The ocurrence of foreign bodies in otorhinolaryngology
|
|
|
- Hillary Long
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Rev Bras Otorrinolaringol 2006;72(2): ORIGINAL ARTICLE Foreign body in ear, nose and oropharynx: experience from a tertiary hospital Romualdo Suzano Louzeiro Tiago 1, Daniel Cauduro Salgado 2, Juliano Piotto Corrêa 3, Márcio Ricardo Barros Pio 4, Ernani Edney Lambert 5 Key words: Ear. Nose. Oropharynx. Summary The ocurrence of foreign bodies in otorhinolaryngology is reason of constant searches for emergency services. Objective: To value the incidence of patients with foreign body, to analyze the clinical situation and the treatment in these cases. Method: The prospective study was realized in 81 patients with diagnosis of foreign body of nose, ear or oropharynx in the otorhinolaryngology service of the Hospital do Servidor Público Municipal de São Paulo between april/2003 and march/2005. Results: 57 cases of foreign body of ear, 13 cases of nose and 11 of oropharynx. These patients, 51.85% were men and 48.15% were women. The age average was 23 years old. The average of the evolution time was days, being that 38.27% these cases were taken care in less 24 hours of evolution. Inside the total of patients, 83.95% received initial attendance in the otorhinolaryngology clinic, and 16.05% came of another service after some previous removal attempt. The most common symptom of the foreign bodies cases of oropharynx it was odinofagia present in 90.91% of the cases; in the foreign bodies of nose, the unilateral rhinorrhea and cacosmia were present in of the cases; in the foreign bodies of ear, 38.60% evolved without symptoms and with hipoacusia. The most frequent foreign body of oropharynx it was the fish spine (54.55%); in the nose it was the paper (30.77%); and in the ear it was the cotton (31.58%). The complications resulting of the presence of foreign body or about the manipulation of these had been found in 13 cases (16.05%). Conclusion: Most cases of foreign body conditions, in which a non-specialist professional or a non-professional person previously handles its removal, have a bad evolution with emerging complications. Such outcomes strengthen the fact that an otorhinolaryngologist using the proper equipment must treat patients with foreign body. 1 MD, MS, PhD in Otorhinolaryngology - UNIFESP. Assistant Physician at the Hospital do Servidor Público Municipal de São Paulo. 2 MD, 2nd year resident of otorhinolaryngology - Hospital do Servidor Público Municipal de São Paulo. 3 MD, 2nd year resident of Otorhinolaryngology - Hospital do Servidor Público Municipal de São Paulo. 4 MD, 3rd year resident of otorhinolaryngology - Hospital do Servidor Público Municipal de São Paulo. 5 MD, 3rd year resident of otorhinolaryngology -Hospital do Servidor Público Municipal de São Paulo. Serviço de Otorrinolaringologia do Hospital do Servidor Público Municipal de São Paulo. Mailing Address: Daniel Cauduro Salgado - Rua dos Tapes 56 apto. 204 C Liberdade São Paulo SP Tel: (0xx11) danimed32@ig.com.br Paper submitted to the ABORL-CCF SGP (Management Publications System) on July 13th, 2005 and accepted for publication on February 22nd,
2 INTRODUCTION Foreign bodies (FBs) in the nose, ears and the oropharynx are reason for frequent visits to otorhinolaryngology emergency units. FB cases rarely go without symptoms, which are determined by the time or duration the FB stays in place before removal. In the nose initial symptoms are sneezing, serous coryza and nasal obstruction, eventually progressing after a few days to unilateral foul smelling purulent rhinorrhea. In the ear initial symptoms may be hypoacusis, otorrhagia, otorrhea or buzzing and the diagnosis may be confirmed by otoscopy. The main symptom in oropharynx FBs is odynophagia 1. FBs may vary widely in shape, size and composition. Schulze et al. (2002), in a retrospective study of 698 ear FB cases, proposed an 8-class classification system based on FB shape and texture 2. FBs may also be classified according to the introduction mode, either voluntary or accidental. Voluntary placement of FBs occurs mostly in children and accidental introduction is usually of live animals 3. The shape and size of FBs establishes the level of difficulty in their removal. In ear FBs complications may arise as the external auditory canal is small and important anatomical structures are close.4 Removal may be difficult when the FB is close to the tympanic membrane or the bony external auditory canal because of intense pain due to increased sensitivity. Frequent complications include: laceration of the external auditory canal, tympanic perforation, external otitis and hematomas. FBs in the nose may progress with epistaxis, septal perforation and rhinosinusitis depending on the time the FB has been in place and its location 1. Complications may also arise frequently during FB removal, making it essential for ENT specialists to treat these cases. Bressler et al. (1993) reviewed prospectively 98 ear FB cases, concluding that FBs not removed by primary medical care should be referred to expert evaluation 4. Ikino et al. (1998) reviewed 88 ear and nose FB cases in pediatric patients and suggested that prevention is the preferred option and that parents and relatives should be informed about the risks of foreign objects introduced in the ear and nose.6 Marques et al. (1998) conducted a prospective review of 477 nose, ear and oral cavity FB cases and noted a high complication rate in those cases where removal was attempted by untrained or unprepared professionals 1. In a retrospective review of 162 ear FB cases, Thompson et al. (2003) concluded that successful FB removal depends on patient cooperation, the ability of the physician to see the FB, the type of FB, prior manipulation and available instruments 5. The aim of this study was to establish the incidence of patients with FBs in the otorhinolaryngology unit at the Sao Paulo Municipal Servidor Publico Hospital (HSPM) (Hospital do Servidor Publico Municipal de Sao Paulo) and to study the clinical findings and the treatment of these patients. MATERIAL AND METHODS A prospective study of 81 patients admitted to the HSPM Otorhinolaryngology Unit between April 2003 and March 2005 with a diagnosis of foreign objects in the nose, ear or oropharynx that had underwent a complete otorhinolaryngological examination followed by FB removal. The initial clinical assessment and the FB removal procedure were performed by one of the resident physicians monitored by a senior physician of the HSPM Otorhinolaryngology Unit. A specific protocol form was filled in for all cases, including the following points: age; main complaint; associated symptoms; duration of the condition; location; nature of the FB; strategy and complications. Data were collected by the ENT specialist who was responsible for the patient, based on the interview of the patient or child caretaker. One of the following instruments was used to remove ear FBs: a curette, an alligator forceps, ear syringing or irrigation and bayonet forceps. In selected cases a microscope was used to facilitate FB handling. Instruments used for nasal FB were: Itard s catheter, alligator forceps or a curette. Instruments used to remove pharyngeal FBs were: a Hartmann forceps a bayonet forceps or digital maneuvers, always with local anesthesia with 10% lidocaine. Alcohol was instilled in the external auditory canal prior to removing live FBs. General anesthesia was required in only one patient to remove the FB. RESULTS Our study included 81 cases of otorhinolaryngological FBs: 57 (70.37%) in the ear, 13 (16.05%) in the nose and 11 (13.58%) in the oropharynx. Age varied from 2 to 84 years (average 23 years). The 0-3 year group was the most frequently affected groups for nose FBs, with 11 cases (84.61%). The 4-20 years group was the most frequently affected group for ear FBs, with 27 cases (47.37%). Pharyngeal FBs were more frequent in patients over 20 years of age, with 9 cases (81.82%) (Table 1). Gender distribution was 42 men (51.85%) and 39 women (48.15%) (Table 2). The average FB duration time was days; 31 cases (38.27%) were seen within 24 hours of FB duration. Foreign objects in the ear cases had an average FB duration time of days. Foreign objects in the nose cases had an average FB duration time of days. Foreign objects in the oropharynx cases had an average FB duration time of 1.72 days. First treatment was given in the otorhinolaryngology clinic in 83.95% of patients; 16.05% were referred from other clinical units following some attempt at removal. 178
3 Table 1. Frequency of cases with foreign bodies according to the age group and the site of the foreign body. Table 2. Frequency of cases with foreign bodies according to gender and the site of the foreign body. AGE SITE 0-3 years 4-20 years >20 years Total Ear Oropharynx Nose Total GENDER SITE Male Female Ear Oropharynx 5 6 Nose 5 8 Total The location of FBs was as follows: of 57 ear FBs, 29 (50.88%) were placed in the right ear, 24 (42.11%) in the left ear and 4 (7.02%) in both ears. Nasal FBs were 8 cases (61.54%) in the right naris and 5 (38.46%) in the left naris. Of 11 pharyngeal FB cases 4 (36.36%) were in the right tonsil, 4 (36.36%) in the left tonsil and 3 (27.27%) at the base of the tongue. The most common symptom in oropharyngeal FBs was odinofagia in ten cases (90.91%). Unilateral rhinorrhea and cacosmia were found in six cases (46.15%) of nasal FBs, followed by unilateral rhinorrhea in four cases (30.77%). No symptoms were found in 22 cases (38.60%) of ear FBs; 16 (28.07%) developed hypoacusis and 9 (15.79%) presented otalgia (Table 3). Of 57 patients with ear FBs, 23 (40.35%) were removed with alligator forceps, 18 (31.58%) with irrigation, 8 (14.04%) with a curette and 8 (14.04%) using more than one method. Of 13 patients with nasal FBs, extraction was done using Itard s catheter in 9 (69.23%), alligator forceps in 2 (15.38%) and more than one method in 2 (15.38%). Of 11 pharyngeal FBs, 7 (63.64%) were removed with a Hartmann forceps, 2 (18.18%) with a bayonet forceps and 2 (18.18%) using digital maneuvers. FBs were classified as animate organic, inanimate organic and inorganic. There were 49 (85.96%) inanimate organic FBs in the ear, 5 (877%) inorganic FBs and 3 (5.26%) animate organic FBs. There were 12 (92.31%) inanimate organic FBs in the nose and 1 (7.69%) inorganic FB. There were 11 (100%) inanimate organic FBs in the pharynx. The most frequent FB in the oropharynx was fish spine, with 6 cases (54.55%). Paper was the most frequent object in the nose, with 4 cases (30.77%), followed by sponges, with 3 cases (23.08%). The most frequent FB in the ear was cotton, with 18 cases (31.58%), followed by plastic, with 7 cases (12.28%) (Table 4). Complications resulting from FBs and previous removal attempts were seen in 13 cases (16.05%). Oropharyngeal FBs did not present complications. Seven ear FB cases (12.28%) presented with acute external otitis and one case (1.75%) had a laceration in the external audi- tory canal. Three nasal FB cases (23.08%) presented with rhinosinusitis; one (7.69%) had epistaxis and one (7.69%) had a rhinolith. DISCUSSION In this study there was a slight predominance of FBs in men (51.85%) compared to women (48.15%), similar to results published by other authors.5 The average age was 23 years, similar to Bressler s et al. review (1993) 4. Nose FBs were more frequent in children, particularly in the 0-3 years age group (84.61%), as seen in another review 1. The incidence fell with age; no FBs in the nose were seen in patients over 20 years of age. This reflects the sense of curiosity and self-discovery typical of children. With growth and cognitive development, placing FBs in the nose be- Chart 1. Symptoms related to foreign objects according to the site. REGION SYMPTOMS FREQUENCY No symptoms 22 Hypoacusis 16 Otalgia 9 Fever 3 Ear Hypoacusis and otalgia 2 Buzzing 2 Hypoacusis and buzzing 1 Foul smelling otorrhea 1 Dizziness 1 Unilateral Rhinorrhea and cacosmia 6 Nose Unilateral Rhinorrhea 4 No symptoms 2 Bilateral Rhinorrhea and fever 1 Oropharynx Odinofagia 10 No symptoms 1 179
4 Chart 2. Frequency of the FB type according to the site. REGION TYPE OF FOREIGN BODY FREQUENCY Ear Nose Oropharynx Cotton 18 Plastic 7 Pencil 5 Silicone 4 Eraser 3 Paper 3 Insect 3 Stone 3 Bean 2 Hair 2 Wax crayon 2 Metal sphere 1 Bead 1 Matchstick 1 Screw 1 Popcorn 1 Paper 4 Sponge 3 Gauze 1 Tangerine seed 1 Metal chain 1 Sponge 1 Corn 1 Bead 1 Fish spine 6 Popcorn 2 Rice seed 2 Green vegetable 1 comes rare and is seen only in psychiatric patients 6. On the other hand, oropharyngeal FBs were more frequent in patients over 20 years of age (81.82%). Only two pediatric patients in this category were seen at our Otorhinolaryngology Unit, probably due to the fact that these patients usually are referred directly to the Endoscopy Unit due to the risk of airway obstruction 6. Ear FB cases had a balanced distribution between the 4-20 years age group (27 cases) and the over 20 years age group (24 cases). FB placement in the 4-20 years age group was seen mostly between 3 and 12 years of age (23 cases), which may be explained by play between children. FB were introduced accidentally in patients over 20 years such as during the act of scratching the ear with cotton (15 cases) or by introducing ear plugs (4 cases). The three cases in which the FB was an insect in the external acoustic canal were over 12 years of age. FB duration in the specific site was less than 24 hours in 38.27% of cases, similar to the study by Ikino et al. (1998) 6. The average FB duration time in the oropharynx was only 1.72 days, explained by the resulting discomfort due to the FB in this site. FBs in the nose, however, had an average FB duration of days due to a rhinolith in a 10-year-old child in which a sponge fragment remained approximately 510 days in the nasal cavity. Rhinolithiasis is a rare disease, characterized by coral-like calcium concretions deposited progressively around a FB,7 uncommon in pediatric patients 8. The average ear FB duration time was days. In symptomatic ear FB cases, the average FB duration was days. Average FB duration in asymptomatic ear FB cases (38.60%) was 4.86 days % of the total number of patients was referred to our unit following an unsuccessful attempt at FB removal at another unit. This percentage is lower compared to other studies. This may be explained by the fact that municipal civil servants first seek medical services at the HSPM (a city hospital for civil servants). There is also a good relationship between the Emergency Room and the Pediatrics Department staff and our Otorhinolaryngology Unit. Oropharyngeal FBs were found in the tonsils or at the base of tongue, probably due to tonsillary crypts that favor food retention. Nose and ear FBs are more frequent to the right. We believe this is due to the fact that most of the population is right-handed. Thompson et al. (2003) noted only a minor predominance of FBs in the right ear (52%) 5. The most frequent symptom in oropharyngeal FB cases was odinofagia (90.91%) which motivated patients to seek medical help earlier (1.72 days). The most frequent symptom in nose FB cases was unilateral rhinorrhea, in 76.92% of patients. The absence of symptoms was the most common presentation in ear FB cases (38.60%) and the most frequent symptom was hypoacusis (28.07%). Removal methods most commonly used for ear, nose and oropharyngeal FBs were similar to those presented in a review by Marques et al. (1998) 1, in order of preference the alligator forceps, Itard s catheter and the Hartmann forceps. No patient required endoscopy or indirect laryngoscopy to remove oropharyngeal FBs. General anesthesia was required in only one case to remove an organic FB (bean) from the right ear, next to the tympanic membrane, in a 9-year-old child. The need for general anesthesia to remove FBs varies in literature, with percentages varying from 8.6% to 30% 5. Complications of ear FBs were seen in 8 patients (14.03%), lower than reported in literature.1 In this group 7 patients presented acute external otitis. This situation generated the debate of whether external otitis was a result of the FB duration in the external acoustic canal or 180
5 if infection in the first place had led the patient to place a FB in the ear to relieve symptoms. External otitis was the most frequent complication in the review by Bressler et al. (1993), with a 7.1% incidence 4. Laceration of the external auditory canal was seen in only 1 case and there was no perforation of the tympanic membrane. Five nose FB cases (38.46%) developed complications: 3 cases of rhinosinusitis, one case of epistaxis and 1 rhinolith. The complication rate for nose FBs was higher than other reports in literature 1. No complications were seen in oropharyngeal FB cases. Of the 13 cases with complications, 7 (53.85%) had undergone prior FB removal attempts in the hands of unprepared professionals or lay persons. In a review by Schulze et al. (2002) ear FB complications were significantly higher in patients who had undergone unsuccessful FB removal attempts 2. This is similar to the findings in Bressler s et al. review (1993), in which laceration of the external acoustic canal was seen in 61.5% of cases which had undergone unsuccessful FB removal attempts. This may be compared with the 5.1% complication rate in patients with no previous FB removal attempt 4, underlining the importance of a ENT specialist to deal with these cases. REFERENCES 1. Marques MPC, Sayuri MC, Nogueira MD, Nogueirol RB, Maestri VC. Tratamento dos corpos estranhos otorrinolaringológicos: um estudo prospectivo. Rev Bras Otorrinolaringol 1998;64: Schulze SL, Kerschner J, Beste D. Pediatric external auditory canal foreign bodies: a review of 698 cases. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2002;127: Hungria H. Patologia do ouvido externo. Em: Hungria H. Otorrinolaringologia. 8 ed. Rio de Janeiro: Guanabara Koogan; p Bressler K, Shelton C. Ear foreign-body removal: a review of 98 consecutive cases. Laryngoscope 1993;103: Thompson SK, Wein RO, Dutcher PO. External auditory canal foreign body removal: management practices and outcomes. Laryngoscope 2003;113: Ikino CMY, D Antonio WEPA, Balbani APS, Sanchez TG, Butugan O. Análise dos atendimentos para retirada de corpos estranhos de ouvido e nariz em crianças. Rev Bras Otorrinolaringol 1998;64: Cavalcanti HVR, Campos GG, Velasco TS, Rego PF, Benetti AP. Rinolito: relato de caso e revisão de literatura. Rev Bras Otorrinolaringol 2004;70: Hadi U, Ghossaini S, Zaytoun G. Rhinolithiasis: a forgotten entity. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2002;126: CONCLUSION Oropharyngeal foreign bodies were more frequent in patients over 20 years of age. The main symptom was odinofagia, which motivated an earlier search for medical services. Ear foreign bodies were more frequent in adults, with cotton as the most common material. Nose foreign bodies were more frequent in the 0-3 year age group and the main symptom was unilateral rhinorrhea. The majority of cases in which unsuccessful foreign body removal attempts by untrained professionals or lay persons had been made developed complications, emphasizing the need for an ENT specialist with adequate instruments to manage such cases. 181
Foreign bodies in otorhinolaryngology: a study of 860 cases managed in medical college hospital.
 ISSN: 2250:0359 Volume 3 Issue 4 2013 Foreign bodies in otorhinolaryngology: a study of 860 cases managed in medical college hospital. Sudhir M Naik 1, Ravishankara S 2, Mohan Appaji 3, Goutham MK 4, N
ISSN: 2250:0359 Volume 3 Issue 4 2013 Foreign bodies in otorhinolaryngology: a study of 860 cases managed in medical college hospital. Sudhir M Naik 1, Ravishankara S 2, Mohan Appaji 3, Goutham MK 4, N
Foreign bodies are one of the most common ENT (Ear,
 Rev Bras Otorrinolaringol 2008;74(1):7-15. ORIGINAL ARTICLE Complications of ent foreign bodies: a retrospective study Ricardo Rodrigues Figueiredo 1, Andréia Aparecida de Azevedo 2, Arthur Octavio de
Rev Bras Otorrinolaringol 2008;74(1):7-15. ORIGINAL ARTICLE Complications of ent foreign bodies: a retrospective study Ricardo Rodrigues Figueiredo 1, Andréia Aparecida de Azevedo 2, Arthur Octavio de
Nasal cavities foreign bodies are common accidents in
 Rev Bras Otorrinolaringol 2006;72(1):18-23 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Nasal foreign bodies: description of types and complications in 420 cases Ricardo Rodrigues Figueiredo 1, Andréia A. Azevedo 2, Arthur Octávio
Rev Bras Otorrinolaringol 2006;72(1):18-23 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Nasal foreign bodies: description of types and complications in 420 cases Ricardo Rodrigues Figueiredo 1, Andréia A. Azevedo 2, Arthur Octávio
Procedural Sedation Use in the ED: Management of Pediatric Ear and Nose Foreign Bodies
 Therapeutics Procedural Sedation Use in the ED: Management of Pediatric and Foreign Bodies LANCE BROWN, MD, MPH, T. KENT DENMARK, MD, WILLIAM A. WITTLAKE, MD, EDWARD J. VARGAS, MD, TIMOTHY WATSON, MD,
Therapeutics Procedural Sedation Use in the ED: Management of Pediatric and Foreign Bodies LANCE BROWN, MD, MPH, T. KENT DENMARK, MD, WILLIAM A. WITTLAKE, MD, EDWARD J. VARGAS, MD, TIMOTHY WATSON, MD,
Objective: To compare types of aural foreign objects between adults and children presenting at two Australian Emergency Departments.
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Volume 4 Number 2 Adult Aural Foreign Bodies C Ryan, A Ghosh, D Smit, B Wilson-Boyd, S O'Leary Citation C Ryan, A Ghosh, D Smit, B Wilson-Boyd, S O'Leary.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Volume 4 Number 2 Adult Aural Foreign Bodies C Ryan, A Ghosh, D Smit, B Wilson-Boyd, S O'Leary Citation C Ryan, A Ghosh, D Smit, B Wilson-Boyd, S O'Leary.
Flexible Fiberoptic Exam
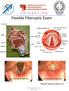 Flexible Fiberoptic Exam True Vocal Cords abducted True Vocal Cords adducted *Fiberoptic endoscopy, image is true. Cerumen Removal Position Patient -Explain Procedure Visualize Canal/Landmarks Determine
Flexible Fiberoptic Exam True Vocal Cords abducted True Vocal Cords adducted *Fiberoptic endoscopy, image is true. Cerumen Removal Position Patient -Explain Procedure Visualize Canal/Landmarks Determine
Vascular Affection of Temporal Bone: Differential Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approach
 Case Report Article Vascular Affection of Temporal Bone: Differential Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approach Teresa Cristina Mendes Higino*, Gustavo Motta Simplício do Nascimento**, Daniel Cauduro Salgado***,
Case Report Article Vascular Affection of Temporal Bone: Differential Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approach Teresa Cristina Mendes Higino*, Gustavo Motta Simplício do Nascimento**, Daniel Cauduro Salgado***,
Rhinolithiasis and value of nasal endoscopy: A Case Report
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Volume 7 Number 2 Rhinolithiasis and value of nasal endoscopy: A Case Report R Singh, S Varshney, S Bist, N Gupta, R Bhatia, S Kishore Citation R Singh,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Volume 7 Number 2 Rhinolithiasis and value of nasal endoscopy: A Case Report R Singh, S Varshney, S Bist, N Gupta, R Bhatia, S Kishore Citation R Singh,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Assessment of symptom improvement following nasal septoplasty with or without turbinectomy
 Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2011;77(5):577-83. ORIGINAL ARTICLE Assessment of symptom improvement following nasal septoplasty with or without turbinectomy Leandro Castro Velasco 1, Lisandra Megumi Arima 2,
Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2011;77(5):577-83. ORIGINAL ARTICLE Assessment of symptom improvement following nasal septoplasty with or without turbinectomy Leandro Castro Velasco 1, Lisandra Megumi Arima 2,
Tympanoplasty is done to eradicate ear pathology and
 Rev Bras Otorrinolaringol 2007;73(3):384-9. ORIGINAL ARTICLE The effect of timpanoplasty on tinnitus in patients with conductive hearing loss: a six month follow-up Adriana da Silva Lima 1, Tanit Ganz
Rev Bras Otorrinolaringol 2007;73(3):384-9. ORIGINAL ARTICLE The effect of timpanoplasty on tinnitus in patients with conductive hearing loss: a six month follow-up Adriana da Silva Lima 1, Tanit Ganz
Pediatric Otolaryngology University of Kentucky April 2009
 Common ENT Problems: How to evaluate and when to refer Maria C. Veling M.D. Pediatric Otolaryngology University of Kentucky April 2009 1 Objectives Identify symptoms and findings of clinically significant
Common ENT Problems: How to evaluate and when to refer Maria C. Veling M.D. Pediatric Otolaryngology University of Kentucky April 2009 1 Objectives Identify symptoms and findings of clinically significant
Prophylactic Tobramycin Drops After Tympanostomy Tube Placement
 International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology 2018; 4(1): 6-10 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijo doi: 10.11648/j.ijo.20180401.12 ISSN: 2472-2405 (Print); ISSN: 2472-2413 (Online) Prophylactic
International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology 2018; 4(1): 6-10 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijo doi: 10.11648/j.ijo.20180401.12 ISSN: 2472-2405 (Print); ISSN: 2472-2413 (Online) Prophylactic
Commen Nose Diseases
 Commen Nose Diseases Symptoms List: Nasal obstruction. Nasal discharge: Anterior (Rhinorrhea). Posterior (Postnasal discharge). Epistaxis. Hyposmia and Anosmia. Headache. Snoring. Nasal Obstruction Definition:
Commen Nose Diseases Symptoms List: Nasal obstruction. Nasal discharge: Anterior (Rhinorrhea). Posterior (Postnasal discharge). Epistaxis. Hyposmia and Anosmia. Headache. Snoring. Nasal Obstruction Definition:
Objectives. Urgent Care in the Family Practice Setting. Disclosures. Urgent Care in the Family Practice Setting. Tanya A.
 Urgent Care in the Family Practice Setting Tanya A. Tupick DO Pennsylvania Osteopathic Family Physicians Society August 3 rd 2018 Disclosures Dr. Tupick has provided no disclosures. Objectives Goals and
Urgent Care in the Family Practice Setting Tanya A. Tupick DO Pennsylvania Osteopathic Family Physicians Society August 3 rd 2018 Disclosures Dr. Tupick has provided no disclosures. Objectives Goals and
KIDS PUT THINGS IN THE CRAZIEST PLACES...
 KIDS PUT THINGS IN THE CRAZIEST PLACES... YOU CAN T MAKE ME EAT MY DINNER! 2 year old observed to stuff corn up right nostril Judith Klein, MD FACEP Assistant Professor of Emergency Medicine UCSF-SFGH
KIDS PUT THINGS IN THE CRAZIEST PLACES... YOU CAN T MAKE ME EAT MY DINNER! 2 year old observed to stuff corn up right nostril Judith Klein, MD FACEP Assistant Professor of Emergency Medicine UCSF-SFGH
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Crooked nose: outcome evaluations in rhinoplasty
 Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2011;77(4):510-5. ORIGINAL ARTICLE Crooked nose: outcome evaluations in rhinoplasty BJORL.org Lisandra Megumi Arima 1, Leandro Castro Velasco 2, Romualdo Suzano Louzeiro Tiago
Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2011;77(4):510-5. ORIGINAL ARTICLE Crooked nose: outcome evaluations in rhinoplasty BJORL.org Lisandra Megumi Arima 1, Leandro Castro Velasco 2, Romualdo Suzano Louzeiro Tiago
JINNAH SINDH MEDICAL UNIVERSITY SEMESTER VII- OTORHINOLARYNGOLOGY (EAR, NOSE THROAT DISEASES)- 2017
 JINNAH SINDH MEDICAL UNIVERSITY SEMESTER VII- OTORHINOLARYNGOLOGY (EAR, NOSE THROAT DISEASES)- 2017 This study guide is meant to be used for semester VII & VIII students of Jinnah Sindh medical university.
JINNAH SINDH MEDICAL UNIVERSITY SEMESTER VII- OTORHINOLARYNGOLOGY (EAR, NOSE THROAT DISEASES)- 2017 This study guide is meant to be used for semester VII & VIII students of Jinnah Sindh medical university.
OTOLARYNGOLOGY HEAD AND NECK SURGERY
 OTOLARYNGOLOGY HEAD AND NECK SURGERY COORDINATOR: ADMINISTRATIVE ASSISTANT: Dr. Murad Husein LHSC - Victoria Hospital, Room B3-440A Phone: 685-8184 Fax: (519) 685-8185 Email: Murad.Husein@lhsc.on.ca Ms.
OTOLARYNGOLOGY HEAD AND NECK SURGERY COORDINATOR: ADMINISTRATIVE ASSISTANT: Dr. Murad Husein LHSC - Victoria Hospital, Room B3-440A Phone: 685-8184 Fax: (519) 685-8185 Email: Murad.Husein@lhsc.on.ca Ms.
WV OTORHINOLARYNGOLOGY. EAR, NOSE AND THROAT MEDICINE
 WV OTORHINOLARYNGOLOGY. EAR, NOSE AND THROAT MEDICINE 1 Societies 11 History 13 Dictionaries. Encyclopaedias. Bibliographies Use for general works only. Classify with specific aspect where possible 15
WV OTORHINOLARYNGOLOGY. EAR, NOSE AND THROAT MEDICINE 1 Societies 11 History 13 Dictionaries. Encyclopaedias. Bibliographies Use for general works only. Classify with specific aspect where possible 15
Otology Workshop Basic
 April 21, 2017 Chicago Otology Basic workshop Jeffrey Fichera, PhD, PA C Updated 2/09/2017 Otology Workshop Basic Clear Instruction Live Demonstration Learn by doing Hands On Practice Identify normal,
April 21, 2017 Chicago Otology Basic workshop Jeffrey Fichera, PhD, PA C Updated 2/09/2017 Otology Workshop Basic Clear Instruction Live Demonstration Learn by doing Hands On Practice Identify normal,
Introduction 4/17/2017. Otology Workshop; Advanced Ryan Marovich, MPAS, PA-C J. Andrew Clark, PA-C Updated 12/03/2015
 March 31, 2016 Orlando, FL Otology Workshop; Advanced Ryan Marovich, MPAS, PA-C J. Andrew Clark, PA-C Updated 12/03/2015 Otology Workshop; Advanced Clear Instruction Live Demonstration Hands On Practice
March 31, 2016 Orlando, FL Otology Workshop; Advanced Ryan Marovich, MPAS, PA-C J. Andrew Clark, PA-C Updated 12/03/2015 Otology Workshop; Advanced Clear Instruction Live Demonstration Hands On Practice
OTOLARYNGOLOGY. A) Introduction. B) Description. C) Objectives
 OTOLARYNGOLOGY Academic Director: Dr. Andrew Petrakos Undergraduate Curriculum Administrator: Kelly Ducharme PHONE: 519-253-3000 ext 4303 EMAIL: kducharm@uwindsor.ca OFFICE LOCATION: Medical Education
OTOLARYNGOLOGY Academic Director: Dr. Andrew Petrakos Undergraduate Curriculum Administrator: Kelly Ducharme PHONE: 519-253-3000 ext 4303 EMAIL: kducharm@uwindsor.ca OFFICE LOCATION: Medical Education
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Assessment of hearing in a municipal public school student population
 Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2011;77(6):716-20. ORIGINAL ARTICLE Assessment of hearing in a municipal public school student population Janaina Cândida Rodrigues Nogueira 1, Maria da Conceição Mendonça 2 BJORL.org
Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2011;77(6):716-20. ORIGINAL ARTICLE Assessment of hearing in a municipal public school student population Janaina Cândida Rodrigues Nogueira 1, Maria da Conceição Mendonça 2 BJORL.org
Learning Objectives for Rotation in Otolaryngology Year 3 Clerkship
 Learning Objectives for Rotation in Otolaryngology Year 3 Clerkship EAR INFECTIONS - OBJECTIVES examine the outer ear, ear canal and tympanic membrane and describe normal versus abnormal findings differentiate
Learning Objectives for Rotation in Otolaryngology Year 3 Clerkship EAR INFECTIONS - OBJECTIVES examine the outer ear, ear canal and tympanic membrane and describe normal versus abnormal findings differentiate
PAEDIATRIC ACUTE CARE GUIDELINE. Otitis Media
 Princess Margaret Hospital for Children PAEDIATRIC ACUTE CARE GUIDELINE Otitis Media Scope (Staff): Scope (Area): All Emergency Department Clinicians Emergency Department This document should be read in
Princess Margaret Hospital for Children PAEDIATRIC ACUTE CARE GUIDELINE Otitis Media Scope (Staff): Scope (Area): All Emergency Department Clinicians Emergency Department This document should be read in
Dubai Standards of Care (Septoplasty)
 Dubai Standards of Care 2017 (Septoplasty) Preface Ear, nose and throat disorders are the most common problem dealt with in daily practice. In Dubai, the management of ear, nose and throat disorders were
Dubai Standards of Care 2017 (Septoplasty) Preface Ear, nose and throat disorders are the most common problem dealt with in daily practice. In Dubai, the management of ear, nose and throat disorders were
Otorhinolaryngologic Evaluation from Leprosy Patients Protocol of a National Reference Center
 Original Article Otorhinolaryngologic Evaluation from Leprosy Patients Protocol of a National Reference Center Giselle Mateus da Silva*, Lucas Gomes Patrocinio**, José Antonio Patrocinio***, Isabela Maria
Original Article Otorhinolaryngologic Evaluation from Leprosy Patients Protocol of a National Reference Center Giselle Mateus da Silva*, Lucas Gomes Patrocinio**, José Antonio Patrocinio***, Isabela Maria
The earlobe occupies a unique position among facial
 Rev Bras Otorrinolaringol 2006;72(4):447-51. ORIGINAL ARTICLE Earlobe cleft reconstructive surgery Lucas Gomes Patrocínio 1, Rodrigo Márcio Morais 2, José Edmundo Pereira 3, José Antônio Patrocínio 4 Keywords:
Rev Bras Otorrinolaringol 2006;72(4):447-51. ORIGINAL ARTICLE Earlobe cleft reconstructive surgery Lucas Gomes Patrocínio 1, Rodrigo Márcio Morais 2, José Edmundo Pereira 3, José Antônio Patrocínio 4 Keywords:
Subspecialty Rotation: Otolaryngology
 Subspecialty Rotation: Otolaryngology Faculty: Evelyn Kluka, M.D. GOAL: Hearing Loss. Understand the morbidity of hearing loss, intervention strategies, and the pediatrician's and other specialists' roles
Subspecialty Rotation: Otolaryngology Faculty: Evelyn Kluka, M.D. GOAL: Hearing Loss. Understand the morbidity of hearing loss, intervention strategies, and the pediatrician's and other specialists' roles
Commissioning Policy Individual Funding Request
 Commissioning Policy Individual Funding Request Referral for Microsuction of Ear Wax, Discharge or Debris Removal in Secondary Care All Ages Criteria Based Access and Prior Approval Policy Date Adopted:
Commissioning Policy Individual Funding Request Referral for Microsuction of Ear Wax, Discharge or Debris Removal in Secondary Care All Ages Criteria Based Access and Prior Approval Policy Date Adopted:
Otorhinolaryngologic Emergencies In Nigeria, Sub-Saharan Africa: Implication for Training.
 8 Otorhinolaryngologic Emergencies In Nigeria, Sub-Saharan Africa: Implication for Training. O.A. Lasisi 1, Z.K. Imam 2, A.A. Adeosun 1, 1 Senior Lecturer/Consultant, 2 Registrar Department of Otorhinolaryngology,
8 Otorhinolaryngologic Emergencies In Nigeria, Sub-Saharan Africa: Implication for Training. O.A. Lasisi 1, Z.K. Imam 2, A.A. Adeosun 1, 1 Senior Lecturer/Consultant, 2 Registrar Department of Otorhinolaryngology,
LESSON ASSIGNMENT , Irrigate an Obstructed Ear. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 6 Irrigate an Obstructed Ear. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 6-1 through 6-9. TASK TAUGHT LESSON OBJECTIVES 081-833-0059, Irrigate an Obstructed Ear. After completing this lesson,
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 6 Irrigate an Obstructed Ear. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 6-1 through 6-9. TASK TAUGHT LESSON OBJECTIVES 081-833-0059, Irrigate an Obstructed Ear. After completing this lesson,
Disclosures. Ear. Management of Chronic Problems in Otolaryngology. Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery 10/21/2013
 Disclosures Management of Chronic Problems in Otolaryngology Patent Pending 61/624, 105 - Sinus diagnostics and therapeutics Consultant, BioInspire Inc Steven D. Pletcher Associate Professor Department
Disclosures Management of Chronic Problems in Otolaryngology Patent Pending 61/624, 105 - Sinus diagnostics and therapeutics Consultant, BioInspire Inc Steven D. Pletcher Associate Professor Department
The Honrubia Technique of Balloon Sinuplasty for the Improvement of Symptoms in Chronic Sinusitis. Patients. Vincent Honrubia MD, FACS
 The Honrubia Technique of Balloon Sinuplasty for the Improvement of Symptoms in Chronic Sinusitis Patients Vincent Honrubia MD, FACS Allyssa Cantu, PA-S Sharon Gelman, MEd, PA-S Rachel Tsai, BS Director,
The Honrubia Technique of Balloon Sinuplasty for the Improvement of Symptoms in Chronic Sinusitis Patients Vincent Honrubia MD, FACS Allyssa Cantu, PA-S Sharon Gelman, MEd, PA-S Rachel Tsai, BS Director,
Section Editor: Rakesh Prasad Shrivastav 1. Examination of the Ear, Nose and Throat 3 Rabindra B Pradhananga
 Contents Section 1: Ent Examination Section Editor: 1. Examination of the Ear, Nose and Throat 3 Section 2: The Ear Section Editor: Hari Bhattarai 2. Anatomy of the Ear and Facial Nerve 7 External Ear
Contents Section 1: Ent Examination Section Editor: 1. Examination of the Ear, Nose and Throat 3 Section 2: The Ear Section Editor: Hari Bhattarai 2. Anatomy of the Ear and Facial Nerve 7 External Ear
The Throat. Image source:
 The Throat Anatomy Image source: http://anatomyforlayla.blogspot.co.za/2007/04/blog-post.html The Throat consists of three parts: 1. The Nasopharynx is the upper part of the throat and it is situated behind
The Throat Anatomy Image source: http://anatomyforlayla.blogspot.co.za/2007/04/blog-post.html The Throat consists of three parts: 1. The Nasopharynx is the upper part of the throat and it is situated behind
The management of ear canal
 D. Dance, BSc, LLB, M. Riley, MD, FRCPC, J.P. Ludemann, MDCM, FRCSC Removal of ear canal foreign bodies in children: What can go wrong and when to refer While the majority of objects lodged in the ear
D. Dance, BSc, LLB, M. Riley, MD, FRCPC, J.P. Ludemann, MDCM, FRCSC Removal of ear canal foreign bodies in children: What can go wrong and when to refer While the majority of objects lodged in the ear
Effective Date: August 31, To provide guidelines for the proper administration of ear irrigation
 SUBJECT: EAR IRRIGATION 1. PURPOSE: COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL NURSING POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SECTION - Treatments POLICY NUMBER: 406 Effective Date: August 31, 2006 To provide guidelines for the proper
SUBJECT: EAR IRRIGATION 1. PURPOSE: COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL NURSING POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SECTION - Treatments POLICY NUMBER: 406 Effective Date: August 31, 2006 To provide guidelines for the proper
Chapter 17: Foreign bodies in the nose. Joselen Ransome. Aetiology. Mode of entry
 Chapter 17: Foreign bodies in the nose Joselen Ransome Foreign bodies in the nose do not feature largely in otolaryngological literature, yet on occasions they may pose a considerable challenge to both
Chapter 17: Foreign bodies in the nose Joselen Ransome Foreign bodies in the nose do not feature largely in otolaryngological literature, yet on occasions they may pose a considerable challenge to both
Study of success rates in endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy with and without stenting. dacryocystorhinostomy with and
 Original Research Article Study of success rates in endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy with and without stenting Kirti Ambani 1, Niraj Suri 2, Hiren Parmar 3* 1 Assistant Professor, ENT Department, GMERS
Original Research Article Study of success rates in endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy with and without stenting Kirti Ambani 1, Niraj Suri 2, Hiren Parmar 3* 1 Assistant Professor, ENT Department, GMERS
2019 HPN Provider Summary Guide St. Rose Parkway, Suite Smoke Ranch Road Henderson, NV Las Vegas, NV 89128
 12.5 EAR NOSE AND THROAT REFERRAL GUIDELINES Contracted Group: Ear Nose and Throat Consultants (ENTC) For Appointments: Telephone Number: (702) 792-6700 Fax: (702) 792-7198 Locations: 3195 St. Rose Parkway,
12.5 EAR NOSE AND THROAT REFERRAL GUIDELINES Contracted Group: Ear Nose and Throat Consultants (ENTC) For Appointments: Telephone Number: (702) 792-6700 Fax: (702) 792-7198 Locations: 3195 St. Rose Parkway,
Endoscopic surgery in the treatment of crista galli pneumatization evolving with localizated frontal headaches
 Original Article Int. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2013;17(3):246-250. DOI: 10.7162/S1809-97772013000300003 Endoscopic surgery in the treatment of crista galli pneumatization evolving with localizated frontal
Original Article Int. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2013;17(3):246-250. DOI: 10.7162/S1809-97772013000300003 Endoscopic surgery in the treatment of crista galli pneumatization evolving with localizated frontal
Rhinosinusitis is a severe sickness and may have serious
 Rev Bras Otorrinolaringol 2007;73(5):684-8. ORIGINAL ARTICLE Orbital complications of acute rhinosinusitis: a new classification Antonio Augusto Velasco e Cruz 1, Ricardo Cassiano Demarco 2, Fabiana Cardoso
Rev Bras Otorrinolaringol 2007;73(5):684-8. ORIGINAL ARTICLE Orbital complications of acute rhinosinusitis: a new classification Antonio Augusto Velasco e Cruz 1, Ricardo Cassiano Demarco 2, Fabiana Cardoso
2018 HPN Provider Summary Guide St. Rose Parkway, Suite Smoke Ranch Road Henderson, NV Las Vegas, NV 89128
 12.5 EAR NOSE AND THROAT REFERRAL GUIDELINES Contracted Group: Ear Nose and Throat Consultants (ENTC) For Appointments: Telephone Number: (702) 792-6700 Fax: (702) 792-7198 Locations: 3195 St. Rose Parkway,
12.5 EAR NOSE AND THROAT REFERRAL GUIDELINES Contracted Group: Ear Nose and Throat Consultants (ENTC) For Appointments: Telephone Number: (702) 792-6700 Fax: (702) 792-7198 Locations: 3195 St. Rose Parkway,
Spectrum of ear, nose and throat disorders among children reporting to the out-patient department of a tertiary care center, Nepal
 International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Chaudhari BK et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018 Sep;4(5):1125-1129 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937
International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Chaudhari BK et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018 Sep;4(5):1125-1129 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937
Nasopharyngeal Biopsy Performed in an Otorhinolaryngology Service - Clinical-histopathological Correlation
 Original Article Nasopharyngeal Biopsy Performed in an Otorhinolaryngology Service - Clinical-histopathological Correlation Marcelo Alexandre Carvalho*, Sebastião Diógenes Pinheiro**, Marcos Rabelo de
Original Article Nasopharyngeal Biopsy Performed in an Otorhinolaryngology Service - Clinical-histopathological Correlation Marcelo Alexandre Carvalho*, Sebastião Diógenes Pinheiro**, Marcos Rabelo de
Conventional Versus Endoscopic Inferior Turbinate Reduction: Technique and Results
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Conventional Versus Endoscopic Inferior Turbinate Reduction: Technique and Results B S Gendeh, MS(ORL-HNS), Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Faculty of Medicine, Hospital Universiti
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Conventional Versus Endoscopic Inferior Turbinate Reduction: Technique and Results B S Gendeh, MS(ORL-HNS), Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Faculty of Medicine, Hospital Universiti
Clinical Practice Guideline: Tonsillectomy in Children, Baugh et al Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery, 2011 J and: 144 (1 supplement) S1 30.
 Pediatric ENT Guidelines Jane Cooper, FNP, CORLN References: Clinical Practice Guideline: Tympanostomy tubes in children, Rosenfeld et al., American Academy of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery Foundation
Pediatric ENT Guidelines Jane Cooper, FNP, CORLN References: Clinical Practice Guideline: Tympanostomy tubes in children, Rosenfeld et al., American Academy of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery Foundation
Is adenoidectomy an effective therapy for otitis media with effusion?
 02 RJR 02 2011.qxd:Interior 4/26/11 11:57 AM Page 80 Romanian Journal of Rhinology, Vol. 1, No. 2, April - June 2011 ORIGINAL PAPERS Is adenoidectomy an effective therapy for otitis media with effusion?
02 RJR 02 2011.qxd:Interior 4/26/11 11:57 AM Page 80 Romanian Journal of Rhinology, Vol. 1, No. 2, April - June 2011 ORIGINAL PAPERS Is adenoidectomy an effective therapy for otitis media with effusion?
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program. Primary Goals for Rotation. Otolaryngology
 The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Otolaryngology 1. GOAL: Hearing Loss. Understand the morbidity of hearing loss, intervention strategies, and the pediatrician's
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Otolaryngology 1. GOAL: Hearing Loss. Understand the morbidity of hearing loss, intervention strategies, and the pediatrician's
Swallowed Foreign Body
 Swallowed Foreign Body Page 1 of 5 INTRODUCTION Swallowed foreign bodies can be divided into five distinct groups: 1 Small blunt objects 2 Large blunt objects 3 Potentially poisonous objects 4 Sharp objects
Swallowed Foreign Body Page 1 of 5 INTRODUCTION Swallowed foreign bodies can be divided into five distinct groups: 1 Small blunt objects 2 Large blunt objects 3 Potentially poisonous objects 4 Sharp objects
Patient profile, indications, complications and Evaluation of Septoplasty outcome in a Base Hospital in Sri Lanka
 Patient profile, indications, complications and Evaluation of Septoplasty outcome in a Base Hospital in Sri Lanka Rubasinghe M.S., De Silva M.D.K., Wanasinghe W.M.S.C.L., De Livera R.J.K., Wimalaratna
Patient profile, indications, complications and Evaluation of Septoplasty outcome in a Base Hospital in Sri Lanka Rubasinghe M.S., De Silva M.D.K., Wanasinghe W.M.S.C.L., De Livera R.J.K., Wimalaratna
Procedures in the ED. MCEP Straight Talk Most $$$ ED CPT Codes (not including E&M codes) EKGs X-rays Ultrasounds.
 Procedures in the ED Most $$$ ED CPT Codes (not including E&M codes) 93010 Electrocardiogram report 31500 Insert emergency airway 36556 Insert non-tunnel CV cath 92950 Heart/lung resuscitation CPR 12001
Procedures in the ED Most $$$ ED CPT Codes (not including E&M codes) 93010 Electrocardiogram report 31500 Insert emergency airway 36556 Insert non-tunnel CV cath 92950 Heart/lung resuscitation CPR 12001
ACUTE MASTOIDITIS IN CHILDREN: SUSCEPTIBILITY FACTORS AND MANAGEMENT
 & ACUTE MASTOIDITIS IN CHILDREN: SUSCEPTIBILITY FACTORS AND MANAGEMENT Slobodan Spremo*, Biljana Udovčić Clinic for Otorhinolaryngology, Clinic Center in Banja Luka, Zdrave Korde 1, 78000 Banja Luka, Bosnia
& ACUTE MASTOIDITIS IN CHILDREN: SUSCEPTIBILITY FACTORS AND MANAGEMENT Slobodan Spremo*, Biljana Udovčić Clinic for Otorhinolaryngology, Clinic Center in Banja Luka, Zdrave Korde 1, 78000 Banja Luka, Bosnia
March 31, 2016 Orlando, FL. ENT Procedures Jose C. Mercado, PA-C, MMS, DFAAPA
 March 31, 2016 Orlando, FL ENT Procedures Jose C. Mercado, PA-C, MMS, DFAAPA Updated 12/03/2015 ENT Procedures Workshop Clear Instruction Live Demonstration Hands-On Practice Learn by doing Removal Foreign
March 31, 2016 Orlando, FL ENT Procedures Jose C. Mercado, PA-C, MMS, DFAAPA Updated 12/03/2015 ENT Procedures Workshop Clear Instruction Live Demonstration Hands-On Practice Learn by doing Removal Foreign
I ntroduction: Bone marrow transplantation (BMT)
 Rev Bras Otorrinolaringol 2006;72(3):328-32. ORIGINAL ARTICLE Chronic GVHD: predictive factor for rhinosinusitis in bone marrow transplantation Erica Ortiz 1, Eulalia Sakano 2, Carmino Antonio De Souza
Rev Bras Otorrinolaringol 2006;72(3):328-32. ORIGINAL ARTICLE Chronic GVHD: predictive factor for rhinosinusitis in bone marrow transplantation Erica Ortiz 1, Eulalia Sakano 2, Carmino Antonio De Souza
NECK MASS. Clinical history and examination: Document detail history of mass. Imaging: US or CT of neck
 ENT ENT Referral Referral Guidelines Guidelines Austin Health ENT Clinic holds fortnightly multidisciplinary meetings with Plastics/ Maxillary Facial and Oncology units to discuss and plan the treatment
ENT ENT Referral Referral Guidelines Guidelines Austin Health ENT Clinic holds fortnightly multidisciplinary meetings with Plastics/ Maxillary Facial and Oncology units to discuss and plan the treatment
Recognize the broad impact of hearing impairment on child and family, including social, psychological, educational and financial consequences.
 Otolaryngology Note: The goals and objectives described in detail below are not meant to be completed in a single one month block rotation but are meant to be cumulative, culminating in a thorough and
Otolaryngology Note: The goals and objectives described in detail below are not meant to be completed in a single one month block rotation but are meant to be cumulative, culminating in a thorough and
Objective assessment of autophony in patients with patulous Eustachian tube
 Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol (7) 264:1387 1391 DOI 1.17/s5-7-374-1 OTOLOGY Objective assessment of autophony in patients with patulous Eustachian tube Yoko Hori Tetsuaki Kawase Takeshi Oshima Shuichi Sakamoto
Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol (7) 264:1387 1391 DOI 1.17/s5-7-374-1 OTOLOGY Objective assessment of autophony in patients with patulous Eustachian tube Yoko Hori Tetsuaki Kawase Takeshi Oshima Shuichi Sakamoto
Use of Magill Forceps to Remove Foreign Bodies in Children
 THIEME Original Article e91 Use of Magill Forceps to Remove Foreign Bodies in Children Murat Oncel, MD 1 Guven Sadi Sunam, MD 1 Cagdas Elsurer, MD 2 Huseyin Yildiran, MD 1 1 Department of Thoracic Surgery,
THIEME Original Article e91 Use of Magill Forceps to Remove Foreign Bodies in Children Murat Oncel, MD 1 Guven Sadi Sunam, MD 1 Cagdas Elsurer, MD 2 Huseyin Yildiran, MD 1 1 Department of Thoracic Surgery,
Department of Pediatric Otolarygnology. ENT Specialty Programs
 Department of Pediatric Otolarygnology ENT Specialty Programs Staffed by fellowship-trained otolaryngologists, assisted by pediatric nurse practitioners, ENT (Otolaryngology) at Nationwide Children s Hospital
Department of Pediatric Otolarygnology ENT Specialty Programs Staffed by fellowship-trained otolaryngologists, assisted by pediatric nurse practitioners, ENT (Otolaryngology) at Nationwide Children s Hospital
Incidence of Odontogenic Sinusitis Experience in a Tertiary Care Centre
 Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/130 Incidence of Odontogenic Sinusitis Experience in a Tertiary Care Centre B G Prakash 1, Suhasini Biyyapu 2 1 Professor, Department of ENT, JSS Medical College,
Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/130 Incidence of Odontogenic Sinusitis Experience in a Tertiary Care Centre B G Prakash 1, Suhasini Biyyapu 2 1 Professor, Department of ENT, JSS Medical College,
Effectiveness of Grommet Insertion in Resistant Otitis Media with Effusion
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 35, No.1, March 2013 Effectiveness of Grommet Insertion in Resistant Otitis Media with Effusion Ali Maeed S Al-Shehri, MD, Fach Arzt* Ahmad Neklawi, MD** Ayed A Shati, MD,
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 35, No.1, March 2013 Effectiveness of Grommet Insertion in Resistant Otitis Media with Effusion Ali Maeed S Al-Shehri, MD, Fach Arzt* Ahmad Neklawi, MD** Ayed A Shati, MD,
CURRICULLUM OF ENT (U.G)
 CURRICULLUM OF ENT (U.G) OBJECTIVES: 1. To enable the student to familiarize himself with the common problems related to the subject of ENT. 2. To enable the student to be competent to evaluate the symptoms,
CURRICULLUM OF ENT (U.G) OBJECTIVES: 1. To enable the student to familiarize himself with the common problems related to the subject of ENT. 2. To enable the student to be competent to evaluate the symptoms,
Effects of adenoidectomy and adenotonsillectomy on the components of Waldeyer ring
 International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Bhat VK et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2017 Apr;3(2):290-297 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937 Original
International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Bhat VK et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2017 Apr;3(2):290-297 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937 Original
PECULIARITIES OF DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF THE ESOPHAGEAL FOREIGN BODIES (COINS) IN CHILDREN CLINICOSTATISTICAL STUDY
 7 CASE STUDIES PECULIARITIES OF DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF THE ESOPHAGEAL FOREIGN BODIES (COINS) IN CHILDREN CLINICOSTATISTICAL STUDY Corneliu Toader 1,3, Miorita Toader 2, Iolanda Cristina Vivisenco 2,3
7 CASE STUDIES PECULIARITIES OF DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF THE ESOPHAGEAL FOREIGN BODIES (COINS) IN CHILDREN CLINICOSTATISTICAL STUDY Corneliu Toader 1,3, Miorita Toader 2, Iolanda Cristina Vivisenco 2,3
Physical Examination
 Otorhinolaryngologic Approach Sasan Dabiri, M.D. Department of Otorhinolaryngology Head & Neck Surgery Amir A lam hospital Tehran University of Medical Sciences General Notes Parts of an : Inspection Palpation
Otorhinolaryngologic Approach Sasan Dabiri, M.D. Department of Otorhinolaryngology Head & Neck Surgery Amir A lam hospital Tehran University of Medical Sciences General Notes Parts of an : Inspection Palpation
Aim: The purpose of this research is to propose a
 Rev Bras Otorrinolaringol. V.71, n.3, 313-7, may/jun. 2005 ARTIGO ORIGINAL ORIGINAL ARTICLE Proposal of measurement of vertical larynx position at rest Osiris de Oliveira Camponês do Brasil 1, Rosiane
Rev Bras Otorrinolaringol. V.71, n.3, 313-7, may/jun. 2005 ARTIGO ORIGINAL ORIGINAL ARTICLE Proposal of measurement of vertical larynx position at rest Osiris de Oliveira Camponês do Brasil 1, Rosiane
Aim: To evaluate the safety of bilateral submandibular
 Rev Bras Otorrinolaringol 2007;73(1):41-5. ORIGINAL ARTICLE Drooling: analysis and evaluation of 31 children who underwent bilateral submandibular gland excision and parotid duct ligation. Dayse Manrique
Rev Bras Otorrinolaringol 2007;73(1):41-5. ORIGINAL ARTICLE Drooling: analysis and evaluation of 31 children who underwent bilateral submandibular gland excision and parotid duct ligation. Dayse Manrique
ENT Referral Guidelines
 ENT Referral Guidelines Austin Health ENT Clinic holds fortnightly multidisciplinary meetings with Plastics/ Maxillary Facial and Oncology units to discuss and plan the treatment of patients with cancerous
ENT Referral Guidelines Austin Health ENT Clinic holds fortnightly multidisciplinary meetings with Plastics/ Maxillary Facial and Oncology units to discuss and plan the treatment of patients with cancerous
Ear, nose and throat problems in Accident and Emergency
 CONTINUING PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT By reading this article and writing a practice profile, you can gain a certificate of learning. You have up to a year to send in your practice profile. Guidelines on
CONTINUING PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT By reading this article and writing a practice profile, you can gain a certificate of learning. You have up to a year to send in your practice profile. Guidelines on
The medical education of internship in surgery and otolaryngology in competence of recovery of deafness caused by cerumen
 The medical education of internship in surgery and otolaryngology in competence of recovery of deafness caused A educação médica no internato de cirurgia e otolaringologia e sua influência na competência
The medical education of internship in surgery and otolaryngology in competence of recovery of deafness caused A educação médica no internato de cirurgia e otolaringologia e sua influência na competência
The Third Annual ENT for the PA-C April 26-28, 2013
 The Third Annual ENT for the PA-C April 26-28, 2013 Presented By American Academy of Otolarynology Head and Neck Surgery Society of Physician Assistants in Head and Neck Surgery Hosted By New York Presbyterian
The Third Annual ENT for the PA-C April 26-28, 2013 Presented By American Academy of Otolarynology Head and Neck Surgery Society of Physician Assistants in Head and Neck Surgery Hosted By New York Presbyterian
Evaluation of Children with Chronic Rhinosinusitis after Adenotonsillectomy
 Iranian Journal of Otorhinolaryngology No.2, Vol.24, Serial No.67, Spring-2012 Original Article Abstract Evaluation of Children with Chronic Rhinosinusitis after Adenotonsillectomy 1* Fatholah Behnoud
Iranian Journal of Otorhinolaryngology No.2, Vol.24, Serial No.67, Spring-2012 Original Article Abstract Evaluation of Children with Chronic Rhinosinusitis after Adenotonsillectomy 1* Fatholah Behnoud
Evaluation of the Use of an Intranasal Metallic Dilator in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome Using CPAP
 Original Article Evaluation of the Use of an Intranasal Metallic Dilator in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome Using CPAP Levon Mekhitarian Neto*, José Francisco de Salles Chagas**, Rogério
Original Article Evaluation of the Use of an Intranasal Metallic Dilator in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome Using CPAP Levon Mekhitarian Neto*, José Francisco de Salles Chagas**, Rogério
Otorhinolaryngology, Head & Neck Surgery
 MB, ChB Phase IV Late Clinical Rotations Year 5-6 Otorhinolaryngology, Head & Neck Surgery Part of Clinical Rotations 65730 541/65730 678 2008 MB, ChB Phase IV: Late Clinical Rotations 2008 OTORHINOLARYNGOLOGY,
MB, ChB Phase IV Late Clinical Rotations Year 5-6 Otorhinolaryngology, Head & Neck Surgery Part of Clinical Rotations 65730 541/65730 678 2008 MB, ChB Phase IV: Late Clinical Rotations 2008 OTORHINOLARYNGOLOGY,
ENT Procedures Workshop
 March 19, 2015 Newport Beach, CA ENT Procedures Jose C. Mercado, PA-C, MMS, DFAAPA Updated 01/24/2015 ENT Procedures Workshop Clear Live Hands On Instruction Demonstration Practice Learn by doing Removal
March 19, 2015 Newport Beach, CA ENT Procedures Jose C. Mercado, PA-C, MMS, DFAAPA Updated 01/24/2015 ENT Procedures Workshop Clear Live Hands On Instruction Demonstration Practice Learn by doing Removal
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Eustachian tube function in adults with intact tympanic membrane. pressure, protecting the middle ear from abrupt pressure changes.
 Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2010;76(3):340-6. ORIGINAL ARTICLE BJORL Eustachian tube function in adults with intact tympanic membrane.org Renata Rumy Makibara 1, Jackeline Yumi Fukunaga 2, Daniela Gil 3 Keywords:
Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2010;76(3):340-6. ORIGINAL ARTICLE BJORL Eustachian tube function in adults with intact tympanic membrane.org Renata Rumy Makibara 1, Jackeline Yumi Fukunaga 2, Daniela Gil 3 Keywords:
East and Central African Journal of Surgery Volume 15 Number 2. July/August 2010.
 Prevalence of Otolaryngological diseases in Nigerians. J.A.E. Eziyi, Y.B. Amusa, O.V. Akinpelu ORL Unit, Department of Surgery, Obafemi Awolowo University, Ile-Ife, Osun State, Nigeria. Correspondence
Prevalence of Otolaryngological diseases in Nigerians. J.A.E. Eziyi, Y.B. Amusa, O.V. Akinpelu ORL Unit, Department of Surgery, Obafemi Awolowo University, Ile-Ife, Osun State, Nigeria. Correspondence
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 4/ Issue 85/ Oct. 22, 2015 Page 14800
 HISTOPATHOLOGY IN CHRONIC TONSILLITIS A RETROSPECTIVE ANALYSIS P. Thirunavukarasu 1, K. Priya 2, S. B. Jothiramalingam 3, Jagadeesh Marthandam 4, P. Preethi 5, S. Prabakaran 6, R. Sivakami 7, R. B. Namasivaya
HISTOPATHOLOGY IN CHRONIC TONSILLITIS A RETROSPECTIVE ANALYSIS P. Thirunavukarasu 1, K. Priya 2, S. B. Jothiramalingam 3, Jagadeesh Marthandam 4, P. Preethi 5, S. Prabakaran 6, R. Sivakami 7, R. B. Namasivaya
Scottish Parliament Region: Lothian. Case : Lothian NHS Board. Summary of Investigation. Category Health: Hospital; cancer; diagnosis
 Scottish Parliament Region: Lothian Case 201202271: Lothian NHS Board Summary of Investigation Category Health: Hospital; cancer; diagnosis Overview The complainant (Mr C) attended the Ear, Nose and Throat
Scottish Parliament Region: Lothian Case 201202271: Lothian NHS Board Summary of Investigation Category Health: Hospital; cancer; diagnosis Overview The complainant (Mr C) attended the Ear, Nose and Throat
CLINICAL PROFILE AND MANAGEMENT AUDIT OF EAR WAX IMPACTION IN OWERRI, SOUTH EAST NIGERIA
 ISSN: 2250-0359 Volume 4 Issue 4 2014 CLINICAL PROFILE AND MANAGEMENT AUDIT OF EAR WAX IMPACTION IN OWERRI, SOUTH EAST NIGERIA IBIAM FA I NDUAGU S I, OBASIKENE G II MBATA G. III 1 ENT Department FMC Owerri
ISSN: 2250-0359 Volume 4 Issue 4 2014 CLINICAL PROFILE AND MANAGEMENT AUDIT OF EAR WAX IMPACTION IN OWERRI, SOUTH EAST NIGERIA IBIAM FA I NDUAGU S I, OBASIKENE G II MBATA G. III 1 ENT Department FMC Owerri
Foreign Body Aspiration in Paediatric Airway
 Available online at www.ijmrhs.com ISSN No: 2319-5886 International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences, 2017, 6(3): 17-21 Foreign Body Aspiration in Paediatric Airway Dhupar Puja 1, Rathod Arun
Available online at www.ijmrhs.com ISSN No: 2319-5886 International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences, 2017, 6(3): 17-21 Foreign Body Aspiration in Paediatric Airway Dhupar Puja 1, Rathod Arun
Acute Otitis Media, Acute Bacterial Sinusitis, and Acute Bacterial Rhinosinusitis
 Acute Otitis Media, Acute Bacterial Sinusitis, and Acute Bacterial Rhinosinusitis This guideline, developed by Larry Simmons, MD, in collaboration with the ANGELS team, on October 3, 2013, is a significantly
Acute Otitis Media, Acute Bacterial Sinusitis, and Acute Bacterial Rhinosinusitis This guideline, developed by Larry Simmons, MD, in collaboration with the ANGELS team, on October 3, 2013, is a significantly
Surgical Privileges Form: ORL - HNS
 Surgical Form: ORL - HNS Clinical Request Applicant s Name:. License No. (If Any):... Date:... Scope of Practice:. Facility:.. Place of Work:. CATEGORY I: GENERAL PRIVILEGES 1. Admitting privileges 2.
Surgical Form: ORL - HNS Clinical Request Applicant s Name:. License No. (If Any):... Date:... Scope of Practice:. Facility:.. Place of Work:. CATEGORY I: GENERAL PRIVILEGES 1. Admitting privileges 2.
Dynamics In The Trend Of Foreign Bodies In ENT Practice In Nigeria: Any Change?
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Volume 14 Number 2 Dynamics In The Trend Of Foreign Bodies In ENT Practice In Nigeria: Any Change? N Onyeagwara, A Okhahku, E Emokpaire, F Ogisi Citation
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Volume 14 Number 2 Dynamics In The Trend Of Foreign Bodies In ENT Practice In Nigeria: Any Change? N Onyeagwara, A Okhahku, E Emokpaire, F Ogisi Citation
Original Article. Relieving Symptoms of Chronic Sinusitis in Children By Adenoidectomy
 Original Article Relieving Symptoms of Chronic Sinusitis in Children By Adenoidectomy * C.A.B.M.S/ENT Summary: Background: To determine the efficacy of adenoidectomy in relieving symptoms of chronic sinusitis
Original Article Relieving Symptoms of Chronic Sinusitis in Children By Adenoidectomy * C.A.B.M.S/ENT Summary: Background: To determine the efficacy of adenoidectomy in relieving symptoms of chronic sinusitis
4 ENT. 4.1 Bone anchored hearing aids. 4.2 Cochlear implants. (
 4 ENT 4.1 Bone anchored hearing aids This commissioning responsibility has transferred to NHS England (http://www.england.nhs.uk/). Queries around treatment availability and eligibility, as well as referrals
4 ENT 4.1 Bone anchored hearing aids This commissioning responsibility has transferred to NHS England (http://www.england.nhs.uk/). Queries around treatment availability and eligibility, as well as referrals
Dine & Learn - Victoria May 2015 Otolaryngology
 Dine & Learn - Victoria May 2015 Otolaryngology Allergic rhinitis Allergic rhinitis guidelines (Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery 2015) Diagnosis: history: allergen + either nasal congestion or runny
Dine & Learn - Victoria May 2015 Otolaryngology Allergic rhinitis Allergic rhinitis guidelines (Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery 2015) Diagnosis: history: allergen + either nasal congestion or runny
A study of comparison between the efficacy of endoscopic septoplasty and traditional septoplasty
 International Surgery Journal Yadav PK et al. Int Surg J. 2016 Aug;3(3):1134-1140 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20162190
International Surgery Journal Yadav PK et al. Int Surg J. 2016 Aug;3(3):1134-1140 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20162190
Paediatric ENT problems
 Paediatric ENT problems Ears Otitis media Otitis media with effusion FBs Otitis externa Ruptured TM Nose FBs Allergic rhinitis Septal perforation expistaxis Throat FB Croup Stidor Tonsillitis Paediatric
Paediatric ENT problems Ears Otitis media Otitis media with effusion FBs Otitis externa Ruptured TM Nose FBs Allergic rhinitis Septal perforation expistaxis Throat FB Croup Stidor Tonsillitis Paediatric
White Paper: Balloon Sinuplasty for Chronic Sinusitis, The Latest Recommendations
 White Paper: Balloon Sinuplasty for Chronic Sinusitis, The Latest Recommendations For Health Plans, Medical Management Organizations and TPAs Executive Summary Despite recent advances in instrumentation
White Paper: Balloon Sinuplasty for Chronic Sinusitis, The Latest Recommendations For Health Plans, Medical Management Organizations and TPAs Executive Summary Despite recent advances in instrumentation
Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery
 WHAT IS FUNCTIONAL ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY (FESS)? The nasal telescope has greatly changes the evaluation and treatment of rhino-sinusitis. This instrument, which provides a view of the structures in
WHAT IS FUNCTIONAL ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY (FESS)? The nasal telescope has greatly changes the evaluation and treatment of rhino-sinusitis. This instrument, which provides a view of the structures in
Rohan R. Walvekar, MD. Basic Sialendoscopy Set. Basic Sialendoscopy Set. Disclosure I have the following relationship(s) with commercial interests.
 UCSF Salivary Endoscopy Course 2014 Basic Set Up and Instruments Rohan R. Walvekar, MD Department of Otolaryngology & Head Neck Surgery Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center New Orleans, LA
UCSF Salivary Endoscopy Course 2014 Basic Set Up and Instruments Rohan R. Walvekar, MD Department of Otolaryngology & Head Neck Surgery Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center New Orleans, LA
Pediatrics Grand Rounds 25 October University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio, Texas
 PEDIATRIC ENT & YOU A PATIENT CARE PARTNERSHIP Disclosure Timothy McEvoy, MD has no relevant relationships with commercial interests to disclose. Timothy McEvoy, MD UTHSCSA Department of Otolaryngology-
PEDIATRIC ENT & YOU A PATIENT CARE PARTNERSHIP Disclosure Timothy McEvoy, MD has no relevant relationships with commercial interests to disclose. Timothy McEvoy, MD UTHSCSA Department of Otolaryngology-
ICD10 CODES CODE DESCRIPTION R Abnormal auditory function study H Abnormal auditory perception, bilateral H Abnormal auditory
 ICD10 CODES CODE DESCRIPTION R94.120 Abnormal auditory function study H93.293 Abnormal auditory perception, bilateral H93.292 Abnormal auditory perception, left ear H93.291 Abnormal auditory perception,
ICD10 CODES CODE DESCRIPTION R94.120 Abnormal auditory function study H93.293 Abnormal auditory perception, bilateral H93.292 Abnormal auditory perception, left ear H93.291 Abnormal auditory perception,
Tonsillectomy Hemorrhage. DR Tran Quoc Huy ENT department
 Tonsillectomy Hemorrhage complication DR Tran Quoc Huy ENT department Topic Outline INTRODUCTION OVERVIEW OF INDICATIONS CONTRAINDICATIONS COMPLICATIONS HEMORRHAGE COMPLICATION INTRODUCTION Tonsillectomy
Tonsillectomy Hemorrhage complication DR Tran Quoc Huy ENT department Topic Outline INTRODUCTION OVERVIEW OF INDICATIONS CONTRAINDICATIONS COMPLICATIONS HEMORRHAGE COMPLICATION INTRODUCTION Tonsillectomy
TOOTH BRUSH INJURY: A CASE REPORT
 TOOTH BRUSH INJURY: A CASE REPORT Veerakumar.R 1 Pavithra.J 2 Rohini.M 2 Suganya.M 2 PRIYADARSHINI DENTAL COLLEGE AND HOSPITAL,THIRUVALLUR. 1. Professor, Head of the Department, Department of Pedodontics
TOOTH BRUSH INJURY: A CASE REPORT Veerakumar.R 1 Pavithra.J 2 Rohini.M 2 Suganya.M 2 PRIYADARSHINI DENTAL COLLEGE AND HOSPITAL,THIRUVALLUR. 1. Professor, Head of the Department, Department of Pedodontics
SD-DS. 34 INTERNATIONAL MEDICAL JOURNAL ON DOWN SYNDROME 2003: vol. 7, núm. 3, pp
 34 INTERNATIONAL MEDICAL JOURNAL ON DOWN SYNDROME 2003: vol. 7, núm. 3, pp. 34-38 Original Relationship between the size of the ear canal and Eustachian tube function in Down syndrome Joan Domènech 1-2,
34 INTERNATIONAL MEDICAL JOURNAL ON DOWN SYNDROME 2003: vol. 7, núm. 3, pp. 34-38 Original Relationship between the size of the ear canal and Eustachian tube function in Down syndrome Joan Domènech 1-2,
TYMPANOPLASTY WITH OR WITHOUT MASTOIDECTOMY SURGICAL INSTRUCTIONS
 Head and Neck Associates of Orange County, Inc. An Incorporated Medical Group Head & Neck Surgery Pediatric & Adult Otolaryngology Facial Reconstructive Surgery TYMPANOPLASTY WITH OR WITHOUT MASTOIDECTOMY
Head and Neck Associates of Orange County, Inc. An Incorporated Medical Group Head & Neck Surgery Pediatric & Adult Otolaryngology Facial Reconstructive Surgery TYMPANOPLASTY WITH OR WITHOUT MASTOIDECTOMY
