Work Design and Industrial Ergonomics - Ear and Noise
|
|
|
- Grant Norton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Department of Industrial Engineering Work Design and Industrial Ergonomics - Ear and Noise
2 Elements of the Office Environment Workstation Design (Physical) Health Outcomes Work Organization (Job design) PERSON Job Satisfaction Psychosocial (Job control, etc) Productivity/Quality
3 Hearing Sound is created by vibrations from a source and is transmitted through a media (such as the atmosphere) to the ear. Sound has two main attributes: Frequency of Sound Waves and Sound intensity 1. Frequency of Sound Waves: When sound is generated, it causes vibration and makes the air molecules to be moved back and forth. This alternation creates corresponding increase and decreases in the air pressure.
4 1. Frequency of Sound Waves The vibration forms sinusoidal (sine) waves. The height of the wave above and below the midline represents the amount of above-normal and below-normal air pressure respectively. The waveform above the midline is the image of the waveform below the midline in a sine wave. The waveform repeats itself again and again in a sine wave. The number of cycles per second is called the frequency of the sound. Frequency is expressed in hertz (Hz) and is equivalent to cycles per second. The human ear is sensitive to frequencies in the range of 20 to 20,000 Hz (highest sensitivity between 1000 to 3000 Hz), but it is not equally sensitive to all frequencies. In addition, people differ in their relative sensitivities to various frequencies.
5 2.Sound intensity It is defined in terms of power per unit area. The Bel (B) is the basic unit for measuring sound. The most convenient measure is the decibel (db), 1 db=0.1b.
6 Complex Sounds Very few sounds are pure. Most complex sounds are nonharmonic. Masking: It is the condition when one component of the sound environment reduces the sensitivity of the ear to another component.
7 AUDIOTORY DISPLAYS There are four types of human functions involved in the reception of auditory signals: 1. Detection 2. Relative discrimination (differentiating between two or more signals presented together) 3. Absolute identification (only one signal is present) 4. Localization (knowing the direction that the signal is coming from)
8 Summary: How Sound Travels Through The Ear Acoustic energy, in the form of sound waves, is channeled into the ear canal by the pinna. Sound waves hit the tympanic membrane and cause it to vibrate, like a drum, changing it into mechanical energy. The malleus, which is attached to the tympanic membrane, starts the ossicles into motion. The stapes moves in and out of the oval window of the cochlea creating a fluid motion, or hydraulic energy. The fluid movement causes membranes in the Organ of Corti to shear against the hair cells. This creates an electrical signal which is sent up the Auditory Nerve to the brain. The brain interprets it as sound!
9 Detection of signals Signals can occur in peaceful surroundings or noisy surroundings. The signal plus the noise (SN) should be distinct from the noise (N) itself. If the above is not the case, the signal can not be detected in the presence of noise. The threshold of the detectability of the signal is elevated. This threshold should be exceeded by the signal if it is to be detected accurately. What Level? Annoyance?
10 Relative Discrimination Relative discrimination of signals on the basis of intensity and frequency depends in part on interactions between these two dimensions. A common measure is the just-noticeable difference (JND). JND is the smallest difference or change along a stimulus dimension that can just be detected 50% of the time by people. The smaller the JND, the easier it is for people to detect differences on the dimension being changed.
11 Absolute Identification The number of levels along a continuum (range or scale) that can identified usually is quiet small. It is better to use more dimensions with fewer steps or levels of each dimension than to use fewer dimensions and more levels of each. Localization The ability to localize (guess the direction of sound) the direction from which the sound is coming from is called stereophony. People mostly relay on intensity and phase of sound to determine the direction of sound.
12 The Outer Ear Consists of The Pinna - cartilaginous, highly variable in appearance, some landmarks. External Auditory Canal (or external auditory meatus) cm tube.
13 Anatomy of the Human Ear
14 Anatomy of the Human Ear
15 Generated by Foxit PDF Creator Foxit Software
16 Main Components of the Hearing Mechanism Outer Ear Middle Ear Inner Ear Central Auditory Nervous System
17 Noise Convection and Conduction
18 Structures of the Outer Ear Auricle (Pinna) Collects sound Helps in sound localization Most efficient in directing high frequency sounds to the eardrum
19 External Auditory Canal Approximately 1¼ inch in length S shaped Lined with cerumen glands Outer 1/3rd cartilage; inner 2/3rds mastoid bone Increases sound pressure at the tympanic membrane by as much as 5-6 db (due to acoustic resonance)
20 Structures of the Inner Ear Cochlea - Snail-shaped organ with a series of fluid-filled tunnels; converts mechanical energy into electrical energy 20
21 Physiology of the Cochlea
22 Cochlea Cilia
23 Operation of the Cochlea
24 Structures of the Inner Ear (Cont.) Oval Window located at the footplate of the stapes; when the footplate vibrates, the cochlear fluid is set into motion Round Window functions as the pressure relief port for the fluid set into motion initially by the movement of the stapes in the oval window
25 Structures of the Inner Ear (Cont.) Oval Window located at the footplate of the stapes; when the footplate vibrates, the cochlear fluid is set into motion Round Window functions as the pressure relief port for the fluid set into motion initially by the movement of the stapes in the oval window
26 Cochlear Functions Transduction- Converting acoustical-mechanical energy into electro-chemical energy. Frequency Analysis-Breaking sound up into its component frequencies Bekesy s Traveling Wave Active Tuning from OHCs
27 Hair Cells q q Frequency-specific High pitch sounds = base of cochlea Low pitch sounds = apex of cochlea When the basilar membrane moves, a shearing action between the tectorial membrane and the organ of Corti causes hair cells to bend
28 Healthy Cochlea The cilia ( sensory hairs) appear normal
29 Central Auditory System 8th Cranial Nerve or Auditory Nerve carries signals from cochlea to brain Fibers of the auditory nerve are present in the hair cells of the inner ear Auditory Cortex: Temporal lobe of the brain where sound is perceived and analyzed
30 Hearing
31 NOISE Noise is referred to as unwanted sound. In the context of information theory, noise is defined as that auditory stimulus of stimuli bearing no informational relationship to the presence or completion of the immediate task. How loud is it? Loudness depends on intensity and frequency. A low frequency tone will not sound as loud as a high frequency sound of the same intensity.
32 NOISE Noise is any annoying, disturbing or unwanted sound. Noise effects on people : irritate people; interfere with verbal communication; reduce working efficiency; disturb sleep; damage hearing. The effects of noise: Deafness The main effect of noise is the development of deafness, especially when you are exposed to high levels of continuous noise. This may result in 'noise-induced occupational deafness'.
33 NOISE Noise is distracting Interfere with communication Affects the ability to concentrate Excessive Noise can result in hearing loss Hearing can be affected by a noise level of 85dBA over an 8 hour exposure, this usually affects the ability to hear higher frequency sounds
34 How loud is it? One of the most important effects of noise is hearing loss. Occupational hearing loss. Temporary loss, permanent loss. Continuous noise or non-continuous noise. Physiological effects of noise.
35 Sound Levels
36 Hearing Protection when is it required? There are regulations that state when hearing protection is mandatory; however, a good rule of thumb is that hearing protection should be used if you have to shout at someone standing 3 feet away from you to be heard over the noise. The two most frequent problems L&I encounters are people not wearing the hearing protection when it is required or not wearing it correctly.
37 Effects of Noise Exposure Hearing Loss From Noise Exposure Hearing loss from noise exposure is usually not noticed because it is so gradual. Usually a person loses the ability to hear higher pitches first. Often the first noticeable effect is difficulty in hearing speech.
38 Effects of Noise Exposure The damage from exposure to noise occurs in the inner ear. There are tiny hair cells in this part of the ear that are flattened out when exposed to noise. If the exposure is short, the hair cells raise back up. If the exposure is long or extremely loud, the hair cells don t recover and hearing ability is reduced. When all the hair cells are damaged, complete deafness occurs. People who say they are used to the noise often have already lost some of their hearing. Damage occurs in this part of the ear
39 Types of Hearing Protection earmuffs The WISHA noise regulations require that we have at least 2 types of hearing protection to choose from. There are three types of hearing protection ear muffs, earplugs and ear caps. Ear muffs and earplugs provide about equal protection, ear caps somewhat less. earplugs ear caps
40 Hearing Protection Types of Hearing Protectors All hearing protectors are designed to reduce the intensity (loudness) of noise to the inner ear. They work much better than wads of cotton or bits of cloth stuffed in the ear. All three types have advantages and disadvantages and people vary on which they prefer to use. Cotton doesn t work!!
41 Ear Plugs Earplugs are made of foam, rubber or plastic and are either one-size-fits-all or in sizes small, medium and large. Some are disposable, some are reusable. They are lightweight, and require no maintenance. They are inserted into the ear canal. Some earplugs have little handles for use in dirty environments. 41
42 Inserting Foam Earplugs Foam type earplugs are one-size-fits-all and must be inserted properly into the ear. Roll earplug into small cylinder first, then insert in ear. The technique for inserting earplugs is to first, roll the earplug into a small cylinder, pull the ear up and back, this opens the ear canal. Push the ear plug into the ear canal and hold there for a few seconds until it expands and fills the ear canal. This will provide the tightest fit and greatest protection. 42
43 Inserting Foam Earplugs Earplug incorrectly inserted Earplug correctly inserted The left picture shows plugs only partially inserted into the ear canal a common mistake.
44 Facts About Ear caps Do not have same noise reduction as earplugs or ear muffs because they do not penetrate the ear canal and the seal is not as tight as earplugs More expensive than earplugs and disposable tips are not as readily available People tend to use when dirty like the ones in the photo Not the best choice for a logging environment
45 Attached Earmuffs Some muffs are attached to hardhats or goggles and are somewhat less protective than stand alone earmuffs. Some high-tech muffs can filter out certain frequencies or have radios inside for communication in high noise areas. Earplugs can be worn under earmuffs for really loud noise levels
46 Employer s Responsibility What the WISHA Rules Require Hearing Protection--The employer must provide hearing protection for all employees that have an eight hour time weighted exposure of 85 dba or above, who have any continuous exposure at or above 115 dba, or who have an exposure to any impulse noise levels above 140 db.
47 Effects of Noise Exposure Daily Allowable Exposure Times to Noise The table below shows noise levels and how long a person can be exposed without hearing protection before there is damage to the ear. Noise Level Allowable Exposure Time 85 decibels 8 hours 90 decibels 4 hours 100 decibels 1 hour 105 decibels 30 minutes 110 decibels 15 minutes 115 decibels 0 minutes
48 Noise and performance Noise causes fatigue and loss of concentration and efficiency, resulting in a decrease in work output and an increase in the number of mistakes made. The World Health Organization (WHO) provides some guidance on acceptable levels of noise in the community.
49 Noise and Loudness
50 NOISE EXPOSURE CAN BE REDUCED BY SUBSTITUTE WITH A QUIETER PROCESS OR EQUIPMENT SEPARATE EMPLOYEES FROM NOISY EQUIPMENT CHANGE THE DIRECTION OF THE NOISE ABSORB THE NOISE WITH SOUND DAMPENERS
51 Recently Measured Noise Levels in Logging Cutters 11 Monitored Ranged from 90.3 up to 96.8 dba Saws were Stihl and Husky
52 Measured Noise Levels in Logging Chasers 21 monitored Noise levels ranged from 87.8 up to 95.7 dba Wide range of equipment configurations Yarder Shovel Power saw Operators 8 Monitored Skidders, Shovels and Yarders were all in the 90 decibel range ( dba Noise levels can vary greatly depending on whether the doors & windows are open or closed on the machines.
53 Two Types of Hearing Loss Conductive Sensory
54 Conductive Hearing Loss Caused by damage to or a malfunction of the outer and middle ear Some causes excessive ear wax fluid in the ear a torn eardrum Colds Usually hearing is restored once the cause is diagnosed and treated
55 Sensory Hearing Loss Caused by damage to or a malfunction of the inner ear, auditory nerve, or the brain Causes of sensory hearing loss Aging, Damage to fetus, Hereditary, Noise, Disease, Injury, Drugs
56 Damaged Cochlea Loss of cilia as a result of Noise
57 NOISE HAZARD EVALUATION Purpose To identify noise hazardous areas To document the magnitude of the noise hazard To aid in the implementation of a hearing conservation program To protect personnel from developing a noise-induced hearing loss To implement engineering controls
58 Survey Intervals Annually-in all areas to identify potential noise hazards AND to re-survey all previously identified noise hazards Within 30 days of a procedural or equipment change that affect ambient noise Whenever noise makes it difficult for two people, with good hearing, to converse at arm s length
59 Who can perform sound level surveys? Audiologist Industrial Hygienist A suitably trained technician
60 Sound Level Meters Calibrated noise measuring device which meets the criteria of ANSI Standard S (R 1983) Microphone (transducer) Amplifier Weighting network Slow/fast averager Display meter Analog Digital
61 Type I Precision SLM Tolerance of + or 1 db accuracy Individual octave band measurements Required for booth certification Cost: $2,000.00
62 Type II SLM Used routinely for surveys in the field Has individual weightings networks: A weighing B weighing C weighing Cost: $ to $600.00
63 Procedures for operation Check electroacoustic calibration date-must be within one year Set meter response to appropriate weighing for calibrator, and slow response Check meter response with field calibrator must be within 1 db of calibration source level Set weighing to A and meter response to Slow Adjust meter range until display is seen Read display Record results on NEHC form 5100/17Recheck field calibration Maintain records for 40 years
64 Source of Error Reading (averaging) errors Wrong scale setting Wrong microphone position
65 Distance from Source Inverse square law applies: Each time the distance from a source is doubled, in a free field, the sound pressure level drops by 6dB This principal is used to define the noise hazard radius
66 Care of SLM things to Avoid Excessive heat High humidity (>90%) Hard blows or shocks Handling of microphone Excessive dust Strong electromagnetic fields Pegging the needle
67 Sound Levels and Hearing Conservation Noise measurements are essential HCP enrollment base on: Noise survey data-sound level surveys or dosimetry Job/task factors-length of exposure, level of noise/vibration Patient specific factors-pre-existing hearing loss or ear disease
68 Test Room Certification Principals of Sound Reduction Permit test signal to be heard at threshold levels Reduce sound by producing an acoustical barrier to sound transmission Reduce high frequencies more than low
69 Factors Affecting Performance Vibration Vibration isolators or shock mounts for control Ventilation systems and muffler Door seals Test with the light test or paper test Lighting
70 Accuracy of Sound Level Readings Affecting Factors The body baffle effect Shielding effect Wind noise
71 Masking Masking Effect: when two sounds are present at the same time One signal may mask or cover up the other This can result in false threshold for hearing during audiometric testing Masking typically occurs when the interfering noise is low in frequency White Noise
72 OSHA Noise Standard 2 Program Strategy Noise Exposure Program 90 dba 8 hour TWA(Equivalent Exposure Concept) Hearing Conservation Program 85 dba 8 hour TWA TWA- Time Weighted Average
73 Noise Measuring Equipment Sound Level Meters (SLM) Continuous on-mobile sources Noise Dosimeters Mobile/variable noise sources
Work Design and Industrial Ergonomics - Ear and Noise
 Department of Industrial Engineering Work Design and Industrial Ergonomics - Ear and Noise Learning outcomes After finishing this chapter, You should be able to Define the sound (physically) and how it
Department of Industrial Engineering Work Design and Industrial Ergonomics - Ear and Noise Learning outcomes After finishing this chapter, You should be able to Define the sound (physically) and how it
ENT 318 Artificial Organs Physiology of Ear
 ENT 318 Artificial Organs Physiology of Ear Lecturer: Ahmad Nasrul Norali The Ear The Ear Components of hearing mechanism - Outer Ear - Middle Ear - Inner Ear - Central Auditory Nervous System Major Divisions
ENT 318 Artificial Organs Physiology of Ear Lecturer: Ahmad Nasrul Norali The Ear The Ear Components of hearing mechanism - Outer Ear - Middle Ear - Inner Ear - Central Auditory Nervous System Major Divisions
E4061 Hearing Conservation: Are You Listening, Jim? Leader s Guide
 E4061 Hearing Conservation: Are You Listening, Jim? Leader s Guide ARE YOU LISTENING, JIM? This easy-to-use Leader s Guide is provided to assist in conducting a successful presentation. Featured are: INTRODUCTION
E4061 Hearing Conservation: Are You Listening, Jim? Leader s Guide ARE YOU LISTENING, JIM? This easy-to-use Leader s Guide is provided to assist in conducting a successful presentation. Featured are: INTRODUCTION
Health, Safety, Security and Environment
 Document owner and change code Document Owner Aaron Perronne Title HSSE Manager Mark X Change Code Description X N/A First Issue A Typographical/Grammatical correction; formatting change; text clarification-no
Document owner and change code Document Owner Aaron Perronne Title HSSE Manager Mark X Change Code Description X N/A First Issue A Typographical/Grammatical correction; formatting change; text clarification-no
Protect Your Hearing
 S-76 Purdue University Cooperative Extension Service West Lafayette, IN 47907 Protect Your Hearing F. R. Willsey Professor Emeritus of Agricultural Engineering Most people think of farming as the quiet
S-76 Purdue University Cooperative Extension Service West Lafayette, IN 47907 Protect Your Hearing F. R. Willsey Professor Emeritus of Agricultural Engineering Most people think of farming as the quiet
NOISE CONTROL AND HEARING CONSERVATION PROGRAM
 NOISE CONTROL AND HEARING CONSERVATION PROGRAM R1 PAGE 1 OF 13 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.0 INTRODUCTION 2.0 SCOPE AND APPLICATION 3.0 CRITERIA FOR NOISE EXPOSURE 3.1 Individual Exposure 3.2 Noise Areas 4.0 PROGRAM
NOISE CONTROL AND HEARING CONSERVATION PROGRAM R1 PAGE 1 OF 13 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.0 INTRODUCTION 2.0 SCOPE AND APPLICATION 3.0 CRITERIA FOR NOISE EXPOSURE 3.1 Individual Exposure 3.2 Noise Areas 4.0 PROGRAM
Hearing. and other senses
 Hearing and other senses Sound Sound: sensed variations in air pressure Frequency: number of peaks that pass a point per second (Hz) Pitch 2 Some Sound and Hearing Links Useful (and moderately entertaining)
Hearing and other senses Sound Sound: sensed variations in air pressure Frequency: number of peaks that pass a point per second (Hz) Pitch 2 Some Sound and Hearing Links Useful (and moderately entertaining)
Sound. Audition. Physics of Sound. Properties of sound. Perception of sound works the same way as light.
 Sound Audition Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
Sound Audition Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
Audition. Sound. Physics of Sound. Perception of sound works the same way as light.
 Audition Sound Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
Audition Sound Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
College of Medicine Dept. of Medical physics Physics of ear and hearing /CH
 College of Medicine Dept. of Medical physics Physics of ear and hearing /CH 13 2017-2018 ***************************************************************** o Introduction : The ear is the organ that detects
College of Medicine Dept. of Medical physics Physics of ear and hearing /CH 13 2017-2018 ***************************************************************** o Introduction : The ear is the organ that detects
NC Employees Workplace Program Requirements for Safety and Health. Hearing Conservation
 Scope NC Employees Workplace Program Requirements for Hearing Conservation The employer shall administer a continuing, effective hearing conservation program, whenever employee noise exposures equal or
Scope NC Employees Workplace Program Requirements for Hearing Conservation The employer shall administer a continuing, effective hearing conservation program, whenever employee noise exposures equal or
Vision Painting Inc. Safety Management System
 HEARING / NOISE CONSERVATION 1. INTRODUCTION Written in 1983, the OSHA Hearing Conservation Standard (29CFR1910.95 Occupational Noise Exposure) requires that employers implement a hearing conservation
HEARING / NOISE CONSERVATION 1. INTRODUCTION Written in 1983, the OSHA Hearing Conservation Standard (29CFR1910.95 Occupational Noise Exposure) requires that employers implement a hearing conservation
Occupational Noise & Hearing Loss Presented at CopperPoint SafetyWorks 2016 By Ms. Robyn Steiner, MSPH CIH CSP June 8 and 15, 2016
 & Hearing Loss Presented at CopperPoint SafetyWorks 2016 By Ms. Robyn Steiner, MSPH CIH CSP June 8 and 15, 2016 www.atcgroupservices.com Can You Imagine? Not being able to Hear what the other person is
& Hearing Loss Presented at CopperPoint SafetyWorks 2016 By Ms. Robyn Steiner, MSPH CIH CSP June 8 and 15, 2016 www.atcgroupservices.com Can You Imagine? Not being able to Hear what the other person is
HEARING CONSERVATION PROCEDURE
 HEARING CONSERVATION PROCEDURE 1. PURPOSE The purpose of this procedure is to prevent permanent and temporary occupational hearing loss that may result from impulsive, intermittent or continuous noise
HEARING CONSERVATION PROCEDURE 1. PURPOSE The purpose of this procedure is to prevent permanent and temporary occupational hearing loss that may result from impulsive, intermittent or continuous noise
Occupational Noise Exposure
 Occupational Noise Exposure Hearing Conservation Training Program Presented by the Office of Environmental Health and Safety Did You Know? About 30 million workers are exposed to hazardous noise on the
Occupational Noise Exposure Hearing Conservation Training Program Presented by the Office of Environmental Health and Safety Did You Know? About 30 million workers are exposed to hazardous noise on the
SOUTHERN UTAH UNIVERSITY S WRITTEN HEARING CONSERVATION PROGRAM December 2017
 SOUTHERN UTAH UNIVERSITY S WRITTEN HEARING CONSERVATION PROGRAM December 2017 1.0 PURPOSE: The objective of the Southern Utah University hearing conservation program is to minimize occupational hearing
SOUTHERN UTAH UNIVERSITY S WRITTEN HEARING CONSERVATION PROGRAM December 2017 1.0 PURPOSE: The objective of the Southern Utah University hearing conservation program is to minimize occupational hearing
3882 Hearing Conservation Training for Employees. Leader s Guide ERI Safety Videos
 3882 Hearing Conservation Training for Employees Leader s Guide 2008 ERI Safety Videos HEARING CONSERVATION TRAINING FOR EMPLOYEES This easy-to-use Leader s Guide is provided to assist in conducting a
3882 Hearing Conservation Training for Employees Leader s Guide 2008 ERI Safety Videos HEARING CONSERVATION TRAINING FOR EMPLOYEES This easy-to-use Leader s Guide is provided to assist in conducting a
North Dakota State University Noise/Hearing Conservation
 North Dakota State University Noise/Hearing Conservation I. Introduction A number of job functions at NDSU may require varying degrees of hearing protection against the effects of hazardous noise. When
North Dakota State University Noise/Hearing Conservation I. Introduction A number of job functions at NDSU may require varying degrees of hearing protection against the effects of hazardous noise. When
Hearing Conservation Program
 Hearing Conservation Program 1.0 Scope and Application The following procedures describe procedures for assessing and controlling excessive occupational noise exposure as directed by University policy
Hearing Conservation Program 1.0 Scope and Application The following procedures describe procedures for assessing and controlling excessive occupational noise exposure as directed by University policy
Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis. Lecture 29. Hearing
 Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 29 A dangerous device. Hearing The sound stimulus is changes in pressure The simplest sounds vary in: Frequency: Hertz, cycles per second. How fast the
Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 29 A dangerous device. Hearing The sound stimulus is changes in pressure The simplest sounds vary in: Frequency: Hertz, cycles per second. How fast the
PSY 310: Sensory and Perceptual Processes 1
 Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 29 A dangerous device. Hearing The sound stimulus is changes in pressure The simplest sounds vary in: Frequency: Hertz, cycles per second. How fast the
Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 29 A dangerous device. Hearing The sound stimulus is changes in pressure The simplest sounds vary in: Frequency: Hertz, cycles per second. How fast the
Hearing Conservation Program
 1. Introduction The University of Denver (HCP) is written in accordance with the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) General Industry Standard Occupational Exposure to Noise CFR 1910.95
1. Introduction The University of Denver (HCP) is written in accordance with the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) General Industry Standard Occupational Exposure to Noise CFR 1910.95
noise induced Working Together to Prevent Hearing Loss
 noise induced hearing loss (NIHL) Working Together to Prevent Hearing Loss NOISE INDUCED HEARING LOSS Noise and its Effects Noise is a serious and widespread problem in many New Brunswick workplaces. Over
noise induced hearing loss (NIHL) Working Together to Prevent Hearing Loss NOISE INDUCED HEARING LOSS Noise and its Effects Noise is a serious and widespread problem in many New Brunswick workplaces. Over
Required Slide. Session Objectives
 Auditory Physiology Required Slide Session Objectives Auditory System: At the end of this session, students will be able to: 1. Characterize the range of normal human hearing. 2. Understand the components
Auditory Physiology Required Slide Session Objectives Auditory System: At the end of this session, students will be able to: 1. Characterize the range of normal human hearing. 2. Understand the components
Hearing. istockphoto/thinkstock
 Hearing istockphoto/thinkstock Audition The sense or act of hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves Sound waves are composed of changes in air pressure unfolding over time. Acoustical transduction: Conversion
Hearing istockphoto/thinkstock Audition The sense or act of hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves Sound waves are composed of changes in air pressure unfolding over time. Acoustical transduction: Conversion
THE MECHANICS OF HEARING
 CONTENTS The mechanics of hearing Hearing loss and the Noise at Work Regulations Loudness and the A weighting network Octave band analysis Hearing protection calculations Worked examples and self assessed
CONTENTS The mechanics of hearing Hearing loss and the Noise at Work Regulations Loudness and the A weighting network Octave band analysis Hearing protection calculations Worked examples and self assessed
E3586. What?! Protect Your Hearing. Leader s Guide
 E3586 What?! Protect Your Hearing Leader s Guide 1 What?! Protect Your Hearing This easy-to-use Leader s Guide is provided to assist in conducting a successful presentation. Featured are: INTRODUCTION:
E3586 What?! Protect Your Hearing Leader s Guide 1 What?! Protect Your Hearing This easy-to-use Leader s Guide is provided to assist in conducting a successful presentation. Featured are: INTRODUCTION:
MECHANISM OF HEARING
 MECHANISM OF HEARING Sound: Sound is a vibration that propagates as an audible wave of pressure, through a transmission medium such as gas, liquid or solid. Sound is produced from alternate compression
MECHANISM OF HEARING Sound: Sound is a vibration that propagates as an audible wave of pressure, through a transmission medium such as gas, liquid or solid. Sound is produced from alternate compression
Hearing ConservationTraining
 Hearing ConservationTraining Introduction Employees who are exposed to hazardous levels of noise in the workplace are at risk for developing noise-induced hearing loss. Noise-induced hearing loss is 100
Hearing ConservationTraining Introduction Employees who are exposed to hazardous levels of noise in the workplace are at risk for developing noise-induced hearing loss. Noise-induced hearing loss is 100
Chapter 11: Sound, The Auditory System, and Pitch Perception
 Chapter 11: Sound, The Auditory System, and Pitch Perception Overview of Questions What is it that makes sounds high pitched or low pitched? How do sound vibrations inside the ear lead to the perception
Chapter 11: Sound, The Auditory System, and Pitch Perception Overview of Questions What is it that makes sounds high pitched or low pitched? How do sound vibrations inside the ear lead to the perception
Intro to Audition & Hearing
 Intro to Audition & Hearing Lecture 16 Chapter 9, part II Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Fall 2017 1 Sine wave: one of the simplest kinds of sounds: sound for which pressure
Intro to Audition & Hearing Lecture 16 Chapter 9, part II Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Fall 2017 1 Sine wave: one of the simplest kinds of sounds: sound for which pressure
Deafness and hearing impairment
 Auditory Physiology Deafness and hearing impairment About one in every 10 Americans has some degree of hearing loss. The great majority develop hearing loss as they age. Hearing impairment in very early
Auditory Physiology Deafness and hearing impairment About one in every 10 Americans has some degree of hearing loss. The great majority develop hearing loss as they age. Hearing impairment in very early
HEARING CONSERVATION FACILITATOR S GUIDE
 HEARING CONSERVATION FACILITATOR S GUIDE What s Inside 1 Facilitator s Guidelines 1-a Overview 1-b Getting Started 1-c Presentation Guidelines 1-d Lesson Plan 1-f Frequently Asked Questions 2 Why These
HEARING CONSERVATION FACILITATOR S GUIDE What s Inside 1 Facilitator s Guidelines 1-a Overview 1-b Getting Started 1-c Presentation Guidelines 1-d Lesson Plan 1-f Frequently Asked Questions 2 Why These
This presentation covers information on noise, hearing loss and how to protect your ears.
 This presentation covers information on noise, hearing loss and how to protect your ears. Remember, this information applies to the activities you do at school, at work and at home. 1 OSHA defines noise
This presentation covers information on noise, hearing loss and how to protect your ears. Remember, this information applies to the activities you do at school, at work and at home. 1 OSHA defines noise
3M Center for Hearing Conservation
 3M Center for Hearing Conservation Key Terms in Occupational Hearing Conservation Absorption A noise control method featuring sound-absorbing materials that are placed in an area to reduce the reflection
3M Center for Hearing Conservation Key Terms in Occupational Hearing Conservation Absorption A noise control method featuring sound-absorbing materials that are placed in an area to reduce the reflection
INTRODUCTION TO AUDIOLOGY Hearing Balance Tinnitus - Treatment
 INTRODUCTION TO AUDIOLOGY Hearing Balance Tinnitus - Treatment What is Audiology? Audiology refers to the SCIENCE OF HEARING AND THE STUDY OF THE AUDITORY PROCESS (Katz, 1986) Audiology is a health-care
INTRODUCTION TO AUDIOLOGY Hearing Balance Tinnitus - Treatment What is Audiology? Audiology refers to the SCIENCE OF HEARING AND THE STUDY OF THE AUDITORY PROCESS (Katz, 1986) Audiology is a health-care
The Ear. The ear can be divided into three major parts: the outer ear, the middle ear and the inner ear.
 The Ear The ear can be divided into three major parts: the outer ear, the middle ear and the inner ear. The Ear There are three components of the outer ear: Pinna: the fleshy outer part of the ear which
The Ear The ear can be divided into three major parts: the outer ear, the middle ear and the inner ear. The Ear There are three components of the outer ear: Pinna: the fleshy outer part of the ear which
M Hearing Conservation. Leader s Guide
 M 3196 Hearing Conservation Leader s Guide HEARING CONSERVATION AND SAFETY This easy-to-use Leader s Guide is provided to assist in conducting a successful presentation. Featured are: INTRODUCTION: A brief
M 3196 Hearing Conservation Leader s Guide HEARING CONSERVATION AND SAFETY This easy-to-use Leader s Guide is provided to assist in conducting a successful presentation. Featured are: INTRODUCTION: A brief
The University of Texas at El Paso
 The University of Texas at El Paso Hearing Conservation Program PURPOSE The purpose of the Hearing Conservation Program is to provide information for the protection of University employees from long term
The University of Texas at El Paso Hearing Conservation Program PURPOSE The purpose of the Hearing Conservation Program is to provide information for the protection of University employees from long term
THE EAR AND HEARING Be sure you have read and understand Chapter 16 before beginning this lab. INTRODUCTION: hair cells outer ear tympanic membrane
 BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ****************************************************************************************************** THE EAR AND HEARING ******************************************************************************************************
BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ****************************************************************************************************** THE EAR AND HEARING ******************************************************************************************************
Before taking field measurements, it is important to determine the type of information required. The person making the measurement must understand:
 Why measure noise in the workplace? Measuring noise levels and workers' noise exposures is the most important part of a workplace hearing conservation and noise control program. It helps identify work
Why measure noise in the workplace? Measuring noise levels and workers' noise exposures is the most important part of a workplace hearing conservation and noise control program. It helps identify work
Procedure Number 310 TVA Safety Procedure Page 1 of 6 Hearing Conservation Revision 0 January 6, 2003
 Procedure Number 310 TVA Safety Procedure Page 1 of 6 Hearing Conservation Revision 0 January 6, 2003 1. Purpose 1.1. The purpose of this procedure is to establish a TVA Hearing Conservation Program (HCP)
Procedure Number 310 TVA Safety Procedure Page 1 of 6 Hearing Conservation Revision 0 January 6, 2003 1. Purpose 1.1. The purpose of this procedure is to establish a TVA Hearing Conservation Program (HCP)
HEARING CONSERVATION & NOISE EXPOSURE. 10/1/99 Created By: C. Miterko 1
 HEARING CONSERVATION & NOISE EXPOSURE 10/1/99 Created By: C. Miterko 1 Objectives What is sound? How the ear works How to measure noise What does OSHA says about noise? Reading hearing tests Hearing Protection
HEARING CONSERVATION & NOISE EXPOSURE 10/1/99 Created By: C. Miterko 1 Objectives What is sound? How the ear works How to measure noise What does OSHA says about noise? Reading hearing tests Hearing Protection
UCSD HEARING CONSERVATION PROGRAM Environment, Health & Safety (EH&S) and Center for Occupational & Environmental Medicine (COEM) 2017
 UCSD HEARING CONSERVATION PROGRAM Environment, Health & Safety (EH&S) and Center for Occupational & Environmental Medicine (COEM) 2017 Table of Contents Purpose Applicable Regulations and Standards Responsibilities
UCSD HEARING CONSERVATION PROGRAM Environment, Health & Safety (EH&S) and Center for Occupational & Environmental Medicine (COEM) 2017 Table of Contents Purpose Applicable Regulations and Standards Responsibilities
Learning Targets. Module 20. Hearing Explain how the ear transforms sound energy into neural messages.
 Learning Targets Module 20 Hearing 20-1 Describe the characteristics of air pressure waves that we hear as sound. 20-2 Explain how the ear transforms sound energy into neural messages. 20-3 Discuss how
Learning Targets Module 20 Hearing 20-1 Describe the characteristics of air pressure waves that we hear as sound. 20-2 Explain how the ear transforms sound energy into neural messages. 20-3 Discuss how
HEARING CONSERVATION PROGRAM Texas Christian University
 HEARING CONSERVATION PROGRAM Texas Christian University I. PURPOSE. It is the intent of Texas Christian University to provide every employee with a safe and healthful working environment. Any faculty or
HEARING CONSERVATION PROGRAM Texas Christian University I. PURPOSE. It is the intent of Texas Christian University to provide every employee with a safe and healthful working environment. Any faculty or
HEARING CONSERVATION PROGRAM
 I. INTRODUCTION The University of Wyoming (UW) is committed to protecting the health and safety of students, employees, faculty, and volunteers at the various UW facilities. Therefore, it is UW s policy
I. INTRODUCTION The University of Wyoming (UW) is committed to protecting the health and safety of students, employees, faculty, and volunteers at the various UW facilities. Therefore, it is UW s policy
LISTEN! You might be going deaf DEPARTMENT OF LABOUR TE TARI MAHI OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY & HEALTH SERVICE
 LISTEN! You might be going deaf OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY & HEALTH SERVICE 1 DEPARTMENT OF LABOUR TE TARI MAHI GET THE ANSWERS ABOUT HOW NOISE AFFECTS YOU. Issued by the Occupational Safety & Health Service,
LISTEN! You might be going deaf OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY & HEALTH SERVICE 1 DEPARTMENT OF LABOUR TE TARI MAHI GET THE ANSWERS ABOUT HOW NOISE AFFECTS YOU. Issued by the Occupational Safety & Health Service,
Chapter 13 Physics of the Ear and Hearing
 Hearing 100 times greater dynamic range than vision Wide frequency range (20 ~ 20,000 Hz) Sense of hearing Mechanical system that stimulates the hair cells in the cochlea Sensors that produce action potentials
Hearing 100 times greater dynamic range than vision Wide frequency range (20 ~ 20,000 Hz) Sense of hearing Mechanical system that stimulates the hair cells in the cochlea Sensors that produce action potentials
Hearing Conservation Program
 Hearing Conservation Program Subject Matter Expert Brandi E. Kissel bek66@cornell.edu 607-882-5273 Page 1 of 9 Contents 1.0 INTRODUCTION... 2 2.0 OBJECTIVES AND METRICS... 2 3.0 SCOPE... 2 4.0 ROLES AND
Hearing Conservation Program Subject Matter Expert Brandi E. Kissel bek66@cornell.edu 607-882-5273 Page 1 of 9 Contents 1.0 INTRODUCTION... 2 2.0 OBJECTIVES AND METRICS... 2 3.0 SCOPE... 2 4.0 ROLES AND
Environmental Health & Safety Policy Manual
 Environmental Health & Safety Policy Manual Issue Date: 1/23/2014 Policy # EHS-400.14 Hearing Conservation Program 1.0 PURPOSE: To establish policy that defines the minimum requirements for the LSUHSC
Environmental Health & Safety Policy Manual Issue Date: 1/23/2014 Policy # EHS-400.14 Hearing Conservation Program 1.0 PURPOSE: To establish policy that defines the minimum requirements for the LSUHSC
This refresher covers protecting your eyes and hearing. Remember, this information applies to activities you do at school, work and home.
 This refresher covers protecting your eyes and hearing. Remember, this information applies to activities you do at school, work and home. Collision shops can be noisy, especially when you work with loud
This refresher covers protecting your eyes and hearing. Remember, this information applies to activities you do at school, work and home. Collision shops can be noisy, especially when you work with loud
Contents. 1) Purpose ) Policy ) Definitions ) Procedure a) Requirements b) Noise standard... 4
 Contents 1) Purpose... 3 2) Policy... 3 3) Definitions... 3 4) Procedure... 4 a) Requirements... 4 b) Noise standard... 4 c) Responsibilites... 5 d) Exposure Monitoring and Assessments... 6 e) Employee
Contents 1) Purpose... 3 2) Policy... 3 3) Definitions... 3 4) Procedure... 4 a) Requirements... 4 b) Noise standard... 4 c) Responsibilites... 5 d) Exposure Monitoring and Assessments... 6 e) Employee
Hearing Conservation and Noise Control
 Hearing Conservation and Noise Control Objectives What is sound? How the ear works How to measure noise What the Regulations say about noise Reading hearing tests Hearing Protection What is Sound? Hertz
Hearing Conservation and Noise Control Objectives What is sound? How the ear works How to measure noise What the Regulations say about noise Reading hearing tests Hearing Protection What is Sound? Hertz
NOISE IN THE WORKPLACE
 NOISE IN THE WORKPLACE Not all sound is noise noise is unwanted or unpleasant sound. Noise can cause stress and interfere with concentration. Noise can mask or interfere with conversation and may contribute
NOISE IN THE WORKPLACE Not all sound is noise noise is unwanted or unpleasant sound. Noise can cause stress and interfere with concentration. Noise can mask or interfere with conversation and may contribute
Hearing Conservation Training Program
 Hearing Conservation Training Program For 49 CFR Part 227 2009 Transportation Occupational Medicine Consultants, Inc. 1 Introduction This presentation is intended to provide you with the information and
Hearing Conservation Training Program For 49 CFR Part 227 2009 Transportation Occupational Medicine Consultants, Inc. 1 Introduction This presentation is intended to provide you with the information and
Receptors / physiology
 Hearing: physiology Receptors / physiology Energy transduction First goal of a sensory/perceptual system? Transduce environmental energy into neural energy (or energy that can be interpreted by perceptual
Hearing: physiology Receptors / physiology Energy transduction First goal of a sensory/perceptual system? Transduce environmental energy into neural energy (or energy that can be interpreted by perceptual
How Do Our Ears Work? Quiz
 The Marvelous Ear How Do Our Ears Work? Quiz 1. How do humans hear sounds? 2. How does human hearing work? Sketch and label the system. 3. Do you know any sensors that detect sound and how they might do
The Marvelous Ear How Do Our Ears Work? Quiz 1. How do humans hear sounds? 2. How does human hearing work? Sketch and label the system. 3. Do you know any sensors that detect sound and how they might do
Hearing Conservation Program
 Last Reviewed Date: 3/07/2018 Last Revised Date: 7/27/2017 Effective Date: 6/27/1994 Applies To: Employees, Faculty, Students, Others For More Information contact: EHS, Coordinator at 860-486-3613 or valerie.brangan@uconn.edu
Last Reviewed Date: 3/07/2018 Last Revised Date: 7/27/2017 Effective Date: 6/27/1994 Applies To: Employees, Faculty, Students, Others For More Information contact: EHS, Coordinator at 860-486-3613 or valerie.brangan@uconn.edu
HEARING PROTECTION. Technical Data Information Earplugs Earmuffs
 HEARING PROTECTION Technical Data Information Earplugs Earmuffs Technical Data Information Noise Hazard Humans have a multitude of senses, sight, hearing, taste, smell and touch. They are all as important
HEARING PROTECTION Technical Data Information Earplugs Earmuffs Technical Data Information Noise Hazard Humans have a multitude of senses, sight, hearing, taste, smell and touch. They are all as important
Reference: Mark S. Sanders and Ernest J. McCormick. Human Factors Engineering and Design. McGRAW-HILL, 7 TH Edition. NOISE
 NOISE NOISE: It is considered in an information-theory context, as that auditory stimulus or stimuli bearing no informational relationship to the presence or completion of the immediate task. Human ear
NOISE NOISE: It is considered in an information-theory context, as that auditory stimulus or stimuli bearing no informational relationship to the presence or completion of the immediate task. Human ear
Hearing Sound. The Human Auditory System. The Outer Ear. Music 170: The Ear
 Hearing Sound Music 170: The Ear Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) November 17, 2016 Sound interpretation in the auditory system is done by
Hearing Sound Music 170: The Ear Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) November 17, 2016 Sound interpretation in the auditory system is done by
Music 170: The Ear. Tamara Smyth, Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) November 17, 2016
 Music 170: The Ear Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) November 17, 2016 1 Hearing Sound Sound interpretation in the auditory system is done by
Music 170: The Ear Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) November 17, 2016 1 Hearing Sound Sound interpretation in the auditory system is done by
Sound and its characteristics. The decibel scale. Structure and function of the ear. Békésy s theory. Molecular basis of hair cell function.
 Hearing Sound and its characteristics. The decibel scale. Structure and function of the ear. Békésy s theory. Molecular basis of hair cell function. 19/11/2014 Sound A type of longitudinal mass wave that
Hearing Sound and its characteristics. The decibel scale. Structure and function of the ear. Békésy s theory. Molecular basis of hair cell function. 19/11/2014 Sound A type of longitudinal mass wave that
RISK ASSESMENT AND PERSONAL PROTECTIVE EQUIPMENTS
 RISK ASSESMENT AND PERSONAL PROTECTIVE EQUIPMENTS Ahmet ERSOY Occupational Health and Safety Expert Ankara Personal Protection and PPE OHS aims to protect the health, safety and welfare of people at work.
RISK ASSESMENT AND PERSONAL PROTECTIVE EQUIPMENTS Ahmet ERSOY Occupational Health and Safety Expert Ankara Personal Protection and PPE OHS aims to protect the health, safety and welfare of people at work.
Gettysburg College. Hearing Conservation Program
 Gettysburg College Hearing Conservation Program Adopted Aug 28, 2008 Reviewed and Updated July 2015 Table of Contents I. Introduction A. Purpose B. Scope II. Responsibility A. Associate Director of Environmental
Gettysburg College Hearing Conservation Program Adopted Aug 28, 2008 Reviewed and Updated July 2015 Table of Contents I. Introduction A. Purpose B. Scope II. Responsibility A. Associate Director of Environmental
San Diego State University Environmental Health and Safety
 Occupational Hearing Conservation Program (HCP) Making Hearing Health a Workplace Wellness Priority Lake Health Walter Vieweg, DO, D.PM., M.A. Occupational Physician Certified NRCME, MRO, Civil Surgeon,
Occupational Hearing Conservation Program (HCP) Making Hearing Health a Workplace Wellness Priority Lake Health Walter Vieweg, DO, D.PM., M.A. Occupational Physician Certified NRCME, MRO, Civil Surgeon,
HEARING LOSS PREVENTION PROGRAM AND PROCEDURES
 HEARING LOSS PREVENTION PROGRAM AND PROCEDURES UW Environmental Health & Safety Department April 2014 1.0 Policy In an effort to prevent permanent hearing loss caused by excessive noise, UW maintains a
HEARING LOSS PREVENTION PROGRAM AND PROCEDURES UW Environmental Health & Safety Department April 2014 1.0 Policy In an effort to prevent permanent hearing loss caused by excessive noise, UW maintains a
Hearing Conservation Program
 1500 - Hearing Conservation Program DOCUMENT HISTORY Version Date Comments 1.0 January, 2016 Initial Hearing Conservation Program 2.0 July, 2017 Annual Review This document will be reviewed routinely and
1500 - Hearing Conservation Program DOCUMENT HISTORY Version Date Comments 1.0 January, 2016 Initial Hearing Conservation Program 2.0 July, 2017 Annual Review This document will be reviewed routinely and
Occupational Noise Exposure 29 CFR
 Occupational Noise Exposure 29 CFR 1910.95 Is There a Problem? More than 30 million Americans are exposed to hazardous sound levels on a regular basis 10 million have suffered irreversible noise induced
Occupational Noise Exposure 29 CFR 1910.95 Is There a Problem? More than 30 million Americans are exposed to hazardous sound levels on a regular basis 10 million have suffered irreversible noise induced
Hearing Conservation Program
 Hearing Conservation Program Table of Contents I. Program Goals and Objectives... 2 II. Scope and Application... 2 III. Regulatory Authority and Related Information... 2 IV. Definitions... 2 V. Responsibilities...
Hearing Conservation Program Table of Contents I. Program Goals and Objectives... 2 II. Scope and Application... 2 III. Regulatory Authority and Related Information... 2 IV. Definitions... 2 V. Responsibilities...
Auditory System. Barb Rohrer (SEI )
 Auditory System Barb Rohrer (SEI614 2-5086) Sounds arise from mechanical vibration (creating zones of compression and rarefaction; which ripple outwards) Transmitted through gaseous, aqueous or solid medium
Auditory System Barb Rohrer (SEI614 2-5086) Sounds arise from mechanical vibration (creating zones of compression and rarefaction; which ripple outwards) Transmitted through gaseous, aqueous or solid medium
 Page 1 of 5 Prevention & Control of Hazards Personal Protective Equipment Hearing Protectors How can I protect my hearing at work? What are some things I should know about selecting hearing protection
Page 1 of 5 Prevention & Control of Hazards Personal Protective Equipment Hearing Protectors How can I protect my hearing at work? What are some things I should know about selecting hearing protection
Environmental Health & Safety Programs
 1.0 Introduction Worker exposure to noise of sufficient intensity and duration can result in permanent hearing damage. Noise-induced hearing loss rarely results from a single exposure; it can progress
1.0 Introduction Worker exposure to noise of sufficient intensity and duration can result in permanent hearing damage. Noise-induced hearing loss rarely results from a single exposure; it can progress
Gettysburg College. Hearing Conservation Program
 Gettysburg College Hearing Conservation Program September 10, 2007 Table of Contents I. Introduction A. Purpose B. Scope II. III. IV. Responsibility A. President of Gettysburg College/Director of Risk
Gettysburg College Hearing Conservation Program September 10, 2007 Table of Contents I. Introduction A. Purpose B. Scope II. III. IV. Responsibility A. President of Gettysburg College/Director of Risk
Hearing Conservation Program
 Hearing Conservation Program June 2018 Hearing Conservation Program Table of Contents I. Purpose II. III. Responsibilities Program Directives A. Noise Exposure Monitoring B. Audiometric Testing C. Control
Hearing Conservation Program June 2018 Hearing Conservation Program Table of Contents I. Purpose II. III. Responsibilities Program Directives A. Noise Exposure Monitoring B. Audiometric Testing C. Control
PSY 215 Lecture 10 Topic: Hearing Chapter 7, pages
 PSY 215 Lecture 10 Topic: Hearing Chapter 7, pages 189-197 Corrections: NTC 09-1, page 3, the Superior Colliculus is in the midbrain (Mesencephalon). Announcements: Movie next Monday: Case of the frozen
PSY 215 Lecture 10 Topic: Hearing Chapter 7, pages 189-197 Corrections: NTC 09-1, page 3, the Superior Colliculus is in the midbrain (Mesencephalon). Announcements: Movie next Monday: Case of the frozen
Outline. The ear and perception of sound (Psychoacoustics) A.1 Outer Ear Amplifies Sound. Introduction
 The ear and perception of sound (Psychoacoustics) 1 Outline A. Structure of the Ear B. Perception of Pitch C. Perception of Loudness D. Timbre (quality of sound) E. References Updated 01Aug0 Introduction
The ear and perception of sound (Psychoacoustics) 1 Outline A. Structure of the Ear B. Perception of Pitch C. Perception of Loudness D. Timbre (quality of sound) E. References Updated 01Aug0 Introduction
East Carolina University
 East Carolina University Office of Environmental Health & Safety 211 S Jarvis Street, Suite 102 Greenville, NC 27858 P: (252) 328-6166 F: (252) 737-1458 www.ecu.edu/oehs Hearing Conservation Program ii
East Carolina University Office of Environmental Health & Safety 211 S Jarvis Street, Suite 102 Greenville, NC 27858 P: (252) 328-6166 F: (252) 737-1458 www.ecu.edu/oehs Hearing Conservation Program ii
Environmental Health and Safety. Hearing Conservation Program
 Environmental Health and Safety Hearing Conservation Program Date of Issuance: 07/23/2018 Revision Number: Initial Revision Date: Prepared by: EH&S 1. Purpose Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) has developed
Environmental Health and Safety Hearing Conservation Program Date of Issuance: 07/23/2018 Revision Number: Initial Revision Date: Prepared by: EH&S 1. Purpose Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) has developed
UC Merced Hearing Conservation Program
 Hearing Conservation Program www.ucmerced.edu Version 2015-1 Table of Contents Section Page 1.0 PURPOSE... 1 2.0 REGULATIONS AND OTHER APPLICABLE STANDARDS... 1 3.0 RESPONSIBILITIES... 1 3.1 Department
Hearing Conservation Program www.ucmerced.edu Version 2015-1 Table of Contents Section Page 1.0 PURPOSE... 1 2.0 REGULATIONS AND OTHER APPLICABLE STANDARDS... 1 3.0 RESPONSIBILITIES... 1 3.1 Department
Perception of Sound. To hear sound, your ear has to do three basic things:
 Perception of Sound Your ears are extraordinary organs. They pick up all the sounds around you and then translate this information into a form your brain can understand. One of the most remarkable things
Perception of Sound Your ears are extraordinary organs. They pick up all the sounds around you and then translate this information into a form your brain can understand. One of the most remarkable things
The Basics of Hearing Protection
 2008 The Basics of Hearing Protection hearing protection, more than any other safety related issue is one that tends to be ignored by workers. This is why a clear understanding of the long range effects
2008 The Basics of Hearing Protection hearing protection, more than any other safety related issue is one that tends to be ignored by workers. This is why a clear understanding of the long range effects
HEAR YE! HEAR YE! (1.5 Hours)
 HEAR YE! HEAR YE! (1.5 Hours) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 4 Grade Range: 3-5 OVERVIEW In this activity, students will construct a model ear to learn how different materials transmit sound. Topic:
HEAR YE! HEAR YE! (1.5 Hours) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 4 Grade Range: 3-5 OVERVIEW In this activity, students will construct a model ear to learn how different materials transmit sound. Topic:
HEARING. Structure and Function
 HEARING Structure and Function Rory Attwood MBChB,FRCS Division of Otorhinolaryngology Faculty of Health Sciences Tygerberg Campus, University of Stellenbosch Analyse Function of auditory system Discriminate
HEARING Structure and Function Rory Attwood MBChB,FRCS Division of Otorhinolaryngology Faculty of Health Sciences Tygerberg Campus, University of Stellenbosch Analyse Function of auditory system Discriminate
Hearing. By: Jimmy, Dana, and Karissa
 Hearing By: Jimmy, Dana, and Karissa Anatomy - The ear is divided up into three parts - Sound enters in through the outer ear and passes into the middle where the vibrations are received and sent to the
Hearing By: Jimmy, Dana, and Karissa Anatomy - The ear is divided up into three parts - Sound enters in through the outer ear and passes into the middle where the vibrations are received and sent to the
HEARING CONSERVATION PURPOSE
 HEARING CONSERVATION PURPOSE The purpose of a Hearing Conservation Policy (HCP) is to prevent occupational noise exposures which could lead to noise-induced hearing loss and to comply with existing Occupational
HEARING CONSERVATION PURPOSE The purpose of a Hearing Conservation Policy (HCP) is to prevent occupational noise exposures which could lead to noise-induced hearing loss and to comply with existing Occupational
Safety Services Guidance. Occupational Noise
 Occupational Noise Key word(s): Occupational noise, sound, hearing, decibel, noise induced hearing loss (NIHL), Noise at Work Regulations 2005 Target audience: Managers and staff with responsibility to
Occupational Noise Key word(s): Occupational noise, sound, hearing, decibel, noise induced hearing loss (NIHL), Noise at Work Regulations 2005 Target audience: Managers and staff with responsibility to
managing safely Noise at Work Course Notes Mark Mallen Group Health and Safety Manager December 2005 Noise at Work: Version 1 Page 1 of 23
 Noise at Work Course Notes Mark Mallen Group Health and Safety Manager December 2005 Noise at Work: Version 1 Page 1 of 23 Course Content 1. What is noise? 2. Sound - Sound Waves 3. How do we hear? - The
Noise at Work Course Notes Mark Mallen Group Health and Safety Manager December 2005 Noise at Work: Version 1 Page 1 of 23 Course Content 1. What is noise? 2. Sound - Sound Waves 3. How do we hear? - The
PSY 214 Lecture # (11/9/2011) (Sound, Auditory & Speech Perception) Dr. Achtman PSY 214
 PSY 214 Lecture 16 Topic: Sound, Auditory System & Speech Perception Chapter 11, pages 270-289 Corrections: None Announcements: CD is available outside Dr Achtman s office if you would like to see demonstrations
PSY 214 Lecture 16 Topic: Sound, Auditory System & Speech Perception Chapter 11, pages 270-289 Corrections: None Announcements: CD is available outside Dr Achtman s office if you would like to see demonstrations
Prepared By: Blake Smith/James Stubbs
 Title: Hearing Conservation Program Print Date: Revision # Effective Date: Prepared By: Blake Smith/James Stubbs Reviewed By: Jen Stones Josh Manning Date Prepared: 09.2017 Date Reviewed: 10.26.2017 10.26.2017
Title: Hearing Conservation Program Print Date: Revision # Effective Date: Prepared By: Blake Smith/James Stubbs Reviewed By: Jen Stones Josh Manning Date Prepared: 09.2017 Date Reviewed: 10.26.2017 10.26.2017
Hearing Protection. Basic
 Hearing Protection Basic OSHA's hearing conservation program is designed to protect workers with significant occupational noise exposures from hearing impairment even if they are subject to such noise
Hearing Protection Basic OSHA's hearing conservation program is designed to protect workers with significant occupational noise exposures from hearing impairment even if they are subject to such noise
Hearing Conservation Program
 Hearing Conservation Program Revised: September 2017 2009-2017. University of New Hampshire Office of Environmental Health and Safety. All rights reserved. The most current version of this document can
Hearing Conservation Program Revised: September 2017 2009-2017. University of New Hampshire Office of Environmental Health and Safety. All rights reserved. The most current version of this document can
Before we talk about the auditory system we will talk about the sound and waves
 The Auditory System PHYSIO: #3 DR.LOAI ZAGOUL 24/3/2014 Refer to the slides for some photos. Before we talk about the auditory system we will talk about the sound and waves All waves have basic characteristics:
The Auditory System PHYSIO: #3 DR.LOAI ZAGOUL 24/3/2014 Refer to the slides for some photos. Before we talk about the auditory system we will talk about the sound and waves All waves have basic characteristics:
Hearing Conservation and You. Leader s Guide and Quiz
 4670 Hearing Conservation and You Leader s Guide and Quiz HEARING CONSERVATION AND YOU INTRODUCTION Follow along as Steve, Jerry and a group of co-workers receive their annual training on hearing conservation.
4670 Hearing Conservation and You Leader s Guide and Quiz HEARING CONSERVATION AND YOU INTRODUCTION Follow along as Steve, Jerry and a group of co-workers receive their annual training on hearing conservation.
Systems Neuroscience Oct. 16, Auditory system. http:
 Systems Neuroscience Oct. 16, 2018 Auditory system http: www.ini.unizh.ch/~kiper/system_neurosci.html The physics of sound Measuring sound intensity We are sensitive to an enormous range of intensities,
Systems Neuroscience Oct. 16, 2018 Auditory system http: www.ini.unizh.ch/~kiper/system_neurosci.html The physics of sound Measuring sound intensity We are sensitive to an enormous range of intensities,
ID# Final Exam PS325, Fall 1997
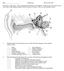 ID# Final Exam PS325, Fall 1997 Good luck on this exam. Answer each question carefully and completely. Keep your eyes foveated on your own exam, as the Skidmore Honor Code is in effect (as always). Have
ID# Final Exam PS325, Fall 1997 Good luck on this exam. Answer each question carefully and completely. Keep your eyes foveated on your own exam, as the Skidmore Honor Code is in effect (as always). Have
Hearing Conservation Program Regulations and Recommendations Summary
 ITEM # OSHA 29 CFR 1910.95 MSHA 30 CFR Part 62 NIOSH DHHS Pub. No. 98-126 NOISE MEASUREMENT NOISE MEASUREMENT NOISE MEASUREMENT 1 Methods: Not specified Not specified Conform to ANSI S12.19-1996 without
ITEM # OSHA 29 CFR 1910.95 MSHA 30 CFR Part 62 NIOSH DHHS Pub. No. 98-126 NOISE MEASUREMENT NOISE MEASUREMENT NOISE MEASUREMENT 1 Methods: Not specified Not specified Conform to ANSI S12.19-1996 without
Structure, Energy Transmission and Function. Gross Anatomy. Structure, Function & Process. External Auditory Meatus or Canal (EAM, EAC) Outer Ear
 Gross Anatomy Structure, Energy Transmission and Function IE N O ME 1 Structure, Function & Process 4 External Auditory Meatus or Canal (EAM, EAC) Outer third is cartilaginous Inner 2/3 is osseous Junction
Gross Anatomy Structure, Energy Transmission and Function IE N O ME 1 Structure, Function & Process 4 External Auditory Meatus or Canal (EAM, EAC) Outer third is cartilaginous Inner 2/3 is osseous Junction
Auditory Physiology Richard M. Costanzo, Ph.D.
 Auditory Physiology Richard M. Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1. Describe the morphology and function of the following structures:
Auditory Physiology Richard M. Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1. Describe the morphology and function of the following structures:
