Producing and Detecting Sound
|
|
|
- Barnaby Eaton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Sound Producing and Detecting Sound What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement or a D if you disagree. After you ve read this lesson, reread the statements to see if you have changed your mind. Before Statement After 1. Sound waves travel fastest in empty space. 2. Hearing loss is mainly caused by brief, loud sounds, such as a firecracker. Key Concepts How is sound produced? How does sound move from one place to another? Why does sound travel at different speeds through various materials? What are the functions of the different parts of the human ear? What is sound? Everywhere you look, people seem to have something on their ears! Some talk on cell phones, some listen to music, and others wear ear protection to prevent damage to their hearing. All of these devices have something to do with sound. Sound is produced by sound waves longitudinal waves that can only travel through matter. A longitudinal wave is a wave that makes the particles in the material that carries the wave move back and forth along the direction the wave travels. Sources of Sound Every sound, from the buzzing of a bee to a loud siren, results from a vibration. A vibration is a rapid, back-and-forth motion that can occur in solids, liquids, or gases. The energy carried by a sound wave is caused by vibration. For example, as you pull on a guitar string, you transfer energy to the string. When you let go, the string snaps back and vibrates. As the string vibrates, it collides with nearby air particles and transfers energy to these particles. The air particles collide with other air particles and pass on energy. The string vibrates in a back-and-forth motion. This motion causes a disturbance in the air that carries energy outward from the source of the sound. This disturbance is a sound wave. Identify the Main Ideas As you read, write one sentence to summarize the main idea in each paragraph. Write the main ideas on a sheet of paper or in your notebook to study later. Key Concept Check 1. Determine How is sound produced? Reading Essentials Sound 285
2 SCIENCE USE V. COMMON USE media Science Use plural form of medium; forms of matter through which sound travels Common Use a type of mass communication, such as radio Visual Check 2. Identify As a speaker is producing sound, when does a rarefaction occur? Compression Compression Energy How Sound Waves Travel Vibrating objects cause sound waves that occur only in matter. So, sound waves must travel through a solid, a liquid, or a gas. A material in which a wave travels is a medium. You usually hear sound through the medium of air. But sound waves also can travel through other media, such as water, wood, and metal. Sound waves cannot travel through empty space, because empty space has no medium to carry the energy. From a Sound Source to Your Ear Sound waves move away from a sound source, such as the speaker below, as compressions and rarefactions. If you touch a speaker, you can feel it vibrate as it produces sound waves. Air particles fill a room. Each time the speaker cone moves forward, it pushes air particles ahead of it in the room. This push forces the particles closer together, increasing air pressure in that area. A region of a longitudinal wave where the particles in the medium are closest together is a compression. The image on the left in the figure below illustrates a compression. With each vibration, the speaker cone moves forward and then back. When the speaker cone moves back, it leaves behind a low-pressure region with fewer air particles. The image on the right in the figure illustrates this low-pressure region, called a rarefaction. A rarefaction (rayr uh FAK shun) is a region of a longitudinal wave where the particles are farthest apart. Normal air pressure When the speaker cone moves out, it forces particles in the air closer together. This produces a high pressure area, or compression. How Sound Waves Move Rarefaction Rarefaction Compression Energy Normal air pressure When the speaker cone moves back, it leaves behind an area with fewer particles. This is a low pressure area called a rarefaction. 286 Sound Reading Essentials
3 Energy in Sound Waves Imagine someone at the back of a line bumping into the next person. That person bumps the next person and then returns to his or her original place. The energy of the bump continues down the line. In the same way, particles of a medium vibrate back and forth as a sound wave carries energy away from a source. The figure at right shows this process. Speed of Sound Sound waves travel faster in water than in air. The table compares the speed of sound in different media. Direction of Sound Energy Direction of energy The Speed of Sound Material Compression Rarefaction Vibration of an individual particle Speed (m/s) Material Two factors that affect the speed of sound waves are the density and the stiffness of Air (0 C) Air (20 C) Water (20 C) ,481 the material, or medium. Water (0 C) 1,500 Density is how closely the Seawater (25 C) 1,533 particles are packed. Gas particles are far apart and do not collide as often as do the particles of a liquid or a solid. Therefore, sound energy transfers more slowly in a gas Ice (0 C) Iron Glass 3,500 5,130 5,640 than in a liquid or a solid. In a stiff or rigid solid, where particles are packed close together, the particles collide and transfer energy quickly. Sound waves travel faster in seawater than in freshwater. Seawater contains dissolved salts and has a higher density than freshwater. Temperature The temperature of a medium also affects the speed of sound. As the temperature of a gas increases, the particles move faster and collide more often. This increase in collisions transfers more energy in less time. Notice that sound waves travel faster in air at 20 C than in air at 0 C. In liquids and solids, temperature has the opposite effect. Why do sound waves travel faster in water at 0 C than at 20 C? As water cools, the molecules move closer together, colliding more often. Sound waves travel even faster when the water freezes into ice because ice is rigid. Visual Check 3. Describe What happens to particles of matter as sound waves travel? Key Concept Check 4. Explain How do sound waves travel? Interpreting Tables 5. Predict Based on the data in the table, do you think sound will move faster in cool pond water or in warm bath water? Key Concept Check 6. Explain Why does sound travel at different speeds through various materials? Reading Essentials Sound 287
4 Key Concept Check 7. Identify What are the functions of the different parts of the human ear? Visual Check 8. Analyze How does the eardrum help you hear? Detecting Sound The fennec fox is a small fox with large ears. How do you think having large ears helps a fennec fox? Sound waves fill the air, and the large outer ear helps funnel sound waves to the inner ear, where sound is detected. Ears also tell the direction a sound comes from. With its large ears, the fennec fox can hear predators approach from greater distances. The fox s ears can even detect prey moving underground. The Human Ear Have you ever cupped your hand around the back of your ear so you could hear better? Why does that work? The human ear has three main parts. The outer ear collects sound waves. By cupping your hand around your ear, you extend the outer ear and collect more waves. The middle ear amplifies sound. The inner ear sends signals about sound to the brain. As shown in the figure below, each part of the ear has a special shape with different parts that help it perform its function. Functions of Human Ear Parts 1 The outer ear collects sounds. Cupping your hand around your ear makes the collector bigger, so it gathers more sounds. The ear canal is also part of the outer ear. The ear canal directs collected sounds to the middle ear. Ear canal 3 2 The middle ear amplifies sound. The eardrum, a structure like a drumhead, lies between the outer and the middle ear. Sound waves entering the outer ear cause the eardrum to vibrate. The vibrations transfer to three tiny bones called the hammer, the anvil, and the stirrup. The vibrations of these bones conduct the sound toward the inner ear. Outer ear Middle ear Inner ear Hammer Eardrum Anvil Stirrup Cochlea The inner ear contains small, fluid-filled chambers called the cochlea (KOH klee uh). Sound waves passing through the cochlea cause tiny hairlike cells to vibrate. The movement of the hair cells produces nerve signals that travel to the brain. The brain interprets these signals as sound. 288 Sound Reading Essentials
5 Hearing Loss The harder you pound on a drum, the farther the drumhead travels as it vibrates. What would a drum sound like if the drumhead had a big tear in it? Like a drumhead, the eardrum can be damaged. The eardrum vibrates as pressure changes in the ear. The louder the sound is, the farther the eardrum moves in and out as it vibrates. A very loud sound can make the eardrum vibrate so hard that it tears. Damage to the eardrum can cause hearing loss. Also, the tear can allow bacteria into the ear, causing infection. The tear may heal, but thick, uneven scar tissue can make the eardrum less sensitive to sounds. Listening to loud music over a long period of time also can damage the ears. Locate the cochlea in the figure on the previous page. Infection or loud sounds can damage tiny hair cells in the cochlea. Cells that are damaged or die do not grow back. As a result, hearing becomes less sensitive. Many people who work around loud machines, construction, or traffic wear ear protection to prevent damage. Wearing a headset while listening to loud music, however, traps the pressure changes in the ear. This can lead to permanent hearing loss. Make a vertical three-tab book to organize your notes about sound. How Sound Is Produced How Sound Travels How Sound Is Detected Reading Check 9. Analyze Why can a very loud sound cause the eardrum to tear? Reading Check 10. Name some things that might happen to your ear to cause hearing loss. Reading Essentials Sound 289
6 Mini Glossary compression: a region of a longitudinal wave where the particles in the medium are closest together longitudinal wave: a wave that makes the particles in the material that carries the wave move back and forth along the direction that the wave travels medium: a material in which a wave travels rarefaction (rayr uh FAK shun): a region of a longitudinal wave where the particles are farthest apart sound wave: longitudinal wave that travels only through matter vibration: a rapid back-and-forth motion that can occur in solids, liquids, or gases 1. Review the terms and their definitions in the Mini Glossary. Write a sentence that identifies the media through which sound can travel. 2. In the table below, describe the function of each main area of the ear. Then identify the parts within each area. Outer Ear Middle Ear Inner Ear function: function: function: parts: parts: parts: 3. How did summarizing the main ideas help you learn about sound? In the space below, summarize one main idea that you learned from your notes. What do you think Reread the statements at the beginning of the lesson. Fill in the After column with an A if you agree with the statement or a D if you disagree. Did you change your mind? ConnectED Log on to ConnectED.mcgraw-hill.com and access your textbook to find this lesson s resources. END OF LESSON 290 Sound Reading Essentials
Sound Waves. Making Sound Waves
 Benchmarks SC.B.1.3.6 Annually Assessed (pp. 195, 197): The student knows the properties of waves; that each wave consists of a number of crests and troughs; and the effects of different media on waves;
Benchmarks SC.B.1.3.6 Annually Assessed (pp. 195, 197): The student knows the properties of waves; that each wave consists of a number of crests and troughs; and the effects of different media on waves;
17.4 Sound and Hearing
 You can identify sounds without seeing them because sound waves carry information to your ears. People who work in places where sound is very loud need to protect their hearing. Properties of Sound Waves
You can identify sounds without seeing them because sound waves carry information to your ears. People who work in places where sound is very loud need to protect their hearing. Properties of Sound Waves
Sound Waves. Sound waves can only travel through matter. The energy carried by a sound wave is transferred by the collisions between the
 Sound Waves Making Sound Waves How does the motion of a drummer s drumsticks produce sound waves? The impact of the sticks on the head of a drum causes the drum head to vibrate. These vibrations transfer
Sound Waves Making Sound Waves How does the motion of a drummer s drumsticks produce sound waves? The impact of the sticks on the head of a drum causes the drum head to vibrate. These vibrations transfer
Chapter 17 Sound Sound and Hearing. Properties of Sound Waves 1/20/2017. Pearson Prentice Hall Physical Science: Concepts in Action
 Pearson Prentice Hall Physical Science: Concepts in Action Chapter 17 Sound Standing Waves in Music When the string of a violin is played with a bow, it vibrates and creates standing waves. Some instruments,
Pearson Prentice Hall Physical Science: Concepts in Action Chapter 17 Sound Standing Waves in Music When the string of a violin is played with a bow, it vibrates and creates standing waves. Some instruments,
DeltaScience. Content Readers. Summary. Science Background. Objectives. Reading Comprehension Skills. Supporting English Learners
 DeltaScience Content Readers TM Red Edition Grade 3 4 reading level Purple Edition Grade 4 5 reading level Objectives Describe how vibrating objects make sound waves. Explain how sound waves move through
DeltaScience Content Readers TM Red Edition Grade 3 4 reading level Purple Edition Grade 4 5 reading level Objectives Describe how vibrating objects make sound waves. Explain how sound waves move through
Wonderlab. Sound. The Statoil Gallery. The science and maths behind the exhibits LIGHT WONDERLAB: THE STATOIL GALLERY LEVEL 3, SCIENCE MUSEUM LONDON
 Wonderlab The Statoil Gallery and maths s Sound Age (s) Topic 7 11 LIGHT INFORMATION 11-14 Location WONDERLAB: THE STATOIL GALLERY LEVEL 3, SCIENCE MUSEUM LONDON 1 What s the science? What more will you
Wonderlab The Statoil Gallery and maths s Sound Age (s) Topic 7 11 LIGHT INFORMATION 11-14 Location WONDERLAB: THE STATOIL GALLERY LEVEL 3, SCIENCE MUSEUM LONDON 1 What s the science? What more will you
Sound A Science A Z Physical Series Word Count: 1,093
 Sound A Science A Z Physical Series Word Count: 1,093 Written by Robert N. Knight Visit www.sciencea-z.com www.sciencea-z.com Sound KEY ELEMENTS USED IN THIS BOOK The Big Idea: Sound is made of waves that
Sound A Science A Z Physical Series Word Count: 1,093 Written by Robert N. Knight Visit www.sciencea-z.com www.sciencea-z.com Sound KEY ELEMENTS USED IN THIS BOOK The Big Idea: Sound is made of waves that
AND THE EARS HAVE IT! (1 Hour)
 (1 Hour) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 3 Grade Range: K-2 OVERVIEW In this activity, students will explore the nature of human hearing by attempting to determine the location at different locations
(1 Hour) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 3 Grade Range: K-2 OVERVIEW In this activity, students will explore the nature of human hearing by attempting to determine the location at different locations
Low? High or. v vv \T\ \ C\ [ \(\(\(\(\ PITCH FREQUENCY CHAPTER4
 CHAPTER4 High or Low? PITCH Another quality that an oscilloscope shows is pitch. Pitch is a measurement of how high or low a sound is. If you make your voice high and squeaky, then it has a high pitch.
CHAPTER4 High or Low? PITCH Another quality that an oscilloscope shows is pitch. Pitch is a measurement of how high or low a sound is. If you make your voice high and squeaky, then it has a high pitch.
Norwood Science Center
 Norwood Science Center Energy Grade 5 Background Information: The sense of hearing involves the ear, the auditory nerve, and a special center within the brain. We hear because our ears respond to vibrations
Norwood Science Center Energy Grade 5 Background Information: The sense of hearing involves the ear, the auditory nerve, and a special center within the brain. We hear because our ears respond to vibrations
Please visit the website hearingandsound.weebly.com to help you study, as well as viewing the videos and booklet posted.
 Hearing and Sound Study Guide Please visit the website hearingandsound.weebly.com to help you study, as well as viewing the videos and booklet posted. 1. Sounds make vibrations and vibrations move in all
Hearing and Sound Study Guide Please visit the website hearingandsound.weebly.com to help you study, as well as viewing the videos and booklet posted. 1. Sounds make vibrations and vibrations move in all
Transfer of Sound Energy through Vibrations
 secondary science 2013 16 Transfer of Sound Energy through Vibrations Content 16.1 Sound production by vibrating sources 16.2 Sound travel in medium 16.3 Loudness, pitch and frequency 16.4 Worked examples
secondary science 2013 16 Transfer of Sound Energy through Vibrations Content 16.1 Sound production by vibrating sources 16.2 Sound travel in medium 16.3 Loudness, pitch and frequency 16.4 Worked examples
The Nature of Sound. Section 1: What Is Sound? (p. 534)
 CHAPTER 21 DIRECTED READING WORKSHEET The Nature of Sound As you read Chapter 21, which begins on page 532 of your textbook, answer the following questions. Would You Believe...? (p. 532) 1. What did Marco
CHAPTER 21 DIRECTED READING WORKSHEET The Nature of Sound As you read Chapter 21, which begins on page 532 of your textbook, answer the following questions. Would You Believe...? (p. 532) 1. What did Marco
5. Which word refers to making
 Name: Date: WEEK 6 1 Read the text and then answer the questions. How do people hear? Look in a mirror, and you will see that your ears are shaped a little like a funnel. That shape amplifies sounds you
Name: Date: WEEK 6 1 Read the text and then answer the questions. How do people hear? Look in a mirror, and you will see that your ears are shaped a little like a funnel. That shape amplifies sounds you
Draw a cross section of the human ear and label its parts.
 Human Ear 1. Open the Human Ear session and follow the instructions. 2. Complete the Human Ear worksheet as you progress through the session. Draw a cross section of the ear and label its parts. 3. Using
Human Ear 1. Open the Human Ear session and follow the instructions. 2. Complete the Human Ear worksheet as you progress through the session. Draw a cross section of the ear and label its parts. 3. Using
The Human Ear. Grade Level: 4 6
 The Human Ear Grade Level: 4 6 Teacher Guidelines pages 1 2 Instructional Pages pages 3 5 Practice Pages pages 6 7 Homework Page page 8 Answer Key page 9 Classroom Procedure: 1. Give a blank sheet of paper,
The Human Ear Grade Level: 4 6 Teacher Guidelines pages 1 2 Instructional Pages pages 3 5 Practice Pages pages 6 7 Homework Page page 8 Answer Key page 9 Classroom Procedure: 1. Give a blank sheet of paper,
SENDING SECRET MESSAGES (1 Hour)
 SENDING SECRET MESSAGES (1 Hour) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 3 Grade Range: K-2 OVERVIEW In this activity, students explore how sound waves travel through various materials. They will build a sound
SENDING SECRET MESSAGES (1 Hour) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 3 Grade Range: K-2 OVERVIEW In this activity, students explore how sound waves travel through various materials. They will build a sound
9.3 Sound The frequency of sound Frequency and pitch pitch Most sound has more than one frequency The frequency spectrum
 9.3 Sound Like other waves, sound has frequency, wavelength, amplitude, and speed. Because sound is part of your daily experience, you already know its properties but by different names. You may never
9.3 Sound Like other waves, sound has frequency, wavelength, amplitude, and speed. Because sound is part of your daily experience, you already know its properties but by different names. You may never
IT S A SECRET! (1 Hour) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 4 Grade Range: K-2
 IT S A SECRET! (1 Hour) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 4 Grade Range: K-2 OVERVIEW In this activity, students explore how sound waves travel through various materials. They will build a sound transmission
IT S A SECRET! (1 Hour) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 4 Grade Range: K-2 OVERVIEW In this activity, students explore how sound waves travel through various materials. They will build a sound transmission
Chapter 2. The Senses
 Chapter 2. The Senses 2.1 Sensory Receptors (p.25-27) sensory receptors - specialized nerve cells whose function is to collect information about changes in the surrounding environment. sensory organs -
Chapter 2. The Senses 2.1 Sensory Receptors (p.25-27) sensory receptors - specialized nerve cells whose function is to collect information about changes in the surrounding environment. sensory organs -
Hearing Loss. How does the hearing sense work? Test your hearing
 Hearing Loss You may have hearing loss and not even be aware of it. People of all ages experience gradual hearing loss, often due to the natural aging process or long exposure to loud noise. Other causes
Hearing Loss You may have hearing loss and not even be aware of it. People of all ages experience gradual hearing loss, often due to the natural aging process or long exposure to loud noise. Other causes
Perception of Sound. To hear sound, your ear has to do three basic things:
 Perception of Sound Your ears are extraordinary organs. They pick up all the sounds around you and then translate this information into a form your brain can understand. One of the most remarkable things
Perception of Sound Your ears are extraordinary organs. They pick up all the sounds around you and then translate this information into a form your brain can understand. One of the most remarkable things
9.3 Sound. The frequency of sound. pitch - the perception of high or low that you hear at different frequencies of sound.
 9.3 Sound Like other waves, sound has frequency, wavelength, amplitude, and speed. Because sound is part of your daily experience, you already know its properties but by different names. You may never
9.3 Sound Like other waves, sound has frequency, wavelength, amplitude, and speed. Because sound is part of your daily experience, you already know its properties but by different names. You may never
Hearing and Sound Study Guide
 Hearing and Sound Study Guide I made the following website as a study tool to help you prepare for Thursday with videos and sample questions hearingandsound.weebly.com 1. Sounds make vibrations and vibrations
Hearing and Sound Study Guide I made the following website as a study tool to help you prepare for Thursday with videos and sample questions hearingandsound.weebly.com 1. Sounds make vibrations and vibrations
Sound Travels How sound travels is explained and demonstrated using a spoon and some string to get the vibrations, then sound, to the students ears.
 Sound Travels How sound travels is explained and demonstrated using a spoon and some string to get the vibrations, then sound, to the students ears. Grade Level Used This activity was done with 4 th graders.
Sound Travels How sound travels is explained and demonstrated using a spoon and some string to get the vibrations, then sound, to the students ears. Grade Level Used This activity was done with 4 th graders.
2. Drumming on My Ear BUILD KNOWLEDGE
 2. Drumming on My Ear BUILD KNOWLEDGE INTRODUCTION What Students Do in this Activity Students learn more about the form that sound waves take and how humans hear sound. They build a model of a human eardrum
2. Drumming on My Ear BUILD KNOWLEDGE INTRODUCTION What Students Do in this Activity Students learn more about the form that sound waves take and how humans hear sound. They build a model of a human eardrum
Sound and hearing 2 The outside of the ear. Sound and hearing 1 How sounds get to our ears
 Sound and hearing 1 How sounds get to our ears 1. What are some of the sounds you would hear if you were camping on a quiet night? 2. How would you feel if you couldn t hear anything? When you listen to
Sound and hearing 1 How sounds get to our ears 1. What are some of the sounds you would hear if you were camping on a quiet night? 2. How would you feel if you couldn t hear anything? When you listen to
Directions: Review the sound vocabulary words. In the pre column place a 2, 1, or 0 2 = expert 1 = heard of it 0 = do not know it
 Directions: Review the sound vocabulary words. In the pre column place a 2, 1, or 0 2 = expert 1 = heard of it 0 = do not know it pre Sound Vocabulary Absorption Amplitude Compression Crest Decibels Echo
Directions: Review the sound vocabulary words. In the pre column place a 2, 1, or 0 2 = expert 1 = heard of it 0 = do not know it pre Sound Vocabulary Absorption Amplitude Compression Crest Decibels Echo
Sound Workshop. What is sound Longitudinal Waves Frequency and pitch Hearing ranges Sounds in solids, liquids and gases Sound in a vacuum
 Sound Workshop a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. k. l. What is sound Longitudinal Waves Frequency and pitch Hearing ranges Sounds in solids, liquids and gases Sound in a vacuum Echoes Ultrasound Loudspeakers
Sound Workshop a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. k. l. What is sound Longitudinal Waves Frequency and pitch Hearing ranges Sounds in solids, liquids and gases Sound in a vacuum Echoes Ultrasound Loudspeakers
Unit 3 Lesson 3 How Do Cells Work Together? Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 How Cells Are Organized Cells are organized to work together so the body functions smoothly. How do cells work together? Classwork 1: Question 1 How do cells work together? Classwork 1: Question 2 Organ
How Cells Are Organized Cells are organized to work together so the body functions smoothly. How do cells work together? Classwork 1: Question 1 How do cells work together? Classwork 1: Question 2 Organ
Sound. Chapter Test A. Multiple Choice. 1 Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
 _ Sound Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. _ 1. Sound is a disturbance that travels through a medium as a a. longitudinal wave. b. surface wave.
_ Sound Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. _ 1. Sound is a disturbance that travels through a medium as a a. longitudinal wave. b. surface wave.
Structure, Movement, and Control
 Human Body Systems Structure, Movement, and Control What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with
Human Body Systems Structure, Movement, and Control What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with
Sound All Around. Visit for thousands of books and materials.
 Sound All Around A Reading A Z Level M Leveled Reader Word Count: 432 LEVELED READER M Written by Penny Atcheson Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of books and materials. www.readinga-z.com Sound
Sound All Around A Reading A Z Level M Leveled Reader Word Count: 432 LEVELED READER M Written by Penny Atcheson Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of books and materials. www.readinga-z.com Sound
Structure, Movement, and Control
 Lesson 2 Structure, Movement, and Control Scan Lesson 2. Read the lesson titles and bold words. Look at the pictures. Identify three facts you discovered about the structure, movement, and control of the
Lesson 2 Structure, Movement, and Control Scan Lesson 2. Read the lesson titles and bold words. Look at the pictures. Identify three facts you discovered about the structure, movement, and control of the
If sound waves needs molecules, how do astronauts in the vacuum of space talk to each other?
 Worksheet 16 A lesson from the Native Access to Engineering Programme Sound sound: saund (noun) 13 th century 1 a : a particular auditory impression : b : the sensation perceived by the sense of hearing
Worksheet 16 A lesson from the Native Access to Engineering Programme Sound sound: saund (noun) 13 th century 1 a : a particular auditory impression : b : the sensation perceived by the sense of hearing
Formatting notes: Bold black text are questions to ask your students to answer Blue bold: learning goals write these on the board.
 These slides could be used in the classroom but are designed with the intent of describing the lesson. When we tested this material with students, we did not project these slides. The teacher used them
These slides could be used in the classroom but are designed with the intent of describing the lesson. When we tested this material with students, we did not project these slides. The teacher used them
Hearing. istockphoto/thinkstock
 Hearing istockphoto/thinkstock Audition The sense or act of hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves Sound waves are composed of changes in air pressure unfolding over time. Acoustical transduction: Conversion
Hearing istockphoto/thinkstock Audition The sense or act of hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves Sound waves are composed of changes in air pressure unfolding over time. Acoustical transduction: Conversion
Science - Year 4. Sound Block 4S. Listen Up! Session 2 Resource Pack
 Science - Year 4 Sound Block 4S Listen Up! Session 2 Resource Pack Original resource copyright Hamilton Trust, who give permission for it to be adapted as wished by individual users. We refer you to our
Science - Year 4 Sound Block 4S Listen Up! Session 2 Resource Pack Original resource copyright Hamilton Trust, who give permission for it to be adapted as wished by individual users. We refer you to our
COMMON CORE Lessons & Activities SAMPLE
 COMMON CORE Lessons & Activities TEACH IT TODAY! About this Book This Common Core Lessons and Activities Book allows you to immediately meet new Common Core State Standards for English Language Arts, as
COMMON CORE Lessons & Activities TEACH IT TODAY! About this Book This Common Core Lessons and Activities Book allows you to immediately meet new Common Core State Standards for English Language Arts, as
2 Sensing the Environment
 CHAPTER 17 2 Sensing the Environment SECTION Communication and Control California Science Standards 7.5.a, 7.5.b, 7.5.g, 7.6.b BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer
CHAPTER 17 2 Sensing the Environment SECTION Communication and Control California Science Standards 7.5.a, 7.5.b, 7.5.g, 7.6.b BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer
Structure and Movement
 Structure and Movement The Skin Key Concepts What does the skin do? How do the three layers of skin differ? How does the skin interact with other body systems? What do you think? Read the two statements
Structure and Movement The Skin Key Concepts What does the skin do? How do the three layers of skin differ? How does the skin interact with other body systems? What do you think? Read the two statements
SENSORY SYSTEM VII THE EAR PART 1
 SENSORY SYSTEM VII THE EAR PART 1 Waves Sound is a compression wave The Ear Ear Outer Ear Pinna Outer ear: - Made up of the pinna and the auditory canal Auditory Canal Outer Ear Pinna (also called the
SENSORY SYSTEM VII THE EAR PART 1 Waves Sound is a compression wave The Ear Ear Outer Ear Pinna Outer ear: - Made up of the pinna and the auditory canal Auditory Canal Outer Ear Pinna (also called the
Sound. Audition. Physics of Sound. Properties of sound. Perception of sound works the same way as light.
 Sound Audition Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
Sound Audition Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
Audition. Sound. Physics of Sound. Perception of sound works the same way as light.
 Audition Sound Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
Audition Sound Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
E4061 Hearing Conservation: Are You Listening, Jim? Leader s Guide
 E4061 Hearing Conservation: Are You Listening, Jim? Leader s Guide ARE YOU LISTENING, JIM? This easy-to-use Leader s Guide is provided to assist in conducting a successful presentation. Featured are: INTRODUCTION
E4061 Hearing Conservation: Are You Listening, Jim? Leader s Guide ARE YOU LISTENING, JIM? This easy-to-use Leader s Guide is provided to assist in conducting a successful presentation. Featured are: INTRODUCTION
Sound from Left or Right?
 Sound from Left or Right? Pre-Activity Quiz 1. How does our sense of hearing work? 2. Why do we have two ears? 3. How does a stethoscope work? (A device used by doctors to listen to the sound of your heart.)
Sound from Left or Right? Pre-Activity Quiz 1. How does our sense of hearing work? 2. Why do we have two ears? 3. How does a stethoscope work? (A device used by doctors to listen to the sound of your heart.)
ISLAMABAD ACADEMY PHYSICS FOR 10TH CLASS (UNIT # 13)
 PHYSICS FOR 10TH CLASS (UNIT # 13) SHORT QUESTIONS How sound is produced? It is produced from a vibrating body which transfers in air from one place to other in the form of compression waves. A medium
PHYSICS FOR 10TH CLASS (UNIT # 13) SHORT QUESTIONS How sound is produced? It is produced from a vibrating body which transfers in air from one place to other in the form of compression waves. A medium
Hearing. PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers. Module 14. Hearing. Hearing
 PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Hearing Module 14 2 Hearing Hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves The
PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Hearing Module 14 2 Hearing Hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves The
How Sound Works. Visit for thousands of books and materials.
 How Sound Works A Reading A Z Level U Leveled Reader Word Count: 1,637 LEVELED READER U Written by Penny Atcheson Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of books and materials. www.readinga-z.com How Sound
How Sound Works A Reading A Z Level U Leveled Reader Word Count: 1,637 LEVELED READER U Written by Penny Atcheson Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of books and materials. www.readinga-z.com How Sound
Sensation and Perception. 8.2 The Senses
 Sensation and Perception 8.2 The Senses I. Introduction A. You probably think that you have just five senses: vision, hearing, taste, smell, and touch. In addition, people have two more internal senses:
Sensation and Perception 8.2 The Senses I. Introduction A. You probably think that you have just five senses: vision, hearing, taste, smell, and touch. In addition, people have two more internal senses:
Respiration and Circulation
 Respiration and Circulation lood Key Concepts What does the do? How do the parts of the differ? What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place
Respiration and Circulation lood Key Concepts What does the do? How do the parts of the differ? What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place
Biological Psychology. Unit Two AE Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology
 Biological Psychology Unit Two AE Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology Vision How do our brains make 3-D images out of 2-D inputs? We live in a 3-dimensional world, but each of our eyes is only capable
Biological Psychology Unit Two AE Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology Vision How do our brains make 3-D images out of 2-D inputs? We live in a 3-dimensional world, but each of our eyes is only capable
How Do Our Ears Work? Quiz
 The Marvelous Ear How Do Our Ears Work? Quiz 1. How do humans hear sounds? 2. How does human hearing work? Sketch and label the system. 3. Do you know any sensors that detect sound and how they might do
The Marvelous Ear How Do Our Ears Work? Quiz 1. How do humans hear sounds? 2. How does human hearing work? Sketch and label the system. 3. Do you know any sensors that detect sound and how they might do
Two ears are better than one.
 Two ears are better than one. Two ears for a reason. Hearing with both ears, as nature intended, is called binaural hearing. It allows us to hear sounds accurately and more naturally. Especially in noisy
Two ears are better than one. Two ears for a reason. Hearing with both ears, as nature intended, is called binaural hearing. It allows us to hear sounds accurately and more naturally. Especially in noisy
A Kazoo For You. Science Activity.
 A Kazoo For You Science Activity www.apologia.com A Kazoo For You Science Activity Published by Apologia Educational Ministries, Inc. 1106 Meridian Street, Suite 340 Anderson, IN 46016 www.apologia.com
A Kazoo For You Science Activity www.apologia.com A Kazoo For You Science Activity Published by Apologia Educational Ministries, Inc. 1106 Meridian Street, Suite 340 Anderson, IN 46016 www.apologia.com
Our Sense Organs Ears
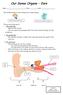 Our Sense Organs Ears Name: Class: Date: Ears enable people to hear things and to keep balance. This boy can hear with his ear. This boy s ears help him to balance. The ear has three parts: 1. The Outer
Our Sense Organs Ears Name: Class: Date: Ears enable people to hear things and to keep balance. This boy can hear with his ear. This boy s ears help him to balance. The ear has three parts: 1. The Outer
NERVOUS SYSTEM & SENSES TEACHER COPY
 NERVOUS SYSTEM & SENSES TEACHER COPY FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM What are the three functions of the Nervous System? 1. Receives information about what is happening inside and outside of your body
NERVOUS SYSTEM & SENSES TEACHER COPY FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM What are the three functions of the Nervous System? 1. Receives information about what is happening inside and outside of your body
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Functions of the Nervous System nervous system stimulus response Neuron structure and function neurons nerve impulses dendrite
 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Functions of the Nervous System The nervous system is a network of communication used by body parts to maintain homeostasis and bodily functions. The nervous system gathers information
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Functions of the Nervous System The nervous system is a network of communication used by body parts to maintain homeostasis and bodily functions. The nervous system gathers information
Cell Structure and Function
 CHAPTER 10 Cell Structure and Function LESSON 3 Moving Cellular Material What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column
CHAPTER 10 Cell Structure and Function LESSON 3 Moving Cellular Material What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column
Sound (11-16) Click here to buy the clear version of Sound (11-16). This pdf file can be downloaded and used on your PC or tablet.
 Sound (11-16) Click here to buy clear version of Sound (11-16). This pdf file can be downloaded and used on your PC or tablet. NOT AVAILABLE YET TEST PAGES ONLY Contents Topic Page Contents Page Sound
Sound (11-16) Click here to buy clear version of Sound (11-16). This pdf file can be downloaded and used on your PC or tablet. NOT AVAILABLE YET TEST PAGES ONLY Contents Topic Page Contents Page Sound
Converting Sound Waves into Neural Signals, Part 1. What happens to initiate neural signals for sound?
 The Ear Outer Ear: Pinna. Collects sounds. Middle Ear: Chamber between eardrum and cochlea containing three tiny bones (hammer, anvil, stirrup) that concentrate the vibrations of the eardrum on the cochlea
The Ear Outer Ear: Pinna. Collects sounds. Middle Ear: Chamber between eardrum and cochlea containing three tiny bones (hammer, anvil, stirrup) that concentrate the vibrations of the eardrum on the cochlea
Hearing The ice show was in its final moments and the music was louder than ever. There was a final chord that echoed across the arena.
 Hearing Hearing The ice show was in its final moments and the music was louder than ever. There was a final chord that echoed across the arena. The audience rose to its feet to applaud. Wow, that was really
Hearing Hearing The ice show was in its final moments and the music was louder than ever. There was a final chord that echoed across the arena. The audience rose to its feet to applaud. Wow, that was really
HEAR YE! HEAR YE! (1.5 Hours)
 HEAR YE! HEAR YE! (1.5 Hours) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 4 Grade Range: 3-5 OVERVIEW In this activity, students will construct a model ear to learn how different materials transmit sound. Topic:
HEAR YE! HEAR YE! (1.5 Hours) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 4 Grade Range: 3-5 OVERVIEW In this activity, students will construct a model ear to learn how different materials transmit sound. Topic:
This presentation covers information on noise, hearing loss and how to protect your ears.
 This presentation covers information on noise, hearing loss and how to protect your ears. Remember, this information applies to the activities you do at school, at work and at home. 1 OSHA defines noise
This presentation covers information on noise, hearing loss and how to protect your ears. Remember, this information applies to the activities you do at school, at work and at home. 1 OSHA defines noise
How the Nervous System Works (pp )
 How the Nervous System Works (pp. 600 604) This section describes what the nervous system does in the body. It also tells how nerve impulses travel. Use Target Reading Skills As you read, identify the
How the Nervous System Works (pp. 600 604) This section describes what the nervous system does in the body. It also tells how nerve impulses travel. Use Target Reading Skills As you read, identify the
The Senses. senses are almost impossible to describe, and yet we use them every moment of the day.
 The Senses Objectives 31.4.1 Discuss the sense of touch and identify the various types of sensory receptors in the skin. THINK ABOUT IT We live in a world of sensations. Think about how many of your experiences
The Senses Objectives 31.4.1 Discuss the sense of touch and identify the various types of sensory receptors in the skin. THINK ABOUT IT We live in a world of sensations. Think about how many of your experiences
Name Date Class. How the Nervous System Works (pages ) 2. Is the following sentence true or false? You can move without your
 CHAPTER 15 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM SECTION 15 1 How the Nervous System Works (pages 486-490) This section describes what the nervous system does in the body. It also tells how nerve impulses travel. Functions
CHAPTER 15 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM SECTION 15 1 How the Nervous System Works (pages 486-490) This section describes what the nervous system does in the body. It also tells how nerve impulses travel. Functions
Unit 4P.1: Sound. How sounds are made? Loudness and pitch Hearing sound Noise Traveling of sound Echo
 Unit 4P.1: How sounds are made? Loudness and pitch Hearing sound Noise Traveling of sound Echo Science skills: Predicting Observing and classifying UBy the end of this unit you should: Know that sound
Unit 4P.1: How sounds are made? Loudness and pitch Hearing sound Noise Traveling of sound Echo Science skills: Predicting Observing and classifying UBy the end of this unit you should: Know that sound
Hearing for life Facts about hearing. How hearing works, how hearing fades and how to assist your hearing
 Hearing for life Facts about hearing How hearing works, how hearing fades and how to assist your hearing 3 Our hearing develops fully while we are still in the womb Our hearing is the only one of our senses
Hearing for life Facts about hearing How hearing works, how hearing fades and how to assist your hearing 3 Our hearing develops fully while we are still in the womb Our hearing is the only one of our senses
Sensing the Environment
 2 Sensing the Environment Key Concept Your organ systems have specialized structures and functions to sense and gather information. What You Will Learn Pressure, temperature, pain, and vibration are four
2 Sensing the Environment Key Concept Your organ systems have specialized structures and functions to sense and gather information. What You Will Learn Pressure, temperature, pain, and vibration are four
Protect Your Hearing!
 Protect Your Hearing! What is noise? Loud sounds if they are over 85 db can be damaging. How do I know if I am listening to levels above 85dB? It is invisible, tasteless, odorless, and IGNORED as a form
Protect Your Hearing! What is noise? Loud sounds if they are over 85 db can be damaging. How do I know if I am listening to levels above 85dB? It is invisible, tasteless, odorless, and IGNORED as a form
Senses. hear. smell. see. taste. touch. Your senses gather information from the outside world. They help you see, hear, taste, smell and touch things.
 Human Body Senses 1 Senses Your senses gather information from the outside world. They help you see, hear, taste, smell and touch things. They also help you to detect pain, pressure, and temperature. All
Human Body Senses 1 Senses Your senses gather information from the outside world. They help you see, hear, taste, smell and touch things. They also help you to detect pain, pressure, and temperature. All
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
 Name: Block: Chapter 7: The Nervous System Lesson 1: How the Nervous System Works What is the Role of the Nervous System? Your nervous system receives information about what is happening both inside and
Name: Block: Chapter 7: The Nervous System Lesson 1: How the Nervous System Works What is the Role of the Nervous System? Your nervous system receives information about what is happening both inside and
Ear Exam and Hearing Tests
 Ear Exam and Hearing Tests Test Overview A thorough evaluation of a person's hearing requires an ear exam and hearing tests. In children, normal hearing is important for language to develop correctly.
Ear Exam and Hearing Tests Test Overview A thorough evaluation of a person's hearing requires an ear exam and hearing tests. In children, normal hearing is important for language to develop correctly.
Sound and Music. Acoustical Society of America 2
 Sound and Music Acoustical Society of America 2 What is Sound? Sit quietly and listen to the sounds around you. Today you will be Sound Detectives 3 What is Sound? Strike the tuning fork with a rubber
Sound and Music Acoustical Society of America 2 What is Sound? Sit quietly and listen to the sounds around you. Today you will be Sound Detectives 3 What is Sound? Strike the tuning fork with a rubber
Learning Targets. Module 20. Hearing Explain how the ear transforms sound energy into neural messages.
 Learning Targets Module 20 Hearing 20-1 Describe the characteristics of air pressure waves that we hear as sound. 20-2 Explain how the ear transforms sound energy into neural messages. 20-3 Discuss how
Learning Targets Module 20 Hearing 20-1 Describe the characteristics of air pressure waves that we hear as sound. 20-2 Explain how the ear transforms sound energy into neural messages. 20-3 Discuss how
Biology. Slide 1 of 49. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 49 2 of 49 Sensory Receptors Neurons that react directly to stimuli from the environment are called sensory receptors. Sensory receptors react to stimuli by sending impulses to other neurons
Biology 1 of 49 2 of 49 Sensory Receptors Neurons that react directly to stimuli from the environment are called sensory receptors. Sensory receptors react to stimuli by sending impulses to other neurons
HEARING GUIDE PREPARED FOR CLINICAL PROFESSIONALS HEARING.HEALTH.MIL. HCE_ClinicalProvider-Flip_FINAL01.indb 1
 HEARING GUIDE PREPARED FOR CLINICAL PROFESSIONALS HCE_ClinicalProvider-Flip_FINAL01.indb 1 TEMPORAL MUSCLE TEMPORAL BONE EXTERNAL AUDITORY CANAL MALLEUS INCUS STAPES SEMICUIRCULAR CANALS COCHLEA VESTIBULAR
HEARING GUIDE PREPARED FOR CLINICAL PROFESSIONALS HCE_ClinicalProvider-Flip_FINAL01.indb 1 TEMPORAL MUSCLE TEMPORAL BONE EXTERNAL AUDITORY CANAL MALLEUS INCUS STAPES SEMICUIRCULAR CANALS COCHLEA VESTIBULAR
Lecture 9: Sound Localization
 Lecture 9: Sound Localization Localization refers to the process of using the information about a sound which you get from your ears, to work out where the sound came from (above, below, in front, behind,
Lecture 9: Sound Localization Localization refers to the process of using the information about a sound which you get from your ears, to work out where the sound came from (above, below, in front, behind,
Ear Disorders and Problems
 Ear Disorders and Problems Introduction Your ear has three main parts: outer, middle and inner. You use all of them to hear. There are many disorders and problems that can affect the ear. The symptoms
Ear Disorders and Problems Introduction Your ear has three main parts: outer, middle and inner. You use all of them to hear. There are many disorders and problems that can affect the ear. The symptoms
Organs of the Nervous System: brain, spinal cord, and nerves
 Nervous System The Nervous System functions as a control center and coordinates all actions and reactions, sending immediate and specific information as electrical impulses. Organs of the Nervous System:
Nervous System The Nervous System functions as a control center and coordinates all actions and reactions, sending immediate and specific information as electrical impulses. Organs of the Nervous System:
Nervous System. Made of two parts. Central Peripheral
 Nervous System Made of two parts Central Peripheral The Central Nervous System is made of the brain and the spinal cord. The Central Nervous System controls everything in the body. A system that controls
Nervous System Made of two parts Central Peripheral The Central Nervous System is made of the brain and the spinal cord. The Central Nervous System controls everything in the body. A system that controls
This refresher covers protecting your eyes and hearing. Remember, this information applies to activities you do at school, work and home.
 This refresher covers protecting your eyes and hearing. Remember, this information applies to activities you do at school, work and home. Collision shops can be noisy, especially when you work with loud
This refresher covers protecting your eyes and hearing. Remember, this information applies to activities you do at school, work and home. Collision shops can be noisy, especially when you work with loud
E3586. What?! Protect Your Hearing. Leader s Guide
 E3586 What?! Protect Your Hearing Leader s Guide 1 What?! Protect Your Hearing This easy-to-use Leader s Guide is provided to assist in conducting a successful presentation. Featured are: INTRODUCTION:
E3586 What?! Protect Your Hearing Leader s Guide 1 What?! Protect Your Hearing This easy-to-use Leader s Guide is provided to assist in conducting a successful presentation. Featured are: INTRODUCTION:
X-Plain Tinnitus Reference Summary
 X-Plain Tinnitus Reference Summary Introduction Tinnitus causes a person to hear a persistent sound in the ear when no sound exists. According to the American Tinnitus Association, at least 12 million
X-Plain Tinnitus Reference Summary Introduction Tinnitus causes a person to hear a persistent sound in the ear when no sound exists. According to the American Tinnitus Association, at least 12 million
Prisoner of Echo. 45 minutes. A sound wave needs a medium through which it is transmitted.
 LESSON ACTIVITY: Prisoner of Echo Prisoner of Echo is a physical science learning game aligned to Common Core and Next Generation Science standards. Partner with Jenkins, a helpful but slightly snarky
LESSON ACTIVITY: Prisoner of Echo Prisoner of Echo is a physical science learning game aligned to Common Core and Next Generation Science standards. Partner with Jenkins, a helpful but slightly snarky
The Outer and Middle Ear PERIPHERAL AUDITORY SYSTEM HOW WE HEAR. The Ear in Action AUDITORY NEUROPATHY: A CLOSER LOOK. The 3 parts of the ear
 AUDITORY NEUROPATHY: A CLOSER LOOK HOW WE HEAR The 3 parts of the ear The ear consists of three main parts: 1. The outer ear The part you see, which is called the auricle (ohr-a-kal). 2. The middle ear
AUDITORY NEUROPATHY: A CLOSER LOOK HOW WE HEAR The 3 parts of the ear The ear consists of three main parts: 1. The outer ear The part you see, which is called the auricle (ohr-a-kal). 2. The middle ear
LISTEN! You might be going deaf DEPARTMENT OF LABOUR TE TARI MAHI OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY & HEALTH SERVICE
 LISTEN! You might be going deaf OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY & HEALTH SERVICE 1 DEPARTMENT OF LABOUR TE TARI MAHI GET THE ANSWERS ABOUT HOW NOISE AFFECTS YOU. Issued by the Occupational Safety & Health Service,
LISTEN! You might be going deaf OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY & HEALTH SERVICE 1 DEPARTMENT OF LABOUR TE TARI MAHI GET THE ANSWERS ABOUT HOW NOISE AFFECTS YOU. Issued by the Occupational Safety & Health Service,
Science5 (SoundMulberry4th)
 Science5 (SoundMulberry4th) Name: Date: 1. The figure below shows a glass partly filled with water. Grace tapped the glass with a metal spoon and heard a sound. Which action would raise the pitch when
Science5 (SoundMulberry4th) Name: Date: 1. The figure below shows a glass partly filled with water. Grace tapped the glass with a metal spoon and heard a sound. Which action would raise the pitch when
Assistive Technology Project. Presented By: Rose Aldan
 Assistive Technology Project Presented By: Rose Aldan Hearing Aid How Your Ear Works An auditory wonder Your ears appear to be relatively simple structures. But they are, in fact, only part of the complex
Assistive Technology Project Presented By: Rose Aldan Hearing Aid How Your Ear Works An auditory wonder Your ears appear to be relatively simple structures. But they are, in fact, only part of the complex
SOUNDS LIKE FUN SCIENCE GRADE 4 STELLA BIZZIO. TIME ALLOTMENT: One 50-minute class.
 SOUNDS LIKE FUN TIME ALLOTMENT: One 50-minute class. OVERVIEW: Using hands-on activities and demonstrations the lesson will focus on the production of sound as energy that can make matter vibrate. Students
SOUNDS LIKE FUN TIME ALLOTMENT: One 50-minute class. OVERVIEW: Using hands-on activities and demonstrations the lesson will focus on the production of sound as energy that can make matter vibrate. Students
What is otosclerosis?
 What is otosclerosis? The term otosclerosis describes a condition of abnormal growth in the tiny bones of the middle ear, which leads to a fixation of the stapes bone. The stapes bone must move freely
What is otosclerosis? The term otosclerosis describes a condition of abnormal growth in the tiny bones of the middle ear, which leads to a fixation of the stapes bone. The stapes bone must move freely
Bacteria and Viruses
 CHAPTER 13 LESSON 3 Bacteria and Viruses What are viruses? Key Concepts What are viruses? How do viruses affect human health? What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree
CHAPTER 13 LESSON 3 Bacteria and Viruses What are viruses? Key Concepts What are viruses? How do viruses affect human health? What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree
Angel International School - Manipay 2 nd Term Examination March, 2018 Physics
 Grade 08 Angel International School - Manipay 2 nd Term Examination March, 2018 Duration: 2.00 Hours 1) Underline the correct answer: Part 1 Index No:- 1) Which is necessary for producing a sound? a) air
Grade 08 Angel International School - Manipay 2 nd Term Examination March, 2018 Duration: 2.00 Hours 1) Underline the correct answer: Part 1 Index No:- 1) Which is necessary for producing a sound? a) air
Senses and Sense Organs
 Senses and Sense Organs SENSORY SYSTEMS Human experience is effected by both internal and external stimuli. Humans are able to distinguish among many different types of stimuli by means of a highly developed
Senses and Sense Organs SENSORY SYSTEMS Human experience is effected by both internal and external stimuli. Humans are able to distinguish among many different types of stimuli by means of a highly developed
FUNNELS OF SOUND. Activity Pack. Explore how sound travels using ear defenders and funnels to create giant ears. Neurosciences and Mental Health
 FUNNELS OF SOUND Activity Pack Description: Duration of Activity: Age: Topic: Key words: Resources: Related Activities: Explore how sound travels using ear defenders and funnels to create giant ears No
FUNNELS OF SOUND Activity Pack Description: Duration of Activity: Age: Topic: Key words: Resources: Related Activities: Explore how sound travels using ear defenders and funnels to create giant ears No
PSY 215 Lecture 10 Topic: Hearing Chapter 7, pages
 PSY 215 Lecture 10 Topic: Hearing Chapter 7, pages 189-197 Corrections: NTC 09-1, page 3, the Superior Colliculus is in the midbrain (Mesencephalon). Announcements: Movie next Monday: Case of the frozen
PSY 215 Lecture 10 Topic: Hearing Chapter 7, pages 189-197 Corrections: NTC 09-1, page 3, the Superior Colliculus is in the midbrain (Mesencephalon). Announcements: Movie next Monday: Case of the frozen
HOW DO HUMAN SENSORS WORK? - UNDERSTANDING HUMAN SENSORS AND COMPARING THEM WITH THOSE IN A ROBOT
 HOW DO HUMAN SENSORS WORK? - UNDERSTANDING HUMAN SENSORS AND COMPARING THEM WITH THOSE IN A ROBOT (50 MINUTES) PRE/POST- ASSESSMENT SHEET HOW DO HUMAN SENSORS WORK? 1. What sensors or senses do we humans
HOW DO HUMAN SENSORS WORK? - UNDERSTANDING HUMAN SENSORS AND COMPARING THEM WITH THOSE IN A ROBOT (50 MINUTES) PRE/POST- ASSESSMENT SHEET HOW DO HUMAN SENSORS WORK? 1. What sensors or senses do we humans
Ganglion Cells Blind Spot Cornea Pupil Visual Area of the Bipolar Cells Thalamus Rods and Cones Lens Visual cortex of the occipital lobe
 How We See How We See Cornea Ganglion Cells whose axons form the optic nerve Blind Spot the exit point at the back of the retina Pupil which is controlled by the iris Bipolar Cells Visual Area of the Thalamus
How We See How We See Cornea Ganglion Cells whose axons form the optic nerve Blind Spot the exit point at the back of the retina Pupil which is controlled by the iris Bipolar Cells Visual Area of the Thalamus
