Related KidsHealth Links
|
|
|
- Abigail Williams
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards This guide correlates with the following National Health Education Standards: Comprehend concepts related to health promotion and disease prevention to enhance health. Analyze the influence of family, peers, culture, media, technology, and other factors on health behaviors. access valid information and products and services to enhance health. use interpersonal communication skills to enhance health and avoid or reduce health risks. use decision-making skills to enhance health. use goal-setting skills to enhance health. practice health-enhancing behaviors and avoid or reduce health risks. advocate for personal, family, and community health. National Health Education Standards: healthyschools/sher/standards/ index.htm Your students might not realize the damaging effects that loud noises in their everyday environment can have. These activities will help your students realize the importance of protecting their hearing, as well as understand the challenges faced by hearing-impaired teens. Related KidsHealth Links Articles for Teens: Ears TeensHealth.org/en/teens/ears.html Earbuds TeensHealth.org/en/teens/earbuds.html Impairment TeensHealth.org/en/teens/hearingimpairment.html Aids TeensHealth.org/en/teens/hearing-aids.html Swimmer s Ear (External Otitis) TeensHealth.org/en/teens/swimmers-ear.html Perforated Eardrum TeensHealth.org/en/teens/eardrums.html Special Needs Factsheet for Teachers: Impairments KidsHealth.org/en/parents/hearing-factsheet.html Discussion Questions Note: The following questions are written in language appropriate for sharing with your students. 1. Name some of the causes of hearing loss. 2. How do your ears get messages to your brain so you can interpret sounds around you? 3. Name some ways to care for your ears and protect your hearing. 4. Are you listening? is a common question asked by teachers. Are listening and hearing the same thing? 5. What do your ears help you do besides hear? 6. What challenges do hearing impaired teens face?
2 Activities for Students Note: The following activities are written in language appropriate for sharing with your students. Turning Down Loss Risks Objectives: Demonstrate an understanding of how to prevent noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL) Materials: Computer with Internet access, TeensHealth.org articles related to hearing Posterboard, markers, audiovisual recording and viewing equipment Class Time: 1 to 4 hours, depending on materials produced (can be divided into multiple sessions) Activity: Noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL) is caused by too much exposure to loud noises, which can permanently damage the hairs on cells in the cochlea. One of the main causes of NIHL among U.S. teens is the use of portable music players. Concerts, video games, TVs, movie theaters, automobile traffic, power tools, and even some appliances can also be too noisy for many people. Fortunately, NIHL is almost 100% preventable if people take steps to protect their ears. To help local kids avoid this problem, create a multimedia awareness campaign for middle schoolers to alert them to the risks and consequences of noise-induced hearing impairment, especially related to earbuds. Create a brief public service announcement (PSA) audio clip, no longer than 30 seconds, to be played during school announcements. Also create posters offering tips to avoid NIHL, as well as a PowerPoint presentation, or an online slideshow, video, or music video featuring tips about protecting hearing and caring for the ears. Make sure the materials you create are age-appropriate and engaging for your intended audience, and that they include fun and memorable messages. [Note to instructor: You can divide your class into small groups and assign each media type to a different group.] Extension: Have your class present its awareness campaign to a middle school class or middle school assembly.
3 Impairment Q&A Objectives: Experience and understand the challenges that can accompany hearing impairment Materials: Ear plugs, sound-blocking headphones or other sound-blocking devices Paper, pencil or pen Class Time: At least 90 minutes outside school Activity: To help you understand the challenges faced by people with hearing impairment or deafness, you re going to experience the challenges yourself. Spend at least 1 hour over a Saturday or Sunday wearing ear plugs, soundblocking headphones or another sound-blocking device. You ll have to be especially careful during some basic activities, such as crossing a street or other things that you might partially depend on hearing to do. Then write a report about how your day without hearing went. Make sure to include interactions with people around you and the emotions you felt. Extension: With a partner, check out books or online resources on American Sign Language (ASL) and learn enough signs to demonstrate a brief, casual conversation in front of the class. Demonstrate your conversation twice the first time silently, and the second time speaking aloud while using your ASL signs so the class can listen in on your conversation. Reproducible Materials Quiz: KidsHealth.org/classroom/9to12/body/functions/hearing_quiz.pdf Answer Key: KidsHealth.org/classroom/9to12/body/functions/hearing_quiz_answers.pdf KidsHealth.org is devoted to providing the latest children s health information. The site, which is widely recommended by educators, libraries, and school associations, has received the Teachers Choice Award for the Family and the prestigious Pirelli Award for Best Educational Media for Students. KidsHealth comes from the nonprofit Nemours Foundation. Check out to see the latest additions!
4 Human Body Series Name: Date: Quiz Instructions: Answer each question. 1. Your ears: a. collect and process sounds b. send signals to your brain c. help you keep your balance d. all of the above 2. The connects your middle ear to the upper part of your throat and helps equalize the pressure on both sides of the eardrum. 3.True or false: Earwax contains chemicals that fight off infections inside the ear canal. 4. Listening to music on earbuds too loud over a long period of time can cause: a. auditory processing disorder b. otitis media c. noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL) 5. hearing loss is present at birth. hearing loss happens later in life. 6. A ringing, humming, buzzing, roaring, or clicking in the ears is called. 7. True or false: loss is the most common birth defect. 8. Name three things that can cause hearing impairment: 9. The snail shell-shaped, fluid-filled converts the vibrations from the middle ear into nerve impulses. 10. The three smallest bones in the body, located just past the eardrum, are: a. the tibia, the fibula, and the phalange b. the malleus, the incus, and the stapes c. the morpheus, the incubus, and the hades 11. The, in the middle ear, is the smallest bone in the body. 12. The part of the ear that is visible on the side of your head is called the or auricle. It s made of covered by skin, and its main job is to gather sounds and funnel them to the ear.
5 Human Body Series Quiz Answer Key 1. Your ears: a. collect and process sounds b. send signals to your brain c. help you keep your balance d. all of the above 2. The eustachian tube the pressure on both sides of the eardrum. connects your middle ear to the upper part of your throat and helps equalize 3.True or false: Earwax contains chemicals that fight off infections inside the ear canal. 4. Listening to music on earbuds too loud over a long period of time can cause: a. auditory processing disorder b. otitis media c. noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL) 5. Congenital hearing loss is present at birth. Acquired hearing loss happens later in life. 6. A ringing, humming, buzzing, roaring, or clicking in the ears is called tinnitus. 7. True or false: loss is the most common birth defect. 8. Name three things that can cause hearing impairment: (any three of the following: genes, head injuries, infections or illnesses, loud noises, medications) 9. The snail shell-shaped, fluid-filled cochlea converts the vibrations from the middle ear into nerve impulses. 10. The three smallest bones in the body, located just past the eardrum, are: a. the tibia, the fibula, and the phalange b. the malleus, the incus, and the stapes c. the morpheus, the incubus, and the hades 11. The stapes, in the middle ear, is the smallest bone in the body. 12. The part of the ear that is visible on the side of your head is called the pinna or auricle. It s made of cartilage covered by skin, and its main job is to gather sounds and funnel them to the ear canal.
Related KidsHealth Links
 K to Grade 2 Human Body Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards This guide
K to Grade 2 Human Body Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards This guide
Related KidsHealth Links. Discussion Questions
 Grades 6 to 8 Human Body Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards This
Grades 6 to 8 Human Body Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards This
The Human Ear. Grade Level: 4 6
 The Human Ear Grade Level: 4 6 Teacher Guidelines pages 1 2 Instructional Pages pages 3 5 Practice Pages pages 6 7 Homework Page page 8 Answer Key page 9 Classroom Procedure: 1. Give a blank sheet of paper,
The Human Ear Grade Level: 4 6 Teacher Guidelines pages 1 2 Instructional Pages pages 3 5 Practice Pages pages 6 7 Homework Page page 8 Answer Key page 9 Classroom Procedure: 1. Give a blank sheet of paper,
Become a good listener LESSON PLAN / MARCH 2015 SPONSORED BY
 Become a good listener LESSON PLAN / MARCH 2015 SPONSORED BY WHO KNOWS WHAT HEARING IS? Hearing, auditory perception, or audition is the ability to perceive sound by detecting vibrations, changes in the
Become a good listener LESSON PLAN / MARCH 2015 SPONSORED BY WHO KNOWS WHAT HEARING IS? Hearing, auditory perception, or audition is the ability to perceive sound by detecting vibrations, changes in the
Related KidsHealth Links
 K to Grade 2 Human Body Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards This guide
K to Grade 2 Human Body Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards This guide
Related KidsHealth Links
 Grades 3 to 5 Personal Health Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards
Grades 3 to 5 Personal Health Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards
Related KidsHealth Links
 K to Grade 2 Health Problems Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards This
K to Grade 2 Health Problems Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards This
Related KidsHealth Links. Discussion Questions
 Grades 3 to 5 Health Problems Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards
Grades 3 to 5 Health Problems Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards
Related KidsHealth Links. Discussion Questions
 K to Grade 2 Human Body Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards This guide
K to Grade 2 Human Body Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards This guide
The bloom guide to better hearing. Find out what you need to know about hearing loss and hearing aids with this helpful guide
 The bloom guide to better hearing Find out what you need to know about hearing loss and hearing aids with this helpful guide Let us help you find the best solution for your hearing Coming to terms with
The bloom guide to better hearing Find out what you need to know about hearing loss and hearing aids with this helpful guide Let us help you find the best solution for your hearing Coming to terms with
Protect Your Hearing!
 Protect Your Hearing! What is noise? Loud sounds if they are over 85 db can be damaging. How do I know if I am listening to levels above 85dB? It is invisible, tasteless, odorless, and IGNORED as a form
Protect Your Hearing! What is noise? Loud sounds if they are over 85 db can be damaging. How do I know if I am listening to levels above 85dB? It is invisible, tasteless, odorless, and IGNORED as a form
Related KidsHealth Links
 Grades 3 to 5 Human Body Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards This
Grades 3 to 5 Human Body Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards This
Related KidsHealth Links
 Grades 9 to 12 Personal Health Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards
Grades 9 to 12 Personal Health Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards
HEARING GUIDE PREPARED FOR CLINICAL PROFESSIONALS HEARING.HEALTH.MIL. HCE_ClinicalProvider-Flip_FINAL01.indb 1
 HEARING GUIDE PREPARED FOR CLINICAL PROFESSIONALS HCE_ClinicalProvider-Flip_FINAL01.indb 1 TEMPORAL MUSCLE TEMPORAL BONE EXTERNAL AUDITORY CANAL MALLEUS INCUS STAPES SEMICUIRCULAR CANALS COCHLEA VESTIBULAR
HEARING GUIDE PREPARED FOR CLINICAL PROFESSIONALS HCE_ClinicalProvider-Flip_FINAL01.indb 1 TEMPORAL MUSCLE TEMPORAL BONE EXTERNAL AUDITORY CANAL MALLEUS INCUS STAPES SEMICUIRCULAR CANALS COCHLEA VESTIBULAR
Related KidsHealth Links
 Grades 3 to 5 Human Body Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards This
Grades 3 to 5 Human Body Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards This
SENSORY SYSTEM VII THE EAR PART 1
 SENSORY SYSTEM VII THE EAR PART 1 Waves Sound is a compression wave The Ear Ear Outer Ear Pinna Outer ear: - Made up of the pinna and the auditory canal Auditory Canal Outer Ear Pinna (also called the
SENSORY SYSTEM VII THE EAR PART 1 Waves Sound is a compression wave The Ear Ear Outer Ear Pinna Outer ear: - Made up of the pinna and the auditory canal Auditory Canal Outer Ear Pinna (also called the
INTRODUCTION TO AUDIOLOGY Hearing Balance Tinnitus - Treatment
 INTRODUCTION TO AUDIOLOGY Hearing Balance Tinnitus - Treatment What is Audiology? Audiology refers to the SCIENCE OF HEARING AND THE STUDY OF THE AUDITORY PROCESS (Katz, 1986) Audiology is a health-care
INTRODUCTION TO AUDIOLOGY Hearing Balance Tinnitus - Treatment What is Audiology? Audiology refers to the SCIENCE OF HEARING AND THE STUDY OF THE AUDITORY PROCESS (Katz, 1986) Audiology is a health-care
Hearing Loss. How does the hearing sense work? Test your hearing
 Hearing Loss You may have hearing loss and not even be aware of it. People of all ages experience gradual hearing loss, often due to the natural aging process or long exposure to loud noise. Other causes
Hearing Loss You may have hearing loss and not even be aware of it. People of all ages experience gradual hearing loss, often due to the natural aging process or long exposure to loud noise. Other causes
Related KidsHealth Links
 Grades 6 to 8 Health Problem Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards This
Grades 6 to 8 Health Problem Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards This
X-Plain Tinnitus Reference Summary
 X-Plain Tinnitus Reference Summary Introduction Tinnitus causes a person to hear a persistent sound in the ear when no sound exists. According to the American Tinnitus Association, at least 12 million
X-Plain Tinnitus Reference Summary Introduction Tinnitus causes a person to hear a persistent sound in the ear when no sound exists. According to the American Tinnitus Association, at least 12 million
Related KidsHealth Links
 K to Grade 2 Health Problems Series KidsHealth.org/classroom These activities will help your students understand what asthma is, how it affects kids, and how kids deal with asthma triggers and flare-ups.
K to Grade 2 Health Problems Series KidsHealth.org/classroom These activities will help your students understand what asthma is, how it affects kids, and how kids deal with asthma triggers and flare-ups.
HEARING GUIDE PREPARED FOR HEARING HEALTH PROFESSIONALS HEARING.HEALTH.MIL. HCE_HealthProvider-Flip_FINAL02.indb 1
 HEARING GUIDE PREPARED FOR HEARING HEALTH PROFESSIONALS HCE_HealthProvider-Flip_FINAL02.indb 1 In both on- and off-duty settings, hearing is an important element of life. ON DUTY Situational awareness
HEARING GUIDE PREPARED FOR HEARING HEALTH PROFESSIONALS HCE_HealthProvider-Flip_FINAL02.indb 1 In both on- and off-duty settings, hearing is an important element of life. ON DUTY Situational awareness
Related KidsHealth Links
 Grades 9 to 12 Health Problems Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials is so common
Grades 9 to 12 Health Problems Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials is so common
i Can t Hear You Developed by David Kleehammer Brockport High School For the My Environment, My Health, My Choices project
 i Can t Hear You Developed by David Kleehammer Brockport High School For the project University of Rochester Rochester, NY Abstract: Personal listening devices, MP3 players, and ipods are a significant
i Can t Hear You Developed by David Kleehammer Brockport High School For the project University of Rochester Rochester, NY Abstract: Personal listening devices, MP3 players, and ipods are a significant
Ear Disorders and Problems
 Ear Disorders and Problems Introduction Your ear has three main parts: outer, middle and inner. You use all of them to hear. There are many disorders and problems that can affect the ear. The symptoms
Ear Disorders and Problems Introduction Your ear has three main parts: outer, middle and inner. You use all of them to hear. There are many disorders and problems that can affect the ear. The symptoms
Assisting in Otolaryngology
 Assisting in Otolaryngology Learning Objectives Identify the structures and explain the functions of the external, middle, and internal ear. Describe the conditions that can lead to hearing loss, including
Assisting in Otolaryngology Learning Objectives Identify the structures and explain the functions of the external, middle, and internal ear. Describe the conditions that can lead to hearing loss, including
HEAR YE! HEAR YE! (1.5 Hours)
 HEAR YE! HEAR YE! (1.5 Hours) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 4 Grade Range: 3-5 OVERVIEW In this activity, students will construct a model ear to learn how different materials transmit sound. Topic:
HEAR YE! HEAR YE! (1.5 Hours) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 4 Grade Range: 3-5 OVERVIEW In this activity, students will construct a model ear to learn how different materials transmit sound. Topic:
Hearing. By Jack & Tori
 Hearing By Jack & Tori 3 Main Components of the Human Ear. Outer Ear. Middle Ear. Inner Ear Outer Ear Pinna: >Visible part of ear and ear canal -Acts as a funnel to direct sound Eardrum: >Airtight membrane
Hearing By Jack & Tori 3 Main Components of the Human Ear. Outer Ear. Middle Ear. Inner Ear Outer Ear Pinna: >Visible part of ear and ear canal -Acts as a funnel to direct sound Eardrum: >Airtight membrane
Main Idea and Details Sort
 Main Idea and Details Sort Students are given 4 different main ideas and 12 details. Students must match up the details to the correct main idea. Print the main ideas (page 25) in one color and the details
Main Idea and Details Sort Students are given 4 different main ideas and 12 details. Students must match up the details to the correct main idea. Print the main ideas (page 25) in one color and the details
HEARING CONSERVATION FACILITATOR S GUIDE
 HEARING CONSERVATION FACILITATOR S GUIDE What s Inside 1 Facilitator s Guidelines 1-a Overview 1-b Getting Started 1-c Presentation Guidelines 1-d Lesson Plan 1-f Frequently Asked Questions 2 Why These
HEARING CONSERVATION FACILITATOR S GUIDE What s Inside 1 Facilitator s Guidelines 1-a Overview 1-b Getting Started 1-c Presentation Guidelines 1-d Lesson Plan 1-f Frequently Asked Questions 2 Why These
Learning Targets. Module 20. Hearing Explain how the ear transforms sound energy into neural messages.
 Learning Targets Module 20 Hearing 20-1 Describe the characteristics of air pressure waves that we hear as sound. 20-2 Explain how the ear transforms sound energy into neural messages. 20-3 Discuss how
Learning Targets Module 20 Hearing 20-1 Describe the characteristics of air pressure waves that we hear as sound. 20-2 Explain how the ear transforms sound energy into neural messages. 20-3 Discuss how
2. Drumming on My Ear BUILD KNOWLEDGE
 2. Drumming on My Ear BUILD KNOWLEDGE INTRODUCTION What Students Do in this Activity Students learn more about the form that sound waves take and how humans hear sound. They build a model of a human eardrum
2. Drumming on My Ear BUILD KNOWLEDGE INTRODUCTION What Students Do in this Activity Students learn more about the form that sound waves take and how humans hear sound. They build a model of a human eardrum
Related KidsHealth Links
 K to Grade 2 Personal Health Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards This
K to Grade 2 Personal Health Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards This
Related KidsHealth Links
 K to Grade 2 Human Body Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards This guide
K to Grade 2 Human Body Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards This guide
Scrub In. What is the function of cerumen? Which part of the ear collects sound waves and directs them into the auditory canal?
 Scrub In What is the function of cerumen? a. Keeps the ear canal from collapsing b. Helps transmit sound waves c. Protection d. Lubrication Which part of the ear collects sound waves and directs them into
Scrub In What is the function of cerumen? a. Keeps the ear canal from collapsing b. Helps transmit sound waves c. Protection d. Lubrication Which part of the ear collects sound waves and directs them into
Hearing Health Presentation
 Hearing Health Presentation Communication around you Hearing connects us with: Family and friends Sounds in our environment Music we love When hearing loss is present it can put limits on your life. How
Hearing Health Presentation Communication around you Hearing connects us with: Family and friends Sounds in our environment Music we love When hearing loss is present it can put limits on your life. How
Hearing Conservation for Children
 Hearing Conservation for Children How Loud is too Loud? 160 db Jet Airplane DANGER ZONE 150 db Helicoptor 140 db Rock Concert 130 db Ambulance Siren 120 db School Dance 110 db Power Saw 100 db Cement Mixer
Hearing Conservation for Children How Loud is too Loud? 160 db Jet Airplane DANGER ZONE 150 db Helicoptor 140 db Rock Concert 130 db Ambulance Siren 120 db School Dance 110 db Power Saw 100 db Cement Mixer
Diagnosing and Treating Adults with Hearing Loss
 Diagnosing and Treating Adults with Hearing Loss Diana Callesano, Au.D., CCC-A Eric Nelson, Au.D., CCC-A Clinical Audiologists Department of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery Hearing and Speech Services
Diagnosing and Treating Adults with Hearing Loss Diana Callesano, Au.D., CCC-A Eric Nelson, Au.D., CCC-A Clinical Audiologists Department of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery Hearing and Speech Services
Protect your Hearing
 Protect your Hearing 3 Your hearing is precious Throughout our lives we are bombarded with a steady stream of sound in schools, at home, at work and out and about. And sometimes these sounds get so loud
Protect your Hearing 3 Your hearing is precious Throughout our lives we are bombarded with a steady stream of sound in schools, at home, at work and out and about. And sometimes these sounds get so loud
Related KidsHealth Links. Discussion Questions
 K to Grade 2 Health Problems Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards This
K to Grade 2 Health Problems Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards This
E4061 Hearing Conservation: Are You Listening, Jim? Leader s Guide
 E4061 Hearing Conservation: Are You Listening, Jim? Leader s Guide ARE YOU LISTENING, JIM? This easy-to-use Leader s Guide is provided to assist in conducting a successful presentation. Featured are: INTRODUCTION
E4061 Hearing Conservation: Are You Listening, Jim? Leader s Guide ARE YOU LISTENING, JIM? This easy-to-use Leader s Guide is provided to assist in conducting a successful presentation. Featured are: INTRODUCTION
Hearing for life Protecting your hearing. Tips on how you can best preserve your hearing
 Hearing for life Protecting your hearing Tips on how you can best preserve your hearing 3 Your hearing is precious Throughout our lives we are bombarded with a steady stream of sound in school, at home,
Hearing for life Protecting your hearing Tips on how you can best preserve your hearing 3 Your hearing is precious Throughout our lives we are bombarded with a steady stream of sound in school, at home,
Hearing for life Protecting your hearing. Tips on how you can best preserve your hearing
 Hearing for life Protecting your hearing Tips on how you can best preserve your hearing 3 Your hearing is precious Throughout our lives we are bombarded with a steady stream of sound in schools, at home,
Hearing for life Protecting your hearing Tips on how you can best preserve your hearing 3 Your hearing is precious Throughout our lives we are bombarded with a steady stream of sound in schools, at home,
Related KidsHealth Links. Discussion Questions
 Grades 9-12 Personal Health Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards This
Grades 9-12 Personal Health Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards This
5. Which word refers to making
 Name: Date: WEEK 6 1 Read the text and then answer the questions. How do people hear? Look in a mirror, and you will see that your ears are shaped a little like a funnel. That shape amplifies sounds you
Name: Date: WEEK 6 1 Read the text and then answer the questions. How do people hear? Look in a mirror, and you will see that your ears are shaped a little like a funnel. That shape amplifies sounds you
Learning about Tinnitus
 Learning about Tinnitus Guide to help you understand and manage your tinnitus Content Your health and your goals!........................................... 4 What s that ringing in my ears?........................................
Learning about Tinnitus Guide to help you understand and manage your tinnitus Content Your health and your goals!........................................... 4 What s that ringing in my ears?........................................
Children s hearing. A guide for parents
 Children s hearing A guide for parents Creating the future Children are our future. By giving them access to a world full of sounds, we can help them to develop the hearing skills they need to build their
Children s hearing A guide for parents Creating the future Children are our future. By giving them access to a world full of sounds, we can help them to develop the hearing skills they need to build their
Assistive Technology Project. Presented By: Rose Aldan
 Assistive Technology Project Presented By: Rose Aldan Hearing Aid How Your Ear Works An auditory wonder Your ears appear to be relatively simple structures. But they are, in fact, only part of the complex
Assistive Technology Project Presented By: Rose Aldan Hearing Aid How Your Ear Works An auditory wonder Your ears appear to be relatively simple structures. But they are, in fact, only part of the complex
Hearing. istockphoto/thinkstock
 Hearing istockphoto/thinkstock Audition The sense or act of hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves Sound waves are composed of changes in air pressure unfolding over time. Acoustical transduction: Conversion
Hearing istockphoto/thinkstock Audition The sense or act of hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves Sound waves are composed of changes in air pressure unfolding over time. Acoustical transduction: Conversion
Related KidsHealth Links
 Grades 3 to 5 Personal Health Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards
Grades 3 to 5 Personal Health Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards
Perception of Sound. To hear sound, your ear has to do three basic things:
 Perception of Sound Your ears are extraordinary organs. They pick up all the sounds around you and then translate this information into a form your brain can understand. One of the most remarkable things
Perception of Sound Your ears are extraordinary organs. They pick up all the sounds around you and then translate this information into a form your brain can understand. One of the most remarkable things
Related KidsHealth Links
 K to Grade 2 Personal Health Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards This
K to Grade 2 Personal Health Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards This
Learning about Tinnitus
 Learning about Tinnitus Guide to help you understand and manage your tinnitus Content Your health and your goals 4 What is that sound in your ears? 5 What causes tinnitus? 6 Tinnitus and your brain 7 What
Learning about Tinnitus Guide to help you understand and manage your tinnitus Content Your health and your goals 4 What is that sound in your ears? 5 What causes tinnitus? 6 Tinnitus and your brain 7 What
Receptors / physiology
 Hearing: physiology Receptors / physiology Energy transduction First goal of a sensory/perceptual system? Transduce environmental energy into neural energy (or energy that can be interpreted by perceptual
Hearing: physiology Receptors / physiology Energy transduction First goal of a sensory/perceptual system? Transduce environmental energy into neural energy (or energy that can be interpreted by perceptual
how we hear. Better understanding of hearing loss The diagram above illustrates the steps involved.
 How we hear Better understanding of hearing loss begins by understanding how we hear. The diagram above illustrates the steps involved. 1. Sound waves are collected by the outer ear and channeled along
How we hear Better understanding of hearing loss begins by understanding how we hear. The diagram above illustrates the steps involved. 1. Sound waves are collected by the outer ear and channeled along
Related KidsHealth Links. Discussion Questions
 K to Grade 2 Personal Health Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards This
K to Grade 2 Personal Health Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards This
Noise Exposure Module Quiz
 265 East 400 South Box 291 Raymond Alberta T0K 2S0 Tel: 403 752-4585 Fax: 403 752-3643 Email: safetyctr@abfarmsafety.com Website: abfarmsafety.com Rural Safety Sense Contest Quiz DVD development and contest
265 East 400 South Box 291 Raymond Alberta T0K 2S0 Tel: 403 752-4585 Fax: 403 752-3643 Email: safetyctr@abfarmsafety.com Website: abfarmsafety.com Rural Safety Sense Contest Quiz DVD development and contest
Sound. Audition. Physics of Sound. Properties of sound. Perception of sound works the same way as light.
 Sound Audition Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
Sound Audition Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
Audition. Sound. Physics of Sound. Perception of sound works the same way as light.
 Audition Sound Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
Audition Sound Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
Draw a cross section of the human ear and label its parts.
 Human Ear 1. Open the Human Ear session and follow the instructions. 2. Complete the Human Ear worksheet as you progress through the session. Draw a cross section of the ear and label its parts. 3. Using
Human Ear 1. Open the Human Ear session and follow the instructions. 2. Complete the Human Ear worksheet as you progress through the session. Draw a cross section of the ear and label its parts. 3. Using
Guide to Your Hearing Health
 X Guide to Your Hearing Health Hearing loss is the 3rd most common chronic physical condition in the U.S. Don t suffer in silence we ve got solutions to help keep you connected! Are you having difficulty
X Guide to Your Hearing Health Hearing loss is the 3rd most common chronic physical condition in the U.S. Don t suffer in silence we ve got solutions to help keep you connected! Are you having difficulty
ID# Exam 2 PS 325, Fall 2003
 ID# Exam 2 PS 325, Fall 2003 As always, the Honor Code is in effect and you ll need to write the code and sign it at the end of the exam. Read each question carefully and answer it completely. Although
ID# Exam 2 PS 325, Fall 2003 As always, the Honor Code is in effect and you ll need to write the code and sign it at the end of the exam. Read each question carefully and answer it completely. Although
Hearing The ice show was in its final moments and the music was louder than ever. There was a final chord that echoed across the arena.
 Hearing Hearing The ice show was in its final moments and the music was louder than ever. There was a final chord that echoed across the arena. The audience rose to its feet to applaud. Wow, that was really
Hearing Hearing The ice show was in its final moments and the music was louder than ever. There was a final chord that echoed across the arena. The audience rose to its feet to applaud. Wow, that was really
Chapter 13 Physics of the Ear and Hearing
 Hearing 100 times greater dynamic range than vision Wide frequency range (20 ~ 20,000 Hz) Sense of hearing Mechanical system that stimulates the hair cells in the cochlea Sensors that produce action potentials
Hearing 100 times greater dynamic range than vision Wide frequency range (20 ~ 20,000 Hz) Sense of hearing Mechanical system that stimulates the hair cells in the cochlea Sensors that produce action potentials
Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis. Lecture 29. Hearing
 Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 29 A dangerous device. Hearing The sound stimulus is changes in pressure The simplest sounds vary in: Frequency: Hertz, cycles per second. How fast the
Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 29 A dangerous device. Hearing The sound stimulus is changes in pressure The simplest sounds vary in: Frequency: Hertz, cycles per second. How fast the
PSY 310: Sensory and Perceptual Processes 1
 Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 29 A dangerous device. Hearing The sound stimulus is changes in pressure The simplest sounds vary in: Frequency: Hertz, cycles per second. How fast the
Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 29 A dangerous device. Hearing The sound stimulus is changes in pressure The simplest sounds vary in: Frequency: Hertz, cycles per second. How fast the
UNDERSTANDING HEARING LOSS
 Helping Babies and Toddlers get a Strong Start UNDERSTANDING HEARING LOSS You have recently been told that your child has a hearing loss. You may feel emotional and overwhelmed as you begin to learn more
Helping Babies and Toddlers get a Strong Start UNDERSTANDING HEARING LOSS You have recently been told that your child has a hearing loss. You may feel emotional and overwhelmed as you begin to learn more
UNDERSTANDING HEARING LOSS
 Helping Babies and Toddlers get a Strong Start UNDERSTANDING HEARING LOSS You have recently been told that your child has a hearing loss. You may feel emotional and overwhelmed as you begin to learn more
Helping Babies and Toddlers get a Strong Start UNDERSTANDING HEARING LOSS You have recently been told that your child has a hearing loss. You may feel emotional and overwhelmed as you begin to learn more
How Do Our Ears Work? Quiz
 The Marvelous Ear How Do Our Ears Work? Quiz 1. How do humans hear sounds? 2. How does human hearing work? Sketch and label the system. 3. Do you know any sensors that detect sound and how they might do
The Marvelous Ear How Do Our Ears Work? Quiz 1. How do humans hear sounds? 2. How does human hearing work? Sketch and label the system. 3. Do you know any sensors that detect sound and how they might do
Hearing Conservation and Noise Control
 Hearing Conservation and Noise Control Objectives What is sound? How the ear works How to measure noise What the Regulations say about noise Reading hearing tests Hearing Protection What is Sound? Hertz
Hearing Conservation and Noise Control Objectives What is sound? How the ear works How to measure noise What the Regulations say about noise Reading hearing tests Hearing Protection What is Sound? Hertz
THE EAR AND HEARING Be sure you have read and understand Chapter 16 before beginning this lab. INTRODUCTION: hair cells outer ear tympanic membrane
 BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ****************************************************************************************************** THE EAR AND HEARING ******************************************************************************************************
BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ****************************************************************************************************** THE EAR AND HEARING ******************************************************************************************************
Hearing Loss. Understanding hearing loss, its effects and available solutions.
 Hearing Loss Understanding hearing loss, its effects and available solutions. Hearing loss is a very common health condition in adults but it is often unrecognised and untreated. Introduction Hearing loss
Hearing Loss Understanding hearing loss, its effects and available solutions. Hearing loss is a very common health condition in adults but it is often unrecognised and untreated. Introduction Hearing loss
Hearing Loss. This year, the weather people in South Texas are warning us to expect a big snow fall in July. Goals and Objectives
 Hearing Loss Janet Reed District 4 Education Chair Assisted by Andrew B. Crocker Extension Program Specialist III, Gerontology Health September 13, 2017 Page 1 Educational programs of the Texas A&M AgriLife
Hearing Loss Janet Reed District 4 Education Chair Assisted by Andrew B. Crocker Extension Program Specialist III, Gerontology Health September 13, 2017 Page 1 Educational programs of the Texas A&M AgriLife
Required Slide. Session Objectives
 Auditory Physiology Required Slide Session Objectives Auditory System: At the end of this session, students will be able to: 1. Characterize the range of normal human hearing. 2. Understand the components
Auditory Physiology Required Slide Session Objectives Auditory System: At the end of this session, students will be able to: 1. Characterize the range of normal human hearing. 2. Understand the components
MIDDLE EAR SURGERY. For Better Health and Hearing
 MIDDLE EAR SURGERY For Better Health and Hearing Help for Ongoing Ear Problems Your doctor has found a problem with your middle ear. This is a part of the ear that you can t see. You may have taken medication,
MIDDLE EAR SURGERY For Better Health and Hearing Help for Ongoing Ear Problems Your doctor has found a problem with your middle ear. This is a part of the ear that you can t see. You may have taken medication,
3882 Hearing Conservation Training for Employees. Leader s Guide ERI Safety Videos
 3882 Hearing Conservation Training for Employees Leader s Guide 2008 ERI Safety Videos HEARING CONSERVATION TRAINING FOR EMPLOYEES This easy-to-use Leader s Guide is provided to assist in conducting a
3882 Hearing Conservation Training for Employees Leader s Guide 2008 ERI Safety Videos HEARING CONSERVATION TRAINING FOR EMPLOYEES This easy-to-use Leader s Guide is provided to assist in conducting a
LISTEN! You might be going deaf DEPARTMENT OF LABOUR TE TARI MAHI OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY & HEALTH SERVICE
 LISTEN! You might be going deaf OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY & HEALTH SERVICE 1 DEPARTMENT OF LABOUR TE TARI MAHI GET THE ANSWERS ABOUT HOW NOISE AFFECTS YOU. Issued by the Occupational Safety & Health Service,
LISTEN! You might be going deaf OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY & HEALTH SERVICE 1 DEPARTMENT OF LABOUR TE TARI MAHI GET THE ANSWERS ABOUT HOW NOISE AFFECTS YOU. Issued by the Occupational Safety & Health Service,
E3586. What?! Protect Your Hearing. Leader s Guide
 E3586 What?! Protect Your Hearing Leader s Guide 1 What?! Protect Your Hearing This easy-to-use Leader s Guide is provided to assist in conducting a successful presentation. Featured are: INTRODUCTION:
E3586 What?! Protect Your Hearing Leader s Guide 1 What?! Protect Your Hearing This easy-to-use Leader s Guide is provided to assist in conducting a successful presentation. Featured are: INTRODUCTION:
Sound Travels How sound travels is explained and demonstrated using a spoon and some string to get the vibrations, then sound, to the students ears.
 Sound Travels How sound travels is explained and demonstrated using a spoon and some string to get the vibrations, then sound, to the students ears. Grade Level Used This activity was done with 4 th graders.
Sound Travels How sound travels is explained and demonstrated using a spoon and some string to get the vibrations, then sound, to the students ears. Grade Level Used This activity was done with 4 th graders.
PSY 214 Lecture # (11/9/2011) (Sound, Auditory & Speech Perception) Dr. Achtman PSY 214
 PSY 214 Lecture 16 Topic: Sound, Auditory System & Speech Perception Chapter 11, pages 270-289 Corrections: None Announcements: CD is available outside Dr Achtman s office if you would like to see demonstrations
PSY 214 Lecture 16 Topic: Sound, Auditory System & Speech Perception Chapter 11, pages 270-289 Corrections: None Announcements: CD is available outside Dr Achtman s office if you would like to see demonstrations
Nervous System. Made of two parts. Central Peripheral
 Nervous System Made of two parts Central Peripheral The Central Nervous System is made of the brain and the spinal cord. The Central Nervous System controls everything in the body. A system that controls
Nervous System Made of two parts Central Peripheral The Central Nervous System is made of the brain and the spinal cord. The Central Nervous System controls everything in the body. A system that controls
Related TeensHealth Links
 Grades 9 to 12 Health Problems Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards
Grades 9 to 12 Health Problems Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards
Trusted content provider for family-friendly, age-appropriate health & wellness information
 An Introduction to What Is KidsHealth Trusted content provider for family-friendly, age-appropriate health & wellness information Creators of print, video, and online resources about children s health
An Introduction to What Is KidsHealth Trusted content provider for family-friendly, age-appropriate health & wellness information Creators of print, video, and online resources about children s health
Deafness and hearing impairment
 Auditory Physiology Deafness and hearing impairment About one in every 10 Americans has some degree of hearing loss. The great majority develop hearing loss as they age. Hearing impairment in very early
Auditory Physiology Deafness and hearing impairment About one in every 10 Americans has some degree of hearing loss. The great majority develop hearing loss as they age. Hearing impairment in very early
Acquired Deafness Loss of hearing that occurs or develops sometime in the course of a lifetime, but is not present at birth.
 Page 1 of 5 URMC» Audiology Glossary of Terms A Acoustic Neuroma A tumor, usually benign, which develops on the hearing and balance nerves and can cause gradual hearing loss, tinnitus, and dizziness. Acquired
Page 1 of 5 URMC» Audiology Glossary of Terms A Acoustic Neuroma A tumor, usually benign, which develops on the hearing and balance nerves and can cause gradual hearing loss, tinnitus, and dizziness. Acquired
ENT 318 Artificial Organs Physiology of Ear
 ENT 318 Artificial Organs Physiology of Ear Lecturer: Ahmad Nasrul Norali The Ear The Ear Components of hearing mechanism - Outer Ear - Middle Ear - Inner Ear - Central Auditory Nervous System Major Divisions
ENT 318 Artificial Organs Physiology of Ear Lecturer: Ahmad Nasrul Norali The Ear The Ear Components of hearing mechanism - Outer Ear - Middle Ear - Inner Ear - Central Auditory Nervous System Major Divisions
Use it or Lose It: The Importance Of Hearing Protection
 Use it or Lose It: The Importance Of Hearing Protection Amjad Awawdeh Arlington Laboratories BAA South West Regional Study Day Wednesday 9 March 2016 Hearing Conservation WHY this topic is so important
Use it or Lose It: The Importance Of Hearing Protection Amjad Awawdeh Arlington Laboratories BAA South West Regional Study Day Wednesday 9 March 2016 Hearing Conservation WHY this topic is so important
MECHANISM OF HEARING
 MECHANISM OF HEARING Sound: Sound is a vibration that propagates as an audible wave of pressure, through a transmission medium such as gas, liquid or solid. Sound is produced from alternate compression
MECHANISM OF HEARING Sound: Sound is a vibration that propagates as an audible wave of pressure, through a transmission medium such as gas, liquid or solid. Sound is produced from alternate compression
Pediatric Hearing Screening Training for the PCA. Gouverneur Healthcare Services 227 Madison Street New York, NY 10002
 Pediatric Hearing Screening Training for the PCA Gouverneur Healthcare Services 227 Madison Street New York, NY 10002 Preface The purpose of any hearing screening program is to ensure early identification
Pediatric Hearing Screening Training for the PCA Gouverneur Healthcare Services 227 Madison Street New York, NY 10002 Preface The purpose of any hearing screening program is to ensure early identification
The Outer and Middle Ear PERIPHERAL AUDITORY SYSTEM HOW WE HEAR. The Ear in Action AUDITORY NEUROPATHY: A CLOSER LOOK. The 3 parts of the ear
 AUDITORY NEUROPATHY: A CLOSER LOOK HOW WE HEAR The 3 parts of the ear The ear consists of three main parts: 1. The outer ear The part you see, which is called the auricle (ohr-a-kal). 2. The middle ear
AUDITORY NEUROPATHY: A CLOSER LOOK HOW WE HEAR The 3 parts of the ear The ear consists of three main parts: 1. The outer ear The part you see, which is called the auricle (ohr-a-kal). 2. The middle ear
HEARING CONSERVATION & NOISE EXPOSURE. 10/1/99 Created By: C. Miterko 1
 HEARING CONSERVATION & NOISE EXPOSURE 10/1/99 Created By: C. Miterko 1 Objectives What is sound? How the ear works How to measure noise What does OSHA says about noise? Reading hearing tests Hearing Protection
HEARING CONSERVATION & NOISE EXPOSURE 10/1/99 Created By: C. Miterko 1 Objectives What is sound? How the ear works How to measure noise What does OSHA says about noise? Reading hearing tests Hearing Protection
Converting Sound Waves into Neural Signals, Part 1. What happens to initiate neural signals for sound?
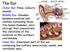 The Ear Outer Ear: Pinna. Collects sounds. Middle Ear: Chamber between eardrum and cochlea containing three tiny bones (hammer, anvil, stirrup) that concentrate the vibrations of the eardrum on the cochlea
The Ear Outer Ear: Pinna. Collects sounds. Middle Ear: Chamber between eardrum and cochlea containing three tiny bones (hammer, anvil, stirrup) that concentrate the vibrations of the eardrum on the cochlea
au/images/conductive-loss-new.jpg
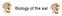 Biology of the ear http://www.nal.gov. au/images/conductive-loss-new.jpg Agenda Pre-test Lecture Group Gesture Types of hearing losses Audiograms Views Post-test Pretest!! See how much you know Answer
Biology of the ear http://www.nal.gov. au/images/conductive-loss-new.jpg Agenda Pre-test Lecture Group Gesture Types of hearing losses Audiograms Views Post-test Pretest!! See how much you know Answer
photo courtesy of Oticon Glossary
 photo courtesy of Oticon Glossary 404.591.1884 www.childrensent.com American Sign Language (ASL): a manual language with its own word order and grammar, used primarily by people who are Deaf. Atresia (aural):
photo courtesy of Oticon Glossary 404.591.1884 www.childrensent.com American Sign Language (ASL): a manual language with its own word order and grammar, used primarily by people who are Deaf. Atresia (aural):
You ve got to be kidding Dad. You wouldn t be able to hear anything with ear plugs. Sure I could, his father said. Your mother and I wore them when
 Hearing Hearing The ice show was ending. The music was louder than ever. One last chord echoed across the arena. The audience stood and clapped. Wow, that was really something! Jake said. They really put
Hearing Hearing The ice show was ending. The music was louder than ever. One last chord echoed across the arena. The audience stood and clapped. Wow, that was really something! Jake said. They really put
Hearing. By: Jimmy, Dana, and Karissa
 Hearing By: Jimmy, Dana, and Karissa Anatomy - The ear is divided up into three parts - Sound enters in through the outer ear and passes into the middle where the vibrations are received and sent to the
Hearing By: Jimmy, Dana, and Karissa Anatomy - The ear is divided up into three parts - Sound enters in through the outer ear and passes into the middle where the vibrations are received and sent to the
An Introduction to. the #1, most-visited site devoted to children s health & parenting
 An Introduction to the #1, most-visited site devoted to children s health & parenting About KidsHealth Our Mission: To positively impact the health of children by providing knowledge, perspective, advice,
An Introduction to the #1, most-visited site devoted to children s health & parenting About KidsHealth Our Mission: To positively impact the health of children by providing knowledge, perspective, advice,
NERVOUS SYSTEM & SENSES TEACHER COPY
 NERVOUS SYSTEM & SENSES TEACHER COPY FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM What are the three functions of the Nervous System? 1. Receives information about what is happening inside and outside of your body
NERVOUS SYSTEM & SENSES TEACHER COPY FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM What are the three functions of the Nervous System? 1. Receives information about what is happening inside and outside of your body
Glue Ear a guide for Teachers
 Glue Ear a guide for Teachers HOW THIS FACTSHEET CAN HELP This factsheet has been produced to help teachers understand the medical condition, glue ear, and offer appropriate support to children who have
Glue Ear a guide for Teachers HOW THIS FACTSHEET CAN HELP This factsheet has been produced to help teachers understand the medical condition, glue ear, and offer appropriate support to children who have
Sound from Left or Right?
 Sound from Left or Right? Pre-Activity Quiz 1. How does our sense of hearing work? 2. Why do we have two ears? 3. How does a stethoscope work? (A device used by doctors to listen to the sound of your heart.)
Sound from Left or Right? Pre-Activity Quiz 1. How does our sense of hearing work? 2. Why do we have two ears? 3. How does a stethoscope work? (A device used by doctors to listen to the sound of your heart.)
