06/11/1431. The head and neck. Chapter 6. Ra'eda Almashaqba 1. The Head. Ra'eda Almashaqba 2
|
|
|
- Lily Flowers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The head and neck Chapter 6 Ra'eda Almashaqba 1 The Head Ra'eda Almashaqba 2 1
2 The Head Ra'eda Almashaqba 3 Common or concern symptom History of: Headache Vertigo Headaches/Migraines Head injury Syncope- dizziness vs vertigo Neck pain- Lumps or swelling Epistaxis Head or Neck surgery Ra'eda Almashaqba 4 2
3 Head Look for scars, lumps, rashes, hair loss, or other lesions. Look for facial asymmetry, involuntary movements, or edema. Palpate to identify any areas of tenderness or deformity. Ra'eda Almashaqba 5 Hydrocephalus: enlarged skull Cushing s syndrome: moon like face with red cheeks duo to increased adrenal gland production. Nephrotic syndrome: the face is edematous and often pale. Acromegaly: enlargement of both bone and soft tissue. Parkinson s disease: masklik face Ra'eda Almashaqba 6 3
4 The Eye Ra'eda Almashaqba 7 Ra'eda Almashaqba 8 4
5 Ra'eda Almashaqba 9 Assessment of the Eye History: Pain Redness or swelling Eye tearing or other discharge Injury to eye Surgery procedure to the eye Medication that may effect the eye Ra'eda Almashaqba 10 5
6 Assessment of the eye Eyebrows: Symmetrical, Curving outward, No crusting or infection, No lesion. Eye Lids: Inspect for: Position,Color, Condition of surface, Condition and direction of eyelashes, Ability to close or blink. Ra'eda Almashaqba 11 Eye Lids Ptosis-abnormal drooping of the lid over the pupil Ectropin- lid margin that turns out Entropin- lid margin that turn in Redness Edema Lacrimal Glands Assess for edema at the inner canthus of the eye, Observe for signs of infection Ra'eda Almashaqba 12 6
7 Conjunctiva and Sclera Covers the exposed surface of the eyeball; lines the eyelids, Normally transparent, assess for Conjunctivitis. Assessment of Pupils: Shape and size of pupil Contracts- when exposed to light or focus in on a near object Dilates- in the dark or when focus on a distant object Average size 3-7mm Miosis: constriction of the pupils Mydriasis: dilatation of the pupils Ra'eda Almashaqba 13 Pupillary Reactions to Light Look for both the direct (same eye) and consensual (other eye) reactions. Accommodation If the pupillary reactions to light are diminished or absent, check the reaction to accommodation (near reaction): Hold your finger about 10cm from the patient's nose. Ask them to alternate looking into the distance and at your finger. Observe the pupillary response in each eye. Ra'eda Almashaqba 14 7
8 Visual Acuity Does the client wear glasses or contacts? Assess ability to read Snellen Chart. E Chart Normal vision 20/20 20N standard distance you stand from chart Myopia: impaired far vision. Presbyopia: impaired near vision. Ra'eda Almashaqba 15 For example, 20/40 means that at 20 feet the patient can only read letters a "normal" person can read from twice that distance (at 40 feet). Ra'eda Almashaqba 16 8
9 Visual Fields When a person using both eyes, the tow visual field over lap in an area of binoculer vision. Lateraly vision is mononoculer Ra'eda Almashaqba 17 Visual Fields (Confrontation test) Assess for peripheral vision Have patient sit or stand 2ft away, facing you at eye level Move a finger equal distance from the patient and yourself outside the field of vision and then bring back in slowly; patient states when he/she spots the finger Ra'eda Almashaqba 18 9
10 Cover and Uncover test Used to detect weakness in the eye muscles- Nystagmus Stand in front of client- cover one eye with a piece of paper, observe uncovered eye for movement indicating re-fixation of the gaze Remove cover and observe the previously covered eye for movement Repeat for the other eye Ra'eda Almashaqba 19 Extraocular movements-eom Six muscles guide the movement of each eye Movement of the eyes should be parallel Ra'eda Almashaqba 20 10
11 Extraocular Movement Client stands about 2ft away; nurse hold up a finger about 6-12 inches from clients eyes; the client is to keep head in a fixed position facing the nurse; the client follows the movement of the finger with eyes only; the nurse assess for abnormalities. nystagmus (involuntary movement of the eye)( fine rythmatic oscillation of the eye). Ra'eda Almashaqba 21 Ophthalmoscope Exam Ra'eda Almashaqba 22 11
12 Darken the room as much as possible. Adjust the ophthalmoscope so that the light is no brighter than necessary. Adjust the aperture to a plain white circle. Set the diopter dial to zero unless you have determined a better setting for your eyes. Use your left hand and left eye to examine the patient's left eye. Use your right hand and right eye to examine the patient's right eye. Place your free hand on the patient's shoulder for better control. Ask the patient to stare at a point on the wall or corner of the room. Ra'eda Almashaqba 23 Look through the ophthalmoscope and shine the light into the patient's eye from about two feet away. You should see the retina as a "red reflex." Follow the red color to move within a few inches of the patient's eye. Adjust the diopter dial to bring the retina into focus. Find a blood vessel and follow it to the optic disk. Use this as a point of reference. Inspect outward from the optic disk in at least four quadrants and note any abnormalities. Move nasally from the disk to observe the macula. Repeat for the other eye. Ra'eda Almashaqba 24 12
13 Ra'eda Almashaqba 25 Special Tests Upper Eyelid Eversion Ask the patient to look down. Gently grasp the patient's upper eyelashes and pull them out and down. Place the shaft of an applicator or tongue blade about 1 cm from the lid margin. Pull the lid upward using the applicator as a fulcrum to turn the lid "inside out." Do not press down on the eye itself. Pin the eyelid in this position by pressing the lashes against the eyebrow while you examine the palpebral conjuntiva. Ask the patient to blink several times to return the lid to normal. Ra'eda Almashaqba 26 13
14 The Ear Ra'eda Almashaqba 27 The Ear The ear consists of external, middle, and inner structures. External ear consist of auricle and ear canal. Middle ear consist of tympanic membrane and 3 ossicles Inner ear consist of cochlea and cochlear nerve Ra'eda Almashaqba 28 14
15 Ra'eda Almashaqba 29 Pathway of Hearing Conductive Phase: transmission of sound vibration from the external ear to the ear canal then through the ear drum and ossicles to the cochlea Sensorineural Phase: Transmission of vibration from the cochlea, cochlear nerve then to the brain. Ra'eda Almashaqba 30 15
16 Changes with Aging Diminished hearing acuity ( presbycusis) - start with high- pitch sound - extend to the sound in middle and lower range - evident after the age of 50. Ra'eda Almashaqba 31 Health History Hearing problems :( How is your hearing?, Have you had any trouble with your ears?) hearing loss: ( one or both ears, Sudden or gradual loss, Any associated symptoms? ) Dose the patient have special difficulty understanding people as they talk. what difference does a noisy environment make worse -- Sensorineural Better-- conductive Ra'eda Almashaqba 32 16
17 Ask about medication ( lasix, Aspirin, NSAID s) Earache (pain, fever, discharge, sore throat, URT infection) Tinnitus Vertigo: point problem in the labyrinths of the inner ear, or lesions in CN VIII (dizzy, room spinning, being pulled) Ra'eda Almashaqba 33 Ear Exam Inspect auricle and surrounding tissues Deformities Lumps Skin lesions If pain, discharge, inflammation palpate pinna and tragus for tenderness Tug test: movement of the auricle and tragus Painful in acute Otitis externa (swimmer s ear) Palpate mastoid process for tenderness Otitis media Ra'eda Almashaqba 34 17
18 Fundamentals of Otoscopy To see the ear canal and ear drum. Use the largest ear speculum that the canal will accommodate Position the patient s head so that you can see comfortably Straighten the ear canal by grasping the auricle firmly and pulling it upward, backward, and slightly away from the head Ra'eda Almashaqba 35 Holding the scope between your thumb and forefingers, brace your hand against the patient s face This allows your hand and instrument to follow unexpected movements by the patient You may use the right hand to examine both the right and the left ears Ra'eda Almashaqba 36 18
19 Viewing Insert the speculum gently into the ear canal Direct it down and forward and through the hair in the canal if present Cerumen (ear wax) may be present and may totally obscure your view; it varies from yellow and flaky to brown and sticky Ra'eda Almashaqba 37 Viewing Inspect ear canal for discharge, foreign body, redness, swelling Inspect the eardrum, noting color and contour Should have a bright reflection of light ( cone of light) Identify the insertion of the handle of the malleus, and short process of the malleus Gently move the speculum so you can see as much of the drum as possible Ra'eda Almashaqba 38 19
20 Examination of the EARS Otoscopic exam Pull the ear upwards and backwards to straighten the canal. Insert the otoscope Inspect the ear canal and middle ear structures noting any redness, drainage, or deformity. Ra'eda Almashaqba 39 Ra'eda Almashaqba 40 20
21 Viewing Abnormalities to be on the look out for: Swollen, red, canal: swimmer s ear (Otitis externa) Bulging, red eardrum: ear infection (Otitis media) Amber eardrum: fluid (allergies) Ra'eda Almashaqba 41 Ear Exam Auditory Acuity: Assess hearing one ear at a time with whisper test tuning fork (512 Hz), ticking watch, or others. If hearing is abnormal, perform the Weber and Rinne tests to assess for Sensorineural and/or conductive hearing loss Ra'eda Almashaqba 42 21
22 Examination of the Ears Weber Test: lateralization Base of tuning fork (512 Hz) on top of head Ask where patient hears it; in conductive loss, sound heard in the impaired ear vs. Sensorineural loss where it is heard in the good ear Compare air and bone conduction: Rinne Tuning fork on mastoid and in front of ear Conductive loss: BC>AC, heard longer through bone Sensorineural loss: AC>BC, air is longer than bone Ra'eda Almashaqba 43 Ra'eda Almashaqba 44 22
23 Rinne Test (To compare AC & BC) A positive Rinne test is a normal test: air conduction should be longer than bone conduction. Sensorineural hearing loss produces a positive Rinne test: AC>BC Conductive hearing loss produces a negative Rinne test: AC<BC or AC=BC Ra'eda Almashaqba 45 Ra'eda Almashaqba 46 23
24 Diseases Causing Hearing Loss Conductive Hearing loss: Lesion between the receptors and environment (Ossicles lesion, Otitis media, otosclerosis, impacted cerumen) Sensorineural hearing loss: Lesion of the receptors or its pathway (Aging, drug toxicity, noise damage, acoustic neuroma) Ra'eda Almashaqba 47 The nose and paranasal sinuses Ra'eda Almashaqba 48 24
25 Anatomy of the Nose External 1. Nasal bridge 2. Tip 3. Anterior naris 4. Vestibule 5. Ala nasi Internal 1. Nasal Septum 2. Turbinate - Superior - middle - inferior 3. Frontal and Maxillary Sinus Ra'eda Almashaqba 49 The nose Ra'eda Almashaqba 50 25
26 The Nose & Sinus Health history: Rhinorrhea: drainage from the nose Nasal discharge or runny nose--continuous, watery, purulent, mucoid, bloody Nasal congestion---stuffy nose, sneezing, watery eyes, throat discomfort, itching in the eyes, nose, throat. Frequent or severe colds How often? Remedies? Sinus pain Headache, tenderness, fever Ra'eda Almashaqba 51 The Nose Health history: Trauma Breath through nose? Any obstruction? Epistaxis bleeding from nose How much? Teaspoon, does it pour out? From one or both nostrils? How do you treat them? Difficult to stop? Allergies Pollen, dust, hair? Aggravating environment Inhalers? Spray, drops Any change in sense of smell Ra'eda Almashaqba 52 26
27 Examination of the Nose and paranasal sinuses Inspect the anterior and inferior surface of the nose ( note symmetry, deformity) Test for nasal obstruction Inspect the inside of the nose with the otoscope using the largest ear speculum Ra'eda Almashaqba 53 Observe the 1. nasal septum for deviation, inflammation, perforation. 2. Nasal Mucosa: color, swelling, bleeding, exudates 3. Any abnormalities such as ulcers or polyps. Palpate for sinus tenderness Ra'eda Almashaqba 54 27
28 The Nose Palpate sinus areas with thumbs Frontal sinus, below eyebrows Maxillary sinus, below cheekbones Firm pressure, no pain Note tenderness (chronic allergy, acute infection sinusitis) Transillumination of sinuses An inflamed sinus does not illuminate Ra'eda Almashaqba 55 Normal Findings The septum is in the middle and the turbinate project into the nasal passages. There is sufficient room for the nasal passages. The mucous membrane is red and compact over the turbinate. There may be a small amount of thin secretions. Ra'eda Almashaqba 56 28
29 Special Tests Sinus Transillumination Darken the room as much as possible. Place a bright otoscope or other point light source on the maxilla. Ask the patient to open their mouth and look for an orange glow on the hard palate. A decreased or absent glow suggests that the sinus is filled with something other than air. Ra'eda Almashaqba 57 Mouth & Oropharynx Ra'eda Almashaqba 58 29
30 Ra'eda Almashaqba 59 Mouth & Pharynx Anatomy of the Mouth: Lips, gingiva, intredental papillae, labial frenulum, labial mucosa, alveolar mucosa Anatomy of the tongue: papillae ( red dots on the tongue surface), lingual frenulum, submandibular gland duct (Wharton s duct), parotid duct (Stensen s duct), buccal mucosa Ra'eda Almashaqba 60 30
31 Changes with aging Diminished salivary secretion Decreased sense of taste Teeth become abraded with time Ra'eda Almashaqba 61 Health history Sore throat How frequent? Since when? Cough, fever, fatigue, headache, hoarseness, postnasal drip Sores or lesions in mouth or tongue For how long? Single or multiple? Stress, food, season change? Altered taste Bleeding gums--gingivitis Toothache Ra'eda Almashaqba 62 31
32 Hoarseness Acute or chronic Overuse of voice Allergy, smoking, other inhaled irritants Hypothyroidism Tumors Dysphagia difficulty swallowing Gastroesophageal reflux disease, neurological, esophageal cancer Pharyngitis-- Swollen glands or lumps in neck Ra'eda Almashaqba 63 Mouth and Throat Exam Inspect using penlight The Lips Color, moisture, cracking, Scaliness, lesions, ulcers Pallor shock and anemia Cyanosis hypoxemia and chilling Cherry red lips carbon monoxide poisoning, acidosis, ketoacidosis Blisters (herpes simplex) Ulcer (chancre sore) Edema Cleft lip Ra'eda Almashaqba 64 32
33 Oral mucosa: look in pt mouth with the help of light and tongue blade look for: Color, ulcers, white patches, and nodule The Gum&Teeth Gum: color gum margin, interdental papillae: for swelling or ulceration Teeth: missing, discolored, misshapen, abnormally positioned Ra'eda Almashaqba 65 1-The roof of the mouth: Inspect color and shape of hard palate (roof of mouth) * Cleft palate * Midline lobulated bony growth: (Torus palatinus) 2-The tongue and the floor of the mouth: for symmetry( test for hypoglossal nerve, CN XII) - Note color and texture of the tongue Dry mouth with dehydration, fever, deep vertical fissures, Decreased/ excess saliva - Inspect the sides and the undersurface of the tongue and the floor of the mouth for ( white or reddened area, nodules, ulceration loss of movement Ra'eda Almashaqba 66 33
34 Inspect the U-shape under the tongue Note white patches, redness, nodules, ulcerations Any lesion or ulcer persisting more than 2 weeks should be followed Palpate the tongue for indurations 3-The Pharynx: Ask patient to say Ah while depressing tongue to check pharynx note integrity and mobility as person phonates Failure of soft palate to raise with "aah" and deviation of uvula to opposite side: (Paralysis of Vagus CN X) Check gag reflex (Glossopharangeal CN IX, and Vagus CN Ra'eda Almashaqba 67 Pharyngeal wall note color, any exudates, lesions Redness, swelling, pus : (Pharyngitis: Viral, Strep) Grayish exudates (Diphtheria) Inspect soft palate, anterior and posterior pillars, uvula, tonsils, and pharynx color, symmetry, exudates, swelling, ulceration, tonsillar enlargement Ra'eda Almashaqba 68 34
35 The Neck Anatomy divided into 2 triangles Anterior: bounded above by the mandible, laterally by sternomastoid muscle, and medially by the midline of the neck Posterior: extended from the sternomastoid to the trapezius and bounded below by the clavicle Midline structure: 1. Hyoid bone 2. Thyroid cartilage 3. Cricoid cartilage 4. Tracheal ring 5. Thyroid gland Ra'eda Almashaqba 69 The pharynx and larynx Ra'eda Almashaqba 70 35
36 Lymph Nodes Ra'eda Almashaqba 71 Health HX of the Neck Ask the pt if he notice any swollen gland or lumps in the neck Enlarged thyroid gland goiter Thyroid function Temperature intolerance and sweating Do you prefer hot or cold weather Do you dress more warmly or less warmly than other people? Palpitations? Change in weight? Ra'eda Almashaqba 72 36
37 Examination of the Neck Inspect the neck note any masses or scare, enlarged gland, visible lymph node Palpate LN: 1. By using the pads of the middle and ring finger 2. The pt should be relaxed, neck flexed forward and towered the side being examined Ra'eda Almashaqba 73 Feel in sequence: Preauricular: in front of the ear Posterior auricular: anterior to the mastoid Occipital: at the base of the skull posteriorlly Tonsillar: at angle of mandible Submandibular: midway between the angle and the tip of the mandible submental: at the midline few cm behind the tip of the mandible Superficial cervical: superficial to the sternomastoid Posterior cervical: along the anterior edge of the trapezius Deep cervical: deep to the sternomastoid muscle Supraclavicular: deep in the angle formed by the clavicle and sternomastoid (suggests thoracic or abdominal malignancy) Ra'eda Almashaqba 74 37
38 Note shape, size, delimitation, mobility, consistency, and any tenderness Small, mobile, discrete, nontender nodes are common and termed shotty Nodes are abnormal if greater than 1 cm and/or present greater than one month Hard nodes suggest malignancy Tender nodes suggest infection Rubbery nodes suggest lymphoma Ra'eda Almashaqba 75 The Trachea & the Thyroid gland Inspection of the trachea for deviation then feel for deviation by: place your finger along one side of the trachea and note the space between it and the sternomastoid. Inspect the neck for thyroid gland: - ask the pt to tilt head back by using a light from downward the tip of pt chin inspect the region below the Cricoid cartilage for the gland - ask pt to sip water and to extend the neck and swallow, watch for upward movement of the thyroid gland noting it s contour and symmetry Ra'eda Almashaqba 76 38
39 Palpation of the thyroid gland: from behind the pt - ask the pt to flex the neck -Place the finger of both hands on the pt s neck - Ask the pt to sip and swallow water, feel the isthmus - Displace the trachea to the Rt, with the Rt hand fingers, palpate the thyroid in space between displaced trachea and relaxes sternomastoid, in similar way examine the Lt lobe - Note size, shape, and consistency of the gland, ID any nodules or tenderness Ra'eda Almashaqba 77 If the thyroid gland is enlarged listen over the lateral lobe with stethoscope to detect bruit ( similar to the cardiac murmur but of noncardic origin). Normal: Right side slightly larger than left Ra'eda Almashaqba 78 39
40 Questions Ra'eda Almashaqba Ra'eda Almashaqba Ra'eda Almashaqba 80 40
PCM1 Physical Exam Skills Session: Head and Neck FACILITATOR & STUDENT COPY
 PATIENT CENTERED MEDICINE - 1 GOALS & OUTCOMES: PCM1 Physical Exam Skills Session: Head and Neck FACILITATOR & STUDENT COPY 1. To introduce the applied anatomy relevant for the examination of the head
PATIENT CENTERED MEDICINE - 1 GOALS & OUTCOMES: PCM1 Physical Exam Skills Session: Head and Neck FACILITATOR & STUDENT COPY 1. To introduce the applied anatomy relevant for the examination of the head
Unit # 10 B Assessment of Ears
 In The Name of God (A PROJECT OF NEW LIFE HEALTH CARE SOCIETY KARACHI) Unit # 10 B Assessment of Ears Shahzad Bashir RN, BScN, DCHN, MScN (Std. DUHS) Instructor New Life College of Nursing Updated, January
In The Name of God (A PROJECT OF NEW LIFE HEALTH CARE SOCIETY KARACHI) Unit # 10 B Assessment of Ears Shahzad Bashir RN, BScN, DCHN, MScN (Std. DUHS) Instructor New Life College of Nursing Updated, January
Head and Neck Examination
 Head and Neck Examination Statement of Goals Understand and perform an examination of the head and neck. Learning Objectives Head Ears Nose Sinus A. Describe the anatomy of the head, including regions
Head and Neck Examination Statement of Goals Understand and perform an examination of the head and neck. Learning Objectives Head Ears Nose Sinus A. Describe the anatomy of the head, including regions
Module Three. Application of Health Assessment NUR 225. Physical examination of Head and Neck. King Saud University. Collage of Nursing
 King Saud University Collage of Nursing Medical Surgical Nursing depart Application of Health Assessment NUR 225 Module Three Physical examination of Head and Neck 1 Physical Examination techniques for
King Saud University Collage of Nursing Medical Surgical Nursing depart Application of Health Assessment NUR 225 Module Three Physical examination of Head and Neck 1 Physical Examination techniques for
Physical examination- inspection Internal Medicine 3rd year. Dr. Székely Hajnal
 Physical examination- inspection Internal Medicine 3rd year Dr. Székely Hajnal 2017.10.03. Inspection The book recommends examining the patient from the patient s right side Often you will need to examine
Physical examination- inspection Internal Medicine 3rd year Dr. Székely Hajnal 2017.10.03. Inspection The book recommends examining the patient from the patient s right side Often you will need to examine
EAR, NOSE AND THROAT (ENT) ASSESSMENT
 This decision support tool is effective as of October 2016. For more information or to provide feedback on this or any other decision support tool, email certifiedpractice@crnbc.ca EAR, NOSE AND THROAT
This decision support tool is effective as of October 2016. For more information or to provide feedback on this or any other decision support tool, email certifiedpractice@crnbc.ca EAR, NOSE AND THROAT
EAR, NOSE AND THROAT (ENT) ASSESSMENT
 RN First Call Certified Practice This decision support tool is effective as of October 2016. For more information or to provide feedback on this or any other decision support tool, email certifiedpractice@crnbc.ca
RN First Call Certified Practice This decision support tool is effective as of October 2016. For more information or to provide feedback on this or any other decision support tool, email certifiedpractice@crnbc.ca
EAR, NOSE AND THROAT (ENT) ASSESSMENT
 For more information or to provide feedback on this or any other decision support tool, email certifiedpractice@bccnp.ca EAR, NOSE AND THROAT (ENT) ASSESSMENT Nurses with Remote Nursing Certified Practice
For more information or to provide feedback on this or any other decision support tool, email certifiedpractice@bccnp.ca EAR, NOSE AND THROAT (ENT) ASSESSMENT Nurses with Remote Nursing Certified Practice
REVIEW/PREVIEW OF HEAD AND NECK ANATOMY FOR ENT EXAM
 REVIEW/PREVIEW OF HEAD AND NECK ANATOMY FOR ENT EXAM - 2017 PALPATE CAROTID ARTERY: AT LEVEL OF CAROTID BIFURCATION VERTEBRAL LEVEL C4 Sternocleidomastoid Muscle INTERNAL CAROTID EXTERNAL CAROTID COMMON
REVIEW/PREVIEW OF HEAD AND NECK ANATOMY FOR ENT EXAM - 2017 PALPATE CAROTID ARTERY: AT LEVEL OF CAROTID BIFURCATION VERTEBRAL LEVEL C4 Sternocleidomastoid Muscle INTERNAL CAROTID EXTERNAL CAROTID COMMON
Cranial Nerves Exam. 1. To learn how to examine the functions of the 12 pairs of cranial nerves.
 Cranial Nerves Exam [Purpose] 1. To learn how to examine the functions of the 12 pairs of cranial nerves. 2. To understand the function of the 12 pairs of cranial nerves. [Principle] The cranial nerves
Cranial Nerves Exam [Purpose] 1. To learn how to examine the functions of the 12 pairs of cranial nerves. 2. To understand the function of the 12 pairs of cranial nerves. [Principle] The cranial nerves
EAR, NOSE AND THROAT (ENT) ASSESSMENT
 For more information or to provide feedback on this or any other decision support tool, email certifiedpractice@bccnp.ca EAR, NOSE AND THROAT (ENT) ASSESSMENT Nurses with Remote Nursing Certified Practice
For more information or to provide feedback on this or any other decision support tool, email certifiedpractice@bccnp.ca EAR, NOSE AND THROAT (ENT) ASSESSMENT Nurses with Remote Nursing Certified Practice
Lecture 07. Lymphatic's of Head & Neck. By: Dr Farooq Amanullah Khan PMC
 Lecture 07 Lymphatic's of Head & Neck By: Dr Farooq Amanullah Khan PMC Dated: 28.11.2017 Lymphatic Vessels Of the 800 lymph nodes in the human body, 300 are in the Head & neck region. The lymphatic vessels
Lecture 07 Lymphatic's of Head & Neck By: Dr Farooq Amanullah Khan PMC Dated: 28.11.2017 Lymphatic Vessels Of the 800 lymph nodes in the human body, 300 are in the Head & neck region. The lymphatic vessels
CERVICAL LYMPH NODES
 CERVICAL LYMPH NODES (ANATOMY & EXAMINATION) Hemant (DTCD 1 st YEAR) 1. Lymphatic Tissues: A Type of connective tissue that contains large numbers of lymphocytes. 2. Lymphatic Vessels: Are Tubes that assist
CERVICAL LYMPH NODES (ANATOMY & EXAMINATION) Hemant (DTCD 1 st YEAR) 1. Lymphatic Tissues: A Type of connective tissue that contains large numbers of lymphocytes. 2. Lymphatic Vessels: Are Tubes that assist
Primary Care ENT. Dr Layth Delaimy
 Primary Care ENT Dr Layth Delaimy EAR NOSE THROAT Examinations Inspecting the external ear Swab any discharge, and remove any wax. Look for obvious signs of abnormality: Size and shape of pinna Extra cartilage
Primary Care ENT Dr Layth Delaimy EAR NOSE THROAT Examinations Inspecting the external ear Swab any discharge, and remove any wax. Look for obvious signs of abnormality: Size and shape of pinna Extra cartilage
Neurological Assessment Part 1
 Neurological Assessment Part 1 MOTOR EXAMINATION: Look at bulk, contour and symmetry of individual muscles: muscles of face upper arm arm thigh lower leg Look for atrophy--may help to localize the site
Neurological Assessment Part 1 MOTOR EXAMINATION: Look at bulk, contour and symmetry of individual muscles: muscles of face upper arm arm thigh lower leg Look for atrophy--may help to localize the site
ASSESSING THE EYES. Structures. Eyelids Extraocularmuscles Eyelashes Lacrimal glands: Lacrimal ducts Cornea Conjunctiva Sclera Pupils Iris.
 ASSESSING THE EYES Structures External Eyelids Extraocularmuscles Eyelashes Lacrimal glands: Lacrimal ducts Cornea Conjunctiva Sclera Pupils Iris 1 2 Structures Internal Optic disc Physiological cup Retinal
ASSESSING THE EYES Structures External Eyelids Extraocularmuscles Eyelashes Lacrimal glands: Lacrimal ducts Cornea Conjunctiva Sclera Pupils Iris 1 2 Structures Internal Optic disc Physiological cup Retinal
Module Three. Application of Health Assessment NUR 225. Physical examination of Head and Neck. King Saud University. Collage of Nursing
 King Saud University Collage of Nursing Medical Surgical Nursing depart Application of Health Assessment NUR 225 Module Three Physical examination of Head and Neck 1 Physical Examination techniques for
King Saud University Collage of Nursing Medical Surgical Nursing depart Application of Health Assessment NUR 225 Module Three Physical examination of Head and Neck 1 Physical Examination techniques for
BIOE221. Session 03. Head and Neck Assessment. Bioscience Department. Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au
 BIOE221 Session 03 Head and Neck Assessment Bioscience Department Session Objectives Understand the importance and rationale for the examinations of the mouth and throat Understand the importance and rationale
BIOE221 Session 03 Head and Neck Assessment Bioscience Department Session Objectives Understand the importance and rationale for the examinations of the mouth and throat Understand the importance and rationale
NURS 221 HEALTH ASSESSMENT (Practical) Procedure Guide and Performance Checklist
 King Saud University College of Nursing Medical Surgical Department NURS 221 HEALTH ASSESSMENT (Practical) Procedure Guide and Performance Checklist Module Three Physical Examination of the Head, Neck
King Saud University College of Nursing Medical Surgical Department NURS 221 HEALTH ASSESSMENT (Practical) Procedure Guide and Performance Checklist Module Three Physical Examination of the Head, Neck
BATES VISUAL GUIDE TO PHYSICAL EXAMINATION. Vol. 7: Head, Eyes, and Ears
 BATES VISUAL GUIDE TO PHYSICAL EXAMINATION Vol. 7: Head, Eyes, and Ears Your learning objectives for mastering the examination of the head, eyes, and ears are: to identify and examine key structures basic
BATES VISUAL GUIDE TO PHYSICAL EXAMINATION Vol. 7: Head, Eyes, and Ears Your learning objectives for mastering the examination of the head, eyes, and ears are: to identify and examine key structures basic
Special Senses. Unit 6.7 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.7 (7 th Edition)
 Special Senses Unit 6.7 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.7 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the five special senses. Identify the four general senses. Trace the pathway of light rays as they pass
Special Senses Unit 6.7 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.7 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the five special senses. Identify the four general senses. Trace the pathway of light rays as they pass
Unit 4 - REGULATORY SYSTEMS Special Senses Lecture Notes
 Unit 4 - REGULATORY SYSTEMS Special Senses Lecture Notes 4.04 Describe the Special Senses A. Smell Smell occurs when specialized cells in the nose (chemoreceptors) detect certain chemicals resulting in
Unit 4 - REGULATORY SYSTEMS Special Senses Lecture Notes 4.04 Describe the Special Senses A. Smell Smell occurs when specialized cells in the nose (chemoreceptors) detect certain chemicals resulting in
Module Three. Application of Health Assessment NUR 225. Physical examination of Head and Neck. King Saud University. Collage of Nursing
 King Saud University Collage of Nursing Medical Surgical Nursing depart Application of Health Assessment NUR 225 Module Three Physical examination of Head and Neck 1 Physical Examination techniques for
King Saud University Collage of Nursing Medical Surgical Nursing depart Application of Health Assessment NUR 225 Module Three Physical examination of Head and Neck 1 Physical Examination techniques for
Assisting in Otolaryngology
 Assisting in Otolaryngology Learning Objectives Identify the structures and explain the functions of the external, middle, and internal ear. Describe the conditions that can lead to hearing loss, including
Assisting in Otolaryngology Learning Objectives Identify the structures and explain the functions of the external, middle, and internal ear. Describe the conditions that can lead to hearing loss, including
Compliance Department ELEMENTS OF EAR, NOSE AND THROAT EXAMINATION 11/2010
 Compliance Department ELEMENTS OF EAR, NOSE AND THROAT EXAMINATION 11/2010 System/ Body Area Constitutional Measurement of any three of the following seven vital signs: 1) sitting or standing blood pressure,
Compliance Department ELEMENTS OF EAR, NOSE AND THROAT EXAMINATION 11/2010 System/ Body Area Constitutional Measurement of any three of the following seven vital signs: 1) sitting or standing blood pressure,
The white of the eye and the part that maintains its shape is know n as the:
 Scrub In The white of the eye and the part that maintains its shape is know n as the: a. Cornea b. Pupil c. Retina d. Sclera The structure that is found in the ear and contains the organ of hearing is
Scrub In The white of the eye and the part that maintains its shape is know n as the: a. Cornea b. Pupil c. Retina d. Sclera The structure that is found in the ear and contains the organ of hearing is
Inner ear: Cochlea Vestibule utricle & saccule 3 semi-circular canals Auditory nerve. rworks.
 Intended learning outcomes ENT Health Assessment Julia Booth Senior Lecturer To recognise the need for clinical assessment in relation to ENT conditions Demonstrate the ability to obtain a detailed relevant
Intended learning outcomes ENT Health Assessment Julia Booth Senior Lecturer To recognise the need for clinical assessment in relation to ENT conditions Demonstrate the ability to obtain a detailed relevant
Head and Neck Exam. Dr. Gary Mumaugh Western Physical Assessment
 Head and Neck Exam Dr. Gary Mumaugh Western Physical Assessment Eyes Common or Concerning Symptoms Visual disturbances, spots (scotomas), flashing lights, use of corrective lenses, pain, redness, excessive
Head and Neck Exam Dr. Gary Mumaugh Western Physical Assessment Eyes Common or Concerning Symptoms Visual disturbances, spots (scotomas), flashing lights, use of corrective lenses, pain, redness, excessive
Veins of the Face and the Neck
 Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
The Ear The ear consists of : 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR 2-THE MIDDLE EAR, OR TYMPANIC CAVITY 3-THE INTERNAL EAR, OR LABYRINTH 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR.
 The Ear The ear consists of : 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR 2-THE MIDDLE EAR, OR TYMPANIC CAVITY 3-THE INTERNAL EAR, OR LABYRINTH 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR Made of A-AURICLE B-EXTERNAL AUDITORY MEATUS A-AURICLE It consists
The Ear The ear consists of : 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR 2-THE MIDDLE EAR, OR TYMPANIC CAVITY 3-THE INTERNAL EAR, OR LABYRINTH 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR Made of A-AURICLE B-EXTERNAL AUDITORY MEATUS A-AURICLE It consists
Program Script. Nursing Assessment The Head-to-Toe Assessment
 Program Script Nursing Assessment The Head-to-Toe Assessment This document comprises the complete script for this program including chapter titles. This is provided to instructors to enhance the educational
Program Script Nursing Assessment The Head-to-Toe Assessment This document comprises the complete script for this program including chapter titles. This is provided to instructors to enhance the educational
INTRODUCTION: ANATOMY UNDERLYING CLINICAL TESTS OF CRANIAL NERVES
 INTRODUCTION: ANATOMY UNDERLYING CLINICAL TESTS OF CRANIAL NERVES CRANIAL NERVE I - OLFACTORY I - OLFACTORY NERVE - SMELL TEST: SMELL ODORS (note: not ammonia; pain in nasal cavity CN5 DAMAGE: LOSS OF
INTRODUCTION: ANATOMY UNDERLYING CLINICAL TESTS OF CRANIAL NERVES CRANIAL NERVE I - OLFACTORY I - OLFACTORY NERVE - SMELL TEST: SMELL ODORS (note: not ammonia; pain in nasal cavity CN5 DAMAGE: LOSS OF
Head and Neck Exam. Charlie Goldberg, M.D. Professor of Medicine, UCSD SOM
 Head and Neck Exam Charlie Goldberg, M.D. Professor of Medicine, UCSD SOM Charles.Goldberg@va.gov Observation and Palpation Note right sided neck/jaw area swelling and R v L asymmetry Inspection face &
Head and Neck Exam Charlie Goldberg, M.D. Professor of Medicine, UCSD SOM Charles.Goldberg@va.gov Observation and Palpation Note right sided neck/jaw area swelling and R v L asymmetry Inspection face &
CRANIAL NERVES. Dr. Amani A. Elfaki Associate Professor Department of Anatomy
 CRANIAL NERVES Dr. Amani A. Elfaki Associate Professor Department of Anatomy LEARNING OBJECTIVES Named the cranial nerves Identify the funcunal component of each cranial nerve Identify the effect of each
CRANIAL NERVES Dr. Amani A. Elfaki Associate Professor Department of Anatomy LEARNING OBJECTIVES Named the cranial nerves Identify the funcunal component of each cranial nerve Identify the effect of each
Neurological Assessment. Lecture 8
 Neurological Assessment Lecture 8 Nervous System Central Nervous System Brain Spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Central Nervous System-Brain Central Nervous System-Spinal
Neurological Assessment Lecture 8 Nervous System Central Nervous System Brain Spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Central Nervous System-Brain Central Nervous System-Spinal
Physical Examination
 Otorhinolaryngologic Approach Sasan Dabiri, M.D. Department of Otorhinolaryngology Head & Neck Surgery Amir A lam hospital Tehran University of Medical Sciences General Notes Parts of an : Inspection Palpation
Otorhinolaryngologic Approach Sasan Dabiri, M.D. Department of Otorhinolaryngology Head & Neck Surgery Amir A lam hospital Tehran University of Medical Sciences General Notes Parts of an : Inspection Palpation
By Wayne Rodrigues, M.ED., ATC, EMT-P
 By Wayne Rodrigues, M.ED., ATC, EMT-P Purpose is to look for Fluid Perforations Foreign Objects Excessive Cerumen Inflammation Redness Swelling Cuppett, 2012 Translucent Pearly gray in color Concave
By Wayne Rodrigues, M.ED., ATC, EMT-P Purpose is to look for Fluid Perforations Foreign Objects Excessive Cerumen Inflammation Redness Swelling Cuppett, 2012 Translucent Pearly gray in color Concave
PRACTICE OF MEDICINE. Physical Examination of Head, Neck, Eyes, Ears, Nose, Throat 2 December I. Head and Neck
 PRACTICE OF MEDICINE Physical Examination of Head, Neck, Eyes, Ears, Nose, Throat 2 December 2002 I. Head and Neck GOALS: 1) Review landmarks of head and neck exam 2) Learn to examine thyroid gland EVIDENCE-BASED
PRACTICE OF MEDICINE Physical Examination of Head, Neck, Eyes, Ears, Nose, Throat 2 December 2002 I. Head and Neck GOALS: 1) Review landmarks of head and neck exam 2) Learn to examine thyroid gland EVIDENCE-BASED
Dr. Sami Zaqout Faculty of Medicine IUG
 Auricle External Ear External auditory meatus The Ear Middle Ear (Tympanic Cavity) Auditory ossicles Internal Ear (Labyrinth) Bony labyrinth Membranous labyrinth External Ear Auricle External auditory
Auricle External Ear External auditory meatus The Ear Middle Ear (Tympanic Cavity) Auditory ossicles Internal Ear (Labyrinth) Bony labyrinth Membranous labyrinth External Ear Auricle External auditory
Face. Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face
 Face Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face The muscle of facial expression (include the muscle of the face and the scalp). All are derived
Face Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face The muscle of facial expression (include the muscle of the face and the scalp). All are derived
Examination and Diseases of Cranial Nerves
 Cranial nerve evaluation is an important part of a neurologic exam. There are some differences in the assessment of cranial nerves with different species but the general principles are the same. Going
Cranial nerve evaluation is an important part of a neurologic exam. There are some differences in the assessment of cranial nerves with different species but the general principles are the same. Going
Ear, Nose, and Throat Disorders
 Health Reference Series Second Edition Basic Consumer Health Information about Disorders of the Ears, Hearing Loss, Vestibular Disorders, Nasal and Sinus Problems, Throat and Vocal Cord Disorders, and
Health Reference Series Second Edition Basic Consumer Health Information about Disorders of the Ears, Hearing Loss, Vestibular Disorders, Nasal and Sinus Problems, Throat and Vocal Cord Disorders, and
The Ear. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 The Ear Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology The Ear The ear consists of the external ear; the middle ear (tympanic cavity); and the internal ear (labyrinth), which contains
The Ear Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology The Ear The ear consists of the external ear; the middle ear (tympanic cavity); and the internal ear (labyrinth), which contains
WOMEN'S INTERAGENCY HIV STUDY ORAL PROTOCOL FORM OP 4: ORAL MUCOSAL TISSUE EXAM
 WOMEN'S INTERAGENCY HIV STUDY ORAL PROTOCOL FORM OP 4: ORAL MUCOSAL TISSUE EXAM COMPLETING THE FORM GENERAL INFORMATION Affix the Participant ID label in the space indicated. Record the visit number. Be
WOMEN'S INTERAGENCY HIV STUDY ORAL PROTOCOL FORM OP 4: ORAL MUCOSAL TISSUE EXAM COMPLETING THE FORM GENERAL INFORMATION Affix the Participant ID label in the space indicated. Record the visit number. Be
Lab Activity 19 & 20. Cranial Nerves General Senses. Portland Community College BI 232
 Lab Activity 19 & 20 Cranial Nerves General Senses Portland Community College BI 232 Cranial Nerves Nerves that originate from the brain rather than the spinal cord Part of the peripheral nervous system
Lab Activity 19 & 20 Cranial Nerves General Senses Portland Community College BI 232 Cranial Nerves Nerves that originate from the brain rather than the spinal cord Part of the peripheral nervous system
The Sensory Systems. Lesson 7.1: The Eye Lesson 7.2: The Ear Lesson 7.3: Smell and Taste
 7 The Sensory Systems Lesson 7.1: The Eye Lesson 7.2: The Ear Lesson 7.3: Smell and Taste Chapter 7: The Sensory Systems Lesson 7.1 The Eye The Eye anatomy of the eye external internal vision injuries,
7 The Sensory Systems Lesson 7.1: The Eye Lesson 7.2: The Ear Lesson 7.3: Smell and Taste Chapter 7: The Sensory Systems Lesson 7.1 The Eye The Eye anatomy of the eye external internal vision injuries,
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. Physical Assessment of the Sensory System (HEENT). After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 2 Physical Assessment of the Sensory System (HEENT). LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 2-1 through 2-10. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 2-1.
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 2 Physical Assessment of the Sensory System (HEENT). LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 2-1 through 2-10. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 2-1.
NURSE-UP RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 NURSE-UP RESPIRATORY SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pulmonary Ventilation - Breathing Gas exchanger External Respiration between lungs and bloodstream Internal Respiration between bloodstream
NURSE-UP RESPIRATORY SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pulmonary Ventilation - Breathing Gas exchanger External Respiration between lungs and bloodstream Internal Respiration between bloodstream
o A cushion of fat surrounds most of the eye
 Name Period SPECIAL SENSES The Senses of touch o Temperature o Pressure o Pain o Smell o Taste o Sight o Hearing o Equilibrium The Eye and Vision are in the eyes has over a o Most of the eye is enclosed
Name Period SPECIAL SENSES The Senses of touch o Temperature o Pressure o Pain o Smell o Taste o Sight o Hearing o Equilibrium The Eye and Vision are in the eyes has over a o Most of the eye is enclosed
3-Deep fascia: is absent (except over the parotid gland & buccopharngeal fascia covering the buccinator muscle)
 The Face 1-Skin of the Face The skin of the face is: Elastic Vascular (bleed profusely however heal rapidly) Rich in sweat and sebaceous glands (can cause acne in adults) It is connected to the underlying
The Face 1-Skin of the Face The skin of the face is: Elastic Vascular (bleed profusely however heal rapidly) Rich in sweat and sebaceous glands (can cause acne in adults) It is connected to the underlying
LESSON ASSIGNMENT , Irrigate an Obstructed Ear. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 6 Irrigate an Obstructed Ear. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 6-1 through 6-9. TASK TAUGHT LESSON OBJECTIVES 081-833-0059, Irrigate an Obstructed Ear. After completing this lesson,
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 6 Irrigate an Obstructed Ear. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 6-1 through 6-9. TASK TAUGHT LESSON OBJECTIVES 081-833-0059, Irrigate an Obstructed Ear. After completing this lesson,
The Neck the lower margin of the mandible above the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle
 The Neck is the region of the body that lies between the lower margin of the mandible above and the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle below Nerves of the neck Cervical Plexus Is formed
The Neck is the region of the body that lies between the lower margin of the mandible above and the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle below Nerves of the neck Cervical Plexus Is formed
Perenial Allergic Rhinosinusitis and OMM
 Perenial Allergic Rhinosinusitis and OMM Robert Hostoffer, DO Devi Jhaveri, DO Allergic Symptoms Sinus Pressure Nasal Congestion Rhinorrhea Post Nasal Drainage Physical Examination Findings That Suggest
Perenial Allergic Rhinosinusitis and OMM Robert Hostoffer, DO Devi Jhaveri, DO Allergic Symptoms Sinus Pressure Nasal Congestion Rhinorrhea Post Nasal Drainage Physical Examination Findings That Suggest
Senses. hear. smell. see. taste. touch. Your senses gather information from the outside world. They help you see, hear, taste, smell and touch things.
 Human Body Senses 1 Senses Your senses gather information from the outside world. They help you see, hear, taste, smell and touch things. They also help you to detect pain, pressure, and temperature. All
Human Body Senses 1 Senses Your senses gather information from the outside world. They help you see, hear, taste, smell and touch things. They also help you to detect pain, pressure, and temperature. All
Scrub In. What is the function of cerumen? Which part of the ear collects sound waves and directs them into the auditory canal?
 Scrub In What is the function of cerumen? a. Keeps the ear canal from collapsing b. Helps transmit sound waves c. Protection d. Lubrication Which part of the ear collects sound waves and directs them into
Scrub In What is the function of cerumen? a. Keeps the ear canal from collapsing b. Helps transmit sound waves c. Protection d. Lubrication Which part of the ear collects sound waves and directs them into
Laryngoscopy Examinations
 Laryngoscopy Examinations Laryngoscopy is a visual examination of the back of the throat where the voice box (larynx) and vocal cords are located. The procedure is done by using hand mirrors and a light
Laryngoscopy Examinations Laryngoscopy is a visual examination of the back of the throat where the voice box (larynx) and vocal cords are located. The procedure is done by using hand mirrors and a light
Ears. Mouth. Jowls 6 Major Bones of the Face Nasal bone Two
 1 2 3 4 5 Chapter 25 Injuries to the Face, Neck, and Eyes Injuries to the Face and Neck Face and neck are to injury Relatively unprotected positions on body Some injuries are life-threatening. trauma to
1 2 3 4 5 Chapter 25 Injuries to the Face, Neck, and Eyes Injuries to the Face and Neck Face and neck are to injury Relatively unprotected positions on body Some injuries are life-threatening. trauma to
EDITORIAL FOR THE MONTH OF MARCH 2010 COMMON E.N.T. PROBLEMS IN MY PRACTICE. Most common problems that I have encountered in my practice are:
 EDITORIAL FOR THE MONTH OF MARCH 2010 COMMON E.N.T. PROBLEMS IN MY PRACTICE Most common problems that I have encountered in my practice are: I) Allergic vasomotor rhinitis II) Cholesteatoma III) Deafness
EDITORIAL FOR THE MONTH OF MARCH 2010 COMMON E.N.T. PROBLEMS IN MY PRACTICE Most common problems that I have encountered in my practice are: I) Allergic vasomotor rhinitis II) Cholesteatoma III) Deafness
Kingdom of Bahrain Arabian Gulf University College of Medicine and Medical Sciences Year 6 ENT SMC Otitis Media (Dr.
 Kingdom of Bahrain Arabian Gulf University College of Medicine and Medical Sciences Year 6 ENT SMC Otitis Media (Dr. Jalal Almarzooq) - Anatomy of the ear: The ear is divided into 3 parts: External ear.
Kingdom of Bahrain Arabian Gulf University College of Medicine and Medical Sciences Year 6 ENT SMC Otitis Media (Dr. Jalal Almarzooq) - Anatomy of the ear: The ear is divided into 3 parts: External ear.
MARYWOOD UNIVERSITY PHYSICIAN ASSISTANT PROGRAM HISTORY, PHYSICAL, ASSESSMENT AND PLAN
 MARYWOOD UNIVERSITY PHYSICIAN ASSISTANT PROGRAM HISTORY, PHYSICAL, ASSESSMENT AND PLAN PA: PRECEPTOR: MARYWOOD STAFF: PATIENT ID: AGE: SEX: DATE: Chief Complaint: History of Present Illness: 1 Medications:
MARYWOOD UNIVERSITY PHYSICIAN ASSISTANT PROGRAM HISTORY, PHYSICAL, ASSESSMENT AND PLAN PA: PRECEPTOR: MARYWOOD STAFF: PATIENT ID: AGE: SEX: DATE: Chief Complaint: History of Present Illness: 1 Medications:
CRANIAL NERVE TESTING FOR THE PRIMARY CARE OPTOMETRIST
 CRANIAL NERVE TESTING FOR THE PRIMARY CARE OPTOMETRIST Hannah Shinoda, OD Caroline Ooley, OD, FAAO Assistant Professors Pacific University College of Optometry The authors have no financial interest in
CRANIAL NERVE TESTING FOR THE PRIMARY CARE OPTOMETRIST Hannah Shinoda, OD Caroline Ooley, OD, FAAO Assistant Professors Pacific University College of Optometry The authors have no financial interest in
Facial Accupressure Massage. Taha Haque, D.O. CAM Workshop
 Facial Accupressure Massage Taha Haque, D.O. CAM Workshop 1 10July2015 Benefits of facial accupressure Enhance local blood flow Firm and tone face and neck Mild to moderate symptomatic relief of headaches,
Facial Accupressure Massage Taha Haque, D.O. CAM Workshop 1 10July2015 Benefits of facial accupressure Enhance local blood flow Firm and tone face and neck Mild to moderate symptomatic relief of headaches,
Lab Activities 16, 17, & 18
 Lab Activities 16, 17, & 18 Olfaction & Taste Vision Hearing & Equilibrium Portland Community College BI 232 Lingual Papilla Papilla are epithelial projections on the superior surface of the tongue Circumvallate
Lab Activities 16, 17, & 18 Olfaction & Taste Vision Hearing & Equilibrium Portland Community College BI 232 Lingual Papilla Papilla are epithelial projections on the superior surface of the tongue Circumvallate
The Throat. Image source:
 The Throat Anatomy Image source: http://anatomyforlayla.blogspot.co.za/2007/04/blog-post.html The Throat consists of three parts: 1. The Nasopharynx is the upper part of the throat and it is situated behind
The Throat Anatomy Image source: http://anatomyforlayla.blogspot.co.za/2007/04/blog-post.html The Throat consists of three parts: 1. The Nasopharynx is the upper part of the throat and it is situated behind
PH-04A: Clinical Photography Production Checklist With A Small Camera
 PH-04A: Clinical Photography Production Checklist With A Small Camera Operator Name Total 0-49, Passing 39 Your Score Patient Name Date of Series Instructions: Evaluate your Series of photographs first.
PH-04A: Clinical Photography Production Checklist With A Small Camera Operator Name Total 0-49, Passing 39 Your Score Patient Name Date of Series Instructions: Evaluate your Series of photographs first.
Essential questions. What are the structures of the sensory system? 3.03 Remember the structures of the sensory system 2
 Essential questions What are the structures of the sensory system? 3.03 Remember the structures of the sensory system 2 The Senses Eyes Sight Ears Hearing Nose Smell Tongue Taste Skin Touch 3.03 Remember
Essential questions What are the structures of the sensory system? 3.03 Remember the structures of the sensory system 2 The Senses Eyes Sight Ears Hearing Nose Smell Tongue Taste Skin Touch 3.03 Remember
INTRA/EXTRA ORAL EXAMINATION
 INTRA/EXTRA ORAL EXAMINATION www.dentalelle.com Dentalelle Tutoring Intraoral/Extraoral Examination 1. If you notice a typical finding after reviewing the head and neck on a new patient, what does this
INTRA/EXTRA ORAL EXAMINATION www.dentalelle.com Dentalelle Tutoring Intraoral/Extraoral Examination 1. If you notice a typical finding after reviewing the head and neck on a new patient, what does this
NECK MASS. Clinical history and examination: Document detail history of mass. Imaging: US or CT of neck
 ENT ENT Referral Referral Guidelines Guidelines Austin Health ENT Clinic holds fortnightly multidisciplinary meetings with Plastics/ Maxillary Facial and Oncology units to discuss and plan the treatment
ENT ENT Referral Referral Guidelines Guidelines Austin Health ENT Clinic holds fortnightly multidisciplinary meetings with Plastics/ Maxillary Facial and Oncology units to discuss and plan the treatment
2 Sensing the Environment
 CHAPTER 17 2 Sensing the Environment SECTION Communication and Control California Science Standards 7.5.a, 7.5.b, 7.5.g, 7.6.b BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer
CHAPTER 17 2 Sensing the Environment SECTION Communication and Control California Science Standards 7.5.a, 7.5.b, 7.5.g, 7.6.b BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer
Sinus Surgery. Middle Meatus
 Sinus Surgery Introduction Sinus surgery is a very common and safe operation. Your doctor may recommend that you have sinus surgery. The decision whether or not to have sinus surgery is also yours. This
Sinus Surgery Introduction Sinus surgery is a very common and safe operation. Your doctor may recommend that you have sinus surgery. The decision whether or not to have sinus surgery is also yours. This
Dr. Sami Zaqout Faculty of Medicine IUG
 The Nose External Nose Nasal Cavity External Nose Blood and Nerve Supplies of the External Nose Blood Supply of the External Nose The skin of the external nose Branches of the ophthalmic and the maxillary
The Nose External Nose Nasal Cavity External Nose Blood and Nerve Supplies of the External Nose Blood Supply of the External Nose The skin of the external nose Branches of the ophthalmic and the maxillary
Basic Anatomy and Physiology of the Lips and Oral Cavity. Dr. Faghih
 Basic Anatomy and Physiology of the Lips and Oral Cavity Dr. Faghih It is divided into seven specific subsites : 1. Lips 2. dentoalveolar ridges 3. oral tongue 4. retromolar trigone 5. floor of mouth 6.
Basic Anatomy and Physiology of the Lips and Oral Cavity Dr. Faghih It is divided into seven specific subsites : 1. Lips 2. dentoalveolar ridges 3. oral tongue 4. retromolar trigone 5. floor of mouth 6.
Anatomy: There are 6 muscles that move your eye.
 Thyroid Eye Disease Your doctor thinks you have thyroid orbitopathy. This is an autoimmune condition where your body's immune system is producing factors that stimulate enlargement of the muscles that
Thyroid Eye Disease Your doctor thinks you have thyroid orbitopathy. This is an autoimmune condition where your body's immune system is producing factors that stimulate enlargement of the muscles that
SPECIAL SENSES PART I: OLFACTION & GUSTATION
 SPECIAL SENSES PART I: OLFACTION & GUSTATION 5 Special Senses Olfaction Gustation Vision Equilibrium Hearing Olfactory Nerves Extend through cribriform plate into nasal cavity on both sides of nasal septum
SPECIAL SENSES PART I: OLFACTION & GUSTATION 5 Special Senses Olfaction Gustation Vision Equilibrium Hearing Olfactory Nerves Extend through cribriform plate into nasal cavity on both sides of nasal septum
20-20,000 Hertz range of human hearing
 20-20,000 Hertz range of human hearing accommodation automatic adjustment in focal length of the lens of the eye; changing the shape of the lens aqueous humor Watery fluid in the anterior chambers of the
20-20,000 Hertz range of human hearing accommodation automatic adjustment in focal length of the lens of the eye; changing the shape of the lens aqueous humor Watery fluid in the anterior chambers of the
93.62% HEENT Results Turned In Health Assessment - August 2016, NUR 101. Experience Overview. Results for Sarah Smith
 HEENT Results Turned In Health Assessment - August 2016, NUR 101 Results for Sarah Smith Overview Experience Overview Transcript Subjective Data Collection Objective Data Collection Patient: Tina Jones
HEENT Results Turned In Health Assessment - August 2016, NUR 101 Results for Sarah Smith Overview Experience Overview Transcript Subjective Data Collection Objective Data Collection Patient: Tina Jones
PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA
 PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Outline Anatomical Structure and Boundaries Foramina and Communications with other spaces and cavities Contents Pterygopalatine Ganglion Especial emphasis on certain arteries and
PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Outline Anatomical Structure and Boundaries Foramina and Communications with other spaces and cavities Contents Pterygopalatine Ganglion Especial emphasis on certain arteries and
SPECIAL SENSES. Anatomy & Physiology
 SPECIAL SENSES Anatomy & Physiology BELL WORK: DEFINE LACRIMAL ACHROMATIC OTOSCOPE TENNITIS VERTIGO STANDARD 25) Define key terms associated with vision disorders, ear disorders, nose disorders, and mouth
SPECIAL SENSES Anatomy & Physiology BELL WORK: DEFINE LACRIMAL ACHROMATIC OTOSCOPE TENNITIS VERTIGO STANDARD 25) Define key terms associated with vision disorders, ear disorders, nose disorders, and mouth
Subdivided into Vestibule & Oral cavity proper
 Extends from the lips to the oropharyngeal isthmus The oropharyngeal isthmus: Is the junction of mouth and pharynx. Is bounded: Above by the soft palate and the palatoglossal folds Below by the dorsum
Extends from the lips to the oropharyngeal isthmus The oropharyngeal isthmus: Is the junction of mouth and pharynx. Is bounded: Above by the soft palate and the palatoglossal folds Below by the dorsum
ATI Skills Modules Checklist for Medication Administration 2
 For faculty use only Educator s name Score Date ATI Skills Modules Checklist for Medication Administration 2 Student s name Date Verify order Patient record Assess for procedure need Identify, gather,
For faculty use only Educator s name Score Date ATI Skills Modules Checklist for Medication Administration 2 Student s name Date Verify order Patient record Assess for procedure need Identify, gather,
Eye and Ocular Adnexa, Auditory Systems
 Eye and Ocular Adnexa, Auditory Systems CPT copyright 2011 American Medical Association. All rights reserved. Fee schedules, relative value units, conversion factors and/or related components are not assigned
Eye and Ocular Adnexa, Auditory Systems CPT copyright 2011 American Medical Association. All rights reserved. Fee schedules, relative value units, conversion factors and/or related components are not assigned
o A cushion of fat surrounds most of the eye
 Name Period SPECIAL SENSES The Senses General senses of touch o Temperature o Pressure o Pain Special senses o Smell o Taste o Sight o Hearing o Equilibrium The Eye and Vision 70 percent of all sensory
Name Period SPECIAL SENSES The Senses General senses of touch o Temperature o Pressure o Pain Special senses o Smell o Taste o Sight o Hearing o Equilibrium The Eye and Vision 70 percent of all sensory
Gangguan Telinga. Ruptur Gendang Telinga. Mula Tarigan, S.Kp
 Gangguan Telinga Ruptur Gendang Telinga Mula Tarigan, S.Kp Ruptured eardrum Introduction A ruptured (perforated) eardrum is a tear or a hole in eardrum (tympanic membrane), the thin membrane that separates
Gangguan Telinga Ruptur Gendang Telinga Mula Tarigan, S.Kp Ruptured eardrum Introduction A ruptured (perforated) eardrum is a tear or a hole in eardrum (tympanic membrane), the thin membrane that separates
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Respiration Includes Pulmonary ventilation Air moves in and out of lungs Continuous replacement of gases in alveoli (air sacs) External respiration Gas exchange between blood and
The Respiratory System Respiration Includes Pulmonary ventilation Air moves in and out of lungs Continuous replacement of gases in alveoli (air sacs) External respiration Gas exchange between blood and
TENTATIVE DIAGNOSES Based on the information provided so far, what are the potential diagnoses?
 Case Study #4 PEDIATRIC CASE STUDY SCENARIO Mary Jennings has brought her son Joe to your office. Joe is a 6-year old Jordanian male. He presents with the complaint of an itchy red eye. Mary states that
Case Study #4 PEDIATRIC CASE STUDY SCENARIO Mary Jennings has brought her son Joe to your office. Joe is a 6-year old Jordanian male. He presents with the complaint of an itchy red eye. Mary states that
THE INTERIOR OF THE PHARYNX. By Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi
 THE INTERIOR OF THE PHARYNX By Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi The Cavity The cavity of the pharynx is divided into: 1. The Nasal part (called Nasopharynx) 2. The Oral part (called the Oropharynx), 3. And the
THE INTERIOR OF THE PHARYNX By Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi The Cavity The cavity of the pharynx is divided into: 1. The Nasal part (called Nasopharynx) 2. The Oral part (called the Oropharynx), 3. And the
Washington State Dental Association s 2016 Pacific Northwest Dental Conference. Presents
 Washington State Dental Association s 2016 Pacific Northwest Dental Conference Presents Physical Examination of the Head and Neck for Dental Health Care Providers Theresa Gonzales, DMD Thursday, June 16,
Washington State Dental Association s 2016 Pacific Northwest Dental Conference Presents Physical Examination of the Head and Neck for Dental Health Care Providers Theresa Gonzales, DMD Thursday, June 16,
Upper Respiratory Tract Infections / 42
 Upper Respiratory Tract Infections 1 Upper Respiratory Tract Infections Acute tonsillitispharyngitis Acute otitis media Acute sinusitis Common cold Acute laryngitis Otitis externa Mastoiditis Acute apiglottis
Upper Respiratory Tract Infections 1 Upper Respiratory Tract Infections Acute tonsillitispharyngitis Acute otitis media Acute sinusitis Common cold Acute laryngitis Otitis externa Mastoiditis Acute apiglottis
What are the causes of nasal congestion?
 Stuffy Noses Nasal congestion, stuffiness, or obstruction to nasal breathing is one of the oldest and most common human complaints. For some, it may only be a nuisance; for others, nasal congestion can
Stuffy Noses Nasal congestion, stuffiness, or obstruction to nasal breathing is one of the oldest and most common human complaints. For some, it may only be a nuisance; for others, nasal congestion can
Chapter 13: Mass in the Neck. Raymond P. Wood II:
 Chapter 13: Mass in the Neck Raymond P. Wood II: In approaching the problem of a mass in the neck, one immediately encounters the fact that there are normally palpable masses in the neck (eg, almost all
Chapter 13: Mass in the Neck Raymond P. Wood II: In approaching the problem of a mass in the neck, one immediately encounters the fact that there are normally palpable masses in the neck (eg, almost all
What is Otolaryngology? (pronounced oh/toe/lair/in/goll/oh/jee) is the oldest medical specialty in the United States.
 What is Otolaryngology? (pronounced oh/toe/lair/in/goll/oh/jee) is the oldest medical specialty in the United States. Otolaryngologists are physicians trained in the medical and surgical management and
What is Otolaryngology? (pronounced oh/toe/lair/in/goll/oh/jee) is the oldest medical specialty in the United States. Otolaryngologists are physicians trained in the medical and surgical management and
Chapter 2. The Senses
 Chapter 2. The Senses 2.1 Sensory Receptors (p.25-27) sensory receptors - specialized nerve cells whose function is to collect information about changes in the surrounding environment. sensory organs -
Chapter 2. The Senses 2.1 Sensory Receptors (p.25-27) sensory receptors - specialized nerve cells whose function is to collect information about changes in the surrounding environment. sensory organs -
Flexible Fiberoptic Exam
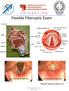 Flexible Fiberoptic Exam True Vocal Cords abducted True Vocal Cords adducted *Fiberoptic endoscopy, image is true. Cerumen Removal Position Patient -Explain Procedure Visualize Canal/Landmarks Determine
Flexible Fiberoptic Exam True Vocal Cords abducted True Vocal Cords adducted *Fiberoptic endoscopy, image is true. Cerumen Removal Position Patient -Explain Procedure Visualize Canal/Landmarks Determine
Anatomy of Oral Cavity DR. MAAN AL-ABBASI
 Anatomy of Oral Cavity DR. MAAN AL-ABBASI By the end of this lecture you should be able to: 1. Differentiate different parts of the oral cavity 2. Describe the blood and nerve supply of mucosa and muscles
Anatomy of Oral Cavity DR. MAAN AL-ABBASI By the end of this lecture you should be able to: 1. Differentiate different parts of the oral cavity 2. Describe the blood and nerve supply of mucosa and muscles
Percussion These 4 techniques are the foundation of the physical exam. Respiration Blood pressure Body
 1 Chapter 11: Physical Exam Techniques 2 Introduction Although patient assessment formally starts with the, the physical examination actually begins when you first set eyes on your patient. The purpose
1 Chapter 11: Physical Exam Techniques 2 Introduction Although patient assessment formally starts with the, the physical examination actually begins when you first set eyes on your patient. The purpose
The Sense Organs 10/13/2016. The Human Eye. 1. Sclera 2. Choroid 3. Retina. The eye is made up of three layers:
 The human body gathers information from the outside world by using the five senses of: The Sense Organs 12.3 Sight Hearing Taste Smell Touch This information is essential in helping the body maintain homeostasis.
The human body gathers information from the outside world by using the five senses of: The Sense Organs 12.3 Sight Hearing Taste Smell Touch This information is essential in helping the body maintain homeostasis.
Head: Special Senses. Taste Smell Vision Hearing/Balance
 Head: Special Senses Taste Smell Vision Hearing/Balance TASTE: how does it work? Taste buds on tongue on fungiform papillae ( mushroom-like projections) Each bud contains several cell types in microvilli
Head: Special Senses Taste Smell Vision Hearing/Balance TASTE: how does it work? Taste buds on tongue on fungiform papillae ( mushroom-like projections) Each bud contains several cell types in microvilli
Special Senses. Accessory Structures of the Eye. The Eye and Vision. Accessory Structures of the Eye. Accessory Structures of the Eye
 8 PART A Special Senses PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Senses General senses
8 PART A Special Senses PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Senses General senses
