Analysis of the Abfraction Lesions Formation Mechanism by the Finite Element Method
|
|
|
- Ashlie Curtis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 241 ORIGINAL PAPER doi: /aim ACTA INFORM MED AUG 22(4): Received: 16 May 2014 Accepted: 15 July 2014 AVICENA 2014 Analysis of the Abfraction Lesions Formation Mechanism by the Finite Element Method Selma Jakupovic 1, Edin Cerjakovic 4, Alan Topcic 4, Muhamed Ajanovic 3, Alma Konjhodzic-Prcic 1, Amra Vukovic 2 Department of Restorative Dentistry and Endodontics, Faculty of Dentistry, University of Sarajevo, Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina 1 Department of Dental Morphology with Dental Anthropology and Forensics, Faculty of Dentistry, University of Sarajevo, Sarajevo, Bosnia and Hercegovina 2 Department of Prosthodontics, Faculty of Dentistry, University of Sarajevo, Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina 3 Department of Production Engineering, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, University of Tuzla, Tuzla, Bosnia and Herzegovina 4 Corresponding author: Selma Jakupovic, MDD. Department of Restorative dentistry and Endodontics, Faculty of Dentistry, University of Sarajevo, Bolnička 4a, Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina. Phone: (203); jakupovic_selma@yahoo.com ABSTRACT Introduction: An abfraction lesion is a type of a non-carious cervical lesion (NCCL) that represents a sharp defect on the cervical part of tooth, caused by occlusal biomechanical forces. The largest prevalence of the NCCL is found on the mandibular first premolar. The goal of the study is, by means of a numerical method the finite element method (FEM), in an appropriate computer program, conduct a stress analysis of the mandibular premolar under various static loads, with a special reference to the biomechanics of cervical tooth region. Material and methods: A three-dimensional model of the mandibular premolar is gained from a µct x-ray image. By using the FEM, straining of the enamel, dentin, peridontal ligament and alveolar bone under axial and paraxial forces of 200 [N] is analyzed. The following software were used in the analysis: CT images processing CTAn program and FEM analysis AnsysWorkbench Results: According to results obtained through the FEM method, the calculated stress is higher with eccentric forces within all tested tooth tissue. The occlusal load leads to a significant stress in the cervical tooth area, especially in the sub-superficial layer of the enamel (over 50 MPa). The measured stress in the peridontal ligament is approximately three times higher under paraxial load with regard to the axial load, while stress calculated in the alveolar bone under paraxial load is almost ten times higher with regard to the axial load. The highest stress values were calculated in the cervical part of the alveoli, where bone resorption is most commonly seen. Conclusion: Action of occlusal forces, especially paraxial ones, leads to significant stress in the cervical part of tooth. The stress values in the cervical sub-superficial enamel layer are almost 5 times higher in relation to the superficial enamel, which additionally confirms complexity of biomechanical processes in the creation of abfraction lesions. Key words: abfraction, finite element method, occlusion, stress. 1. INTRODUCTION Teeth are made of several types of tissue (enamel, dentin, cement, pulp) with various mechanical properties and morphology, which makes analysis of distribution and concentration of stress alongside these structures very complex process (1). By definition, external forces that act on the body cause internal forces between body particles, so their reduction to a unit of surface represents stress/ straining (2). Stress distribution through a certain structure depends on a shape and mechanical properties of the material through which is distributed, as well as types of stress. Fractures of hard tooth tissue are directly related to stress intensity in a certain period of time (3). A special clinical appearance called abfraction is in a relation to stress distribution through tooth tissue. Abfraction lesion is a type of a non-carious cervical lesion (NCCL) which represents a microstructure loss of tooth tissue, created under action of occlusal biomechanical forces in the area of the highest stress concentration, that is, in the cervical region. Constant tension and compression of this area result in severing chemical bonds among hydroxyapatite crystals of enamel and dentin, allowing small molecules to penetrate, which prevent re-establishing of bonds (4,5) Such a loss of hard tooth tissue in the cervical area Grippo (6) 1991 named abfraction, so that these le- Figure 1. Abfraction lessions
2 242 Analysis of the Abfraction Lesions Formation Mechanism by the Finite Element Method sions could clinically differentiate from lesions caused by erosion and abrasion. Abfraction lessions are typically shaped as a wedgeshaped tissue defect, with sharp internal and external edges (Figure 1). Incidence of non-carious cervical lesion rises with patient s age, which also points out to the tissue fatigue component through a longer period of time (1,7). The mandibular first premolar is the tooth with highest prevalence of non-carious cervical lesions (7,8,9). A specific morphology and occlusion of this tooth surely significantly affect these results. Previously modeled 3D volumetric tooth structures are linked in one unit a complex model. Mutual relation of elements as well as boundary conditions are defined. Using AnsysWorkbench, a finite element mesh of the complex model is formed and the tooth model is divided into finite elements, namely: for volumetric bodies Solid187, for contact areas Targe179 and conta174, and for boundary conditions and area of the force action a Surf154 type net. The size of the basic element of meshed model was 0.1 mm, so that the model consisted knots and elements (Figure 4). 2. MATERIALS AND METHODS Intact mandibular first premolar was scanned by a µct 1076 SkyScan scanner (Kontich, Belgium)(10,11) at the Center for Translational and Clinic Research, School of Medicine of University of Zagreb. The images were reconstructed using Nrecon (ScyScan) program into transaxial sections. By scanning, then by additional reduction of input data, around 576 horizontal sections 0,0361 [mm] thick, with a clearly visible internal tooth structures (resolution up to px in each section) were chosen for the reconstruction of 3D model (Figure 2). Data was analyzed by CTAn program (SkyScan). Figure 2. Micro CT images of the mandibular first premolar Based on the µct section, pre-processing of the data and generating a volumetric 3D CAD tooth model was conducted. For that purpose, program packages Matlab, CreoParametic 1.0 was used. This way, two 3D solid models of enamel and dentin were obtained, which are in mutual contact alongside the entire dentin enamel junction. On the other side, the pulp is modeled as an empty space, since Young's modulus of pulp elasticity is negligibly small in relation to adjacent structures. The peridontal ligament is modeled as a membrane 0.3 mm thin, which surrounds the root of the tooth, which corresponds to real anatomic values (12), and additionally a segment of the alveolar bone is modeled (Figure 3). Figure 3. Three-dimensional volumetric tooth tissue models reconstructed from µct images; (a) enamel, (b) dentin, (c) pulp, (d) periodontal ligament (e) reconstructed segment of the alveolar bone Figure 4. Image of the finite elements mesh Characteristics of the materials used in the research, obtained after a detailed literature research are, given in Table 1. For the purpose of the analysis, it was assumed that all materials are isotropic, homogenous and linearly elastic. Material Young`s modulus of elasticity [MPa] Poisson koefficient Enamel Dentin Periodontal ligament Alveolar bone Table 1. Material characteristics Literature source The load is distributed to regions that correspond to antagonists contacts in the central occlusion (Figure 5a). For the purpose of presenting actions of the paraxial load, a laterotrusive movement of the mandibular first premolar, at 40 angle on the external side of the buccal cusp (14, 16) (Figure 5b) was simulated. The values of the maximum simulated load were 200 [N] (3,17,18), and it is assumed that the character of force action is static. The tooth tissue tension values were calculated by the Finite Element Method, which proved to be an adequate method for predicting the biomechanical behavior of the tooth under load (19). The analysis was done in the AnsysWorkbench 14.0 program package. There are various criteria to grade stress in ORIGINAL PAPER / ACTA INFORM MED AUG 22(4):
3 243 Figure 5. Image of contact tooth regions in (a) central occlusion (b) laterotrusion a material, and with it, to evaluate possible material breaking. In bodies of complex morphology, such as teeth, it is a very rare occurrence to find a single type of stress (straining, compressive or shearing). Almost always, it is a case of combined action of the aforementioned stresses, which results in complex stress. For that reason, in order to show the complex stress the hypothesis of the highest distortion energy (Von Mises stress) was used, which allows determining the total of resulting stress in every point of the observed object tooth element. 3. RESULTS Results obtained by the finite element method are represented in the form of relevant images where the stress values are presented through a color scale, which allows a clear visual image with numeric stress Figure 8. Stress distribution in the enamel under (a) axial and (b) paraxial load of 200 [N]. Maxumum values of Von Mises stress obtained on the tooth model are spotted in the enamel under the paraxial load in the contact region. Figure 9. Stress distribution in the dentin under (a) axial and (b) paraxial load of 200 [N]. There is a significant difference in the stress of the cervical part of dentin under axial in relation to paraxial load. Figure 6. Stress distribution in the cervical part of the tooth under (a) axial (b) paraxial load of 200 [N]. The values of Von Mises stress in the cervical part of the tooth are almost 5 times higher under the paraxial than under axial load. Figure 10. Stress distribution in the peridontal ligament under (a) axial and (b) paraxial load of 200 [N]. Stress values in the peridontal ligament under paraxial load are almost three times higher than the ones in the central occlusion. Figure 11. Stress distribution in the alveolar bone under (a) axial and (b) paraxial load of 200 [N]. The measured stress under paraxial load is almost ten times higher than the ones in the central occlusion. The highest bone stress is spotted alongside the upper edge of the alveolar socket. Figure 7. Stress distribution on the sagital section of the intact tooth under paraxial load of 200 [N]. It was noted that stress values in the cervical part of the tooth are higher in the subsuperficial than in the superficial area of the enamel, which suggested that the initial breaking off of the enamel might happen exactly in these layers. values (the left side of the image). It is necessary to mention that the given selected values represent extreme calculated values. 4. DISCUSSION This research presents effects of two types of occlusal load on the intact tooth. Since the contact sur-
4 244 Analysis of the Abfraction Lesions Formation Mechanism by the Finite Element Method face and masticatory force intensity are extremely variable, two types of occlusal contacts (Figure 5 a and 5 b) were chosen in order to show effects of a favorable and unfavorable situation for the tooth and surrounding tissues. Results of this research show that calculated stress values on tested models are higher with eccentric forces in all tooth tissues. Maximum load on the tooth model under both types of loads are spotted in contact regions, that is, region of force action, and under axial load measured 205 [MPa] (Figure 8 a), and under paraxial load MPa (Figure 8 b). The result of high stress values on a small surface, the contact region, is in accordance with Anusavice s (21) claim who, with that, explains wearing out of occlusal composite fillings. The action of occlusal forces led to a significant stress in the cervical region of the tooth. The calculated Von Mises stress in the cervical tooth part under axial load is not high and measure up to 12 MPa (Figure 6 a), whereas the stresses in the same part of the tooth under paraxial load are significantly higher and measure over 50 MPa (Figure 6 b), which corresponds the results of the study of Poiata et al (22). The elasticity modules of enamel and dentin are different, so the occlusal load is dominantly transferred through the enamel because of a far greater hardness (23). Significantly lower values of Von Misses stress are measured in the dentin in relation to the enamel and measured for axial (Figure 9 a) and MPa for paraxial load (Figure 9 b). The highest stress is spotted in the crown and the cervical part of the tooth and reduces towards to tooth apex. By analyzing forming mechanisms of abfraction lesions Rees and Hammadeh (24) presented a theory of a possible undermining of the enamel due to stress concentration on the dentin enamel junction. The results of this research confirm observations of aforementioned authors, since the values of calculated stress in the cervical part of the tooth are higher in the sub-superficial than in the superficial region of the enamel (Figure 7), which indicates that breaking of the bonds between enamel prisms might occur in these layers exactly. Cervical lesion progression can additionally be improved through erosion and abrasion. Also, microscopic studies show that the sub-superficial enamel is structurally inferior, with a lower percentage of a mineral component, a higher percentage of protein and higher porosity compared to the superficial layer (25). The periodontal ligament (PDL) is an extremely important tissue in tooth movement evaluation. The role of the PDL cannot be ignored in an attempt of imitating a real situation. Maximum stress values in the PDL are spotted alongside the upper edge of the ligament, in cervical part of tooth, for both types of load. The calculated stress under load in the central occlusion equals 5 MPa (Figure 10 a), whereas under the paraxial load it is almost three times higher and equals 13.5 MPa (Figure 10 b). The calculated values are not high thanks to the fact that the PDL is made of discrete collagen fibers, which allows a high-elasticity behavior under load, that is, works as a stressabsorber (26). A small difference between spotted stress intensity under two types of load proves that the PDL well absorbs paraxial forces. In the alveolar bone, the highest stress was registered alongside the top of the tooth socket. The calculated bone stress under paraxial load equals 112 MPa (Figure 11 a) and are almost ten times higher than under axial load whose values equal 17 MPa (Figure 11 b). This results clearly presents the mode of transmission eccentric occlusal forces onto surrounding alveolar bone structures, as well as their role in the possible creation of bone resorption. 5. CONCLUSIONS The largest influence on stress intensity has the type of loading the teeth. Calculated stress values on tested models are higher with eccentric occlusal forces in all tooth tissues. Occlusal load, besides in the contact region, leads to occurrence of significant stress in the cervical part of the tooth. Stress values in the sub-superficial layer of the cervical enamel are almost 5 times higher in relation to superficial enamel. Stress under occlusal forces is dominantly transferred through the enamel where the highest stress values were measured. Stress calculated under paraxial load in the periodontal ligament is almost three times higher than stress obtained in the central occlusion. Stress calculated under paraxial load in the alveolar bone is almost ten times higher than stress obtained in the central occlusion. The highest stress in the bone is spotted along the top edge of the alveolar socket. This research give a clear image of stress distribution in one moment of tooth straining, and represents a good basis for observation and conclusion of cause-effect links during creation of lesions, but still many questions will remain open. They rely on the fact that the acting force in this research is assumed as a static, not a dynamic occurrence, with a relatively large number of repetitions, as it is in reality. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS Authors owe great gratitude to the personnel of Center for Translational and Clinic Research of School of Medicine of University of Zagreb for technical aid during the creation and reconstruction of µct tooth images. CONFLICT OF INTEREST: NONE DECLARED. REFERENCES 1. Palamara JEA, Palamara D, Messer HH, Tyas M J. Tooth morphology and characteristics of noncarious cervical lesions. J Dent. 2006; 34: ORIGINAL PAPER / ACTA INFORM MED AUG 22(4):
5 Alfirević I, Bjelovučić D, Budin I, Matijašević B, Modlic B, Mulc A, Z. Šikić, Taboršak D, Tešnjak S. Inženjerski priručnik - Temelji inžinjerskih znanja, I izdanje, Školska knjiga Zagreb, Republika Hrvatska, Borčić J. Antonić R. Muhović Urek M. Petričević N. Nola-Fuchs P. Ćatić A. Smojver I. 3-d stress analysis in first maxillary premolar. Coll Antropol. 2007; 31: Pegoraro LF, Scolaro JM, Conti PC, Telles D, Pegoraro TA. Noncarious cervical lesions in adults, Prevalence and occlusal aspects. JADA. 2005; 136: Wood I, Jawad Z, Paisley C, Brunton P. Non-carious cervical tooth surface loss: a literature review. J Dent. 2008; 36(10): Grippo J O. Abfractions: a new classification of hard tissue lesion of teeth. Journal Esthet Dent. 1991; 3: Jakupović S, Vuković A, Korać S, Tahmiščija I, Bajsman A. The prevalence, distribution and expression of noncarious cervical lesions (NCCL) in permanent dentition. Mater Sociomed. 2010; 22(4): Aw C, Lepe X, Johnson G H, Mancl L. Caracteristics of noncarious cervical lesions, A clinical investigation. JADA. 2002; 133: Borčić J, Anić I, Urek M M, Ferreri S. The prevalence of non-carious cervical lesions in permanent dentition. J Oral Rehabil. 2004; 31: Tajima K, Chen KK, Takahashi N, Noda N, Nagamatsu Y, Kakigawa H. Dent Mater J. Three-dimensional finite element modeling from CT images of tooth and its validation. 2009; 28(2): Magne P, Oganesyan T. Premolar cuspal flexure as a function of restorative material and occlusal contact location. Quintessence Int. 2009; 40(5): Ichim I. Schmidlin PR, Kieser JA, Swain MV. Mechanical evaluation of cervical glass ionomer restorations; 3 D finite element study. J Dent. 2007; 35: Lertchirakarn V, Palamara JEA, Messer HH. Finite element analysis and strain gauge studies of vertical root fracture. J Endod. 2003; 29: Rees J S, The effect of variation in occlusal loading on the development of abfraction lesions: a finite element study. J Oral Rehabil. 2002; 29: Li L, Wang l, Bai Z, Mao Y, Gao B, Xin H, Zhou B, Zhang Y Liu B. Three dimensional finite element analysis of weakened roots restored with different cements in combination with titanium alloy posts. Chinese Med Jour. 2006; 119(4): Ichim I, Li Q, Loughran J, Swain M V, Kieser J. Restoration of noncarious cervical lesions Part I. Modeling of restorative fracture. Dent Mats. 2003; 23: Borčić J, Anić I, Smojver I, Ćatić A, Miletić I, Ribarić SP. 3D finite element model and cervical lesion formation in normal occlusion and in malocclusion. J Oral Rehabil. 2005; 32: Romeed SA, Malik R, Dunne SM. Stress analysis of occlusal forces in canine teeth and their role in the development of non-carious cervical lesions: abfraction. Int J Dent. 2012; doi: /2012/ Michael JA, Townsend GC, Greenwood LF, Kaidonis JA. Abfraction: separating fact from fiction. Aust Dent J. 2009, 54(1): Dejak B, Mlotkowski A, Romanowicz M. Finite element analysis of mechanism of cervical lesion formation in simulated molars during mastication and parafunction. J Prosthet Dent. 2005; 94: Anusavice KJ. Phillip s science of dental materials. 10 th ed. WB Saunders, Philadelphia, USA, 1996; Poiate IA, Vasconcellos AB, Poiate Junior E, Dias KR. Stress distribution in the cervical region of an upper central incisor in a 3D finite element model. Braz Oral Res. 2009; 23(2): Lee WC, Eakle WS. Stress-induced cervical lesions: Review of advances in the past 10 years. J Prosthet Dent. 1996; 75: Rees JS, Hammadeh M. Undermining of enamel as a mechanisam of abfraction lesion formation: a finite element study. Eur J Oral Sci. 2004; 112: Poole DFG, Newman HN, Dibdin GH. Structure and porosity of human cervical enamel studied by polarizing microscopy and transmission electron microscopy. Arch Oral Biol. 1981; 26: Geramy A, Sherafoddin F. Abfraction: 3d analysis by means of the finite element method. Quint Int. 2003; 34:
The Prevalence, Distribution and Expression of Noncarious Cervical Lesions (NCCL) in Permanent Dentition
 The Prevalence, Distribution and Expression of Noncarious Cervical Lesions (NCCL) in Permanent Dentition Selma Jakupovic, Amra Vukovic, Samra Korac, Irmina Tahmiscija, Anita Bajsman Faculty of Dental Medicine,
The Prevalence, Distribution and Expression of Noncarious Cervical Lesions (NCCL) in Permanent Dentition Selma Jakupovic, Amra Vukovic, Samra Korac, Irmina Tahmiscija, Anita Bajsman Faculty of Dental Medicine,
Tooth Abfraction in Relationship to Occlusal Load Stresses: A Case Report
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 10 Ver. I (Oct. 2017), PP 80-84 www.iosrjournals.org Tooth Abfraction in Relationship to Occlusal
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 10 Ver. I (Oct. 2017), PP 80-84 www.iosrjournals.org Tooth Abfraction in Relationship to Occlusal
The Role of Cuspal Flexure And the Weakening Effect of occlusal Amalgam Restoration in the Development of Abfraction Lesions A Finite Element Study
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 7 Ver. VII (July. 2017), PP 10-17 www.iosrjournals.org The Role of Cuspal Flexure And the Weakening
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 7 Ver. VII (July. 2017), PP 10-17 www.iosrjournals.org The Role of Cuspal Flexure And the Weakening
Performance Assessment of Various Molar Crown Designs
 2012 2nd International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Technology IPCBEE vol. 34 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore Performance Assessment of Various Molar Crown Designs Rashmi Uddanwadiker
2012 2nd International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Technology IPCBEE vol. 34 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore Performance Assessment of Various Molar Crown Designs Rashmi Uddanwadiker
ENDODONTOLOGY ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION
 To Analyze the Distribution of Root Canal Stresses after Simulated Canal Preparation of Different Canal Taper in Mandibular First Premolar by Finite Element Study An In Vitro Study. DHANYA KUMAR N. M.
To Analyze the Distribution of Root Canal Stresses after Simulated Canal Preparation of Different Canal Taper in Mandibular First Premolar by Finite Element Study An In Vitro Study. DHANYA KUMAR N. M.
FEM analysis of the mandibular first premolar with different post diameters
 Odontology (2011) 99:148 154 DOI 10.1007/s10266-011-0011-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLE FEM analysis of the mandibular first premolar with different post diameters Je-Kang Du Wei-Ko Lin Chau-Hsiang Wang Huey-Er Lee
Odontology (2011) 99:148 154 DOI 10.1007/s10266-011-0011-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLE FEM analysis of the mandibular first premolar with different post diameters Je-Kang Du Wei-Ko Lin Chau-Hsiang Wang Huey-Er Lee
Ⅰ. INTRODUCTION. Department of Conservative dentistry, College of Dentistry, Pusan National University
 Effects of occlusal load on the stress distribution of four cavity configurations of noncarious cervical lesions: A three-dimensional finite element analysis study Effects of occlusal load on the stress
Effects of occlusal load on the stress distribution of four cavity configurations of noncarious cervical lesions: A three-dimensional finite element analysis study Effects of occlusal load on the stress
Finite element analysis of thermal stress distribution in different restorative materials used in class V cavities
 Original Article Finite element analysis of thermal stress distribution in different restorative materials used in class V cavities MS Guler, C Guler 1, F Cakici 2, EB Cakici 2, S Sen 3 Department of Maritime
Original Article Finite element analysis of thermal stress distribution in different restorative materials used in class V cavities MS Guler, C Guler 1, F Cakici 2, EB Cakici 2, S Sen 3 Department of Maritime
Key words : Non-carious cervical lesion, Stress distribution, Composite resin, Elastic modulus, Finite element analysis
 대한치과보존학회지 : Vol. 33, No. 3, 2008 The influence of combining composite resins with different elastic modulus on the stress distribution of class V restoration: A three-dimensional finite element study Jeong-Kil
대한치과보존학회지 : Vol. 33, No. 3, 2008 The influence of combining composite resins with different elastic modulus on the stress distribution of class V restoration: A three-dimensional finite element study Jeong-Kil
Stress distribution in the cervical region of an upper central incisor in a 3D finite element model
 Universidade de São Paulo Biblioteca Digital da Produção Intelectual - BDPI Outros departamentos - IF/Outros Artigos e Materiais de Revistas Científicas - IF/Outros 2009 Stress distribution in the cervical
Universidade de São Paulo Biblioteca Digital da Produção Intelectual - BDPI Outros departamentos - IF/Outros Artigos e Materiais de Revistas Científicas - IF/Outros 2009 Stress distribution in the cervical
Available online at ScienceDirect
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 69 ( 2014 ) 1251 1257 24th DAAAM International Symposium on Intelligent Manufacturing and Automation, 2013 Comparative Study
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 69 ( 2014 ) 1251 1257 24th DAAAM International Symposium on Intelligent Manufacturing and Automation, 2013 Comparative Study
In-Silico approach on Offset placement of implant-supported bridges placed in bone of different density in Orthodontics.
 In-Silico approach on Offset placement of implant-supported bridges placed in bone of different density in Orthodontics. Chandrasenan.P 1, Vishnu.G 2, Akshay K Nair 3 1M Tech student, Department of Mechanical
In-Silico approach on Offset placement of implant-supported bridges placed in bone of different density in Orthodontics. Chandrasenan.P 1, Vishnu.G 2, Akshay K Nair 3 1M Tech student, Department of Mechanical
Evaluation of Stress Distribution in Bone of Different Densities Using Different Implant Designs: A Three-Dimensional Finite Element Analysis
 J Indian Prosthodont Soc (Oct-Dec 2013) 13(4):555 559 DOI 10.1007/s13191-012-0189-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Evaluation of Stress Distribution in Bone of Different Densities Using Different Implant Designs: A
J Indian Prosthodont Soc (Oct-Dec 2013) 13(4):555 559 DOI 10.1007/s13191-012-0189-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Evaluation of Stress Distribution in Bone of Different Densities Using Different Implant Designs: A
IJCPD Biomechanical Stress Analysis of Mandibular First Permanent Molar; Restored with Amalgam and Composite Resin
 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-1047 IJCPD Biomechanical Stress Analysis of Mandibular First Permanent Molar; Restored with and Resin ORIGINAL ARTICLE Biomechanical Stress Analysis of Mandibular First Permanent
10.5005/jp-journals-10005-1047 IJCPD Biomechanical Stress Analysis of Mandibular First Permanent Molar; Restored with and Resin ORIGINAL ARTICLE Biomechanical Stress Analysis of Mandibular First Permanent
Experimental and Numerical Comparison of Stresses Level between Titanium and Novel Composite Single Tooth Implant
 International Journal of Mechanical & Mechatronics Engineering IJMME-IJENS Vol:15 No:06 84 Experimental and Numerical Comparison of Stresses Level between Titanium and Novel Composite Single Tooth Implant
International Journal of Mechanical & Mechatronics Engineering IJMME-IJENS Vol:15 No:06 84 Experimental and Numerical Comparison of Stresses Level between Titanium and Novel Composite Single Tooth Implant
Three-dimensional finite element analysis of the application of attachment for obturator framework in unilateral maxillary defect
 Journal of Oral Rehabilitation 2007 Three-dimensional finite element analysis of the application of attachment for obturator framework in unilateral maxillary defect S. JIAN*, J. TING*, T. YING &W.DONG-MEI
Journal of Oral Rehabilitation 2007 Three-dimensional finite element analysis of the application of attachment for obturator framework in unilateral maxillary defect S. JIAN*, J. TING*, T. YING &W.DONG-MEI
Diagnosing and Educating Patients About Occlusal Disease
 Diagnosing and Educating Patients About Occlusal Disease A new standard of care for recognizing this highly destructive, littleunderstood problem Jose-Luis Ruiz, DDS, FAGD Many patients are surprised to
Diagnosing and Educating Patients About Occlusal Disease A new standard of care for recognizing this highly destructive, littleunderstood problem Jose-Luis Ruiz, DDS, FAGD Many patients are surprised to
EFFECT OF RESTORATION TYPE ON THE STRESS DISTRIBUTION OF ENDODONTICALLY TREATED MAXILLARY PREMOLARS; THREE-DIMENSIONAL FINITE ELEMENT STUDY
 대한치과보존학회지 : Vol. 34, No. 1, 2009 EFFECT OF RESTORATION TYPE ON THE STRESS DISTRIBUTION OF ENDODONTICALLY TREATED MAXILLARY PREMOLARS; THREE-DIMENSIONAL FINITE ELEMENT STUDY Heun-Sook Jung 1, Hyeon-Cheol
대한치과보존학회지 : Vol. 34, No. 1, 2009 EFFECT OF RESTORATION TYPE ON THE STRESS DISTRIBUTION OF ENDODONTICALLY TREATED MAXILLARY PREMOLARS; THREE-DIMENSIONAL FINITE ELEMENT STUDY Heun-Sook Jung 1, Hyeon-Cheol
Keyong Yuan 1, Chenguang Niu 1, Qian Xie 2, Wenxin Jiang 1, Li Gao 1, Zhengwei Huang 1, Rui Ma 1
 Eur J Oral Sci 2016; 124: 591 596 DOI: 10.1111/eos.12303 Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved Ó 2016 Eur J Oral Sci European Journal of Oral Sciences Comparative evaluation of the impact of minimally
Eur J Oral Sci 2016; 124: 591 596 DOI: 10.1111/eos.12303 Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved Ó 2016 Eur J Oral Sci European Journal of Oral Sciences Comparative evaluation of the impact of minimally
OUR EXPERIENCE WITH GRADIA DIRECT IN THE RESTORATION OF ANTERIOR TEETH
 ISSN: 1312-773X (Online) Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers) 2006, vol. 12, issue 2 OUR EXPERIENCE WITH GRADIA DIRECT IN THE RESTORATION OF ANTERIOR TEETH Snezhanka Topalova-Pirinska,
ISSN: 1312-773X (Online) Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers) 2006, vol. 12, issue 2 OUR EXPERIENCE WITH GRADIA DIRECT IN THE RESTORATION OF ANTERIOR TEETH Snezhanka Topalova-Pirinska,
Scanning electron microscope characterization of abrasion in human teeth
 Dental Journal Mahidol Dental Journal Original Article Scanning electron microscope characterization of abrasion in human teeth B.Sc., D.D.S., Specialty Certificate in Oral Pathology, M.S. Department of
Dental Journal Mahidol Dental Journal Original Article Scanning electron microscope characterization of abrasion in human teeth B.Sc., D.D.S., Specialty Certificate in Oral Pathology, M.S. Department of
FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF PERIODONTAL STRESSES IN FIXED PROSTHODONTICS
 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF PERIODONTAL STRESSES IN FIXED PROSTHODONTICS Valeria Pendefunda, Arina Ciocan Pendefunda, Nicoleta Ioanid, Alina Apostu, Oana Ţănculescu Odontology, Periodontology and Fixed
FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF PERIODONTAL STRESSES IN FIXED PROSTHODONTICS Valeria Pendefunda, Arina Ciocan Pendefunda, Nicoleta Ioanid, Alina Apostu, Oana Ţănculescu Odontology, Periodontology and Fixed
Medical NBDE-II. Dental Board Exams Part I.
 Medical NBDE-II Dental Board Exams Part I http://killexams.com/exam-detail/nbde-ii Question: 149 Anatomically, the term "clinical root" can be defined as which of the following: A. The space in the tooth
Medical NBDE-II Dental Board Exams Part I http://killexams.com/exam-detail/nbde-ii Question: 149 Anatomically, the term "clinical root" can be defined as which of the following: A. The space in the tooth
Prosthetic Options in Implant Dentistry. Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor
 Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION
 ABSTRACT Purpose: Evaluation of stress distribution maxilla under parafunctional loading on short dental implant using 3-dimensional (3D) finite element models. Material and method: 3D maxillary and mandibular
ABSTRACT Purpose: Evaluation of stress distribution maxilla under parafunctional loading on short dental implant using 3-dimensional (3D) finite element models. Material and method: 3D maxillary and mandibular
Finite Element Analysis of Dental Implant as Orthodontic Anchorage
 JCDP 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1044 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Finite Element Analysis of Dental Implant as Orthodontic Anchorage Finite Element Analysis of Dental Implant as Orthodontic Anchorage Anirban Sarmah,
JCDP 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1044 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Finite Element Analysis of Dental Implant as Orthodontic Anchorage Finite Element Analysis of Dental Implant as Orthodontic Anchorage Anirban Sarmah,
AN EXPERT SYSTEM FOR STRESS ANALYSIS OF HUMAN TEETH. Qiong Li. Dissertation. Submitted to the Faculty of the. Graduate School of Vanderbilt University
 AN EXPERT SYSTEM FOR STRESS ANALYSIS OF HUMAN TEETH By Qiong Li Dissertation Submitted to the Faculty of the Graduate School of Vanderbilt University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the
AN EXPERT SYSTEM FOR STRESS ANALYSIS OF HUMAN TEETH By Qiong Li Dissertation Submitted to the Faculty of the Graduate School of Vanderbilt University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the
Dental Morphology and Vocabulary
 Dental Morphology and Vocabulary Palate Palate Palate 1 2 Hard Palate Rugae Hard Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate 4 Palate Hard Palate Soft Palate Maxillary Arch (Maxilla) (Uppers)
Dental Morphology and Vocabulary Palate Palate Palate 1 2 Hard Palate Rugae Hard Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate 4 Palate Hard Palate Soft Palate Maxillary Arch (Maxilla) (Uppers)
Part II National Board Review Operative Dentistry. Module 3D General Questions Answers in BOLD (usually the first answer)
 Part II National Board Review Operative Dentistry Module 3D General Questions Answers in BOLD (usually the first answer) Howard E. Strassler, DMD University of Maryland Dental School With special acknowledgements
Part II National Board Review Operative Dentistry Module 3D General Questions Answers in BOLD (usually the first answer) Howard E. Strassler, DMD University of Maryland Dental School With special acknowledgements
Stress and Displacement Analysis of Dental Implant Threads Using Three-Dimensional Finite Element Analysis
 1 Research Article Stress and Displacement Analysis of Dental Implant Threads Using Three-Dimensional Finite Element Analysis Aswin Yodrux* Department of Materials Handling and Logistics for Engineering,
1 Research Article Stress and Displacement Analysis of Dental Implant Threads Using Three-Dimensional Finite Element Analysis Aswin Yodrux* Department of Materials Handling and Logistics for Engineering,
J Bagh College Dentistry Vol. 27(1), March 2015 The influence of
 The influence of shifting the class I cavity position prepared in posterior teeth buccally and lingualy on stress distribution (Finite element analysis study) Abdulsalm Rasheed Al-Zahawi, B.D.S., H.D.D.,
The influence of shifting the class I cavity position prepared in posterior teeth buccally and lingualy on stress distribution (Finite element analysis study) Abdulsalm Rasheed Al-Zahawi, B.D.S., H.D.D.,
Dental Anatomy and Occlusion
 CHAPTER 53 Dental Anatomy and Occlusion Ma Lou C. Sabino DDS, and Emily G. Smythe, DDS What numerical system is used most commonly in the United States for designating the adult dentition? Pediatric dentition?
CHAPTER 53 Dental Anatomy and Occlusion Ma Lou C. Sabino DDS, and Emily G. Smythe, DDS What numerical system is used most commonly in the United States for designating the adult dentition? Pediatric dentition?
Finite Element Evaluation of Stress Distribution in Mature and Immature Teeth
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Finite Element Evaluation of Stress Distribution in Mature and Immature Teeth Ali Talati 1, Reza Disfani 1, Maryam Javidi 1*, Ashkan Afshar 2, Akbar Fallah Rastegar 3 1. Department of
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Finite Element Evaluation of Stress Distribution in Mature and Immature Teeth Ali Talati 1, Reza Disfani 1, Maryam Javidi 1*, Ashkan Afshar 2, Akbar Fallah Rastegar 3 1. Department of
The Influence of Cervical Cavity Shape on the Restoration Material Retention A finite element method study
 The Influence of Cervical Cavity Shape on the Restoration Material Retention A finite element method study ANAMARIA FLORESCU, STEFAN MANEA, VIOLETA HANCU, ROXANA MANU*, CORNELIA FLORENTINA BICLESANU Titu
The Influence of Cervical Cavity Shape on the Restoration Material Retention A finite element method study ANAMARIA FLORESCU, STEFAN MANEA, VIOLETA HANCU, ROXANA MANU*, CORNELIA FLORENTINA BICLESANU Titu
Comparative analysis of the stress distribution in five anatomical types of maxillary central incisor
 Technology and Health Care 25 (2017) S53 S62 DOI 10.3233/THC-171306 IOS Press S53 Comparative analysis of the stress distribution in five anatomical types of maxillary central incisor Lei Sun a, Xifeng
Technology and Health Care 25 (2017) S53 S62 DOI 10.3233/THC-171306 IOS Press S53 Comparative analysis of the stress distribution in five anatomical types of maxillary central incisor Lei Sun a, Xifeng
Modal analysis of maxillary central incisor tooth
 African Journal of Biotechnology Vol. 8 (19), pp. 5088-5096, 5 October, 2009 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/ajb ISSN 1684 5315 2009 Academic Journals Full Length Research Paper Modal
African Journal of Biotechnology Vol. 8 (19), pp. 5088-5096, 5 October, 2009 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/ajb ISSN 1684 5315 2009 Academic Journals Full Length Research Paper Modal
International Journal of Engineering Technology and Scientific Innovation PHOTOELASTIC AND FINITE ELEMENT STRESS ANALYSIS OF HUMAN TEETH
 PHOTOELASTIC AND FINITE ELEMENT STRESS ANALYSIS OF HUMAN TEETH Sadiq J. Abass, Noora A. Abdul-Alhussain, Jamal A. Hassan Al-Nahrain University, Collage of Engineering, Biomedical Engineering Department
PHOTOELASTIC AND FINITE ELEMENT STRESS ANALYSIS OF HUMAN TEETH Sadiq J. Abass, Noora A. Abdul-Alhussain, Jamal A. Hassan Al-Nahrain University, Collage of Engineering, Biomedical Engineering Department
FRACTURES AND LUXATIONS OF PERMANENT TEETH
 FRACTURES AND LUXATIONS OF PERMANENT TEETH 1. Treatment guidelines and alveolar bone Followup Procedures INFRACTION Clinical findings Radiographic findings Treatment Follow-Up Favorable Outcome Unfavorable
FRACTURES AND LUXATIONS OF PERMANENT TEETH 1. Treatment guidelines and alveolar bone Followup Procedures INFRACTION Clinical findings Radiographic findings Treatment Follow-Up Favorable Outcome Unfavorable
Continually Fluoride Releasing Aesthetic Dental Restorative Material
 Continually Fluoride Releasing Aesthetic Dental Restorative Material Research is our best product Image provided by Dr. Sushil Koirala BEAUTIFIL II More than just filling BEAUTIFIL II stands out for its
Continually Fluoride Releasing Aesthetic Dental Restorative Material Research is our best product Image provided by Dr. Sushil Koirala BEAUTIFIL II More than just filling BEAUTIFIL II stands out for its
6610 NE 181st Street, Suite #1, Kenmore, WA
 660 NE 8st Street, Suite #, Kenmore, WA 9808 www.northshoredentalacademy.com.08.900 READ CHAPTER The Professional Dental Assistant (p.-9) No Key Terms Recall Questions:,,,, and 6 CLASS SYLLABUS DAY READ
660 NE 8st Street, Suite #, Kenmore, WA 9808 www.northshoredentalacademy.com.08.900 READ CHAPTER The Professional Dental Assistant (p.-9) No Key Terms Recall Questions:,,,, and 6 CLASS SYLLABUS DAY READ
Interdisciplinary Treatment of a Fused Lower Premolar with Supernumerary Tooth
 Interdisciplinary Treatment of a Fused Lower Premolar with Supernumerary Tooth Cengiz Gadimli a Zafer Sari b Abstract The objective of this report is to describe combined orthodontic and endodontic treatment
Interdisciplinary Treatment of a Fused Lower Premolar with Supernumerary Tooth Cengiz Gadimli a Zafer Sari b Abstract The objective of this report is to describe combined orthodontic and endodontic treatment
OCCLUSION: PHYSIOLOGIC vs. NON-PHYSIOLOGIC
 Oral Anatomy and Occlusion Prosthodontic Component OCCLUSION: PHYSIOLOGIC vs. NON-PHYSIOLOGIC By: Dr. Babak Shokati, DDS, MSc. MSc. Prosthodontics Definition of Masticatory System by The Academy of Prosthodontics
Oral Anatomy and Occlusion Prosthodontic Component OCCLUSION: PHYSIOLOGIC vs. NON-PHYSIOLOGIC By: Dr. Babak Shokati, DDS, MSc. MSc. Prosthodontics Definition of Masticatory System by The Academy of Prosthodontics
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adult performance horse dental care in, 505 519 bit seat reduction in, 514 515 canine teeth disorders, 515 diagnostic nerve blocks in,
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adult performance horse dental care in, 505 519 bit seat reduction in, 514 515 canine teeth disorders, 515 diagnostic nerve blocks in,
Effect of Screw Profile on Stress Distribution Pattern of Dental Implants by FEA
 ISSN 2395-1621 Effect of Screw Profile on Stress Distribution Pattern of Dental Implants by FEA #1 RaiphaleGovind, #2 Shinde B.M. 1 govindaraiphale@gmail.com*1 2bharat.shinde@zealeducation.com 1 (M.E Student
ISSN 2395-1621 Effect of Screw Profile on Stress Distribution Pattern of Dental Implants by FEA #1 RaiphaleGovind, #2 Shinde B.M. 1 govindaraiphale@gmail.com*1 2bharat.shinde@zealeducation.com 1 (M.E Student
Finite element analysis and fatigue test on the bicuspids to support theory of abfraction
 Scholars' Mine Masters Theses Student Research & Creative Works Fall 2010 Finite element analysis and fatigue test on the bicuspids to support theory of abfraction Madhuchandra Mahadevaswamy Follow this
Scholars' Mine Masters Theses Student Research & Creative Works Fall 2010 Finite element analysis and fatigue test on the bicuspids to support theory of abfraction Madhuchandra Mahadevaswamy Follow this
Recent advances in composite CAD/CAM blocks
 MAINJOT Recent advances in composite CAD/CAM blocks Amélie Mainjot, DDS, MS, PhD Dental Biomaterials Research Unit (d-bru) and Department of Fixed Prosthodontics Institute of Dentistry, University of Liège
MAINJOT Recent advances in composite CAD/CAM blocks Amélie Mainjot, DDS, MS, PhD Dental Biomaterials Research Unit (d-bru) and Department of Fixed Prosthodontics Institute of Dentistry, University of Liège
Development of teeth. 5.DM - Pedo
 Development of teeth 5.DM - Pedo Tooth development process of continuous changes in predetermined order starts from dental lamina A band of ectodermal cells growing from the epithelium of the embryonic
Development of teeth 5.DM - Pedo Tooth development process of continuous changes in predetermined order starts from dental lamina A band of ectodermal cells growing from the epithelium of the embryonic
Push-out of root canal filling using the material testing stage (MTS) inside a Micro-CT: preliminary observations
 Push-out of root canal filling using the material testing stage (MTS) inside a Micro-CT: preliminary observations G.B. Leoni, 1 M.Brito-Júnior, 1 E.A. Gomes, 2 J.Chaves, 1 Y.T.C. Silva-Sousa, 2 M.D.Sousa-Neto
Push-out of root canal filling using the material testing stage (MTS) inside a Micro-CT: preliminary observations G.B. Leoni, 1 M.Brito-Júnior, 1 E.A. Gomes, 2 J.Chaves, 1 Y.T.C. Silva-Sousa, 2 M.D.Sousa-Neto
Periodontal Ligament Stress Analysis During Periodontal Resorption
 , June 29 - July 1, 2016, London, U.K. Periodontal Ligament Stress Analysis During Periodontal Resorption R.A. Moga, C.G. Chiorean Abstract Conservation of the PDL(periodontal ligament) height during the
, June 29 - July 1, 2016, London, U.K. Periodontal Ligament Stress Analysis During Periodontal Resorption R.A. Moga, C.G. Chiorean Abstract Conservation of the PDL(periodontal ligament) height during the
A finite element analysis of ferrule design on restoration resistance and distribution of stress within a root
 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2006.01085.x A finite element analysis of ferrule design on restoration resistance and distribution of stress within a root I. Ichim 1, D. V. Kuzmanovic 2 & R. M. Love 2 1 Department
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2006.01085.x A finite element analysis of ferrule design on restoration resistance and distribution of stress within a root I. Ichim 1, D. V. Kuzmanovic 2 & R. M. Love 2 1 Department
Finite element stress analysis of restored primary teeth: A comparative evaluation between stainless steel crowns and preformed zirconia crowns
 Original Article Finite element stress analysis of restored primary teeth: A comparative evaluation between stainless steel crowns and preformed zirconia crowns Atiguppe Ramasetty Prabhakar, Amrita Chakraborty
Original Article Finite element stress analysis of restored primary teeth: A comparative evaluation between stainless steel crowns and preformed zirconia crowns Atiguppe Ramasetty Prabhakar, Amrita Chakraborty
There had been controversies concerning how to achieve maximum anchorage in the first premolar extraction cases.
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC DENTAL SCIENCE Research Article Comparison Between the Stresses Induced on Vital Structures During Two Steps and En-Masse Retraction Methods of Upper Anterior Segment Depending
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC DENTAL SCIENCE Research Article Comparison Between the Stresses Induced on Vital Structures During Two Steps and En-Masse Retraction Methods of Upper Anterior Segment Depending
Finite element analysis: A Boon To Dental Research
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dental Science Volume 6 Number 2 Finite element analysis: A Boon To Dental Research G Vasudeva Citation G Vasudeva. Finite element analysis: A Boon To Dental Research.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dental Science Volume 6 Number 2 Finite element analysis: A Boon To Dental Research G Vasudeva Citation G Vasudeva. Finite element analysis: A Boon To Dental Research.
Clinical UM Guideline
 Clinical UM Guideline Subject: Clinical Crown Lengthening Guideline #: 04-206 Current Effective Date: 03/24/2017 Status: New Last Review Date: 02/08/2017 Description This document addresses the procedure
Clinical UM Guideline Subject: Clinical Crown Lengthening Guideline #: 04-206 Current Effective Date: 03/24/2017 Status: New Last Review Date: 02/08/2017 Description This document addresses the procedure
SPACE MAINTAINER. Multimedia Health Education. Disclaimer
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage your health. All decisions about the management of premature loss of primary teeth and use of space maintainers must
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage your health. All decisions about the management of premature loss of primary teeth and use of space maintainers must
Esthetic Rehabilitation of Severely Discolored Maxillary Anterior Teeth with Porcelain Laminate Veneers: A Case Report
 Esthetic Rehabilitation of Severely Discolored Maxillary Anterior Teeth with Porcelain Laminate Veneers: A Case Report Dr. Shikha Nandal 1, Dr. Himanshu Shekhawat 2 1 M.D.S. (Prosthodontics) Senior Resident,
Esthetic Rehabilitation of Severely Discolored Maxillary Anterior Teeth with Porcelain Laminate Veneers: A Case Report Dr. Shikha Nandal 1, Dr. Himanshu Shekhawat 2 1 M.D.S. (Prosthodontics) Senior Resident,
Anisotropy of Tensile Strengths of Bovine Dentin Regarding Dentinal Tubule Orientation and Location
 Original paper Dental Materials Journal 21 (1): 32-43, 2002 Anisotropy of Tensile Strengths of Bovine Dentin Regarding Dentinal Tubule Orientation and Location Toshiko INOUE, Hidekazu TAKAHASHI and Fumio
Original paper Dental Materials Journal 21 (1): 32-43, 2002 Anisotropy of Tensile Strengths of Bovine Dentin Regarding Dentinal Tubule Orientation and Location Toshiko INOUE, Hidekazu TAKAHASHI and Fumio
An Investigation into Non Carious Tooth Wear and Associated Clinical findings
 39 An Investigation into Non Carious Tooth Wear and Associated Clinical findings Faraedon M. Zardawi PhD School of Dentistry University of Sulaimani,Iraq Corresponding Author: Faraedon M. Zardawi Email:
39 An Investigation into Non Carious Tooth Wear and Associated Clinical findings Faraedon M. Zardawi PhD School of Dentistry University of Sulaimani,Iraq Corresponding Author: Faraedon M. Zardawi Email:
THE PROSTHETIC VALUE OF THE TEETH ACCORDING TO THEIR PERIODONTAL ATTACHMENT LEVEL
 THE PROSTHETIC VALUE OF THE TEETH ACCORDING TO THEIR PERIODONTAL ATTACHMENT LEVEL Nicoleta Ioanid 1, Gabriela Ifteni, Irina Grădinaru 2, Silvia Mârțu 1, Oana Țănculescu 1 1 Gr. T. Popa" U.M.Ph. - Iași,
THE PROSTHETIC VALUE OF THE TEETH ACCORDING TO THEIR PERIODONTAL ATTACHMENT LEVEL Nicoleta Ioanid 1, Gabriela Ifteni, Irina Grădinaru 2, Silvia Mârțu 1, Oana Țănculescu 1 1 Gr. T. Popa" U.M.Ph. - Iași,
Stress distributions in adhesively cemented ceramic and resin-composite Class II inlay restorations: a 3D-FEA study
 Dental Materials (2004) 20, 862 872 www.intl.elsevierhealth.com/journals/dema Stress distributions in adhesively cemented ceramic and resin-composite Class II inlay restorations: a 3D-FEA study Pietro
Dental Materials (2004) 20, 862 872 www.intl.elsevierhealth.com/journals/dema Stress distributions in adhesively cemented ceramic and resin-composite Class II inlay restorations: a 3D-FEA study Pietro
A clinical case involving severe erosion of the maxillary anterior teeth restored with direct composite resin restorations
 SETHI A clinical case involving severe erosion of the maxillary anterior teeth restored with direct composite resin restorations Sanjay Sethi, BDS (Lond.) Square Mile Dental Centre, 7-9 White Kennett Street,
SETHI A clinical case involving severe erosion of the maxillary anterior teeth restored with direct composite resin restorations Sanjay Sethi, BDS (Lond.) Square Mile Dental Centre, 7-9 White Kennett Street,
Periodontal Disease. Radiology of Periodontal Disease. Periodontal Disease. The Role of Radiology in Assessment of Periodontal Disease
 Radiology of Periodontal Disease Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Periodontal Disease! Includes several disorders of the periodontium! Gingivitis! Marginal Periodontitis! Localized
Radiology of Periodontal Disease Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Periodontal Disease! Includes several disorders of the periodontium! Gingivitis! Marginal Periodontitis! Localized
Complex esthetic and functional rehabilitation using glass-ceramic materials - long-term documentation of a restoration
 C L I N I C A L Complex esthetic and functional rehabilitation using glass-ceramic materials - long-term documentation of a restoration Daniel Edelhoff 1 and Oliver Brix 2 1 Prof. Dr Daniel Edelhoff, Munich
C L I N I C A L Complex esthetic and functional rehabilitation using glass-ceramic materials - long-term documentation of a restoration Daniel Edelhoff 1 and Oliver Brix 2 1 Prof. Dr Daniel Edelhoff, Munich
Parafunction poses a risk for any. Predictable Esthetics through Functional Design: The Role of Harmonious Disclusion
 Predictable Esthetics through Functional Design: The Role of Harmonious Disclusion BRIAN S. VENCE, DDS* ABSTRACT The goal of this clinical report is to describe and illustrate the principles for achieving
Predictable Esthetics through Functional Design: The Role of Harmonious Disclusion BRIAN S. VENCE, DDS* ABSTRACT The goal of this clinical report is to describe and illustrate the principles for achieving
Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development. Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L.
 Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L. Dennis Proximal contact areas Contact areas are on the mesial and
Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L. Dennis Proximal contact areas Contact areas are on the mesial and
T O O T H A T L A S C O U R S E G U I D E A S S I S T A N T E D I T I O N
 T O O T H A T L A S C O U R S E G U I D E A S S I S T A N T E D I T I O N The information in this guide was prepared by ehuman with contributions from: Cara Miyasaki, RDHEF, MS, Foothill College Kay Murphy,
T O O T H A T L A S C O U R S E G U I D E A S S I S T A N T E D I T I O N The information in this guide was prepared by ehuman with contributions from: Cara Miyasaki, RDHEF, MS, Foothill College Kay Murphy,
ADHESIVE RECONSTRUCTION IN HELP OF THE ORTHODONTIC TREATMENT
 ISSN: 1312-773X (Online) Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers) 2006, vol. 12, issue 2 ADHESIVE RECONSTRUCTION IN HELP OF THE ORTHODONTIC TREATMENT Snezhanka Topalova-Pirinska 1, R. Pirinska
ISSN: 1312-773X (Online) Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers) 2006, vol. 12, issue 2 ADHESIVE RECONSTRUCTION IN HELP OF THE ORTHODONTIC TREATMENT Snezhanka Topalova-Pirinska 1, R. Pirinska
Dr Mohammed Alfarsi Page 1 9 December Principles of Occlusion
 Dr Mohammed Alfarsi Page 1 9 December 2013 Principles of Occlusion Overview: The occlusion is a very large, yet easy to manage once properly understood, topic. Thus, no one handout is enough to fully understand
Dr Mohammed Alfarsi Page 1 9 December 2013 Principles of Occlusion Overview: The occlusion is a very large, yet easy to manage once properly understood, topic. Thus, no one handout is enough to fully understand
A DAMAGE/REPAIR MODEL FOR ALVEOLAR BONE REMODELING
 A DAMAGE/REPAIR MODEL FOR ALVEOLAR BONE REMODELING M. Mengoni 1 and J.-P. Ponthot 2 1. ABSTRACT Tooth movements obtained through orthodontic appliances result from a complex biochemical process of bone
A DAMAGE/REPAIR MODEL FOR ALVEOLAR BONE REMODELING M. Mengoni 1 and J.-P. Ponthot 2 1. ABSTRACT Tooth movements obtained through orthodontic appliances result from a complex biochemical process of bone
Transactions on Biomedicine and Health vol 1, 1993 WIT Press, ISSN
 2d and 3d modelling comparison for a human first premolar to determine an appropriate cavityfillingmaterial B. Ekici, E. Giingor, M. Akyiiz & S. Altintas Bogazigi University, Istanbul, Turkey ABSTRACT
2d and 3d modelling comparison for a human first premolar to determine an appropriate cavityfillingmaterial B. Ekici, E. Giingor, M. Akyiiz & S. Altintas Bogazigi University, Istanbul, Turkey ABSTRACT
Plaque and Occlusion in Periodontal Disease Wednesday, February 25, :54 AM
 Plaque and Occlusion in Periodontal Disease Wednesday, February 25, 2015 9:54 AM 1. The definition of Trauma From Occlusion: Primary TFO, Secondary TFO, and Combined TFO 2. Clinical and Radiographic signs
Plaque and Occlusion in Periodontal Disease Wednesday, February 25, 2015 9:54 AM 1. The definition of Trauma From Occlusion: Primary TFO, Secondary TFO, and Combined TFO 2. Clinical and Radiographic signs
Finite element analysis to study the effects of using CAD/CAM glass-fiber post system in a severely damaged anterior tooth
 Bio-Medical Materials and Engineering 26 (2015) S519 S525 DOI 10.3233/BME-151341 IOS Press S519 Finite element analysis to study the effects of using CAD/CAM glass-fiber post system in a severely damaged
Bio-Medical Materials and Engineering 26 (2015) S519 S525 DOI 10.3233/BME-151341 IOS Press S519 Finite element analysis to study the effects of using CAD/CAM glass-fiber post system in a severely damaged
Treatment Options for the Compromised Tooth
 New Edition Treatment Options for the Compromised Tooth A Decision Guide American Association of Endodontists www.aae.org/treatmentoptions TREATMENT PLANNING CONSIDERATIONS The Treatment Options for the
New Edition Treatment Options for the Compromised Tooth A Decision Guide American Association of Endodontists www.aae.org/treatmentoptions TREATMENT PLANNING CONSIDERATIONS The Treatment Options for the
All-ceramic crowns have been introduced in
 Influence of Core Thickness on a Restored Crown of a First Premolar Using Finite Element Analysis Kaarel A. Proos, BEng, PhD a Michael V. Swain, BSc, PhD b Jim Ironside, BDS, MDS, PhD c Grant P. Steven,
Influence of Core Thickness on a Restored Crown of a First Premolar Using Finite Element Analysis Kaarel A. Proos, BEng, PhD a Michael V. Swain, BSc, PhD b Jim Ironside, BDS, MDS, PhD c Grant P. Steven,
Abfraction: Etiology, Treatment and Prognosis
 International Journal of Dental Sciences and Research, 2017, Vol. 5, No. 5, 125-131 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ijdsr/5/5/3 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.12691/ijdsr-5-5-3 Abfraction:
International Journal of Dental Sciences and Research, 2017, Vol. 5, No. 5, 125-131 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ijdsr/5/5/3 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.12691/ijdsr-5-5-3 Abfraction:
Effect of Extension and Type of Composite-Restored Class II Cavities on Biomechanical Properties of Teeth: A Three Dimensional Finite Element Analysis
 Original Article Effect of Extension and Type of Composite-Restored Class II Cavities on Biomechanical Properties of Teeth: A Three Dimensional Finite Element Analysis Azam Valian 1, Elham Moravej-Salehi
Original Article Effect of Extension and Type of Composite-Restored Class II Cavities on Biomechanical Properties of Teeth: A Three Dimensional Finite Element Analysis Azam Valian 1, Elham Moravej-Salehi
Howard E. Strassler, DMD University of Maryland School of Dentistry
 Part II National Board Review Operative Dentistry-Biomaterials Structures, chemical properties, physical properties BASIC CONCEPTS ON HOW DENTAL MATERIALS WORK! Howard E. Strassler, DMD University of Maryland
Part II National Board Review Operative Dentistry-Biomaterials Structures, chemical properties, physical properties BASIC CONCEPTS ON HOW DENTAL MATERIALS WORK! Howard E. Strassler, DMD University of Maryland
Strain Analysis of a Human Tooth with Support Tissues Resorption
 , July 3-5, 2013, London, U.K. Strain Analysis of a Human Tooth with Support Tissues Resorption R. A. Moga, C. G. Chiorean Abstract The conservative and reconstructive dentistry took, in the last years,
, July 3-5, 2013, London, U.K. Strain Analysis of a Human Tooth with Support Tissues Resorption R. A. Moga, C. G. Chiorean Abstract The conservative and reconstructive dentistry took, in the last years,
Resin-bonded casting used as an anterior fixed partial denture retainer: A clinical report
 Resin-bonded casting used as an anterior fixed partial denture retainer: A clinical report Hideo Matsumura, DDS, PhD, a Hiroyasu Koizumi, DDS, PhD, a and Naomi Tanoue, DDS, PhD b a Department of Crown
Resin-bonded casting used as an anterior fixed partial denture retainer: A clinical report Hideo Matsumura, DDS, PhD, a Hiroyasu Koizumi, DDS, PhD, a and Naomi Tanoue, DDS, PhD b a Department of Crown
A Finite Element Model of Apical Force Distribution From Orthodontic Tooth Movement
 Original Article A Finite Element Model of Apical Force Distribution From Orthodontic Tooth Movement David J. Rudolph, DDS, PhD a ; Michael G. Willes, DDS, MS b ; Glenn T. Sameshima, DDS, PhD c Abstract:
Original Article A Finite Element Model of Apical Force Distribution From Orthodontic Tooth Movement David J. Rudolph, DDS, PhD a ; Michael G. Willes, DDS, MS b ; Glenn T. Sameshima, DDS, PhD c Abstract:
how to technique Issue How to improve the longevity of porcelain veneers.
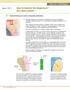 Issue 4 2013 How to improve the longevity of porcelain veneers. 1. Avoid finishing on a resin composite restoration. longer term weak spot Although tempting in the interests of minimal tooth removal, finishing
Issue 4 2013 How to improve the longevity of porcelain veneers. 1. Avoid finishing on a resin composite restoration. longer term weak spot Although tempting in the interests of minimal tooth removal, finishing
Evaluation of fixed partial denture in relation to gingival recession and other factors
 Evaluation of fixed partial denture in relation to gingival recession and other factors Faiza M. Abdul Ameer,B.D.S., M. Sc. (1) Zainab M. Abdul Ameer,B.D.S., M. Sc (2) ABSTRACT Background: Gingival recession
Evaluation of fixed partial denture in relation to gingival recession and other factors Faiza M. Abdul Ameer,B.D.S., M. Sc. (1) Zainab M. Abdul Ameer,B.D.S., M. Sc (2) ABSTRACT Background: Gingival recession
NUMERICAL STUDY OF STRESSES IN DENTAL MATERIALS BY USING FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS
 NUMERICAL STUDY OF STRESSES IN DENTAL MATERIALS BY USING FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS Gunjal Vinayak B. PG Student, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Rajarambapu Institute of Technology, Sakharale, India
NUMERICAL STUDY OF STRESSES IN DENTAL MATERIALS BY USING FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS Gunjal Vinayak B. PG Student, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Rajarambapu Institute of Technology, Sakharale, India
Stress Analysis of Ceramic Laminate Veneer for Diastema Closure with Different Extensions and Different Directions of Applied Load
 International Journal of Dental Sciences and Research, 2018, Vol. 6, No. 2, 33-38 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ijdsr/6/2/3 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.12691/ijdsr-6-2-3 Stress
International Journal of Dental Sciences and Research, 2018, Vol. 6, No. 2, 33-38 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ijdsr/6/2/3 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.12691/ijdsr-6-2-3 Stress
Three-dimensional finite element modeling from CT images of tooth and its validation
 Dental Materials Journal 2009; 28(2): 219-226 Original Paper Three-dimensional finite element modeling from CT images of tooth and its validation Kiyoshi TAJIMA 1, Ker-Kong CHEN 2, Nobusuke TAKAHASHI 1,
Dental Materials Journal 2009; 28(2): 219-226 Original Paper Three-dimensional finite element modeling from CT images of tooth and its validation Kiyoshi TAJIMA 1, Ker-Kong CHEN 2, Nobusuke TAKAHASHI 1,
Effect of Three Different Core Materials on the Fracture Resistance of Endodontically Treated Deciduous Mandibular Second Molars: An in vitro Study
 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1097 Preetam Shah et al ORIGINAL RESEARCH Effect of Three Different Core Materials on the Fracture Resistance of Endodontically Treated Deciduous Mandibular Second Molars: An
10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1097 Preetam Shah et al ORIGINAL RESEARCH Effect of Three Different Core Materials on the Fracture Resistance of Endodontically Treated Deciduous Mandibular Second Molars: An
Splints and stress transmission to teeth: an in vitro experiment
 Journal of Dentistry 28 (2000) 475 480 Journal of Dentistry www.elsevier.com/locate/jdent Splints and stress transmission to teeth: an in vitro experiment M. Halachmi a, *, A. Gavish a, E. Gazit a, E.
Journal of Dentistry 28 (2000) 475 480 Journal of Dentistry www.elsevier.com/locate/jdent Splints and stress transmission to teeth: an in vitro experiment M. Halachmi a, *, A. Gavish a, E. Gazit a, E.
Case Study. Case # 1 Author: Dr. Suheil Boutros (USA) 2013 Zimmer Dental, Inc. All rights reserved. 6557, Rev. 03/13.
 Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Initial force systems during bodily tooth movement with plastic aligners and composite attachments: A three-dimensional finite element analysis
 Original Article Initial force systems during bodily tooth movement with plastic aligners and composite attachments: A three-dimensional finite element analysis Juan Pablo Gomez a ; Fabio Marcelo Peña
Original Article Initial force systems during bodily tooth movement with plastic aligners and composite attachments: A three-dimensional finite element analysis Juan Pablo Gomez a ; Fabio Marcelo Peña
Original Article INTRODUCTION. Amandeep Kaur, Meena N, Shubhashini N, Anitha Kumari, Ashish Shetty
 Original Article A comparative study of intra canal stress pattern in endodontically treated teeth with average sized canal diameter and reinforced wide canals with three different post systems using finite
Original Article A comparative study of intra canal stress pattern in endodontically treated teeth with average sized canal diameter and reinforced wide canals with three different post systems using finite
Lauren Gueits, RDH, BS
 Lauren Gueits, RDH, BS The Dental Hygienist s Role in Identifying Malocclusion and the Benefits of Tooth Alignment Sponsored by Our Time Together.. Ortho 101: Perio-Ortho-Systemic Connections Long Term
Lauren Gueits, RDH, BS The Dental Hygienist s Role in Identifying Malocclusion and the Benefits of Tooth Alignment Sponsored by Our Time Together.. Ortho 101: Perio-Ortho-Systemic Connections Long Term
Evidence of pulp disease in the inlayed teeth of the ancient Mayans: a micro-ct study
 Evidence of pulp disease in the inlayed teeth of the ancient Mayans: a micro-ct study M. A. Versiani 1, J. D. Pécora 1, M. D. Sousa-Neto 1 1 Department of Restorative Dentistry, Faculty of Dentistry, University
Evidence of pulp disease in the inlayed teeth of the ancient Mayans: a micro-ct study M. A. Versiani 1, J. D. Pécora 1, M. D. Sousa-Neto 1 1 Department of Restorative Dentistry, Faculty of Dentistry, University
Modelling of temporomandibular joint and FEM analysis
 Acta of Bioengineering and Biomechanics Vol. 8, No. 1, 2006 Modelling of temporomandibular joint and FEM analysis MARTINA FRIOVÁ, ZDENK HORÁK, SVATAVA KONVIKOVÁ Laboratory of Biomechanics, Department of
Acta of Bioengineering and Biomechanics Vol. 8, No. 1, 2006 Modelling of temporomandibular joint and FEM analysis MARTINA FRIOVÁ, ZDENK HORÁK, SVATAVA KONVIKOVÁ Laboratory of Biomechanics, Department of
Comparative Evaluation of Fracture Resistance of Dental Amalgam, Z350 Composite Resin and Cention-N Restoration In Class II Cavity
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 4 Ver.1 April. (2018), PP 52-56 www.iosrjournals.org Comparative Evaluation of Fracture Resistance
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 4 Ver.1 April. (2018), PP 52-56 www.iosrjournals.org Comparative Evaluation of Fracture Resistance
Three-dimensional simulation of human teeth and its application in dental education and research
 Original Article Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran (MJIRI) Iran University of Medical Sciences Three-dimensional simulation of human teeth and its application in dental education and research
Original Article Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran (MJIRI) Iran University of Medical Sciences Three-dimensional simulation of human teeth and its application in dental education and research
Human Healed Trauma Skull
 Human Healed Trauma Skull Product Number: Specimen Evaluated: BC-303 Original Specimen Skeletal Inventory: 1 Cranium with full dentition (teeth ##1-16) 1 Mandible with full dentition (teeth ##17-32) Osteological
Human Healed Trauma Skull Product Number: Specimen Evaluated: BC-303 Original Specimen Skeletal Inventory: 1 Cranium with full dentition (teeth ##1-16) 1 Mandible with full dentition (teeth ##17-32) Osteological
Unusual transmigration of canines report of two cases in a family
 ISSN: Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2014 Jan-Mar;11(1):88-92 Case Report Article Unusual transmigration of canines report of two cases in a family Sulabha A. Narsapur 1 Sameer Choudhari 2 Shrishal
ISSN: Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2014 Jan-Mar;11(1):88-92 Case Report Article Unusual transmigration of canines report of two cases in a family Sulabha A. Narsapur 1 Sameer Choudhari 2 Shrishal
All Ceramic Inlays - Coming of Age
 CASE REPORT All Ceramic Inlays - Coming of Age Ahmad Naeem 1 & Bashir Taseer 2 Quick Response Code ABSTRACT: In the past decade and a half there has been an explosion in the introduction of restorative
CASE REPORT All Ceramic Inlays - Coming of Age Ahmad Naeem 1 & Bashir Taseer 2 Quick Response Code ABSTRACT: In the past decade and a half there has been an explosion in the introduction of restorative
ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION /jp-journals
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1677 Finite Element Analysis of the Endodontically-treated Maxillary Premolars restored with Composite Resin along with Glass Fiber Insertion in Various Positions
ORIGINAL RESEARCH 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1677 Finite Element Analysis of the Endodontically-treated Maxillary Premolars restored with Composite Resin along with Glass Fiber Insertion in Various Positions
Key points for starting off
 Key points for starting off First off, the five questions to ask yourself about a loose tooth before identifying it are: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Category (incisor, canine, premolar or molar)? Permanent or deciduous?
Key points for starting off First off, the five questions to ask yourself about a loose tooth before identifying it are: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Category (incisor, canine, premolar or molar)? Permanent or deciduous?
