Linear dimensional changes in plaster die models using different elastomeric materials
|
|
|
- Lawrence Wheeler
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Prosthodontics Prosthodontics Linear dimensional changes in plaster die models using different elastomeric materials Jefferson Ricardo Pereira (a) Karina Yumi Murata (b) Accácio Lins do Valle (c) Janaina Salomon Ghizoni (d) Fábio Kenji Shiratori (e) (a) PhD, Department of Prosthodontics, Dental School, University of Southern Santa Catarina (UNISUL), Tubarão, SC, Brazil. (b) DDS; (c) PhD; (e) MSc Department of Prosthodontics, Bauru Dental School, University of São Paulo (USP), Bauru, SP, Brazil. (d) MSc, Department of Periodontology, Dental School, University of South of Santa Catarina (UNISUL), Tubarão, SC, Brazil. Abstract: Dental impression is an important step in the preparation of prostheses since it provides the reproduction of anatomic and surface details of teeth and adjacent structures. The objective of this study was to evaluate the linear dimensional alterations in gypsum dies obtained with different elastomeric materials, using a resin coping impression technique with individual shells. A master cast made of stainless steel with fixed prosthesis characteristics with two prepared abutment teeth was used to obtain the impressions. References points (A, B, C, D, E and F) were recorded on the occlusal and buccal surfaces of abutments to register the distances. The impressions were obtained using the following materials: polyether, mercaptan-polysulfide, addition silicone, and condensation silicone. The transfer impressions were made with custom trays and an irreversible hydrocolloid material and were poured with type IV gypsum. The distances between identified points in gypsum dies were measured using an optical microscope and the results were statistically analyzed by ANOVA (p < 0.05) and Tukey s test. The mean of the distances were registered as follows: addition silicone (AB = 13.6 µm, CD = 15.0 µm, EF = 14.6 µm, GH = 15.2 µm), mercaptan-polysulfide (AB = 36.0 µm, CD = 36.0 µm, EF = 39.6 µm, GH = 40.6 µm), polyether (AB = 35.2 µm, CD = 35.6 µm, EF = 39.4 µm, GH = 41.4 µm) and condensation silicone (AB = 69.2 µm, CD = 71.0 µm, EF = 80.6 µm, GH = 81.2 µm). All of the measurements found in gypsum dies were compared to those of a master cast. The results demonstrated that the addition silicone provides the best stability of the compounds tested, followed by polyether, polysulfide and condensation silicone. No statistical differences were obtained between polyether and mercaptan-polysulfide materials. Descriptors: Dental impression materials; Dental impression technique; Dental prosthesis. Corresponding author: Jefferson Ricardo Pereira Rua Pd Bernardo Freuser, 306-D - Sala 202 Tubarão - SC - Brazil CEP: jeffripe@rocketmail.com Received for publication on Mar 22, 2010 Accepted for publication on Jun 17, 2010 Introduction Successful dental prosthesis is dependent upon the dimensional precision of impression materials and techniques. The cervical limits of abutment teeth, especially when they are located in subgingival regions, can be unsatisfactory because of the challenges involved in obtaining accurate impressions. This is because the impression materials are not able to keep away gingival tissues, thus methods are needed to handle such tissues to better reproduce structural details in these regions. 1-3 Many me- 336 Braz Oral Res Jul-Sep;24(3):336-41
2 Pereira JR, Murata KY, Valle AL, Ghizoni JS, Shiratori FK chanical, chemical or chemical-mechanical methods have emerged to facilitate gingival retraction. 4-5 Today, many clinicians employ the individual shell technique with mechanical gingival retraction that was initially described by Cannistraci. 6 Livaditis 7 favoured the technique of orienting the impression material distribution to mould the gingival sulcus without additional procedures such as retractor wires or chemical substances. However, even with mechanical gingival retraction, the tissue trauma or gingival bleeding is minimal. Aside from the impression technique, the materials used are also very important in order to obtain gypsum casts. Addition silicones, mercaptanpolysulfides, and polyetheres are the most common additives for this procedure The thickness of the impression material, in addition to the effects of temperature and the materials used, influences the mould, producing excessive distortion of the impression. 9,10 The individual shell technique is advantageous because the thickness of the material is less and it thus produces only minor dimensional changes in the impression. 9,10 In this way, the objective of this study was to analyze the linear dimensional changes of those dental impression materials. The hypothesis was that there was significant difference on the linear dimensional alterations in gypsum dies obtained with different elastomeric materials. Material and Methods One master cast was made with stainless steel, simulating two posterior abutment teeth prepared to receive a fixed prosthesis intercalated between two bridges. The occlusal and vestibular surfaces were marked reference points named A, B, C, D (occlusal), E, F, G, and H (vestibular). In this way, inter abutment distances AB, CD, EF and GH can be identified, as shown in Figure 1. The distances between the points (2,538 µm) were measured microscopically (Mitutoyo SC-6 COOE TOO-113, Mitutoyo INC, Kanagawa, Japan). These measurements were compared to those obtained from gypsum casts from a master cast made using the different elastomeric materials. To ensure the correct positioning of the master cast and the tray, a device aimed at standardizing the position during the impressions was utilized. This device holds the master cast enveloped in a container fabricated with condensation silicone (Elite Double 8, Zhermack, Badia Polesine, RO, Italy) and three resin abutments (Clássico Artigos Odontológicos, S/A, São Paulo, SP, Brazil) juxtapositioned on a glass plate with dimensions of 12 x 8 cm. In the lateral portions of the container were two fixed pivot-abutments to prevent the horizontal displacement of the tray, and in the opposite lateral section, another pivot was fixed to support the cable of the tray while preventing its vertical displacement. To make the shells, the prosthetic abutments of the master cast were reproduced by alginate (Jeltrate, Dentsply, Petrópolis, RJ, Brazil) and a partial perforated tray, thus producing the preliminary cast (Herodent Vigodent, Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brazil). Forty shells made of acrylic resin with the correct cervical adaptation were produced from this preliminary cast. One individual tray was made to transfer the shells. This tray was composed of a posterior length, and two grooves to allow the tray to keep the same position on the device during the impression, thus preventing all displacement. The shells were each filled with the four group impression materials to obtain the impressions, five repetitions each, thus resulting in twenty samples. The groupings are as follows; Group MERC: Impres- AB CD EF GH Figure 1 - Schematic drawing representing the master cast and the inter abutment distances (A, B, C and D occlusal) (E, F, G and H vestibular). Braz Oral Res Jul-Sep;24(3):
3 Linear dimensional changes in plaster die models using different elastomeric materials sion with mercaptan-polysulfide (Permlastic Regular - Kerr, Orange, CA, USA); Group CS: Impression with condensation silicone (Optosil/Xantopren - Heraeus-Kulzer, Wasserburg, Germany); Group AS: Impression with addition silicone (Aquasil Soft Putty/Aquasil LV - Dentsply do Brasil, Petrópolis, RJ, Brasil); Group POLY: Impression with polyether (Impregum F - Espe, St. Paul, Minnesota, USA). A thin layer of adhesive was applied to the shells, as recommended by the manufacturer. After the drying of the adhesive, the impression material was put on the shells, and the shells were slowly positioned on the abutments in the master cast. A static load of 400 g was applied to the shells during the polymerization of each material. All steps were done by one operator. In order to the remove the shells, the individual trays were filled with alginate (Jeltrate- Dentsply, Petrópolis, RJ, Brazil) and positioned on the master cast, maintaining the shells in the position favored by the device for the placement of the master cast and tray. After evaluation, the impressions were poured with special gypsum (Velmix Kerr, Orange, CA, USA) followed by spatulation in a vacuum for 5 minutes. To further diminish the formation of the bubbles, a vibrator (DCL, Campinas, SP, Brazil) was used to pour the impression, and 45 minutes were allowed to elapse in order to harden the gypsum. The cast gypsum was then removed. After the casts were evaluated via microscopy with a magnification of 30 times and precision of 5 micrometers (MITUTOYO SC-6 COOE-113, MITUTOYO INC, Kanagawa, Japan), they were measured using the reference points described above, thus allowing us to obtain the dimension of the inter abutment distances. The dimensions of master casts and the gypsum casts were obtained by the same observer who had no previous knowledge regarding which group of impression material was used in the casts. The measures of each point were made three times and the final mean was considered to be the distance between the points. Statistical analysis of the results was performed using analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey test. Values of p < 0.05 were considered statistically significant. Results The difference of the distance between the points (AB, CD, EF, and GH) from each gypsum cast in relation to the master cast was registered in micrometers. The measures of the distances between the points (AB, CD, EF, and GH) were analyzed separately and the mean of the dimensional changes of each of the utilized materials and the standard deviation are reported in Table 1. Table 2 shows the percentages of alteration related to the master cast. Discussion This study accepted the hypothesis that there was significant difference on the linear dimensional alterations in gypsum dies obtained with different elastomeric materials. In the clinic, the dental surgeon faces the possibility of destroyed dental elements. According to the level of the destruction of such teeth, professionals have the option to recommend direct or indirect restorations. One of the most important steps in the indirect metallic or non-metallic restoration is obtaining an accurate impression of the tooth to be restored and its adjacent tissues in attempt to reproduce the correct relationship among all of the structures in the buccal cavity. In line with this, researchers have established the use of a shell similar to an individual dental tray for a prepared tooth, like an abutment tooth, thus allowing more control of the minimal thickness of the material and generating a smaller disturbance compared to an individual dental tray. 2,7 With regard to gingival retraction, Dimashkieh and Morgano 2 reported that the use of the retractor wire was the most popular treatment in comparison to a shell. However, this method takes more time and requires the use of chemical agents that could damage local tissues, cause undesirable systemic effects, and alter the polymerization of the rubber material. In this work, gypsum die abutments from impressions with addition silicone presented lower 338 Braz Oral Res Jul-Sep;24(3):336-41
4 Pereira JR, Murata KY, Valle AL, Ghizoni JS, Shiratori FK Table 1 - Average of the dimensional changes (µm) and the standard deviation of each of the materials in relation to evaluated distances (standard deviation of each material related to all of the analyzed distances). Material AB CD EF GH X dp X dp X dp X dp Merc 36.0 a a a a 1.51 Poly 35.2 a a a a 0.89 CS 69.2 b b b b 0.83 AS 13.6 c c c c 0.83 Groups with the same letter, in columns, are not statistically different (P < 0.05). Merc: mercaptan-polysulfide. Poly: polyether. CS: condensation silicone. AS: addition silicone. distortion. (Table 1) This was most likely due to the insignificant contraction of the material. In the dental office, this situation enables an accurate adaptation of the metallic structure. The results of the present study confirm the excellent dimensional stability and the reproduction of details achieved when using this material, as described previously The condensation silicone shows low resistance to rip and higher deformation than other elastomeric materials, and increased distortion when it is stored prior to pouring. The dimensional instability may be due to ethylic alcohol, which could be produced as a by-product of the chemical reaction of this silicone. This was confirmed by comparison of the addition and condensation silicone, indicating the first is a choice material. 12 The data from the present study confirmed the dimensional instability of the condensation silicone, since the casts from the impressions made with this material presented a higher dimensional linear alteration of the inter abutment teeth (AB = 69.2 µm, CD = 71.0 µm, EF = 80.6 µm, GH = 81.2 µm). Therefore, we do not recommend the use of condensation silicone in this technique. To further elucidate the characteristics of polyether, the authors evaluated this common dental clinic material. High elasticity of the polyether was observed. There was difficulty in the removal of the shell and transfer of the impression. However, the shells were removed and carefully repositioned on an alginate mold. The dimensional stability of this material was noted; the abutment dies were a little larger than the master cast (Table 1), but this difference was not clinically significant. The polyether has a higher modulus of elasticity than mercaptan-polysulfide and the silicones, Table 2 - Percentages of alteration related to the master cast. Material % Merc 1.50 Poly 1.49 CS 2.97 AS 0.57 Merc: mercaptan-polysulfide. Poly: polyether. CS: condensation silicone. AS: addition silicone. and it frequently does need a substantial force for its removal from the buccal cavity. 11 The rigidity and inferior resistance to ripping of the polyether prevented its indication for use in interproximal and subgingival prepared tooth areas. Thus, the authors recommend applying a large amount of material between the tray and prepared tooth area with this compound. The polyether is stable, has less of a permanent deformation than polysulfide, and good reproduction of structural details. The high degree of dimensional stability is explained by the absence of volatile products during polymerization. Another studied material was polysulfide. It presented similar results to those of polyether. The dimensional stability of polysulfide is low because of the loss of volatile components causing significant contractions in the impression. 14 The dimensional change of the mercaptan-polysulfide was also due to handling of the material, time of mixture, time of waiting to pour the impression, amount of material, morphological characteristics of the tray, and accommodation of the adhesive. 15 However, the mercaptan-polysulfide had the same measures of inter-abutment distances as the polyether and addition or condensation silicones Braz Oral Res Jul-Sep;24(3):
5 Linear dimensional changes in plaster die models using different elastomeric materials when an individual tray was used. 16,17 The polysulfide presented better results than the addition or condensation silicones in the study of the capacity of copy of elastomeric materials. 12 Despite the abominable smell, fast time of handling, prolongable time of polymerization, and high sensitivity to temperature and humidity, the mercaptan-polysulfide has an effective union with the tray, proper adhesive, and flexible time for the pouring of impressions, low cost, and higher resistance to ripping. Although many works have confirmed the dimensional instability of mercaptan-polysulfide, 14 other researchers agree with its good quality Besides that, in this work, the minimal thickness of the material obtained in the use of the individual shell allowed the secure impression. Therefore, materials not good for obtaining impressions, when used together with the other techniques (i.e.: individual shell), have their qualities raised. The American Dental Association (ADA) admits dimensional changes of elastomers less than 0.5% are clinically acceptable. The addition silicone showed 0.57% of alteration related to the master cast, followed by 1.49% of polyether, 1.50% of the mercaptan-polysulfide and 2.97% of condensation silicone. The authors observed that the addition silicone was the most stable material, while condensation silicone had the higher mean of distortion. The dies obtained by impression with polyether and mercaptan-polysulfide showed a similar interabutment distance and casts a little bigger than the master cast. This is clinically important because it provides space for the cement agent. Therefore, the polyether and the mercaptan-polysulfide are materials that could indicate the use of the individual shell technique. The impression materials are produced as a solution to the limitations of the older materials. Thus, dental professionals should be informed about the advantages and disadvantages of each material to adequately use them in clinical practice. As such, the professional will be able to adjust the more precise reproduction of the prepared tooth, aiming for final satisfaction in the case. Conclusions According to results, it is possible to conclude: The addition silicone showed the best stability compared to the three other groups, followed by polyether, mercaptan-polysulfide, and condensation silicone. Condensation silicone was significantly different from the three other groups. Polyether and the mercaptan-polysulfide did not present a significant difference from each other, but they were worse than addition silicone and better than condensation silicone. Acknowledgements The authors would like to thank FAPESP (São Paulo Research Foundation). The authors want to thank Prof. Dr. José Roberto Pereira Lauris for the statistical analysis. References 1. Millar B. How to make a good impression (crown and bridge). Br Dent J Oct;191(7):402-3, Dimashkieh MR, Morgano SM. A procedure for making fixed prosthodontic impressions with the use of preformed crown shells. J Prosthet Dent Jan;73(1): Johnson GH, Mancl LA, Schwedhelm ER, Verhoef DR, Lepe X. Clinical trial investigating success rates for polyether and vinyl polysiloxane impressions made with full-arch and dualarch plastic trays. J Prosthet Dent Jan;103(1): Donovan TE, Chee WW. Current concepts in gingival displacement. Dent Clin North Am Apr;48(2): Kumbuloglu O, User A, Toksavul S, Boyacioglu H. Clinical evaluation of different gingival retraction cords. Quintessence Int Feb;38(2):e Cannistraci AJ. A new approach to impression taking for crown and bridge. Dent Clin North Am Mar;29: Livaditis GJ. The matrix impression system for fixed prosthodontics. J Prosthet Dent Feb;79(2): Rubel BS. Impression materials: a comparative review of impression materials most commonly used in restorative dentistry. Dent Clin North Am Jul;51(3): Braz Oral Res Jul-Sep;24(3):336-41
6 Pereira JR, Murata KY, Valle AL, Ghizoni JS, Shiratori FK 9. Millstein P, Maya A, Segura C. Determining the accuracy of stock and custom tray impression/casts. J Oral Rehabil Aug;25(8): Donovan TE, Chee WW. A review of contemporary impression materials and techniques. Dent Clin North Am Apr;48(2): Farah JW, Clark AE, Ainpour PR. Elastomeric impression materials. Oper Dent Jan;6(1): Johnson GH, Craig RG. Accuracy of addition silicone as a function of technique. J Prosthet Dent Feb;55(2): Faria ACL, Rodrigues RCS, Macedo AP, Mattos MGC, Ribeiro RF. Accuracy of stone casts obtained by different impression materials. Braz Oral Res Oct-Dec;22(4): Phillips RW. Skinner s science of dental materials, 10 th ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders; p. 15. Walters RA, Spurrier S. An effect of tray design and material retention on the linear dimensional changes in polysulfide impressions. J Prosthet Dent Mar;63(3): Johnson GH, Craig RG. Accuracy of four types of rubber impression materials compared with time of pour and a repeat pour of models. J Prosthet Dent Apr;53(4): Boulton JL, Gage JP, Vincent PF, Basford KE. A laboratory study of dimensional changes for three elastomeric impression materials using custom and stock trays. Aust Dent J Dec;41(6): Braz Oral Res Jul-Sep;24(3):
Al-Qarni AA. Dimensional Accuracy of Multiple Pour Cast from
 IJopRD IJOPRD ORIGINAL ARTICLE Dimensional Accuracy of Multiple Pour Cast from Different 10.5005/jp-journals-10019-1155 Elastomer Impression Techniques Dimensional Accuracy of Multiple Pour Cast from Different
IJopRD IJOPRD ORIGINAL ARTICLE Dimensional Accuracy of Multiple Pour Cast from Different 10.5005/jp-journals-10019-1155 Elastomer Impression Techniques Dimensional Accuracy of Multiple Pour Cast from Different
Evaluation of the Effect of Temperature Changes on the Dimensional Stability of poly (Vinyl Siloxane) Impression Material.
 IOR Journal of Dental and Medical ciences (IOR-JDM e-in: 2279-0853, p-in: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 12 Ver. VIII (Dec. 2017, PP 10-15 www.iosrjournals.org Evaluation of the Effect of Temperature Changes
IOR Journal of Dental and Medical ciences (IOR-JDM e-in: 2279-0853, p-in: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 12 Ver. VIII (Dec. 2017, PP 10-15 www.iosrjournals.org Evaluation of the Effect of Temperature Changes
Research Article Accuracy of Single-Step versus 2-Step Double-Mix Impression Technique
 International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Dentistry Volume 2011, Article ID 341546, 5 pages doi:10.5402/2011/341546 Research Article Accuracy of Single-Step versus 2-Step Double-Mix Impression Technique
International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Dentistry Volume 2011, Article ID 341546, 5 pages doi:10.5402/2011/341546 Research Article Accuracy of Single-Step versus 2-Step Double-Mix Impression Technique
Impressions in fixed partial denture: A review update
 Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Experimental Biology, 2015, 5(12):1-5 Impressions in fixed partial denture: A review update ISSN: 2248 9215 CODEN (USA): EJEBAU Yeshwante
Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Experimental Biology, 2015, 5(12):1-5 Impressions in fixed partial denture: A review update ISSN: 2248 9215 CODEN (USA): EJEBAU Yeshwante
Lect. 14 Prosthodontics Dr. Osama
 Lect. 14 Prosthodontics Dr. Osama Principles of Removable Partial Denture Design Difference in Prosthesis Support and Influence on Design: For a tooth-supported prosthesis, the movement potential is less
Lect. 14 Prosthodontics Dr. Osama Principles of Removable Partial Denture Design Difference in Prosthesis Support and Influence on Design: For a tooth-supported prosthesis, the movement potential is less
Impression Materials and Storage Time Influence on Cast Models Accuracy
 10.5005/jp-journals-10029-1033 Fabiana Santos Gonçalves et al ORIGINAL ARTICLE Impression Materials and Storage Time Influence on Cast Models Accuracy Fabiana Santos Gonçalves, Wallace de Freitas Oliveira,
10.5005/jp-journals-10029-1033 Fabiana Santos Gonçalves et al ORIGINAL ARTICLE Impression Materials and Storage Time Influence on Cast Models Accuracy Fabiana Santos Gonçalves, Wallace de Freitas Oliveira,
Effect of Intermixing Brands on the Dimensional Accuracy of Master Cast using Putty-wash Impression Technique
 Mohammed E Sayed et al ORIGINAL RESEARCH 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1921 Effect of Intermixing Brands on the Dimensional Accuracy of Master Cast using Putty- Impression Technique 1 Mohammed E Sayed, 2 Bandar
Mohammed E Sayed et al ORIGINAL RESEARCH 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1921 Effect of Intermixing Brands on the Dimensional Accuracy of Master Cast using Putty- Impression Technique 1 Mohammed E Sayed, 2 Bandar
Journal of Clinical and Translational Research; 2018; 4(1): xxx-xxx
 Journal of Clinical and Translational Research; 2018; 4(1): xxx-xxx ORINIAL ARTICLE Viscosity effects of polyvinyl siloxane impression materials on the accuracy of the stone die produced Warren Ho 1, Liang
Journal of Clinical and Translational Research; 2018; 4(1): xxx-xxx ORINIAL ARTICLE Viscosity effects of polyvinyl siloxane impression materials on the accuracy of the stone die produced Warren Ho 1, Liang
J Bagh College Dentistry Vol. 21(1), 2009 The effect of using different..
 The effect of using different impression techniques and materials on vertical tissue displacement in free end extension ridges. (Dental survey and clinical study) Rawia. N. AL- Dafaii, B.D.S., MSc. (1)
The effect of using different impression techniques and materials on vertical tissue displacement in free end extension ridges. (Dental survey and clinical study) Rawia. N. AL- Dafaii, B.D.S., MSc. (1)
Comparison of the surface roughness of gypsum models constructed using various impression materials and gypsum products
 Journal of Dental Sciences (2013) xx, 1e6 + MODEL Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.e-jds.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of the surface roughness of gypsum models constructed
Journal of Dental Sciences (2013) xx, 1e6 + MODEL Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.e-jds.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of the surface roughness of gypsum models constructed
Tooth preparation for posterior fi xed partial denture (FPD) Tooth preparation for anterior fi xed partial denture (FPD)
 CHAPTER 17 Tooth preparation for posterior fi xed partial denture (FPD) 1 Defi nition and feature of FPD 2 Actual sequence of tooth preparation for posterior FPD Verify abutment teeth Occlusal guide groove
CHAPTER 17 Tooth preparation for posterior fi xed partial denture (FPD) 1 Defi nition and feature of FPD 2 Actual sequence of tooth preparation for posterior FPD Verify abutment teeth Occlusal guide groove
Complete denture impressions
 Lec.5 Complete denture impressions د. غسان الطائي Dental Impression: a negative imprint of an oral structure used to produce a positive replica of the structure to be used as a permanent record or in the
Lec.5 Complete denture impressions د. غسان الطائي Dental Impression: a negative imprint of an oral structure used to produce a positive replica of the structure to be used as a permanent record or in the
Acknowledgments Introduction p. 1 Objectives p. 1 Goals p. 2 History of Dental Materials p. 3 The Oral Environment p. 4 Characteristics of the Ideal
 Preface p. v Acknowledgments p. vii Introduction p. 1 Objectives p. 1 Goals p. 2 History of Dental Materials p. 3 The Oral Environment p. 4 Characteristics of the Ideal Dental Material p. 5 Quality Assurance
Preface p. v Acknowledgments p. vii Introduction p. 1 Objectives p. 1 Goals p. 2 History of Dental Materials p. 3 The Oral Environment p. 4 Characteristics of the Ideal Dental Material p. 5 Quality Assurance
MAURO FRADEANI, MD, DDS
 ESTHETIC REHABILITATION IN FIXED PROSTHODONTICS PROSTHETIC MAURO FRADEANI, MD, DDS Private Practice Pesaro and Milan, Italy TREATMENT A SYSTEMATIC APPROACH TO ESTHETIC, BIOLOGIC, AND FUNCTIONAL INTEGRATION
ESTHETIC REHABILITATION IN FIXED PROSTHODONTICS PROSTHETIC MAURO FRADEANI, MD, DDS Private Practice Pesaro and Milan, Italy TREATMENT A SYSTEMATIC APPROACH TO ESTHETIC, BIOLOGIC, AND FUNCTIONAL INTEGRATION
Original Research. Matrix impression system Kumar MP et al
 Received: 08 th January 2015 Accepted: 03 rd April 2014 Conflicts of Interest: None Source of Support: Nil Original Research A Comparison of Accuracy of Matrix Impression System with Putty Reline Technique
Received: 08 th January 2015 Accepted: 03 rd April 2014 Conflicts of Interest: None Source of Support: Nil Original Research A Comparison of Accuracy of Matrix Impression System with Putty Reline Technique
ABSTRACT I INTRODUCTION. J Appl Oral Sci. 2008;16(4):280-5
 www.fob.usp.br/jaos or www.scielo.br/jaos J Appl Oral Sci. 2008;16(4):280-5 EFFECT OF CONVENTIONAL AND EXPERIMENTAL GINGIVAL RETRACTION SOLUTIONS ON THE TENSILE STRENGTH AND INHIBITION OF POLYMERIZATION
www.fob.usp.br/jaos or www.scielo.br/jaos J Appl Oral Sci. 2008;16(4):280-5 EFFECT OF CONVENTIONAL AND EXPERIMENTAL GINGIVAL RETRACTION SOLUTIONS ON THE TENSILE STRENGTH AND INHIBITION OF POLYMERIZATION
Prosthodontic Rehabilitation with Overdenture Using Modified Impression Technique: A Case Report
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 10 Ver.VII (Oct. 2015), PP 102-107 www.iosrjournals.org Prosthodontic Rehabilitation with Overdenture
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 10 Ver.VII (Oct. 2015), PP 102-107 www.iosrjournals.org Prosthodontic Rehabilitation with Overdenture
International Journal of Dentistry and Oral Science (IJDOS) ISSN:
 International Journal of Dentistry and Oral Science (IJDOS) ISSN: 2377-8075 A Novel Functional Impression Procedure for Distal-Extension Removable Partial Dentures Li QL *, Cao Y Case Report Department
International Journal of Dentistry and Oral Science (IJDOS) ISSN: 2377-8075 A Novel Functional Impression Procedure for Distal-Extension Removable Partial Dentures Li QL *, Cao Y Case Report Department
DIMENSIONAL STABILITY OF IMPRESSION BODY USING THE SILICONE INDEX TOOTH TRAY IMPRESSION SYSTEM
 DIMENSIONAL STABILITY OF IMPRESSION BODY USING THE SILICONE INDEX TOOTH TRAY IMPRESSION SYSTEM Kyu-Young Lee, DDS, M.S*, Seung-Mi Jeong, DDS, PhD*, June-Sung Shim, DDS, PhD**, Byeong-Gap Choi, DDS, PhD**,
DIMENSIONAL STABILITY OF IMPRESSION BODY USING THE SILICONE INDEX TOOTH TRAY IMPRESSION SYSTEM Kyu-Young Lee, DDS, M.S*, Seung-Mi Jeong, DDS, PhD*, June-Sung Shim, DDS, PhD**, Byeong-Gap Choi, DDS, PhD**,
INFLUENCE OF APPLICATION SITE OF PROVISIONAL CEMENT ON THE MARGINAL ADAPTATION OF PROVISIONAL CROWNS
 www.fob.usp.br/jaos or www.scielo.br/jaos J Appl Oral Sci. 2008;16(3):214-8 INFLUENCE OF APPLICATION SITE OF PROVISIONAL CEMENT ON THE MARGINAL ADAPTATION OF PROVISIONAL CROWNS Mayra CARDOSO 1, Marcelo
www.fob.usp.br/jaos or www.scielo.br/jaos J Appl Oral Sci. 2008;16(3):214-8 INFLUENCE OF APPLICATION SITE OF PROVISIONAL CEMENT ON THE MARGINAL ADAPTATION OF PROVISIONAL CROWNS Mayra CARDOSO 1, Marcelo
Impression for crown and bridge work
 Lec.9 Crown & Bridge ims Impression for crown and bridge work Definition: an impression is a negative reproduction or likeness of an object, from which, a positive reproduction (or cast) could be obtained.
Lec.9 Crown & Bridge ims Impression for crown and bridge work Definition: an impression is a negative reproduction or likeness of an object, from which, a positive reproduction (or cast) could be obtained.
IMPRESSION PROCEDURES TRAINING MANUAL
 IMPRESSION PROCEDURES TRAINING MANUAL 01 01 A.B. DENTAL A.B. Dental is proud to present this impression taking procedure protocol. This manual explains, step by step, the procedure while using A.B. Dental
IMPRESSION PROCEDURES TRAINING MANUAL 01 01 A.B. DENTAL A.B. Dental is proud to present this impression taking procedure protocol. This manual explains, step by step, the procedure while using A.B. Dental
International J. of Healthcare and Biomedical Research, Volume: 04, Issue: 03, April 2016, 83-92
 Original article: Impression materials and techniques used and followed for the fixed partial denture treatment by private dental practitioners in Maharashtra state: A questionnaire study 1Dr.Amruta P.
Original article: Impression materials and techniques used and followed for the fixed partial denture treatment by private dental practitioners in Maharashtra state: A questionnaire study 1Dr.Amruta P.
DENTAL MATERIALS STUDY GUIDE
 DENTAL MATERIALS STUDY GUIDE WORKSHEET Dentalelle Tutoring www.dentalelle.com Study Guide for Dental Materials Dentalelle Tutoring 1. When completing a large composite restoration, how should the composite
DENTAL MATERIALS STUDY GUIDE WORKSHEET Dentalelle Tutoring www.dentalelle.com Study Guide for Dental Materials Dentalelle Tutoring 1. When completing a large composite restoration, how should the composite
Using technology to create the perfect impression
 The take-aways ȜȜ ȜȜ Taking impressions with traditional stock impress trays and many closed bite systems can be challenging. Clinician s Choice HeatWave system offers an accurate fit out of the box, allowing
The take-aways ȜȜ ȜȜ Taking impressions with traditional stock impress trays and many closed bite systems can be challenging. Clinician s Choice HeatWave system offers an accurate fit out of the box, allowing
INSTRUCTIONS FOR THE DENTIST. synocta impression procedure, Screw-retained and Snap-on. Screw-retained (Open tray) Snap-on (Closed tray)
 INSTRUCTIONS FOR THE DENTIST synocta impression procedure, Screw-retained and Snap-on Screw-retained (Open tray) Snap-on (Closed tray) click 1. Attach synocta Impression caps to implants. Hand-tighten
INSTRUCTIONS FOR THE DENTIST synocta impression procedure, Screw-retained and Snap-on Screw-retained (Open tray) Snap-on (Closed tray) click 1. Attach synocta Impression caps to implants. Hand-tighten
Reference to primary publication Properties of alginates in ZWP 4/2014 Xantalgin Crono - Introduction
 Reference to primary publication in ZWP 4/2014 Dr. Marcus Holzmeier, Wuerzburg Xantalgin Crono - Highly accurate alginate impressions. Introduction Even today when digital impression techniques are gaining
Reference to primary publication in ZWP 4/2014 Dr. Marcus Holzmeier, Wuerzburg Xantalgin Crono - Highly accurate alginate impressions. Introduction Even today when digital impression techniques are gaining
Clinical trial investigating success rates for polyether and vinyl polysiloxane impressions made with full-arch and dual-arch plastic trays
 Clinical trial investigating success rates for polyether and vinyl polysiloxane impressions made with full-arch and dual-arch plastic trays Glen H. Johnson, DDS, MS, a Lloyd A. Mancl, PhD, b E. Ricardo
Clinical trial investigating success rates for polyether and vinyl polysiloxane impressions made with full-arch and dual-arch plastic trays Glen H. Johnson, DDS, MS, a Lloyd A. Mancl, PhD, b E. Ricardo
An in vitro study to evaluate the effect on dimensional changes of elastomers during cold sterilization
 Original Article An in vitro study to evaluate the effect on dimensional changes of elastomers during cold sterilization Poonam K. Khinnavar, B. H. Dhanya Kumar, D. B. Nandeeshwar Department of Prosthodontics,
Original Article An in vitro study to evaluate the effect on dimensional changes of elastomers during cold sterilization Poonam K. Khinnavar, B. H. Dhanya Kumar, D. B. Nandeeshwar Department of Prosthodontics,
IMPRESSION MATERIALS
 IMPRESSION MATERIALS Function of Impression Materials To make a negative copy of an oral structure single tooth, quadrant, or arch edentulous or dentulous Negative copy must be accurate to produce an accurate
IMPRESSION MATERIALS Function of Impression Materials To make a negative copy of an oral structure single tooth, quadrant, or arch edentulous or dentulous Negative copy must be accurate to produce an accurate
CASE REPORT ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION. AIMS AND OBJECTIVES Aims
 An in vitro Study to Compare the Accuracy of Master Cast Fabricated by Three Different 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1143 Transfer Techniques for Single Tooth CASE REPORT An in vitro Study to Compare the Accuracy
An in vitro Study to Compare the Accuracy of Master Cast Fabricated by Three Different 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1143 Transfer Techniques for Single Tooth CASE REPORT An in vitro Study to Compare the Accuracy
B U J O D. Invited Review IMPLANT IMPRESSIONS SIMPLIFIED. Reddy et al. Vol. 2 Issue-3 Sept
 Invited Review IMPLANT IMPRESSIONS SIMPLIFIED AUTHORS: Vahini Reddy*, Venkateswara Allu Reddy**, Sadhvi K.V*** Introduction It is said that you never get a second chance to make a first impression but
Invited Review IMPLANT IMPRESSIONS SIMPLIFIED AUTHORS: Vahini Reddy*, Venkateswara Allu Reddy**, Sadhvi K.V*** Introduction It is said that you never get a second chance to make a first impression but
Double-casting method for fixed prosthodontics with functionally generated path
 Double-casting method for fixed prosthodontics with functionally generated path Shogo Minagi, DDS, PhD, a Toshiyuki Tanaka, DDS, b Takashi Sato, DDS, PhD, c and Tadashi Matsunaga, DDS, PhD d Department
Double-casting method for fixed prosthodontics with functionally generated path Shogo Minagi, DDS, PhD, a Toshiyuki Tanaka, DDS, b Takashi Sato, DDS, PhD, c and Tadashi Matsunaga, DDS, PhD d Department
Annotation to the lesson 21 Topic: Methods of provisory crowns fabrication. Chair-side technique. Evaluation of
 Annotation to the lesson 21 Topic: Methods of provisory crowns fabrication. Chair-side technique. Evaluation of crown fitting quality Contemporary methods of restoration of tooth tissues pathology, using
Annotation to the lesson 21 Topic: Methods of provisory crowns fabrication. Chair-side technique. Evaluation of crown fitting quality Contemporary methods of restoration of tooth tissues pathology, using
Precision. Hydrophilicity. V-Posil. Dimensional stability. Intraoral setting time. Working time. Precision impression material, A-silicone-based
 Dimensional stability Precision Working time Toughness Intraoral setting time Hydrophilicity Precision impression material, A-silicone-based Addition silicone impression material impressively precise Models
Dimensional stability Precision Working time Toughness Intraoral setting time Hydrophilicity Precision impression material, A-silicone-based Addition silicone impression material impressively precise Models
Comparison of Dimensional Accuracy of Four Different Die Materials before and after Disinfection of the Impression: An in vitro Study
 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1383 Yamini Nandini et al ORIGINAL RESEARCH Comparison of Dimensional Accuracy of Four Different Die Materials before and after Disinfection of the Impression: An in vitro Study
10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1383 Yamini Nandini et al ORIGINAL RESEARCH Comparison of Dimensional Accuracy of Four Different Die Materials before and after Disinfection of the Impression: An in vitro Study
ACOMPARATIVEEVALUATIONOFEASY REMOVALOFDENTALCASTSFROMALGINATE IMPRESSIONSUSINGDIFFERENTBRANDSOF DENTALSTONE-ANINVITROSTUDY
 ORIGINALRESEARCHARTICLE ACOMPARATIVEEVALUATIONOFEASY REMOVALOFDENTALCASTSFROMALGINATE IMPRESSIONSUSINGDIFFERENTBRANDSOF DENTALSTONE-ANINVITROSTUDY ABSTRACT: Background: The fracture of teeth on removal
ORIGINALRESEARCHARTICLE ACOMPARATIVEEVALUATIONOFEASY REMOVALOFDENTALCASTSFROMALGINATE IMPRESSIONSUSINGDIFFERENTBRANDSOF DENTALSTONE-ANINVITROSTUDY ABSTRACT: Background: The fracture of teeth on removal
Frequent use for the preparation of prosthetic products
 laboratory use Frequent use for the preparation of prosthetic products Silicones gain more and more use for the preparation of prosthetic products. ERGAMIX addition silicone (polyvinylsiloxane) and ERGASIL
laboratory use Frequent use for the preparation of prosthetic products Silicones gain more and more use for the preparation of prosthetic products. ERGAMIX addition silicone (polyvinylsiloxane) and ERGASIL
Chapter 12. Prosthodontics
 Chapter 12 Prosthodontics Golbarg Kolahi 1 Prosthesis [prahs-thee-sis] A replacement for a missing body part Golbarg Kolahi 2 Prosthesis In the dental field, it is a fixed or removable appliance replacing
Chapter 12 Prosthodontics Golbarg Kolahi 1 Prosthesis [prahs-thee-sis] A replacement for a missing body part Golbarg Kolahi 2 Prosthesis In the dental field, it is a fixed or removable appliance replacing
Psychological Impact of Communication
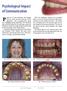 Psychological Impact of Communication Patient is a 47 year old female was unhappy with her smile and self conscience of her appearance. She is missing teeth, which was impinging during mastication. The
Psychological Impact of Communication Patient is a 47 year old female was unhappy with her smile and self conscience of her appearance. She is missing teeth, which was impinging during mastication. The
Evaluation of hardness and surface roughness of two maxillofacial silicones following disinfection
 Maxillofacial Prosthesis Maxillofacial Prosthesis Evaluation of hardness and surface roughness of two maxillofacial silicones following disinfection Marcelo Coelho Goiato (a) Aldiéris Alves Pesqueira (b)
Maxillofacial Prosthesis Maxillofacial Prosthesis Evaluation of hardness and surface roughness of two maxillofacial silicones following disinfection Marcelo Coelho Goiato (a) Aldiéris Alves Pesqueira (b)
Shadeguides Ceramic Veneers: Tooth Preparation for Enamel Preservation
 Ajay Juneja Shadeguides Ceramic Veneers: Tooth Preparation for Enamel Preservation 1 Feb 2016 The rationale of having minimal preparation and having ceramic veneers cemented to enamel in order for the
Ajay Juneja Shadeguides Ceramic Veneers: Tooth Preparation for Enamel Preservation 1 Feb 2016 The rationale of having minimal preparation and having ceramic veneers cemented to enamel in order for the
Peninsula Dental Social Enterprise (PDSE)
 Peninsula Dental Social Enterprise (PDSE) Laboratory Procedures for Dentures and Indirect Restorations Version 1.0 Date approved: November 2016 Approved by: The Board Review due: November 2019 Policy will
Peninsula Dental Social Enterprise (PDSE) Laboratory Procedures for Dentures and Indirect Restorations Version 1.0 Date approved: November 2016 Approved by: The Board Review due: November 2019 Policy will
The effect of immersion disinfection procedures on dimensional stability of two elastomeric impression materials
 441 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 50, No. 4, 441-446, 2008 Original The effect of immersion disinfection procedures on dimensional stability of two elastomeric impression materials Dario Melilli, Antonio
441 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 50, No. 4, 441-446, 2008 Original The effect of immersion disinfection procedures on dimensional stability of two elastomeric impression materials Dario Melilli, Antonio
Prosthodontic Management of Combination Syndrome Case with Metal Reinforced Maxillary Complete Denture and Mandibular Teeth supported Overdenture
 Case Report imedpub Journals www.imedpub.com Periodontics and Prosthodontics DOI: 10.21767/2471-3082.100041 Prosthodontic Management of Combination Syndrome Case with Metal Reinforced Maxillary Complete
Case Report imedpub Journals www.imedpub.com Periodontics and Prosthodontics DOI: 10.21767/2471-3082.100041 Prosthodontic Management of Combination Syndrome Case with Metal Reinforced Maxillary Complete
Accuracy 9 articles 4 Posters Shade measurement 1 article. Technology comparison 1 article
 Accuracy 9 articles 4 Posters Shade measurement 1 article Technology comparison 1 article 3Shape TRIOS Color had the best agreement of all included methods for the color chroma and hue... whereas the
Accuracy 9 articles 4 Posters Shade measurement 1 article Technology comparison 1 article 3Shape TRIOS Color had the best agreement of all included methods for the color chroma and hue... whereas the
Removable partial dentures
 Removable partial dentures Feb, 4, 2015 McCracken's Removable Partial Prosthodontics, Twelfth Edition Carr, Alan B 1 Prosthesis that replaces the missing teeth and associated supporting structures in a
Removable partial dentures Feb, 4, 2015 McCracken's Removable Partial Prosthodontics, Twelfth Edition Carr, Alan B 1 Prosthesis that replaces the missing teeth and associated supporting structures in a
Evaluating the Effect of a Sloping Shoulder and a Shoulder Bevel on the Marginal Integrity of Porcelain-Fused-to-Metal (PFM) Veneer Crowns
 Evaluating the Effect of a Sloping Shoulder and a Shoulder Bevel on the Marginal Integrity of Porcelain-Fused-to-Metal (PFM) Veneer Crowns Abstract Aim: A porcelain-fused-to-metal (PFM) veneer crown restoration
Evaluating the Effect of a Sloping Shoulder and a Shoulder Bevel on the Marginal Integrity of Porcelain-Fused-to-Metal (PFM) Veneer Crowns Abstract Aim: A porcelain-fused-to-metal (PFM) veneer crown restoration
A Simplified Technique for Implant-Abutment Level Impression After Soft Tissue Adaptation Around Provisional Restoration
 University of Kentucky UKnowledge Oral Health Practice Faculty Publications Oral Health Practice 5-24-2016 A Simplified Technique for Implant-Abutment Level Impression After Soft Tissue Adaptation Around
University of Kentucky UKnowledge Oral Health Practice Faculty Publications Oral Health Practice 5-24-2016 A Simplified Technique for Implant-Abutment Level Impression After Soft Tissue Adaptation Around
Modification of sectional impression technique using polyvinyl siloxane for fabrication of interim complete dentures
 Modification of sectional impression technique using polyvinyl siloxane for fabrication of interim complete dentures Post graduate student, Department of Prosthodontics and Jayakar Shetty Professor and
Modification of sectional impression technique using polyvinyl siloxane for fabrication of interim complete dentures Post graduate student, Department of Prosthodontics and Jayakar Shetty Professor and
ARAB AMERICAN UNIVERSITY. Lab. Manual. Prosthetic Dentistry1; Removable Prosthodontics. 3 rd year
 ARAB AMERICAN UNIVERSITY Lab. Manual Prosthetic Dentistry1; Removable Prosthodontics 3 rd year Department of Fixed and removable prosthetic Dentistry Faculty of Dentistry 2012/2013 Course Instructor Dr.
ARAB AMERICAN UNIVERSITY Lab. Manual Prosthetic Dentistry1; Removable Prosthodontics 3 rd year Department of Fixed and removable prosthetic Dentistry Faculty of Dentistry 2012/2013 Course Instructor Dr.
E x p r e s s 2. Clinical Cases. VPS Impression Material. Clinical case 1:
 E x p r e s s 2 VPS Impression Material Clinical case 1: Anterior all-ceramic Lava Zirconia Bridge using Express 2 Penta Putty Soft in combination with Express 2 Regular Body VPS Impression Material in
E x p r e s s 2 VPS Impression Material Clinical case 1: Anterior all-ceramic Lava Zirconia Bridge using Express 2 Penta Putty Soft in combination with Express 2 Regular Body VPS Impression Material in
When faced with an element which is the
 USE OF DENTAL IMPRESSION MATERIALS IN THE ANALYSIS OF TOOL MARKS TO IDENTIFY CAUSAL ELEMENTS National Institute of Legal Medicine and Forensic Sciences, Special Edition SUMMARY When faced with an element
USE OF DENTAL IMPRESSION MATERIALS IN THE ANALYSIS OF TOOL MARKS TO IDENTIFY CAUSAL ELEMENTS National Institute of Legal Medicine and Forensic Sciences, Special Edition SUMMARY When faced with an element
KAREN O. From Failure to Fantastic
 KAREN O From Failure to Fantastic THE Pi TEAM THOMAS J. BALSHI, DDS, PhD, FACP GLENN J. WOLFINGER, DMD, FACP JAMES R. BOWERS, DDS IAN SMITH, DMD KAREN O Karen suffered from painful and swollen gum tissue
KAREN O From Failure to Fantastic THE Pi TEAM THOMAS J. BALSHI, DDS, PhD, FACP GLENN J. WOLFINGER, DMD, FACP JAMES R. BOWERS, DDS IAN SMITH, DMD KAREN O Karen suffered from painful and swollen gum tissue
Department of Prosthodontics, Faculty of Dentistry, Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand
 Dental Journal Mahidol Dental Journal Original Article Dimensional stability of compression and injection molding denture bases in long and short curing procedures Noppavan Nagaviroj, Krantarat Wanitchanont,
Dental Journal Mahidol Dental Journal Original Article Dimensional stability of compression and injection molding denture bases in long and short curing procedures Noppavan Nagaviroj, Krantarat Wanitchanont,
FLEXCEED EXCEEDS YOUR EXPECTATIONS
 EXCEEDS YOUR EXPECTATIONS 1 because FIRST IMPRESSION lasts GC introduces FLEXCEED, a new vinyl polysiloxane impression material that is affordable yet accurately replicates the highest level of detail
EXCEEDS YOUR EXPECTATIONS 1 because FIRST IMPRESSION lasts GC introduces FLEXCEED, a new vinyl polysiloxane impression material that is affordable yet accurately replicates the highest level of detail
Prosthetic Options in Implant Dentistry. Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor
 Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Removable Partial Dentures
 Removable Partial Dentures Replacement of missing teeth Fixed partial denture Removable partial denture Complete removable Transitional denture Partial removable Implant retained prosthodontics No prosthetic
Removable Partial Dentures Replacement of missing teeth Fixed partial denture Removable partial denture Complete removable Transitional denture Partial removable Implant retained prosthodontics No prosthetic
hydrorise implant SIMPLY ACCURATE High-rigidity addition silicone
 hydrorise implant SIMPLY ACCURATE High-rigidity addition silicone 2 Hydrorise Implant, simply accurate Dental implants represent a solid solution in prosthetic dentistry and are considered the privileged
hydrorise implant SIMPLY ACCURATE High-rigidity addition silicone 2 Hydrorise Implant, simply accurate Dental implants represent a solid solution in prosthetic dentistry and are considered the privileged
Evaluation of a New Intraoral Paralleling Device for Creating Guiding Planes: A Pilot Study
 Evaluation of a New Intraoral Paralleling Device for Creating Guiding Planes: A Pilot Study Alexandre Luiz Souto Borges, DDS, MsC, PhD; Alessandra Bühler Borges, DDS, MsC, PhD; Eduardo Shigueyuki Uemura,
Evaluation of a New Intraoral Paralleling Device for Creating Guiding Planes: A Pilot Study Alexandre Luiz Souto Borges, DDS, MsC, PhD; Alessandra Bühler Borges, DDS, MsC, PhD; Eduardo Shigueyuki Uemura,
Comparison of the accuracy and dimensional stability of interocclusal recording materials - An in- vitro study.
 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 5, Issue 7, July 2015 1 Comparison of the accuracy and dimensional stability of interocclusal recording materials - An in- vitro study.
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 5, Issue 7, July 2015 1 Comparison of the accuracy and dimensional stability of interocclusal recording materials - An in- vitro study.
Fabricaction of immediate interim complete dentures using modified Poly vinyl siloxane sectional impression technique: A Case Report
 Case Report Fabricaction of immediate interim complete dentures using modified Poly vinyl siloxane sectional impression technique: A Case Report Vinay Pavan Kumar Kadavakolanu 1,*, Nitin H C 2, Jayakar
Case Report Fabricaction of immediate interim complete dentures using modified Poly vinyl siloxane sectional impression technique: A Case Report Vinay Pavan Kumar Kadavakolanu 1,*, Nitin H C 2, Jayakar
Basic information on the. Straumann Pro Arch TL. Straumann Pro Arch TL
 Basic information on the Straumann Pro Arch TL Straumann Pro Arch TL Contents 1. Introduction 2 1.1 Discover more treatment options with the 4 mm Short Implant 2 2. Technical information 3 3. Step-by-step
Basic information on the Straumann Pro Arch TL Straumann Pro Arch TL Contents 1. Introduction 2 1.1 Discover more treatment options with the 4 mm Short Implant 2 2. Technical information 3 3. Step-by-step
synocta Meso abutment for cement-retained restorations PROSTHETICS Step-by-step instructions
 synocta Meso abutment for cement-retained restorations PROSTHETICS Step-by-step instructions INTRODUCTION synocta Meso abutment for cement-retained restorations 1 The synocta Meso abutments, available
synocta Meso abutment for cement-retained restorations PROSTHETICS Step-by-step instructions INTRODUCTION synocta Meso abutment for cement-retained restorations 1 The synocta Meso abutments, available
MODIFIED FUNCTIONAL IMPRESSION TECHNIQUE FOR RESORBED MANDIBULAR RIDGE: TWO CASE STUDIES
 Prosthetic dentistry MODIFIED FUNCTIONAL IMPRESSION TECHNIQUE FOR RESORBED MANDIBULAR RIDGE: TWO CASE STUDIES Divia CHUGH 1, Siddharth PHULL 2, Arpan RANA 1, Yashendra SAINI 1 1 Resident (Prosthodontics)
Prosthetic dentistry MODIFIED FUNCTIONAL IMPRESSION TECHNIQUE FOR RESORBED MANDIBULAR RIDGE: TWO CASE STUDIES Divia CHUGH 1, Siddharth PHULL 2, Arpan RANA 1, Yashendra SAINI 1 1 Resident (Prosthodontics)
cement-retained single crowns using cementable abutments
 cement-retained single crowns using cementable abutments cement-retained restorations cement-retained single crowns using cementable abutments Cement-retained implant restorations are similar to conventional
cement-retained single crowns using cementable abutments cement-retained restorations cement-retained single crowns using cementable abutments Cement-retained implant restorations are similar to conventional
Restoration of the worn dentition
 Clin Dent Rev (2017) 1:4 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41894-017-0003-3 TREATMENT Restoration of the worn dentition Paul King 1 Received: 16 March 2017 / Accepted: 31 May 2017 / Published online: 30 June 2017
Clin Dent Rev (2017) 1:4 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41894-017-0003-3 TREATMENT Restoration of the worn dentition Paul King 1 Received: 16 March 2017 / Accepted: 31 May 2017 / Published online: 30 June 2017
Oral Rehabilitation with CAMLOG implants after loss of dentition due to an accident
 Case Report 13 2011 Oral Rehabilitation with CAMLOG implants after loss of dentition due to an accident Dr Hitoshi Minagawa Tokyo, Japan Prosthetics Dr Hitoshi Minagawa successfully completed his studies
Case Report 13 2011 Oral Rehabilitation with CAMLOG implants after loss of dentition due to an accident Dr Hitoshi Minagawa Tokyo, Japan Prosthetics Dr Hitoshi Minagawa successfully completed his studies
Stress Distribution in Natural Tooth and Implant Supported Removable Partial Denture with Different Attachment Types: A Photoelastic Analysis
 Original Article Stress Distribution in Natural Tooth and Implant Supported Removable Partial Denture with Different Attachment Types: A Photoelastic Analysis M. Naser Khaki 1, A. Shishehian 2. 1 Assistant
Original Article Stress Distribution in Natural Tooth and Implant Supported Removable Partial Denture with Different Attachment Types: A Photoelastic Analysis M. Naser Khaki 1, A. Shishehian 2. 1 Assistant
Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers) 2016, vol. 22, issue 3
 Journal of IMAB ISSN: 1312-773X http://dx.doi.org/10.5272/jimab.2016223.1296 Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers) 2016, vol. 22, issue 3 COMPARISON OF INTERFACIAL SURFACE TENSION AND
Journal of IMAB ISSN: 1312-773X http://dx.doi.org/10.5272/jimab.2016223.1296 Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers) 2016, vol. 22, issue 3 COMPARISON OF INTERFACIAL SURFACE TENSION AND
Hex-Lock Abutment System. Restorative Manual
 System Restorative Manual 32 Restorative options with s s are manufactured from titanium alloy and used as the support foundation for single- or multiple-unit cement-retained, partially edentulous fixed
System Restorative Manual 32 Restorative options with s s are manufactured from titanium alloy and used as the support foundation for single- or multiple-unit cement-retained, partially edentulous fixed
Prof. Dr. Hikmat J. Al-Judy B.D.S., M.Sc., Ph.D in Prosthodontic, College of Dentistry/ Baghdad University/ Baghdad, Iraq.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 7 Ver. V (July. 2015), PP 35-40 www.iosrjournals.org Comparison of the effect of sectional
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 7 Ver. V (July. 2015), PP 35-40 www.iosrjournals.org Comparison of the effect of sectional
(Images are at the end of article)
 Long term provisionalization during periodontal surgery and extraction site tissue grafting: A Case Review Michael Tischler, DDS Diplomate American Board Of Oral Implantology/Implant Dentistry (Images
Long term provisionalization during periodontal surgery and extraction site tissue grafting: A Case Review Michael Tischler, DDS Diplomate American Board Of Oral Implantology/Implant Dentistry (Images
Making an implant level cast with the angled abutment and acrylic resin cap : A clinical report
 Medical Communication Biosci. Biotech. Res. Comm. 10(2): 319-323 (2017) Making an implant level cast with the angled abutment and acrylic resin cap : A clinical report Hamid Neshandar Asli 1 and Bardia
Medical Communication Biosci. Biotech. Res. Comm. 10(2): 319-323 (2017) Making an implant level cast with the angled abutment and acrylic resin cap : A clinical report Hamid Neshandar Asli 1 and Bardia
INTRODUCTION. Why Choose Cortex Prosthetics?
 Prosthetic Manual 4 INDEX Introduction 6-14 Impression Techniques 15-29 Abutments Selection Handling 30-33 Temporary Restorations 34-38 Screw Reiained Restorations 39-52 Removable Restorations 53-63 5
Prosthetic Manual 4 INDEX Introduction 6-14 Impression Techniques 15-29 Abutments Selection Handling 30-33 Temporary Restorations 34-38 Screw Reiained Restorations 39-52 Removable Restorations 53-63 5
Dimensional Stability of Two Polyvinyl Siloxane Impression Materials in Different Time Intervals
 Journal of Dental Biomaterials. 2015;2(4) Original Article Dimensional Stability of Two Polyvinyl Siloxane Impression Materials in Different Time Intervals Aalaei Sh a, Rezaei Adli A a, Mansoorali MR b,
Journal of Dental Biomaterials. 2015;2(4) Original Article Dimensional Stability of Two Polyvinyl Siloxane Impression Materials in Different Time Intervals Aalaei Sh a, Rezaei Adli A a, Mansoorali MR b,
Immediate Complete Denture: A Case Report
 Human Journals Case Report July 2018 Vol.:10, Issue:1 All rights are reserved by Ruby et al. Immediate Complete Denture: A Case Report Keywords: immediate denture, dental prosthesis ABSTRACT Ruby*, Manish
Human Journals Case Report July 2018 Vol.:10, Issue:1 All rights are reserved by Ruby et al. Immediate Complete Denture: A Case Report Keywords: immediate denture, dental prosthesis ABSTRACT Ruby*, Manish
IMPRESSION TRAYS. Stainless Steel Edentulous Impression Trays. 73
 IMPRESSION TRAYS Standard Stainless Steel Trays Perforated stainless steel impression trays - the most popular type. Retention is assured by holes over the whole surface of the tray. A rim on the back
IMPRESSION TRAYS Standard Stainless Steel Trays Perforated stainless steel impression trays - the most popular type. Retention is assured by holes over the whole surface of the tray. A rim on the back
SCD Case Study. Attachments in Prosthodontics
 SCD Case Study Attachments in Prosthodontics Precision attachments are retention units milled out of alloy. They have male and female parts that fit together with tolerances of 10 microns. It is important
SCD Case Study Attachments in Prosthodontics Precision attachments are retention units milled out of alloy. They have male and female parts that fit together with tolerances of 10 microns. It is important
"Designing a fixed partial denture without a pontic"- Case report
 Article ID: ISSN 2046-1690 "Designing a fixed partial denture without a pontic"- Peer review status: No Corresponding Author: Dr. Khurshid Mattoo, Assistant Professor, Prosthodontics, College of Dental
Article ID: ISSN 2046-1690 "Designing a fixed partial denture without a pontic"- Peer review status: No Corresponding Author: Dr. Khurshid Mattoo, Assistant Professor, Prosthodontics, College of Dental
Universal Plunger Loc Attachment
 Universal Plunger Loc Attachment www.preat.com 800-232-7732 Universal Plunger Loc Complete Universal 7.5mm length TI plunger attachment. Compatible with Lew Passive and Swiss Loc NG. 1.5mm plunger, 7.5mm
Universal Plunger Loc Attachment www.preat.com 800-232-7732 Universal Plunger Loc Complete Universal 7.5mm length TI plunger attachment. Compatible with Lew Passive and Swiss Loc NG. 1.5mm plunger, 7.5mm
Soft Tissue Transfer Utilizing Digital Impressions of Anterior Implants
 Soft Tissue Transfer Utilizing Digital Impressions of Anterior Implants Pacific Coast Society for Prosthodontics Anchorage, Alaska June 28, 2013 Kenneth F. Hinds DDS Traditional(Analog) ImpressionTechnique
Soft Tissue Transfer Utilizing Digital Impressions of Anterior Implants Pacific Coast Society for Prosthodontics Anchorage, Alaska June 28, 2013 Kenneth F. Hinds DDS Traditional(Analog) ImpressionTechnique
Lingual Veneers, a conservative approach
 Ajay Juneja Lingual Veneers, a conservative approach 24 Sep 2016 It is known that bulimia nervosa can cause quite a rapid deterioration of tooth tissues. In severe cases, full-coverage crowns may be the
Ajay Juneja Lingual Veneers, a conservative approach 24 Sep 2016 It is known that bulimia nervosa can cause quite a rapid deterioration of tooth tissues. In severe cases, full-coverage crowns may be the
Nagri D et al. Linear occlusion and Neutral Zone recording for severely resorbed ridges
 Doi:10.21276/ledent.2018.02.01.02 Case Report LINEAR OCCLUSION AND NEUTRAL ZONE RECORDING USING TISSUE CONDITIONER REPORT OF A SEVERELY RESORBED RIDGE Divya Nagri, 1Ashish Kakkar, 2Neeraj Mittal, 3Lovely
Doi:10.21276/ledent.2018.02.01.02 Case Report LINEAR OCCLUSION AND NEUTRAL ZONE RECORDING USING TISSUE CONDITIONER REPORT OF A SEVERELY RESORBED RIDGE Divya Nagri, 1Ashish Kakkar, 2Neeraj Mittal, 3Lovely
Dimensional Accuracy of Optical Bite Registration in Single and Multiple Unit Restorations
 Ó Operative Dentistry, 2013, 38-3, 309-315 Dimensional Accuracy of Bite Registration in Single and Multiple Unit Restorations Y Iwaki N Wakabayashi Y Igarashi Clinical Relevance Based on the dimensional
Ó Operative Dentistry, 2013, 38-3, 309-315 Dimensional Accuracy of Bite Registration in Single and Multiple Unit Restorations Y Iwaki N Wakabayashi Y Igarashi Clinical Relevance Based on the dimensional
Impression techniques for removable partial dentures: A review
 Review Article DOI: 10.18231/2455-8486.2017.0012 Impression techniques for removable partial dentures: A review Reeta Jain 1,*, Supriya 2, Shweta 3, Kimmi 4 1 Professor & HOD, 2,3,4 PG Student, Dept. of
Review Article DOI: 10.18231/2455-8486.2017.0012 Impression techniques for removable partial dentures: A review Reeta Jain 1,*, Supriya 2, Shweta 3, Kimmi 4 1 Professor & HOD, 2,3,4 PG Student, Dept. of
The Sheffield Fit Test - Revisited. Academic Unit of Restorative Dentistry, School of Clinical Dentistry, University of
 The Sheffield Fit Test - Revisited Dr A. Johnson 1 MMedSci; PhD; LCGI; MCGI; FHEA, Dr C.A. Miller 2 BEng (hons), PhD. Dr G.E. White 1 MMedSci; PhD; CGIA. 1 Academic Unit of Restorative Dentistry, School
The Sheffield Fit Test - Revisited Dr A. Johnson 1 MMedSci; PhD; LCGI; MCGI; FHEA, Dr C.A. Miller 2 BEng (hons), PhD. Dr G.E. White 1 MMedSci; PhD; CGIA. 1 Academic Unit of Restorative Dentistry, School
SS Implant System 2013 PROSTHETIC PROCEDURE
 SS Implant System 2013 PROSTHETIC PROCEDURE Contents TS Implant System Cement retained restoration 06 Cement-retained bridges with the Solid abutment system (non-modified abutment) 16 Cement-retained bridges
SS Implant System 2013 PROSTHETIC PROCEDURE Contents TS Implant System Cement retained restoration 06 Cement-retained bridges with the Solid abutment system (non-modified abutment) 16 Cement-retained bridges
Review Article Techniques of Fabrication of Provisional Restoration: An Overview
 International Dentistry Volume 2011, Article ID 134659, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2011/134659 Review Article Techniques of Fabrication of Provisional Restoration: An Overview K. M. Regish, Deeksha Sharma, and
International Dentistry Volume 2011, Article ID 134659, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2011/134659 Review Article Techniques of Fabrication of Provisional Restoration: An Overview K. M. Regish, Deeksha Sharma, and
Restoration of Smile And Function in Partially Edentulous Patient With worn out Anterior Dentition
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 1 Ver. XII (January. 2017), PP 18-22 www.iosrjournals.org Restoration of Smile And Function
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 1 Ver. XII (January. 2017), PP 18-22 www.iosrjournals.org Restoration of Smile And Function
A PERIO-PROSTHETIC. with the BIO-GLASS. DR. Mirko Paoli (DDS) DT. Roberto Fabris ABUTMENT SYSTEM
 A PERIO-PROSTHETIC with the TREATMENT use of ABUTMENT SYSTEM BIO-GLASS DR. Mirko Paoli (DDS) DT. Roberto Fabris 110 SUMMER 2015 The implant therapy in dentistry has allowed the modification of prosthetic
A PERIO-PROSTHETIC with the TREATMENT use of ABUTMENT SYSTEM BIO-GLASS DR. Mirko Paoli (DDS) DT. Roberto Fabris 110 SUMMER 2015 The implant therapy in dentistry has allowed the modification of prosthetic
Rahul Nagrath Manesh Lahori Manjari Agrawal
 J Indian Prosthodont Soc (December 2014) 14(Suppl. 1):S59 S66 DOI 10.1007/s13191-014-0365-z ORIGINAL ARTICLE A Comparative Evaluation of Dimensional Accuracy and Surface Detail Reproduction of Four Hydrophilic
J Indian Prosthodont Soc (December 2014) 14(Suppl. 1):S59 S66 DOI 10.1007/s13191-014-0365-z ORIGINAL ARTICLE A Comparative Evaluation of Dimensional Accuracy and Surface Detail Reproduction of Four Hydrophilic
Solid Zirconia Full-Arch Implant Prosthesis (Protocol C All-CAD with Multi-Unit Abutments) BruxZir. FIRST Appointment. The BruxZir
 (Protocol C All-CAD with Multi-Unit Abutments) Step-by-Step Restorative Protocol C The BruxZir Full-Arch Implant Prosthesis offers a fixed, all-zirconia implant solution for edentulous patients desiring
(Protocol C All-CAD with Multi-Unit Abutments) Step-by-Step Restorative Protocol C The BruxZir Full-Arch Implant Prosthesis offers a fixed, all-zirconia implant solution for edentulous patients desiring
Virtual The hydrophilic precision impression material
 Impressive Impressions The hydrophilic precision impression material Hydrophilic: exactly where you need it Single-phase impressions with Hydrophilicity and contact angle Excellent wettability Excellent
Impressive Impressions The hydrophilic precision impression material Hydrophilic: exactly where you need it Single-phase impressions with Hydrophilicity and contact angle Excellent wettability Excellent
Exclusively distributed in the USA and Canada by: DMG America LLC Englewood, New Jersey 07631, U.S., Phone: (800)
 LuxaBite With the friendly cooperation of : David Hornbrook, DDS, FAACD, La Mesa, Calif. (USA) Ross Nash, DDS, Charlotte, NC (USA) Mark Montgomery, DMD, Salem, OR (USA) Exclusively distributed in the USA
LuxaBite With the friendly cooperation of : David Hornbrook, DDS, FAACD, La Mesa, Calif. (USA) Ross Nash, DDS, Charlotte, NC (USA) Mark Montgomery, DMD, Salem, OR (USA) Exclusively distributed in the USA
International Journal of Recent Advances in Multidisciplinary Research Vol. 02, Issue 03, pp , March, 2015
 sz International journal Journal of of Research Recent and Advances Review in in Health Multidisciplinary Sciences, July -2014 Research, March -2015 International Journal of Recent Advances in Multidisciplinary
sz International journal Journal of of Research Recent and Advances Review in in Health Multidisciplinary Sciences, July -2014 Research, March -2015 International Journal of Recent Advances in Multidisciplinary
EFFECTIVE DATE: 04/24/14 REVISED DATE: 04/23/15, 04/28/16, 06/22/17, 06/28/18 POLICY NUMBER: CATEGORY: Dental
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: DENTAL IMPLANTS PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product (including an Essential
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: DENTAL IMPLANTS PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product (including an Essential
INDICATIONS. Fixed Appliances are indicated when precise tooth movements are required
 DEFINITION Fixed Appliances are devices or equipments that are attached to the teeth, cannot be removed by the patient and are capable of causing tooth movement. INDICATIONS Fixed Appliances are indicated
DEFINITION Fixed Appliances are devices or equipments that are attached to the teeth, cannot be removed by the patient and are capable of causing tooth movement. INDICATIONS Fixed Appliances are indicated
IMPRESSION TECHNIQUE AND MATERIALS
 IMPRESSION TECHNIQUE AND MATERIALS DR ZURYATI AB GHANI BDS (WALES), Grad Dip Clin Dent (Adelaide), Doctor in Clinical Dentistry (prosthodontics( prosthodontics), Adelaide, FRACDS (Australia). 29.06.08
IMPRESSION TECHNIQUE AND MATERIALS DR ZURYATI AB GHANI BDS (WALES), Grad Dip Clin Dent (Adelaide), Doctor in Clinical Dentistry (prosthodontics( prosthodontics), Adelaide, FRACDS (Australia). 29.06.08
Essentials of. Dental Assisting. Edition 6. Debbie S. Robinson Doni L. Bird
 Essentials of Dental Assisting Edition 6 Debbie S. Robinson Doni L. Bird CHAPTER21 Restorative Procedures http://evolve.elsevier.com/robinson/essentials/ LEARNING OBJECTIVES KEY TERMS 1. Pronounce, define,
Essentials of Dental Assisting Edition 6 Debbie S. Robinson Doni L. Bird CHAPTER21 Restorative Procedures http://evolve.elsevier.com/robinson/essentials/ LEARNING OBJECTIVES KEY TERMS 1. Pronounce, define,
