ABSTRACT I INTRODUCTION. J Appl Oral Sci. 2008;16(4):280-5
|
|
|
- Roger Wilkinson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 or J Appl Oral Sci. 2008;16(4):280-5 EFFECT OF CONVENTIONAL AND EXPERIMENTAL GINGIVAL RETRACTION SOLUTIONS ON THE TENSILE STRENGTH AND INHIBITION OF POLYMERIZATION OF FOUR TYPES OF IMPRESSION MATERIALS Sérgio SÁBIO 1, Paulo Afonso FRANCISCONE 2, José MONDELLI 3 1- DDS, MSc, PhD student, Department of Operative Dentistry, Endodontics and Dental Materials, Bauru School of Dentistry, University of São Paulo, Bauru, SP, Brazil. 2- DDS, PhD, Associate Professor, Department of Operative Dentistry, Endodontics and Dental Materials, Bauru School of Dentistry, University of São Paulo, Bauru, SP, Brazil. 3- DDS. MSc, PhD, Full Professor, Department of Operative Dentistry, Endodontics and Dental Materials, Bauru School of Dentistry, University of São Paulo, Bauru, SP, Brazil. Corresponding address: Dr. Sérgio SÁBIO - Departamento de Odontologia da Universidade Estadual de Maringá - R. Luis de Camões, 130 ap Maringá, PR, Brasil - Phone: ssabio@wnet.com.br Received: July 23, Modification: September 18, Accepted: March 1, 2008 ABSTRACT I n the present study, two types of tests (tensile strength test and polymerization inhibition test) were performed to evaluate the physical and chemical properties of four impression materials [a polysulfide (Permlastic), a polyether (Impregum), a condensation silicone (Xantopren) and a polyvinylsiloxane (Aquasil)] when polymerized in contact with of one conventional (Hemostop) and two experimental (Vislin and Afrin) gingival retraction solutions. For the tensile strength test, the impression materials were mixed and packed into a steel plate with perforations that had residues of the gingival retraction solutions. After polymerization, the specimens were tested in tensile strength in a universal testing machine. For the polymerization inhibition test, specimens were obtained after taking impressions from a matrix with perforations that contained 1 drop of the gingival retraction solutions. Two independent examiners decided on whether or not impression material remnants remained unpolymerized, indicating interference of the chemical solutions. Based on the analysis of the results of both tests, the following conclusions were reached: 1. The tensile strength of the polysulfide decreased after contact with Hemostop and Afrin. 2. None of the chemical solutions inhibited the polymerization of the polysulfide; 3. The polyether presented lower tensile strength after polymerization in contact with the three gingival retraction agents; 4. The polyether had its polymerization inhibited only by Hemostop; 5. None of the chemical solutions affected the tensile strength of the condensation silicone; 6. Only Hemostop inhibited the polymerization of the condensation silicone; 7. The polyvinylsiloxane specimens polymerized in contact with Hemostop had significantly lower tensile strength; 8. Neither of the chemical solutions (Afrin and Vislin) affected the tensile strength of the polyvinylsiloxane and the condensation silicone; 9. Results of the tensile strength and polymerization inhibition tests suggest that Vislin can be used as substance of gingival retraction without affecting the tested properties of four impression materials. Key words: Gingival retraction. Dental impression materials. Drug effects. Silicone elastomers. Elasticity. INTRODUCTION The use of chemical substances to cease bleeding of a gingival tissue ulcerated during dental preparation or to obtain gingival retraction during impression procedures has been extensively investigated 1,2,8,10,12,16,17,18,23. The main points assessed in these works are the influence of the use of epinephrine and astringents, the behavior of the impression materials when set in contact with chemical substances and the quality of gingival retraction. With the use of 2-step putty-wash impression technique, gingival retraction is necessary to exposes the subgingival cervical level of tooth preparation and this step has great influence on the final impression. Several undesirable characteristics have been reported during use of gingival restriction solutions. Buchanann and Thayler 17 (1982) report that epinephrine can cause cardiovascular effects. Benson, et al. 10 (1986) have reported that although it does not present cardiovascular effects, aluminum chloride can cause long-term injury to the gingival 280
2 EFFECT OF CONVENTIONAL AND EXPERIMENTAL GINGIVAL RETRACTION SOLUTIONS ON THE TENSILE STRENGTH AND INHIBITION OF POLYMERIZATION OF FOUR TYPES OF IMPRESSION MATERIALS tissue and it has to be moist during application in order to avoid gingival laceration and bleeding recurrence. O mahony, et al. 21 (2000) found in an in vitro study that ferric subsulfate, ferric sulfate, and aluminum chloride interfere in the quality of reproduction of polyvinylsiloxane impression, possibly due to the sulfur that delays or inhibits polymerization. Recently Bowles, et al. 16 (1991) have suggested the use of sympathomimetic amines, capable of producing local vasoconstriction with minimal side-effect as gingival retraction agents. These substances are the active ingredient in several ophthalmic or nasal decongestants. The results obtained by these authors encourage their use for presenting a response equal or superior to that the epinephrine, without causing blood pressure alterations. However, there is a lack of studies evaluating the effect of these gingival retraction agents regarding the physical and chemical integrity of the impression materials. The purpose of this study was to investigate whether four commonly used types of impression materials have their physical and chemical properties altered when polymerized in contact with conventional and experimental gingival retraction agents. MATERIAL AND METHODS Two types of tests (tensile strength test and polymerization inhibition test) were performed to evaluate the physical and chemical properties of impression materials [a polysulfide (Permlastic; Kerr, Romulus, MI, USA), a polyether (Impregum; 3M/ESPE, St. Paul, MN, USA), a condensation silicone (Xantopren; Bayer, Germany) and a polyvinylsiloxane (Aquasil; Dentsply, DeTrey, Konstanz, Germany)] when polymerized in contact with one conventional (Hemostop; Dentsply Ind. e Com. Ltda., Petrópolis, RJ, Brazil) and two experimental (tetrahydrozoline hydrochloride - Vislin; Alcon Laboratórios do Brasil Ltda., São Paulo, SP, Brazil and oxymetazoline hydrochloride - Afrin; Schering-Plough Produtos Farmacêuticos, São Paulo, SP, Brazil) gingival retraction solutions. Tensile Strength Test For each impression material, 40 specimens were fabricated and randomly assigned to 4 groups (n=10): three test groups, in which the material was mixed and packed into a matrix that previously received one of the three gingival retraction solutions and a control group, which had not been in contact with the chemicals. The matrix consisted of a steel plate with dumbbell-shaped perforations fabricated in accordance with the specifications of ISO 37:1994(E) standard, with dimensions corresponding to 20% of those described in this normative. All specimens were fabricated by the same operator. The specimens in the control group were prepared as follows. The impression material was mixed according to the manufacturer s instructions and packed into the matrix that was placed onto a glass slab, without contact with the gingival retraction solutions. A second glass slab was positioned over the matrix and the whole set received the application of a 5 kg load during the time recommended by each manufacturer for removal of the mould from the mouth. After setting, the specimens had the excess of impression material removed and were carefully trimmed with a scissor. The specimens in the test groups were fabricated in the same way as described above, except for the fact that the impression material completed its polymerization in contact with residues of Afrin, Vislin or Hemostop. For such purpose, before the materials were packed into the matrix, 1 ml of each the gingival retraction solution was placed on the glass slab, left undisturbed for 1 min and then removed with either an air stream (Afrin and Vislin) or an air/water spray (Hemostop). Hemostop was removed in a different way from the other solutions because it was observed in the pilot study that air blowing of Hemostop was not sufficient to produce polyether specimens in conditions to be submitted to the tensile strength test. After storage at a temperature of 23 ± 2ºC and relative humidity of 50 ± 10% during 24 h, the specimens were tested in a Vitrodyne universal testing machine John Chatillon & Sons, Greensboro, NC, USA). Specimen dimensions were recorded with a digital caliper (Mitutoyo, Tokyo, Japan) before testing. Three areas of each specimen were measured and checked three times to accurately establish their width and thickness, which were averaged to obtain a final measurement. Specimens that were not in accordance with this measurement were discarded. Each specimen had its ends fixed to an apparatus of the Vitrodyne machine and was tested in tensile strength at a crosshead speed of 500 mm/min until its complete fracture. The values were recorded in N and converted into kgf. The final values that were submitted to statistical analysis were obtained with the following equation: TS = Fm/W.t, where TS= tensile strength in MPa, Fm: maximum force of specimen rupture, W= average specimen width in the central area, t= average specimen thickness in the central area. Data were analyzed statistically by one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett s and Kruskal Wallis tests using SigmaStat Statistical Analysis software (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) (Table1). Polymerization Inhibition Test For each impression material, 20 specimens were fabricated and randomly assigned to 4 groups: three test groups (gingival retraction solutions) and a control group. For specimen preparation, a rectangular steel matrix perfectly fit to a white plastic plate was fabricated. A vertical and a horizontal line virtually divided the matrix in four segments, each one containing 5 perforations (0.9 cm diameter, 2 mm deep), which totalized 20 perforations in the matrix. The white plastic plate was adapted to the matrix and each circle formed by the perforations was demarcated on plate surface with a #3216 diamond bur in the exact place. The circles drawn on the plastic plate were numbered I, II, III, IV and V to identify each perforation. A notch was prepared with the bur on the plate and on the matrix in such a way that one adapted to 281
3 SÁBIO S, FRANCISCONE P A, MONDELLI J the other always in the same position. For each material, the first group of 5 perforations served as the control group, that is, no gingival retraction solution was applied. In a clockwise direction, the other three groups of 5 perforations in the matrix received, respectively, one drop of Hemostop, Afrin and Vislin in each perforation. After impression, the sequence of the solutions was modified so that the frequency of location of residues did not influence the judgment. Each material was mixed according to the manufacturer s instructions and packed into the matrix perforations. The white plate was placed onto the matrix in the previously demarcated position and kept for 10 min. Thereafter, the plate was separated from the matrix with a plaster knife and was examined by two independent examiners (experienced professors of the Department of Dentistry, State University of Maringá). These observers should decide on whether or not there were unpolymerized impression material remnants within the circles drawn on the plastic plate and register their opinion in a chart with a similar drawing to that of the plate. Four impressions were made for each material, in such a way that 20 specimens (4 impressions x 5 perforations) were obtained for each condition (control, Hemostop, Afrin and Vislin). Data were analyzed statistically by Cochran s Q nonparametric statistical test using SigmaStat Statistical Analysis software (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) (Table 1). RESULTS Tensile Strength Test For the polysulfide, Dunnett s multiple-comparison test was used for comparison with the control group. Hemostop and Afrin presented statistically significant lower tensile TABLE 1- Statistically significant differences and the type of statistical test used in agreement with the interaction between the impression material and the type of substance of gingival retraction Statistical significance difference Hemostop Afrin Vislin Control (MPa, means) Polysulfide (Permlastic) Yes p<0.05 Dunnett s test Yes p<0.05 Dunnett s test No p=0.135 Dunnett s test Polyether (Impregum) Polyvinil siloxane (Aquasil) No p=0.03 No p= Condensation silicone (Xantopren) No - p=0.238 (Kruskal Wallis) No - p=0.238 (Kruskal Wallis) No - p=0.238 (Kruskal Wallis) FIGURE 1- Tensile bond strength means for the four impression materials polymerized in contact with different gingival retraction solutions 282
4 EFFECT OF CONVENTIONAL AND EXPERIMENTAL GINGIVAL RETRACTION SOLUTIONS ON THE TENSILE STRENGTH AND INHIBITION OF POLYMERIZATION OF FOUR TYPES OF IMPRESSION MATERIALS strength than the control group (p<0.05), but no significant difference (p>0.05) was observed between Vislin and the control. For the polyether, the specimens prepared in contact with the gingival retraction solutions presented significantly lower tensile strength (p<0.05) than the control specimens. For the condensation silicone, there was no statistically significant difference among the control and test groups (p=0.238). Kruskal-Wallis test was used. For the polyvinylsiloxane, only the group prepared in contact with Hemostop presented significantly lower tensile strength than the control group. Tensile strength test data are presented in Table 1 and Figure 1. Polymerization Inhibition For the condensation silicone and polyether, Hemostop differed significantly from the other gingival retraction solutions (p<0.05) with inhibition of polymerization in 30 over 40 tests performed. For the polyvinylsiloxane and polysulfide, there was no statistically significant difference (p>0.05) between the gingival retraction solutions and the control group, that is, the results were negative for polymerization inhibition in all 40 tests. DISCUSSION The use of nasal decongestant and eye drops, as substances for gingival retraction is a real possibility suggested by Bowles, et al. 16 (1991). The main goal of the tests performed in the present study was to evaluate some of the physical and chemical properties of impression materials that set in contact with substances used for gingival retraction. With the 2-step putty-wash impression technique, frequently used for prosthetic preparations, gingival retraction is a key factor for obtaining a reliable reproduction. Several gingival retraction agents are currently used and they present different characteristics. These chemical substances are used in association with mechanical means, such as the gingival retraction cords, to retract the gingival tissue. Several undesirable characteristics may interfere with the quality of reproduction and justify the search for new materials that come to behave satisfactorily and improve the accuracy of the models. The tensile strength of elastomeric materials is a type of physical test recommended by the ISO 37:1994 standard and used by Polyzois, et al. 23 (2000) to evaluate physical properties of elastomeric materials. Inhibition of polymerization is an efficient method to assess the effects of chemical substances on the process of polymerization of the impression materials, and has scientific acceptance in the literature 3-7,9,11,14,15,19, Due to their different properties and chemical compositions, the four materials evaluated in the present study behaved differently, as expected. The tested polysulfide (Permlastic) is an elastomeric impression material that has been in the market for a long time. It is a slow-polymerization material in which the reaction continues even after clinical polymerization. Because of this characteristic, this material is relatively slow to develop elasticity. The polysulfide specimens made in contact with Afrin and Hemostop had their tensile strength decreased in comparison to the control specimens. These results show that this impression material can have this physical characteristics altered by the contact with residues of these products, even in the presence of small amounts, which suggests that care should be taken in the use of these two substances for gingival retraction. On the other hand, no gingival retraction solution evaluated in this study affected significantly the polymerization of the polysulfide, even the chemical agent being applied in a great amount in relation to the amount of material, which does not occur under clinical conditions because most part of the gingival retraction solution is eliminated prior to the impressions procedures. A nonparametric test was used for analysis of these data because the proposed methodology did not try to quantify the amount of unpolymerized material, but only the presence or absence of unpolymerized material. Based on the results of both tests, the impression technique in which Afrin and Hemostop are used as gingival retraction agents should be performed with care to avoid contact with the material. For Vislin, on the other hand, neither of the tests proved any change in the polysulfide behavior, which suggests its use for gingival retraction procedures with this material. Impregum is a fast-cure polyether impression material that accurately registers the surface of the prepared tooth and has good elastic recovery to the deformation due to its high level of cross-linking in the polymeric chain. Probably due to these characteristics this material presented more significant differences when set in contact with Hemostop, Afrin and Vislin compared to the control group. Afrin and Vislin had a significant impact on the properties of the polyether material compared to the control group. While Afrin and Vislin were air-blown after 1 min, Hemostop was removed with an air/water spray, which means that the specimens in the Afrin and Vislin groups set in contact with a larger amount of chemical solution than the specimens of the Hemostop group. Both Afrin and Vislin use water as a vehicle in its composition. Impregum is known to be watersensitive due to its water-sorption capacity, which can explain the alterations observed. However, the tensile strength test alone is not capable to separate the influence that each component has on the impression material. For the polymerization inhibition test, it was observed that Hemostop was the only one to affect the polymerization of the polyether, differing significantly from the control group. In this test, a greater amount of the gingival retraction solution was in contact with the impression material because the goal was to verify if the material was chemically affected during the polymerization, and there was no concern with respect to the amount of substance. Neither Afrin nor Vislin interfered with Impregum polymerization, possibly due to the fact that the components of these products do not interact chemically with the components of this polyether. 283
5 SÁBIO S, FRANCISCONE P A, MONDELLI J It is assumed that under clinical conditions residues of these products used for gingival retraction procedures will not inhibit the polymerization of the impression material. The use of gingival retraction substances is necessary during impression. However, it is a component of instability to be strictly controlled. In the present study, the polyether presented incompatibilities with the three analyzed substances, once physically they alter its response. Even in small amounts as used in the tests, they can jeopardize the integrity of the obtained impressions. Once obtained the effects of gingival retraction, the substances should be totally removed with air jets (Afrin and Vislin) or air/water sprays (Hemostop). Xantopren is a condensation silicone also known as type 1 silicone. In the present study, the use of gingival retraction solutions did not affect significantly the tensile strength of this material. However, this material had its polymerization inhibited by Hemostop, though polymerization in contact with the other gingival retractions solutions (Vislin and Afrin) was not affected. This change increases the importance of eliminating this aluminum chloride of the gingival sulcus after the gingival retraction. Air/water spraying seems to be sufficient as the material presented no significant alteration on polymerization after this procedure, as observed in the tensile strength test. The fact that neither Afrin nor Vislin presented any negative effect on material polymerization indicates a favorable response to the two substances. Aquasil is classified as a type 2 silicone or a polyvinylsiloxane. In this study, only the specimens made in contact with Hemostop had their tensile strength decreased. These results were obtained even after air/water spraying of this agent from the matrix. Hemostop composition does not necessarily affect the polymerization process as the polymerization inhibition that showed negative results. Both experimental substances also presented a good response with no adverse effects on polymerization inhibition. These results encourage the conduction of further research with these experimental gingival retraction substances. CONCLUSIONS Based on the analysis of the results of both tests, the following conclusions were reached: 1. The tensile strength of the polysulfide decreased after contact with Hemostop and Afrin. 2. None of the chemical solutions inhibited the polymerization of the polysulfide; 3. The polyether presented lower tensile strength after polymerization in contact with the three gingival retraction agents; 4. The polyether had its polymerization inhibited only by Hemostop; 5. None of the chemical solutions affected the tensile strength of the condensation silicone; 6. Only Hemostop inhibited the polymerization of the condensation silicone; 7. The polyvinylsiloxane specimens polymerized in contact with Hemostop had significantly lower tensile strength; 8. Neither of the chemical solutions (Afrin and Vislin) affected the tensile strength of the polyvinylsiloxane and the condensation silicone; 9. Results of the tensile strength and polymerization inhibition tests suggest that Vislin can be used as substance of gingival retraction without affecting the tested properties of four impression materials. REFERENCES 1- Allen EP, Baine SC, Brodine AH, Cronin RJ Jr, Donovan TE, Kois JC, et al. Annual review of selected dental literature: report of the committee on scientific investigation of the American Academy of Restorative Dentistry. J Prosthet Dent. 2002;88(1): Allen EP, Baine SC, Brodine AH, Cronin RJ Jr, Donovan TE, Kois JC, et al. Annual review of selected dental literature: Report of the committee on scientific investigation of the American Academy of Restorative Dentistry. J Prosthet Dent. 2003;90(1): Araújo PA, Jörgensen KD, Araújo CRP. Effect of undercuts on the accuracy of reheated addition-reaction silicone impressions. Rev Odontol Univ Sao Paulo. 1990;4(3): Araújo PA, Jörgensen KD. Effect of material bulk and undercuts on the accuracy of impression materials. J Prosthet Dent. 1985;54(6): Araújo PA, Jörgenesen KD. Improved accuracy by reheating addition-reaction silicone impressions. J Prosthet Dent. 1986;55(1): Ayers HD. Detail duplication test used to evaluate elastic impression materials. J Prosthet Dent. 1960;10(2): Augsburger RH. Accuracy of casts from three impression materials and effect of a gypsum hardener. Oper Dent. 1981;6(1): Bader JD, Bonito AJ, Shugars DA. A systematic review of cardiovascular effects of epinephrine hypertensive dental patients. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2002;93(6): Bell JW, von Fraunhofer JA. The handling of elastomeric impression materials: a review. J Dent. 1975;3(5): Benson W, Bomberg TJ, Hatch RA, Hoffman W. Tissue displacement methods in fixed prosthodontics. J Prosthet Dent. 1986;55(2): Blatz MB, Sadan A, Burguess TO, Mercante D, Hoist S. Selected characteristics of a new polyvinyl siloxane impression material: a randomized clinical trial. Quintessence Int. 2005;36(2): Boening KW, Walter MH, Schuette U. Clinical significance of surface activation of silicone impression materials. J Dent. 1998;26(5/ 6): Bomberg TJ, Goldfogel MH, Hoffman W Jr, Bomberg SE. Consideration for adhesion of impression materials to impression tray. J Prosthet Dent. 1988;60(6): Brown D. Factors affecting the dimensional stability of elastic impression materials. J Dent. 1973;1(6): Boulton JL, Gage JP, Vincent PF, Basford KE. A laboratory study of dimensional changes for three elastomeric impression materials using custom and stock trays. Aust Dent J. 1996;41(6): Bowles WH, Tardy SJ, Vahady A. Evaluation of new gingival retraction agents. J Dent. Res. 1991;70(11):
6 EFFECT OF CONVENTIONAL AND EXPERIMENTAL GINGIVAL RETRACTION SOLUTIONS ON THE TENSILE STRENGTH AND INHIBITION OF POLYMERIZATION OF FOUR TYPES OF IMPRESSION MATERIALS 17- Buchanan WT, Thayer KE. Systemic effects of epinephrineimpregnated retraction cord in fixed partial denture prosthodontics. J Am Dent Assoc. 1982;104: Camargo LM, Chee WWL, Donovan TE. Inhibition of polymerization of polyvinyl siloxanes by medicaments used on gingival retraction cords. J Prosthet Dent. 1993;70(2): Causton BE, Burke FJT, Wilson NHF. Implications of the presence of dithiocarbamate in latex gloves. Dent Mater. 1993;9: Lewinstein I, Craig RG. Accuracy of impression materials measured with a vertical height gauge. J Oral Rehabil. 1990;17: O Mahony A, Spencer P, Williams K. Effect of 3 medicaments on the dimensional accuracy and surface detail reproduction of polyvinylsiloxane impressions. Quintessence Int. 2000;31(3): Peregrina A, Land MF, Foil P, Price C. Effects of two types of latex gloves and surfactants on polymerization inhibition of three polyvinylsiloxane impression materials. J Prosthet Dent. 2003;90(3): Polyzois GL, Tarantil PA, Frangon MJ, Andreopolous AG. Physical properties of a silicone prosthetic elastomers stored in simulated skin secretions. J Prosthet Dent. 2000;83(5): Purton DG. Impression materials and gingival retraction techniques for crowns and bridges. N Z Dent J. 1988;84(377):
Objectives: This study investigated the possible interactions between three addition
 www.scielo.br/jaos Effects of sulfur-based hemostatic agents and gingival retraction cords handled with latex gloves on the polymerization of polyvinyl siloxane impression materials Carlos Eduardo Palhares
www.scielo.br/jaos Effects of sulfur-based hemostatic agents and gingival retraction cords handled with latex gloves on the polymerization of polyvinyl siloxane impression materials Carlos Eduardo Palhares
Linear dimensional changes in plaster die models using different elastomeric materials
 Prosthodontics Prosthodontics Linear dimensional changes in plaster die models using different elastomeric materials Jefferson Ricardo Pereira (a) Karina Yumi Murata (b) Accácio Lins do Valle (c) Janaina
Prosthodontics Prosthodontics Linear dimensional changes in plaster die models using different elastomeric materials Jefferson Ricardo Pereira (a) Karina Yumi Murata (b) Accácio Lins do Valle (c) Janaina
Comparative Evaluation of Dimensional Accuracy and Surface Detail Reproduction of Elastomeric Impression Material when Treated
 Comparative Evaluation of Dimensional Accuracy and Surface Detail Reproduction of Elastomeric Impression Material when Treated with Three Retraction Cord Medicaments : An In Vitro Study Pravin Raipure
Comparative Evaluation of Dimensional Accuracy and Surface Detail Reproduction of Elastomeric Impression Material when Treated with Three Retraction Cord Medicaments : An In Vitro Study Pravin Raipure
Al-Qarni AA. Dimensional Accuracy of Multiple Pour Cast from
 IJopRD IJOPRD ORIGINAL ARTICLE Dimensional Accuracy of Multiple Pour Cast from Different 10.5005/jp-journals-10019-1155 Elastomer Impression Techniques Dimensional Accuracy of Multiple Pour Cast from Different
IJopRD IJOPRD ORIGINAL ARTICLE Dimensional Accuracy of Multiple Pour Cast from Different 10.5005/jp-journals-10019-1155 Elastomer Impression Techniques Dimensional Accuracy of Multiple Pour Cast from Different
Imprint 3. Technical Data Sheet. VPS Impression Material. Indications. Introduction
 VPS Impression Material Technical Data Sheet Indications All dual-phase impressions, e.g. crown, bridge, inlay and onlay preparations, implant abutments, orthodontic impressions and related impressions
VPS Impression Material Technical Data Sheet Indications All dual-phase impressions, e.g. crown, bridge, inlay and onlay preparations, implant abutments, orthodontic impressions and related impressions
Original Research. Matrix impression system Kumar MP et al
 Received: 08 th January 2015 Accepted: 03 rd April 2014 Conflicts of Interest: None Source of Support: Nil Original Research A Comparison of Accuracy of Matrix Impression System with Putty Reline Technique
Received: 08 th January 2015 Accepted: 03 rd April 2014 Conflicts of Interest: None Source of Support: Nil Original Research A Comparison of Accuracy of Matrix Impression System with Putty Reline Technique
INFLUENCE OF APPLICATION SITE OF PROVISIONAL CEMENT ON THE MARGINAL ADAPTATION OF PROVISIONAL CROWNS
 www.fob.usp.br/jaos or www.scielo.br/jaos J Appl Oral Sci. 2008;16(3):214-8 INFLUENCE OF APPLICATION SITE OF PROVISIONAL CEMENT ON THE MARGINAL ADAPTATION OF PROVISIONAL CROWNS Mayra CARDOSO 1, Marcelo
www.fob.usp.br/jaos or www.scielo.br/jaos J Appl Oral Sci. 2008;16(3):214-8 INFLUENCE OF APPLICATION SITE OF PROVISIONAL CEMENT ON THE MARGINAL ADAPTATION OF PROVISIONAL CROWNS Mayra CARDOSO 1, Marcelo
Impression for crown and bridge work
 Lec.9 Crown & Bridge ims Impression for crown and bridge work Definition: an impression is a negative reproduction or likeness of an object, from which, a positive reproduction (or cast) could be obtained.
Lec.9 Crown & Bridge ims Impression for crown and bridge work Definition: an impression is a negative reproduction or likeness of an object, from which, a positive reproduction (or cast) could be obtained.
Evaluation of the Effect of Temperature Changes on the Dimensional Stability of poly (Vinyl Siloxane) Impression Material.
 IOR Journal of Dental and Medical ciences (IOR-JDM e-in: 2279-0853, p-in: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 12 Ver. VIII (Dec. 2017, PP 10-15 www.iosrjournals.org Evaluation of the Effect of Temperature Changes
IOR Journal of Dental and Medical ciences (IOR-JDM e-in: 2279-0853, p-in: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 12 Ver. VIII (Dec. 2017, PP 10-15 www.iosrjournals.org Evaluation of the Effect of Temperature Changes
Research Article Accuracy of Single-Step versus 2-Step Double-Mix Impression Technique
 International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Dentistry Volume 2011, Article ID 341546, 5 pages doi:10.5402/2011/341546 Research Article Accuracy of Single-Step versus 2-Step Double-Mix Impression Technique
International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Dentistry Volume 2011, Article ID 341546, 5 pages doi:10.5402/2011/341546 Research Article Accuracy of Single-Step versus 2-Step Double-Mix Impression Technique
Rahul Nagrath Manesh Lahori Manjari Agrawal
 J Indian Prosthodont Soc (December 2014) 14(Suppl. 1):S59 S66 DOI 10.1007/s13191-014-0365-z ORIGINAL ARTICLE A Comparative Evaluation of Dimensional Accuracy and Surface Detail Reproduction of Four Hydrophilic
J Indian Prosthodont Soc (December 2014) 14(Suppl. 1):S59 S66 DOI 10.1007/s13191-014-0365-z ORIGINAL ARTICLE A Comparative Evaluation of Dimensional Accuracy and Surface Detail Reproduction of Four Hydrophilic
EFFECT OF THERMOCYCLING ON THE TENSILE AND SHEAR BOND STRENGTHS OF THREE SOFT LINERS TO A DENTURE BASE RESIN
 www.fob.usp.br/revista or www.scielo.br/jaos J Appl Oral Sci. 2007;15(1):18-23 EFFECT OF THERMOCYCLING ON THE TENSILE AND SHEAR BOND STRENGTHS OF THREE SOFT LINERS TO A DENTURE BASE RESIN Carlos Nelson
www.fob.usp.br/revista or www.scielo.br/jaos J Appl Oral Sci. 2007;15(1):18-23 EFFECT OF THERMOCYCLING ON THE TENSILE AND SHEAR BOND STRENGTHS OF THREE SOFT LINERS TO A DENTURE BASE RESIN Carlos Nelson
IMPRESSION MATERIALS
 IMPRESSION MATERIALS Function of Impression Materials To make a negative copy of an oral structure single tooth, quadrant, or arch edentulous or dentulous Negative copy must be accurate to produce an accurate
IMPRESSION MATERIALS Function of Impression Materials To make a negative copy of an oral structure single tooth, quadrant, or arch edentulous or dentulous Negative copy must be accurate to produce an accurate
Impression Materials and Storage Time Influence on Cast Models Accuracy
 10.5005/jp-journals-10029-1033 Fabiana Santos Gonçalves et al ORIGINAL ARTICLE Impression Materials and Storage Time Influence on Cast Models Accuracy Fabiana Santos Gonçalves, Wallace de Freitas Oliveira,
10.5005/jp-journals-10029-1033 Fabiana Santos Gonçalves et al ORIGINAL ARTICLE Impression Materials and Storage Time Influence on Cast Models Accuracy Fabiana Santos Gonçalves, Wallace de Freitas Oliveira,
J Bagh College Dentistry Vol. 21(1), 2009 The effect of using different..
 The effect of using different impression techniques and materials on vertical tissue displacement in free end extension ridges. (Dental survey and clinical study) Rawia. N. AL- Dafaii, B.D.S., MSc. (1)
The effect of using different impression techniques and materials on vertical tissue displacement in free end extension ridges. (Dental survey and clinical study) Rawia. N. AL- Dafaii, B.D.S., MSc. (1)
Comparison of the surface roughness of gypsum models constructed using various impression materials and gypsum products
 Journal of Dental Sciences (2013) xx, 1e6 + MODEL Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.e-jds.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of the surface roughness of gypsum models constructed
Journal of Dental Sciences (2013) xx, 1e6 + MODEL Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.e-jds.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of the surface roughness of gypsum models constructed
Journal of Clinical and Translational Research; 2018; 4(1): xxx-xxx
 Journal of Clinical and Translational Research; 2018; 4(1): xxx-xxx ORINIAL ARTICLE Viscosity effects of polyvinyl siloxane impression materials on the accuracy of the stone die produced Warren Ho 1, Liang
Journal of Clinical and Translational Research; 2018; 4(1): xxx-xxx ORINIAL ARTICLE Viscosity effects of polyvinyl siloxane impression materials on the accuracy of the stone die produced Warren Ho 1, Liang
Evaluation of Bond Strength of Silicone and Acrylic Resin Based Resilient Denture Liners Over A Period of Storage in Water.
 DOI: 0.2276/aimdr.208.4..DE4 Original Article ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-284 Evaluation of Bond Strength of Silicone and Acrylic Resin Based Resilient Denture Liners Over A Period of Storage in
DOI: 0.2276/aimdr.208.4..DE4 Original Article ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-284 Evaluation of Bond Strength of Silicone and Acrylic Resin Based Resilient Denture Liners Over A Period of Storage in
Bond Strength of Composite Resin Luting Cements to Fiber-reinforced Composite Root Canal Post
 Bond Strength of Composite Resin Luting Cements to Fiber-reinforced Composite Root Canal Post Abstract Aims: The aim of this study was to compare the attachment of different composite resin luting cements
Bond Strength of Composite Resin Luting Cements to Fiber-reinforced Composite Root Canal Post Abstract Aims: The aim of this study was to compare the attachment of different composite resin luting cements
Acknowledgments Introduction p. 1 Objectives p. 1 Goals p. 2 History of Dental Materials p. 3 The Oral Environment p. 4 Characteristics of the Ideal
 Preface p. v Acknowledgments p. vii Introduction p. 1 Objectives p. 1 Goals p. 2 History of Dental Materials p. 3 The Oral Environment p. 4 Characteristics of the Ideal Dental Material p. 5 Quality Assurance
Preface p. v Acknowledgments p. vii Introduction p. 1 Objectives p. 1 Goals p. 2 History of Dental Materials p. 3 The Oral Environment p. 4 Characteristics of the Ideal Dental Material p. 5 Quality Assurance
Tooth preparation for posterior fi xed partial denture (FPD) Tooth preparation for anterior fi xed partial denture (FPD)
 CHAPTER 17 Tooth preparation for posterior fi xed partial denture (FPD) 1 Defi nition and feature of FPD 2 Actual sequence of tooth preparation for posterior FPD Verify abutment teeth Occlusal guide groove
CHAPTER 17 Tooth preparation for posterior fi xed partial denture (FPD) 1 Defi nition and feature of FPD 2 Actual sequence of tooth preparation for posterior FPD Verify abutment teeth Occlusal guide groove
DIMENSIONAL STABILITY OF IMPRESSION BODY USING THE SILICONE INDEX TOOTH TRAY IMPRESSION SYSTEM
 DIMENSIONAL STABILITY OF IMPRESSION BODY USING THE SILICONE INDEX TOOTH TRAY IMPRESSION SYSTEM Kyu-Young Lee, DDS, M.S*, Seung-Mi Jeong, DDS, PhD*, June-Sung Shim, DDS, PhD**, Byeong-Gap Choi, DDS, PhD**,
DIMENSIONAL STABILITY OF IMPRESSION BODY USING THE SILICONE INDEX TOOTH TRAY IMPRESSION SYSTEM Kyu-Young Lee, DDS, M.S*, Seung-Mi Jeong, DDS, PhD*, June-Sung Shim, DDS, PhD**, Byeong-Gap Choi, DDS, PhD**,
Facts About. Express. Penta Putty/ Ultra-Light Body. Vinyl Polysiloxane Precision Impression Materials
 Facts About Express Penta Putty/ Vinyl Polysiloxane Precision Impression Materials European Field Evaluation Results May August 2004 Ultra Light Body Contents 1 Innovative VPS Impression Materials....................
Facts About Express Penta Putty/ Vinyl Polysiloxane Precision Impression Materials European Field Evaluation Results May August 2004 Ultra Light Body Contents 1 Innovative VPS Impression Materials....................
A comparative evaluation of three different techniques for single step border molding
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH A comparative evaluation of three different techniques for single step border molding Kheur M 1, Jambhekar S 2, Sethi T 3, Kheur S 4 1Professor, 3 PG student, Dept. of Prosthodontics,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH A comparative evaluation of three different techniques for single step border molding Kheur M 1, Jambhekar S 2, Sethi T 3, Kheur S 4 1Professor, 3 PG student, Dept. of Prosthodontics,
Comparison of Flexural Strength of two Provisional Materials Used In Fixed Prosthodontics -An in Vitro Study.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 9 Ver. XII (September). 2016), PP 54-58 www.iosrjournals.org Comparison of Flexural Strength
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 9 Ver. XII (September). 2016), PP 54-58 www.iosrjournals.org Comparison of Flexural Strength
Original Research. The Effect of temperature on the strength of luting cements Patil SG et al
 Received: 03 rd August 2014 Accepted: 27 th November 2014 Conflicts of Interest: None Source of Support: Nil Original Research The Effect of Temperature on Compressive and Tensile Strengths of Commonly
Received: 03 rd August 2014 Accepted: 27 th November 2014 Conflicts of Interest: None Source of Support: Nil Original Research The Effect of Temperature on Compressive and Tensile Strengths of Commonly
A New Category of Impression Material VPES - A Breakthrough Technology
 A New Category of Impression Material VPES - A Breakthrough Technology Key Concern in Taking Consistent and Accurate Impressions VPES Vinyl PolyEther Silicone #1 Concern When Taking An Impression Involving
A New Category of Impression Material VPES - A Breakthrough Technology Key Concern in Taking Consistent and Accurate Impressions VPES Vinyl PolyEther Silicone #1 Concern When Taking An Impression Involving
ARAB AMERICAN UNIVERSITY. Lab. Manual. Prosthetic Dentistry1; Removable Prosthodontics. 3 rd year
 ARAB AMERICAN UNIVERSITY Lab. Manual Prosthetic Dentistry1; Removable Prosthodontics 3 rd year Department of Fixed and removable prosthetic Dentistry Faculty of Dentistry 2012/2013 Course Instructor Dr.
ARAB AMERICAN UNIVERSITY Lab. Manual Prosthetic Dentistry1; Removable Prosthodontics 3 rd year Department of Fixed and removable prosthetic Dentistry Faculty of Dentistry 2012/2013 Course Instructor Dr.
DURATEMP Temporary Crown & Bridge Material. Temrex Corporation October 2009
 DURATEMP Temporary Crown & Bridge Material Temrex Corporation October 2009 DURATEMP Temporary Crown & Bridge Material Overview Product Characteristics Physical Properties Case Report Instructions Ordering
DURATEMP Temporary Crown & Bridge Material Temrex Corporation October 2009 DURATEMP Temporary Crown & Bridge Material Overview Product Characteristics Physical Properties Case Report Instructions Ordering
Effect of cavity preparation design on the fracture resistance of directly and indirectly restored premolars
 Braz J Oral Sci. October/December 2008 - Vol. 7 - Number 27 Effect of cavity preparation design on the fracture resistance of directly and indirectly restored premolars Denise Sá Maia Casselli 1 ; André
Braz J Oral Sci. October/December 2008 - Vol. 7 - Number 27 Effect of cavity preparation design on the fracture resistance of directly and indirectly restored premolars Denise Sá Maia Casselli 1 ; André
Clinical trial investigating success rates for polyether and vinyl polysiloxane impressions made with full-arch and dual-arch plastic trays
 Clinical trial investigating success rates for polyether and vinyl polysiloxane impressions made with full-arch and dual-arch plastic trays Glen H. Johnson, DDS, MS, a Lloyd A. Mancl, PhD, b E. Ricardo
Clinical trial investigating success rates for polyether and vinyl polysiloxane impressions made with full-arch and dual-arch plastic trays Glen H. Johnson, DDS, MS, a Lloyd A. Mancl, PhD, b E. Ricardo
Analysis of the properties of commercially available silicone elastomers for maxillofacial prostheses
 Analysis of the properties of commercially available silicone elastomers for maxillofacial prostheses Zubeda Begum, 1 Mohammed Zaheer Kola, 2 Paran Joshi 3 ABSTRACT Aim - Maxillofacial prosthetic materials
Analysis of the properties of commercially available silicone elastomers for maxillofacial prostheses Zubeda Begum, 1 Mohammed Zaheer Kola, 2 Paran Joshi 3 ABSTRACT Aim - Maxillofacial prosthetic materials
Frequent use for the preparation of prosthetic products
 laboratory use Frequent use for the preparation of prosthetic products Silicones gain more and more use for the preparation of prosthetic products. ERGAMIX addition silicone (polyvinylsiloxane) and ERGASIL
laboratory use Frequent use for the preparation of prosthetic products Silicones gain more and more use for the preparation of prosthetic products. ERGAMIX addition silicone (polyvinylsiloxane) and ERGASIL
DENTAL MATERIALS STUDY GUIDE
 DENTAL MATERIALS STUDY GUIDE WORKSHEET Dentalelle Tutoring www.dentalelle.com Study Guide for Dental Materials Dentalelle Tutoring 1. When completing a large composite restoration, how should the composite
DENTAL MATERIALS STUDY GUIDE WORKSHEET Dentalelle Tutoring www.dentalelle.com Study Guide for Dental Materials Dentalelle Tutoring 1. When completing a large composite restoration, how should the composite
International J. of Healthcare and Biomedical Research, Volume: 04, Issue: 03, April 2016, 83-92
 Original article: Impression materials and techniques used and followed for the fixed partial denture treatment by private dental practitioners in Maharashtra state: A questionnaire study 1Dr.Amruta P.
Original article: Impression materials and techniques used and followed for the fixed partial denture treatment by private dental practitioners in Maharashtra state: A questionnaire study 1Dr.Amruta P.
B U J O D. Invited Review IMPLANT IMPRESSIONS SIMPLIFIED. Reddy et al. Vol. 2 Issue-3 Sept
 Invited Review IMPLANT IMPRESSIONS SIMPLIFIED AUTHORS: Vahini Reddy*, Venkateswara Allu Reddy**, Sadhvi K.V*** Introduction It is said that you never get a second chance to make a first impression but
Invited Review IMPLANT IMPRESSIONS SIMPLIFIED AUTHORS: Vahini Reddy*, Venkateswara Allu Reddy**, Sadhvi K.V*** Introduction It is said that you never get a second chance to make a first impression but
Impressions in fixed partial denture: A review update
 Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Experimental Biology, 2015, 5(12):1-5 Impressions in fixed partial denture: A review update ISSN: 2248 9215 CODEN (USA): EJEBAU Yeshwante
Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Experimental Biology, 2015, 5(12):1-5 Impressions in fixed partial denture: A review update ISSN: 2248 9215 CODEN (USA): EJEBAU Yeshwante
Precision. Hydrophilicity. V-Posil. Dimensional stability. Intraoral setting time. Working time. Precision impression material, A-silicone-based
 Dimensional stability Precision Working time Toughness Intraoral setting time Hydrophilicity Precision impression material, A-silicone-based Addition silicone impression material impressively precise Models
Dimensional stability Precision Working time Toughness Intraoral setting time Hydrophilicity Precision impression material, A-silicone-based Addition silicone impression material impressively precise Models
Effect of Intermixing Brands on the Dimensional Accuracy of Master Cast using Putty-wash Impression Technique
 Mohammed E Sayed et al ORIGINAL RESEARCH 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1921 Effect of Intermixing Brands on the Dimensional Accuracy of Master Cast using Putty- Impression Technique 1 Mohammed E Sayed, 2 Bandar
Mohammed E Sayed et al ORIGINAL RESEARCH 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1921 Effect of Intermixing Brands on the Dimensional Accuracy of Master Cast using Putty- Impression Technique 1 Mohammed E Sayed, 2 Bandar
Color stability and colorant effect on maxillofacial elastomers. Part I: Colorant effect on physical properties
 Color stability and colorant effect on maxillofacial elastomers. Part I: Colorant effect on physical properties Steven P. Haug, DDS, MSD, a Carl J. Andres, DDS, MSD, a and B. Keith Moore, PhD b Indiana
Color stability and colorant effect on maxillofacial elastomers. Part I: Colorant effect on physical properties Steven P. Haug, DDS, MSD, a Carl J. Andres, DDS, MSD, a and B. Keith Moore, PhD b Indiana
INSTRUCTIONS FOR THE DENTIST. synocta impression procedure, Screw-retained and Snap-on. Screw-retained (Open tray) Snap-on (Closed tray)
 INSTRUCTIONS FOR THE DENTIST synocta impression procedure, Screw-retained and Snap-on Screw-retained (Open tray) Snap-on (Closed tray) click 1. Attach synocta Impression caps to implants. Hand-tighten
INSTRUCTIONS FOR THE DENTIST synocta impression procedure, Screw-retained and Snap-on Screw-retained (Open tray) Snap-on (Closed tray) click 1. Attach synocta Impression caps to implants. Hand-tighten
2 (Cercon) Comparison of marginal fit in zirconia-based all-ceramic frameworks (cercon) made by two approaches (Direct and Wax-up scanning)
 (1391 1 25 ) () ( scanning) 2 2 2 1 - - - -1-2 Comparison of marginal fit in zirconia-based all-ceramic frameworks (cercon) made by two approaches ( and scanning) Naser Golshah 1, Habib Hajimiragha 2,
(1391 1 25 ) () ( scanning) 2 2 2 1 - - - -1-2 Comparison of marginal fit in zirconia-based all-ceramic frameworks (cercon) made by two approaches ( and scanning) Naser Golshah 1, Habib Hajimiragha 2,
The art and science of impression making was first
 THE IMPRESSION: A BLUEPRINT TO RESTORATIVE SUCCESS DOUGLAS A. TERRY 1, KARL F. LEINFELDER 2, ERNESTO A. LEE 3, ALEJANDRO JAMES 4 The art and science of impression making was first described in 1755 when
THE IMPRESSION: A BLUEPRINT TO RESTORATIVE SUCCESS DOUGLAS A. TERRY 1, KARL F. LEINFELDER 2, ERNESTO A. LEE 3, ALEJANDRO JAMES 4 The art and science of impression making was first described in 1755 when
SDR has proven reliability in high C-factor cavities 2
 R R SDR has proven reliability in high C-factor cavities 2 SDR was introduced by DENTSPLY DETREY, Konstanz, Germany in 200 and has since been used in over 20 million restorations across the globe. SDR
R R SDR has proven reliability in high C-factor cavities 2 SDR was introduced by DENTSPLY DETREY, Konstanz, Germany in 200 and has since been used in over 20 million restorations across the globe. SDR
Dimensional Stability of Two Polyvinyl Siloxane Impression Materials in Different Time Intervals
 Journal of Dental Biomaterials. 2015;2(4) Original Article Dimensional Stability of Two Polyvinyl Siloxane Impression Materials in Different Time Intervals Aalaei Sh a, Rezaei Adli A a, Mansoorali MR b,
Journal of Dental Biomaterials. 2015;2(4) Original Article Dimensional Stability of Two Polyvinyl Siloxane Impression Materials in Different Time Intervals Aalaei Sh a, Rezaei Adli A a, Mansoorali MR b,
EXAIMPLANT HYDROPHILIC VINYL POLYSILOXANE IMPRESSION MATERIAL (FOR DENTAL IMPLANTS) RECOMMENDED INDICATIONS CONTRAINDICATIONS
 EXAIMPLANT HYDROPHILIC VINYL POLYSILOXANE IMPRESSION MATERIAL (FOR DENTAL IMPLANTS) Prior to use, carefully read the instructions for use. For use only by a dental professional in the recommended indications.
EXAIMPLANT HYDROPHILIC VINYL POLYSILOXANE IMPRESSION MATERIAL (FOR DENTAL IMPLANTS) Prior to use, carefully read the instructions for use. For use only by a dental professional in the recommended indications.
NARROW DIAMETER implant
 ND NARROW DIAMETER implant TABLE OF CONTENTS ND - NARROW DIAMETER implant Implant characteristics page 04 Dental implant page 05 Open Tray Impression Transfer page 06 Titanium Abutments page 07 O-Ball
ND NARROW DIAMETER implant TABLE OF CONTENTS ND - NARROW DIAMETER implant Implant characteristics page 04 Dental implant page 05 Open Tray Impression Transfer page 06 Titanium Abutments page 07 O-Ball
Bond strength test of acrylic artificial teeth with prosthetic base
 Bond strength test of acrylic artificial teeth with prosthetic base (Erna Kurnikasari et al.) Bond strength test of acrylic artificial teeth with prosthetic base Erna Kurnikasari, Muslich Mahmud, Hasna
Bond strength test of acrylic artificial teeth with prosthetic base (Erna Kurnikasari et al.) Bond strength test of acrylic artificial teeth with prosthetic base Erna Kurnikasari, Muslich Mahmud, Hasna
Excellent temporaries
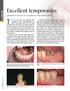 Excellent temporaries User report on Structur 2 SC and Structur 2 Premium from VOCO T he use of acrylic and composite type materials for the provisionalisation of crown and bridge work has been well established
Excellent temporaries User report on Structur 2 SC and Structur 2 Premium from VOCO T he use of acrylic and composite type materials for the provisionalisation of crown and bridge work has been well established
Using technology to create the perfect impression
 The take-aways ȜȜ ȜȜ Taking impressions with traditional stock impress trays and many closed bite systems can be challenging. Clinician s Choice HeatWave system offers an accurate fit out of the box, allowing
The take-aways ȜȜ ȜȜ Taking impressions with traditional stock impress trays and many closed bite systems can be challenging. Clinician s Choice HeatWave system offers an accurate fit out of the box, allowing
Evaluation of hardness and surface roughness of two maxillofacial silicones following disinfection
 Maxillofacial Prosthesis Maxillofacial Prosthesis Evaluation of hardness and surface roughness of two maxillofacial silicones following disinfection Marcelo Coelho Goiato (a) Aldiéris Alves Pesqueira (b)
Maxillofacial Prosthesis Maxillofacial Prosthesis Evaluation of hardness and surface roughness of two maxillofacial silicones following disinfection Marcelo Coelho Goiato (a) Aldiéris Alves Pesqueira (b)
Transverse Strength of Reinforced Denture Base Resin with Metal Wire and E-Glass Fibers
 Original Article Transverse Strength of Reinforced Denture Base Resin with Metal Wire and E-Glass Fibers M. Vojdani 1, AAR. Khaledi 2 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Prosthodontics, Faculty of Dentistry,
Original Article Transverse Strength of Reinforced Denture Base Resin with Metal Wire and E-Glass Fibers M. Vojdani 1, AAR. Khaledi 2 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Prosthodontics, Faculty of Dentistry,
ACOMPARATIVEEVALUATIONOFEASY REMOVALOFDENTALCASTSFROMALGINATE IMPRESSIONSUSINGDIFFERENTBRANDSOF DENTALSTONE-ANINVITROSTUDY
 ORIGINALRESEARCHARTICLE ACOMPARATIVEEVALUATIONOFEASY REMOVALOFDENTALCASTSFROMALGINATE IMPRESSIONSUSINGDIFFERENTBRANDSOF DENTALSTONE-ANINVITROSTUDY ABSTRACT: Background: The fracture of teeth on removal
ORIGINALRESEARCHARTICLE ACOMPARATIVEEVALUATIONOFEASY REMOVALOFDENTALCASTSFROMALGINATE IMPRESSIONSUSINGDIFFERENTBRANDSOF DENTALSTONE-ANINVITROSTUDY ABSTRACT: Background: The fracture of teeth on removal
Double-casting method for fixed prosthodontics with functionally generated path
 Double-casting method for fixed prosthodontics with functionally generated path Shogo Minagi, DDS, PhD, a Toshiyuki Tanaka, DDS, b Takashi Sato, DDS, PhD, c and Tadashi Matsunaga, DDS, PhD d Department
Double-casting method for fixed prosthodontics with functionally generated path Shogo Minagi, DDS, PhD, a Toshiyuki Tanaka, DDS, b Takashi Sato, DDS, PhD, c and Tadashi Matsunaga, DDS, PhD d Department
Vin ylsi loxan xane:
 Product portfolio Silginat Preliminary Impressions Vinylsiloxanether: Identium Precision Impressions Impressions Restoratives Visalys Temp Temporaries Kettenbach LP w w w.kettenbachusa.com Vinylpoly siloxane:
Product portfolio Silginat Preliminary Impressions Vinylsiloxanether: Identium Precision Impressions Impressions Restoratives Visalys Temp Temporaries Kettenbach LP w w w.kettenbachusa.com Vinylpoly siloxane:
FLEXCEED EXCEEDS YOUR EXPECTATIONS
 EXCEEDS YOUR EXPECTATIONS 1 because FIRST IMPRESSION lasts GC introduces FLEXCEED, a new vinyl polysiloxane impression material that is affordable yet accurately replicates the highest level of detail
EXCEEDS YOUR EXPECTATIONS 1 because FIRST IMPRESSION lasts GC introduces FLEXCEED, a new vinyl polysiloxane impression material that is affordable yet accurately replicates the highest level of detail
Aquasil. Ultra+ Smart Wetting Impression Material. For Implant Impressions. No Compromise.
 Aquasil Ultra+ Smart Wetting Impression Material For Implant Impressions. No Compromise. I M P R E SS I O N M AT E R I A L F O R I M P L A N TS MAKE THE CL EAR CHOICE 67% OF DENTISTS ARE INTERESTED IN
Aquasil Ultra+ Smart Wetting Impression Material For Implant Impressions. No Compromise. I M P R E SS I O N M AT E R I A L F O R I M P L A N TS MAKE THE CL EAR CHOICE 67% OF DENTISTS ARE INTERESTED IN
Exclusively distributed in the USA and Canada by: DMG America LLC Englewood, New Jersey 07631, U.S., Phone: (800)
 LuxaBite With the friendly cooperation of : David Hornbrook, DDS, FAACD, La Mesa, Calif. (USA) Ross Nash, DDS, Charlotte, NC (USA) Mark Montgomery, DMD, Salem, OR (USA) Exclusively distributed in the USA
LuxaBite With the friendly cooperation of : David Hornbrook, DDS, FAACD, La Mesa, Calif. (USA) Ross Nash, DDS, Charlotte, NC (USA) Mark Montgomery, DMD, Salem, OR (USA) Exclusively distributed in the USA
AVADENT-WAGNER EZ GUIDE PROTOCOL
 APPOINTMENT A. Final Impressions 1 APPOINTMENT 2 APPOINTMENT 3 D. Seat Wagner EZ Guide Try-In B. Papillameter Measurement E. Refine Anterior Teeth C. Tooth Mould Selection F. Interocclusal Record G. Deliver
APPOINTMENT A. Final Impressions 1 APPOINTMENT 2 APPOINTMENT 3 D. Seat Wagner EZ Guide Try-In B. Papillameter Measurement E. Refine Anterior Teeth C. Tooth Mould Selection F. Interocclusal Record G. Deliver
AVADENT-WAGNER EZ GUIDE PROTOCOL
 APPOINTMENT 1 APPOINTMENT 2 APPOINTMENT 3 A. Final Impressions D. Seat Try-In B. Papillameter Measurement E. Refine Anterior Teeth C. Tooth Mould Selection F. Interocclusal Record G. Deliver Final Dentures
APPOINTMENT 1 APPOINTMENT 2 APPOINTMENT 3 A. Final Impressions D. Seat Try-In B. Papillameter Measurement E. Refine Anterior Teeth C. Tooth Mould Selection F. Interocclusal Record G. Deliver Final Dentures
Natural Tooth Pontic using Fiber-reinforced Composite for Immediate Tooth Replacement
 10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1035 CLINICAL ARTICLE Natural Tooth Pontic using Fiber-reinforced Composite for Immediate Tooth Replacement Natural Tooth Pontic using Fiber-reinforced Composite for Immediate
10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1035 CLINICAL ARTICLE Natural Tooth Pontic using Fiber-reinforced Composite for Immediate Tooth Replacement Natural Tooth Pontic using Fiber-reinforced Composite for Immediate
Effect of Thickness and Recycling on Transverse Strength of Relined Acrylic Resin Denture
 ISSN: 1812 1217 Effect of Thickness and Recycling on Transverse Strength of Relined Acrylic Resin Denture Base. Nadira A Hatim BDS, MSc ( Prof) Aliaa W AL-Omari BDS, MSc (Asst Lec) Department of Prosthetic
ISSN: 1812 1217 Effect of Thickness and Recycling on Transverse Strength of Relined Acrylic Resin Denture Base. Nadira A Hatim BDS, MSc ( Prof) Aliaa W AL-Omari BDS, MSc (Asst Lec) Department of Prosthetic
Dimensional Accuracy of Optical Bite Registration in Single and Multiple Unit Restorations
 Ó Operative Dentistry, 2013, 38-3, 309-315 Dimensional Accuracy of Bite Registration in Single and Multiple Unit Restorations Y Iwaki N Wakabayashi Y Igarashi Clinical Relevance Based on the dimensional
Ó Operative Dentistry, 2013, 38-3, 309-315 Dimensional Accuracy of Bite Registration in Single and Multiple Unit Restorations Y Iwaki N Wakabayashi Y Igarashi Clinical Relevance Based on the dimensional
Bond strengths between composite resin and auto cure glass ionomer cement using the co-cure technique
 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Australian Dental Journal 2006;51:(2):175-179 Bond strengths between composite resin and auto cure glass ionomer cement using the co-cure technique GM Knight,* JM McIntyre,* Mulyani*
SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Australian Dental Journal 2006;51:(2):175-179 Bond strengths between composite resin and auto cure glass ionomer cement using the co-cure technique GM Knight,* JM McIntyre,* Mulyani*
ISO 1567 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD. Dentistry Denture base polymers. Art dentaire Polymères pour base de prothèses dentaires. Third edition
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 1567 Third edition 1999-02-15 Dentistry Denture base polymers Art dentaire Polymères pour base de prothèses dentaires A Reference number Contents 1 Scope...1 2 Normative references...1
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 1567 Third edition 1999-02-15 Dentistry Denture base polymers Art dentaire Polymères pour base de prothèses dentaires A Reference number Contents 1 Scope...1 2 Normative references...1
Reference to primary publication Properties of alginates in ZWP 4/2014 Xantalgin Crono - Introduction
 Reference to primary publication in ZWP 4/2014 Dr. Marcus Holzmeier, Wuerzburg Xantalgin Crono - Highly accurate alginate impressions. Introduction Even today when digital impression techniques are gaining
Reference to primary publication in ZWP 4/2014 Dr. Marcus Holzmeier, Wuerzburg Xantalgin Crono - Highly accurate alginate impressions. Introduction Even today when digital impression techniques are gaining
A comparative evaluation of the marginal accuracy of crowns fabricated from four commercially available provisional materials: An in vitro study
 A comparative evaluation of the marginal accuracy of crowns fabricated from four commercially available provisional materials: An in vitro study Bhavya Mohandas Amin, Meena Ajay Aras, Vidya Chitre Abstract
A comparative evaluation of the marginal accuracy of crowns fabricated from four commercially available provisional materials: An in vitro study Bhavya Mohandas Amin, Meena Ajay Aras, Vidya Chitre Abstract
Peninsula Dental Social Enterprise (PDSE)
 Peninsula Dental Social Enterprise (PDSE) Laboratory Procedures for Dentures and Indirect Restorations Version 1.0 Date approved: November 2016 Approved by: The Board Review due: November 2019 Policy will
Peninsula Dental Social Enterprise (PDSE) Laboratory Procedures for Dentures and Indirect Restorations Version 1.0 Date approved: November 2016 Approved by: The Board Review due: November 2019 Policy will
IMPRESSION TRAYS. Stainless Steel Edentulous Impression Trays. 73
 IMPRESSION TRAYS Standard Stainless Steel Trays Perforated stainless steel impression trays - the most popular type. Retention is assured by holes over the whole surface of the tray. A rim on the back
IMPRESSION TRAYS Standard Stainless Steel Trays Perforated stainless steel impression trays - the most popular type. Retention is assured by holes over the whole surface of the tray. A rim on the back
Core build-up using post systems
 Core build-up using post systems Dr. Gergely Pataky Department of Conservative Dentistry What to speak about today General considerations Classification of post systems Dowel-core or fibre post? Biologic
Core build-up using post systems Dr. Gergely Pataky Department of Conservative Dentistry What to speak about today General considerations Classification of post systems Dowel-core or fibre post? Biologic
Evaluation of a New Intraoral Paralleling Device for Creating Guiding Planes: A Pilot Study
 Evaluation of a New Intraoral Paralleling Device for Creating Guiding Planes: A Pilot Study Alexandre Luiz Souto Borges, DDS, MsC, PhD; Alessandra Bühler Borges, DDS, MsC, PhD; Eduardo Shigueyuki Uemura,
Evaluation of a New Intraoral Paralleling Device for Creating Guiding Planes: A Pilot Study Alexandre Luiz Souto Borges, DDS, MsC, PhD; Alessandra Bühler Borges, DDS, MsC, PhD; Eduardo Shigueyuki Uemura,
ISO INTERNATIONAL STANDARD. Dentistry Reversible-irreversible hydrocolloid impression material systems
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 13716 First edition 1999-05-01 Dentistry Reversible-irreversible hydrocolloid impression material systems Art dentaire Systèmes de produits pour empreintes à base d'hydrocolloïdes
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 13716 First edition 1999-05-01 Dentistry Reversible-irreversible hydrocolloid impression material systems Art dentaire Systèmes de produits pour empreintes à base d'hydrocolloïdes
Effect of Incorporation of Disinfectant Solutions on Setting Time, Linear Dimensional Stability, and Detail Reproduction in Dental Stone Casts
 Effect of Incorporation of Disinfectant Solutions on Setting Time, Linear Dimensional Stability, and Detail Reproduction in Dental Stone Casts Matheus Guilherme Lucas, DDS, MSc, 1 João Neudenir rioli-filho,
Effect of Incorporation of Disinfectant Solutions on Setting Time, Linear Dimensional Stability, and Detail Reproduction in Dental Stone Casts Matheus Guilherme Lucas, DDS, MSc, 1 João Neudenir rioli-filho,
BUILD IT FAST. MAKE IT LAST.
 EDUCATION SUPPORT COMMITTED TO CONTINUOUS LEARNING WE RE HERE FOR YOU Clinical Education Service & Support The Dentsply Sirona Academy, Charlotte is a state-of-the-art training facility for dental professionals
EDUCATION SUPPORT COMMITTED TO CONTINUOUS LEARNING WE RE HERE FOR YOU Clinical Education Service & Support The Dentsply Sirona Academy, Charlotte is a state-of-the-art training facility for dental professionals
STEP-BY-STEP-ANLEITUNG
 STEP-BY-STEP-ANLEITUNG VON TECHNIKERN FÜR TECHNIKER LABORATORY PROCEDURES, STEP BY STEP BY TECHNICIANS FOR TECHNICIANS Eclipse junior Laboratory Procedures, Step by Step* Splints Drilling Stents Temporaries
STEP-BY-STEP-ANLEITUNG VON TECHNIKERN FÜR TECHNIKER LABORATORY PROCEDURES, STEP BY STEP BY TECHNICIANS FOR TECHNICIANS Eclipse junior Laboratory Procedures, Step by Step* Splints Drilling Stents Temporaries
The development of modern Oral
 RESEARCH In Vitro Evaluation of the Removal Force of Abutments in Frictional Dental Implants João César Zielak, DDS, MSc, PhD* Murilo Rorbacker, DDS Rodrigo Gomes, DDS Celso Yamashita, DDS, MSc, PhD Carla
RESEARCH In Vitro Evaluation of the Removal Force of Abutments in Frictional Dental Implants João César Zielak, DDS, MSc, PhD* Murilo Rorbacker, DDS Rodrigo Gomes, DDS Celso Yamashita, DDS, MSc, PhD Carla
Virtual The hydrophilic precision impression material
 Impressive Impressions The hydrophilic precision impression material Hydrophilic: exactly where you need it Single-phase impressions with Hydrophilicity and contact angle Excellent wettability Excellent
Impressive Impressions The hydrophilic precision impression material Hydrophilic: exactly where you need it Single-phase impressions with Hydrophilicity and contact angle Excellent wettability Excellent
WHAT IS CLEAN BASE? Custom Base 4/9/2013
 The simultaneous delivery of multiple brackets onto the tooth surface via a polyvinylsiloxane or clear plastic tray. Accurate Bracket Placement Better Utilization of Staff Reduced Chairside Stress Less
The simultaneous delivery of multiple brackets onto the tooth surface via a polyvinylsiloxane or clear plastic tray. Accurate Bracket Placement Better Utilization of Staff Reduced Chairside Stress Less
The effect of a plastic-wrapped LED light curing unit and curing distance variances on diametral tensile strength of composite resin
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS The effect of a plastic-wrapped LED light curing unit and curing distance variances on diametral tensile strength of composite resin To cite this
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS The effect of a plastic-wrapped LED light curing unit and curing distance variances on diametral tensile strength of composite resin To cite this
CAD/CAM Dentures. CAD/CAM Dentures. AvaDent Digital Dentures. Disclosure 5/25/15. Summary of Advantages of CAD/CAM Complete Dentures CAD/CAM
 5/25/15 CAD/CAM Dentures CAD/CAM Dentures Computer Aided Design Computer Aided Manufacturing Objective: In this lecture you will learn how complete dentures can be fabricated using CAD/CAM technology.
5/25/15 CAD/CAM Dentures CAD/CAM Dentures Computer Aided Design Computer Aided Manufacturing Objective: In this lecture you will learn how complete dentures can be fabricated using CAD/CAM technology.
3M ESPE Astringent Retraction Paste. Suited for polyether, VPS and digital impressions! Technical Data Sheet
 3M ESPE Astringent Retraction Paste Suited for polyether, VPS and digital impressions! Technical Data Sheet 1 Retraction made easy by the 3M ESPE Astringent Retraction Paste For more than 45 years, 3M
3M ESPE Astringent Retraction Paste Suited for polyether, VPS and digital impressions! Technical Data Sheet 1 Retraction made easy by the 3M ESPE Astringent Retraction Paste For more than 45 years, 3M
International Journal of Dentistry and Oral Science (IJDOS) ISSN:
 International Journal of Dentistry and Oral Science (IJDOS) ISSN: 2377-8075 A Novel Functional Impression Procedure for Distal-Extension Removable Partial Dentures Li QL *, Cao Y Case Report Department
International Journal of Dentistry and Oral Science (IJDOS) ISSN: 2377-8075 A Novel Functional Impression Procedure for Distal-Extension Removable Partial Dentures Li QL *, Cao Y Case Report Department
Polyether Impression Material. Technical Product Profile Impregum. L DuoSoft Quick
 Polyether Impression Material Technical Product Profile Impregum Penta Soft Penta H DuoSoft Penta L DuoSoft Garant L DuoSoft Penta Soft Quick Penta H DuoSoft Quick L DuoSoft Quick 2 Table of Contents Introduction...................................................................5
Polyether Impression Material Technical Product Profile Impregum Penta Soft Penta H DuoSoft Penta L DuoSoft Garant L DuoSoft Penta Soft Quick Penta H DuoSoft Quick L DuoSoft Quick 2 Table of Contents Introduction...................................................................5
MDJ Evaluation the effect of eugenol containing temporary Vol.:9 No.:2 2012
 MDJ Evaluation the effect of eugenol containing temporary fillings on shear bond strength of composite restoration Dr. Farid G. Numan B.D.S., M.Sc Abstract The purpose of this in-vitro study was to evaluate
MDJ Evaluation the effect of eugenol containing temporary fillings on shear bond strength of composite restoration Dr. Farid G. Numan B.D.S., M.Sc Abstract The purpose of this in-vitro study was to evaluate
Smile design with composites: A case study
 Clinical Smile design with composites: A case study Eduardo Mahn 1 and Christian Coachman 2 Adhesive dentistry has improved dramatically over the last decade. Not only are adhesives more reliable and easier
Clinical Smile design with composites: A case study Eduardo Mahn 1 and Christian Coachman 2 Adhesive dentistry has improved dramatically over the last decade. Not only are adhesives more reliable and easier
Fatigue life prediction methodology of automotive rubber component. *Chang-Su Woo 1)
 Fatigue life prediction methodology of automotive rubber component *Chang-Su Woo 1) 1) Department of Nano Mechanics, KIMM, Daejeon 305-345, Korea 1) cswoo@kimm.re.kr ABSTRACT Fatigue life prediction and
Fatigue life prediction methodology of automotive rubber component *Chang-Su Woo 1) 1) Department of Nano Mechanics, KIMM, Daejeon 305-345, Korea 1) cswoo@kimm.re.kr ABSTRACT Fatigue life prediction and
UNDERSTANDING DIGITAL DENTISTRY: CBCT AND INTRA-ORAL 30 SCANNING
 UNDERSTANDING DIGITAL DENTISTRY: CBCT AND INTRA-ORAL 30 SCANNING -=- & UNDERSTANDING DIGITAL DENTISTRY: CBCT AND INTRA-ORAL 30 SCANNING ----CBCTi-------iTERO------ NewTom VGi *Vertical Patient Positioning
UNDERSTANDING DIGITAL DENTISTRY: CBCT AND INTRA-ORAL 30 SCANNING -=- & UNDERSTANDING DIGITAL DENTISTRY: CBCT AND INTRA-ORAL 30 SCANNING ----CBCTi-------iTERO------ NewTom VGi *Vertical Patient Positioning
Esthetic Rehabilitation of Severely Discolored Maxillary Anterior Teeth with Porcelain Laminate Veneers: A Case Report
 Esthetic Rehabilitation of Severely Discolored Maxillary Anterior Teeth with Porcelain Laminate Veneers: A Case Report Dr. Shikha Nandal 1, Dr. Himanshu Shekhawat 2 1 M.D.S. (Prosthodontics) Senior Resident,
Esthetic Rehabilitation of Severely Discolored Maxillary Anterior Teeth with Porcelain Laminate Veneers: A Case Report Dr. Shikha Nandal 1, Dr. Himanshu Shekhawat 2 1 M.D.S. (Prosthodontics) Senior Resident,
Dentistry continues to evolve. Esthetic Templates for Complex Restorative Cases: Rationale and Management
 Esthetic Templates for Complex Restorative Cases: Rationale and Management DEAN E. KOIS, DMD* KYLE K. SCHMIDT, DDS* ARIEL J. RAIGRODSKI, DMD, MS ABSTRACT Complex restorative cases require difficult clinical
Esthetic Templates for Complex Restorative Cases: Rationale and Management DEAN E. KOIS, DMD* KYLE K. SCHMIDT, DDS* ARIEL J. RAIGRODSKI, DMD, MS ABSTRACT Complex restorative cases require difficult clinical
FRACTURE STRENGTH OF PALATAL DENTURE BASE CONSTRUCTED FROM DIFFERENT ACRYLIC DENTURE BASE MATERIALS
 FRACTURE STRENGTH OF PALATAL DENTURE BASE CONSTRUCTED FROM DIFFERENT ACRYLIC DENTURE BASE MATERIALS Faten Khalid Ali Al-Kadi, MSc Jwan Fatih Abdulkareem, PhD Cheman Abdulrahman Al-jmoor, MSc College of
FRACTURE STRENGTH OF PALATAL DENTURE BASE CONSTRUCTED FROM DIFFERENT ACRYLIC DENTURE BASE MATERIALS Faten Khalid Ali Al-Kadi, MSc Jwan Fatih Abdulkareem, PhD Cheman Abdulrahman Al-jmoor, MSc College of
Annotation to the lesson 21 Topic: Methods of provisory crowns fabrication. Chair-side technique. Evaluation of
 Annotation to the lesson 21 Topic: Methods of provisory crowns fabrication. Chair-side technique. Evaluation of crown fitting quality Contemporary methods of restoration of tooth tissues pathology, using
Annotation to the lesson 21 Topic: Methods of provisory crowns fabrication. Chair-side technique. Evaluation of crown fitting quality Contemporary methods of restoration of tooth tissues pathology, using
Dimensional Accuracy of 2 Irreversible Hydrocolloid Alternative Impression Materials with Immediate and Delayed Pouring
 ca Applied Research Cite this article as: J Can Dent Assoc 2010;76:aXXX 2012;78:c2 Dimensional Accuracy of 2 Irreversible Hydrocolloid Alternative Impression Materials with Immediate and Delayed Pouring
ca Applied Research Cite this article as: J Can Dent Assoc 2010;76:aXXX 2012;78:c2 Dimensional Accuracy of 2 Irreversible Hydrocolloid Alternative Impression Materials with Immediate and Delayed Pouring
Traxodent Hemodent Paste Retraction System
 new! Unit Dose Traxodent Hemodent Paste Retraction System Saves on chair time and provides predictable results for your patients well being. The #1 retraction paste 1 is now available in syringe or unit
new! Unit Dose Traxodent Hemodent Paste Retraction System Saves on chair time and provides predictable results for your patients well being. The #1 retraction paste 1 is now available in syringe or unit
Removal efficiency of propolis paste dressing from the root canal
 Universidade de São Paulo Biblioteca Digital da Produção Intelectual - BDPI Departamento de Dentística, Endodontia e Materiais Odontológicos - FOB/BAD Artigos e Materiais de Revistas Científicas - FOB/BAD
Universidade de São Paulo Biblioteca Digital da Produção Intelectual - BDPI Departamento de Dentística, Endodontia e Materiais Odontológicos - FOB/BAD Artigos e Materiais de Revistas Científicas - FOB/BAD
The Reinforced Removable Retainer
 The Reinforced Removable Retainer Abstract The aim of this paper is to present a new type of orthodontic removable retainer, which is of great help to the orthodontist as well as to the patient. The procedures
The Reinforced Removable Retainer Abstract The aim of this paper is to present a new type of orthodontic removable retainer, which is of great help to the orthodontist as well as to the patient. The procedures
Frequently Asked Questions
 General Is a true 3M polyether material? Impregum Super Quick Material is a real 3M polyether impression material but with a faster setting time. The base monomer and the setting mechanism are still the
General Is a true 3M polyether material? Impregum Super Quick Material is a real 3M polyether impression material but with a faster setting time. The base monomer and the setting mechanism are still the
Protemp Crown Temporization Material
 Clinical Case Studies Introduction from 3M ESPE is the world s first preformed, malleable temporary crown, providing speed and simplicity in temporization like never before. With this revolutionary light-curable
Clinical Case Studies Introduction from 3M ESPE is the world s first preformed, malleable temporary crown, providing speed and simplicity in temporization like never before. With this revolutionary light-curable
Fiber post reconstruction: fast and furious style
 Stefan Koubi Fiber post reconstruction: fast and furious style 18 Dec 2017 Fiber post cementation management is crucial to prosthetic treatment success, as 70% of prosthetic treatments are performed on
Stefan Koubi Fiber post reconstruction: fast and furious style 18 Dec 2017 Fiber post cementation management is crucial to prosthetic treatment success, as 70% of prosthetic treatments are performed on
Gender Based Comparison of Gingival Zenith Esthetics Humagain M, Rokaya D, Srii R, Dixit S, Kafle D
 Gender Based Comparison of Gingival Zenith Esthetics Humagain M, Rokaya D, Srii R, Dixit S, Kafle D ABSTRACT Background Department of Dentistry Kathmandu University School of Medical Sciences, Dhulikhel,
Gender Based Comparison of Gingival Zenith Esthetics Humagain M, Rokaya D, Srii R, Dixit S, Kafle D ABSTRACT Background Department of Dentistry Kathmandu University School of Medical Sciences, Dhulikhel,
2. Gap closure and replacement of the missing tooth 35 with directly modelled bridge region 34-36
 GrandTEC Test Kit Dear User, This Test Kit has been put together to enable you to test GrandTEC on the model before using it in a clinical situation. GrandTEC is a resin-impregnated glass fibre strip.
GrandTEC Test Kit Dear User, This Test Kit has been put together to enable you to test GrandTEC on the model before using it in a clinical situation. GrandTEC is a resin-impregnated glass fibre strip.
