Verrucous carcinoma arising from a previous cystic lesion: a case report
|
|
|
- Jesse Brooks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Kang and Leem Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery (2018) 40:31 Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery CASE REPORT Open Access Verrucous carcinoma arising from a previous cystic lesion: a case report Sunghyun Kang 1 and Dae Ho Leem 2* Abstract Background: Verrucous carcinoma (VC) accounts for 1 10% of cases of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) in the oral cavity, and 75% of VC occur in the oral cavity. Only 3% of primary intraosseous squamous cell carcinomas (PIOSCC), which means SCC occurring primarily in the bone, are VC. Verrucous carcinoma arising from odontogenic cysts (OC) is very rare, with only seven cases reported to date. Case presentation: This study reported a case of a patient who underwent partial maxillectomy and neck dissection for VC that occurred in the right anterior maxilla. The patient was admitted to the emergency department at our institution 8 years ago and showed cystic lesions in the anterior maxilla on facial computed tomography (CT) images. Treatment through other departments including assessment of laceration in the mental region and only suture was performed. This report highlights a very rare case of VC in the right anterior maxilla arising from a previous cystic lesion. Conclusions: Since PIOSCC can arise from OC, appropriate treatment of intraosseous cysts and regular radiologic evaluation are necesssary. Surgical exicision of the primary lesion without neck dissection can lead to good prognosis for patients with primary intraosseous verrucous carcinoma. Keywords: Verrucous carcinoma, Intraosseous verrucous carcinoma, Primary intraosseous carcinoma, Odontogenic cyst, Maxilla Background Verrucous carcinoma (VC), first reported by Ackerman in 1948, is characterized by exophytic and papillary friable lesions. It is slowly growing, well differentiated, and verrucous in nature and often extensive with a tendency to invade local structures. The main causes of VC are poor oral hygiene, smoking, and alcohol abuse [1, 2]. Kraus and Perezmesa reported that VC can occur in various epithelial lining, but is most common in the oral cavity, larynx, esophagus, and genitalia [3]. Verrucous carcinoma is characterized by diffuse and exophytic lesions covered by leukoplakic patches. It grows slowly over several years and forms a cauliflower-like lesion cm in size with indolent pain within a few months after turning into a small wart-like mass. It shows aggressive local invasion of associated structures * Correspondence: idisho@jbnu.ac.kr 2 Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, School of Dentistry, Chonbuk National University, 567 Baekje-daero, Deokjin-gu, Jeonju-si, Jeollabuk-do 54896, South Korea Full list of author information is available at the end of the article such as the bone and cartilage around the primary lesion and rarely spreads to the lymph nodes. Verrucous carcinoma has relatively good prognosis due to its low metastatic and invasive potential and is treated by surgical excision without radical neck dissection [4]. Carcinoma within the bone is a very rare form of VC and often arises from odontogenic cysts (OC) [4]. Borrás-Ferreres et al. reported the rate of carcinomatous transformation of OC of % [5]. Carcinomatous transformation of OC is characterized by pain and swelling, but may be detected on panoramic radiographs without accompanied symptoms. Histologically, OC transformation to well-differentiated SCC is reported as the most common finding. With regard to OC transformation to SCC, Schwimmer et al. reported that 60% of SCC arose from residual or radicular cysts, 35% arose from dentigerous cysts or odontogenic keratocytes, and 11% arose from lateral periodontal cysts and other types of cysts [6]. Bodner et al. reported 116 cases of primary intraosseous squamous cell carcinoma (PIOSCC) which means SCC occurring primarily in the bone that The Author(s) Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
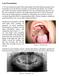
2 Kang and Leem Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery (2018) 40:31 Page 2 of 8 occurred at OC [7]. Primary intraosseous squamous cell carcinoma refers to carcinoma originated in the jaw as primary site of lesion and accounts for 1 2% of all OC. Roughly 85% of PIOSCC is well-to-moderately differentiated SCC, and only 3% is VC. VC arising from OC is a type of PIOSCC and is referred to as primary intraosseous verrucous carcinoma (PIOVC) [8]. Verrucous carcinoma arising from an OC is very rare, with only seven cases reported to date. Diagnosis of carcinoma originating in the jaw, especially carcinoma arising from an OC, is difficult because it is necessary to determine if the carcinoma is primary, originating from another site or spreading through the alveolar bone if the carcinoma occurs on the mucous membrane, or originating from the maxillary sinus. In case of carcinoma arising from an OC, it is difficult to confirm through histology that the carcinoma originated from OC. Therefore, there are very few cases of carcinoma arising from OC reported to date, and VC arising from OC is extremely rare [9]. This study reported a case of partial maxillectomy and neck dissection performed for VC that occurred on the labial surface of the edentulous alveolar ridge in the anterior maxilla and in the middle of the palate. Facial CT imaging 8 years ago indicated that the patient had an odontogenic cystic lesion on the ipsilateral side. At the time, the patient visited the emergency department at the present institution for laceration in the mental region and underwent suturing. The patient underwent assessment for the presence of jaw fracture subsequent to the facial CT but was not informed regarding the prognosis of or treatment for the cystic lesion in the maxilla. This case report highlighted the possibility of VC arising from a previous cystic lesion, with a comparative review of similar cases. Case presentation A 76-year-old patient visited a private clinic in May 2016 after developing a lesion inside his mouth. Incisional biopsy showed a lesion on the labial surface of the edentulous alveolar ridge in the anterior maxilla, and the patient was diagnosed with VC. The patient was referred to the Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery at Chonbuk National University Dental Hospital in June At the time of admission, the patient showed painless exophytic verrucous proliferation measuring 2 cm 2 cm on the labial surface of the edentulous alveolar ridge in the anterior maxilla and 1 cm 1 cm in the middle of the palate. The lesions surfaces were covered with thick, white keratin (Fig. 1). The patient had been diagnosed with hypertension and prostatism 6 years ago, which were being controlled through medication. The patient had stopped taking aspirins 3 months ago. At the time of visit to the Emergency Department of Chonbuk Fig. 1 Clinical photograph showing papillary exophytic growths of the labial parts of the maxillary right anterior edentulous ridge and middle of the palate National University Dental Hospital for laceration in the mental region 8 years ago, facial CT through referral from another department indicated the presence of cystic lesion surrounded by the unperforated cortical bone in the right anterior maxilla (Fig. 2). However, through facial CT performed at the time of the admission to the Emergency Department explained to the patient only about there was no facial bone fracture. The patient reported that he had not been informed of the presence of cystic lesion in the maxilla at the time of visit to the emergency department 8 years ago and not received any treatment due to absence of symptoms. The patient underwent full-mouth extraction for the remaining maxillary and mandibular teeth 3 months before visiting the private clinic and has been wearing maxillary and mandibular complete dentures since then. Based on results from incisional biopsy of the lesion performed at Chonbuk National University Dental Hospital at the time of admission, the patient was diagnosed with VC. Since the time of initial detection 8 years ago, the cystic lesion in the right maxilla was more widespread, with surrounding bone destruction, unclear border, and irregularly absorbed nasal mucous, anterior maxilla and palatine bones (Fig. 3). MRI test showed heterogeneous enhancement in the right maxilla with accompanied bony erosion, with invasion of the levator labii superioris muscle, and zygomatic muscle in the anterior direction (Fig. 4). Heterogeneous enhancement with maximum 1 cm radius was observed in the lymph node at the right cervical chain levels I and II, so metastasis was suspected. On FDG PET/CT, an enlarged lymph node with FDG uptake was observed at the right cervical levels IB and II. Supraomohyoid neck dissection (SOHND) was planned under suspicion of invasion of the neck. Findings from chest radiographs, electrocardiograms, and blood tests presented no contraindication for general
3 Kang and Leem Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery (2018) 40:31 Page 3 of 8 Fig. 2 Facial CT image acquired 8 years ago at the emergency room showing a well-circumscribed, corticated, expansile, unilocular, and radiolucency lesion in the right anterior maxillary area. a Axial view. b Coronal view. c Sagittal view anesthesia, in addition, the chest radiographs revealed absence of specific lesions. In July 2016, partial maxillectomy of the right maxilla and SOHND were performed (Fig. 5) under general anesthesia. Partial maxillectomy with safety margin of 1 cm and frozen biopsy were performed; results showed negative findings. In addition, result from frozen biopsy of the enlarged lymph node showed negative findings. Furacid gauze packing was performed at the site of partial maxillectomy, and a premade obturator was fixed on the maxilla through using a screw. Cross-sectional image of the excised right maxillary lesion showed presence of a solid mass with unclear border surrounding the tissues and with white papillary appearance. In addition, the lesion on the edentulous alveolar ridge of the right anterior maxilla and the lesion in the middle of thepalatewasfoundtobeasingleexposedmasswithinthe oral cavity. Finally, the patient was diagnosed with VC based onthebiopsyresults.thelesionwasstagedaspt4an0 since no metastasis was observed in the lymph nodes. Follow-up evaluation at 6 months (Fig. 6), 1 year (Fig. 7), and 2 years (Fig. 5d) after surgery revealed the absence of recurrence or metastasis. Histopathologic findings An incisional biopsy of the lesion in the right maxillary alveolar ridge performed at the present institution showed downward growth of numerous thickened and bulbous rete ridges of squamous cells. With regard to biomarker testing, the lesion was p16 positive and had lower proliferation based on Ki-67 detection; as a result, the patient was initially diagnosed with VC (Fig. 8a). Histological examination performed after surgery showed epithelial cells with exophytic surfaces and prominent keratin layer arranged in compressed invaginating folds that proliferated downward (Fig. 8b). In addition, blunt club-shaped projections of hyperplastic epithelium rather than infiltration were observed, and the basal layer exhibited dysplasia and hyperplasia (Fig. 8c). Groups of epithelial cells proliferating within the maxilla associated with bony destruction was observed (Fig. 8d). Finally, the patient was diagnosed with VC based on the observation of exo-endophytic growth pattern, deep extension of thick, parakeratotic, squamous epithelial cell layer, and bulbous rete ridges with borders extending toward the adjacent tissue with locally invasive patterns. The diagnosis of VC is based on histopathological findings as well as clinical symptoms, since the biopsy specimen does not always represent the full thickness of the epithelium [10]. Our patient exhibited clinical and histopathological characteristics of VC including epithelial cells with associated destruction of the bone within the maxilla and proliferation with combined dysplasia and hyperplasia. Since the patient had a cystic lesion in Fig. 3 Facial CT image acquired at the first visit in 2016 showing a dome-shaped radiolucent area in the right maxilla with expansion to the nasal floor and jagged margin of the cortical bone. a Axial view. b Coronal view. c Sagittal view
4 Kang and Leem Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery (2018) 40:31 Page 4 of 8 Fig. 4 PET and MRI scans acquired before surgery. a 18-FDG PET/CT coronal view showing hot FDG spot on the right maxillary area. b T2-weighted MRI scan, axial view. c T2-weighted MRI scan, sagittal view the same area, it was concluded that the patient had VC arising from a previous cystic lesion. Conclusions The remaining epithelium after odontogenesis proliferates and differentiates due to unknown stimuli and forms an odontogenic tumor. The cysts or tumors may undergo metaplastic transformation into squamous epithelium to develop into malignant tumors [11]. Gardner analyzed 63 cases of carcinoma arising from OC reported since the first report of carcinoma arising from OC by Herrmann until 1967 and reported that long-standing chronic inflammation is the major factor promoting the transformation of cysts to carcinoma [12]. In 1971, the WHO defined primary intraosseous carcinoma as SCC within the jaw that originates from remnants of odontogenic epithelium rather than the oral mucosa [13]. Although there is controversy regarding the cause of carcinomatous transformation of OC, most studies explain that long-standing chronic inflammation may act as a malignant transformation factor, and that the connective tissue infiltration of lymphocytes and plasma cells may be the major cause of transformation. In 1963, Ward and Cohen classified the causes of carcinoma arising from OC: first, metastasis of carcinoma from another site to an existing cyst; second, transformation of carcinoma into cyst; and third, malignant changes of the cyst [14]. Gardner proposed the following criteria for SCC originating from OC in 1975: microscopy findings of transition area from benign cystic epithelial lining to invasive SCC, absence of carcinomatous changes in the overlying Fig. 5 Preoperative and postoperative clinical photograph. a Pre-operative image. b Excisional specimen (the right side of the maxilla, red arrow; the palatal side, yellow arrow). c Verrucous proliferation pattern can be seen on the surface of the lesion inside the bone. d At 2-years post-surgery, there is no recurrence of findings
5 Kang and Leem Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery (2018) 40:31 Page 5 of 8 Fig. 6 PET and MRI scans acquired 6 months after surgery indicate no recurrence of findings. a 18-FDG PET/CT coronal view showing only slight spots around the partial maxillectomy area due to the surgery. b T2-weighted MRI scan, axial view. c T2-weighted MRI scan, sagittal view epithelium, and no source of carcinoma in the adjacent structures [12]. To et al. proposed the following criteria for PIOSSC diagnosis in 1991: histology finding of intrabony SCC with no evidence of associated oral disease, negative finding on chest radiograph, and 6 months survival with no evidence of occult primary or negative autopsy [15]. Suei et al. explained that the possibility of occurrence of primary tumor in another site must be ruled out in order to diagnose PIOSCC [9]. However, since the causal relationship is unclear, a follow-up period of at least 6 months that includes chest radiography is necessary to rule out the possibility of lesions from another site [15]. Mucosal changes or metastasis from another lesion should be ruled out for the diagnosis of PIOSCC arising from OC. Differentiating between the origins of histologically similar PIOSCC at OC and PIOSCC that metastasized from a distant lesion such as the mucosal membrane, or that of highly advanced PIOSCC is difficult [16]. Therefore, a radiologic examination is useful for diagnosing PIOSCC. A lesion with radiographic findings of surrounding bone can be assumed to be of intraosseous origin [9]. Whereas, OC generally presents as a round or oval radiolucent lesion with well-defined borders on radiographs; OC that has undergone malignant transformation shows jagged margins, indentations, and indistinct borders. In addition, it is characterized by bony expansion with thinning of the cortex of the maxilla and mandible [12]. It also shows resorption of the adjacent dental roots in addition to bone erosion in the buccal (labial) and palatal (lingual) sides [17]. Bodner et al. reviewed 116 cases of PIOSCC [7]. However, VC arising from OC is very rare, with only seven cases reported to date (Table 1) [2, 4, 8, 18 21]. Takeda reported that the risk of malignant change of OC was four times higher in the mandible than in the maxilla [22]. In addition, the risk of VC is reported to be two times higher in the mandible than in the maxilla and four times higher among men than women, with the mean age at onset of 53.9 years [23]. However, of the total eight reported cases of OC transforming to VC including the present case, six cases showed transformation in the maxilla (75%), and seven cases were male (87.5%). The mean age at onset of VC was 61.0 years. Characteristics of each reported case Enriquez et al. reported the first case in 1980 of VC at OC in the mandible [2]. The second case was by Anand et al. in 1994 on VC in the maxilla with odontogenic keratocysts [18]. The third case was reported by Pomatto et al. in 2011, on VC at OC in the maxilla following tooth extraction in the left posterior maxilla; the authors claimed that VC originated from post-extraction remnants and introduced the term PIOVC [8]. The fourth case was reported by Fig. 7 Facial CT image acquired 1 year after surgery indicates no recurrence of findings. a Axial view. b Coronal view. c Sagittal view
6 Kang and Leem Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery (2018) 40:31 Page 6 of 8 Fig. 8 Histopathologic microphotographs of the specimen with hematoxylin and eosin staining. a Incisional biopsy before surgery showing downward growth of numerous thickened, bulbous rete ridges of squamous cells ( 100). b Surgical specimen showing exophytic growth pattern with prominent keratin layer arranged in compressed invaginating fold ( 50). c Hyperplastic epithelium showing blunt projections rather than infiltration of the underlying tissue with dysplasia and hyperplasia of the basal cell layer ( 50). d A group of epithelial cells proliferating within the maxillary bone with bony destruction ( 50) Mohtashm et al. in 2008, on VC at OC in the maxilla [4]. Mohtashm et al. explained that since metastasis of VC is extremely rare, surgical exicision without radical neck dissection is the best treatment option for VC. The fifth case was reported by Imaue et al. in 2013, on VC at OC in the maxilla [19]. Similar to the present case, a dome-shaped radiopaque mass with well-defined margins was observed in the left maxilla on radiograph, with expansion toward the maxillary sinus, nasal septum, and zygomatic arch. Partial maxillectomy was performed. The sixth case was reported by Peng et al. in 2015, on VC at OC in the mandible [24]. Peng et al. summarized all reports regarding VC and explained that since PIOVC has no recurrence or metastasis, it does not require any forms of neck dissection, and removal of primary lesion alone can lead to good prognosis. The seventh case was reported by Kamarthi et al. in 2016, on VC at OC in the maxilla with confirmed verrucous transformation of the cystic lining [21]. Early histological findings of VC include keratin piling on the surface, with initiation of downgrowth of epithelial projections. With progression of VC, club-shaped fingers of hyperplastic epithelium that gradually project into rather than infiltrate the deeper tissues are observed. At this point, the epithelium is well-differentiated while the Table 1 Reported cases of verrucous carcinoma arising from odontogenic cystic lesion Author (year) Age/sex Site Symptom Diagnosis Prognosis, follower-up period, month Enriquez et al. (1980) [2] 56/M Mandible Painless lesion, fistulous tract VC arising from OC No recurrence or metastasis, 48 Anand et al. (1994) [18] 46/M Maxilla Discomfort VC arising from OKC No recurrence or metastasis, 24 Pomatto et al. (2001) [8] NA/F Maxilla Recurrent swelling VC arising from DC No recurrence or metastasis, 8 Mohtasham et al. (2008) [4] 58/M Maxilla Non-tender on palpation, VC arising from OKC No recurrence or metastasis, 20 exophytic lesion Imaue et al. (2013) [19] 52/M Maxilla Painless exophytic lesion VC arising from POC No recurrence or metastasis, NA Peng et al. (2015) [24] 74/M Mandible Swelling with mild pain VC arising from DC No recurrence or metastasis, 5 Kamarthi et al. (2016) [21] 65/M Maxilla Painful swelling VC arising from OKC No recurrence or metastasis, 6 Present case (2018) 76/M Maxilla Painless exophytic lesion VC arising from POC No recurrence or metastasis, 24 VC Verrucous carcinoma, OC odontogenic cyst, OKC odontogenic keratocyst, DC dentigerous cyst, POC previous odontogenic cystic lesion, NA not available
7 Kang and Leem Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery (2018) 40:31 Page 7 of 8 basement membrane is intact. With growth of VC, cleftlike spaces with degenerating keratin project deeply. Chronic inflammation of the connective tissues, plasma cells, and mononuclear cells may ensue [1]. Odontogenic cyst that has undergone malignant transformation is characterized by chronic infiltration of lymphocytes and plasma cells in the connective tissue of the cyst wall. Cyst walls exhibit hyperplastic epithelium, and tumor cells exhibit pleomorphism and hyperchromatism. Cholesterol crystal clefts may be observed, and they may invade fibrous cystic walls. The cyst walls may have normal epithelial surface on some parts and naive epithelial surface on the others [12]. Maxymiw and Wood reported a case of OC advanced to SCC in the mandible, and based on the finding of transition of the cellular lining of the cyst wall from benign epithelium to carcinoma, it was confirmed that OC originated from carcinoma. In this case, malignant transformation occurred through chronic infiltration by lymphocytes and plasma cells of the cyst walls connective tissues. Cysts are partially or fully lined with dyskeratotic squamous epithelium. The stratified squamous epithelium with linings can transform to invasive SCC from the normal squamous epithelium and proliferate into the connective tissues of the cyst [17]. Verrucous carcinoma arising from OC is characterized by the transformation of the lining epithelium of the cyst to verrucous hyperplastic epithelium. In addition, moderate chronic inflammatory cells infiltrate the fibrous cystic wall. Proliferation of hyperparakeratotic-stratified squamous cyst lining epithelium can occur, and down-growth of broad and bulbous epithelial ridges with pushing-border invasion, which is generally observed in VC, can occur in the fibrous cystic wall. Thick prominent rete pegs with well-preserved basement membrane and well-differentiated squamous cells which penetrate deeply into the underlying tissue are also observed. Cell nuclei is prominent, and cellular pleomorphism is observed, with mild dysplasia, focal dyskeratosis, and atypical squamous cells. In addition, mitotic figures of the basal and parabasal epithelial cells are observed [2, 20]. Most reports indicate that surgical excision of the primary lesion is sufficient for VC, and VC shows higher 5-year survival rate than SCC. McClure et al. reported that although more aggressive excisions are necessary for large tumors, neck dissection is not necessary, since in most cases, VC is inflammatory rather than metastatic even in cases with lymphadenopathy at preoperative examinations [10]. However, Walvekar et al. recommended that considering the uncertainty of pathological diagnosis in cases with suspicious lymphadenopathy, it is reasonable to perform selective neck dissection such as SOHND. According to his analysis of 101 cases of VC within the oral cavity, the rate of recurrent VC was 28%, and the 5-year survival rate after surgery was 77.6% [23]. Ackerman reported that while radiotherapy may be effective for small superficial VC, surgical excision must be accompanied for cases with VC affecting a large area [1]. Few studies have reported that irradiation of VC, which is radiosensitive, can cause high-recurrence rates and anaplastic transformation of the neoplasm leading to rapid metastatic dissemination [3, 10]. Gardner analyzed 25 cases of carcinoma arising from OC and reported patients mortality rate of 20% within months after surgery [12]. In studies including 27 cases each of carcinoma arising from OC, Eversole et al. reported a 2-year survival rate of 53% and Schiwmmer et al. that of 63% [6, 25]. In a study including 116 cases, Bodner et al. reported that 46% of cases with PIOSCC underwent surgery, and 38% underwent surgery and radiotherapy; follow-up revealed a 2-year survival rate of 62% and 5-year survival rate of 38%; and only 6 out of 116 cases with neck metastasis; however, despite the low rate of neck metastasis, neck dissection was performed in 59 of 116 cases (51%) [7]. In the seven reported cases of VC arising from odontogenic cystic lesion, excluding the present case report, neck dissection and radiotherapy were not performed. In this case report, neck dissection was performed due to PET/MRI characteristic of enlarged lymph node, but radiotherapy was not performed. Surgical excision of the primary lesion led to good prognosis. As suggested by the criteria, VC which is less malignant than SCC, with primary lesion in the jaw without distant lesion, low metastatic potential, and low recurrence rate may lead to good prognosis. Our patient showed cystic lesion surrounded by the cortical bone at the site of carcinoma since 8 years ago, clear histological characteristics of VC, bony destruction of the maxilla, and cancer cell infiltration of the jaw; based on these findings, the patient was diagnosed with PIOVC. However, based on the diagnostic criteria for PIOSCC, the presence of radiolucent cystic lesions at the site of VC observed 8 years ago, characteristics of the carcinoma cells differentiating within the bone, and absence of distant lesion, as well as previous reports, the patient was diagnosed with VC arising from odontogenic cystic lesion. In conclusion, this case report highlights that patients with OC must be promptly diagnosed and managed due to the possibility of malignant transformation of OC. Careful monitoring of lesions through CT is necessary for patients with OC. In addition, their prognosis must be carefully observed through regular follow-up x-ray examination. As reported in previous studies, surgical excision of the primary lesion without neck dissection can lead to good prognosis of PIOVC. However, if a patient exhibits combined lymphadenopathy, the possibility of future occurrence of metastasis must be completely eliminated through selective neck dissection.
8 Kang and Leem Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery (2018) 40:31 Page 8 of 8 Abbreviations 18-FDG PET/CT: Positron emission tomography with 2-deoxy-2-fluorine-18- fluoro- D-glucose integrated with computed tomography; CT: Computed tomography; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; OC: Odontogenic cyst; PIOSCC: Primary intraosseous squamous cell carcinoma; PIOVC: Primary intraosseous verrucous carcinoma; SOHND: Supraomohyoid neck dissection; VC: Verrucous carcinoma Acknowledgements We thank Professor Nampyo Cho for assistance with histologic findings. Authors contributions DHL performed the surgery and reviewed the manuscript; SHK participated in the operation as primary care physician, reviewed the literature, and wrote the manuscript. Both authors read and approved the final manuscript. Ethics approval and consent to participate Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this case report and accompanying images. Consent for publication The patient consented to the publication of this case report. Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Publisher s Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. Author details 1 Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Chonbuk National University Hospital, 20 Geonjiro, Deokjin-gu, Jeonju-si, Jeollabuk-do 54907, South Korea. 2 Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, School of Dentistry, Chonbuk National University, 567 Baekje-daero, Deokjin-gu, Jeonju-si, Jeollabuk-do 54896, South Korea. 13. Kramer IR, Pindborg JJ, Shear M (1992) The WHO histological typing of odontogenic tumours. A commentary on the second edition. Cancer 70: Ward TG, Cohen B (1963) Squamous carcinoma in a mandibular cyst. Br J Oral Surg 1: To EH, Brown JS, Avery BS, Ward-Booth RP (1991) Primary intraosseous carcinoma of the jaws. Three new cases and a review of the literature. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 29: Alevizos I, Blaeser B, Gallagher G, Ohyama H, Wong DT, Todd R (2002) Odontogenic carcinoma: a functional genomic comparison with oral mucosal squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol 38: Maxymiw WG, Wood RE (1991) Carcinoma arising in a dentigerous cyst: a case report and review of the literature. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 49: Anand VK, Arrowood JP Jr, Krolls SO (1994) Malignant potential of the odontogenic keratocyst. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 111: Imaue S, Tomihara K, Takei R, Arai N, Noguchi M (2013) Verrucous carcinoma of the maxilla possibly originating from a previous cyst: a case report. J Oral Maxillofac Surg Med Pathol 25: Peng Q, Wang Y, Quan H, Li Y, Tang Z (2016) Oral verrucous carcinoma: from multifactorial etiology to diverse treatment regimens (review). Int J Oncol 49: Kamarthi N, Palakshappa SG, Wadhwan V, Mohan RS (2016) Intraosseous verrucous carcinoma arising from an orthokeratinized odontogenic keratocyst: a report of a rarest entity. Contemp Clin Dent 7: Takeda Y (1991) Intra-osseous squamous cell carcinoma of the maxilla: probably arisen from non-odontogenic epithelium. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 29: Walvekar RR, Chaukar DA, Deshpande MS, Pai PS, Chaturvedi P, Kakade A, Kane SV, D'Cruz AK (2009) Verrucous carcinoma of the oral cavity: a clinical and pathological study of 101 cases. Oral Oncol 45: Peng CY, Huang YF, Lu MY, Lee YH, Yu CH (2015) Intraosseous verrucous carcinoma arising from an infected dentigerous cyst-a case report. J Formos Med Assoc 114: Eversole LR, Sabes WR, Rovin S (1975) Aggressive growth and neoplastic potential of odontogenic cysts: with special reference to central epidermoid and mucoepidermoid carcinomas. Cancer 35: Received: 8 August 2018 Accepted: 31 August 2018 References 1. Ackerman LV (1948) Verrucous carcinoma of the oral cavity. Surgery 23: Enriquez RE, Ciola B, Bahn SL (1980) Verrucous carcinoma arising in an odontogenic cyst. Report of a case. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 49: Kraus FT, Perezmesa C (1966) Verrucous carcinoma. Clinical and pathologic study of 105 cases involving oral cavity, larynx and genitalia. Cancer 19: Mohtasham N, Babazadeh F, Jafarzadeh H (2008) Intraosseous verrucous carcinoma originating from an odontogenic cyst: a case report. J Oral Sci 50: Borras-Ferreres J, Sanchez-Torres A, Gay-Escoda C (2016) Malignant changes developing from odontogenic cysts: a systematic review. J Clin Exp Dent 8: e622 e Schwimmer AM, Aydin F, Morrison SN (1991) Squamous cell carcinoma arising in residual odontogenic cyst. Report of a case and review of literature. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 72: Bodner L, Manor E, Shear M, van der Waal I (2011) Primary intraosseous squamous cell carcinoma arising in an odontogenic cyst: a clinicopathologic analysis of 116 reported cases. J Oral Pathol Med 40: Pomatto E, Carbone V, Giangrandi D, Falco V (2001) Primary intraosseous verrucous carcinoma developing from a maxillary odontogenic cyst: case report. Tumori 87: Suei Y, Tanimoto K, Taguchi A, Wada T (1994) Primary intraosseous carcinoma: review of the literature and diagnostic criteria. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 52: McClure DL, Gullane PJ, Slinger RP, Wysocki GP (1984) Verrucous carcinoma--changing concepts in management. J Otolaryngol 13: Anneroth G, Hansen LS (1982) Variations in keratinizing odontogenic cysts and tumors. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 54: Gardner AF (1975) A survey of odontogenic cysts and their relationship to squamous cell carcinoma. Dent J 41:
Primary intraosseous squamous cell carcinoma of the maxilla possibly arising from an infected residual cyst: A case report
 ONCOLOGY LETTERS 9: 131-135, 2015 Primary intraosseous squamous cell carcinoma of the maxilla possibly arising from an infected residual cyst: A case report SHINTARO SUKEGAWA 1, HIDENOBU MATSUZAKI 2, NAOKI
ONCOLOGY LETTERS 9: 131-135, 2015 Primary intraosseous squamous cell carcinoma of the maxilla possibly arising from an infected residual cyst: A case report SHINTARO SUKEGAWA 1, HIDENOBU MATSUZAKI 2, NAOKI
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Arising in a Residual Cyst: A Case Report
 Squamous Cell Carcinoma Arising in a Residual Cyst: A Case Report Abstract Aim: The purpose of this report is to present a case of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) arising from a mandibular residual cyst.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Arising in a Residual Cyst: A Case Report Abstract Aim: The purpose of this report is to present a case of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) arising from a mandibular residual cyst.
Central Poorly Differentiated Adenocarcinoma of the Maxilla: Report of a Case
 Kobe J. Med. Sci., Vol. 49, No. 2, pp. 45-49, 2003 Central Poorly Differentiated Adenocarcinoma of the Maxilla: Report of a Case MASAHIRO UMEDA 1), SATOSHI YOKOO 1), YASUYUKI SHIBUYA 1), TAKAHIDE KOMORI
Kobe J. Med. Sci., Vol. 49, No. 2, pp. 45-49, 2003 Central Poorly Differentiated Adenocarcinoma of the Maxilla: Report of a Case MASAHIRO UMEDA 1), SATOSHI YOKOO 1), YASUYUKI SHIBUYA 1), TAKAHIDE KOMORI
Maxillary Verrucous Carcinoma Coincident With Cervical Lymph Node Metastasis of Colon Adenocarcinoma
 Int Surg 2012;97:270 274 Case Report Maxillary Verrucous Carcinoma Coincident With Cervical Lymph Node Metastasis of Colon Adenocarcinoma Hatsumi Yano Kato 1, Hiroaki Ishibashi 1, Yoshiki Nariai 1, Katsumi
Int Surg 2012;97:270 274 Case Report Maxillary Verrucous Carcinoma Coincident With Cervical Lymph Node Metastasis of Colon Adenocarcinoma Hatsumi Yano Kato 1, Hiroaki Ishibashi 1, Yoshiki Nariai 1, Katsumi
Ameloblastic Carcinoma of the Mandible: a Rare Case Report
 IBIMA Publishing Journal of Research and Practice in Dentistry http://www.ibimapublishing.com/journals/dent/dent.html Vol. 2015 (2015), Article ID 672596, 6 pages DOI: 10.5171/2015.672596 Case Report Ameloblastic
IBIMA Publishing Journal of Research and Practice in Dentistry http://www.ibimapublishing.com/journals/dent/dent.html Vol. 2015 (2015), Article ID 672596, 6 pages DOI: 10.5171/2015.672596 Case Report Ameloblastic
MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS
 MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS Squamous cell carcinoma Osteogenic sarcoma Chondrosarcoma Fibrosarcoma Malignant lymphomas (incl. Burkitt s) Multiple myeloma Ameloblastoma Secondary
MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS Squamous cell carcinoma Osteogenic sarcoma Chondrosarcoma Fibrosarcoma Malignant lymphomas (incl. Burkitt s) Multiple myeloma Ameloblastoma Secondary
Case Report Malignant Transformation of an Odontogenic Cyst in aperiodof10years
 Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 762969, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/762969 Case Report Malignant Transformation of an Odontogenic Cyst in aperiodof10years Juliane Pirágine Araújo, 1 Luiz
Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 762969, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/762969 Case Report Malignant Transformation of an Odontogenic Cyst in aperiodof10years Juliane Pirágine Araújo, 1 Luiz
Orthokeratinized Odontogenic Cyst: A Rarity
 aijoc AIJOC Case Report 1 Heena Sonawane, 2 Freny R Karjodkar, 3 Kaustubh Sansare, 4 Nimish Prakash ABSTRACT Orthokeratinized odontogenic cyst (OOC) was first identified as the rare variant of keratocystic
aijoc AIJOC Case Report 1 Heena Sonawane, 2 Freny R Karjodkar, 3 Kaustubh Sansare, 4 Nimish Prakash ABSTRACT Orthokeratinized odontogenic cyst (OOC) was first identified as the rare variant of keratocystic
Glandular Odontogenic Cyst Coexisting with a Dentigerous Cyst: Case Report
 SmyrnaMed Case 2018;2(1): 1-5 ISSN (Online): 2564-6869 www.smyrnamed.com Glandular Odontogenic Cyst Coexisting with a Dentigerous Cyst: Case Report Assist.Prof.Dr. Serap Keskin Tunç 1, Dt. Erkan Feslihan
SmyrnaMed Case 2018;2(1): 1-5 ISSN (Online): 2564-6869 www.smyrnamed.com Glandular Odontogenic Cyst Coexisting with a Dentigerous Cyst: Case Report Assist.Prof.Dr. Serap Keskin Tunç 1, Dt. Erkan Feslihan
Clear cell odontogenic carcinoma mimicking a cystic lesion: a case of misdiagnosis
 CASE REPORT http://dx.doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2014.40.4.199 pissn 2234-7550 eissn 2234-5930 Clear cell odontogenic carcinoma mimicking a cystic lesion: a case of misdiagnosis Minkyu Kim 1, Eunae Cho 2,
CASE REPORT http://dx.doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2014.40.4.199 pissn 2234-7550 eissn 2234-5930 Clear cell odontogenic carcinoma mimicking a cystic lesion: a case of misdiagnosis Minkyu Kim 1, Eunae Cho 2,
Dysplasia, Mimics and Other Controversies
 Dysplasia, Mimics and Other Controversies Mary S. Richardson, MD Dept. of Pathology Medical University of South Carolina Charleston, SC Notice of Faculty Disclosure In accordance with ACGME guidelines,
Dysplasia, Mimics and Other Controversies Mary S. Richardson, MD Dept. of Pathology Medical University of South Carolina Charleston, SC Notice of Faculty Disclosure In accordance with ACGME guidelines,
Origin of Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors
 Origin of Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors Odontogenic Apparatus Origin of Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors Odontogenic Apparatus Remnants of dental lamina Reduced enamel epithelium Odontogenic rests Basal cell layer
Origin of Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors Odontogenic Apparatus Origin of Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors Odontogenic Apparatus Remnants of dental lamina Reduced enamel epithelium Odontogenic rests Basal cell layer
An Expansile Large Odontogenic Keratocyst Maxilla: A Case Report.
 RESEARCH AND REVIEWS: JOURNAL OF DENTAL SCIENCES An Expansile Large Odontogenic Keratocyst Maxilla: A Case Report. Nasib Chand Khabra 1, Ish Pandhi 1 *, Kiran DN 2, Sunil Alipuria 1, Bhawna Gulati 1, and
RESEARCH AND REVIEWS: JOURNAL OF DENTAL SCIENCES An Expansile Large Odontogenic Keratocyst Maxilla: A Case Report. Nasib Chand Khabra 1, Ish Pandhi 1 *, Kiran DN 2, Sunil Alipuria 1, Bhawna Gulati 1, and
04/09/2018. Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions. Agenda. Squamous Dysplasia. Squamo-proliferative lesions. Architectural features
 Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical
Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical
Mucous and ciliated cell metaplasia in epithelial linings of odontogenic inflammatory and developmental cysts
 77 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 47, No. 2, 77-81, 2005 Original Mucous and ciliated cell metaplasia in epithelial linings of odontogenic inflammatory and developmental cysts Yasunori Takeda, Yuko Oikawa,
77 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 47, No. 2, 77-81, 2005 Original Mucous and ciliated cell metaplasia in epithelial linings of odontogenic inflammatory and developmental cysts Yasunori Takeda, Yuko Oikawa,
Reconstruction of large oroantral defects using a pedicled buccal fat pad
 Yang et al. Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery (2018) 40:7 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40902-018-0144-6 Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery CASE REPORT Open Access Reconstruction
Yang et al. Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery (2018) 40:7 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40902-018-0144-6 Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery CASE REPORT Open Access Reconstruction
Cystic carcinoma of the neck
 Case Report Brunei Int Med J. 2010; 6 (1): 56-60 Cystic carcinoma of the neck Prathibha Parampalli SUBRHAMANYA, Ghazala KAFEEL, Hla OO, Pemasiri Upali TELISINGHE, Department of Pathology, RIPAS Hospital,
Case Report Brunei Int Med J. 2010; 6 (1): 56-60 Cystic carcinoma of the neck Prathibha Parampalli SUBRHAMANYA, Ghazala KAFEEL, Hla OO, Pemasiri Upali TELISINGHE, Department of Pathology, RIPAS Hospital,
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Case Report Orthokeratinized Odontogenic Cyst: A Case Report- A Milder Variant of OKC or an Independent Entity Mariyam
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Case Report Orthokeratinized Odontogenic Cyst: A Case Report- A Milder Variant of OKC or an Independent Entity Mariyam
Papillary verrucous lesion of the oral mucosa: A need for detailed histopathological examination
 Case report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18320/jimd/201502.03163 JOURNAL OF INTERNATIONAL MEDICINE AND DENTISTRY To search..to know...to share p-issn: 2454-8847 e-issn: 2350-045X Papillary verrucous lesion
Case report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18320/jimd/201502.03163 JOURNAL OF INTERNATIONAL MEDICINE AND DENTISTRY To search..to know...to share p-issn: 2454-8847 e-issn: 2350-045X Papillary verrucous lesion
Large Dentigerous Cyst
 Volume 16.2.1 Feb 2016 This Lecture Series qualifies for 0.5 Informal CPD Learning Hours Large Dentigerous Cyst By Dr Hassem Geha A 55 year-old male presented with a painless swelling in the right mandible.
Volume 16.2.1 Feb 2016 This Lecture Series qualifies for 0.5 Informal CPD Learning Hours Large Dentigerous Cyst By Dr Hassem Geha A 55 year-old male presented with a painless swelling in the right mandible.
Peripheral Odontogenic Fibroma: A rare case report
 Annals of Dental Research (2013) Vol 3 (1): 10-14 HATAM Publishers: All Rights Reserved Annals of Dental Research www.hgpub.com www.adres.yolasite.com Case Report Peripheral Odontogenic Fibroma: A rare
Annals of Dental Research (2013) Vol 3 (1): 10-14 HATAM Publishers: All Rights Reserved Annals of Dental Research www.hgpub.com www.adres.yolasite.com Case Report Peripheral Odontogenic Fibroma: A rare
Primary Intra-Osseous Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Mandible - A Case Report
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 9 Ver. VI (September). 2016), PP 66-70 www.iosrjournals.org Primary Intra-Osseous Squamous
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 9 Ver. VI (September). 2016), PP 66-70 www.iosrjournals.org Primary Intra-Osseous Squamous
Case Report Basal Cell Ameloblastoma of Mandible: A Rare Case Report with Review
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 187820, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/187820 Case Report Basal Cell Ameloblastoma of Mandible: A Rare Case Report with Review Hemant Shakya, 1
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 187820, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/187820 Case Report Basal Cell Ameloblastoma of Mandible: A Rare Case Report with Review Hemant Shakya, 1
Carcinoma of Unknown Primary site (CUP) in HEAD & NECK SURGERY
 Carcinoma of Unknown Primary site (CUP) in HEAD & NECK SURGERY SEARCHING FOR THE PRIMARY? P r o f J P P r e t o r i u s H e a d : C l i n i c a l U n i t C r i t i c a l C a r e U n i v e r s i t y O f
Carcinoma of Unknown Primary site (CUP) in HEAD & NECK SURGERY SEARCHING FOR THE PRIMARY? P r o f J P P r e t o r i u s H e a d : C l i n i c a l U n i t C r i t i c a l C a r e U n i v e r s i t y O f
Clinical details: Details of scan: CONE BEAM CT REPORT: Name: H. B. Gender: Reason for referral: Referred by:
 Name: H. B. Gender: Male DOB: 11/12/1950 Age: 64 Date taken: 16/11/2015 Date reported: 19/11/2015 Clinical details: Reason for referral: Referred by: Investigate symptoms related to left TMJ. Reconstructed
Name: H. B. Gender: Male DOB: 11/12/1950 Age: 64 Date taken: 16/11/2015 Date reported: 19/11/2015 Clinical details: Reason for referral: Referred by: Investigate symptoms related to left TMJ. Reconstructed
Cholesterol granuloma of the jaws: report of two cases
 Cholesterol granuloma of the jaws: report of two cases Pages with reference to book, From 15 To 17 Alper Alkan, Osman Etoz ( Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Erciyes University, Faculty of
Cholesterol granuloma of the jaws: report of two cases Pages with reference to book, From 15 To 17 Alper Alkan, Osman Etoz ( Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Erciyes University, Faculty of
MALAYSIAN DENTAL JOURNAL. Primary Intraosseous Squamous Cell Carcinoma: An Incidental Finding
 MALAYSIAN DENTAL JOURNAL Primary Intraosseous Squamous Cell Carcinoma: An Incidental Finding Yew CC 1, Abd Ghani N 1, Jamal Din SKK 2, Najar Din MY 3 1 Dental Officer, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial
MALAYSIAN DENTAL JOURNAL Primary Intraosseous Squamous Cell Carcinoma: An Incidental Finding Yew CC 1, Abd Ghani N 1, Jamal Din SKK 2, Najar Din MY 3 1 Dental Officer, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial
NASAL SEPTUM ADENOID CYSTIC CARCINOMA: A CASE REPORT
 NASAL SEPTUM ADENOID CYSTIC CARCINOMA: A CASE REPORT Shu-Yu Tai, 1 Chen-Yu Chien, 2 Chih-Feng Tai, 2,4 Wen-Rei Kuo, 2,4 Wan-Ting Huang, 3 and Ling-Feng Wang 2,4 Departments of 1 Family Medicine, 2 Otolaryngology
NASAL SEPTUM ADENOID CYSTIC CARCINOMA: A CASE REPORT Shu-Yu Tai, 1 Chen-Yu Chien, 2 Chih-Feng Tai, 2,4 Wen-Rei Kuo, 2,4 Wan-Ting Huang, 3 and Ling-Feng Wang 2,4 Departments of 1 Family Medicine, 2 Otolaryngology
Management of Neck Metastasis from Unknown Primary
 Management of Neck Metastasis from Unknown Primary.. Definition Histologic evidence of malignancy in the cervical lymph node (s) with no apparent primary site of original tumour Diagnosis after a thorough
Management of Neck Metastasis from Unknown Primary.. Definition Histologic evidence of malignancy in the cervical lymph node (s) with no apparent primary site of original tumour Diagnosis after a thorough
Inter-radicular Radiolucencies
 Inter-radicular Radiolucencies Differential Diagnosis Laterally Displaced Radicular Cyst Accessory canals Root fracture Lateral Periodontal Cyst Botryoid variant Odontogenic Keratocyst Incisive Canal Cyst
Inter-radicular Radiolucencies Differential Diagnosis Laterally Displaced Radicular Cyst Accessory canals Root fracture Lateral Periodontal Cyst Botryoid variant Odontogenic Keratocyst Incisive Canal Cyst
Proceedings of the 36th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 36th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA Oct. 14-17, 2011 Jeju, Korea Next Congress: http://www.ivis.org October 14(Fri) ~ 17(Mon) 2011 ICC Jeju, Korea 2011 WSAVA
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 36th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA Oct. 14-17, 2011 Jeju, Korea Next Congress: http://www.ivis.org October 14(Fri) ~ 17(Mon) 2011 ICC Jeju, Korea 2011 WSAVA
Problem diagnoses. Current issues in Anatomic pathology. Problem Diagnoses in Tumors of the Oral Cavity 5/29/2009
 Current issues in Anatomic pathology Problem Diagnoses in Tumors of the Oral Cavity Richard Jordan DDS PhD FRCPath Professor of Oral Pathology & Pathology Director, UCSF Oral Pathology Diagnostic Laboratory
Current issues in Anatomic pathology Problem Diagnoses in Tumors of the Oral Cavity Richard Jordan DDS PhD FRCPath Professor of Oral Pathology & Pathology Director, UCSF Oral Pathology Diagnostic Laboratory
CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA PRESENTING AS UNILOCULAR RADIOLUCENCY IN POSTERIOR MANDIBLE A CASE REPORT
 IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 Case Report CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA PRESENTING AS UNILOCULAR RADIOLUCENCY IN POSTERIOR MANDIBLE A CASE REPORT S. Aruleena Shaminey 1, G.
IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 Case Report CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA PRESENTING AS UNILOCULAR RADIOLUCENCY IN POSTERIOR MANDIBLE A CASE REPORT S. Aruleena Shaminey 1, G.
A case of orthokeratinizing odontogenic cyst in the mandible
 114 J Meikai Dent Med 44 1, 114 118, 2015 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 2 1 46 A case of orthokeratinizing odontogenic cyst in the mandible Nobuaki TAMURA 1, Hiroshi TAKESHIMA 1, Kentaro KIKUCHI
114 J Meikai Dent Med 44 1, 114 118, 2015 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 2 1 46 A case of orthokeratinizing odontogenic cyst in the mandible Nobuaki TAMURA 1, Hiroshi TAKESHIMA 1, Kentaro KIKUCHI
Case Presentation: Figure 1. Palatal lesion. Figure 2. Panoramic xray
 Case Presentation: A 10-year-old girl presented with a hard palatal mass that had been progressively increasing in size for the last 4 months, as reported by her dentist. Two months previously, her dentist
Case Presentation: A 10-year-old girl presented with a hard palatal mass that had been progressively increasing in size for the last 4 months, as reported by her dentist. Two months previously, her dentist
高雄醫學大學 口腔醫學院 口腔病理影像科 牙科 X 光影像判讀 教學範例
 高雄醫學大學 口腔醫學院 口腔病理影像科 牙科 X 光影像判讀 教學範例 Content Image No. 001 Dentigerous cyst over left upper embedded canine--------------------- 頁 1 Image No. 002---------------------------------------------------------------
高雄醫學大學 口腔醫學院 口腔病理影像科 牙科 X 光影像判讀 教學範例 Content Image No. 001 Dentigerous cyst over left upper embedded canine--------------------- 頁 1 Image No. 002---------------------------------------------------------------
MULTILOCULAR AMELOBLASTOMA OF MANDIBLE-A CASE REPORT
 International Journal of Advancements in Research & Technology, Volume 2, Issue2, February-2013 1 MULTILOCULAR AMELOBLASTOMA OF MANDIBLE-A CASE REPORT DR SANTOSH KUMAR SUBUDHI*, DR SUMIT DASH**, DR.K..PREMANANDA***,
International Journal of Advancements in Research & Technology, Volume 2, Issue2, February-2013 1 MULTILOCULAR AMELOBLASTOMA OF MANDIBLE-A CASE REPORT DR SANTOSH KUMAR SUBUDHI*, DR SUMIT DASH**, DR.K..PREMANANDA***,
Ameloblastic Carcinoma-Secondary Type,A Rare Case Report and Distinction from Malignant Ameloblastoma
 Ameloblastic Carcinoma-Secondary Type,A Rare Case Report and Distinction from Malignant Ameloblastoma Rajesh B Dhirawani, Sumit Asrani, Anshalika Agrawal, Sauvik Singha* and Kshitij Aggarwal Department
Ameloblastic Carcinoma-Secondary Type,A Rare Case Report and Distinction from Malignant Ameloblastoma Rajesh B Dhirawani, Sumit Asrani, Anshalika Agrawal, Sauvik Singha* and Kshitij Aggarwal Department
Kidney Case 1 SURGICAL PATHOLOGY REPORT
 Kidney Case 1 Surgical Pathology Report February 9, 2007 Clinical History: This 45 year old woman was found to have a left renal mass. CT urography with reconstruction revealed a 2 cm medial mass which
Kidney Case 1 Surgical Pathology Report February 9, 2007 Clinical History: This 45 year old woman was found to have a left renal mass. CT urography with reconstruction revealed a 2 cm medial mass which
Squamous cell carcinoma of the maxillary sinus mimicking periodontitis
 Squamous cell carcinoma of the maxillary sinus mimicking periodontitis 저자저널명발행기관 NDSL URL Na, Ji Yeon ; Kang, Joo Hyun ; Choi, Seong-Ho ; Jeong, Ho-Gul ; Han, Sang-Sun 大韓齒科醫師協會誌 = The journal of the Korean
Squamous cell carcinoma of the maxillary sinus mimicking periodontitis 저자저널명발행기관 NDSL URL Na, Ji Yeon ; Kang, Joo Hyun ; Choi, Seong-Ho ; Jeong, Ho-Gul ; Han, Sang-Sun 大韓齒科醫師協會誌 = The journal of the Korean
Da Costa was the first to coin the term. Marjolin s Ulcer: A Case Report and Literature Review. Case Report. Introduction
 E-Da Medical Journal 2016;3(2):24-28 Case Report Marjolin s Ulcer: A Case Report and Literature Review Yue-Chiu Su 1, Li-Ren Chang 2 Marjolin s ulcer is an aggressive cutaneous malignancy, which is common
E-Da Medical Journal 2016;3(2):24-28 Case Report Marjolin s Ulcer: A Case Report and Literature Review Yue-Chiu Su 1, Li-Ren Chang 2 Marjolin s ulcer is an aggressive cutaneous malignancy, which is common
CLINICAL EXPERIENCE OF ORAL VERRUCOUS CARCINOMA IN CENTRAL INDIA POPULATION: A PROSPECTIVE STUDY
 Official publication of Foundation for Head & Neck oncology of India www.jhnps.weebly.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE CLINICAL EXPERIENCE OF ORAL VERRUCOUS CARCINOMA IN CENTRAL INDIA POPULATION: A PROSPECTIVE STUDY
Official publication of Foundation for Head & Neck oncology of India www.jhnps.weebly.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE CLINICAL EXPERIENCE OF ORAL VERRUCOUS CARCINOMA IN CENTRAL INDIA POPULATION: A PROSPECTIVE STUDY
Pharmacologyonline 2: (2008) Young Researchers Gavasova and Budev EPULIS FISSURATUM CLINICAL APPEARANCE AND TREATMENT. Dr G.Gavasova, Dr I.
 EPULIS FISSURATUM CLINICAL APPEARANCE AND TREATMENT Dr G.Gavasova, Dr I.Budev Medical University, Faculty of Dental Medicine Oral Surgery Department Head: Prof. Dr D. Atanasov, Ph.D, MD. Summary Continuous
EPULIS FISSURATUM CLINICAL APPEARANCE AND TREATMENT Dr G.Gavasova, Dr I.Budev Medical University, Faculty of Dental Medicine Oral Surgery Department Head: Prof. Dr D. Atanasov, Ph.D, MD. Summary Continuous
SALIVARY GLAND DISEASES. Omar alnoubani MD,MRCS
 SALIVARY GLAND DISEASES Omar alnoubani MD,MRCS Salivary Glands Overview Parotid gland Sublingual gland Submandibular gland Salivary glands - Types 3 Major Salivary Glands Parotid Submandibular Sublingual
SALIVARY GLAND DISEASES Omar alnoubani MD,MRCS Salivary Glands Overview Parotid gland Sublingual gland Submandibular gland Salivary glands - Types 3 Major Salivary Glands Parotid Submandibular Sublingual
AMELOBLASTIC CARCINOMA OF
 AMELOBLASTIC CARCINOMA OF MANDIBLE- A Rare Case Report with Review of Literature Mubeen K (1), Shakya HK (2), Jigna VR (3) (1) MDS, Professor and Head of Department, Department of Oral Medicine and Radiology,
AMELOBLASTIC CARCINOMA OF MANDIBLE- A Rare Case Report with Review of Literature Mubeen K (1), Shakya HK (2), Jigna VR (3) (1) MDS, Professor and Head of Department, Department of Oral Medicine and Radiology,
Oral Verrucous Carcinoma and Ameloblastoma: A Rare Coincidence
 Case Report Iranian Journal of Otorhinolaryngology, Vol.27 (2), Serial No.79, Mar 2015 Abstract Oral Verrucous Carcinoma and Ameloblastoma: A Rare Coincidence * Zohreh Dalirsani 1, Farnaz Falaki 2, Nooshin
Case Report Iranian Journal of Otorhinolaryngology, Vol.27 (2), Serial No.79, Mar 2015 Abstract Oral Verrucous Carcinoma and Ameloblastoma: A Rare Coincidence * Zohreh Dalirsani 1, Farnaz Falaki 2, Nooshin
SQUAMOUS ODONTOGENIC TUMOUR: REPORT OF FIVE CASES FROM NIGERIA AND REVIEW OF LITERATURE
 African Journal of Oral Health Volume 3 Numbers 1&2, 2006:1-5 REFEREED ARTICLE SQUAMOUS ODONTOGENIC TUMOUR: REPORT OF FIVE CASES FROM NIGERIA AND REVIEW OF LITERATURE Adebiyi K.E., Odukoya O., Taiwo, E.O.
African Journal of Oral Health Volume 3 Numbers 1&2, 2006:1-5 REFEREED ARTICLE SQUAMOUS ODONTOGENIC TUMOUR: REPORT OF FIVE CASES FROM NIGERIA AND REVIEW OF LITERATURE Adebiyi K.E., Odukoya O., Taiwo, E.O.
IN THE NAME OF GOD. Dr.kheirandish DDS,MSC Oral and maxillofacial pathology
 IN THE NAME OF GOD Dr.kheirandish DDS,MSC Oral and maxillofacial pathology ODONTOGENIC CYSTS AND TUMORS Chapter 15 I. DENTIGEROUS CYST II. III. IV. ERUPTION CYST ODONTOGENIC KERATOCYST Orthokeratinized
IN THE NAME OF GOD Dr.kheirandish DDS,MSC Oral and maxillofacial pathology ODONTOGENIC CYSTS AND TUMORS Chapter 15 I. DENTIGEROUS CYST II. III. IV. ERUPTION CYST ODONTOGENIC KERATOCYST Orthokeratinized
[ 06-10] Dr. B. Siva Reddy, Dr. B. Ajay Reginald, Dr. D. Sireesha, Dr. Meda Samatha India Abstract: Keywords ARTICLE 20/07/ /09/2018
![[ 06-10] Dr. B. Siva Reddy, Dr. B. Ajay Reginald, Dr. D. Sireesha, Dr. Meda Samatha India Abstract: Keywords ARTICLE 20/07/ /09/2018 [ 06-10] Dr. B. Siva Reddy, Dr. B. Ajay Reginald, Dr. D. Sireesha, Dr. Meda Samatha India Abstract: Keywords ARTICLE 20/07/ /09/2018](/thumbs/87/95905171.jpg) Dentigerous Cyst Associated with an Impacted Mesiodens: A Rare Case Report with Review of Literature [PP: 06-10] Dr. B. Siva Reddy, Dr. B. Ajay Reginald, Dr. D. Sireesha, Dr. Meda Samatha, Department of
Dentigerous Cyst Associated with an Impacted Mesiodens: A Rare Case Report with Review of Literature [PP: 06-10] Dr. B. Siva Reddy, Dr. B. Ajay Reginald, Dr. D. Sireesha, Dr. Meda Samatha, Department of
Ameoblastic carcinoma of mandible - A rare case report with review of literature
 Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Case report doi:10.4317/jced.2.e100 Ameoblastic carcinoma of mandible - A rare case report with review of literature K Mubeen 1, Hemant Kumar
Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Case report doi:10.4317/jced.2.e100 Ameoblastic carcinoma of mandible - A rare case report with review of literature K Mubeen 1, Hemant Kumar
CONCURRENT EXTRAVASATION MUCOCELE AND EPIDERMOID CYST OF THE LOWER LIP: A CASE REPORT
 Mucocele and epidermoid cyst CONCURRENT EXTRAVASATION MUCOCELE AND EPIDERMOID CYST OF THE LOWER LIP: A CASE REPORT Wen-Chen Wang, Li-Min Lin, Yee-Hsiung Shen, 1 Yu-Ju Lin, and Yuk-Kwan Chen Departments
Mucocele and epidermoid cyst CONCURRENT EXTRAVASATION MUCOCELE AND EPIDERMOID CYST OF THE LOWER LIP: A CASE REPORT Wen-Chen Wang, Li-Min Lin, Yee-Hsiung Shen, 1 Yu-Ju Lin, and Yuk-Kwan Chen Departments
A COMPARATIVE HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY OF EPITHELIAL linings OF ODONTOGENIC CYSTS AND UNICYSTIC AMElOBlASTOMAS
 A COMPARATIVE HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY OF EPITHELIAL linings OF ODONTOGENIC CYSTS AND UNICYSTIC AMElOBlASTOMAS J Sudiono, RB Zain. A Comparative Histopathological Study of Epithelial Linings of Odontogenic
A COMPARATIVE HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY OF EPITHELIAL linings OF ODONTOGENIC CYSTS AND UNICYSTIC AMElOBlASTOMAS J Sudiono, RB Zain. A Comparative Histopathological Study of Epithelial Linings of Odontogenic
A Case Report of Odontogenic Keratocyst in Anterior Mandibule Position
 A Case Report of Odontogenic Keratocyst in Anterior Mandibule Position Malihe Moeini 1, Seyed Ehsan Anvar 2, Rasool Barzegari Bafghi 3* 1.Resident of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, Faculty of Dentistry,
A Case Report of Odontogenic Keratocyst in Anterior Mandibule Position Malihe Moeini 1, Seyed Ehsan Anvar 2, Rasool Barzegari Bafghi 3* 1.Resident of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, Faculty of Dentistry,
Ghost Cell Odontogenic Carcinoma Arising from Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor: A Case Report
 The Korean Journal of Pathology 2012; 46: 478-482 CASE REPORT Ghost Cell Odontogenic Carcinoma Arising from Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor: A Case Report Zhi-Yu Zhu Zhi-Gang Chu 1 Yu Chen Wei-Ping
The Korean Journal of Pathology 2012; 46: 478-482 CASE REPORT Ghost Cell Odontogenic Carcinoma Arising from Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor: A Case Report Zhi-Yu Zhu Zhi-Gang Chu 1 Yu Chen Wei-Ping
Yoshihide OTA, Kazunari KARAKIDA, Daisuke WATANABE, Muneo MIYASAKA and Keiichi TSUKINOKI
 Tokai J Exp Clin Med., Vol. 23, No. 4, pp.157-165, 1998 A Case of Central Carcinoma of the Mandible Arising from a Recurrent Odontogenic Keratocyst : Delineation of Surgical Margins and Reconstruction
Tokai J Exp Clin Med., Vol. 23, No. 4, pp.157-165, 1998 A Case of Central Carcinoma of the Mandible Arising from a Recurrent Odontogenic Keratocyst : Delineation of Surgical Margins and Reconstruction
Glandular odontogenic cyst associated with ameloblastoma: Case report and review of the literature
 Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Case Report doi:10.4317/jced.53775 http://dx.doi.org/10.4317/jced.53775 : Case report and review of the literature Timothée Cousin 1, Samuel
Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Case Report doi:10.4317/jced.53775 http://dx.doi.org/10.4317/jced.53775 : Case report and review of the literature Timothée Cousin 1, Samuel
Central odontogenic fibroma of the mandible: a case report
 457 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 51, No. 3, 457-461, 2009 Case Report Central odontogenic fibroma of the mandible: a case report Ioanna Daskala 1), Demos Kalyvas 2), Markos Kolokoudias 2), Dimitris Vlachodimitropoulos
457 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 51, No. 3, 457-461, 2009 Case Report Central odontogenic fibroma of the mandible: a case report Ioanna Daskala 1), Demos Kalyvas 2), Markos Kolokoudias 2), Dimitris Vlachodimitropoulos
The clinical appearance and diagnosis of odontogenic cysts. SE Arc-Állcsont-Szájsebészeti és Fogászati Klinika BUDAPEST
 The clinical appearance and diagnosis of odontogenic cysts SE Arc-Állcsont-Szájsebészeti és Fogászati Klinika BUDAPEST DEFINITION A cyst is a sac with walls of connective tissue, lined by epithelium, containing
The clinical appearance and diagnosis of odontogenic cysts SE Arc-Állcsont-Szájsebészeti és Fogászati Klinika BUDAPEST DEFINITION A cyst is a sac with walls of connective tissue, lined by epithelium, containing
Head & Neck Case # 1
 DISCHARGE SUMMARY Head & Neck Case # 1 Date of Admission: 10/30/2010 Date of Discharge: 11/02/2010 Present Medical History: The patient is a 33-year-old lady with a history of right superior alveolar ridge
DISCHARGE SUMMARY Head & Neck Case # 1 Date of Admission: 10/30/2010 Date of Discharge: 11/02/2010 Present Medical History: The patient is a 33-year-old lady with a history of right superior alveolar ridge
Head and Neck Case 1 PATIENT HISTORY
 Head and Neck Case 1 PATIENT HISTORY Patient History May 7, 2007 Otolaryngology Head & Neck Subjective: Patient was recently seen by a dentist, who noted a roughness in his lower alveolus, and wanted to
Head and Neck Case 1 PATIENT HISTORY Patient History May 7, 2007 Otolaryngology Head & Neck Subjective: Patient was recently seen by a dentist, who noted a roughness in his lower alveolus, and wanted to
Treatment Modalities of Odontogenic Keratocyst of Maxilla and Mandible: Our Experience
 wjd Parveen Akhter Lone et al Original Research 10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1344 Treatment Modalities of Odontogenic Keratocyst of Maxilla and Mandible: Our Experience 1 Parveen Akhter Lone, 2 Mohan Singh,
wjd Parveen Akhter Lone et al Original Research 10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1344 Treatment Modalities of Odontogenic Keratocyst of Maxilla and Mandible: Our Experience 1 Parveen Akhter Lone, 2 Mohan Singh,
Case Report A Rare Cutaneous Adnexal Tumor: Malignant Proliferating Trichilemmal Tumor
 Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 742920, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/742920 Case Report A Rare Cutaneous Adnexal Tumor: Malignant Proliferating Trichilemmal Tumor Omer Alici,
Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 742920, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/742920 Case Report A Rare Cutaneous Adnexal Tumor: Malignant Proliferating Trichilemmal Tumor Omer Alici,
Disclosure. Educational Objectives. Terminology. Odontogenic Cysts. Terminology
 Disclosure Lisa J. Koenig BChD, DDS, MS Professor & Program Director, Oral Medicine and Oral Radiology Marquette University School of Dentistry Consultant to Soredex for the Scanora 3D and 3Dx Author/Editor
Disclosure Lisa J. Koenig BChD, DDS, MS Professor & Program Director, Oral Medicine and Oral Radiology Marquette University School of Dentistry Consultant to Soredex for the Scanora 3D and 3Dx Author/Editor
Management of Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumour With Marsupialisation, Enucleation and Carnoy s Solution Application: A Case Report
 Management of Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumour With Marsupialisation, Enucleation and Carnoy s Solution Application: A Case Report Aydin Ozkan 1, Gurkan Rasit Bayar 2, Hasan Ayberk Altug 2, Metin Sencimen
Management of Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumour With Marsupialisation, Enucleation and Carnoy s Solution Application: A Case Report Aydin Ozkan 1, Gurkan Rasit Bayar 2, Hasan Ayberk Altug 2, Metin Sencimen
DISORDERS OF THE SALIVARY GLANDS Neoplasms Dr.M.Baskaran Selvapathy S IV
 DISORDERS OF THE SALIVARY GLANDS Neoplasms Dr.M.Baskaran Selvapathy S IV NEOPLASMS A) Epithelial I. Benign Pleomorphic adenoma( Mixed tumour) Adenolymphoma (Warthin s tumour) Oxyphil adenoma (Oncocytoma)
DISORDERS OF THE SALIVARY GLANDS Neoplasms Dr.M.Baskaran Selvapathy S IV NEOPLASMS A) Epithelial I. Benign Pleomorphic adenoma( Mixed tumour) Adenolymphoma (Warthin s tumour) Oxyphil adenoma (Oncocytoma)
Autologous Bone Augmentation in Combination with an Ameloblastoma in the Maxillary Region- A Case Report?
 Archives of Clinical and Medical Case Reports doi: 10.26502/acmcr.96550023 Volume 2, Issue 2 Case Report Autologous Bone Augmentation in Combination with an Ameloblastoma in the Maxillary Region- A Case
Archives of Clinical and Medical Case Reports doi: 10.26502/acmcr.96550023 Volume 2, Issue 2 Case Report Autologous Bone Augmentation in Combination with an Ameloblastoma in the Maxillary Region- A Case
PAPILLARY THYROID CARCINOMA PRESENTING AS A LATERAL NECK MASS MASS. Dr. Pamela Hanson DO PGY3
 PAPILLARY THYROID CARCINOMA PRESENTING AS A LATERAL NECK MASS MASS Dr. Pamela Hanson DO PGY3 MK CASE PRESENTATION 28 yo Female presented to the ENT Clinic in October 2016, with the complaint of chronic
PAPILLARY THYROID CARCINOMA PRESENTING AS A LATERAL NECK MASS MASS Dr. Pamela Hanson DO PGY3 MK CASE PRESENTATION 28 yo Female presented to the ENT Clinic in October 2016, with the complaint of chronic
Oral cancer: Prognosis & Treatment. Dr. Hani Al Sheikh Radhi
 Oral cancer: Prognosis & Treatment Dr. Hani Al Sheikh Radhi Prognostic factors in Oral caner TNM staging T stage N stage M stage Site Histological Factors Vascular & Perineural Invasion Surgical Margins
Oral cancer: Prognosis & Treatment Dr. Hani Al Sheikh Radhi Prognostic factors in Oral caner TNM staging T stage N stage M stage Site Histological Factors Vascular & Perineural Invasion Surgical Margins
PhD in Oral Surgery (50 Credit Hours)
 PhD in Oral Surgery (50 Credit Hours) First Semester (9 Credit Hours) OSRG 701 Oral Surgery I 1 OSRG 791 Oral Surgery Clinics I 2 OSRG 706 Applied Surgical Anatomy 1 OSRG 707 Pain and Anxiety Control 1
PhD in Oral Surgery (50 Credit Hours) First Semester (9 Credit Hours) OSRG 701 Oral Surgery I 1 OSRG 791 Oral Surgery Clinics I 2 OSRG 706 Applied Surgical Anatomy 1 OSRG 707 Pain and Anxiety Control 1
Carcinoma ex Pleomorphic Adenoma on Right Parotid Gland: A Case Report. School of Dentistry, Kyungpook National University
 Korean Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology 2017;41(4):189-194 ISSN:1225-1577(Print); 2384-0900(Online) Available online at http://journal.kaomp.org https://doi.org/10.17779/kaomp.2017.41.4.006
Korean Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology 2017;41(4):189-194 ISSN:1225-1577(Print); 2384-0900(Online) Available online at http://journal.kaomp.org https://doi.org/10.17779/kaomp.2017.41.4.006
INFLAMMATORY DENTIGEROUS CYST OR INFLAMMATORY CYSTIC LESIONS OF MIXED DENTITION?: A REPORT OF THREE CASES
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 03, Issue 03 INFLAMMATORY DENTIGEROUS CYST OR INFLAMMATORY CYSTIC LESIONS OF MIXED DENTITION?: A REPORT OF THREE CASES Pritam K Mankapure
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 03, Issue 03 INFLAMMATORY DENTIGEROUS CYST OR INFLAMMATORY CYSTIC LESIONS OF MIXED DENTITION?: A REPORT OF THREE CASES Pritam K Mankapure
ORAL MELANOMA Definition Epidemiology Clinical Presentation
 ORAL MELANOMA Definition Melanoma is a highly malignant neoplasia, arising from melanocytes, the cells that produce the brownish pigment melanin. Melanin is the determinant in skin colour and protects
ORAL MELANOMA Definition Melanoma is a highly malignant neoplasia, arising from melanocytes, the cells that produce the brownish pigment melanin. Melanin is the determinant in skin colour and protects
Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor : What radiologist needs to know?
 Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor : What radiologist needs to know? Poster No.: C-0444 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit K. El Karzazi, J. M. Villanueva Rincón, R. Corrales,
Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor : What radiologist needs to know? Poster No.: C-0444 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit K. El Karzazi, J. M. Villanueva Rincón, R. Corrales,
My Journey into the World of Salivary Gland Sebaceous Neoplasms
 My Journey into the World of Salivary Gland Sebaceous Neoplasms Douglas R. Gnepp Warren Alpert Medical School at Brown University Rhode Island Hospital Pathology Department Providence RI Asked to present
My Journey into the World of Salivary Gland Sebaceous Neoplasms Douglas R. Gnepp Warren Alpert Medical School at Brown University Rhode Island Hospital Pathology Department Providence RI Asked to present
Ameloblastomatous Gorlin s cyst
 319 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 49, No. 4, 319-323, 2007 Case Report Ameloblastomatous Gorlin s cyst Mala Kamboj 1) and Manish Juneja 2) 1) Department of Oral Pathology and Microbiology, U.P. King George
319 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 49, No. 4, 319-323, 2007 Case Report Ameloblastomatous Gorlin s cyst Mala Kamboj 1) and Manish Juneja 2) 1) Department of Oral Pathology and Microbiology, U.P. King George
ONCOLOGY LETTERS 10: , 2015
 ONCOLOGY LETTERS 10: 749-753, 2015 Inability of PET/CT to identify a primary sinonasal inverted papilloma with squamous cell carcinoma in a patient with a submandibular lymph node metastasis: A case report
ONCOLOGY LETTERS 10: 749-753, 2015 Inability of PET/CT to identify a primary sinonasal inverted papilloma with squamous cell carcinoma in a patient with a submandibular lymph node metastasis: A case report
Neoplasia 2018 Lecture 2. Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath
 Neoplasia 2018 Lecture 2 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. List the differences between benign and malignant tumors. 2. Recognize the histological features of malignancy. 3. Define dysplasia and understand
Neoplasia 2018 Lecture 2 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. List the differences between benign and malignant tumors. 2. Recognize the histological features of malignancy. 3. Define dysplasia and understand
Ortho keratinized Odontogenic Cyst of Mandible: A Rare Case Report
 Journal of Dental School 2015; 33(3): 233-237 Case Report Ortho keratinized Odontogenic Cyst of Mandible: A Rare Case Report 1 Soudabeh Sargolzaei 1 Fatemeh Mashhadi Abbas *2 Leila Hesami Moghadam 3 Sanaa
Journal of Dental School 2015; 33(3): 233-237 Case Report Ortho keratinized Odontogenic Cyst of Mandible: A Rare Case Report 1 Soudabeh Sargolzaei 1 Fatemeh Mashhadi Abbas *2 Leila Hesami Moghadam 3 Sanaa
Los Angeles Radiological Society 62 nd Annual Midwinter Radiology Conference January 31, 2010
 Los Angeles Radiological Society 62 nd Annual Midwinter Radiology Conference January 31, 2010 Self Assessment Module on Nuclear Medicine and PET/CT Case Review FDG PET/CT IN LYMPHOMA AND MELANOMA Submitted
Los Angeles Radiological Society 62 nd Annual Midwinter Radiology Conference January 31, 2010 Self Assessment Module on Nuclear Medicine and PET/CT Case Review FDG PET/CT IN LYMPHOMA AND MELANOMA Submitted
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences MUCOEPIDERMOID CARCINOMA OF MINOR SALIVARY GLAND-PALATE: ABSTRACT
 Case report Biosciences International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 MUCOEPIDERMOID CARCINOMA OF MINOR SALIVARY GLAND-PALATE: SHIVAKUMAR.S 1 AND SUBAIR VC 2 1 Professor, Department of
Case report Biosciences International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 MUCOEPIDERMOID CARCINOMA OF MINOR SALIVARY GLAND-PALATE: SHIVAKUMAR.S 1 AND SUBAIR VC 2 1 Professor, Department of
Diagnostic difficulties with lesions of the oral mucosa
 BDIAP London, November 2010 School of Clinical Dentistry University of Sheffield Diagnostic difficulties with lesions of the oral mucosa Paul M Speight Dept Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology University of
BDIAP London, November 2010 School of Clinical Dentistry University of Sheffield Diagnostic difficulties with lesions of the oral mucosa Paul M Speight Dept Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology University of
Disclosure. Acknowledgement. What is the Best Workup for Rectal Cancer Staging: US/MRI/PET? Rectal cancer imaging. None
 What is the Best Workup for Rectal Cancer Staging: US/MRI/PET? Zhen Jane Wang, MD Assistant Professor in Residence UC SF Department of Radiology Disclosure None Acknowledgement Hueylan Chern, MD, Department
What is the Best Workup for Rectal Cancer Staging: US/MRI/PET? Zhen Jane Wang, MD Assistant Professor in Residence UC SF Department of Radiology Disclosure None Acknowledgement Hueylan Chern, MD, Department
Dentigerous cyst associated with an impacted mesiodens: report of 2 cases
 Imaging Science in Dentistry 2012; 42 : 255-60 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2012.42.4.255 Dentigerous cyst associated with an impacted mesiodens: report of 2 cases Neha Khambete, Rahul Kumar*, Mukund
Imaging Science in Dentistry 2012; 42 : 255-60 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2012.42.4.255 Dentigerous cyst associated with an impacted mesiodens: report of 2 cases Neha Khambete, Rahul Kumar*, Mukund
Differential Diagnosis of Oral Masses. Palatal Lesions
 Differential Diagnosis of Oral Masses Palatal Lesions Palatal Masses Periapical Abscess Torus Palatinus Mucocele Lymphoid Hyperplasia Adenomatous Hyperplasia Benign Salivary Neoplasms Malignant Salivary
Differential Diagnosis of Oral Masses Palatal Lesions Palatal Masses Periapical Abscess Torus Palatinus Mucocele Lymphoid Hyperplasia Adenomatous Hyperplasia Benign Salivary Neoplasms Malignant Salivary
Successful Conservative Surgical Treatment of Ameloblastic Fibroma in the Posterior Maxilla : A Case Report
 http://dx.doi.org/10.5933/jkapd.2013.40.4.321 ISSN (print) 1226-8496 Successful Conservative Surgical Treatment of Ameloblastic Fibroma in the Posterior Maxilla : A Case Report Youngeun Lee 1, Hyojung
http://dx.doi.org/10.5933/jkapd.2013.40.4.321 ISSN (print) 1226-8496 Successful Conservative Surgical Treatment of Ameloblastic Fibroma in the Posterior Maxilla : A Case Report Youngeun Lee 1, Hyojung
A Case Report on Surgical Management of Odontogenic Keratocyst
 World Journal of Medical Sciences 10 (2): 212-216, 2014 ISSN 1817-3055 IDOSI Publications, 2014 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.wjms.2014.10.2.82185 A Case Report on Surgical Management of Odontogenic Keratocyst 1
World Journal of Medical Sciences 10 (2): 212-216, 2014 ISSN 1817-3055 IDOSI Publications, 2014 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.wjms.2014.10.2.82185 A Case Report on Surgical Management of Odontogenic Keratocyst 1
A Case of Squamous Cell Carcinoma Arising from Branchial Cleft Cyst
 Oral Science International, November 2008, p.135 140 Copyright 2008, Japanese Stomatology Society. All Rights Reserved. A Case of Squamous Cell Carcinoma Arising from Branchial Cleft Cyst Takashi Saito
Oral Science International, November 2008, p.135 140 Copyright 2008, Japanese Stomatology Society. All Rights Reserved. A Case of Squamous Cell Carcinoma Arising from Branchial Cleft Cyst Takashi Saito
Objectives. Atypical Glandular Cells. Atypical Endocervical Cells. Reactive Endocervical Cells
 2013 California Society of Pathologists 66 th Annual Meeting San Francisco, CA Atypical Glandular Cells to Early Invasive Adenocarcinoma: Cervical Cytology and Histology Christina S. Kong, MD Associate
2013 California Society of Pathologists 66 th Annual Meeting San Francisco, CA Atypical Glandular Cells to Early Invasive Adenocarcinoma: Cervical Cytology and Histology Christina S. Kong, MD Associate
Periapical central giant cell granuloma misdiagnosed as odontogenic cyst
 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2006.01107.x CLINICAL ARTICLE Periapical central giant cell granuloma misdiagnosed as odontogenic cyst T. Lombardi 1, M. Bischof 1,2, R. Nedir 1,2, D. Vergain 1, C. Galgano 3,
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2006.01107.x CLINICAL ARTICLE Periapical central giant cell granuloma misdiagnosed as odontogenic cyst T. Lombardi 1, M. Bischof 1,2, R. Nedir 1,2, D. Vergain 1, C. Galgano 3,
Esophageal Cancer Initially Thought to be Accompanied by a Solitary Metastasis to an Intrathoracic Paraaortic Lymph Node
 2012 66 5 417 421 Esophageal Cancer Initially Thought to be Accompanied by a Solitary Metastasis to an Intrathoracic Paraaortic Lymph Node a b* a a a a a a a b ʼ 418 Horio et al. Acta Med. Okayama Vol.
2012 66 5 417 421 Esophageal Cancer Initially Thought to be Accompanied by a Solitary Metastasis to an Intrathoracic Paraaortic Lymph Node a b* a a a a a a a b ʼ 418 Horio et al. Acta Med. Okayama Vol.
LARYNGEAL DYSPLASIA. Tomas Fernandez M; 3 rd year ENT resident, Son Espases University Hospital
 LARYNGEAL DYSPLASIA Tomas Fernandez M; 3 rd year ENT resident, Son Espases University Hospital INTRODUCTION Laryngeal cancer constitutes 1-2% of all malignancies diagnosed worldwide Survival is related
LARYNGEAL DYSPLASIA Tomas Fernandez M; 3 rd year ENT resident, Son Espases University Hospital INTRODUCTION Laryngeal cancer constitutes 1-2% of all malignancies diagnosed worldwide Survival is related
A Rare case of Tubercular Gingivitis Case Report
 Case Report A Rare case of Tubercular Gingivitis Case Report *Dr. Ansh Chugh 1, Dr. Firoz A Hakkim 2, Dr. Rajesh. V 3, Dr. Raghava Sharma 4 1: JUNIOR RESIDENT IN GENERAL MEDICINE 2: SENIOR RESIDENT IN
Case Report A Rare case of Tubercular Gingivitis Case Report *Dr. Ansh Chugh 1, Dr. Firoz A Hakkim 2, Dr. Rajesh. V 3, Dr. Raghava Sharma 4 1: JUNIOR RESIDENT IN GENERAL MEDICINE 2: SENIOR RESIDENT IN
Myoepithelial Carcinoma: A Rare Case Report with Review
 Review article: Myoepithelial Carcinoma: A Rare Case Report with Review Dr. Shilpa Parikh 1, *Dr. Bhavik Mavani 2, Dr. Jigna Shah 3,Dr.Sheetal Sharma 4 1 Professor, Dept of Oral Medicine & Radiology, Govt.
Review article: Myoepithelial Carcinoma: A Rare Case Report with Review Dr. Shilpa Parikh 1, *Dr. Bhavik Mavani 2, Dr. Jigna Shah 3,Dr.Sheetal Sharma 4 1 Professor, Dept of Oral Medicine & Radiology, Govt.
Merkel Cell Carcinoma Case # 2
 DISCHARGE SUMMARY Admitted: 10/11/2010 Discharged: 10/13/2010 Merkel Cell Carcinoma Case # 2 Chief Compliant: A 79 year old lady status post tumor on the scalp excision and left neck likely dissection
DISCHARGE SUMMARY Admitted: 10/11/2010 Discharged: 10/13/2010 Merkel Cell Carcinoma Case # 2 Chief Compliant: A 79 year old lady status post tumor on the scalp excision and left neck likely dissection
The future of health is digital
 Dated: XX/XX/XXXX Name: XXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXX Birth Date: XX/XX/XXXX Date of scan: XX/XX/XXXX Examination of the anatomical volume: The following structures are reviewed and evaluated for bilateral symmetry,
Dated: XX/XX/XXXX Name: XXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXX Birth Date: XX/XX/XXXX Date of scan: XX/XX/XXXX Examination of the anatomical volume: The following structures are reviewed and evaluated for bilateral symmetry,
AGGRESSIVE VARIANT OF ORAL VERRUCOUS CARCINOMA WITH EXTENSIVE MANDIBULAR INVOLVEMENT: A RARE CASE REPORT
 AGGRESSIVE VARIANT OF ORAL VERRUCOUS CARCINOMA WITH EXTENSIVE MANDIBULAR INVOLVEMENT: A RARE CASE REPORT Dr. R.S. Sathawane 1, Dr. Nikita Agrawal 2, Dr. Abhijeet Deoghare 3, Dr. Deepti Patel 2 1. Professor
AGGRESSIVE VARIANT OF ORAL VERRUCOUS CARCINOMA WITH EXTENSIVE MANDIBULAR INVOLVEMENT: A RARE CASE REPORT Dr. R.S. Sathawane 1, Dr. Nikita Agrawal 2, Dr. Abhijeet Deoghare 3, Dr. Deepti Patel 2 1. Professor
Polymorphous Low-Grade. December 5 th, 2008
 Polymorphous Low-Grade Adenocarcinoma December 5 th, 2008 Epidemiology Represents 2 nd or 3 rd most common minor salivary gland malignancy (17-26%) 1 st mucoepidermoid carcinoma Rare in reported Asian
Polymorphous Low-Grade Adenocarcinoma December 5 th, 2008 Epidemiology Represents 2 nd or 3 rd most common minor salivary gland malignancy (17-26%) 1 st mucoepidermoid carcinoma Rare in reported Asian
FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATION OF ENLARGED LYMPH NODE: Metastatic squamous cell carcinoma
 Case Scenario 1 HNP: A 70 year old white male presents with dysphagia. The patient is a current smoker, current user of alcohol and is HPV positive. A CT of the Neck showed mass in the left pyriform sinus.
Case Scenario 1 HNP: A 70 year old white male presents with dysphagia. The patient is a current smoker, current user of alcohol and is HPV positive. A CT of the Neck showed mass in the left pyriform sinus.
A CASE OF A Huge Submandibular Pleomorphic Adenoma
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery Volume 4 Number 2 S VERMA Citation S VERMA.. The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery. 2009 Volume 4 Number 2. Abstract Pleomorphic adenoma
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery Volume 4 Number 2 S VERMA Citation S VERMA.. The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery. 2009 Volume 4 Number 2. Abstract Pleomorphic adenoma
