CORRELATION STUDY OF PLAQUE AND GINGIVAL INDEXES OF MOTHERS AND THEIR CHILDREN
|
|
|
- Evangeline Fields
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 or J Appl Oral Sci 2005; 13(3): CORRELATION STUDY OF PLAQUE AND GINGIVAL INDEXES OF MOTHERS AND THEIR CHILDREN ESTUDO DA CORRELAÇÃO DOS ÍNDICES DE PLACA E GENGIVAL EM MÃES E FILHOS Ana Cláudia Durante RAMIRES-ROMITO 1, Luciana Butini OLIVEIRA 2, Giuseppe Alexandre ROMITO 3 Márcia Pinto Alves MAYER 4, Célia Regina Martins Delgado RODRIGUES 5 1- DDS, MSc, PhD, Graduate student (Doctor degree), Department of Dental Materials, University of São Paulo. 2- DDS, MSc, PhD, Graduate student (Doctor degree), Department of Orthodontics and Pediatric Dentistry, University of São Paulo. 3- DDS, MSc, PhD, Assistant Professor, Department of Stomatology, University of São Paulo. 4- DDS, MSc, PhD, Associate Professor, Department of Microbiology, University of São Paulo. 5- DDS, MSc, PhD, Associate Professor, Department of Orthodontics and Pediatric Dentistry, University of São Paulo. Corresponding adress: Dra. Célia Regina Martins Delgado Rodrigues - Universidade de São Paulo - Departamento de Ortodontia e Odontopediatria Av. Prof Lineu Prestes, 2227, São Paulo, SP, Brasil. - Tel/Fax: celiadr@usp.br Received: April 26, Modification: June 21, Accepted: April 15, ABSTRACT T his study aimed to compare the periodontal condition between plaque and gingival indexes in 30 pairs of mother and child with mixed dentition, as well as to correlate the findings with some of their social and oral hygiene habits. Mother s and child s plaque and gingival indexes were recorded during clinical examination. Periapical and bitewing radiographs were taken in order to assess the presence of any pathologic bone loss. Questionnaires answered by the mothers were used to collect information regarding the mother s and the child s habits of tooth hygiene and the mother s job, instruction level and family income. The data collected from the mothers group and from the children s group were statistically analyzed both separately and with the two groups together. From the statistical analyses (Pearson correlation test, student test and Covariance analysis), it was possible to conclude that there was a greater correlation between the plaque and gingival indexes in the mothers group than in the children s group. No significant correlation between plaque and gingival indexes could be found between the pairs. Also, bone loss and plaque and gingival indexes in the children did not show any correlation. The mothers plaque indexes increased with age and decreased when they flossed everyday and when they had a job. The children s plaque indexes were lower when they had their tooth hygiene done by their mothers, when the latter had declared that they flossed their children s teeth everyday, and also when the mothers had a job. Children s gingival indexes increased with age and decreased when they brushed their teeth more often, when their mothers had a job and when their mothers declared they are used to flossing every day. Uniterms: Periodontal disease; Plaque and gingival indexes; Oral hygiene habits; Mothers; Children. RESUMO O objetivo deste estudo foi comparar a condição periodontal em 30 pares de mães e crianças com dentição mista, através dos índices de placa e gengival, bem como verificar sua correlação com alguns aspectos sociais e hábitos de higiene oral. No exame clínico foram registrados o índice de placa (IP) e índice gengival (IG) e, em seguida, foram realizadas tomadas radiográficas periapicais e interproximais que possibilitaram avaliar a possível presença de perdas ósseas em mães e crianças. Através de questionários, foram colhidas informações a respeito dos hábitos de higiene oral das mães e crianças, nível de escolaridade da mãe, se a mãe trabalhava fora e a renda familiar. Após análise estatística (Teste de Correlação de Pearson; test t de Student; Análise de Covariância), concluiu-se que houve maior correlação entre os índices de placa e gengival composto por adultos do que no grupo de crianças. Não foi encontrada correlação significante entre os índices de placa e gengival nos pares de mães e crianças. Não foi encontrada nenhuma correlação significante entre perda óssea e os índices de placa ou gengival dos pares. O índice de placa total das mães aumentou a idade e diminuiu quando a mãe utilizava fio dental diariamente e quando esta trabalhava fora. O índice gengival total das mães também foi reduzido quando elas trabalhavam fora. Houve redução no índice de placa total da criança quando a mãe a auxiliava durante a escovação, quando a mãe utilizava fio dental diariamente e quando esta trabalhava fora. O índice gengival total da criança foi maior com o aumento da idade e foi reduzido com aumento da sua freqüência de escovação, quando a mãe utilizava fio dental diariamente e quando a mãe trabalhava fora. Unitermos: Doença periodontal; Índices de placa e gengival; Hábitos de higiene oral; Mães; Crianças.
2 CORRELATION STUDY OF PLAQUE AND GINGIVAL INDEXES OF MOTHERS AND THEIR CHILDREN INTRODUCTION Periodontal disease is one of the main causes for tooth loss. Damage to tissues occurs due to an interaction of specific bacterial and host s factors (Bimstein, et al ). The role of dental plaque as the primary etiologic agent in gingivitis has been demonstrated in classic studies of experimental gingivitis in adults (Theilade, et al. 24, 1966) and children (Mackler and Crawford 12, 1973; Matsson 13, 1978; Parfitt 17, 1957). Little correlation between plaque presence and gingivitis has been reported in pre-school children (Mackler and Crawford 12, 1973; Matsson and Goldberg 14, 1985; Parfitt 17, 1957), probably due to age-related bacteriological differences and/or differences in the immune response between children and adults (Bimstein and Ebersole 4, 1989; Matsson 13, 1978; Morinushi, et al. 16, 2000; Parfitt 17, 1957). Furthermore, a hormonal influence is strongly suggested on the gingival inflammatory process concomitant to pre-puberty and puberty (Parfitt 17, 1957; Peretz, et al. 18, 1993; Peretz, et al. 19, 1996). During the mixed dentition, similar amounts of gingival inflammation are observed in permanent and deciduous teeth (Matsson and Goldberg 14, 1985; Ramberg, et al. 21, 1994). Although the severity of gingivitis is less intense in children than in adults (Mackler and Crawford 12, 1973; Matsson and Goldberg 14, 1985), periodontitis may occur in children and adolescents (Albandar, et al. 1, 1995; Bimstein, et al. 6 ; 1996). The early colonization by highly virulent organisms and/or an impaired host response are associated to the etiology of early-onset periodontitis, although local factors such as presence of carious cavities may also influence attachment loss (Albandar, et al. 1, 1995). The familial environment has been considered as the main source of pathogenic organisms and also influences the establishment of long-lasting habits, including tooth cleaning (Li and Caufield 9, 1995; Von Troil-Lindén, et al. 25, 1995). Studies have demonstrated the similarity of the microbiota between mother/child, considering both cariogenic or periodontal pathogenic organisms such as Streptococcus mutans and Prevotella intermedia (Caufield, et al. 7, 1993; Könönen, et al. 8 ; 1994; Matsson 13, 1978; Matsson and Goldberg 15, 1986). The periodontal conditions of mothers and their children may also correlate (Löe and Silness 10, 1963). However, very few studies correlated the clinical variables in pairs of mother and their children with mixed dentition, with reported habits. The aim of the present study was to assess the periodontal conditions in terms of plaque and gingival indexes and alveolar bone loss of mothers and children with mixed dentition. The clinical findings were also correlated with reported social conditions and oral hygiene habits. MATERIAL AND METHODS The study group was formed by thirty pairs of mothers (29 to 49 years old, mean ± 5.17) and children with mixed dentition (7 to 11 years old, mean 8.67 ± 0.92). The children were selected among those selected for treatment at the Department of Orthodontics and Pediatric Dentistry at the Dental School of University of São Paulo. The patients had not taken antibiotics at least for the last three months before the exam. The procedures, possible discomforts or risks, as well as the benefits of this study were fully explained to the subjects involved, and their informed consent was obtained prior to the investigation. This study was reviewed and approved by Ethics Committee of the University of São Paulo. Information about medical and dental history of each subject was obtained during the anamnesis. A dentist interviewed children s mothers about their oral hygiene habits and social economical conditions using a questionnaire. Mothers who did not present first molars and incisors were excluded from the study group. Children should have the four first permanent molars (n=4) at least with two thirds erupted, maxillary and mandibular incisors fully erupted, no proximal caries lesion (checked through bite-wing radiographs) and no fistula. Deciduous teeth with more than one third of root resorption were not considered. One trained examiner performed the all clinical examination. Gingival inflammation was determined by Löe and Silness 10 (1963), and dental plaque and gingival indexes were assessed according to Silness and Löe 22 (1964). Four surfaces per tooth (buccal, lingual, mesial and distal) were examined in every permanent and deciduous tooth (except for third molars in the mothers group). Plaque and gingival indexes were calculated separately for every mother and child. Two X-rays from molar region (bitewing) and two from the anterior region (periapical) were taken from each subject to assess the distance from the cementoenamel junction to the alveolar bone crest (CEJ-ABC distance). Measurements were made by transferring the radiographic images to a computer program (Image Lab - Oral Pathology Department Program Dental School, University of São Paulo, Brazil). Pearson s correlation test was done in order to determine the correlation between: 1) plaque and gingival indexes of mother/child pairs; 2) CEJ-ABC distances and plaque and gingival indexes (measured only in mothers, on the mesial surfaces of maxillary central incisors and on first molars); and 3) The mean value of all CEJ-ABC distances measured in mothers and children s total gingival indexes. The influence of some behavioral and social factors in plaque and gingival indexes of mothers and children was assessed by using the covariance analysis tests. Results at the 5% (p<0.05) level of probability were considered statistically significant. RESULTS The mean values of plaque and gingival indexes from the children and their mothers are shown in Table 1. Correlation analysis between plaque and gingival indexes in the group of children (C) and in the group of mothers (M) are shown in Table 2. Significant correlations between plaque and gingival indexes were found in both groups. However, a stronger correlation between total plaque and gingival index was observed in the adults (M Total PI x M Total GI, r = ) 228
3 RAMIRES-ROMITO A C D, OLIVEIRA L B, ROMITO G A, MAYER M P A, RODRIGUES C R M D than in the children (C Total PI x C Total GI, r = ). The correlation of Plaque and Gingival Indexes between the pairs of mother/child analyzing selected groups of teeth (Incisors or Molars) or all teeth (TOTAL) is shown in Table 3. A significant but weak correlation was shown between Total plaque index from children and their mothers (C Total PI x M Total PI, r = ). However, a higher correlation in plaque index for the region of first molars between both groups was demonstrated (C Molars PI x M Molars PI, r = ). No significant correlation between mother and child was obtained by analyzing the gingival index. The distances CEJ-ABC were measured to detect alveolar bone loss. Children exhibited no bone loss, as evidenced by measures of CEJ-ABC of less than 3mm in every tooth examined (mean value = 1.22 mm ± 0.28). Eighteen out of 30 (60%) mothers presented at least one value of CEJ-ABC higher than 3mm. CEJ-ABC distance values higher than 5mm were observed only in 3 subjects in the mothers group (10%). No correlation between gingival index in children and alveolar bone loss in mothers was detected (r = , p = ). The reported behavioral and social factors were correlated to plaque and gingival indexes of children and their mothers. TABLE 1- Mean values of plaque and gingival indexes of children and mothers for incisors, first permanent molars and total teeth The data obtained between these reported variables and Total Plaque Index and in Total Gingival Index the mothers group are shown in Table 4. The variables that were associated to mother s plaque index were mother s age, frequency of flossing and the fact of having a job. The fact of having a job was the only significant variable that was associated to gingival index in the group of mothers. The reported behavior and social status were also correlated to clinical indexes in children, and the results are shown in Table 5. Plaque Index in the children was correlated to variables such as mother s frequency of flossing, mother s support during child s toothbrushing and mother s having a job. Children s Gingival Index was correlated to the variables mother s frequency of flossing, mother with a job, children s frequency of tooth brushing and children s age. DISCUSSION Periodontal conditions in children have been a subject of researches for decades (Bimstein and Ebersole 4, 1989; Matsson 13, 1978; Matsson and Goldberg 14, 1985; Parfit 17, 1957; Peretz, et al. 19, 1996; Ramberg, et al. 21, 1994). However, very little is known about the correlation between the presence of periodontal disease in mothers and the establishment of gingival or periodontal disease in their children. The influence of the family in the establishment of a pathogenic microbiota in children has been very well TABLE 3- Pearson s correlation between the pairs of children (C) and mothers (M) when variables of plaque and gingival indexes for total, molars and incisors teeth are considered *Mean value of Plaque Index ± standard deviation **Mean value of Gengival Index ± standard deviation ***n = 27 TABLE 2- Pearson s correlation between the variables incisors, molars and total teeth considering the plaque (PI) and gingival indexes (GI) of children (C) and mothers (M) TABLE 4- Covariance analyses for mother s total plaque and gingival indexes 229 *Statistically significant (p<0.01)
4 CORRELATION STUDY OF PLAQUE AND GINGIVAL INDEXES OF MOTHERS AND THEIR CHILDREN documented (Könönen, et al. 8 ; 1994; Morinushi, et al. 16, 2000). However, other factors such as hereditary immune response and behavioral factors including tooth cleaning habits should also contribute for the increased prevalence of periodontal disease in certain families. In the present study, a very homogeneous population with a well-limited age range was analyzed, differing from other studies in the literature (Beaty, et al. 3, 1993; Zambon, et al. 26, 1983). Lower correlation values between plaque and gingival indexes were obtained in the group of children than in the group of mothers. These findings are in agreement with Matsson and Goldberg 15 (1986) who reported less gingival inflammation in children than in adults in the presence of similar amounts of plaque accumulation, indicating a difference in the pathogenic potential of dental plaque or in the host response. Significant correlation of plaque between mother-child was found only when Total (low correlation) or Molar (moderate correlation) plaque index was considered (Table 3). The significant correlation for plaque index in molar region but not significant in the region of incisors may represent different abilities of plaque removal between mothers and children. In the children s group, the eventual absence of proximal contact in the region of incisors may have also contributed to a lower plaque index. Although the oldest children did not show the highest values for plaque accumulation, they exhibited the highest total gingival index values, indicating an increase in gingival reaction to dental plaque accumulation with age, as described in the literature (Bimstein and Matsson 5, 1999; Matsson 13, 1978; Matsson and Goldberg 15, 1986). There was no correlation between CEJ-ABC distance and plaque or gingival indexes among mothers. Only 3 subjects in the mothers group presented distances values higher than 5mm. Other studies have also reported that supragingival plaque accumulation was not directly related to alveolar bone loss. In addition, preventive measures alone, aiming to control plaque accumulation, might not be effective in controlling destructive periodontal disease (Albandar, et al. 1, 1995; Bartold, et al. 2, 1998). Declared family income or the socioeconomic class did not influence the oral health of the groups, in contrast to the results found in other studies (MacGregor, Baldin 11, 1991; TABLE 5- Covariance analyses for children s total plaque and gingival indexes Tan, et al. 23, 1981). Although the social class was not homogeneous in the study group, it should be noticed that these subjects were seeking free treatment at the University. Mothers total gingival index was influenced by the fact of having a job. Those who reported that they worked outside home presented the lowest values for total gingival index. The reduced plaque and gingival indexes in these mothers may reflect an increased self-esteem, need for a better appearance and possibility of getting more information than those at home. A lower total plaque index in the group of children was also demonstrated when their mother reported having a job. These data contribute to the findings that dental health behavior appears to be a part of a person s lifestyle and a significant association between self-esteem and toothbrushing frequency has already been reported (MacGregor and Baldin 11, 1991). Regardless almost all parents usually consider tooth brushing as important for oral health, only 11 mothers reported helping the children in their oral hygiene. A lower total plaque index in the group of children was demonstrated when the mothers helped the children to brush their teeth. As expected, parents supervision improved the quality of tooth cleaning. A Dutch study pointed out that a quarter of 12 years-old children were not supervised in their oral home care (Petersen 20, 1992). In countries where high levels of caries reduction were achieved such in Denmark, three-quarters of the parents of 6 years old children answered that they believed children less than 10 years old need help from adults in toothbrushing (Petersen 20, 1992). Total gingival index was decreased with an increase in frequency of children s tooth brushing and when their mothers declared they are used to flossing everyday. Children s plaque index was also reduced when their mothers answered that they flossed always, showing that mother s frequency of flossing may reflect their awareness of the importance of oral hygiene, which could be transmitted and stimulated in the children. It has been long before when it was reported that children follow the example of their parents. Therefore, it is more effective to change behavior through the route of behavior itself than through the route of knowledge. This information may be also useful to be aware that it is not very effective to direct the efforts in dental health education solely to the youngsters (Tan, et al. 23, 1981). Although no clinically significant correlation in plaque or periodontal indexes between mothers and their children could be found, mothers awareness to oral health, represented by flossing and attention to child s oral hygiene, was significantly correlated to children s better oral health. These data reinforce the need for family participation in oral health campaigns and not only school-based programs. REFERENCES 1- Albandar JM, Buischi YAP, Oliveira LB, Axelsson P. Lack of effect of oral hygiene training on periodontal disease progression over three years in adolescents. J Periodontol. 1995;66: *p< 0.01 **p<
5 RAMIRES-ROMITO A C D, OLIVEIRA L B, ROMITO G A, MAYER M P A, RODRIGUES C R M D 2- Bartold GJ, Syemour MP, Cullinan MP, Westerman B. Effect of increased community and professional awareness of plaque control on the management of inflammatory periodontal diseases. Int Dent J. 1998;48: Beaty TH, Colyer CR, Chang YC, Liag KY, Graybeal JC, Muhammad NK, et al. Familial aggregation of periodontal indices. J Dent Res. 1993;72: Bimstein E, Ebersole JE. The age-dependent reaction of periodontal tissues to dental plaque. J Dent Child. 1989;56: Bimstein E, Matsson L. Growth and development considerations in the diagnosis of gingivitis and periodontitis in children. Pediatr Dent. 1999;21: Bimstein E, Ram D, Naor R, Sela MN. The composition of subgengival microflora in two groups of children with and without primary dentition alveolar bone loss. Pediatr Dent 1996;18: Caufield PW, Cutter GR, Dasanayake AP. Initial acquisition of mutans streptococci by infants: evidence for a discrete window of infectivity. J Dent Res. 1993;72: Könönen E, Saarela M, Karjalainen J, Jousimies-Somer H, Alaluusua S, Asikainen S. Transmission of oral Prevotella melanonogenica between a mother and her young child. Relationship between oral gram negative anaerobic bacteria in saliva of mother and the colonization of her edentulous infant. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 1994;9: Ramberg PW, Lindhe J, Gaffar A. Plaque and gingivitis in the deciduous and permanent dentition. J Clin Periodontol. 1994;21: Silness P, Löe H. Periodontal disease in pregnancy II. Acta Odontol Scand. 1964;22: Tan H, Ter Horst G, Dekking YM. Dental knowledge, attitude and behavior in 12-year-old dutch suburban children. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 1981;9: Theilade E, Wright WH, Jensen SB, Löe H. Experimental gingivitis in man. II. A longitudinal clinical and bacteriological investigation. J Periodontal Res. 1966;1: Von Troil-Lindén B, Torkko H, Alaluusua S, Wolf J, Jousimies- Somer H, Asikainen S. Periodontal findings in spouses - A clinical, radiographic and microbiological study. J Clin Periodontol. 1995;2: Zambon JJ, Christersson LA, Slots J. Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans in human periodontal disease. Prevalence in patient groups and distribution of biotypes and serotypes within families. J Periodontol. 1983;54: Li Y, Caulfield PW. The fidelity of initial acquisition of mutans streptococci by infants from their mothers. J Dent Res. 1995;74: Löe H, Silness P. Periodontal disease in pregnancy I. Acta Odontol Scand. 1963;21: MacGregor IDM, Baldin JW. Self-esteem as a predictor of tooth brushing behavior in young adolescents. J Clin Periodontol. 1991;18: Mackler SB, Crawford JJ. Plaque development and gingivitis in the primary dentition. J Periodontol. 1973;44: Matsson L. Development of gingivits in pre-school children and young adults. J Clin Periodontol. 1978;5: Matsson L, Goldberg P. Gingival inflammatory reaction in children at different ages. J Clin Periodontol. 1985;12: Matsson L, Goldberg P. Gingival inflammation at deciduous and permanent teeth. J Clin Periodontol. 1986;13: Morinushi T, Lopatin DE, Poperin NV, Ueda Y. The relationship between gingivitis and colonization by Porphyromonas gingivalis and Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans in children. J Periodontol. 2000; 71: Parfitt GJ. A five year longitudinal study of the gingival conditions of a group of children in England. J Periodontol. 1957;28: Peretz B, Machtei EM, Bimstein E. Changes in periodontal status of children and young adolescence: a one-year longitudinal study. J Clin Pediatr Dent. 1993;18: Peretz B, Machtei EM, Bimstein E. Periodontal status in childhood and early adolescence: three-year follow up. J Clin Pediatr Dent. 1996;20: Petersen PE. Oral health behavior of 6-year-old Danish children. Acta Odontol Scand. 1992;50:
Effect of oral anticipatory guidance on oral health and oral hygiene practices in preschool children
 Effect of oral anticipatory guidance on oral health and oral hygiene practices in preschool children Débora Conçalves Farias, DDS* / Soraya Coelho Leal, DDS,MS,PhD** / Orlando Ayrton de Toledo, DDS,PhD***
Effect of oral anticipatory guidance on oral health and oral hygiene practices in preschool children Débora Conçalves Farias, DDS* / Soraya Coelho Leal, DDS,MS,PhD** / Orlando Ayrton de Toledo, DDS,PhD***
Relato de Caso / Case Report
 Relato de Caso / Case Report IJD ISSN:1806-146X Clinical and Psychological Approaches during Periodontal Treatment in Adolescents Abordagem clínica e psicológica durante o tratamento periodontal de adolescentes
Relato de Caso / Case Report IJD ISSN:1806-146X Clinical and Psychological Approaches during Periodontal Treatment in Adolescents Abordagem clínica e psicológica durante o tratamento periodontal de adolescentes
Oral Health Status of Pregnant Women
 Oral Health Status of Pregnant Women Ingrida Vasiliauskiene Stomatologija, Baltic Dental and Maxillofacial Journal, 5:57-61, 2003 SUMMARY The aim of the study was to determine the prevalence and severity
Oral Health Status of Pregnant Women Ingrida Vasiliauskiene Stomatologija, Baltic Dental and Maxillofacial Journal, 5:57-61, 2003 SUMMARY The aim of the study was to determine the prevalence and severity
Objectives: The purpose of this study was to evaluate the prevalence of alveolar bone
 www.scielo.br/jaos Prevalence of alveolar bone loss in healthy children treated at private pediatric dentistry clinics Maria do Carmo Machado GUIMARÃES 1, Valéria Martins de ARAÚJO 2, Márcia Raquel AVENA
www.scielo.br/jaos Prevalence of alveolar bone loss in healthy children treated at private pediatric dentistry clinics Maria do Carmo Machado GUIMARÃES 1, Valéria Martins de ARAÚJO 2, Márcia Raquel AVENA
Concordance of Porphyromonas gingivalis Colonization in Families
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Feb. 1997, p. 455 461 Vol. 35, No. 2 0095-1137/97/$04.00 0 Copyright 1997, American Society for Microbiology Concordance of Porphyromonas gingivalis Colonization in Families
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Feb. 1997, p. 455 461 Vol. 35, No. 2 0095-1137/97/$04.00 0 Copyright 1997, American Society for Microbiology Concordance of Porphyromonas gingivalis Colonization in Families
Rare case of generalised aggressive periodontitis in the primary dentition
 Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2014 Rare case of generalised aggressive periodontitis in the primary dentition
Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2014 Rare case of generalised aggressive periodontitis in the primary dentition
Plaque removal by manual and electric toothbrushing among children. Remoção de placa bacteriana pela escovação elétrica e manual em crianças
 Pesqui Odontol Bras v. 15, n. 4, p. 296-301, out./dez. 2001. Odontopediatria Plaque removal by manual and electric ing among children Remoção de placa bacteriana pela escovação elétrica e manual em crianças
Pesqui Odontol Bras v. 15, n. 4, p. 296-301, out./dez. 2001. Odontopediatria Plaque removal by manual and electric ing among children Remoção de placa bacteriana pela escovação elétrica e manual em crianças
Periodontal conditions of teeth presenting pathologic migration Condições periodontais de dentes com migração dentária patológica
 Braz Oral Res 2004;18(4):301-5 Periodontics Periodontal conditions of teeth presenting pathologic migration Condições periodontais de dentes com migração dentária patológica Maurício Ribeiro Costa* Karina
Braz Oral Res 2004;18(4):301-5 Periodontics Periodontal conditions of teeth presenting pathologic migration Condições periodontais de dentes com migração dentária patológica Maurício Ribeiro Costa* Karina
Protecting All Children s Teeth Caries
 Protecting All Children s Teeth Caries 1 http://www.aap.org/oralhealth/pact Introduction used with permission from Ian Van Dinther Caries is an infectious transmissible disease resulting from tooth adherent
Protecting All Children s Teeth Caries 1 http://www.aap.org/oralhealth/pact Introduction used with permission from Ian Van Dinther Caries is an infectious transmissible disease resulting from tooth adherent
PERINATAL CARE AND ORAL HEALTH
 PERINATAL CARE AND ORAL HEALTH Lakshmi Mallavarapu, DDS Terry Reilly Health Services Boise, Idaho CE objectives Recognize the necessity of Oral Care during Perinatal Period Examine and assess teeth and
PERINATAL CARE AND ORAL HEALTH Lakshmi Mallavarapu, DDS Terry Reilly Health Services Boise, Idaho CE objectives Recognize the necessity of Oral Care during Perinatal Period Examine and assess teeth and
Early Childhood Caries (ECC) KEVIN ZIMMERMAN DMD
 Early Childhood Caries (ECC) KEVIN ZIMMERMAN DMD What Is Early Childhood Caries? Early Childhood Caries (ECC) is a transmissible infectious process that affects children younger than age 6 and results
Early Childhood Caries (ECC) KEVIN ZIMMERMAN DMD What Is Early Childhood Caries? Early Childhood Caries (ECC) is a transmissible infectious process that affects children younger than age 6 and results
Pathogens in Relation to Periodontal Status
 J Dent Res 74(11): 1789-1793, November, 1995 Salivary Levels of Suspected Periodontal Pathogens in Relation to Periodontal Status and Treatment B. von Troil-Lindenl*, H. Torkko2, S. Alaluusua3, H. Jousimies-Somer4,
J Dent Res 74(11): 1789-1793, November, 1995 Salivary Levels of Suspected Periodontal Pathogens in Relation to Periodontal Status and Treatment B. von Troil-Lindenl*, H. Torkko2, S. Alaluusua3, H. Jousimies-Somer4,
SCIENTIFIC ARTICLES. Longitudinal evaluation of caries patterns from the primary to the mixed dentition
 PEDIATRIC DENTlSTRYKopyright 0 1990 by The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry Volume 12. Number 5 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLES Longitudinal evaluation of caries patterns from the primary to the mixed dentition
PEDIATRIC DENTlSTRYKopyright 0 1990 by The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry Volume 12. Number 5 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLES Longitudinal evaluation of caries patterns from the primary to the mixed dentition
Relationship between gingival health and dental caries in children aged 7-12 years
 151 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 42, No. 3, 151-155, 2000 Relationship between gingival health and dental caries in children aged 7-12 years Mitsugi Okada, Satsuki Kuwahara, Yasutaka Kaihara, Hiroyuki
151 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 42, No. 3, 151-155, 2000 Relationship between gingival health and dental caries in children aged 7-12 years Mitsugi Okada, Satsuki Kuwahara, Yasutaka Kaihara, Hiroyuki
Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development. Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L.
 Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L. Dennis Proximal contact areas Contact areas are on the mesial and
Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L. Dennis Proximal contact areas Contact areas are on the mesial and
Comparative Evaluation of 0.2 percent Chlorhexidine and Magnetized Water as a Mouth Rinse on Streptococcus mutans in Children
 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-1108 Nidhi ORIGINAL Gupta, Manohar ARTICLE Bhat Comparative Evaluation of 0.2 percent Chlorhexidine and Magnetized Water as a Mouth Rinse on Streptococcus mutans in Children 1
10.5005/jp-journals-10005-1108 Nidhi ORIGINAL Gupta, Manohar ARTICLE Bhat Comparative Evaluation of 0.2 percent Chlorhexidine and Magnetized Water as a Mouth Rinse on Streptococcus mutans in Children 1
Introduction. Clinical Periodontal Examination 11/1/16
 Is Radiologic Assessment of Alveolar Crest Height Useful to Monitor Periodontal Disease Activity? Based on DCNA chapter: Hattan A.M. Zaki, Kenneth R. Hoffmann, Ernest Hausmann, Frank A. Scannapieco Periodontitis,
Is Radiologic Assessment of Alveolar Crest Height Useful to Monitor Periodontal Disease Activity? Based on DCNA chapter: Hattan A.M. Zaki, Kenneth R. Hoffmann, Ernest Hausmann, Frank A. Scannapieco Periodontitis,
Dental Morphology and Vocabulary
 Dental Morphology and Vocabulary Palate Palate Palate 1 2 Hard Palate Rugae Hard Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate 4 Palate Hard Palate Soft Palate Maxillary Arch (Maxilla) (Uppers)
Dental Morphology and Vocabulary Palate Palate Palate 1 2 Hard Palate Rugae Hard Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate 4 Palate Hard Palate Soft Palate Maxillary Arch (Maxilla) (Uppers)
Clinical Management of an Unusual Case of Gingival Enlargement
 Clinical Management of an Unusual Case of Gingival Enlargement Abstract Aim: The purpose of this article is to report a case of conditioned gingival enlargement managed by nonsurgical periodontal therapy.
Clinical Management of an Unusual Case of Gingival Enlargement Abstract Aim: The purpose of this article is to report a case of conditioned gingival enlargement managed by nonsurgical periodontal therapy.
Evaluation of Marginal Alveolar Bone Height for Early Detection of Periodontal Disease in Pediatric Population: Clinical and Radiographic Study
 Evaluation of Marginal Alveolar Bone Height for Early Detection of Periodontal 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1485 Disease in Pediatric Population Original RESEARCH Evaluation of Marginal Alveolar Bone Height
Evaluation of Marginal Alveolar Bone Height for Early Detection of Periodontal 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1485 Disease in Pediatric Population Original RESEARCH Evaluation of Marginal Alveolar Bone Height
Intrusion of Incisors to Facilitate Restoration: The Impact on the Periodontium
 Note: This is a sample Eoster. Your EPoster does not need to use the same format style. For example your title slide does not need to have the title of your EPoster in a box surrounded with a pink border.
Note: This is a sample Eoster. Your EPoster does not need to use the same format style. For example your title slide does not need to have the title of your EPoster in a box surrounded with a pink border.
Toothbrushing Frequency as It Relates to Plaque Development and Gingival Health*
 Toothbrushing Frequency as It Relates to Plaque Development and Gingival Health* by NIKLAUS P. LANG* BOYD R. CUMMING*** HARALD LÖE** EPIDEMIOLOGICAL and experimental studies have demonstrated that gingival
Toothbrushing Frequency as It Relates to Plaque Development and Gingival Health* by NIKLAUS P. LANG* BOYD R. CUMMING*** HARALD LÖE** EPIDEMIOLOGICAL and experimental studies have demonstrated that gingival
Bacterial Plaque and Its Relation to Dental Diseases. As a hygienist it is important to stress the importance of good oral hygiene and
 Melissa Rudzinski Preventive Dentistry Shaunda Clark November 2013 Bacterial Plaque and Its Relation to Dental Diseases As a hygienist it is important to stress the importance of good oral hygiene and
Melissa Rudzinski Preventive Dentistry Shaunda Clark November 2013 Bacterial Plaque and Its Relation to Dental Diseases As a hygienist it is important to stress the importance of good oral hygiene and
Influence Of Orthodontic Treatment On Gingival Condition
 Influence Of Orthodontic Treatment On Gingival Condition Irinel Panainte, DMD Department of Orthodontics, Faculty of Dental Medicine, University of Medicine and Pharmacy Tirgu Mures, Romania Ramona Vlad,
Influence Of Orthodontic Treatment On Gingival Condition Irinel Panainte, DMD Department of Orthodontics, Faculty of Dental Medicine, University of Medicine and Pharmacy Tirgu Mures, Romania Ramona Vlad,
6610 NE 181st Street, Suite #1, Kenmore, WA
 660 NE 8st Street, Suite #, Kenmore, WA 9808 www.northshoredentalacademy.com.08.900 READ CHAPTER The Professional Dental Assistant (p.-9) No Key Terms Recall Questions:,,,, and 6 CLASS SYLLABUS DAY READ
660 NE 8st Street, Suite #, Kenmore, WA 9808 www.northshoredentalacademy.com.08.900 READ CHAPTER The Professional Dental Assistant (p.-9) No Key Terms Recall Questions:,,,, and 6 CLASS SYLLABUS DAY READ
STATISTICAL STUDY REGARDING THE PREVALENCE OF THE PERIODONTAL PATHOLOGY ON THE TEENAGER PATIENT
 STATISTICAL STUDY REGARDING THE PREVALENCE OF THE PERIODONTAL PATHOLOGY ON THE TEENAGER PATIENT Oana Potârnichie 1*, Sorina Solomon 2, Liliana Păsărin 1, Alexandra Mârțu 3, Irina Ursărescu 4, Diana Cristala
STATISTICAL STUDY REGARDING THE PREVALENCE OF THE PERIODONTAL PATHOLOGY ON THE TEENAGER PATIENT Oana Potârnichie 1*, Sorina Solomon 2, Liliana Păsărin 1, Alexandra Mârțu 3, Irina Ursărescu 4, Diana Cristala
An Overview of Gingival and Periodontal Diseases in 12 to 15 years using Gingivitis and Periodontitis Site Prevalence Index (WHO, 1978)
 10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1079 ORIGINL RESERCH WJD n Overview of Gingival and Periodontal Diseases in 12 to 15 years n Overview of Gingival and Periodontal Diseases in 12 to 15 years using Gingivitis and
10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1079 ORIGINL RESERCH WJD n Overview of Gingival and Periodontal Diseases in 12 to 15 years n Overview of Gingival and Periodontal Diseases in 12 to 15 years using Gingivitis and
Risk Assessment. Full Summary. Description and Use:
 Risk Assessment Full Summary Description and Use: Risk assessment is a strategy for improving the efficiency and effectiveness of prevention procedures and programs. Risk assessment protocols that are
Risk Assessment Full Summary Description and Use: Risk assessment is a strategy for improving the efficiency and effectiveness of prevention procedures and programs. Risk assessment protocols that are
Prevalence of Gingival recession in Dental college students: A Clinical investigation
 American Journal of Advances in Medical Science www.arnaca.com eissn: 2347-2766 Original Research Article Prevalence of Gingival recession in Dental college students: A Clinical Ninad Moon 1, Prasant Pillai
American Journal of Advances in Medical Science www.arnaca.com eissn: 2347-2766 Original Research Article Prevalence of Gingival recession in Dental college students: A Clinical Ninad Moon 1, Prasant Pillai
THE AMERICAN ACADEMY OF PERIODONTOLOGY
 THE AMERICAN ACADEMY OF PERIODONTOLOGY Suite 800 737 North Michigan Avenue Chicago, Illinois 60611-2690 www.perio.org 2005 The American Academy of Periodontology PDW PERIODONTAL DISEASES what you need
THE AMERICAN ACADEMY OF PERIODONTOLOGY Suite 800 737 North Michigan Avenue Chicago, Illinois 60611-2690 www.perio.org 2005 The American Academy of Periodontology PDW PERIODONTAL DISEASES what you need
THE MOST COMMON CHIEF COMPLAINT AMONG JORDANIAN CHILDREN AT FIRST DENTAL VISIT
 Pedodontics Original Article THE MOST COMMON CHIEF COMPLAINT AMONG JORDANIAN CHILDREN AT FIRST DENTAL VISIT 1 YAHYA MA DRAIDI, BDS (Jordan), MDENTSC in Restorative Dentistry (Periodontics) (Leeds-UK) 2
Pedodontics Original Article THE MOST COMMON CHIEF COMPLAINT AMONG JORDANIAN CHILDREN AT FIRST DENTAL VISIT 1 YAHYA MA DRAIDI, BDS (Jordan), MDENTSC in Restorative Dentistry (Periodontics) (Leeds-UK) 2
Rate of cultivable subgingival periodontopathogenic bacteria in chronic periodontitis
 157 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 46, No. 3, 157-161, 2004 Original Rate of cultivable subgingival periodontopathogenic bacteria in chronic periodontitis Mohammad Hossein Salari and Zainab Kadkhoda Department
157 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 46, No. 3, 157-161, 2004 Original Rate of cultivable subgingival periodontopathogenic bacteria in chronic periodontitis Mohammad Hossein Salari and Zainab Kadkhoda Department
Infant and Toddler Oral Health
 Infant and Toddler Oral Health Photo CD Decompressor are needed to use this picture Greater New York Dental Meeting December 1, 2002 Steven Chussid D.D.S. Timing of First Visit Guidelines of the American
Infant and Toddler Oral Health Photo CD Decompressor are needed to use this picture Greater New York Dental Meeting December 1, 2002 Steven Chussid D.D.S. Timing of First Visit Guidelines of the American
Best Practices in Oral Health for Older Adults -How to Keep My Bite in My Life!
 Best Practices in Oral Health for Older Adults -How to Keep My Bite in My Life! Mr. has most of his natural teeth. Mr. JB Age 78. In for rehab from stroke; will return home. Non-dominant hand/arm paralyzed.
Best Practices in Oral Health for Older Adults -How to Keep My Bite in My Life! Mr. has most of his natural teeth. Mr. JB Age 78. In for rehab from stroke; will return home. Non-dominant hand/arm paralyzed.
Dental caries prevention. Preventive programs for children 5DM
 Dental caries prevention Preventive programs for children 5DM Definition of Terms Preventive dentistry: usage of all the means to achieve and maintain the optimal oral health prevention of dental caries,
Dental caries prevention Preventive programs for children 5DM Definition of Terms Preventive dentistry: usage of all the means to achieve and maintain the optimal oral health prevention of dental caries,
Parental Attitudes and Tooth Brushing Habits in Preschool Children in Mangalore, Karnataka: A Cross-sectional Study
 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-1210 Fawaz Pullishery et al RESEARCH ARTICLE Parental Attitudes and Tooth Brushing Habits in Preschool Children in Mangalore, Karnataka: A Cross-sectional Study Fawaz Pullishery,
10.5005/jp-journals-10005-1210 Fawaz Pullishery et al RESEARCH ARTICLE Parental Attitudes and Tooth Brushing Habits in Preschool Children in Mangalore, Karnataka: A Cross-sectional Study Fawaz Pullishery,
AETIOLOGY AND SEVERITY OF GINGIVAL RECESSION AMONG YOUNG INDIVIDUALS IN BELGAUM DISTRICT IN INDIA
 AETIOLOGY AND SEVERITY OF GINGIVAL RECESSION AMONG YOUNG INDIVIDUALS IN BELGAUM DISTRICT IN INDIA V. Dodwad. Aetiology and severity of gingival recession among young individuals in Belgaum district in
AETIOLOGY AND SEVERITY OF GINGIVAL RECESSION AMONG YOUNG INDIVIDUALS IN BELGAUM DISTRICT IN INDIA V. Dodwad. Aetiology and severity of gingival recession among young individuals in Belgaum district in
Th.e effectiveness of interdental flossing w=th and without a fluoride dentifrice
 /Copyright 1980 by The American Academy of Pedodontics/VoL 2, No. 2 Th.e effectiveness of interdental flossing w=th and without a fluoride dentifrice Gerald Z. Wright, D.D.S., M.S.D., F.R.C.D.(C) W. H.
/Copyright 1980 by The American Academy of Pedodontics/VoL 2, No. 2 Th.e effectiveness of interdental flossing w=th and without a fluoride dentifrice Gerald Z. Wright, D.D.S., M.S.D., F.R.C.D.(C) W. H.
Attachment G. Orthodontic Criteria Index Form Comprehensive D8080. ABBREVIATIONS CRITERIA for Permanent Dentition YES NO
 First Review IL HFS Dental Program Models Second Review Ortho cad Attachment G Orthodontic Criteria Index Form Comprehensive D8080 Ceph Film X-Rays Photos Narrative Patient Name: DOB: ABBREVIATIONS CRITERIA
First Review IL HFS Dental Program Models Second Review Ortho cad Attachment G Orthodontic Criteria Index Form Comprehensive D8080 Ceph Film X-Rays Photos Narrative Patient Name: DOB: ABBREVIATIONS CRITERIA
Periodontal Disease. Radiology of Periodontal Disease. Periodontal Disease. The Role of Radiology in Assessment of Periodontal Disease
 Radiology of Periodontal Disease Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Periodontal Disease! Includes several disorders of the periodontium! Gingivitis! Marginal Periodontitis! Localized
Radiology of Periodontal Disease Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Periodontal Disease! Includes several disorders of the periodontium! Gingivitis! Marginal Periodontitis! Localized
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Quintessence Int. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2011 August 6.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Quintessence Int. 2007 April ; 38(4): e213 e217. Microbial acid production (Clinpro Cario L-Pop) and dental caries in infants and
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Quintessence Int. 2007 April ; 38(4): e213 e217. Microbial acid production (Clinpro Cario L-Pop) and dental caries in infants and
Prosthetic Options in Implant Dentistry. Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor
 Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Mesial Step Class I or Class III Dependent upon extent of step seen clinically and patient s growth pattern Refer for early evaluation (by 8 years)
 Orthodontics and Dentofacial Development Overview Development of Dentition Treatment Retention and Relapse Growth of Naso-Maxillary Complex Develops postnatally entirely by intramenbranous ossification
Orthodontics and Dentofacial Development Overview Development of Dentition Treatment Retention and Relapse Growth of Naso-Maxillary Complex Develops postnatally entirely by intramenbranous ossification
EFFECT OF ORAL HYGIENE INSTRUCTIONS ON GINGIVAL INDEX AND PLAQUE SCORE AMONG PERIODONTAL PATIENTS VISITING THE UNIVERSITY OF NAIROBI DENTAL HOSPITAL.
 EFFECT OF ORAL HYGIENE INSTRUCTIONS ON GINGIVAL INDEX AND PLAQUE SCORE AMONG PERIODONTAL PATIENTS VISITING THE UNIVERSITY OF NAIROBI DENTAL HOSPITAL. INVESTIGATOR KAGURU GEORGE KARIUKI BDS III 2004/2005
EFFECT OF ORAL HYGIENE INSTRUCTIONS ON GINGIVAL INDEX AND PLAQUE SCORE AMONG PERIODONTAL PATIENTS VISITING THE UNIVERSITY OF NAIROBI DENTAL HOSPITAL. INVESTIGATOR KAGURU GEORGE KARIUKI BDS III 2004/2005
EFFECTIVENESS OF ORAL HYGIENE INSTRUCTION MEDIA ON PERIODONTAL HEALTH AMONG HEARING IMPAIRED CHILDREN
 EFFECTIVENESS OF ORAL HYGIENE INSTRUCTION MEDIA ON PERIODONTAL HEALTH AMONG HEARING IMPAIRED CHILDREN Malee Arunakul, Yosvimol Kuphasuk 2 and Romcharee Boonyathanasit 3 Department of Pediatric Dentistry,
EFFECTIVENESS OF ORAL HYGIENE INSTRUCTION MEDIA ON PERIODONTAL HEALTH AMONG HEARING IMPAIRED CHILDREN Malee Arunakul, Yosvimol Kuphasuk 2 and Romcharee Boonyathanasit 3 Department of Pediatric Dentistry,
A Clinical Evaluation of Anatomic Features of Gingiva in Dental Students in Tabriz, Iran
 Received 26 October 2007; Accepted 11 February 2008 A Clinical Evaluation of Anatomic Features of Gingiva in Dental Students in Tabriz, Iran Adileh Shirmohammadi 1 Masoumeh Faramarzie 1 * Ardeshir Lafzi
Received 26 October 2007; Accepted 11 February 2008 A Clinical Evaluation of Anatomic Features of Gingiva in Dental Students in Tabriz, Iran Adileh Shirmohammadi 1 Masoumeh Faramarzie 1 * Ardeshir Lafzi
Relationship Between Gingivitis and Anterior Teeth Irregularities Among 18 to 26 Years Age Group: A Hospital Based Study in Belgaum, Karnataka
 Relationship Between Gingivitis and Anterior Teeth Irregularities Among 18 to 26 Years Age Group: A Hospital Based Study in Belgaum, Karnataka V Chandrasekhara Reddy, BR Ashok Kumar, Anil Ankola ABSTRACT
Relationship Between Gingivitis and Anterior Teeth Irregularities Among 18 to 26 Years Age Group: A Hospital Based Study in Belgaum, Karnataka V Chandrasekhara Reddy, BR Ashok Kumar, Anil Ankola ABSTRACT
Persson GR, Salvi GE, Heitz-Mayfield LJA et al. Antimicrobial therapy using a local drug delivery system (Arestin) in the treatment of
 Persson GR, Salvi GE, Heitz-Mayfield LJA et al. Antimicrobial therapy using a local drug delivery system (Arestin) in the treatment of peri-implantitis I: microbiological outcomes. Clin Oral Imp Res 2006;
Persson GR, Salvi GE, Heitz-Mayfield LJA et al. Antimicrobial therapy using a local drug delivery system (Arestin) in the treatment of peri-implantitis I: microbiological outcomes. Clin Oral Imp Res 2006;
Problems of First Permanent Molars - The first group of permanent teeth erupt in the oral cavity. - Deep groove and pit
 Management of the poor first permanent e molar Assoc. Prof. Kadkao Vongsavan * Asst. Prof. Praphasri Rirattanapong* Dr. Pongsakorn Sakkamathya** ** * Department of Pediatric Dentistry Faculty of Dentistry,
Management of the poor first permanent e molar Assoc. Prof. Kadkao Vongsavan * Asst. Prof. Praphasri Rirattanapong* Dr. Pongsakorn Sakkamathya** ** * Department of Pediatric Dentistry Faculty of Dentistry,
Improving quality and efficiency in dental hygiene Journal of Genrotological Nursing, Vol. 15, No. 6
 Data Sheet no.4 in support of the Collis Curve Toothbrush Improving quality and efficiency in dental hygiene Journal of Genrotological Nursing, Vol. 15, No. 6 David Collis and the Collis Curve Toothbrush
Data Sheet no.4 in support of the Collis Curve Toothbrush Improving quality and efficiency in dental hygiene Journal of Genrotological Nursing, Vol. 15, No. 6 David Collis and the Collis Curve Toothbrush
Dental Care and Health An Update. Dr. Ranjini Pillai, DDS, MPH, FAGD, FICOI
 Dental Care and Health An Update Dr. Ranjini Pillai, DDS, MPH, FAGD, FICOI WHO s Definition of Health? Health is a state of complete physical, mental, and social wellbeing and not merely the absence of
Dental Care and Health An Update Dr. Ranjini Pillai, DDS, MPH, FAGD, FICOI WHO s Definition of Health? Health is a state of complete physical, mental, and social wellbeing and not merely the absence of
Evaluation of fixed partial denture in relation to gingival recession and other factors
 Evaluation of fixed partial denture in relation to gingival recession and other factors Faiza M. Abdul Ameer,B.D.S., M. Sc. (1) Zainab M. Abdul Ameer,B.D.S., M. Sc (2) ABSTRACT Background: Gingival recession
Evaluation of fixed partial denture in relation to gingival recession and other factors Faiza M. Abdul Ameer,B.D.S., M. Sc. (1) Zainab M. Abdul Ameer,B.D.S., M. Sc (2) ABSTRACT Background: Gingival recession
Cognitive Impairment and Oral Health
 Geriatric Lectures Series: Cognitive Impairment and Oral Health Dr. Leo Marchini, DDS, MSD, PhD Department of Preventive and Community Dentistry University of Iowa College of Dentistry and Dental Clinics
Geriatric Lectures Series: Cognitive Impairment and Oral Health Dr. Leo Marchini, DDS, MSD, PhD Department of Preventive and Community Dentistry University of Iowa College of Dentistry and Dental Clinics
Alveolar Growth in Japanese Infants: A Comparison between Now and 40 Years ago
 Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2017) 58(1): 9 18 Original Article doi:10.2209/tdcpublication.2016-0500 Alveolar Growth in Japanese Infants: A Comparison between Now and 40 Years ago Hiroki Imai 1), Tetsuhide Makiguchi
Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2017) 58(1): 9 18 Original Article doi:10.2209/tdcpublication.2016-0500 Alveolar Growth in Japanese Infants: A Comparison between Now and 40 Years ago Hiroki Imai 1), Tetsuhide Makiguchi
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
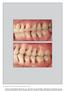 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 395 Clinical Case Report on Treatment of Generalized Aggressive Periodontitis: 5-Year Follow-up Kai-Fang Hu, DDS, MD 1 /Ya-Ping Ho, DDS,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 395 Clinical Case Report on Treatment of Generalized Aggressive Periodontitis: 5-Year Follow-up Kai-Fang Hu, DDS, MD 1 /Ya-Ping Ho, DDS,
Tribal Distribution of Aggressive Periodontitis in Sudanese School Children (12-16 years) in Khartoum State
 American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences 2017, 7(9): 338-343 DOI: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20170709.03 Tribal Distribution of Aggressive Periodontitis in Sudanese School Children (12-16 years) in Khartoum
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences 2017, 7(9): 338-343 DOI: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20170709.03 Tribal Distribution of Aggressive Periodontitis in Sudanese School Children (12-16 years) in Khartoum
Histologic characteristics of the gingiva associated with the primary and permanenteeth of children
 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Histologic characteristics of the gingiva associated with the primary and permanenteeth of children Enrique Bimstein, CD Lars Matsson, DDS, Odont Dr Aubrey W. Soskolne, BDS, PhD Joshua
SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Histologic characteristics of the gingiva associated with the primary and permanenteeth of children Enrique Bimstein, CD Lars Matsson, DDS, Odont Dr Aubrey W. Soskolne, BDS, PhD Joshua
Microbiota and Oral Disease Prof. Dennis Cvitkovitch
 1 Professor Dennis Cvitkovitch Faculty of Dentistry Dental Research Institute University of Toronto The human microbiome We are a composite species: eukaryotic, bacterial, archeal Every human harbors over
1 Professor Dennis Cvitkovitch Faculty of Dentistry Dental Research Institute University of Toronto The human microbiome We are a composite species: eukaryotic, bacterial, archeal Every human harbors over
The inhibitory effects of different mouthwash brands on the zone of inhibition of. Micrococcus luteus and Escherichia coli
 The inhibitory effects of different mouthwash brands on the zone of inhibition of Micrococcus luteus and Escherichia coli George Kendros Bio 2290 Section 001 TM Gray 2013 04 10 Abstract The use of mouthwash
The inhibitory effects of different mouthwash brands on the zone of inhibition of Micrococcus luteus and Escherichia coli George Kendros Bio 2290 Section 001 TM Gray 2013 04 10 Abstract The use of mouthwash
Changes of the Marginal Periodontium as a Result of
 Changes of the Marginal Periodontium as a Result of Labial Tooth Movement in Monkeys G. G. Steiner,* J. K. Pearson,f J. Ainamo^ Tooth position has been suggested to be an important factor in gingival recession.
Changes of the Marginal Periodontium as a Result of Labial Tooth Movement in Monkeys G. G. Steiner,* J. K. Pearson,f J. Ainamo^ Tooth position has been suggested to be an important factor in gingival recession.
The pediatricians role in the oral health of children
 The pediatricians role in the oral health of children Nuket Sandalli 1, Senem Selvi Kuvvetli 2, Sule Kavaloglu Cildir 3, Semra Ergeneli 4 Abstract Objectives: To determine the pediatricians knowledge,
The pediatricians role in the oral health of children Nuket Sandalli 1, Senem Selvi Kuvvetli 2, Sule Kavaloglu Cildir 3, Semra Ergeneli 4 Abstract Objectives: To determine the pediatricians knowledge,
Original Research Article Artigo Original de Pesquisa. Abstract
 ISSN: Versão impressa: 1806-7727 Versão eletrônica: 1984-5685 Original Research Article Artigo Original de Pesquisa Morphometric study of length and grooves of lower central incisors roots Estudo morfométrico
ISSN: Versão impressa: 1806-7727 Versão eletrônica: 1984-5685 Original Research Article Artigo Original de Pesquisa Morphometric study of length and grooves of lower central incisors roots Estudo morfométrico
Supragingival Plaque Removal with and without Dentifrice: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial
 Braz Dent J (2012) 23(3): 235-240 Toothbrushing with or without dentifrice ISSN 0103-6440 235 Supragingival Plaque Removal with and without Dentifrice: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial Fabricio B.
Braz Dent J (2012) 23(3): 235-240 Toothbrushing with or without dentifrice ISSN 0103-6440 235 Supragingival Plaque Removal with and without Dentifrice: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial Fabricio B.
Relationship of cariogenic bacteria levels with periodontal status and root surface caries in elderly Japanese
 Original article Relationship of cariogenic bacteria levels with periodontal status and root surface caries in elderly Japanese Yasuhiko Saotome 1,3, Akio Tada 2, Nobuhiro Hanada 4, Akihiro Yoshihara 5,
Original article Relationship of cariogenic bacteria levels with periodontal status and root surface caries in elderly Japanese Yasuhiko Saotome 1,3, Akio Tada 2, Nobuhiro Hanada 4, Akihiro Yoshihara 5,
Microbial Complexes Detected in the Second/Third Molar Region in Patients With Asymptomatic Third Molars
 J Oral Maxillofac Surg 60:1234-1240, 2002 Microbial Complexes Detected in the Second/Third Molar Region in Patients With Asymptomatic Third Molars Raymond P. White, Jr, DDS, PhD,* Phoebus N. Madianos,
J Oral Maxillofac Surg 60:1234-1240, 2002 Microbial Complexes Detected in the Second/Third Molar Region in Patients With Asymptomatic Third Molars Raymond P. White, Jr, DDS, PhD,* Phoebus N. Madianos,
The relative lack of information and. Growth and development considerations in the diagnosis of gingivitis and periodontitis in children
 Literature Review Growth and development considerations in the diagnosis of gingivitis and periodontitis in children Enrique Bimstein, CD Lars Matsson, DDS Dr. Bimstein is a Professor, Department of Pediatric
Literature Review Growth and development considerations in the diagnosis of gingivitis and periodontitis in children Enrique Bimstein, CD Lars Matsson, DDS Dr. Bimstein is a Professor, Department of Pediatric
CLINICAL EVALUATION OF GINGIVAL SULCUS DEPTH IN PRIMARY DENTITION BY COMPUTERIZED, PRESSURE- SENSITIVE FLORIDA PROBE
 GMJ GULF MEDICAL JOURNAL ORAL PROCEEDINGS CLINICAL EVALUATION OF GINGIVAL SULCUS DEPTH IN PRIMARY DENTITION BY COMPUTERIZED, PRESSURE- SENSITIVE FLORIDA PROBE Anukriti Pathak 1 *, B. Nandlal 2 1Specialist
GMJ GULF MEDICAL JOURNAL ORAL PROCEEDINGS CLINICAL EVALUATION OF GINGIVAL SULCUS DEPTH IN PRIMARY DENTITION BY COMPUTERIZED, PRESSURE- SENSITIVE FLORIDA PROBE Anukriti Pathak 1 *, B. Nandlal 2 1Specialist
The Effect of X Ray Vertical Angulation on Radiographic Assessment of Alveolar Bone Loss
 1 The Effect of X Ray Vertical Angulation on Radiographic Assessment of Alveolar Bone Loss ABSTRACT M. Mehdizadeh MD*, M. Amintavakoli MD**, M. Allahverdi MD*** Introduction: Radiographs provide unique
1 The Effect of X Ray Vertical Angulation on Radiographic Assessment of Alveolar Bone Loss ABSTRACT M. Mehdizadeh MD*, M. Amintavakoli MD**, M. Allahverdi MD*** Introduction: Radiographs provide unique
Case Report Management of Neglected Severe Early Childhood Caries in a Six Year Old Female Child: A Three Year Follow Up
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS DENTAL SCIENCE Case Report Management of Neglected Severe Early Childhood Caries in a Six Year Old Female Child: A Three Year Follow Up Mansi Jain 1, Shalini Garg 2 *, Abhishek Dhindsa
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS DENTAL SCIENCE Case Report Management of Neglected Severe Early Childhood Caries in a Six Year Old Female Child: A Three Year Follow Up Mansi Jain 1, Shalini Garg 2 *, Abhishek Dhindsa
Logistics of Presentation. My Philosophy & Background. Course Objectives. Early Childhood Caries. Early Childhood Caries
 Oral Health: Early Intervention for Expectant Mothers and Children and the Impact on Overall Health Michelle Stafford, DDS Board Certified Pediatric Dentist October 11 th, 2014 Logistics of Presentation
Oral Health: Early Intervention for Expectant Mothers and Children and the Impact on Overall Health Michelle Stafford, DDS Board Certified Pediatric Dentist October 11 th, 2014 Logistics of Presentation
Journal of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
 Comparison of Systemic Ciprofloxacin in Elimination of A.a from Active Sites with Combination of Metronidzole and Amoxicillin in Patients with Aggressive Periodontitis: A Randomized Double Blind Controlled
Comparison of Systemic Ciprofloxacin in Elimination of A.a from Active Sites with Combination of Metronidzole and Amoxicillin in Patients with Aggressive Periodontitis: A Randomized Double Blind Controlled
Generalized gingival enlargement associated with aggressive periodontitis in a 20-year-old patient: case report and literature review
 J Oral Diag [online] 2016; 01:e20160024. ORIGINAL ARTICLE Marcos Custódio 1 * Paula Verona Ragusa da Silva 1 Norberto Nobuo Sugaya 1 Celso Augusto Lemos 1 Claudio Mendes Pannuti 1 Paulo Henrique Braz-Silva
J Oral Diag [online] 2016; 01:e20160024. ORIGINAL ARTICLE Marcos Custódio 1 * Paula Verona Ragusa da Silva 1 Norberto Nobuo Sugaya 1 Celso Augusto Lemos 1 Claudio Mendes Pannuti 1 Paulo Henrique Braz-Silva
Advanced Probing Techniques
 Module 21 Advanced Probing Techniques MODULE OVERVIEW The clinical periodontal assessment is one of the most important functions performed by dental hygienists. This module begins with a review of the
Module 21 Advanced Probing Techniques MODULE OVERVIEW The clinical periodontal assessment is one of the most important functions performed by dental hygienists. This module begins with a review of the
Small Animal Dentistry. Presented by: Rebecca Dodge, CVT
 Small Animal Dentistry Presented by: Rebecca Dodge, CVT Topics to be discussed Anatomy and oral examination Common dental problems for canines and felines Client knowledge and prevention tips Anatomy Dog
Small Animal Dentistry Presented by: Rebecca Dodge, CVT Topics to be discussed Anatomy and oral examination Common dental problems for canines and felines Client knowledge and prevention tips Anatomy Dog
Electronic Dental Records
 Electronic Dental Records Dr. Douglas K Benn, Professor of Maxillofacial Radiology & Director of Oral Diagnostic Systems, University of Florida and Health Conundrums LLC 8/2/2008 Dr Benn, University of
Electronic Dental Records Dr. Douglas K Benn, Professor of Maxillofacial Radiology & Director of Oral Diagnostic Systems, University of Florida and Health Conundrums LLC 8/2/2008 Dr Benn, University of
Frequency of Class II Cavities in Molars Requiring Root Canal Treatment in Pakistani Population
 Frequency of Class II Cavities in Molars Requiring Root Canal Treatment in Pakistani Population Dr Huma Sarwar, MDS resident 1, Dr Fazal ur-rehman Qazi, Associate Professor 1 Dr Shahbaz Ahmed, Associate
Frequency of Class II Cavities in Molars Requiring Root Canal Treatment in Pakistani Population Dr Huma Sarwar, MDS resident 1, Dr Fazal ur-rehman Qazi, Associate Professor 1 Dr Shahbaz Ahmed, Associate
Oral health status and behaviour in Jordanian adolescents aged years
 Oral health status and behaviour in Jordanian adolescents aged 12 18 years Leena Smadi Jordan University, Jordan RESEARCH Please cite this paper as: Smadi L. Oral health status and behaviour in Jordanian
Oral health status and behaviour in Jordanian adolescents aged 12 18 years Leena Smadi Jordan University, Jordan RESEARCH Please cite this paper as: Smadi L. Oral health status and behaviour in Jordanian
Factors affecting dental biofilm in patients wearing fixed orthodontic appliances
 Mei et al. Progress in Orthodontics (2017) 18:4 DOI 10.1186/s40510-016-0158-5 RESEARCH Open Access Factors affecting dental biofilm in patients wearing fixed orthodontic appliances Li Mei 1*, Joyce Chieng
Mei et al. Progress in Orthodontics (2017) 18:4 DOI 10.1186/s40510-016-0158-5 RESEARCH Open Access Factors affecting dental biofilm in patients wearing fixed orthodontic appliances Li Mei 1*, Joyce Chieng
Periodontal Maintenance
 Periodontal Maintenance Friday, February 20, 2015 1:06 PM Periodontal disease control always begins with patient education - Plaque control, diet, smoking cessation, impact that systemic health has on
Periodontal Maintenance Friday, February 20, 2015 1:06 PM Periodontal disease control always begins with patient education - Plaque control, diet, smoking cessation, impact that systemic health has on
Oral bacterial interactions in periodontal health and disease
 Vol. 6(5), pp. 51-57, August 2014 DOI: 10.5897/JDOH2014.0127 Article Number: 84910BB46956 ISSN 2006-9871 Copyright 2014 Author(s) retain the copyright of this article http://www.academicjournals.org/jdoh
Vol. 6(5), pp. 51-57, August 2014 DOI: 10.5897/JDOH2014.0127 Article Number: 84910BB46956 ISSN 2006-9871 Copyright 2014 Author(s) retain the copyright of this article http://www.academicjournals.org/jdoh
Self-check with plaque disclosing solution improves oral hygiene in schoolchildren living in a children s home
 Nagashima et al. Archives of Public Health (2018) 76:50 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13690-018-0296-y RESEARCH Open Access Self-check with plaque disclosing solution improves oral hygiene in schoolchildren
Nagashima et al. Archives of Public Health (2018) 76:50 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13690-018-0296-y RESEARCH Open Access Self-check with plaque disclosing solution improves oral hygiene in schoolchildren
Evaluation of the relationship between obesity, dental caries and periodontal disease in adolescents
 G. Vallogini*, V. Nobili**, R. Rongo***, S. De Rosa*, F. Magliarditi*, V. D Antò***, A. Galeotti* *Bambino Gesù Children s Hospital, Department of Paediatric Dentistry, Rome, Italy **Bambino Gesù Children
G. Vallogini*, V. Nobili**, R. Rongo***, S. De Rosa*, F. Magliarditi*, V. D Antò***, A. Galeotti* *Bambino Gesù Children s Hospital, Department of Paediatric Dentistry, Rome, Italy **Bambino Gesù Children
Case report Biological Restorations: An Alternative Esthetic Treatment for Restoration of Severely Mutilated Primary Anterior Teeth
 Jaypee s International Journal of Clinical Grewal Pediatric N, Reeshu Dentistry, S September-December 2008;1(1):42-47 Case report Biological Restorations: An Alternative Esthetic Treatment for Restoration
Jaypee s International Journal of Clinical Grewal Pediatric N, Reeshu Dentistry, S September-December 2008;1(1):42-47 Case report Biological Restorations: An Alternative Esthetic Treatment for Restoration
Point of Care. Question 1. Reference
 The Point of Care section of JCDA answers everyday clinical questions by providing practical information that aims to be useful at the point of patient care. The responses reflect the opinions of the contributors
The Point of Care section of JCDA answers everyday clinical questions by providing practical information that aims to be useful at the point of patient care. The responses reflect the opinions of the contributors
Prevalence of Gingival Recession and its Relationship to Past Orthodontic Treatment in Nepalese Young Adults
 Research Article Prevalence of and its Relationship to Past Orthodontic Treatment in Nepalese Young Adults Dr Bhageshwar Dhami, 1 Dr Priti Shrestha, 2 Dr Sujaya Gupta, 3 Dr Sujita Shrestha, 4 Dr Rabindra
Research Article Prevalence of and its Relationship to Past Orthodontic Treatment in Nepalese Young Adults Dr Bhageshwar Dhami, 1 Dr Priti Shrestha, 2 Dr Sujaya Gupta, 3 Dr Sujita Shrestha, 4 Dr Rabindra
Oral Health: A component of the Patient Centered Medical home
 Oral Health: A component of the Patient Centered Medical home Mark Deutchman MD University of Colorado Schools of Medicine, Dental Medicine and Public Health 1 Oral Health is a Fit for PCMH Patient centered
Oral Health: A component of the Patient Centered Medical home Mark Deutchman MD University of Colorado Schools of Medicine, Dental Medicine and Public Health 1 Oral Health is a Fit for PCMH Patient centered
Diagnosis. overt Examination. Definitive Examination. History. atient interview. Personal History. Clinical Examination.
 Diagnosis overt Examination History Definitive Examination atient interview Personal History Mental Attitude Medical History Dental History Clinical Examination Extra Oral Oral Radiographic Evaluation
Diagnosis overt Examination History Definitive Examination atient interview Personal History Mental Attitude Medical History Dental History Clinical Examination Extra Oral Oral Radiographic Evaluation
CLINICAL. Periodontal disease in healthy children: two clinical reports
 PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY/Copyright 1984 by The American Academy of PedodonticsAlol. 6 No. I CLINICAL Periodontal disease in healthy children: two clinical reports Ronald B. Cogen, DDS, PhD Wesam A1-Joburi,
PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY/Copyright 1984 by The American Academy of PedodonticsAlol. 6 No. I CLINICAL Periodontal disease in healthy children: two clinical reports Ronald B. Cogen, DDS, PhD Wesam A1-Joburi,
Risk indicators for aggressive periodontitis in an untreated isolated young population from Brazil
 Periodontics Periodontology Risk indicators for aggressive periodontitis in an untreated isolated young population from Brazil Priscila Corraini (a) Cláudio Mendes Pannuti (b) Alessandro Nautili Pustiglioni
Periodontics Periodontology Risk indicators for aggressive periodontitis in an untreated isolated young population from Brazil Priscila Corraini (a) Cláudio Mendes Pannuti (b) Alessandro Nautili Pustiglioni
Dental Anatomy and Occlusion
 CHAPTER 53 Dental Anatomy and Occlusion Ma Lou C. Sabino DDS, and Emily G. Smythe, DDS What numerical system is used most commonly in the United States for designating the adult dentition? Pediatric dentition?
CHAPTER 53 Dental Anatomy and Occlusion Ma Lou C. Sabino DDS, and Emily G. Smythe, DDS What numerical system is used most commonly in the United States for designating the adult dentition? Pediatric dentition?
Materials and Methods: Literature review and Authors opinion.
 Haffajee AD, Bogren A, Hasturk H et al. Subgingival microbiota of chronic periodontitis subjects from different geographic locations. J Clin Periodontol 2004; 31:996-1002. Purpose: To compare the subgingival
Haffajee AD, Bogren A, Hasturk H et al. Subgingival microbiota of chronic periodontitis subjects from different geographic locations. J Clin Periodontol 2004; 31:996-1002. Purpose: To compare the subgingival
ORIGINAL RESEARCH. Self-reported Awareness of Oral Health and Infant Oral Health among Pregnant Women in Mangalore, India- A Prenatal Survey
 Dr. Varghese Chacko M.D.S (Paedodontics & Preventive Dentistry) is Associate Professor, Department of Pedodontics & Preventive Dentistry, Manipal College of Dental Sciences (Mangalore), Manipal University,
Dr. Varghese Chacko M.D.S (Paedodontics & Preventive Dentistry) is Associate Professor, Department of Pedodontics & Preventive Dentistry, Manipal College of Dental Sciences (Mangalore), Manipal University,
Patient had no significant findings in medical history. Her vital signs were 130/99, pulse 93.
 Julia Collins Den 1200 Journal #4 1. Demographics Patient is J.S. age 29, Heavy/II 2. Assessment Patient had no significant findings in medical history. Her vital signs were 130/99, pulse 93. Patient does
Julia Collins Den 1200 Journal #4 1. Demographics Patient is J.S. age 29, Heavy/II 2. Assessment Patient had no significant findings in medical history. Her vital signs were 130/99, pulse 93. Patient does
PERIODONTAL CASE PRESENTATION - 1
 PERIODONTAL CASE PRESENTATION - 1 Overview A 32 year-old patient presented with generalized aggressive periodontitis. Treatment included non-surgical therapy with adjunctive antibiotics and surgical treatment.
PERIODONTAL CASE PRESENTATION - 1 Overview A 32 year-old patient presented with generalized aggressive periodontitis. Treatment included non-surgical therapy with adjunctive antibiotics and surgical treatment.
Primary Teeth Chapter 18. Dental Anatomy 2016
 Primary Teeth Chapter 18 Dental Anatomy 2016 Primary Teeth - Introduction Synonyms deciduous teeth, baby teeth, temporary teeth, milk teeth. There are 20 primary teeth, designated as A thru T in the Universal
Primary Teeth Chapter 18 Dental Anatomy 2016 Primary Teeth - Introduction Synonyms deciduous teeth, baby teeth, temporary teeth, milk teeth. There are 20 primary teeth, designated as A thru T in the Universal
Appendix. CPT only copyright 2007 American Medical Association. All rights reserved. NTHSteps Dental Guidelines
 Appendix NTHSteps Dental Guidelines N N.1 American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry Periodicity Guidelines.................. N-2 N.2 American Dental Association Guidelines for Prescribing Dental Radiographs.........
Appendix NTHSteps Dental Guidelines N N.1 American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry Periodicity Guidelines.................. N-2 N.2 American Dental Association Guidelines for Prescribing Dental Radiographs.........
MDJ Lower Arch Crowding In Relation To Periodontal Disease Vol.:5 No.:2 2008
 MDJ Lower Arch Crowding In Relation To Periodontal Disease Dr. Barzam Abdulwahab, B.D.S M.sc. (periodontics) Abstract A clinical examination was done to study the relationship between crowding and periodontal
MDJ Lower Arch Crowding In Relation To Periodontal Disease Dr. Barzam Abdulwahab, B.D.S M.sc. (periodontics) Abstract A clinical examination was done to study the relationship between crowding and periodontal
Relationship between pulpal involvement of primary molars and eruption pattern of premolars
 Relationship between pulpal involvement of primary molars and eruption pattern of premolars G. P. PINI PRATO, T. BACCETTI, L. FRANCHI, R. GIORGETTI*, A. MARINELLI SUMMARY. Aim This study s aim was to investigate
Relationship between pulpal involvement of primary molars and eruption pattern of premolars G. P. PINI PRATO, T. BACCETTI, L. FRANCHI, R. GIORGETTI*, A. MARINELLI SUMMARY. Aim This study s aim was to investigate
Dental health status of Hong Kong preschool children. Citation Hong Kong Dental Journal, 2009, v. 6 n. 1, p. 6-12
 Title Dental health status of Hong Kong preschool children Author(s) Lo, ECM; Loo, EKY; Lee, CK Citation Hong Kong Dental Journal, 2009, v. 6 n. 1, p. 6-12 Issued Date 2009 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/58042
Title Dental health status of Hong Kong preschool children Author(s) Lo, ECM; Loo, EKY; Lee, CK Citation Hong Kong Dental Journal, 2009, v. 6 n. 1, p. 6-12 Issued Date 2009 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/58042
Essentials of Oral Health
 Essentials of Oral Health Oral Development Developing teeth from the prenatal period through adolescence benefit from fluoride and good nutrition and are susceptible to the damaging effects of injuries,
Essentials of Oral Health Oral Development Developing teeth from the prenatal period through adolescence benefit from fluoride and good nutrition and are susceptible to the damaging effects of injuries,
