Localized scleroderma in childhood: review of the literature and case report
|
|
|
- Darren Park
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY/Copyright!987 by The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry Volume 9 Number 3 Localized scleroderma in childhood: review of the literature and case report W. Kim Seow, BDS, MDSc, FRACDS W. Young, BDSc, MSc, PhD, FRCD(C) Abstract Although the dental manifestations of the rare dermatologic disorder generalized scleroderma have been well described in adults, the oral manifestations of localized scleroderma in childhood are not well documented. A case of localized scleroderma in a female child is described which highlights the problems of dental management of the defects that interfere with dental and alveolar development. Literature Review Scleroderma, a relatively uncommon collagen disease of unknown etiology, was recognized more than 2 centuries ago (Capusan 1972). It is characterized induration and fixation of the skin to the deeper subcutaneous tissues. It may begin in children and young adults with females being twice as frequently affected as males (Weisman and Calcaterra 1978). The disease may occur in both the localized and systemic forms. In the localized form, also known as morphea, the changes are confined to skin and subcutaneous tissue with occasional involvement of deeper tissues (Kornreich et al. 1977). The cutaneous lesions are described as white or yellowish plaques, slightly elevated or depressed, and may occur as linear bands or ribbons, often termed en coup de sabre since they resemble the marks produced by a sabre sword (Shafer et al. 1983). The systemic form of the disease is characterized by diffuse fibrosis of the skin and certain internal organs, primarily the blood vessels, gastrointestinal tract, lungs, heart, and kidneys (Eversole et al. 1974; Shafer et al. 1983). The chief manifestations include thickening and induration of the skin, digital pitting, sclerodactyly, pigmentations, telangiectasia, 1 and Raynaud s phenomenon. The oral manifestations of scleroderma include fibrosis and rigidity of facial skin, tongue, soft palate, larynx, ~ salivary glands, and buccal mucous membrane lkass et al. 1966; Dabich et al. 1974; Eversole et al. 1974; Kornreich et al. 1977; Sharer et al ~ Eversole et al. 1974; Weisman and Calcaterra 1978; Marmary et al. 1981; Naylor leading to microstomia, dysarthria, dysphagia, and xerostomia. Periodontal manifestations such as loss of attached gingiva and multiple foci of recession have been reported (Eversole et al. 1974). It is suggested that the external pressure created by the skin changes may result in resorption of the alveolar bone, tilting of the teeth, delayed tooth eruption and early exfoliation of the teeth (Looby and Burket 1942). Radiographic signs include characteristic widening of the periodontal ligament space without increased tooth mobility and resorption of the coronoid process, condyle, and posterior aspect of the ascending ramus of the mandible. 3 These changes in the mandible and TMJ cause impaired growth and development as well as functional problems such as subluxation and abnormal motion (Nandakumar et al. 1983). Although scleroderma usually is classified into clinical categories of localized and systemic forms, this distinction is not always clear-cut. Several authors now have suggested that localized cutaneous scleroderma in the form of morphea or linear bands does not preclude the 4 development of progressive systemic sclerosis. The oral signs of scleroderma have been described mainly in adults. Although there are several reports on childhood scleroderma in the medical literature, only minimal information is available on the oral aspects. The first case report on the dental manifestations of localized childhood scleroderma was presented by Looby and Burket in Two decades later, Hoggins and Hamilton (1969) described a similar case. This paper presents patient with localized scleroderma, emphasizing the early features and dental management of this rare dermatologic disorder. Clinical Report A Caucasian female patient 5.5 years of age was referred to the University Dental School by her derma- 3 Seifert et al. 1975; White et al. 1977; Marmary et al. 1981; Nandakumar et al Rocinan and Fennell 1962; Kass et al. 1966; Kornreich et al. 1977; Masi et al. 1980; Kuto et al LOCALIZED SCLERODERMA IN CHILDHOOD: SEOW AND YOUNG
2 tologist who had diagnosed a condition of localized scleroderma after biopsy of a skin lesion on her cheek. She was of normal intelligence, with height 113 cm (50th percentile) and weight 17.0 kg (25th percentile). A linear, flat, white scar-like lesion, approximately 0.5 cm wide, extended from the bridge of the nose through the right ala and the right side of the philtrum of the lip (Fig 1). A 2-cm white, non-raised, indurated plaque with superficial hemorrhagic crusting (which was the site of the biopsy, Fig 2) was noted on her right cheek just below the malar eminence. No other skin lesions were apparent and no developmental dysmorphological features were noted. diagnosis of scleroderma was confirmed by histopathology- Tests to exclude systemic involvement of the disease such as anticentromere antibody were negative. However, blood tests revealed raised erythrocyte sedimentation rate as well as increased neutrophil and eosinophil counts. Antinuclear antibody tests were done to exclude systemic lupus erythematosus and these were negative. As there appeared to be no systemic involvement, no medical treatment was given at this stage. Dental Manifestations The patient's dental problems first were noted by her general dental practitioner when, after her fall, he observed that the maxillary right primary central incisor FIG 2. The plaque was an irregular, ivory-colored sclerosis of the skin with loss of normal skin creases. The scab is at the site of the biopsy (2x). FIG 1. Two lesions of localized scleroderma on the face of a 6- year-old girl. A coup de sabre linear scar extends through the right ala and philtrum and a plaque is present on the right cheek. Medical History The patient was the product of a normal full-term pregnancy of a nonconsanguinous marriage. She weighed 3.1 kg at birth. Apart from mild jaundice at birth and occasional asthma which was controlled by Ventolin syrup, her medical history was insignificant. The skin lesions and dental problems appeared to date from about 2 years previously when she sustained a fall, striking and loosening the root of her maxillary right primary central incisor. She was taken to a medical general practitioner who in turn referred her to a dermatologist. A punch biopsy of skin was performed and was loose and displaced mesially. There was a deep periodontal pocket on the mesial aspect of the tooth. A periapical radiograph taken at that time revealed extensive bone loss around the maxillary incisors (Fig 3, next page). The maxillary right primary central incisor was subsequently extracted. When the patient first presented to the University Dental School, it was observed that there was a large defect of the labial gingiva and maxillary alveolus where the right primary central incisor had been lost (Fig4, next page). At approximately 10 mm from the alveolar crest, the labial surface of the crown of the permanent right central incisor was exposed about 5 mm. The alveolar defect appeared to coincide in line with the scar on the philtrum. The maxillary right primary lateral incisor and the left primary central incisor appeared to be tilted toward the alveolar defect. The maxillary right primary lateral incisor was only slightly mobile despite a large area of exposed root surface on its mesial and labial aspect. Periodontal probing did not reveal any pockets greater than 2 mm. PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY: SEPTEMBERl987/VoL. 9 No
3 FIG 4. The maxillary anterior dentition 2 months after tooth exfoliation. There is a large alveolar defect on the right, the permanent central incisor crown is exposed, and there is loss of periodontal support on the mesial of the right primary lateral incisor. FIG 3. Periapical radiograph of the maxillary incisors taken at first detection of scleroderma. The right central incisor was loosened secondary to a fall. There is widening of the periodontal membrane and proximal bone loss between the primary incisors. An orthopantogram revealed all permanent teeth except the third molars to be present. An anterior maxillary occlusal radiograph showed that the permanent maxillary right central incisor had a slight palatal inclination relative to the left incisor (Fig 5). No bone abnormalities were detected in those radiographs or in full-mouth periapical radiographs. In addition, the periapical films showed no evidence of an increase in periodontal membrane spaces frequently reported in diffuse scleroderma (Marmary et al. 1981). A soft-tissue radiograph revealed no evidence of calcification in the cheek lesion. The lips, tongue, floor of the mouth, soft palate, and pharynx were of normal mobility. No dysphagia was reported and speech was normal. Histopathology Sections stained with H&E (Fig 6) showed dense sclerosis of dermal collagen extending into superficial subcutaneous fat. There was loss of dermal appendages particularly the sweat glands and atrophy of the epithelium with loss of rete pegs. Blood vessels were few and sclerotic changes were seen in their walls. The maxillary right primary central incisor had been kept in a dried state by the patient's mother. A ground section of this tooth showed no defect in enamel or dentin formation. The apical third of the root was tapered and the dentin was thinner than in the mid-third. Over this thinned dentin a thick layer of normal cellular cementum was present and showed evidence of a moderate amount of external resorption along the lateral aspects of the root and mildly at the apex. These findings were consistent with tooth exfoliation secondary to loss of periodontal support. Dental Management The immediate dental management was directed at the prevention of further loss of support surrounding the maxillary incisors. Although this loss of support was thought to be due to scleroderma, the prevention of further resorption secondary to periodontal inflammation from plaque on the primary lateral and left central FIG 5. Anterior maxillary occlusal radiograph of the affected area. Note palatal inclination of the permanent right central incisor which may be the result of a dilaceration. The radiolucency on the cingulum of this tooth may be a developmental pit. 242 LOCALIZED SCLERODERMA IN CHILDHOOD: SHOW AND YOUNG
4 incisor was the first priority. The patient and her mother were instructed in meticulous oral cleaning of the site. She was recalled monthly and no further progression of bone resorption was found. The permanent maxillary right central incisor which is due to erupt within the next 2 years may present several problems. First, it is possible that local fibrosis may impede tooth eruption and alveolar growth. Second, if orthodontic movement is required to encourage eruption or to correct the slight palatal inclination of this tooth, it may not respond normally to orthodontic forces. Third, the lack of labial attached gingiva may present an esthetic problem, already compromised by lack of alveolar growth in this region. This may be corrected by gingival grafts; however, the success of these grafts in scleroderma is unknown. Discussion Although the oral manifestations of systemic scleroderma have been well documented, particularly in the adult patient, there are only 2 reports in the dental literature of the dentofacial aspects of childhood scleroderma. Manifestations similar to those in this case such as localized facial skin fibrosis, loss of periodontal support, early exfoliationof primary teeth, lack of alveolar growth, and eruption of permanent teeth have been reported previously in an 8-year-old female patient (Looby and Burket 1942). Lack of alveolar growth in the localized affected region has been described in a 6-year-old female. Her left primary lateral incisor was tilted distally and the primary canine and first molar failed to reach occlusion (Rodnan, 1979). Since the histologic features of the involved tooth are normal in this case, the lesion most likely developed with the local scleroderma after dental formation had occurred. Children presenting with localized scleroderma must be assessed carefully, not only for oral problems but also for systemic manifestations as well. Long-term follow-up into adulthood is necessary since systemic involvement may supervene. The present report appears to conform to the clinical and histological parameters of localized scleroderma with no attendant features of the generalized form. Accordingly, no systemic treatment is underway and the patient is under 6-month observation by her dermatologists. She will be monitored for dental and alveolar development and esthetics. Dr. Seow is a lecturer, paediatric dentistry, and Dr. Young is an associate professor, oral biology, University of Queensland Dental School. Reprint requests should be sent to: Dr. W. Kim Seow, Dept, of Paediatric Dentistry, University of Queensland, Dental School, Turbot St., Brisbane, Queensland, Australia ' " CapusanI: Crusio's case of scleroderma. Ann Intern Med 76:146-50, Dabich L, Sullivan DB, Cassidy JT: Scleroderma in the child. J Pediatr 85:770-75,1974. Eversole LR, Jacobsen PL, Stone CE: Oral and gingival changes in systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). J Periodontol 55:175-78,1974. ~[?:? %r:';-. % \.'V*',^--/^* ; ' "_^a ^>.' '^Ar V 3r-" ; *' '^, V-'^V- -' /'- ^:T:^^' V r^'l^ " : : -^^V^^:^^'^>"' - ^ ' i^«*^*cq> ; ; ;f' V^-'T"-^ A >.- -^ -- v :J^:^.:-'>rr'- J " /i- < ^1*^*2* -' Y*..-. v - v / d: >i." ' - -i.-.' i» w?z. ^^^^-^m^m«m ^':mf^i^:^i^mim FIG 6. Section of affected skin of right cheek showing thinned epidermis, atrophy of skin adnexal structures and rete ridges, dermal sclerosis with excess collagen, and avascularity (H&E, 200x). Hoggins GS, Hamilton MC: Dentofacial defects associated with scleroderma. Oral Surg 27:734-36,1969. Kass H, Hansen V, Patrick J: Scleroderma in childhood. J Pediatr 68:243-56, Kornreich HK, King KK, Bernstein BH, Singsen BH, Hanson V: Scleroderma in childhood. Arthritis Rheum 20:343-50, Kuto F, Sakaguchi T, Horasawa Y, Hayashi M, Hirasawa Y, Tokuhiro H: Total hemiatrophy. Association with localised scleroderma, Schonlein-Henoch nephritis and paroxysmal nocternal hemoglobinuria. Arch Intern Med 145: ,1985. Looby JP, Burket LW: Scleroderma of the face with involvement of the alveolar process. Am J Orthod Oral Surg 28:493-98,1942. Marmary Y, GlaissR, PisantyS: Scleroderma: oral manifestations. Oral Surg 52:32-37,1981. PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY: SEPTEMBERl987/VoL. 9 No
5 Masi AT, Rodnan GP, Medsger TA et al: Preliminary criteria for the classification of systemic.sclerosis (scleroderma). Arthritis Rheum 23:581-86, Nandakumar E, Kumar V, Cherian M]: Mandibular osteolysis in progressive systemic sclerosis. Australas Radio127:167-69,1983. Naylor WP: Oral management of the scleroderma patient, l Am Dent Assoc 105:814-17, Rodnan GP, Fennell RH: Progressive systemic sclerosis (sderoderma). J Am Med Assoc 180:665-70, Rodnan GP: Progressive systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). Philadelphia; Lea and Febiger, 1979 pp Ryatt KS, Hopper FE, Cottrell JA: Mandibular resorption in systemic sclerosis. Br J Dermatol 107:711-14, Seifert MH, Steigerwolf JC, Cliff MM: Bone resorption of the mandible in progressive systemic,sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum 18:507-11, Shafer WG, Hine MK, Levy BM: Textbook of Oral Pathology. Philadelphia; WB Saunders Co, 1983 pp Weisman RA, Calcaterra TC: Head and neck manifestations of scleroderma. Ann Oto187:332-39, White SC, Frey NW, Blaschke DD, Ross MD, Clements PJ, Furst DE, Paulus HE: Oral radiographic changes in patients with PSS (scleroderma). J Am Dent Assoc 94: , Immunization: new U.S. schedule Getting your children fully immunized has become easier. The most recent guidelines from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control alter the schedule of vaccinations, reducing the number of visits needed to complete the process. Until now, a child had to be taken for immunization at 15 months for the combined measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccine, and again at 18 months for the third dose of oral poliovirus (OPV) vaccine and the fourth of diphtheria-tetanus-pertussis (DTP) vaccine. Now, children 15 months or older can be given these three immunizations simultaneously. One less visit may also prevent overlooking a vital immunization, thereby increasing the number of children who receive the complete series of vaccinations. It is important for parents to consult their doctor for his/her recommendations for a child s immunization schedule. Some physicians may prefer to continue giving MMR at 15 months, followed by DTP/OPV at 18 months, especially if other purposes are served by the additional visit to the doctor. New Immunization Schedule for Healthy Infants and Children 2 months 4 months 6 months 15 months 24 months 4-6 years Every 10 years First diphtheria-tetanus-pertussis (DTP) and oral polio (OPV) Second DTP and OPV Third DTP Measles-mumps-rubella (MMR), fourth DTP, and third OPV Hemophilus influenza type b (HBPV) Fifth DTP and fourth OPV Diphtheria/tetanus booster 244 LOCALIZED SCLERODERMA IN CHILDHOOD: SEOW AND YOUNG
Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development. Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L.
 Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L. Dennis Proximal contact areas Contact areas are on the mesial and
Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L. Dennis Proximal contact areas Contact areas are on the mesial and
Dental Morphology and Vocabulary
 Dental Morphology and Vocabulary Palate Palate Palate 1 2 Hard Palate Rugae Hard Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate 4 Palate Hard Palate Soft Palate Maxillary Arch (Maxilla) (Uppers)
Dental Morphology and Vocabulary Palate Palate Palate 1 2 Hard Palate Rugae Hard Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate 4 Palate Hard Palate Soft Palate Maxillary Arch (Maxilla) (Uppers)
Oral Embryology and Histology
 Oral Embryology and Histology Chapter 8 Copyright 2018, Elsevier Inc. All Rights Reserved. 1 Learning Objectives Lesson 8.1: Oral Embryology 1. Pronounce, define, and spell the key terms. 2. Define embryology
Oral Embryology and Histology Chapter 8 Copyright 2018, Elsevier Inc. All Rights Reserved. 1 Learning Objectives Lesson 8.1: Oral Embryology 1. Pronounce, define, and spell the key terms. 2. Define embryology
6610 NE 181st Street, Suite #1, Kenmore, WA
 660 NE 8st Street, Suite #, Kenmore, WA 9808 www.northshoredentalacademy.com.08.900 READ CHAPTER The Professional Dental Assistant (p.-9) No Key Terms Recall Questions:,,,, and 6 CLASS SYLLABUS DAY READ
660 NE 8st Street, Suite #, Kenmore, WA 9808 www.northshoredentalacademy.com.08.900 READ CHAPTER The Professional Dental Assistant (p.-9) No Key Terms Recall Questions:,,,, and 6 CLASS SYLLABUS DAY READ
Prosthetic Options in Implant Dentistry. Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor
 Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
1. What is the highest and sharpest cusp on the lower first deciduous molar? 2. Which of the following is NOT the correct location of an embrasure?
 1 1. What is the highest and sharpest cusp on the lower first deciduous molar? a. mesiobuccal b. distobuccal c. distolingual d.mesiolingual 2. Which of the following is NOT the correct location of an embrasure?
1 1. What is the highest and sharpest cusp on the lower first deciduous molar? a. mesiobuccal b. distobuccal c. distolingual d.mesiolingual 2. Which of the following is NOT the correct location of an embrasure?
Attachment G. Orthodontic Criteria Index Form Comprehensive D8080. ABBREVIATIONS CRITERIA for Permanent Dentition YES NO
 First Review IL HFS Dental Program Models Second Review Ortho cad Attachment G Orthodontic Criteria Index Form Comprehensive D8080 Ceph Film X-Rays Photos Narrative Patient Name: DOB: ABBREVIATIONS CRITERIA
First Review IL HFS Dental Program Models Second Review Ortho cad Attachment G Orthodontic Criteria Index Form Comprehensive D8080 Ceph Film X-Rays Photos Narrative Patient Name: DOB: ABBREVIATIONS CRITERIA
Dental Anatomy and Occlusion
 CHAPTER 53 Dental Anatomy and Occlusion Ma Lou C. Sabino DDS, and Emily G. Smythe, DDS What numerical system is used most commonly in the United States for designating the adult dentition? Pediatric dentition?
CHAPTER 53 Dental Anatomy and Occlusion Ma Lou C. Sabino DDS, and Emily G. Smythe, DDS What numerical system is used most commonly in the United States for designating the adult dentition? Pediatric dentition?
Academic Affiliate Fellowship Practice Exam: 2018
 Academic Affiliate Fellowship Practice Exam: 2018 Current History: A patient presents to your practice complaining of a tight feeling in her perioral tissue area. She is unable to open her mouth fully
Academic Affiliate Fellowship Practice Exam: 2018 Current History: A patient presents to your practice complaining of a tight feeling in her perioral tissue area. She is unable to open her mouth fully
Primary Teeth Chapter 18. Dental Anatomy 2016
 Primary Teeth Chapter 18 Dental Anatomy 2016 Primary Teeth - Introduction Synonyms deciduous teeth, baby teeth, temporary teeth, milk teeth. There are 20 primary teeth, designated as A thru T in the Universal
Primary Teeth Chapter 18 Dental Anatomy 2016 Primary Teeth - Introduction Synonyms deciduous teeth, baby teeth, temporary teeth, milk teeth. There are 20 primary teeth, designated as A thru T in the Universal
Shell teeth m management from the mixed to the permanent dentition: case report Rosamund Harrison, DMD, MS, MRCD(C) CASE REPORTS.
 Shell teeth m management from the mixed to the permanent dentition: case report Rosamund Harrison, DMD, MS, MRCD(C) David Kennedy, BDS, MSD, FRCD(C) CASE REPORTS Introduction Relatively few cases of shell
Shell teeth m management from the mixed to the permanent dentition: case report Rosamund Harrison, DMD, MS, MRCD(C) David Kennedy, BDS, MSD, FRCD(C) CASE REPORTS Introduction Relatively few cases of shell
Plaque and Occlusion in Periodontal Disease Wednesday, February 25, :54 AM
 Plaque and Occlusion in Periodontal Disease Wednesday, February 25, 2015 9:54 AM 1. The definition of Trauma From Occlusion: Primary TFO, Secondary TFO, and Combined TFO 2. Clinical and Radiographic signs
Plaque and Occlusion in Periodontal Disease Wednesday, February 25, 2015 9:54 AM 1. The definition of Trauma From Occlusion: Primary TFO, Secondary TFO, and Combined TFO 2. Clinical and Radiographic signs
SCLERODERMA 101. Maureen D. Mayes, MD, MPH Professor of Medicine University of Texas - Houston
 SCLERODERMA 101 Maureen D. Mayes, MD, MPH Professor of Medicine University of Texas - Houston TYPES OF SCLERODERMA Localized versus Systemic Two Kinds of Scleroderma Localized Scleroderma Morphea Linear
SCLERODERMA 101 Maureen D. Mayes, MD, MPH Professor of Medicine University of Texas - Houston TYPES OF SCLERODERMA Localized versus Systemic Two Kinds of Scleroderma Localized Scleroderma Morphea Linear
Arrangement of the artificial teeth:
 Lecture Prosthodontic Dr. Osama Arrangement of the artificial teeth: It s the placement of the teeth on a denture with definite objective in mind or it s the setting of teeth on temporary bases. Rules
Lecture Prosthodontic Dr. Osama Arrangement of the artificial teeth: It s the placement of the teeth on a denture with definite objective in mind or it s the setting of teeth on temporary bases. Rules
Advanced Probing Techniques
 Module 21 Advanced Probing Techniques MODULE OVERVIEW The clinical periodontal assessment is one of the most important functions performed by dental hygienists. This module begins with a review of the
Module 21 Advanced Probing Techniques MODULE OVERVIEW The clinical periodontal assessment is one of the most important functions performed by dental hygienists. This module begins with a review of the
Lecture 2 Maxillary central incisor
 Lecture 2 Maxillary central incisor Generally The deciduous tooth appears in the mouth at 3 18 months of age, with 6 months being the average and is replaced by the permanent tooth around 7 8 years of
Lecture 2 Maxillary central incisor Generally The deciduous tooth appears in the mouth at 3 18 months of age, with 6 months being the average and is replaced by the permanent tooth around 7 8 years of
The future of health is digital
 Dated: XX/XX/XXXX Name: XXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXX Birth Date: XX/XX/XXXX Date of scan: XX/XX/XXXX Examination of the anatomical volume: The following structures are reviewed and evaluated for bilateral symmetry,
Dated: XX/XX/XXXX Name: XXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXX Birth Date: XX/XX/XXXX Date of scan: XX/XX/XXXX Examination of the anatomical volume: The following structures are reviewed and evaluated for bilateral symmetry,
RAJ M. SAINI, DDS, MSD
 Restoring and Maintaining Periodontal Health with Orthodontic Treatment RAJ M. SAINI, DDS, MSD rajmsaini@yahoo.com Diplomate Of The American Board Of Orthodontics Clinical Professor Of Orthodontics New
Restoring and Maintaining Periodontal Health with Orthodontic Treatment RAJ M. SAINI, DDS, MSD rajmsaini@yahoo.com Diplomate Of The American Board Of Orthodontics Clinical Professor Of Orthodontics New
Unusual transmigration of canines report of two cases in a family
 ISSN: Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2014 Jan-Mar;11(1):88-92 Case Report Article Unusual transmigration of canines report of two cases in a family Sulabha A. Narsapur 1 Sameer Choudhari 2 Shrishal
ISSN: Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2014 Jan-Mar;11(1):88-92 Case Report Article Unusual transmigration of canines report of two cases in a family Sulabha A. Narsapur 1 Sameer Choudhari 2 Shrishal
Morphology of an Anatomic Crown. By: Assistant Professor Dr. Baydaa Ali Al - Rawi
 Morphology of an Anatomic Crown By: Assistant Professor Dr. Baydaa Ali Al - Rawi October 4, 2009 Elevated landmarks Depressed landmarks A) Elevated landmarks : 1. Dental lobe : is one of the primary centers
Morphology of an Anatomic Crown By: Assistant Professor Dr. Baydaa Ali Al - Rawi October 4, 2009 Elevated landmarks Depressed landmarks A) Elevated landmarks : 1. Dental lobe : is one of the primary centers
Hereditary Opalescent Dentin: A Report of Two Cases
 Hereditary Opalescent Dentin: A Report of Two Cases Siddharth Gupta, BDS, MDS; Rahul R. Bhowate, BDS, MDS; Ashok Bhati, BDS, MDS Abstract Aim: The aim of this case report is to present the clinical and
Hereditary Opalescent Dentin: A Report of Two Cases Siddharth Gupta, BDS, MDS; Rahul R. Bhowate, BDS, MDS; Ashok Bhati, BDS, MDS Abstract Aim: The aim of this case report is to present the clinical and
Correction of a maxillary canine-first premolar transposition using mini-implant anchorage
 CASE REPORT Correction of a maxillary canine-first premolar transposition using mini-implant anchorage Mehmet Oguz Oztoprak, DDS, MSc, a Cigdem Demircan, DDS, b Tulin Arun, PhD, DDS, MSc c Transposition
CASE REPORT Correction of a maxillary canine-first premolar transposition using mini-implant anchorage Mehmet Oguz Oztoprak, DDS, MSc, a Cigdem Demircan, DDS, b Tulin Arun, PhD, DDS, MSc c Transposition
Diagnosis. overt Examination. Definitive Examination. History. atient interview. Personal History. Clinical Examination.
 Diagnosis overt Examination History Definitive Examination atient interview Personal History Mental Attitude Medical History Dental History Clinical Examination Extra Oral Oral Radiographic Evaluation
Diagnosis overt Examination History Definitive Examination atient interview Personal History Mental Attitude Medical History Dental History Clinical Examination Extra Oral Oral Radiographic Evaluation
Journal of Pediatric Sciences
 Journal of Pediatric Sciences Progressive facial hemiatrophy with contralateral maxillary mucocele Mohd Ashraf, Sheikh Javeed Sultan, Javed Ahmad Journal of Pediatric Sciences 2010;2:e11 How to cite this
Journal of Pediatric Sciences Progressive facial hemiatrophy with contralateral maxillary mucocele Mohd Ashraf, Sheikh Javeed Sultan, Javed Ahmad Journal of Pediatric Sciences 2010;2:e11 How to cite this
Large Dentigerous Cyst
 Volume 16.2.1 Feb 2016 This Lecture Series qualifies for 0.5 Informal CPD Learning Hours Large Dentigerous Cyst By Dr Hassem Geha A 55 year-old male presented with a painless swelling in the right mandible.
Volume 16.2.1 Feb 2016 This Lecture Series qualifies for 0.5 Informal CPD Learning Hours Large Dentigerous Cyst By Dr Hassem Geha A 55 year-old male presented with a painless swelling in the right mandible.
Progressive systemic sclerosis in a child: case report
 CASE REPORT Progressive systemic sclerosis in a child: case report C.C.E. Tai, P. Lee, MD R.E. Wood, DDS, MSc Abstract A case o,fpediatric progressive systemic sclerosis is reported and a literature review
CASE REPORT Progressive systemic sclerosis in a child: case report C.C.E. Tai, P. Lee, MD R.E. Wood, DDS, MSc Abstract A case o,fpediatric progressive systemic sclerosis is reported and a literature review
Dr.Sepideh Falah-kooshki
 Dr.Sepideh Falah-kooshki MAXILLA Premaxillary/median palatal suture (radiolucent). Incisive fossa and foramen (radiolucent). Nasal passages (radiolucent). Nasal septum (radiopaque). Anterior nasal spine
Dr.Sepideh Falah-kooshki MAXILLA Premaxillary/median palatal suture (radiolucent). Incisive fossa and foramen (radiolucent). Nasal passages (radiolucent). Nasal septum (radiopaque). Anterior nasal spine
Clinical details: Details of scan: CONE BEAM CT REPORT: Name: H. B. Gender: Reason for referral: Referred by:
 Name: H. B. Gender: Male DOB: 11/12/1950 Age: 64 Date taken: 16/11/2015 Date reported: 19/11/2015 Clinical details: Reason for referral: Referred by: Investigate symptoms related to left TMJ. Reconstructed
Name: H. B. Gender: Male DOB: 11/12/1950 Age: 64 Date taken: 16/11/2015 Date reported: 19/11/2015 Clinical details: Reason for referral: Referred by: Investigate symptoms related to left TMJ. Reconstructed
The periodontium attempts to accommodate to the forces exerted to the crown. This adaptive capacity varies in different persons and in the same person
 The periodontium attempts to accommodate to the forces exerted to the crown. This adaptive capacity varies in different persons and in the same person at different times. The effect of occlusal forces
The periodontium attempts to accommodate to the forces exerted to the crown. This adaptive capacity varies in different persons and in the same person at different times. The effect of occlusal forces
NATIONAL EXAMINING BOARD FOR DENTAL NURSES
 NATIONAL EXAMINING BOARD FOR DENTAL NURSES NATIONAL DIPLOMA EXAMINATION DENTAL CHARTING NEBDN is a limited company registered in England & Wales No. 5580200 Registered with the Charity Commisioners No.
NATIONAL EXAMINING BOARD FOR DENTAL NURSES NATIONAL DIPLOMA EXAMINATION DENTAL CHARTING NEBDN is a limited company registered in England & Wales No. 5580200 Registered with the Charity Commisioners No.
FRACTURES AND LUXATIONS OF PERMANENT TEETH
 FRACTURES AND LUXATIONS OF PERMANENT TEETH 1. Treatment guidelines and alveolar bone Followup Procedures INFRACTION Clinical findings Radiographic findings Treatment Follow-Up Favorable Outcome Unfavorable
FRACTURES AND LUXATIONS OF PERMANENT TEETH 1. Treatment guidelines and alveolar bone Followup Procedures INFRACTION Clinical findings Radiographic findings Treatment Follow-Up Favorable Outcome Unfavorable
Dental Anatomy High Yield Notes. **Atleast 35 questions comes from these areas of old lectures**
 Dental Anatomy High Yield Notes **Atleast 35 questions comes from these areas of old lectures** This review notes compiled and prepared by my sister for her own study, as a last day review session for
Dental Anatomy High Yield Notes **Atleast 35 questions comes from these areas of old lectures** This review notes compiled and prepared by my sister for her own study, as a last day review session for
Prevalence of root dilaceration in adult dental patients in Croatia
 Prevalence of root dilaceration in adult dental patients in Croatia Ana Malčić, DDS, a Silvana Jukić, DDS, PhD, b Valentina Brzović, DDS, a Ivana Miletić, DDS,PhD, b Ivica Pelivan, DDS, d and Ivica Anić,
Prevalence of root dilaceration in adult dental patients in Croatia Ana Malčić, DDS, a Silvana Jukić, DDS, PhD, b Valentina Brzović, DDS, a Ivana Miletić, DDS,PhD, b Ivica Pelivan, DDS, d and Ivica Anić,
COMBINED PERIODONTAL-ENDODONTIC LESION. By Dr. P.K. Agrawal Sr. Prof and Head Dept. Of Periodontia Govt. Dental College, Jaipur
 COMBINED PERIODONTAL-ENDODONTIC LESION By Dr. P.K. Agrawal Sr. Prof and Head Dept. Of Periodontia Govt. Dental College, Jaipur Differential diagnosis For differential diagnostic purposed the endo-perio
COMBINED PERIODONTAL-ENDODONTIC LESION By Dr. P.K. Agrawal Sr. Prof and Head Dept. Of Periodontia Govt. Dental College, Jaipur Differential diagnosis For differential diagnostic purposed the endo-perio
You know you would like to stop swearing at the computer after each shot. Troubleshooting oral radiography
 You know you would like to stop swearing at the computer after each shot Troubleshooting oral radiography Goals of oral radiology Achieve diagnostic images of the teeth and surrounding bone. Images should
You know you would like to stop swearing at the computer after each shot Troubleshooting oral radiography Goals of oral radiology Achieve diagnostic images of the teeth and surrounding bone. Images should
Tooth Variations. Suruedee Chinthakanan
 Tooth Variations Suruedee Chinthakanan Tooth variations Dental anomalies Cause : hereditary factor Developmental disturbances of teeth www.ectodermaldysplsia.org Tooth variations Enamel is formed from
Tooth Variations Suruedee Chinthakanan Tooth variations Dental anomalies Cause : hereditary factor Developmental disturbances of teeth www.ectodermaldysplsia.org Tooth variations Enamel is formed from
Evidence-based decision making in periodontal tooth prognosis
 Clin Dent Rev (2017) 1:3 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41894-017-0004-2 TREATMENT Evidence-based decision making in periodontal tooth prognosis Carlos Ernesto Nemcovsky 1 Received: 12 April 2017 / Accepted:
Clin Dent Rev (2017) 1:3 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41894-017-0004-2 TREATMENT Evidence-based decision making in periodontal tooth prognosis Carlos Ernesto Nemcovsky 1 Received: 12 April 2017 / Accepted:
Periodontal Diagnosis Form
 Periodontal Diagnosis Form Notes on the use of the form 1. The form that follows is a comprehensive analysis of your patient, taking into account many factors that might contribute to oral conditions.
Periodontal Diagnosis Form Notes on the use of the form 1. The form that follows is a comprehensive analysis of your patient, taking into account many factors that might contribute to oral conditions.
Appendix 4. Case Summary Template. Social history. Patient (Name and Date of birth): Presenting complaints. History Medical history
 Appendix 4 Case Summary Template Patient (Name and Date of birth): Presenting complaints Chief complaint Subsidiary complaints History of complaints Patient s expectations History Medical history Medical
Appendix 4 Case Summary Template Patient (Name and Date of birth): Presenting complaints Chief complaint Subsidiary complaints History of complaints Patient s expectations History Medical history Medical
Core build-up using post systems
 Core build-up using post systems Dr. Gergely Pataky Department of Conservative Dentistry What to speak about today General considerations Classification of post systems Dowel-core or fibre post? Biologic
Core build-up using post systems Dr. Gergely Pataky Department of Conservative Dentistry What to speak about today General considerations Classification of post systems Dowel-core or fibre post? Biologic
A survey of biopsied oral lesions in pediatric dental patients
 PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY/Copyright 1986 by The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry Volume 8 Number 2 A survey of biopsied oral lesions in pediatric dental patients Robert L. Skinner, MS W.D. Davenport,
PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY/Copyright 1986 by The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry Volume 8 Number 2 A survey of biopsied oral lesions in pediatric dental patients Robert L. Skinner, MS W.D. Davenport,
Total Impaction of Deciduous Maxillary Molars: Two Case Reports
 Total Impaction of Deciduous Maxillary Molars: Two Case Reports Abstract Aim: The purpose of this report is to present two cases of totally impacted maxillary deciduous molars, considered a rarity in dental
Total Impaction of Deciduous Maxillary Molars: Two Case Reports Abstract Aim: The purpose of this report is to present two cases of totally impacted maxillary deciduous molars, considered a rarity in dental
PERIODONTAL CASE PRESENTATION - 1
 PERIODONTAL CASE PRESENTATION - 1 Overview A 32 year-old patient presented with generalized aggressive periodontitis. Treatment included non-surgical therapy with adjunctive antibiotics and surgical treatment.
PERIODONTAL CASE PRESENTATION - 1 Overview A 32 year-old patient presented with generalized aggressive periodontitis. Treatment included non-surgical therapy with adjunctive antibiotics and surgical treatment.
Problems of First Permanent Molars - The first group of permanent teeth erupt in the oral cavity. - Deep groove and pit
 Management of the poor first permanent e molar Assoc. Prof. Kadkao Vongsavan * Asst. Prof. Praphasri Rirattanapong* Dr. Pongsakorn Sakkamathya** ** * Department of Pediatric Dentistry Faculty of Dentistry,
Management of the poor first permanent e molar Assoc. Prof. Kadkao Vongsavan * Asst. Prof. Praphasri Rirattanapong* Dr. Pongsakorn Sakkamathya** ** * Department of Pediatric Dentistry Faculty of Dentistry,
The influence of sensor size and orientation on image quality in intra-oral periapical radiography
 Clinical The influence of sensor size and orientation on image quality in intra-oral periapical radiography Tony Druttman 1 The periapical view is one of the standard intra-oral radiographs by which diagnostic
Clinical The influence of sensor size and orientation on image quality in intra-oral periapical radiography Tony Druttman 1 The periapical view is one of the standard intra-oral radiographs by which diagnostic
Periodontal Disease. Radiology of Periodontal Disease. Periodontal Disease. The Role of Radiology in Assessment of Periodontal Disease
 Radiology of Periodontal Disease Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Periodontal Disease! Includes several disorders of the periodontium! Gingivitis! Marginal Periodontitis! Localized
Radiology of Periodontal Disease Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Periodontal Disease! Includes several disorders of the periodontium! Gingivitis! Marginal Periodontitis! Localized
Development of teeth. 5.DM - Pedo
 Development of teeth 5.DM - Pedo Tooth development process of continuous changes in predetermined order starts from dental lamina A band of ectodermal cells growing from the epithelium of the embryonic
Development of teeth 5.DM - Pedo Tooth development process of continuous changes in predetermined order starts from dental lamina A band of ectodermal cells growing from the epithelium of the embryonic
Mesial Step Class I or Class III Dependent upon extent of step seen clinically and patient s growth pattern Refer for early evaluation (by 8 years)
 Orthodontics and Dentofacial Development Overview Development of Dentition Treatment Retention and Relapse Growth of Naso-Maxillary Complex Develops postnatally entirely by intramenbranous ossification
Orthodontics and Dentofacial Development Overview Development of Dentition Treatment Retention and Relapse Growth of Naso-Maxillary Complex Develops postnatally entirely by intramenbranous ossification
JOURNAL OF INTERNATIONAL ACADEMIC RESEARCH FOR MULTIDISCIPLINARY Impact Factor 3.114, ISSN: , Volume 5, Issue 3, April 2017
 THE INFLUENCE OF BILATERAL IMPACTED THIRD MOLAR ANGULATION AND POSITION ON THE INCISORS CROWDING HAZEM HASSAN* *Professor, Dept. of orthodontic, Faculty of Dentistry, Al-Andalus University for Medical
THE INFLUENCE OF BILATERAL IMPACTED THIRD MOLAR ANGULATION AND POSITION ON THE INCISORS CROWDING HAZEM HASSAN* *Professor, Dept. of orthodontic, Faculty of Dentistry, Al-Andalus University for Medical
Development of occlusion
 Development of occlusion The development of dentition is an important part of craniofacial growth as the formation, eruption, exfoliation and exchange of teeth take place during this period. Term occlusion
Development of occlusion The development of dentition is an important part of craniofacial growth as the formation, eruption, exfoliation and exchange of teeth take place during this period. Term occlusion
IMPACTED CANINES. Unfortunately, this important tooth is the second most common tooth to be impacted after third molars
 IMPACTED CANINES After we talked about impacted third molars, today we ll discuss about maxillary impacted canines in upper dental arch, how to manage these cases as a dental surgeon. You will study about
IMPACTED CANINES After we talked about impacted third molars, today we ll discuss about maxillary impacted canines in upper dental arch, how to manage these cases as a dental surgeon. You will study about
Case report: Idiopathic pre-eruptive coronal resorption of a maxillary permanent canine
 Case report: Idiopathic pre-eruptive coronal resorption of a maxillary permanent canine N.M. Manan*, S.K. Mallineni**, N.M. King*** *Paediatric Dentistry and Orthodontics Dept., Faculty of Dentistry, University
Case report: Idiopathic pre-eruptive coronal resorption of a maxillary permanent canine N.M. Manan*, S.K. Mallineni**, N.M. King*** *Paediatric Dentistry and Orthodontics Dept., Faculty of Dentistry, University
Radiology. & supporting structures. Lec. 14 Common diseases of teeth Dr. Areej
 Radiology Lec. 14 Common diseases of teeth Dr. Areej & supporting structures A radiograph is only one part of the diagnostic process. Usually one does NOT make a diagnosis solely from a radiograph. A diagnosis
Radiology Lec. 14 Common diseases of teeth Dr. Areej & supporting structures A radiograph is only one part of the diagnostic process. Usually one does NOT make a diagnosis solely from a radiograph. A diagnosis
Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report
 Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Relationship between pulpal involvement of primary molars and eruption pattern of premolars
 Relationship between pulpal involvement of primary molars and eruption pattern of premolars G. P. PINI PRATO, T. BACCETTI, L. FRANCHI, R. GIORGETTI*, A. MARINELLI SUMMARY. Aim This study s aim was to investigate
Relationship between pulpal involvement of primary molars and eruption pattern of premolars G. P. PINI PRATO, T. BACCETTI, L. FRANCHI, R. GIORGETTI*, A. MARINELLI SUMMARY. Aim This study s aim was to investigate
Canine Extrusion Technique with SmartClip Self-Ligating Brackets
 Canine Extrusion Technique with SmartClip Self-Ligating Brackets Dr. Luis Huanca Ghislanzoni Dr. Luis Huanca received his DDS in 2006 and the MS and Specialist in Orthodontics in 2009 from the University
Canine Extrusion Technique with SmartClip Self-Ligating Brackets Dr. Luis Huanca Ghislanzoni Dr. Luis Huanca received his DDS in 2006 and the MS and Specialist in Orthodontics in 2009 from the University
1. Anterior-posterior movement of the mandible (APM):
 Dental Anatomy A. Terminology: Over the past few years there have been several acronyms introduced into the equine dentistry industry. These terms should help you describe and understand equine dental
Dental Anatomy A. Terminology: Over the past few years there have been several acronyms introduced into the equine dentistry industry. These terms should help you describe and understand equine dental
Applications in Dermatology, Dentistry and LASIK Eye Surgery using LASERs
 Applications in Dermatology, Dentistry and LASIK Eye Surgery using LASERs http://www.medispainstitute.com/menu_laser_tattoo.html http://www.life123.com/bm.pix/bigstockphoto_close_up_of_eye_surgery_catar_2264267.s600x600.jpg
Applications in Dermatology, Dentistry and LASIK Eye Surgery using LASERs http://www.medispainstitute.com/menu_laser_tattoo.html http://www.life123.com/bm.pix/bigstockphoto_close_up_of_eye_surgery_catar_2264267.s600x600.jpg
Lecture. Permanent maxillary premolars
 Lecture Permanent maxillary premolars Permanent premolars The maxillary premolars are four in number: two in the right and two in the left. They are posterior to the canines and anterior to the molars.
Lecture Permanent maxillary premolars Permanent premolars The maxillary premolars are four in number: two in the right and two in the left. They are posterior to the canines and anterior to the molars.
Medical NBDE-II. Dental Board Exams Part I.
 Medical NBDE-II Dental Board Exams Part I http://killexams.com/exam-detail/nbde-ii Question: 149 Anatomically, the term "clinical root" can be defined as which of the following: A. The space in the tooth
Medical NBDE-II Dental Board Exams Part I http://killexams.com/exam-detail/nbde-ii Question: 149 Anatomically, the term "clinical root" can be defined as which of the following: A. The space in the tooth
Controlled tooth movement to correct an iatrogenic problem
 CASE REPORT Controlled tooth movement to correct an iatrogenic problem Rhita Cristina Cunha Almeida, a Felipe de Assis R. Carvalho, a Marco Antonio Almeida, b Jonas Capelli Junior, c and Walter Augusto
CASE REPORT Controlled tooth movement to correct an iatrogenic problem Rhita Cristina Cunha Almeida, a Felipe de Assis R. Carvalho, a Marco Antonio Almeida, b Jonas Capelli Junior, c and Walter Augusto
Postnatal Growth. The study of growth in growing children is for two reasons : -For health and nutrition assessment
 Growth of The Soft Tissues Postnatal Growth Postnatal growth is defined as the first 20 years of growth after birth krogman 1972 The study of growth in growing children is for two reasons : -For health
Growth of The Soft Tissues Postnatal Growth Postnatal growth is defined as the first 20 years of growth after birth krogman 1972 The study of growth in growing children is for two reasons : -For health
Upper arch. 1Prosthodontics. Dr.Bassam Ali Al-Turaihi. Basic anatomy & & landmark of denture & mouth
 1Prosthodontics Lecture 2 Dr.Bassam Ali Al-Turaihi Basic anatomy & & landmark of denture & mouth Upper arch Palatine process of maxilla: it form the anterior three quarter of the hard palate. Horizontal
1Prosthodontics Lecture 2 Dr.Bassam Ali Al-Turaihi Basic anatomy & & landmark of denture & mouth Upper arch Palatine process of maxilla: it form the anterior three quarter of the hard palate. Horizontal
Paediatric Dentistry Avulsion: Case reports
 Australian Dental Journal 1997;42.(6):361-6 Paediatric Dentistry Avulsion: Case reports J. E. Rutar, BDSc(Qld), GCEd(Qld)* Abstract Children may present at a dental surgery for management of oro-facial
Australian Dental Journal 1997;42.(6):361-6 Paediatric Dentistry Avulsion: Case reports J. E. Rutar, BDSc(Qld), GCEd(Qld)* Abstract Children may present at a dental surgery for management of oro-facial
Indication for Intentional Replantation of Teeth
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 12 Ver. V (Dec. 2017), PP 36-42 www.iosrjournals.org Indication for Intentional Replantation
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 12 Ver. V (Dec. 2017), PP 36-42 www.iosrjournals.org Indication for Intentional Replantation
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo. Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
 Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
Treatment planning of nonskeletal problems. in preadolescent children
 In the name of GOD Treatment planning of nonskeletal problems in preadolescent children Presented by: Dr Somayeh Heidari Orthodontist Reference: Contemporary Orthodontics Chapter 7 William R. Proffit,
In the name of GOD Treatment planning of nonskeletal problems in preadolescent children Presented by: Dr Somayeh Heidari Orthodontist Reference: Contemporary Orthodontics Chapter 7 William R. Proffit,
Alveolar Growth in Japanese Infants: A Comparison between Now and 40 Years ago
 Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2017) 58(1): 9 18 Original Article doi:10.2209/tdcpublication.2016-0500 Alveolar Growth in Japanese Infants: A Comparison between Now and 40 Years ago Hiroki Imai 1), Tetsuhide Makiguchi
Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2017) 58(1): 9 18 Original Article doi:10.2209/tdcpublication.2016-0500 Alveolar Growth in Japanese Infants: A Comparison between Now and 40 Years ago Hiroki Imai 1), Tetsuhide Makiguchi
Buccally Malposed Mesially Angulated Maxillary Canine Management
 Buccally Malposed Mesially Angulated Maxillary Canine Management Suhad. H. Manhal,* Summery: Maxillary canine is an important tooth in all fields of dentistry. However, malposed upper canine is seemed
Buccally Malposed Mesially Angulated Maxillary Canine Management Suhad. H. Manhal,* Summery: Maxillary canine is an important tooth in all fields of dentistry. However, malposed upper canine is seemed
The Treatment of Traumatic Dental Injuries
 The Recommended Guidelines of the American Association of Endodontists for The Treatment of Traumatic Dental Injuries 2013 American Association of Endodontists Revised 9/13 The Recommended Guidelines of
The Recommended Guidelines of the American Association of Endodontists for The Treatment of Traumatic Dental Injuries 2013 American Association of Endodontists Revised 9/13 The Recommended Guidelines of
The unerupted maxillary canine - a post-surgical review.
 The unerupted maxillary canine - a post-surgical review. Item Type Article Authors O'Dowling, Ian Citation The unerupted maxillary canine--a post-surgical review., 55 (5):232-6 J Ir Dent Assoc Publisher
The unerupted maxillary canine - a post-surgical review. Item Type Article Authors O'Dowling, Ian Citation The unerupted maxillary canine--a post-surgical review., 55 (5):232-6 J Ir Dent Assoc Publisher
An Unusual Association of Odontomas with Primary Teeth
 An Unusual Association of Odontomas with Primary Teeth Gülsün Yıldırım-Öz a, DDS, PhD Gül Tosun b, DDS, PhD Dilek Kızıloğlu c, DDS Ercan Durmuş d, DDS, PhD Yağmur Şener e, DDS, PhD Abstract Odontomas generally
An Unusual Association of Odontomas with Primary Teeth Gülsün Yıldırım-Öz a, DDS, PhD Gül Tosun b, DDS, PhD Dilek Kızıloğlu c, DDS Ercan Durmuş d, DDS, PhD Yağmur Şener e, DDS, PhD Abstract Odontomas generally
All Dentistry is Cosmetic Betsy Bakeman, DDS Arkansas State Dental Association
 All Dentistry is Cosmetic Betsy Bakeman, DDS Arkansas State Dental Association Patients have traditionally sought treatment when concerned with the way their teeth look, function or feel. Over the past
All Dentistry is Cosmetic Betsy Bakeman, DDS Arkansas State Dental Association Patients have traditionally sought treatment when concerned with the way their teeth look, function or feel. Over the past
Esthetic Crown Lengthening
 Esthetic Crown Lengthening Esthetic Crown Lengthening ACCELERATED OSTEOGENIC ORTHODOTNICS (WILKODONTICS) It is a technique developed by Wilko brothers. has roots in orthopedics, back to the early 1900s
Esthetic Crown Lengthening Esthetic Crown Lengthening ACCELERATED OSTEOGENIC ORTHODOTNICS (WILKODONTICS) It is a technique developed by Wilko brothers. has roots in orthopedics, back to the early 1900s
DENTAL RADIOGRAPH INTERPRETATION
 DENTAL RADIOGRAPH INTERPRETATION Brook A. Niemiec, DVM Diplomate, American Veterinary Dental College Fellow, Academy of Veterinary Dentistry www.vetdentaltraning.com www.vetdentalrad.com Interpreting dental
DENTAL RADIOGRAPH INTERPRETATION Brook A. Niemiec, DVM Diplomate, American Veterinary Dental College Fellow, Academy of Veterinary Dentistry www.vetdentaltraning.com www.vetdentalrad.com Interpreting dental
Connective Tissue Graft for Gingival Recession in Mandibular Incisor Area: A Case Report
 Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2017) 58(3): 155 162 Case Report doi:10.2209/tdcpublication.2016-0038 Connective Tissue Graft for Gingival Recession in Mandibular Incisor Area: A Case Report Masahiro Egawa 1), Satoru
Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2017) 58(3): 155 162 Case Report doi:10.2209/tdcpublication.2016-0038 Connective Tissue Graft for Gingival Recession in Mandibular Incisor Area: A Case Report Masahiro Egawa 1), Satoru
A Clinical Evaluation of Anatomic Features of Gingiva in Dental Students in Tabriz, Iran
 Received 26 October 2007; Accepted 11 February 2008 A Clinical Evaluation of Anatomic Features of Gingiva in Dental Students in Tabriz, Iran Adileh Shirmohammadi 1 Masoumeh Faramarzie 1 * Ardeshir Lafzi
Received 26 October 2007; Accepted 11 February 2008 A Clinical Evaluation of Anatomic Features of Gingiva in Dental Students in Tabriz, Iran Adileh Shirmohammadi 1 Masoumeh Faramarzie 1 * Ardeshir Lafzi
ALABAMA DENTAL HYGIENE PROGRAM 50 QUESTIONS PRE ENTRANCE EXAM
 ALABAMA DENTAL HYGIENE PROGRAM 50 QUESTIONS PRE ENTRANCE EXAM NAME DATE RETURN COMPLETED EXAM WITH APPLICATION You may copy for future reference 1. One cause of decay is the Streptococcus mutans bacteria
ALABAMA DENTAL HYGIENE PROGRAM 50 QUESTIONS PRE ENTRANCE EXAM NAME DATE RETURN COMPLETED EXAM WITH APPLICATION You may copy for future reference 1. One cause of decay is the Streptococcus mutans bacteria
INFECTED DENTIGEROUS CYST IN IMPACTED CANINE- A case report
 Case Report INFECTED DENTIGEROUS CYST IN IMPACTED CANINE- A case report Gazala Fatima Parveen, M.D. Akheel 1 Department of oral & maxillofacial surgery, MCDRC Lucknow, U.P.,India 1-Department of Oral &
Case Report INFECTED DENTIGEROUS CYST IN IMPACTED CANINE- A case report Gazala Fatima Parveen, M.D. Akheel 1 Department of oral & maxillofacial surgery, MCDRC Lucknow, U.P.,India 1-Department of Oral &
Interdisciplinary management of Impacted teeth in an adult with Orthodontics & Free Gingival graft : A Case Report
 Original article: Interdisciplinary management of Impacted teeth in an adult with Orthodontics & Free Gingival graft : A Case Report Dr Renuka Patel, Dr Falguni Mehta, Dr. Ashish Pandey Assistant Professor,
Original article: Interdisciplinary management of Impacted teeth in an adult with Orthodontics & Free Gingival graft : A Case Report Dr Renuka Patel, Dr Falguni Mehta, Dr. Ashish Pandey Assistant Professor,
THE PREVALENCE OF IMPACTED PERMANENT MAXILLARY CANINES IN MALTESE SCHOOL CHILDREN: A PILOT STUDY
 Maltese Medical Journal 42 Volufne VII Issue I 1995 THE PREVALENCE OF IMPACTED PERMANENT MAXILLARY CANINES IN MALTESE SCHOOL CHILDREN: A PILOT STUDY S. Camilleri Keywords: Maxillary permanent canine, impacted,
Maltese Medical Journal 42 Volufne VII Issue I 1995 THE PREVALENCE OF IMPACTED PERMANENT MAXILLARY CANINES IN MALTESE SCHOOL CHILDREN: A PILOT STUDY S. Camilleri Keywords: Maxillary permanent canine, impacted,
Development of occlusion:
 : Dr.Issam Aljorani (BDS, MSc. Ortho.) Postnatal development of the dentition When a child is born, mineralization of all the primary tooth crowns is well underway, with this process also beginning in
: Dr.Issam Aljorani (BDS, MSc. Ortho.) Postnatal development of the dentition When a child is born, mineralization of all the primary tooth crowns is well underway, with this process also beginning in
Eruption and Shedding of Teeth
 Eruption and Shedding of Teeth Mixed Dentition: Presence of both dentitions Figure from Ten Cate s Oral Histology, Ed., Antonio Nanci, 6 th edition Tooth eruption is the process by which developing teeth
Eruption and Shedding of Teeth Mixed Dentition: Presence of both dentitions Figure from Ten Cate s Oral Histology, Ed., Antonio Nanci, 6 th edition Tooth eruption is the process by which developing teeth
Permanent 2 nd Maxillary Molars
 Permanent 2 nd Maxillary Molars In comparison to the first max molar First molars appears in the oral cavity at the age of 6 years old.. While 2 nd molar 3 rd molar Max. 2 nd molar have long roots (sometimes
Permanent 2 nd Maxillary Molars In comparison to the first max molar First molars appears in the oral cavity at the age of 6 years old.. While 2 nd molar 3 rd molar Max. 2 nd molar have long roots (sometimes
Tooth eruption and movement
 Tooth eruption and movement Dr. Krisztián Nagy Diphydont dentition Deciduous dentition primary dentition Diphydont dentition Permanent dentition secondary dentition Mixed Dentition: Presence of both dentitions
Tooth eruption and movement Dr. Krisztián Nagy Diphydont dentition Deciduous dentition primary dentition Diphydont dentition Permanent dentition secondary dentition Mixed Dentition: Presence of both dentitions
Figure (2-6): Labial frenum and labial notch.
 The anatomy of the edentulous ridge in the maxilla and mandible is very important for the design of a complete denture. The consistency of the mucosa and architecture of the underlying bone is different
The anatomy of the edentulous ridge in the maxilla and mandible is very important for the design of a complete denture. The consistency of the mucosa and architecture of the underlying bone is different
Elevators. elevators:- There are three major components of the elevator are:-
 Elevators Elevators:- Are exo-levers, instrument designed to elevate or luxate the teeth or roots from their bony socket in close or surgical method of extraction to force a tooth or root along the line
Elevators Elevators:- Are exo-levers, instrument designed to elevate or luxate the teeth or roots from their bony socket in close or surgical method of extraction to force a tooth or root along the line
Classifications for Gingival Recession: A Mini Review
 Galore International Journal of Health Sciences and Research Vol.3; Issue: 1; Jan.-March 2018 Website: www.gijhsr.com Review Article P-ISSN: 2456-9321 Classifications for Gingival Recession: A Mini Review
Galore International Journal of Health Sciences and Research Vol.3; Issue: 1; Jan.-March 2018 Website: www.gijhsr.com Review Article P-ISSN: 2456-9321 Classifications for Gingival Recession: A Mini Review
Dental Anatomy and Physiology for Clinical Dental Technicians. with Marnie Hayward
 Dental Anatomy and Physiology for Clinical Dental Technicians with Marnie Hayward Salivary glands Parotid Submandibular Sublingual Salivary glands position Parotid glands Lie below ear and behind angle
Dental Anatomy and Physiology for Clinical Dental Technicians with Marnie Hayward Salivary glands Parotid Submandibular Sublingual Salivary glands position Parotid glands Lie below ear and behind angle
Management of Crowded Class 1 Malocclusion with Serial Extractions: Report of a Case
 Management of Crowded Class 1 Malocclusion with Serial Extractions: Report of a Case Hayder A. Hashim, BDS, MSc Abstract Aim: The purpose of this article is to show the value of serial extractions in a
Management of Crowded Class 1 Malocclusion with Serial Extractions: Report of a Case Hayder A. Hashim, BDS, MSc Abstract Aim: The purpose of this article is to show the value of serial extractions in a
Case Report: Long-Term Outcome of Class II Division 1 Malocclusion Treated with Rapid Palatal Expansion and Cervical Traction
 Case Report Case Report: Long-Term Outcome of Class II Division 1 Malocclusion Treated with Rapid Palatal Expansion and Cervical Traction Roberto M. A. Lima, DDS a ; Anna Leticia Lima, DDS b Abstract:
Case Report Case Report: Long-Term Outcome of Class II Division 1 Malocclusion Treated with Rapid Palatal Expansion and Cervical Traction Roberto M. A. Lima, DDS a ; Anna Leticia Lima, DDS b Abstract:
DonnishJournals
 DonnishJournals 2041-3144 Donnish Journal of Dentistry and Oral Hygiene Vol 1(2) pp. 007-011 May, 2015 http:///djdoh Copyright 2015 Donnish Journals Original Research Article Orthodontic Management of
DonnishJournals 2041-3144 Donnish Journal of Dentistry and Oral Hygiene Vol 1(2) pp. 007-011 May, 2015 http:///djdoh Copyright 2015 Donnish Journals Original Research Article Orthodontic Management of
Correction of Crowding using Conservative Treatment Approach
 Case Report Correction of Crowding using Conservative Treatment Approach Dr Tapan Shah, 1 Dr Tarulatha Shyagali, 2 Dr Kalyani Trivedi 3 1 Senior Lecturer, 2 Professor, Department of Orthodontics, Darshan
Case Report Correction of Crowding using Conservative Treatment Approach Dr Tapan Shah, 1 Dr Tarulatha Shyagali, 2 Dr Kalyani Trivedi 3 1 Senior Lecturer, 2 Professor, Department of Orthodontics, Darshan
PERMANENT MANDIBULAR INCISORS
 PERMANENT MANDIBULAR INCISORS (Central and Lateral) DR.AHMED AL-JOBORY LEC. 5 PERMANENT MANDIBULAR INCISORS ARE 4 IN NUMBER : 2 CENTRAL (RIGHT &LEFT) AND 2 LATERAL INCISORS (RIGHT &LEFT). CHARACTERISTIC
PERMANENT MANDIBULAR INCISORS (Central and Lateral) DR.AHMED AL-JOBORY LEC. 5 PERMANENT MANDIBULAR INCISORS ARE 4 IN NUMBER : 2 CENTRAL (RIGHT &LEFT) AND 2 LATERAL INCISORS (RIGHT &LEFT). CHARACTERISTIC
Surgical Therapy. Tuesday, April 2, 13. Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS
 Surgical Therapy Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS Periodontal Flap: a surgical procedure in which incisions are made in the gingiva or mucosa to allow for separation of the epithelium and connective tissues
Surgical Therapy Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS Periodontal Flap: a surgical procedure in which incisions are made in the gingiva or mucosa to allow for separation of the epithelium and connective tissues
Intrusion of Incisors to Facilitate Restoration: The Impact on the Periodontium
 Note: This is a sample Eoster. Your EPoster does not need to use the same format style. For example your title slide does not need to have the title of your EPoster in a box surrounded with a pink border.
Note: This is a sample Eoster. Your EPoster does not need to use the same format style. For example your title slide does not need to have the title of your EPoster in a box surrounded with a pink border.
#45 Ortho-Tain, Inc PREVENTIVE ERUPTION GUIDANCE -- PREVENTIVE OCCLUSAL DEVELOPMENT
 #45 Ortho-Tain, Inc. 1-800-541-6612 PREVENTIVE ERUPTION GUIDANCE -- PREVENTIVE OCCLUSAL DEVELOPMENT Analysis and Diagnosis of Occlusion: The ideal child of 5 y ears of age that probably has the best chance
#45 Ortho-Tain, Inc. 1-800-541-6612 PREVENTIVE ERUPTION GUIDANCE -- PREVENTIVE OCCLUSAL DEVELOPMENT Analysis and Diagnosis of Occlusion: The ideal child of 5 y ears of age that probably has the best chance
Ectopic upper canine associated to ectopic lower second bicuspid. Case report
 Original Article Published on 15-06-2001 In Italiano, per favore En Español, por favor Ectopic upper canine associated to ectopic lower second bicuspid. Case report A.R. Mazzocchi* * MD DDS. Corresponding
Original Article Published on 15-06-2001 In Italiano, per favore En Español, por favor Ectopic upper canine associated to ectopic lower second bicuspid. Case report A.R. Mazzocchi* * MD DDS. Corresponding
Abstract. A Case Of External Resorption
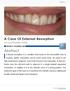 SHGDDS 1 BY Steven H. Goldstein, DDS Abstract External resorption is a condition that leads to the irreversible loss of enamel, dentin, cementum, and in some cases bone. Its cause is not fully understood,
SHGDDS 1 BY Steven H. Goldstein, DDS Abstract External resorption is a condition that leads to the irreversible loss of enamel, dentin, cementum, and in some cases bone. Its cause is not fully understood,
