The effects of acid-etching on enamel from different clinical variants of amelogenesis imperfecta: an SEM study
|
|
|
- Juliana Shepherd
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The effects of acid-etching on enamel from different clinical variants of amelogenesis imperfecta: an SEM study W. Kim Seow MDSc, DDSc, PhD, FRACDS A. Amaratunge RDS, PhD Abstract fissure sealants, and splinting of teeth. 1_4 Acid etching Purpose: Successful bonding of resins to teeth affected of enamel results in many surface irregularities, which by amelogenesis imperfecta (AI) may be highly dependent on how the enamel responds to acid etching. The ing, as well as its wetability, which enhances the flow greatly increases the surface area for mechanical bond- aim of this study was to determine, using scanning electron microscopy (SEM), the types of etching pattern The distinct morphological surface changes caused of resin. ~4 achieved with 37% phosphoric acid on dental enamel of by acid etching have been clearly demonstrated by 5 clinical variants of AI, namely, pitted hypoplastic, SEM. 4 In general, the surface modifications may be smoot hypoplastic, X-linked (male), X-linked (female), classified into three types of etching patterns. 4 In the and hypomineralized. type 1 pattern, a honeycomb appearance is produced Methods: A normal premolar and primary molar3ckom by prism core material being preferentially removed, two healthy patients were used as controls. The enamel was leaving the prism peripherally intact. In the type 2 scanned before and after acid etching for 1 min. In the pattern, a cobblestone effect is produced by the peripheral regions of the prisms being dissolved pref- normal, control teeth, the three classical etching patterns were produced: type 1, in which the prism cores are preferentially removed; type 2, in which the prism peripher- 3 pattern, surface loss occurs without exposing the erentially, leaving the prism cores intact. In the type ies are removed, and type 3 in which the removal of enamel underlying enamel prisms. Although the relative significance of the etching patterns to bond strength is does not relate to prism structure. Results: In the normal primary molar, patterns of types still unclear, it is likely that all three types contribute 1 to clinical bonding on any one surface. 2 and 3 were generallyproduced. In the AI teeth, the effects of acid etching reflected the clinical variant ofai. All While the etching patterns produced in normal three etch patterns were observed in the enamel surrounding the pits in the pitted type of AI and in the bands of enamel have been well described, little is known regarding the changes produced in abnormal enamel, normal enamel in the female with X-linked AL as well as and in particular, for developmental abnormalities in the hypomineralized variant. In contrast, no typical etch patterns could be detected in the enamel j~om the male such as amelogenesis imperfecta (AI). M is a heterogenous group of inherited conditions affecting enamel, patient with X-linked variant, as well ashore the enamel affected by the smoot hypoplastic variant. and shows prevalence rates ranging from 1:4000 to Condusions: The lack of typical etchingpatterns these 1:14, As the diagnosis and classification of M variants may be the result of abnormal prism structure, or based on molecular criteria 8-1 are yet to be determined, the standard etching time and~or acid concentration may diagnosis of AI is usually based on clinical and inheritance criteria. ~-J3 Witkop 7 suggested four broad cat- be inappropriate for the abnormal enamel. The results of this study may have useful applications in the restoration of egories of AI in his classification, namely, hypoplastic, teeth affected by AL (Pediatr Dent 20:137-42, 1998) hypocalcified, hypomaturation, and hypomaturation! hypoplastic with taurodontism, and included several subtypes dependant on inheritance patterns. In clini- Aa cid etching of enamel to create a surface suit ble for bonding resins is now a cornerstone echnique of clinical dentistry. Phosphoric acid at a concentration of 37% is now the most widely used acid in bonding techniques for esthetic restorations, cal practice, however, the lack of clear familial histories in the majority of patients often prevents definitive diagnosis of affected individuals into a particular subtype. Furthermore, extensive overlap of clinical pre- Pediatric Dentistry , 1998 American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry 37
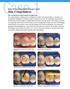
2 sentations of the hypocalcified and hypomaturation types often make it extremely difficult to distinguish clinically between these two types of Al. Hence, for practical purposes, three broad clinical variants are generally recognized, namely, 1) hypoplastic, in which the enamel is deficient in quantity, 2) hypomineralized/ hypomaturation in which mineralization/maturation of enamel is altered, and 3) X-linked, in which females classically display vertical striping of enamel, and males show an even loss of enamel. Because a significant complication of Al is poor esthetics, an important aspect of clinical management is improvement of the appearance using bonded resins. 12 ' 15 However, in many patients with Al, adhesive restorations may show high failure rates that are associated with inadequate bonding between the restorations and enamel. This area of restorative dentistry for Al has not been well investigated. As the bond between enamel and restoration is highly dependent on the enamel surface changes after acid etching, the examination of these surfaces may provide clues as to the potential success of the acid etch technique on the different types of enamel surfaces in Al variants. The aim of this investigation was to use SEM to examine the effects of acid-etching on teeth from patients with different variants of Al compared with normal teeth. Methods Naturally exfoliated primary teeth, as well as premolar teeth extracted for orthodontic reasons, were donated by patients. All the Al patients had been previously diagnosed by Dr. Seow using clinical and radiographic criteria. 12 '" The teeth had been kept dry by the patients until the time of study. One tooth from a patient of each of the following clinical variants of Al was randomly selected for study: 1) pitted hypoplastic, 2) rough hypoplastic, 3) X-linked hypoplastic (female), 4) X-linked hypoplastic (male), and 5) hypomineralized. A total of five Al-affected teeth and two normal control teeth were used for the study. The teeth were cleaned in an ultrasonic bath containing 0.5% sodium hypochlorite solution for 30 min to remove surface debris, and dried with compressed air. Half the facial surface of each tooth was masked with masking tape and the unmasked half treated with 37% phosphoric acid for 1 min, thoroughly washed with distilled water for another minute, and dried with compressed air. The teeth were then vacuum coated with 50 mm of silver and prepared for SEM in a Phillips 505 scanning electron microscope (Phillips Electronic Eindhoven, Netherlands). Results Control Teeth A premolar extracted for orthodontic reasons from a healthy female was used as a control tooth for the Al-affected premolar. A naturally exfoliated mandibular primary first molar from a healthy male was used as a comparison for the Al-affected primary teeth. Normal maxillary premolar-untreated Low-power SEM showed a generally uniform surface with distinct perikymata showing as wave-like horizontal bands. Higher magnification showed the surface to be covered with many shallow depressions and a few micropits. Normal maxillary premolar-acid etched After treatment with acid, the etched area generally showed a type 1 pattern with the prism cores preferentially removed (Fig 1). However, in small, isolated areas the etching pattern was similar to that of type 2, i.e., prism peripheries were preferentially removed. A type 3 etching pattern (general removal of tooth structure without exposing prism structure) was also observed in other isolated areas. Normal primary mandibular molar-untreated Rounded enamel rod endings were faintly visible on the surface of the normal primary molar, and gave it a uniformly speckled appearance. Apart from a few scratches, the untreated enamel surface was generally unremarkable. Normal primary mandibular molar-acid etched Acid etching generally produced a type 2 pattern. 4 Fig 1. Facial surface of normal premolar after treatment with phosphoric acid. Type 1 etch pattern in which the prism cores were preferentially removed was generally observed. Mag. x3000 > Fig 2. Facial surface of normal primary molar treated with phosphoric acid. Type 2 etch pattern was predominantly present Mag. xlooo 38 American Academy ofpediatric Dentistry Pediatric Dentistry -20:1, 1998
3 In some isolated areas, the removal of tooth mineral around the prism borders appeared more extensive, leaving behind irregular clumps of fractured sheets of enamel prisms. Hypoplastic pined Al Clinically, all permanent teeth of the patient showed many round, pin head-sized pits, which were concentrated mainly on the occlusal half of the facial and lingual surfaces. Maxillary premolar-untreated In the untreated surface, the pits appeared round or elongated oval under low-power SEM, arranged linearly, and surrounded by apparently normal enamel (Fig 3a). At high magnification, the pits were clearly demarcated as depressed areas containing rough, dysplastic enamel and organic material. The enamel surface in the cervical parts of the tooth appeared to be normal, although containing a few pits. Maxillary premolar-acid etched After acid etching, the enamel surrounding the pits generally showed mixture of either type 1 or type 2 patterns (Fig 3b). In other isolated areas, the pattern of etching was generally that of type 3. Smooth, hypoplastic Al In this patient, the entire primary dentition showed thin enamel which appeared extremely abraded. Primary mandibular first molar-untreated The untreated tooth surface of the primary first molar tooth showed a generally unremarkable and relatively smooth surface (Fig 4a). Primary mandibular first molar-acid etched After acid etching, the enamel showed a generally uniform fibrillar surface, without any of the classical features of etched enamel (Fig 4b). X-linked Hypoplastic (Male) Clinically, the entire primary dentition of the patient showed thin enamel, of normal color, and appeared smooth on the surface. Primary maxillary incisor-untreated Low-power SEM of a primary maxillary incisor from this patient showed extensive surface loss of enamel from abrasion. Higher magnification showed the intact parts of the enamel surface to be relatively smooth (Fig 5a). Primary maxillary incisor-acid etched In the areas where intact surface enamel was present, acid etching showed patchy loss of surface tooth structure without evidence of etching patterns (Fig 5b). X-linked Hypoplastic (Female) The primary dentition of this patient was heavily restored with amalgam and showed areas of extensive breakdown. The enamel appeared rough and grooved. Primary maxillary first molar-untreated Low-power SEM showed alternating bands of relatively smooth, normal-appearing enamel inter- 4 Fig 3a. Untreated facial surface of premolar affected with pined hypoplastic Al. The pits were mainly concentrated on the occlusal halves of the facial and lingual surfaces. Mag. x30 * Fig 3d. Facial surface of premolar affected with pined hypoplastic Al after treatment with phosphoric acid. In the center is a large oval pit Filled arrow shows area of type 1 etch pattern. Open arrow shows area of type 2 etch pattern. In the areas Immediately adjacent to the pit, a type 3 etch pattern was found. Mag. xsoo 4 Fig 4a. Untreated facial surface of primary molar affected with the smooth hypoplastic variant of Al. Apart from a few narrow linear depressions, the surface was generally unremarkable. Mag. xf 000 > Fig 4b. Facial surface of primary molar affected with the smooth hypoplastic variant of Al after treatment with phosphoric acid. The enamel shows a uniform fibrillar surface without any of the classical features of etching. Mag. xlooo Pediatric Dentistry -20:1, 1998 American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry 39
4 4 Fig 5a. Untreated facial surface of a primary incisor from a male affected with X- linked Al. The right side of the figure depicts an area of relatively smooth, intact surface, wheras the left side shows areas of abrasion with a granular appearance and shallow grooves and pits. Mag. xsoo ^ Fig 5b. Primary incisor from a male affected with X-linked Al after phosphoric acid treatment On the right, there was patchy loss of surface enamel with no etch pattern. On the -' left, which had partial loss of surface enamel, there was irregular removal of tooth structure [type 3 etch pattern). Mag. xluo spersed with abnormal, granular, and rough enamel. Higher magnification of the abnormal areas showed a complex pattern of interconnecting rounded ridges separated by furrows (Fig 6a) containing rough granular enamel and small pits (Fig 6b). Primary maxillary first molar-acid etched Acid etching of the surface revealed a variety of etching appearances. In the bands of smooth normal enamel, a type 2 etching pattern predominated (Fig 6c). In areas of abnormal granular enamel, there was irregular removal of tooth structure without definite etching patterns. HypomineralizedAI A premolar was available from a female who had been diagnosed as having hypomineralized variant Al. Clinically, both primary and permanent teeth of the patient appeared yellow-brown, and showed areas of posteruptive fracture and abrasion. Maxillary premolar-untreated Fig 7a shows the intact areas of the facial surface. Higher magnification of this area showed the presence of many irregular, shallow pits and fine cracks. The mesial half of the facial surface showed a large area of partial enamel loss. SEM of the fractured enamel in this area revealed a rough surface containing irregular patches of rough, granular enamel (Fig 7b). In the vertical parts of the fractured enamel surface, irregular, longitudinal prism structure was observed (Fig 7c). Maxillary premolar-acid etched Acid etching of the enamel surface with phosphoric acid produced a random mixture of the three classical etching patterns. Discussion As the failure rates of adhesive restorations in Al may be high, the question often arises as to whether this type of dental enamel may be successfully etched. The present study addresses this important clinical issue in five clinical variants of Al, namely, pitted hypoplastic, smooth hypoplastic, X-linked (female), X- linked (male), and hypomineralized, using extracted premolar and exfoliated primary teeth. The common features of normal enamel, as well as the abnormal enamel in Al, have been described in previous publications. 15 " 23 Our results on the untreated surfaces of the different variants of Al showed many of these abnormalities. However, there have been no previous studies comparing the effects of acid Fig 6a. Ontreated facial surface of a primary first molar from a female affected with the X-linked variant of Al. The surface showed a complex pattern of interconnecting, rounded ridges separated by grooves. Mag. X110 Fig 6b. Untreated facial surface of a primary first molar from a female affected with the X-linked variant of Al. Higher magnification of a furrow between two bands of normal enamel showed the presence of rough, granular enamel and small pits. Mag. X800 Fig 6c. Facial surface of a primary first molar from a female affected with the X- linked variant of Al after treatment with phosphoric acid. A type 2 etch pattern was generally observed in the bands of normal enamel depicted in Fig 6a. Mag American Academy ofpediatric Dentistry Pediatric Dentistry - 20:1, 1998
5 etching on enamel from different Al variants. Our study shows that the three classical acid-etching patterns found in normal enamel may be produced in most of the clinical variants of Al, although each variant tended to show a predominant etch pattern. In the case of the pitted hypoplastic variant, the predominant etch pattern was that of type 1, in which the prism cores were preferentially removed. In contrast, in the X-linked (female) variant, the main etching pattern was type 2, in which the peripheral boundaries of the prisms were dissolved. In the X-linked (male) variant, the etched enamel generally showed a type 3 pattern, in which the pattern of prism dissolution was irregular and did not appear to be related to prism structure. In the hypomineralized type of Al, all three types of etching patterns were found to be distributed equally. In contrast, the enamel surface of the smooth hypoplastic variant did not change significantly after etching with phosphoric acid. It is possible that removal of a thin surface layer of enamel had occurred without production of etch patterns because of abnormalities in prism structure, such as the presence of a prismless layer. Alternatively, it is also likely that, because of smaller or weaker prisms, the length of time of the acid etch or the concentration of etchant may not be optimal to produce the classical etch patterns. These hypotheses are based on findings of previous studies which found abnormalities of prism structure, as well as reduction in enamel thickness by more than half compared with normal enamel in the smooth hypoplastic variant of Al.' 8 In the hypomineralized variant, the findings on the untreated surface such as micropits and cracks are similar to those noted in a previous report. 17 The fact that acid etching produced all the three classical etch patterns suggested that the prism structure in this variant may be generally normal, a finding which had been observed in a previous ultrastructural study on this Al variant. 19 Thus, based on the findings of this study, acid etching for bonded restorations may be possible in hypomineralized Al despite the presence of hypomineralization abnormalities and morphological changes detected at the crystallite level. 19 In this regard, pretreatment of enamel with 5% sodium hypochlorite had been shown to be effective in removing excess protein from teeth affected by the hypomineralized Al, with enhancement of clinical bonding. 21 Of further interest is the recent finding of Wright et al. 24 that decreased mineral content and increased protein was found not only in hypomineralized Al, but also in the hypomaturation and hypoplastic variants. This suggests that pretreatment with sodium hypochlorite is likely to be of value in enhancing the effect of acid etching in cases of Al in general. However, our use of only 0.5% sodium hypochlorite in the ultrasonication bath was mainly for the removal of gross plaque and other organic debris present on the tooth surface. This low concentration of the reagent would be unlikely to have affected the tooth surface to significantly alter the effects of the acid etching as reported by Venezie et al. 21 Our study thus showed that the presence or absence of useful etch patterns for bonding largely reflects the preoperative clinical appearance/ morphology of the Al-affected teeth. In this regard, it is of interest to note the differences between male and female teeth in the X-linked variant. Because of the homozygous Al gene defect in the males, the tooth from the male patient showed uniformly abnormal enamel. When treated with acid, classical etch patterns did not appear, suggesting abnormal prism structure on the entire surface. In contrast, in the female patient, the untreated enamel presented in al- Fig 7a. low-power SEN of facial surface of unteated premolar of patient affected by hypomineralized Al. A few cracks were present most likely the result of extraction. On the left side (arrow) are areas of shallow depressions containing rough, granular enamel. Mag. X100 Fig 7b. Higher magnification of area showing surface loss of enamel in Fig. la. The surface showed rounded ridges and depressions which appear to contain shallow, irregular honeycomb outlines resembling a developing enamel morphology. Mag. X2000 Fig 7c. Facial surface of premolar of patient affected by hypomineralized Al after treatment with phosphoric acid. A mixture of the three clasical etch patterns were observed on the surface. Mag.X2000 Pediatric Dentistry - 20:1, 1998 American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry 41
6 ternating bands of normal and abnormal enamel as a result of the Lyonization phenomenon which may be observed in X-linked conditions. 21 After treatment with acid, only the bands with normal enamel showed the typical etch patterns, suggesting that enamel with normal prism structure was found only in the bands containing normal enamel. From a clinical viewpoint, the presence of the typical etch patterns in most variants of AI suggests that bonding of composite resins may be feasible in most patients with AI. High failure rates of adhesive restorations on M-affected teeth compared with normal teeth could be due to factors other than bond failure, such as fractures within weak enamel or dentin supporting the restorations. Alternatively, total or partial loss of enamel may have occurred prior to placement of restorations, so that reduced areas were available for bonding. Conclusions 1. In the pitted hypoplastic and hypomineratized variants of AI, classical etch patterns as seen in normal, control enamel may be produced after treatment with phosphoric acid 2. In the smooth hypoplastic and male X-linked variants, classical etch patterns are generally not observed, and in the female X-linked variant, these are seen only in the bands of normal enamel which alternate with the abnormal bands. The authors thank staffofthe Electron Microscope Division, Center for Microscopy and Microanalysis, University of Queensland for use of SEM facilities. Dr. Seow is associate professor in pediatric dentistry, University of Queensland Dental School, Brisbane, Australia. Dr. Amaratunge is senior dentist, Aboriginal and Islander Community Health Service, Woolloongabba, Australia. References l. Gwinnett AJ: A study of enamel adhesives. The physical relationship between enamel and adhesive. Arch Oral Biol 12: , RetiefDH: Effect of conditioning the enamel surface with phosphoric acid. J Dent Res 52:333-41, Gwinnett AJ: Histologic changes in human enamel following treatment with acidic adhesive conditioning agents. Arch Oral Biol 16:731-38, Silverstone LM, Saxton CA, Dogon IL, Fejerskov O: Variation in the pattern of acid etching of human dental enamel examined by scanning electron microscopy. Caries Res 9:373-87, Backman B, Holm AK: Amelogenesis imperfecta: prevalence and incidence in a northern Swedish county. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 14:43-47, Sundell S, Koch G: Hereditary amelogenesis imperfecta. I. Epidemiology and clinical classification in a Swedish child population. Swed Dent J 9:157-69, Witkop CJ Jr: Amelogenesis imperfecta, dentinogenesis imperfecta and dentin dysplasia revisited: problems in classification. J Oral Pathol 17:547-53, Forsman K, Lind L, Backman B, Westermark E, Holmgren G: Localization ofa gene for autosomal dominant amelogenesis imperfecta (ADAI) to chromosome 4q. Hum Mol Genet 3: , Lagerstrom-Fermer M, Nilsson M, Backman B, Salido E, Shapiro L, Pettersson U, Landegren U: Amelogenin signal peptide mutation: correlation between mutations in the amelogenin gene (AMGX) and manifestations of X-linked amelogenesis imperfecta. Genomics 26:15962, Moore GE: Molecular genetic approaches to the study of human craniofacial dysmorphologies. Int Rev Cytol 158:215-77, Sundell S: Hereditary amelogenesis imperfecta. I. Oral health in children. Swed Dent J 10:151-63, Seow WK: Clinical diagnosis and management strategies ofamelogenesis imperfecta variants. Pediatr Dent 15:384-93, Seow WK: Dental development in amelogenesis imperfecta: a controlled study. Pediatr Dent 17:26-30, Rada RE, Hasiakos PS: Current treatment modalities in the conservative restoration ofamelogenesis imperfecta: a case report. Quintessence Int 21: , Newman HN, Poole DF: Observations with scanning and transmission electron microscopy on the structure of human surface enamel. Arch Oral Biol 19: , Shroff FR, Romaniuk K: A preliminary investigation of the surface structure of the enamel of erupted deciduous teeth. NZ Dent J 60:299_305, Sauk JJ Jr, Cotton WR, Lyon HW, Witkop CJ: Electronoptic analyses ofhypomineralized amelogenesis imperfecta in man. Arch Oral Biol 17: , Wright JT, Robinson C, Shore R: Characterization of the enamel ultrastructure and mineral content in hypoplastic amelogenesis imperfecta. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 72: , Wright JT, Duggal MS, Robinson C, Kirkham J, Shore R: The mineral composition and enamel ultrastructure of hypocalcified amelogenesis imperfecta. J Craniofac Genet Dev Biol 13:117-26, Backman B, Anneroth G, Horstedt P: amelogensis imperfecta: a scanning electron microscopic and microradiographic study. J Oral Pathol Med 18:140-45, Venezie RD, Vadiakas G, Christensen JR, Wright JT: Enamel pretreatment with sodium hypochlorite to enhance bonding in hypopcalcified amelogenesis imperfecta: case report and SEM analysis. Pediatr Dent 16:433-36, Wright JT, Aldred MJ, Crawford pj, Kirkham J, Robinson C: Enamel ultrastructure and protein content in X-linked amelogenesis imperfecta. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 76:192-99, Gwinnett AJ: Structure and composition of enamel. Oper Dent 5:10-17, Wright JT, Deaton TG, Hall KI, Yamauchi M: The mineral and protein content of enamel in amelogenesis imperfecta. Connect Tissue Res 32:247-52, American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry Pediatric Dentistry , 1998
Scanning electron microscope characterization of abrasion in human teeth
 Dental Journal Mahidol Dental Journal Original Article Scanning electron microscope characterization of abrasion in human teeth B.Sc., D.D.S., Specialty Certificate in Oral Pathology, M.S. Department of
Dental Journal Mahidol Dental Journal Original Article Scanning electron microscope characterization of abrasion in human teeth B.Sc., D.D.S., Specialty Certificate in Oral Pathology, M.S. Department of
Evidence for a genetic disorder affecting tooth
 Studies on the Early Paleolithic site of Melka Kunture, Ethiopia - 2004: 703-713. Paleoanthropology Evidence for a genetic disorder affecting tooth formation in the Garba IV child Uri Zilberman 1,Patricia
Studies on the Early Paleolithic site of Melka Kunture, Ethiopia - 2004: 703-713. Paleoanthropology Evidence for a genetic disorder affecting tooth formation in the Garba IV child Uri Zilberman 1,Patricia
DH220 Dental Materials
 DH220 Dental Materials Lecture #5 Prof. Lamanna RDH, MS Restorative Dentistry: Glass Ionomer Bird & Robinson p.740-741 I. Use Liner Base Luting agent Restorative material: Class III, V, & eroded/abraded
DH220 Dental Materials Lecture #5 Prof. Lamanna RDH, MS Restorative Dentistry: Glass Ionomer Bird & Robinson p.740-741 I. Use Liner Base Luting agent Restorative material: Class III, V, & eroded/abraded
Oral Rehabilitation of a Young Adult with Amelogenesis Imperfecta: A Clinical Report
 J Indian Prosthodont Soc (Oct-Dec 2010) 10(4):240 245 DOI 10.1007/s13191-010-0037-6 CLINICAL REPORT Oral Rehabilitation of a Young Adult with Amelogenesis Imperfecta: A Clinical Report Y. Bharath Shetty
J Indian Prosthodont Soc (Oct-Dec 2010) 10(4):240 245 DOI 10.1007/s13191-010-0037-6 CLINICAL REPORT Oral Rehabilitation of a Young Adult with Amelogenesis Imperfecta: A Clinical Report Y. Bharath Shetty
BASCD Trainers Pack for Caries Prevalence Studies. Updated: June 2014 for UK Training & Calibration exercise for the Deciduous Dentition
 BASCD Trainers Pack for Caries Prevalence Studies Updated: June 2014 for UK Training & Calibration exercise for the Deciduous Dentition Prepared by Helen Paisley, Cynthia Pine and Girvan Burnside Administrative
BASCD Trainers Pack for Caries Prevalence Studies Updated: June 2014 for UK Training & Calibration exercise for the Deciduous Dentition Prepared by Helen Paisley, Cynthia Pine and Girvan Burnside Administrative
The Effects of the Acid Etch and Direct Bonding Technique in Orthodontics on Enamel Surface Topography
 J. Dent. Ass. S. Afr. Vol. 31, No 10 pp 509-513 The Effects of the Acid Etch and Direct Bonding Technique in Orthodontics on Enamel Surface Topography P L Sadowsky and D H Retief Department of Orthodontics,
J. Dent. Ass. S. Afr. Vol. 31, No 10 pp 509-513 The Effects of the Acid Etch and Direct Bonding Technique in Orthodontics on Enamel Surface Topography P L Sadowsky and D H Retief Department of Orthodontics,
Key points for starting off
 Key points for starting off First off, the five questions to ask yourself about a loose tooth before identifying it are: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Category (incisor, canine, premolar or molar)? Permanent or deciduous?
Key points for starting off First off, the five questions to ask yourself about a loose tooth before identifying it are: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Category (incisor, canine, premolar or molar)? Permanent or deciduous?
SCIENTIFIC. Effects of various acids on the buccal surface of human permanent teeth: a study using scanning electron microscopy*
 PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY/Copyright 1979 by The American Academy o! Pedodontics/VoL 1, No. 3/Printed in U.S.A. SCIENTIFIC Effects of various acids on the buccal surface of human permanent teeth: a study using
PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY/Copyright 1979 by The American Academy o! Pedodontics/VoL 1, No. 3/Printed in U.S.A. SCIENTIFIC Effects of various acids on the buccal surface of human permanent teeth: a study using
Table Clinical Features Related to Level of Spinal Cord Injury. Level of Spinal Cord Damage. Associated Clinical Features. respiratory paralysis
 Table 17.1. Clinical Features Related to Level of Spinal Cord Injury Level of Spinal Cord Damage C1 to C4 C4 to C5 C5 to C6 C6 to C7 T11 to T12 T12 to L1 S3 to S5 Associated Clinical Features Death secondary
Table 17.1. Clinical Features Related to Level of Spinal Cord Injury Level of Spinal Cord Damage C1 to C4 C4 to C5 C5 to C6 C6 to C7 T11 to T12 T12 to L1 S3 to S5 Associated Clinical Features Death secondary
Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development. Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L.
 Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L. Dennis Proximal contact areas Contact areas are on the mesial and
Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L. Dennis Proximal contact areas Contact areas are on the mesial and
The clinical effectiveness of a colored pit and fisssure sealant at 24 months
 PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY/Copyright 1980 by The American Academy of Pedodontics/Vol. 2, No. 1 The clinical effectiveness of a colored pit and fisssure sealant at 24 months Richard J. Simonsen, B.A., B.S., D.D.S.
PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY/Copyright 1980 by The American Academy of Pedodontics/Vol. 2, No. 1 The clinical effectiveness of a colored pit and fisssure sealant at 24 months Richard J. Simonsen, B.A., B.S., D.D.S.
Morphology of an Anatomic Crown. By: Assistant Professor Dr. Baydaa Ali Al - Rawi
 Morphology of an Anatomic Crown By: Assistant Professor Dr. Baydaa Ali Al - Rawi October 4, 2009 Elevated landmarks Depressed landmarks A) Elevated landmarks : 1. Dental lobe : is one of the primary centers
Morphology of an Anatomic Crown By: Assistant Professor Dr. Baydaa Ali Al - Rawi October 4, 2009 Elevated landmarks Depressed landmarks A) Elevated landmarks : 1. Dental lobe : is one of the primary centers
Etching with EDTA- An in vitro study
 ISSN 0970-4388 Etching with EDTA- An in vitro study BOGRA P a, KASWAN S b ABSTRACT: In the present study, 25% EDTA, in gel form, was used to analyse its micromorphological effects on tooth surfaces with
ISSN 0970-4388 Etching with EDTA- An in vitro study BOGRA P a, KASWAN S b ABSTRACT: In the present study, 25% EDTA, in gel form, was used to analyse its micromorphological effects on tooth surfaces with
Shell teeth m management from the mixed to the permanent dentition: case report Rosamund Harrison, DMD, MS, MRCD(C) CASE REPORTS.
 Shell teeth m management from the mixed to the permanent dentition: case report Rosamund Harrison, DMD, MS, MRCD(C) David Kennedy, BDS, MSD, FRCD(C) CASE REPORTS Introduction Relatively few cases of shell
Shell teeth m management from the mixed to the permanent dentition: case report Rosamund Harrison, DMD, MS, MRCD(C) David Kennedy, BDS, MSD, FRCD(C) CASE REPORTS Introduction Relatively few cases of shell
Pits and fissures: etch resistance in prismless enamel walls
 ADRF REPORT Australian Dental Journal 2001;46:(4):258-262 Pits and fissures: etch resistance in prismless enamel walls MF Burrow,* JF Burrow, OF Makinson Abstract Background: In a previous study to examine
ADRF REPORT Australian Dental Journal 2001;46:(4):258-262 Pits and fissures: etch resistance in prismless enamel walls MF Burrow,* JF Burrow, OF Makinson Abstract Background: In a previous study to examine
Dr Milen Mariam Rajeev et al, SPJPBS.2015.,3(1), ISSN PROSTHETIC REHABILITATION OF AMELOGENESIS IMPERFECTA A CASE REPORT
 PROSTHETIC REHABILITATION OF AMELOGENESIS IMPERFECTA A CASE REPORT 1. Dr Milen Mariam Rajeev*, III year post graduate,department of Prosthodontics, 2. Dr Alex Mathews Muruppel, MDS, Head of the Department,
PROSTHETIC REHABILITATION OF AMELOGENESIS IMPERFECTA A CASE REPORT 1. Dr Milen Mariam Rajeev*, III year post graduate,department of Prosthodontics, 2. Dr Alex Mathews Muruppel, MDS, Head of the Department,
Filtek LS Low Shrink Posterior Restorative System Case 1: Cusp build-up
 Case 1 This case study focuses on the restoration of an upper molar. Filtek LS Low Shrink Posterior Restorative System Case 1: Cusp build-up The existing, inadequate restoration led to the development
Case 1 This case study focuses on the restoration of an upper molar. Filtek LS Low Shrink Posterior Restorative System Case 1: Cusp build-up The existing, inadequate restoration led to the development
Indications The selection of amalgam as a restorative material for class V cavity should involve the following considerations:
 1 Lec.7 د.عبد املنعم اخلفاجي CLASS V CAVITY PREPARATION FOR AMAGLAM Indications The selection of amalgam as a restorative material for class V cavity should involve the following considerations: 1- Caries:
1 Lec.7 د.عبد املنعم اخلفاجي CLASS V CAVITY PREPARATION FOR AMAGLAM Indications The selection of amalgam as a restorative material for class V cavity should involve the following considerations: 1- Caries:
Practice Impact Questionnaire
 Practice Impact Questionnaire Your practitioner identifier is: XXXXXXXX It is very important that ONLY YOU complete this questionnaire because your responses will be compared to responses that you provided
Practice Impact Questionnaire Your practitioner identifier is: XXXXXXXX It is very important that ONLY YOU complete this questionnaire because your responses will be compared to responses that you provided
Primary Teeth Chapter 18. Dental Anatomy 2016
 Primary Teeth Chapter 18 Dental Anatomy 2016 Primary Teeth - Introduction Synonyms deciduous teeth, baby teeth, temporary teeth, milk teeth. There are 20 primary teeth, designated as A thru T in the Universal
Primary Teeth Chapter 18 Dental Anatomy 2016 Primary Teeth - Introduction Synonyms deciduous teeth, baby teeth, temporary teeth, milk teeth. There are 20 primary teeth, designated as A thru T in the Universal
A prospective clinical trial comparing preformed metal crowns and cast restorations for defective first permanent molars
 A prospective clinical trial comparing preformed metal crowns and cast restorations for defective first permanent molars A.M. ZAGDWON, S.A. FAYLE, M.A. POLLARD ABSTRACT. Aim This study investigated two
A prospective clinical trial comparing preformed metal crowns and cast restorations for defective first permanent molars A.M. ZAGDWON, S.A. FAYLE, M.A. POLLARD ABSTRACT. Aim This study investigated two
1. What is the highest and sharpest cusp on the lower first deciduous molar? 2. Which of the following is NOT the correct location of an embrasure?
 1 1. What is the highest and sharpest cusp on the lower first deciduous molar? a. mesiobuccal b. distobuccal c. distolingual d.mesiolingual 2. Which of the following is NOT the correct location of an embrasure?
1 1. What is the highest and sharpest cusp on the lower first deciduous molar? a. mesiobuccal b. distobuccal c. distolingual d.mesiolingual 2. Which of the following is NOT the correct location of an embrasure?
OUR EXPERIENCE WITH GRADIA DIRECT IN THE RESTORATION OF ANTERIOR TEETH
 ISSN: 1312-773X (Online) Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers) 2006, vol. 12, issue 2 OUR EXPERIENCE WITH GRADIA DIRECT IN THE RESTORATION OF ANTERIOR TEETH Snezhanka Topalova-Pirinska,
ISSN: 1312-773X (Online) Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers) 2006, vol. 12, issue 2 OUR EXPERIENCE WITH GRADIA DIRECT IN THE RESTORATION OF ANTERIOR TEETH Snezhanka Topalova-Pirinska,
Anisotropy of Tensile Strengths of Bovine Dentin Regarding Dentinal Tubule Orientation and Location
 Original paper Dental Materials Journal 21 (1): 32-43, 2002 Anisotropy of Tensile Strengths of Bovine Dentin Regarding Dentinal Tubule Orientation and Location Toshiko INOUE, Hidekazu TAKAHASHI and Fumio
Original paper Dental Materials Journal 21 (1): 32-43, 2002 Anisotropy of Tensile Strengths of Bovine Dentin Regarding Dentinal Tubule Orientation and Location Toshiko INOUE, Hidekazu TAKAHASHI and Fumio
W. Kim Seow, MDSc, DDSc, PhD, FRACDS P.C. Lu L. H. McAllan, BDS, MSc
 Scientific Article Prevalence of pre-eruptive intracoronal dentin defects from panoramic radiographs W. Kim Seow, MDSc, DDSc, PhD, FRACDS P.C. Lu L. H. McAllan, BDS, MSc Dr. Seow is associate professor,
Scientific Article Prevalence of pre-eruptive intracoronal dentin defects from panoramic radiographs W. Kim Seow, MDSc, DDSc, PhD, FRACDS P.C. Lu L. H. McAllan, BDS, MSc Dr. Seow is associate professor,
1 24% 25 49% 50 74% 75 99% Every time or 100% 2. Do you assess caries risk for individual patients in any way? Yes
 1. When you examine patients to determine if they have a primary caries lesion, on what percent of these patients do you use airdrying to help diagnose the lesion? Never or 0% (skip to question 3) 1 24%
1. When you examine patients to determine if they have a primary caries lesion, on what percent of these patients do you use airdrying to help diagnose the lesion? Never or 0% (skip to question 3) 1 24%
Lecture. Permanent maxillary premolars
 Lecture Permanent maxillary premolars Permanent premolars The maxillary premolars are four in number: two in the right and two in the left. They are posterior to the canines and anterior to the molars.
Lecture Permanent maxillary premolars Permanent premolars The maxillary premolars are four in number: two in the right and two in the left. They are posterior to the canines and anterior to the molars.
Amelogenesis Imperfecta with Taurodontism, Microdontia and Minor Thalassemia: A Case Report
 Case Report Amelogenesis Imperfecta with Taurodontism, Microdontia and Minor Thalassemia: A Case Report Fatemeh Mazhari 1, Negar Mokhtari Amirmajdi 2 1 Dental Material Research Center, Faculty of Dentistry,
Case Report Amelogenesis Imperfecta with Taurodontism, Microdontia and Minor Thalassemia: A Case Report Fatemeh Mazhari 1, Negar Mokhtari Amirmajdi 2 1 Dental Material Research Center, Faculty of Dentistry,
Point of Care. Question 1. Reference
 The Point of Care section of JCDA answers everyday clinical questions by providing practical information that aims to be useful at the point of patient care. The responses reflect the opinions of the contributors
The Point of Care section of JCDA answers everyday clinical questions by providing practical information that aims to be useful at the point of patient care. The responses reflect the opinions of the contributors
General dentists in private practice place numerous
 PROACTIVE INTERVENTION DENTISTRY Incorporating Glass Ionomers into Everyday Dental Practice Todd Snyder, DDS, FAACD, FIADFE Introduction General dentists in private practice place numerous direct tooth
PROACTIVE INTERVENTION DENTISTRY Incorporating Glass Ionomers into Everyday Dental Practice Todd Snyder, DDS, FAACD, FIADFE Introduction General dentists in private practice place numerous direct tooth
Lecture 2 Maxillary central incisor
 Lecture 2 Maxillary central incisor Generally The deciduous tooth appears in the mouth at 3 18 months of age, with 6 months being the average and is replaced by the permanent tooth around 7 8 years of
Lecture 2 Maxillary central incisor Generally The deciduous tooth appears in the mouth at 3 18 months of age, with 6 months being the average and is replaced by the permanent tooth around 7 8 years of
Case Report Typical Radiographic Findings of Dentin Dysplasia Type 1b with Dental Fluorosis
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 902861, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/902861 Case Report Typical Radiographic Findings of Dentin Dysplasia Type 1b with Dental Fluorosis S. Venkata
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 902861, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/902861 Case Report Typical Radiographic Findings of Dentin Dysplasia Type 1b with Dental Fluorosis S. Venkata
A NOVEL APPROACH FOR TREATING FISSURE CARIES. The problem of hidden caries. Current diagnostic methods
 A NOVEL APPROACH FOR TREATING FISSURE CARIES Daniel W. Boston, DMD. Associate Professor and Chairman Temple University School of Dentistry Department of Restorative Dentistry 3223 North Broad Street Philadelphia,
A NOVEL APPROACH FOR TREATING FISSURE CARIES Daniel W. Boston, DMD. Associate Professor and Chairman Temple University School of Dentistry Department of Restorative Dentistry 3223 North Broad Street Philadelphia,
The spectrum of dental manifestations in vitamin D-resistant rickets: implications for management
 PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY/Copyright 1986 by The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry Volume 8 Number 3 The spectrum of dental manifestations in vitamin D-resistant rickets: implications for management W.
PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY/Copyright 1986 by The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry Volume 8 Number 3 The spectrum of dental manifestations in vitamin D-resistant rickets: implications for management W.
Dental erosion: In vitro model of wine assessor s erosion
 ADRF REPORT Australian Dental Journal 21;46:(4):263-268 Dental erosion: In vitro model of wine assessor s erosion Tong Bee Mok,* J McIntyre,* D Hunt* Abstract Background: Wine makers and assessors frequently
ADRF REPORT Australian Dental Journal 21;46:(4):263-268 Dental erosion: In vitro model of wine assessor s erosion Tong Bee Mok,* J McIntyre,* D Hunt* Abstract Background: Wine makers and assessors frequently
Shadeguides Ceramic Veneers: Tooth Preparation for Enamel Preservation
 Ajay Juneja Shadeguides Ceramic Veneers: Tooth Preparation for Enamel Preservation 1 Feb 2016 The rationale of having minimal preparation and having ceramic veneers cemented to enamel in order for the
Ajay Juneja Shadeguides Ceramic Veneers: Tooth Preparation for Enamel Preservation 1 Feb 2016 The rationale of having minimal preparation and having ceramic veneers cemented to enamel in order for the
Part II National Board Review Operative Dentistry. Module 3D General Questions Answers in BOLD (usually the first answer)
 Part II National Board Review Operative Dentistry Module 3D General Questions Answers in BOLD (usually the first answer) Howard E. Strassler, DMD University of Maryland Dental School With special acknowledgements
Part II National Board Review Operative Dentistry Module 3D General Questions Answers in BOLD (usually the first answer) Howard E. Strassler, DMD University of Maryland Dental School With special acknowledgements
Title. Citation 北海道歯学雑誌, 38(Special issue): Issue Date Doc URL. Type. File Information.
 Title The ICDAS (International Caries Detection & Assessme Author(s)Kanehira, Takashi; Takehara, Junji; Nakamura, Kimiya Citation 北海道歯学雑誌, 38(Special issue): 180-183 Issue Date 2017-09 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/67359
Title The ICDAS (International Caries Detection & Assessme Author(s)Kanehira, Takashi; Takehara, Junji; Nakamura, Kimiya Citation 北海道歯学雑誌, 38(Special issue): 180-183 Issue Date 2017-09 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/67359
Lec. 3-4 Dr. Saif Alarab Clinical Technique for Class I Amalgam Restorations The outline form
 Lec. 3-4 Dr. Saif Alarab Clinical Technique for Class I Amalgam Restorations Class I refers to -Restorations on the occlusal surfaces of posterior teeth, - The occlusal two thirds of facial and lingual
Lec. 3-4 Dr. Saif Alarab Clinical Technique for Class I Amalgam Restorations Class I refers to -Restorations on the occlusal surfaces of posterior teeth, - The occlusal two thirds of facial and lingual
The Use of Glass-fibers Ribbon and Composite for Prosthetic Restoration of Missing Primary Teeth-Laboratory and Clinical Research
 Send Orders of Reprints at reprints@benthamscience.net 220 The Open Dentistry Journal, 2014, 8, 220-228 Open Access The Use of Glass-fibers Ribbon and Composite for Prosthetic Restoration of Missing Primary
Send Orders of Reprints at reprints@benthamscience.net 220 The Open Dentistry Journal, 2014, 8, 220-228 Open Access The Use of Glass-fibers Ribbon and Composite for Prosthetic Restoration of Missing Primary
Caries Experience of Fluoride-related and Unrelated Enamel Malformations
 Oral Med Pathol 9 (2004) 61 Caries Experience of Fluoride-related and Unrelated Enamel Malformations Yue Nakahara 1, Kaori Sato 2, Hisao Yagishita 2, Yuuichi Soeno 2, Masaaki Ogawa 3 and Takaaki Aoba 2
Oral Med Pathol 9 (2004) 61 Caries Experience of Fluoride-related and Unrelated Enamel Malformations Yue Nakahara 1, Kaori Sato 2, Hisao Yagishita 2, Yuuichi Soeno 2, Masaaki Ogawa 3 and Takaaki Aoba 2
Stainless Steel Crowns
 Stainless Steel Crowns Objectives Indications for use of stainless steel crowns Technique used in preparing and placing a stainless steel crown restoration on a primary molar. Indications for SSC Restoration
Stainless Steel Crowns Objectives Indications for use of stainless steel crowns Technique used in preparing and placing a stainless steel crown restoration on a primary molar. Indications for SSC Restoration
A scanning electron microscopy comparison of enamel polishing methods after air-rotor stripping
 A scanning electron microscopy comparison of enamel polishing methods after air-rotor stripping Cesare Piacentini, DMD, DDS," and Giuseppe Sfondrini, DMD, DDS ~ Pavia, Italy In the last few years, orthodontic
A scanning electron microscopy comparison of enamel polishing methods after air-rotor stripping Cesare Piacentini, DMD, DDS," and Giuseppe Sfondrini, DMD, DDS ~ Pavia, Italy In the last few years, orthodontic
Enamel protein in smooth hypoplastic amelogenesis imperfecta
 Enamel protein in smooth hypoplastic amelogenesis imperfecta John Timothy Wright,DDS, MS Colin Robinson, PhD Jennifer Kirkham, PhD Abstract Amelogenesis imperfecta (AI) remains a poorly understood group
Enamel protein in smooth hypoplastic amelogenesis imperfecta John Timothy Wright,DDS, MS Colin Robinson, PhD Jennifer Kirkham, PhD Abstract Amelogenesis imperfecta (AI) remains a poorly understood group
Clinical report. Drs Paul and Alexandre MIARA and F. CONNOLLY COMPOSITE POSTERIOR FILLINGS. How to control. layering? 8 - Dentoscope n 124
 COMPOSITE POSTERIOR FILLINGS How to control layering? 8 - Dentoscope n 124 CV FLASH Dr Paul MIARA Dental surgeon Dr Alexandre MIARA Dental surgeon Dr F. CONNOLLY Dental surgeon Thanks to continuous improvements
COMPOSITE POSTERIOR FILLINGS How to control layering? 8 - Dentoscope n 124 CV FLASH Dr Paul MIARA Dental surgeon Dr Alexandre MIARA Dental surgeon Dr F. CONNOLLY Dental surgeon Thanks to continuous improvements
Esthetic Rehabilitation of Severely Discolored Maxillary Anterior Teeth with Porcelain Laminate Veneers: A Case Report
 Esthetic Rehabilitation of Severely Discolored Maxillary Anterior Teeth with Porcelain Laminate Veneers: A Case Report Dr. Shikha Nandal 1, Dr. Himanshu Shekhawat 2 1 M.D.S. (Prosthodontics) Senior Resident,
Esthetic Rehabilitation of Severely Discolored Maxillary Anterior Teeth with Porcelain Laminate Veneers: A Case Report Dr. Shikha Nandal 1, Dr. Himanshu Shekhawat 2 1 M.D.S. (Prosthodontics) Senior Resident,
Prosthetic and Surgical Approach for Oral Rehabilitation in a Patient with Amelogenesis Imperfecta: A Clinical Report
 Case Report Prosthetic and Surgical Approach for Oral Rehabilitation in a Patient with Amelogenesis Imperfecta: A Clinical Report H. Sazegara 1, K. Seyedan 2, H. Behnia 3, P. Ghaderi 2 1 Associate Professor,
Case Report Prosthetic and Surgical Approach for Oral Rehabilitation in a Patient with Amelogenesis Imperfecta: A Clinical Report H. Sazegara 1, K. Seyedan 2, H. Behnia 3, P. Ghaderi 2 1 Associate Professor,
ADHESIVE RECONSTRUCTION IN HELP OF THE ORTHODONTIC TREATMENT
 ISSN: 1312-773X (Online) Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers) 2006, vol. 12, issue 2 ADHESIVE RECONSTRUCTION IN HELP OF THE ORTHODONTIC TREATMENT Snezhanka Topalova-Pirinska 1, R. Pirinska
ISSN: 1312-773X (Online) Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers) 2006, vol. 12, issue 2 ADHESIVE RECONSTRUCTION IN HELP OF THE ORTHODONTIC TREATMENT Snezhanka Topalova-Pirinska 1, R. Pirinska
Molar Incisor Hypomineralisation: restorative management
 Molar Incisor Hypomineralisation: restorative management S.A. FAYLE ABSTRACT. Aim The methods for the restoration of permanent molars and incisors affected by Molar Incisor Hypomineralisation are reviewed.
Molar Incisor Hypomineralisation: restorative management S.A. FAYLE ABSTRACT. Aim The methods for the restoration of permanent molars and incisors affected by Molar Incisor Hypomineralisation are reviewed.
SCIENTIFIC ARTICLES. Longitudinal evaluation of caries patterns from the primary to the mixed dentition
 PEDIATRIC DENTlSTRYKopyright 0 1990 by The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry Volume 12. Number 5 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLES Longitudinal evaluation of caries patterns from the primary to the mixed dentition
PEDIATRIC DENTlSTRYKopyright 0 1990 by The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry Volume 12. Number 5 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLES Longitudinal evaluation of caries patterns from the primary to the mixed dentition
Colourf low. light cured dental flowable composite
 Colourf low light cured dental flowable composite DENTAL LIFE SCIENCES (mfg) Ltd. Unit A3, Wigan Enterprise Court, Wigan Enterprise Park, WN2 2LE United Kingdom www.dentallifesciences.com Colourf low flowable
Colourf low light cured dental flowable composite DENTAL LIFE SCIENCES (mfg) Ltd. Unit A3, Wigan Enterprise Court, Wigan Enterprise Park, WN2 2LE United Kingdom www.dentallifesciences.com Colourf low flowable
Ghost Teeth: A Rare Developmental Anomaly of the Dental Tissues
 Science Journal of Medicine and Clinical Trials ISSN: 2276-7487 http://www.sjpub.org Author(s) 2014. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Published By Science Journal Publication International Open Access Publisher
Science Journal of Medicine and Clinical Trials ISSN: 2276-7487 http://www.sjpub.org Author(s) 2014. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Published By Science Journal Publication International Open Access Publisher
Hereditary Opalescent Dentin: A Report of Two Cases
 Hereditary Opalescent Dentin: A Report of Two Cases Siddharth Gupta, BDS, MDS; Rahul R. Bhowate, BDS, MDS; Ashok Bhati, BDS, MDS Abstract Aim: The aim of this case report is to present the clinical and
Hereditary Opalescent Dentin: A Report of Two Cases Siddharth Gupta, BDS, MDS; Rahul R. Bhowate, BDS, MDS; Ashok Bhati, BDS, MDS Abstract Aim: The aim of this case report is to present the clinical and
Annals and Essences of Dentistry
 doi:10.5368/aedj.2012.4.4.3.2 COMPREHENSIVE MANAGEMENT OF AN ADULT PATIENT WITH DENTAL FLUOROSIS 1 Kapil Dua 2 Kavitha Eappen 3 Ajit Kumar Jaiswal 4 Anjuman Khurana Dua 1 Associate Professor 2 Assistant
doi:10.5368/aedj.2012.4.4.3.2 COMPREHENSIVE MANAGEMENT OF AN ADULT PATIENT WITH DENTAL FLUOROSIS 1 Kapil Dua 2 Kavitha Eappen 3 Ajit Kumar Jaiswal 4 Anjuman Khurana Dua 1 Associate Professor 2 Assistant
CAS. Asymmetrical tooth defects observed in hypoplastic primary teeth and amelogenesis imperfecta: case reports
 PEDIATRIC DENTiSTRY/Copyright The American Academy of Pediatric Volume 9 Number 2 1987 by Dentistry CAS Asymmetrical tooth defects observed in hypoplastic primary teeth and amelogenesis imperfecta: case
PEDIATRIC DENTiSTRY/Copyright The American Academy of Pediatric Volume 9 Number 2 1987 by Dentistry CAS Asymmetrical tooth defects observed in hypoplastic primary teeth and amelogenesis imperfecta: case
AMELOGENESIS IMPERFECTA - A CASE REPORT WITH FULL MOUTH REHABILITATION
 International Journal of Dental Research & Development (IJDRD) ISSN(P): 2250-2386; ISSN(E): 2321-0117 Vol. 6, Issue 5, Oct 2016, 1-8 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd. AMELOGENESIS IMPERFECTA - A CASE REPORT WITH FULL MOUTH
International Journal of Dental Research & Development (IJDRD) ISSN(P): 2250-2386; ISSN(E): 2321-0117 Vol. 6, Issue 5, Oct 2016, 1-8 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd. AMELOGENESIS IMPERFECTA - A CASE REPORT WITH FULL MOUTH
values is of great interest.
 User Report Dr. Ralph Schönemann, May 21, 2008 There are numerous self-etchbonding systems on the market that sometimes differ very much from one another with regards to their chemical composition. It
User Report Dr. Ralph Schönemann, May 21, 2008 There are numerous self-etchbonding systems on the market that sometimes differ very much from one another with regards to their chemical composition. It
Amelogenesis Imperfecta: A Series of
 Case Report Amelogenesis Imperfecta: A Series of Case Report Nuzula Begum 1, Gowri P Bhandarkar 2, Raghavendra Kini 3, Vathsala Naik 4, K Rashmi 1, Lizzy Carol D Souza 1 1 Post Graduate Student, Department
Case Report Amelogenesis Imperfecta: A Series of Case Report Nuzula Begum 1, Gowri P Bhandarkar 2, Raghavendra Kini 3, Vathsala Naik 4, K Rashmi 1, Lizzy Carol D Souza 1 1 Post Graduate Student, Department
Molar-Incisor Hypomineralization (MIH): An Unusual Case with Literature Review
 ADVANCES IN MEDICAL AND DENTAL SCIENCES 2017. 6(1): 6-10 ISSN: 1995-0764 EISSN: 1998-1082 Journal home page: http://arnmsmb.com/amds/ RESARCH ARTICLE Molar-Incisor Hypomineralization (MIH): An Unusual
ADVANCES IN MEDICAL AND DENTAL SCIENCES 2017. 6(1): 6-10 ISSN: 1995-0764 EISSN: 1998-1082 Journal home page: http://arnmsmb.com/amds/ RESARCH ARTICLE Molar-Incisor Hypomineralization (MIH): An Unusual
Planning and Care for Children and Adolescents with Dental Enamel Defects
 Planning and Care for Children and Adolescents with Dental Enamel Defects Etiology, Research and Contemporary Management Bernadette K. Drummond Nicola Kilpatrick Editors 123 Planning and Care for Children
Planning and Care for Children and Adolescents with Dental Enamel Defects Etiology, Research and Contemporary Management Bernadette K. Drummond Nicola Kilpatrick Editors 123 Planning and Care for Children
Natural Tooth Pontic using Fiber-reinforced Composite for Immediate Tooth Replacement
 10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1035 CLINICAL ARTICLE Natural Tooth Pontic using Fiber-reinforced Composite for Immediate Tooth Replacement Natural Tooth Pontic using Fiber-reinforced Composite for Immediate
10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1035 CLINICAL ARTICLE Natural Tooth Pontic using Fiber-reinforced Composite for Immediate Tooth Replacement Natural Tooth Pontic using Fiber-reinforced Composite for Immediate
CPR for Complex Dental Treatment; From Concept, to Prototype, to Restoration
 Reality or Resin; Free Hand Artistry with Anterior Bonding Dennis B. Hartlieb, DDS CPR for Complex Dental Treatment; From Concept, to Prototype, to Restoration Wish List: 1. Reversible (no prep/ minimal
Reality or Resin; Free Hand Artistry with Anterior Bonding Dennis B. Hartlieb, DDS CPR for Complex Dental Treatment; From Concept, to Prototype, to Restoration Wish List: 1. Reversible (no prep/ minimal
Complex esthetic and functional rehabilitation using glass-ceramic materials - long-term documentation of a restoration
 C L I N I C A L Complex esthetic and functional rehabilitation using glass-ceramic materials - long-term documentation of a restoration Daniel Edelhoff 1 and Oliver Brix 2 1 Prof. Dr Daniel Edelhoff, Munich
C L I N I C A L Complex esthetic and functional rehabilitation using glass-ceramic materials - long-term documentation of a restoration Daniel Edelhoff 1 and Oliver Brix 2 1 Prof. Dr Daniel Edelhoff, Munich
Examination and Treatment Protocols for Dental Caries and Inflammatory Periodontal Disease
 Examination and Treatment Protocols for Dental Caries and Inflammatory Periodontal Disease Dental Caries The current understanding of the caries process supports the shift in caries management from a restorative-only
Examination and Treatment Protocols for Dental Caries and Inflammatory Periodontal Disease Dental Caries The current understanding of the caries process supports the shift in caries management from a restorative-only
Lecture Content and learning outcomes
 DIPLOMA IN PAEDIATRIC DENTISTRY Subject Lecture Content and learning outcomes Craniofacial growth and development The process of pre-natal development The process of post-natal craniofacial growth The
DIPLOMA IN PAEDIATRIC DENTISTRY Subject Lecture Content and learning outcomes Craniofacial growth and development The process of pre-natal development The process of post-natal craniofacial growth The
The Premolars. Chapter 17 Permanent Posterior Teeth (p )
 The Premolars Chapter 17 Permanent Posterior Teeth (p. 230-244) General Information Function: u Hold and grind food u Work with molars in mastication. u Even without molars one may be able to chew well
The Premolars Chapter 17 Permanent Posterior Teeth (p. 230-244) General Information Function: u Hold and grind food u Work with molars in mastication. u Even without molars one may be able to chew well
WaveOne Gold reciprocating instruments: clinical application in the private practice: Part 2
 C L I N I C A L WaveOne Gold reciprocating instruments: clinical application in the private practice: Part 2 Peet van der Vyver 1 and Martin Vorster 2 1 Department of Odontology, School of Dentistry, University
C L I N I C A L WaveOne Gold reciprocating instruments: clinical application in the private practice: Part 2 Peet van der Vyver 1 and Martin Vorster 2 1 Department of Odontology, School of Dentistry, University
riva helping you help your patients
 riva helping you help your patients what is a glass ionomer? how will a dentist benefit from using glass ionomers? how will a patient benefit from their glass ionomer? Glass ionomer is the generic name
riva helping you help your patients what is a glass ionomer? how will a dentist benefit from using glass ionomers? how will a patient benefit from their glass ionomer? Glass ionomer is the generic name
2. Gap closure and replacement of the missing tooth 35 with directly modelled bridge region 34-36
 GrandTEC Test Kit Dear User, This Test Kit has been put together to enable you to test GrandTEC on the model before using it in a clinical situation. GrandTEC is a resin-impregnated glass fibre strip.
GrandTEC Test Kit Dear User, This Test Kit has been put together to enable you to test GrandTEC on the model before using it in a clinical situation. GrandTEC is a resin-impregnated glass fibre strip.
Amelogenesis imperfecta (AI)
 2010 JCO, Inc. May not be distributed without permission. www.jco-online.com CASE REPORT Interdisciplinary Treatment of a Patient with Amelogenesis Imperfecta MARGARITA VARELA MORALES, MD, DDS, PHD JOSE-MARÍA
2010 JCO, Inc. May not be distributed without permission. www.jco-online.com CASE REPORT Interdisciplinary Treatment of a Patient with Amelogenesis Imperfecta MARGARITA VARELA MORALES, MD, DDS, PHD JOSE-MARÍA
Bond strengths between composite resin and auto cure glass ionomer cement using the co-cure technique
 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Australian Dental Journal 2006;51:(2):175-179 Bond strengths between composite resin and auto cure glass ionomer cement using the co-cure technique GM Knight,* JM McIntyre,* Mulyani*
SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Australian Dental Journal 2006;51:(2):175-179 Bond strengths between composite resin and auto cure glass ionomer cement using the co-cure technique GM Knight,* JM McIntyre,* Mulyani*
Problems of First Permanent Molars - The first group of permanent teeth erupt in the oral cavity. - Deep groove and pit
 Management of the poor first permanent e molar Assoc. Prof. Kadkao Vongsavan * Asst. Prof. Praphasri Rirattanapong* Dr. Pongsakorn Sakkamathya** ** * Department of Pediatric Dentistry Faculty of Dentistry,
Management of the poor first permanent e molar Assoc. Prof. Kadkao Vongsavan * Asst. Prof. Praphasri Rirattanapong* Dr. Pongsakorn Sakkamathya** ** * Department of Pediatric Dentistry Faculty of Dentistry,
ORIGINAL STUDY BRACKET BONDING TO ENAMEL AND DENTIN - ESEM STUDIES -
 MEDICINĂ, no 1, 2013 ORIGINAL STUDY BRACKET BONDING TO ENAMEL AND DENTIN - ESEM STUDIES - Delia Ioana Ciocan 1, Florin Miculescu 2, Lucian Toma Ciocan 3, Dragos Stanciu 1 1 Orthodontics and Dento-Facial
MEDICINĂ, no 1, 2013 ORIGINAL STUDY BRACKET BONDING TO ENAMEL AND DENTIN - ESEM STUDIES - Delia Ioana Ciocan 1, Florin Miculescu 2, Lucian Toma Ciocan 3, Dragos Stanciu 1 1 Orthodontics and Dento-Facial
Restoration of teeth using lithium disilicate glass-ceramics in a patient with Dentinogenesis Imperfecta
 Clinical Restoration of teeth using lithium disilicate glass-ceramics in a patient with Dentinogenesis Imperfecta Daniel Edelhoff 1, Oliver Brix 2 and Josef Schweiger 1 Introduction The availability of
Clinical Restoration of teeth using lithium disilicate glass-ceramics in a patient with Dentinogenesis Imperfecta Daniel Edelhoff 1, Oliver Brix 2 and Josef Schweiger 1 Introduction The availability of
Patient demand for esthetic dentistry
 PROFILE Masters of Esthetic Dentistry Keys to Success in Creating Esthetic Class IV Restorations Robert C. Margeas, DDS Current occupation Private Practice Adjunct Professor, Department of Operative Dentistry,
PROFILE Masters of Esthetic Dentistry Keys to Success in Creating Esthetic Class IV Restorations Robert C. Margeas, DDS Current occupation Private Practice Adjunct Professor, Department of Operative Dentistry,
Dental Health Considerations & Solutions in Patients with Turner Syndrome
 Dental Health Considerations & Solutions in Patients with Turner Syndrome Robert Korwin, D.M.D. Post Graduate Certificate in General Practice Master, Academy of General Dentistry Master, International
Dental Health Considerations & Solutions in Patients with Turner Syndrome Robert Korwin, D.M.D. Post Graduate Certificate in General Practice Master, Academy of General Dentistry Master, International
stabilisation and surface protection
 Guiding the way to caries stabilisation and surface protection Fissure sealing MI restorations Pulp capping Hypersensitivity Protection Caries stabilisation Fuji Triage from GC. Temporary restorations
Guiding the way to caries stabilisation and surface protection Fissure sealing MI restorations Pulp capping Hypersensitivity Protection Caries stabilisation Fuji Triage from GC. Temporary restorations
6610 NE 181st Street, Suite #1, Kenmore, WA
 660 NE 8st Street, Suite #, Kenmore, WA 9808 www.northshoredentalacademy.com.08.900 READ CHAPTER The Professional Dental Assistant (p.-9) No Key Terms Recall Questions:,,,, and 6 CLASS SYLLABUS DAY READ
660 NE 8st Street, Suite #, Kenmore, WA 9808 www.northshoredentalacademy.com.08.900 READ CHAPTER The Professional Dental Assistant (p.-9) No Key Terms Recall Questions:,,,, and 6 CLASS SYLLABUS DAY READ
The use of pit and fissure sealants in dentistry, present status and future developments
 PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY/Copyright 1982 by The American Academy of Pedodontics/Vol. 4, No. 1 The use of pit and fissure sealants in dentistry, present status and future developments Leon M. Silverstone, BChD,
PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY/Copyright 1982 by The American Academy of Pedodontics/Vol. 4, No. 1 The use of pit and fissure sealants in dentistry, present status and future developments Leon M. Silverstone, BChD,
Amelogenesis Imperfecta: Current Understanding of Genotype-Phenotype
 Amelogenesis Imperfecta: Current Understanding of Genotype-Phenotype 5 John Timothy Wright Abstract There are nearly 100 hereditary conditions that affect enamel formation. Hereditary enamel conditions
Amelogenesis Imperfecta: Current Understanding of Genotype-Phenotype 5 John Timothy Wright Abstract There are nearly 100 hereditary conditions that affect enamel formation. Hereditary enamel conditions
Introduction. B. Jälevik 1 A. Szigyarto Matei 2 A. Robertson 1
 https://doi.org/10.1007/s40368-018-0347-7 ORIGINAL SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE The prevalence of developmental defects of enamel, a prospective cohort study of adolescents in Western Sweden: a Barn I TAnadvarden
https://doi.org/10.1007/s40368-018-0347-7 ORIGINAL SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE The prevalence of developmental defects of enamel, a prospective cohort study of adolescents in Western Sweden: a Barn I TAnadvarden
Amelogenesis Imperfecta- A Review. Pankhuri Nigam, Vijay Pal Singh, Krishnadeo Prasad, Jalaj Tak, Anju Sinha, Parveen Grewal
 Review Article Amelogenesis Imperfecta- A Review Pankhuri Nigam, Vijay Pal Singh, Krishnadeo Prasad, Jalaj Tak, Anju Sinha, Parveen Grewal Department of Oral Pathology, S.B.B.D.C, Ghaizabad, U.P, India
Review Article Amelogenesis Imperfecta- A Review Pankhuri Nigam, Vijay Pal Singh, Krishnadeo Prasad, Jalaj Tak, Anju Sinha, Parveen Grewal Department of Oral Pathology, S.B.B.D.C, Ghaizabad, U.P, India
Total Impaction of Deciduous Maxillary Molars: Two Case Reports
 Total Impaction of Deciduous Maxillary Molars: Two Case Reports Abstract Aim: The purpose of this report is to present two cases of totally impacted maxillary deciduous molars, considered a rarity in dental
Total Impaction of Deciduous Maxillary Molars: Two Case Reports Abstract Aim: The purpose of this report is to present two cases of totally impacted maxillary deciduous molars, considered a rarity in dental
Mutational Spectrum of FAM83H: The C-Terminal Portion is Required for Tooth Enamel Calcification
 HUMAN MUTATION Mutation in Brief #1014, 29:E95-E99, (2008) Online MUTATION IN BRIEF Mutational Spectrum of FAM83H: The C-Terminal Portion is Required for Tooth Enamel Calcification Sook-Kyung Lee 1, Jan
HUMAN MUTATION Mutation in Brief #1014, 29:E95-E99, (2008) Online MUTATION IN BRIEF Mutational Spectrum of FAM83H: The C-Terminal Portion is Required for Tooth Enamel Calcification Sook-Kyung Lee 1, Jan
Peninsula Dental Social Enterprise (PDSE)
 Peninsula Dental Social Enterprise (PDSE) Paediatric Pathway - Restorative Version 2.0 Date approved: May 2018 Approved by: The Board Review due: May 2020 Page 1 of 7 Routine assessment: Clinical Examination
Peninsula Dental Social Enterprise (PDSE) Paediatric Pathway - Restorative Version 2.0 Date approved: May 2018 Approved by: The Board Review due: May 2020 Page 1 of 7 Routine assessment: Clinical Examination
PREVALENCE AND FACTORS ASSOCIATED WITH TOOTH DISCOLORATION AMONG UAE UNIVERSITY STUDENTS
 GMJ GULF MEDICAL JOURNAL ORAL PROCEEDINGS PREVALENCE AND FACTORS ASSOCIATED WITH TOOTH Omar Barakat 1 *, Ardeshir Amirhosseini 1, Mohammad Ahmad 1, Sara Al-Fallahi 1, Talal Atassi 1, Walid El-Sayed 2 1Final
GMJ GULF MEDICAL JOURNAL ORAL PROCEEDINGS PREVALENCE AND FACTORS ASSOCIATED WITH TOOTH Omar Barakat 1 *, Ardeshir Amirhosseini 1, Mohammad Ahmad 1, Sara Al-Fallahi 1, Talal Atassi 1, Walid El-Sayed 2 1Final
Dental Anatomy and Occlusion
 CHAPTER 53 Dental Anatomy and Occlusion Ma Lou C. Sabino DDS, and Emily G. Smythe, DDS What numerical system is used most commonly in the United States for designating the adult dentition? Pediatric dentition?
CHAPTER 53 Dental Anatomy and Occlusion Ma Lou C. Sabino DDS, and Emily G. Smythe, DDS What numerical system is used most commonly in the United States for designating the adult dentition? Pediatric dentition?
Supplemental mandibular incisors: a Recherché
 CASE REPORT 34 Supplemental mandibular incisors: a Recherché Sankriti Murthy Introduction: Supernumerary teeth are a developmental disturbance encountered in the dental arches. These teeth are in excess
CASE REPORT 34 Supplemental mandibular incisors: a Recherché Sankriti Murthy Introduction: Supernumerary teeth are a developmental disturbance encountered in the dental arches. These teeth are in excess
Direct composite restorations for large posterior cavities extended range of applications for high-performance materials
 Direct composite restorations for large posterior cavities extended range of applications for high-performance materials A case study by Ann-Christin Meier, Dr. med. dent., Stapelfeld, Germany When large
Direct composite restorations for large posterior cavities extended range of applications for high-performance materials A case study by Ann-Christin Meier, Dr. med. dent., Stapelfeld, Germany When large
Annals and Essences of Dentistry
 10.5368/aedj.2017.9.3.2.8 FIBRE REINFORCED COMPOSITE RESIN PROSTHESIS AS INTERIM REPLACEMENT FOR CONGENITALLY MISSING PERMANENT MANDIBULAR CENTRAL INCISORS:A CASE REPORT 1 Patel P 2 Kohli S 3 Deep S 4
10.5368/aedj.2017.9.3.2.8 FIBRE REINFORCED COMPOSITE RESIN PROSTHESIS AS INTERIM REPLACEMENT FOR CONGENITALLY MISSING PERMANENT MANDIBULAR CENTRAL INCISORS:A CASE REPORT 1 Patel P 2 Kohli S 3 Deep S 4
Root Surface Protection Simple. Effective. Important.
 GC Fuji VII / Fuji VII EP Root Surface Protection Simple. Effective. Important. Brush up your painting skills and help your patients Q&A Prof. Laurie Walsh University of Queensland lifestyle factors (frequency
GC Fuji VII / Fuji VII EP Root Surface Protection Simple. Effective. Important. Brush up your painting skills and help your patients Q&A Prof. Laurie Walsh University of Queensland lifestyle factors (frequency
Journal of Oral & Dental Health
 Research Article X-ray Microanalysis of ormal Primary Tooth Dentine and Primary Tooth Dentine in Teeth Diagnosed Dentinogenesis Imperfecta Type II oren JG 1 *, Sabel 1 and Cornell DH 2 Journal of Oral
Research Article X-ray Microanalysis of ormal Primary Tooth Dentine and Primary Tooth Dentine in Teeth Diagnosed Dentinogenesis Imperfecta Type II oren JG 1 *, Sabel 1 and Cornell DH 2 Journal of Oral
swed dent j 2010; 34: hasselkvist, johansson, johansson
 swed dent j 2010; 34: 187-195 hasselkvist, johansson, johansson swedish dental journal vol. 34 issue 4 2010 187 swed dent j 2010; 34: 187-195 hasselkvist, johansson, johansson 188 swedish dental journal
swed dent j 2010; 34: 187-195 hasselkvist, johansson, johansson swedish dental journal vol. 34 issue 4 2010 187 swed dent j 2010; 34: 187-195 hasselkvist, johansson, johansson 188 swedish dental journal
OCCLUSION. Principles & Treatment. José dos Santos, Jr, DDS, PhD. São Paulo, Brazil
 OCCLUSION Principles & Treatment José dos Santos, Jr, DDS, PhD São Paulo, Brazil Former Professor Division of Occlusion Department of Restorative Dentistry University of Texas Health Science Center at
OCCLUSION Principles & Treatment José dos Santos, Jr, DDS, PhD São Paulo, Brazil Former Professor Division of Occlusion Department of Restorative Dentistry University of Texas Health Science Center at
Root Dentine Sensitivity
 Indian Medical Gazette JULY 2012 269 Original Study Root Dentine Sensitivity Jyoti Ajay Khade, Associate Professor, Dept. of Dentistry, Rajiv Gandhi Institute of Medical Sciences (RIMS) Adilabad, A.P.
Indian Medical Gazette JULY 2012 269 Original Study Root Dentine Sensitivity Jyoti Ajay Khade, Associate Professor, Dept. of Dentistry, Rajiv Gandhi Institute of Medical Sciences (RIMS) Adilabad, A.P.
Class I Cavity Preparation. Alaa Sabrah, BDS, MSD, PhD Nov,
 بسم اهلل الرحمن الرحيم Class I Cavity Preparation Alaa Sabrah, BDS, MSD, PhD Nov, 2015 15 Goals and Objectives?Define class I carious lesion.1 Describe the clinical technique for treating class I?carious
بسم اهلل الرحمن الرحيم Class I Cavity Preparation Alaa Sabrah, BDS, MSD, PhD Nov, 2015 15 Goals and Objectives?Define class I carious lesion.1 Describe the clinical technique for treating class I?carious
Selection and arrangement of teeth in rpd
 Selection and arrangement of teeth in rpd upon completion of the articulator mounting and a thorough assessment of the occlusal requirements, the practitioner should be able to perform the proper arrangement
Selection and arrangement of teeth in rpd upon completion of the articulator mounting and a thorough assessment of the occlusal requirements, the practitioner should be able to perform the proper arrangement
A clinical case involving severe erosion of the maxillary anterior teeth restored with direct composite resin restorations
 SETHI A clinical case involving severe erosion of the maxillary anterior teeth restored with direct composite resin restorations Sanjay Sethi, BDS (Lond.) Square Mile Dental Centre, 7-9 White Kennett Street,
SETHI A clinical case involving severe erosion of the maxillary anterior teeth restored with direct composite resin restorations Sanjay Sethi, BDS (Lond.) Square Mile Dental Centre, 7-9 White Kennett Street,
Treatment management of first permanent molars in children with Molar-Incisor Hypomineralisation
 Treatment management of first permanent molars in children with Molar-Incisor Hypomineralisation N. KOTSANOS*, E.G. KAKLAMANOS**, K. ARAPOSTATHIS* ABSTRACT. Aim To study the treatment management of first
Treatment management of first permanent molars in children with Molar-Incisor Hypomineralisation N. KOTSANOS*, E.G. KAKLAMANOS**, K. ARAPOSTATHIS* ABSTRACT. Aim To study the treatment management of first
