Mutational Spectrum of FAM83H: The C-Terminal Portion is Required for Tooth Enamel Calcification
|
|
|
- Mabel Anderson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 HUMAN MUTATION Mutation in Brief #1014, 29:E95-E99, (2008) Online MUTATION IN BRIEF Mutational Spectrum of FAM83H: The C-Terminal Portion is Required for Tooth Enamel Calcification Sook-Kyung Lee 1, Jan C-C. Hu 2, John D. Bartlett 3, Kyung-Eun Lee 1, Brent P-J. Lin 4, James P. Simmer 2, and Jung-Wook Kim 1,5* 1 Department of Cell and Developmental Biology & Dental Research Institute, School of Dentistry, Seoul National University, Yongon-dong, Chongno-gu, Seoul , Korea; 2 Department of Biologic and Materials Sciences, University of Michigan Dental Research Lab, 1210 Eisenhower Place, Ann Arbor, MI 48108; 3 Harvard- Forsyth Department of Oral Biology, Department of Cytokine Biology, The Forsyth Institute, 140 The Fenway, Boston, MA 02115; 4 Department of Growth and Development, University of California, San Francisco, School of Dentistry, San Francisco, CA ; 5 Department of Pediatric Dentistry & Dental Research Institute, School of Dentistry, Seoul National University, Yongon-dong, Chongno-gu, Seoul , Korea. *Correspondence to Jung-Wook Kim, Dental Genetics Laboratory, Department of Cell and Developmental Biology, Department of Pediatric Dentistry & Dental Research Institute, School of Dentistry, Seoul National University, Yongon-dong, Chongno-gu, Seoul , Korea; Tel.: ; Fax: ; pedoman@snu.ac.kr Communicated by Mark H. Paalman Dental enamel forms through the concerted activities of specialized extracellular matrix proteins, including amelogenin, enamelin, MMP20, and KLK4. Defects in the genes encoding these proteins cause non-syndromic inherited enamel malformations collectively designated as amelogenesis imperfecta (AI). These genes, however, account for only about a quarter of all AI cases. Recently we identified mutations in FAM83H that caused autosomal dominant hypocalcified amelogenesis imperfecta (ADHCAI). Unlike other genes that cause AI, FAM83H does not encode an extracellular matrix protein. Its location inside the cell is completely unknown, as is its function. We here report novel FAM83H mutations in four kindreds with ADHCAI. All are nonsense mutations in the last exon (c.1243g>t, p.e415x; c.891t>a, p.y297x; c.1380g>a, p.w460x; and c.2029c>t, p.q677x). These mutations delete between 503 and 883 amino acids from the C-terminus of a protein normally comprised of 1179 residues. The reason these mutations cause such extreme defects in the enamel layer without affecting other parts of the body is not known yet. However it seems evident that the large C-terminal part of the protein is essential for proper enamel calcification Wiley-Liss, Inc. KEY WORDS: amelogenesis imperfecta; hypocalcification; enamel; matrix; FAM83H INTRODUCTION Dental enamel is the hardest tissue in the human body. It consists of a highly organized layer of calcium hydroxyapatite crystals that covers dentin to form the crown of a tooth. Dental enamel contains less than 1% Received 29 January 2008; accepted revised manuscript 20 February WILEY-LISS, INC. DOI: /humu.20789
2 E96 Lee et al. organic material, whereas other mineralized tissues contain about 20% organics (Nanci, 2008). Amelogenesis imperfecta (AI) is a collection of inherited conditions exhibiting malformations in tooth enamel, usually in the absence of other symptoms (Hu, et al., 2007; Wright, 2006). The enamel phenotype in AI varies, but can be broadly categorized as hypoplastic (abnormally thin), hypomaturation (normal thickness, but soft), and hypocalcified (irregular thickness and soft) (Witkop, 1988). Dental enamel forms in an extracellular space by matrix-mediated biomineralization (Simmer and Fincham, 1995). Defects in the genes encoding four secreted enamel matrix proteins are known to cause non-syndromic hereditary enamel defects. Mutations in the amelogenin gene (AMELX; MIM# ) cause X-linked hypoplastic and hypomaturation AI. Mutations in the enamelin gene (ENAM; MIM# ) cause autosomal dominant or recessive hypoplastic AI, while mutations in the genes encoding the enamel proteases enamelysin (MMP20; MIM# ) and kallikrein 4 (KLK4; MIM# ), cause autosomal recessive hypomaturation AI. These genes, however, were found to cause the disease in only 6 out of 24 AI families screened by mutational analyses using the known candidate genes (Kim, et al., 2006). Recently, a form of autosomal dominant AI was linked to a 2.1 MB region of chromosome 8 (Mendoza, et al., 2007), and we discerned that defects in FAM83H (family with sequence similarity 83 member H) within this linked interval caused autosomal dominant hypocalcified amelogenesis imperfecta (ADHCAI) in two Korean families (Kim, et al., 2008). The aim of this study was to further investigate for FAM83H (8q24.3) mutations in other kindreds with ADHCAI. MATERIALS AND METHODS Subjects The study protocol and subject consents were reviewed and approved by the Institution Review Boards at the Seoul National University Hospital and the University of Michigan and appropriate informed consent was obtained from all subjects. Among the 37 AI families, we selected 7 ADHCAI families based on the clinical phenotype. DNA extraction, PCR amplification and Mutational Analysis Ten cc of peripheral whole blood was obtained from participating family members. Genomic DNA was obtained by a conventional salting out method. we amplified and sequenced all exons and exon/intron boundaries of the FAM83H gene as previously described (Kim, et al., 2008). PCR amplifications were performed using the HiPi DNA polymerase premix (ElpisBio, Korea). PCR amplification products were purified by the PCR Purification Kit and protocol (ElpisBio, Korea) and used as template for DNA sequencing, which was performed at the DNA sequencing center (Macrogen, Korea). DNA mutation numbering system is based on cdna sequence. For cdna numbering, nucleotide numbering reflects cdna numbering with +1 corresponding to the A of the ATG translation initiation codon in the reference sequence (NM_ ), according to journal guidelines ( Paternity Testing Genomic DNA from the proband of family 2 (AI#12) and his parents were analyzed by a commercial laboratory (DowGene, Korea) using 15 genetic markers (D3S1358, D21S11, D5S818, D13S317, D7S820, CSF1PO, TPOX, FGA, VWA, D16S539, D8S1179, D18S51, THO1, PentaE, PentaD). RESULTS Nonsense mutations were identified in the last exon (exon 5) of FAM83H in four families with hypocalcified amelogenesis imperfecta (Table 1). In three of the families (1,3,4) the pattern of inheritance is autosomal dominant (Figure 1). The mutation in family 2 is spontaneous, as the mutation is present in the proband but absent in his biological parents (confirmed by paternity testing), who have normal dentitions.
3 Mutational spectrum of FAM83H E97 Table 1. Novel FAM83H mutations of detected in this study Site Family* Race Mutation** Protein Pattern of Inheritance Exon 5 1(AI#8) Hispanic c.1243g>t p.e415x autosomal dominant Exon 5 2(AI#12) Asian c.891t>a p.y297x spontaneous Exon 5 3(AI#21) Caucasian c.1380g>a p.w460x autosomal dominant Exon 5 4(AI#24) Caucasian c.2029c>t p.q677x autosomal dominant *Family ID in parenthesis correspond to families in previous report (Kim, et al., 2006). **DNA mutation numbering system is based on cdna sequence. For cdna numbering, nucleotide numbering reflects cdna numbering with +1 corresponding to the A of the ATG translation initiation codon in the reference sequence (NM_ ), according to journal guidelines ( Figure 1. A: Pedigree of family 1 (p.e415x). Oral photographs show the proband (IV-4). Upper photo is the mandibular incisors at age 7 years and 11 months. Lower one is a photo at age 10 years and 10 months. B: Pedigree of family 2 (p.y297x) and oral photograph of proband (II-1). C: Pedigree of family 3 (p.w460x) and oral photograph of proband at age 8. D: Pedigree of family 4 (p.q677x) with panorex and oral photographs of proband (IV-2) at age 13 years and 5 months.
4 E98 Lee et al. The dental enamel in the affected members of our four AI kindreds is cheesy soft in consistency, light yellow in shade, and nearly normal in thickness until erupting into function. Thereafter the enamel layer is rapidly lost due to attrition. The abraded teeth lose contour, often becoming tapered toward the incisal edge or occlusal surface. The abraded surfaces are rough in texture, take up stain rapidly, and are sensitive to thermal changes. Most of the enamel crown is rapidly lost, but sporadic islands of enamel are retained for years and appear to be of near-normal hardness. The clinical phenotype is most consistent with a diagnosis of hypocalcified AI. There are now 6 FAM83H mutations that have been identified in families affected with autosomal dominant hypocalcification amelogenesis imperfecta (ADHCAI). All of the observed mutations introduce premature translation termination codons in exon 5 (Figure 2). Figure 2. Gene diagram showing the 5 exons (boxes) and 4 introns (bars) of FAM83H. The non-coding regions in exons are shaded. The number of base pairs (bp) in an intron is shown above the intron. The number of base pairs in an exon is below the exon, followed by the number of amino acid codons in the exon and the range of amino acids encoded by the exon. The disease-causing mutations reported here are marked in bold above exon 5. The disease-causing mutations reported previously are marked in bold below exon 5. DISCUSSION Previously we conducted mutational analyses on 24 kindreds with amelogenesis imperfecta (Kim, et al., 2006). Seven candidate genes for AI were studied: amelogenin (AMELX), enamelin (ENAM), ameloblastin (AMBN), tuftelin (TUFT1), distal-less homeobox 3 (DLX3), enamelysin (MMP20), and kallikrein 4 (KLK4). The causative mutation was identified in 6 of the 24 families: two in the amelogenin, three in the enamelin and one in the enamelysin gene. We have now found non-identical FAM83H mutations in the affected members of four of these families, so the genetic etiologies of about half of the families are now known. These findings suggest that FAM83H is a major contributor to the etiology of AI, but other causative genes remain to be discovered. FAM83H is unique among the candidate genes for AI because it does not encode an enamel matrix protein. FAM83H maps to chromosome 8q24.3, comprises 5 exons and encodes a protein having 1179 amino acids, most of which (933 aa) are encoded by the last exon. It is particularly intriguing that the 6 FAM83H mutations are all premature stop codons in the last exon, which allows the mutated transcripts to avoid nonsense-mediated mrna decay. This means that FAM83H translation products lacking between 503 and 883 amino acids are synthesized along with an equal number of molecules expressed from the normal FAM83H allele. If the amino-terminal half of the FAM83H protein normally associates with another protein (as in homo- or heteromeric interactions) then the mutant and full-length proteins might be equally capable of forming these associations, but only complexes containing the full-length FAM83H protein could carry out their combined function. If so, expressing the truncated protein would be worse than expressing the normal protein in diminished amounts. Another possibility is that protein(s) functionally interacting with FAM83H might play a role in the pathogenesis of AI. Currently it is not known if FAM83H interacts with other proteins or if FAM83H haploinsufficiency results in an enamel phenotype.
5 Mutational spectrum of FAM83H E99 However it seems evident that the large C-terminal part of the protein (after 676 amino acids) is essential for proper enamel calcification, based on mutational spectrum of the FAM83H in the ADHCAI families. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS We thank the participants in this study for their cooperation. This work was supported in part by a grant from the Korea Health 21 R&D Project, Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (A060010), the Korea Science and Engineering Foundation (KOSEF) through the Biotechnology R&D program (# ), and NIDCR/NIH Grants DE and DE REFERENCES Hu JC, Chun YH, Al Hazzazzi T, Simmer JP Enamel formation and amelogenesis imperfecta. Cells Tissues Organs 186: Kim JW, Lee SK, Lee ZH, Park JC, Lee KE, Lee MH, Park JT, Seo BM, Hu JC, Simmer JP FAM83H Mutations in Families with Autosomal-Dominant Hypocalcified Amelogenesis Imperfecta. Am J Hum Genet 82: Kim JW, Simmer JP, Lin BP, Seymen F, Bartlett JD, Hu JC Mutational analysis of candidate genes in 24 amelogenesis imperfecta families. Eur J Oral Sci 114: Suppl. (1):3-12. Mendoza G, Pemberton TJ, Lee K, Scarel-Caminaga R, Mehrian-Shai R, Gonzalez-Quevedo C, Ninis V, Hartiala J, Allayee H, Snead ML, Leal SM, Line SR, Patel PI A new locus for autosomal dominant amelogenesis imperfecta on chromosome 8q24.3. Hum Genet 120: Nanci A, editor Ten Cate's Oral Histology Development, Structure, and Function. 7th ed. St. Louis, MO, USA: Mosby. p 411. Simmer JP, Fincham AG Molecular mechanisms of dental enamel formation. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med 6: Witkop CJ, Jr Amelogenesis imperfecta, dentinogenesis imperfecta and dentin dysplasia revisited: problems in classification. J Oral Pathol 17: Wright JT The molecular etiologies and associated phenotypes of amelogenesis imperfecta. Am J Med Genet A 140:
Fibers and extracellular matrix of hard tissues - Collagen and non-collagen proteins in hard tissues
 Fibers and extracellular matrix of hard tissues - Collagen and non-collagen proteins in hard tissues Dr. Gábor Varga Department of Oral Biology February, 2016 Radiograph of teeth remarkable harmony of
Fibers and extracellular matrix of hard tissues - Collagen and non-collagen proteins in hard tissues Dr. Gábor Varga Department of Oral Biology February, 2016 Radiograph of teeth remarkable harmony of
Amelogenesis Imperfecta: A Series of
 Case Report Amelogenesis Imperfecta: A Series of Case Report Nuzula Begum 1, Gowri P Bhandarkar 2, Raghavendra Kini 3, Vathsala Naik 4, K Rashmi 1, Lizzy Carol D Souza 1 1 Post Graduate Student, Department
Case Report Amelogenesis Imperfecta: A Series of Case Report Nuzula Begum 1, Gowri P Bhandarkar 2, Raghavendra Kini 3, Vathsala Naik 4, K Rashmi 1, Lizzy Carol D Souza 1 1 Post Graduate Student, Department
Evidence for a genetic disorder affecting tooth
 Studies on the Early Paleolithic site of Melka Kunture, Ethiopia - 2004: 703-713. Paleoanthropology Evidence for a genetic disorder affecting tooth formation in the Garba IV child Uri Zilberman 1,Patricia
Studies on the Early Paleolithic site of Melka Kunture, Ethiopia - 2004: 703-713. Paleoanthropology Evidence for a genetic disorder affecting tooth formation in the Garba IV child Uri Zilberman 1,Patricia
Amelogenesis Imperfecta type IV: A Challenge to Esthetics & Function
 aaaasasasss Shanila MA et al.: Amelogenesis Imperfecta type IV Amelogenesis Imperfecta type IV: A Challenge to Esthetics & Function Shanila A Majid 1, Manasa A Meundi 2, Namitha Jayapal 3, Chaya M David
aaaasasasss Shanila MA et al.: Amelogenesis Imperfecta type IV Amelogenesis Imperfecta type IV: A Challenge to Esthetics & Function Shanila A Majid 1, Manasa A Meundi 2, Namitha Jayapal 3, Chaya M David
Dr Milen Mariam Rajeev et al, SPJPBS.2015.,3(1), ISSN PROSTHETIC REHABILITATION OF AMELOGENESIS IMPERFECTA A CASE REPORT
 PROSTHETIC REHABILITATION OF AMELOGENESIS IMPERFECTA A CASE REPORT 1. Dr Milen Mariam Rajeev*, III year post graduate,department of Prosthodontics, 2. Dr Alex Mathews Muruppel, MDS, Head of the Department,
PROSTHETIC REHABILITATION OF AMELOGENESIS IMPERFECTA A CASE REPORT 1. Dr Milen Mariam Rajeev*, III year post graduate,department of Prosthodontics, 2. Dr Alex Mathews Muruppel, MDS, Head of the Department,
Amelogenesis Imperfecta- A Review. Pankhuri Nigam, Vijay Pal Singh, Krishnadeo Prasad, Jalaj Tak, Anju Sinha, Parveen Grewal
 Review Article Amelogenesis Imperfecta- A Review Pankhuri Nigam, Vijay Pal Singh, Krishnadeo Prasad, Jalaj Tak, Anju Sinha, Parveen Grewal Department of Oral Pathology, S.B.B.D.C, Ghaizabad, U.P, India
Review Article Amelogenesis Imperfecta- A Review Pankhuri Nigam, Vijay Pal Singh, Krishnadeo Prasad, Jalaj Tak, Anju Sinha, Parveen Grewal Department of Oral Pathology, S.B.B.D.C, Ghaizabad, U.P, India
S erine protease functionality is based on nucleophilic
 545 LETTER TO JMG Mutation in kallikrein 4 causes autosomal recessive hypomaturation amelogenesis imperfecta P S Hart, T C Hart, M D Michalec, O H Ryu, D Simmons, S Hong, J T Wright... S erine protease
545 LETTER TO JMG Mutation in kallikrein 4 causes autosomal recessive hypomaturation amelogenesis imperfecta P S Hart, T C Hart, M D Michalec, O H Ryu, D Simmons, S Hong, J T Wright... S erine protease
MODULE NO.14: Y-Chromosome Testing
 SUBJECT Paper No. and Title Module No. and Title Module Tag FORENSIC SIENCE PAPER No.13: DNA Forensics MODULE No.21: Y-Chromosome Testing FSC_P13_M21 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning Outcome 2. Introduction:
SUBJECT Paper No. and Title Module No. and Title Module Tag FORENSIC SIENCE PAPER No.13: DNA Forensics MODULE No.21: Y-Chromosome Testing FSC_P13_M21 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning Outcome 2. Introduction:
Molecular Basis of Human Enamel Defects
 BALKAN JOURNAL OF DENTAL MEDICINE ISSN 2335-0245 STOMATOLOGICAL SOCIETY Molecular Basis of Human Enamel Defects SUMMARY During eruption of teeth in the oral cavity, the effect of gene variations and environmental
BALKAN JOURNAL OF DENTAL MEDICINE ISSN 2335-0245 STOMATOLOGICAL SOCIETY Molecular Basis of Human Enamel Defects SUMMARY During eruption of teeth in the oral cavity, the effect of gene variations and environmental
Endocrine Surgery. Characteristics of the Germline MEN1 Mutations in Korea: A Literature Review ORIGINAL ARTICLE. The Korean Journal of INTRODUCTION
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE ISSN 1598-1703 (Print) ISSN 2287-6782 (Online) Korean J Endocrine Surg 2014;14:7-11 The Korean Journal of Endocrine Surgery Characteristics of the Germline MEN1 Mutations in Korea: A Literature
ORIGINAL ARTICLE ISSN 1598-1703 (Print) ISSN 2287-6782 (Online) Korean J Endocrine Surg 2014;14:7-11 The Korean Journal of Endocrine Surgery Characteristics of the Germline MEN1 Mutations in Korea: A Literature
ANAR PATEL*, A.R. CHAUDHARY**, BHAVIN DUDHIA***, NARESH SONI****, ABHISHEK BAROT***** ABSTRACT
 AMELOGENESIS IMPERFECTA Clinical Report ANAR PATEL*, A.R. CHAUDHARY**, BHAVIN DUDHIA***, NARESH SONI****, ABHISHEK BAROT***** ABSTRACT Amelogenesis Imperfecta (AI) is a diverse collection of inherited
AMELOGENESIS IMPERFECTA Clinical Report ANAR PATEL*, A.R. CHAUDHARY**, BHAVIN DUDHIA***, NARESH SONI****, ABHISHEK BAROT***** ABSTRACT Amelogenesis Imperfecta (AI) is a diverse collection of inherited
Hereditary Opalescent Dentin: A Report of Two Cases
 Hereditary Opalescent Dentin: A Report of Two Cases Siddharth Gupta, BDS, MDS; Rahul R. Bhowate, BDS, MDS; Ashok Bhati, BDS, MDS Abstract Aim: The aim of this case report is to present the clinical and
Hereditary Opalescent Dentin: A Report of Two Cases Siddharth Gupta, BDS, MDS; Rahul R. Bhowate, BDS, MDS; Ashok Bhati, BDS, MDS Abstract Aim: The aim of this case report is to present the clinical and
Amelogenesis Imperfecta: Current Understanding of Genotype-Phenotype
 Amelogenesis Imperfecta: Current Understanding of Genotype-Phenotype 5 John Timothy Wright Abstract There are nearly 100 hereditary conditions that affect enamel formation. Hereditary enamel conditions
Amelogenesis Imperfecta: Current Understanding of Genotype-Phenotype 5 John Timothy Wright Abstract There are nearly 100 hereditary conditions that affect enamel formation. Hereditary enamel conditions
Clinical and molecular analysis of the enamelin gene ENAM in Colombian families with autosomal dominant amelogenesis imperfecta
 Research Article Genetics and Molecular Biology, 35, 3, 557-566 (2012) Copyright 2012, Sociedade Brasileira de Genética. Printed in Brazil www.sbg.org.br Clinical and molecular analysis of the enamelin
Research Article Genetics and Molecular Biology, 35, 3, 557-566 (2012) Copyright 2012, Sociedade Brasileira de Genética. Printed in Brazil www.sbg.org.br Clinical and molecular analysis of the enamelin
Amelogenesis Imperfecta: Review of Literature with a case report
 Case Report Journal of Applied Dental and Medical Sciences NLM ID: 101671413 ISSN:2454-2288 Volume 2 Issue 1 January - March 2016 Amelogenesis Imperfecta: Review of Literature with a case report Vijender
Case Report Journal of Applied Dental and Medical Sciences NLM ID: 101671413 ISSN:2454-2288 Volume 2 Issue 1 January - March 2016 Amelogenesis Imperfecta: Review of Literature with a case report Vijender
Genome - Wide Linkage Mapping
 Biological Sciences Initiative HHMI Genome - Wide Linkage Mapping Introduction This activity is based on the work of Dr. Christine Seidman et al that was published in Circulation, 1998, vol 97, pgs 2043-2048.
Biological Sciences Initiative HHMI Genome - Wide Linkage Mapping Introduction This activity is based on the work of Dr. Christine Seidman et al that was published in Circulation, 1998, vol 97, pgs 2043-2048.
D uring mammalian tooth formation, two proteinases are
 271 LEER O JM MMP-20 mutation in autosomal recessive pigmented hypomaturation amelogenesis imperfecta J-W Kim, J P Simmer, Hart, P S Hart, M D Ramaswami, J D Bartlett, J - Hu... D uring mammalian tooth
271 LEER O JM MMP-20 mutation in autosomal recessive pigmented hypomaturation amelogenesis imperfecta J-W Kim, J P Simmer, Hart, P S Hart, M D Ramaswami, J D Bartlett, J - Hu... D uring mammalian tooth
An Investigation of The Impact of Amelogenesis Imperfecta (AI) on Children and Adolescents.
 An Investigation of The Impact of Amelogenesis Imperfecta (AI) on Children and Adolescents. Mohammad Almehateb D.D.S (USA) In partial fulfilment of the degree of Clinical Doctorate in Paediatric Dentistry
An Investigation of The Impact of Amelogenesis Imperfecta (AI) on Children and Adolescents. Mohammad Almehateb D.D.S (USA) In partial fulfilment of the degree of Clinical Doctorate in Paediatric Dentistry
Statistical Evaluation of Sibling Relationship
 The Korean Communications in Statistics Vol. 14 No. 3, 2007, pp. 541 549 Statistical Evaluation of Sibling Relationship Jae Won Lee 1), Hye-Seung Lee 2), Hyo Jung Lee 3) and Juck-Joon Hwang 4) Abstract
The Korean Communications in Statistics Vol. 14 No. 3, 2007, pp. 541 549 Statistical Evaluation of Sibling Relationship Jae Won Lee 1), Hye-Seung Lee 2), Hyo Jung Lee 3) and Juck-Joon Hwang 4) Abstract
CANCER GENETICS PROVIDER SURVEY
 Dear Participant, Previously you agreed to participate in an evaluation of an education program we developed for primary care providers on the topic of cancer genetics. This is an IRB-approved, CDCfunded
Dear Participant, Previously you agreed to participate in an evaluation of an education program we developed for primary care providers on the topic of cancer genetics. This is an IRB-approved, CDCfunded
Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein
 Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein BEFORE CLASS: Reading: Read the introduction on p. 333, skip the beginning of Concept 17.1 from p. 334 to the bottom of the first column on p. 336, and
Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein BEFORE CLASS: Reading: Read the introduction on p. 333, skip the beginning of Concept 17.1 from p. 334 to the bottom of the first column on p. 336, and
Introduction to Genetics
 Introduction to Genetics Table of contents Chromosome DNA Protein synthesis Mutation Genetic disorder Relationship between genes and cancer Genetic testing Technical concern 2 All living organisms consist
Introduction to Genetics Table of contents Chromosome DNA Protein synthesis Mutation Genetic disorder Relationship between genes and cancer Genetic testing Technical concern 2 All living organisms consist
Dentin Formation(Dentinogenesis)
 Lecture four Dr. Wajnaa Oral Histology Dentin Formation(Dentinogenesis) Dentinogenesis begins at the cusp tips after the odontoblasts have differentiated and begin collagen production. Dentinogenesis growth
Lecture four Dr. Wajnaa Oral Histology Dentin Formation(Dentinogenesis) Dentinogenesis begins at the cusp tips after the odontoblasts have differentiated and begin collagen production. Dentinogenesis growth
Beta Thalassemia Case Study Introduction to Bioinformatics
 Beta Thalassemia Case Study Sami Khuri Department of Computer Science San José State University San José, California, USA sami.khuri@sjsu.edu www.cs.sjsu.edu/faculty/khuri Outline v Hemoglobin v Alpha
Beta Thalassemia Case Study Sami Khuri Department of Computer Science San José State University San José, California, USA sami.khuri@sjsu.edu www.cs.sjsu.edu/faculty/khuri Outline v Hemoglobin v Alpha
Oral Rehabilitation of a Young Adult with Amelogenesis Imperfecta: A Clinical Report
 J Indian Prosthodont Soc (Oct-Dec 2010) 10(4):240 245 DOI 10.1007/s13191-010-0037-6 CLINICAL REPORT Oral Rehabilitation of a Young Adult with Amelogenesis Imperfecta: A Clinical Report Y. Bharath Shetty
J Indian Prosthodont Soc (Oct-Dec 2010) 10(4):240 245 DOI 10.1007/s13191-010-0037-6 CLINICAL REPORT Oral Rehabilitation of a Young Adult with Amelogenesis Imperfecta: A Clinical Report Y. Bharath Shetty
Case Report Typical Radiographic Findings of Dentin Dysplasia Type 1b with Dental Fluorosis
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 902861, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/902861 Case Report Typical Radiographic Findings of Dentin Dysplasia Type 1b with Dental Fluorosis S. Venkata
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 902861, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/902861 Case Report Typical Radiographic Findings of Dentin Dysplasia Type 1b with Dental Fluorosis S. Venkata
Identification of a novel duplication mutation in the VHL gene in a large Chinese family with Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) syndrome
 Identification of a novel duplication mutation in the VHL gene in a large Chinese family with Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) syndrome L.H. Cao 1, B.H. Kuang 2, C. Chen 1, C. Hu 2, Z. Sun 1, H. Chen 2, S.S. Wang
Identification of a novel duplication mutation in the VHL gene in a large Chinese family with Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) syndrome L.H. Cao 1, B.H. Kuang 2, C. Chen 1, C. Hu 2, Z. Sun 1, H. Chen 2, S.S. Wang
Shell teeth m management from the mixed to the permanent dentition: case report Rosamund Harrison, DMD, MS, MRCD(C) CASE REPORTS.
 Shell teeth m management from the mixed to the permanent dentition: case report Rosamund Harrison, DMD, MS, MRCD(C) David Kennedy, BDS, MSD, FRCD(C) CASE REPORTS Introduction Relatively few cases of shell
Shell teeth m management from the mixed to the permanent dentition: case report Rosamund Harrison, DMD, MS, MRCD(C) David Kennedy, BDS, MSD, FRCD(C) CASE REPORTS Introduction Relatively few cases of shell
Disturbances in tooth development lead to various dental anomalies,
 RESEARCH REPORTS Clinical S.A. Frazier-Bowers 1, D.C. Guo 2, A. Cavender 1, L. Xue 2, B. Evans 3, T. King 2, D. Milewicz 2, and R.N. D'Souza 1* 1 Department of Orthodontics, Dental Branch, Suite 371, and
RESEARCH REPORTS Clinical S.A. Frazier-Bowers 1, D.C. Guo 2, A. Cavender 1, L. Xue 2, B. Evans 3, T. King 2, D. Milewicz 2, and R.N. D'Souza 1* 1 Department of Orthodontics, Dental Branch, Suite 371, and
MUTATIONS, MUTAGENESIS, AND CARCINOGENESIS. (Start your clickers)
 MUTATIONS, MUTAGENESIS, AND CARCINOGENESIS (Start your clickers) How do mutations arise? And how do they affect a cell and its organism? Mutations: heritable changes in genes Mutations occur in DNA But
MUTATIONS, MUTAGENESIS, AND CARCINOGENESIS (Start your clickers) How do mutations arise? And how do they affect a cell and its organism? Mutations: heritable changes in genes Mutations occur in DNA But
Role of Paired Box9 (PAX9) (rs ) and Muscle Segment Homeobox1 (MSX1) (581C>T) Gene Polymorphisms in Tooth Agenesis
 EC Dental Science Special Issue - 2017 Role of Paired Box9 (PAX9) (rs2073245) and Muscle Segment Homeobox1 (MSX1) (581C>T) Gene Polymorphisms in Tooth Agenesis Research Article Dr. Sonam Sethi 1, Dr. Anmol
EC Dental Science Special Issue - 2017 Role of Paired Box9 (PAX9) (rs2073245) and Muscle Segment Homeobox1 (MSX1) (581C>T) Gene Polymorphisms in Tooth Agenesis Research Article Dr. Sonam Sethi 1, Dr. Anmol
PREVALENCE AND FACTORS ASSOCIATED WITH TOOTH DISCOLORATION AMONG UAE UNIVERSITY STUDENTS
 GMJ GULF MEDICAL JOURNAL ORAL PROCEEDINGS PREVALENCE AND FACTORS ASSOCIATED WITH TOOTH Omar Barakat 1 *, Ardeshir Amirhosseini 1, Mohammad Ahmad 1, Sara Al-Fallahi 1, Talal Atassi 1, Walid El-Sayed 2 1Final
GMJ GULF MEDICAL JOURNAL ORAL PROCEEDINGS PREVALENCE AND FACTORS ASSOCIATED WITH TOOTH Omar Barakat 1 *, Ardeshir Amirhosseini 1, Mohammad Ahmad 1, Sara Al-Fallahi 1, Talal Atassi 1, Walid El-Sayed 2 1Final
JULY 21, Genetics 101: SCN1A. Katie Angione, MS CGC Certified Genetic Counselor CHCO Neurology
 JULY 21, 2018 Genetics 101: SCN1A Katie Angione, MS CGC Certified Genetic Counselor CHCO Neurology Disclosures: I have no financial interests or relationships to disclose. Objectives 1. Review genetic
JULY 21, 2018 Genetics 101: SCN1A Katie Angione, MS CGC Certified Genetic Counselor CHCO Neurology Disclosures: I have no financial interests or relationships to disclose. Objectives 1. Review genetic
The Histology of Dentin
 The Histology of Dentin Pauline Hayes Garrett, D.D.S. Department of Endodontics, Prosthodontics, and Operative Dentistry University of Maryland, Baltimore This material was taken from: Essentials of Oral
The Histology of Dentin Pauline Hayes Garrett, D.D.S. Department of Endodontics, Prosthodontics, and Operative Dentistry University of Maryland, Baltimore This material was taken from: Essentials of Oral
Amelogenesis Imperfecta with Taurodontism, Microdontia and Minor Thalassemia: A Case Report
 Case Report Amelogenesis Imperfecta with Taurodontism, Microdontia and Minor Thalassemia: A Case Report Fatemeh Mazhari 1, Negar Mokhtari Amirmajdi 2 1 Dental Material Research Center, Faculty of Dentistry,
Case Report Amelogenesis Imperfecta with Taurodontism, Microdontia and Minor Thalassemia: A Case Report Fatemeh Mazhari 1, Negar Mokhtari Amirmajdi 2 1 Dental Material Research Center, Faculty of Dentistry,
IVF Michigan, Rochester Hills, Michigan, and Reproductive Genetics Institute, Chicago, Illinois
 FERTILITY AND STERILITY VOL. 80, NO. 4, OCTOBER 2003 Copyright 2003 American Society for Reproductive Medicine Published by Elsevier Inc. Printed on acid-free paper in U.S.A. CASE REPORTS Preimplantation
FERTILITY AND STERILITY VOL. 80, NO. 4, OCTOBER 2003 Copyright 2003 American Society for Reproductive Medicine Published by Elsevier Inc. Printed on acid-free paper in U.S.A. CASE REPORTS Preimplantation
Enamel protein in smooth hypoplastic amelogenesis imperfecta
 Enamel protein in smooth hypoplastic amelogenesis imperfecta John Timothy Wright,DDS, MS Colin Robinson, PhD Jennifer Kirkham, PhD Abstract Amelogenesis imperfecta (AI) remains a poorly understood group
Enamel protein in smooth hypoplastic amelogenesis imperfecta John Timothy Wright,DDS, MS Colin Robinson, PhD Jennifer Kirkham, PhD Abstract Amelogenesis imperfecta (AI) remains a poorly understood group
Amelogenesis imperfecta caused by N-terminal enamelin point mutations in mice and men is driven by endoplasmic reticulum stress
 Human Molecular Genetics, 2017, Vol. 26, No. 10 1863 1876 doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddx090 Advance Access Publication Date: 11 March 2017 Original Article ORIGINAL ARTICLE Amelogenesis imperfecta caused by N-terminal
Human Molecular Genetics, 2017, Vol. 26, No. 10 1863 1876 doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddx090 Advance Access Publication Date: 11 March 2017 Original Article ORIGINAL ARTICLE Amelogenesis imperfecta caused by N-terminal
AMELOGENESIS. Prof. Shaleen Chandra
 AMELOGENESIS Epithelial Enamel Organ Outer Enamel Epithelium Stellate Reticulum Stratum Intermedium Inner Enamel Epithelium Cervical Loop Life Cycle of Ameloblasts Morphogenic stage Organizing Stage Formative
AMELOGENESIS Epithelial Enamel Organ Outer Enamel Epithelium Stellate Reticulum Stratum Intermedium Inner Enamel Epithelium Cervical Loop Life Cycle of Ameloblasts Morphogenic stage Organizing Stage Formative
The coiled-coil domain containing protein CCDC40 is essential for motile cilia function and left-right axis formation
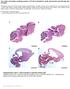 The coiled-coil domain containing protein CCDC40 is essential for motile cilia function and left-right axis formation Anita Becker-Heck#, Irene Zohn#, Noriko Okabe#, Andrew Pollock#, Kari Baker Lenhart,
The coiled-coil domain containing protein CCDC40 is essential for motile cilia function and left-right axis formation Anita Becker-Heck#, Irene Zohn#, Noriko Okabe#, Andrew Pollock#, Kari Baker Lenhart,
Dentinogenesis imperfecta type II: A case report with 17 years of follow-up
 Imaging Science in Dentistry 2017; 47: 129-33 https://doi.org/10.5624/isd.2017.47.2.129 Dentinogenesis imperfecta type II: A case report with 17 years of follow-up Francisco José Reis Gama 1, Isabella
Imaging Science in Dentistry 2017; 47: 129-33 https://doi.org/10.5624/isd.2017.47.2.129 Dentinogenesis imperfecta type II: A case report with 17 years of follow-up Francisco José Reis Gama 1, Isabella
Tumor suppressor genes D R. S H O S S E I N I - A S L
 Tumor suppressor genes 1 D R. S H O S S E I N I - A S L What is a Tumor Suppressor Gene? 2 A tumor suppressor gene is a type of cancer gene that is created by loss-of function mutations. In contrast to
Tumor suppressor genes 1 D R. S H O S S E I N I - A S L What is a Tumor Suppressor Gene? 2 A tumor suppressor gene is a type of cancer gene that is created by loss-of function mutations. In contrast to
Bioinformatics Laboratory Exercise
 Bioinformatics Laboratory Exercise Biology is in the midst of the genomics revolution, the application of robotic technology to generate huge amounts of molecular biology data. Genomics has led to an explosion
Bioinformatics Laboratory Exercise Biology is in the midst of the genomics revolution, the application of robotic technology to generate huge amounts of molecular biology data. Genomics has led to an explosion
Ghost Teeth: A Rare Developmental Anomaly of the Dental Tissues
 Science Journal of Medicine and Clinical Trials ISSN: 2276-7487 http://www.sjpub.org Author(s) 2014. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Published By Science Journal Publication International Open Access Publisher
Science Journal of Medicine and Clinical Trials ISSN: 2276-7487 http://www.sjpub.org Author(s) 2014. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Published By Science Journal Publication International Open Access Publisher
Molecular Characterization of the NF2 Gene in Korean Patients with Neurofibromatosis Type 2: A Report of Four Novel Mutations
 Korean J Lab Med 2010;30:190-4 DOI 10.3343/kjlm.2010.30.2.190 Original Article Diagnostic Genetics Molecular Characterization of the NF2 Gene in Korean Patients with Neurofibromatosis Type 2: A Report
Korean J Lab Med 2010;30:190-4 DOI 10.3343/kjlm.2010.30.2.190 Original Article Diagnostic Genetics Molecular Characterization of the NF2 Gene in Korean Patients with Neurofibromatosis Type 2: A Report
DENTIN It a hard vital tissue, surrounds the pulp & underlies the enamel on the crown & the cementum on the roots of the teeth.
 Lec. 7 Dr. Ali H.Murad DENTIN It a hard vital tissue, surrounds the pulp & underlies the enamel on the crown & the cementum on the roots of the teeth. Physical properties: 1-Dentin is pale yellow in color,
Lec. 7 Dr. Ali H.Murad DENTIN It a hard vital tissue, surrounds the pulp & underlies the enamel on the crown & the cementum on the roots of the teeth. Physical properties: 1-Dentin is pale yellow in color,
The effects of acid-etching on enamel from different clinical variants of amelogenesis imperfecta: an SEM study
 The effects of acid-etching on enamel from different clinical variants of amelogenesis imperfecta: an SEM study W. Kim Seow MDSc, DDSc, PhD, FRACDS A. Amaratunge RDS, PhD Abstract fissure sealants, and
The effects of acid-etching on enamel from different clinical variants of amelogenesis imperfecta: an SEM study W. Kim Seow MDSc, DDSc, PhD, FRACDS A. Amaratunge RDS, PhD Abstract fissure sealants, and
Enamel: Composition, Formation & Structure PROF. DR. KARTHIKEYAN RAMALINGAM
 Enamel: Composition, Formation & Structure PROF. DR. KARTHIKEYAN RAMALINGAM ENAMEL It is the hardest calcified matrix in the body. Ameloblasts are the cells responsible for enamel formation. These cells
Enamel: Composition, Formation & Structure PROF. DR. KARTHIKEYAN RAMALINGAM ENAMEL It is the hardest calcified matrix in the body. Ameloblasts are the cells responsible for enamel formation. These cells
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier
 Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name and description (please provide any alternative names Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name and description (please provide any alternative names Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Muscular Dystrophy. Biol 405 Molecular Medicine
 Muscular Dystrophy Biol 405 Molecular Medicine Duchenne muscular dystrophy Duchenne muscular dystrophy is a neuromuscular disease that occurs in ~ 1/3,500 male births. The disease causes developmental
Muscular Dystrophy Biol 405 Molecular Medicine Duchenne muscular dystrophy Duchenne muscular dystrophy is a neuromuscular disease that occurs in ~ 1/3,500 male births. The disease causes developmental
Genome 371, Autumn 2018 Quiz Section 9: Genetics of Cancer Worksheet
 Genome 371, Autumn 2018 Quiz Section 9: Genetics of Cancer Worksheet All cancer is due to genetic mutations. However, in cancer that clusters in families (familial cancer) at least one of these mutations
Genome 371, Autumn 2018 Quiz Section 9: Genetics of Cancer Worksheet All cancer is due to genetic mutations. However, in cancer that clusters in families (familial cancer) at least one of these mutations
Restoration of teeth using lithium disilicate glass-ceramics in a patient with Dentinogenesis Imperfecta
 Clinical Restoration of teeth using lithium disilicate glass-ceramics in a patient with Dentinogenesis Imperfecta Daniel Edelhoff 1, Oliver Brix 2 and Josef Schweiger 1 Introduction The availability of
Clinical Restoration of teeth using lithium disilicate glass-ceramics in a patient with Dentinogenesis Imperfecta Daniel Edelhoff 1, Oliver Brix 2 and Josef Schweiger 1 Introduction The availability of
Benefits of conducting research while completing the DDS program Critical thinking skills and opportunity to publish scientific papers NIH/NIDCR
 Benefits of conducting research while completing the DDS program Critical thinking skills and opportunity to publish scientific papers NIH/NIDCR training opportunities (basic and clinical research) Presentation
Benefits of conducting research while completing the DDS program Critical thinking skills and opportunity to publish scientific papers NIH/NIDCR training opportunities (basic and clinical research) Presentation
What is the inheritance pattern (e.g., autosomal, sex-linked, dominant, recessive, etc.)?
 Module I: Introduction to the disease Give a brief introduction to the disease, considering the following: the symptoms that define the syndrome, the range of phenotypes exhibited by individuals with the
Module I: Introduction to the disease Give a brief introduction to the disease, considering the following: the symptoms that define the syndrome, the range of phenotypes exhibited by individuals with the
Medical NBDE-II. Dental Board Exams Part I.
 Medical NBDE-II Dental Board Exams Part I http://killexams.com/exam-detail/nbde-ii Question: 149 Anatomically, the term "clinical root" can be defined as which of the following: A. The space in the tooth
Medical NBDE-II Dental Board Exams Part I http://killexams.com/exam-detail/nbde-ii Question: 149 Anatomically, the term "clinical root" can be defined as which of the following: A. The space in the tooth
Chapter 11 Gene Expression
 Chapter 11 Gene Expression 11-1 Control of Gene Expression Gene Expression- the activation of a gene to form a protein -a gene is on or expressed when it is transcribed. -cells do not always need to produce
Chapter 11 Gene Expression 11-1 Control of Gene Expression Gene Expression- the activation of a gene to form a protein -a gene is on or expressed when it is transcribed. -cells do not always need to produce
SPACE MAINTAINER. Multimedia Health Education. Disclaimer
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage your health. All decisions about the management of premature loss of primary teeth and use of space maintainers must
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage your health. All decisions about the management of premature loss of primary teeth and use of space maintainers must
22q11.2 DELETION SYNDROME. Anna Mª Cueto González Clinical Geneticist Programa de Medicina Molecular y Genética Hospital Vall d Hebrón (Barcelona)
 22q11.2 DELETION SYNDROME Anna Mª Cueto González Clinical Geneticist Programa de Medicina Molecular y Genética Hospital Vall d Hebrón (Barcelona) Genomic disorders GENOMICS DISORDERS refers to those diseases
22q11.2 DELETION SYNDROME Anna Mª Cueto González Clinical Geneticist Programa de Medicina Molecular y Genética Hospital Vall d Hebrón (Barcelona) Genomic disorders GENOMICS DISORDERS refers to those diseases
Double Teeth: A challenge for dentists
 Double Teeth: A challenge for dentists Neeraja.R 1, Umapathy 2 Corresponding Author Dr.Neeraja.R No 73, 7 th cross Cambridge layout Bangalore-8 Karnataka ph no- 8197919680 Email id: neeraja_pedo@yahoo.com
Double Teeth: A challenge for dentists Neeraja.R 1, Umapathy 2 Corresponding Author Dr.Neeraja.R No 73, 7 th cross Cambridge layout Bangalore-8 Karnataka ph no- 8197919680 Email id: neeraja_pedo@yahoo.com
MUTATIONS, MUTAGENESIS, AND CARCINOGENESIS
 MUTATIONS, MUTAGENESIS, AND CARCINOGENESIS How do different alleles arise? ( allele : form of a gene; specific base sequence at a site on DNA) Mutations: heritable changes in genes Mutations occur in DNA
MUTATIONS, MUTAGENESIS, AND CARCINOGENESIS How do different alleles arise? ( allele : form of a gene; specific base sequence at a site on DNA) Mutations: heritable changes in genes Mutations occur in DNA
Index. osteonecrosis, 104 prophylactic antibiotics, 105
 A Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans, 34 AI. See Amelogenesis imperfecta (AI) Alloplastic tooth replacement, 59 Alveolar bone mass dental radiographs, 30 eruption pathway, 12 exfoliation, 33 periodontitis,
A Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans, 34 AI. See Amelogenesis imperfecta (AI) Alloplastic tooth replacement, 59 Alveolar bone mass dental radiographs, 30 eruption pathway, 12 exfoliation, 33 periodontitis,
Immunolocalization of gene products responsible for Amelogenesis Imperfecta and Dentinogenesis Imperfecta in mice
 Boston University OpenBU Theses & Dissertations http://open.bu.edu Boston University Theses & Dissertations 2016 Immunolocalization of gene products responsible for Amelogenesis Imperfecta and Dentinogenesis
Boston University OpenBU Theses & Dissertations http://open.bu.edu Boston University Theses & Dissertations 2016 Immunolocalization of gene products responsible for Amelogenesis Imperfecta and Dentinogenesis
Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development. Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L.
 Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L. Dennis Proximal contact areas Contact areas are on the mesial and
Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L. Dennis Proximal contact areas Contact areas are on the mesial and
DOES THE BRCAX GENE EXIST? FUTURE OUTLOOK
 CHAPTER 6 DOES THE BRCAX GENE EXIST? FUTURE OUTLOOK Genetic research aimed at the identification of new breast cancer susceptibility genes is at an interesting crossroad. On the one hand, the existence
CHAPTER 6 DOES THE BRCAX GENE EXIST? FUTURE OUTLOOK Genetic research aimed at the identification of new breast cancer susceptibility genes is at an interesting crossroad. On the one hand, the existence
5Recommended Shade-Matching Protocol
 5Recommended Shade-Matching Protocol In this chapter: Seven steps to a successful shade match 5 Recommended Shade-Matching Protocol Figs 5-1 and 5-2 Conventional methods of shade selection, when used alone,
5Recommended Shade-Matching Protocol In this chapter: Seven steps to a successful shade match 5 Recommended Shade-Matching Protocol Figs 5-1 and 5-2 Conventional methods of shade selection, when used alone,
The spectrum of dental manifestations in vitamin D-resistant rickets: implications for management
 PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY/Copyright 1986 by The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry Volume 8 Number 3 The spectrum of dental manifestations in vitamin D-resistant rickets: implications for management W.
PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY/Copyright 1986 by The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry Volume 8 Number 3 The spectrum of dental manifestations in vitamin D-resistant rickets: implications for management W.
Advances in genetic diagnosis of neurological disorders
 Acta Neurol Scand 2014: 129 (Suppl. 198): 20 25 DOI: 10.1111/ane.12232 2014 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd ACTA NEUROLOGICA SCANDINAVICA Review Article Advances in genetic diagnosis
Acta Neurol Scand 2014: 129 (Suppl. 198): 20 25 DOI: 10.1111/ane.12232 2014 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd ACTA NEUROLOGICA SCANDINAVICA Review Article Advances in genetic diagnosis
Biology 2C03: Genetics What is a Gene?
 Biology 2C03: Genetics What is a Gene? September 9 th, 2013 Model Organisms - E. coli - Yeast - Worms - Arabodopsis - Fruitflie - Mouse What is a Gene? - Define, recognize, describe and apply Mendel s
Biology 2C03: Genetics What is a Gene? September 9 th, 2013 Model Organisms - E. coli - Yeast - Worms - Arabodopsis - Fruitflie - Mouse What is a Gene? - Define, recognize, describe and apply Mendel s
CHAPTER IV RESULTS Microcephaly General description
 47 CHAPTER IV RESULTS 4.1. Microcephaly 4.1.1. General description This study found that from a previous study of 527 individuals with MR, 48 (23 female and 25 male) unrelated individuals were identified
47 CHAPTER IV RESULTS 4.1. Microcephaly 4.1.1. General description This study found that from a previous study of 527 individuals with MR, 48 (23 female and 25 male) unrelated individuals were identified
The Meaning of Genetic Variation
 Activity 2 The Meaning of Genetic Variation Focus: Students investigate variation in the beta globin gene by identifying base changes that do and do not alter function, and by using several CD-ROM-based
Activity 2 The Meaning of Genetic Variation Focus: Students investigate variation in the beta globin gene by identifying base changes that do and do not alter function, and by using several CD-ROM-based
Polycarbonate Crowns for Primary teeth Revisited. Restorative options, Technique & Case reports
 Polycarbonate Crowns for Primary teeth Revisited Restorative options, Technique & Case reports Karthik Venkataraghavan 1, John Chan 2 1 Pediatric Dentist, Vibha Dental Care Centre, Bangalore, India. 2
Polycarbonate Crowns for Primary teeth Revisited Restorative options, Technique & Case reports Karthik Venkataraghavan 1, John Chan 2 1 Pediatric Dentist, Vibha Dental Care Centre, Bangalore, India. 2
Biochemistry 2000 Sample Question Transcription, Translation and Lipids. (1) Give brief definitions or unique descriptions of the following terms:
 (1) Give brief definitions or unique descriptions of the following terms: (a) exon (b) holoenzyme (c) anticodon (d) trans fatty acid (e) poly A tail (f) open complex (g) Fluid Mosaic Model (h) embedded
(1) Give brief definitions or unique descriptions of the following terms: (a) exon (b) holoenzyme (c) anticodon (d) trans fatty acid (e) poly A tail (f) open complex (g) Fluid Mosaic Model (h) embedded
Insulin mrna to Protein Kit
 Insulin mrna to Protein Kit A 3DMD Paper BioInformatics and Mini-Toober Folding Activity Student Handout www.3dmoleculardesigns.com Insulin mrna to Protein Kit Contents Becoming Familiar with the Data...
Insulin mrna to Protein Kit A 3DMD Paper BioInformatics and Mini-Toober Folding Activity Student Handout www.3dmoleculardesigns.com Insulin mrna to Protein Kit Contents Becoming Familiar with the Data...
MEDICAL GENOMICS LABORATORY. Next-Gen Sequencing and Deletion/Duplication Analysis of NF1 Only (NF1-NG)
 Next-Gen Sequencing and Deletion/Duplication Analysis of NF1 Only (NF1-NG) Ordering Information Acceptable specimen types: Fresh blood sample (3-6 ml EDTA; no time limitations associated with receipt)
Next-Gen Sequencing and Deletion/Duplication Analysis of NF1 Only (NF1-NG) Ordering Information Acceptable specimen types: Fresh blood sample (3-6 ml EDTA; no time limitations associated with receipt)
PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES ISSN:
 PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN: 2072 1625 Pac. J. Med. Sci. (PJMS) www.pacjmedsci.com. Email: pacjmedsci@gmail.com. UNUSUAL OCCURRENCE OF EPIDERMOLYSIS BULLOSA
PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN: 2072 1625 Pac. J. Med. Sci. (PJMS) www.pacjmedsci.com. Email: pacjmedsci@gmail.com. UNUSUAL OCCURRENCE OF EPIDERMOLYSIS BULLOSA
Primary Teeth Chapter 18. Dental Anatomy 2016
 Primary Teeth Chapter 18 Dental Anatomy 2016 Primary Teeth - Introduction Synonyms deciduous teeth, baby teeth, temporary teeth, milk teeth. There are 20 primary teeth, designated as A thru T in the Universal
Primary Teeth Chapter 18 Dental Anatomy 2016 Primary Teeth - Introduction Synonyms deciduous teeth, baby teeth, temporary teeth, milk teeth. There are 20 primary teeth, designated as A thru T in the Universal
Dental Anatomy and Occlusion
 CHAPTER 53 Dental Anatomy and Occlusion Ma Lou C. Sabino DDS, and Emily G. Smythe, DDS What numerical system is used most commonly in the United States for designating the adult dentition? Pediatric dentition?
CHAPTER 53 Dental Anatomy and Occlusion Ma Lou C. Sabino DDS, and Emily G. Smythe, DDS What numerical system is used most commonly in the United States for designating the adult dentition? Pediatric dentition?
MRC-Holland MLPA. Description version 19;
 SALSA MLPA probemix P6-B2 SMA Lot B2-712, B2-312, B2-111, B2-511: As compared to the previous version B1 (lot B1-11), the 88 and 96 nt DNA Denaturation control fragments have been replaced (QDX2). SPINAL
SALSA MLPA probemix P6-B2 SMA Lot B2-712, B2-312, B2-111, B2-511: As compared to the previous version B1 (lot B1-11), the 88 and 96 nt DNA Denaturation control fragments have been replaced (QDX2). SPINAL
FAM20A Mutations Can Cause Enamel-Renal Syndrome (ERS)
 Can Cause Enamel-Renal Syndrome (ERS) Shih-Kai Wang 1,2, Parissa Aref 3, Yuanyuan Hu 1, Rachel N. Milkovich 1, James P. Simmer 1, Mohammad El- Khateeb 4, Hinda Daggag 4, Zaid H. Baqain 5, Jan C-C. Hu 1
Can Cause Enamel-Renal Syndrome (ERS) Shih-Kai Wang 1,2, Parissa Aref 3, Yuanyuan Hu 1, Rachel N. Milkovich 1, James P. Simmer 1, Mohammad El- Khateeb 4, Hinda Daggag 4, Zaid H. Baqain 5, Jan C-C. Hu 1
Therapy-related acute myeloid leukemia with germline TP53 mutation (Li-Fraumeni syndrome) SH Chelsey Deel MD Teresa Scordino MD
 Therapy-related acute myeloid leukemia with germline TP53 mutation (Li-Fraumeni syndrome) SH2017-167 Chelsey Deel MD Teresa Scordino MD Clinical History HPI: 44 year old Caucasian female referred for evaluation
Therapy-related acute myeloid leukemia with germline TP53 mutation (Li-Fraumeni syndrome) SH2017-167 Chelsey Deel MD Teresa Scordino MD Clinical History HPI: 44 year old Caucasian female referred for evaluation
Clinical and Molecular Genetic Spectrum of Slovenian Patients with CGD
 Clinical and Molecular Genetic Spectrum of Slovenian Patients with CGD Avčin T, Debeljak M, Markelj G, Anderluh G*, Glavnik V, Kuhar M University Children s Hospital Ljubljana and *Biotechnical Faculty,
Clinical and Molecular Genetic Spectrum of Slovenian Patients with CGD Avčin T, Debeljak M, Markelj G, Anderluh G*, Glavnik V, Kuhar M University Children s Hospital Ljubljana and *Biotechnical Faculty,
Human Genetic Diseases (Ch. 15)
 Human Genetic Diseases (Ch. 15) 1 2 2006-2007 3 4 5 6 Genetic counseling Pedigrees can help us understand the past & predict the future Thousands of genetic disorders are inherited as simple recessive
Human Genetic Diseases (Ch. 15) 1 2 2006-2007 3 4 5 6 Genetic counseling Pedigrees can help us understand the past & predict the future Thousands of genetic disorders are inherited as simple recessive
Section Chapter 14. Go to Section:
 Section 12-3 Chapter 14 Go to Section: Content Objectives Write these Down! I will be able to identify: The origin of genetic differences among organisms. The possible kinds of different mutations. The
Section 12-3 Chapter 14 Go to Section: Content Objectives Write these Down! I will be able to identify: The origin of genetic differences among organisms. The possible kinds of different mutations. The
Prosthetic and Surgical Approach for Oral Rehabilitation in a Patient with Amelogenesis Imperfecta: A Clinical Report
 Case Report Prosthetic and Surgical Approach for Oral Rehabilitation in a Patient with Amelogenesis Imperfecta: A Clinical Report H. Sazegara 1, K. Seyedan 2, H. Behnia 3, P. Ghaderi 2 1 Associate Professor,
Case Report Prosthetic and Surgical Approach for Oral Rehabilitation in a Patient with Amelogenesis Imperfecta: A Clinical Report H. Sazegara 1, K. Seyedan 2, H. Behnia 3, P. Ghaderi 2 1 Associate Professor,
SALSA MLPA KIT P060-B2 SMA
 SALSA MLPA KIT P6-B2 SMA Lot 111, 511: As compared to the previous version B1 (lot 11), the 88 and 96 nt DNA Denaturation control fragments have been replaced (QDX2). Please note that, in contrast to the
SALSA MLPA KIT P6-B2 SMA Lot 111, 511: As compared to the previous version B1 (lot 11), the 88 and 96 nt DNA Denaturation control fragments have been replaced (QDX2). Please note that, in contrast to the
Single Gene (Monogenic) Disorders. Mendelian Inheritance: Definitions. Mendelian Inheritance: Definitions
 Single Gene (Monogenic) Disorders Mendelian Inheritance: Definitions A genetic locus is a specific position or location on a chromosome. Frequently, locus is used to refer to a specific gene. Alleles are
Single Gene (Monogenic) Disorders Mendelian Inheritance: Definitions A genetic locus is a specific position or location on a chromosome. Frequently, locus is used to refer to a specific gene. Alleles are
TRANSLATION: 3 Stages to translation, can you guess what they are?
 TRANSLATION: Translation: is the process by which a ribosome interprets a genetic message on mrna to place amino acids in a specific sequence in order to synthesize polypeptide. 3 Stages to translation,
TRANSLATION: Translation: is the process by which a ribosome interprets a genetic message on mrna to place amino acids in a specific sequence in order to synthesize polypeptide. 3 Stages to translation,
Examples of independent inheritance
 GENETIC PROBLEMS Examples of independent inheritance The amelogenesis imperfecta is is a disorder of tooth development that causes development of abnormally small, discolored teeth. The disease is caused
GENETIC PROBLEMS Examples of independent inheritance The amelogenesis imperfecta is is a disorder of tooth development that causes development of abnormally small, discolored teeth. The disease is caused
Role of genes in oro-dental diseases
 REVIEW ARTICLE www.ijdr.in B Kavitha, Vijayashree Priyadharshini, B Sivapathasundharam, TR Saraswathi Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology, Meenakshi Ammal Dental College and Hospital, Chennai,
REVIEW ARTICLE www.ijdr.in B Kavitha, Vijayashree Priyadharshini, B Sivapathasundharam, TR Saraswathi Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology, Meenakshi Ammal Dental College and Hospital, Chennai,
Abstract. Introduction. RBMOnline - Vol 8. No Reproductive BioMedicine Online; on web 10 December 2003
 RBMOnline - Vol 8. No 2. 224-228 Reproductive BioMedicine Online; www.rbmonline.com/article/1133 on web 10 December 2003 Article Preimplantation genetic diagnosis for early-onset torsion dystonia Dr Svetlana
RBMOnline - Vol 8. No 2. 224-228 Reproductive BioMedicine Online; www.rbmonline.com/article/1133 on web 10 December 2003 Article Preimplantation genetic diagnosis for early-onset torsion dystonia Dr Svetlana
SSN SBPM Workshop Exam One. Short Answer Questions & Answers
 SSN SBPM Workshop Exam One Short Answer Questions & Answers 1. Describe the effects of DNA damage on the cell cycle. ANS : DNA damage causes cell cycle arrest at a G2 checkpoint. This arrest allows time
SSN SBPM Workshop Exam One Short Answer Questions & Answers 1. Describe the effects of DNA damage on the cell cycle. ANS : DNA damage causes cell cycle arrest at a G2 checkpoint. This arrest allows time
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier
 Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name Choroideremia OMIM number for disease 303100 Disease alternative names please
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name Choroideremia OMIM number for disease 303100 Disease alternative names please
Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 8 Questions
 Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 8 Questions Linkage Analysis Question Question 8.1 Affected members of the pedigree above have an autosomal dominant disorder, and cytogenetic analyses using conventional
Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 8 Questions Linkage Analysis Question Question 8.1 Affected members of the pedigree above have an autosomal dominant disorder, and cytogenetic analyses using conventional
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier
 Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name Genetic Causes of Hypothyroidism 1. Loss of function mutations in TSHR cause thyroid
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name Genetic Causes of Hypothyroidism 1. Loss of function mutations in TSHR cause thyroid
Human Genetic Disorders
 Human Genetic Disorders HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOMES Human somatic cells have 23 pairs of homologous chromosomes 23 are inherited from the mother and 23 from the father HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOMES Autosomes o Are
Human Genetic Disorders HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOMES Human somatic cells have 23 pairs of homologous chromosomes 23 are inherited from the mother and 23 from the father HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOMES Autosomes o Are
Supplementary Table 1. PIK3CA mutation in colorectal cancer
 Liao X et al. PIK3CA Mutation in Colorectal Cancer. Page 1 Supplementary Table 1. PIK3CA mutation in colorectal cancer Exon Domain Nucleotide change* Amino acid change* cases 9 Helical c.1621t>a p.e541t
Liao X et al. PIK3CA Mutation in Colorectal Cancer. Page 1 Supplementary Table 1. PIK3CA mutation in colorectal cancer Exon Domain Nucleotide change* Amino acid change* cases 9 Helical c.1621t>a p.e541t
Early Embryonic Development
 Early Embryonic Development Maternal effect gene products set the stage by controlling the expression of the first embryonic genes. 1. Transcription factors 2. Receptors 3. Regulatory proteins Maternal
Early Embryonic Development Maternal effect gene products set the stage by controlling the expression of the first embryonic genes. 1. Transcription factors 2. Receptors 3. Regulatory proteins Maternal
Chapter 1 : Genetics 101
 Chapter 1 : Genetics 101 Understanding the underlying concepts of human genetics and the role of genes, behavior, and the environment will be important to appropriately collecting and applying genetic
Chapter 1 : Genetics 101 Understanding the underlying concepts of human genetics and the role of genes, behavior, and the environment will be important to appropriately collecting and applying genetic
Hands-On Ten The BRCA1 Gene and Protein
 Hands-On Ten The BRCA1 Gene and Protein Objective: To review transcription, translation, reading frames, mutations, and reading files from GenBank, and to review some of the bioinformatics tools, such
Hands-On Ten The BRCA1 Gene and Protein Objective: To review transcription, translation, reading frames, mutations, and reading files from GenBank, and to review some of the bioinformatics tools, such
Multistep nature of cancer development. Cancer genes
 Multistep nature of cancer development Phenotypic progression loss of control over cell growth/death (neoplasm) invasiveness (carcinoma) distal spread (metastatic tumor) Genetic progression multiple genetic
Multistep nature of cancer development Phenotypic progression loss of control over cell growth/death (neoplasm) invasiveness (carcinoma) distal spread (metastatic tumor) Genetic progression multiple genetic
