Wenjian Zhang 1*, Adam Skrypczak 2 and Robin Weltman 3
|
|
|
- Brice Johns
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Zhang et al. BMC Oral Health (2015) 15:65 DOI /s RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Anterior maxilla alveolar ridge dimension and morphology measurement by cone beam computerized tomography (CBCT) for immediate implant treatment planning Wenjian Zhang 1*, Adam Skrypczak 2 and Robin Weltman 3 Abstract Background: Implants have been widely used to restore missing teeth. Limited information on applied anatomy at the anterior maxilla compromises the clinical outcome for implant placement in this region. In the current study, Cone Beam Computerized Tomography (CBCT) was used to measure alveolar ridge and buccal undercut dimension at the anterior maxilla to help develop treatment planning for immediate implant placement. Methods: CBCT scans were screened to include 51 subjects with full dentition at right maxilla. Measurements were taken at the cross sectional views in the middle of the maxillary right central incisor, lateral incisor, and canine regions. Alveolar height was measured from the alveolar crest to floor of nasal fossa. Alveolar width was measured from the buccal to palatal cortical plate at the coronal, middle, and apical third of the distance from the alveolar crest to floor of the nasal fossa. Buccal undercut location was measured from where the buccal cortical plate started dipping to a line extending at the alveolar crest that was perpendicular to the long axis of the alveolar ridge. The buccal undercut depth was measured from the deepest point of the undercut at the buccal plate to a line tangent to the buccal plate paralleling the long axis of ridge. Results: Alveolar width increased from coronal to apical direction for each tooth. Mean alveolar widths (mm) were: central incisor, 9.55; lateral incisor, 8.30; canine, The lateral incisor had a significantly smaller alveolar width than the other anterior teeth. No significant difference in ridge height was noted among the teeth. Undercut locations from the alveolar crest (mm) were: central incisor, 5.84; lateral incisor, 3.59; canine, Undercut depths (mm) were: central incisor, 0.76; lateral incisor, 0.87; canine, The percentages of teeth with buccal undercuts were: central incisor, 41 %, lateral incisor, 77 %, and canine 33 %. Male demonstrate significant larger ridge width compared with females for all three teeth. Conclusions: At anterior maxilla, the lateral incisor has the thinnest alveolar bone, and most frequently exhibits a buccal undercut which is the closest to alveolar ridge compared with other maxillary anterior teeth. Keywords: Anterior maxilla, CBCT, Alveolar ridge, Buccal undercut, Implant * Correspondence: Wenjian.Zhang@uth.tmc.edu 1 Department of Diagnostic and Biomedical Sciences, The University of Texas School of Dentistry at Houston, 7500 Cambridge Street, Houston, TX 77054, USA Full list of author information is available at the end of the article 2015 Zhang et al. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly credited. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
2 Zhang et al. BMC Oral Health (2015) 15:65 Page 2 of 8 Background Oral rehabilitation with implant-supported prostheses has been very successful in restoration of single or multiple missing teeth [1 5]. Successful implant treatment depends on precise planning. Information on the height, width, morphology, and density of alveolar bone surrounding the proposed implant site is very critical for determination of the size of the implant and angle of placement [6 8]. Conventional radiographic techniques such as intraoral, panoramic, and cephalometric images used to be the standard methods for implant treatment planning [9]. However, imaging distortion and superimposition compromise the accuracy of treatment planning with these techniques [10]. The improvement in sectional imaging techniques advocates the use of tomographic technique in the investigation of potential implant sites [10]. The recent introduction of cone beam computerized tomography (CBCT) in dentistry, opens up a new horizon in providing comprehensive preoperative implant site assessment and sophisticated surgical guide in dental implantology [11]. The American Academy of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology (AAOMR) recently recommendedcbctastheimagingmodalityofchoicefor implant treatment planning [12]. CBCT provides high-resolution and accurate multiple planar reformatted images at a relatively low radiation dosage and affordable price [13 16]. Dimensional measurement by CBCT can achieve sub-millimeter accuracy which is comparable to the level of multi-slice computerized tomography (MSCT) [17], and precision of the measurement will not be affected by variations in voxel settings in the imaging acquisition protocol [18]. Implant length in initial planning with panoramic radiographs tends to be overestimated, which could be attributed to the inherent magnification in panoramic imaging leading to an overestimation of the available bone for implant placement [19, 20]. This inaccuracy may result in a greater risk of injury to adjacent anatomic structures, such as floor of maxillary sinus or inferior alveolar nerve. Implant sizes estimated by CBCT images are narrower and shorter than those obtained from panoramic radiographs [21], suggesting that CBCT exams lead to a safer decision. Maxillary anterior region may be the implant site that requires the most rigorous pre-operative assessment, because alveolar dimension and morphology will have a direct influence on aesthetic outcome and stability of implant placement [22]. Previous experience has shown that adequate alveolar height is not the only prerequisite for a successful implant placement. Deficiency of transversal ridge width would lead to length reduction or even impossible implant insertion [23]. However, very few studies have evaluated bone parameters for implant treatment at this region. In the present study, CBCT images were used to evaluate alveolar ridge dimension and the presence and size of buccal undercut at the maxillary anterior region. The correlation of ridge height and width with the age and gender of the subjects was also analyzed. This study was aimed to provide more quantitative information to help immediate implant treatment at the maxillary anterior area. Methods Subjects The subjects who had CBCT scans performed at the University of Texas School of Dentistry at Houston Radiology Division since 2011 were screened according to the selection criteria. The exclusion criteria were: 1) systemic/endocrine diseases that influence bone metabolism, e.g., osteoporosis, hyperparathyroidism, Paget s disease, and renal osteodystrophy; 2) topical conditions that may affect bone quantity and quality at anterior maxilla, e.g., moderate to severe periodontal disease, cyst, neoplasm, prior trauma or surgery. A total of 51 subjects with full dentition at right maxilla were included in the study. There were 20 males and 31 females, with an age range of years old (45.25 ± 17.72, Table 1). Institutional Review Board (IRB) exemption was obtained for the study after internal review. CBCT imaging acquisition All included CBCT scans covered both maxillary and mandibular arches with a field of view (FOV) of 150 x 90 mm 2. The scans were acquired at 90 kv (kv), 10 ma (ma), 16 s, and a 0.2 mm 3 voxel size with a Kodak 9500 unit (Carestream Health, Inc, Rochester, NY). CBCT images were reconstructed with Anatomage Invivo 5.1 software at 1 mm thickness. All images were displayed on a 19-in. flat panel screen (HP Development Company, Palo Alto, CA) with a 1920 X 1080 pixel resolution and viewed in a dimly lit environment. Measurements To ensure consistent head placement, all CBCT scans were checked and re-orientated, if necessary, to position Table 1 Patient age and gender information Age Males Females Total 20 31
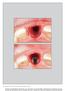
3 Zhang et al. BMC Oral Health (2015) 15:65 Page 3 of 8 the occlusal plane parallel to the floor (Fig. 1a). Cross sectional views perpendicular to alveolar ridge were taken in the middle of maxillary right central incisor, lateral incisor, and canine regions (Fig. 1b and c). The linear measurements were done as described below (also see Fig. 2). Absence or presence of buccal undercut was demonstrated in a right maxillary canine (Fig. 3a) and a right maxillary lateral incisor (Fig. 3b), respectively. All the measurements were taken by one examiner. 1. Alveolar height A line was drawn from alveolar crest paralleling with the long axis of alveolar ridge. The distance from alveolar crest to the floor of nasal fossa was defined as alveolar height. (Fig. 2a). 2. Alveolar width Alveolar height was divided into coronal, middle, and apical third. In the middle of each third, a line was drawn perpendicular to the long axis of alveolar ridge. The distance between buccal and palatal cortical plate was defined as alveolar width (Fig. 2a). The overall alveolar width for each tooth was the average of coronal, middle, and apical third of alveolar width measurements. 3. Buccal undercut location For a tooth identified to have buccal undercut, a line was extended from alveolar crest which was perpendicular to the long axis of the alveolar ridge. The distance from where the buccal cortical plate started dipping to the aforementioned line was defined as buccal undercut location (Fig. 2b). This value demonstrated how close the buccal undercut was to the alveolar crest. 4. Buccal undercut depth For a tooth identified to have buccal undercut, a line tangent to buccal cortical plate and parallel to the long axis of alveolar ridge was drawn. The distance from the deepest point of the buccal undercut to the aforementioned line was defined as the buccal undercut depth (Fig. 2b). 5. Percent of teeth with buccal undercut For maxillary right central incisors, lateral incisors, and canines, the formula to calculate the percent of teeth with buccal undercut was: (the number of teeth with buccal undercut)/(total number of teeth evaluated)x100. Statistical analysis Kolmogorov Smirnov test was used to determine the normality of the data. One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's honestly significant difference (HSD) test and Kruskal-Wallis test were used to detect statistical difference among the groups for normal and non-normal distributed data, respectively. The correlations between subjects age and gender with alveolar height and width measurements were evaluated by Spearman s correlation analysis. Data were reported as means ± standard deviation (SD). The statistical difference was set at a p value less than All of the statistical analysis was run with SAS 9.2 program (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC). Fig. 1 Reformatted CBCT views. a. Reformatted panoramic view demonstrates that the occlusal plane is parallel to the floor. b. Axial view at the maxillary arch level. The green lines are perpendicular to alveolar ridge. They indicate where the cross sectional views were taken. c. Series of cross sectional views. The view in the middle panel (corresponding to the middle green line in B) was used for alveolar volume and buccal undercut measurements
4 Zhang et al. BMC Oral Health (2015) 15:65 Page 4 of 8 Fig. 2 Diagrams for alveolar ridge and buccal undercut measurements. a. Alveolar height and width measurements. Line a represents the floor of nasal fossa. Green line represents the distance from alveolar crest to the floor of nasal fossa, and is designated as alveolar height. The alveolar height is divided into thirds (shown by the purple dots). In the middle of each third, a dotted purple line is drawn perpendicular to the long axis of the ridge and extends from buccal to palatal cortical plate. The distance between the two plates is designated as alveolar width at apical third, middle third, and coronal third, respectively. b. Buccal undercut location and depth measurements. Line b is the alveolar crest line perpendicular to the long axis of alveolar ridge. Blue dot is where buccal cortical plate starts dipping. The distance from the blue dot to line b is designated as buccal undercut location. Line c is tangent to buccal cortical plate and parallel to the long axis of alveolar ridge. The pink dot represents the deepest point on the buccal undercut. The green line representing the distance between the deepest point and tangent line is designated as the buccal undercut depth Results ThenormalityofthedatawastestedbyKolmogorov Smirnov test. It was found that the data for alveolar height and width had normal distribution, therefore, Fig. 3 Cross sectional views demonstrate absence or presence of buccal undercut. a. No buccal undercut for this maxillary right canine. b. Presence of buccal undercut for this maxillary right lateral incisor one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's honestly significant difference (HSD) test was used to detect statistical difference among the three maxillary anterior teeth. The data for buccal undercut location and depth had non-normal distribution, and Kruskal-Wallis test was
5 Zhang et al. BMC Oral Health (2015) 15:65 Page 5 of 8 used to detect the statistical difference among the teeth. Mean alveolar height for the maxillary right central incisor, lateral incisor, and canine was ± 3.23, ± 2.53, ± 2.81 mm, respectively. There was no significant difference in the ridge height among these teeth (Fig. 4). Coronal, middle, and apical third alveolar width for maxillary right central incisors was 8.07 ± 0.93, 8.67 ± 1.62,11.91 ± 2.38 mm, lateral incisors was 7.08 ± 0.80, 7.35 ± 1.39, ± 1.81 mm, and canines was 8.94 ± 1.08, 8.72 ± 1.35, ± 2.06 mm, respectively. The alveolar width increased from the coronal to apical direction for all three teeth. The mean alveolar width for maxillary central incisors, lateral incisors, and canines was 9.55 ± 1.45, 8.30 ± 1.10, 9.62 ± 1.30 mm, respectively. The lateral incisors demonstrated significantly thinner alveolar width than the other two anterior teeth (p = , Fig. 5). For the correlation between subjects age/gender and alveolar volume measurements, it was found that male demonstrated significantly larger alveolar width compared to female for all three maxillary anterior teeth (Fig. 6). Male and female alveolar width (mm) for maxillary right central incisor were ± 1.36 and 8.96 ± 1.14, (r =0.5, p = ), for maxillary right lateral incisor were 8.97 ± 0.87, 7.84 ± 0.94 (r = 0.52, p = ), for maxillary right canine were ± 1.20 and 9.13 ± 1.07 (r =0.44,p = ), respectively (Fig. 6). Among the maxillary right anterior teeth, 41 % of central incisors, 77 % of lateral incisors, and 33 % of canines had buccal undercut. The mean distance of buccal undercuts to the alveolar ridge (mm) for central incisors, lateral incisors, and canines was 5.84 ± 2.52, 3.59 ± 2.21, 5.11 ± 2.99, respectively. The buccal undercut for lateral incisors was the closest to alveolar ridge compared to the other anterior teeth (p = , Fig. 7). The buccal undercut depth (mm) for central incisor, lateral incisor, and canine was 0.76 ± 0.47, 0.87 ± 0.41, 0.73 ± 0.37, Fig. 5 Alveolar width measurements. Lateral incisor demonstrates significantly thinner alveolar ridge compared with central incisor and canine. Asterisk denotes p = N = 51 for all three teeth respectively. There was no statistically significant difference in buccal undercut depth among these three maxillary anterior teeth (Fig. 8). Discussion The alveolar process after tooth extraction normally undergoes resorption resulting in decreased alveolar height and width [24 28]. The alveolar dimension prior to tooth extraction is considered one of the prognostic factors in determining the available alveolar volume for implant placement following extraction [29]. It has been a general consensus that a precise preoperative evaluation of alveolar dimension at the future implant site is very important to develop an appropriate placement strategy and to preserve adjacent anatomical structures, especially for cases in need of immediate implant placement [23]. In the anterior maxilla, implant placement presents more challenges due to the demand for well-anchored implant as well as for satisfactory esthetic result [30, 31]. Fig. 4 Alveolar height measurements. There is no significant difference in alveolar height among maxillary central incisor, later incisor, and canine. N = 51 for all three teeth Fig. 6 Male demonstrates significant larger alveolar width compared to female for maxillary central incisor, lateral incisor, and canine. Stars indicate statistically significant difference (p = , , and for central incisor, lateral incisor, and canine, respectively). N = 20 for male, N = 31 for female for all three teeth
6 Zhang et al. BMC Oral Health (2015) 15:65 Page 6 of 8 Fig. 7 Measurements for buccal undercut location. Lateral incisor has buccal undercut which is the closest to alveolar ridge compared with central incisor and canine. Asterisk denotes p = N =51 for all three teeth There is scarce information in the current literature on the alveolar dimension in the maxillary anterior area. Several studies have evaluated the buccal bone wall thickness at anterior maxilla, and the data suggest that a minimal 2 mm in thickness is ideal to achieve an optimal biological and esthetic outcome [32 34]. However, the overall alveolar dimension and morphology at anterior maxilla have not been fully evaluated yet. In the present study, the averaged alveolar height and width at maxillary anterior region ranged between ~ mm and 8.30 ~ 9.62 mm, respectively, for the selected population. The lateral incisor had the thinnest alveolar ridge compared with the central incisor and canine, probably due to the presence of a lateral fossa which creates the buccal concavity adjacent to lateral incisor [35]. The alveolar width increased from the coronal to apical direction for all three anterior teeth, demonstrating a general bell curve-shaped ridge in anterior maxilla. Male demonstrated significantly wider alveolar ridge compared to female for all three maxillary anterior teeth, which was consistent with what was reported in the literature for other dentoalveolar region [29]. All the subjects included in the study had full dentition at right maxillary anterior region, which eliminated the influence of alveolar atrophy due to edentulism. In the current study, 41 % of central incisors, 77 % of lateral incisors, and 33 % of canines have been found to have buccal undercuts. Except for the much higher incidence of undercut associated with lateral incisor, this result was similar to what has been reported for mandibular posterior area [29, 36]. Presence of lingual undercuts above the mandible canal was observed in % of mandible molars [29, 36]. A buccal or lingual undercut increases the risk of alveolar cortical plate perforation and surgical complication, or indicates the need for additional grafting procedures. To compensate for this anatomical variation, an implant may have to be placed off-axially and restored with an angled abutment [37]. Based on the current study, it appears that without additional grafting procedures, implant placement in the lateral incisor region would incur highest risk of perforation of the buccal plate, whereas the canine region would be the least likely for such an event in the anterior maxilla. The lateral incisor has the thinnest alveolar ridge and highest incidence of buccal undercut. In addition, its undercut is most coronally positioned among the three anterior teeth. The parameters for canine were opposite for the most part. A careful preoperative evaluation of anterior maxilla, especially of the lateral incisor region, is invaluable for selection of the optimal treatment approach and reducing surgical complications. Although we minimized the variables as much as possible, there are still some limitations in the study. Some of these include a relatively small sample size and variations in ethnicities of patients. Future investigation with larger sample size and different ethnic background would be needed to further validate current findings. Conclusions An average alveolar dimension at anterior maxilla is approximately 18 ~ 19 mm in height and 8 ~ 9 mm in width for the selected population. At least one third of maxillary anterior teeth have buccal undercut with various depth and location. Careful treatment planning with CBCT is critical for successful implant placement, especially at the lateral incisor region due to limited availability of alveolar bone. Fig. 8 Measurements for buccal undercut depth. There is no significant difference in buccal undercut depth among maxillary central incisor, later incisor, and canine. N = 51 for all three teeth Abbreviations CBCT: Cone Beam Computerized Tomography; AAOMR: The American Academy of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology; MSCT: Multi-slice Computerized Tomography; IRB: Institutional Review Board; FOV: Field of View; KV: Kilovolt; MA: Milliampere; HSD: Tukey's honestly significant difference; SD: Standard Deviation.
7 Zhang et al. BMC Oral Health (2015) 15:65 Page 7 of 8 Competing interests The authors declared that they have no competing interests. Authors contributions WZ conceived of the study, participated in its design and interpretation of the data, and drafted the manuscript. AS did all the measurements and analyzed the data. RW contributed to the design of the study and critically revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Acknowledgements This project was supported by internal funding. Author details 1 Department of Diagnostic and Biomedical Sciences, The University of Texas School of Dentistry at Houston, 7500 Cambridge Street, Houston, TX 77054, USA. 2 Junior Dental Student, The University of Texas School of Dentistry at Houston, 7500 Cambridge Street, Houston, TX 77054, USA. 3 Department of Periodontics and Dental Hygiene, The University of Texas School of Dentistry at Houston, 7500 Cambridge Street, Houston, TX 77054, USA. Received: 2 March 2015 Accepted: 3 June 2015 References 1. Karoussis IK, Salvi GE, Heitz-Mayfield LJ, Bragger U, Hammerle CH, Lang NP. Long-term implant prognosis in patients with and without a history of chronic periodontitis: a 10-year prospective cohort study of the ITI Dental Implant System. Clinical oral implants research. 2003;14(3): Romeo E, Lops D, Amorfini L, Chiapasco M, Ghisolfi M, Vogel G. Clinical and radiographic evaluation of small-diameter (3.3-mm) implants followed for 1 7 years: a longitudinal study. Clinical oral implants research. 2006;17(2): Romeo E, Lops D, Margutti E, Ghisolfi M, Chiapasco M, Vogel G. Long-term survival and success of oral implants in the treatment of full and partial arches: a 7-year prospective study with the ITI dental implant system. The International journal of oral & maxillofacial implants. 2004;19(2): Wennstrom JL, Ekestubbe A, Grondahl K, Karlsson S, Lindhe J. Oral rehabilitation with implant-supported fixed partial dentures in periodontitis-susceptible subjects. A 5-year prospective study. J Clin Periodontol. 2004;31(9): Wennstrom JL, Ekestubbe A, Grondahl K, Karlsson S, Lindhe J. Implant-supported single-tooth restorations: a 5-year prospective study. J Clin Periodontol. 2005;32(6): de Oliveira RC, Leles CR, Normanha LM, Lindh C, Ribeiro-Rotta RF. Assessments of trabecular bone density at implant sites on CT images. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2008;105(2): Eufinger H, Konig S, Eufinger A, Machtens E: [Significance of the height and width of the alveolar ridge in implantology in the edentulous maxilla. Analysis of 95 cadaver jaws and 24 consecutive patients]. Mund Kiefer Gesichtschir 1999, 3 Suppl 1:S Roze J, Babu S, Saffarzadeh A, Gayet-Delacroix M, Hoornaert A, Layrolle P. Correlating implant stability to bone structure. Clinical oral implants research. 2009;20(10): Harris D, Buser D, Dula K, Grondahl K, Haris D, Jacobs R, et al. E.A.O. Guidelines fo the use of diagnostic imaging in implant dentistry. A consensus workshop organized by the european association for osseointegration in trinity college Dublin. Clinical oral implants research. 2002;13(5): Garg AK, Vicari A. Radiographic modalities for diagnosis and treatment planning in implant dentistry. Implant Soc. 1995;5(5): Benavides E, Rios HF, Ganz SD, An CH, Resnik R, Reardon GT, et al. Use of cone beam computed tomography in implant dentistry: the international congress of oral implantologists consensus report. Implant Dent. 2012;21(2): Tyndall DA, Price JB, Tetradis S, Ganz SD, Hildebolt C, Scarfe WC. American academy of O, maxillofacial R: position statement of the american academy of oral and maxillofacial radiology on selection criteria for the use of radiology in dental implantology with emphasis on cone beam computed tomography. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2012;113(6): Carrafiello G, Dizonno M, Colli V, Strocchi S, Pozzi Taubert S, Leonardi A, et al. Comparative study of jaws with multislice computed tomography and cone-beam computed tomography. Radiol Med. 2010;115(4): Kobayashi K, Shimoda S, Nakagawa Y, Yamamoto A. Accuracy in measurement of distance using limited cone-beam computerized tomography. The International journal of oral & maxillofacial implants. 2004;19(2): Silva MA, Wolf U, Heinicke F, Bumann A, Visser H, Hirsch E. Cone-beam computed tomography for routine orthodontic treatment planning: a radiation dose evaluation. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2008;133(5):640 e Sukovic P. Cone beam computed tomography in craniofacial imaging. Orthod Craniofac Res. 2003;6 Suppl 1:31 6. discussion Loubele M, Van Assche N, Carpentier K, Maes F, Jacobs R, van Steenberghe D, et al. Comparative localized linear accuracy of small-field cone-beam CT and multislice CT for alveolar bone measurements. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2008;105(4): Menezes CC, Janson G, Massaro CS, Cambiaghi L, Garib DG. Reproducibility of bone plate thickness measurements with Cone-Beam Computed Tomography using different image acquisition protocols. Dental Press J Orthod. 2010;15(5): Batenburg RH, Stellingsma K, Raghoebar GM, Vissink A. Bone height measurements on panoramic radiographs: the effect of shape and position of edentulous mandibles. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1997;84(4): Choi YG, Kim YK, Eckert SE, Shim CH. Cross-sectional study of the factors that influence radiographic magnification of implant diameter and length. The International journal of oral & maxillofacial implants. 2004;19(4): Correa LR, Spin-Neto R, Stavropoulos A, Schropp L, da Silveira HE, Wenzel A. Planning of dental implant size with digital panoramic radiographs, CBCTgenerated panoramic images, and CBCT cross-sectional images. Clinical oral implants research. 2014;25(6): Wakimoto M, Matsumura T, Ueno T, Mizukawa N, Yanagi Y, Iida S. Bone quality and quantity of the anterior maxillary trabecular bone in dental implant sites. Clinical oral implants research. 2012;23(11): Eufinger H, Konig S, Eufinger A. The role of alveolar ridge width in dental implantology. Clin Oral Investig. 1997;1(4): Araujo MG, Lindhe J. Dimensional ridge alterations following tooth extraction. An experimental study in the dog Journal of clinical periodontology. 2005;32(2): Araujo MG, Wennstrom JL, Lindhe J. Modeling of the buccal and lingual bone walls of fresh extraction sites following implant installation. Clinical oral implants research. 2006;17(6): Cardaropoli G, Araujo M, Hayacibara R, Sukekava F, Lindhe J. Healing of extraction sockets and surgically produced - augmented and non-augmented - defects in the alveolar ridge. An experimental study in the dog Journal of clinical periodontology. 2005;32(5): Ferrus J, Cecchinato D, Pjetursson EB, Lang NP, Sanz M, Lindhe J. Factors influencing ridge alterations following immediate implant placement into extraction sockets. Clinical oral implants research. 2010;21(1): Schropp L, Wenzel A, Kostopoulos L, Karring T. Bone healing and soft tissue contour changes following single-tooth extraction: a clinical and radiographic 12-month prospective study. The International journal of periodontics & restorative dentistry. 2003;23(4): Braut V, Bornstein MM, Lauber R, Buser D. Bone dimensions in the posterior mandible: a retrospective radiographic study using cone beam computed tomography. Part 1 analysis of dentate sites. The International journal of periodontics & restorative dentistry. 2012;32(2): Belser UC, Buser D, Hess D, Schmid B, Bernard JP, Lang NP. Aesthetic implant restorations in partially edentulous patients a critical appraisal. Periodontology ;17: Buser D, Martin W, Belser UC. Optimizing esthetics for implant restorations in the anterior maxilla: anatomic and surgical considerations. The International journal of oral & maxillofacial implants. 2004;19(Suppl): Braut V, Bornstein MM, Belser U, Buser D. Thickness of the anterior maxillary facial bone wall-a retrospective radiographic study using cone beam computed tomography. The International journal of periodontics & restorative dentistry. 2011;31(2): Grunder U, Gracis S, Capelli M. Influence of the 3-D bone-to-implant relationship on esthetics. The International journal of periodontics & restorative dentistry. 2005;25(2): Huynh-Ba G, Pjetursson BE, Sanz M, Cecchinato D, Ferrus J, Lindhe J, et al. Analysis of the socket bone wall dimensions in the upper maxilla in relation to immediate implant placement. Clinical oral implants research. 2010;21(1): White SC, Pharoah MJ. Oral radiology principles and interpretation. 6th ed. St. Louis, Missouri: Mosby Elsevier; 2009.
8 Zhang et al. BMC Oral Health (2015) 15:65 Page 8 of Watanabe H, Mohammad Abdul M, Kurabayashi T, Aoki H. Mandible size and morphology determined with CT on a premise of dental implant operation. Surgical and radiologic anatomy : SRA. 2010;32(4): Chan HL, Benavides E, Yeh CY, Fu JH, Rudek IE, Wang HL. Risk assessment of lingual plate perforation in posterior mandibular region: a virtual implant placement study using cone-beam computed tomography. J Periodontol. 2011;82(1): Submit your next manuscript to BioMed Central and take full advantage of: Convenient online submission Thorough peer review No space constraints or color figure charges Immediate publication on acceptance Inclusion in PubMed, CAS, Scopus and Google Scholar Research which is freely available for redistribution Submit your manuscript at
Analysis of the socket bone wall dimensions in the upper maxilla in relation to immediate implant placement
 Guy Huynh-Ba Bjarni E. Pjetursson Mariano Sanz Denis Cecchinato Jorge Ferrus Jan Lindhe Niklaus P. Lang Analysis of the socket bone wall dimensions in the upper maxilla in relation to immediate implant
Guy Huynh-Ba Bjarni E. Pjetursson Mariano Sanz Denis Cecchinato Jorge Ferrus Jan Lindhe Niklaus P. Lang Analysis of the socket bone wall dimensions in the upper maxilla in relation to immediate implant
Reliability of Orthopantomography and Cone-beam Computed Tomography in Presurgical Implant Planning: A Clinical Study
 JCDP Original Research Reliability of OPG and CBCT 10.5005/jp-journals-00000-0000 in Presurgical Implant Planning Reliability of Orthopantomography and Cone-beam Computed Tomography in Presurgical Implant
JCDP Original Research Reliability of OPG and CBCT 10.5005/jp-journals-00000-0000 in Presurgical Implant Planning Reliability of Orthopantomography and Cone-beam Computed Tomography in Presurgical Implant
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss. Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor
 Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
The Application of Cone Beam CT Image Analysis for the Mandibular Ramus Bone Harvesting
 44 The Application of Cone Beam CT Image Analysis for the Mandibular Ramus Bone Harvesting LivingWell Institute of Dental Research Lee, Jang-yeol, Youn, Pil-sang, Kim, Hyoun-chull, Lee Sang-chull Ⅰ. Introduction
44 The Application of Cone Beam CT Image Analysis for the Mandibular Ramus Bone Harvesting LivingWell Institute of Dental Research Lee, Jang-yeol, Youn, Pil-sang, Kim, Hyoun-chull, Lee Sang-chull Ⅰ. Introduction
Digital Implant Dentistry Workflow
 Digital Implant Dentistry Workflow Ahmad Kutkut, DDS, MS, FICOI, DICOI Director of Predoctoral Implant Program Chair UKCD Implant Board ahmad.kutkut@uky.edu Disclaimer Neither I or any of my immediate
Digital Implant Dentistry Workflow Ahmad Kutkut, DDS, MS, FICOI, DICOI Director of Predoctoral Implant Program Chair UKCD Implant Board ahmad.kutkut@uky.edu Disclaimer Neither I or any of my immediate
Dental Implant Planning using Cone Beam CT imaging: a pictorial guide.
 Dental Implant Planning using Cone Beam CT imaging: a pictorial guide. Poster No.: C-1970 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. R. Rice, G. Price, S. Morley, T. Beale; London/UK Keywords:
Dental Implant Planning using Cone Beam CT imaging: a pictorial guide. Poster No.: C-1970 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. R. Rice, G. Price, S. Morley, T. Beale; London/UK Keywords:
Prosthetic Options in Implant Dentistry. Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor
 Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
CASE REPORT. CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration
 Computer Aided Implantology Academy Newsletter - Newsletter 20 - July 2009 CASE REPORT CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration Case Report
Computer Aided Implantology Academy Newsletter - Newsletter 20 - July 2009 CASE REPORT CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration Case Report
CBCT Specific Guidelines for South African Practice as Indicated by Current Literature:
 CBCT Specific Guidelines for South African Practice as Indicated by Current Literature: CF Hoogendijk Maxillo- facial and Oral surgery: Trauma: 1. Facial trauma for the confirmation or exclusion of fractures
CBCT Specific Guidelines for South African Practice as Indicated by Current Literature: CF Hoogendijk Maxillo- facial and Oral surgery: Trauma: 1. Facial trauma for the confirmation or exclusion of fractures
Saif Fahad Alrahaimi 1, Elluru Venkatesh 2. Division of Periodontics, Ministry of Health, 2
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE https://doi.org/0.55/jkaoms.07.43..00 pissn 347550 eissn 345930 Localization of mandibular canal and assessment of the remaining alveolar bone in posterior segment of the mandible with
ORIGINAL ARTICLE https://doi.org/0.55/jkaoms.07.43..00 pissn 347550 eissn 345930 Localization of mandibular canal and assessment of the remaining alveolar bone in posterior segment of the mandible with
International Journal of Current Medical and Pharmaceutical Research
 ISSN: 2395-6429 International Journal of Current Medical and Pharmaceutical Research Available Online at http://www.journalcmpr.com DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.24327/23956429.ijcmpr20170169 RESEARCH ARTICLE
ISSN: 2395-6429 International Journal of Current Medical and Pharmaceutical Research Available Online at http://www.journalcmpr.com DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.24327/23956429.ijcmpr20170169 RESEARCH ARTICLE
Labial and lingual/palatal bone thickness of maxillary and mandibular anteriors in human cadavers in Koreans
 Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2011;41:60-66 doi: 10.5051/jpis.2011.41.2.60 Labial and lingual/palatal bone thickness of maxillary and mandibular anteriors in human cadavers in Koreans Ji Young
Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2011;41:60-66 doi: 10.5051/jpis.2011.41.2.60 Labial and lingual/palatal bone thickness of maxillary and mandibular anteriors in human cadavers in Koreans Ji Young
Dr. Muhannad Abdulrhman Muhammed Halwani, Rakan Saed Safar Al Thobaiti and Abdallah Ali M Asker
 2018; 4(3): 276-280 ISSN Print: 2394-7489 ISSN Online: 2394-7497 IJADS 2018; 4(3): 276-280 2018 IJADS www.oraljournal.com Received: 01-05-2018 Accepted: 05-06-2018 Dr. Muhannad Abdulrhman Muhammed Halwani
2018; 4(3): 276-280 ISSN Print: 2394-7489 ISSN Online: 2394-7497 IJADS 2018; 4(3): 276-280 2018 IJADS www.oraljournal.com Received: 01-05-2018 Accepted: 05-06-2018 Dr. Muhannad Abdulrhman Muhammed Halwani
Flapless, Immediate Implantation & Immediate Loading with Socket Preservation in the Esthetic Area Using the Alpha-Bio Tec's NeO Implants
 Flapless Surgery Case Study 48 Flapless, Immediate Implantation & Immediate Loading with Socket Preservation in the Esthetic Area Using the Alpha-Bio Tec's NeO Implants Dr. Gadi Schneider DMD, Specialist
Flapless Surgery Case Study 48 Flapless, Immediate Implantation & Immediate Loading with Socket Preservation in the Esthetic Area Using the Alpha-Bio Tec's NeO Implants Dr. Gadi Schneider DMD, Specialist
JCDP. Original research ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION
 JCDP Original research Roentgenographic 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-2295 Predictability of Lengths of Implant Evaluation of Predictability of Suitable Implant Lengths as related to Accurate Treatment Planning
JCDP Original research Roentgenographic 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-2295 Predictability of Lengths of Implant Evaluation of Predictability of Suitable Implant Lengths as related to Accurate Treatment Planning
ANTHROPOMETRIC EVALUATION OF BUCCAL ALVEOLAR BONE DIMENSION OF MAXILLARY ANTERIOR TEETH IN INDIAN POPULATION: A CONE BEAM COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY STUDY
 International Journal of Dental Research &Development (IJDRD) ISSN(P): 2250-2386; ISSN(E): 2321-0117 Vol. 6, Issue 6, Dec 2016, 23-32 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd ANTHROPOMETRIC EVALUATION OF BUCCAL ALVEOLAR BONE DIMENSION
International Journal of Dental Research &Development (IJDRD) ISSN(P): 2250-2386; ISSN(E): 2321-0117 Vol. 6, Issue 6, Dec 2016, 23-32 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd ANTHROPOMETRIC EVALUATION OF BUCCAL ALVEOLAR BONE DIMENSION
Immediate Implant Placement:
 Immediate Implant Placement: Parameters Influencing Tissue Remodeling Bernard Touati, DDS and Mario Groisman, DDS In esthetic implant therapy, the patient s objective is to obtain an imperceptible, natural-looking
Immediate Implant Placement: Parameters Influencing Tissue Remodeling Bernard Touati, DDS and Mario Groisman, DDS In esthetic implant therapy, the patient s objective is to obtain an imperceptible, natural-looking
Factors influencing ridge alterations following immediate implant placement into extraction sockets
 Jorge Ferrus Denis Cecchinato E. Bjarni Pjetursson Niklaus P. Lang Mariano Sanz Jan Lindhe Factors influencing ridge alterations following immediate implant placement into extraction sockets Authors affiliations:
Jorge Ferrus Denis Cecchinato E. Bjarni Pjetursson Niklaus P. Lang Mariano Sanz Jan Lindhe Factors influencing ridge alterations following immediate implant placement into extraction sockets Authors affiliations:
Utilizing Digital Treatment Planning and Guided Surgery in Conjunction with Narrow Body Implants. by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD
 Utilizing Digital Treatment Planning and Guided Surgery in Conjunction with Narrow Body Implants by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant dentistry is undergoing some amazing transformations. With the
Utilizing Digital Treatment Planning and Guided Surgery in Conjunction with Narrow Body Implants by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant dentistry is undergoing some amazing transformations. With the
Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy.
 Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy. Salvi GE, Brägger U. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24 Suppl:69-85. Department of Periodontology, School of Dental Medicine, University of Bern,
Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy. Salvi GE, Brägger U. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24 Suppl:69-85. Department of Periodontology, School of Dental Medicine, University of Bern,
Monday Morning Pearls of Practice by Bobby Baig
 Dec 19, 2016 Monday Morning Pearls of Practice by Bobby Baig baig@buildyoursmile.com Prosthodontic Associates 2300 Yonge St, suite 905 Toronto, M4P1E4 www.buildyoursmile.com CBCT and Implant Dentistry:
Dec 19, 2016 Monday Morning Pearls of Practice by Bobby Baig baig@buildyoursmile.com Prosthodontic Associates 2300 Yonge St, suite 905 Toronto, M4P1E4 www.buildyoursmile.com CBCT and Implant Dentistry:
CHAPTER 6. Zygogiannis K Aartman IHA Parsa A van der Stelt PF Wismeijer D. Accepted
 CHAPTER 6 Implant size selection and location of anatomical structures prior to implant placement to retain mandibular overdentures: panoramic radiographs vs cone beam computed tomography Zygogiannis K
CHAPTER 6 Implant size selection and location of anatomical structures prior to implant placement to retain mandibular overdentures: panoramic radiographs vs cone beam computed tomography Zygogiannis K
Devoted to the Advancement of Implant Dentistry
 Devoted to the Advancement of Implant Dentistry Devoted to the Advancement of Implant Dentistry Our ultimate goal is to provide you and your patients with the highest standards in implant case planning
Devoted to the Advancement of Implant Dentistry Devoted to the Advancement of Implant Dentistry Our ultimate goal is to provide you and your patients with the highest standards in implant case planning
Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report
 Clinical Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report Rabih Abi Nader 1 and Carine Tabarani 2 Abstract Soft tissue contour depends on the underlying bone anatomy. Following tooth extraction,
Clinical Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report Rabih Abi Nader 1 and Carine Tabarani 2 Abstract Soft tissue contour depends on the underlying bone anatomy. Following tooth extraction,
The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges
 Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
Radiographic Evaluation of Bone Formation and Density Changes after Mandibular Third Molar Extraction: A 6 Month Follow up
 Original Article Radiographic Evaluation of Bone Formation and Density Changes after Mandibular Third Molar Extraction: A Follow up Abbas Haghighat, Ehsan Hekmatian, Mehrdad Abdinian, Ezzeddin Sadeghkhani
Original Article Radiographic Evaluation of Bone Formation and Density Changes after Mandibular Third Molar Extraction: A Follow up Abbas Haghighat, Ehsan Hekmatian, Mehrdad Abdinian, Ezzeddin Sadeghkhani
Assessment of Response of Dental Clinicians and Patients towards Different Imaging Modalities Used In Diagnostic Evaluation of Dental Implant Therapy.
 Assessment of Response of Dental Clinicians and Patients towards Different Imaging Modalities Used In Diagnostic Evaluation of Dental Implant Therapy. Khairnar Mayur Sudhakar, Raut Darshana Hemant, Bakshi
Assessment of Response of Dental Clinicians and Patients towards Different Imaging Modalities Used In Diagnostic Evaluation of Dental Implant Therapy. Khairnar Mayur Sudhakar, Raut Darshana Hemant, Bakshi
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 3 Influence of the 3-D Bone-to-Implant Relationship on Esthetics Ueli Grunder, DMD* Stefano Gracis, DMD** Matteo Capelli, DMD** There are
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 3 Influence of the 3-D Bone-to-Implant Relationship on Esthetics Ueli Grunder, DMD* Stefano Gracis, DMD** Matteo Capelli, DMD** There are
SCD Case Study. Implant-supported overdentures
 SCD Case Study Implant-supported overdentures An implant-retained overdenture may be indicated in patients with changed anatomy, neuromuscular disorders, significant gag reflex or considerable ridge resorption
SCD Case Study Implant-supported overdentures An implant-retained overdenture may be indicated in patients with changed anatomy, neuromuscular disorders, significant gag reflex or considerable ridge resorption
Intramembranous autogenous bone graft is the gold
 CASE LETTER CBCT Morphologic Analysis of Edentulous Posterior Mandible for Mandibular Body Bone Graft Jae-Min Song, DDS, MSD, PhD 1 Jae-Yeol Lee, DDS, MSD, PhD 1,2 Yong-Deok Kim, DDS, MSD, PhD 2,3 * INTRODUCTION
CASE LETTER CBCT Morphologic Analysis of Edentulous Posterior Mandible for Mandibular Body Bone Graft Jae-Min Song, DDS, MSD, PhD 1 Jae-Yeol Lee, DDS, MSD, PhD 1,2 Yong-Deok Kim, DDS, MSD, PhD 2,3 * INTRODUCTION
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 401 Guidelines for Selecting the Implant Diameter During Immediate Implant Placement of a Fresh Extraction Socket: A Case Series Ariádene
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 401 Guidelines for Selecting the Implant Diameter During Immediate Implant Placement of a Fresh Extraction Socket: A Case Series Ariádene
Maxillary Central Incisor Incisive Canal Relationship: A Cone Beam Computed Tomography Study
 Maxillary Central Incisor Incisive Canal Relationship: A Cone Beam Computed Tomography Study Joseph Y.K. Kan, DDS, MS Professor, Department of Restorative Dentistry, Loma Linda University School of Dentistry,
Maxillary Central Incisor Incisive Canal Relationship: A Cone Beam Computed Tomography Study Joseph Y.K. Kan, DDS, MS Professor, Department of Restorative Dentistry, Loma Linda University School of Dentistry,
THE USE OF KEYSTONE EASYGUIDE CT SCANNING SOFTWARE FOR DIAGNOSIS, DIRECTION AND DEPTH DETERMINATION
 CT DIAGNOSTICS IN 3D IMPLANT TREATMENT PLANNING THE USE OF KEYSTONE EASYGUIDE CT SCANNING SOFTWARE FOR DIAGNOSIS, DIRECTION AND DEPTH DETERMINATION Timothy Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Assistant Clinical Professor
CT DIAGNOSTICS IN 3D IMPLANT TREATMENT PLANNING THE USE OF KEYSTONE EASYGUIDE CT SCANNING SOFTWARE FOR DIAGNOSIS, DIRECTION AND DEPTH DETERMINATION Timothy Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Assistant Clinical Professor
Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report
 Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
An Introduction to Dental Implants
 An Introduction to Dental Implants Aims: This article provides an introduction to dental implants, outlining the categories of dental implants, the phases involved in implant dentistry and assessing a
An Introduction to Dental Implants Aims: This article provides an introduction to dental implants, outlining the categories of dental implants, the phases involved in implant dentistry and assessing a
Sang-Sun Han, 1 Kwang-Min Lee, 2 and Kee-Deog Kim Introduction
 BioMed Research International Volume 2015, Article ID 808625, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/808625 Research Article Availability of Software-Based Correction of Mandibular Plane for the Vertical
BioMed Research International Volume 2015, Article ID 808625, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/808625 Research Article Availability of Software-Based Correction of Mandibular Plane for the Vertical
Benefits of CBCT in Implant Planning
 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1032 CLINICAL SCIENCE 1 Gregori M Kurtzman, 2 Douglas F Dompkowski 1 Private General Practice in Silver Spring, Maryland, USA 2 Private Periodontal Practice in Bethesda, Maryland,
10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1032 CLINICAL SCIENCE 1 Gregori M Kurtzman, 2 Douglas F Dompkowski 1 Private General Practice in Silver Spring, Maryland, USA 2 Private Periodontal Practice in Bethesda, Maryland,
Comparison of accuracy of digital radiography and panoramic radiography in dental implants procedure - A literature review
 Review Article Comparison of accuracy of digital radiography and panoramic radiography in dental implants procedure - A literature review M. Keerthna, Ashish R. Jain* ABSTRACT Appropriate treatment planning
Review Article Comparison of accuracy of digital radiography and panoramic radiography in dental implants procedure - A literature review M. Keerthna, Ashish R. Jain* ABSTRACT Appropriate treatment planning
Consensus Statements and Recommended Clinical Procedures Regarding Contemporary Surgical and Radiographic Techniques in Implant Dentistry
 Group 1 and Recommended Clinical Procedures Regarding Contemporary Surgical and Radiographic Techniques in Implant Dentistry Michael M. Bornstein, PD Dr Med Dent 1 /Bilal Al-Nawas, Prof Dr Med, Dr Med
Group 1 and Recommended Clinical Procedures Regarding Contemporary Surgical and Radiographic Techniques in Implant Dentistry Michael M. Bornstein, PD Dr Med Dent 1 /Bilal Al-Nawas, Prof Dr Med, Dr Med
Contemporary Implant Dentistry
 Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
University of Groningen. Immediate dental implant placement in the aesthetic zone Slagter, Kirsten
 University of Groningen Immediate dental implant placement in the aesthetic zone Slagter, Kirsten IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
University of Groningen Immediate dental implant placement in the aesthetic zone Slagter, Kirsten IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
Digital Imaging from a new perspective
 TREATMENT CENTRES HANDPIECES HYGIENE SYSTEMS X-RAY SYSTEMS CEREC TREATMENT CENTRES HANDPIECES HYGIENE SYSTEMS X-RAY SYSTEMS CEREC SIRONA CREATING AND MAINTAINING VALUE. You are right to expect a great
TREATMENT CENTRES HANDPIECES HYGIENE SYSTEMS X-RAY SYSTEMS CEREC TREATMENT CENTRES HANDPIECES HYGIENE SYSTEMS X-RAY SYSTEMS CEREC SIRONA CREATING AND MAINTAINING VALUE. You are right to expect a great
Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry
 Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry AUTHORS Dr. Daniel Capitán Maraver Dr. Manuel Fuentes Ortiz Visiting lecturers in the Master s Degree in Clinical Practice in Implantology and
Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry AUTHORS Dr. Daniel Capitán Maraver Dr. Manuel Fuentes Ortiz Visiting lecturers in the Master s Degree in Clinical Practice in Implantology and
Maxillary Sinus Measurements in Different Age Groups of Human Cadavers
 Tikrit Journal for Dental Sciences 1(2013)107-112 Maxillary Sinus Measurements in Different Age Groups of Human Cadavers Mohammad A. Abd-alla BDS, MSc., Ph.D. (1) Abdul-Jabbar J. Mahdi BDS, MSc., Ph.D.
Tikrit Journal for Dental Sciences 1(2013)107-112 Maxillary Sinus Measurements in Different Age Groups of Human Cadavers Mohammad A. Abd-alla BDS, MSc., Ph.D. (1) Abdul-Jabbar J. Mahdi BDS, MSc., Ph.D.
The advent of computerized tomography (CT) greatly
 RESEARCH A Comparison of Computed Tomography Scans and Digital Periapical Radiographs Ridge Height Measurements Ravichandra Juluri, BDS, MS 1 Maria Moran, DMD, MS 2 Jon B. Suzuki, DDS, PhD 3 Ahmed Khocht,
RESEARCH A Comparison of Computed Tomography Scans and Digital Periapical Radiographs Ridge Height Measurements Ravichandra Juluri, BDS, MS 1 Maria Moran, DMD, MS 2 Jon B. Suzuki, DDS, PhD 3 Ahmed Khocht,
The future of health is digital
 Dated: XX/XX/XXXX Name: XXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXX Birth Date: XX/XX/XXXX Date of scan: XX/XX/XXXX Examination of the anatomical volume: The following structures are reviewed and evaluated for bilateral symmetry,
Dated: XX/XX/XXXX Name: XXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXX Birth Date: XX/XX/XXXX Date of scan: XX/XX/XXXX Examination of the anatomical volume: The following structures are reviewed and evaluated for bilateral symmetry,
Assessment of the relationship between the maxillary molars and adjacent structures using cone beam computed tomography
 Imaging Science in Dentistry 2012; 42 : 219-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2012.42.4.219 Assessment of the relationship between the maxillary molars and adjacent structures using cone beam computed tomography
Imaging Science in Dentistry 2012; 42 : 219-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2012.42.4.219 Assessment of the relationship between the maxillary molars and adjacent structures using cone beam computed tomography
CBCT as an Emerging Gold Standard for Presurgical Planning in Implant Restorations
 10.5005/jp-journals-10011-1344 M Shiva Shankar et al CASE REPORT CBCT as an Emerging Gold Standard for Presurgical Planning in Implant Restorations M Shiva Shankar, Bhupinder Pal, Nitesh Rai, Digvijaya
10.5005/jp-journals-10011-1344 M Shiva Shankar et al CASE REPORT CBCT as an Emerging Gold Standard for Presurgical Planning in Implant Restorations M Shiva Shankar, Bhupinder Pal, Nitesh Rai, Digvijaya
Oral Rehabilitation with CAMLOG implants after loss of dentition due to an accident
 Case Report 13 2011 Oral Rehabilitation with CAMLOG implants after loss of dentition due to an accident Dr Hitoshi Minagawa Tokyo, Japan Prosthetics Dr Hitoshi Minagawa successfully completed his studies
Case Report 13 2011 Oral Rehabilitation with CAMLOG implants after loss of dentition due to an accident Dr Hitoshi Minagawa Tokyo, Japan Prosthetics Dr Hitoshi Minagawa successfully completed his studies
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo. Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
 Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report
 C A S E R E P O R T Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report Rhoodie Garrana 1 and Govindrau Mohangi
C A S E R E P O R T Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report Rhoodie Garrana 1 and Govindrau Mohangi
Osseointegrated implant-supported
 CLINICAL SCREWLESS FIXED DETACHABLE PARTIAL OVERDENTURE TREATMENT FOR ATROPHIC PARTIAL EDENTULISM OF THE ANTERIOR MAXILLA Dennis Flanagan, DDS This is a case report of the restoration of a partially edentulous
CLINICAL SCREWLESS FIXED DETACHABLE PARTIAL OVERDENTURE TREATMENT FOR ATROPHIC PARTIAL EDENTULISM OF THE ANTERIOR MAXILLA Dennis Flanagan, DDS This is a case report of the restoration of a partially edentulous
COMPUTER TOMOGRAPHY ASSESSMENT OF ALVEOLAR RIDGE MODIFICATIONS IN ELDERLY PATIENTS
 COMPUTER TOMOGRAPHY ASSESSMENT OF ALVEOLAR RIDGE MODIFICATIONS IN ELDERLY PATIENTS Adina Mosnegu, Alexandru Nem Department of Geriatric Stomatology, Dental Medicine Faculty, University of Medicine and
COMPUTER TOMOGRAPHY ASSESSMENT OF ALVEOLAR RIDGE MODIFICATIONS IN ELDERLY PATIENTS Adina Mosnegu, Alexandru Nem Department of Geriatric Stomatology, Dental Medicine Faculty, University of Medicine and
Periodontal Disease. Radiology of Periodontal Disease. Periodontal Disease. The Role of Radiology in Assessment of Periodontal Disease
 Radiology of Periodontal Disease Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Periodontal Disease! Includes several disorders of the periodontium! Gingivitis! Marginal Periodontitis! Localized
Radiology of Periodontal Disease Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Periodontal Disease! Includes several disorders of the periodontium! Gingivitis! Marginal Periodontitis! Localized
Oral Health and Dentistry
 Page 107 to 118 Volume 1 Issue 2 2017 Case Report Oral Health and Dentistry ISSN: 2573-4989 Full Mouth Implants Rehabilitation of a Patient with Ectodermal Dysplasia After 3-Ds Ridge Augmentation and Bilateral
Page 107 to 118 Volume 1 Issue 2 2017 Case Report Oral Health and Dentistry ISSN: 2573-4989 Full Mouth Implants Rehabilitation of a Patient with Ectodermal Dysplasia After 3-Ds Ridge Augmentation and Bilateral
Distribution of the maxillary artery related to sinus graft surgery for implantation
 42 Distribution of the maxillary artery related to sinus graft surgery for implantation LvingWell Dental Hospital LivingWell Institute of Dental Research Jang-yeol Lee, Hyoun-chull Kim, Il-hae Park, Sang-chull
42 Distribution of the maxillary artery related to sinus graft surgery for implantation LvingWell Dental Hospital LivingWell Institute of Dental Research Jang-yeol Lee, Hyoun-chull Kim, Il-hae Park, Sang-chull
Evaluation of Cone Beam Computed Tomography in Diagnosis and Treatment Plan of Impacted Maxillary Canines
 Original Research Evaluation of Cone Beam Computed Tomography in Diagnosis and Treatment Plan of Impacted Maxillary Canines Seyed Hossein Hoseini Zarch 1, Farzin Heravi 2, Adineh Javadian Langaroodi 3,
Original Research Evaluation of Cone Beam Computed Tomography in Diagnosis and Treatment Plan of Impacted Maxillary Canines Seyed Hossein Hoseini Zarch 1, Farzin Heravi 2, Adineh Javadian Langaroodi 3,
Assessment of Lingual Concavities in Submandibular Fossa Region in Patients requiring Dental Implants A Cone Beam Computed Tomography Study
 Assessment of Lingual Concavities in Submandibular Fossa via 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-2427 Cone Beam Computed Tomography ORIGINAL ARTICLE Assessment of Lingual Concavities in Submandibular Fossa Region
Assessment of Lingual Concavities in Submandibular Fossa via 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-2427 Cone Beam Computed Tomography ORIGINAL ARTICLE Assessment of Lingual Concavities in Submandibular Fossa Region
Esthetic management of multiple missing anterior teeth A Case report
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 13, Issue 1 Ver. II (Jan. 2014), PP 97-101 Esthetic management of multiple missing anterior teeth A
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 13, Issue 1 Ver. II (Jan. 2014), PP 97-101 Esthetic management of multiple missing anterior teeth A
The Use of Freeze-Dried Bone Allograft as an Alternative to Autogenous Bone Graft in the Atrophic Maxilla: A 3-Year Clinical Follow-up
 643 The Use of Freeze-Dried Bone Allograft as an Alternative to Autogenous Bone Graft in the Atrophic Maxilla: A 3-Year Clinical Follow-up Marco Aurélio Bianchini, DDS, MSc, PhD 1 André R. Buttendorf,
643 The Use of Freeze-Dried Bone Allograft as an Alternative to Autogenous Bone Graft in the Atrophic Maxilla: A 3-Year Clinical Follow-up Marco Aurélio Bianchini, DDS, MSc, PhD 1 André R. Buttendorf,
CT Scan Technology. An Evolving Tool for Avoiding Complications and Achieving Predictable Implant Placement and Restoration SCOTT D.
 CT Scan Technology An Evolving Tool for Avoiding Complications and Achieving Predictable Implant Placement and Restoration SCOTT D. GANZ, DMD / USA Abstract Implant dentistry, one of the most predictable
CT Scan Technology An Evolving Tool for Avoiding Complications and Achieving Predictable Implant Placement and Restoration SCOTT D. GANZ, DMD / USA Abstract Implant dentistry, one of the most predictable
SEDENTEXCT: Guidelines and evidence-based use of CBCT
 : Guidelines and evidence-based use of CBCT Keith Horner John Dalton Rutherford Bragg UK largest single-site University 34,000 students University Dental Hospital of Manchester 90,000 patients attend
: Guidelines and evidence-based use of CBCT Keith Horner John Dalton Rutherford Bragg UK largest single-site University 34,000 students University Dental Hospital of Manchester 90,000 patients attend
In-Office Cone Beam Computerized Tomography: Technology Review and Clinical Examples Michael Tischler, DDS
 Page 1 of 8 Issue Date: June 2008, Posted On: 6/26/2008 In-Office Cone Beam Computerized Tomography: Technology Review and Clinical Examples Michael Tischler, DDS Electronic Medical Record Research EMR
Page 1 of 8 Issue Date: June 2008, Posted On: 6/26/2008 In-Office Cone Beam Computerized Tomography: Technology Review and Clinical Examples Michael Tischler, DDS Electronic Medical Record Research EMR
A cone-beam computed tomography evaluation of buccal bone thickness following maxillary expansion
 Imaging Science in Dentistry 2013; 43: 85-90 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2013.43.2.85 A cone-beam computed tomography evaluation of buccal bone thickness following maxillary expansion Sercan Akyalcin,
Imaging Science in Dentistry 2013; 43: 85-90 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2013.43.2.85 A cone-beam computed tomography evaluation of buccal bone thickness following maxillary expansion Sercan Akyalcin,
Evaluation of Morphology and Anatomical Measurement of Nasopalatine Canal Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography
 Original Article Evaluation of Morphology and Anatomical Measurement of Nasopalatine Canal Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography Mehrdad Panjnoush 1, Hamideh Norouzi 2, Yasaman Kheirandish 3, Ahmad Reza
Original Article Evaluation of Morphology and Anatomical Measurement of Nasopalatine Canal Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography Mehrdad Panjnoush 1, Hamideh Norouzi 2, Yasaman Kheirandish 3, Ahmad Reza
Anatomy and morphology of the nasopalatine canal using cone-beam computed tomography
 Imaging Science in Dentistry 23; 43: 273-8 http://dx.doi.org/.24/isd.23.43.4.273 Anatomy and morphology of the nasopalatine canal using cone-beam computed tomography Arpita Rai Thakur, Krishna Burde 2,
Imaging Science in Dentistry 23; 43: 273-8 http://dx.doi.org/.24/isd.23.43.4.273 Anatomy and morphology of the nasopalatine canal using cone-beam computed tomography Arpita Rai Thakur, Krishna Burde 2,
Case Study. Case # 1 Author: Dr. Suheil Boutros (USA) 2013 Zimmer Dental, Inc. All rights reserved. 6557, Rev. 03/13.
 Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Case Report. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
 Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
Planning for esthetics Part II: adjacent implant restorations
 C L I N I C A L Planning for esthetics Part II: adjacent implant restorations William C Martin, 1 Emma Lewis, 2 Dean Morton 3 1 DMD, MS, Associate Professor & Clinical Director, Center for Implant Dentistry,
C L I N I C A L Planning for esthetics Part II: adjacent implant restorations William C Martin, 1 Emma Lewis, 2 Dean Morton 3 1 DMD, MS, Associate Professor & Clinical Director, Center for Implant Dentistry,
Cephalometric Analysis
 Cephalometric Analysis of Maxillary and Mandibular Growth and Dento-Alveolar Change Part III In two previous articles in the PCSO Bulletin s Faculty Files, we discussed the benefits and limitations of
Cephalometric Analysis of Maxillary and Mandibular Growth and Dento-Alveolar Change Part III In two previous articles in the PCSO Bulletin s Faculty Files, we discussed the benefits and limitations of
Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3)
 B. Klinge Thomas F. Flemmig Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3) Members of working group: Matteo Chiapasco Jan-Eirik Ellingsen Ronald Jung Friedrich Neukam Isabella Rocchietta
B. Klinge Thomas F. Flemmig Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3) Members of working group: Matteo Chiapasco Jan-Eirik Ellingsen Ronald Jung Friedrich Neukam Isabella Rocchietta
Periapical Radiography
 Periapical Radiography BARBARA E. DIXON B.D.S., M.Sc., D.P.D.S. Main Indications Detection of Apical infection/inflammation Assessment of the periodontal status After trauma Assessment of Unerupted teeth
Periapical Radiography BARBARA E. DIXON B.D.S., M.Sc., D.P.D.S. Main Indications Detection of Apical infection/inflammation Assessment of the periodontal status After trauma Assessment of Unerupted teeth
Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases
 52 STARGET 1 I 12 StraUMaNN CareS r ry vincenzo MiriSOLA Di TOrreSANTO AND LUCA COrDArO Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases Background A 41-year-old woman with
52 STARGET 1 I 12 StraUMaNN CareS r ry vincenzo MiriSOLA Di TOrreSANTO AND LUCA COrDArO Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases Background A 41-year-old woman with
AAO 115th Annual Session San Francisco, CA May 17 (Sunday), 1:15-2:00 pm, 2015
 AAO 115th Annual Session San Francisco, CA May 17 (Sunday), 1:15-2:00 pm, 2015 Title: Clinical and iomechanical Considerations of TADs in Challenging Cases: Sagittal Correction beyond Orthodontic oundaries
AAO 115th Annual Session San Francisco, CA May 17 (Sunday), 1:15-2:00 pm, 2015 Title: Clinical and iomechanical Considerations of TADs in Challenging Cases: Sagittal Correction beyond Orthodontic oundaries
The thickness of alveolar bone at the maxillary canine and premolar teeth in normal occlusion
 Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2012;42:173-178 http://dx.doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2012.42.5.173 The of alveolar bone at the maxillary canine and premolar teeth in normal occlusion Seong-Ho Jin
Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2012;42:173-178 http://dx.doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2012.42.5.173 The of alveolar bone at the maxillary canine and premolar teeth in normal occlusion Seong-Ho Jin
Implant Imaging JCD /jp-journals REVIEW ARTICLE ABSTRACT
 JCD 10.5005/jp-journals-10031-1051 REVIEW ARTICLE Ajay R Bhoosreddy, Seema Bhoosreddy, Vinayak Umesh Shirsekar ABSTRACT Implants improve the quality of life for patients who are unable to keep their natural
JCD 10.5005/jp-journals-10031-1051 REVIEW ARTICLE Ajay R Bhoosreddy, Seema Bhoosreddy, Vinayak Umesh Shirsekar ABSTRACT Implants improve the quality of life for patients who are unable to keep their natural
The influence of sensor size and orientation on image quality in intra-oral periapical radiography
 Clinical The influence of sensor size and orientation on image quality in intra-oral periapical radiography Tony Druttman 1 The periapical view is one of the standard intra-oral radiographs by which diagnostic
Clinical The influence of sensor size and orientation on image quality in intra-oral periapical radiography Tony Druttman 1 The periapical view is one of the standard intra-oral radiographs by which diagnostic
Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas
 2 Long-term follow-up of 2.5mm NDIs supporting a fixed prosthesis Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas EDUARDO ANITUA, DDS, MD, PHD¹,² A narrow-diameter implant (NDI) is an implant with
2 Long-term follow-up of 2.5mm NDIs supporting a fixed prosthesis Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas EDUARDO ANITUA, DDS, MD, PHD¹,² A narrow-diameter implant (NDI) is an implant with
Dentascan Evaluation of Hard Tissue Changes around Implants Placed in Healed Sockets: A Cross-sectional Study
 JDSOR ORIGINAL ARTICLE Dentascan Evaluation of Hard Tissue Changes around 10.5005/jp-journals-10039-1099 Implants Placed in Healed Sockets Dentascan Evaluation of Hard Tissue Changes around Implants Placed
JDSOR ORIGINAL ARTICLE Dentascan Evaluation of Hard Tissue Changes around 10.5005/jp-journals-10039-1099 Implants Placed in Healed Sockets Dentascan Evaluation of Hard Tissue Changes around Implants Placed
Proposed score for occlusal-supporting ability
 Open Journal of Stomatology, 2013, 3, 230-234 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojst.2013.33040 Published Online June 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojst/) OJST Proposed score for occlusal-supporting ability
Open Journal of Stomatology, 2013, 3, 230-234 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojst.2013.33040 Published Online June 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojst/) OJST Proposed score for occlusal-supporting ability
A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive. maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years.
 Original Article A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years follow up Myat Nyan Department of Prosthodontics,
Original Article A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years follow up Myat Nyan Department of Prosthodontics,
POST-IMPLANT NEUROLOGICAL COMPLICATIONS IN THE HORIZONTAL MANDIBULAR ARCH
 Maxillofacial Surgery POST-IMPLANT NEUROLOGICAL COMPLICATIONS IN THE HORIZONTAL MANDIBULAR ARCH O. Stamatin¹, Maria Voroneanu², Carmen Stelea³ 1. PhD Student, Dept of OMF Surgery, Faculty of Med Dent,
Maxillofacial Surgery POST-IMPLANT NEUROLOGICAL COMPLICATIONS IN THE HORIZONTAL MANDIBULAR ARCH O. Stamatin¹, Maria Voroneanu², Carmen Stelea³ 1. PhD Student, Dept of OMF Surgery, Faculty of Med Dent,
Diagnostics and treatment planning. Dr. Attila Szűcs DDS
 Diagnostics and treatment planning. Dr. Attila Szűcs DDS Considering both surgical Aim and prosthetic aspects in the planning of implant prosthetics Arrangements for implant therapy Preliminary examinations
Diagnostics and treatment planning. Dr. Attila Szűcs DDS Considering both surgical Aim and prosthetic aspects in the planning of implant prosthetics Arrangements for implant therapy Preliminary examinations
Computed tomography for dental implants: the influence of the gantry angle and mandibular positioning on the bone height and width
 (2005) 34, 9 15 q 2005 The British Institute of Radiology http://dmfr.birjournals.org RESEARCH Computed tomography for dental implants: the influence of the gantry angle and mandibular positioning on the
(2005) 34, 9 15 q 2005 The British Institute of Radiology http://dmfr.birjournals.org RESEARCH Computed tomography for dental implants: the influence of the gantry angle and mandibular positioning on the
GuidedService. The ultimate guide for precise implantations
 GuidedService The ultimate guide for precise implantations ABGuidedService The ultimate guide for precise implantations At A.B. Dental we've brought implantology into the future with a 3D digitally planned
GuidedService The ultimate guide for precise implantations ABGuidedService The ultimate guide for precise implantations At A.B. Dental we've brought implantology into the future with a 3D digitally planned
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2013) Vol. 52, Page
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2013) Vol. 52, Page 544 554 Role of Multislice Dental CT in Assessment of Dental Implants Safa A Elaty *, Ahmed M Monib *, Yasser A Mohamed *,Ahmed F Abd
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2013) Vol. 52, Page 544 554 Role of Multislice Dental CT in Assessment of Dental Implants Safa A Elaty *, Ahmed M Monib *, Yasser A Mohamed *,Ahmed F Abd
CLASSIFICATIONS. Established in 1994 as a subcommittee of the. Prosthodontic Care Committee
 CLASSIFICATIONS Established in 1994 as a subcommittee of the Prosthodontic Care Committee Committee Members Thomas J. McGarry, DDS, Chair Arthur Nimmo, DDS James F. Skiba, DDS Christopher R. Smith, DDS
CLASSIFICATIONS Established in 1994 as a subcommittee of the Prosthodontic Care Committee Committee Members Thomas J. McGarry, DDS, Chair Arthur Nimmo, DDS James F. Skiba, DDS Christopher R. Smith, DDS
Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis
 CASE REPORT Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis Dr Ashish Yadav 1, Dr Aratee Gupta 2, Dr Archana Singh 3, 1,3-
CASE REPORT Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis Dr Ashish Yadav 1, Dr Aratee Gupta 2, Dr Archana Singh 3, 1,3-
Implant surgery of the edentulous premaxilla
 Evaluation of Maxillary Incisive Canal Characteristics Related to Dental Implant Treatment With Computerized Tomography: A Clinical Multicenter Study Tolga F. Tözüm,* Güliz N. Güncü,* Yağmur D. Yıldırım,*
Evaluation of Maxillary Incisive Canal Characteristics Related to Dental Implant Treatment With Computerized Tomography: A Clinical Multicenter Study Tolga F. Tözüm,* Güliz N. Güncü,* Yağmur D. Yıldırım,*
E.A.O. Guidelines for the use of Diagnostic Imaging in Implant Dentistry
 David Harris Daniel Buser Karl Dula Kerstin Gröndahl David Harris Reinhilde Jacobs Ulf Lekholm Richard Nakielny Daniel van Steenberghe Paul van der Stelt E.A.O. Guidelines for the use of Diagnostic Imaging
David Harris Daniel Buser Karl Dula Kerstin Gröndahl David Harris Reinhilde Jacobs Ulf Lekholm Richard Nakielny Daniel van Steenberghe Paul van der Stelt E.A.O. Guidelines for the use of Diagnostic Imaging
Bone grafts are widely used in the reconstruction of
 RESEARCH Cone Beam Computerized Tomography Measurement of Alveolar Ridge at Posterior Mandible for Implant Graft Estimation Wenjian Zhang, DDS, MS, PhD 1 * Justin Tullis, BS 2 Robin Weltman, DDS, MS 3
RESEARCH Cone Beam Computerized Tomography Measurement of Alveolar Ridge at Posterior Mandible for Implant Graft Estimation Wenjian Zhang, DDS, MS, PhD 1 * Justin Tullis, BS 2 Robin Weltman, DDS, MS 3
REGENERATIONTIME. A Case Report by. Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor
 A Case Report by Dr. Daniele Cardaropoli Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor The Situation An adult female patient presented with an endodontic/prosthetic failure
A Case Report by Dr. Daniele Cardaropoli Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor The Situation An adult female patient presented with an endodontic/prosthetic failure
The Quality Leader in 3D Cone Beam CT
 The Quality Leader in 3D Cone Beam CT The Complete 2-in-1 or 3-in-1 Multi-modality Solution PreXion, with over 15 years of innovation in the medical and dental fields, introduces the PreXion3D Eclipse.
The Quality Leader in 3D Cone Beam CT The Complete 2-in-1 or 3-in-1 Multi-modality Solution PreXion, with over 15 years of innovation in the medical and dental fields, introduces the PreXion3D Eclipse.
Alveolar Bone Remodeling and Development after Immediate Orthodontic Root Movement
 Journal of Dental Health, Oral Disorders & Therapy Alveolar Bone Remodeling and Development after Immediate Orthodontic Root Abstract Introduction: Adult orthodontics is rapidly expanding primarily due
Journal of Dental Health, Oral Disorders & Therapy Alveolar Bone Remodeling and Development after Immediate Orthodontic Root Abstract Introduction: Adult orthodontics is rapidly expanding primarily due
MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Comparison of panoramic radiography with cone beam CT in predicting the relationship of the mandibular third molar roots to the alveolar canal
 Imaging Science in Dentistry 2013; 43: 105-9 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2013.43.2.105 Comparison of panoramic radiography with cone beam CT in predicting the relationship of the mandibular third molar
Imaging Science in Dentistry 2013; 43: 105-9 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2013.43.2.105 Comparison of panoramic radiography with cone beam CT in predicting the relationship of the mandibular third molar
The treatment protocol for replacing
 RESEARCH Detection of the Mandibular Canal and the Mental Foramen in Panoramic Radiographs: Intraexaminer Agreement Jamil A. Shibli, DDS, PhD 1 Marília C. Martins, DDS, PhD 2 Leonor C. M. Loffredo, PhD
RESEARCH Detection of the Mandibular Canal and the Mental Foramen in Panoramic Radiographs: Intraexaminer Agreement Jamil A. Shibli, DDS, PhD 1 Marília C. Martins, DDS, PhD 2 Leonor C. M. Loffredo, PhD
3 Dimensional Diagnosis Unravelling Prognosis of Multiple Impacted Teeth A Case Report
 3 Dimensional Diagnosis Unravelling Prognosis of Multiple Impacted Teeth A Case Report Adusumilli Gopinath 1, Naveen Admala Reddy 2, Mayur G Rohra 3 1 Professor, Department of Orthodontics, AME S Dental
3 Dimensional Diagnosis Unravelling Prognosis of Multiple Impacted Teeth A Case Report Adusumilli Gopinath 1, Naveen Admala Reddy 2, Mayur G Rohra 3 1 Professor, Department of Orthodontics, AME S Dental
Case study 2. A Retrospective Multi-Center Study on the Spiral Implant
 Case study 2 A Retrospective Multi-Center Study on the Spiral Implant Benny Karmon DMD, Jerry Kohen DMD, Ariel Lor DMD, Yiftach Gratciany DMD, Zvi Laster DMD, Gideon Hallel DMD MPA, Tsvia Karmon A Retrospective
Case study 2 A Retrospective Multi-Center Study on the Spiral Implant Benny Karmon DMD, Jerry Kohen DMD, Ariel Lor DMD, Yiftach Gratciany DMD, Zvi Laster DMD, Gideon Hallel DMD MPA, Tsvia Karmon A Retrospective
Periapical radiography and cone beam computed tomography for assessment of the periapical bone defect 1 week and 12 months after root-end resection
 (2009) 38, 531 536 2009 The British Institute of Radiology http://dmfr.birjournals.org RESEARCH Periapical radiography and cone beam computed tomography for assessment of the periapical bone defect 1 week
(2009) 38, 531 536 2009 The British Institute of Radiology http://dmfr.birjournals.org RESEARCH Periapical radiography and cone beam computed tomography for assessment of the periapical bone defect 1 week
