IMMUNOPATHOLOGY OF CICATRICIAL PEMPHIGOID: STUDIES OF COMPLEMENT DEPOSITION
|
|
|
- Francine Hunter
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
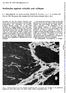
1 THE JOURNAl. or I NVE.~TIGATIVE DERMA rolog\, 68: i Copyright@ 1977 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 68. No. I Printed tn U..A. IMMUNOPATHOLOGY OF CICATRICIAL PEMPHIGOID: STUDIES OF COMPLEMENT DEPOSITION R. s. ROGERS, III, M.D., H. 0. PERRY, M.D., S. F. BEAN, M.D., AND R. E. JORDON, M.D. Cutaneous Immunopathology Unit and the Departments of Dermatology and Immunology, Mayo Clinic and Mayo Foundation, Rochester, M innesota, and the Diagnostic Clinic of Houston (SFB) Houston, Texas, U.S. A. Im munopathologic investigations were conducted on t he sera and oral mucosal tissue specimens of 23 patients with cicatricial pemphigoid. A linear, continuous basement membrane zone pattern was noted in 83% of oral mucosal biopsy specimens studied. This pattern is indistinguishable from the pattern noted in immunofluorescence studies of bullous pemphigoid, herpes gestationis, and some cases of desquamative gingivitis. Complement studies provided data supportive of classical pathway activation in cicatricial pemphigoid tissue. Deposition oflga with Factor B, properdin, and C3 raised the possibility of alternative pathway activation, a question requiring further study. Circulating antibasement membrane zone antibodies were noted in the sera of two patients with cicatricial pemphigoid. Cicatricial (benjgn mucous membrane) pemphigoid (CP) is a well-defined disease characterized by its chronic course, its scarring nature, and its predilection for the mucosal surfaces. Civatte [1) and Lever [2] separated CP from pemphigus vulgaris by the presence of subepithelial bullae in CP. Lever!3 ], Hardy et al [4), and Shklar and McCarthy!51 reported large series defining the distinct clinical nature of the disease. Lortat-Jacob [6] described a disease. dermatite bulleuse mucosynechante et atrophiante, which is indistinguishable from CP (7]. The clinical and histopathologic characteristics of CP suggest an etiologic relationship between CP and bullous pemphigoid (BP). Several recent investigations [7-14] have demonstrated the presence of tissue-bound immunoglobulin and complement components C3 and C4 at the basement membrane zone (BMZ) in CP. The linear pattern of this BMZ staining is identical to the immunofluorescent (IF) pattern of BP. The identical direct IF findings lend credence to an etiologic relationship between CP and BP. Further support for this relationship is the presence of Manuscript received June 14, 1976; accepted for publication August 15, This investigation was supported in part by Research Grant Al from the. ational Institutes of Health. Public Health Service. and by grants from the Minnesota Chapter of the Arthritis Foundation. Presented in part at the Annual Meeting of the American Federation for Clinical Re!';earch. Atlantic City. New Jersey, May 4, Reprint requests to: Dr. R.. Rogers, Ill. Department of Dermatology, Mayo Clinic. Rochester. Minnesota Abbreviations: BP: bullous pemphigoid BMZ: ba.,ement membrane wne C: complement CP: cicatricial pemphigoid IF: immunofluorescent lg: immunoglobulin 39 circulating anti-bmz antibodies in the sera of several patients with cicatricial pemphigoid [15-18]. We have investigated sera and tissue samples from 23 patients with CP by IF techniques. Two of 21 patients' sera demonstrated cir culating anti BMZ antibodies. Nineteen of 23 patients' tissues demonstrated linear BMZ deposition of immunoglobulins as well as components of both the classical and alternative complement pathways and fibrin. PATIE:-.:T~ A:\0 :\1ETHOD, Twenty-three patients with CP were studied. Four of these patients. whose clinical. histopathologic, and immunopathologic findings have been reported elsewhere [19 ], had their disea e begin as desquamative gingivitis which then e\ olved into CP. Almo t all immunopathologic tests had been conducted since the inception of our Cutaneous Immunopathology Unit in June erum and tissue samples were obtamed by standard procedures and were tested immediateh or were stored at - I0 C until tested. Oral mucosal specimens were obtained in all 23 patients, skin specimens in 2 patients. and vaginal mucosal specimens in l patient. Twenty of 23 of the oral mucosal histopathologic specimens revealed subepithelial bullae. In 3 patients, the histopathologic specimens were nonspecific. Controls consisted of sera and tissues from other patients with oral mucosal inflammatory diseases. the results of which have been reported elsewhere [20 ). Antihuman lgg was prepared in goats, assayed. and conjugated with fluorescein i8othiocyanate by methods pre\ iously reiewed in detail [21]. Labeled antisera to lgm. * lga. * C3," and fibrin.* as well as unlabeled antisera to C4t and labeled goat antirabbit and rabbit antigoat IgG, * were purchased. Hyland Division, Travenol Laboratories. Inc.. Costa Mesa, Calif t Behring Diagnostics, American Hoechst Pharmaceuticals, Sommerville, N. J
2 40 ROGERS ET AL Rabbit antisera t.o Clq and to properdin Factor B were prepared and tested by the methods of Morse and Christian [22] and Gotze and Miiller-Eberhard [23), respectively. Goat antiserum to properdin was made after isolating human properdin by the method of Pensky et al [24]. Details of the preparation and use of these antisera (to Clq. Factor B. and properdin) have been published previously in detail [25-27 ]. All antisera were checked for specificity by both double immunodiffussion (Ouchterlony) and immunoelectrophoresis. Units of antisera, fluorescein-protein ratios, antibody protein assays, and dilutions at which the conjugated antisera were used conformed to previously determined standards [21). Serum specimens were tested for circulating antibodies by t he indirect IF staining technique according to established procedures [21) using monkey esophageal mucosal sections. Tissue specimens were tested for fixed immunoglobulins and complement components by both the di.rect and the modified indirect IF procedures as previously reported in detail [21-29]. Direct IF testing of C'P tissue specimens was conducted with antisera to lgg, IgA, lgm, fibrin, and C3 by previously described methods [21-27). The modified indirect IF staining method [25-29] was used to test for the presence of Clq. C4. Factor B, and properdin. Briefly, this method involves treating tissue specimens first with rabbit anti-clq, rabbit anti-c4. or rabbit anti-factor B and then with labeled goat antirabbit lgg. In a similar fashion goat antiproperdin was used first, followed by labeled rabbit antigoat lgg. The specificity controls for the modified indirect IF technique have been reported [25-27]. RESL;LTS The Table is a summary of our immunopathologic observations of the oral mucosal lesions of 23 patients with CP. Both cutaneous lesions and the vaginal mucosal lesion also demonstrated a linear BMZ pattern by direct IF testing with deposition of immunoglobulins and complement components. A continuous, linear BMZ pattern was found in 19 of 23 or 83% of the oral mucosal biopsy specimens by the direct IF test. All 19 tissue specimens had the deposition of one or more TABLE. Summary of immunopathologic obseruations of cicatricial pemphigoid mucosal lesions J\nti~era Linear BMZ panern :--lumber Percent positive lgg 9/ lga 8/20 40 lgm 6/21 29 C3 17/21 81 C!q 7/11 64 C4 2/4 50 Factor B 5/10 50 Properdin" 7/11 64 Fibrin 15/23 65 P ositive BMZ pattern 19/23 83 Modified indirect ff staining employed Vol. 68, No. 1 F1c. l. Linear. continuous deposition of lga at the basement membrane zone of an oral mucosal biopsy specimen. This pattern is typical of the pemphigoid spectrum of disease ( x 250). complement components at the BMZ. Thirteen of the 19 positive tissue specimens had the deposition of 1 or more immunoglobulin at the BMZ. Interestingly, lgg deposition was noted in ouly 9 of 23 tissues tested. lga deposition (Fig. 1) occurred in 8 of 20 and IgM in 6 of 21 tissues tested, respectively. Six had deposition of 2 or more complement components and fibrin at the BMZ. A continuous. linear BMZ pattern similar to the one that we report herein has been seen only in oral mucosal specimens from patients with desquamative gingivitis [19] and BP. Only 2 results (C3 and fibrin in a linear BMZ pattern) in 42 patients with miscellaneous oral mucosal diseases have been noted that could be questionably interpreted as positive linear BMZ staining [20]. Evidence for activation of the classical complement pathway in lesions of CP can be gleaned from the deposition of Clq, one of the subunits of the first component of complement, and C4, another early reacting component of the classical sequence These components were noted in 7 of 11 and 2 of 4 specimens. respectively. lga deposition (Fig. 1) in 8 of 20 tissue specimens studied is noteworthy as this immunoglobulin does not characteristically activate the classical complement pathway but can activate the alternative pathway [23]. Alternative pathway compo-
3 Jan CICATRICIAL PEMPHIGOID 41 nents, Factor B and properdin, were present in a high percentage of lesions studied. in 5 of 10 and 7 of 11 specimens, respectively. In 4 patients' tissues, lga, C3, Factor B, and properdin deposition were apparent at the BMZ in serial sections. As in pemphigus [25] and BP [26}. specific absorption of anti-factor B with Factor B and antiproperdin with properdin resulted in blocking of the IF staining. Circulating anti-bmz antibodies were present in 2 of 23 patients with CP. In both patients t he antibodies were present for a short period of time (1 month and 4 months), after which the antibodies were absent on repeated testing. The titers were 1:320 and 1:80. The substrate for indirect IF testing at the time of the positive tests was guinea-pig esophagus. Both of these patients represent somewhat atypical cases of CP and will be reported elsewhere. No positive indirect IF tests have been noted since June 1973, when monkey esophageal mucosa became our standard substrate. 01. CUSS I O~ Our findings are consistent with the reports of others [7-13 ] who have noted deposition of immunoglobulins C3 and C4 at the BMZ of CP lesions. Nineteen of 23 (83%) of the oral mucosal biopsy specimens studied were positive. Thirteen of the 19 specimens had the deposition of 1 or more immunoglobulin with or without 1 or more complement components at the BMZ in a continuous, linear pat tern. The presence of 2 or more complement components in the oral mucosal specimens, even in the absence of immunoglobulin deposition, increased the number of positive results from 13 of 23 to 19 of 23 patients. A few of our patients had negative results on the first oral mucosal biopsy specimen. onl~, to have a positive result when the study was repeated on " better" tissue. The mucosal surfaces of CP are prone to separation from the submucosa due to the nature of the subepithelial bullous process. With the loss of the mucosal-submucosal interface. specificity of immunopathologic interpretation is lost. Also, tissue which has been ulcerated or eroded is inadequate for interpretation. For these reasons, we have selected the areas of perilesional erythema as the site of our biopsy specimens. With " better" tissue selection positive results are much more frequent and add an important diagnostic method to t he study of CP. The IF pattern reported here (Figs. 1. 2) is a linear. continuous deposition of immunoreactive proteins at the BMZ. This pattern is distinctive for the pemphigoid spectrum of diseases which now appears to include CP, BP, herpes gestationis [27,28,30 j, and perhaps desquamative gingivitis [19]. The Jack of lgg deposition in the majority of tissues tested is somewhat puzzling, however, in FIG. 2. Linear, continuous deposition of C3 at the basement membrane zone of an oral mucosal biopsy specimen (Y. 250). light of the other reports [8,10, 12). Only 9 of 23 CP biopsies tested by us demonstrated IgG deposition to the BMZ. The explanation for this finding is not clear at the present time, although similar findings have recently been noted in both BP (31] and herpes gestations [27]. Deposition of C3. a pivotal protein in the complement sequence which appears at the interface of both the classical and alternative pathways, appears to be a more sensitive. specific immunopathologic finding in all of these diseases. Provost and Tomasi [28,29] and Jordon et al [261 have reported deposition of Clq, C4, and C3, in addition to IgG and IgM at the BMZ of cutaneous lesions of BP by IF techniques. These studies provide immunopathologic evidence for activation of the classical pathway in CP. Immunoglobulins G and M characteristically acti, ate the classical pathway and were present in 11 of 23 patients. Early classical pathway components. Clq and C4. were present in the majority of tissue specimens so tested, and C3 was present in 17 of 21 tissue specimens. On the other hand, one cannot state unequivocally that the classical pathway is activated on the basis of immunopathologic observations alone. although our data would support this contention. The finding of lga deposition in about one-half of CP tissue specimens tested is also worthy of note. Alt hough all immunoglobulins when aggregated or altered may activate the alternative path-
4 42 ROGERS ET AL way,:): lga may activate complement only by that pathway [23 ]. Factor B and properdin, two components of the alternative pathway, were found bound to the BMZ in 5 of 10 and 7 of 11 specimens, respectively. In addition, 4 of our patients' tissues demonstrated IgA, C3, Factor B, and properdin at the BMZ in serial sections. Similar findings have been noted in a few patients with dermatitis herpetiformis [32] where IgA deposition characteristically occurs. Binding of Factor B and properdin in tissues, however, may not be indicative of true alternative pathway activation. Recently Schreiber et al [33] and Fearon and Austen {34] have demonstrated that Factor B and properdin can bind to C3b, thus stabilizing the ''C3b-dependent C3 convertase." Classical pathway activation of C3, which was apparent in all specimens with Factor B and properdin deposition (i.e., Clq and C4 deposition as well), produces C3b which presumably binds to the BMZ with other immunoreactive proteins. Thus, deposition of Factor B and properdin can be explained by their binding to C3b at the BMZ. Similar findings in BP [26,28,29] and. more recently, in herpes gestationis [27,30] are also best explained by this phenomenon. The question of true alternative pathway activation, independent of generation of the C3b-dependent C3 convertase, in all of these diseases requires further study. The presence of circulating anti-bmz antibodies in the sera of 2 of these patients was a transient phenomenon lasting only 1 and 4 months until consistently negative results were obtained. The disease characteristics and substrate specificities have been discussed by other investigators [15-18]. These two patients and a third with circulating anti-bmz antibodies will be reported in a separate communication. REFERENCES 1. Civatte A: Le diagnostic des dermatoses butleuses an laboratorie. Arch Belg Dermatol Syphiligr 5: Lever WF: Pemphigus: a histopathologic study. Arch Dermatol 64: , Lever WF: Pemphigus and Pemphigoid. Springfield, Ill, Thomas Hardy KM, Perry HO, Pingree GC, Kirby TJ Jr: Benign mucous membrane pemphigoid. Arch Dermatol 104: , Shklar G, McCarthy P: Oral lesions of mucous membrane pemphigoid. Arch Oto!aryngol 93: Lortat-Jacob E: Benign mucosal pemphigoid: dermatite bulleuse muco-synechante et atrophiante. Br J Dermatol 70: , Kuffer R, Umbert P: Etude en immunofluorescence de quatre affections bulleuses de Ia muqueuse buccale. Rev Stomatol 75: Bean SF. Waisman M, Michel B, Thomas CI, Knox :j: Frank MM. Gaither T, Adkinson F, Terry WD, May JE: Activation of the alternative complement pathway by human immunoglobulins, Proceedings. Sixth International Complement Workshop, Sarasota, Florida, Vol. 68, No. I JM. Levine M: Cicatricial pemphigoid: immunofluorescent studies. Arch Dermatol 106: , Heydenreich G. From E, Diederichsen H: Some unusual findings obtained by the immunfluorescence method in bullous pemphigoid and benign mucous membrane pemphigoid. Acta Derm Venereol (Stockh) 52: , Holubar K, Honigsmann H. Wolff' K : Cicatricial pemphigoid: immunofluorescence investigations Arch Dermatol 108:50-52, Hood Cl : Essential shrinking of the conjunctiva, chronic cicatrizing conjunctivitis, beni,:m mucous membrane pemphigoid. Invest Opbthalmol 12: , 1973 J 2. Griffith MR, Fukuyama K, Tuffanelli D. ilverman S Jr: Immunofluorescent studies in mucous membrane pemphigoid. Arch Dermatol 109: , Huron BE: Immunological aspects of cicatricial pemphigoid. Am J Ophthalmol 79: , Rogers R TII. J ordon RE: Immunofluorescent studies of cicatricial pemphigoid. Clin Res 23:459A, Dantzig P: Circulating antibodies in cicatricial pem phigoid. Arch Dermatol 108: Dabelsteen E, Ullman S. Thomsen K, Rygaard J : Demonstration of basement membrane autoantibodies in patients with benign mucous membrane pemphigoid. Acta Derm Venereol (Stockh) 54: Tagani H, Imamura S: Beni,:m mucous membrane pemphigoid: demonstration of circulating and tis sue-bound membrane antibodies. Arch Dermatol 109: , Bean SF: Cicatricial pemphigoid : immunofluorescent studies. Arch Dermawl 110:552-5;> Rogers RS lll, Sheridan PJ. Jordon RE: Desquama (ive gin)!ivitis: clinical. histopatholo)!ic and immunopathologic investigations. Oral urg 42: Rogers RS ill. Jordon RE: Immunopathology of oral mucosal inflammatorv diseases (abstrl. J Invest Dermatol 66: Beutner EH. Chorzelski TP. Jordon RE: Autosensitization in Pemphigoid and Bullous Pemphigoid. Springfield. Ill, Thomas Morse.JH. Ch.ristian C'L: Immunological studies of the lis prolein component of t he human complement system. J Exp Med 119: Gotze 0, Muller-Eherhard HJ: The C3-acrivator system: an alternate pathway of complement activation. J Exp Med l34:90s-108s Pensky J, Hinz CF' Jr. Todd EW. Wedgewood RJ. Boyer JT, Lepow IH: Properties of highly purified human properdin. J l mmunol 100: , Jordon RE, chroeter AL, Rogers RS Ill. Perry HO: Classical and alternate pathway activation of complement in pemphigus vulgaris lesions.,j Invest Dermatol 63: , Jordon RE, Schroeter AL, Good RA, Day NK: The complement system in bullous pemphigoid. n. lmm"unofluorescent evidence for both classical and alternate pathway activation of complement. C1in Immunol lmmunopathol 3: , J ordon RE, Heine KG, Tappeiner G, Bushkell LL, Provost IT: The immunopathology of herpes gestationis: immunofluorescence studies and characterization of ''HG factor.",j Clin lnvest 57: , Provost TT, Tomasi TB Jr: Evidence for complement activation via the alternate pathway in skin diseases. L Herpes gestationis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and bullous pemphigoid. J Clin Invest 52: , Provost TT, Tomasi TB Jr: Immunopathology of
5 Jan bullous pemphigoid: basement membrane deposition of lge, alternate pathway components and fibrin. Clin Exp lmmunol 18: , Katz Sl, Hertz KC, Yaoita H: Herpes gestationis: Immunopathology and characterization of HG factor. J Clio Invest 57: , Jordon RE: Complement activation in pemphigus and bullous pemphigoid. Jlnvest Dermatol67: , Provost IT, Tomasi TB Jr: Evidence for the activation of complement via the alternate pathway in CICATRICIAL PEMPHIGOID 43 skin diseases. II. Dermatitis herpetiformis. Clin lmmunol Immunopathol 3: , Schreiber RD, Medicus RG, Gotz 0, Multer-Eberhard HJ: Properdin and nephritic factor dependent C3 convertases: requirement of native C3 for enzyme formation and the function of bound C3b as properdin receptor. J Exp Med 142: , Fearon DT, Austen KF: Properdin: binding to C3b and stabilization of the C3b-dependent C3 convertase. J Exp Med 142: , 1975
The Immunopathology of Herpes Gestationis
 The Immunopathology of Herpes Gestationis IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE STUDIES AND CHARACTERIZATION OF "HG FACTOR" ROBERT E. JORDON, KARL G. HEINE, GERHARD TAPPEINER, LAWRENCE L. BUSHKELL, and THOMAS T. PROVOST
The Immunopathology of Herpes Gestationis IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE STUDIES AND CHARACTERIZATION OF "HG FACTOR" ROBERT E. JORDON, KARL G. HEINE, GERHARD TAPPEINER, LAWRENCE L. BUSHKELL, and THOMAS T. PROVOST
pemphigoid. a clinical and immunopathological study
 British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1989, 73, 52-56 Conjunctival involvement in cicatricial and bullous pemphigoid. a clinical and immunopathological study PEGGY A FRITH,' AND A J BRON' V A VENNING,2 F WOJNAROWSKA,2
British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1989, 73, 52-56 Conjunctival involvement in cicatricial and bullous pemphigoid. a clinical and immunopathological study PEGGY A FRITH,' AND A J BRON' V A VENNING,2 F WOJNAROWSKA,2
Immunoglobulin and complement
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 321 Immunoglobulin and complement deposition in skin of rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus patients ARNOLD L. SCHROETER, DOYT L. CONN, AND ROBERT E. JORDON
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 321 Immunoglobulin and complement deposition in skin of rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus patients ARNOLD L. SCHROETER, DOYT L. CONN, AND ROBERT E. JORDON
COMPLEMENT ACTIVATION IN PEMPHIGUS AND BULLOUS PEMPHIGOID
 THE JOURNAL OF NVESTGATVE DERMATOLOGY, 67:366-371, 1976 Copyright 1976 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 67, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. COMPLEMENT ACTVATON N PEMPHGUS AND BULLOUS PEMPHGOD ROBERT E. JORDON,
THE JOURNAL OF NVESTGATVE DERMATOLOGY, 67:366-371, 1976 Copyright 1976 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 67, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. COMPLEMENT ACTVATON N PEMPHGUS AND BULLOUS PEMPHGOD ROBERT E. JORDON,
Direct immunofluorescence of skin using formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded sections
 Direct immunofluorescence of skin using formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded sections SL MERA, EW YOUNG, AND JWB BRADFIELD J Clin Pathol 1980; 33: 365-369 From the University Department ofpathology, University
Direct immunofluorescence of skin using formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded sections SL MERA, EW YOUNG, AND JWB BRADFIELD J Clin Pathol 1980; 33: 365-369 From the University Department ofpathology, University
Original Contribution
 Direct Immunofluorescence Test of Skin Biopsy Samples Results of 204 Cases Kabir AN, 1 Das RK, 2 Kamal M 3 Direct immunofluorescence (DIF) test of skin and renal biopsy specimens is being done on regular
Direct Immunofluorescence Test of Skin Biopsy Samples Results of 204 Cases Kabir AN, 1 Das RK, 2 Kamal M 3 Direct immunofluorescence (DIF) test of skin and renal biopsy specimens is being done on regular
THE USE OF HUMAN SKIN FOR THE DETECTION OF ANTI- EPITHELIAL AUTOANTIBODIES A DIAGNOSTIC AND PROGNOSTIC TEST*
 Tlia JOUStNAL OF INVF5T1WTiVF DEBM.,TLGY Copyright 1969 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 53, No. 6 Printed 'in U.S.A. THE USE OF HUMAN SKIN FOR THE DETECTION OF ANTI- EPITHELIAL AUTOANTIBODIES A DIAGNOSTIC
Tlia JOUStNAL OF INVF5T1WTiVF DEBM.,TLGY Copyright 1969 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 53, No. 6 Printed 'in U.S.A. THE USE OF HUMAN SKIN FOR THE DETECTION OF ANTI- EPITHELIAL AUTOANTIBODIES A DIAGNOSTIC
A cross-sectional study of clinical, histopathological and direct immmunofluorescence diagnosis in autoimmune bullous diseases
 Original Article A cross-sectional study of clinical, histopathological and direct immmunofluorescence diagnosis in autoimmune bullous diseases Anchal Jindal, MD 1 Rushikesh Shah, MBBS 2 Neela Patel, MD
Original Article A cross-sectional study of clinical, histopathological and direct immmunofluorescence diagnosis in autoimmune bullous diseases Anchal Jindal, MD 1 Rushikesh Shah, MBBS 2 Neela Patel, MD
Autoimmune Diseases with Oral Manifestations
 Autoimmune Diseases with Oral Manifestations Martin S. Greenberg DDS, FDS RCSEd Professor Emeritus Department of Oral Medicine University of Pennsylvania Disclosure Statement I have no actual or potential
Autoimmune Diseases with Oral Manifestations Martin S. Greenberg DDS, FDS RCSEd Professor Emeritus Department of Oral Medicine University of Pennsylvania Disclosure Statement I have no actual or potential
t Dr. Small is a Fellow of the Medical Research
 THE JoURNAL or INVESTIGATIVE DERMATOLOGY, 64:441-445, 1975 Copyright 1975 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 64, No.6 Printed in U.S.A. HUMAN NECROTIZING VASCULITIS: IMMUNOGLOBULINS AND COMPLEMENT IN VESSEL
THE JoURNAL or INVESTIGATIVE DERMATOLOGY, 64:441-445, 1975 Copyright 1975 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 64, No.6 Printed in U.S.A. HUMAN NECROTIZING VASCULITIS: IMMUNOGLOBULINS AND COMPLEMENT IN VESSEL
The Complement System in Bullous Pemphigoid
 The Complement System in Bullous Pemphigoid I. COMPLEMENT AND COMPONENT LEVELS IN SERA AND BLISTER FLUIDS R. E. JoRDoN-, N. K. DAY, WV. MI. SAMS, JR., and R. A. GOOD From the Department of Pathology, University
The Complement System in Bullous Pemphigoid I. COMPLEMENT AND COMPONENT LEVELS IN SERA AND BLISTER FLUIDS R. E. JoRDoN-, N. K. DAY, WV. MI. SAMS, JR., and R. A. GOOD From the Department of Pathology, University
Definitive and Differential Diagnosis of Desquamative Gingivitis Through Direct Immunofluorescence Studies
 Volume 83 Number 10 Definitive and Differential Diagnosis of Desquamative Gingivitis Through Direct Immunofluorescence Studies Lakshmanan Suresh* and Mirdza E. Neiders* Background: Desquamative gingivitis
Volume 83 Number 10 Definitive and Differential Diagnosis of Desquamative Gingivitis Through Direct Immunofluorescence Studies Lakshmanan Suresh* and Mirdza E. Neiders* Background: Desquamative gingivitis
Properdin Deposition in the Dermal- Epidermal Junction in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
 Clinical Significance of Serum Properdin Levels and Properdin Deposition in the Dermal- Epidermal Junction in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus MARKc A. SCmHAGER and NAOMI F. ROTHFIELD From the Division of
Clinical Significance of Serum Properdin Levels and Properdin Deposition in the Dermal- Epidermal Junction in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus MARKc A. SCmHAGER and NAOMI F. ROTHFIELD From the Division of
Interesting Case Series. Linear IgA Bullous Dermatosis
 Interesting Case Series Linear IgA Bullous Dermatosis Sean Chen, BA, a Peter Mattei, MD, a Max Fischer, MD, MPH, a Joshua D. Gay, PA-C, b Stephen M. Milner, MBBS, BDS, FRCS (Ed), FACS, b and Leigh Ann
Interesting Case Series Linear IgA Bullous Dermatosis Sean Chen, BA, a Peter Mattei, MD, a Max Fischer, MD, MPH, a Joshua D. Gay, PA-C, b Stephen M. Milner, MBBS, BDS, FRCS (Ed), FACS, b and Leigh Ann
Clinicopathological correlation of blistering diseases of skin
 Bangladesh Med Res Counc Bull 2008; 34: 48-53 Copyright 2008 by Bangladesh Medical Research Council Clinicopathological correlation of blistering diseases of skin A.K.M. Nurul Kabir 1, Mohammed Kamal 1
Bangladesh Med Res Counc Bull 2008; 34: 48-53 Copyright 2008 by Bangladesh Medical Research Council Clinicopathological correlation of blistering diseases of skin A.K.M. Nurul Kabir 1, Mohammed Kamal 1
Indirect cutaneous immunofluorescence1
 J. clin. Path., 1973, 26, 268-272 Indirect cutaneous immunofluorescence1 II Clinical significance THOMAS K. BURNHAM From the Department ofdermatology, Henry Ford Hospital, Detroit, Michigan, USA SYNOPSIS
J. clin. Path., 1973, 26, 268-272 Indirect cutaneous immunofluorescence1 II Clinical significance THOMAS K. BURNHAM From the Department ofdermatology, Henry Ford Hospital, Detroit, Michigan, USA SYNOPSIS
Introduction to Pemphigoid: Spectrum of Disease & Treatment
 Introduction to Pemphigoid: Spectrum of Disease & Treatment A Razzaque Ahmed, MD Center for Blistering Diseases Boston, MA A.Razzaque.Ahmed@tufts.edu centerforblisteringdiseases.com SPECTRUM OF PEMPHIGOID
Introduction to Pemphigoid: Spectrum of Disease & Treatment A Razzaque Ahmed, MD Center for Blistering Diseases Boston, MA A.Razzaque.Ahmed@tufts.edu centerforblisteringdiseases.com SPECTRUM OF PEMPHIGOID
Pemphigus in younger age group in Bangladeshi population
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE in younger age group in Bangladeshi population Abdul Wahab 1, MD, Lubna Khondker 1, MD, Jamal Uddin 1, MD, Ishrat Bhuiyan 2, MD Shirajul Islam Khan 3, MD, Zafrul Islam 1, MD, Rahmat Ali
ORIGINAL ARTICLE in younger age group in Bangladeshi population Abdul Wahab 1, MD, Lubna Khondker 1, MD, Jamal Uddin 1, MD, Ishrat Bhuiyan 2, MD Shirajul Islam Khan 3, MD, Zafrul Islam 1, MD, Rahmat Ali
Background information of DIF
 Napa Dermatopathology Meeting 2018: Immunobullous Disease Whitney A. High, MD, JD, MEng whitney.high@ucdenver.edu Professor of Dermatology & Pathology Vice-Chairman, Dermatology Director of Dermatopathology
Napa Dermatopathology Meeting 2018: Immunobullous Disease Whitney A. High, MD, JD, MEng whitney.high@ucdenver.edu Professor of Dermatology & Pathology Vice-Chairman, Dermatology Director of Dermatopathology
Department of Dermatology, Nippon Medical School, 1-1-5, Sendagi, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo , Japan 2
 Dermatology Research and Practice Volume 2010, Article ID 931340, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2010/931340 Case Report Paraneoplastic Pemphigus Presenting as Mild Cutaneous Features of Pemphigus Foliaceus and Lichenoid
Dermatology Research and Practice Volume 2010, Article ID 931340, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2010/931340 Case Report Paraneoplastic Pemphigus Presenting as Mild Cutaneous Features of Pemphigus Foliaceus and Lichenoid
Absence of Intercellular Antigens in the Deep Layers of the Epidermis in Pemphigus Foliaceus
 Absence of Intercellular Antigens in the Deep Layers of the Epidermis in Pemphigus Foliaceus Jean-Claude Bystryn, Jose Rodriguez J Clin Invest. 1978;61(2):339-348. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci108944. Research
Absence of Intercellular Antigens in the Deep Layers of the Epidermis in Pemphigus Foliaceus Jean-Claude Bystryn, Jose Rodriguez J Clin Invest. 1978;61(2):339-348. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci108944. Research
Immunopathology of Psoriasis: A Comparison with Other Parakeratotic Lesions
 0022-202X/ 82/ 7803-0256$02.00/0 THE JOURNAL 0~' INVESTIGATIVE DERMATOLOGY, 78:256-260, 982 Copyright 982 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 78, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. Immunopathology of Psoriasis: A
0022-202X/ 82/ 7803-0256$02.00/0 THE JOURNAL 0~' INVESTIGATIVE DERMATOLOGY, 78:256-260, 982 Copyright 982 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 78, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. Immunopathology of Psoriasis: A
IMMUNOELECTRONMICROSCOPIC LOCALIZATION OF IgA IN SKIN OF PATIENTS WITH DERMATITIS HERPETIFORMIS HIDEO YAOITA, M.D., AND STEPHEN 1. KATZ, M.D., PH.D.
 THE JOURNAL OF INVESTIGATIVE DERMATOLOGY. 67:502-506. 1976 Copyright 1976 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 67. :-':0. 4 Printed in U.S.A. REPORTS IMMUNOELECTRONMICROSCOPIC LOCALIZATION OF IgA IN SKIN
THE JOURNAL OF INVESTIGATIVE DERMATOLOGY. 67:502-506. 1976 Copyright 1976 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 67. :-':0. 4 Printed in U.S.A. REPORTS IMMUNOELECTRONMICROSCOPIC LOCALIZATION OF IgA IN SKIN
Mucous membrane pemphigoid in a patient with hypertension treated with atenolol: a case report
 Kanjanabuch et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2012, 6:373 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Mucous membrane pemphigoid in a patient with hypertension treated with atenolol: a
Kanjanabuch et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2012, 6:373 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Mucous membrane pemphigoid in a patient with hypertension treated with atenolol: a
A Clinical Study of Oral Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid
 The Journal of International Medical Research 2003; 31: 340 344 A Clinical Study of Oral Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid A ALKAN 1, Ö GÜNHAN 3, A ALKAN 2 AND F OTAN 2 1 Department of Oral and Maxillofacial
The Journal of International Medical Research 2003; 31: 340 344 A Clinical Study of Oral Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid A ALKAN 1, Ö GÜNHAN 3, A ALKAN 2 AND F OTAN 2 1 Department of Oral and Maxillofacial
Glomerular Complement Components
 Glomerular Complement Components in Human Glomerulonephritis PIERRE J. VERROUST, CURIns B. WILSON, NEIL R. CoopER, THOMAS S. EDGINGTON, and FRANK J. DIXON From the Department of Experimental Pathology,
Glomerular Complement Components in Human Glomerulonephritis PIERRE J. VERROUST, CURIns B. WILSON, NEIL R. CoopER, THOMAS S. EDGINGTON, and FRANK J. DIXON From the Department of Experimental Pathology,
A case of bullous pemphigoid following pemphigus foliaceus
 #2228 A case of bullous pemphigoid following pemphigus foliaceus Priyanka Vedak MD 1, Danielle Levine MD 1,3, Lyn Duncan MD 2,3, Hensin Tsao 1,3, Daniela Kroshinsky MD MPH 1,3 1. Department of Dermatology,
#2228 A case of bullous pemphigoid following pemphigus foliaceus Priyanka Vedak MD 1, Danielle Levine MD 1,3, Lyn Duncan MD 2,3, Hensin Tsao 1,3, Daniela Kroshinsky MD MPH 1,3 1. Department of Dermatology,
and Isolation of Antibody in Linear Immunoglobulin A Bullous Dermatosis
 Identification of the Cutaneous Basement Membrane Zone Antigen and Isolation of Antibody in Linear Immunoglobulin A Bullous Dermatosis John J. Zone, Ted B. Taylor, Donald P. Kadunce, and Laurence J. Meyer
Identification of the Cutaneous Basement Membrane Zone Antigen and Isolation of Antibody in Linear Immunoglobulin A Bullous Dermatosis John J. Zone, Ted B. Taylor, Donald P. Kadunce, and Laurence J. Meyer
INFLAMMATORY DISEASES PART I. Immunopathology Part I
 INFLAMMATORY DISEASES PART I Immunopathology Part I Nonspecific & T Cell Mediated Mucosal Inflammatory Lesions Nonspecific and Idiopathic Mucositis Hypersensitivity and Autoimmune T cell mediated Immunoglobulin
INFLAMMATORY DISEASES PART I Immunopathology Part I Nonspecific & T Cell Mediated Mucosal Inflammatory Lesions Nonspecific and Idiopathic Mucositis Hypersensitivity and Autoimmune T cell mediated Immunoglobulin
Epidermolysis Bullosa Acquisita
 Introduction Epidermolysis Bullosa Acquisita Pages with reference to book, From 192 To 194 Nasser Rashid Dar ( Departments of Dermatology, Combined Military Hospital, Peshawar. ) Ahsan Hameed, Ashfaq Ahmad
Introduction Epidermolysis Bullosa Acquisita Pages with reference to book, From 192 To 194 Nasser Rashid Dar ( Departments of Dermatology, Combined Military Hospital, Peshawar. ) Ahsan Hameed, Ashfaq Ahmad
Comment on Association of bullous pemphigoid with malignancy: A systematic review and meta-analysis
 Accepted Manuscript Comment on Association of bullous pemphigoid with malignancy: A systematic review and meta-analysis Maglie Roberto, MD, Antiga Emiliano, MD, PhD, Caproni Marzia, MD, PhD PII: S0190-9622(17)32812-8
Accepted Manuscript Comment on Association of bullous pemphigoid with malignancy: A systematic review and meta-analysis Maglie Roberto, MD, Antiga Emiliano, MD, PhD, Caproni Marzia, MD, PhD PII: S0190-9622(17)32812-8
Secondary fluorescent staining of virus antigens by rheumatoid factor and fluorescein-conjugated anti-lgm
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1973), 32, 53 Secondary fluorescent staining of virus antigens by rheumatoid factor and fluorescein-conjugated anti-lgm P. V. SHIRODARIA, K. B. FRASER, AND F. STANFORD From the Department
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1973), 32, 53 Secondary fluorescent staining of virus antigens by rheumatoid factor and fluorescein-conjugated anti-lgm P. V. SHIRODARIA, K. B. FRASER, AND F. STANFORD From the Department
Immunofluorescence in Oral Dermatological Disorders- No Shiny Matter
 Journal of Academy of Dental Education Journal of Academy of Dental Education, 24-28, DOI: 10.18311/jade/2015-2016/15951 ISSN (Print): 2348-1595 ISSN (Online) : 2348-2621 Immunofluorescence in Oral Dermatological
Journal of Academy of Dental Education Journal of Academy of Dental Education, 24-28, DOI: 10.18311/jade/2015-2016/15951 ISSN (Print): 2348-1595 ISSN (Online) : 2348-2621 Immunofluorescence in Oral Dermatological
IMMUNOFLUORESCENT LOCALIZATION OF BASEMENT MEMBRANE IN LESIONS OF DERMATITIS HERPETIFORMIS
 THE JOURNAL OF INVESTIGATIVE DERMATOLOGY, 67:683-687, 1976 Copyri ght 1976 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 67, No. 6 Printed ill U.S.A. REPORTS IMMUNOFLUORESCENT LOCALIZATION OF BASEMENT MEMBRANE IN
THE JOURNAL OF INVESTIGATIVE DERMATOLOGY, 67:683-687, 1976 Copyri ght 1976 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 67, No. 6 Printed ill U.S.A. REPORTS IMMUNOFLUORESCENT LOCALIZATION OF BASEMENT MEMBRANE IN
Erythema gyratumrepens-like eruption in a patient with epidermolysisbullosaacquisita associated with ulcerative colitis
 Erythema gyratumrepens-like eruption in a patient with epidermolysisbullosaacquisita associated with ulcerative colitis A. España C. Sitaru* M. Pretel L. Aguado J. Jimenez# Department of Dermatology, University
Erythema gyratumrepens-like eruption in a patient with epidermolysisbullosaacquisita associated with ulcerative colitis A. España C. Sitaru* M. Pretel L. Aguado J. Jimenez# Department of Dermatology, University
When your patient complains of
 WILLIAM LAWSON, MD, DDS Mount Sinai School of Medicine ABSTRACT: Certain clues can help you identify the cause of bullous oral lesions. Diffuse oral and labial bullous erosions, sometimes accompanied by
WILLIAM LAWSON, MD, DDS Mount Sinai School of Medicine ABSTRACT: Certain clues can help you identify the cause of bullous oral lesions. Diffuse oral and labial bullous erosions, sometimes accompanied by
atorvastatin 10mg, amlodipine 5mg and dilitazem 60mg. He had unexplained iron deficiency anaemia (hemoglobin-8.4gm/dl, ferritin- 4.73ng/ml, total iron
 Pemphigus herpetiformis : A rare clinical variant of pemphigus Shrestha P 1, Tajhya RB 2, Pokharel A 3 1,2 Consultant Dermatologist, Department of Dermatology, Vayodha Hospital Pvt. Ltd, Balkhu, Kathmandu,
Pemphigus herpetiformis : A rare clinical variant of pemphigus Shrestha P 1, Tajhya RB 2, Pokharel A 3 1,2 Consultant Dermatologist, Department of Dermatology, Vayodha Hospital Pvt. Ltd, Balkhu, Kathmandu,
Immunobullous Diseases: Review and Update. May P. Chan, MD Associate Professor of Pathology and Dermatology University of Michigan
 Immunobullous Diseases: Review and Update May P. Chan, MD Associate Professor of Pathology and Dermatology University of Michigan Diagnosis of Immunobullous Diseases Clinical H&E DIF DIAGNOSIS IIF ELISA
Immunobullous Diseases: Review and Update May P. Chan, MD Associate Professor of Pathology and Dermatology University of Michigan Diagnosis of Immunobullous Diseases Clinical H&E DIF DIAGNOSIS IIF ELISA
THE ALTERNATE COMPLEMENT PATHWAY IN INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE
 GASTROENTEROWGY 70:181-185, 1976 Copyright 1976 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 70, No.2 Printed in U.S.A. THE ALTERNATE COMPLEMENT PATHWAY IN INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE Quantitation of the C3 proactivator
GASTROENTEROWGY 70:181-185, 1976 Copyright 1976 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 70, No.2 Printed in U.S.A. THE ALTERNATE COMPLEMENT PATHWAY IN INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE Quantitation of the C3 proactivator
To Correlate Clinical Diagnosis with Histopathology and DIF Pattern of Autoimmune Based Vesiculobullous Disorders In A Tertiary Teaching Hospital
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 7 Ver. 2 (July. 2018), PP 01-06 www.iosrjournals.org To Correlate Clinical Diagnosis with Histopathology
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 7 Ver. 2 (July. 2018), PP 01-06 www.iosrjournals.org To Correlate Clinical Diagnosis with Histopathology
Indian Journal of Dermatopathology and Diagnostic Dermatology
 Volume 1 Issue 1 Jan-Jun 2014 Online full text at www.ijdpdd.com Indian Journal of Dermatopathology and Diagnostic Dermatology DSI IADVL Karnataka Branch Official Publication of Dermatopathology Society
Volume 1 Issue 1 Jan-Jun 2014 Online full text at www.ijdpdd.com Indian Journal of Dermatopathology and Diagnostic Dermatology DSI IADVL Karnataka Branch Official Publication of Dermatopathology Society
Autoimmune bullous dermatoses
 Autoimmune bullous dermatoses Overview of serological diagnostics in autoimmune blister-forming diseases of the skin Pemphigoid diseases Pemphigus diseases Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita Dermatitis herpetiformis
Autoimmune bullous dermatoses Overview of serological diagnostics in autoimmune blister-forming diseases of the skin Pemphigoid diseases Pemphigus diseases Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita Dermatitis herpetiformis
S003 CPC Self-Assessment
 S003 CPC Self-Assessment Alina G. Bridges, D.O. Associate Professor Program Director, Dermatopathology Fellowship Department of Dermatology, Division of Dermatopathology and Cutaneous Immunopathology Mayo
S003 CPC Self-Assessment Alina G. Bridges, D.O. Associate Professor Program Director, Dermatopathology Fellowship Department of Dermatology, Division of Dermatopathology and Cutaneous Immunopathology Mayo
Immunoglobulin in Clinically Uninvolved Skin
 Immunoglobulin in Clinically Uninvolved Skin in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus ASSOCIATION WITH RENAL DISEASE JAMES N. GILLIAM, DON E. CHEATUM, ERIC R. Hunn, PETR STASTNY, and MoRMs ZIFF From the Department
Immunoglobulin in Clinically Uninvolved Skin in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus ASSOCIATION WITH RENAL DISEASE JAMES N. GILLIAM, DON E. CHEATUM, ERIC R. Hunn, PETR STASTNY, and MoRMs ZIFF From the Department
Department of Dermatology, Christian Medical College and Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India.
 Bullous pemphigoid mimicking granulomatous inflammation Abhilasha Williams, Emy Abi Thomas. Department of Dermatology, Christian Medical College and Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India. Egyptian Dermatology
Bullous pemphigoid mimicking granulomatous inflammation Abhilasha Williams, Emy Abi Thomas. Department of Dermatology, Christian Medical College and Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India. Egyptian Dermatology
Bullous Pemphigoid with Lymphocytic Colitis: A Case Report and Short Literature Review
 Dermatol Ther (Heidelb) (2016) 6:437 441 DOI 10.1007/s13555-016-0135-4 CASE REPORT Bullous Pemphigoid with Lymphocytic Colitis: A Case Report and Short Literature Review Alexandra Sperl. Johann W. Bauer.
Dermatol Ther (Heidelb) (2016) 6:437 441 DOI 10.1007/s13555-016-0135-4 CASE REPORT Bullous Pemphigoid with Lymphocytic Colitis: A Case Report and Short Literature Review Alexandra Sperl. Johann W. Bauer.
Epidermolysis Bullosa Acquisita: A Retrospective Clinical Analysis of 30 Cases
 Acta Derm Venereol 2011 Epub ahead of print CLINICAL REPORT Epidermolysis Bullosa Acquisita: A Retrospective Clinical Analysis of 30 Cases Jong Hoon Kim 1, Yeon Hee Kim 2 and Soo-Chan Kim 1 1 Department
Acta Derm Venereol 2011 Epub ahead of print CLINICAL REPORT Epidermolysis Bullosa Acquisita: A Retrospective Clinical Analysis of 30 Cases Jong Hoon Kim 1, Yeon Hee Kim 2 and Soo-Chan Kim 1 1 Department
PEMPIDGUS ANTIBODIES: THEIR ROLE IN DISEASE*
 TH.E JoURNAL or h.-vestigative DEBMAToLoGY Copyright 1971 by The Wi!Uams & Wilkillll Co. Vol. 66, No.6 P-rinted in U.S.A. PEMPIDGUS ANTIBODIES: THEIR ROLE IN DISEASE* W. MITCHELL SAMS, Ja., M.D. AND ROBERT
TH.E JoURNAL or h.-vestigative DEBMAToLoGY Copyright 1971 by The Wi!Uams & Wilkillll Co. Vol. 66, No.6 P-rinted in U.S.A. PEMPIDGUS ANTIBODIES: THEIR ROLE IN DISEASE* W. MITCHELL SAMS, Ja., M.D. AND ROBERT
Immunofluorescence in Oral Pathology Part III: Pathology and Immunofluorescent Patterns in Intraepithelial Immunobullous Disorders
 10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1157 Roopa S Rao et al REVIEW ARTICLE Immunofluorescence in Oral Pathology Part III: Pathology and Immunofluorescent Patterns in Intraepithelial Immunobullous Disorders Roopa
10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1157 Roopa S Rao et al REVIEW ARTICLE Immunofluorescence in Oral Pathology Part III: Pathology and Immunofluorescent Patterns in Intraepithelial Immunobullous Disorders Roopa
IN THE NAME OF GOD. Dr.kheirandish DDS,MSC Oral and maxillofacial pathology
 IN THE NAME OF GOD Dr.kheirandish DDS,MSC Oral and maxillofacial pathology Dermatologic Diseases Chapter 16 ECTODERMAL DYSPLASIA o Two or more ectodermally derived anatomic structures fail to develop o
IN THE NAME OF GOD Dr.kheirandish DDS,MSC Oral and maxillofacial pathology Dermatologic Diseases Chapter 16 ECTODERMAL DYSPLASIA o Two or more ectodermally derived anatomic structures fail to develop o
Comparative study of indirect immunofluorescence, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, and the Tzanck smear test for the diagnosis of pemphigus
 (2016) 45: 786 790 2016 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd wileyonlinelibrary.com/journal/jop doi: 10.1111/jop.12439 Comparative study of indirect immunofluorescence, enzyme-linked
(2016) 45: 786 790 2016 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd wileyonlinelibrary.com/journal/jop doi: 10.1111/jop.12439 Comparative study of indirect immunofluorescence, enzyme-linked
Classification: 1. Infective: 2. Traumatic: 3. Idiopathic: Recurrent Aphthous Stomatitis (RAS) 4. Associated with systemic disease:
 Classification: 1. Infective: 2. Traumatic: 3. Idiopathic: Recurrent Aphthous Stomatitis (RAS) 4. Associated with systemic disease: Hematological GIT Behcet s HIV 5. Associated with dermatological diseases:
Classification: 1. Infective: 2. Traumatic: 3. Idiopathic: Recurrent Aphthous Stomatitis (RAS) 4. Associated with systemic disease: Hematological GIT Behcet s HIV 5. Associated with dermatological diseases:
External ocular findings in lupus erythematosus: a
 BnrtishJournal ofophthalmology, 1990, 74, 163-167 163 Department of Ophthalmology, Oxford Eye Hospital P Frith Departments of Dermatology, Slade Hospital, Oxford, and High Wycombe General Hospital S M
BnrtishJournal ofophthalmology, 1990, 74, 163-167 163 Department of Ophthalmology, Oxford Eye Hospital P Frith Departments of Dermatology, Slade Hospital, Oxford, and High Wycombe General Hospital S M
The incidence of internal malignancies in autoimmune bullous diseases
 Tokai J Exp Clin Med., Vol. 32, No. 1, pp. 42-47, 2007 The incidence of internal malignancies in autoimmune bullous diseases Kenichi IWASHITA, Takashi MATSUYAMA, Emiko AKASAKA, Kimihiko MIZUTANI, Kozo
Tokai J Exp Clin Med., Vol. 32, No. 1, pp. 42-47, 2007 The incidence of internal malignancies in autoimmune bullous diseases Kenichi IWASHITA, Takashi MATSUYAMA, Emiko AKASAKA, Kimihiko MIZUTANI, Kozo
Role of direct immunofluorescence on Tzanck smear and plucked hair in the diagnosis of pemphigus vulgaris
 Original Article Role of direct immunofluorescence on Tzanck smear and plucked hair in the diagnosis of pemphigus vulgaris Kehkshan Tahir, Saelah Batool, Muhammad Shahid, Shahbaz Aman Department of Dermatology,
Original Article Role of direct immunofluorescence on Tzanck smear and plucked hair in the diagnosis of pemphigus vulgaris Kehkshan Tahir, Saelah Batool, Muhammad Shahid, Shahbaz Aman Department of Dermatology,
ULTRASTRUCTURAL LOCALIZATION OF IMMUNOGLOBULINS IN BULLOUS PEMPHIGOID SKIN
 THE JOUIINAL OF INVJISTIGATJVE DBRMATOLOG~, 64:220-227, 1975 Copyright@ 1975 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 64, No.4 Printed in U.S.A. ULTRASTRUCTURAL LOCALIZATION OF IMMUNOGLOBULINS IN BULLOUS PEMPHIGOID
THE JOUIINAL OF INVJISTIGATJVE DBRMATOLOG~, 64:220-227, 1975 Copyright@ 1975 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 64, No.4 Printed in U.S.A. ULTRASTRUCTURAL LOCALIZATION OF IMMUNOGLOBULINS IN BULLOUS PEMPHIGOID
Bullous pemphigoid (BP) is the most common autoimmune. ActaDV ActaDV
 6 CLINICAL REPORT Diagnostic Value of Linear Fluorescence Along the Basement Membrane of Sweat Gland Ducts in Bullous Pemphigoid Işın SINEM BAĞCI,, Orsolya N. HORVÁTH, Enno SCHMIDT,, Thomas RUZICKA and
6 CLINICAL REPORT Diagnostic Value of Linear Fluorescence Along the Basement Membrane of Sweat Gland Ducts in Bullous Pemphigoid Işın SINEM BAĞCI,, Orsolya N. HORVÁTH, Enno SCHMIDT,, Thomas RUZICKA and
Case Rep Dermatol 2009;1:66 70 DOI: / Key Words Coma Blister Barbiturate Overdose Meningoencephalitis
 66 Coma Blisters Joana Rocha a Teresa Pereira a Filipa Ventura a Fernando Pardal b Celeste Brito a Departments of a Dermatology and b Pathology, Hospital de São Marcos, Braga, Portugal Key Words Coma Blister
66 Coma Blisters Joana Rocha a Teresa Pereira a Filipa Ventura a Fernando Pardal b Celeste Brito a Departments of a Dermatology and b Pathology, Hospital de São Marcos, Braga, Portugal Key Words Coma Blister
2018 Oregon Dental Conference Course Handout Denis Lynch, DDS, PhD
 2018 Oregon Dental Conference Course Handout Denis Lynch, DDS, PhD Course 9148: Diagnosis and Treatment of Recurrent Oral Ulcers Friday, April 6 9 am - 12 pm Diagnosis and Treatment of Recurrent Oral Ulcers
2018 Oregon Dental Conference Course Handout Denis Lynch, DDS, PhD Course 9148: Diagnosis and Treatment of Recurrent Oral Ulcers Friday, April 6 9 am - 12 pm Diagnosis and Treatment of Recurrent Oral Ulcers
Clinical application of a new nephelometric technique
 J Clin Pathol 1983;36:793-797 Clinical application of a new nephelometric technique to measure complement activation D VERGAN, L BEVS, BA NASARUDDN, G MEL-VERGAN,* DEH TEE From the Departments ofmmunology
J Clin Pathol 1983;36:793-797 Clinical application of a new nephelometric technique to measure complement activation D VERGAN, L BEVS, BA NASARUDDN, G MEL-VERGAN,* DEH TEE From the Departments ofmmunology
Acquired and Inherited Bullous Diseases
 Acquired and Inherited Bullous Diseases Erin Wei MD Brigham and Women s Hospital, Department of Dermatology Instructor, Harvard Medical School Director, Bullous Disease Clinic No disclosures Conflict of
Acquired and Inherited Bullous Diseases Erin Wei MD Brigham and Women s Hospital, Department of Dermatology Instructor, Harvard Medical School Director, Bullous Disease Clinic No disclosures Conflict of
MESACUP BP180 ELISA Kit
 Semi-quantitative test kit for anti-bp180 antibodies ELISA Kit for measuring anti BP180 antibodies MESACUP BP180 ELISA Kit CONTENTS INTENDED USE... 1 SUMMARY AND EXPLANATION... 1 PRINCIPLE... 1 BRIEF ASSAY
Semi-quantitative test kit for anti-bp180 antibodies ELISA Kit for measuring anti BP180 antibodies MESACUP BP180 ELISA Kit CONTENTS INTENDED USE... 1 SUMMARY AND EXPLANATION... 1 PRINCIPLE... 1 BRIEF ASSAY
Original Article ABSTRACT
 Original Article doi: 10.5146/tjpath.2015.01345 Utility of Direct Immunofluorescence Studies in Subclassification of Autoimmune Sub-Epidermal Bullous Diseases: A 2-Year Study in a Tertiary Care Hospital
Original Article doi: 10.5146/tjpath.2015.01345 Utility of Direct Immunofluorescence Studies in Subclassification of Autoimmune Sub-Epidermal Bullous Diseases: A 2-Year Study in a Tertiary Care Hospital
Pemphigus foliaceus: a clinical study of 32 cases in Hong Kong 32
 H.K. Dermatol. Venereol. Bull. (2004) 12, 126-132 Original Article Pemphigus foliaceus: a clinical study of 32 cases in Hong Kong 32 This is a cross-sectional, retrospective study of 32 Hong Kong Chinese
H.K. Dermatol. Venereol. Bull. (2004) 12, 126-132 Original Article Pemphigus foliaceus: a clinical study of 32 cases in Hong Kong 32 This is a cross-sectional, retrospective study of 32 Hong Kong Chinese
Original Article. Direct Immunofluorescence in Clinically Diagnosed Oral Lichen Planus
 JOMP Journal of Oral Medicine and Pain Original Article pissn 2288-9272 eissn 2383-8493 J Oral Med Pain 2016;41(1):16-20 http://dx.doi.org/10.14476/jomp.2016.41.1.16 Direct Immunofluorescence in Clinically
JOMP Journal of Oral Medicine and Pain Original Article pissn 2288-9272 eissn 2383-8493 J Oral Med Pain 2016;41(1):16-20 http://dx.doi.org/10.14476/jomp.2016.41.1.16 Direct Immunofluorescence in Clinically
Differentiating Anti-Lamina Lucida and Anti-Sublamina Densa Anti BMZ Antibodies by Indirect Immunofluorescence on 1.0 M Sodium Chloride-Separated Skin
 0022-202X/84/8202-0 139$02.00/ 0 THE JOURNAL O F INVESTIGATIVE Dlli!MATO LOGY, 82:139-144, 1984 Copyright I 984 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 82, No.2 Printed in U.S.A. Differentiating Anti-Lamina
0022-202X/84/8202-0 139$02.00/ 0 THE JOURNAL O F INVESTIGATIVE Dlli!MATO LOGY, 82:139-144, 1984 Copyright I 984 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 82, No.2 Printed in U.S.A. Differentiating Anti-Lamina
Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal Vol. 6 No 1: 14, June 2010
 Wells Syndrome H. Gammaz, H. Amer, A. Adly and S. Mahmoud Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal 6 (1): 14 Al-Haud Al-Marsoud Hospital, Cairo, Egypt e-mail: hananderma@hotmail.com Submitted: April 15, 2010
Wells Syndrome H. Gammaz, H. Amer, A. Adly and S. Mahmoud Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal 6 (1): 14 Al-Haud Al-Marsoud Hospital, Cairo, Egypt e-mail: hananderma@hotmail.com Submitted: April 15, 2010
AUTOIMMUNE BLISTERING DISEASES; WINDOW TO SYSTEMIC DISEASE
 AUTOIMMUNE BLISTERING DISEASES; WINDOW TO SYSTEMIC DISEASE Ron Feldman, MD, PhD Assistant Professor of Dermatology Emory University ron.j.feldman@emory.edu Disclosures I have no conflict of interest to
AUTOIMMUNE BLISTERING DISEASES; WINDOW TO SYSTEMIC DISEASE Ron Feldman, MD, PhD Assistant Professor of Dermatology Emory University ron.j.feldman@emory.edu Disclosures I have no conflict of interest to
Study of early diagnosis of various vesiculobullous lesions of the skin using histopathology
 Original article: Study of early of various vesiculobullous lesions of the skin using histopathology Dr Sachin Parhe* Department of Pathology, DVVPF s Medical College & Hospital, Ahmednagar -414111. Corresponding
Original article: Study of early of various vesiculobullous lesions of the skin using histopathology Dr Sachin Parhe* Department of Pathology, DVVPF s Medical College & Hospital, Ahmednagar -414111. Corresponding
B. Autoimmune blistering diseases
 Go Back to the Top To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details formation immediately above the basal layer. The dermal papillae, which are covered by basal cells in the single layer that is left in
Go Back to the Top To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details formation immediately above the basal layer. The dermal papillae, which are covered by basal cells in the single layer that is left in
DERMATOLOGY VOLUME 40 NUMBER 5 PART 1 MAY 1999
 CONTINUING MEDICAL EDUCATION The new pemphigus variants Journal of the American Academy of DERMATOLOGY VOLUME 40 NUMBER 5 PART 1 MAY 1999 Neha D. Robinson, MD, a Takashi Hashimoto, MD, b Masayuki Amagai,
CONTINUING MEDICAL EDUCATION The new pemphigus variants Journal of the American Academy of DERMATOLOGY VOLUME 40 NUMBER 5 PART 1 MAY 1999 Neha D. Robinson, MD, a Takashi Hashimoto, MD, b Masayuki Amagai,
Pharmacologyonline 1: 1-6 (2010) Case Report Ravishankar and Hiremath CIPROFLOXACIN INDUCED BULLOUS PEMPHIGOID: A CASE REPORT
 CIPROFLOXACIN INDUCED BULLOUS PEMPHIGOID: A CASE REPORT Ravishankar AC 1*, Hiremath SV 1 1 Dept of Pharmacology and Pharmacotherapeutics, JN Medical College, Belgaum, India. Summary Bullous pemphigoid
CIPROFLOXACIN INDUCED BULLOUS PEMPHIGOID: A CASE REPORT Ravishankar AC 1*, Hiremath SV 1 1 Dept of Pharmacology and Pharmacotherapeutics, JN Medical College, Belgaum, India. Summary Bullous pemphigoid
Immunoglobulin Binding in Cardiomyopathic Hearts
 Immunoglobulin Binding in Cardiomyopathic Hearts By SUNIL K. DAS, M.D., JEFFERY P. CALLEN, B.A., VERNON N. DODSON, M.D., AND JAMES T. CASSIDY, M.D. SUMMARY Bound gamma globulin was demonstrated by the
Immunoglobulin Binding in Cardiomyopathic Hearts By SUNIL K. DAS, M.D., JEFFERY P. CALLEN, B.A., VERNON N. DODSON, M.D., AND JAMES T. CASSIDY, M.D. SUMMARY Bound gamma globulin was demonstrated by the
Effect of Substrate on Indirect Immunofluorescence Test for Canine Pemphigus Foliaceus
 Vet Pathol33:332336 (1996) Effect of Substrate on Indirect Immunofluorescence Test for Canine Pemphigus Foliaceus T. IWASAKI, M. SHIMIZU, H. OBATA, M. OGATA, M. NAGATA, T. YANAI, H. KITAGAWA, AND Y. SASAKI
Vet Pathol33:332336 (1996) Effect of Substrate on Indirect Immunofluorescence Test for Canine Pemphigus Foliaceus T. IWASAKI, M. SHIMIZU, H. OBATA, M. OGATA, M. NAGATA, T. YANAI, H. KITAGAWA, AND Y. SASAKI
Index. in tissue, 87-89
 ANA titers, 79-84 Adult atopic dermatitis, 239 Allergens, contact dermatitis, 253 Allergic contact dermatitis Acontact sensitivity, cellular participants in, 258 factors influencing incidence of, 254 'hardening',
ANA titers, 79-84 Adult atopic dermatitis, 239 Allergens, contact dermatitis, 253 Allergic contact dermatitis Acontact sensitivity, cellular participants in, 258 factors influencing incidence of, 254 'hardening',
MUCOCUTANEOUS LESIONS Normal structures in epithelium cell adhesion to each other and to underlying connective tissue:
 ORAL DERMATOSES AND MUCOSAL/GINGIVAL LESIONS MUCOCUTANEOUS LESIONS Normal structures in epithelium cell adhesion to each other and to underlying connective tissue: Diagram taken from: Oral and Maxillofacial
ORAL DERMATOSES AND MUCOSAL/GINGIVAL LESIONS MUCOCUTANEOUS LESIONS Normal structures in epithelium cell adhesion to each other and to underlying connective tissue: Diagram taken from: Oral and Maxillofacial
CLINCOPATHOLOGICAL CASE
 CLINCOPATHOLOGICAL CASE Generalized vesiculo-bullous and pustular eruption in an adult man Hassab El-Naby H, MD, El-Khalawany M, MD Department of Dermatology, Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt CLINICAL
CLINCOPATHOLOGICAL CASE Generalized vesiculo-bullous and pustular eruption in an adult man Hassab El-Naby H, MD, El-Khalawany M, MD Department of Dermatology, Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt CLINICAL
Paul K. Shitabata, M.D. Dermatopathology Institute
 Paul K. Shitabata, M.D. Dermatopathology Institute Technical Considerations Storage of slides at room temperature
Paul K. Shitabata, M.D. Dermatopathology Institute Technical Considerations Storage of slides at room temperature
BULLOUS SYSTEMIC lupus erythematosus
 OBSERVATION Bullous Systemic Lupus Erythematosus With Autoantibodies Recognizing Multiple Skin Basement Membrane Components, Bullous Pemphigoid Antigen 1, Laminin-5, Laminin-6, and Type VII Collagen Lawrence
OBSERVATION Bullous Systemic Lupus Erythematosus With Autoantibodies Recognizing Multiple Skin Basement Membrane Components, Bullous Pemphigoid Antigen 1, Laminin-5, Laminin-6, and Type VII Collagen Lawrence
University of Groningen. Acantholysis in pemphigus van der Wier, Gerda
 University of Groningen Acantholysis in pemphigus van der Wier, Gerda IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the
University of Groningen Acantholysis in pemphigus van der Wier, Gerda IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the
In contrast to the flaccid blisters, erosions, and crusted. disease that occurs during the second or third trimester of
 Pemphigus and Pemphigoid as Paradigms of Organ-specific, Autoantibody-mediated Diseases John R. Stanley Dermatology Branch, National Cancer Institute, National Institutes ofhealth, Bethesda, Maryland 20892
Pemphigus and Pemphigoid as Paradigms of Organ-specific, Autoantibody-mediated Diseases John R. Stanley Dermatology Branch, National Cancer Institute, National Institutes ofhealth, Bethesda, Maryland 20892
REF: Chap 1 (Pemphigus vulgaris/etiology and
 Chapter 1: Vesiculobullous Diseases Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Intercellular deposits of IgG are consistently found in oral epithelium in which of the following? a. Cicatricial pemphigoid b. Lichen planus
Chapter 1: Vesiculobullous Diseases Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Intercellular deposits of IgG are consistently found in oral epithelium in which of the following? a. Cicatricial pemphigoid b. Lichen planus
ANS: C REF: Chap 1 (Pemphigus vulgaris/etiology and pathogenesis), p 11
 Chapter 1: Vesiculobullous Diseases Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Intercellular deposits of IgG are consistently found in oral epithelium in which of the following? a. Cicatricial pemphigoid b. Lichen planus
Chapter 1: Vesiculobullous Diseases Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Intercellular deposits of IgG are consistently found in oral epithelium in which of the following? a. Cicatricial pemphigoid b. Lichen planus
Complement Antibodies and Proteins
 COMPLEMENT ANTIBODIES AND PROTEINS FROM CEDARLANE INTERNATIONAL VERSION www.cedarlanelabs.com For over 50 years, Cedarlane has provided complement related products to the life science research and diagnostic
COMPLEMENT ANTIBODIES AND PROTEINS FROM CEDARLANE INTERNATIONAL VERSION www.cedarlanelabs.com For over 50 years, Cedarlane has provided complement related products to the life science research and diagnostic
Complement Fixation by Pemphigus Antibody. I. In Vitro Fixation to Organ and Tissue Culture Skin
 0022-202X/84/ 8205-0506$02.00/ 0 T!! E JOUHNA L OF I NVESTIGATIVE D ERMATOLOGY, 82:506-510, 1984 Copyri ght 1984 by T he Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 82, No. 5 Printed i11 U.S. A. Complement Fixation by
0022-202X/84/ 8205-0506$02.00/ 0 T!! E JOUHNA L OF I NVESTIGATIVE D ERMATOLOGY, 82:506-510, 1984 Copyri ght 1984 by T he Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 82, No. 5 Printed i11 U.S. A. Complement Fixation by
Mucous membrane pemphigoid presenting as bleeding gums and burning sensation of mouth: a case report
 Archives of Orofacial Sciences www.dental.usm.my/aos/ Penerbit Universiti Sains Malaysia. 2018 print ISSN: 1823-8602 e-issn: 2231-7163 Case Report Arch Orofac Sci (2018), 13(1): 45-49. Mucous membrane
Archives of Orofacial Sciences www.dental.usm.my/aos/ Penerbit Universiti Sains Malaysia. 2018 print ISSN: 1823-8602 e-issn: 2231-7163 Case Report Arch Orofac Sci (2018), 13(1): 45-49. Mucous membrane
test. It appeared that the MHA-TP test could be
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Mar. 1983, p. 405-409 0095-1137/83/030405-05$02.00/0 Copyright 1983, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 17, No. 3 Reactivity of Microhemagglutination, Fluorescent
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Mar. 1983, p. 405-409 0095-1137/83/030405-05$02.00/0 Copyright 1983, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 17, No. 3 Reactivity of Microhemagglutination, Fluorescent
Antibodies against reticulin
 nn. rheum. Dis. (1977), 36, Supplement p. 51 ntibodies against reticulin and collagen E. J. HOLBOROW, W. PGE FULK, HELEN K. BERD, ND L. B. CONOCHIE From the MRC Rheumatism Unit, Canadian Red Cross Memorial
nn. rheum. Dis. (1977), 36, Supplement p. 51 ntibodies against reticulin and collagen E. J. HOLBOROW, W. PGE FULK, HELEN K. BERD, ND L. B. CONOCHIE From the MRC Rheumatism Unit, Canadian Red Cross Memorial
Case Report DOI: /ourd Georgia Dermatopathology Associates, Atlanta, Georgia, USA 2
 Case Report DOI: 10.7241/ourd.20143.72 CENTRAL CENTRIFUGAL CICATRICIAL ALOPECIA AMALGAMATED WITH ALOPECIA AREATA: IMMUNOLOGIC FINDINGS Ana Maria Abreu Velez 1, Bruce R. Smoller 2, Michael S. Howard 1 Source
Case Report DOI: 10.7241/ourd.20143.72 CENTRAL CENTRIFUGAL CICATRICIAL ALOPECIA AMALGAMATED WITH ALOPECIA AREATA: IMMUNOLOGIC FINDINGS Ana Maria Abreu Velez 1, Bruce R. Smoller 2, Michael S. Howard 1 Source
DESCRIPTIONS FOR MED 3 ROTATIONS Dermatology A3S
 Regardless of your future field of practice, you will be exposed to a considerable amount of dermatology and this rotation provides you the chance to see a range of skin diseases. You will have the opportunity
Regardless of your future field of practice, you will be exposed to a considerable amount of dermatology and this rotation provides you the chance to see a range of skin diseases. You will have the opportunity
The purpose of this paper is to investigate the. were carried out to determine the immunoglobulin
 Gut, 1974, 15, 284-288 Studies on the nature and significance of connective tissue antibodies in adult coeliac disease and Crohn's disease A. F. N. MAGALHAES, T. J. PETERS, AND WILLIAM F. DOE From the
Gut, 1974, 15, 284-288 Studies on the nature and significance of connective tissue antibodies in adult coeliac disease and Crohn's disease A. F. N. MAGALHAES, T. J. PETERS, AND WILLIAM F. DOE From the
Antibodies Produced by Rabbits Immunized
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Dec. 1971, p. 715-719 Copyright 1971 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 4, No. 6 Printed in U.S.A. Antibodies Produced by Rabbits Immunized ith Visna Virus SEUNG C. KARL AND
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Dec. 1971, p. 715-719 Copyright 1971 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 4, No. 6 Printed in U.S.A. Antibodies Produced by Rabbits Immunized ith Visna Virus SEUNG C. KARL AND
Evidence for an immune complex vasculitis in
 Evidence for an immune complex vasculitis in neonatal necrotising enterocolitis ELIZABETH S GRAY, DAVID J LLOYD, STANLEY S MILLER, ALAN I DAVIDSON, NICOLA J BALCH, CHARLES HW HORNE J Clin Pathol 1981 ;34:759-763
Evidence for an immune complex vasculitis in neonatal necrotising enterocolitis ELIZABETH S GRAY, DAVID J LLOYD, STANLEY S MILLER, ALAN I DAVIDSON, NICOLA J BALCH, CHARLES HW HORNE J Clin Pathol 1981 ;34:759-763
Laboratory Procedure Handout RHEUMATOID FACTORS
 KING ABDULAZIA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF APPLIED MEDICAL SCIENCES DEPARTEMENT OF LABORATORY MEDICAL TECHNOLOGY Laboratory Procedure Handout RHEUMATOID FACTORS RF Latex agglutination for detection of RF INTRODUCTION
KING ABDULAZIA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF APPLIED MEDICAL SCIENCES DEPARTEMENT OF LABORATORY MEDICAL TECHNOLOGY Laboratory Procedure Handout RHEUMATOID FACTORS RF Latex agglutination for detection of RF INTRODUCTION
Title. CitationBritish Journal of Dermatology, 155(5): Issue Date Doc URL. Rights. Type. File Information
 Title Childhood epidermolysis bullosa acquisita with autoa collagen : case report and review of the literature Author(s)Mayuzumi, M.; Akiyama, M.; Nishie, W.; Ukae, S.; Abe CitationBritish Journal of Dermatology,
Title Childhood epidermolysis bullosa acquisita with autoa collagen : case report and review of the literature Author(s)Mayuzumi, M.; Akiyama, M.; Nishie, W.; Ukae, S.; Abe CitationBritish Journal of Dermatology,
Interaction of Complex Polysaccharides with the Complement System: Effect of Calcium Depletion on Terminal Component Consumption
 INFECTION AND IMMUNrrY, Feb. 1975, p. 273-279 Copyright 0 1975 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 11, No. 2 Printed in U.SA. Interaction of Complex Polysaccharides with the Complement System: Effect
INFECTION AND IMMUNrrY, Feb. 1975, p. 273-279 Copyright 0 1975 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 11, No. 2 Printed in U.SA. Interaction of Complex Polysaccharides with the Complement System: Effect
Complement-fixing ability of antinuclear
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1971), 30, 640 Complement-fixing ability of antinuclear factors Studies in adult and juvenile rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus P. M. COSSIO, R. M. ARANA, 0. GARCIA
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1971), 30, 640 Complement-fixing ability of antinuclear factors Studies in adult and juvenile rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus P. M. COSSIO, R. M. ARANA, 0. GARCIA
Case Report Ocular Involvement and Blindness Secondary to Linear IgA Dermatosis
 Ophthalmology Volume 2010, Article ID 280396, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2010/280396 Case Report Ocular Involvement and Blindness Secondary to Linear IgA Dermatosis Cinthya Ramos-Castellón, 1 Gabriela Ortiz-Nieva,
Ophthalmology Volume 2010, Article ID 280396, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2010/280396 Case Report Ocular Involvement and Blindness Secondary to Linear IgA Dermatosis Cinthya Ramos-Castellón, 1 Gabriela Ortiz-Nieva,
however, and the present communication is concerned with some of
 THE AGGLUTINATION OF HUMAN ERYTHROCYTES MODIFIED BY TREATMENT WITH NEWCASTLE DISEASE AND INFLUENZA VIRUS' ALFRED L. FLORMAN' Pediatric Service and Division of Bacteriology, The Mount Sinai Hospital, New
THE AGGLUTINATION OF HUMAN ERYTHROCYTES MODIFIED BY TREATMENT WITH NEWCASTLE DISEASE AND INFLUENZA VIRUS' ALFRED L. FLORMAN' Pediatric Service and Division of Bacteriology, The Mount Sinai Hospital, New
