For more information about how to cite these materials visit
|
|
|
- Gervase Garrett
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Author(s): University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Cell and Developmental Biology License:Unless otherwise noted, the content of this course material is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial Share Alike 3.0 License. We have reviewed this material in accordance with U.S. Copyright Law and have tried to maximize your ability to use, share, and adapt it. The citation key on the following slide provides information about how you may share and adapt this material. Copyright holders of content included in this material should contact open.michigan@umich.edu with any questions, corrections, or clarification regarding the use of content. For more information about how to cite these materials visit Any medical information in this material is intended to inform and educate and is not a tool for self-diagnosis or a replacement for medical evaluation, advice, diagnosis or treatment by a healthcare professional. Please speak to your physician if you have questions about your medical condition. Viewer discretion is advised: Some medical content is graphic and may not be suitable for all viewers.
2 CitationKey formoreinformationsee: Use+Share+Adapt {Contentthecopyrightholder,author,orlawpermitsyoutouse,shareandadapt.} PublicDomain Government:WorksthatareproducedbytheU.S.Government.(17 USC 105) PublicDomain Expired:Worksthatarenolongerprotectedduetoanexpiredcopyrightterm. PublicDomain SelfDedicated:Worksthatacopyrightholderhasdedicatedtothepublicdomain. CreativeCommons ZeroWaiver CreativeCommons AttributionLicense CreativeCommons AttributionShareAlikeLicense CreativeCommons AttributionNoncommercialLicense CreativeCommons AttributionNoncommercialShareAlikeLicense GNU FreeDocumentationLicense MakeYourOwnAssessment {ContentOpen.Michiganbelievescanbeused,shared,andadaptedbecauseitisineligibleforcopyright.} PublicDomain Ineligible:WorksthatareineligibleforcopyrightprotectionintheU.S.(17 USC 102(b))*lawsin yourjurisdictionmaydiffer {ContentOpen.MichiganhasusedunderaFairUsedetermination.} FairUse:UseofworksthatisdeterminedtobeFairconsistentwiththeU.S.CopyrightAct.(17 USC 107)*lawsinyour jurisdictionmaydiffer OurdeterminationDOESNOTmeanthatallusesofthis3rd-partycontentareFairUsesandweDONOTguaranteethat youruseofthecontentisfair. Tousethiscontentyoushoulddoyourownindependentanalysis todeterminewhetherornotyourusewillbefair.
3 CellsandTissuesSequence MedicalHistology IntegumentarySystem, Glands/mammarygland Fall,2008 CellandDevelopmentalBiology
4 1.Skin: TheIntegument EpidermisandDermis Hypodermis(a.k.a.superficialfascia) 2.Appendages:Specializationofepidermis A.Pilosebaceousapparatus Hair Sebaceousglands Arrectopilimuscle B.Sweatglands Eccrinesweatglands Apocrine(odoriferous)sweatglands C. Nail Mammarygland
5 Theskinconsistsof epidermisanddermis andisthelargest organinthebody, accountingforabout 16%ofthebody weight. UMMedicalSchoolAnatomyLaboratoryManual
6 Functionsofskin 1.Protection(fromabrasion,friction,infection,UVrays) Keratin,melanin 2.PermeabilityBarrier(preventionofextremewaterloss) Keratin,lipid,sebum 3.Thermoregulation Sweatglands,bloodvessels,fat 4.SensoryPerception Freeandencapsulatednerveendings 5.ImmunologicDefense Keratinocytes,Langerhanscells 6.Dermatoglyphics(fingerprints)
7 MichiganMedicalSchoolHistologySlideCollection Skin Epidermis: Keratinized,strat.sq. epithelium Dermis: Denseirregularct. TypeIIIand TypeIcollagen Elasticfibers SweatGlands: Eccrineand Apocrineglands Hypodermis(superficialfascia): Fattyconn.Tissue
8 CellsoftheEpidermis Keratinocytes(80%) Melanocytes(5-10%) Langerhanscells(5%) Merkelcells(<1%) MichiganMedicalSchoolHistologySlideCollection
9 CellularLayersoftheEpidermis Epidermis Epidermis Dermis Dermis MichiganMedicalSchoolHistologySlideCollection Weiss,L.,CellandTissueBiology6 th ed.p.543
10 CellsoftheStratumBasale St.Spinosum St.Basale Dermis Source Undetermined
11 Stratumspinosum Source Undetermined
12 BlisteringSkinDisorders Pemphigus:Separation ofepidermalcellsfrom eachother(acantholysis) causedbylossof desmosomefunctions. Bullouspemphigoid: Separationofepidermis fromthedermisdueto blisteringinthebasement membranecausedby lossofanchoring filamentsand hemidesmosomes. Source Undetermined
13 StratumGranulosum KeratohyalinGranules(KG) Histidine-richprotein(filaggrin:filamentaggregating proteinthatcross-linkskeratin) Polysaccharidesandlipids Membrane-coatinggranules(MCG) (a.k.a.lamellargranules,odlandbodies) Primaryintercellularlipidbarriertowater-ceramide cross-linkscellmembranes.
14 KeratohyalinGranules Weiss,L.,CellandTissueBiology6 th ed.p.549
15 MembraneCoatingGranules Primary intercellular barriertowater Weiss,CellandTissueBilogy6 th ed.p.547
16 Stratumcorneum 15-20layersofnonnucleatedflattenedcells filledwithkeratainfilaments. Keratinfilamentsarecrosslinkedwithfilaggrin. Thekeratin-filaggrin depositedontheinsideof theplasmamembraneform athickenedcellenvelope. Source Undetermined
17 Thickandthinskin Source Undetermined Bluearrows:Cellsofthestratumgranulosum
18 Melanocytes Skincolor Redbloodcellsinthedermalvascularbeds. Carotenesfromexogenousfoodsstoredinfatty tissues. Hemoglobinandbilirubin(endogenousdegradation products). Melanin(pigmentproducedbymelanocytes)
19 Melanocytes (neuralcrestorigin) MichiganMedicalSchoolHistologySlideCollection Rhodin,Histology,pp.485
20 MelanocytesproduceMelanin Melanin: Eumelanin Pheomelanin Tyrosinase(deficiency:albinism) Tyrosine 3,4-dihydroxyphenyalanine(dopa) dopaquinone Melanin
21 Epidermal- melaninunit Cytocrinesecretion Source Undetermined
22 Ross/Romrell,Histology2 nd ed.p.356
23 Pigmentdistributioninlight(left)anddark(right)skin MichiganMedicalSchoolHistologySlideCollection MichiganMedicalSchoolHistologySlideCollection
24 Merkel scell Langerhanscell Bonemarrowderived Bind,processand presentantigentotlymphocytes Roleinimmunologic skinreactions. Fawcett,Histology,pp.536
25 ProliferationandMaturationofEpithelialCells Source Undetermined
26 Source Undetermined Psoriasis
27 Dermis PapillaryDermis ReticularDermis Containsbloodandlymphaticvessels,nerves, hairfollicles,sebaceousglands,arrectopili muscle,andsweat(eccrineandapocrine) glands Hypodermis (superficialfasciawithfatcells)
28 EpithelialPegsandDermalPapillae Source Undetermined Source Undetermined
29 Papillary(PL)andReticular(RL)Dermis TypeIIICollagen Elasticfibers(EF) Source Undetermined TypeICollagen
30 PapillaryDermis housesbloodvessels,nerveendings,etc. Epidermis Papillarydermis Reticulardermis MichiganMedicalSchoolHistologySlideCollection SourceUndetermined
31 Dermisandskincirculation WheaterFig.9.18 Wheater 9.18
32 MichiganMedicalSchoolHistologySlideCollection MichiganMedicalSchoolHistologySlideCollection Sebaceous gland Arrecto pile muscle Pilosebaceous apparatus hair,sebaceousgland andarrectopilemuscle hair Swaet gland
33 Hairfollicle:hairbulbandhairshaft (B,C) (A) Young/HeathWheater shistology4 th ed.p.167 (D) Ross/Romrell,Histology2 nd ed.p.361 SourceUndetermined
34 GrowthCycleoftheHairFollicle Weiss, pg. 562 testosterone 5αdihydrotestosterone, whichbindsthe intracellularreceptorsand Inhibitsthemetabolismof condemnedfollicles. 5α-reductase(?)
35 Source Undetermined Pilo-sebaceousApparatus
36 Source Undetermined HolocrineSecretion
37 ModeofSecretion Merocrine(Exocytosis) Almostallexocrineglands,includingeccrine andapocrinesweatglands. Apocrine(somepartsofcellsaresecreted) Mammaryglands(lipidsecretion) Holocrine(wholecellsaresecreted) Sebaceousglands Source Undetermined
38 Tsaitgaist,,Wikipedia Hairfollicle andit s associated structures
39 EccrineSweatGlands MichiganMedicalSchoolHistologySlideCollection
40 Secretoryportion Eccrine Sweat Gland Myoepithelialcells Ducts Secretoryportion MichiganMedicalSchoolHistologySlideCollection
41 Source Undetermined MyoepithelialCells
42 ApocrineSweatGlands MichiganMedicalSchoolHistologySlideCollection
43 MichiganMedicalSchoolHistologySlideCollection ApocrineSweatGlands Myoepithelialcells
44 SecretoryPortionsof EccrineandApocrineSweatGlands MichiganMedicalSchoolHistologySlideCollection
45 Source Undetermined
46 GlandularLobulesandLobes ManyLobulesformaLobe. Source Undetermined Adapted and modified from Leson TS, Leson CR, Paparo AA: Text/Atlas of Histology. Philadelphia, WB Saunders, 1988
47 Gray s Anatomy, Wikimedia Commons US Federal Government
48 ChangeinMammaryGlandAlveoliandDucts Inactive:Noalveoliand undifferentiatedterminal ducts. Active(duringpregnancy): Proliferationand differentiationofalveoli. Active(lactating):Secretion ofmilkandaccumulationin alveolarlumen. Source Undetermined
49 Inactiveandactivemammaryglands Inactivegland(left): Lobulesarearranged sparselyandeachlobule consistsofmainlybluntly endingductswithno secretoryalveoli. Activegland(right): Lobulesarewelldeveloped andpackthegland.ineach lobule,secretoryalveolihave formedandtheirlumensare highlydilated. MichiganMedicalSchoolHistologySlideCollection(allimages)
50 Thestromaofthemammarygland Lactiferous duct InterlobularCT IntralobularCT MichiganMedicalSchoolHistologySlideCollection Source Undetermined Lobule Theloose,morecellularandlessfibrous,intralobular connectivetissuemakesthestromadistensibleforthe hypertrophyoftheepithelialelementsanddifferentiationofthe alveoli.numerousplasmacells(arrowsabove),whichappear intheintralobularconnectivetissueduringpregnancyand lactation,produceimmunoglobuliniga.igaistakenupbythe epithelialcells,secretedinthemilk,andtransportedtothe infant sintestinewheretheantibodiesresistbacterial infection.
51 Theantibodiesresistentericinfections. Image of mother breastfeeding infant antibodies removed Source Undetermined
52 Nipple-Lactiferousducts Lactiferousducts 15-20independentlactiferousducts, eachdrainingoneofthelobesofthe gland,openatthetipofthenipple. Withinthenipple,eachductisslightly dilatedtoformalactiferoussinus(inset). Gray s Anatomy, Wikimedia Commons MichiganMedicalSchoolHistologySlideCollection
53 #265(nipple)Lactiferousducts Thelactiferousductislined byasuperficiallayerof cuboidalepithelialcellsand abasallayerof myoepithelialcells(arrows). MichiganMedicalSchoolHistologySlideCollection
54 LearningObjectives Beabletoidentifyprincipallayersoftheskin(epidermis,dermisand hypodermis)atthelightmicroscopelevelandknowthemajorfunctionsofeach layer. Beabletoidentifythestrataoftheepidermisinthickandthinskinandknowthe majorcellulareventsthattakeplaceineachlayerintheprocessof keratinization. Beabletoidentifythecellsindifferentlayeroftheepidermisattheelectron microscopelevelbyrecognizingcharacteristicorganellesandstructurespresent ineachlayer. Beabletorecognizemelanocytesandknowtheprocessofpigmentformationin theskin. Beabletoidentifyeccrineandapocrinesweatglandsatthelightmicroscope levelanddistinguishductalandsecretoryportions. Beabletoidentifythecomponentsofthepilosebacousapparatusandknowthe structuralrelationshipbetweeneachcomponentandtheepidermis. Beabletoidentifythemammarygland,byrecognizingitsstructuralcomponents (lactiferousducts,alveoli,lobules,thestromalconnectivetissue),andknowthe histologicaldifferencesinactiveandinactiveglands.
55 AdditionalSourceInformation formoreinformationsee: Slide 5: UM Medical School Anatomy Laboratory Manual Slide 7: Michigan Medical School Histology Slide Collection Slide 8: Michigan Medical School Histology Slide Collection Slide 9: Michigan Medical School Histology Slide Collection ; Source Undetermined Slide 10: Source Undetermined Slide 11: Source Undetermined Slide 12: Source Undetermined Slide 14: Source Undetermined Slide 15: Source Undetermined Slide 16: Source Undetermined Slide 17: Source Undetermined Slide 19: Michigan Medical School Histology Slide Collection ; Source Undetermined; Slide 21: Source Undetermined Slide 22: Source Undetermined; Slide 23: Michigan Medical School Histology Slide Collection ; Source Undetermined Slide 24: Source Undetermined Slide 25: Source Undetermined Slide 26: Source Undetermined Slide 28: Source Undetermined Slide 29: Source Undetermined Slide 30: Michigan Medical School Histology Slide Collection ; Source Undetermined Slide 31: Wheater 9.18 Slide 32: Michigan Medical School Histology Slide Collection Slide 33: Sources Undetermined Slide 34: Weiss, pg. 562 Slide 35: Source Undetermined
56 Slide 36: Source Undetermined Slide 37: Source Undetermined Slide 38: Tsaitgaist, Wikipeda, Slide 39: Michigan Medical School Histology Slide Collection Slide 40: Michigan Medical School Histology Slide Collection Slide 41: Source Undetermined Slide 42: Michigan Medical School Histology Slide Collection Slide 43: Michigan Medical School Histology Slide Collection Slide 44: Michigan Medical School Histology Slide Collection ; Source Undetermined Slide 45: Source Undetermined Slide 46: Adapted and modified from Leson TS, Leson CR, Paparo AA: Text/Atlas of Histology. Philadelphia, WB Saunders, 1988; Source Undetermined Slide 47: Gray s Anatomy, Wikimedia Commons, U.S. Federal Government Slide 48: Source Undetermined Slide 49: Michigan Medical School Histology Slide Collection Slide 50: Michigan Medical School Histology Slide Collection ; Source Undetermined Slide 51: Source Undetermined; Slide 52: Gray s Anatomy, Wikimedia Commons, Michigan Medical School Histology Slide Collection Slide 53: Michigan Medical School Histology Slide Collection
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author: John Williams, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author: John Williams, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author: Michael Jibson, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Author: Michael Jibson, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Prachi Agarwal M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Prachi Agarwal M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author: Michael Jibson, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Author: Michael Jibson, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Gerald Abrams, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Gerald Abrams, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author: Jonathan Trobe, MD, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
Author: Jonathan Trobe, MD, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Gerald Abrams, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Gerald Abrams, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Gerald Abrams, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Gerald Abrams, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author: Michael Jibson, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Author: Michael Jibson, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Kathleen A. Stringer, Pharm. D, 2011 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Kathleen A. Stringer, Pharm. D, 2011 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology
 Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Louis D Alecy, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Louis D Alecy, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Arno Kumagai, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Arno Kumagai, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author: John Williams, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author: John Williams, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Cell and Developmental Biology License: Unless otherwise noted, the content of this course material is licensed under a Creative Commons
Author(s): University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Cell and Developmental Biology License: Unless otherwise noted, the content of this course material is licensed under a Creative Commons
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Silas P. Norman, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Silas P. Norman, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Louis D Alecy, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Louis D Alecy, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Rachel Glick, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Rachel Glick, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Louis D Alecy, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Louis D Alecy, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology
 Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Michael Heung, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Michael Heung, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Rachel Glick, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Rachel Glick, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology
 Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology
 Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Rajesh Mangrulkar, M.D., 2011 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Rajesh Mangrulkar, M.D., 2011 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Louis D Alecy, D.M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License:
Author(s): Louis D Alecy, D.M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License:
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): John G. Younger, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Author(s): John G. Younger, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
The Integumentary System
 The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep to it Two distinct regions Epidermis Dermis PHL 212 1 Function
The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep to it Two distinct regions Epidermis Dermis PHL 212 1 Function
Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology
 Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author: Thomas Sisson, MD, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author: Thomas Sisson, MD, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Kerby Shedden, Ph.D., 2010 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Kerby Shedden, Ph.D., 2010 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Louis D Alecy, D.M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License:
Author(s): Louis D Alecy, D.M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License:
Document Title: The Management of Acute Ischemic Stroke & TIA
 Project: Ghana Emergency Medicine Collaborative Document Title: The Management of Acute Ischemic Stroke & TIA Author(s): Rashmi U. Kothari, M.D. (KCMS/MSU), 2012 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material
Project: Ghana Emergency Medicine Collaborative Document Title: The Management of Acute Ischemic Stroke & TIA Author(s): Rashmi U. Kothari, M.D. (KCMS/MSU), 2012 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material
Integument. Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Melanoma. Largest organ 30% of all clinical diagnoses 1/3 of all tumors
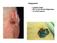 Squamous Cell Carcinoma Integument Largest organ 30% of all clinical diagnoses 1/3 of all tumors Melanoma Epidermis Stratified, squamous keratinized epithelium Derived from ectoderm Appendages hair follicles
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Integument Largest organ 30% of all clinical diagnoses 1/3 of all tumors Melanoma Epidermis Stratified, squamous keratinized epithelium Derived from ectoderm Appendages hair follicles
Cell Types in Epidermis
 Epidermis Stratified, squamous keratinized epithelium Appendages hair follicles nails sweat glands sebaceous glands mammary glands Dermis Dense, irregular connective tissue Hypodermis Superficial fascia
Epidermis Stratified, squamous keratinized epithelium Appendages hair follicles nails sweat glands sebaceous glands mammary glands Dermis Dense, irregular connective tissue Hypodermis Superficial fascia
Skin. Kristine Krafts, M.D.
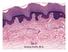 Skin Kristine Krafts, M.D. Skin Lecture Objectives Describe the functions of skin. Describe the structure, location and function of the cell types found in epidermis: keratinocytes, melanocytes, Langerhans
Skin Kristine Krafts, M.D. Skin Lecture Objectives Describe the functions of skin. Describe the structure, location and function of the cell types found in epidermis: keratinocytes, melanocytes, Langerhans
Lab 7: Integumentary System Hamilton ANSWERS TO PRE- LAB ASSIGNMENTS
 Lab 7: Integumentary System Hamilton ANSWERS TO PRE- LAB ASSIGNMENTS Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. a. epidermis b. dermis c. hypodermis d. adipose tissue e. hair f. sebaceous gland g. sweat gland 2. a Pre-Lab
Lab 7: Integumentary System Hamilton ANSWERS TO PRE- LAB ASSIGNMENTS Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. a. epidermis b. dermis c. hypodermis d. adipose tissue e. hair f. sebaceous gland g. sweat gland 2. a Pre-Lab
Author(s): C. James Holliman, M.D. (Penn State University), 2008
 Project: Ghana Emergency Medicine Collaborative Document Title: Status Epilepticus (SE) Author(s): C. James Holliman, M.D. (Penn State University), 2008 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is
Project: Ghana Emergency Medicine Collaborative Document Title: Status Epilepticus (SE) Author(s): C. James Holliman, M.D. (Penn State University), 2008 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is
Author(s): Rockefeller A. Oteng, M.D., University of Michigan
 Project: Ghana Emergency Medicine Collaborative Document Title: Pulmonary Embolism Part 2 (2012) Author(s): Rockefeller A. Oteng, M.D., University of Michigan License: Unless otherwise noted, this material
Project: Ghana Emergency Medicine Collaborative Document Title: Pulmonary Embolism Part 2 (2012) Author(s): Rockefeller A. Oteng, M.D., University of Michigan License: Unless otherwise noted, this material
Chapter 4 Opener Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 4 Opener Introduction The integumentary system is composed of: Skin Hair Nails Sweat glands Oil glands Mammary glands The skin is the most visible organ of the body Clinicians can tell a lot about
Chapter 4 Opener Introduction The integumentary system is composed of: Skin Hair Nails Sweat glands Oil glands Mammary glands The skin is the most visible organ of the body Clinicians can tell a lot about
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Michael Hortsch, Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Michael Hortsch, Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
11/8/2012. Chapter 6 Part 1 Objectives: Skin = Integument = Cutaneous Membrane. The Structure of Skin. Epidermis
 Chapter 6 Part 1 Objectives: Define organ, and associate the skin as an organ of the integumentary system. List the general functions of the skin. Describe the structure of the layers of the skin. Summarize
Chapter 6 Part 1 Objectives: Define organ, and associate the skin as an organ of the integumentary system. List the general functions of the skin. Describe the structure of the layers of the skin. Summarize
Skin and Body Membranes
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 4 Skin and Body Membranes Slides 4.1 4.32 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Skin and Body Membranes Function
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 4 Skin and Body Membranes Slides 4.1 4.32 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Skin and Body Membranes Function
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author: John Williams, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author: John Williams, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Skin (Integumentary System) Wheater, Chap. 9
 Skin (Integumentary System) Wheater, Chap. 9 Skin (Integument) Consists of skin and associated derivatives Largest organ of body (21 ft 2 ; 9 lbs.; has 11 miles of blood vessels) Functions: Protection
Skin (Integumentary System) Wheater, Chap. 9 Skin (Integument) Consists of skin and associated derivatives Largest organ of body (21 ft 2 ; 9 lbs.; has 11 miles of blood vessels) Functions: Protection
Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology David Shier Jackie Butler Ricki Lewis Created by Dr. Melissa Eisenhauer Head Athletic Trainer/Assistant Professor Trevecca Nazarene University Chapter 6
Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology David Shier Jackie Butler Ricki Lewis Created by Dr. Melissa Eisenhauer Head Athletic Trainer/Assistant Professor Trevecca Nazarene University Chapter 6
ABCD rule. apocrine glands. arrector pili. ceruminous glands. contact dermatitis
 ABCD rule assessing moles: asymmetric, broder irregularity, color, diameter (larger than 6mm) apocrine glands arrector pili sweat glands in the pubic and underarm areas that secrete thicker sweat, that
ABCD rule assessing moles: asymmetric, broder irregularity, color, diameter (larger than 6mm) apocrine glands arrector pili sweat glands in the pubic and underarm areas that secrete thicker sweat, that
Skin Histology. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Skin Histology Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Integumentary system The skin is considered the largest organ of the body Basic Skin Histology The skin is composed of two
Skin Histology Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Integumentary system The skin is considered the largest organ of the body Basic Skin Histology The skin is composed of two
Skin and Body Membranes
 4 Skin and Body Membranes PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Skin and Body Membranes
4 Skin and Body Membranes PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Skin and Body Membranes
Study Guide for Bio 101 Lecture Exam 3
 Study Guide for Bio 101 Lecture Exam 3 Please note that this study guide is a listing of objectives that you are required to master for this course. However, items mentioned in class or in laboratory as
Study Guide for Bio 101 Lecture Exam 3 Please note that this study guide is a listing of objectives that you are required to master for this course. However, items mentioned in class or in laboratory as
Ex. 7: Integumentary
 Collin County Community College BIOL. 2401 Ex. 7: Integumentary. Skin or Integument Consists of three major regions Epidermis outermost superficial region Dermis middle region Hypodermis (superficial fascia)
Collin County Community College BIOL. 2401 Ex. 7: Integumentary. Skin or Integument Consists of three major regions Epidermis outermost superficial region Dermis middle region Hypodermis (superficial fascia)
M1 - Renal, Fall 2007
 University of Michigan Deep Blue deepblue.lib.umich.edu 2007-09 M1 - Renal, Fall 2007 Lyons, R.; Burney, R. Lyons, R., Burney, R. (2008, August 07). Renal. Retrieved from Open.Michigan - Educational Resources
University of Michigan Deep Blue deepblue.lib.umich.edu 2007-09 M1 - Renal, Fall 2007 Lyons, R.; Burney, R. Lyons, R., Burney, R. (2008, August 07). Renal. Retrieved from Open.Michigan - Educational Resources
CHAPTER 5 INTEGUMENTARY
 CHAPTER 5 INTEGUMENTARY skin under the skin other stuff cutaneous layer hypodermis (subcutaneous) accessory structures Cutaneous layer = skin epithelial layers = connective tissue layer = dermis Subcutaneous
CHAPTER 5 INTEGUMENTARY skin under the skin other stuff cutaneous layer hypodermis (subcutaneous) accessory structures Cutaneous layer = skin epithelial layers = connective tissue layer = dermis Subcutaneous
Introduction. Skin and Body Membranes. Cutaneous Membranes Skin 9/14/2017. Classification of Body Membranes. Classification of Body Membranes
 Introduction Skin and Body Membranes Body membranes Cover surfaces Line body cavities Form protective and lubricating sheets around organs Classified in 5 categories Epithelial membranes 3 types- cutaneous,
Introduction Skin and Body Membranes Body membranes Cover surfaces Line body cavities Form protective and lubricating sheets around organs Classified in 5 categories Epithelial membranes 3 types- cutaneous,
Unit 4 - The Skin and Body Membranes 1
 Unit 4 - The Skin and Body Membranes 1 I. Unit 4: Skin and Body Membranes A. Body Membranes 1. Function of body membranes a) Cover body surfaces b) Line body cavities c) Form protective sheets around organs
Unit 4 - The Skin and Body Membranes 1 I. Unit 4: Skin and Body Membranes A. Body Membranes 1. Function of body membranes a) Cover body surfaces b) Line body cavities c) Form protective sheets around organs
The Integumentary System
 The Integumentary System The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep to it Two distinct regions Epidermis Dermis
The Integumentary System The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep to it Two distinct regions Epidermis Dermis
The Integumentary System
 The Integumentary System The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system (See if you can name some appendages) A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep
The Integumentary System The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system (See if you can name some appendages) A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep
Ch. 4: Skin and Body Membranes
 Ch. 4: Skin and Body Membranes I. Body Membranes A. Function of body membranes 1. Cover body surfaces 2. Line body cavities 3. Form protective sheets around organs II. Classification of Body Membranes
Ch. 4: Skin and Body Membranes I. Body Membranes A. Function of body membranes 1. Cover body surfaces 2. Line body cavities 3. Form protective sheets around organs II. Classification of Body Membranes
SKIN HISTOLOGY the microscopic anatomy of the Integument. Mikrogeo. com
 SKIN HISTOLOGY the microscopic anatomy of the Integument Mikrogeo. com Hair follicles, sweat glands, sebaceous glands (even teeth) are products of the epidermis,embryologically speaking ectododerm, that
SKIN HISTOLOGY the microscopic anatomy of the Integument Mikrogeo. com Hair follicles, sweat glands, sebaceous glands (even teeth) are products of the epidermis,embryologically speaking ectododerm, that
Integumentary System
 Chapter 5 Integumentary System 5-1 Skin: composed of dermis and epidermis Dermis. Gives structural strength. C.T. with many fibers, fibroblasts, macrophages. Some adipocytes and blood vessels. Contains
Chapter 5 Integumentary System 5-1 Skin: composed of dermis and epidermis Dermis. Gives structural strength. C.T. with many fibers, fibroblasts, macrophages. Some adipocytes and blood vessels. Contains
Anatomy and Physiology I Student Outline The Integumentary System. Integumentary System. Page 1
 Anatomy and Physiology I Student Outline The Integumentary System Integumentary System Page 1 Have a very clear understanding of the each particular tissue and their unique functions in each layer of the
Anatomy and Physiology I Student Outline The Integumentary System Integumentary System Page 1 Have a very clear understanding of the each particular tissue and their unique functions in each layer of the
Integumentary System. Remember: Types of Membranes: Bio 250
 Integumentary System Bio 250 Remember: Tissue: Group of cells that are similar in appearance and perform similar function Organ: Two or more tissues grouped together and performing a specialized function
Integumentary System Bio 250 Remember: Tissue: Group of cells that are similar in appearance and perform similar function Organ: Two or more tissues grouped together and performing a specialized function
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 5 The Integumentary System Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails,
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 5 The Integumentary System Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails,
Chapter 6 Skin and the Integumentary System. Skin Cells. Layers of Skin. Epidermis Dermis Subcutaneous layer beneath dermis not part of skin
 Chapter 6 Skin and the Integumentary System Composed of several tissues Maintains homeostasis Protective covering Retards water loss Regulates body temperature Houses sensory receptors Contains immune
Chapter 6 Skin and the Integumentary System Composed of several tissues Maintains homeostasis Protective covering Retards water loss Regulates body temperature Houses sensory receptors Contains immune
Figure 6.1 Transparency Master 37
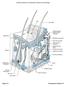 Pore Hair shaft Epidermis Dermal papillae (papillary layer of dermis) Meissner s corpuscle Dermis Free nerve ending Reticular layer of dermis Sebaceous (oil) gland Arrector pili muscle Sensory nerve fiber
Pore Hair shaft Epidermis Dermal papillae (papillary layer of dermis) Meissner s corpuscle Dermis Free nerve ending Reticular layer of dermis Sebaceous (oil) gland Arrector pili muscle Sensory nerve fiber
1. Introduction (Open your text to the image of a cross section of skin) i. Organ of the Integument. Connective Tissues. Epithelial Tissues
 Integumentary System 1. Introduction (Open your text to the image of a cross section of skin) A. Integumentary System i. Organ of the Integument a. Tissues Connective Tissues * Tissue / Location Relationships
Integumentary System 1. Introduction (Open your text to the image of a cross section of skin) A. Integumentary System i. Organ of the Integument a. Tissues Connective Tissues * Tissue / Location Relationships
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 5 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 5 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
This section covers the basic knowledge of normal skin structure and function required to help understand how skin diseases occur.
 Background Knowledge Functions of normal skin Background Knowledge This section covers the basic knowledge of normal skin structure and function required to help understand how skin diseases occur. Learning
Background Knowledge Functions of normal skin Background Knowledge This section covers the basic knowledge of normal skin structure and function required to help understand how skin diseases occur. Learning
Overview of the Integumentary System. Lab #7. Layers of the epidermis are known as strata. Organization of the Epidermis: Layers of the Epidermis
 Overview of the Integumentary System Lab #7 Integumentary System Organization of the Epidermis: Layers of the epidermis are known as strata Figure 5 2 Layers of the Epidermis Top: Free surface of skin
Overview of the Integumentary System Lab #7 Integumentary System Organization of the Epidermis: Layers of the epidermis are known as strata Figure 5 2 Layers of the Epidermis Top: Free surface of skin
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes 4 Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes 4 Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities
The Integumentary System: An Overview
 The Integumentary System: An Overview Functions: Protective covering Helps regulate body temperature Retards water loss from deeper tissues Houses sensory receptors Synthesizes biochemicals Excretes small
The Integumentary System: An Overview Functions: Protective covering Helps regulate body temperature Retards water loss from deeper tissues Houses sensory receptors Synthesizes biochemicals Excretes small
Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad. Lab 1
 Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad Lab 1 1 Tissues are groups of cells with a common structure (form) and function (job). There are (4) types of tissue: 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Nervous 2 Epithelial cells
Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad Lab 1 1 Tissues are groups of cells with a common structure (form) and function (job). There are (4) types of tissue: 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Nervous 2 Epithelial cells
Skin is a multilayered organ that covers and protects the body.
 Section 1: Skin is a multilayered organ that covers and protects the body. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions What are the four tissue types that are found in
Section 1: Skin is a multilayered organ that covers and protects the body. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions What are the four tissue types that are found in
Epidermis. Integumentary system
 Epidermis the doctor mentioned at the begging of the lecture that the slides is from different sources and has information and details that is enough for us so we don t have to go back and read from the
Epidermis the doctor mentioned at the begging of the lecture that the slides is from different sources and has information and details that is enough for us so we don t have to go back and read from the
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author: Brent C. Williams, M.D., M.P.H., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Author: Brent C. Williams, M.D., M.P.H., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Ch 4. Skin and Body Membranes
 Ch 4 Skin and Body Membranes TITLE HISTOLOGY SLIDES & NOTES ESSENTIAL QUESTION What tissues compose the integumentary system? Stratified Squamous Epithelium Stratified = several layers; Squamous = shape
Ch 4 Skin and Body Membranes TITLE HISTOLOGY SLIDES & NOTES ESSENTIAL QUESTION What tissues compose the integumentary system? Stratified Squamous Epithelium Stratified = several layers; Squamous = shape
Tissues. Tissues - Overview. Bio 101 Laboratory 3. Epithelial Tissues and Integument
 Bio 101 Laboratory 3 Epithelial Tissues and Integument 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue Integument Connective Tissue **We will be doing muscle and nervous tissues
Bio 101 Laboratory 3 Epithelial Tissues and Integument 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue Integument Connective Tissue **We will be doing muscle and nervous tissues
Science that studies adverse skin effects and the substances that produce them
 Science that studies adverse skin effects and the substances that produce them Leena A. Nylander-French, Ph.D., CIH 159 Rosenau Tel: 966.3826 E-mail: leena_french@unc.edu Occupational skin diseases are
Science that studies adverse skin effects and the substances that produce them Leena A. Nylander-French, Ph.D., CIH 159 Rosenau Tel: 966.3826 E-mail: leena_french@unc.edu Occupational skin diseases are
Chapter 5: Integumentary System
 Chapter 5: Integumentary System I. Overview of the Integumentary System A. List the five major functions of the integumentary system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Il. Skin A. Epidermis 1. The epidermis consists of 2.
Chapter 5: Integumentary System I. Overview of the Integumentary System A. List the five major functions of the integumentary system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Il. Skin A. Epidermis 1. The epidermis consists of 2.
Integumentary System Practice & McDaniel,
 Name: Period: Date: Adapted from: Akkaraju, Liachovitzky Integumentary System Practice & McDaniel, 2010-11 Objectives Checklist. After completion of this packet you should be able to: list the general
Name: Period: Date: Adapted from: Akkaraju, Liachovitzky Integumentary System Practice & McDaniel, 2010-11 Objectives Checklist. After completion of this packet you should be able to: list the general
Integumentary System (Script) Slide 1: Integumentary System. Slide 2: An overview of the integumentary system
 Integumentary System (Script) Slide 1: Integumentary System Slide 2: An overview of the integumentary system Skin is the body s largest and heaviest organ making up 15% of body weight. Most skin is 1 to
Integumentary System (Script) Slide 1: Integumentary System Slide 2: An overview of the integumentary system Skin is the body s largest and heaviest organ making up 15% of body weight. Most skin is 1 to
Ch 5: Integumentary System
 Ch 5: Integumentary System You gotta have skin; All you really need is skin. Skin's the thing, that if you've got it outside, It helps keep your insides in. Alan Sherman (1924-1973) Developed by John Gallagher,
Ch 5: Integumentary System You gotta have skin; All you really need is skin. Skin's the thing, that if you've got it outside, It helps keep your insides in. Alan Sherman (1924-1973) Developed by John Gallagher,
Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs
 Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs Classification of Body Membranes Epithelial membranes Cutaneous
Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs Classification of Body Membranes Epithelial membranes Cutaneous
Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary
 Due in Lab 1. Skeletal System 33-34 2. Skeletal System 26 3. PreLab 6 Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary Cell Defenses and the Sunshine
Due in Lab 1. Skeletal System 33-34 2. Skeletal System 26 3. PreLab 6 Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary Cell Defenses and the Sunshine
Before you begin, think about your skin. It covers your entire body! What questions do you have about skin and skin color?
 Before you begin, think about your skin. It covers your entire body! What questions do you have about skin and skin color? Watch the entire animation once through. Go through it once more, stopping at
Before you begin, think about your skin. It covers your entire body! What questions do you have about skin and skin color? Watch the entire animation once through. Go through it once more, stopping at
Integumentary System. Packet #12
 Integumentary System Packet #12 Introduction Skin/Integument Skin, considered an organ, is the major component of the integumentary system. The integumentary system is also composed of other accessory
Integumentary System Packet #12 Introduction Skin/Integument Skin, considered an organ, is the major component of the integumentary system. The integumentary system is also composed of other accessory
Chapter 5: The Integumentary System - Introduction and Epidermis
 Chapter 5: The Integumentary System - Introduction and Epidermis The Integument Means Covering Composed: Skin Hair Nails Sweat glands Oil glands The Integument Thickness 1.5 4 mm (or more) Weight 9 11
Chapter 5: The Integumentary System - Introduction and Epidermis The Integument Means Covering Composed: Skin Hair Nails Sweat glands Oil glands The Integument Thickness 1.5 4 mm (or more) Weight 9 11
The integumentary system includes
 Survivor The integumentary system includes What are 3 of the 5 basic functions of the integumentary system? The integumentary system protects against what types of tissue damage? List at least two types
Survivor The integumentary system includes What are 3 of the 5 basic functions of the integumentary system? The integumentary system protects against what types of tissue damage? List at least two types
Levels of Organization
 Levels of Organization Oklahoma Laws Violators can be fined, arrested or jailed for making ugly faces at a dog. Females are forbidden from doing their own hair without being licensed by the state. Dogs
Levels of Organization Oklahoma Laws Violators can be fined, arrested or jailed for making ugly faces at a dog. Females are forbidden from doing their own hair without being licensed by the state. Dogs
Anatomy Ch 6: Integumentary System
 Anatomy Ch 6: Integumentary System Introduction: A. Organs are body structures composed of two or more different tissues. B. The skin and its accessory organs make up the integumentary system. Types of
Anatomy Ch 6: Integumentary System Introduction: A. Organs are body structures composed of two or more different tissues. B. The skin and its accessory organs make up the integumentary system. Types of
Integumentary System and Body Membranes
 Integumentary System and Body Membranes The Skin and its appendages hair, nails, and skin glands Anatomy/Physiology NHS http://www.lab.anhb.uwa.edu.au/mb140/corepages/integumentary/integum.htm I. System
Integumentary System and Body Membranes The Skin and its appendages hair, nails, and skin glands Anatomy/Physiology NHS http://www.lab.anhb.uwa.edu.au/mb140/corepages/integumentary/integum.htm I. System
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author: Brent C. Williams, M.D., M.P.H., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Author: Brent C. Williams, M.D., M.P.H., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
7/10/18. Introduction. Integumentary System. Physiology. Anatomy. Structure of the Skin. Epidermis
 Introduction Integumentary System Chapter 22 Skin is largest and heaviest organ of body (7% of body weight) Houses receptors for touch, heat, cold, movement, and vibration No other body system is more
Introduction Integumentary System Chapter 22 Skin is largest and heaviest organ of body (7% of body weight) Houses receptors for touch, heat, cold, movement, and vibration No other body system is more
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition. Mrs. Hummer. Chapter 6
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 6 1 Chapter 6 Skin and the Integumentary System Composed of several tissues Maintains homeostasis Protective covering Retards water
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 6 1 Chapter 6 Skin and the Integumentary System Composed of several tissues Maintains homeostasis Protective covering Retards water
Histology of Skin. dr. Alya Amila Fitrie, M.Kes dr. Radita Nur Anggraeni Department of Histology Medical Faculty University of North Sumatera 2008
 Histology of Skin dr. Alya Amila Fitrie, M.Kes dr. Radita Nur Anggraeni Department of Histology Medical Faculty University of North Sumatera 2008 1 INTRODUCTION The heaviest single organ of the body, 16%
Histology of Skin dr. Alya Amila Fitrie, M.Kes dr. Radita Nur Anggraeni Department of Histology Medical Faculty University of North Sumatera 2008 1 INTRODUCTION The heaviest single organ of the body, 16%
CH 05 THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
 CH 05 THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM This system consists of skin and its derivatives. The skin is one of the largest organs of the body in terms of surface area. The functions of the integumentary system include:
CH 05 THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM This system consists of skin and its derivatives. The skin is one of the largest organs of the body in terms of surface area. The functions of the integumentary system include:
Comparative Anatomical Factors Affecting Topical Delivery
 Comparative Anatomical Factors Affecting Topical Delivery Nancy A. Monteiro-Riviere, Ph.D., Fellow ATS Professor of Investigative Dermatology and Toxicology Center for Chemical Toxicology Research and
Comparative Anatomical Factors Affecting Topical Delivery Nancy A. Monteiro-Riviere, Ph.D., Fellow ATS Professor of Investigative Dermatology and Toxicology Center for Chemical Toxicology Research and
Chapter 5. Integumentary System 5-1
 Chapter 5 Integumentary System 5-1 Structures that are part of the integument Skin Hair Nails Glands Overview of Functions Protection Sensation Temperature regulation Vitamin D production Excretion Immunity
Chapter 5 Integumentary System 5-1 Structures that are part of the integument Skin Hair Nails Glands Overview of Functions Protection Sensation Temperature regulation Vitamin D production Excretion Immunity
