EFFECTS OF COMBINATION OF CYCLOSPORINE WITH LOSARTAN OR ENALAPRIL ON KIDNEY FUNCTION IN UREMIC RATS
|
|
|
- Emerald Wright
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Copyright 2002 by Institute of Pharmacology Polish Academy of Sciences Polish Journal of Pharmacology Pol. J. Pharmacol., 2002, 54, ISSN EFFECTS OF COMBINATION OF CYCLOSPORINE WITH LOSARTAN OR ENALAPRIL ON KIDNEY FUNCTION IN UREMIC RATS Arsalan Azzadin 1, Jolanta Ma³yszko 2, Jacek S. Ma³yszko 2, Anna Tankiewicz 1, Micha³ Myœliwiec 2, W³odzimierz Buczko 1,# Department of Pharmacodynamics, Medical Academy of Bia³ystok, Mickiewicza 2c, PL Bia³ystok, Poland; Department of Nephrology and Internal Medicine, Medical Academy of Bia³ystok, urawia 14, PL Bia³ystok, Poland Effects of combination of cyclosporine with losartan or enalapril on kidney function in uremic rats. A. AZZADIN, J. MA YSZKO, J.S. MA YSZKO, A. TANKIEWICZ, M. MYŒLIWIEC, W. BUCZKO. Pol. J. Pharmacol., 2002, 54, Long-term treatment with cyclosporine in solid organ transplantation has been shown to be associated with the development of hypertension and nephrotoxicity. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors have well-known nephroprotective properties and may prevent cyclosporine A (CYA)-induced hypertension. Angiotensin receptor 1 antagonists have similar properties. The purpose of this study was to investigate if losartan or enalapril could be administered with CYA to reduce its nephrotoxic effect in uremic rats. The studies were performed on the following groups of rats: group I control; group II control rats + losartan; group III control rats + CYA; group IV uremic rats; group V uremic rats + losartan; group VI uremic rats + CYA; group VII uremic rats + losartan + CYA, group VIII control rats + enalapril; group IX control rats + enalapril + CYA; group X uremic rats + enalapril; group XI uremic rats + enalapril + CYA. Pretreatment with CYA, losartan or enalapril in uremic rats resulted in a significant increase in urea and creatinine levels and a decrease in hematocrit. The same effect was observed when uremic rats were given CYA + losartan or CYA + enalapril. Pretreatment with losartan was associated with the increase in the level of CYA much higher than with CYA treatment alone. Similarly, pretreatment with enalapril resulted in a significant increase in CYA concentration in both groups of rats given CYA: uremic and non-uremic. Results of our study show that the treatment with cyclosporine and a combination of losartan or enalapril results in an increase in creatinine and urea levels and a decrease in hematocrit. Therefore, physicians should exercise caution, when they give losartan and enalapril to kidney allograft recipients treated with cyclosporine, particularly with impaired allograft function. Key words: cyclosporine, enalapril, losartan, uremia correspondence
2 A. Azzadin, J. Ma³yszko, J.S. Ma³yszko, A. Tankiewicz, M. Myœliwiec, W. Buczko Abbreviations: ACE angiotensin-converting enzyme, AT angiotensin receptor 1, CYA cyclosporine A, LOS losartan, NO nitric oxide INTRODUCTION Cyclosporine A (CYA) is a potent immunosuppressive drug that selectively inhibits transcription of interleukin-2 and several other cytokines, mainly in T-helper lymphocytes [2]. Its introduction has dramatically improved the outcome of solid organ transplantation and CYA is also used with increasing frequency for the treatment of autoimmune diseases. However, the long-term treatment with CYA in solid organ transplantation has been shown to be associated with the development of hypertension and nephrotoxicity [8]. The pathophysiology of CYA-induced acute nephrotoxicity is not fully understood but glomerular hypoperfusion following CYA administration has been shown [11, 14]. Several mechanisms, including endothelin-mediated systemic and renal vasoconstriction, sodium retension, impaired vasodilatation secondary to reduction in nitric oxide (NO), and altered cytosolic calcium translocation have been proposed to underline CYA-induced hypertension [12, 15]. The renin-angiotensin system plays a major role in the physiological regulation of the kidney function, including the control of renal microvascular and tubular function. Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and angiotensin receptor 1 (AT 1 ) antagonist losartan (LOS) are widely used for the treatment of hypertension, but caution is advised because these drugs may induce reversible renal failure [5, 9]. Although this has been ascribed in some cases to nephrotoxicity, hypertension, hypersensitivity reaction and interstitial nephritis, most cases have been associated with stenosis of the renal arteries or arterioles occurring in either native or transplanted kidneys [5, 9]. The AT 1 receptor recently has been shown to play an important role in the stimulation by angiotensin II of a number of renal vasodilator substances, including bradykinin and NO [4]. On the other hand, ACE inhibitors have well-known nephroprotective properties and may prevent CYA-induced hypertension and deterioration of kidney function in spontaneously hypertensive rats [10]. The purpose of this study was to investigate if losartan (LOS) or enalapril could be administered with CYA to reduce its nephrotoxic effect in uremic rats. MATERIAL and METHODS The study was carried out on male Wistar rats ( g, 20 animals per group). Experimental chronic renal failure was evoked using the method of subtotal nephrectomy under pentobarbital anesthesia (50 mg/kg ip) [13]. The right kidney was totally resected and 60% of the left one was removed [13]. Four weeks after the surgery serum creatinine, urea and hematocrit were assayed to prove the development of renal insufficiency. Then, the administration of the studied drugs (CYA, Neoral, Novartis, Switzerland, LOS, MSD Inc., USA, enalapril, KRKA, Slovenia) started and continued for 8 weeks. LOS was given at a dose of 10 mg/kg po, enalapril at a dose of 10 mg/kg po, and CYA at a dose of 15 mg/kg ip. Rats were divided into the following groups: group I control; group II control rats + LOS; group III control rats + CYA; group IV uremic rats; group V uremic rats + LOS; group VI uremic rats + CYA; group VII uremic rats + LOS + CYA, group VIII control rats + enalapril; group IX control rats + enalapril + CYA; group X uremic rats + enalapril; group XI uremic rats + enalapril + CYA. At the end of the therapy, mean serum creatinine and urea levels, and hematocrit were assayed by standard laboratory methods and whole blood CYA level (by TDX) was recorded. All the results are presented in Table 1 and data are expressed as means ± SD. Completely randomized analyses of variances was used for comparison among groups, followed by Dunnet s test for multiple comparisons. Statistical significance was defined at p < RESULTS We assessed creatinine (0.34 ± 0.08 mg%), and urea (27.5 ± 3.14 mg%) levels, and hematocrit (45.4 ± 3.75%) in control rats in order to establish their normal ranges. As expected, chronic renal failure induced a marked rise in both creatinine and urea concentrations (0.68 ± 0.11 mg% and 57.3 ± 9.47 mg% vs 0.34 ± 0.08 and 27.5 ± 3.14 mg%, respectively) and a decrease in hematocrit (33.85 ± 2.34% vs 45.4 ± 3.75%) when compared to the control group. Moreover, these parameters increased (creatinine and urea) and decreased (hematocrit) in uremic rats treated with CYA (0.8 ± 0.1 mg%, ± 35.9 mg% and 35.2 ± 3.1%, respectively), uremic rats treated with LOS (0.75 ± Pol. J. Pharmacol., 2002, 54,
3 CYCLOSPORINE AND THE KIDNEY Table 1. Creatinine, urea and cyclosporine A (CYA) concentrations, and hematocrit value in control and uremic rats treated with losartan or enalapril and CYA No. Group Creatinine (mg/dl) Urea (mg/dl) Hematocrit (%) CYA concentration (ng/ml) I Control 0.34 ± ± ± II Control + losartan 0.52 ± ± ± III Control + CYA 0.64 ± = ± ± ± 6 IV Uremia 0.68 ± ± ± V Uremia + losartan 0.75 ± 0.14 >@ ± ± 0 VI Uremia + CYA 0.80 ± 0.08 > ± ± ± 21.2 >? VII Uremia + CYA + losartan 1.33 ± 0.18 = ± ± 1.29?A 409 ± 36.6? VIII Control + enalapril 0.64 ± 0.05 E ± 5.53 E ± 2.00 E 0 IX Control + CYA + enalapril 0.92 ± 0.11?E ± 12.34?E ± 2.30?E 1461 ± 88.22? X Uremia + enalapril 0.93 ± 0.05 B ± B ± 1.36 B 0 XI Uremia + CYA + enalapril 1.07 ± 0.09 D ± C ± 3.16 C ± C = p < group I vs II, III and IV vs V, VI, VII; > p < group VII vs V, VI;? p < group III vs VI, VII, p<0.001 group V vs II and VII vs V; A p < group VII vs II; B p < group VIII vs X; C p < group IX vs XI; D p < 0.01 group IX vs XI, E p < group I vs VIII, IX mg%, 70.5 ± 10.7 mg%, 33.6± 2.7 mg%) and uremic rats treated with enalapril (0.93 ± 0.05 mg%, 98.3 ± 17.5 mg%, 24.7 ± 1.4%). They were extremely elevated (creatinine and urea) or decreased (hematocrit) in uremic rats treated with both CYA and LOS (1.33 ± 0.18 mg%, ± 72.6 mg% and 25.4 ± 1.3 %, respectively) and CYA and enalapril (1.07 ± 0.09 mg%, ± 17.5 mg%, ± 3.16%) when compared to the control group. CYA concentration in uremic rats was significantly higher than those observed in non-uremic rats treated with CYA (117 ± 21.2 ng/ml vs 46.5 ± 6 ng/ml). Pretreatment with LOS was associated with the increase in the level of CYA much higher than with CYA alone (409 ± 36.6 vs 46.5 ± 6 and 117 ± 21.2 ng/ml, respectively). Similarly, pretreatment with enalapril resulted in a significant increase in CYA concentration in both groups of rats given CYA (uremic + CYA + enalapril, control + CYA + enalapril) reaching ± ng/ml and 1461 ± 88.2 ng/ml, respectively, when compared to the control or uremic rats given CYA. DISCUSSION We have demonstrated that administration of CYA to uremic rats further increases creatinine and urea concentration when compared to uremic rats. Similar but more pronounced changes were observed after the administration of LOS or enalapril to uremic rats. Combining these two drugs (CYA and LOS or CYA and enalapril) resulted in further increase in urea and creatinine concentration in uremic rats. The same pattern of changes was observed after the administration of CYA, LOS or both drugs together to non-uremic rats as well as CYA, enalapril or both drugs together to nonuremic rats. Administration of the combination of both drugs (CYA and LOS or CYA and enalapril) to uremic or non-uremic rats caused a statistically significant increase in urea and creatinine levels when compared to the rats given only one of these drugs. LOS or CYA did not affect hematocrit in control rats, whereas administration of enalapril resulted in a significant decrease in hematocrit in the control rats. Control rats given CYA have significantly higher hematocrit than control rats given LOS or enalapril. It may be due to the fact, that CYA may induce erythrocytosis (in kidney allograft recipients this phenomenon is called posttransplant erythrocytosis) [3]. However, hematocrit in uremic rats treated with LOS did not differ significantly from hematocrit in uremic rats given CYA, whereas in uremic rats given enalapril hematocrit was significantly lower than in rats given CYA. Uremic rats given CYA and LOS had significantly lower hematocrit than uremic rats given only ISSN
4 A. Azzadin, J. Ma³yszko, J.S. Ma³yszko, A. Tankiewicz, M. Myœliwiec, W. Buczko one of these drugs, whereas in uremic rats given combination of CYA and enalapril, hematocrit was not significantly lower when compared to the uremic rats given only enalapril. LOS was shown to have paradoxical effects on renal function [5, 9]. On the one hand, it caused renal vasodilatation, prevented the slow deterioration of glomerular filtration rate in hypertension, reduced proteinuria and improved morbidity and mortality in diabetic nephropathy, while on the other hand, in states of low fixed renal blood flow such as those arising in bilateral artery stenosis, severe congestive heart failure, and severe sodium and volume depletion, it could worsen renal function and even precipitate acute renal failure [5, 9]. The usual interpretation suggests that in these states renal function is angiotensin-dependent [5, 9]. In our study, control or uremic rats did not show any evidence of low fixed renal blood flow. They had tap water available ad libitum, they were fed standard chow, they were not on diuretics, and no evidence of heart failure or bilateral renal artery stenosis was noted. Therefore, the exacerbation of renal failure remained interesting, but difficult to explain. According to hitherto existing evidence, LOS is exceptionally well-tolerated. There are no data about lowering of hematocrit or aggravating anemia by LOS in end-stage renal failure or in dialysis population. However, since CYA may contribute to posttransplant erythrocytosis [3], patients with this particular pathology might benefit from this combination. LOS given to renal allograft recipients caused a significant decrease in hematocrit and hemoglobin after 6 months of the therapy [1]. It has been suggested that LOS might blunt erythropoiesis by dampening angiotensin II-driven erythropoietin production in the kidney. Moreover, to date no clinically important LOS interactions have been described. Studying effects of enalapril on kidney function, we observed a deterioration of kidney function in control and uremic rats treated with this drug. In kidney transplant recipients given enalapril, no significant change in CYA concentration was observed but impairment in allograft function in the patients with non-optimal allograft function (renal failure) was found [7]. In spontaneously hypertensive rats on a high-sodium diet, enalapril and valsartan equally prevented the CYA-induced deterioration of kidney function [6]. Therefore, taking into consideration the results of our study such as an increase in creatinine level by a combination of LOS or enalapril with CYA, physicians should exercise caution, when they give LOS and enalapril to kidney allograft recipients treated with CYA, particularly with impaired allograft function. REFERENCES 1. Boran M., Gonenc F., Cetin S.: Losartan in renal allograft recipients receiving cyclosporine A. Nephron, 1999, 83, Borel J.F., Feurer C., Magnee C., Stahelin H.: Effects of the new antilymphocytic peptide cyclosporine A in animals. Immunology, 1977, 32, Brox A.G., Mangel J., Hanley J.A., Louis G.St., Mongrain S., Gagnon R.F.: Erythrocytosis after renal transplantation represents an abnormality of insulin-like growth factor-i and its binding proteins. Transplantation, 1998, 66, Douglas J.G.: The curtain rises on the renin-angiotensin system: AT2 receptors are in the spotlight. J. Clin. Invest., 1996, 97, Goodfriend T.L., Elliott M.E., Catt K.J.: Angiotensin receptors and their antagonist. N. Engl. J. Med., 1996, 334, Lassila M., Finckenberg P., Pere A.K., Krogerus L., Ahonen J., Vapaatalo H., Nurminen M.L.: Comparison of enalapril and valsartan in cyclosporine A-induced hypertension and nephrotoxicity in spontaneously hypertensive rats on high-sodium diet. Brit. J. Pharmacol., 2000, 130, Martinez-Castelao A., Hueso M., Sanz V., Rejas J., Alsina J., Grinyo J.M.: Treatment of hypertension after renal transplantation: long-term efficacy of verapamil, enalapril, and doxazosin. Kidney Int., 1998, 68, Suppl., S130 S Mason J.: Pathophysiology and toxicology of cyclosporine in humans and animals. Pharmacol. Rev., 1989, 42, Matsukawa T., Ichikawa I.: Biological functions of angiotensin and its receptors. Ann. Rev. Physiol., 1997, 59, Mervaala E., Lassila M., Vaskonen T., Krogerus L., Lahteenmaki T., Vapaatalo H., Karppanen H.: Effects of ACE inhibition on cyclosporine A-induced hypertension and nephrotoxicity in spontaneously hypertensive rats on a high-sodium diet. Blood Press., 1999, 8, Murray B.M., Paller M.S., Ferris T.F.: Effect of CsA administration on renal hemodynamics in conscious rats. Kidney Int., 1985, 28, Pichler R.H., Franceschini N., Young B.A., Hugo C., Ando H.T.F., Burdmann E.A., Shankland S.J.: Pathogenesis of cyclosporine nephropathy: roles of angiotensin II and osteopontin. J. Amer. Soc. Nephrol., 1995, 4, Pol. J. Pharmacol., 2002, 54,
5 CYCLOSPORINE AND THE KIDNEY 13. Rutkowski B., Hoppe A., Manitius A.: Blood glucose and insulin levels following glucose load in rats with chronic renal failure. Acta Med. Pol., 1981,3, Sullivan B.A., Hak L.J., Finn W.F.: Cyclosporine nephrotoxicity: studies in laboratory animals. Transplant. Proc., 1985, 17, Van der Schaaf M.R., Hene R.J., Floor M., Blankestijn P.J., Koomans H.A.: Hypertension after renal transplantation. Calcium channel or converting enzyme blockade? Hypertension, 1995, 25, Received: March 21, 2002; in revised form: July 8, ISSN
renoprotection therapy goals 208, 209
 Subject Index Aldosterone, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 induction 163, 164, 168 Aminopeptidases angiotensin II processing 64 66, 214 diabetic expression 214, 215 Angiotensin I intrarenal compartmentalization
Subject Index Aldosterone, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 induction 163, 164, 168 Aminopeptidases angiotensin II processing 64 66, 214 diabetic expression 214, 215 Angiotensin I intrarenal compartmentalization
The CARI Guidelines Caring for Australasians with Renal Impairment. ACE Inhibitor and Angiotensin II Antagonist Combination Treatment GUIDELINES
 ACE Inhibitor and Angiotensin II Antagonist Combination Treatment Date written: September 2004 Final submission: September 2005 Author: Kathy Nicholls GUIDELINES No recommendations possible based on Level
ACE Inhibitor and Angiotensin II Antagonist Combination Treatment Date written: September 2004 Final submission: September 2005 Author: Kathy Nicholls GUIDELINES No recommendations possible based on Level
Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
 Early Treatment is the Key Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Stage Description GFR (ml/min/1.73 m 2 ) >90 1 Kidney damage with normal or GFR 2 Mild decrease in GFR 60-89 3 Moderate decrease in GFR
Early Treatment is the Key Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Stage Description GFR (ml/min/1.73 m 2 ) >90 1 Kidney damage with normal or GFR 2 Mild decrease in GFR 60-89 3 Moderate decrease in GFR
HYPERTENSION IN CKD. LEENA ONGAJYOOTH, M.D., Dr.med RENAL UNIT SIRIRAJ HOSPITAL
 HYPERTENSION IN CKD LEENA ONGAJYOOTH, M.D., Dr.med RENAL UNIT SIRIRAJ HOSPITAL Stages in Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease and Therapeutic Strategies Complications Normal Increased risk Damage GFR
HYPERTENSION IN CKD LEENA ONGAJYOOTH, M.D., Dr.med RENAL UNIT SIRIRAJ HOSPITAL Stages in Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease and Therapeutic Strategies Complications Normal Increased risk Damage GFR
M2 TEACHING UNDERSTANDING PHARMACOLOGY
 M2 TEACHING UNDERSTANDING PHARMACOLOGY USING CVS SYSTEM AS AN EXAMPLE NIGEL FONG 2 JAN 2014 TODAY S OBJECTIVE Pharmacology often seems like an endless list of mechanisms and side effects to memorize. To
M2 TEACHING UNDERSTANDING PHARMACOLOGY USING CVS SYSTEM AS AN EXAMPLE NIGEL FONG 2 JAN 2014 TODAY S OBJECTIVE Pharmacology often seems like an endless list of mechanisms and side effects to memorize. To
Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009 São Paulo, Brazil - 2009 Next WSAVA Congress : Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of the Congress Organizers PROTEINURIA
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009 São Paulo, Brazil - 2009 Next WSAVA Congress : Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of the Congress Organizers PROTEINURIA
PRODUCT CIRCULAR. Tablets COZAAR (losartan potassium) I. THERAPEUTIC CLASS II. INDICATIONS III. DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION PAK-CZR-T
 PRODUCT CIRCULAR Tablets I. THERAPEUTIC CLASS, the first of a new class of agents for the treatment of hypertension, is an angiotensin II receptor (type AT 1 ) antagonist. also provides a reduction in
PRODUCT CIRCULAR Tablets I. THERAPEUTIC CLASS, the first of a new class of agents for the treatment of hypertension, is an angiotensin II receptor (type AT 1 ) antagonist. also provides a reduction in
Prof. Armando Torres Nephrology Section Hospital Universitario de Canarias University of La Laguna Tenerife, Canary Islands, Spain.
 Does RAS blockade improve outcomes after kidney transplantation? Armando Torres, La Laguna, Spain Chairs: Hans De Fijter, Leiden, The Netherlands Armando Torres, La Laguna, Spain Prof. Armando Torres Nephrology
Does RAS blockade improve outcomes after kidney transplantation? Armando Torres, La Laguna, Spain Chairs: Hans De Fijter, Leiden, The Netherlands Armando Torres, La Laguna, Spain Prof. Armando Torres Nephrology
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Transplant Proc. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2010 July 14.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Transplant Proc. 1990 February ; 22(1): 17 20. The Effects of FK 506 on Renal Function After Liver Transplantation J. McCauley, J.
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Transplant Proc. 1990 February ; 22(1): 17 20. The Effects of FK 506 on Renal Function After Liver Transplantation J. McCauley, J.
VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease in Primary Care (2008) PROVIDER REFERENCE CARDS Chronic Kidney Disease
 VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease in Primary Care (2008) PROVIDER REFERECE CARDS Chronic Kidney Disease CKD VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management
VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease in Primary Care (2008) PROVIDER REFERECE CARDS Chronic Kidney Disease CKD VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management
Recurrent Idiopathic Membranous Glomerulonephritis After Kidney Transplantation and Successful Treatment With Rituximab
 TRANSPLANTATION Recurrent Idiopathic Membranous Glomerulonephritis After Kidney Transplantation and Successful Treatment With Rituximab Khadijeh Makhdoomi, 1,2 Saeed Abkhiz, 1,2 Farahnaz Noroozinia, 1,3
TRANSPLANTATION Recurrent Idiopathic Membranous Glomerulonephritis After Kidney Transplantation and Successful Treatment With Rituximab Khadijeh Makhdoomi, 1,2 Saeed Abkhiz, 1,2 Farahnaz Noroozinia, 1,3
Antihypertensive drugs: I. Thiazide and other diuretics:
 Clinical assessment of hypertensive patient: You have to take history regarding the presence of other risk factors for CAb like diabetes mellitus, smoking, etc. Take history whether the patient takes medications
Clinical assessment of hypertensive patient: You have to take history regarding the presence of other risk factors for CAb like diabetes mellitus, smoking, etc. Take history whether the patient takes medications
Renal Disease and PK/PD. Anjay Rastogi MD PhD Division of Nephrology
 Renal Disease and PK/PD Anjay Rastogi MD PhD Division of Nephrology Drugs and Kidneys Kidney is one of the major organ of drug elimination from the human body Renal disease and dialysis alters the pharmacokinetics
Renal Disease and PK/PD Anjay Rastogi MD PhD Division of Nephrology Drugs and Kidneys Kidney is one of the major organ of drug elimination from the human body Renal disease and dialysis alters the pharmacokinetics
Pearls in Acute Heart Failure Management
 Pearls in Acute Heart Failure Management Best Practices Juan M. Aranda Jr., M.D. Professor of Medicine Medical Director of Heart Failure/ Transplant Program University of Florida College of Medicine Disclosures:
Pearls in Acute Heart Failure Management Best Practices Juan M. Aranda Jr., M.D. Professor of Medicine Medical Director of Heart Failure/ Transplant Program University of Florida College of Medicine Disclosures:
Antihypertensive Agents Part-2. Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia
 Antihypertensive Agents Part-2 Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Agents that block production or action of angiotensin Angiotensin-converting
Antihypertensive Agents Part-2 Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Agents that block production or action of angiotensin Angiotensin-converting
Metabolic Consequences of Anti Hypertensives: Is It Clinically Important?
 Metabolic Consequences of Anti Hypertensives: Is It Clinically Important?,FACA,FICA,MASH,FVBWG,MISCP CONSULTANT OF CARDIOLOGY DIRECTOR OF PORT-FOUAD HOSPITAL CCU Consideration of antihypertensive agents
Metabolic Consequences of Anti Hypertensives: Is It Clinically Important?,FACA,FICA,MASH,FVBWG,MISCP CONSULTANT OF CARDIOLOGY DIRECTOR OF PORT-FOUAD HOSPITAL CCU Consideration of antihypertensive agents
Metabolic Syndrome and Chronic Kidney Disease
 Metabolic Syndrome and Chronic Kidney Disease Definition of Metabolic Syndrome National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Adult Treatment Panel (ATP) III Abdominal obesity, defined as a waist circumference
Metabolic Syndrome and Chronic Kidney Disease Definition of Metabolic Syndrome National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Adult Treatment Panel (ATP) III Abdominal obesity, defined as a waist circumference
HLA and Non-HLA Antibodies in Transplantation and their Management
 HLA and Non-HLA Antibodies in Transplantation and their Management Luca Dello Strologo October 29 th, 2016 Hystory I 1960 donor specific antibodies (DSA): first suggestion for a possible role in deteriorating
HLA and Non-HLA Antibodies in Transplantation and their Management Luca Dello Strologo October 29 th, 2016 Hystory I 1960 donor specific antibodies (DSA): first suggestion for a possible role in deteriorating
The CARI Guidelines Caring for Australians with Renal Impairment. Specific effects of calcium channel blockers in diabetic nephropathy GUIDELINES
 Specific effects of calcium channel blockers in diabetic nephropathy Date written: September 2004 Final submission: September 2005 Author: Kathy Nicholls GUIDELINES a. Non-dihydropyridine calcium channel
Specific effects of calcium channel blockers in diabetic nephropathy Date written: September 2004 Final submission: September 2005 Author: Kathy Nicholls GUIDELINES a. Non-dihydropyridine calcium channel
Amlodipine plus Lisinopril Tablets AMLOPRES-L
 Amlodipine plus Lisinopril Tablets AMLOPRES-L COMPOSITION AMLOPRES-L Each uncoated tablet contains: Amlodipine besylate equivalent to Amlodipine 5 mg and Lisinopril USP equivalent to Lisinopril (anhydrous)
Amlodipine plus Lisinopril Tablets AMLOPRES-L COMPOSITION AMLOPRES-L Each uncoated tablet contains: Amlodipine besylate equivalent to Amlodipine 5 mg and Lisinopril USP equivalent to Lisinopril (anhydrous)
Diabetic Nephropathy 2009
 Diabetic Nephropathy 2009 Michael T McDermott MD Director, Endocrinology and Diabetes Practice University of Colorado Hospital Michael.mcdermott@ucdenver.edu Diabetic Nephropathy Clinical Stages Hyperfunction
Diabetic Nephropathy 2009 Michael T McDermott MD Director, Endocrinology and Diabetes Practice University of Colorado Hospital Michael.mcdermott@ucdenver.edu Diabetic Nephropathy Clinical Stages Hyperfunction
The effect of losartan on hemoglobin concentration and renal outcome in diabetic nephropathy of type 2 diabetes
 original article http://www.kidney-international.org & 2008 International Society of Nephrology The effect of losartan on hemoglobin concentration and renal outcome in diabetic nephropathy of type 2 diabetes
original article http://www.kidney-international.org & 2008 International Society of Nephrology The effect of losartan on hemoglobin concentration and renal outcome in diabetic nephropathy of type 2 diabetes
THE KIDNEY IN HYPOTENSIVE STATES. Benita S. Padilla, M.D.
 THE KIDNEY IN HYPOTENSIVE STATES Benita S. Padilla, M.D. Objectives To discuss what happens when the kidney encounters low perfusion To discuss new developments and clinical application points in two scenarios
THE KIDNEY IN HYPOTENSIVE STATES Benita S. Padilla, M.D. Objectives To discuss what happens when the kidney encounters low perfusion To discuss new developments and clinical application points in two scenarios
LXIV: DRUGS: 4. RAS BLOCKADE
 LXIV: DRUGS: 4. RAS BLOCKADE ACE Inhibitors Components of RAS Actions of Angiotensin i II Indications for ACEIs Contraindications RAS blockade in hypertension RAS blockade in CAD RAS blockade in HF Limitations
LXIV: DRUGS: 4. RAS BLOCKADE ACE Inhibitors Components of RAS Actions of Angiotensin i II Indications for ACEIs Contraindications RAS blockade in hypertension RAS blockade in CAD RAS blockade in HF Limitations
Chronic Kidney Disease for the Primary Care Physician in What do the Kidneys do? CKD in the US
 1:25-2:25pm Managing Chronic Kidney Disease in 2019 SPEAKERS Adriana Dejman, MD Chronic Kidney Disease for the Primary Care Physician in 2019 Adriana Dejman, MD Assistant Professor of Clinical Medicine
1:25-2:25pm Managing Chronic Kidney Disease in 2019 SPEAKERS Adriana Dejman, MD Chronic Kidney Disease for the Primary Care Physician in 2019 Adriana Dejman, MD Assistant Professor of Clinical Medicine
Prevalence of anemia and cardiovascular diseases in chronic kidney disease patients: a single tertiary care centre study
 International Journal of Advances in Medicine Sathyan S et al. Int J Adv Med. 2017 Feb;4(1):247-251 http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20170120
International Journal of Advances in Medicine Sathyan S et al. Int J Adv Med. 2017 Feb;4(1):247-251 http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20170120
General introduction of nephrology. Xiaoqiang Ding M.D., Ph.D. Department of nephrology Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University
 General introduction of nephrology Xiaoqiang Ding M.D., Ph.D. Department of nephrology Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University Terminology Kidney,renal Nephrology Scope of nephrology Kidney diseases and
General introduction of nephrology Xiaoqiang Ding M.D., Ph.D. Department of nephrology Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University Terminology Kidney,renal Nephrology Scope of nephrology Kidney diseases and
Cyclosporine Nephrotoxicity and Early Posttransplant Hyperkalemia in Living-Donor Renal Recipients: Report of 4 Cases
 case report Cyclosporine Nephrotoxicity and Early Posttransplant Hyperkalemia in Living-Donor Renal Recipients: Report of 4 Cases Svetlana Pavleska-Kuzmanovska, 1 Zivko Popov, 2 Ognen Ivanovski, 2 Vesna
case report Cyclosporine Nephrotoxicity and Early Posttransplant Hyperkalemia in Living-Donor Renal Recipients: Report of 4 Cases Svetlana Pavleska-Kuzmanovska, 1 Zivko Popov, 2 Ognen Ivanovski, 2 Vesna
THE KIDNEY AND SLE LUPUS NEPHRITIS
 THE KIDNEY AND SLE LUPUS NEPHRITIS JACK WATERMAN DO FACOI 2013 NEPHROLOGY SIR RICHARD BRIGHT TERMINOLOGY RENAL INSUFFICIENCY CKD (CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE) ESRD (ENDSTAGE RENAL DISEASE) GLOMERULONEPHRITIS
THE KIDNEY AND SLE LUPUS NEPHRITIS JACK WATERMAN DO FACOI 2013 NEPHROLOGY SIR RICHARD BRIGHT TERMINOLOGY RENAL INSUFFICIENCY CKD (CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE) ESRD (ENDSTAGE RENAL DISEASE) GLOMERULONEPHRITIS
The Diabetes Kidney Disease Connection Missouri Foundation for Health February 26, 2009
 The Diabetes Kidney Disease Connection Missouri Foundation for Health February 26, 2009 Teresa Northcutt, RN BSN Primaris Program Manager, Prevention - CKD MO-09-01-CKD This material was prepared by Primaris,
The Diabetes Kidney Disease Connection Missouri Foundation for Health February 26, 2009 Teresa Northcutt, RN BSN Primaris Program Manager, Prevention - CKD MO-09-01-CKD This material was prepared by Primaris,
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Wanner C, Inzucchi SE, Lachin JM, et al. Empagliflozin and
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Wanner C, Inzucchi SE, Lachin JM, et al. Empagliflozin and
ANGIOTENSIN II RECEPTOR BLOCKERS: MORE THAN THE ALTERNATIVE PRESENTATION BY: PATRICK HO, USC PHARM D. CANDIDATE OF 2017 MENTOR: DR.
 ANGIOTENSIN II RECEPTOR BLOCKERS: MORE THAN THE ALTERNATIVE PRESENTATION BY: PATRICK HO, USC PHARM D. CANDIDATE OF 2017 MENTOR: DR. CRAIG STERN, PHARMD, MBA, RPH, FASCP, FASHP, FICA, FLMI, FAMCP RENIN-ANGIOTENSIN
ANGIOTENSIN II RECEPTOR BLOCKERS: MORE THAN THE ALTERNATIVE PRESENTATION BY: PATRICK HO, USC PHARM D. CANDIDATE OF 2017 MENTOR: DR. CRAIG STERN, PHARMD, MBA, RPH, FASCP, FASHP, FICA, FLMI, FAMCP RENIN-ANGIOTENSIN
Chapter 22: Hematological Complications
 Chapter 22: Hematological Complications 22.1: Perform a complete blood count at least (Not Graded): daily for 7 days, or until hospital discharge, whichever is earlier; two to three times per week for
Chapter 22: Hematological Complications 22.1: Perform a complete blood count at least (Not Graded): daily for 7 days, or until hospital discharge, whichever is earlier; two to three times per week for
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Stages. CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE Treatment Options. Incident counts & adjusted rates, by primary diagnosis Figure 2.
 Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Stages Stage 1 GFR > 90 (evidence of renal disease) Stage 2 GFR 60-89 Stage 3 GFR 30-59 Stage 4 GFR 15-29 Stage 5 GFR
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Stages Stage 1 GFR > 90 (evidence of renal disease) Stage 2 GFR 60-89 Stage 3 GFR 30-59 Stage 4 GFR 15-29 Stage 5 GFR
Left ventricular hypertrophy: why does it happen?
 Nephrol Dial Transplant (2003) 18 [Suppl 8]: viii2 viii6 DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfg1083 Left ventricular hypertrophy: why does it happen? Gerard M. London Department of Nephrology and Dialysis, Manhes Hospital,
Nephrol Dial Transplant (2003) 18 [Suppl 8]: viii2 viii6 DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfg1083 Left ventricular hypertrophy: why does it happen? Gerard M. London Department of Nephrology and Dialysis, Manhes Hospital,
ALLHAT RENAL DISEASE OUTCOMES IN HYPERTENSIVE PATIENTS STRATIFIED INTO 4 GROUPS BY BASELINE GLOMERULAR FILTRATION RATE (GFR)
 1 RENAL DISEASE OUTCOMES IN HYPERTENSIVE PATIENTS STRATIFIED INTO 4 GROUPS BY BASELINE GLOMERULAR FILTRATION RATE (GFR) 6 / 5 / 1006-1 2 Introduction Hypertension is the second most common cause of end-stage
1 RENAL DISEASE OUTCOMES IN HYPERTENSIVE PATIENTS STRATIFIED INTO 4 GROUPS BY BASELINE GLOMERULAR FILTRATION RATE (GFR) 6 / 5 / 1006-1 2 Introduction Hypertension is the second most common cause of end-stage
ROLE OF ANGIOTENSIN CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS AND ANGIOTENSIN RECEPTOR BLOCKERS IN TYPE I DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY DR.NASIM MUSA
 ROLE OF ANGIOTENSIN CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS AND ANGIOTENSIN RECEPTOR BLOCKERS IN TYPE I DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY DR.NASIM MUSA Type I IDDM is characterized by The abrupt onset of symptoms Insulinopenia
ROLE OF ANGIOTENSIN CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS AND ANGIOTENSIN RECEPTOR BLOCKERS IN TYPE I DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY DR.NASIM MUSA Type I IDDM is characterized by The abrupt onset of symptoms Insulinopenia
CRAIOVA UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY FACULTY OF MEDICINE ABSTRACT DOCTORAL THESIS
 CRAIOVA UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY FACULTY OF MEDICINE ABSTRACT DOCTORAL THESIS RISK FACTORS IN THE EMERGENCE OF POSTOPERATIVE RENAL FAILURE, IMPACT OF TREATMENT WITH ACE INHIBITORS Scientific
CRAIOVA UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY FACULTY OF MEDICINE ABSTRACT DOCTORAL THESIS RISK FACTORS IN THE EMERGENCE OF POSTOPERATIVE RENAL FAILURE, IMPACT OF TREATMENT WITH ACE INHIBITORS Scientific
Case Study in Chronic Renal Failure
 Case Study in Chronic Renal Failure Development of Knowledge Base: There were over 14,500 articles dealing with chronic renal failure entered into PubMed during 2000 2004. A current concept in this array
Case Study in Chronic Renal Failure Development of Knowledge Base: There were over 14,500 articles dealing with chronic renal failure entered into PubMed during 2000 2004. A current concept in this array
COMPLETE INHIBITION OF RENAL RESERVE IN CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE BY A COMBINATION OF ACEI AND ARB
 COMPLETE INHIBITION OF RENAL RESERVE IN CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE BY A COMBINATION OF ACEI AND ARB CG Musso ¹, J Reynaldi¹, N Imperiali ¹, L Algranati ¹, DG Oreopoulos ² Nephrology Department Hospital Italiano
COMPLETE INHIBITION OF RENAL RESERVE IN CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE BY A COMBINATION OF ACEI AND ARB CG Musso ¹, J Reynaldi¹, N Imperiali ¹, L Algranati ¹, DG Oreopoulos ² Nephrology Department Hospital Italiano
Management of Hypertension
 Clinical Practice Guidelines Management of Hypertension Definition and classification of blood pressure levels (mmhg) Category Systolic Diastolic Normal
Clinical Practice Guidelines Management of Hypertension Definition and classification of blood pressure levels (mmhg) Category Systolic Diastolic Normal
Chronic Kidney Disease
 Chronic Kidney Disease Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Educational Objectives Outline Demographics Propose Strategies to slow progression and improve outcomes Plan for treatment of CKD Chronic Kidney Disease
Chronic Kidney Disease Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Educational Objectives Outline Demographics Propose Strategies to slow progression and improve outcomes Plan for treatment of CKD Chronic Kidney Disease
Introduction. 1. Introduction
 1. Introduction Chronic kidney disease (CKD) encompasses a spectrum of different pathophysiologic processes associated with abnormal kidney function, and a progressive decline in glomerular filtration
1. Introduction Chronic kidney disease (CKD) encompasses a spectrum of different pathophysiologic processes associated with abnormal kidney function, and a progressive decline in glomerular filtration
The Cardiorenal Syndrome in Heart Failure
 The Cardiorenal Syndrome in Heart Failure Van N Selby, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Advanced Heart Failure Program, UCSF October 9, 2015 Disclosures None 1 Cardiorenal Syndrome (CRS) A pathophysiologic
The Cardiorenal Syndrome in Heart Failure Van N Selby, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Advanced Heart Failure Program, UCSF October 9, 2015 Disclosures None 1 Cardiorenal Syndrome (CRS) A pathophysiologic
ACEIs / ARBs NDHP dihydropyridine ( DHP ) ACEIs ARBs ACEIs ARBs NDHP. ( GFR ) 60 ml/min/1.73m ( chronic kidney disease, CKD )
 005 16 175-180 1 1 ( chronic kidney disease, CKD ) 003 ( end-stage renal disease, ESRD ) Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors ( ) angiotensin receptor blockers ( ) nondihydropyridine ( NDHP ) / NDHP
005 16 175-180 1 1 ( chronic kidney disease, CKD ) 003 ( end-stage renal disease, ESRD ) Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors ( ) angiotensin receptor blockers ( ) nondihydropyridine ( NDHP ) / NDHP
RENAL FAILURE IN CHILDREN Dr. Mai Mohamed Elhassan Assistant Professor Jazan University
 RENAL FAILURE IN CHILDREN Dr. Mai Mohamed Elhassan Assistant Professor Jazan University OBJECTIVES By the end of this lecture each student should be able to: Define acute & chronic kidney disease(ckd)
RENAL FAILURE IN CHILDREN Dr. Mai Mohamed Elhassan Assistant Professor Jazan University OBJECTIVES By the end of this lecture each student should be able to: Define acute & chronic kidney disease(ckd)
Disclosures. Topics. Staging and GFR. K-DOQI Staging of Chronic Kidney Disease. Definition of Chronic Kidney Disease. Chronic Kidney Disease
 Disclosures Chronic Kidney Disease Consultant: Baxter Healthcare J. Kevin Tucker, M.D. Brigham and Women s Hospital Massachusetts General Hospital Topics Staging of chronic kidney disease (CKD) How to
Disclosures Chronic Kidney Disease Consultant: Baxter Healthcare J. Kevin Tucker, M.D. Brigham and Women s Hospital Massachusetts General Hospital Topics Staging of chronic kidney disease (CKD) How to
Intruduction PSI MODE OF ACTION AND PHARMACOKINETICS
 Multidisciplinary Insights on Clinical Guidance for the Use of Proliferation Signal Inhibitors in Heart Transplantation Andreas Zuckermann, MD et al. Department of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery, Medical University
Multidisciplinary Insights on Clinical Guidance for the Use of Proliferation Signal Inhibitors in Heart Transplantation Andreas Zuckermann, MD et al. Department of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery, Medical University
RENAAL, IRMA-2 and IDNT. Three featured trials linking a disease spectrum IDNT RENAAL. Death IRMA 2
 Treatment of Diabetic Nephropathy and Proteinuria Background End stage renal disease is a major cause of death and disability among diabetics BP reduction is important to slow the progression of diabetic
Treatment of Diabetic Nephropathy and Proteinuria Background End stage renal disease is a major cause of death and disability among diabetics BP reduction is important to slow the progression of diabetic
Over- and underfill: not all nephrotic states are equal. Detlef Bockenhauer
 Over- and underfill: not all nephrotic states are equal Detlef Bockenhauer Objectives Review pathophysiology of oedema: undervs overfill Treatment options The clinical setting: case 1 A6-y old girl with
Over- and underfill: not all nephrotic states are equal Detlef Bockenhauer Objectives Review pathophysiology of oedema: undervs overfill Treatment options The clinical setting: case 1 A6-y old girl with
SLOWING PROGRESSION OF KIDNEY DISEASE. Mark Rosenberg MD University of Minnesota
 SLOWING PROGRESSION OF KIDNEY DISEASE Mark Rosenberg MD University of Minnesota OUTLINE 1. Epidemiology of progression 2. Therapy to slow progression a. Blood Pressure control b. Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone
SLOWING PROGRESSION OF KIDNEY DISEASE Mark Rosenberg MD University of Minnesota OUTLINE 1. Epidemiology of progression 2. Therapy to slow progression a. Blood Pressure control b. Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone
OBJECTVES OF LEARNING
 OBJECTVES OF LEARNING ACUTE RENAL FAILURE AND RENAL REPLACEMENT THERAPY DR.TAI CHENG SHENG RECOGNITION OF DEFINITION OF ARF RECOGNITION OF CAUSE OF ARF RECOGNITION OF PATHOGENESIS OF ARF RECOGNITION OF
OBJECTVES OF LEARNING ACUTE RENAL FAILURE AND RENAL REPLACEMENT THERAPY DR.TAI CHENG SHENG RECOGNITION OF DEFINITION OF ARF RECOGNITION OF CAUSE OF ARF RECOGNITION OF PATHOGENESIS OF ARF RECOGNITION OF
The CARI Guidelines Caring for Australasians with Renal Impairment. Protein Restriction to prevent the progression of diabetic nephropathy GUIDELINES
 Protein Restriction to prevent the progression of diabetic nephropathy Date written: September 2004 Final submission: September 2005 Author: Kathy Nicholls GUIDELINES a. A small volume of evidence suggests
Protein Restriction to prevent the progression of diabetic nephropathy Date written: September 2004 Final submission: September 2005 Author: Kathy Nicholls GUIDELINES a. A small volume of evidence suggests
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Transplant Proc. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2011 April 6.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Transplant Proc. 1991 December ; 23(6): 2777 2779. Pharmacokinetics of Cyclosporine and Nephrotoxicity in Orthotopic Liver Transplant
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Transplant Proc. 1991 December ; 23(6): 2777 2779. Pharmacokinetics of Cyclosporine and Nephrotoxicity in Orthotopic Liver Transplant
Doppler ultrasound, see Ultrasonography. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), kidney oxygenation assessment 75
 Subject Index Acidemia, cardiorenal syndrome type 3 146 Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative (ADQI) acute kidney injury biomarkers, see Acute kidney injury; specific biomarkers cardiorenal syndrome, see specific
Subject Index Acidemia, cardiorenal syndrome type 3 146 Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative (ADQI) acute kidney injury biomarkers, see Acute kidney injury; specific biomarkers cardiorenal syndrome, see specific
(renoprotective (end-stage renal disease, ESRD) therapies) (JAMA)
 [1], 1., 2. 3. (renoprotective (end-stage renal disease, ESRD) therapies) (JAMA) (multiple risk (renal replacement therapy, RRT) factors intervention treatment MRFIT) [2] ( 1) % (ESRD) ( ) ( 1) 2001 (120
[1], 1., 2. 3. (renoprotective (end-stage renal disease, ESRD) therapies) (JAMA) (multiple risk (renal replacement therapy, RRT) factors intervention treatment MRFIT) [2] ( 1) % (ESRD) ( ) ( 1) 2001 (120
Rejection or Not? Interhospital Renal Meeting 10 Oct Desmond Yap & Sydney Tang Queen Mary Hospital
 Rejection or Not? Interhospital Renal Meeting 10 Oct 2007 Desmond Yap & Sydney Tang Queen Mary Hospital Case Presentation F/61 End stage renal failure due to unknown cause Received HD in private hospital
Rejection or Not? Interhospital Renal Meeting 10 Oct 2007 Desmond Yap & Sydney Tang Queen Mary Hospital Case Presentation F/61 End stage renal failure due to unknown cause Received HD in private hospital
Published trials point to a detrimental relationship
 ANEMIA, CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE, AND CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE: THE CLINICAL TRIALS Steven Fishbane, MD* ABSTRACT Clinical trials have shown a strong detrimental relationship among anemia, chronic kidney disease
ANEMIA, CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE, AND CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE: THE CLINICAL TRIALS Steven Fishbane, MD* ABSTRACT Clinical trials have shown a strong detrimental relationship among anemia, chronic kidney disease
efficacy of verapamil, enalapril, and doxazosin
 Kidney International, Vol. 54, Suppl. 68 (1998), pp. S-130 S-134 Treatment of hypertension after renal transplantation: Long-term efficacy of verapamil, enalapril, and doxazosin ALBERTO MARTÍNEZ-CASTELAO,
Kidney International, Vol. 54, Suppl. 68 (1998), pp. S-130 S-134 Treatment of hypertension after renal transplantation: Long-term efficacy of verapamil, enalapril, and doxazosin ALBERTO MARTÍNEZ-CASTELAO,
Section 3, Lecture 2
 59-291 Section 3, Lecture 2 Diuretics: -increase in Na + excretion (naturesis) Thiazide and Related diuretics -decreased PVR due to decreases muscle contraction -an economical and effective treatment -protect
59-291 Section 3, Lecture 2 Diuretics: -increase in Na + excretion (naturesis) Thiazide and Related diuretics -decreased PVR due to decreases muscle contraction -an economical and effective treatment -protect
Principles of Renal Physiology. 4th Edition
 Principles of Renal Physiology 4th Edition Principles of Renal Physiology 4th Edition Chris Lote Professor of Experimental Nephrology, University of Birmingham, UK SPRINGER SCIENCE+BUSINESS MEDIA, B.V.
Principles of Renal Physiology 4th Edition Principles of Renal Physiology 4th Edition Chris Lote Professor of Experimental Nephrology, University of Birmingham, UK SPRINGER SCIENCE+BUSINESS MEDIA, B.V.
Hypertension in Systemic Diseases
 Hypertension in Systemic Diseases Prof. Andrzej Więcek FRCP (Edin.), FERA Department of Nephrology, Transplantation and Internal Medicine Medical University of Silesia, Katowice, Poland Hypertension in
Hypertension in Systemic Diseases Prof. Andrzej Więcek FRCP (Edin.), FERA Department of Nephrology, Transplantation and Internal Medicine Medical University of Silesia, Katowice, Poland Hypertension in
KDIGO Controversies Conference on Management of Patients with Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease
 KDIGO Controversies Conference on Management of Patients with Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease February 5-8, 2015 Vancouver, Canada Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) is an international
KDIGO Controversies Conference on Management of Patients with Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease February 5-8, 2015 Vancouver, Canada Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) is an international
Reversal of Microalbuminuria A Causative Factor of Diabetic Nephropathy is Achieved with ACE Inhibitors than Strict Glycemic Control
 ISSN 0976 3333 Available Online at www.ijpba.info International Journal of Pharmaceutical & Biological Archives 2013; 4(5): 923-928 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Reversal of Microalbuminuria A Causative Factor
ISSN 0976 3333 Available Online at www.ijpba.info International Journal of Pharmaceutical & Biological Archives 2013; 4(5): 923-928 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Reversal of Microalbuminuria A Causative Factor
Case Presentation Turki Al-Hussain, MD
 Case Presentation Turki Al-Hussain, MD Director, Renal Pathology Chapter Saudi Society of Nephrology & Transplantation Consultant Nephropathologist & Urological Pathologist Department of Pathology & Laboratory
Case Presentation Turki Al-Hussain, MD Director, Renal Pathology Chapter Saudi Society of Nephrology & Transplantation Consultant Nephropathologist & Urological Pathologist Department of Pathology & Laboratory
DIABETES AND YOUR KIDNEYS
 DIABETES AND YOUR KIDNEYS OR AS WE CALL IT DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY The latest guidelines to keep you safe, healthy, fit, and out of danger from needing dialysis A UCLA HEALTH EDUCATIONAL SEMINAR Ramy M. Hanna
DIABETES AND YOUR KIDNEYS OR AS WE CALL IT DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY The latest guidelines to keep you safe, healthy, fit, and out of danger from needing dialysis A UCLA HEALTH EDUCATIONAL SEMINAR Ramy M. Hanna
Prevention And Treatment of Diabetic Nephropathy. MOH Clinical Practice Guidelines 3/2006 Dr Stephen Chew Tec Huan
 Prevention And Treatment of Diabetic Nephropathy MOH Clinical Practice Guidelines 3/2006 Dr Stephen Chew Tec Huan Prevention Tight glucose control reduces the development of diabetic nephropathy Progression
Prevention And Treatment of Diabetic Nephropathy MOH Clinical Practice Guidelines 3/2006 Dr Stephen Chew Tec Huan Prevention Tight glucose control reduces the development of diabetic nephropathy Progression
Diabetic Nephropathy
 Diabetic Nephropathy Objectives: Know what Diabetic Nephropathy means. Know how common is Diabetic nephropathy in Saudi Arabia and to appreciate how bad are this complications. Know the risk factors of
Diabetic Nephropathy Objectives: Know what Diabetic Nephropathy means. Know how common is Diabetic nephropathy in Saudi Arabia and to appreciate how bad are this complications. Know the risk factors of
Analysis of Factors Causing Hyperkalemia
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Analysis of Factors Causing Hyperkalemia Kenmei Takaichi 1, Fumi Takemoto 1, Yoshifumi Ubara 1 and Yasumichi Mori 2 Abstract Objective Patients with impaired renal function or diabetes
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Analysis of Factors Causing Hyperkalemia Kenmei Takaichi 1, Fumi Takemoto 1, Yoshifumi Ubara 1 and Yasumichi Mori 2 Abstract Objective Patients with impaired renal function or diabetes
Dr. Mehmet Kanbay Department of Medicine Division of Nephrology Istanbul Medeniyet University School of Medicine Istanbul, Turkey.
 The uric acid dilemma: causal risk factor for hypertension and CKD or mere bystander? Mehmet Kanbay, Istanbul, Turkey Chairs: Anton H. van den Meiracker, Rotterdam, The Netherlands Claudia R.C. Van Roeyen,
The uric acid dilemma: causal risk factor for hypertension and CKD or mere bystander? Mehmet Kanbay, Istanbul, Turkey Chairs: Anton H. van den Meiracker, Rotterdam, The Netherlands Claudia R.C. Van Roeyen,
COMPOSITION. A film coated tablet contains. Active ingredient: irbesartan 75 mg, 150 mg or 300 mg. Rotazar (Film coated tablets) Irbesartan
 Rotazar (Film coated tablets) Irbesartan Rotazar 75 mg, 150 mg, 300 mg COMPOSITION A film coated tablet contains Active ingredient: irbesartan 75 mg, 150 mg or 300 mg. Rotazar 75 mg, 150 mg, 300 mg PHARMACOLOGICAL
Rotazar (Film coated tablets) Irbesartan Rotazar 75 mg, 150 mg, 300 mg COMPOSITION A film coated tablet contains Active ingredient: irbesartan 75 mg, 150 mg or 300 mg. Rotazar 75 mg, 150 mg, 300 mg PHARMACOLOGICAL
Literature Review Transplantation
 Literature Review 2010- Transplantation Alexander Wiseman, M.D. Associate Professor, Division of Renal Diseases and Hypertension Medical Director, Kidney and Pancreas Transplant Programs University of
Literature Review 2010- Transplantation Alexander Wiseman, M.D. Associate Professor, Division of Renal Diseases and Hypertension Medical Director, Kidney and Pancreas Transplant Programs University of
THE RENIN-ANGIOTENSIN-ALDOSTERONE SYSTEM
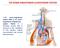 THE RENIN-ANGIOTENSIN-ALDOSTERONE SYSTEM The renin angiotensin system (RAS) or the renin angiotensin aldosterone system (RAAS) is a hormone system that is involved in the regulation of the plasma sodium
THE RENIN-ANGIOTENSIN-ALDOSTERONE SYSTEM The renin angiotensin system (RAS) or the renin angiotensin aldosterone system (RAAS) is a hormone system that is involved in the regulation of the plasma sodium
Renal Transporters- pathophysiology of drug - induced renal disorders. Lisa Harris, Pharmacist, John Hunter Hospital, Newcastle, 2015 November
 Renal Transporters- pathophysiology of drug - induced renal disorders Lisa Harris, Pharmacist, John Hunter Hospital, Newcastle, 2015 November Renal Failure Up to 25% of acute renal failure is drug induced
Renal Transporters- pathophysiology of drug - induced renal disorders Lisa Harris, Pharmacist, John Hunter Hospital, Newcastle, 2015 November Renal Failure Up to 25% of acute renal failure is drug induced
Special Challenges and Co-Morbidities
 Special Challenges and Co-Morbidities Renal Disease/ Hypertension/ Diabetes in African-Americans M. Keith Rawlings, MD Medical Director Peabody Health Center AIDS Arms, Inc Dallas, TX Chair, Internal Medicine
Special Challenges and Co-Morbidities Renal Disease/ Hypertension/ Diabetes in African-Americans M. Keith Rawlings, MD Medical Director Peabody Health Center AIDS Arms, Inc Dallas, TX Chair, Internal Medicine
Cardiorenal Syndrome Prof. Dr. Bülent ALTUN Hacettepe University Faculty of Medicine Department of Internal Medicine Division of Nephrology
 Cardiorenal Syndrome Prof. Dr. Bülent ALTUN Hacettepe University Faculty of Medicine Department of Internal Medicine Division of Nephrology Heart and Kidney The kidney yin dominates water, The heart yang
Cardiorenal Syndrome Prof. Dr. Bülent ALTUN Hacettepe University Faculty of Medicine Department of Internal Medicine Division of Nephrology Heart and Kidney The kidney yin dominates water, The heart yang
The hypertensive kidney and its Management
 The hypertensive kidney and its Management Dr H0 Chung Ping Hypertension Management Seminar 20061124 Hypertensive kidney Kidney damage asymptomatic till late stage Viscous cycle to augment renal damage
The hypertensive kidney and its Management Dr H0 Chung Ping Hypertension Management Seminar 20061124 Hypertensive kidney Kidney damage asymptomatic till late stage Viscous cycle to augment renal damage
Antihypertensive drugs SUMMARY Made by: Lama Shatat
 Antihypertensive drugs SUMMARY Made by: Lama Shatat Diuretic Thiazide diuretics The loop diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics *Hydrochlorothiazide *Chlorthalidone *Furosemide *Torsemide *Bumetanide Aldosterone
Antihypertensive drugs SUMMARY Made by: Lama Shatat Diuretic Thiazide diuretics The loop diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics *Hydrochlorothiazide *Chlorthalidone *Furosemide *Torsemide *Bumetanide Aldosterone
University of Groningen. Evaluation of renal end points in nephrology trials Weldegiorgis, Misghina Tekeste
 University of Groningen Evaluation of renal end points in nephrology trials Weldegiorgis, Misghina Tekeste IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish
University of Groningen Evaluation of renal end points in nephrology trials Weldegiorgis, Misghina Tekeste IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish
CKD FOR INTERNISTS. Dr Ahmed Hossain Associate professor Medicine Sir Salimullah Medical College
 CKD FOR INTERNISTS Dr Ahmed Hossain Associate professor Medicine Sir Salimullah Medical College INTRODUCTION In 2002, the National Kidney Foundation s Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative(KDOQI)
CKD FOR INTERNISTS Dr Ahmed Hossain Associate professor Medicine Sir Salimullah Medical College INTRODUCTION In 2002, the National Kidney Foundation s Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative(KDOQI)
HUGE EQUATION ACCURACY FOR SCREENING CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE: A PROSPECTIVE STUDY
 Journal of Aging Research & Clinical Practice Volume 6, 2017 J Aging Res Clin Practice 2017;inpress Published online in press HUGE EQUATION ACCURACY FOR SCREENING CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE: A PROSPECTIVE
Journal of Aging Research & Clinical Practice Volume 6, 2017 J Aging Res Clin Practice 2017;inpress Published online in press HUGE EQUATION ACCURACY FOR SCREENING CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE: A PROSPECTIVE
DRUGS USED TO TREAT HYPERTENSION BY ALI ALALAWI
 DRUGS USED TO TREAT HYPERTENSION BY ALI ALALAWI 3. Vasodilators Drugs which dilate blood vessels ( decrease peripheral vascular resistance) by acting on smooth muscle cells through non-autonomic mechanisms:
DRUGS USED TO TREAT HYPERTENSION BY ALI ALALAWI 3. Vasodilators Drugs which dilate blood vessels ( decrease peripheral vascular resistance) by acting on smooth muscle cells through non-autonomic mechanisms:
Diabetes and Hypertension
 Diabetes and Hypertension M.Nakhjvani,M.D Tehran University of Medical Sciences 20-8-96 Hypertension Common DM comorbidity Prevalence depends on diabetes type, age, BMI, ethnicity Major risk factor for
Diabetes and Hypertension M.Nakhjvani,M.D Tehran University of Medical Sciences 20-8-96 Hypertension Common DM comorbidity Prevalence depends on diabetes type, age, BMI, ethnicity Major risk factor for
Comparison between the efficacy of double blockade and single blockade of RAAS in diabetic kidney disease
 International Journal of Advances in Medicine Gupta A et al. Int J Adv Med. 2018 Aug;5(4):931-935 http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20183122
International Journal of Advances in Medicine Gupta A et al. Int J Adv Med. 2018 Aug;5(4):931-935 http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20183122
Reducing proteinuria
 Date written: May 2005 Final submission: October 2005 Author: Adrian Gillin Reducing proteinuria GUIDELINES a. The beneficial effect of treatment regimens that include angiotensinconverting enzyme inhibitors
Date written: May 2005 Final submission: October 2005 Author: Adrian Gillin Reducing proteinuria GUIDELINES a. The beneficial effect of treatment regimens that include angiotensinconverting enzyme inhibitors
Antihypertensives. Antihypertensive Classes. RAAS Inhibitors. Renin-Angiotensin Cascade. Angiotensin Receptors. Approaches to Hypertension Treatment
 Approaches to Hypertension Treatment Antihypertensives Inhibit Sympathetic impulses Inhibit contractility Inhibit heart rate Inhibit vasoconstriction Inhibit smooth muscle function Inhibit RAAS Inhibit
Approaches to Hypertension Treatment Antihypertensives Inhibit Sympathetic impulses Inhibit contractility Inhibit heart rate Inhibit vasoconstriction Inhibit smooth muscle function Inhibit RAAS Inhibit
Introductory Clinical Pharmacology Chapter 41 Antihypertensive Drugs
 Introductory Clinical Pharmacology Chapter 41 Antihypertensive Drugs Blood Pressure Normal = sys
Introductory Clinical Pharmacology Chapter 41 Antihypertensive Drugs Blood Pressure Normal = sys
Preoperative Serum Bicarbonate Levels Predict Acute Kidney Iinjry after Cardiac Surgery
 International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN (USA): IJCRGG, ISSN: 0974-4290, ISSN(Online):2455-9555 Vol.11 No.06, pp 203-208, 2018 Preoperative Serum Bicarbonate Levels Predict Acute Kidney Iinjry
International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN (USA): IJCRGG, ISSN: 0974-4290, ISSN(Online):2455-9555 Vol.11 No.06, pp 203-208, 2018 Preoperative Serum Bicarbonate Levels Predict Acute Kidney Iinjry
Objectives. Pre-dialysis CKD: The Problem. Pre-dialysis CKD: The Problem. Objectives
 The Role of the Primary Physician and the Nephrologist in the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease () By Brian Young, M.D. Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA
The Role of the Primary Physician and the Nephrologist in the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease () By Brian Young, M.D. Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA
6/10/2014. Chronic Kidney Disease - General management and standard of care. Management of CKD according to stage (KDOQI 2002)
 Chronic Kidney Disease - General management and standard of care Dr Nathalie Demoulin, Prof Michel Jadoul Cliniques universitaires Saint-Luc Université Catholique de Louvain What should and can be done
Chronic Kidney Disease - General management and standard of care Dr Nathalie Demoulin, Prof Michel Jadoul Cliniques universitaires Saint-Luc Université Catholique de Louvain What should and can be done
Analgesic and NSAID-induced Kidney Disease
 Analgesic and NSAID-induced Kidney Disease Edited by J.H.STEWART Associate Dean, Western Clinical School University of Sydney, Australia Oxford New York Tokyo Melbourne OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS 1993 CONTENTS
Analgesic and NSAID-induced Kidney Disease Edited by J.H.STEWART Associate Dean, Western Clinical School University of Sydney, Australia Oxford New York Tokyo Melbourne OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS 1993 CONTENTS
Salt Sensitivity: Mechanisms, Diagnosis, and Clinical Relevance
 Salt Sensitivity: Mechanisms, Diagnosis, and Clinical Relevance Matthew R. Weir, MD Professor and Director Division of Nephrology University of Maryland School of Medicine Overview Introduction Mechanisms
Salt Sensitivity: Mechanisms, Diagnosis, and Clinical Relevance Matthew R. Weir, MD Professor and Director Division of Nephrology University of Maryland School of Medicine Overview Introduction Mechanisms
Acute Kidney Injury for the General Surgeon
 Acute Kidney Injury for the General Surgeon UCSF Postgraduate Course in General Surgery Maui, HI March 20, 2011 Epidemiology & Definition Pathophysiology Clinical Studies Management Summary Hobart W. Harris,
Acute Kidney Injury for the General Surgeon UCSF Postgraduate Course in General Surgery Maui, HI March 20, 2011 Epidemiology & Definition Pathophysiology Clinical Studies Management Summary Hobart W. Harris,
Case Report Beneficial Effect of Conversion to Belatacept in Kidney-Transplant Patients with a Low Glomerular-Filtration Rate
 Case Reports in Transplantation, Article ID 190516, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/190516 Case Report Beneficial Effect of Conversion to Belatacept in Kidney-Transplant Patients with a Low Glomerular-Filtration
Case Reports in Transplantation, Article ID 190516, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/190516 Case Report Beneficial Effect of Conversion to Belatacept in Kidney-Transplant Patients with a Low Glomerular-Filtration
Cardiorenal Syndrome
 Cardiorenal Syndrome Peenida Skulratanasak, M.D. Division of Nephrology, Department of Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Siriraj Hospital, Mahidol University Definition of Cardiorenal syndrome (CRS) Structural
Cardiorenal Syndrome Peenida Skulratanasak, M.D. Division of Nephrology, Department of Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Siriraj Hospital, Mahidol University Definition of Cardiorenal syndrome (CRS) Structural
Urine Formation by the Kidneys: I. Glomerular Filtration, Renal Blood Flow and Their Control.
 Urine Formation by the Kidneys: I. Glomerular Filtration, Renal Blood Flow and Their Control. Chapter 26 Yanal A Shafagoj. MD. PhD Lecture-1 Introduction 31/3/2015 1 University of Jordan Faculty of Medicine
Urine Formation by the Kidneys: I. Glomerular Filtration, Renal Blood Flow and Their Control. Chapter 26 Yanal A Shafagoj. MD. PhD Lecture-1 Introduction 31/3/2015 1 University of Jordan Faculty of Medicine
Figure 1 LVH: Allowed Cost by Claim Volume (Data generated from a Populytics analysis).
 Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD): The New Silent Killer Nelson Kopyt D.O. Chief of Nephrology, LVH Valley Kidney Specialists For the past several decades, the health care needs of Americans have shifted from
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD): The New Silent Killer Nelson Kopyt D.O. Chief of Nephrology, LVH Valley Kidney Specialists For the past several decades, the health care needs of Americans have shifted from
Analysis of AVP functions via V1a and V1b receptors with knockout mice. Akito Tanoue
 Analysis of AVP functions via V1a and V1b receptors with knockout mice Akito Tanoue Department of Pharmacology, National Research Institute for Child Health and Development Arginine-Vasopressin (AVP) is
Analysis of AVP functions via V1a and V1b receptors with knockout mice Akito Tanoue Department of Pharmacology, National Research Institute for Child Health and Development Arginine-Vasopressin (AVP) is
Prof. Andrzej Wiecek Department of Nephrology, Endocrinology and Metabolic Diseases Medical University of Silesia Katowice, Poland.
 What could be the role of renal denervation in chronic kidney disease? Andrzej Wiecek, Katowice, Poland Chairs: Peter J. Blankestijn, Utrecht, The Netherlands Jonathan Moss, Glasgow, UK Prof. Andrzej Wiecek
What could be the role of renal denervation in chronic kidney disease? Andrzej Wiecek, Katowice, Poland Chairs: Peter J. Blankestijn, Utrecht, The Netherlands Jonathan Moss, Glasgow, UK Prof. Andrzej Wiecek

 www.usrds.org www.usrds.org 1 1,749 + (2,032) 1,563 to
www.usrds.org www.usrds.org 1 1,749 + (2,032) 1,563 to