Fed state. Fasting state. Glucagon (alpha cell) Pancreas. Insulin (beta cell) Glucose output. Glucose uptake. Blood glucose. Liver
|
|
|
- Gregory Lester
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Physiopathology of Diabetes & Diagnosis Contents Normal physiology of glucose control Classification of diabetes Type 2 diabetes Type 1 diabetes Diagnosis of diabetes ١
2 Insulin and Glucagon Regulate Normal Glucose Homeostasis Glucagon (alpha cell) Fasting state Pancreas Fed state Release of gut hormones Incretins 1,2 (GLP-1 & GIP) Insulin (beta cell) Glucose output Liver Blood glucose Glucose uptake Muscle Adipose tissue Porte D Jr, Kahn SE. Clin Invest Med. 1995;18: Adapted from Kahn CR, Saltiel AR. In: Kahn CR et al, eds. Joslin s Diabetes Mellitus. 14th ed. Lippincott Williams & ٢ Wilkins; 2005:
3 Insulin Action in Muscle and Fat Cells Mobilization o of GLUT4 to the Cell Surface Plasma membrane Insulin receptor Intracellular signaling cascades Intracellular GLUT4 vesicles Insulin GLUT4 vesicle mobilization to plasma membrane GLUT4 vesicle integration into plasma membrane Glucose entry into cell via GLUT4 GLUT4=glucose transporter 4 ٣
4 Classification of Diabetes Mellitus by Etiology Type 1 β-cell destruction complete lack of insulin Type 2 β-cell dysfunction and insulin resistance Gestational β-cell dysfunction and insulin resistance during pregnancy Other specific types Genetic defects df of β-cell function Exocrine pancreatic diseases Endocrinopathies Drug- or chemical-induced Other rare forms ۴
5 Etiology of Type 2 Diabetes Impaired Insulin Secretion and Insulin Resistance Genes and environment Impaired insulin secretion + Insulin resistance Impaired glucose tolerance Type 2 diabetes ۵
6 Natural History of Type 2 Diabetes Progression Years from diagnosis Insulin resistance Insulin secretion Pre-diabetes Onset Microvascular Macrovascular complications complications Diagnosis Type 2 diabetes (T2DM) ۶
7 Pathogenesis of Type 1 Diabetes One Defect No hepatic insulin effect Absent insulin secretion No muscle/fat insulin effect Unrestrained glucose production Hyperglycemia Impaired glucose clearance More glucose enters the blood Glycosuria Less glucose enters peripheral tissues ٧
8 Natural History Of Pre Type 1 Diabetes β-cell mass 100% Putative trigger Cellular autoimmunity Circulating autoantibodies (ICA, GAD65) Genetic predisposition Insulitis β-cell injury Loss of first-phase insulin response (IVGTT) Glucose intolerance (OGTT) Pre - diabetes Diabetes Clinical onset only 10% of β-cells remain Time Eisenbarth GS. N Engl J Med. 1986;314: ٨
9 Glucose Tolerance Categories FPG 2-h PPG (OGTT) Plasma glucose (mg/dl) Diabetes Mellitus Diabetes Mellitus IGT Plasma glucose (mmol/l) IFG 100 Normal 80 Normal American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care. 2007;30(suppl 1) ٩
10 Criteria for the Diagnosis of Diabetes Mellitus Symptoms of diabetes plus random blood glucose concentration 11.1mmol/L (200 mg/dl) Fasting plasma glucose 7.0 mmol/l (126 mg/dl) Two-hour plasma glucose 11.1 mmol/l (140 mg/dl) during an oral glucose tolerance testc or or ١٠
11 Diabetes Mellitus Complications ١١
12 Acute Complications of DM Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar State (HHS) Both disorders are associated with absolute or relative insulin deficiency, volume depletion, and acid-base abnormalities ١٢
13 Hyperglycemia The Defining i Feature of Diabetes Excessive glucose production Hyperglycemia Impaired glucose clearance Tissue injury ١٣ 1
14 Two Mechanisms of Tissue Injury by Hyperglycemia Glycation Hyperglycemia Sorbitol pathway pathway Glycated proteins (eg, A1C) Advanced glycation gy end products (AGEs) Sorbitol and fructose Altered function or turnover Receptor-mediated cytokine effects Osmotic effects Oxidative effects Brownlee M. Metabolism. 2000;49(suppl 1):9-13; Greene DA et al. N Engl J Med. 1987;316: ; Sheetz MJ, King GL. JAMA. 2002;288: ١۴
15 Chronic Complications of DM Microvascular Macrovascular Other Gastrointestinal Genitourinary i Dermatologic Infectious Cataracts Glaucoma ١۵
16 Eye What are the Microvascular Complications? Hyperglycemia Kidney Nerves Retinopathy Macular edema Nephropathy Neuropathy Microalbuminuria i i Peripheral Gross albuminuria Autonomic Blindness Kidney failure Amputation Death and/or disability ١۶
17 Retinopathy Normal retina Proliferative retinopathy ١٧
18 What are the Macrovascular Complications? Metabolic injury to large vessels Heart Brain Extremities Coronary artery disease Cerebrovascular diseaseperipheral vascular Coronary syndrome MI CHF TIA CVA Cognitive impairment disease Ulceration Gangrene Amputation ١٨
19 Macrovascular disease at diagnosis in Type 2 diabetes Cerebrovascular disease 1% 75% of all deaths in people with Type 2 diabetes are due to Abnormal ECG 18% cardiovascular disease Hypertension 35% Absent foot pulses 13% Intermittent claudication 3% UKPDS Group. Diabetes Res 1990; 13: ١٩
20 Risk of Microvascular Complications vs. A1C in Type 1 Diabetes Results From the DCCT Relative risk Retinopathy progression Neuropathy progression o Microalbuminuria progression A1C (%) Skyler JS. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 1996;25: ٢٠
21 Risk of Microvascular Events vs. A1C in Type 2 Diabetes Hazard ratio 10 8 Results From Epidemiologic Analysis of the UKPDS % change per 1% change in A1C 2 0 Stratton IM et al. BMJ. 2000;321: A1C (%) ٢١
22 A1C Predicts Myocardial Infarction in Type 2 Diabetes UKPDS Relative risk Patients Followed for 10 Years* <6 6 to <7 7 to <8 8 to <9 9 to <10 10 *Adjusted for age, sex, and duration of diabetes Stratton IM et al. BMJ. 2000;321: A1C (%) ٢٢
23 TREATMENT ٢٣
24 Guidelines: Limitations Despite many current guidelines for glycaemic control there is still a lack of consensus on ideal target and intervention values Incorporation of guidelines into clinical practice can be difficult large-scale studies have shown the need for improved glycaemic control, but many patients fail to reach goals for glycaemic gy control the complexity of the individual s characteristics, risk factors, needs and personal goals still need to be taken into account ٢۴
25 Current guidelines recommend targets for HbA1c, FPG and PPBG levels Glucose control Healthy ADA 1 AACE 3 IDF 4 ADA/ EASD 5 HbA 1c * (%) <6.0 1 < <6.5 <7.0 FBG, mmol/l (mg/dl) < <6.0 (< ) ( ) ( ) (< ) ( ) PPBG, mmol/l <7.8** <10.0** 7.8** <8.0** <10 (mg/dl) (< ) (< ) ( ) (< ) (< ) *DCCT aligned; **1 2 hours postprandial 1. American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 2006;29(suppl 1):S4 S42 S American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 2006;29(suppl 1):S American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists. Endocr Pract 2002;8(suppl 1): International Diabetes Federation. Global Guideline for Type 2 Diabetes. Brussels: International Diabetes Federation, Nathan D, et al. Diabetologia 2006;49; ٢۵
26 Insulin and Glucagon Regulate Normal Glucose Homeostasis Glucagon (alpha cell) Fasting state Pancreas Fed state Release of gut hormones Incretins 1,2 (GLP-1 & GIP) Insulin (beta cell) Glucose output Liver Blood glucose Glucose uptake Muscle Adipose tissue Porte D Jr, Kahn SE. Clin Invest Med. 1995;18: Adapted from Kahn CR, Saltiel AR. In: Kahn CR et al, eds. Joslin s Diabetes Mellitus. 14th ed. Lippincott Williams & ٢۶ Wilkins; 2005:
27 Treatment of Diabetes Non-pharmacologic Oral agents Insulin ٢٧
28 Non-pharmacologic Nutrition Exercise Life-style Change ٢٨
29 Treatment of T2DM Is Accomplished by Different Agents via Different Modes of Action Insulin secretagogues Insulin Inhibitors of gluconeogenesis Inhibitors of glucose absorption Insulin sensitizers Insulin secretion Liver/gut glucose delivery Insulin resistance Glucose toxicity Blood glucose Glucose toxicity ٢٩
30 Oral Anti-Diabetes Agents OADs INSULIN SENSITIZERS OTHERS α-glucosidase Inhibitor INSULIN SECRETAGOGUES acarbose GLUCOBAY (Bayer) Biguanidesid Thiazolidinediones / Sulphonylureas l Non-Sulphonylureas l Glitazone (TZD) metformin roziglitazone AVANDIA (GSK) chlorpropamide DIABENESE (Pfizer) glibenclamide repaglinide NOVONORM (Novo) nateglinide GLUCOPHAGE (Merck) pioglitazone ACTOS (Eli Lilly) DAONIL (Aventis) gliclazide DIAMICRON (Servier) glipizide MINIDIAB (Pfizer) glimepiride AMARYL (Aventis) STARLIX (Novartis) ٣٠
31 How Different Agents Regulate Hyperglycemia y in Diabetes Pancreatic beta cells Liver Amelioration of hyperglycemia Sulfonylureas Meglitinides Stimulate insulin release Muscle PPARs (TZDs or glitazones) Biguanides Insulin Inhibit glucose production Gut PPARs (TZDs or glitazones) Biguanides Insulin Stimulate glucose uptake Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors Retard glucose reflux into circulation PPAR=peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor agonist. Williams G, Pickup JC, eds. Handbook of Diabetes. 3rd ed. Malden, Ma: Blackwell Publishing, 2004; DeFronzo RA. Ann Intern Med. 1999;131: ; Buse JB et al. In: Williams Textbook of Endocrinology. 10th ed. Philadelphia, Pa: Saunders, 2003: ٣١ Adapted from DeFronzo RA. Ann Intern Med. 1999;131:
32 Therapeutic Effects and Limitations Class Sulfonylureas Meglitinides Biguanides (metformin) PPARs Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors Insulin Primary Effect HbA1c PPG HbA1c HbA1c PPG HbA1c Limitations Hypoglycemia, weight gain Hypoglycemia, weight gain GI adverse effects, lactic acidosis (rare) Weight gain, edema, anemia, potential for liver toxicity GI adverse effects Injectable route, hypoglycemia, weight ih gain PPG=postprandial glucose; GI=gastrointestinal gastrointestinal. DeFronzo RA. Ann Intern Med. 1999;131: ; Williams G, Pickup JC, eds. Handbook of Diabetes. 3rd ed. Malden, Ma: Blackwell Publishing, 2004; Holz GG, Chepurny OG. Curr Med Chem. 2003;10: ; Meneilly GS et al. Diabetes Care. 2003;26: ; Ahrén B et al. Diabetes Care. 2002;25: ; Moller DE. Nature. 2001;414: ٣٢
33 Insulin Deficiency and Resistance Type 2 DM 250 Relative e Function (%) β-cell failure Insulin resistance Insulin level Duration of Diabetes (years) Adapted from Bergenstal RM. In: Endocrinology. Philadelphia, Pa: W.B. Saunders Co; 2001: ٣٣
34 The Number of Medications Taken Usually Increases With Duration of Disease 100 Diabetes diagnosed Monotherapy failure Requiring insulin Beta-ce ell functi ion (%) IGT Monotherapy Dual-drug regimens Multidrug combination +/ insulin Insulinbased regimens Approximate time (years) IGT=impaired glucose tolerance. UKPDS 16. Diabetes. 1995;44: Turner RC et al. JAMA. 1999;281: ; Warren RE. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2004;65:S3 S8; Lebovitz HE. Med Clin N Am. 2004;88: ٣۴
35 Oral Monotherapy: Failure Is Inevitable Type 2 DM Failure rates for oral monotherapy in type 2 diabetes* 1,2 Study 3 Years 6 Years 9 Years UKPDS 49 >45% NS >75% (N=4075) UKPDS 24 NS 52% NS (N=458) *Failure rates defined as A1C concentration >7% in UKPDS 49 and >8% in UKPDS 24. NS, not studied; UKPDS, United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study. 1. Turner RC et al. JAMA. 1999;281: UKPDS 24. Ann Intern Med. 1998;128: ٣۵
36 Insulin Therapy ٣۶
37 Action of Insulin Time Breakfast Lunch Supper ٣٧
38 Normal Insulin Secretion: The Basal-Bolus Bolus Insulin Concept In nsulin Ef ffect Endogenous Insulin Bolus Insulin Basal Insulin B B, breakfast; L, lunch; D, dinner; HS, bedtime. L D Time of Administration HS Adapted from: 1. Leahy JL. In: Leahy JL, Cefalu WT, eds. Insulin Therapy. New York, NY: Marcel Dekker, Inc.; Bolli GB et al. Diabetologia. 1999;42: ٣٨
39 Comparison of Human Insulins and Analogues Insulin Preparations Onset of Action Peak of Action (h) Duration of Action (h) Short-acting Regular human min Rapid Acting Lispro/Aspart/Glulisine 5-15 min Intermediate-acting acting NPH 1-3 h Lente 1-3 h Long-acting Glargine 1-2 h Peakless >24 Ultralente 2-4 h 8-14 <20 Time course of action of any insulin can vary in different people or at different times in the same person; thus, time periods indicated here should only be considered general guidelines. Leahy JL. In: Leahy JL, Cefalu WT, eds. Insulin Therapy. New York, NY: Marcel Dekker, Inc.; ٣٩
40 Insulin Time Action Curves Effect Relative e Insulin Rapid (Lispro, Aspart/Glulisine) Short (Regular) Intermediate (NPH) Prolonged Intermediate (Ultralente) Long (Glargine, Detemir) Time (Hours) ۴٠
41 Twice-daily pre-mixed insulins Pla asma levels Breakfast Lunch Dinner Snack Normal endogenous insulin Regular insulin NPH insulin Both insulins combined Risk of hyperglycaemia Risk of hypoglycaemia Time of day NPH=neutral protamine Hagedorn. Leahy JL. In: Leahy JL, Cefalu WT, eds. Insulin Therapy. New York, NY: Marcel Dekker, Inc; 2002: Bolli GB et al. Diabetologia. 1999;42: ۴١
42 Insulin Treatment Regimens OAD + Basal OAD + Bolus Premix Mischinsulin 25/ Basal + Bolus
43 Basal insulins: The choices Generic name Brand name Insulin analogues Insulin glargine Insulin detemir NPH [Neutral Protamine Hagedorn] insulin Lantus Levemir Insulatard, Novolin N, Protaphane Human insulin Lente insulin (zinc suspension) Ultralente insulin (extended zinc suspension) Iletin Lente, Insulin Lente Pork (Humulin L*, Novolin L*) (Humulin U*, Ultratard *) *Discontinued ۴٣
44 Basal Insulin Long acting (e.g. glargine) Intermediate acting (e.g. NPH, lente) - Provides optimal basal insulin coverage with a once daily dosing - Less optimal as a basal insulin, because it doesn t have a flat insulin release profile - Lower risk of hypoglycemia - More hypoglycemic episodes - Flat release profile ۴۴
45 Prandial insulin promotes total flexibility in meal timing Ultra short/rapid acting insulin analogues (lispro) - Rapid onset of action - Forms monomers and thus is absorbed rapidly - Duration of action lasts for 4 hours regardless of the dose given Short acting insulin (regular insulin) - Less optimal profile as compared to rapid acting analogues - Forms hexamers and has slower absorption - Sustained duration of action may lead to post-prandial prandial hypoglycemia - Less hypoglycemia ۴۵
46 Limitations of Intermediate Insulins: NPH Does not mimick basal insulin profile 1,2 Variable absorption Pronounced peak hour duration Requires twice-daily administration to provide 24-hour basal insulin coverage Fear of hypoglycaemia 3 Major factor limiting insulin adjustments 1. Chan JL et al. Mayo Clin Proc. 2003;78: Leahy JL. In: Leahy JL, Cefalu WT, eds. Insulin Therapy. New York, NY: Marcel Dekker, Inc.; Bergenstal RM et al. In: DeGroot LJ, Jameson JL, eds. Endocrinology. 4th ed. Philadelphia, Pa: WB Saunders Co.; 2001: ۴۶
47 The Ideal Basal Insulin 1 injection daily covers 24 hours No peaks Low incidence id of hypoglycaemia Good glycaemic control Less weight gain Safe Predictable Easy handling Injection at different sites Injection at different times No mixing i necessary/clear solution High treatment satisfaction and acceptance ۴٧
48 Characteristics of Insulin Glargine Recombinant human insulin analogue 1 Basal (long-acting) insulin 1 Relatively constant peakless concentration over 24 hours 1,2 Once-daily SC administration 1 For adult and paediatric (aged 6 years) patients with type 1 diabetes and adults with type 2 diabetes 1,2 Lower risk of hypoglycaemia than with traditional basal insulins 1 Flexible dosing 1 1. Lantus (insulin glargine) EMEA Summary of Product Characteristics Lantus receives European approval for pediatric use. Aventis Pharma Web site. Available at: Accessed March 19, ۴٨
49 ADA/EASD consensus algorithm for type 2 diabetes mellitus (2006) Diagnosis Lifestyle intervention and metformin No HbA 1c 7% Yes a Add basal insulin c most effective Add sulfonylurea least expensive Add glitazone no hypoglycemia No HbA 1c 7% Yes a No HbA 1c 7% Yes a No HbA 1c 7% Yes a Intensify insulin c Add glitazone b Add basal insulin Add sulfonylurea b No HbA 1c 7% Yes a No HbA 1c 7% Yes a Add basal or intensify insulin c Intensive insulin + metformin +/ glitazone a Check HbA 1c every 3 months until HbA 1c is <7%, and then at least every 6 months. b Although three oral agents can be used, initiation and intensification of insulin therapy is preferred based on effectiveness and expense. c See Nathan et al for initiation and adjustment of insulin. Nathan D, et al. Diabetologia 2006;49:
50 ADA/EASD consensus algorithm for type 2 diabetes mellitus ( ) At diagnosis: Lifestyle + Metformin Tier 1: well-validated therapies Lifestyle + Metformin + Basal insulin Lifestyle + Metformin + Sulfonylureas Lifestyle + Metformin + Intensive insulin STEP 1 STEP 2 STEP 3 Tier 2: Less well validated therapies Lifestyle + Metformin + Pioglitazone No hypoglycaemia Oedema/CHF Bone loss Lifestyle + metformin +GLP1 GLP-1 agonist No hypoglycaemia Weight loss Nausea/vomiting Lifestyle + metformin + Pioglitazone + Sulfonylurea Lifestyle + metformin + Pioglitazone + Basal insulin Nathan DM, et al. Diabetes Care 2008;31:1 11.
Mae Sheikh-Ali, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Endocrinology University of Florida College of Medicine- Jacksonville
 Mae Sheikh-Ali, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Endocrinology University of Florida College of Medicine- Jacksonville Pathogenesis of Diabetes Mellitus (DM) Criteria for the diagnosis
Mae Sheikh-Ali, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Endocrinology University of Florida College of Medicine- Jacksonville Pathogenesis of Diabetes Mellitus (DM) Criteria for the diagnosis
Agenda. Indications Different insulin preparations Insulin initiation Insulin intensification
 Insulin Therapy F. Hosseinpanah Obesity Research Center Research Institute for Endocrine sciences Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences November 11, 2017 Agenda Indications Different insulin preparations
Insulin Therapy F. Hosseinpanah Obesity Research Center Research Institute for Endocrine sciences Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences November 11, 2017 Agenda Indications Different insulin preparations
Management of Type 2 Diabetes. Why Do We Bother to Achieve Good Control in DM2. Insulin Secretion. The Importance of BP and Glucose Control
 Insulin Secretion Management of Type 2 Diabetes DG van Zyl Why Do We Bother to Achieve Good Control in DM2 % reduction 0-5 -10-15 -20-25 -30-35 -40 The Importance of BP and Glucose Control Effects of tight
Insulin Secretion Management of Type 2 Diabetes DG van Zyl Why Do We Bother to Achieve Good Control in DM2 % reduction 0-5 -10-15 -20-25 -30-35 -40 The Importance of BP and Glucose Control Effects of tight
第十五章. Diabetes Mellitus
 Diabetes-1/9 第十五章 Diabetes Mellitus 陳曉蓮醫師 2/9 - Diabetes 羅東博愛醫院 Management of Diabetes mellitus A. DEFINITION OF DIABETES MELLITUS Diabetes Mellitus is characterized by chronic hyperglycemia with disturbances
Diabetes-1/9 第十五章 Diabetes Mellitus 陳曉蓮醫師 2/9 - Diabetes 羅東博愛醫院 Management of Diabetes mellitus A. DEFINITION OF DIABETES MELLITUS Diabetes Mellitus is characterized by chronic hyperglycemia with disturbances
Comprehensive Diabetes Treatment
 Comprehensive Diabetes Treatment Joshua L. Cohen, M.D., F.A.C.P. Professor of Medicine Interim Director, Division of Endocrinology & Metabolism The George Washington University School of Medicine Diabetes
Comprehensive Diabetes Treatment Joshua L. Cohen, M.D., F.A.C.P. Professor of Medicine Interim Director, Division of Endocrinology & Metabolism The George Washington University School of Medicine Diabetes
Society for Ambulatory Anesthesia Consensus Statement on Perioperative Blood Glucose Management in Diabetic Patients Undergoing Ambulatory Surgery
 Society for Ambulatory Anesthesia Consensus Statement on Perioperative Blood Glucose Management in Diabetic Patients Undergoing Ambulatory Surgery Girish P. Joshi, MB BS, MD, FFARCSI Anesthesia & Analgesia
Society for Ambulatory Anesthesia Consensus Statement on Perioperative Blood Glucose Management in Diabetic Patients Undergoing Ambulatory Surgery Girish P. Joshi, MB BS, MD, FFARCSI Anesthesia & Analgesia
Current Diabetes Care for Internists:2011
 Current Diabetes Care for Internists:2011 Petch Rawdaree, DM, MSc, DLSHTM Faculty of Medicine Vajira Hospital University of Bangkok Metropolis 19 th January 2011 ก ก 1. ก ก ก ก 2. ก ก ก ก ก 3. ก ก ก ก
Current Diabetes Care for Internists:2011 Petch Rawdaree, DM, MSc, DLSHTM Faculty of Medicine Vajira Hospital University of Bangkok Metropolis 19 th January 2011 ก ก 1. ก ก ก ก 2. ก ก ก ก ก 3. ก ก ก ก
Management of Type 2 Diabetes
 Management of Type 2 Diabetes Pathophysiology Insulin resistance and relative insulin deficiency/ defective secretion Not immune mediated No evidence of β cell destruction Increased risk with age, obesity
Management of Type 2 Diabetes Pathophysiology Insulin resistance and relative insulin deficiency/ defective secretion Not immune mediated No evidence of β cell destruction Increased risk with age, obesity
Abbreviations DPP-IV dipeptidyl peptidase IV DREAM Diabetes REduction Assessment with ramipril and rosiglitazone
 Index Abbreviations DPP-IV dipeptidyl peptidase IV DREAM Diabetes REduction Assessment with ramipril and rosiglitazone Medication GAD glutamic acid decarboxylase GLP-1 glucagon-like peptide 1 NPH neutral
Index Abbreviations DPP-IV dipeptidyl peptidase IV DREAM Diabetes REduction Assessment with ramipril and rosiglitazone Medication GAD glutamic acid decarboxylase GLP-1 glucagon-like peptide 1 NPH neutral
Clinical Overview of Combination Therapy with Sitagliptin and Metformin
 Clinical Overview of Combination Therapy with Sitagliptin and Metformin 1 Contents Pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes and mechanism of action of sitagliptin Clinical data overview of sitagliptin: Monotherapy
Clinical Overview of Combination Therapy with Sitagliptin and Metformin 1 Contents Pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes and mechanism of action of sitagliptin Clinical data overview of sitagliptin: Monotherapy
Timely!Insulinization In!Type!2! Diabetes,!When!and!How
 Timely!Insulinization In!Type!2! Diabetes,!When!and!How, FACP, FACE, CDE Professor of Internal Medicine UT Southwestern Medical Center Dallas, Texas Current Control and Targets 1 Treatment Guidelines for
Timely!Insulinization In!Type!2! Diabetes,!When!and!How, FACP, FACE, CDE Professor of Internal Medicine UT Southwestern Medical Center Dallas, Texas Current Control and Targets 1 Treatment Guidelines for
Diabetes: Definition Pathophysiology Treatment Goals. By Scott Magee, MD, FACE
 Diabetes: Definition Pathophysiology Treatment Goals By Scott Magee, MD, FACE Disclosures No disclosures to report Definition of Diabetes Mellitus Diabetes Mellitus comprises a group of disorders characterized
Diabetes: Definition Pathophysiology Treatment Goals By Scott Magee, MD, FACE Disclosures No disclosures to report Definition of Diabetes Mellitus Diabetes Mellitus comprises a group of disorders characterized
Obesity, Insulin Resistance, Metabolic Syndrome, and the Natural History of Type 2 Diabetes
 Obesity, Insulin Resistance, Metabolic Syndrome, and the Natural History of Type 2 Diabetes Genetics, environment, and lifestyle (obesity, inactivity, poor diet) Impaired fasting glucose Decreased β-cell
Obesity, Insulin Resistance, Metabolic Syndrome, and the Natural History of Type 2 Diabetes Genetics, environment, and lifestyle (obesity, inactivity, poor diet) Impaired fasting glucose Decreased β-cell
Update on Insulin-based Agents for T2D. Harry Jiménez MD, FACE
 Update on Insulin-based Agents for T2D Harry Jiménez MD, FACE Harry Jiménez MD, FACE Has received honorarium as Speaker and/or Consultant for the following pharmaceutical companies: Eli Lilly Merck Boehringer
Update on Insulin-based Agents for T2D Harry Jiménez MD, FACE Harry Jiménez MD, FACE Has received honorarium as Speaker and/or Consultant for the following pharmaceutical companies: Eli Lilly Merck Boehringer
Oral Hypoglycemics and Risk of Adverse Cardiac Events: A Summary of the Controversy
 Oral Hypoglycemics and Risk of Adverse Cardiac Events: A Summary of the Controversy Jeffrey Boord, MD, MPH Advances in Cardiovascular Medicine Kingston, Jamaica December 7, 2012 VanderbiltHeart.com Outline
Oral Hypoglycemics and Risk of Adverse Cardiac Events: A Summary of the Controversy Jeffrey Boord, MD, MPH Advances in Cardiovascular Medicine Kingston, Jamaica December 7, 2012 VanderbiltHeart.com Outline
Glyceamic control is indicated by 1. Fasting blood sugar less than 126 mg/dl 2. Random blood sugar 3. HbA1c less than 6.5 % Good glycaemic control
 Glyceamic control is indicated by 1. Fasting blood sugar less than 126 mg/dl 2. Random blood sugar 3. HbA1c less than 6.5 % Good glycaemic control can prevent many of early type 1 DM(in DCCT trail ). UK
Glyceamic control is indicated by 1. Fasting blood sugar less than 126 mg/dl 2. Random blood sugar 3. HbA1c less than 6.5 % Good glycaemic control can prevent many of early type 1 DM(in DCCT trail ). UK
INSULIN THERAPY. Rungnapa Laortanakul, MD Maharat Nakhon Ratchasima hospital
 INSULIN THERAPY Rungnapa Laortanakul, MD Maharat Nakhon Ratchasima hospital 3 Sep. 2013 Case Somsak is a 64-year-old man was diagnosed with T2DM, HT, and dyslipidemia 9 years ago. No history of hypoglycemia
INSULIN THERAPY Rungnapa Laortanakul, MD Maharat Nakhon Ratchasima hospital 3 Sep. 2013 Case Somsak is a 64-year-old man was diagnosed with T2DM, HT, and dyslipidemia 9 years ago. No history of hypoglycemia
Diabetes Mellitus. Raja Nursing Instructor. Acknowledgement: Badil 09/03/2016
 Diabetes Mellitus Raja Nursing Instructor 09/03/2016 Acknowledgement: Badil Objective: Define Diabetes Mellitus (DM) & types of DM. Understand the pathophysiology of Type-I & II DM. List the clinical features
Diabetes Mellitus Raja Nursing Instructor 09/03/2016 Acknowledgement: Badil Objective: Define Diabetes Mellitus (DM) & types of DM. Understand the pathophysiology of Type-I & II DM. List the clinical features
OBJECTIVES 4/7/2014. Diabetes Update Overview of the Diabetes Epidemic in the United States. ISHP Annual Spring Meeting
 Diabetes Update 2014 ISHP Annual Spring Meeting Hayley Miller MD April 13, 2014 OBJECTIVES Review diabetes guidelines. Understand diabetes management targets. Discuss current therapeutic strategies. Overview
Diabetes Update 2014 ISHP Annual Spring Meeting Hayley Miller MD April 13, 2014 OBJECTIVES Review diabetes guidelines. Understand diabetes management targets. Discuss current therapeutic strategies. Overview
Modulating the Incretin System: A New Therapeutic Strategy for Type 2 Diabetes
 Modulating the Incretin System: A New Therapeutic Strategy for Type 2 Diabetes Geneva Clark Briggs, PharmD, BCPS Adjunct Professor at University of Appalachia College of Pharmacy Clinical Associate, Medical
Modulating the Incretin System: A New Therapeutic Strategy for Type 2 Diabetes Geneva Clark Briggs, PharmD, BCPS Adjunct Professor at University of Appalachia College of Pharmacy Clinical Associate, Medical
YOU HAVE DIABETES. Angie O Connor Community Diabetes Nurse Specialist 25th September 2013
 YOU HAVE DIABETES Angie O Connor Community Diabetes Nurse Specialist 25th September 2013 Predicated 2015 figures are already met 1 in 20 have diabetes:1in8 over 60years old Definite Diagnosis is key Early
YOU HAVE DIABETES Angie O Connor Community Diabetes Nurse Specialist 25th September 2013 Predicated 2015 figures are already met 1 in 20 have diabetes:1in8 over 60years old Definite Diagnosis is key Early
Diabetes mellitus. Treatment
 Diabetes mellitus Treatment Recommended glycemic targets for the clinical management of diabetes(ada) Fasting glycemia: 80-110 mg/dl Postprandial : 100-145 mg/dl HbA1c: < 6,5 % Total cholesterol: < 200
Diabetes mellitus Treatment Recommended glycemic targets for the clinical management of diabetes(ada) Fasting glycemia: 80-110 mg/dl Postprandial : 100-145 mg/dl HbA1c: < 6,5 % Total cholesterol: < 200
2008 Age-Adjusted Estimates of the % Obese Adults in PA
 Outline The Sugar Fix : Practical Approaches to Blood Glucose Management in Diabetes Monica DiNardo, RN, APNP, BC, CDE VA Pittsburgh Health Care System, University of Pittsburgh School of Nursing PhD Program
Outline The Sugar Fix : Practical Approaches to Blood Glucose Management in Diabetes Monica DiNardo, RN, APNP, BC, CDE VA Pittsburgh Health Care System, University of Pittsburgh School of Nursing PhD Program
INSULIN 101: When, How and What
 INSULIN 101: When, How and What Alice YY Cheng @AliceYYCheng Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or transmitted in any form
INSULIN 101: When, How and What Alice YY Cheng @AliceYYCheng Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or transmitted in any form
Insulin Therapy Management. Insulin Therapy
 Insulin Therapy Management Insulin Therapy Contents Insulin and its effect on glycemic control Physiology of insulin secretion Insulin pharmacokinetics and regimens Insulin dose adjustment for pregnancy
Insulin Therapy Management Insulin Therapy Contents Insulin and its effect on glycemic control Physiology of insulin secretion Insulin pharmacokinetics and regimens Insulin dose adjustment for pregnancy
Pancreatic b-cell Dysfunction in Type 2 Diabetes ZIAD KAHWASH, M.D. Insulin resistance: Defects in Insulin Signaling
 Plasma insulin (mu/ml) ZIAD KAHWASH, M.D. resistance: Defects in Signaling Increased glucose production Glucose Insufficient glucose disposal X Liver glucagon insulin Pancreas Peripheral tissues (skeletal
Plasma insulin (mu/ml) ZIAD KAHWASH, M.D. resistance: Defects in Signaling Increased glucose production Glucose Insufficient glucose disposal X Liver glucagon insulin Pancreas Peripheral tissues (skeletal
Pathogenesis of Type 2 Diabetes
 9/23/215 Multiple, Complex Pathophysiological Abnmalities in T2DM incretin effect gut carbohydrate delivery & absption pancreatic insulin secretion pancreatic glucagon secretion HYPERGLYCEMIA? Pathogenesis
9/23/215 Multiple, Complex Pathophysiological Abnmalities in T2DM incretin effect gut carbohydrate delivery & absption pancreatic insulin secretion pancreatic glucagon secretion HYPERGLYCEMIA? Pathogenesis
INSIGHT INTO MANAGING AND TREATING TYPE 2 DIABETES ISRAEL HARTMAN MD FACE
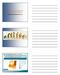 INSIGHT INTO MANAGING AND TREATING TYPE 2 DIABETES ISRAEL HARTMAN MD FACE Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) Is an Epidemic The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention statistics from 2007 estimated that
INSIGHT INTO MANAGING AND TREATING TYPE 2 DIABETES ISRAEL HARTMAN MD FACE Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) Is an Epidemic The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention statistics from 2007 estimated that
Mr Rab Burtun. Dr David Kim. 8:30-10:30 WS #2: Diabetes Basic 11:00-13:00 WS #9: Diabetes Basic (Repeated)
 Dr David Kim Endocrinologist and General Physician Waitemata DHB and Apollo Specialist Clinic Albany Auckland Mr Rab Burtun Diabetes Nurse Specialist Waitemata DHB Waitakere Hospital Auckland 8:30-10:30
Dr David Kim Endocrinologist and General Physician Waitemata DHB and Apollo Specialist Clinic Albany Auckland Mr Rab Burtun Diabetes Nurse Specialist Waitemata DHB Waitakere Hospital Auckland 8:30-10:30
Cardiovascular Management of a Patient with Diabetes
 Cardiovascular Management of a Patient with Diabetes Dr Jeremy Krebs Clinical Leader Endocrinology and Diabetes Wellington Hospital Summary People with diabetes take a lot of medication Compliance and
Cardiovascular Management of a Patient with Diabetes Dr Jeremy Krebs Clinical Leader Endocrinology and Diabetes Wellington Hospital Summary People with diabetes take a lot of medication Compliance and
Update on Insulin-based Agents for T2D
 Update on Insulin-based Agents for T2D Injectable Therapies for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) and Obesity This presentation will: Describe established and newly available insulin therapies for treatment
Update on Insulin-based Agents for T2D Injectable Therapies for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) and Obesity This presentation will: Describe established and newly available insulin therapies for treatment
INSULIN THERAY دکتر رحیم وکیلی استاد غدد ومتابولیسم کودکان دانشگاه علوم پزشکی مشهد
 INSULIN THERAY DIABETES1 IN TYPE دکتر رحیم وکیلی استاد غدد ومتابولیسم کودکان دانشگاه علوم پزشکی مشهد Goals of management Manage symptoms Prevent acute and late complications Improve quality of life Avoid
INSULIN THERAY DIABETES1 IN TYPE دکتر رحیم وکیلی استاد غدد ومتابولیسم کودکان دانشگاه علوم پزشکی مشهد Goals of management Manage symptoms Prevent acute and late complications Improve quality of life Avoid
UKPDS: Over Time, Need for Exogenous Insulin Increases
 UKPDS: Over Time, Need for Exogenous Insulin Increases Patients Requiring Additional Insulin (%) 60 40 20 Oral agents By 6 Chlorpropamide years, Glyburide more than 50% of UKPDS patients required insulin
UKPDS: Over Time, Need for Exogenous Insulin Increases Patients Requiring Additional Insulin (%) 60 40 20 Oral agents By 6 Chlorpropamide years, Glyburide more than 50% of UKPDS patients required insulin
Medications for Diabetes
 Medications for Diabetes Sweet, but not too sweet Colette Raymond, Pharm D June 15, 2011 Learning Objectives At the end of this presentation you should be able to: Understand the prevalence and types of
Medications for Diabetes Sweet, but not too sweet Colette Raymond, Pharm D June 15, 2011 Learning Objectives At the end of this presentation you should be able to: Understand the prevalence and types of
Diabetes Guidelines in View of Recent Clinical Trials Are They Still Applicable?
 Diabetes Guidelines in View of Recent Clinical Trials Are They Still Applicable? Jay S. Skyler, MD, MACP Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism and Diabetes Research Institute University of
Diabetes Guidelines in View of Recent Clinical Trials Are They Still Applicable? Jay S. Skyler, MD, MACP Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism and Diabetes Research Institute University of
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus 2011
 2011 Michael T. McDermott MD Director, Endocrinology and Diabetes Practice University of Colorado Hospital Michael.mcdermott@ucdenver.edu Diabetes Mellitus Diagnosis 2011 Diabetes Mellitus Fasting Glucose
2011 Michael T. McDermott MD Director, Endocrinology and Diabetes Practice University of Colorado Hospital Michael.mcdermott@ucdenver.edu Diabetes Mellitus Diagnosis 2011 Diabetes Mellitus Fasting Glucose
Chief of Endocrinology East Orange General Hospital
 Targeting the Incretins System: Can it Improve Our Ability to Treat Type 2 Diabetes? Darshi Sunderam, MD Darshi Sunderam, MD Chief of Endocrinology East Orange General Hospital Age-adjusted Percentage
Targeting the Incretins System: Can it Improve Our Ability to Treat Type 2 Diabetes? Darshi Sunderam, MD Darshi Sunderam, MD Chief of Endocrinology East Orange General Hospital Age-adjusted Percentage
Treatment Options for Diabetes: An Update
 Treatment Options for Diabetes: An Update A/Prof. Marg McGill Manager, Diabetes Centre Dr. Ted Wu Staff Specialist Endocrinologist Diabetes Centre Centre of Health Professional Education Education Provider
Treatment Options for Diabetes: An Update A/Prof. Marg McGill Manager, Diabetes Centre Dr. Ted Wu Staff Specialist Endocrinologist Diabetes Centre Centre of Health Professional Education Education Provider
Type 2 Diabetes: Where Do We Start with Treatment? DIABETES EDUCATION. Diabetes Mellitus: Complications and Co-Morbid Conditions
 Diabetes Mellitus: Complications and Co-Morbid Conditions ADA Guidelines for Glycemic Control: 2016 Retinopathy Between 2005-2008, 28.5% of patients with diabetes 40 years and older diagnosed with diabetic
Diabetes Mellitus: Complications and Co-Morbid Conditions ADA Guidelines for Glycemic Control: 2016 Retinopathy Between 2005-2008, 28.5% of patients with diabetes 40 years and older diagnosed with diabetic
The Diabetes Guidelines Trek: The Next Generation. Inpatient Diabetes Guidelines. Learning Objectives. Current Inpatient Guidelines
 The Diabetes Guidelines Trek: The Next Generation J. Christopher Lynch, PharmD, BCACP Southern Illinois University Edwardsville School of Pharmacy Susan Cornell BS, PharmD, CDE, FAPhA, FAADE Midwestern
The Diabetes Guidelines Trek: The Next Generation J. Christopher Lynch, PharmD, BCACP Southern Illinois University Edwardsville School of Pharmacy Susan Cornell BS, PharmD, CDE, FAPhA, FAADE Midwestern
Modulating the Incretin System: A New Therapeutic Strategy for Type 2 Diabetes. Overview. Prevalence of Overweight in the U.S.
 Modulating the Incretin System: A New Therapeutic Strategy for Type 2 Diabetes Geneva Clark Briggs, PharmD, BCPS Overview Underlying defects with Type 2 diabetes Importance of managing postprandial glucose
Modulating the Incretin System: A New Therapeutic Strategy for Type 2 Diabetes Geneva Clark Briggs, PharmD, BCPS Overview Underlying defects with Type 2 diabetes Importance of managing postprandial glucose
Objectives 2/13/2013. Figuring out the dose. Sub Optimal Glycemic Control: Moving to the Appropriate Treatment
 Sub Optimal Glycemic Control: Moving to the Appropriate Treatment Judy Thomas, MSN, FNP-BC Holt and Walton, Rheumatology and Endocrinology Objectives Upon completion of this session you will be better
Sub Optimal Glycemic Control: Moving to the Appropriate Treatment Judy Thomas, MSN, FNP-BC Holt and Walton, Rheumatology and Endocrinology Objectives Upon completion of this session you will be better
Drugs used in Diabetes. Dr Andrew Smith
 Drugs used in Diabetes Dr Andrew Smith Plan Introduction Insulin Sensitising Drugs: Metformin Glitazones Insulin Secretagogues: Sulphonylureas Meglitinides Others: Acarbose Incretins Amylin Analogues Damaglifozin
Drugs used in Diabetes Dr Andrew Smith Plan Introduction Insulin Sensitising Drugs: Metformin Glitazones Insulin Secretagogues: Sulphonylureas Meglitinides Others: Acarbose Incretins Amylin Analogues Damaglifozin
Diabetes Mellitus 糖尿病. Dr Shiu Cho Tak MD FRCP
 Diabetes Mellitus 糖尿病 Dr Shiu Cho Tak MD FRCP Glucose Tolerance Categories FPG 2-hr PG on OGTT mg/dl mg/dl 126 Diabetes Mellitus 200 Diabetes Mellitus 100 and
Diabetes Mellitus 糖尿病 Dr Shiu Cho Tak MD FRCP Glucose Tolerance Categories FPG 2-hr PG on OGTT mg/dl mg/dl 126 Diabetes Mellitus 200 Diabetes Mellitus 100 and
Optimizing Treatment Strategies to Improve Patient Outcomes in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes
 Optimizing Treatment Strategies to Improve Patient Outcomes in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes Philip Raskin, MD Professor of Medicine The University of Texas, Southwestern Medical Center NAMCP Spring
Optimizing Treatment Strategies to Improve Patient Outcomes in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes Philip Raskin, MD Professor of Medicine The University of Texas, Southwestern Medical Center NAMCP Spring
3. NEW DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA, NEW CLASSIFICATION OF DM AND MODERN THERAPY APPROACH
 3. NEW DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA, NEW CLASSIFICATION OF DM AND MODERN THERAPY APPROACH 1.1 Introduction Ivana Pavlić-Renar, Ph.D. Vuk Vrhovac University Clinic, Zagreb, Croatia The current classification of
3. NEW DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA, NEW CLASSIFICATION OF DM AND MODERN THERAPY APPROACH 1.1 Introduction Ivana Pavlić-Renar, Ph.D. Vuk Vrhovac University Clinic, Zagreb, Croatia The current classification of
Update on Diabetes Mellitus
 Update on Diabetes Mellitus Treatment: Targeting the Incretin System Overview Underlying defects with Type 2 diabetes Importance of managing postprandial glucose control Amylin Incretin Hormones New therapies
Update on Diabetes Mellitus Treatment: Targeting the Incretin System Overview Underlying defects with Type 2 diabetes Importance of managing postprandial glucose control Amylin Incretin Hormones New therapies
Initiating Insulin in Primary Care for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Dr Manish Khanolkar, Diabetologist, Auckland Diabetes Centre
 Initiating Insulin in Primary Care for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Dr Manish Khanolkar, Diabetologist, Auckland Diabetes Centre Outline How big is the problem? Natural progression of type 2 diabetes What
Initiating Insulin in Primary Care for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Dr Manish Khanolkar, Diabetologist, Auckland Diabetes Centre Outline How big is the problem? Natural progression of type 2 diabetes What
GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) Agonists (Byetta, Bydureon, Tanzeum, Trulicity, Victoza ) Step Therapy and Quantity Limit Criteria Program Summary
 OBJECTIVE The intent of the GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) s (Byetta/exenatide, Bydureon/ exenatide extended-release, Tanzeum/albiglutide, Trulicity/dulaglutide, and Victoza/liraglutide) Step Therapy
OBJECTIVE The intent of the GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) s (Byetta/exenatide, Bydureon/ exenatide extended-release, Tanzeum/albiglutide, Trulicity/dulaglutide, and Victoza/liraglutide) Step Therapy
Early treatment for patients with Type 2 Diabetes
 Israel Society of Internal Medicine Kibutz Hagoshrim, June 22, 2012 Early treatment for patients with Type 2 Diabetes Eduard Montanya Hospital Universitari Bellvitge-IDIBELL CIBERDEM University of Barcelona
Israel Society of Internal Medicine Kibutz Hagoshrim, June 22, 2012 Early treatment for patients with Type 2 Diabetes Eduard Montanya Hospital Universitari Bellvitge-IDIBELL CIBERDEM University of Barcelona
Initiating Injectable Therapy in Type 2 Diabetes
 Initiating Injectable Therapy in Type 2 Diabetes David Doriguzzi, PA C Learning Objectives To understand current Diabetes treatment guidelines To understand how injectable medications fit into current
Initiating Injectable Therapy in Type 2 Diabetes David Doriguzzi, PA C Learning Objectives To understand current Diabetes treatment guidelines To understand how injectable medications fit into current
Choosing a Diabetes Strategy Where to Start and Where to Go
 Choosing a Diabetes Strategy Where to Start and Where to Go Erin Keely, MD, FRCPC; and Sharon Brez, RN, BScN, MA(Ed), CDE As presented at the University of Ottawa's 52nd Annual Refresher Course for Family
Choosing a Diabetes Strategy Where to Start and Where to Go Erin Keely, MD, FRCPC; and Sharon Brez, RN, BScN, MA(Ed), CDE As presented at the University of Ottawa's 52nd Annual Refresher Course for Family
Table 1. Antihyperglycemic agents for use in type 2 diabetes
 Table 1. Antihyperglycemic agents for use in type 2 diabetes DRUG IN ALPHA-GLUCOSIDASE INHIBITOR: inhibits pancreatic alpha-amyle and intestinal alpha-glucoside Acarbose (Glucobay) 0.6% Negligible Not
Table 1. Antihyperglycemic agents for use in type 2 diabetes DRUG IN ALPHA-GLUCOSIDASE INHIBITOR: inhibits pancreatic alpha-amyle and intestinal alpha-glucoside Acarbose (Glucobay) 0.6% Negligible Not
Insulin and Post Prandial
 Insulin and Post Prandial Pr Luc Martinez PCDE Meeting Barcelona 2016 Conflicts of interest disclosure Advis consultant f Amgen Inc.; AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals LP; GlaxoSmithKline; Ipsen; Lilly; Mayoly
Insulin and Post Prandial Pr Luc Martinez PCDE Meeting Barcelona 2016 Conflicts of interest disclosure Advis consultant f Amgen Inc.; AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals LP; GlaxoSmithKline; Ipsen; Lilly; Mayoly
I. General Considerations
 1 2 3 I. General Considerations A. Type I ( Juvenile Onset or IDDM) IDDM results from autoimmune destruction of beta cells inability to secrete insulin --> ketone formation --> DKA 4 Diabetic Ketoacidosis
1 2 3 I. General Considerations A. Type I ( Juvenile Onset or IDDM) IDDM results from autoimmune destruction of beta cells inability to secrete insulin --> ketone formation --> DKA 4 Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Insulin Initiation and Intensification. Disclosure. Objectives
 Insulin Initiation and Intensification Neil Skolnik, M.D. Associate Director Family Medicine Residency Program Abington Memorial Hospital Professor of Family and Community Medicine Temple University School
Insulin Initiation and Intensification Neil Skolnik, M.D. Associate Director Family Medicine Residency Program Abington Memorial Hospital Professor of Family and Community Medicine Temple University School
Diabetes Mellitus: Implications of New Clinical Trials and New Medications
 Diabetes Mellitus: Implications of New Clinical Trials and New Medications Estimates of Diagnosed Diabetes in Adults, 2005 Alka M. Kanaya, MD Asst. Professor of Medicine UCSF, Primary Care CME October
Diabetes Mellitus: Implications of New Clinical Trials and New Medications Estimates of Diagnosed Diabetes in Adults, 2005 Alka M. Kanaya, MD Asst. Professor of Medicine UCSF, Primary Care CME October
Hot Topics: The Future of Diabetes Management Cutting Edge Medication and Technology-Based Care
 Hot Topics: The Future of Diabetes Management Cutting Edge Medication and Technology-Based Care Mary Jean Christian, MA, MBA, RD, CDE Diabetes Program Coordinator UC Irvine Health Hot Topics: Diabetes
Hot Topics: The Future of Diabetes Management Cutting Edge Medication and Technology-Based Care Mary Jean Christian, MA, MBA, RD, CDE Diabetes Program Coordinator UC Irvine Health Hot Topics: Diabetes
Role of Insulin Analogs in
 Role of Insulin Analogs in Type 2 Diabetes Supported by an educational grant from Novo Nordisk Inc. This program is supported by an educational grant from Novo Nordisk Inc. It has been accredited by the
Role of Insulin Analogs in Type 2 Diabetes Supported by an educational grant from Novo Nordisk Inc. This program is supported by an educational grant from Novo Nordisk Inc. It has been accredited by the
Insulin Intensification: A Patient-Centered Approach
 MARTIN J. ABRAHAMSON, MD Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA Insulin Intensification: A Patient-Centered Approach Dr Abrahamson is associate professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and medical director
MARTIN J. ABRAHAMSON, MD Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA Insulin Intensification: A Patient-Centered Approach Dr Abrahamson is associate professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and medical director
Why is Earlier and More Aggressive Treatment of T2 Diabetes Better?
 Blood glucose (mmol/l) Why is Earlier and More Aggressive Treatment of T2 Diabetes Better? Disclosures Dr Kennedy has provided CME, been on advisory boards or received travel or conference support from:
Blood glucose (mmol/l) Why is Earlier and More Aggressive Treatment of T2 Diabetes Better? Disclosures Dr Kennedy has provided CME, been on advisory boards or received travel or conference support from:
Oral and Injectable Non-insulin Antihyperglycemic Agents
 Appendix 5: Diabetes Education and Medical Management in Adults with Diabetes Oral and Injectable Non-insulin s This directive will be implemented by RPhs, RNs or RDs who have been deemed authorized implementers.
Appendix 5: Diabetes Education and Medical Management in Adults with Diabetes Oral and Injectable Non-insulin s This directive will be implemented by RPhs, RNs or RDs who have been deemed authorized implementers.
Endo 2 SLO Practice (online) Page 1 of 7
 Endo 2 SLO Practice (online) Page 1 of 7 1. A long- acting insulin, like Lantus is for? A. When the next meal is within 30-60 minutes of the injection B. Over night use or for ½ of the day often combined
Endo 2 SLO Practice (online) Page 1 of 7 1. A long- acting insulin, like Lantus is for? A. When the next meal is within 30-60 minutes of the injection B. Over night use or for ½ of the day often combined
Newer Drugs in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
 Newer Drugs in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Dr. C. Dinesh M. Naidu Professor of Pharmacology, Kamineni Institute of Medical Sciences, Narketpally. 1 Presentation Outline Introduction Pathogenesis
Newer Drugs in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Dr. C. Dinesh M. Naidu Professor of Pharmacology, Kamineni Institute of Medical Sciences, Narketpally. 1 Presentation Outline Introduction Pathogenesis
Professor Rudy Bilous James Cook University Hospital
 Professor Rudy Bilous James Cook University Hospital Rate per 100 patient years Rate per 100 patient years 16 Risk of retinopathy progression 16 Risk of developing microalbuminuria 12 12 8 8 4 0 0 5 6
Professor Rudy Bilous James Cook University Hospital Rate per 100 patient years Rate per 100 patient years 16 Risk of retinopathy progression 16 Risk of developing microalbuminuria 12 12 8 8 4 0 0 5 6
Diabetes in the UK: Update on Diabetes Treatment and Care. Why is diabetes increasing? Obesity Increased waist circumference.
 Update on Diabetes Treatment and Care Tahseen A Chowdhury Consultant Diabetologist Royal London and Mile End Hospitals Diabetes prevalence (thousands) Diabetes in the UK: 1995-21 3 25 2 15 1 5 Type 1 Type
Update on Diabetes Treatment and Care Tahseen A Chowdhury Consultant Diabetologist Royal London and Mile End Hospitals Diabetes prevalence (thousands) Diabetes in the UK: 1995-21 3 25 2 15 1 5 Type 1 Type
Hanyang University Guri Hospital Chang Beom Lee
 Hanyang University Guri Hospital Chang Beom Lee Meal prayer, Van Brekelenkam 17 th C Introduction 2012 ADA/EASD Position Statement Proper Patients for Pioglitazone β-cell Preservation by Pioglitazone Benefit
Hanyang University Guri Hospital Chang Beom Lee Meal prayer, Van Brekelenkam 17 th C Introduction 2012 ADA/EASD Position Statement Proper Patients for Pioglitazone β-cell Preservation by Pioglitazone Benefit
Julie White, MS Administrative Director Boston University School of Medicine Continuing Medical Education
 MENTOR QI Diabetes Performance Improvement Initiative, Getting Patients to Goal in Glycemic Control: Current Data Julie White, MS Administrative Director Boston University School of Medicine Continuing
MENTOR QI Diabetes Performance Improvement Initiative, Getting Patients to Goal in Glycemic Control: Current Data Julie White, MS Administrative Director Boston University School of Medicine Continuing
A New Therapeutic Strategey for Type II Diabetes: Update 2008
 Live, One Hour Webinar A New Therapeutic Strategey for Type II Diabetes: Update 2008 Geneva Clark Briggs, PharmD, BCPS Adjunct Professor at University of Appalachia College of Pharmacy in Grundy, Virginia.
Live, One Hour Webinar A New Therapeutic Strategey for Type II Diabetes: Update 2008 Geneva Clark Briggs, PharmD, BCPS Adjunct Professor at University of Appalachia College of Pharmacy in Grundy, Virginia.
Non-insulin treatment in Type 1 DM Sang Yong Kim
 Non-insulin treatment in Type 1 DM Sang Yong Kim Chosun University Hospital Conflict of interest disclosure None Committee of Scientific Affairs Committee of Scientific Affairs Insulin therapy is the mainstay
Non-insulin treatment in Type 1 DM Sang Yong Kim Chosun University Hospital Conflict of interest disclosure None Committee of Scientific Affairs Committee of Scientific Affairs Insulin therapy is the mainstay
Drug Therapy for Diabetes Mellitus. Adj A/Prof Daniel Chew Dept of Endocrinology 8 th July 2017
 Drug Therapy for Diabetes Mellitus Adj A/Prof Daniel Chew Dept of Endocrinology 8 th July 2017 Diabetes Subtypes Optimal Treatment Ominous Octet DeFronzo. DIABETES, VOL. 58, APRIL 2009 Schematic Overview
Drug Therapy for Diabetes Mellitus Adj A/Prof Daniel Chew Dept of Endocrinology 8 th July 2017 Diabetes Subtypes Optimal Treatment Ominous Octet DeFronzo. DIABETES, VOL. 58, APRIL 2009 Schematic Overview
Diabetes Mellitus. Intended Learning Objectives:
 Intended Learning Objectives: Diabetes Mellitus 1. Compare and contrast the differences between the drug therapy recommendations of several of the latest and leading diabetes guidelines. 2. Assess the
Intended Learning Objectives: Diabetes Mellitus 1. Compare and contrast the differences between the drug therapy recommendations of several of the latest and leading diabetes guidelines. 2. Assess the
In-Hospital Management of Diabetes. Dr Benjamin Schiff Assistant Professor McGill University
 In-Hospital Management of Diabetes Dr Benjamin Schiff Assistant Professor McGill University No conflict of interest to declare CLINICAL SCENARIO 62 y/o male with hx of DM 2, COPD, and HT is admitted with
In-Hospital Management of Diabetes Dr Benjamin Schiff Assistant Professor McGill University No conflict of interest to declare CLINICAL SCENARIO 62 y/o male with hx of DM 2, COPD, and HT is admitted with
Insulin Prior Authorization with optional Quantity Limit Program Summary
 Insulin Prior Authorization with optional Quantity Limit Program Summary 1-13,16-19, 20 FDA LABELED INDICATIONS Rapid-Acting Insulins Humalog (insulin lispro) NovoLog (insulin aspart) Apidra (insulin glulisine)
Insulin Prior Authorization with optional Quantity Limit Program Summary 1-13,16-19, 20 FDA LABELED INDICATIONS Rapid-Acting Insulins Humalog (insulin lispro) NovoLog (insulin aspart) Apidra (insulin glulisine)
What s New in Type 2? Peter Hammond Consultant Physician Harrogate District Hospital
 What s New in Type 2? Peter Hammond Consultant Physician Harrogate District Hospital Therapy considerations in T2DM Thiazoledinediones DPP IV inhibitors GLP 1 agonists Insulin Type Delivery Horizon scanning
What s New in Type 2? Peter Hammond Consultant Physician Harrogate District Hospital Therapy considerations in T2DM Thiazoledinediones DPP IV inhibitors GLP 1 agonists Insulin Type Delivery Horizon scanning
SIMPLICITY IN T2DM MANAGEMENT WITH DPP4 INHIBITORS: SPECIAL POPULATION
 SIMPLICITY IN T2DM MANAGEMENT WITH DPP4 INHIBITORS: SPECIAL POPULATION DR ROSE ZHAO-WEI TING ( 丁昭慧醫生 ) MBBS (HK), MRCP (UK), FHKCP, FHKAM (MEDICINE) Specialist in Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism
SIMPLICITY IN T2DM MANAGEMENT WITH DPP4 INHIBITORS: SPECIAL POPULATION DR ROSE ZHAO-WEI TING ( 丁昭慧醫生 ) MBBS (HK), MRCP (UK), FHKCP, FHKAM (MEDICINE) Specialist in Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism
Reviewing Diabetes Guidelines. Newsletter compiled by Danny Jaek, Pharm.D. Candidate
 Reviewing Diabetes Guidelines Newsletter compiled by Danny Jaek, Pharm.D. Candidate AL AS KA N AT IV E DI AB ET ES TE A M Volume 6, Issue 1 Spring 2011 Dia bet es Dis pat ch There are nearly 24 million
Reviewing Diabetes Guidelines Newsletter compiled by Danny Jaek, Pharm.D. Candidate AL AS KA N AT IV E DI AB ET ES TE A M Volume 6, Issue 1 Spring 2011 Dia bet es Dis pat ch There are nearly 24 million
Diabetes: What is the scope of the problem?
 Diabetes: What is the scope of the problem? Elizabeth R. Seaquist MD Division of Endocrinology and Diabetes Department of Medicine Director, General Clinical Research Center Pennock Family Chair in Diabetes
Diabetes: What is the scope of the problem? Elizabeth R. Seaquist MD Division of Endocrinology and Diabetes Department of Medicine Director, General Clinical Research Center Pennock Family Chair in Diabetes
TABLE 1A: Formulary Coverage of Insulin Therapies & Indications for Use in Various Populations
 177 TABLE 1A: Formulary Coverage of Insulin Therapies & Indications for Use in Various Populations TABLE 1A : Formulary Coverage of Insulin Therapies & Indications for Use in Various Populations Formulary
177 TABLE 1A: Formulary Coverage of Insulin Therapies & Indications for Use in Various Populations TABLE 1A : Formulary Coverage of Insulin Therapies & Indications for Use in Various Populations Formulary
TREATMENT OF DIABETES AFTER METFORMIN GREGG GERETY, MD ALBANY MEDICAL COLLEGE, DIVISION OF COMMUNITY ENDOCRINOLOGY JULY 14, 2017
 TREATMENT OF DIABETES AFTER METFORMIN GREGG GERETY, MD ALBANY MEDICAL COLLEGE, DIVISION OF COMMUNITY ENDOCRINOLOGY JULY 14, 2017 Outline Review treatment algorithms from ADA/ EASD & ACE/AACE. Review positive
TREATMENT OF DIABETES AFTER METFORMIN GREGG GERETY, MD ALBANY MEDICAL COLLEGE, DIVISION OF COMMUNITY ENDOCRINOLOGY JULY 14, 2017 Outline Review treatment algorithms from ADA/ EASD & ACE/AACE. Review positive
Diabetes Mellitus in Older Adults. Presenter Disclosure Information
 Diabetes Mellitus in Older Adults Medha Munshi, M.D. Joslin Diabetes Center Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Harvard Medical School Presenter Disclosure Information Medha Munshi Research grant from
Diabetes Mellitus in Older Adults Medha Munshi, M.D. Joslin Diabetes Center Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Harvard Medical School Presenter Disclosure Information Medha Munshi Research grant from
No disclosures. Diabetes Test Topics. Case #1. Diabetes Family Medicine Board Review: Improving Clinical Care Across the Lifespan
 Diabetes Family Medicine Board Review: Improving Clinical Care Across the Lifespan No disclosures Sarah Kim, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Clinical Medicine, UCSF Division of Endocrinology, SFGH March
Diabetes Family Medicine Board Review: Improving Clinical Care Across the Lifespan No disclosures Sarah Kim, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Clinical Medicine, UCSF Division of Endocrinology, SFGH March
TABLE 1A : Formulary Coverage of Insulin Therapies & Indications for Use in Various Populations
 177 TABLE 1A : Formulary Coverage of Insulin Therapies & Indications for Use in Various Populations Formulary Coverage Indication for use with: INSULIN THERAPY NS NB NL PE ADULTS PEDIATRICS PREGNANCY BOLUS
177 TABLE 1A : Formulary Coverage of Insulin Therapies & Indications for Use in Various Populations Formulary Coverage Indication for use with: INSULIN THERAPY NS NB NL PE ADULTS PEDIATRICS PREGNANCY BOLUS
DM in OPD for Internist. Rungnapa Laortanakul, MD Maharat Nakhon Ratchasima hospital 28 Oct 2013
 DM in OPD for Internist Rungnapa Laortanakul, MD Maharat Nakhon Ratchasima hospital 28 Oct 2013 Outlines DM management GDM Case Somjit is a 43-year-old woman Check-up No abnormal symptom Laboratory FBS
DM in OPD for Internist Rungnapa Laortanakul, MD Maharat Nakhon Ratchasima hospital 28 Oct 2013 Outlines DM management GDM Case Somjit is a 43-year-old woman Check-up No abnormal symptom Laboratory FBS
Glycemic control a matter of life and death
 Glycemic control a matter of life and death Linda Garcia Mellbin MD PhD Specialist in Cardiology & Internal medicine Dep of Cardiology Karolinska University Hospital /Karolinska Institutet Mortality (%)
Glycemic control a matter of life and death Linda Garcia Mellbin MD PhD Specialist in Cardiology & Internal medicine Dep of Cardiology Karolinska University Hospital /Karolinska Institutet Mortality (%)
Insulin Initiation, titration & Insulin switch in the Primary Care-KISS
 Insulin Initiation, titration & Insulin switch in the Primary Care-KISS Rotorua GP CME 9 June 2012 Dr Kingsley Nirmalaraj FRACP Endocrinologist, BOPDHB & Suite 9, Promed House, Tenth Ave, Tauranga Linda
Insulin Initiation, titration & Insulin switch in the Primary Care-KISS Rotorua GP CME 9 June 2012 Dr Kingsley Nirmalaraj FRACP Endocrinologist, BOPDHB & Suite 9, Promed House, Tenth Ave, Tauranga Linda
Learning Objectives. Impact of Diabetes II UPDATES IN TYPE 2 DIABETES. David Doriguzzi, PA-C
 UPDATES IN TYPE 2 DIABETES David Doriguzzi, PA-C Learning Objectives Upon completion of this educational activity, the participant should be able to: Overcome barriers and attitudes that limit Clinician/Patient
UPDATES IN TYPE 2 DIABETES David Doriguzzi, PA-C Learning Objectives Upon completion of this educational activity, the participant should be able to: Overcome barriers and attitudes that limit Clinician/Patient
Diabetes 2013: Achieving Goals Through Comprehensive Treatment. Session 2: Individualizing Therapy
 Diabetes 2013: Achieving Goals Through Comprehensive Treatment Session 2: Individualizing Therapy Joshua L. Cohen, M.D., F.A.C.P. Professor of Medicine Interim Director, Division of Endocrinology & Metabolism
Diabetes 2013: Achieving Goals Through Comprehensive Treatment Session 2: Individualizing Therapy Joshua L. Cohen, M.D., F.A.C.P. Professor of Medicine Interim Director, Division of Endocrinology & Metabolism
Inernal Medicine by Prof. El Sayed Abdel Fatah Eid. Diabetes Mellitus. Prof. El Sayed Abdel Fattah Eid. Lecturer of Internal Medicine Delta University
 Diabetes Mellitus By Prof. El Sayed Abdel Fattah Eid Lecturer of Internal Medicine Delta University (Diabetes Mellitus) Definition: Diabetes mellitus comprises a heterogeneous group of metabolic diseases
Diabetes Mellitus By Prof. El Sayed Abdel Fattah Eid Lecturer of Internal Medicine Delta University (Diabetes Mellitus) Definition: Diabetes mellitus comprises a heterogeneous group of metabolic diseases
Glucose Control drug treatments
 Glucose Control drug treatments It should be noted that glitazones are under suspicion of precipitating acute cardiac events and current recommendations contraindicate the use of glitazones in patients
Glucose Control drug treatments It should be noted that glitazones are under suspicion of precipitating acute cardiac events and current recommendations contraindicate the use of glitazones in patients
MANAGEMENT OF TYPE 1 DIABETES MELLITUS
 MANAGEMENT OF TYPE 1 DIABETES MELLITUS INVESTIGATIONS AND TREATMENT MANSI NAIK VII SEMESTER INVESTIGATIONS FASTING BLOOD SUGAR PLASMA GLUCOSE HEMOGLOBIN A 1c SYMPTOMS OF TYPE 1 DIABETES MELLITUS Polyuria
MANAGEMENT OF TYPE 1 DIABETES MELLITUS INVESTIGATIONS AND TREATMENT MANSI NAIK VII SEMESTER INVESTIGATIONS FASTING BLOOD SUGAR PLASMA GLUCOSE HEMOGLOBIN A 1c SYMPTOMS OF TYPE 1 DIABETES MELLITUS Polyuria
DR HJ BODANSKY MD FRCP CONSULTANT PHYSICIAN LEEDS TEACHING HOSPITALS ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR, UNIVERSITY OF LEEDS
 DR HJ BODANSKY MD FRCP CONSULTANT PHYSICIAN LEEDS TEACHING HOSPITALS ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR, UNIVERSITY OF LEEDS DIABETETES UPDATE 2015 AIMS OF THE SEMINAR Diagnosis Investigation Management When to refer
DR HJ BODANSKY MD FRCP CONSULTANT PHYSICIAN LEEDS TEACHING HOSPITALS ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR, UNIVERSITY OF LEEDS DIABETETES UPDATE 2015 AIMS OF THE SEMINAR Diagnosis Investigation Management When to refer
DIABETES. overview of pharmacologic agents used in the management of. Overview 4/3/2014 OBJECTIVES. Injectable Agents
 overview of pharmacologic agents used in the management of DIABETES Kyle Roberts, Pharm.D. PGY-1 Pharmacy Resident Saint Alphonsus RMC 1. List the different classes of diabetes medications, including the
overview of pharmacologic agents used in the management of DIABETES Kyle Roberts, Pharm.D. PGY-1 Pharmacy Resident Saint Alphonsus RMC 1. List the different classes of diabetes medications, including the
Initiation and Titration of Insulin in Diabetes Mellitus Type 2
 Initiation and Titration of Insulin in Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 Greg Doelle MD, MS April 6, 2016 Disclosure I have no actual or potential conflicts of interest in relation to the content of this lecture.
Initiation and Titration of Insulin in Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 Greg Doelle MD, MS April 6, 2016 Disclosure I have no actual or potential conflicts of interest in relation to the content of this lecture.
Age-adjusted Percentage of U.S. Adults Who Were Obese or Who Had Diagnosed Diabetes
 Age-adjusted Percentage of U.S. Adults Who Were Obese or Who Had Diagnosed Diabetes Obesity (BMI 30 kg/m 2 ) 1994 2000 2009 No Data 26.0% Diabetes 1994 2000 2009
Age-adjusted Percentage of U.S. Adults Who Were Obese or Who Had Diagnosed Diabetes Obesity (BMI 30 kg/m 2 ) 1994 2000 2009 No Data 26.0% Diabetes 1994 2000 2009
What the Pill Looks Like. How it Works. Slows carbohydrate absorption. Reduces amount of sugar made by the liver. Increases release of insulin
 Diabetes s Oral s - Pills These are some of the pills that are currently available in Canada to treat diabetes. Each medication has benefits and side effects you should be aware of. Your diabetes team
Diabetes s Oral s - Pills These are some of the pills that are currently available in Canada to treat diabetes. Each medication has benefits and side effects you should be aware of. Your diabetes team
GLP 1 agonists Winning the Losing Battle. Dr Bernard SAMIA. KCS Congress: Impact through collaboration
 GLP 1 agonists Winning the Losing Battle Dr Bernard SAMIA KCS Congress: Impact through collaboration CONTACT: Tel. +254 735 833 803 Email: kcardiacs@gmail.com Web: www.kenyacardiacs.org Disclosures I have
GLP 1 agonists Winning the Losing Battle Dr Bernard SAMIA KCS Congress: Impact through collaboration CONTACT: Tel. +254 735 833 803 Email: kcardiacs@gmail.com Web: www.kenyacardiacs.org Disclosures I have
FUNDING: MICIS mandated by Maine Legislature, funded by fees collected from pharmaceutical companies as a cost of doing business in the state.
 GOAL: To improve clinical outcomes by delivering upto-date, evidence-based prescribing information, using data and guidelines developed by noncommercial sources FUNDING: MICIS mandated by Maine Legislature,
GOAL: To improve clinical outcomes by delivering upto-date, evidence-based prescribing information, using data and guidelines developed by noncommercial sources FUNDING: MICIS mandated by Maine Legislature,
Glycemic control what can be achieved with life-style and when and how to use pharmacological agents?
 Glycemic control what can be achieved with life-style and when and how to use pharmacological agents? Eberhard Standl Munich Diabetes Research Institute At the Munich Helmholtz Center Pathogenetic key
Glycemic control what can be achieved with life-style and when and how to use pharmacological agents? Eberhard Standl Munich Diabetes Research Institute At the Munich Helmholtz Center Pathogenetic key
ประช มว ชาการสาหร บแพทย ท ปฏ บ ต งานในหน วยบร การปฐมภ ม
 ประช มว ชาการสาหร บแพทย ท ปฏ บ ต งานในหน วยบร การปฐมภ ม Update DM 21 ส งหาคม 2558 พญ.ร งนภา ลออธนก ล, พบ 2015 Outlines DM OPD management Case scenario Case Somjit is a 43-year-old woman Check-up No abnormal
ประช มว ชาการสาหร บแพทย ท ปฏ บ ต งานในหน วยบร การปฐมภ ม Update DM 21 ส งหาคม 2558 พญ.ร งนภา ลออธนก ล, พบ 2015 Outlines DM OPD management Case scenario Case Somjit is a 43-year-old woman Check-up No abnormal
