ERA-EDTA Registry Annual Report 2001
|
|
|
- Jennifer Barber
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ERA-EDTA Registry Annual Report 2001
2 Suggested citation ERA-EDTA Registry: ERA-EDTA Registry 2001 Annual Report. Academic Medical Center, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, June i
3 ERA-EDTA Registry Dept. of Medical Informatics Academic Medical Center, J2-254 PO Box DE Amsterdam The Netherlands Telephone Fax Website ERA-EDTA Registry Committee JD Briggs, chairman G Colasanti, Italy T Feest, United Kingdom C Grönhagen-Riska, Finland AJ van der Heijden, The Netherlands HJ Schober-Halstenberg, Germany K Simpson, Scotland B Stengel, France D Tsakiris, Greece K Verrier-Jones, United Kingdom Registry Office Staff S Bos, database manager - website developer R Cornet, senior medical informatician FW Dekker, senior epidemiologist PCW van Dijk, medical informatician EF Güggenheim - van der Hout, secretary KJ Jager, managing director - epidemiologist VS Stel, epidemiologist ii
4 Acknowledgements The ERA-EDTA Registry would like to thank the patients and staff of all the dialysis and transplant units who have contributed data via their national and regional renal registries. In addition, we would like to thank the following persons for their contribution to the work of the ERA-EDTA Registry. Registry For contribution to Section A Austria Belgium - Dutch-speaking Belgium - French-speaking Denmark Finland Greece Iceland Norway Spain - Basque country Spain - Catalonia Spain - Valencia Sweden The Netherlands United Kingdom - England/Wales United Kingdom - Scotland For contribution to Section B Bosnia - Herzegovina Croatia Czech Republic Estonia Germany Russia Serbia and Montenegro Tunesia Turkey R Kramar and HK Stummvoll H Augustijn and J Donck F Collart H Løkkegaard C Grönhagen-Riska and P Finne GA Ioannidis P Ásmundsson T Leivestad Á Magaz, J Aranzabal and I Lampreabe M Clèries and E Vela O Zurriaga and MJ García Blasco S Schön F de Charro D Ansell and T Feest K Simpson E Mešić and H Resić S Čala J Lachmanova and F Lopot M Ots, M Luman and K Lilienthal HJ Schober-Halstenberg and K Haas N Tomilina and B Bikbov L Djukanovic and M Radovic N Cherni and H Trimech K Serdengeçti and G Suleymanlar The ERA-EDTA Registry is funded by the ERA-EDTA. The following companies have committed funds in the form of unrestricted educational grants to assist the ERA- EDTA in the financial support of the Registry: Amgen, Baxter, Fresenius Medical Care, Gambro, Hoffmann-La Roche, Hospal, Ortho-Biotech and Shire. iii
5 Index I Introduction - 10 II Methods - 11 III Reference tables SECTION A - 15 A1 AFFILIATED REGISTRY INFORMATION FOR 2001 Table A General population of the country/region and percent coverage of general population in 2001 Table A Renal centres: total number of centres and number collaborating A2 INCIDENT PATIENTS ACCEPTED FOR RRT IN 2001 (residents only) AT DAY 1 Table A Incident counts and percentage at day 1, by age and gender Table A Gender, mean and median age of incident patients at day 1 Table A Incident rates per million population, unadjusted at day 1, by age and gender Table A Incident rates per million population, unadjusted at day 1, by cause of renal failure Table A Incident rates per million population, adjusted at day 1, by cause of renal failure, adjusted for age and gender A3 INCIDENT PATIENTS ACCEPTED FOR RRT IN 2001 (residents only) AT DAY 90 Table A Incident counts and percentage at day 90, by age and gender Table A Gender, mean and median age of incident patients at day 90 Table A Incident rates per million population, unadjusted at day 90, by age and gender Table A Incident rates per million population, unadjusted at day 90, by cause of renal failure iv
6 Table A Incident rates per million population, adjusted at day 90, by cause of renal failure, adjusted for age and gender Table A Incident counts at day 90, by established therapy Table A Incident rates per million population, unadjusted at day 90, by established therapy Table A Incident rates per million population, adjusted at day 90, by established therapy, adjusted for age and gender Table A Percentage of established therapy, unadjusted at day 90 Table A Percentage of established therapy, unadjusted at day 90, by age, gender and primary diagnosis A4 PREVALENT PATIENTS ON RRT IN 2001 (residents only) Table A Prevalence counts and percentage prevalent patients on December 31, by age and gender Table A Gender, mean and median age prevalent patients on December 31 Table A Prevalence per million population, unadjusted prevalent patients on December 31, by age and gender Table A Prevalence per million population and percentage, unadjusted prevalent patients on December 31, by cause of renal failure Table A Prevalence per million population, adjusted prevalent patients on December 31, by cause of renal failure, adjusted for age and gender Table A Prevalence counts prevalent patients on December 31, by established therapy Table A Prevalence per million population, unadjusted prevalent patients on December 31, by established therapy Table A Prevalence per million population, adjusted prevalent patients on December 31, by established therapy, adjusted for age and gender Table A Percentage of established therapy, unadjusted prevalent patients on December 31 v
7 Table A Percentage of established therapy, unadjusted prevalent patients on December 31, by age, gender and primary diagnosis Table A Patients living on a functioning graft, unadjusted prevalent patients on December 31 A5 SURVIVAL PROBABILITY (residents only) Patient Survival on Renal Replacement Therapy (RRT) Table A day, one-, two- and five-year survival probabilities (cohort ): Incident RRT patients, unadjusted from day 1 to 90 days, one, two and five years, by age, gender and primary diagnosis Table A day, one-, two- and five-year survival probabilities (cohort ): Incident RRT patients, adjusted from day 1 to 90 days, one, two and five years, adjusted for age, gender and primary diagnosis Table A One-, two- and five-year survival probabilities (cohort ): Incident RRT patients, unadjusted from day 91 to one, two and five years + 90 days, by age, gender and primary diagnosis Table A One-, two- and five-year survival probabilities (cohort ): Incident RRT patients, adjusted from day 91 to one, two and five years + 90 days, adjusted for age, gender and primary diagnosis Table A day, one- and two-year survival probabilities (cohort ): Incident RRT patients, unadjusted from day 1 to 90 days, one and two years, by age, gender and primary diagnosis Table A day, one- and two-year survival probabilities (cohort ): Incident RRT patients, adjusted from day 1 to 90 days, one and two years, adjusted for age, gender and primary diagnosis Table A One- and two-year survival probabilities (cohort ): Incident RRT patients, unadjusted from day 91 to one and two years + 90 days, by age, gender and primary diagnosis Table A One- and two-year survival probabilities (cohort ): Incident RRT patients, adjusted from day 91 to one and two years + 90 days, adjusted for age, gender and primary diagnosis Patient Survival on Dialysis Table A day, one-, two- and five-year survival probabilities (cohort ): Incident dialysis patients, unadjusted from day 1 to 90 days, one, two and five years, by age, gender and primary diagnosis Table A day, one-, two- and five-year survival probabilities (cohort ): Incident dialysis patients, adjusted from day 1 to 90 days, one, two and five years, adjusted for age, gender and primary diagnosis Table A One-, two- and five-year survival probabilities (cohort ): Incident dialysis patients, unadjusted from day 91 to one, two and five years + 90 days, by age, gender and primary diagnosis Table A One-, two- and five-year survival probabilities (cohort ): Incident dialysis patients, adjusted from day 91 to one, two and five years + 90 days, adjusted for age, gender and primary diagnosis Table A day, one- and two-year survival probabilities (cohort ): Incident dialysis patients, unadjusted from day 1 to 90 days, one and two years, by age, gender and primary diagnosis vi
8 Table A day, one- and two-year survival probabilities (cohort ): Incident dialysis patients, adjusted from day 1 to 90 days, one and two years, adjusted for age, gender and primary diagnosis Table A One- and two-year survival probabilities (cohort ): Incident dialysis patients, unadjusted from day 91 to one and two years + 90 days, by age, gender and primary diagnosis Table A One- and two-year survival probabilities (cohort ): Incident dialysis patients, adjusted from day 91 to one and two years + 90 days, adjusted for age, gender and primary diagnosis Patient Survival after First Transplant (cadaver donor) Table A One-, two- and five-year survival probabilities (cohort ): First transplant patients (cadaver donor), unadjusted from day of transplant to one, two and five years, by age, gender and primary diagnosis Table A One-, two- and five-year survival probabilities (cohort ): First transplant patients (cadaver donor), adjusted from day of transplant to one, two and five years, adjusted for age, gender and primary diagnosis Table A One- and two-year survival probabilities (cohort ): First transplant patients (cadaver donor), unadjusted from day of transplant to one and two years, by age, gender and primary diagnosis Table A One- and two-year survival probabilities (cohort ): First transplant patients (cadaver donor), adjusted from day of transplant to one and two years, adjusted for age, gender and primary diagnosis Patient Survival after First Transplant (living donor) Table A One-, two- and five-year survival probabilities (cohort ): First transplant patients (living donor), unadjusted from day of transplant to one, two and five years, by age, gender and primary diagnosis Table A One-, two- and five-year survival probabilities (cohort ): First transplant patients (living donor), adjusted from day of transplant to one, two and five years, adjusted for age, gender and primary diagnosis Table A One- and two-year survival probabilities (cohort ): First transplant patients (living donor), unadjusted from day of transplant to one and two years, by age, gender and primary diagnosis Table A One- and two-year survival probabilities (cohort ): First transplant patients (living donor), adjusted from day of transplant to one and two years, adjusted for age, gender and primary diagnosis Graft Survival after First transplant (cadaver donor) Table A One-, two- and five-year survival probabilities (cohort ): First graft (cadaver donor), unadjusted from day of transplant to one, two and five years, by age, gender and primary diagnosis Table A One-, two- and five-year survival probabilities (cohort ): First graft (cadaver donor), adjusted from day of transplant to one, two and five years, adjusted for age, gender and primary diagnosis Table A One- and two-year survival probabilities (cohort ): First graft (cadaver donor), unadjusted from day of transplant to one and two years, by age, gender and primary diagnosis Table A One- and two-year survival probabilities (cohort ): First graft (cadaver donor), adjusted from day of transplant to one and two years, adjusted for age, gender and primary diagnosis vii
9 Graft Survival after First Transplant (living donor) Table A One-, two- and five-year survival probabilities (cohort ): First graft (living donor), unadjusted from day of transplant to one, two and five years, by age, gender and primary diagnosis Table A One-, two- and five-year survival probabilities (cohort ): First graft (living donor), adjusted from day of transplant to one, two and five years, adjusted for age, gender and primary diagnosis Table A One- and two-year survival probabilities (cohort ): First graft (living donor), unadjusted from day of transplant to one and two years, by age, gender and primary diagnosis Table A One- and two-year survival probabilities (cohort ): First graft (living donor, adjusted from day of transplant to one and two years, adjusted for age, gender and primary diagnosis IV Reference tables SECTION B - 60 B1 AFFILIATED REGISTRY INFORMATION FOR 2001 Table B General population of the country/region and percent coverage of general population in 2001 Table B Renal centres: total number of centres and number collaborating B2 INCIDENT PATIENTS ACCEPTED FOR RRT IN 2001 (residents only) AT DAY 1 Table B Incident counts and incident rates per million population, unadjusted at day 1 Table B Gender, mean and median age of incident patients at day 1 Table B Incident rates per million population, adjusted at day 1, adjusted for age and gender Table B Incident rates per million population and percentage, unadjusted at day 1, by cause of renal failure B3 INCIDENT PATIENTS ACCEPTED FOR RRT IN 2001 (residents only) AT DAY 90 Table B Incident counts and incident rates per million population, unadjusted at day 90 Table B Gender, mean and median age of incident patients at day 90 Table B Incident rates per million population, adjusted at day 90, adjusted for age and gender viii
10 Table B Incident rates per million population and percentage, unadjusted at day 90, by cause of renal failure Table B Incident counts at day 90, by established therapy Table B Incident rates per million population, unadjusted at day 90, by established therapy Table B Percentage of established therapy, unadjusted at day 90 B4 PREVALENT PATIENTS ON RRT IN 2001 (residents only) Table B Prevalent counts and per million population, unadjusted prevalent patients on December 31 Table B Gender, mean and median age prevalent patients on December 31 Table B Prevalence per million population, adjusted prevalent patients on December 31, adjusted for age and gender Table B Prevalence per million population and percentage, unadjusted prevalent patients on December 31, by cause of renal failure Table B Prevalence counts prevalent patients on December 31, by established therapy Table B Prevalence per million population, unadjusted prevalent patients on December 31, by established therapy Table B Percentage of established therapy, unadjusted prevalent patients on December 31 Table B Renal transplants, number and percentage by donor type ix
11 I Introduction This is the second year in which the Amsterdam based ERA-EDTA Registry has published an annual report. Section A of this report includes tables with 2001 data based on the analyses of data sets received from national and regional registries collecting individual patient data that are included in the ERA-EDTA Registry database. These data are published after receipt of the data sets and subsequent analysis by the Registry office and the following permission for publication from the country involved. Section B relates to the countries collecting individual patient data, centre questionnaire data or information from health authorities. Their data are not included in the ERA-EDTA Registry database. These countries complete the tables themselves and return them to the ERA-EDTA Registry office for inclusion in this annual report. 10
12 II Methods Section A The tables in this section are based on the analyses of data sets received from national and regional registries collecting individual patient data, which are included in the ERA-EDTA Registry database. The databases serving as a basis for the analyses were received on the dates shown in the following table. Registry Date Austria 19 June 2002 Belgium Dutch-speaking 6 January 2003 Belgium French-speaking 28 April 2003 Denmark 6 January 2003 Finland 19 December 2002 Greece 6 February 2003 Iceland 3 April 2003 Norway 3 February 2003 Spain Basque country 19 March 2003 Spain Catalonia 17 October 2002 Spain Valencia 10 September 2002 Sweden 8 July 2002 The Netherlands 25 March 2003 United Kingdom - England/Wales 28 March 2003 United Kingdom - Scotland 3 April 2003 Registry data are subject to continuous alteration and improvement. Small differences between ERA-EDTA Registry data and the data presented in the national/regional registry s own annual reports may therefore result from different times of data extraction. Differences in data collection between collaborating registries and inclusion of their data into the ERA-EDTA Registry database In the comparison of data between registries it should be recognised that there may be small differences between registries in definitions and in the collection of their data. The different registries do not for example collect data at the same level of detail, especially with regard to the different subtypes of the treatment modalities. Also, registries may handle temporary changes in the treatment modality of the individual patient differently. The data from England/Wales (United Kingdom) exclude patients younger than 18 years of age in the data sets provided to the ERA-EDTA Registry. Inclusion of those would add 2 pmp to the overall UK incidence rate and 12 pmp to the UK prevalence. In addition, it should be noted that the prevalence figures produced by the UK Renal Registry are slightly higher than those produced by the ERA-EDTA Registry. This is due to the fact that the UK Renal Registry calculates prevalence rates from the electronic quarterly data returns (which are not part of the ERA- EDTA Registry data set) rather than from the timeline which can be incomplete for some patients. 11
13 Incidence and prevalence The incidence tables refer to all patients who started RRT for ESRD in 2001 and the prevalence tables to all patients who were alive and on RRT on 31 December General population data for the year 2001, provided by Eurostat, the national bureaus of statistics or the national or regional registry, served as the population base. The grouping of renal diseases is provided in Appendix 1. For the adjustment of incidence and prevalence for age and gender we used the age and gender distribution of the European population of 1995 as provided by Eurostat. Survival analysis For the analysis of survival data we used two five-year cohorts: for the presentation of 90-day (for survival on RRT and on dialysis), one-, two- and five-year survival probabilities. These analyses were based on data from Austria, Basque Country (Spain), Catalonia (Spain), Denmark, Dutch-speaking Belgium, Finland, French-speaking Belgium, Greece, Iceland, Norway, Scotland (United Kingdom), Sweden, The Netherlands and Valencia (Spain) for the presentation of 90-day (for survival on RRT and on dialysis), one- and two-year survival probabilities. These analyses were based on data from Austria, Basque Country (Spain), Catalonia (Spain), Denmark, Dutch-speaking Belgium, England/Wales (United Kingdom), Finland, Frenchspeaking Belgium, Greece, Iceland, Norway, Scotland (United Kingdom), Sweden, The Netherlands and Valencia (Spain). With regard to the inclusion of data, some further comments need to be made. The data were used from the date from which they were available, which in a small number of cases was later than the first cohort year, this being due to the fact that the national or regional registry was established later. Survival was analysed from day 1 and from day 91 onwards for those patients alive and on RRT on those days. All patients had the opportunity to complete the entire follow-up period with the exception of patients starting in the last 90 days of a cohort in a survival analysis from day 91. For the different types of survival analysis we defined the following events and censoring. Survival type Event Censoring Patients on renal replacement therapy Death of patient Recovery of renal function Loss to follow-up End of follow-up time Patients on dialysis Death of patient Transplantation Recovery of renal function Loss to follow-up End of follow-up time First transplant recipients Death of patient Loss to follow-up End of follow-up time First graft Death of patient Graft failure Loss to follow-up End of follow-up time As the ERA-EDTA Registry database is still growing with respect to the coverage of European countries, we chose to adjust for fixed parameters in our survival analyses. The values for adjustment are shown in the following table. 12
14 Survival type Age Gender Renal disease Patients on renal 60 years 60% male DM - non DM 20/80 replacement therapy Patients on dialysis 60 years 60% male DM - non DM 20/80 First transplant recipients 45 years 60% male DM - non DM 10/90 (cadaver donor) First transplant recipients 45 years 60% male DM - non DM 10/90 (living donor) First graft (cadaver donor) 45 years 60% male DM - non DM 10/90 First graft (living donor) 45 years 60% male DM - non DM 10/90 In unadjusted survival analysis the cells in the tables were left blank when there were less than 30 patients in that cell. In the adjusted survival analysis, cells with less than 30 events were left empty. The latter analysis excluded patients for whom age, gender, or primary renal disease was missing. Section B These tables relate to countries collecting individual patient data, centre questionnaire data or information from health authorities. Their data are not included in the ERA-EDTA Registry database. The tables were completed by national and regional registries and sent to the ERA-EDTA Registry for inclusion in this annual report. The incidence tables refer to all patients who started RRT for ESRD in 2001 and the prevalence tables to all patients who were alive and on RRT on 31 December General population data for the year 2001 were provided by the national or regional registries. For the adjustment of incidence and prevalence for age and gender they used the age and gender distribution of the European population of Appendix 1 - Grouping of renal diseases Primary Renal Disease (PRD) PRD code code Group Glomerulonephritis; histologically NOT examined I Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis with nephrotic syndrome in children I IgA nephropathy (proven by immunofluorescence, not code 76 and not 85) I Dense deposit disease; membrano-proliferative GN; type II (proven by I immunofluorescence and/or electron microscopy) Membranous nephropathy I Membrano-proliferative GN; type I (proven by immunofluorescence and/or I electron microscopy - not code 84 or 89) Crescentic (extracapillary) glomerulonephritis (type I, II, III) I Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis with nephrotic syndrome in adults I Glomerulonephritis; histologically examined, not given above I Pyelonephritis cause not specified II Pyelonephritis associated with neurogenic bladder II Pyelonephritis due to congenital obstructive uropathy with/without vesico-ureteric II reflux Pyelonephritis due to acquired obstructive uropathy II 13
15 Primary Renal Disease (PRD) PRD code code Group Pyelonephritis due to vesico-ureteric reflux without obstruction II Pyelonephritis due to urolithiasis II Pyelonephritis due to other cause II Interstitial nephritis (not pyelonephritis) due to other cause, or unspecified (not VII mentioned above) Nephropathy (interstitial) due to analgesic drugs VII Nephropathy (interstitial) due to cis-platinum VII Nephropathy (interstitial) due to cyclosporin A VII Lead induced nephropathy (interstitial) 34 VII Drug induced nephropathy (interstitial) not mentioned above VII Cystic kidney disease - type unspecified VII Polycystic kidneys; adult type (dominant) III Polycystic kidneys; infantile (recessive) VII Medullary cystic disease; including nephronophthisis VII Cystic kidney disease - other specified type VII Hereditary/Familial nephropathy - type unspecified VII Hereditary nephritis with nerve deafness (Alport's Syndrome) VII Cystinosis VII Primary oxalosis VII Fabry's disease VII Hereditary nephropathy - other specified type VII Renal hypoplasia (congenital) - type unspecified VII Oligomeganephronic hypoplasia VII Congenital renal dysplasia with or without urinary tract malformation VII Syndrome of agenesis of abdominal muscles (Prune Belly) VII Renal vascular disease - type unspecified V Renal vascular disease due to malignant hypertension IV Renal vascular disease due to hypertension IV Renal vascular disease due to polyarteritis VII Wegener's granulomatosis VII Glomerulonephritis related to liver cirrhosis VII Cryoglobulinaemic glomerulonephritis 78 VII Renal vascular disease - due to other cause (not given above and not code V 88) Diabetes glomerulosclerosis or diabetic nephropathy - Type I VI Diabetes glomerulosclerosis or diabetic nephropathy - Type II VI Myelomatosis/light chain deposit disease VII Amyloid VII Lupus erythematosus VII Henoch-Schoenlein purpura VII Goodpasture's Syndrome VII Systemic sclerosis (scleroderma) VII Haemolytic Uraemic Syndrome (including Moschcowitz Syndrome) VII Multi-system disease - other (not mentioned above) VII Tubular necrosis (irreversible) or cortical necrosis (different from 88) VII Tuberculosis VII Gout VII Nephrocalcinosis and hypercalcaemic nephropathy VII Balkan nephropathy VII Kidney tumour VII Traumatic or surgical loss of kidney VII Other identified renal disorders VII Chronic renal failure; aetiology uncertain VIII I Glomerulonephritis/sclerosis; II Pyelonephritis; III Polycystic kidneys, adult type; IV Hypertension ;V Renal vascular disease; VI Diabetes mellitus; VII Miscellaneous; VIII Unknown 14
16 III Reference tables SECTION A 15
17 Table A.1.1 General population of the country/region and percent coverage of general population in 2001 General population in thousands % Coverage of general population Austria 8, Belgium, Dutch-speaking 5, Belgium, French-speaking 4, Denmark 5, Finland 5, Greece 10, Iceland Norway 4, Spain, Basque country 2, Spain, Catalonia 6, Spain, Valencia 4, Sweden 8, The Netherlands 15, UK, England/Wales 52, UK, Scotland 5,
18 Table A.1.2 Renal centres: total number of centres and number collaborating Total number of renal centres Number of renal centres collaborating with the registry Austria Belgium, Dutch-speaking Belgium, French-speaking Denmark Finland Greece Iceland 1 1 Norway Spain, Basque country Spain, Catalonia Spain, Valencia Sweden The Netherlands UK, England/Wales UK, Scotland
19 Table A.2.1 Incident counts and percentage at day 1, by age and gender All Men Women All Men Women All Men Women All Men Women All Men Women All Men Women All N % N % N % N % N % N % N % N % N % N % N % N % N % N % N % N % N % N % Austria Belgium, Dutch-speaking Belgium, French-speaking Denmark Finland Greece Iceland Norway Spain, Basque country Spain, Catalonia Spain, Valencia Sweden The Netherlands UK, England/Wales UK, Scotland Percentages are row percentages Categories may not add up to total or to 100% because of missing values 18
20 Table A.2.2 Gender, mean and median age of incident patients at day 1 All Men Women % Mean (years) (SD) Median (years) % Mean (years) (SD) Median (years) % Mean (years) (SD) Median (years) Austria (15.0) (15.2) (14.3) 67.5 Belgium, Dutch-speaking (14.4) (14.1) (15.0) 70.4 Belgium, French-speaking (16.2) (16.5) (15.9) 68.4 Denmark (15.4) (15.4) (15.6) 66.2 Finland (16.9) (16.7) (17.2) 63.3 Greece (14.9) (15.2) (14.3) 69.5 Iceland (18.4) (21.5) (14.9) 58.6 Norway (17.3) (17.3) (17.3) 64.7 Spain, Basque country (15.8) (15.1) (17.2) 64.9 Spain, Catalonia (15.9) (15.7) (16.4) 69.3 Spain, Valencia (16.2) (16.6) (15.2) 67.6 Sweden (16.4) (15.8) (17.5) 65.4 The Netherlands (16.6) (16.6) (16.6) 62.4 UK, England/Wales (16.1) (16.0) (16.4) 64.0 UK, Scotland (17.3) (17.6) (16.9)
21 Table A.2.3 Incident rates per million population, unadjusted at day 1, by age and gender All Men Women All Men Women All Men Women All Men Women All Men Women All Men Women All Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Austria Belgium, Dutch-speaking Belgium, French-speaking Denmark Finland Greece Iceland Norway Spain, Basque country Spain, Catalonia Spain, Valencia Sweden The Netherlands UK, England/Wales UK, Scotland
22 Table A.2.4 Incident rates per million population, unadjusted at day 1, by cause of renal failure Total GN PN Cause of renal failure DM PKD Type I Type II Both HT RVD Misc Unkn Missing Pmp % Pmp % Pmp % Pmp % Pmp % Pmp % Pmp % Pmp % Pmp % Pmp % Pmp % Pmp % Austria Belgium, Dutch-speaking Belgium, French-speaking Denmark Finland Greece Iceland Norway Spain, Basque country * Spain, Catalonia Spain, Valencia Sweden The Netherlands UK, England/Wales UK, Scotland Abbreviations used: GN: glomerulonephritis/sclerosis; PN: pyelonephritis; PKD: polycystic kidneys, adult type; DM: diabetes mellitus; HT: hypertension; RVD: renal vascular disease; Misc: miscellaneous; Unkn: Categories may not add up to total or to 100% because of missing values * Data on cause of renal failure from Basque country were not available at the ERA-EDTA Registry 21
23 Table A.2.5 Incident rates per million population, adjusted at day 1, by cause of renal failure, adjusted for age and gender Cause of renal failure DM Total GN PN PKD Type I Type II Both HT RVD Misc Unkn Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Austria Belgium, Dutch-speaking Belgium, French-speaking Denmark Finland Greece Iceland Norway Spain, Basque country * Spain, Catalonia Spain, Valencia Sweden The Netherlands UK, England/Wales UK, Scotland Abbreviations used: GN: glomerulonephritis/sclerosis; PN: pyelonephritis; PKD: polycystic kidneys, adult type; DM: diabetes mellitus; HT: hypertension; RVD: renal vascular disease; Misc: miscellaneous; Unkn: Categories may not add up to total or to 100% because of missing values * Data on cause of renal failure from Basque country were not available at the ERA-EDTA Registry 22
24 Table A.3.1 Incident counts and percentage at day 90, by age and gender All Men Women All Men Women All Men Women All Men Women All Men Women All Men Women All N % N % N % N % N % N % N % N % N % N % N % N % N % N % N % N % N % N % Austria Belgium, Dutch-speaking Belgium, French-speaking Denmark Finland Greece Iceland Norway Spain, Basque country Spain, Catalonia Spain, Valencia Sweden The Netherlands UK, England/Wales UK, Scotland Percentages are row percentages Categories may not add up to total or to 100% because of missing values 23
25 Table A.3.2 Gender, mean and median age of incident patients at day 90 All Men Women % Mean (Years) (SD) Median (years) % Mean (Years) (SD) Median (years) % Mean (Years) (SD) Median (years) Austria (15.1) (15.3) (14.5) 66.2 Belgium, Dutch-speaking (14.5) (14.2) (14.9) 69.8 Belgium, French-speaking (16.1) (16.4) (15.8) 68.0 Denmark (15.5) (15.5) (15.5) 65.3 Finland (17.0) (16.7) (17.4) 62.9 Greece (14.9) (15.2) (14.4) 69.0 Iceland (18.4) (21.5) (14.9) 58.6 Norway (17.3) (17.4) (17.3) 61.0 Spain, Basque country (15.9) (15.1) (17.3) 64.4 Spain, Catalonia (16.0) (15.6) (16.7) 69.1 Spain, Valencia (16.4) (16.9) (15.3) 67.4 Sweden (16.5) (16.0) (17.4) 64.4 The Netherlands (16.7) (16.8) (16.5) 60.9 UK, England/Wales (17.5) (17.3) (17.8) 61.2 UK, Scotland (17.9) (18.3) (17.5)
26 Table A.3.3 Incident rates per million population, unadjusted at day 90, by age and gender All Men Women All Men Women All Men Women All Men Women All Men Women All Men Women All Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Austria Belgium, Dutch-speaking Belgium, French-speaking Denmark Finland Greece Iceland Norway Spain, Basque country Spain, Catalonia Spain, Valencia Sweden The Netherlands UK, England/Wales UK, Scotland
27 Table A.3.4 Incident rates per million population, unadjusted at day 90, by cause of renal failure Total GN PN Cause of renal failure DM PKD Type I Type II Both HT RVD Misc Unkn Pmp % Pmp % Pmp % Pmp % Pmp % Pmp % Pmp % Pmp % Pmp % Pmp % Pmp % Austria Belgium, Dutch-speaking Belgium, French-speaking Denmark Finland Greece Iceland Norway Spain, Basque country * Spain, Catalonia Spain, Valencia Sweden The Netherlands UK, England/Wales UK, Scotland Abbreviations used: GN: glomerulonephritis/sclerosis; PN: pyelonephritis; PKD: polycystic kidneys, adult type; DM: diabetes mellitus; HT: hypertension; RVD: renal vascular disease; Misc: miscellaneous; Unkn: Categories may not add up to total or to 100% because of missing values * Data on cause of renal failure from Basque country were not available at the ERA-EDTA Registry 26
28 Table A.3.5 Incident rates per million population, adjusted at day 90, by cause of renal failure, adjusted for age and gender Total GN PN Cause of renal failure DM PKD Type I Type II Both HT RVD Misc Unkn Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Austria Belgium, Dutch-speaking Belgium, French-speaking Denmark Finland Greece Iceland Norway Spain, Basque country * Spain, Catalonia Spain, Valencia Sweden The Netherlands UK, England/Wales UK, Scotland Abbreviations used: GN: glomerulonephritis/sclerosis; PN: pyelonephritis; PKD: polycystic kidneys, adult type; DM: diabetes mellitus; HT: hypertension; RVD: renal vascular disease; Misc: miscellaneous; Unkn: Categories may not add up to total or to 100% because of missing values * Data on cause of renal failure from Basque country were not available at the ERA-EDTA Registry 27
29 Table A.3.6 Incident counts at day 90, by established therapy Total Haemodialysis Peritoneal dialysis Transplant Unknown Missing Hospital/ centre Home HD, type HF HDF Total HD/ HF/HDF APD CAPD PD, type N N N N N N N N N N N Total PD Living Cadaver Tx, type Total Tx N N N N N N Austria Belgium, Dutch-speaking Belgium, French-speaking Denmark Finland Greece Iceland Norway Spain, Basque country Spain, Catalonia Spain, Valencia Sweden The Netherlands UK, England/Wales UK, Scotland " " is unavailable 28
30 Table A.3.7 Incident rates per million population, unadjusted at day 90, by established therapy Total Haemodialysis Peritoneal dialysis Transplant Unknown Missing Hospital/ centre Home HD, type HF HDF Total HD/ HF/HDF APD CAPD PD, type Total PD Living Cadaver Tx, type Total Tx Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Austria Belgium, Dutch-speaking Belgium, French-speaking Denmark Finland Greece Iceland Norway Spain, Basque country Spain, Catalonia Spain, Valencia Sweden The Netherlands UK, England/Wales UK, Scotland " " is unavailable 29
31 Table A.3.8 Incident rates per million population, adjusted at day 90, by established therapy, adjusted for age and gender Total Haemodialysis Peritoneal dialysis Transplant Unknown Missing Hospital/ centre Home HD, type HF HDF Total HD/ HF/HDF APD CAPD PD, type Total PD Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Living Cadaver Tx, type Total Tx Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Pmp Austria Belgium, Dutch-speaking Belgium, French-speaking Denmark Finland Greece Iceland Norway Spain, Basque country Spain, Catalonia Spain, Valencia Sweden The Netherlands UK, England/Wales UK, Scotland " " is unavailable 30
32 Table A.3.9 Percentage of established therapy, unadjusted at day 90 Total Haemodialysis Peritoneal dialysis Transplant Unknown Missing Hospital/ centre Home HD, type HF HDF Total HD/ HF/HDF APD CAPD PD, type % % % % % % % % % % % Total PD Living Cadaver Tx, type Total Tx % % % % % % Austria Belgium, Dutch-speaking Belgium, French-speaking Denmark Finland Greece Iceland Norway Spain, Basque country Spain, Catalonia Spain, Valencia Sweden The Netherlands UK, England/Wales UK, Scotland Categories may not add up to total or to 100% because of missing values " " is unavailable 31
Appendix G Coding: Ethnicity, EDTA Primary Renal Diagnoses, EDTA Causes of Death and Treatment Timeline Modality Codes
 Coding: Ethnicity, EDTA Primary Renal Diagnoses, EDTA Causes of Death and Treatment Timeline Modality Codes G1: Ethnicity coding Ethnicity data is recorded in the clinical information systems in the individual
Coding: Ethnicity, EDTA Primary Renal Diagnoses, EDTA Causes of Death and Treatment Timeline Modality Codes G1: Ethnicity coding Ethnicity data is recorded in the clinical information systems in the individual
RENINE Annual Report 2015
 RENINE Annual Report 2015 T. Hoekstra, M.H. Hemmelder, F.J. van Ittersum In cooperation with the sectie Registratie (Registration division) of the Nederlandse Federatie voor Nefrologie (NfN; Dutch federation
RENINE Annual Report 2015 T. Hoekstra, M.H. Hemmelder, F.J. van Ittersum In cooperation with the sectie Registratie (Registration division) of the Nederlandse Federatie voor Nefrologie (NfN; Dutch federation
ESRD Dialysis Prevalence - One Year Statistics
 Age Group IL Other Total 00-04 12 1 13 05-09 5 2 7 10-14 15 1 16 15-19 55 2 57 20-24 170 10 180 25-29 269 14 283 30-34 381 9 390 35-39 583 14 597 40-44 871 20 891 45-49 1,119 20 1,139 50-54 1,505 35 1,540
Age Group IL Other Total 00-04 12 1 13 05-09 5 2 7 10-14 15 1 16 15-19 55 2 57 20-24 170 10 180 25-29 269 14 283 30-34 381 9 390 35-39 583 14 597 40-44 871 20 891 45-49 1,119 20 1,139 50-54 1,505 35 1,540
RENINE year report 2016
 RENINE year report 216 T. Hoekstra, F.J. van Ittersum and M.H. Hemmelder In cooperation with the sectie Registratie (Registration division) of the Nederlandse Federatie voor Nefrologie (NfN; Dutch federation
RENINE year report 216 T. Hoekstra, F.J. van Ittersum and M.H. Hemmelder In cooperation with the sectie Registratie (Registration division) of the Nederlandse Federatie voor Nefrologie (NfN; Dutch federation
Chapter 8: ESRD Among Children, Adolescents, and Young Adults
 Chapter 8: ESRD Among Children, Adolescents, and Young Adults The number of children beginning end-stage renal disease (ESRD) care decreased by 6% in 2014, totaling 1,398 (Figure 8.1.a). 9,721 children
Chapter 8: ESRD Among Children, Adolescents, and Young Adults The number of children beginning end-stage renal disease (ESRD) care decreased by 6% in 2014, totaling 1,398 (Figure 8.1.a). 9,721 children
USRDS UNITED STATES RENAL DATA SYSTEM
 USRDS UNITED STATES RENAL DATA SYSTEM Chapter 8: Pediatric ESRD 1,462 children in the United States began end-stage renal disease (ESRD) care in 2013. 9,921 children were being treated for ESRD on December
USRDS UNITED STATES RENAL DATA SYSTEM Chapter 8: Pediatric ESRD 1,462 children in the United States began end-stage renal disease (ESRD) care in 2013. 9,921 children were being treated for ESRD on December
Chapter 1. Incidence of End Stage Kidney Disease. Contents:
 Chapter 1 Incidence of End Stage Kidney Disease Contents: Incidence of End Stage Kidney Disease 1-1 Stock and Flow 1-2 Incident patients 1-3 Incident Rates 1-3 Late Referral 1-7 Co-Morbidities 1-9 Primary
Chapter 1 Incidence of End Stage Kidney Disease Contents: Incidence of End Stage Kidney Disease 1-1 Stock and Flow 1-2 Incident patients 1-3 Incident Rates 1-3 Late Referral 1-7 Co-Morbidities 1-9 Primary
Chapter 7: ESRD among Children, Adolescents, and Young Adults
 Chapter 7: ESRD among Children, Adolescents, and Young Adults The one-year end-stage renal disease (ESRD) patient mortality among the 0-4 year age group has declined approximately 41.6% over the past decade.
Chapter 7: ESRD among Children, Adolescents, and Young Adults The one-year end-stage renal disease (ESRD) patient mortality among the 0-4 year age group has declined approximately 41.6% over the past decade.
CHAPTER 2 NEW PATIENTS COMMENCING TREATMENT IN 2007
 CHAPTER 2 NEW PATIENTS COMMENCING TREATMENT IN 27 Stephen McDonald Leonie Excell Hannah Dent NEW PATIENTS ANZDATA Registry 28 Report Figure 2.1 Annual Intake of New Patients 23-27 (Number Per Million Population)
CHAPTER 2 NEW PATIENTS COMMENCING TREATMENT IN 27 Stephen McDonald Leonie Excell Hannah Dent NEW PATIENTS ANZDATA Registry 28 Report Figure 2.1 Annual Intake of New Patients 23-27 (Number Per Million Population)
Report Finnish Registry for Kidney Diseases. Number of patients at end of year y y. 5 9 y. 0 4 y
 Finnish Registry for Kidney Diseases Number of patients at end of year 14 13 12 11 1 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1-9 -95 - -5-1 15 19 y 1 14 y 5 9 y 4 y Finnish Registry for Kidney Diseases Contents Finnish Registry
Finnish Registry for Kidney Diseases Number of patients at end of year 14 13 12 11 1 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1-9 -95 - -5-1 15 19 y 1 14 y 5 9 y 4 y Finnish Registry for Kidney Diseases Contents Finnish Registry
Renal Transplant Registry Report 2008
 Renal Transplant Registry Report 28 Contents:. Introduction Page 2. Summary of transplant activity 27-28 Page 2 3. Graft and Patient Survival analysis 989-28 Page 3 4. Acute rejection 989-28 Page 24. Comparison
Renal Transplant Registry Report 28 Contents:. Introduction Page 2. Summary of transplant activity 27-28 Page 2 3. Graft and Patient Survival analysis 989-28 Page 3 4. Acute rejection 989-28 Page 24. Comparison
TRENDS IN RENAL REPLACEMENT THERAPY IN BOSNIA AND HERZEGOVINA
 & TRENDS IN RENAL REPLACEMENT THERAPY IN BOSNIA AND HERZEGOVINA 2002-2008 Halima Resić* 1, Enisa Mešić 2 1 Clinic for Hemodialysis, University of Sarajevo Clinics Centre, Bolnička 25, 71000 Sarajevo, Bosnia
& TRENDS IN RENAL REPLACEMENT THERAPY IN BOSNIA AND HERZEGOVINA 2002-2008 Halima Resić* 1, Enisa Mešić 2 1 Clinic for Hemodialysis, University of Sarajevo Clinics Centre, Bolnička 25, 71000 Sarajevo, Bosnia
2014 /2018 ERA-EDTA PRD Code ERA-EDTA PRD code 1996 ERA-EDTA. SNOMED CT concept identifier Convert ERA-EDTA Primary Renal Diagnosis (PRD) Term
 Convert Primary Renal Diagnosis (PRD) Term ERA_EDTA diagnosis 3380 901.1.C 90 Acute kidney injury Acute Renal Failure 14669001 Miscellaneous renal disorders 3398 901.2.C 90 Acute kidney injury due to hypovolaemia
Convert Primary Renal Diagnosis (PRD) Term ERA_EDTA diagnosis 3380 901.1.C 90 Acute kidney injury Acute Renal Failure 14669001 Miscellaneous renal disorders 3398 901.2.C 90 Acute kidney injury due to hypovolaemia
Chapter 15: Report of the Paediatric Renal Registry 1999
 Chapter 15: Report of the Paediatric Renal Registry 1999 Prepared by Dr M Lewis Introduction In parallel with the creation of the National Renal Registry, the British Association for Paediatric Nephrology
Chapter 15: Report of the Paediatric Renal Registry 1999 Prepared by Dr M Lewis Introduction In parallel with the creation of the National Renal Registry, the British Association for Paediatric Nephrology
ERA-EDTA ERA-EDTA Primary Renal Diagnosis (PRD) Term ERA-EDTA PRD classification SNOMED CT PRD Code 1/1/2015
 1003 Adult nephrotic syndrome - no histology Immunological Glomerulopathy 52254009 1019 Nephrotic syndrome of childhood - steroid sensitive - no histology Immunological Glomerulopathy 445119005 1026 Congenital
1003 Adult nephrotic syndrome - no histology Immunological Glomerulopathy 52254009 1019 Nephrotic syndrome of childhood - steroid sensitive - no histology Immunological Glomerulopathy 445119005 1026 Congenital
Chapter IX. Pediatric End Stage Renal Disease. Incidence of Reported Pediatric ESRD
 Annual Data Report Chapter IX T his chapter examines the incidence, prevalence, modalities of treatment, and survival outcomes specific to the national pediatric ESRD population. Children with advanced
Annual Data Report Chapter IX T his chapter examines the incidence, prevalence, modalities of treatment, and survival outcomes specific to the national pediatric ESRD population. Children with advanced
Chapter 10. Cancer. ANZDATA gratefully acknowledges the contributions of the Cancer Working Group convened by Germaine Wong.
 Chapter Cancer ANZDATA gratefully acknowledges the contributions of the Cancer Working Group convened by Germaine Wong Contents: Cancer -1 Incidence of Cancer on Renal Replacement Therapy -2 Kidney Cancer
Chapter Cancer ANZDATA gratefully acknowledges the contributions of the Cancer Working Group convened by Germaine Wong Contents: Cancer -1 Incidence of Cancer on Renal Replacement Therapy -2 Kidney Cancer
End Stage Kidney Disease Among Indigenous Peoples of Australia and New Zealand
 Chapter 12 End Stage Kidney Disease Among Indigenous Peoples of and New Zealand 216 ANZDATA Registry 39th Annual Report Data to 31-Dec-215 Introduction In this chapter, rates of end-stage kidney disease
Chapter 12 End Stage Kidney Disease Among Indigenous Peoples of and New Zealand 216 ANZDATA Registry 39th Annual Report Data to 31-Dec-215 Introduction In this chapter, rates of end-stage kidney disease
Chapter 10. Cancer. ANZDATA Registry 39th Annual Report. Data to 31-Dec-2015
 Chapter Cancer 216 ANZDATA Registry 39th Annual Report Data to 31-Dec-215 Incidence of Cancer on Renal Replacement Therapy Figures.1-.6 and table.1 show the cumulative incidence of non-skin cancer in patients
Chapter Cancer 216 ANZDATA Registry 39th Annual Report Data to 31-Dec-215 Incidence of Cancer on Renal Replacement Therapy Figures.1-.6 and table.1 show the cumulative incidence of non-skin cancer in patients
Chapter 12. End Stage Kidney Disease in Indigenous Peoples of Australia and Aotearoa/New Zealand. ANZDATA Registry 39th Annual Report
 Chapter 12 End Stage Kidney Disease in Indigenous Peoples of and Aotearoa/ 216 ANZDATA Registry 39th Annual Report Data to 31-Dec-215 Introduction In this chapter, the rates and practice patterns for end-stage
Chapter 12 End Stage Kidney Disease in Indigenous Peoples of and Aotearoa/ 216 ANZDATA Registry 39th Annual Report Data to 31-Dec-215 Introduction In this chapter, the rates and practice patterns for end-stage
Finnish Registry for Kidney Diseases Report 2001
 Finnish Registry for Kidney Diseases Report 2001 Contents Finnish Registry for Kidney Diseases 2001...ii Board of the Finnish Registry for Kidney Diseases...iii The Finnish population and its distribution
Finnish Registry for Kidney Diseases Report 2001 Contents Finnish Registry for Kidney Diseases 2001...ii Board of the Finnish Registry for Kidney Diseases...iii The Finnish population and its distribution
Report Finnish Registry for Kidney Diseases. Proportion of patients reaching treatment target (%) 100. Healthcare districts Regions
 Finnish Registry for Kidney Diseases Proportion of patients reaching treatment target (%) 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 Healthcare districts Regions Finnish Registry for Kidney Diseases Contents Finnish
Finnish Registry for Kidney Diseases Proportion of patients reaching treatment target (%) 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 Healthcare districts Regions Finnish Registry for Kidney Diseases Contents Finnish
Chapter 15: Causes of Death on Renal Replacement Therapy
 Chapter 15: Causes of Death on Renal Replacement Therapy Summary Cardiovascular disease is the most common cause of death in the renal population and is most evident in diabetics. Patients on renal replacement
Chapter 15: Causes of Death on Renal Replacement Therapy Summary Cardiovascular disease is the most common cause of death in the renal population and is most evident in diabetics. Patients on renal replacement
Chapter IV. Incidence and Causes of Treated ESRD. Methods
 Annual Data Report Chapter IV Incidence and Causes of Treated ESRD T he statistics in this chapter show a continued increase in the annual incidence rate of newly treated ESRD in the United States. The
Annual Data Report Chapter IV Incidence and Causes of Treated ESRD T he statistics in this chapter show a continued increase in the annual incidence rate of newly treated ESRD in the United States. The
by Karlijn van Stralen, Marjolein Bonthuis, Enrico Verrina, Franz Schaefer and Kitty Jager
 Registry of the European Society for Paediatric Nephrology and the European Renal Association and European Dialysis and Transplantation Association ESPN http://espn.cardiff.ac.uk ESPN/ERA-EDTA Registry
Registry of the European Society for Paediatric Nephrology and the European Renal Association and European Dialysis and Transplantation Association ESPN http://espn.cardiff.ac.uk ESPN/ERA-EDTA Registry
Glomerular pathology in systemic disease
 Glomerular pathology in systemic disease Lecture outline Lupus nephritis Diabetic nephropathy Glomerulonephritis Associated with Bacterial Endocarditis and Other Systemic Infections Henoch-Schonlein Purpura
Glomerular pathology in systemic disease Lecture outline Lupus nephritis Diabetic nephropathy Glomerulonephritis Associated with Bacterial Endocarditis and Other Systemic Infections Henoch-Schonlein Purpura
SCOTTISH REAL BIOPSY REGISTRY: SURVEY OF NATIVE KIDNEY BIOPSY IN SCOTLAND 2015
 Scottish Renal Registry Report SECTION N SCOTTISH REAL BIOPSY REGISTRY: SURVEY OF NATIVE KIDNEY BIOPSY IN SCOTLAND All centres in Scotland were able to provide date of birth, sex (except centre), indication
Scottish Renal Registry Report SECTION N SCOTTISH REAL BIOPSY REGISTRY: SURVEY OF NATIVE KIDNEY BIOPSY IN SCOTLAND All centres in Scotland were able to provide date of birth, sex (except centre), indication
RaDaR Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria. Diagnosis Inclusion Criteria Exclusion Criteria. Alport Syndrome definite or probable
 Alport Syndrome and Type IV collagenopathies APRT Deficiency Alport Syndrome definite or probable Alport carrier definite or probable Thin basement membrane nephropathy APRT Deficiency confirmed Abolished
Alport Syndrome and Type IV collagenopathies APRT Deficiency Alport Syndrome definite or probable Alport carrier definite or probable Thin basement membrane nephropathy APRT Deficiency confirmed Abolished
Kidney Transplant. Description
 Section: Surgery Effective Date: October 15, 2015 Subject: Kidney Transplant Page: 1 of 9 Last Review Status/Date: September 2015 Kidney Transplant Description A kidney transplant involves the surgical
Section: Surgery Effective Date: October 15, 2015 Subject: Kidney Transplant Page: 1 of 9 Last Review Status/Date: September 2015 Kidney Transplant Description A kidney transplant involves the surgical
Epidemiology of CKD in Children
 Epidemiology of CKD in Children Ali Düzova, M.D. Hacettepe University Faculty of Medicine Pediatric Nephrology and Rheumatology Unit Ankara CKD Course 03 June 2011, İstanbul Aim & Plan Causes of CKD in
Epidemiology of CKD in Children Ali Düzova, M.D. Hacettepe University Faculty of Medicine Pediatric Nephrology and Rheumatology Unit Ankara CKD Course 03 June 2011, İstanbul Aim & Plan Causes of CKD in
WCPT COUNTRY PROFILE December 2017 SWEDEN
 WCPT COUNTRY PROFILE December 2017 SWEDEN SWEDEN NUMBERS WCPT Members Practising physical therapists 11,043 Total number of physical therapist members in your member organisation 17,906 Total number of
WCPT COUNTRY PROFILE December 2017 SWEDEN SWEDEN NUMBERS WCPT Members Practising physical therapists 11,043 Total number of physical therapist members in your member organisation 17,906 Total number of
WCPT COUNTRY PROFILE December 2017 SERBIA
 WCPT COUNTRY PROFILE December 2017 SERBIA SERBIA NUMBERS WCPT Members Practising physical therapists 622 Total number of physical therapist members in your member organisation 3,323 Total number of practising
WCPT COUNTRY PROFILE December 2017 SERBIA SERBIA NUMBERS WCPT Members Practising physical therapists 622 Total number of physical therapist members in your member organisation 3,323 Total number of practising
WCPT COUNTRY PROFILE December 2017 HUNGARY
 WCPT COUNTRY PROFILE December 2017 HUNGARY HUNGARY NUMBERS WCPT Members Practising physical therapists 727 Total number of physical therapist members in your member organisation 4,000 Total number of practising
WCPT COUNTRY PROFILE December 2017 HUNGARY HUNGARY NUMBERS WCPT Members Practising physical therapists 727 Total number of physical therapist members in your member organisation 4,000 Total number of practising
NAPRTCS Annual Transplant Report
 North American Pediatric Renal Trials and Collaborative Studies NAPRTCS 2014 Annual Transplant Report This is a privileged communication not for publication. TABLE OF CONTENTS PAGE II TRANSPLANTATION Section
North American Pediatric Renal Trials and Collaborative Studies NAPRTCS 2014 Annual Transplant Report This is a privileged communication not for publication. TABLE OF CONTENTS PAGE II TRANSPLANTATION Section
NAPRTCS Annual Transplant Report
 North American Pediatric Renal Trials and Collaborative Studies NAPRTCS 2010 Annual Transplant Report This is a privileged communication not for publication. TABLE OF CONTENTS PAGE I INTRODUCTION 1 II
North American Pediatric Renal Trials and Collaborative Studies NAPRTCS 2010 Annual Transplant Report This is a privileged communication not for publication. TABLE OF CONTENTS PAGE I INTRODUCTION 1 II
Special Feature. Carmine Zoccali 1, Anneke Kramer 2 and Kitty J. Jager 2. Introduction
 NDT Plus (2010) 3: 213213 224 doi: 10.1093/ndtplus/sfp127 Advance Access publication 12 October 2009 Special Feature Chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease a review produced to contribute to
NDT Plus (2010) 3: 213213 224 doi: 10.1093/ndtplus/sfp127 Advance Access publication 12 October 2009 Special Feature Chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease a review produced to contribute to
THIS chapter presents basic information about
 II. Incidence and Prevalence of ESRD INDEX WORDS: Cause of ESRD; diabetic ESRD; dialysis patient counts; ESRD growth rates; ESRD incidence; ESRD Medical Evidence Form 2728; ESRD Medicare; ESRD prevalence;
II. Incidence and Prevalence of ESRD INDEX WORDS: Cause of ESRD; diabetic ESRD; dialysis patient counts; ESRD growth rates; ESRD incidence; ESRD Medical Evidence Form 2728; ESRD Medicare; ESRD prevalence;
NAPRTCS Annual Report
 North American Pediatric Renal Trials and Collaborative Studies NAPRTCS 2006 Annual Report Renal Transplantation Dialysis Chronic Renal Insufficiency This is a privileged communication not for publication.
North American Pediatric Renal Trials and Collaborative Studies NAPRTCS 2006 Annual Report Renal Transplantation Dialysis Chronic Renal Insufficiency This is a privileged communication not for publication.
. Time to transplant listing is dependent on. . In 2003, 9.1% of all prevalent transplant. . Patients with diabetes mellitus are less
 Chapter 5: Joint Analyses with UK Transplant in England and Wales; Access to the Renal Transplant Waiting List, Time to Listing, Diabetic Access to Transplantation and the Influence of Social Deprivation
Chapter 5: Joint Analyses with UK Transplant in England and Wales; Access to the Renal Transplant Waiting List, Time to Listing, Diabetic Access to Transplantation and the Influence of Social Deprivation
UK Renal Registry 20th Annual Report: Chapter 4 Demography of the UK Paediatric Renal Replacement Therapy Population in 2016
 Nephron 2018;139(suppl1):105 116 DOI: 10.1159/000490962 Published online: July 11, 2018 UK Renal Registry 20th Annual Report: Chapter 4 Demography of the UK Paediatric Renal Replacement Therapy Population
Nephron 2018;139(suppl1):105 116 DOI: 10.1159/000490962 Published online: July 11, 2018 UK Renal Registry 20th Annual Report: Chapter 4 Demography of the UK Paediatric Renal Replacement Therapy Population
North American Pediatric Renal Transplant Cooperative Study (NAPRTCS) 2005 Annual Report. Renal Transplantation. Chronic Renal Insufficiency
 North American Pediatric Renal Transplant Cooperative Study (NAPRTCS) 2005 Annual Report Renal Transplantation Dialysis Chronic Renal Insufficiency This is a privileged communication not for publication.
North American Pediatric Renal Transplant Cooperative Study (NAPRTCS) 2005 Annual Report Renal Transplantation Dialysis Chronic Renal Insufficiency This is a privileged communication not for publication.
Incidence of new patients starting RRT
 SECTION A INCIDENCE A1 Incidence of new patients starting RRT A1.1 Incidence of new patients starting RRT 196-213 3 25 2 Number of 15 patients 1 5 367 425 749 119 169 2319 Year starting RRT 2799 2924 2635
SECTION A INCIDENCE A1 Incidence of new patients starting RRT A1.1 Incidence of new patients starting RRT 196-213 3 25 2 Number of 15 patients 1 5 367 425 749 119 169 2319 Year starting RRT 2799 2924 2635
RECURRENT AND DE NOVO RENAL DISEASES IN THE ALLOGRAFT. J. H. Helderman,MD,FACP,FAST
 RECURRENT AND DE NOVO RENAL DISEASES IN THE ALLOGRAFT J. H. Helderman,MD,FACP,FAST Vanderbilt University Medical Center Professor of Medicine, Pathology and Immunology Medical Director, Vanderbilt Transplant
RECURRENT AND DE NOVO RENAL DISEASES IN THE ALLOGRAFT J. H. Helderman,MD,FACP,FAST Vanderbilt University Medical Center Professor of Medicine, Pathology and Immunology Medical Director, Vanderbilt Transplant
Renal replacement therapy in Europe a summary of the 2010 ERA EDTA Registry Annual Report
 Clin Kidney J (2013) 6: 105 115 doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfs164 Special Feature Renal replacement therapy in Europe a summary of the 2010 ERA EDTA Registry Annual Report Anneke Kramer 1, Vianda S. Stel 1, José
Clin Kidney J (2013) 6: 105 115 doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfs164 Special Feature Renal replacement therapy in Europe a summary of the 2010 ERA EDTA Registry Annual Report Anneke Kramer 1, Vianda S. Stel 1, José
3/5/18. Background. Registry Reports. Dialysis Registry Update and Future Directions
 Dialysis Registry Update and Future Directions Annabelle N. Chua, MD March 4, 2018 Background Founded in 1987 as a transplant registry Expanded registry to include dialysis (1992) and CKD (1994) Patient
Dialysis Registry Update and Future Directions Annabelle N. Chua, MD March 4, 2018 Background Founded in 1987 as a transplant registry Expanded registry to include dialysis (1992) and CKD (1994) Patient
Epidemiological Data Chronic Kidney Diseases in Estonia Annual Report 2012
 Epidemiological Data Chronic Kidney Diseases in Estonia Annual Report 2012 Toimetaja: Mai Rosenberg Tartu Ülikooli Sisekliinik Puusepa 6, Tartu ISSN 2346-5689 Eesti Ülikoolide Kirjastus OÜ www.eyk.ee Acknowledgments
Epidemiological Data Chronic Kidney Diseases in Estonia Annual Report 2012 Toimetaja: Mai Rosenberg Tartu Ülikooli Sisekliinik Puusepa 6, Tartu ISSN 2346-5689 Eesti Ülikoolide Kirjastus OÜ www.eyk.ee Acknowledgments
RaDaR Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria. Diagnosis Inclusion Criteria Exclusion Criteria. Alport Syndrome definite or probable
 Alport Syndrome and Type IV collagenopathies APRT Deficiency Alport Syndrome definite or probable Alport carrier definite or probable Thin basement membrane nephropathy APRT Deficiency confirmed Abolished
Alport Syndrome and Type IV collagenopathies APRT Deficiency Alport Syndrome definite or probable Alport carrier definite or probable Thin basement membrane nephropathy APRT Deficiency confirmed Abolished
CHAPTER 12 END-STAGE KIDNEY DISEASE AMONG INDIGENOUS PEOPLES OF AUSTRALIA AND NEW ZEALAND. Stephen McDonald. Matthew Jose. Kylie Hurst INDIGENOUS 12-1
 ANZDATA Registry 213 Report INDIGENOUS END-STAGE KIDNEY DISEASE AMONG INDIGENOUS PEOPLES OF AUSTRALIA AND NEW ZEALAND CHAPTER 12 Stephen McDonald Matthew Jose Kylie Hurst 213 Annual Report - 36th Edition
ANZDATA Registry 213 Report INDIGENOUS END-STAGE KIDNEY DISEASE AMONG INDIGENOUS PEOPLES OF AUSTRALIA AND NEW ZEALAND CHAPTER 12 Stephen McDonald Matthew Jose Kylie Hurst 213 Annual Report - 36th Edition
Final Report: Update on Prior Living Donors Who Were Subsequently Placed on the Waiting List
 OPTN/UNOS Minority Affairs Committee Descriptive Data Request Final Report: Update on Prior Living Donors Who Were Subsequently Placed on the Waiting List Prepared for: Minority Affairs Committee Meeting
OPTN/UNOS Minority Affairs Committee Descriptive Data Request Final Report: Update on Prior Living Donors Who Were Subsequently Placed on the Waiting List Prepared for: Minority Affairs Committee Meeting
Report Finnish Registry for Kidney Diseases. PD n=364. In-center HD n=1408. Kidney transplantation n=2945. Home HD n=138
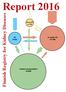 Finnish Registry for Kidney Diseases PD n=364 Home HD n=138 Kidney transplantation n=2945 In-center HD n=1408 Finnish Registry for Kidney Diseases Content Board of the Finnish Registry for Kidney Diseases...
Finnish Registry for Kidney Diseases PD n=364 Home HD n=138 Kidney transplantation n=2945 In-center HD n=1408 Finnish Registry for Kidney Diseases Content Board of the Finnish Registry for Kidney Diseases...
SPECIALISED SERVICES NATIONAL DEFINITIONS SET (THIRD EDITION 2008) Specialised Renal Services (adult) - Definition No. 11
 SPECIALISED SERVICES NATIONAL DEFINITIONS SET (THIRD EDITION 2008) Specialised Renal Services (adult) - Definition No. 11 Preface This definition is part of the third edition of the Specialised Services
SPECIALISED SERVICES NATIONAL DEFINITIONS SET (THIRD EDITION 2008) Specialised Renal Services (adult) - Definition No. 11 Preface This definition is part of the third edition of the Specialised Services
Measles and rubella monitoring January 2015
 Measles and rubella monitoring January 215 Reporting on January December 214 surveillance data and epidemic intelligence data to the end of January 215 Main developments Measles During the 12-month period
Measles and rubella monitoring January 215 Reporting on January December 214 surveillance data and epidemic intelligence data to the end of January 215 Main developments Measles During the 12-month period
ESPN/ERA-EDTA Registry
 ESPN/ERA-EDTA Registry Registry of the European Society for Paediatric Nephrology and the European Renal Association and European Dialysis and Transplantation Association ESPN http://espn.cardiff.ac.uk
ESPN/ERA-EDTA Registry Registry of the European Society for Paediatric Nephrology and the European Renal Association and European Dialysis and Transplantation Association ESPN http://espn.cardiff.ac.uk
DIABETES MELLITUS. Kidney in systemic diseases. Slower the progression: Pathology: Patients with diabetes mellitus are prone to other renal diseases:
 Kidney in systemic diseases Dr. Badri Paudel The kidneys may be directly involved in a number of multisystem diseases or secondarily affected by diseases of other organs. Involvement may be at a prerenal,
Kidney in systemic diseases Dr. Badri Paudel The kidneys may be directly involved in a number of multisystem diseases or secondarily affected by diseases of other organs. Involvement may be at a prerenal,
Protocol. Kidney Transplant
 Protocol Kidney Transplant (70301) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 01/01/15 Next Review Date: 03/18 Preauthorization Yes Review Dates: 05/09, 05/10, 05/11, 05/12, 05/13, 05/14, 11/14, 11/15, 11/16, 03/17
Protocol Kidney Transplant (70301) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 01/01/15 Next Review Date: 03/18 Preauthorization Yes Review Dates: 05/09, 05/10, 05/11, 05/12, 05/13, 05/14, 11/14, 11/15, 11/16, 03/17
Extract from Cancer survival in Europe by country and age: results of EUROCARE-5 a population-based study
 EUROCARE-5 on-line database Data and methods Extract from Cancer survival in Europe 1999 2007 by country and age: results of EUROCARE-5 a population-based study De Angelis R, Sant M, Coleman MP, Francisci
EUROCARE-5 on-line database Data and methods Extract from Cancer survival in Europe 1999 2007 by country and age: results of EUROCARE-5 a population-based study De Angelis R, Sant M, Coleman MP, Francisci
CHAPTER 5. Paediatric Renal Replacement Therapy
 24th Report of the CHAPTER 5 Paediatric Renal Replacement Therapy Lee Ming Lee Lim Yam Ngo Lynster Liaw Chiew Tung Susan Pee Yap Yok Chin Wan Jazilah Wan Ismail 24th Report of the SECTION A: RRT PROVISION
24th Report of the CHAPTER 5 Paediatric Renal Replacement Therapy Lee Ming Lee Lim Yam Ngo Lynster Liaw Chiew Tung Susan Pee Yap Yok Chin Wan Jazilah Wan Ismail 24th Report of the SECTION A: RRT PROVISION
United States Renal Data System (USRDS) International Data Collection Form
 United States Renal Data System (USRDS) International Data Collection Form This form is designed to solicit information on the population of End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD) patients in your country who
United States Renal Data System (USRDS) International Data Collection Form This form is designed to solicit information on the population of End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD) patients in your country who
NAPRTCS Annual Report
 North American Pediatric Renal Trials and Collaborative Studies NAPRTCS 27 Annual Report Renal Transplantation Dialysis Chronic Renal Insufficiency This is a privileged communication not for publication.
North American Pediatric Renal Trials and Collaborative Studies NAPRTCS 27 Annual Report Renal Transplantation Dialysis Chronic Renal Insufficiency This is a privileged communication not for publication.
DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES CENTERS FOR MEDICARE & MEDICAID SERVICES OMB No
 CENTERS FOR MEDICARE & MEDICAID SERVICES OMB No. 0938-0046 END STAGE RENAL DISEASE MEDICAL EVIDENCE REPORT MEDICARE ENTITLEMENT AND/OR PATIENT REGISTRATION A. COMPLETE FOR ALL ESRD PATIENTS Check one:
CENTERS FOR MEDICARE & MEDICAID SERVICES OMB No. 0938-0046 END STAGE RENAL DISEASE MEDICAL EVIDENCE REPORT MEDICARE ENTITLEMENT AND/OR PATIENT REGISTRATION A. COMPLETE FOR ALL ESRD PATIENTS Check one:
Engagement in language assessment / Regions of Europe
 Summary table: Engagement in language / Regions of This table lists the statistically significant differences in the engagement in activities by the respondents from different s of : If the word or appears
Summary table: Engagement in language / Regions of This table lists the statistically significant differences in the engagement in activities by the respondents from different s of : If the word or appears
2015 Children's Mercy Hospitals and Clinics. All Rights Reserved.
 Growth van Stralen KJ, et al., Kidney Int, 2014 Blood Pressure Management van Stralen KJ, et al., Kidney Int, 2014 Sodium Losses on PD Infants might need higher UF rate per BSA as compared to adults to
Growth van Stralen KJ, et al., Kidney Int, 2014 Blood Pressure Management van Stralen KJ, et al., Kidney Int, 2014 Sodium Losses on PD Infants might need higher UF rate per BSA as compared to adults to
Chapter 5 PAEDIATRIC RENAL REPLACEMENT THERAPY. Lee Ming Lee Lim Yam Ngo Lynster Liaw Susan Pee Wan Jazilah Wan Ismail Yap Yok Chin
 Chapter 5 PAEDIATRIC RENAL REPLACEMENT THERAPY Lee Ming Lee Lim Yam Ngo Lynster Liaw Susan Pee Wan Jazilah Wan Ismail Yap Yok Chin SECTION A: RRT PROVISION FOR PAEDIATRIC PATIENTS This chapter presents
Chapter 5 PAEDIATRIC RENAL REPLACEMENT THERAPY Lee Ming Lee Lim Yam Ngo Lynster Liaw Susan Pee Wan Jazilah Wan Ismail Yap Yok Chin SECTION A: RRT PROVISION FOR PAEDIATRIC PATIENTS This chapter presents
NAPRTCS Annual Report
 North American Pediatric Renal Trials and Collaborative Studies NAPRTCS 28 Annual Report Renal Transplantation Dialysis Chronic Renal Insufficiency This is a privileged communication not for publication.
North American Pediatric Renal Trials and Collaborative Studies NAPRTCS 28 Annual Report Renal Transplantation Dialysis Chronic Renal Insufficiency This is a privileged communication not for publication.
Assisted reproductive technology and intrauterine inseminations in Europe, 2005: results generated from European registers by ESHRE
 Human Reproduction, Vol.1, No.1 pp. 1 21, 2009 doi:10.1093/humrep/dep035 Hum. Reprod. Advance Access published February 18, 2009 ORIGINAL ARTICLE ESHRE Assisted reproductive technology and intrauterine
Human Reproduction, Vol.1, No.1 pp. 1 21, 2009 doi:10.1093/humrep/dep035 Hum. Reprod. Advance Access published February 18, 2009 ORIGINAL ARTICLE ESHRE Assisted reproductive technology and intrauterine
Analgesic and NSAID-induced Kidney Disease
 Analgesic and NSAID-induced Kidney Disease Edited by J.H.STEWART Associate Dean, Western Clinical School University of Sydney, Australia Oxford New York Tokyo Melbourne OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS 1993 CONTENTS
Analgesic and NSAID-induced Kidney Disease Edited by J.H.STEWART Associate Dean, Western Clinical School University of Sydney, Australia Oxford New York Tokyo Melbourne OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS 1993 CONTENTS
RECURRENT AND DE NOVO RENAL DISEASES IN THE ALLOGRAFT
 RECURRENT AND DE NOVO RENAL DISEASES IN THE ALLOGRAFT HISTOPATHOLOGIC DISORDERS AFFECTING THE ALLOGRAFT OTHER THAN REJECTION RECURRENT DISEASE DE NOVO DISEASE TRANSPLANT GLOMERULOPATHY Glomerular Non-glomerular
RECURRENT AND DE NOVO RENAL DISEASES IN THE ALLOGRAFT HISTOPATHOLOGIC DISORDERS AFFECTING THE ALLOGRAFT OTHER THAN REJECTION RECURRENT DISEASE DE NOVO DISEASE TRANSPLANT GLOMERULOPATHY Glomerular Non-glomerular
Q1 What age are you?
 Q1 What age are you? Answered: 504 Skipped: 0 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 4.56% 23 3.77% 19 4.56% 23 6.15% 31 3.97% 20 6.55% 33 5.95% 30 6.75% 34 6.35% 32 4.37% 22 6.75% 34 5.56%
Q1 What age are you? Answered: 504 Skipped: 0 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 4.56% 23 3.77% 19 4.56% 23 6.15% 31 3.97% 20 6.55% 33 5.95% 30 6.75% 34 6.35% 32 4.37% 22 6.75% 34 5.56%
CHAPTER 3. Secondary Glomerulonephritis
 CHAPTER 3 Secondary Glomerulonephritis Rosnawati Yahya Liew Yew Foong 59 3.1: Introduction This chapter covers the main secondary glomerulonephritis that were reported to the MRRB from the year 2005-2010.
CHAPTER 3 Secondary Glomerulonephritis Rosnawati Yahya Liew Yew Foong 59 3.1: Introduction This chapter covers the main secondary glomerulonephritis that were reported to the MRRB from the year 2005-2010.
LEBANON. WCPT COUNTRY PROFILE December 2018
 LEBANON WCPT COUNTRY PROFILE December 2018 LEBANON NUMBERS 1600 1400 1200 1000 800 600 400 200 0 Physical therapists in the country Members in MO 1,480 1,480 Total PTs in country 800000 700000 600000 500000
LEBANON WCPT COUNTRY PROFILE December 2018 LEBANON NUMBERS 1600 1400 1200 1000 800 600 400 200 0 Physical therapists in the country Members in MO 1,480 1,480 Total PTs in country 800000 700000 600000 500000
CHAPTER 2. Prevalence of Renal Replacement Therapy for End Stage Kidney Disease
 CHAPTER 2 Prevalence of Renal Replacement Therapy for End Stage Kidney Disease Summarising the number of prevalent renal replacement therapy patients in Australia and New Zealand, the prevalence rate per
CHAPTER 2 Prevalence of Renal Replacement Therapy for End Stage Kidney Disease Summarising the number of prevalent renal replacement therapy patients in Australia and New Zealand, the prevalence rate per
A report on the epidemiology of selected vaccine-preventable diseases in the European Region 30% 20% 10%
 % of reported measles cases WHO EpiBrief A report on the epidemiology of selected vaccine-preventable diseases in the European Region No. /17 This issue of WHO EpiBrief provides an overview of selected
% of reported measles cases WHO EpiBrief A report on the epidemiology of selected vaccine-preventable diseases in the European Region No. /17 This issue of WHO EpiBrief provides an overview of selected
Alcohol-related harm in Europe and the WHO policy response
 Alcohol-related harm in Europe and the WHO policy response Lars Moller Programme Manager World Health Organization Regional Office for Europe Date of presentation NCD global monitoring framework: alcohol-related
Alcohol-related harm in Europe and the WHO policy response Lars Moller Programme Manager World Health Organization Regional Office for Europe Date of presentation NCD global monitoring framework: alcohol-related
WESTERN EUROPE PREVALENCE AND INCIDENCE OF PERIPHERAL ARTERY DISEASE AND CRITICAL LIMB ISCHEMIA 2017
 WESTERN EUROPE PREVALENCE AND INCIDENCE OF PERIPHERAL ARTERY DISEASE AND CRITICAL LIMB ISCHEMIA 2017 Mary L. Yost 404-520-6652 , LLC 23 Ridge Rd. Beaufort, SC 20097 Copyright Pending 2017 All rights reserved,
WESTERN EUROPE PREVALENCE AND INCIDENCE OF PERIPHERAL ARTERY DISEASE AND CRITICAL LIMB ISCHEMIA 2017 Mary L. Yost 404-520-6652 , LLC 23 Ridge Rd. Beaufort, SC 20097 Copyright Pending 2017 All rights reserved,
Table 6.1 Summary information for colorectal cancer in Ireland,
 6 Colorectal cancer 6.1 Summary Colorectal cancer is the second most common cancer in Ireland (excluding non-melanoma skin cancer). It accounts for 12% of all malignant neoplasia in females and 15% in
6 Colorectal cancer 6.1 Summary Colorectal cancer is the second most common cancer in Ireland (excluding non-melanoma skin cancer). It accounts for 12% of all malignant neoplasia in females and 15% in
DENMARK. WCPT COUNTRY PROFILE December 2018
 DENMARK WCPT COUNTRY PROFILE December 2018 DENMARK NUMBERS 14000 12000 10000 8000 6000 4000 2000 0 Physical therapists in the country Members in MO 11,720 12,975 Total PTs in country 800000 700000 600000
DENMARK WCPT COUNTRY PROFILE December 2018 DENMARK NUMBERS 14000 12000 10000 8000 6000 4000 2000 0 Physical therapists in the country Members in MO 11,720 12,975 Total PTs in country 800000 700000 600000
Renal Disease. Please refer to the assignment page Three online modules TBLs
 Renal Disease Please refer to the assignment page Three online modules TBLs 1 Renal Embryology 2 Lab Tests UA CBC Enzymes Creatinine Creatinine clearance Ammonia Abs C Bx 3 BUN Creatinine Creatinine Clearance
Renal Disease Please refer to the assignment page Three online modules TBLs 1 Renal Embryology 2 Lab Tests UA CBC Enzymes Creatinine Creatinine clearance Ammonia Abs C Bx 3 BUN Creatinine Creatinine Clearance
The new ERA-EDTA PRDs UK Renal SNOMED CT subset TheProject
 The new ERA-EDTA PRDs UK Renal SNOMED CT subset TheProject Keith Simpson UKRR Advisor keith.simpson@nhs.net Thanks to ERA-EDTA Registry: Kitty Jager Managing Dir and members of the Coding and Terminology
The new ERA-EDTA PRDs UK Renal SNOMED CT subset TheProject Keith Simpson UKRR Advisor keith.simpson@nhs.net Thanks to ERA-EDTA Registry: Kitty Jager Managing Dir and members of the Coding and Terminology
CHAPTER 6 PERITONEAL DIALYSIS
 CHAPTER 6 PERITONEAL DIALYSIS Fiona Brown Aarti Gulyani Hannah Dent Kylie Hurst Stephen McDonald PERITONEAL DIALYSIS ANZDATA Registry 11 Report STOCK AND FLOW AUSTRALIA Peritoneal dialysis was used to
CHAPTER 6 PERITONEAL DIALYSIS Fiona Brown Aarti Gulyani Hannah Dent Kylie Hurst Stephen McDonald PERITONEAL DIALYSIS ANZDATA Registry 11 Report STOCK AND FLOW AUSTRALIA Peritoneal dialysis was used to
Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology
 Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
QQuickly take me up into the bright child of your mind. E.E. CUMMINGS, The Enormous Room
 QQuickly take me up into the bright child of your mind. E.E. CUMMINGS, The Enormous Room msix PEDIATrIC ESrD 18 ž 21 ATLAS OF ESRD IN THE UNITED STATES Incident rates of ESRD in children have risen two
QQuickly take me up into the bright child of your mind. E.E. CUMMINGS, The Enormous Room msix PEDIATrIC ESrD 18 ž 21 ATLAS OF ESRD IN THE UNITED STATES Incident rates of ESRD in children have risen two
A clinical syndrome, composed mainly of:
 Nephritic syndrome We will discuss: 1)Nephritic syndrome: -Acute postinfectious (poststreptococcal) GN -IgA nephropathy -Hereditary nephritis 2)Rapidly progressive GN (RPGN) A clinical syndrome, composed
Nephritic syndrome We will discuss: 1)Nephritic syndrome: -Acute postinfectious (poststreptococcal) GN -IgA nephropathy -Hereditary nephritis 2)Rapidly progressive GN (RPGN) A clinical syndrome, composed
CHAPTER 6 PERITONEAL DIALYSIS. Fiona Brown Aarti Gulyani Stephen McDonald Kylie Hurst Annual Report 35th Edition
 CHAPTER 6 PERITONEAL DIALYSIS Fiona Brown Aarti Gulyani Stephen McDonald Kylie Hurst 212 Annual Report 35th Edition PERITONEAL DIALYSIS ANZDATA Registry 212 Report STOCK AND FLOW AUSTRALIA Peritoneal dialysis
CHAPTER 6 PERITONEAL DIALYSIS Fiona Brown Aarti Gulyani Stephen McDonald Kylie Hurst 212 Annual Report 35th Edition PERITONEAL DIALYSIS ANZDATA Registry 212 Report STOCK AND FLOW AUSTRALIA Peritoneal dialysis
GERMANY. WCPT COUNTRY PROFILE December 2018
 GERMANY WCPT COUNTRY PROFILE December 2018 GERMANY NUMBERS 160000 140000 120000 100000 80000 60000 40000 20000 0 Physical therapists in the country Members in MO 21,502 136,000 Total PTs in country 800000
GERMANY WCPT COUNTRY PROFILE December 2018 GERMANY NUMBERS 160000 140000 120000 100000 80000 60000 40000 20000 0 Physical therapists in the country Members in MO 21,502 136,000 Total PTs in country 800000
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE (CKD)
 CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE (CKD) CKD implies longstanding (more than 3 months), and usually progressive, impairment in renal function. In many instances, no effective means are available to reverse the primary
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE (CKD) CKD implies longstanding (more than 3 months), and usually progressive, impairment in renal function. In many instances, no effective means are available to reverse the primary
Smokefree Policies in Europe: Are we there yet?
 Smokefree Policies in Europe: Are we there yet? 14 April 2015, 9:00 10:30am Rue de l Industrie 24, 1040 Brussels Permanent Partners: Temporary Partners: The research for the SFP Smokefree Map was partially
Smokefree Policies in Europe: Are we there yet? 14 April 2015, 9:00 10:30am Rue de l Industrie 24, 1040 Brussels Permanent Partners: Temporary Partners: The research for the SFP Smokefree Map was partially
Etiology and epidemiology of end-stage renal disease in Dutch children
 Pediatr Nephrol (2005) 20:1136 1142 DOI 10.1007/s00467-005-1896-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Daniela Miklovicova Marlies Cornelissen Karlien Cransberg Jaap W. Groothoff Ladislav Dedik Cornelis H. Schrőder Etiology
Pediatr Nephrol (2005) 20:1136 1142 DOI 10.1007/s00467-005-1896-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Daniela Miklovicova Marlies Cornelissen Karlien Cransberg Jaap W. Groothoff Ladislav Dedik Cornelis H. Schrőder Etiology
Department of Biological Standardisation OMCL Network & Healthcare (DBO)
 Department of Biological Standardisation OMCL Network & Healthcare (DBO) Implementation of Pathogen Reduction Technologies for Blood Components for Transfusion: Updated Table 2009-2010 COUNCIL OF EUROPE
Department of Biological Standardisation OMCL Network & Healthcare (DBO) Implementation of Pathogen Reduction Technologies for Blood Components for Transfusion: Updated Table 2009-2010 COUNCIL OF EUROPE
CHAPTER 3. Secondary Glomerulonephritis
 2nd Report of the Malaysian Registry of Renal Biopsy 2008 SECONDARY GLOMERULONEPHRITIS CHAPTER 3 Secondary Glomerulonephritis Rosnawati Yahya Liew Yew Foong 41 SECONDARY GLOMERULONEPHRITIS 2nd Report
2nd Report of the Malaysian Registry of Renal Biopsy 2008 SECONDARY GLOMERULONEPHRITIS CHAPTER 3 Secondary Glomerulonephritis Rosnawati Yahya Liew Yew Foong 41 SECONDARY GLOMERULONEPHRITIS 2nd Report
Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation
 Nephrol Dial Transplant (993) 8-684-689 Original Article Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation Chronic renal failure in India M. K. Mani Renal Unit, Apollo Hospital, Madras, India Abstract. In a series of
Nephrol Dial Transplant (993) 8-684-689 Original Article Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation Chronic renal failure in India M. K. Mani Renal Unit, Apollo Hospital, Madras, India Abstract. In a series of
Prevention of Oral Cancer Special Interest Working Group
 Prevention of Oral Cancer Special Interest Working Group Dr Colwyn Jones, Consultant in Dental Public Health, NHS Health Scotland, 1 South Gyle Crescent, Edinburgh EH12 9EB, Scotland. colwyn.jones@nhs.net
Prevention of Oral Cancer Special Interest Working Group Dr Colwyn Jones, Consultant in Dental Public Health, NHS Health Scotland, 1 South Gyle Crescent, Edinburgh EH12 9EB, Scotland. colwyn.jones@nhs.net
Global trends in ESRD epidemiology and impact on Vascular Access
 Global trends in ESRD epidemiology and impact on Vascular Access Wolfgang Meichelboeck, Dipl.-Ing. Pentenried Germany wolfgang.meichelboeck@t-online.de Please respect the copyright when using slides or
Global trends in ESRD epidemiology and impact on Vascular Access Wolfgang Meichelboeck, Dipl.-Ing. Pentenried Germany wolfgang.meichelboeck@t-online.de Please respect the copyright when using slides or
