Amitriptyline delayed gastric emptying
|
|
|
- Grace Douglas
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Amitriptyline delayed gastric emptying We have given this statement a conditional recommendation, as the quality of evidence is very low. The data mainly relate to national databases of upper GI cancer risk (28, 29), case series on early gastric cancer detection (23) and economic modeling (27). These types of data are indirect and often overestimate the benefit of endoscopy, so clinicians may treat a minority of patients over the age of 60 with empirical therapy provided they feel the risk of upper GI cancer malignancy is low. On the other hand, the risk of upper GI malignancy increases in those who were born and spent their TEENhood in certain geographical regions such as South East Asia and some countries in South America (31). In light of the conditional recommendation with the quality of evidence being low, the age threshold for endoscopy should be lowered in these patients, and possibly others, according to clinical judgment. In borderline cases the sex of the patient may be taken into consideration as age-adjusted upper GI cancer risk is about twice as high in men as it is in women (31). As with all guidelines, clinical decisions should be based on symptoms, patient concerns, physical examination findings, laboratory and radiologic studies, and data from the literature, when available. Intravenous fluids to correct dehydration and replenish electrolytes if nutrition is adequate but symptoms occasionally interrupt the intake of even liquid food. Enteral nutrition which provides liquid food directly into the small intestine, bypassing the paralyzed stomach. Intravenous total parenteral nutrition (TPN) to provide calories and nutrients (TPN is a fluid containing glucose, amino acids, lipids, minerals, and vitamins -everything that is needed for adequate nutrition-intravenously. The fluid usually is delivered into a large vein via a catheter in the arm or upper chest.) Doctors generally prefer enteral nutrition over TPN because long-term use of TPN is associated with infections of the catheter and liver damage. Infection can spread through the blood to the rest of the body, a serious condition called sepsis. Catheter-related sepsis often requires treatment with intravenous antibiotics and removal of the infected catheter or replacement with a new catheter. TPN also can damage the liver, most commonly
2 catheter. TPN also can damage the liver, most commonly causing abnormal liver tests in the blood. TPN-induced liver damage usually is mild and reversible (the liver test abnormalities return to normal after cessation of TPN), but, rarely, irreversible liver failure can occur. Such liver failure may require liver transplantation. Abdominal bloating (upper abdomen feels or actually looks distended, tight after eating). Our ultimate goal is to help your TEEN live as healthy, active and comfortable a life as possible. Applying to GI Fellowship Programs: What You Need to Know. Early satiety (feeling full after only a few bites of food, inability to finish meals). The goals of nutritional management are to ensure adequate calories, and that nutrients are consumed to promote your TEEN's growth and development. Maintaining a healthy diet can help control the symptoms of gastroparesis. Jay W. Marks, MD, is a board-certified internist and gastroenterologist. He graduated from Yale University School of Medicine and trained in internal medicine and gastroenterology at UCLA/Cedars- Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles. Unfortunately, at this time, there is lack of national standardization of test protocol for pediatric patients. Techniques vary in hospitals regarding size or volume of the test meal used, patient positioning, frequency and duration of monitoring. Click Join ACG to access applications and information on ACG Member categories. In patients with refractory symptoms of GERD, investigation for delayed gastric emptying should be considered, since delayed gastric emptying can be associated with GERD and possibly aggravate symptoms of heartburn, regurgitation, and other symptoms associated with GERD. In TEENren, gastroparesis may be an acute primary self-limiting disorder triggered by infection, surgery or excessive weight loss. More commonly, however, pediatric gastroparesis overlaps in an individual patient with other chronic GI motility disorders including: Most published literature describes gastroparesis as delayed gastric emptying without a mechanical obstruction. Entrustable Professional Activities (EPAs) for GI Fellowship Training. Please call the Communications Team at or e- mail. Cisapride is a gastrointestinal, prokinetic agent that increases motility in the gastrointestinal tract by increasing the excitability of the esophagus, small intestine and colon. In comparison, metoclopramide acts only on the small intestine. Cisapride is regulated by the FDA and is only available at select highly specialized institutions. A risk of cisapride is serious cardiac arrhythmias, and for this reason the medication can only be prescribed and dispensed by participating providers to ensure careful monitoring. Patients must meet very strict eligibility criteria and be willing to follow the treatment schedule in order to participate. home / diabetes health center / diabetes a-z list / gastroparesis center. Dietary changes are tailored to each patient and may include:. What drugs relieve pain and nausea from gastroparesis?. Authored by a talented group of GI experts, the College is devoted to the development of new ACG guidelines on gastrointestinal and liver diseases. Our guidelines reflect the current state-of-the-art scientific work and are based on the principles of evidence-based medicine.
3 and are based on the principles of evidence-based medicine. ACG welcomes inquiries about digestive health from the media and can make experts available for interviews upon request. Surgery: Surgery occasionally is used to treat gastroparesis. The goal of surgery is to create a larger opening between the stomac Symptoms of gastroparesis mirror some symptoms of delayed gastric emptying and include:. Patients were randomized to a placebo, 10 mg escitalopram, or 25 mg amitriptyline during a 2-week run-in phase, followed by 50 mg amitriptyline for a total of 12 weeks. They were evaluated at baseline with gastric-emptying tests, nutrient drink tests, and blood draws; a subset of patients also underwent evaluation of gastric accommodation by single-photon emission computed tomography. The SSRI (selective serotonin re-uptake inhibitors) group of antidepressants is generally avoided for use in functional and motility gut disorders, primarily due to their high incidence of side effects of nausea, dizziness and dry mouth as well as sexual dysfunction. Data source: A prospective, randomized, double-blind double-dummy study of 292 patients with functional dyspepsia. Entrustable Professional Activities (EPAs) for GI Fellowship Training. Disclaimer: GPDA's Web site is intended for educational and informational purposes only. Any suggestions provided on the GPDA Web site should never be undertaken without your health care professional's knowledge and guidance. If you have a digestive problem, seek professional care The Gastroparesis & Dysmotilities Association. therapy; this may improve symptoms and the delayed gastric. Journalists access information on digestive health, including the latest ACG news and up-to-date information about ACG's Annual Scientific Meeting and the latest clinical science. Diabetic (29%), postsurgical (13%), and idiopathic (36%) etiologies comprise the majority of cases in tertiary referral setting (8). Diabetes mellitus is the most commonly recognized systemic disease associated with gastroparesis. In the NIH consortium cohort, delayed gastric emptying was more pronounced in patients with type 1 DG (10). The 10-year incidence of gastroparesis has been reported to be 5.2% in type 1 diabetes, 1% in type 2 diabetes, and 0.2% in non-diabetic controls in a US community (5). like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and amylin analogs among diabetics,. Serious ( 1) or very serious ( 2) limitation to study quality. Idiopathic gastroparesis refers to a symptomatic patient from delayed gastric empting with no detectable primary underlying abnormality for the delayed gastric emptying. This may represent the most common form of gastroparesis (10,17). Most patients with IG are women; typically young or middle aged. Symptoms of IG overlap with those of functional dyspepsia; it may be difficult to provide a definitive distinction between the two based on symptoms, and many regard IG and functional dyspepsia with delayed gastric emptying as the same condition. Abdominal pain/discomfort typically is the predominant symptom in functional dyspepsia, whereas nausea, vomiting, early satiety, and bloating predominate in IG. Therefore, measurement of gastric emptying is important, as therapies differ if gastric emptying is delayed, normal, or rapid.
4 therapies differ if gastric emptying is delayed, normal, or rapid. etiological diagnosis. Narcotics and other medications that can. Some ( 1) or major ( 2) uncertainty about directness. Authored by a talented group of GI experts, the College is devoted to the development of new ACG guidelines on gastrointestinal and liver diseases. Our guidelines reflect the current state-of-the-art scientific work and are based on the principles of evidence-based medicine. We comply with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information: verify here. From articles to educational programs, ACG provides you tools and techniques you can use in your practice that will help improve efficiency and increase profitability. Learn from experts at ACG's live and web-based educational programs, read what others are doing in their practice to solve problems they encounter and connect with colleagues online to discuss important issues and share ways to improve practice. ACG GI Circle, Hepatology Circle, ACG & CCF IBD Circle and Functional GI Health and Nutrition Circle. delay gastric emptying should be stopped to establish the diagnosis. Keep up with the latest news and developments on Capitol Hill, CMS and the FDA. ACG has compiled a wealth of resources to help keep members up-to-date on the latest legislative and regulatory actions that impact the gastroenterology practice, as well as tools to help you manage your practice in light of these changes and take action on important issues. You can make a difference. From health care reform to other legislative and regulatory issues that affect your practice; every voice counts. Intro / Digestion / Who gets GP / What happens / Symptoms / Dx / Mild forms / Tx. 1 Department of Gastroenterology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, USA; 2 Temple University, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA; 3 University of Texas, MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, Texas, USA; 4 University of Mississippi, Jackson, Mississippi, USA; 5 Stanford University, Palo Alto, California, USA. chemotherapy patients such as aprepitant ( Emend ), and medical marijuana ( Marinol ). Gastroparesis can be caused either by diseases of the stomach's muscles or the nerves that control the muscles, though often no specific cause is identified. The most common disease causing gastroparesis is diabetes mellitus, which damages the nerves controlling the stomach muscles. Gastroparesis also can result from damage to the vagus nerve, the nerve that controls the stomach's muscles, that occurs during surgery on the esophagus and stomach. Scleroderma is an example of a disease in which gastroparesis is due to damage to the stomach's muscles. Occasionally, gastroparesis is caused by reflexes within the nervous system, for example, when the pancreas is inflamed ( pancreatitis ). In such cases, neither the nerves nor the muscles of the stomach are diseased, but messages are sent through nerves from the pancreas to the stomach, which prevents the muscles from working normally. Other causes of gastroparesis include imbalances of minerals in the blood such as potassium, calcium or magnesium, medications (such as narcotic pain - relievers), and thyroid disease. For a substantial number of patients no cause can be found for the gastroparesis, a
5 patients no cause can be found for the gastroparesis, a condition termed idiopathic gastroparesis. Indeed, idiopathic gastroparesis is the second most frequent cause of gastroparesis after diabetes. Gastroparesis can occur as an isolated problem or it can be associated with weakness of the muscles of other parts of the intestine, including the small intestine, colon, and esophagus. home / diabetes health center / diabetes a-z list / gastroparesis center. Surgery: Surgery occasionally is used to treat gastroparesis. The goal of surgery is to create a larger opening between the stomac Treatment of gastroparesis includes diet, medication, and devices or procedures that facilitate emptying of the stomach. The goals of treatment include: Gastroparesis is a disease of the muscles of the stomach or the nerves controlling the muscles that causes the muscles to stop working. Gastroparesis results in inadequate grinding of food by the stomach, and poor emptying of food from the stomach into the intestine. The primary symptoms of gastroparesis are nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. Gastroparesis is best diagnosed by a test called a gastric emptying study. Gastroparesis usually is treated with nutritional support, drugs for treating nausea and vomiting, drugs that stimulate the muscle to work, and, less often, electrical pacing, and surgery. To provide a diet containing foods that are more easily emptied from the stomach. Controlling underlying conditions that may be aggravating gastroparesis. Relieve symptoms of nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. Stimulate muscle activity in the stomach so that food is properly ground and emptied from the stomach Maintaining adequate nutrition. What drugs relieve pain and nausea from gastroparesis?. How Is Your MS Care Routine? Assess Yourself. What is the treatment for gastroparesis and its symptoms?. What is the treatment for gastroparesis and its symptoms?. What drugs relieve pain and nausea from gastroparesis?. What is the prognosis (long-term outcome) for patients with gastroparesis?. MedicineNet does not provide medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. See additional information. What is the prognosis (long-term outcome) for patients with gastroparesis?. Intravenous fluids to correct dehydration and replenish electrolytes if nutrition is adequate but symptoms occasionally interrupt the intake of even liquid food. Enteral nutrition which provides liquid food directly into the small intestine, bypassing the paralyzed stomach. Intravenous total parenteral nutrition (TPN) to provide calories and nutrients (TPN is a fluid containing glucose, amino acids, lipids, minerals, and vitamins -everything that is needed for adequate nutrition-intravenously. The fluid usually is delivered into a large vein via a catheter in the arm or upper chest.) Doctors generally prefer enteral nutrition over TPN because long-term use of TPN is associated with infections of the catheter and liver damage. Infection can spread through the blood to the rest of the body, a serious condition called sepsis. Catheter-related sepsis often requires treatment with intravenous antibiotics and removal of the infected catheter or replacement with a new catheter. TPN also can damage the liver, most commonly causing abnormal liver tests in the blood.
6 liver, most commonly causing abnormal liver tests in the blood. TPN-induced liver damage usually is mild and reversible (the liver test abnormalities return to normal after cessation of TPN), but, rarely, irreversible liver failure can occur. Such liver failure may require liver transplantation. Drugs used to relieve abdominal pain in gastroparesis include nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs ( NSAIDs ) such as ibuprofen ( Motrin ) and naproxen ( Aleve ), low dose tricyclic antidepressants such as amitriptyline ( Elavil, Endep ), drugs that block nerves that sense pain such as gabapentin ( Neurontin ), and narcotics such as tramadol ( Ultram ) and fentanyl ( Duragesic ). (Nevertheless, narcotics as a group tend to cause constipation and slow emptying of the stomach, and, therefore, should be avoided or used with caution in patients with gastroparesis. Jay W. Marks, MD, is a board-certified internist and gastroenterologist. He graduated from Yale University School of Medicine and trained in internal medicine and gastroenterology at UCLA/Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles. Oral Drugs: There are four oral drugs that are used to stimulate contractions of the stomach's muscles, referred to as pro-motility drugs. These drugs are 1) cisapride ( Propulsid ), 2) domperidone, 3) metoclopramide ( Reglan ), and 4) erythromycin. Cisapride (Propulsid) is an effective drug for treating gastroparesis; however, it was removed from the market because it can cause serious and life-threatening irregular heart rhythms. Despite this fact, it can be obtained for use through the pharmaceutical company that manufactures it (Janssen Pharmaceuticals) under a strictly monitored protocol but only for patients with severe gastroparesis unresponsive to all other measures. Domperidone has not been released for use in the US; however, it too can be obtained if approval is obtained for its use from the US Food and Drug Administration. Metoclopramide (Reglan) is available without restriction and is effective at promoting muscular activity in the stomach; however, there are side effects of metoclopramide that can limit its use. Erythromycin (E-Mycin, Ilosone, etc.), is a uncommonly used antibiotic. At doses lower than those used to treat infections, erythromycin stimulates contractions of the muscles of the stomach and small intestine and is useful for treating gastroparesis. It has been demonstrated that tegaserod ( Zelnorm ), an oral drug used for treating constipation in irritable bowel syndrome ( IBS ), increases emptying from the stomach just as it does from the colon. However, in March of 2007, the FDA asked Novartis to suspend sales of tegaserod ) in the United States because a retrospective analysis of data by Novartis from more than 18,000 patients showed a slight difference in the incidence of cardiovascular events ( heart attacks, strokes, and angina ) among patients on tegaserod compared to placebo. The data showed that cardiovascular events occurred in 13 out of 11,614 patients treated with tegaserod (0.1%), compared to one cardiovascular event in 7,031 (0.01%) placebo-treated patients. However, it is unclear whether tegaserod actually causes heart attacks and strokes. Despite this fact, the availability of tegaserod in the U.S. is limited to emergency situations. There are two important
7 limited to emergency situations. There are two important guidelines in prescribing oral drugs for gastroparesis. First, the drugs must be given at the right times, and second, the drugs must reach the small intestine so that they can be absorbed into the body. Since the goal of treatment is to stimulate muscular contractions during and immediately after a meal, drugs that stimulate contractions should be given before meals. Most drugs must be emptied from the stomach so that they can be absorbed in the small intestine. The majority of patients with gastroparesis have delayed emptying of solid food as well as pills and capsules. As mentioned previously, many patients with gastroparesis have less of a problem emptying liquids as compared with solid food. Therefore, liquid medications usually are more effective than pills or capsules. Intravenous drugs Occasionally, patients have such poor emptying of both liquid and solid food from the stomach that only drugs given intravenously are effective. In such patients, intravenous metoclopramide or erythromycin can be used. A third option is octreotide ( Sandostatin ), a hormone-like drug that can be inj. Diet Emptying from the stomach is faster when there is less food to empty, so smaller, more frequent portions of food are recommended. Soft foods (or preferably liquid) that do not require grinding also are emptied more easily. Moreover, in gastroparesis, the emptying of liquids often is less severely affected than the emptying of solids. Fat causes the release of hormones that slow down the emptying of the stomach. Therefore, foods low in fat empty faster from the stomach. In patients with severe gastroparesis, sometimes only liquid meals are tolerated. It also is recommended that the diet be low in fiber (for example, vegetables) due to the concern about the formation of bezoars, and the fact that fiber slows gastric emptying - at least in normal individuals. Food should be chewed well since the grinding action of the stomach is reduced. Meals should be taken with enough liquids to ensure maximal liquidity of contents in the stomach since liquids usually empty better than solid food; however, if liquid emptying also is slow, too much liquid might create problems. (Only trial and error will determine the effects of increased liquids.) Patients with gastroparesis should have most food early in the day, especially the solid food; they should not lie down for 4-5 hours after their last meal, since when lying, the assistance of gravity on gastric emptying is lost. Multivitamins should be taken because of the likelihood of malnutrition and vitamin and mineral deficiencies.
8
Dr. Patsy Smyth, FNP-BC
 Dr. Patsy Smyth, FNP-BC Gastroparesis literally translated means stomach paralysis. Gastroparesis is a syndrome characterized by delayed gastric emptying in absence of mechanical obstruction of the stomach.
Dr. Patsy Smyth, FNP-BC Gastroparesis literally translated means stomach paralysis. Gastroparesis is a syndrome characterized by delayed gastric emptying in absence of mechanical obstruction of the stomach.
June By: Reza Gholami
 ACG/CAG guideline on Management of Dyspepsia June 2017 By: Reza Gholami DEFINITION OF DYSPEPSIA AND SCOPE OF THE GUIDELINE Dyspepsia was originally defined as any symptoms referable to the upper gastrointestinal
ACG/CAG guideline on Management of Dyspepsia June 2017 By: Reza Gholami DEFINITION OF DYSPEPSIA AND SCOPE OF THE GUIDELINE Dyspepsia was originally defined as any symptoms referable to the upper gastrointestinal
ACG Clinical Guideline: Management of Gastroparesis
 ACG Clinical Guideline: Management of Gastroparesis Michael Camilleri, MD 1, Henry P. Parkman, MD 2, Mehnaz A. Shafi, MD 3, Thomas L. Abell, MD 4 and Lauren Gerson, MD, MSc 5 1 Department of Gastroenterology,
ACG Clinical Guideline: Management of Gastroparesis Michael Camilleri, MD 1, Henry P. Parkman, MD 2, Mehnaz A. Shafi, MD 3, Thomas L. Abell, MD 4 and Lauren Gerson, MD, MSc 5 1 Department of Gastroenterology,
GASTROPARESIS 101: BEGINNERS GUIDE TO UNDERSTANDING GASTROPARESIS By: Dr. Josh Ferguson 2017
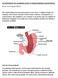 GASTROPARESIS 101: BEGINNERS GUIDE TO UNDERSTANDING GASTROPARESIS By: Dr. Josh Ferguson 2017 This tough looking word, pronounced gas-tro-par-ees-is, is simple enough in its meaning. Gastro means stomach.
GASTROPARESIS 101: BEGINNERS GUIDE TO UNDERSTANDING GASTROPARESIS By: Dr. Josh Ferguson 2017 This tough looking word, pronounced gas-tro-par-ees-is, is simple enough in its meaning. Gastro means stomach.
Outline. Definition (s) Epidemiology Pathophysiology Management With an emphasis on recent developments
 Chronic Dyspepsia Eamonn M M Quigley MD FRCP FACP MACG FRCPI Lynda K and David M Underwood Center for Digestive Disorders Houston Methodist Hospital Houston, Texas Outline Definition (s) Epidemiology Pathophysiology
Chronic Dyspepsia Eamonn M M Quigley MD FRCP FACP MACG FRCPI Lynda K and David M Underwood Center for Digestive Disorders Houston Methodist Hospital Houston, Texas Outline Definition (s) Epidemiology Pathophysiology
Does the Injection of Botulinum Toxin Improve Symptoms in Patients With Gastroparesis?
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2014 Does the Injection of Botulinum Toxin
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2014 Does the Injection of Botulinum Toxin
GASTROPARESIS. C. Prakash Gyawali, MD Professor of Medicine Washington University in St. Louis
 GASTROPARESIS C. Prakash Gyawali, MD Professor of Medicine Washington University in St. Louis Symptom Definitions Nausea: a subjective feeling of wanting to vomit Vomiting: forceful expulsion of gastroduodenal
GASTROPARESIS C. Prakash Gyawali, MD Professor of Medicine Washington University in St. Louis Symptom Definitions Nausea: a subjective feeling of wanting to vomit Vomiting: forceful expulsion of gastroduodenal
Diabetic Gastroparesis. Evan M. Klass, MD, FACP February 16, 2017
 Diabetic Gastroparesis Evan M. Klass, MD, FACP February 16, 2017 Scope of the problem The disorder can affect any part of the GI tract Although 10-20% of the general population suffer from functional GI
Diabetic Gastroparesis Evan M. Klass, MD, FACP February 16, 2017 Scope of the problem The disorder can affect any part of the GI tract Although 10-20% of the general population suffer from functional GI
Gut involvement in PoTS an overview
 Gut involvement in PoTS an overview Qasim Aziz, PhD, FRCP Centre for Neuroscience and Trauma Wingate Institute of Neurogastroenterology Case Hx * 28 year old lady presents with a long hx of constipation
Gut involvement in PoTS an overview Qasim Aziz, PhD, FRCP Centre for Neuroscience and Trauma Wingate Institute of Neurogastroenterology Case Hx * 28 year old lady presents with a long hx of constipation
CHAPTER 11 Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders (FGID) Mr. Ashok Kumar Dept of Pharmacy Practice SRM College of Pharmacy SRM University
 CHAPTER 11 Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders (FGID) Mr. Ashok Kumar Dept of Pharmacy Practice SRM College of Pharmacy SRM University 1 Definition of FGID Chronic and recurrent symptoms of the gastrointestinal
CHAPTER 11 Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders (FGID) Mr. Ashok Kumar Dept of Pharmacy Practice SRM College of Pharmacy SRM University 1 Definition of FGID Chronic and recurrent symptoms of the gastrointestinal
Management of Gastroparesis
 Management of Gastroparesis Bible Class Jan Hendrik Niess As published in Am J Gastroenterol. 2013 Jan;108(1):18-37 What is the definition of gastroparesis? What are cardinal symptoms of gastroparesis?
Management of Gastroparesis Bible Class Jan Hendrik Niess As published in Am J Gastroenterol. 2013 Jan;108(1):18-37 What is the definition of gastroparesis? What are cardinal symptoms of gastroparesis?
A Trip Through the GI Tract: Common GI Diseases and Complaints. Jennifer Curtis, MD
 A Trip Through the GI Tract: Common GI Diseases and Complaints Jennifer Curtis, MD Colon Cancer How does it develop? Most cancers arise from polyps Over time these can turn into cancer Combination of genetic
A Trip Through the GI Tract: Common GI Diseases and Complaints Jennifer Curtis, MD Colon Cancer How does it develop? Most cancers arise from polyps Over time these can turn into cancer Combination of genetic
The Use of Antidepressants in the Treatment of Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Other Functional GI Disorders What are functional GI disorders?
 The Use of Antidepressants in the Treatment of Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Other Functional GI Disorders Christine B. Dalton, PA-C Douglas A. Drossman, MD and Kellie Bunn, PA-C What are functional GI
The Use of Antidepressants in the Treatment of Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Other Functional GI Disorders Christine B. Dalton, PA-C Douglas A. Drossman, MD and Kellie Bunn, PA-C What are functional GI
Amyloidosis & the GI Tract
 Amyloidosis & the GI Tract John O. Clarke, M.D. Director, Esophageal Program Clinical Associate Professor of Medicine Stanford University john.clarke@stanford.edu 2017 Topics to cover 1) Patterns of GI
Amyloidosis & the GI Tract John O. Clarke, M.D. Director, Esophageal Program Clinical Associate Professor of Medicine Stanford University john.clarke@stanford.edu 2017 Topics to cover 1) Patterns of GI
Our evidence. Your expertise. SmartPill : The data you need to evaluate motility disorders.
 Our evidence. Your expertise. SmartPill : The data you need to evaluate motility disorders. SmartPill benefits your practice: Convenient performed right in your office Test standardization Provides direct
Our evidence. Your expertise. SmartPill : The data you need to evaluate motility disorders. SmartPill benefits your practice: Convenient performed right in your office Test standardization Provides direct
Is one of the most common chronic disorders. causing patients to seek medical treatment.
 ILOs After this lecture you should be able to : Define IBS Identify causes and risk factors of IBS Determine the appropriate therapeutic options for IBS Is one of the most common chronic disorders causing
ILOs After this lecture you should be able to : Define IBS Identify causes and risk factors of IBS Determine the appropriate therapeutic options for IBS Is one of the most common chronic disorders causing
PATIENT INFORMATION FROM YOUR SURGEON & SAGES Laparoscopic Anti-Reflux (GERD) Surgery
 Patient Information published on: 03/2004 by the Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons (SAGES) PATIENT INFORMATION FROM YOUR SURGEON & SAGES Laparoscopic Anti-Reflux (GERD) Surgery
Patient Information published on: 03/2004 by the Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons (SAGES) PATIENT INFORMATION FROM YOUR SURGEON & SAGES Laparoscopic Anti-Reflux (GERD) Surgery
The Challenge of Gastroparesis
 The Challenge of Gastroparesis A Guide to Understanding and Management TABLE OF CONTENTS Gastroparesis: A Serious Digestive Problem Gastroparesis: A Serious Digestive Problem....3 How the Stomach Works.................................................................
The Challenge of Gastroparesis A Guide to Understanding and Management TABLE OF CONTENTS Gastroparesis: A Serious Digestive Problem Gastroparesis: A Serious Digestive Problem....3 How the Stomach Works.................................................................
Is a field of radiology that uses unsealed radiation for diagnostic or therapeutic reasons Is a method of physiologic imaging, very different than
 Jeremy Flowers DNP Is a field of radiology that uses unsealed radiation for diagnostic or therapeutic reasons Is a method of physiologic imaging, very different than x-ray or CT that is anatomic imaging
Jeremy Flowers DNP Is a field of radiology that uses unsealed radiation for diagnostic or therapeutic reasons Is a method of physiologic imaging, very different than x-ray or CT that is anatomic imaging
Understanding & Alleviating Constipation. Living (Well!) with Gastroparesis Program Warm-Up Class
 Understanding & Alleviating Constipation Living (Well!) with Gastroparesis Program Warm-Up Class Please Remember The information presented is for educational purposes only and is in no way intended as
Understanding & Alleviating Constipation Living (Well!) with Gastroparesis Program Warm-Up Class Please Remember The information presented is for educational purposes only and is in no way intended as
Gastroparesis. - Recent advances in the pathophysiology and treatment -
 ICDM 2015 Gastroparesis - Recent advances in the pathophysiology and treatment - Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, St. Paul s hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
ICDM 2015 Gastroparesis - Recent advances in the pathophysiology and treatment - Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, St. Paul s hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: gastric_electrical_stimulation 9/2003 5/2017 5/2018 5/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Gastric electrical
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: gastric_electrical_stimulation 9/2003 5/2017 5/2018 5/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Gastric electrical
Gastroparesis and other upper GI problems DR ANDREW DAVIES
 Gastroparesis and other upper GI problems DR ANDREW DAVIES Outline Gastroparesis Hiccoughs Gastroparesis Gastroparesis Definition: A syndrome of objectively delayed gastric emptying in the absence of mechanical
Gastroparesis and other upper GI problems DR ANDREW DAVIES Outline Gastroparesis Hiccoughs Gastroparesis Gastroparesis Definition: A syndrome of objectively delayed gastric emptying in the absence of mechanical
Chapter 20. Assisting With Nutrition and Fluids
 Chapter 20 Assisting With Nutrition and Fluids Food and water: Are physical needs Basics of Nutrition Are necessary for life A poor diet and poor eating habits: Increase the risk for diseases and infection
Chapter 20 Assisting With Nutrition and Fluids Food and water: Are physical needs Basics of Nutrition Are necessary for life A poor diet and poor eating habits: Increase the risk for diseases and infection
National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
 Upper GI Endoscopy National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is upper gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopy? Upper
Upper GI Endoscopy National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is upper gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopy? Upper
Constipation. What is constipation? What is the criteria for having constipation? What are the different types of constipation?
 What is constipation? is defined as having a bowel movement less than 3 times per week. It is usually associated with hard stools or difficulty passing stools. You may have pain while passing stools or
What is constipation? is defined as having a bowel movement less than 3 times per week. It is usually associated with hard stools or difficulty passing stools. You may have pain while passing stools or
Gut complications in autonomic dysfunction Qasim Aziz, PhD, FRCP
 Gut complications in autonomic dysfunction Qasim Aziz, PhD, FRCP Centre for Neuroscience and Trauma Wingate Institute of Neurogastroenterology GI involvement in autonomic dysfunction Conditions Diabetes
Gut complications in autonomic dysfunction Qasim Aziz, PhD, FRCP Centre for Neuroscience and Trauma Wingate Institute of Neurogastroenterology GI involvement in autonomic dysfunction Conditions Diabetes
Neoplastic Disease KNH 406
 Neoplastic Disease KNH 406 Cancer Carcinogenesis - Etiology Genes may be affected by antioxidants, soy, protein, fat, kcal, alcohol Nutritional genomics study of genetic variations that cause different
Neoplastic Disease KNH 406 Cancer Carcinogenesis - Etiology Genes may be affected by antioxidants, soy, protein, fat, kcal, alcohol Nutritional genomics study of genetic variations that cause different
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. Unit 2: Cells & Systems
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Unit 2: Cells & Systems CRACKER DIGESTION OBSERVATION Write down your observations: 1) What does it feel like initially (at the beginning)? 2) What does it feel like after 1 minutes in
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Unit 2: Cells & Systems CRACKER DIGESTION OBSERVATION Write down your observations: 1) What does it feel like initially (at the beginning)? 2) What does it feel like after 1 minutes in
Functional Dyspepsia
 Functional Dyspepsia American College of Gastroenterology Boston Massachusetts, June 2015 Brian E. Lacy, PhD, MD, FACG Professor of Medicine Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth Chief, Section of Gastroenterology
Functional Dyspepsia American College of Gastroenterology Boston Massachusetts, June 2015 Brian E. Lacy, PhD, MD, FACG Professor of Medicine Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth Chief, Section of Gastroenterology
Digestive System. Why do we need to eat? Growth Maintenance (repair tissue) Energy
 Digestive System Why do we need to eat? Growth Maintenance (repair tissue) Energy Nutrients Nutrient = chemical that must be obtained by an organism from it s environment in order to survive; nutrients
Digestive System Why do we need to eat? Growth Maintenance (repair tissue) Energy Nutrients Nutrient = chemical that must be obtained by an organism from it s environment in order to survive; nutrients
Home Total Parenteral Nutrition for Adults
 Home Total Parenteral Nutrition for Adults Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.08.007 05/21/1999 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: PPO, HMO, QUEST Integration 05/27/2016 Section: Home
Home Total Parenteral Nutrition for Adults Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.08.007 05/21/1999 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: PPO, HMO, QUEST Integration 05/27/2016 Section: Home
Digestion. Absorption and Transport. Digestion. Digestion. (Chapter 3) Your GI tract is like a tube!
 Digestion Absorption and Transport Digestion the process of breaking down food into its basic components so they can be absorbed CHO, fat, pro are hydrolysed Vits, mins, water aren t (Chapter 3) Digestion
Digestion Absorption and Transport Digestion the process of breaking down food into its basic components so they can be absorbed CHO, fat, pro are hydrolysed Vits, mins, water aren t (Chapter 3) Digestion
Digestion. Text. What You Don t Know Can Hurt You!
 Digestion Text What You Don t Know Can Hurt You! Digestive Problems Approximately 36.5 million visits annually to ambulatory care facilities due to the diseases of the digestive system Over 4 million ulcers
Digestion Text What You Don t Know Can Hurt You! Digestive Problems Approximately 36.5 million visits annually to ambulatory care facilities due to the diseases of the digestive system Over 4 million ulcers
European Medicines Agency recommends changes to the use of metoclopramide
 20 December 2013 EMA/13239/2014 Corr. 1 European Medicines Agency recommends changes to the use of metoclopramide Changes aim mainly to reduce the risk of neurological side effects On 24 October the European
20 December 2013 EMA/13239/2014 Corr. 1 European Medicines Agency recommends changes to the use of metoclopramide Changes aim mainly to reduce the risk of neurological side effects On 24 October the European
Nutrition for Patients with Cancer or HIV/AIDS Chapter 22
 Nutrition for Patients with Cancer or HIV/AIDS Chapter 22 Nutrition for Patients with Cancer or HIV/AIDS Cancer and HIV/AIDS can cause devastating weight loss and malnutrition. Nutrition therapy Cannot
Nutrition for Patients with Cancer or HIV/AIDS Chapter 22 Nutrition for Patients with Cancer or HIV/AIDS Cancer and HIV/AIDS can cause devastating weight loss and malnutrition. Nutrition therapy Cannot
EXENATIDE (BYETTA ) PROTOCOL, 5mcg and 10mcg SC injection pre-filled pens
 EXENATIDE (BYETTA ) PROTOCOL, 5mcg and 10mcg SC injection pre-filled pens This document should be read in conjunction with the current Summary of Product Characteristics http://www.medicines.org.uk 1.
EXENATIDE (BYETTA ) PROTOCOL, 5mcg and 10mcg SC injection pre-filled pens This document should be read in conjunction with the current Summary of Product Characteristics http://www.medicines.org.uk 1.
Endoscopic Ultrasonography (EUS) Medical Imaging of the Digestive Tract and Internal Organs
 Endoscopic Ultrasonography (EUS) Medical Imaging of the Digestive Tract and Internal Organs More Detailed Pictures for Better Diagnoses Endoscopic ultrasonography allows your doctor to examine your stomach
Endoscopic Ultrasonography (EUS) Medical Imaging of the Digestive Tract and Internal Organs More Detailed Pictures for Better Diagnoses Endoscopic ultrasonography allows your doctor to examine your stomach
Section Coordinator: Jerome W. Breslin, PhD, Assistant Professor of Physiology, MEB 7208, ,
 IDP Biological Systems Gastrointestinal System Section Coordinator: Jerome W. Breslin, PhD, Assistant Professor of Physiology, MEB 7208, 504-568-2669, jbresl@lsuhsc.edu Overall Learning Objectives 1. Characterize
IDP Biological Systems Gastrointestinal System Section Coordinator: Jerome W. Breslin, PhD, Assistant Professor of Physiology, MEB 7208, 504-568-2669, jbresl@lsuhsc.edu Overall Learning Objectives 1. Characterize
Number of studies. Endoscopic finding. Number of subjects. Pooled prevalence 95% CI
 Clinical Approach to the Patient t with Dyspepsia William D. Chey, MD, FACG Professor of Medicine University of Michigan Prevalence of Endoscopic Findings in Individuals with Dyspepsia Systematic Review
Clinical Approach to the Patient t with Dyspepsia William D. Chey, MD, FACG Professor of Medicine University of Michigan Prevalence of Endoscopic Findings in Individuals with Dyspepsia Systematic Review
Pancreatitis. Acute Pancreatitis
 Pancreatitis Pancreatitis is an inflammation of the pancreas. The pancreas is a large gland behind the stomach and close to the duodenum. The duodenum is the upper part of the small intestine. The pancreas
Pancreatitis Pancreatitis is an inflammation of the pancreas. The pancreas is a large gland behind the stomach and close to the duodenum. The duodenum is the upper part of the small intestine. The pancreas
Hepatology Medication With Meals - Color Upgrades(Chinese Edition) By GAO PU JUN READ ONLINE
 Hepatology Medication With Meals - Color Upgrades(Chinese Edition) By GAO PU JUN READ ONLINE Gastroenterology - MedHelp's Gastroenterology Center for Information, Symptoms, Resources, Treatments and Tools
Hepatology Medication With Meals - Color Upgrades(Chinese Edition) By GAO PU JUN READ ONLINE Gastroenterology - MedHelp's Gastroenterology Center for Information, Symptoms, Resources, Treatments and Tools
Dyspepsia is a problem commonly seen by primary
 Concise Review for Clinicians Nonulcer Dyspepsia: What It Is and What It Is Not G. RICHARD LOCKE III, MD Nonulcer dyspepsiais a description of persistent or recurrent upper abdominal pain or discomfort
Concise Review for Clinicians Nonulcer Dyspepsia: What It Is and What It Is Not G. RICHARD LOCKE III, MD Nonulcer dyspepsiais a description of persistent or recurrent upper abdominal pain or discomfort
The Digestive System
 Digestive System 1 Name The Digestive System Purpose: To describe how food moves through the digestive system. To identify the parts of the digestive system. Background Information: Food provides us with
Digestive System 1 Name The Digestive System Purpose: To describe how food moves through the digestive system. To identify the parts of the digestive system. Background Information: Food provides us with
Heartburn, also referred to acid reflux, happens when stomach acid flows back (refluxes) into your esophagus.
 WHILE almost everyone experiences mild heartburn from time to time and many individuals have some antacids or another medication on hand for its relief, talk to your doctor, if you have heartburn more
WHILE almost everyone experiences mild heartburn from time to time and many individuals have some antacids or another medication on hand for its relief, talk to your doctor, if you have heartburn more
Total Parenteral Nutrition and Enteral Nutrition in the Home. Original Policy Date 12:2013
 MP 1.02.01 Total Parenteral Nutrition and Enteral Nutrition in the Home Medical Policy Section Durable Medical Equipment Issue Original Policy Date Last Review Status/Date Return to Medical Policy Index
MP 1.02.01 Total Parenteral Nutrition and Enteral Nutrition in the Home Medical Policy Section Durable Medical Equipment Issue Original Policy Date Last Review Status/Date Return to Medical Policy Index
MEDICAL POLICY: Enteral and Parenteral Nutrition
 POLICY: PG0114 ORIGINAL EFFECTIVE: 02/15/07 LAST REVIEW: 08/14/18 MEDICAL POLICY: Enteral and Parenteral Nutrition GUIDELINES This policy does not certify benefits or authorization of benefits, which is
POLICY: PG0114 ORIGINAL EFFECTIVE: 02/15/07 LAST REVIEW: 08/14/18 MEDICAL POLICY: Enteral and Parenteral Nutrition GUIDELINES This policy does not certify benefits or authorization of benefits, which is
How much magnesium do I need?
 NIH Office of Dietary Supplements Magnesium Fact Sheet for Consumers Table of Contents What is magnesium and what does it do? How much magnesium do I need? What foods provide magnesium? What kinds of magnesium
NIH Office of Dietary Supplements Magnesium Fact Sheet for Consumers Table of Contents What is magnesium and what does it do? How much magnesium do I need? What foods provide magnesium? What kinds of magnesium
Clinical Policy: Gastric Electrical Stimulation Reference Number: CP.MP.40
 Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.MP.40 Effective Date: 09/09 Last Review Date: 10/16 Coding Implications Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and
Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.MP.40 Effective Date: 09/09 Last Review Date: 10/16 Coding Implications Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and
Chapter 23. Nutrition Needs. Copyright 2019 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 23 Nutrition Needs Copyright 2019 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. Lesson 23.1 Define the key terms and key abbreviations in this chapter. Explain the purpose and use of the MyPlate symbol.
Chapter 23 Nutrition Needs Copyright 2019 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. Lesson 23.1 Define the key terms and key abbreviations in this chapter. Explain the purpose and use of the MyPlate symbol.
Subject: Gastric Electric Simulation in Gastroparesis Patient. Review: HJ Hiew Dec Recommendation
 Subject: Gastric Electric Simulation in Gastroparesis Patient Review: HJ Hiew Dec 2014 Recommendation GES may be effective in reducing nausea and vomiting symptoms and need of enteral/parenteral nutrition
Subject: Gastric Electric Simulation in Gastroparesis Patient Review: HJ Hiew Dec 2014 Recommendation GES may be effective in reducing nausea and vomiting symptoms and need of enteral/parenteral nutrition
P A T I E N T H A N D B O O K
 PATIENT HANDBOOK Heal Your Gut, Heal Your Body The gastrointestinal (GI) tract is one of the most sophisticated systems of the human body. We often think of the GI tract for its primary role in digesting
PATIENT HANDBOOK Heal Your Gut, Heal Your Body The gastrointestinal (GI) tract is one of the most sophisticated systems of the human body. We often think of the GI tract for its primary role in digesting
WHAT IS GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD)?
 WHAT IS GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD)? The term gastroesophageal reflux describes the movement (or reflux) of stomach contents back up into the esophagus, the muscular tube that extends from the
WHAT IS GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD)? The term gastroesophageal reflux describes the movement (or reflux) of stomach contents back up into the esophagus, the muscular tube that extends from the
April-May, Diabetes - the Medical Perspective. Diabetes and Food Recipes to Try Menu Suggestions
 April-May, 2017 Diabetes - the Medical Perspective Diabetes and Food Recipes to Try Menu Suggestions Diabetes - the Medical Perspective Gastroparesis Diabetic neuropathy is a potential complication of
April-May, 2017 Diabetes - the Medical Perspective Diabetes and Food Recipes to Try Menu Suggestions Diabetes - the Medical Perspective Gastroparesis Diabetic neuropathy is a potential complication of
Gastrointestinal Involvement in Adult Mitochondrial Disease
 Newcastle Mitochondrial Disease Guidelines At a glance guidelines: Gastrointestinal Involvement in Adult Mitochondrial Disease For full guideline visit: http://www.newcastle-mitochondria.com/service/patient-care-guidelines/
Newcastle Mitochondrial Disease Guidelines At a glance guidelines: Gastrointestinal Involvement in Adult Mitochondrial Disease For full guideline visit: http://www.newcastle-mitochondria.com/service/patient-care-guidelines/
An Introduction to Bariatric Surgery
 An Introduction to Bariatric Surgery What is bariatric surgery? Bariatric surgery is a treatment used to help people with obesity manage their health and weight. Why use surgery to manage obesity? Obesity
An Introduction to Bariatric Surgery What is bariatric surgery? Bariatric surgery is a treatment used to help people with obesity manage their health and weight. Why use surgery to manage obesity? Obesity
Effect of changing lipid formulation in Parenteral Nutrition in the Newborn Experimental Pathology BSc
 Effect of changing lipid formulation in Parenteral Nutrition in the Newborn Experimental Pathology BSc Word count: 6939 0 CONTENTS Abstract...2 Acknowledgements...3 Introduction...4 Materials and Methods...11
Effect of changing lipid formulation in Parenteral Nutrition in the Newborn Experimental Pathology BSc Word count: 6939 0 CONTENTS Abstract...2 Acknowledgements...3 Introduction...4 Materials and Methods...11
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System What is the digestive system? The digestive system is where the digestion of food and liquids occurs. Our bodies are not suited to absorbing the energy contained in food as they are
The Digestive System What is the digestive system? The digestive system is where the digestion of food and liquids occurs. Our bodies are not suited to absorbing the energy contained in food as they are
Motility Conference Ghrelin
 Motility Conference Ghrelin Emori Bizer, M.D. Division of Gastroenterology/Hepatology November 21, 2007 Ghrelin: Basics Hormone produced by the A-like A endocrine cells in the oxyntic mucosa (stomach body
Motility Conference Ghrelin Emori Bizer, M.D. Division of Gastroenterology/Hepatology November 21, 2007 Ghrelin: Basics Hormone produced by the A-like A endocrine cells in the oxyntic mucosa (stomach body
Nivolumab. Other Names: Opdivo. About this Drug. Possible Side Effects (More Common) Warnings and Precautions
 Nivolumab Other Names: Opdivo About this Drug Nivolumab is used to treat cancer. It is given in the vein (IV). Possible Side Effects (More Common) Bone marrow depression. This is a decrease in the number
Nivolumab Other Names: Opdivo About this Drug Nivolumab is used to treat cancer. It is given in the vein (IV). Possible Side Effects (More Common) Bone marrow depression. This is a decrease in the number
Memory Support. NOTE: PURE Products should be taken at least 1 hour before or after prescription medications.
 Memory Support Below are recommendations to help your body achieve and maintain optimal health. Please seek the advice of a qualified medical professional before introducing any recommendations into your
Memory Support Below are recommendations to help your body achieve and maintain optimal health. Please seek the advice of a qualified medical professional before introducing any recommendations into your
There is no single IBD diet
 Nutrition and IBD There is no single IBD diet Nutrition plays an important role in health, during times of IBD disease activity as well as during remission. Although diet does not cause or cure IBD, the
Nutrition and IBD There is no single IBD diet Nutrition plays an important role in health, during times of IBD disease activity as well as during remission. Although diet does not cause or cure IBD, the
WARNING: RISK OF SERIOUS DEHYDRATION IN PEDIATRIC PATIENTS
 June 5, 2018 Synergy Pharmaceuticals Highlights New Data at Digestive Disease Week (DDW) 2018 Linking Uroguanylin Deficiency to Chronic Idiopathic Constipation (CIC) and Irritable Bowel Syndrome with Constipation
June 5, 2018 Synergy Pharmaceuticals Highlights New Data at Digestive Disease Week (DDW) 2018 Linking Uroguanylin Deficiency to Chronic Idiopathic Constipation (CIC) and Irritable Bowel Syndrome with Constipation
Inflammation of the Esophagus (Esophagitis) Basics
 Inflammation of the Esophagus (Esophagitis) Basics OVERVIEW Inflammation of the esophagus typically involves the tubular area of the esophagus itself (known as the esophageal body ) and the muscular area
Inflammation of the Esophagus (Esophagitis) Basics OVERVIEW Inflammation of the esophagus typically involves the tubular area of the esophagus itself (known as the esophageal body ) and the muscular area
GASTROENTEROLOGY Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Examination Blueprint
 GASTROENTEROLOGY Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Examination Blueprint ABIM invites diplomates to help develop the Gastroenterology MOC exam blueprint Based on feedback from physicians that MOC assessments
GASTROENTEROLOGY Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Examination Blueprint ABIM invites diplomates to help develop the Gastroenterology MOC exam blueprint Based on feedback from physicians that MOC assessments
Advancing gastroenterology, improving patient care
 American College of Gastroenterology Advancing gastroenterology, improving patient care Note to Visitors: A fully updated ACG Systematic Review on the Management of Chronic Idiopathic Constipation and
American College of Gastroenterology Advancing gastroenterology, improving patient care Note to Visitors: A fully updated ACG Systematic Review on the Management of Chronic Idiopathic Constipation and
1. Which nutrient is so vital to health that you wouldn't live more than a few days without it? A) vitamins B) water C) minerals D) protein
 Nutrition & You, 4e (Blake) Chapter 1 What Is Nutrition? Legend: For sentences / statements that DO NOT HAVE answer choices, Answer A if TRUE Answer B IF False 1. Which nutrient is so vital to health that
Nutrition & You, 4e (Blake) Chapter 1 What Is Nutrition? Legend: For sentences / statements that DO NOT HAVE answer choices, Answer A if TRUE Answer B IF False 1. Which nutrient is so vital to health that
IBS Irritable Bowel syndrome Therapeutics II PHCL 430
 Salman Bin AbdulAziz University College Of Pharmacy IBS Irritable Bowel syndrome Therapeutics II PHCL 430 Email:- ahmedadel.pharmd@gmail.com Ahmed A AlAmer PharmD R.S is 32-year-old woman experiences intermittent
Salman Bin AbdulAziz University College Of Pharmacy IBS Irritable Bowel syndrome Therapeutics II PHCL 430 Email:- ahmedadel.pharmd@gmail.com Ahmed A AlAmer PharmD R.S is 32-year-old woman experiences intermittent
Identify electrolytes that should be monitored whenever prolonged or severe diarrhea is present
 Chapter 35 Drugs Used to Treat Constipation and Diarrhea Learning Objectives State the underlying causes of constipation Explain the meaning of normal bowel habits Cite nine causes of diarrhea Describe
Chapter 35 Drugs Used to Treat Constipation and Diarrhea Learning Objectives State the underlying causes of constipation Explain the meaning of normal bowel habits Cite nine causes of diarrhea Describe
Lower Gastrointestinal Tract KNH 406
 Lower Gastrointestinal Tract KNH 406 Lower GI Tract A&P Small Intestine Anatomy Duodenum, jejunum, ileum Maximum surface area for digestion and absorption Specialized enterocytes from stem cells of crypts
Lower Gastrointestinal Tract KNH 406 Lower GI Tract A&P Small Intestine Anatomy Duodenum, jejunum, ileum Maximum surface area for digestion and absorption Specialized enterocytes from stem cells of crypts
Copyright The Food Intolerance Testing Group. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be
 Copyright 2018 The Food Intolerance Testing Group All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, distributed, or transmitted in any form or by any means, including photocopying, recording,
Copyright 2018 The Food Intolerance Testing Group All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, distributed, or transmitted in any form or by any means, including photocopying, recording,
A Patient s Guide to Nutraceuticals (Dietary Supplements)
 A Patient s Guide to Nutraceuticals (Dietary Supplements) 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from
A Patient s Guide to Nutraceuticals (Dietary Supplements) 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from
Public Statement: Medical Policy
 ARBenefits Approval: 10/12/11 Medical Policy Title: Gastric Neurostimulation Effective Date: 01/01/2012 Document: ARB0166 Revision Date: Code(s): 0155T Laparoscopy, surgical; implantation or replacement
ARBenefits Approval: 10/12/11 Medical Policy Title: Gastric Neurostimulation Effective Date: 01/01/2012 Document: ARB0166 Revision Date: Code(s): 0155T Laparoscopy, surgical; implantation or replacement
Intravenous (IV) Infusion Therapy
 Intravenous (IV) Infusion Therapy IV vitamin infusion therapy is used in many cases to provide relief from dehydration, fatigue, chronic pain, fibromyalgia, migraine headaches, auto-immune disease, anemia
Intravenous (IV) Infusion Therapy IV vitamin infusion therapy is used in many cases to provide relief from dehydration, fatigue, chronic pain, fibromyalgia, migraine headaches, auto-immune disease, anemia
Parathyroidectomy. Surgery for Parathyroid Problems
 Parathyroidectomy Surgery for Parathyroid Problems Why You Need Parathyroid Surgery Has your doctor just recommended that you have parathyroid surgery? If so, you likely have many questions. What are the
Parathyroidectomy Surgery for Parathyroid Problems Why You Need Parathyroid Surgery Has your doctor just recommended that you have parathyroid surgery? If so, you likely have many questions. What are the
Memory Support. NOTE: PURE Products should be taken at least 1 hour before or after prescription medications.
 Memory Support Below are recommendations to help your body achieve and maintain optimal health. Please seek the advice of a qualified medical professional before introducing any recommendations into your
Memory Support Below are recommendations to help your body achieve and maintain optimal health. Please seek the advice of a qualified medical professional before introducing any recommendations into your
GI Complications in heds and HSD
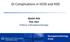 GI Complications in heds and HSD Qasim Aziz PhD, FRCP Professor in Neurogastroenterology Neurogastroenterology Group GUT = Gastrointestinal (GI) tract Oesophagus / gullet Gastro-oesophageal junction Stomach
GI Complications in heds and HSD Qasim Aziz PhD, FRCP Professor in Neurogastroenterology Neurogastroenterology Group GUT = Gastrointestinal (GI) tract Oesophagus / gullet Gastro-oesophageal junction Stomach
I. ALL CLAIMS: HEALTH CARE PROFESSIONALS
 HCP Prescribing Information Date/Version January 2015 Version 2 Page: 1 of 5 I. ALL CLAIMS: HEALTH CARE PROFESSIONALS Indications and Usage Saxenda (liraglutide [rdna origin] injection) is indicated as
HCP Prescribing Information Date/Version January 2015 Version 2 Page: 1 of 5 I. ALL CLAIMS: HEALTH CARE PROFESSIONALS Indications and Usage Saxenda (liraglutide [rdna origin] injection) is indicated as
Chapter 17. Vocabulary. Name Class Date
 Chapter 17 Vocabulary digestion bile nephrons absorption indigestion ureters elimination heartburn bladder mastication hiatal hernia urethra peristalsis appendicitis cystitis gastric juices peptic ulcer
Chapter 17 Vocabulary digestion bile nephrons absorption indigestion ureters elimination heartburn bladder mastication hiatal hernia urethra peristalsis appendicitis cystitis gastric juices peptic ulcer
Nutrition Therapy. Medical Coverage Policy Enteral/Parenteral EFFECTIVE DATE: POLICY LAST UPDATED: 11/20/2018 OVERVIEW
 Medical Coverage Policy Enteral/Parenteral Nutrition Therapy EFFECTIVE DATE: 01 20 2007 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 11/20/2018 OVERVIEW This policy describes the reimbursement for enteral and parenteral nutrition
Medical Coverage Policy Enteral/Parenteral Nutrition Therapy EFFECTIVE DATE: 01 20 2007 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 11/20/2018 OVERVIEW This policy describes the reimbursement for enteral and parenteral nutrition
Medical Policy. MP Ingestible ph and Pressure Capsule
 Medical Policy BCBSA Ref. Policy: 2.01.81 Last Review: 11/15/2018 Effective Date: 11/15/2018 Section: Medicine Related Policies 2.01.20 Esophageal ph Monitoring 6.01.33 Wireless Capsule Endoscopy as a
Medical Policy BCBSA Ref. Policy: 2.01.81 Last Review: 11/15/2018 Effective Date: 11/15/2018 Section: Medicine Related Policies 2.01.20 Esophageal ph Monitoring 6.01.33 Wireless Capsule Endoscopy as a
Laparoscopic Anti-Reflux (GERD) Surgery Patient Information from SAGES
 SAGES Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons https://www.sages.org Laparoscopic Anti-Reflux (GERD) Surgery Patient Information from SAGES Author : SAGES Webmaster Surgery for Heartburn
SAGES Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons https://www.sages.org Laparoscopic Anti-Reflux (GERD) Surgery Patient Information from SAGES Author : SAGES Webmaster Surgery for Heartburn
Methotrexate. About This Drug. Possible Side Effects. Warnings and Precautions
 Methotrexate About This Drug Methotrexate is used to treat cancer. This drug is given in the vein (IV). Possible Side Effects Soreness of the mouth and throat. You may have red areas, white patches, or
Methotrexate About This Drug Methotrexate is used to treat cancer. This drug is given in the vein (IV). Possible Side Effects Soreness of the mouth and throat. You may have red areas, white patches, or
Pediatric Oncology Dietitian BY BRANDON L. LEE, TOIVO PASTO, TINA VEILSON AND ALYSSA RANSANICI
 Pediatric Oncology Dietitian BY BRANDON L. LEE, TOIVO PASTO, TINA VEILSON AND ALYSSA RANSANICI Part 1: What a Pediatric Oncology Dietitian is? A health care professional who has special training in pediatrics
Pediatric Oncology Dietitian BY BRANDON L. LEE, TOIVO PASTO, TINA VEILSON AND ALYSSA RANSANICI Part 1: What a Pediatric Oncology Dietitian is? A health care professional who has special training in pediatrics
Diet and Gastrointestinal Problems
 Chapter 20 Diet and Gastrointestinal Problems Objectives Explain uses of diet therapy in gastrointestinal disturbances Identify foods allowed and disallowed in therapeutic diets discussed Adapt normal
Chapter 20 Diet and Gastrointestinal Problems Objectives Explain uses of diet therapy in gastrointestinal disturbances Identify foods allowed and disallowed in therapeutic diets discussed Adapt normal
Here are some types of gastric bypass surgery:
 Gastric Bypass- Definition By Mayo Clinic staff Weight-loss (bariatric) surgeries change your digestive system, often limiting the amount of food you can eat. These surgeries help you lose weight and can
Gastric Bypass- Definition By Mayo Clinic staff Weight-loss (bariatric) surgeries change your digestive system, often limiting the amount of food you can eat. These surgeries help you lose weight and can
Open to the possibility of a multiple myeloma treatment that works in cells in your body at the DNA level
 If you have multiple myeloma and have already tried at least 2 other types of treatment Open to the possibility of a multiple myeloma treatment that works in cells in your body at the DNA level What is
If you have multiple myeloma and have already tried at least 2 other types of treatment Open to the possibility of a multiple myeloma treatment that works in cells in your body at the DNA level What is
Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions
 Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions 20.1 Overview of GI Processes 1. Describe the functions of digestive system. 2. List and define the four GI Processes: 20.2 Functional Anatomy of the
Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions 20.1 Overview of GI Processes 1. Describe the functions of digestive system. 2. List and define the four GI Processes: 20.2 Functional Anatomy of the
Featured Topic: Weight Loss Fiber, Grape Seed Extract, and Ginger (6 slides)
 Featured Topic: Weight Loss Fiber, Grape Seed Extract, and Ginger (6 slides) America s Obesity Problem 1/3 of children ages 6-19 are overweight or obese 70% of American adults are overweight or obese,
Featured Topic: Weight Loss Fiber, Grape Seed Extract, and Ginger (6 slides) America s Obesity Problem 1/3 of children ages 6-19 are overweight or obese 70% of American adults are overweight or obese,
Understanding Food and Nutrition
 Understanding Food and Nutrition Dr Joan Webster-Gandy Published by Family Doctor Publications Limited in association with the British Medical Association IMPORTANT NOTICE This book is intended not as
Understanding Food and Nutrition Dr Joan Webster-Gandy Published by Family Doctor Publications Limited in association with the British Medical Association IMPORTANT NOTICE This book is intended not as
Section 4: Exercise Physiology. Diet and nutrition and their effect on physical activity and performance
 Section 4: Exercise Physiology Diet and nutrition and their effect on physical activity and performance Learning Objectives 1. Identify the seven classes of food as: carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins,
Section 4: Exercise Physiology Diet and nutrition and their effect on physical activity and performance Learning Objectives 1. Identify the seven classes of food as: carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins,
PARENTERAL NUTRITION THERAPY
 UnitedHealthcare Benefits of Texas, Inc. 1. UnitedHealthcare of Oklahoma, Inc. 2. UnitedHealthcare of Oregon, Inc. UnitedHealthcare of Washington, Inc. UnitedHealthcare West BENEFIT INTERPRETATION POLICY
UnitedHealthcare Benefits of Texas, Inc. 1. UnitedHealthcare of Oklahoma, Inc. 2. UnitedHealthcare of Oregon, Inc. UnitedHealthcare of Washington, Inc. UnitedHealthcare West BENEFIT INTERPRETATION POLICY
Non-Ulcer Dyspepsia: what is it? What can we do with these patients? Overview. Dyspepsia Definition. Functional Dyspepsia. Dyspepsia the Basics
 Non-Ulcer : what is it? What can we do with these patients? Temporal Changes and Geographic Variations in Developing Peptic Ulcer Disease Gastric Cancer 1900 Eamonn M M Quigley MD FACG Alimentary Pharmabiotic
Non-Ulcer : what is it? What can we do with these patients? Temporal Changes and Geographic Variations in Developing Peptic Ulcer Disease Gastric Cancer 1900 Eamonn M M Quigley MD FACG Alimentary Pharmabiotic
UNDERSTANDING CYSTIC FIBROSIS
 UNDERSTANDING CYSTIC FIBROSIS INTRODUCTION Cystic fibrosis is a chronic disease that affects the respiratory and gastrointestinal systems. People with cystic fibrosis have a genetic defect of the lungs
UNDERSTANDING CYSTIC FIBROSIS INTRODUCTION Cystic fibrosis is a chronic disease that affects the respiratory and gastrointestinal systems. People with cystic fibrosis have a genetic defect of the lungs
DYSPEPSIA Dyspepsia indigestion during or after eating Full Heat, burning or pain Note: one of every four people
 What Is Dyspepsia? Dyspepsia, also known as indigestion, can have multiple symptoms. Feelings of indigestion happen during or after eating. If you have indigestion you might feel: Full during a meal. Painful
What Is Dyspepsia? Dyspepsia, also known as indigestion, can have multiple symptoms. Feelings of indigestion happen during or after eating. If you have indigestion you might feel: Full during a meal. Painful
Ingestion Digestion- Absorption- Elimination
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1 FUNCTIONS Organization GI tract==mouth anus Accessory organs Salivary glands, liver, pancreas, gallbladder Major Functions: Ingestion-mouth, teeth, tongue Digestion- chemical and mechanical
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1 FUNCTIONS Organization GI tract==mouth anus Accessory organs Salivary glands, liver, pancreas, gallbladder Major Functions: Ingestion-mouth, teeth, tongue Digestion- chemical and mechanical
