Gastroparesis. - Recent advances in the pathophysiology and treatment -
|
|
|
- Hillary Stone
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ICDM 2015 Gastroparesis - Recent advances in the pathophysiology and treatment - Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, St. Paul s hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea Jung Hwan Oh
2 Etiology Idiopathic -- 40% Diabetes mellitus -- 30% Postsurgical (Gastrectomy/fundoplication) Connective tissue disease Hypothyroidism Malignancy Provocation drugs 2/46 End-stage renal disease
3 Number of people with diabetes (20-79 years), /46 International Diabetes Federation: Diabetes Atlas 6th ed. 2013
4 Prevalence of DM in Korea % / (>30 yo)
5 Prevalence of GI symptoms in DM in Korea 15 % N/V bloating dyspepsia heartburn 5/46 Oh JH, Choi MG et al. Korean J Intern Med 2009
6 Contents Gastroparesis? Prevalence Recent advances in pathophysiology & treatment Summary 6/46
7 What is gastroparesis? Symptoms Absence of obstruction Delayed gastric emptying 7/46
8 Classification Mild gastroparesis Moderate : Compensated gastroparesis moderate symptoms with use of daily medications, maintain nutrition with dietary adjustments Severe : Gastric failure refractory symptoms that are not controlled, inability to maintain oral nutrition 8/46 Stanghellini V. Gut. 2014
9 Typical symptoms? Nausea, vomiting Abdominal discomfort Early satiety Postprandial fullness Bloating 9/46
10 Gastroparesis: separate entity or just a part of FD? FD dus=bad pepto=digestion GP gastro=stomach pa resis=incomplete paralysis FD: Functional dyspepsia, GP: Gastroparesis Stanghellini V. Gut. 2014
11 Diagnosis Scintigraphy Wireless motility capsule (WMC) Breath testing : 13C breath testing using otanoic acid, acetate or spirulina 11/46
12 Gastric Emptying Scintigraphy 20 Min /46 Delayed gastric emptying as greater than 60% retention at 2 hours and/or 10% at 4 hours
13 Consensus recommendations for gastric emptying scintigraphy Normal gastric emptying the retention of <10% of a solid meal at 4 hours Delayed gastric emptying as greater than 60% retention at 2 hours and/or 10% at 4 hours Rapid gastric emptying 30% retention at 1 hour 13/46 Abell TL. Am J Gastroenterol 2008 Tougas G. Am J Gastroenterol 2000
14 Relationship between clinical features and gastric emptying disturbances in diabetes mellitus % Normal GE Delayed GE Rapid GE GE: gastric emptying Bharucha. Clin Endocrinol 2009
15 Before the test Withdrawal Medications stimulating (e.g., metoclopramide) gastric smooth muscle contractions. Inhibiting medications (e.g., narcotics, anticholinergic agents) GLP-1 analogs (exenatide) # DPP IV inhibitors, do not delay gastric emptying Measuring blood glucose 15/46 Hyperglycemia (> 270 mg / dl) should be treated
16 Gastroparesis is uncommon in DM cumulative incidence of developing gastroparesis % Population based study in US 4 16/ Type 1 DM Type 2 DM Controls Choung RS. Am J Gastroenterol 2012
17 the tip of a large hidden iceberg Gastroparesis like syndrome 11%-18% reported symptoms consistent with upper GI dysmotility Mild gastroparesis Increasing incidence of diabetes 17/46 Rey E, J Neurogastroenterol Motil 2012
18 Difference in Type 1 vs 2 Factors Type 1 DM Type 2 DM Age Young Old Delayed gastric emptying Severe Mild Predominant symptom Nausea Early satiety Aggravating factors Neuropathy and poor glycemic control Less clear 18/46
19 Pathophysiology Delayed gastric emptying Sx vs delayed gastric emptying: poor The role of delayed emptying in symptom generation in gastroparesis is unclear. Autonomic neuropathy Sustained hyperglycemia 19/46
20 Pathophysiological changes in diabetic gastroparesis Vagus neuropathy Impaired fundic accommodation Gastric dysrhythmia Loss of nnos Loss of ICC Pylorospasm ICC: Interstitial Cells of Cajal nnos: neuronal nitric oxide synthase Altered function of type 2 Macrophages (CD206-positive M2 macrophages) Incoordinated antroduodenal emptying Kashyap P, Farrugia G. Gut 2010 Tack J, Curr Opin Gastroenterol 2015
21 Pathophysiology Loss of ICC Loss of nnos Delayed gastric emptying Autonomic neuropathy ICC: Interstitial Cells of Cajal nnos: neuronal nitric oxide synthase Oh JH, Pasricha PJ. JNM 2013
22 22/46 Treatment
23 Diet Smaller, more frequent meals Low-fat, more liquid meals efficacy is not proven 23/46
24 Classes of prokinetic agents Prokinetic class Dopamine 2 receptor Antagonists Motilin Receptor Agonists Serotonin 5 -HT4 Agonists Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors GABA B Receptor Agonists Agents Metoclopramide Domperidone Erythromycin Prucalopride Velusetrag Neostigmine Pyridostigmine Baclofen 24/46 Malamood M. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2015
25 Metoclopramide (MCP) Prokinetic and anti-emetic properties D 2 antagonist and 5-HT 3 antagonist the only drug approved by the FDA for gastroparesis Recommended duration : 3 months 25/46
26 Side effects Extrapyramidal side effects, mild restlessness, agitation, and akathisia, overt dystonia and dyskinesia Adverse effects : particularly common in young children and the elderly 26/46
27 Metoclopramide and akathisia % P = Slow (n=154) Slow : 10 mg MCP iv ml NS for 15 min Bolus: 10 mg MCP iv ml NS for 2 min 27/46 Bolus (n=146) Parlak. Emerg Med J 2005
28 28/46
29 Domperidone a dopamine antagonist, peripheral does not cross the blood-brain barrier Available throughout Europe, as well as in Canada but not in the US Side effect? EKG 29/46
30 30/41 Side effect of domperidone
31 Levosulpiride Dopamine antagonist gastric emptying in diabetics improve glycemic control over a 6-month Levosulpiride-induced movement disorders Melga P, Diabetes Care parkinsonism (93.4%), tardive dyskinesia (9.9%) - often irreversible even after the withdrawal 31/46 Shin HW, Mov Disord 2009
32 Drug-induced parkinsonism DM % Case control study in Korea DIP IPD Acute stroke DIP: Drug-induced parkinsonism IPD: Idiopathic Parkinson disease Ma HI, J Neurol Sci 2009
33 Erythromycin Macrolides, a motilin agonist intravenous erythromycin: useful in acute GP long-term oral administration: less obvious Tachyphylaxis 33/46
34 Major pathways used by endogenous ghrelin and motilin to modulate upper GI function AP, area postrema; NTS, nucleus tractus solitarius. Sanger GJ. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015
35 New Ghrelin and motilin receptor agonists in development for the treatment of GP 35/46 Ghrelin receptor agonists TZP-102 (Tranzyme) Relamorelin (RM131) Motilin receptor agonists Camicinal(GSK ) RQ (RaQualia) CEM-031 (Cempra) compound macrocyclic compound a pentapeptide for subcutaneous injection; small-molecule agonist Non-macrolide small molecule Macrolide Rationale Ability to increase gastric emptying and increase appetite Ability to increase gastric emptying Potential additional ability to increase appetite and reduce nausea Effectiveness of low-dose erythromycin
36 Anti-emetics? Associated nausea and vomiting but will not result in improved gastric emptying. Tricyclic antidepressants amitriptyline, nortriptyline, imipramine, desipramine refractory nausea and vomiting doses lower than used for depression higher doses: impairing GI motility 36/46
37 Pain modulators Stop! : narcotic opiate analgesics Tramadol, gabapentin, pregabalin nortriptyline (tricyclic antidepressants) 37/46
38 Other Options Intrapyloric botulinum toxin injection Gastric electrical stimulation Surgery Feeding jejunostomy, vending gastrostomy, partial gastrectomy, pyloplasty 38/46
39 39/46 Botulinum toxin injection
40 40/46 Gastric electrical stimulation (GES)
41 Risk factors for Gastroparesis Longstanding duration Poor glycemic control Severe hyperglycemia ( 270 mg/dl) Neuropathy Female 41/46
42 Predictive factors? Male sex Age 50 y Factors reduced symptoms Initial infectious prodrome antidepressant use Factors associated with NO reduction Overweight or obesity history of smoking use of pain modulators Moderate to severe abdominal pain 4 hr gastric retention>20% Moderate to severe depression Severe gastroesophageal reflex 42/46 Pasricha PJ. Gastroenterology 2015
43 Therapeutic options by symptom severity GLP, glucagon-like peptide; TD, tardive dyskinesia. Stein B, J Clin Gastroenterol 2015
44 Summary Suspected DG Confirm Dx: GET Fluid and electrolytes Dietary modifications: low fat, low fiber Glucose control DG: Diabetic Gastroparesis GET: Gastric Emptying Time 44/46 Prokinetics Anti-emetics (prn)
45 Summary Metoclopramide 5-10mg tid Domperidone 10mg tid Botulinum toxin inj. Refractory Sx? GES Surgery GES: Gastric electrical stimulation 45/46
46 Thank you for your attention
Management of Gastroparesis
 Management of Gastroparesis Bible Class Jan Hendrik Niess As published in Am J Gastroenterol. 2013 Jan;108(1):18-37 What is the definition of gastroparesis? What are cardinal symptoms of gastroparesis?
Management of Gastroparesis Bible Class Jan Hendrik Niess As published in Am J Gastroenterol. 2013 Jan;108(1):18-37 What is the definition of gastroparesis? What are cardinal symptoms of gastroparesis?
GASTROPARESIS. C. Prakash Gyawali, MD Professor of Medicine Washington University in St. Louis
 GASTROPARESIS C. Prakash Gyawali, MD Professor of Medicine Washington University in St. Louis Symptom Definitions Nausea: a subjective feeling of wanting to vomit Vomiting: forceful expulsion of gastroduodenal
GASTROPARESIS C. Prakash Gyawali, MD Professor of Medicine Washington University in St. Louis Symptom Definitions Nausea: a subjective feeling of wanting to vomit Vomiting: forceful expulsion of gastroduodenal
Gastroparesis: Diagnosis and Management
 Gastroparesis: Diagnosis and Management Rodica Pop-Busui MD, PhD Professor of Internal Medicine, Metabolism, Endocrinology and Diabetes, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI Disclosures Astra Zeneca Research
Gastroparesis: Diagnosis and Management Rodica Pop-Busui MD, PhD Professor of Internal Medicine, Metabolism, Endocrinology and Diabetes, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI Disclosures Astra Zeneca Research
ACG Clinical Guideline: Management of Gastroparesis
 ACG Clinical Guideline: Management of Gastroparesis Michael Camilleri, MD 1, Henry P. Parkman, MD 2, Mehnaz A. Shafi, MD 3, Thomas L. Abell, MD 4 and Lauren Gerson, MD, MSc 5 1 Department of Gastroenterology,
ACG Clinical Guideline: Management of Gastroparesis Michael Camilleri, MD 1, Henry P. Parkman, MD 2, Mehnaz A. Shafi, MD 3, Thomas L. Abell, MD 4 and Lauren Gerson, MD, MSc 5 1 Department of Gastroenterology,
Dr. Patsy Smyth, FNP-BC
 Dr. Patsy Smyth, FNP-BC Gastroparesis literally translated means stomach paralysis. Gastroparesis is a syndrome characterized by delayed gastric emptying in absence of mechanical obstruction of the stomach.
Dr. Patsy Smyth, FNP-BC Gastroparesis literally translated means stomach paralysis. Gastroparesis is a syndrome characterized by delayed gastric emptying in absence of mechanical obstruction of the stomach.
Disclosures. Objectives. Gastroparesis: Are We Moving On? Gastroparesis: Clinical Overview
 Gastroparesis: Are We Moving On? Anthony Lembo, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Boston, MA Disclosures Consultant Alkermes, Allergan, Forest,
Gastroparesis: Are We Moving On? Anthony Lembo, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Boston, MA Disclosures Consultant Alkermes, Allergan, Forest,
Gastroparesis and other upper GI problems DR ANDREW DAVIES
 Gastroparesis and other upper GI problems DR ANDREW DAVIES Outline Gastroparesis Hiccoughs Gastroparesis Gastroparesis Definition: A syndrome of objectively delayed gastric emptying in the absence of mechanical
Gastroparesis and other upper GI problems DR ANDREW DAVIES Outline Gastroparesis Hiccoughs Gastroparesis Gastroparesis Definition: A syndrome of objectively delayed gastric emptying in the absence of mechanical
Pharmacodynamic Effects of Ghrelin Agonist Relamorelin (RM-131) in Patients with Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Delayed Gastric Emptying
 Pharmacodynamic Effects of Ghrelin Agonist Relamorelin (RM-131) in Patients with Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Delayed Gastric Emptying Andrea Shin Motility Conference 2/4/15 Disclosures No conflicts
Pharmacodynamic Effects of Ghrelin Agonist Relamorelin (RM-131) in Patients with Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Delayed Gastric Emptying Andrea Shin Motility Conference 2/4/15 Disclosures No conflicts
Outline. Definition (s) Epidemiology Pathophysiology Management With an emphasis on recent developments
 Chronic Dyspepsia Eamonn M M Quigley MD FRCP FACP MACG FRCPI Lynda K and David M Underwood Center for Digestive Disorders Houston Methodist Hospital Houston, Texas Outline Definition (s) Epidemiology Pathophysiology
Chronic Dyspepsia Eamonn M M Quigley MD FRCP FACP MACG FRCPI Lynda K and David M Underwood Center for Digestive Disorders Houston Methodist Hospital Houston, Texas Outline Definition (s) Epidemiology Pathophysiology
What you really need to know about Gastroparesis?
 What you really need to know about Gastroparesis? John M. Wo, MD Division of Gastroenterology/Hepatology Director of GI Motility and Neurogastroenterology 8/3/2016 1/4/2017 1 What you really need to know
What you really need to know about Gastroparesis? John M. Wo, MD Division of Gastroenterology/Hepatology Director of GI Motility and Neurogastroenterology 8/3/2016 1/4/2017 1 What you really need to know
Gastroparesis: A chronic disorder
 Diagnosis and Management of Gastroparesis: The Stomach that Refuses to Empty Improving Symptoms or Gastric Emptying Henry P. Parkman, MD Professor of Medicine Director of GI Motility Laboratory Gastroenterology
Diagnosis and Management of Gastroparesis: The Stomach that Refuses to Empty Improving Symptoms or Gastric Emptying Henry P. Parkman, MD Professor of Medicine Director of GI Motility Laboratory Gastroenterology
Diabetic Gastroparesis. Evan M. Klass, MD, FACP February 16, 2017
 Diabetic Gastroparesis Evan M. Klass, MD, FACP February 16, 2017 Scope of the problem The disorder can affect any part of the GI tract Although 10-20% of the general population suffer from functional GI
Diabetic Gastroparesis Evan M. Klass, MD, FACP February 16, 2017 Scope of the problem The disorder can affect any part of the GI tract Although 10-20% of the general population suffer from functional GI
Functional Dyspepsia
 Functional Dyspepsia American College of Gastroenterology Boston Massachusetts, June 2015 Brian E. Lacy, PhD, MD, FACG Professor of Medicine Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth Chief, Section of Gastroenterology
Functional Dyspepsia American College of Gastroenterology Boston Massachusetts, June 2015 Brian E. Lacy, PhD, MD, FACG Professor of Medicine Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth Chief, Section of Gastroenterology
Subject: Gastric Electric Simulation in Gastroparesis Patient. Review: HJ Hiew Dec Recommendation
 Subject: Gastric Electric Simulation in Gastroparesis Patient Review: HJ Hiew Dec 2014 Recommendation GES may be effective in reducing nausea and vomiting symptoms and need of enteral/parenteral nutrition
Subject: Gastric Electric Simulation in Gastroparesis Patient Review: HJ Hiew Dec 2014 Recommendation GES may be effective in reducing nausea and vomiting symptoms and need of enteral/parenteral nutrition
EDUCATION PRACTICE. Management of Delayed Gastric Emptying. Clinical Scenario. The Problem. Management Strategies and Supporting Evidence
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2005;3:642 646 EDUCATION PRACTICE Management of Delayed Gastric Emptying FRANK K. FRIEDENBERG and HENRY P. PARKMAN Temple University Hospital, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2005;3:642 646 EDUCATION PRACTICE Management of Delayed Gastric Emptying FRANK K. FRIEDENBERG and HENRY P. PARKMAN Temple University Hospital, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
Is a field of radiology that uses unsealed radiation for diagnostic or therapeutic reasons Is a method of physiologic imaging, very different than
 Jeremy Flowers DNP Is a field of radiology that uses unsealed radiation for diagnostic or therapeutic reasons Is a method of physiologic imaging, very different than x-ray or CT that is anatomic imaging
Jeremy Flowers DNP Is a field of radiology that uses unsealed radiation for diagnostic or therapeutic reasons Is a method of physiologic imaging, very different than x-ray or CT that is anatomic imaging
STRATEGIES TO IMPROVE ENTERAL FEEDING TOLERANCE. IS IT WORTH IT? ENGELA FRANCIS RD(SA)
 STRATEGIES TO IMPROVE ENTERAL FEEDING TOLERANCE. IS IT WORTH IT? ENGELA FRANCIS RD(SA) DEFINITION OF ENTERAL FEEDING INTOLERANCE Gastrointestinal feeding intolerance are usually defined as: High gastric
STRATEGIES TO IMPROVE ENTERAL FEEDING TOLERANCE. IS IT WORTH IT? ENGELA FRANCIS RD(SA) DEFINITION OF ENTERAL FEEDING INTOLERANCE Gastrointestinal feeding intolerance are usually defined as: High gastric
Gastrointestinal motility modulating drugs include all compounds which have pharmacological
 Pharmacotherapeutics Gastrointestinal Motility Modulating Drugs Oh Young Lee, MD Department of Internal Medicine, Hanyang University College of Medicine E - mail : leeoy@hanyang.ac.kr J Korean Med Assoc
Pharmacotherapeutics Gastrointestinal Motility Modulating Drugs Oh Young Lee, MD Department of Internal Medicine, Hanyang University College of Medicine E - mail : leeoy@hanyang.ac.kr J Korean Med Assoc
Number of studies. Endoscopic finding. Number of subjects. Pooled prevalence 95% CI
 Clinical Approach to the Patient t with Dyspepsia William D. Chey, MD, FACG Professor of Medicine University of Michigan Prevalence of Endoscopic Findings in Individuals with Dyspepsia Systematic Review
Clinical Approach to the Patient t with Dyspepsia William D. Chey, MD, FACG Professor of Medicine University of Michigan Prevalence of Endoscopic Findings in Individuals with Dyspepsia Systematic Review
Does the Injection of Botulinum Toxin Improve Symptoms in Patients With Gastroparesis?
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2014 Does the Injection of Botulinum Toxin
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2014 Does the Injection of Botulinum Toxin
Use of Prokinetic Agents in Intensive Care Medicine - What is Evidence Based? Dr Martin Sterba PhD EDIC CICM TWH ICU, NSW, Australia
 Use of Prokinetic Agents in Intensive Care Medicine - What is Evidence Based? Dr Martin Sterba PhD EDIC CICM TWH ICU, NSW, Australia Ostrava Ostrava Wollongong Wollongong Wollongong Prokinetics and EBM
Use of Prokinetic Agents in Intensive Care Medicine - What is Evidence Based? Dr Martin Sterba PhD EDIC CICM TWH ICU, NSW, Australia Ostrava Ostrava Wollongong Wollongong Wollongong Prokinetics and EBM
Medical Policy. MP Ingestible ph and Pressure Capsule
 Medical Policy BCBSA Ref. Policy: 2.01.81 Last Review: 11/15/2018 Effective Date: 11/15/2018 Section: Medicine Related Policies 2.01.20 Esophageal ph Monitoring 6.01.33 Wireless Capsule Endoscopy as a
Medical Policy BCBSA Ref. Policy: 2.01.81 Last Review: 11/15/2018 Effective Date: 11/15/2018 Section: Medicine Related Policies 2.01.20 Esophageal ph Monitoring 6.01.33 Wireless Capsule Endoscopy as a
Amitriptyline delayed gastric emptying
 Amitriptyline delayed gastric emptying We have given this statement a conditional recommendation, as the quality of evidence is very low. The data mainly relate to national databases of upper GI cancer
Amitriptyline delayed gastric emptying We have given this statement a conditional recommendation, as the quality of evidence is very low. The data mainly relate to national databases of upper GI cancer
CHAPTER 11 Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders (FGID) Mr. Ashok Kumar Dept of Pharmacy Practice SRM College of Pharmacy SRM University
 CHAPTER 11 Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders (FGID) Mr. Ashok Kumar Dept of Pharmacy Practice SRM College of Pharmacy SRM University 1 Definition of FGID Chronic and recurrent symptoms of the gastrointestinal
CHAPTER 11 Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders (FGID) Mr. Ashok Kumar Dept of Pharmacy Practice SRM College of Pharmacy SRM University 1 Definition of FGID Chronic and recurrent symptoms of the gastrointestinal
Gastroparesis is defined as a syndrome of objectively delayed
 Current and Emerging Therapeutic Options for Gastroparesis Aung S. Myint, DO, Brandon Rieders, MD, Mohammed Tashkandi, MD, Marie L. Borum, MD, EdD, MPH, Joyce M. Koh, MD, Sindu Stephen, MD, and David B.
Current and Emerging Therapeutic Options for Gastroparesis Aung S. Myint, DO, Brandon Rieders, MD, Mohammed Tashkandi, MD, Marie L. Borum, MD, EdD, MPH, Joyce M. Koh, MD, Sindu Stephen, MD, and David B.
Gastroparesis. Abstract and Introduction. Clinical Features. Causes of Gastroparesis.
 1 of 12 1/1/2013 10:59 AM www.medscape.com Gastroparesis William L. Hasler Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2012;28(6):621-628. Abstract and Introduction Abstract Purpose of review: Gastroparesis is a common disorder
1 of 12 1/1/2013 10:59 AM www.medscape.com Gastroparesis William L. Hasler Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2012;28(6):621-628. Abstract and Introduction Abstract Purpose of review: Gastroparesis is a common disorder
June By: Reza Gholami
 ACG/CAG guideline on Management of Dyspepsia June 2017 By: Reza Gholami DEFINITION OF DYSPEPSIA AND SCOPE OF THE GUIDELINE Dyspepsia was originally defined as any symptoms referable to the upper gastrointestinal
ACG/CAG guideline on Management of Dyspepsia June 2017 By: Reza Gholami DEFINITION OF DYSPEPSIA AND SCOPE OF THE GUIDELINE Dyspepsia was originally defined as any symptoms referable to the upper gastrointestinal
GASTROPARESIS 101: BEGINNERS GUIDE TO UNDERSTANDING GASTROPARESIS By: Dr. Josh Ferguson 2017
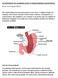 GASTROPARESIS 101: BEGINNERS GUIDE TO UNDERSTANDING GASTROPARESIS By: Dr. Josh Ferguson 2017 This tough looking word, pronounced gas-tro-par-ees-is, is simple enough in its meaning. Gastro means stomach.
GASTROPARESIS 101: BEGINNERS GUIDE TO UNDERSTANDING GASTROPARESIS By: Dr. Josh Ferguson 2017 This tough looking word, pronounced gas-tro-par-ees-is, is simple enough in its meaning. Gastro means stomach.
Lawrence R. Schiller, MD, FACG. Digestive Health Associates of Texas Baylor University Medical Center Dallas, Texas.
 Chronic Nausea & Vomiting Lawrence R. Schiller, MD, FACG Digestive Health Associates of Texas Baylor University Medical Center Dallas, Texas Nausea & Vomiting Common symptoms Quite troubling to patients
Chronic Nausea & Vomiting Lawrence R. Schiller, MD, FACG Digestive Health Associates of Texas Baylor University Medical Center Dallas, Texas Nausea & Vomiting Common symptoms Quite troubling to patients
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: gastric_electrical_stimulation 9/2003 5/2017 5/2018 5/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Gastric electrical
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: gastric_electrical_stimulation 9/2003 5/2017 5/2018 5/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Gastric electrical
DOMPERIDONE BNF 4.6. Domperidone is a dopamine type 2-receptor antagonist. It is structurally related to the
 DOMPERIDONE BNF 4.6 Class: Prokinetic anti-emetic. Indications: Nausea and vomiting, dysmotility dyspepsia, gastro-oesophageal reflux. Pharmacology Domperidone is a dopamine type 2-receptor antagonist.
DOMPERIDONE BNF 4.6 Class: Prokinetic anti-emetic. Indications: Nausea and vomiting, dysmotility dyspepsia, gastro-oesophageal reflux. Pharmacology Domperidone is a dopamine type 2-receptor antagonist.
Treatment of gastrointestinal autonomic neuropathy
 Diabetologia (2016) 59:409 413 DOI 10.1007/s00125-015-3828-9 MINI-REVIEW Treatment of gastrointestinal autonomic neuropathy Hans Törnblom 1 Received: 31 October 2015 /Accepted: 5 November 2015 /Published
Diabetologia (2016) 59:409 413 DOI 10.1007/s00125-015-3828-9 MINI-REVIEW Treatment of gastrointestinal autonomic neuropathy Hans Törnblom 1 Received: 31 October 2015 /Accepted: 5 November 2015 /Published
DIABETIC GASTROPARESIS OBESE VERSUS NON OBESE PATIENTS
 Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Series VI: Medical Sciences Vol. 4 (53) No. 2-2011 DIABETIC GASTROPARESIS OBESE VERSUS NON OBESE PATIENTS L. POANTA 1 D. L. DUMITRAŞCU 1 Abstract: Symptoms
Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Series VI: Medical Sciences Vol. 4 (53) No. 2-2011 DIABETIC GASTROPARESIS OBESE VERSUS NON OBESE PATIENTS L. POANTA 1 D. L. DUMITRAŞCU 1 Abstract: Symptoms
Severe Gastroparesis: Medical Therapy or Gastric Electrical Stimulation
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2010;8:117 124 EDUCATION PRACTICE Severe Gastroparesis: Medical Therapy or Gastric Electrical Stimulation SAVIO C. REDDYMASU, IRENE SAROSIEK, and RICHARD W. McCALLUM
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2010;8:117 124 EDUCATION PRACTICE Severe Gastroparesis: Medical Therapy or Gastric Electrical Stimulation SAVIO C. REDDYMASU, IRENE SAROSIEK, and RICHARD W. McCALLUM
Public Statement: Medical Policy
 ARBenefits Approval: 10/12/11 Medical Policy Title: Gastric Neurostimulation Effective Date: 01/01/2012 Document: ARB0166 Revision Date: Code(s): 0155T Laparoscopy, surgical; implantation or replacement
ARBenefits Approval: 10/12/11 Medical Policy Title: Gastric Neurostimulation Effective Date: 01/01/2012 Document: ARB0166 Revision Date: Code(s): 0155T Laparoscopy, surgical; implantation or replacement
Gut complications in autonomic dysfunction Qasim Aziz, PhD, FRCP
 Gut complications in autonomic dysfunction Qasim Aziz, PhD, FRCP Centre for Neuroscience and Trauma Wingate Institute of Neurogastroenterology GI involvement in autonomic dysfunction Conditions Diabetes
Gut complications in autonomic dysfunction Qasim Aziz, PhD, FRCP Centre for Neuroscience and Trauma Wingate Institute of Neurogastroenterology GI involvement in autonomic dysfunction Conditions Diabetes
The influence of early postoperative enteral feeding and promotility drugs on upper GI tract and gallbladder motility in the critical care setting
 The influence of early postoperative enteral feeding and promotility drugs on upper GI tract and gallbladder motility in the critical care setting Alan Šustić, MD, PhD Dept. of Anesthesiology and ICU Univ.
The influence of early postoperative enteral feeding and promotility drugs on upper GI tract and gallbladder motility in the critical care setting Alan Šustić, MD, PhD Dept. of Anesthesiology and ICU Univ.
Nausea and Vomiting in Palliative Care
 Nausea and Vomiting in Palliative Care Definitions Nausea - an unpleasant feeling of the need to vomit Vomiting - the expulsion of gastric contents through the mouth, caused by forceful and sustained contraction
Nausea and Vomiting in Palliative Care Definitions Nausea - an unpleasant feeling of the need to vomit Vomiting - the expulsion of gastric contents through the mouth, caused by forceful and sustained contraction
Joseph Sellin Editor. Managing Gastrointestinal Complications of Diabetes
 Joseph Sellin Editor Managing Gastrointestinal Complications of Diabetes Managing Gastrointestinal Complications of Diabetes Joseph Sellin Editor Managing Gastrointestinal Complications of Diabetes Editor
Joseph Sellin Editor Managing Gastrointestinal Complications of Diabetes Managing Gastrointestinal Complications of Diabetes Joseph Sellin Editor Managing Gastrointestinal Complications of Diabetes Editor
Gut involvement in PoTS an overview
 Gut involvement in PoTS an overview Qasim Aziz, PhD, FRCP Centre for Neuroscience and Trauma Wingate Institute of Neurogastroenterology Case Hx * 28 year old lady presents with a long hx of constipation
Gut involvement in PoTS an overview Qasim Aziz, PhD, FRCP Centre for Neuroscience and Trauma Wingate Institute of Neurogastroenterology Case Hx * 28 year old lady presents with a long hx of constipation
ESOPHAGEAL MOTOR DISORDERS
 Medicine Dr. Taha Alkarbuli Lecture 1 (Esophageal & GIT Disorders) ESOPHAGEAL DISORDERS: - ESOPHAGEAL MOTOR DISORDERS. - GERD - ESOPHAGEAL TUMORS. ESOPHAGEAL MOTOR DISORDERS Present with chest pain, dysphagia,
Medicine Dr. Taha Alkarbuli Lecture 1 (Esophageal & GIT Disorders) ESOPHAGEAL DISORDERS: - ESOPHAGEAL MOTOR DISORDERS. - GERD - ESOPHAGEAL TUMORS. ESOPHAGEAL MOTOR DISORDERS Present with chest pain, dysphagia,
Review Article Gastroparesis: Concepts, Controversies, and Challenges
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation cienti ca Volume 2012, Article ID 424802, 19 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.6064/2012/424802 Review Article Gastroparesis: Concepts, Controversies, and Challenges Klaus Bielefeldt
Hindawi Publishing Corporation cienti ca Volume 2012, Article ID 424802, 19 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.6064/2012/424802 Review Article Gastroparesis: Concepts, Controversies, and Challenges Klaus Bielefeldt
Management of Functional Dyspepsia (FD)
 Management of Functional Dyspepsia (FD) Amy S. Oxentenko, MD, FACG Program Director and Associate Chair, IM Associate Professor of Medicine Mayo Clinic, Rochester Outline Define functional dyspepsia (FD)
Management of Functional Dyspepsia (FD) Amy S. Oxentenko, MD, FACG Program Director and Associate Chair, IM Associate Professor of Medicine Mayo Clinic, Rochester Outline Define functional dyspepsia (FD)
New Tests and Treatments for Dyspepsia and Irritable Bowel Syndrome
 New Tests and Treatments for Dyspepsia and Irritable Bowel Syndrome Soojong Hong Chae, MD Clinical Assistant Professor Digestive Diseases and Nutrition University of South Florida ROME III Functional dyspepsia
New Tests and Treatments for Dyspepsia and Irritable Bowel Syndrome Soojong Hong Chae, MD Clinical Assistant Professor Digestive Diseases and Nutrition University of South Florida ROME III Functional dyspepsia
Clinical Policy: Gastric Electrical Stimulation Reference Number: CP.MP.40
 Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.MP.40 Effective Date: 09/09 Last Review Date: 10/16 Coding Implications Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and
Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.MP.40 Effective Date: 09/09 Last Review Date: 10/16 Coding Implications Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and
Gender aspects suggestive of gastroparesis in patients with diabetes mellitus: a cross-sectional survey
 Dickman et al. BMC Gastroenterology 2014, 14:34 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Gender aspects suggestive of gastroparesis in patients with diabetes mellitus: a cross-sectional survey Ram Dickman 1,5*, Julio
Dickman et al. BMC Gastroenterology 2014, 14:34 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Gender aspects suggestive of gastroparesis in patients with diabetes mellitus: a cross-sectional survey Ram Dickman 1,5*, Julio
Gastroparesis or Cyclic Vomiting: Does it Matter for Treatment?
 Gastroparesis or Cyclic Vomiting: Does it Matter for Treatment? Brian E. Lacy, MD, PhD, FACG Professor of Medicine Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth Chief, Section of Gastroenterology & Hepatology
Gastroparesis or Cyclic Vomiting: Does it Matter for Treatment? Brian E. Lacy, MD, PhD, FACG Professor of Medicine Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth Chief, Section of Gastroenterology & Hepatology
Clinical Policy: Gastric Electrical Stimulation
 Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.MP.40 Last Review Date: 08/18 Coding Implications Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and legal information. Description
Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.MP.40 Last Review Date: 08/18 Coding Implications Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and legal information. Description
Motility Conference Ghrelin
 Motility Conference Ghrelin Emori Bizer, M.D. Division of Gastroenterology/Hepatology November 21, 2007 Ghrelin: Basics Hormone produced by the A-like A endocrine cells in the oxyntic mucosa (stomach body
Motility Conference Ghrelin Emori Bizer, M.D. Division of Gastroenterology/Hepatology November 21, 2007 Ghrelin: Basics Hormone produced by the A-like A endocrine cells in the oxyntic mucosa (stomach body
GASTRIC EMPTYING STUDY (SOLID)
 GASTRIC EMPTYING STUDY (SOLID) Aim To evaluate patients with symptoms of altered of gastric emptying and/or motility, and quantitatively measure the rate of gastric emptying. This study provides a physiologic,
GASTRIC EMPTYING STUDY (SOLID) Aim To evaluate patients with symptoms of altered of gastric emptying and/or motility, and quantitatively measure the rate of gastric emptying. This study provides a physiologic,
Is one of the most common chronic disorders. causing patients to seek medical treatment.
 ILOs After this lecture you should be able to : Define IBS Identify causes and risk factors of IBS Determine the appropriate therapeutic options for IBS Is one of the most common chronic disorders causing
ILOs After this lecture you should be able to : Define IBS Identify causes and risk factors of IBS Determine the appropriate therapeutic options for IBS Is one of the most common chronic disorders causing
Amyloidosis & the GI Tract
 Amyloidosis & the GI Tract John O. Clarke, M.D. Director, Esophageal Program Clinical Associate Professor of Medicine Stanford University john.clarke@stanford.edu 2017 Topics to cover 1) Patterns of GI
Amyloidosis & the GI Tract John O. Clarke, M.D. Director, Esophageal Program Clinical Associate Professor of Medicine Stanford University john.clarke@stanford.edu 2017 Topics to cover 1) Patterns of GI
Functional Heartburn and Dyspepsia
 Functional Heartburn and Dyspepsia Nicholas Shaheen, MD, MPH Center for Esophageal Diseases and Swallowing University of North Carolina Objectives Understand the means of diagnosing functional heartburn
Functional Heartburn and Dyspepsia Nicholas Shaheen, MD, MPH Center for Esophageal Diseases and Swallowing University of North Carolina Objectives Understand the means of diagnosing functional heartburn
Gut hormones KHATTAB
 Gut hormones PROF:ABD ALHAFIZ HASSAN KHATTAB Gut as an endocrine gland The talk will cover the following : Historical background. Why this subject is chosen. Gastro-intestinal hormones and their function.
Gut hormones PROF:ABD ALHAFIZ HASSAN KHATTAB Gut as an endocrine gland The talk will cover the following : Historical background. Why this subject is chosen. Gastro-intestinal hormones and their function.
The Many Faces of T2DM in Long-term Care Facilities
 The Many Faces of T2DM in Long-term Care Facilities Question #1 Which of the following is a risk factor for increased hypoglycemia in older patients that may suggest the need to relax hyperglycemia treatment
The Many Faces of T2DM in Long-term Care Facilities Question #1 Which of the following is a risk factor for increased hypoglycemia in older patients that may suggest the need to relax hyperglycemia treatment
Postsurgical gastroparesis (PSG), identified as a. Clinical Response to Gastric Electrical Stimulation in Patients With Postsurgical Gastroparesis
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2005;3:49 54 Clinical Response to Gastric Electrical Stimulation in Patients With Postsurgical Gastroparesis RICHARD MCCALLUM,* ZHIYUE LIN,* PAUL WETZEL,* IRENE
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2005;3:49 54 Clinical Response to Gastric Electrical Stimulation in Patients With Postsurgical Gastroparesis RICHARD MCCALLUM,* ZHIYUE LIN,* PAUL WETZEL,* IRENE
IBS Irritable Bowel syndrome Therapeutics II PHCL 430
 Salman Bin AbdulAziz University College Of Pharmacy IBS Irritable Bowel syndrome Therapeutics II PHCL 430 Email:- ahmedadel.pharmd@gmail.com Ahmed A AlAmer PharmD R.S is 32-year-old woman experiences intermittent
Salman Bin AbdulAziz University College Of Pharmacy IBS Irritable Bowel syndrome Therapeutics II PHCL 430 Email:- ahmedadel.pharmd@gmail.com Ahmed A AlAmer PharmD R.S is 32-year-old woman experiences intermittent
GI Pharmacology -4 Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Antiemetics. Dr. Alia Shatanawi
 GI Pharmacology -4 Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Antiemetics Dr. Alia Shatanawi 11-04-2018 Drugs used in Irritable Bowel Syndrome Idiopathic, chronic, relapsing disorder characterized by abdominal discomfort
GI Pharmacology -4 Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Antiemetics Dr. Alia Shatanawi 11-04-2018 Drugs used in Irritable Bowel Syndrome Idiopathic, chronic, relapsing disorder characterized by abdominal discomfort
The PPI Doesn t Work, Now What? PPI Non-responsive Dyspepsia. Disclosures
 The PPI Doesn t Work, Now What? PPI Non-responsive Dyspepsia Lana Bistritz MD FRCPC Royal Alexandra Hospital GI Update 2016 Disclosures I have no relevant financial disclosures I will be discussing off
The PPI Doesn t Work, Now What? PPI Non-responsive Dyspepsia Lana Bistritz MD FRCPC Royal Alexandra Hospital GI Update 2016 Disclosures I have no relevant financial disclosures I will be discussing off
Treatment of Diabetic Gastroparesis by High-Frequency Gastric Electrical Stimulation
 Emerging Treatments and Technologies O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Treatment of Diabetic Gastroparesis by High-Frequency Gastric Electrical Stimulation ZHIYUE LIN, MS 1 JAMESON FORSTER, MD 2 1 IRENE SAROSIEK,
Emerging Treatments and Technologies O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Treatment of Diabetic Gastroparesis by High-Frequency Gastric Electrical Stimulation ZHIYUE LIN, MS 1 JAMESON FORSTER, MD 2 1 IRENE SAROSIEK,
Our evidence. Your expertise. SmartPill : The data you need to evaluate motility disorders.
 Our evidence. Your expertise. SmartPill : The data you need to evaluate motility disorders. SmartPill benefits your practice: Convenient performed right in your office Test standardization Provides direct
Our evidence. Your expertise. SmartPill : The data you need to evaluate motility disorders. SmartPill benefits your practice: Convenient performed right in your office Test standardization Provides direct
Vomiting Approach to diagnosis
 Vomiting Approach to diagnosis By Dr. Sahar El-Gharabawy Associate professor of internal medicine Hepato-gastroenterology Unit )SMH ) Mansoura University Definitions: Nausea: Feeling "sick to the stomach",
Vomiting Approach to diagnosis By Dr. Sahar El-Gharabawy Associate professor of internal medicine Hepato-gastroenterology Unit )SMH ) Mansoura University Definitions: Nausea: Feeling "sick to the stomach",
International Congress of the Italian Association of Companion Animal Veterinarians
 www.ivis.org International Congress of the Italian Association of Companion Animal Veterinarians 2 - May, 201 Rimini, Italy Next Congress : SCIVAC International Congress Ma -, 201 -, Italy Reprinted in
www.ivis.org International Congress of the Italian Association of Companion Animal Veterinarians 2 - May, 201 Rimini, Italy Next Congress : SCIVAC International Congress Ma -, 201 -, Italy Reprinted in
Constipation An Overview. Definition Physiology of GI tract Etiology Assessment Treatment
 CONSTIPATION Constipation An Overview Definition Physiology of GI tract Etiology Assessment Treatment Definition Constipation = the infrequent passage of hard feces Definition of Infrequent The meaning
CONSTIPATION Constipation An Overview Definition Physiology of GI tract Etiology Assessment Treatment Definition Constipation = the infrequent passage of hard feces Definition of Infrequent The meaning
Ingestible ph and Pressure Capsule
 Medical Policy Manual Medicine, Policy No. 117 Ingestible ph and Pressure Capsule Next Review: October 2018 Last Review: October 2017 Effective: December 1, 2017 IMPORTANT REMINDER Medical Policies are
Medical Policy Manual Medicine, Policy No. 117 Ingestible ph and Pressure Capsule Next Review: October 2018 Last Review: October 2017 Effective: December 1, 2017 IMPORTANT REMINDER Medical Policies are
Ingestible ph and Pressure Capsule
 Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Diabesity. Metabolic dysfunction that ranges from mild blood glucose imbalance to full fledged Type 2 DM Signs
 Diabesity Metabolic dysfunction that ranges from mild blood glucose imbalance to full fledged Type 2 DM Signs Abdominal obesity Low HDL, high LDL, and high triglycerides HTN High blood glucose (F>100l,
Diabesity Metabolic dysfunction that ranges from mild blood glucose imbalance to full fledged Type 2 DM Signs Abdominal obesity Low HDL, high LDL, and high triglycerides HTN High blood glucose (F>100l,
Early satiety and postprandial fullness in gastroparesis correlate with gastroparesis severity, gastric emptying, and water load testing
 Received: 16 July 2016 Accepted: 23 September 2016 DOI: 10.1111/nmo.12981 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Early satiety and postprandial fullness in gastroparesis correlate with gastroparesis severity, gastric emptying,
Received: 16 July 2016 Accepted: 23 September 2016 DOI: 10.1111/nmo.12981 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Early satiety and postprandial fullness in gastroparesis correlate with gastroparesis severity, gastric emptying,
State of the art review with literature summary on gastric peroral endoscopic pyloromyotomy for gastroparesis
 bs_bs_banner doi:10.1111/jgh.14293 REVIEW State of the art review with literature summary on gastric peroral endoscopic pyloromyotomy for gastroparesis Tawfik Khoury,*,1 Meir Mizrahi,,1 Mahmud Mahamid,
bs_bs_banner doi:10.1111/jgh.14293 REVIEW State of the art review with literature summary on gastric peroral endoscopic pyloromyotomy for gastroparesis Tawfik Khoury,*,1 Meir Mizrahi,,1 Mahmud Mahamid,
Gastric Electrical Stimulation
 Ontario Health Technology Assessment Series 2006; Vol. 6, No. 16 Gastric Electrical Stimulation An Evidence-Based Analysis August 2006 Medical Advisory Secretariat Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care
Ontario Health Technology Assessment Series 2006; Vol. 6, No. 16 Gastric Electrical Stimulation An Evidence-Based Analysis August 2006 Medical Advisory Secretariat Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care
Chief of Endocrinology East Orange General Hospital
 Targeting the Incretins System: Can it Improve Our Ability to Treat Type 2 Diabetes? Darshi Sunderam, MD Darshi Sunderam, MD Chief of Endocrinology East Orange General Hospital Age-adjusted Percentage
Targeting the Incretins System: Can it Improve Our Ability to Treat Type 2 Diabetes? Darshi Sunderam, MD Darshi Sunderam, MD Chief of Endocrinology East Orange General Hospital Age-adjusted Percentage
Nausea & Vomiting. Dr Eve Lyn TAN Liverpool Hospital NSW, AUSTRALIA
 Nausea & Vomiting Dr Eve Lyn TAN Liverpool Hospital NSW, AUSTRALIA Prevalence prevalence varies *, systemic review 2007 : overall prevalence : nausea 30%, vomiting 20% in last 1-2 weeks of life : nausea
Nausea & Vomiting Dr Eve Lyn TAN Liverpool Hospital NSW, AUSTRALIA Prevalence prevalence varies *, systemic review 2007 : overall prevalence : nausea 30%, vomiting 20% in last 1-2 weeks of life : nausea
University of Louisville
 Core Lecture: Small Bowel Physiology and Motility Disorders John M. Wo, M.D. Director of Swallowing and Motility Center Division of Gastroenterology/Hepatology Jan 18, 2007 Case Presentation 43 yr old
Core Lecture: Small Bowel Physiology and Motility Disorders John M. Wo, M.D. Director of Swallowing and Motility Center Division of Gastroenterology/Hepatology Jan 18, 2007 Case Presentation 43 yr old
CYCLIC VOMITING SYNDROME. C. Prakash Gyawali, MD Professor of Medicine Washington University in St. Louis
 CYCLIC VOMITING SYNDROME C. Prakash Gyawali, MD Professor of Medicine Washington University in St. Louis Case 26 year old male Symptoms began at age 19 yr 5-6 day episodes of recurrent, severe vomiting
CYCLIC VOMITING SYNDROME C. Prakash Gyawali, MD Professor of Medicine Washington University in St. Louis Case 26 year old male Symptoms began at age 19 yr 5-6 day episodes of recurrent, severe vomiting
Adlyxin. (lixisenatide) New Product Slideshow
 Adlyxin (lixisenatide) New Product Slideshow Introduction Brand name: Adlyxin Generic name: Lixisenatide Pharmacological class: Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist Strength and Formulation:
Adlyxin (lixisenatide) New Product Slideshow Introduction Brand name: Adlyxin Generic name: Lixisenatide Pharmacological class: Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist Strength and Formulation:
MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC CONSTIPATION BEYOND LAXATIVES
 Enrique Rey Professor of Medicine Head. Department of Digestive Diseases Hospital Clínico San Carlos Complutense University Madrid, Spain MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC CONSTIPATION BEYOND LAXATIVES CONSTIPATION:
Enrique Rey Professor of Medicine Head. Department of Digestive Diseases Hospital Clínico San Carlos Complutense University Madrid, Spain MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC CONSTIPATION BEYOND LAXATIVES CONSTIPATION:
Practical Strategies for the Clinical Use of Incretin Mimetics CME/CE. CME/CE Released: 09/15/2009; Valid for credit through 09/15/2010
 Practical Strategies for the Clinical Use of Incretin Mimetics CME/CE Robert R. Henry, MD Authors and Disclosures CME/CE Released: 09/15/2009; Valid for credit through 09/15/2010 Introduction Type 2 diabetes
Practical Strategies for the Clinical Use of Incretin Mimetics CME/CE Robert R. Henry, MD Authors and Disclosures CME/CE Released: 09/15/2009; Valid for credit through 09/15/2010 Introduction Type 2 diabetes
Clinical Study Decreased Gastric Motility in Type II Diabetic Patients
 BioMed Research International, Article ID 89487, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/.55/24/89487 Clinical Study Decreased Gastric Motility in Type II Diabetic Patients Yi-Chun Chiu, Ming-Chun Kuo, 2 Christopher
BioMed Research International, Article ID 89487, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/.55/24/89487 Clinical Study Decreased Gastric Motility in Type II Diabetic Patients Yi-Chun Chiu, Ming-Chun Kuo, 2 Christopher
Definition, Pathogenesis, and Management of That Cursed Dyspepsia
 Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2018;16:467 479 Definition, Pathogenesis, and Management of That Cursed Dyspepsia Pramoda Koduru, Malcolm Irani, and Eamonn M. M. Quigley IM F1 김영기 Dyspepsia Umbrella
Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2018;16:467 479 Definition, Pathogenesis, and Management of That Cursed Dyspepsia Pramoda Koduru, Malcolm Irani, and Eamonn M. M. Quigley IM F1 김영기 Dyspepsia Umbrella
Grigoris Leontiadis, MD PhD. McMaster University Upper Gastrointestinal and Pancreatic Diseases Cochrane Group
 Grigoris Leontiadis, MD PhD McMaster University Upper Gastrointestinal and Pancreatic Diseases Cochrane Group No relevant financial relationships with any commercial interests CDDW/CASL Meeting Session:
Grigoris Leontiadis, MD PhD McMaster University Upper Gastrointestinal and Pancreatic Diseases Cochrane Group No relevant financial relationships with any commercial interests CDDW/CASL Meeting Session:
3/31/13 GASTROPARESIS 2013 BACKGROUND, INVESTIGATION AND MANAGEMENT WHAT IS GASTROPARESIS? BACKGROUND WHAT IS GASTROPARESIS? WHAT IS GASTROPARESIS?
 GASTROPARESIS 2013 BACKGROUND, INVESTIGATION AND MANAGEMENT WHAT IS GASTROPARESIS? Definition: Delayed gastric emptying in the absence of mechanical obstruction * C. Gregory Albers, MD FACG Medical Director,
GASTROPARESIS 2013 BACKGROUND, INVESTIGATION AND MANAGEMENT WHAT IS GASTROPARESIS? Definition: Delayed gastric emptying in the absence of mechanical obstruction * C. Gregory Albers, MD FACG Medical Director,
Type 2 DM in Adolescents: Use of GLP-1 RA. Objectives. Scope of Problem: Obesity. Background. Pathophysiology of T2DM
 Type 2 DM in Adolescents: Use of GLP-1 RA Objectives Identify patients in the pediatric population with T2DM that would potentially benefit from the use of GLP-1 RA Discuss changes in glycemic outcomes
Type 2 DM in Adolescents: Use of GLP-1 RA Objectives Identify patients in the pediatric population with T2DM that would potentially benefit from the use of GLP-1 RA Discuss changes in glycemic outcomes
Non-Ulcer Dyspepsia: what is it? What can we do with these patients? Overview. Dyspepsia Definition. Functional Dyspepsia. Dyspepsia the Basics
 Non-Ulcer : what is it? What can we do with these patients? Temporal Changes and Geographic Variations in Developing Peptic Ulcer Disease Gastric Cancer 1900 Eamonn M M Quigley MD FACG Alimentary Pharmabiotic
Non-Ulcer : what is it? What can we do with these patients? Temporal Changes and Geographic Variations in Developing Peptic Ulcer Disease Gastric Cancer 1900 Eamonn M M Quigley MD FACG Alimentary Pharmabiotic
European Medicines Agency recommends changes to the use of metoclopramide
 20 December 2013 EMA/13239/2014 Corr. 1 European Medicines Agency recommends changes to the use of metoclopramide Changes aim mainly to reduce the risk of neurological side effects On 24 October the European
20 December 2013 EMA/13239/2014 Corr. 1 European Medicines Agency recommends changes to the use of metoclopramide Changes aim mainly to reduce the risk of neurological side effects On 24 October the European
Postoperative Ileus. UCSF Postgraduate Course in General Surgery Maui, HI March 20, 2011
 Postoperative Ileus UCSF Postgraduate Course in General Surgery Maui, HI March 20, 2011 Hobart W. Harris, MD, MPH Introduction Pathophysiology Clinical Research Management Summary Postoperative Ileus:
Postoperative Ileus UCSF Postgraduate Course in General Surgery Maui, HI March 20, 2011 Hobart W. Harris, MD, MPH Introduction Pathophysiology Clinical Research Management Summary Postoperative Ileus:
Chronic nausea and vomiting: evaluation and treatment
 Clinical and Systematic Reviews 647 see related editorial on page x Chronic nausea and vomiting: evaluation and treatment Brian E. Lacy, PhD, MD, FACG 1, Henry P. Parkman, MD 2 and Michael Camilleri, MD
Clinical and Systematic Reviews 647 see related editorial on page x Chronic nausea and vomiting: evaluation and treatment Brian E. Lacy, PhD, MD, FACG 1, Henry P. Parkman, MD 2 and Michael Camilleri, MD
Symptom Management. Thomas McKain, MD, ABFM, ABHPM Medical Director
 Symptom Management Nausea & Vomiting Thomas McKain, MD, ABFM, ABHPM Medical Director Mr. Jones has nausea and vomiting. May I initiate Compazine from the Comfort Pak? Objectives 1. Delineate the Differential
Symptom Management Nausea & Vomiting Thomas McKain, MD, ABFM, ABHPM Medical Director Mr. Jones has nausea and vomiting. May I initiate Compazine from the Comfort Pak? Objectives 1. Delineate the Differential
Motor Dysfunctions of the Stomach
 4 Motor Dysfunctions of the Stomach Susan D. Kowalski Motor dysfunctions of the stomach include conditions which present acute, recurrent, or chronic symptoms relating to stasis or rapid transit of stomach
4 Motor Dysfunctions of the Stomach Susan D. Kowalski Motor dysfunctions of the stomach include conditions which present acute, recurrent, or chronic symptoms relating to stasis or rapid transit of stomach
Clinical Policy Title: Gastric electrical stimulation (GES)
 Clinical Policy Title: Gastric electrical stimulation (GES) Clinical Policy Number: 08.02.03 Effective Date: October 1, 2015 Initial Review Date: September 17, 2015 Most Recent Review Date: May 19, 2017
Clinical Policy Title: Gastric electrical stimulation (GES) Clinical Policy Number: 08.02.03 Effective Date: October 1, 2015 Initial Review Date: September 17, 2015 Most Recent Review Date: May 19, 2017
Soliqua (insulin glargine and lixisenatide), Xultophy (insulin degludec and liraglutide)
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.30.48 Subject: Insulin GLP-1 Combinations Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: September 15, 2017 Insulin GLP-1
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.30.48 Subject: Insulin GLP-1 Combinations Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: September 15, 2017 Insulin GLP-1
Chapter 1. General introduction and outline
 Chapter 1 General introduction and outline General introduction The function of the stomach comprises storage of ingested food, production of gastric secretion and mixing food with gastric secretion,
Chapter 1 General introduction and outline General introduction The function of the stomach comprises storage of ingested food, production of gastric secretion and mixing food with gastric secretion,
Multiple Factors Should Be Considered When Setting a Glycemic Goal
 Multiple Facts Should Be Considered When Setting a Glycemic Goal Patient attitude and expected treatment effts Risks potentially associated with hypoglycemia, other adverse events Disease duration Me stringent
Multiple Facts Should Be Considered When Setting a Glycemic Goal Patient attitude and expected treatment effts Risks potentially associated with hypoglycemia, other adverse events Disease duration Me stringent
Diabetic Retinopathy and Neuropathy: 2018 Clinical Practice Guidelines
 Diabetic Retinopathy and Neuropathy: 2018 Clinical Practice Guidelines Richard Arakaki, M.D. Phoenix Area Diabetes Consultant August 9 th 2018 Disclose no conflict of interest Complications and Co-morbidities
Diabetic Retinopathy and Neuropathy: 2018 Clinical Practice Guidelines Richard Arakaki, M.D. Phoenix Area Diabetes Consultant August 9 th 2018 Disclose no conflict of interest Complications and Co-morbidities
Propulsion and mixing of food in the alimentary tract Chapter 63
 Propulsion and mixing of food in the alimentary tract Chapter 63 Types of GI movements: Propulsive movement-peristalsis Propulsion: controlled movement of ingested foods, liquids, GI secretions, and sloughed
Propulsion and mixing of food in the alimentary tract Chapter 63 Types of GI movements: Propulsive movement-peristalsis Propulsion: controlled movement of ingested foods, liquids, GI secretions, and sloughed
HMFP Comprehensive Headache Center Department of Anesthesia, Critical Care and Pain Medicine Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Instructor in
 HMFP Comprehensive Headache Center Department of Anesthesia, Critical Care and Pain Medicine Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Instructor in Anesthesia and Neurology Harvard Medical School Limited time
HMFP Comprehensive Headache Center Department of Anesthesia, Critical Care and Pain Medicine Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Instructor in Anesthesia and Neurology Harvard Medical School Limited time
Clinical Snapshot: Making sense of Autonomic Neuropathy. M S Kamaruddin Consultant Physician South Tees NHS Foundation Trust
 Clinical Snapshot: Making sense of Autonomic Neuropathy M S Kamaruddin Consultant Physician South Tees NHS Foundation Trust Diabetic autonomic neuropathy Classified as clinical or subclinical based on
Clinical Snapshot: Making sense of Autonomic Neuropathy M S Kamaruddin Consultant Physician South Tees NHS Foundation Trust Diabetic autonomic neuropathy Classified as clinical or subclinical based on
Antidepressants: Prof. Riyadh Al_Azzawi F.R.C.Psych
 Antidepressants: Prof. Riyadh Al_Azzawi F.R.C.Psych A. Heterocyclic antidepressants: (tricyclic and tetracyclic ), e.g.amitryptaline,imipramine. B. Monoamine oxidase inhibitors(m.a.o.i), e.g.phenelzine.
Antidepressants: Prof. Riyadh Al_Azzawi F.R.C.Psych A. Heterocyclic antidepressants: (tricyclic and tetracyclic ), e.g.amitryptaline,imipramine. B. Monoamine oxidase inhibitors(m.a.o.i), e.g.phenelzine.
Dyspepsia is a problem commonly seen by primary
 Concise Review for Clinicians Nonulcer Dyspepsia: What It Is and What It Is Not G. RICHARD LOCKE III, MD Nonulcer dyspepsiais a description of persistent or recurrent upper abdominal pain or discomfort
Concise Review for Clinicians Nonulcer Dyspepsia: What It Is and What It Is Not G. RICHARD LOCKE III, MD Nonulcer dyspepsiais a description of persistent or recurrent upper abdominal pain or discomfort
Active ingredients: Metoclopramide Hydrochloride mg Equivalent to metoclopramide hydrochloride anhydrous mg
 Name Primperan 10 mg / 2 ml Metoclopramide hydrochloride anhydrous Solution for I.M. or I.V. injection (Ampoules) Composition Each 2 ml ampoule contains: Active ingredients: Metoclopramide Hydrochloride.
Name Primperan 10 mg / 2 ml Metoclopramide hydrochloride anhydrous Solution for I.M. or I.V. injection (Ampoules) Composition Each 2 ml ampoule contains: Active ingredients: Metoclopramide Hydrochloride.
Management of Type 2 Diabetes
 Management of Type 2 Diabetes Pathophysiology Insulin resistance and relative insulin deficiency/ defective secretion Not immune mediated No evidence of β cell destruction Increased risk with age, obesity
Management of Type 2 Diabetes Pathophysiology Insulin resistance and relative insulin deficiency/ defective secretion Not immune mediated No evidence of β cell destruction Increased risk with age, obesity
