Innovations in Antimicrobials Something Old, Something New
|
|
|
- Kristin Riley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 FSHP Disclosure Innovations in Antimicrobials Something Old, Something New Harrison Bachmeier, PharmD, BCPS Pharmacist Specialist-Infectious Diseases LeeHealth Fort Myers & Cape Coral, FL I do not have (nor does any immediate family member have) a vested interest in or affiliation with any corporate organization offering financial support or grant monies for this continuing education activity, or any affiliation with an organization whose philosophy could potentially bias my presentation. Objectives Identify the role of older antimicrobial agents in the treatment of complicated infections Compare new agents approved for gram negative infections Discuss the role of bezlotoxumab for the prevention of C.difficile recurrence Describe the utility of long-acting agents for gram positive infections Gram Negative Resistance is Rising Resistance, Resistance, Resistance Among 3 rd Gen Cephalosporins K. pneumoniae Pseudomonas aeruginosa imipenem Rahal JJ. Clin Infect Dis. 2009; 49:S4 10 E. coli ceftazidime Resistance, Acinetobacter baumannii ceftazidime amikacin imipenem Classification of β-lactamases Classification Name Common Genes Substrates Class A Broad Spectrum ESBL Carbapenemases PC1 SHV1 TEM1 SHV derived TEM derived CTX-M KPC Penicillins, 1 st gen cephalosporins Penicillins, 1-3 rd gen cephalosporins, aztreonam Penicillins, extended spectrum cephalosporins, aztreonam and carbapenems IMP 1-3 rd gen cephalosporins, cephamycins, and Class B Metallo-β-lactamases VIM carbapenems NDM rd Class C Cephalosporinases AmpC Penicillins, 1-3 gen cephalosporins, cephamycins Class D Oxacillinases OXA-1, 2,10, Pseudomonas OXA-11, 14, 15 Penicillins, 1 st generation cephalosporins 1-3 rd gen cephalosporins, aztreonam Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States, 2013 Pathogen CDC Threat Level Infections per year by species Drug Resistant Infections per year Deaths per year ESBL Enterobacteriaceae SERIOUS 140,000 26,000 1,700 MDR Pseudomonas SERIOUS 51,000 6, MDR Acinetobacter SERIOUS 12,000 7, Carbapenem- Resistant Enterobacteriaceae ESBL= extended spectrum β-lactamase MDR = multiple drug resistant URGENT 140,000 7,900 Klebsiella spp. 1,400 E. coli 600 Misc. $40,000 excess costs/year for each infection At least 3 different antibiotic classes no longer cure Acinetobacter infections Resistant to all or nearly all antibiotics Bush B, Jacoby GA. Antimicrob Agent Chemo 2010;54(3) Acinetobacter OXA-23,24, 58 Above plus cephamycins and carbapenems CDC
2 Are We Entering into a Post-Antibiotic Age? Number of Antibiotics New antibacterial agents approved in the United States Polymyxins: Our Last Line of Defense Polypeptide antibiotics discovered in1947 Formed by both cationic and hydrophobic amino acids Bind to bacterial cell membranes causing permeability changes and ultimately cell death Clinical use began in the 1960s Polymyxin B Susceptible Pathogens Resistant Pathogens Colistin (Polymyxin E) Breakpoint < 2 mcg/ml Pseudomonas spp Proteus spp Acinetobacter spp Serratia spp E. coli Morganella spp. Klebsiella spp Providencia spp. Enterobacter spp. Neisseria spp. Boucher HW et al. Clin Infect Dis. 2009; 48:1 12 Strom DR et al. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46: Sorting Through the Polymyxin Alphabet Soup Colistimethate (CMS) Prodrug of Colistin [active] Labeled as Colistin Base Activity (CBA) 1 MU CMS ~ 44.5 mg CMS 1 MU CMS ~ 30 mg CBA Polymyxin B Active chemical Listed in international units 10,000 units = 1 mg Variability of Polymyxin Serum Drug Concentrations Colistin : 40 fold variability in C ss Polymyxin B: 4 fold variability in C ss 1 Vial = 150 mg CBA = 5 MU CMS = 400 mg CMS 500,000 units = 50 mg = 1 Vial Jian L. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006; 50(12): Lim LM, et al. Pharmacotherapy 2010;30(12): ) Sandri AM et al. Clin Infect Dis 2013;57(4): Garonzik SM et al. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011;55(7): Polymyxin B Pharmacokinetics Colistimethate (CMS) Pharmacokinetics (Tubular reabsorption) Polymyxin B Parameter Polymyxin B Css avg ~3 mg/ml T ½ 12 hours Protein binding 60 Distribution CSF 5 Urine 4 Respiratory (Tubular secretion) Colistimethate (Tubular reabsorption) Colistin Parameter Colistin Css avg mg/ml C max ~7 hours T ½ 9-13 hours Protein binding 50 Distribution CSF 5 Urine 6-70 Respiratory unknown *Up to 7 hours to achieve maximum serum concentrations Nation RL et al, Clin Infect Dis 2014;59(1):88 94 Nation RL et al, Clin Infect Dis 2014;59(1):
3 Impact of Renal Dysfunction Colistimethate Colistin Polymyxin B Polymyxin B is Associated with Less Nephrotoxicity Nephrotoxicity, Comparison of nephrotoxicity rates P=0.08 P=0.003 Acute Renal Failure, P< CMS = Independent Risk Factor for Acute Renal Failure HR: 3.35; (95 CI, 2.05 to 5.48); P<0.001 Polymyxin B Colistin Polymyxin B CMS Nation RL et al, Clin Infect Dis 2014;59(1):88 94 Phe K et al. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2014;58:2740e6 Rigatto MH et al. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2016;60:2443e9. Poor Outcomes Associated with Polymyxins Compared to β-lactams In-Hospital Mortality, Follow up days Retrospective review of 133 patients with P. aeruginosa bacteremia Prospective study with 495 patients with gram-negative infections Median daily dose of polymyxin B: mg Median daily colistin dose: 183mg 83 of comparators received a β-lactam All comparators were β-lactams Factors associated with adjusted in-hospital mortality Multivariate analysis showed increased mortality associated with bacteremia: Polymyxin B - Hazard Ratio 1.9 ( ) p= Adjusted Odds Ratio 1.99 ( ) p= Cumulative Survival, β-lactams 60 Colistin 40 Polymixin-based Combination Therapy Associated with Improved Outcomes Carbapenem- resistant Klebsiella spp. bacteremias are frequently associated with mortality rates around 50 regardless of therapy selected Polymyxin combination therapy seems to be associated with better outcomes but no definitive prospective data is available Polymyxin mono-therapy Polymyxin combo-therapy Mortality Mortality Outcome N, () N, () p- value Tumbarello M, et al CID day mortality 11/22 (50) 13/46 (28) Qureshi ZA, et al AAC day mortality 4/7 (57) 1/7 (14) Zarkotou O, et al Infection related 4/7 (57) 0/14 (0) Clin Micro Infect 2011 mortality Kvitko CH et al. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2011;66(1):175-9 Paul M et al. J Antimicrob Chemother May;65(5): Tumbarello M, et al Clin Infect Dis 2012;55(7): Qureshi ZA, et al Antimicrob Agents Chemo 2012;56(4): Zarkotou O, et al Clin Microbiol Infect 2011; 17: Discrepancies in Approved Colistin Dosing and Target Obtainment Target C ss Attainment, Target C ss Attainment, 1 mg/kg 2.5 mg/kg 3.8 mg/kg 5 mg/kg CBA FDA Dosing/Day Based on ideal body weight OR actual body weight, whichever is lower. > 0.5 mg/l > 1 mg/l > 2 mg/l MIU MIU 9 MIU 9 MIU CMS Europe Medicine Agency Dosing/Day Nation RL et al. Clin Infect Dis 2016;62(5):552 8 Colistin Pharmacokinetic Dosing CMS/colistin pharmacokinetic dosing in critical ill patients (n=102) PK Dosing (MIC < 1 mg/l) Target colistin concentration ~2.5 mg/l Loading Dose CBA (mg) = Colistin target x 2.0 x IBW Maintenance Dose (total daily dose) CBA (mg)/d = colistin target x (1.50 x creatinine clearance + 30) [Q8-12 hour intervals based on renal function] Simplified Dosing Recommendation Based on Updated PK/PD Data (utilized in current NIH study) Loading Dose CrCl >50 ml/min CrCl >30-49 ml/min CrCl >10-29 ml/min 5 mg/kg x 1 (max 300 mg CBA) 5 mg/kg/day divided q8h 3.5 mg/kg/d divided q12h Use ideal body weight or actual body weight, whichever is lower. 2.5 mg/kg/d divided q12h CrCl <10 ml/min or hemodiaylsis 1.5 mg/kg/d divided q24h Garonzik SM et al. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011;55(7): Pogue JM et al. Clin Microbiol Infect 2017;23: Kaye KS ClinicalTrials.gov. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine(US). 2000e Available at: URL of the record NLM Identifier: NCT
4 Polymyxin B Dosing Considerations Polymyxin B clearance does not correlate with creatinine clearance Suggested Polymyxin B Dosing (pathogen MIC<1 mcg/ml) GAINing New Antibiotic Approvals New antibacterial agents approved in the United States Polymyxin B clearance scaled to total body weight Loading Dose 2.5 mg/kg (TBW) Maintenance Dose 1.25 mg/kg (TBW) every 12 hours No adjustment for renal dysfunction Pathogen MIC = 2 mcg/ml 1.5 mg/kg (TBW) Q12H [limited clinical/safety data] Number of Antibiotics Dalbavancin; May 2014 Tedizolid; June 2014 Oritavancin; Aug 2014 Ceftolozane-tazobactam; Dec 2014 Ceftazidime-avibactam; Feb 2015 Delafloxacin; June now Filled diamond: CVVHD patient (wt=250 kg) Filled triangle: CVVHD patient Sandri AM et al. Clin Infect Dis 2013;57(4): Boucher HW et al. Clin Infect Dis. 2009; 48:1 12 Introducing New Gram Negative Agents tazobactam Advance cephalosporin/ Ceftolozane β-lactamase inhibitor combinations Enhanced gram negative spectrum of activity Pseudomonas avibactam Enterobacteriaceae Some ESBLs and AmpC Ceftazidime Avibactam is a novel non-β-lactam β-lactamase inhibitor Expanded coverage KPCs Limited to no activity against Class D (Acinetobacter spp) No activity against Class B (metallo-b-lactamases) Zhanel GG et al. Drugs. 2014; 74:31 51 Zhanel GG et al. Drugs. 2013;73: Expanded Spectrum of Activity Pathogen Ceftolozane-tazobactam Ceftazidime-avibactam MIC Range MIC 50 MIC 90 MIC Range MIC 50 E. coli <0.12 to > < 0.03 to ESBL <0.12 to > < to K. pneumoniae <0.12 to > < 0.06 to ESBL < 0.12 to > to KPC 16 to >16 >16 >16 < 0.06 to Enterobacter spp. < 0.03 to > < 0.03 to > AmpC 0.25 to > to > Pseudomonas < 0.12 to > to > MDR Pseudomonas 0.5 to > < 1 to > Acinetobacter < 0.12 to to > 16 Beta-streptococcus < 0.12 to to S. aureus 4 to to >32 16 >32 Bacteroides fragilis < 0.12 to < 0.06 to > MIC 90 Other Bacteroides spp. < 0.12 to to > >128 Zhanel GG et al. Drugs. 2014; 74:31 51 Zhanel GG et al. Drugs. 2013; 73: Flam RK et al. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis Nov;80(3):233-8 Sader HS et al. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2014;58(3): FDA Susceptibility Breakpoints Comparative Efficacy for cutis Minimum Inhibitory Concentration, mcg/ml Susceptible Intermediate Resistant Ceftolozanetazobactaavibactatazobactaavibactatazobactaavibactam Ceftazidime- Ceftolozane- Ceftazidime- Ceftolozane- Ceftazidime- Microorganism Enterobacteriaceae <2 < >8 >16 Pseudomonas aeruginosa <4 < >16 >16 Streptococcus anginosus Streptococcus constellatus Streptococcus salivarius < >32 -- Bacteroides fragilis <8 ng/ml >32 -- Ceftolozane-tazobactam Levofloxacin Difference, Outcome 1.5g q8h 750 mg q24h 95 CI Median treatment duration 7 days 8 days Composite cure; Symptom resolution (2.3 to14.6) & microbiological response Microbiological eradication (2.9 to 14.3) ESBL-positive (n=118/800) (9.2 to 42.9) Clinical Cure (-0.8 to 6.2) Ceftazidime-avibactam Doripenem Difference, Outcome 2.5g q8hr 500 mg q8hr 95 CI Median IV treatment duration 7 days 8 days Symptom resolution & (0.3 to 13.12) microbiological response Microbiological response (-2.7to 3.56) ceftazidime-nonsusceptible ( to 16.89) pathogen (n=159/810) Clinical Cure (-4.23 to 4.03) Zerbaxa (ceftolozane-tazobactam) for injection. [package insert] Whitehouse Station, NJ; Rev 10/2016 Avycaz (ceftazidime-avibactam) for injection. [package insert] Irvine, Ca: Allergan USA Inc; Rev 01/2017 Wagenlehner FM et al. Lancet 2015; 385: Wagenlehner FM et al. Clin Infect Dis 2016;63(6):
5 Non-Inferior ciai Trial Results Ceftazidime-avibactam 2.5g q8hr Meropenem End Points + metronidazole 1g q8hr Mean treatment duration days days Solomkin J et al. Clin Infect Dis 2015;60(10): Mazuski JE et al. Clin Infect Dis 2016;62(11): Ceftolozane-tazobactam 1.5g q8h Meropenem Difference, End Points + metronidazole 1g q8hr 95 CI MITT population Cure, after days (-8.91 to 0.54) ESBL-positive (n=58/806) CrCl ml/min (n=36) Failure Difference, 95 CI Cure, after days (-8.64 to 1.58) Ceftazidime resistant pathogen (n=111/823) ( to 0.17) CrCl >50 ml/min (-6.17 to 3.97) CrCl ml/min a, b (50.15 to -5.36) Cure, late follow up days ( to 2.79) a. Ceftazidime/avibactam dose adjustment = 1.25g q12 hr (33 less than currently recommended dose) b. Within hrs of treatment initiation, 67.9 showed rapid improvement to CrC >50 ml/min Concerning Outcomes Continue in Serious CRE Infections Shields RK et al. Clin Infect Dis. 2016;63: Castón JJ et al. Int J Infect Dis. 2017;59: King M et al. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017; 61(7):e Shields et al. (2016) N=37 All types of CRE infections case series. APACHE II=34, SOFA=5, Monotherapy in day mortality=24; Clinical success=59 (CRRT=17 vs non-crrt=68) Microbiological failure = 27 (30 resistance to ceftazidime-avibactam) Castón et al. (2017) N=31 Ceftazidime-avibactam (n=8) vs other treatment (n=28) for CRE bacteremia 14-day clinical cure: 85.7 vs 34.8; p= day mortality: 25 vs 52.2; p=0.24 King et al (2017) N=60 All types of CRE infections; Charlson index=4.5, Pitt bacteremia=2, ICU=59 In-hospital mortality = 32; Clinical success = 65 Microbiological cure = 53 Dosing Considerations Ceftolozane-tazobactam FDA indications: complicated UTI & complicated IAI (w/ metronidazole) Renal Dose Adjustments Dose: 1.5 g (1g/500 mg) in 100 ml over 1 hour every 8 hours CrCl Renal adjustment CrCl <50 ml/min UTI/IAI HAP/VAP ml/min 750 mg (500/250) q8hr 1.5g (1g/500mg) q8hr Nosocomial Pneumonia trial (ASPECT-NP) ongoing ml/min 375 mg (250/125) q8hr 750 mg (500/250) q8hr Dose: 3 g (2g/1g) every 8 hours (CrCl >50 ml/min) 750 mg (500mg/250) x1 AWP Cost: $115 per 1.5 g vial (~$345/day) HD NA 150 mg(100/50) q8hr Potential stewardship niche: MDR pseudomonas infections Ceftazidime-avibactam FDA indications: complicated UTIs & complicated IAI (w/ metronidazole) Renal Dose Adjustments Dose: 2.5 g (2g/500mg) in ml over 2 hours every 8 hours CrCl UTI/IAI Renal adjustment: CrCl <50 ml/min ml/min 1.25g (1g/250mg) q8 hr Nosocomial Pneumonia trial (REPROVE) completed ml/min 940 mg (750/190) q12 hr AWP Cost: $359 per 2.5 g vial (~$1,077/day) 6-15 ml/min 940 mg (750/190) q24 hr HD 940 mg (750/190) q48 hr Potential stewardship niche:?cre (KPC) infections Spellberg B. Clin Infect Dis 2016;63(12): Zerbaxa (ceftolozane-tazobactam) for injection. [package insert] Whitehouse Station, NJ; Rev 10/2016 Avycaz (ceftazidime-avibactam) for injection. [package insert] Irvine, Ca: Allergan USA Inc; Rev 01/2017 Xiao AJ et al. J Clin Pharmacol. 2016;56(1): Clinicaltrials.gov NCT &NCT Adverse Effects Similar to Other Cephalosporins Clostridium difficile Incidence and Mortality is Increasing Adverse Effect Ceftolozane-tazobactam cuti n=533 ciai n=482 Ceftazidime-avibactam cuti n=511 ciai n=509 Rates of C. difficile Infection Among Hospitalized Patients, US Annual C. difficile Related Mortality Rates per Million Patients, US Headache Dizziness 1.1 NR NR NR Pyrexia NR 4.5 Nausea Vomiting NA 4.5 Diarrhea Constipation 3.9 NR Rates per 1,000,000 population Historically, advanced generation cephalosporins are associated with increased Clostridium difficile infection risk Wagenlehner FM et al. Lancet 2015; 385: Solomkin J et al. Clin Infect Dis 2015;60(10): Wagenlehner FM et al. Clin Infect Dis 2016;63(6): Mazuski JE et al. Clin Infect Dis 2016;62(11): National Hospital Discharge Survery, United States Redelings MD et al Emerg Infect Dis 2007;13(9):
6 Current Therapy Against C. difficile is Limited Clostridium difficile Frequently Recurs Despite Treatment Standard of care for CDI treatment includes: Oral/IV metronidazole (increasing failure rates) Oral vancomycin Oral fidaxomicin Antibiotic treatment has limited effects in preventing recurrent disease Metronidazole and vancomycin have broad activity against normal microbiota Although reduced compared to vancomycin, recurrence after fidaxomicin may be related to particular strains Percentage of Recurrent CDI Episodes ~40 ~60 Risk Factors Antibiotic use Advanced age Proton pump inhibitor therapy NAP1/BI/027 strain Prior episode of CDI Cohen SH et al. Infect Control Hosp Epi 2010;31(5): Musher DM et al. Clin Infect Dis 2005;40(11): Aslam S et al Lancet Infect Dis. 2005;5: McFarland LV et al. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002; 97: Novel Non-Antimicrobial Strategies Immune response against C. difficile toxins are correlated with reduced recurrences of CDI Successful cases of IVIG use reported in the literature Non-antibacterial toxin binding agents Tolevamer Inferior clinical cure rates compared to metronidazole or vancomycin Significant reduction in CDI recurrences Tolevamer Metronidazole Vancomycin p-value Clinical Cure <0.001 Recurrence <0.001 There are no approved therapies for the prevention of CDI..until now First Approved non-antimicrobial Strategy Against C. difficile Bezlotoxumab Fully human IgG1 monoclonal antibody (mab) that binds to C. difficile toxin B and prevents it s effects on epithelial cells FDA approval : October Indication: Reduce recurrence of CDI in patients 18 years of age who are receiving antibacterial drug treatment of CDI and are at high risk for CDI recurrence Kyne L et al. N Engl J Med. 2000;342: Kyne L et al. Lancet. 2001;357: Johnson S et al. Clin Infec Dis 2014;59(3): Yang Z et al. Infect Immun. 2015;83(2): Zinplava (Bezlotoxumab) for injection [package insert] Whitehouse Station, NJ: Merck & Co., INC; Rev 10/2016 Bezlotoxumab Reduces CDI Recurrence Patients with CDI Recurrence, One time bezlotoxumab 10 mg/kg added to standard treatment for primary or recurrent C. difficile diarrhea (n=2655) p=0.003 p=0.003 p=0.001 ~40 relative reduction Bezlotoxumab Does Not Impact Clinical Cure Rates Overall Clinical Cure Patient with Clinical Cure, Cumulative Incidence of Clinical Cure, Time to Clinical Cure Bezlotoxumab Placebo Days following Infusion Wilcox MH, et al. N Engl J Med 2017;376: Wilcox MH, et al. N Engl J Med 2017;376:
7 Effects on CDI Recurrence Based on Specific Risk Factors CDI Recurrence Rate, Overall Age >65 years < 65 years CDI History (6 months) Yes NO Previous Episodes (ever) >2 <1 Immunocompromised Severe CDI Hypervirulent Strain 027 Strain Yes NO Yes NO Yes NO Yes NO Wilcox MH, et al. N Engl J Med 2017;376: Bezlotoxumab vs Placebo Group Bezlotoxumab Placebo Favors Bezlotoxumab Difference () & 95 CI Overall Age > 65 years Age < 65 years Recent CDI history No Recent CDI history > 2 previous episodes < 1 previous episodes Immunocompromised Not immunocompromised Severe CDI Non-severe CDI Hypervirulent strain positive Non-hypervirulent strain Positive for 027 strain Negative for 027 strain Administration of Bezlotoxumab Dosage 10 mg/kg in 0.9 NaCL (or D5W) single infusion over 60 min No dose adjustments for renal/hepatic dysfunction Administration Given any time during antibiotic therapy for CDI CDI Recurrence Relative to Timing of Administration Bezlotoxumab given relative to SoC treatment Cost (AWP) $ per 1000 mg/40 ml vial Placebo n=773 Bezlotoxumab n= days after days after > 5 days after SoC= standard of care treatment Wilcox MH, et al. N Engl J Med 2017;376: Zinplava (Bezlotoxumab) for injection [package insert] Whitehouse Station, NJ: Merck & Co., INC; Rev 10/2016 Bezlotoxumab: Adverse Effects Adverse effects Infusion related reaction (10) Nausea (7) Pyrexia (5) Headache (4) Warning/precautions Increased risk of serious cardiac adverse effects including mortality in patients with existing heart failure Wilcox MH, et al. N Engl J Med 2017;376: Baseline CHF No Baseline CHF n=325 n=2019 Serious Adverse Effect Bezlotoxumab Bezlotoxumab + Acto Placebo Death Bezlotoxumab Bezlotoxumab + Acto Placebo Adverse effects among subjects with baseline CHF Bezlotoxumab Bezlotoxumab + Acto Placebo n=118 n=103 n=104 Treatment emergent adverse effect Serious Adverse Effect Death Comprehensive Strategies to Reduce Clostridium difficile Recurrences Strengthen infection prevention practices Limit unnecessary antibiotic use Reduce inappropriate acid suppressive therapy Targeted use of fidaxomicin in high risk groups Adjunct bezlotoxumab High risk groups Age > 65 years Immunosuppressed Recent previous CDI episode Prolonged systemic antibiotic use + acid suppressive therapy Reducing C. difficile Exposure Avoid hospital admission Reduce length of stay Limit unnecessary broad spectrum antibiotics Challenge for patients who require IV antibiotic therapy Failed oral antibiotic treatment Questionable compliance Medication/outpatient follow up Risks with prolonged intravenous access Thrombosis Phlebitis Impropriate access (IVDU) IVDU=intravenous drug user Introducing New Gram Positive Antimicrobial Agents Dalbavancin Semisynthetic derivative of teicoplanin Schwalbe RS Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1996;40(10): Steiert M et al. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2002;3(2): Smith JR et al. Infect Dis Ther 2015;4: Karaoui LR et al. Am J Health Syst Pharm 2013;70:23-33 Lipoglycopeptide Enhanced gram-positive activity Multi-modal mechanisms of action Extended half-lives Oritavancin Semisynthetic derivative of vancomycin 7
8 In vitro Activity Against Gram Positive Pathogens MIC 90 mcg/ml Organism Dalbavancin Oritavancin Vancomycin Staphylococcus aureus MRSA VRSA >4 Streptococcus pyogenes Streptococcus agalactiae Viridans group streptococcus Streptococcus pneumoniae Enterococcus faecalis Enterococcus faecium VanA VRE > >512 VanB/C VRE >512 Mechanism of Enhanced Antimicrobial Activity albavancin Template peptidoglycan Cytoplasm Cell Death ritavancin Mature peptidoglycan D-alanyl-d-alanine Lipid II Cell membrane Jones RN et al. J Chemother. 2005;17: Arhin FF et al. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009; 53: Bailey J et al. Am J Health-Syst Pharm. 2008; 65: Zhanel GG et al. Clin Infect Dis 2012;54(S3):S214 9 Highly Bactericidal Agents Against Staphylococcus aureus Log cfu/ml Dalbavancin against MRSA 9 Control 7 Dalbavancin 0.25 mg/l 5 Oritavancin against MRSA Dalbavancin 1 mg/l Oritavancin against VRSA Time, hours Log cfu/ml Log cfu/ml 10 Control Vancomycin Daptomycin Oritavancin Time, hours 10 Control Vancomycin 8 6 Daptomycin 4 FDA Susceptibility Breakpoints Minimum Inhibitory Concentration, mcg/ml Susceptible Intermediate* Resistant* Dalbavancin Oritavancin Dalbavancin Oritavancin Dalbavancin Oritavancin Microorganism Staphylococcus aureus <0.25 < (including MRSA isolates) Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus agalactiae, Streptococcus dysgalactiae, <0.25 < Streptococcus anginosus, Streptococcus constellatus, and Streptococcus intermedius Enterococcus faecalis (vancomycin-susceptible isolates only) <0.25 < *The current absence of data on resistant isolates precludes defining any category other than "Susceptible" 2 Oritavancin McKay GA et al. J Antimic Chemo 2009;63: Time, hours Durata Therapeutics International B.V. Dalbavancin for injection. NDA FDA Briefing Document. March 31, 2014 Orbactiv (oritavancin) for injection [package insert]. Parsippany, NJ: Medicines Company; Rev 08/14 Dalvance (dalbavancin) for injection [package insert]. Parsippany, NJ: Durata Therapeutics; Rev 01/2016 Attractive Pharmacokinetics Oritavancin plasma Dalbavancin plasma concentration, mcg/ml concentration, mg/l Plasma Concentration Time-Profile of 2-Dose Dalbavancin st Dose: Dalbavancin 1000 mg 2 nd Dose: Dalbavancin 5000 mg on day Total Drug Dalbavancin Oritavancin 10 Parameter 1000 mg 1200 mg C max 287 mg/l 138 mcg/ml 1 AUC 0-day mg*h/l 0- : 2800mcg*h/mL Calculated Free Drug Volume of 15.7 L 87.6 L 0.1 distribution Half life 204 hr (8.5 days) 245 hr (10.2 days) 300 Time, Days Clearance L/hr L/hr 100 Plasma Concentration Time-Profile of Single Dose Oritavancin 1200mg Protein binding 10 Renal 33 < 5 elimination Day 14 Orbactiv (oritavancin) for injection [package insert]. Parsippany, NJ: 1 Medicines Company; Rev 08/14 Dalvance (dalbavancin) for injection [package insert]. Parsippany, NJ: Durata Therapeutics; Rev 01/ Time, Days Dalbavancin non-inferior to Standard Care for absssi Dalbavancin* 1000 mg (d1) Vancomycin/ Absolute Difference End Point 500 mg (d8) linezolid (95 CI) No lesion spread at hr DISCOVER ( ) DISCOVER ( ) Both Trials combined ( ) Early >20 reduction of infection area at hr DISCOVER ( ) DISCOVER ( ) Both Trials combined ( ) Investigator s Clinical Cure (-3.0 to 1.5) *Dose adjustment for CrCl <30 ml/min: 750 mg (day 1) & 375 mg on day 8 Boucher HW, et al. N Engl J Med 2014;370:
9 Similar Outcomes with Consolidated Single Dose Dalbavancin Dunne MW, et al. Clin Infect Dis 2016;62(5): Dalbavancin 1500 mg x 1 Dalbavancin 1000 mg (D1) 500 mg (D8) Absolute Difference (95 CI) Assessment at hours Treatment response; >20 decrease in lesion (-8.5 to 2.8) Day 14 Clinical success (-6.1 to 4.1) Day 28 Clinical success ( -4.9 to 4.4) Dose adjustment for CrCl <30 ml/min: 1000 mg x mg (D1) 375 mg (D8) FDA approved single dose CrCl < 30 ml/min = 1125 mg Non-inferiority of Oritavancin for the Treatment of absssi Oritavancin Vancomycin Absolute Difference Outcome 1200 mg x 1 15mg/kg Q12H (95 CI) Primary Endpoint* SOLO I (-1.6 to 8.4) SOLO II (-7.5 to 2.0) Early Lesion size reduction >20 SOLO I ( 0.5 to 8.6) SOLO II (-3.7 to 5.0) Clinical Cure SOLO I ( 2.3 to 6.2) SOLO II (-4.9 to 1.6) *Cessation of spreading or a reduction in the size of the baseline lesion, the absence of fever, and the absence of a need for rescue antibiotic medication Corey RG, et al. N Engl J Med 2014;370: Corey RG, et al Clin Infect Dis 2015;60(2): Potential Interactions with Oritavancin Potential drug-drug interactions Weak CYP 2C9 and CYP2C19 inhibitor Warfarin AUC increased increased omeprazole : 5-hydroxy-omeprazole ratio Weak CYP3A4 and CYP2D6 inducer 18 decrease in midazolam AUC 31 decrease in dextromethorphan metabolism Potential drug-lab interactions Binds to phospholipid reagents in coagulation tests (falsely elevates) activated partial thromboplastin time (aptt) prolonged prothrombin time/international normalized ratio (PT/INR) IV heparin is contraindicated within first 48 hours of oritavancin infusion Adverse Effects Comparison Oritavancin Vancomycin Adverse Effect N=976 N=983 Diarrhea 36 (3.7) 32 (3.4) Nausea 97 (9.9) 103 (10.5) Vomiting 45 (4.6) 46 (4.7) Dizziness 26 (2.7) 26 (2.6) Headache 69 (7.1) 66 (6.7) Infusion site phlebitis 24 (2.5) 15 (1.5) Infusion site reaction 19 (1.9) 34 (3.5) Tachycardia 24 (2.5) 11 (1.1) Abscess 37 (3.8) 23 (2.3) (limb & subcutaneous) AST elevation 27 (2.8) 15 (1.5) ALT elevation 18 (1.8) 15 (1.5) Drug discontinuation 36 (3.7) 41 (4.2) Dalbavancin Comparators Adverse Effect N=1178 N=1224 Serous adverse effect 109 (6.1) 80 (6.5) Drug discontinuation 53 (3) 35 (2.8) Nausea 98 (5.5) 78 (6.4) Vomiting 50 (2.8) 37 (3) Diarrhea 79 (4.4) 72 (5.9) Headache 83 ( (4.8) Rash 48 (2.7) 30 (2.4) Pruritus 38 (2.1) ) ALT 3x ULN 12 (0.8) 2 (0.2) Drug Discontinuation 53 (3.0) 35 (2.9) Orbactiv (oritavancin) for injection [package insert]. Parsippany, NJ: Medicines Company; Rev 08/14 Corey RG, et al. N Engl J Med 2014;370: Corey RG, et al Clin Infect Dis 2015;60(2): Durata Therapeutics International B.V. Dalbavancin for injection. NDA FDA Briefing Document. March 31, 2014 Despite a Long Half Life; Duration of Adverse Effects is Limited Duration of Treatment-Emergent Adverse Events: Pooled Phase II/III Safety Database Durata Therapeutics International B.V. Dalbavancin for injection. NDA FDA Briefing Document. March 31, 2014 Early Interventions to Reduce Healthcare Costs Average hospital length of stay for primary SSSI ~ 3-5 days DRG: $4500-$10,000 Dalbavancin Costs: $4470 Oritavancin Costs: $2700 Shift care from inpatient hospitalization to outpatient infusion centers Identify potential candidates Require IV antibiotic therapy Limited-to-no systemic signs of severe/complicated infection $14,000 $12,000 $10,000 $8,000 $6,000 $4,000 $2,000 $0 Dalbavancin or Oritavancin Jauregui, et al. Clin Infect Dis 2005;41: Kaye K et al. PLoS One 2015; 10(11):1-13 Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP). National and regional estimates on hospital use for all patients from the HCUP National (Nationwide) Inpatient Sample (NIS). Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Rockville, MD. Accessed May 20, 2017 Cost Comparison by Key Components Vancomycin Daptomycin + Linezolid Drug Cost (Inpatient) Drug Cost (outpatient) Inpatient Medical Outpatient Medical 9
10 Patient (& Provider) Counseling Single dose antibiotic = novel approach to antimicrobial therapy Sustained therapeutic drug concentrations x 2 weeks Continued antimicrobial activity post infusion Resolution of lesion takes time Day 1 Day 5 Day 14 Summary Multidrug resistant infections remain a serious healthcare problem Improved pharmacokinetic understanding of polymyxin agents Polymyxin B more attractive than colistin Ceftolozane-tazobactam and ceftazidime-avibactam are welcomed additions to our armamentarium for MDR gram negative infections appropriate use is essential Bezlotoxumab is the first non-antibacterial agent to address and reduce C.difficile recurrent infections Long acting gram positive agents are novel strategies to limit/reduce inpatient hospitalizations FSHP Innovations in Antimicrobial Something Old, Something New Harrison Bachmeier, PharmD, BCPS Pharmacist Specialist-Infectious Diseases LeeHealth Fort Myers & Cape Coral, FL 10
ESCMID Online Lecture Library. by author
 Hospital Universitario Virgen Macarena, Seville New drugs against MRSA and VRE L. Eduardo López Cortés Seville, 8th July Tedizolid Oxazolidinone Ceftaroline // Ceftobiprole 5 th gen cephalosporin Overview
Hospital Universitario Virgen Macarena, Seville New drugs against MRSA and VRE L. Eduardo López Cortés Seville, 8th July Tedizolid Oxazolidinone Ceftaroline // Ceftobiprole 5 th gen cephalosporin Overview
Polymyxin B and Colistin Debate: One of the Same Kind or Mutt and Jeff?
 Polymyxin B and Colistin Debate: One of the Same Kind or Mutt and Jeff? Bruce M. Jones, PharmD, BCPS Clinical Pharmacy Specialist Infectious Diseases St. Joseph's/Candler Health System, Inc. Clinical Adjunct
Polymyxin B and Colistin Debate: One of the Same Kind or Mutt and Jeff? Bruce M. Jones, PharmD, BCPS Clinical Pharmacy Specialist Infectious Diseases St. Joseph's/Candler Health System, Inc. Clinical Adjunct
Antibiotic Treatment of GNR MDR Infections. Stan Deresinski
 Antibiotic Treatment of GNR MDR Infections Stan Deresinski Kucers: The Use of Antibiotics 1st Edition 1972 392 pages Kucers: The Use of Antibiotics 7 th Edition 2017 5338 pages Carbapenem Susceptibility
Antibiotic Treatment of GNR MDR Infections Stan Deresinski Kucers: The Use of Antibiotics 1st Edition 1972 392 pages Kucers: The Use of Antibiotics 7 th Edition 2017 5338 pages Carbapenem Susceptibility
A Snapshot of Colistin Use in South-East Europe and Particularly in Greece
 A Snapshot of Colistin Use in South-East Europe and Particularly in Greece Helen Giamarellou 02.05.2013 When Greek Physicians Prescribe Colistin? It is mainly prescribed in the ICU for VAP, bacteremia
A Snapshot of Colistin Use in South-East Europe and Particularly in Greece Helen Giamarellou 02.05.2013 When Greek Physicians Prescribe Colistin? It is mainly prescribed in the ICU for VAP, bacteremia
Nightmare Bacteria. Disclosures. Technician Objectives. Pharmacist Objectives. Carbapenem Resistance in Carbapenem Resistance in 2017
 Nightmare Bacteria How to Deal with the Reality of Carbapenem-resistant Organisms Disclosures I have no conflicts of interest relative to the content of this presentation Matthew L. Brown, Pharm.D., BCPS
Nightmare Bacteria How to Deal with the Reality of Carbapenem-resistant Organisms Disclosures I have no conflicts of interest relative to the content of this presentation Matthew L. Brown, Pharm.D., BCPS
New Antimicrobials: Now and In the Future
 New Antimicrobials: Now and In the Future David C. Hooper, M.D. Division of Infectious Diseases Infection Control Unit Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Conflicts of Interest Melinta
New Antimicrobials: Now and In the Future David C. Hooper, M.D. Division of Infectious Diseases Infection Control Unit Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Conflicts of Interest Melinta
NDA Briefing Document Anti-Infective Drugs Advisory Committee 05 December 2014
 CEFTAZIDIME-AVIBACTAM FOR INJECTION for Treatment of Complicated Intra-abdominal Infection (used in combination with metronidazole), Complicated Urinary Tract Infection including Acute Pyelonephritis,
CEFTAZIDIME-AVIBACTAM FOR INJECTION for Treatment of Complicated Intra-abdominal Infection (used in combination with metronidazole), Complicated Urinary Tract Infection including Acute Pyelonephritis,
Diane M. Gomes, Pharm.D. Outcomes in Antimicrobial Stewardship Post-Doctoral Pharmacy Fellow Providence Veterans Affairs Medical Center
 Diane M. Gomes, Pharm.D. Outcomes in Antimicrobial Stewardship Post-Doctoral Pharmacy Fellow Providence Veterans Affairs Medical Center The information disseminated in this lecture is given in my personal
Diane M. Gomes, Pharm.D. Outcomes in Antimicrobial Stewardship Post-Doctoral Pharmacy Fellow Providence Veterans Affairs Medical Center The information disseminated in this lecture is given in my personal
XERAVATM (eravacycline): A Novel Fluorocycline Antibacterial
 XERAVATM (eravacycline): A Novel Fluorocycline Antibacterial Matteo Bassetti, MD, PhD Infectious Diseases Division University of Udine and Santa Maria Misericordia University Hospital Udine, Italy Disclosures
XERAVATM (eravacycline): A Novel Fluorocycline Antibacterial Matteo Bassetti, MD, PhD Infectious Diseases Division University of Udine and Santa Maria Misericordia University Hospital Udine, Italy Disclosures
Antibacterial Antibiotic Resistancein 2016 What Should an Internist Know? Disclosures. Objectives 3/6/2016. Achaogen: Allergan:
 Antibacterial Antibiotic Resistancein 2016 What Should an Internist Know? Michael Satlin, MD, MS Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Infectious Diseases Weill Cornell Medicine March 4, 2016 1 Disclosures
Antibacterial Antibiotic Resistancein 2016 What Should an Internist Know? Michael Satlin, MD, MS Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Infectious Diseases Weill Cornell Medicine March 4, 2016 1 Disclosures
Continuous Infusion of Antibiotics In The ICU: What Is Proven? Professor of Medicine Vice-Chairman, Department of Medicine SUNY at Stony Brook
 Continuous Infusion of Antibiotics In The ICU: What Is Proven? Michael S. Niederman, M.D. Chairman, Department of Medicine Winthrop-University Hospital Mineola, NY Professor of Medicine Vice-Chairman,
Continuous Infusion of Antibiotics In The ICU: What Is Proven? Michael S. Niederman, M.D. Chairman, Department of Medicine Winthrop-University Hospital Mineola, NY Professor of Medicine Vice-Chairman,
NEW ANTIMICROBIALS. Sarah McClain, PharmD, BCPS Infectious Diseases Pharmacy Resident Carilion Clinic Roanoke Memorial Hospital April 17, 2015
 NEW ANTIMICROBIALS Sarah McClain, PharmD, BCPS Infectious Diseases Pharmacy Resident Carilion Clinic Roanoke Memorial Hospital April 17, 2015 DISCLOSURES I have no disclosures or conflicts of interest.
NEW ANTIMICROBIALS Sarah McClain, PharmD, BCPS Infectious Diseases Pharmacy Resident Carilion Clinic Roanoke Memorial Hospital April 17, 2015 DISCLOSURES I have no disclosures or conflicts of interest.
Ceftolozane/tazobactam (Zerbaxa, Merck) September 2015 Inpatient Non-Formulary
 Ceftolozane/tazobactam (Zerbaxa, Merck) September 2015 Inpatient n-formulary Criteria for Formulary Consideration of Ceftolozane/tazobactam Efficacy Ceftolozane/tazobactam was approved by the Food and
Ceftolozane/tazobactam (Zerbaxa, Merck) September 2015 Inpatient n-formulary Criteria for Formulary Consideration of Ceftolozane/tazobactam Efficacy Ceftolozane/tazobactam was approved by the Food and
Consultation on the Revision of Carbapenem Breakpoints
 Consultation on the Revision of Carbapenem Breakpoints July 2018 Please send comments to the EUCAST Scientific Secretary at jturnidge@gmail.com by September 15. EUCAST revision of carbapenem breakpoints
Consultation on the Revision of Carbapenem Breakpoints July 2018 Please send comments to the EUCAST Scientific Secretary at jturnidge@gmail.com by September 15. EUCAST revision of carbapenem breakpoints
Giving the Proper Dose: How Can The Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute(CLSI)Help?
 Giving the Proper Dose: How Can The Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute(CLSI)Help? Pranita D. Tamma, M.D., M.H.S. Director, Pediatric Antimicrobial Stewardship Johns Hopkins University School of
Giving the Proper Dose: How Can The Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute(CLSI)Help? Pranita D. Tamma, M.D., M.H.S. Director, Pediatric Antimicrobial Stewardship Johns Hopkins University School of
Public Health Surveillance for Multi Drug Resistant Organisms in Orange County
 Public Health Surveillance for Multi Drug Resistant Organisms in Orange County Matt Zahn, MD Medical Director Epidemiology and Assessment Orange County Public Health Antimicrobial Mechanisms of Action
Public Health Surveillance for Multi Drug Resistant Organisms in Orange County Matt Zahn, MD Medical Director Epidemiology and Assessment Orange County Public Health Antimicrobial Mechanisms of Action
Long-Term Care Updates
 Long-Term Care Updates April 2017 Bezlotoxumab to Prevent Recurrent Infection By Amy Wilson, PharmD and Zara Risoldi Cochrane, PharmD, MS, FASCP Introduction The Gram-positive bacteria is a common cause
Long-Term Care Updates April 2017 Bezlotoxumab to Prevent Recurrent Infection By Amy Wilson, PharmD and Zara Risoldi Cochrane, PharmD, MS, FASCP Introduction The Gram-positive bacteria is a common cause
In Vitro Activity of Ceftazidime-Avibactam Against Isolates. in a Phase 3 Open-label Clinical Trial for Complicated
 AAC Accepted Manuscript Posted Online 21 November 2016 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.01820-16 Copyright 2016, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
AAC Accepted Manuscript Posted Online 21 November 2016 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.01820-16 Copyright 2016, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
The CLSI Approach to Setting Breakpoints
 The CLSI Approach to Setting Breakpoints Jean B. Patel, PhD, D(ABMM) Deputy Director, Office of Antimicrobial Resistance Division of Healthcare Quality Promotion National Center for Emerging and Zoonotic
The CLSI Approach to Setting Breakpoints Jean B. Patel, PhD, D(ABMM) Deputy Director, Office of Antimicrobial Resistance Division of Healthcare Quality Promotion National Center for Emerging and Zoonotic
La farmacologia in aiuto
 Ferrara, 15 giugno 2018 La farmacologia in aiuto Pier Giorgio Cojutti, Federico Pea Istituto di Farmacologia Clinica Azienda Sanitaria Universitaria Integrata di Udine Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Beta-Lactams
Ferrara, 15 giugno 2018 La farmacologia in aiuto Pier Giorgio Cojutti, Federico Pea Istituto di Farmacologia Clinica Azienda Sanitaria Universitaria Integrata di Udine Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Beta-Lactams
Zinplava. (bezlotoxumab) New Product Slideshow
 Zinplava (bezlotoxumab) New Product Slideshow Introduction Brand name: Zinplava Generic name: Bezlotoxumab Pharmacological class: Human IgG1 monoclonal antibody Strength and Formulation: 25mg/mL; solution
Zinplava (bezlotoxumab) New Product Slideshow Introduction Brand name: Zinplava Generic name: Bezlotoxumab Pharmacological class: Human IgG1 monoclonal antibody Strength and Formulation: 25mg/mL; solution
Overcoming the PosESBLities of Enterobacteriaceae Resistance
 Overcoming the PosESBLities of Enterobacteriaceae Resistance Review of current treatment options Jamie Reed, PharmD Pharmacy Grand Rounds August 28, 2018 Rochester, MN 2018 MFMER slide-1 Disclosure No
Overcoming the PosESBLities of Enterobacteriaceae Resistance Review of current treatment options Jamie Reed, PharmD Pharmacy Grand Rounds August 28, 2018 Rochester, MN 2018 MFMER slide-1 Disclosure No
Frequency of Occurrence and Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Bacteria from ICU Patients with Pneumonia
 Frequency of Occurrence and Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Bacteria from ICU Patients with Pneumonia Helio S. Sader, M.D.* Mariana Castanheira, Ph.D. Rodrigo E. Mendes, Ph.D. Robert K. Flamm, Ph.D. JMI
Frequency of Occurrence and Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Bacteria from ICU Patients with Pneumonia Helio S. Sader, M.D.* Mariana Castanheira, Ph.D. Rodrigo E. Mendes, Ph.D. Robert K. Flamm, Ph.D. JMI
Is the package insert correct? PK considerations
 Is the package insert correct? PK considerations Jason A Roberts B Pharm (Hons), PhD, FSHP Professor of Medicine and Pharmacy The University of Queensland, Australia Royal Brisbane and Women s Hospital,
Is the package insert correct? PK considerations Jason A Roberts B Pharm (Hons), PhD, FSHP Professor of Medicine and Pharmacy The University of Queensland, Australia Royal Brisbane and Women s Hospital,
Use of imipenem. with the support of Wallonie-Bruxelles International. Magali Dodémont Microbiology Hospital Erasme Université Libre de Bruxelles
 with the support of Wallonie-Bruxelles International Use of imipenem Magali Dodémont Microbiology Hospital Erasme Université Libre de Bruxelles 1 Β-lactams classification 2 Β-lactams: mode of action Inhibition
with the support of Wallonie-Bruxelles International Use of imipenem Magali Dodémont Microbiology Hospital Erasme Université Libre de Bruxelles 1 Β-lactams classification 2 Β-lactams: mode of action Inhibition
10/4/16. mcr-1. Emerging Resistance Updates. Objectives. National Center for Emerging and Zoonotic Infectious Diseases. Alex Kallen, MD, MPH, FACP
 National Center for Emerging and Zoonotic Infectious Diseases Emerging Resistance Updates Alex Kallen, MD, MPH, FACP Lead Antimicrobial Resistance and Emerging Pathogens Team Prevention and Response Branch
National Center for Emerging and Zoonotic Infectious Diseases Emerging Resistance Updates Alex Kallen, MD, MPH, FACP Lead Antimicrobial Resistance and Emerging Pathogens Team Prevention and Response Branch
Antibiotics to treat multi-drug-resistant bacterial infections
 Antibiotics to treat multi-drug-resistant bacterial infections July 2013 JUNE 2013 Copyright 2013 Tetraphase Pharmaceuticals, Inc. 1 Forward Looking Statements and Other Important Cautions Any statements
Antibiotics to treat multi-drug-resistant bacterial infections July 2013 JUNE 2013 Copyright 2013 Tetraphase Pharmaceuticals, Inc. 1 Forward Looking Statements and Other Important Cautions Any statements
Treatment Options for Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae Infections
 REVIEW ARTICLE Treatment Options for Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae Infections Haley J. Morrill, 1,2 Jason M. Pogue, 3 Keith S. Kaye, 4 and Kerry L. LaPlante 1,2,5 1 Veterans Affairs Medical Center,
REVIEW ARTICLE Treatment Options for Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae Infections Haley J. Morrill, 1,2 Jason M. Pogue, 3 Keith S. Kaye, 4 and Kerry L. LaPlante 1,2,5 1 Veterans Affairs Medical Center,
Infectious Disease in the Critically Ill Patient
 Infectious Disease in the Critically Ill Patient Heather L. Evans, MD MS FACS Director of Surgical Infectious Disease Harborview Medical Center Asst. Professor UW Department of Surgery New Antibiotics:
Infectious Disease in the Critically Ill Patient Heather L. Evans, MD MS FACS Director of Surgical Infectious Disease Harborview Medical Center Asst. Professor UW Department of Surgery New Antibiotics:
Determining the Optimal Carbapenem MIC that Distinguishes Carbapenemase-Producing
 AAC Accepted Manuscript Posted Online 8 August 2016 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.00838-16 Copyright 2016, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 1 2 Determining the
AAC Accepted Manuscript Posted Online 8 August 2016 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.00838-16 Copyright 2016, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 1 2 Determining the
Activity of Ceftolozane/Tazobactam Against a Broad Spectrum of Recent Clinical Anaerobic Isolates
 AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on 25 November 2013 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.02253-13 Copyright 2013, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Activity
AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on 25 November 2013 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.02253-13 Copyright 2013, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Activity
PHARMACOKINETICS OF COLISTIN IN
 PHARMACOKINETICS OF COLISTIN IN CRITICALLY ILL PATIENTS WITH MULTIDRUG-RESISTANT GRAM- NEGATIVE BACILLI INFECTION JOURNAL CLUB PRESENTATION Amal M. Al-Anizi, PharmD Candidate KSU, Infectious disease rotation
PHARMACOKINETICS OF COLISTIN IN CRITICALLY ILL PATIENTS WITH MULTIDRUG-RESISTANT GRAM- NEGATIVE BACILLI INFECTION JOURNAL CLUB PRESENTATION Amal M. Al-Anizi, PharmD Candidate KSU, Infectious disease rotation
ALERT. Clinical microbiology considerations related to the emergence of. New Delhi metallo beta lactamases (NDM 1) and Klebsiella
 ALERT Clinical microbiology considerations related to the emergence of New Delhi metallo beta lactamases (NDM 1) and Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemases (KPC) amongst hospitalized patients in South Africa
ALERT Clinical microbiology considerations related to the emergence of New Delhi metallo beta lactamases (NDM 1) and Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemases (KPC) amongst hospitalized patients in South Africa
NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET
 NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET 1. PRODUCT NAME Zinforo 600 mg powder for injection. 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each vial contains ceftaroline fosamil acetic acid solvate monohydrate equivalent
NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET 1. PRODUCT NAME Zinforo 600 mg powder for injection. 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each vial contains ceftaroline fosamil acetic acid solvate monohydrate equivalent
2/6/14. What s Hot in ID Objectives
 What s Hot in ID 2014 James S. Lewis II, Pharm.D., FIDSA ID Clinical Pharmacy Coordinator Oregon Health and Science University Portland, OR Objectives Describe highlights of the Interscience Conference
What s Hot in ID 2014 James S. Lewis II, Pharm.D., FIDSA ID Clinical Pharmacy Coordinator Oregon Health and Science University Portland, OR Objectives Describe highlights of the Interscience Conference
ABSSSI Case Study days (clinical evaluation)
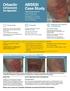 ABSSSI Case Study Cellulitis patient background 44-year-old single father Chronic renal insufficiency Hyperlipidemia, on rosuvastatin Has atrial fibrillation, on apixaban Fell and injured right leg At
ABSSSI Case Study Cellulitis patient background 44-year-old single father Chronic renal insufficiency Hyperlipidemia, on rosuvastatin Has atrial fibrillation, on apixaban Fell and injured right leg At
Cefotaxime Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version th September 2010
 Cefotaxime Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version 1.0 26 th September 2010 Foreword EUCAST The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) is organised by the European
Cefotaxime Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version 1.0 26 th September 2010 Foreword EUCAST The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) is organised by the European
Updates to pharmacological management in the prevention of recurrent Clostridium difficile
 Updates to pharmacological management in the prevention of recurrent Clostridium difficile Julia Shlensky, PharmD PGY2 Internal Medicine Resident September 12, 2017 2017 MFMER slide-1 Clinical Impact Increasing
Updates to pharmacological management in the prevention of recurrent Clostridium difficile Julia Shlensky, PharmD PGY2 Internal Medicine Resident September 12, 2017 2017 MFMER slide-1 Clinical Impact Increasing
NEW DEVELOPMENTS AND CHALLENGING CASES IN HOSPITAL INFECTIOUS DISEASES
 Lisa G. Winston, MD Professor, University of California, San Francisco Vice Chief, Inpatient Medical Services and Hospital Epidemiologist, San Francisco General Hospital NEW DEVELOPMENTS AND CHALLENGING
Lisa G. Winston, MD Professor, University of California, San Francisco Vice Chief, Inpatient Medical Services and Hospital Epidemiologist, San Francisco General Hospital NEW DEVELOPMENTS AND CHALLENGING
NEW DRUGS PART II 7/7/ ANNUAL MEETING ANTIBIOTICS AND ANTIFUNGALS DISCLOSURE BACTERIA OBJECTIVES ANTIBIOTIC RESISTANCE
 ANTIBIOTICS AND ANTIFUNGALS NEW DRUGS PART II JACQUELINE KING, PHARM.D. PHARMACY OPERATIONS SUPERVISOR UFHEALTH CANCER CENTER JACQUELINE.KING@ORLANDOHEALTH.COM TARA MCNULTY, CPHT, RPHT PROJECT MANAGER
ANTIBIOTICS AND ANTIFUNGALS NEW DRUGS PART II JACQUELINE KING, PHARM.D. PHARMACY OPERATIONS SUPERVISOR UFHEALTH CANCER CENTER JACQUELINE.KING@ORLANDOHEALTH.COM TARA MCNULTY, CPHT, RPHT PROJECT MANAGER
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH INCLUDING PATIENT MEDICATION INFORMATION ZERBAXA. Ceftolozane and Tazobactam powder for injection
 PRODUCT MONOGRAPH INCLUDING PATIENT MEDICATION INFORMATION ZERBAXA Ceftolozane and Tazobactam powder for injection 1.5 gram (g) per vial Containing ceftolozane 1 g (as ceftolozane sulfate) and tazobactam
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH INCLUDING PATIENT MEDICATION INFORMATION ZERBAXA Ceftolozane and Tazobactam powder for injection 1.5 gram (g) per vial Containing ceftolozane 1 g (as ceftolozane sulfate) and tazobactam
NONFERMENTING GRAM NEGATIVE RODS. April Abbott Deaconess Health System Evansville, IN
 NONFERMENTING GRAM NEGATIVE RODS April Abbott Deaconess Health System Evansville, IN OBJECTIVES Discuss basic limitations to assessing carbapenem resistance in nonfermenting GNRs Discuss antimicrobial
NONFERMENTING GRAM NEGATIVE RODS April Abbott Deaconess Health System Evansville, IN OBJECTIVES Discuss basic limitations to assessing carbapenem resistance in nonfermenting GNRs Discuss antimicrobial
Plazomicin Versus Meropenem for the Treatment of Complicated Urinary Tract Infection and Acute Pyelonephritis: Results of the EPIC Study
 Plazomicin Versus Meropenem for the Treatment of Complicated Urinary Tract Infection and Acute Pyelonephritis: Results of the EPIC Study Daniel J. Cloutier 1, Loren G. Miller 2, Allison S. Komirenko 1,
Plazomicin Versus Meropenem for the Treatment of Complicated Urinary Tract Infection and Acute Pyelonephritis: Results of the EPIC Study Daniel J. Cloutier 1, Loren G. Miller 2, Allison S. Komirenko 1,
CE Prn. Pharmacy Continuing Education from WF Professional Associates ABOUT WFPA LESSONS TOPICS ORDER CONTACT PHARMACY EXAM REVIEWS
 CE Prn Pharmacy Continuing Education from WF Professional Associates ABOUT WFPA LESSONS TOPICS ORDER CONTACT PHARMACY EXAM REVIEWS New Antimicrobials March 2016 Drug resistant infections are becoming more
CE Prn Pharmacy Continuing Education from WF Professional Associates ABOUT WFPA LESSONS TOPICS ORDER CONTACT PHARMACY EXAM REVIEWS New Antimicrobials March 2016 Drug resistant infections are becoming more
Update on CLSI and EUCAST
 Update on CLSI and EUCAST 1 Completed work» Cephalosporin breakpoints for Enterobacteriaceae ESBL screens MIC versus resistance mechanism» Carbapenem breakpoints for Enterobacteriaceae Modified Hodge Test»
Update on CLSI and EUCAST 1 Completed work» Cephalosporin breakpoints for Enterobacteriaceae ESBL screens MIC versus resistance mechanism» Carbapenem breakpoints for Enterobacteriaceae Modified Hodge Test»
400 mg IV (over 5 to 60 minutes) every 12 hours. > 30 to mg IV (over 5 to 60 minutes ) every 12 hours. 15 to 30
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use TEFLARO safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for TEFLARO. TEFLARO (ceftaroline
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use TEFLARO safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for TEFLARO. TEFLARO (ceftaroline
Open Forum Infectious Diseases MAJOR ARTICLE
 Open Forum Infectious Diseases MAJOR ARTICLE Efficacy and Safety of Oritavancin Relative to Vancomycin for Patients with Acute Bacterial Skin and Skin Structure Infections (ABSSSI) in the Outpatient Setting:
Open Forum Infectious Diseases MAJOR ARTICLE Efficacy and Safety of Oritavancin Relative to Vancomycin for Patients with Acute Bacterial Skin and Skin Structure Infections (ABSSSI) in the Outpatient Setting:
Laboratory CLSI M100-S18 update. Paul D. Fey, Ph.D. Associate Professor/Associate Director Josh Rowland, M.T. (ASCP) State Training Coordinator
 Nebraska Public Health Laboratory 2008 CLSI M100-S18 update Paul D. Fey, Ph.D. Associate Professor/Associate Director Josh Rowland, M.T. (ASCP) State Training Coordinator Agenda Discuss 2008 M100- S18
Nebraska Public Health Laboratory 2008 CLSI M100-S18 update Paul D. Fey, Ph.D. Associate Professor/Associate Director Josh Rowland, M.T. (ASCP) State Training Coordinator Agenda Discuss 2008 M100- S18
May 11, Ceftriaxone for MSSA. Daptomycin Dosing Weight. Candidiasis Treatment
 Diagnostics and Debates: An Update on Rapid Diagnostic Testing and Current Controversies in Infectious Diseases Nicholas Torney, PharmD, BCPS Derek Vander Horst, PharmD Munson Medical Center WMSHP Annual
Diagnostics and Debates: An Update on Rapid Diagnostic Testing and Current Controversies in Infectious Diseases Nicholas Torney, PharmD, BCPS Derek Vander Horst, PharmD Munson Medical Center WMSHP Annual
Antibiotic Usage Related to Microorganisms Pattern and MIC
 Antibiotic Usage Related to Microorganisms Pattern and MIC DR. Dr. Latre Buntaran Sp.MK(K) Secretary General PERDALIN Head of Compartment of Infection Control PERSI Doripenem: Potent
Antibiotic Usage Related to Microorganisms Pattern and MIC DR. Dr. Latre Buntaran Sp.MK(K) Secretary General PERDALIN Head of Compartment of Infection Control PERSI Doripenem: Potent
Cubicin (Daptomycin) Priv.Doz. Dr. med. Markus Rothenburger
 Cubicin (Daptomycin) Priv.Doz. Dr. med. Markus Rothenburger Cubicin (Daptomycin): A new generation of antibiotics First-in-class cyclic natural lipopeptide Activity against major gram positive pathogens
Cubicin (Daptomycin) Priv.Doz. Dr. med. Markus Rothenburger Cubicin (Daptomycin): A new generation of antibiotics First-in-class cyclic natural lipopeptide Activity against major gram positive pathogens
Initial U.S. Approval: 2010
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use TEFLARO safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for TEFLARO. TEFLARO (ceftaroline
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use TEFLARO safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for TEFLARO. TEFLARO (ceftaroline
ICD-10 diagnostic codes consistent with ORBACTIV (oritavancin) indication
 ICD-10 diagnostic codes consistent with ORBACTIV (oritavancin) indication ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Codes Diagnosis INDICATION ORBACTIV (oritavancin) for injection is indicated for the treatment of adult patients
ICD-10 diagnostic codes consistent with ORBACTIV (oritavancin) indication ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Codes Diagnosis INDICATION ORBACTIV (oritavancin) for injection is indicated for the treatment of adult patients
HOW BUGS COMBAT DRUGS: ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE MECHANISMS IN THE MODERN ERA. Romney Humphries, PhD D(ABMM)
 HOW BUGS COMBAT DRUGS: ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE MECHANISMS IN THE MODERN ERA Romney Humphries, PhD D(ABMM) Section Chief, UCLA Clinical Microbiology Los Angeles CA rhumphries@mednet.ucla.edu WHAT WE WILL
HOW BUGS COMBAT DRUGS: ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE MECHANISMS IN THE MODERN ERA Romney Humphries, PhD D(ABMM) Section Chief, UCLA Clinical Microbiology Los Angeles CA rhumphries@mednet.ucla.edu WHAT WE WILL
β-lactamase inhibitors
 β-lactamase inhibitors Properties, microbiology & enzymology DAVID M LIVERMORE Professor of Medical Microbiology, UEA Lead on Antibiotic Resistance, Public Health England β-lactamase classes A B C D Serine
β-lactamase inhibitors Properties, microbiology & enzymology DAVID M LIVERMORE Professor of Medical Microbiology, UEA Lead on Antibiotic Resistance, Public Health England β-lactamase classes A B C D Serine
Sep Oct Nov Dec Total
 LB PAGE 2 LB PAGE 3 Sep Oct Nov Dec 2007 2007 2007 2007 Total Repeat Information Total Repeats 35 15 17 9 76 Repeat Rate 6.01% 0.17% 1.12% 0.39% 2.07% Repeat Chemistry 25 0 2 0 27 Repeat Extraction 1 0
LB PAGE 2 LB PAGE 3 Sep Oct Nov Dec 2007 2007 2007 2007 Total Repeat Information Total Repeats 35 15 17 9 76 Repeat Rate 6.01% 0.17% 1.12% 0.39% 2.07% Repeat Chemistry 25 0 2 0 27 Repeat Extraction 1 0
Presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Microbiology, June 1-5, 2017, New Orleans, LA, USA
 Is Associated With Improved Survival and Safety Compared to Colistin in Serious Carbapenemresistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE) Infections: Results of the CARE Study Lynn E. Connolly 1, Adrian M. Jubb 1,
Is Associated With Improved Survival and Safety Compared to Colistin in Serious Carbapenemresistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE) Infections: Results of the CARE Study Lynn E. Connolly 1, Adrian M. Jubb 1,
Cefuroxime iv Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version th September 2010
 Cefuroxime iv Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version 1.0 26 th September 2010 Foreword EUCAST The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) is organised by the
Cefuroxime iv Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version 1.0 26 th September 2010 Foreword EUCAST The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) is organised by the
Clostridium Difficile Infection: Applying New Treatment Guidelines and Strategies to Reduce Recurrence Rate
 Clostridium Difficile Infection: Applying New Treatment Guidelines and Strategies to Reduce Recurrence Rate Objectives Summarize the changing epidemiology and demographics of patients at risk for Clostridium
Clostridium Difficile Infection: Applying New Treatment Guidelines and Strategies to Reduce Recurrence Rate Objectives Summarize the changing epidemiology and demographics of patients at risk for Clostridium
Lessons from recent studies. João Gonçalves Pereira UCIP DALI
 Lessons from recent studies João Gonçalves Pereira UCIP DALI 1 Patterns of Antimicrobial Activity Concentration C max Aminoglycosides Cmax/MIC>10 Metronidazol Area under the concentration curve Azithromycin
Lessons from recent studies João Gonçalves Pereira UCIP DALI 1 Patterns of Antimicrobial Activity Concentration C max Aminoglycosides Cmax/MIC>10 Metronidazol Area under the concentration curve Azithromycin
Optimizing Antibiotic Therapy in the ICU For Pneumonia Current and Future Approaches
 Optimizing Antibiotic Therapy in the ICU For Pneumonia Current and Future Approaches Andrew F. Shorr, MD, MPH Washington Hospital Center Georgetown Univ. Disclosures I have served as a consultant to, researcher/investigator
Optimizing Antibiotic Therapy in the ICU For Pneumonia Current and Future Approaches Andrew F. Shorr, MD, MPH Washington Hospital Center Georgetown Univ. Disclosures I have served as a consultant to, researcher/investigator
ANNEX I SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS
 ANNEX I SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Doribax 250 mg powder for solution for infusion 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each vial contains doripenem monohydrate
ANNEX I SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Doribax 250 mg powder for solution for infusion 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each vial contains doripenem monohydrate
New Antibiotics. Will Roland, MD
 New Antibiotics Will Roland, MD FDA Approvals 2010 - ceftaroline 2011 - fidaxomicin, telaprevir, boceprevir, spinosad 2012 bedaquiline, raxibacumab, Stribild, 2013 sofosbuvir, simeprevir, dolutegravir
New Antibiotics Will Roland, MD FDA Approvals 2010 - ceftaroline 2011 - fidaxomicin, telaprevir, boceprevir, spinosad 2012 bedaquiline, raxibacumab, Stribild, 2013 sofosbuvir, simeprevir, dolutegravir
Sepsis Treatment: Early Identification Remains the Key Issue
 Sepsis Treatment: Early Identification Remains the Key Issue Marin H. Kollef, MD Professor of Medicine Washington University School of Medicine Director, Medical Critical Care Director, Respiratory Care
Sepsis Treatment: Early Identification Remains the Key Issue Marin H. Kollef, MD Professor of Medicine Washington University School of Medicine Director, Medical Critical Care Director, Respiratory Care
Pharmacologyonline 1: (2010) ewsletter Singh and Kochbar. Optimizing Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamics Principles & Role of
 Optimizing Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamics Principles & Role of Cefoperazone Sulbactam Singh M*, Kochhar P* Medical & Research Division, Pfizer India. Summary Antimicrobial resistance is associated with
Optimizing Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamics Principles & Role of Cefoperazone Sulbactam Singh M*, Kochhar P* Medical & Research Division, Pfizer India. Summary Antimicrobial resistance is associated with
without the permission of the author Not to be copied and distributed to others
 Emperor s Castle interior-prato What is the Role of Inhaled Polymyxins for Treatment of Respiratory Tract Infections? Helen Giamarellou CONCLUSIONS: Patients with Pseudomonas and Acinetobacter VAP may
Emperor s Castle interior-prato What is the Role of Inhaled Polymyxins for Treatment of Respiratory Tract Infections? Helen Giamarellou CONCLUSIONS: Patients with Pseudomonas and Acinetobacter VAP may
Antibiotic Resistance Pattern of Blood and CSF Culture Isolates At NHLS Academic Laboratories (2005)
 Antibiotic Resistance Pattern of Blood and CSF Culture Isolates At NHLS Academic Laboratories (2005) Streptococcus pneumoniae (SP) Blood Culture Isolates Penicillin intermediate Penicillin Cefotaxime 336
Antibiotic Resistance Pattern of Blood and CSF Culture Isolates At NHLS Academic Laboratories (2005) Streptococcus pneumoniae (SP) Blood Culture Isolates Penicillin intermediate Penicillin Cefotaxime 336
Expert rules. for Gram-negatives
 Academic Perspective in Expert rules Emerging Issues of Resistance in Gram-ve Bacteria for Gram-negatives Trevor Winstanley Sheffield Teaching Hospitals Presented on behalf of David Livermore University
Academic Perspective in Expert rules Emerging Issues of Resistance in Gram-ve Bacteria for Gram-negatives Trevor Winstanley Sheffield Teaching Hospitals Presented on behalf of David Livermore University
New insights in antibiotic and antifungal therapy in the compromised host
 New insights in antibiotic and antifungal therapy in the compromised host Claudio Viscoli University of Genova Ospedale Policlinico San Martino, Genova Potential conflicts of interest (last 5 years) Received
New insights in antibiotic and antifungal therapy in the compromised host Claudio Viscoli University of Genova Ospedale Policlinico San Martino, Genova Potential conflicts of interest (last 5 years) Received
PREVENTION AND TREATMENT OF BACTERIAL INFECTIONS IN CIRRHOSIS
 PREVENTION AND TREATMENT OF BACTERIAL INFECTIONS IN CIRRHOSIS Dr. J. Fernández. Head of the Liver Unit Hospital Clinic Barcelona, Spain AEEH Postgraduate Course, Madrid, February 15 2017 Prevalence of
PREVENTION AND TREATMENT OF BACTERIAL INFECTIONS IN CIRRHOSIS Dr. J. Fernández. Head of the Liver Unit Hospital Clinic Barcelona, Spain AEEH Postgraduate Course, Madrid, February 15 2017 Prevalence of
Healthy Adult cuti Patient. Cmax (mcg/ml)(mean ± SD) 73.7 ± ± 113. Vd (L)(mean ± SD) 17.9 ± ± 12.1
 Brand Name: Zemdri Generic Name: plazomicin Manufacturer: Achaogen, Inc Drug Class: aminoglycoside antibacterial Uses: 1-5 Labeled: treatment of complicated urinary tract infections (cuti), including pyelonephritis,
Brand Name: Zemdri Generic Name: plazomicin Manufacturer: Achaogen, Inc Drug Class: aminoglycoside antibacterial Uses: 1-5 Labeled: treatment of complicated urinary tract infections (cuti), including pyelonephritis,
Treatment Options for Urinary Tract Infections Caused by Extended-Spectrum Β-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae
 Treatment Options for Urinary Tract Infections Caused by Extended-Spectrum Β-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae medicine.missouri.edu/jahm/treatment-options-urinary-tract-infections-caused-extended-spectrum-β-lactamase-producingescherichia-coli-klebsiella-pneumoniae/
Treatment Options for Urinary Tract Infections Caused by Extended-Spectrum Β-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae medicine.missouri.edu/jahm/treatment-options-urinary-tract-infections-caused-extended-spectrum-β-lactamase-producingescherichia-coli-klebsiella-pneumoniae/
DORIBAX for injection
 DORIBAX for injection 500 mg Powder for Intravenous Infusion NAME OF THE MEDICINE Doripenem (as monohydrate) PRODUCT INFORMATION The chemical name for doripenem monohydrate is (4R,5S,6S)-3-[((3S,5S)-5-
DORIBAX for injection 500 mg Powder for Intravenous Infusion NAME OF THE MEDICINE Doripenem (as monohydrate) PRODUCT INFORMATION The chemical name for doripenem monohydrate is (4R,5S,6S)-3-[((3S,5S)-5-
DORIPENEM: THE NEWEST MEMBER OF THE CARBAPENEM FAMILY
 Volume 23, Issue 4 January 2008 DORIPENEM: THE NEWEST MEMBER OF THE CARBAPENEM FAMILY as well as for treatment of complicated urinary tract infection (cuti), including pyelonephritis. The following article
Volume 23, Issue 4 January 2008 DORIPENEM: THE NEWEST MEMBER OF THE CARBAPENEM FAMILY as well as for treatment of complicated urinary tract infection (cuti), including pyelonephritis. The following article
Ceftaroline fosamil, as ceftaroline fosamil monoacetate monohydrate.
 PRODUCT INFORMATION ZINFORO ceftaroline fosamil NAME OF THE MEDICINE Ceftaroline fosamil, as ceftaroline fosamil monoacetate monohydrate. The chemical name of ceftaroline fosamil monoacetate monohydrate
PRODUCT INFORMATION ZINFORO ceftaroline fosamil NAME OF THE MEDICINE Ceftaroline fosamil, as ceftaroline fosamil monoacetate monohydrate. The chemical name of ceftaroline fosamil monoacetate monohydrate
Therapy of MDR/XDR Gram-negative bacteria: dealing with the devil. CRE: high dosing, how much? by author
 Therapy of MDR/XDR Gram-negative bacteria: dealing with the devil CRE: high dosing, how much? George L. Daikos, MD National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Laiko General Hospital, Athens, Greece
Therapy of MDR/XDR Gram-negative bacteria: dealing with the devil CRE: high dosing, how much? George L. Daikos, MD National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Laiko General Hospital, Athens, Greece
Adult Inpatient Antibiogram. Antimicrobial Susceptibilities of Frequently Recovered Clinical Isolates. January to December 2016
 Adult Inpatient Antibiogram Antimicrobial Susceptibilities of Frequently Recovered Clinical Isolates January to December 2016 Department of Pathology Camille Hamula, PhD Director, Clinical Microbiology
Adult Inpatient Antibiogram Antimicrobial Susceptibilities of Frequently Recovered Clinical Isolates January to December 2016 Department of Pathology Camille Hamula, PhD Director, Clinical Microbiology
Mechanisms of Resistance to Ceftazidime-Avibactam. Romney M. Humphries, PhD D(ABMM) Chief Scientific Officer Accelerate Diagnostics.
 Mechanisms of Resistance to Ceftazidime-Avibactam Romney M. Humphries, PhD D(ABMM) Chief Scientific Officer Accelerate Diagnostics UCLA, January 2015 62 year old woman with advanced pancreatic cancer Vomiting
Mechanisms of Resistance to Ceftazidime-Avibactam Romney M. Humphries, PhD D(ABMM) Chief Scientific Officer Accelerate Diagnostics UCLA, January 2015 62 year old woman with advanced pancreatic cancer Vomiting
Treatment Strategies for Infections due to MDR-GNR
 Treatment Strategies for Infections due to MDR-GNR Michael Satlin, MD Instructor in Medicine Division of Infectious Diseases Weill Cornell Medical College, New York, NY October 16, 2012 1 2 Faculty Disclosure
Treatment Strategies for Infections due to MDR-GNR Michael Satlin, MD Instructor in Medicine Division of Infectious Diseases Weill Cornell Medical College, New York, NY October 16, 2012 1 2 Faculty Disclosure
Disclosure. Objectives. Evolution of β Lactamases. Extended Spectrum β Lactamases: The New Normal. Prevalence of ESBL Mystic Program
 47 th Annual Meeting August 2-4, 2013 Orlando, FL Extended Spectrum β Lactamases: The New Normal Disclosure I do have a vested interest in or affiliation with the following companies or organizations Triax
47 th Annual Meeting August 2-4, 2013 Orlando, FL Extended Spectrum β Lactamases: The New Normal Disclosure I do have a vested interest in or affiliation with the following companies or organizations Triax
Adenium Biotech. Management: - Peter Nordkild, MD, CEO, ex Novo Nordisk, Ferring, Egalet - Søren Neve, PhD, project director, ex Lundbeck, Novozymes
 Adenium Biotech Management: - Peter Nordkild, MD, CEO, ex Novo Nordisk, Ferring, Egalet - Søren Neve, PhD, project director, ex Lundbeck, Novozymes Board of Directors: - Stephan Christgau, PhD, chairman,
Adenium Biotech Management: - Peter Nordkild, MD, CEO, ex Novo Nordisk, Ferring, Egalet - Søren Neve, PhD, project director, ex Lundbeck, Novozymes Board of Directors: - Stephan Christgau, PhD, chairman,
TP Larry Tsai, MD Chief Medical Officer Tetraphase Pharmaceuticals
 TP-676 Larry Tsai, MD Chief Medical Officer Tetraphase Pharmaceuticals Tetraphase Pharmaceuticals Overview Tetraphase is developing novel antibiotics for serious and life-threatening Gram-negative MDR
TP-676 Larry Tsai, MD Chief Medical Officer Tetraphase Pharmaceuticals Tetraphase Pharmaceuticals Overview Tetraphase is developing novel antibiotics for serious and life-threatening Gram-negative MDR
SBUH Aminoglycoside Dosing Protocol
 Adult Aminoglycoside Dosing for Gram negative infections prior to available serum levels (Excludes patients with cystic fibrosis, OB GYN patients and surgical prophylaxis) Cr Cl 40 ml/min 5 7 mg/kg INT
Adult Aminoglycoside Dosing for Gram negative infections prior to available serum levels (Excludes patients with cystic fibrosis, OB GYN patients and surgical prophylaxis) Cr Cl 40 ml/min 5 7 mg/kg INT
La batteriocidia sierica: passato e presente
 Genova, 23 settembre 2016 La batteriocidia sierica: passato e presente Dott.ssa Maddalena Giannella Clinica di Malattie Infettive AOU Policlinico Sant Orsola Malpighi Case 1 Case 2 Summary: Cured of cancer
Genova, 23 settembre 2016 La batteriocidia sierica: passato e presente Dott.ssa Maddalena Giannella Clinica di Malattie Infettive AOU Policlinico Sant Orsola Malpighi Case 1 Case 2 Summary: Cured of cancer
! Macrolide antibacterial. Fidaxomicin (Dificid ) package labeling. Optimer Pharmaceuticals, Inc. May 2011.
 Disclosure! I have no conflicts of interest related to this presentation Nina Naeger Murphy, Pharm.D., BCPS Clinical Pharmacy Specialist Infectious Diseases MetroHealth Medical Center Learning Objectives!
Disclosure! I have no conflicts of interest related to this presentation Nina Naeger Murphy, Pharm.D., BCPS Clinical Pharmacy Specialist Infectious Diseases MetroHealth Medical Center Learning Objectives!
Long-Term Care Updates
 Long-Term Care Updates April 2018 By Austin Smith, PharmD Candidate and Lindsay Slowiczek, PharmD is the most common healthcare-acquired infection (HAI) in the United States. 1,2 A 2014 prevalence survey
Long-Term Care Updates April 2018 By Austin Smith, PharmD Candidate and Lindsay Slowiczek, PharmD is the most common healthcare-acquired infection (HAI) in the United States. 1,2 A 2014 prevalence survey
OTE. Peramivir: A Novel Intravenous Neuraminidase Inhibitor for the Treatment of Influenza. Vol. 30, Issue 9 June 2015.
 HAR Vol. 30, Issue 9 June 2015 M A N OTE Established 1985 Peramivir: A Novel Intravenous Neuraminidase Inhibitor for the Treatment of Influenza Vincent Solomon, PharmD Peramivir: A Novel Intravenous Neuraminidase
HAR Vol. 30, Issue 9 June 2015 M A N OTE Established 1985 Peramivir: A Novel Intravenous Neuraminidase Inhibitor for the Treatment of Influenza Vincent Solomon, PharmD Peramivir: A Novel Intravenous Neuraminidase
Treatment of febrile neutropenia in patients with neoplasia
 Treatment of febrile neutropenia in patients with neoplasia George Samonis MD, PhD Medical Oncologist Infectious Diseases Specialist Professor of Medicine The University of Crete, Heraklion,, Crete, Greece
Treatment of febrile neutropenia in patients with neoplasia George Samonis MD, PhD Medical Oncologist Infectious Diseases Specialist Professor of Medicine The University of Crete, Heraklion,, Crete, Greece
CLINICAL USE OF GLYCOPEPTIDES. Herbert Spapen Intensive Care Department University Hospital Vrije Universiteit Brussel
 CLINICAL USE OF GLYCOPEPTIDES Herbert Spapen Intensive Care Department University Hospital Vrije Universiteit Brussel Glycopeptides Natural Vancomycin introduced in 1958 Teicoplanin introduced in Europe
CLINICAL USE OF GLYCOPEPTIDES Herbert Spapen Intensive Care Department University Hospital Vrije Universiteit Brussel Glycopeptides Natural Vancomycin introduced in 1958 Teicoplanin introduced in Europe
PHARMACOKINETIC & PHARMACODYNAMIC OF ANTIBIOTICS
 PHARMACOKINETIC & PHARMACODYNAMIC OF ANTIBIOTICS SITI HIR HURAIZAH MD TAHIR Bpharm (UKM), MSc (Clinical Microbiology) (UoN) CLINICAL PHARMACIST HOSPITAL MELAKA WHY STUDY PHARMACOKINETICS (PK) AND PHARMACODYNAMICS
PHARMACOKINETIC & PHARMACODYNAMIC OF ANTIBIOTICS SITI HIR HURAIZAH MD TAHIR Bpharm (UKM), MSc (Clinical Microbiology) (UoN) CLINICAL PHARMACIST HOSPITAL MELAKA WHY STUDY PHARMACOKINETICS (PK) AND PHARMACODYNAMICS
Community Acquired & Nosocomial Pneumonias
 Community Acquired & Nosocomial Pneumonias IDSA/ATS 2007 & 2016 Guidelines José Luis González, MD Clinical Assistant Professor of Medicine Outline Intro - Definitions & Diagnosing CAP treatment VAP & HAP
Community Acquired & Nosocomial Pneumonias IDSA/ATS 2007 & 2016 Guidelines José Luis González, MD Clinical Assistant Professor of Medicine Outline Intro - Definitions & Diagnosing CAP treatment VAP & HAP
HUSRES Annual Report 2009 Martti Vaara
 HUSRES Annual Report 2009 Martti Vaara www.huslab.fi www.intra.hus.fi Martti Vaara, 2/2010 1 The basis of this HUSRES 2009 report is the HUSLAB/Whonet database 2009, which contains susceptibility data
HUSRES Annual Report 2009 Martti Vaara www.huslab.fi www.intra.hus.fi Martti Vaara, 2/2010 1 The basis of this HUSRES 2009 report is the HUSLAB/Whonet database 2009, which contains susceptibility data
Doripenem: pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. Paul M. Tulkens, MD, PhD Françoise Van Bambeke, PharmD, PhD
 16/04/2009 1 Doripenem: pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics Paul M. Tulkens, MD, PhD Françoise Van Bambeke, PharmD, PhD Unité de Pharmacologie cellulaire et moléculaire Louvain Drug Research Institute
16/04/2009 1 Doripenem: pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics Paul M. Tulkens, MD, PhD Françoise Van Bambeke, PharmD, PhD Unité de Pharmacologie cellulaire et moléculaire Louvain Drug Research Institute
ESCMID Online Lecture Library. by author
 Novel PK/PD data on the optimisation of colistin and the carbapenems Diamantis Plachouras Athens, Greece Hot Topics on Infections in the Critically Ill Patient, ESCMID Postgraduate Education Course, 31
Novel PK/PD data on the optimisation of colistin and the carbapenems Diamantis Plachouras Athens, Greece Hot Topics on Infections in the Critically Ill Patient, ESCMID Postgraduate Education Course, 31
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION. 18 October 2006
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 18 October 2006 CUBICIN 350 mg (daptomycin), powder for perfusion solution Box of 1 bottle (CIP code: 567 219-3) CUBICIN
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 18 October 2006 CUBICIN 350 mg (daptomycin), powder for perfusion solution Box of 1 bottle (CIP code: 567 219-3) CUBICIN
The role of an AMR reference laboratory
 The role of an AMR reference laboratory Professor Neil Woodford Antimicrobial Resistance & Healthcare Associated Infections (AMRHAI) Reference Unit Crown copyright Primary purpose: regional AMR threats
The role of an AMR reference laboratory Professor Neil Woodford Antimicrobial Resistance & Healthcare Associated Infections (AMRHAI) Reference Unit Crown copyright Primary purpose: regional AMR threats
ICU Volume 11 - Issue 3 - Autumn Series
 ICU Volume 11 - Issue 3 - Autumn 2011 - Series Impact of Pharmacokinetics of Antibiotics in ICU Clinical Practice Introduction The efficacy of a drug is mainly dependent on its ability to achieve an effective
ICU Volume 11 - Issue 3 - Autumn 2011 - Series Impact of Pharmacokinetics of Antibiotics in ICU Clinical Practice Introduction The efficacy of a drug is mainly dependent on its ability to achieve an effective
Academic Perspective in. David Livermore Prof of Medical Microbiology, UEA Lead on Antibiotic resistance PHE
 Academic Perspective in Emerging No, we can t Issues treat of carbapenemase Resistance and ESBL in Gram-ve producers Bacteria based on MIC David Livermore Prof of Medical Microbiology, UEA Lead on Antibiotic
Academic Perspective in Emerging No, we can t Issues treat of carbapenemase Resistance and ESBL in Gram-ve producers Bacteria based on MIC David Livermore Prof of Medical Microbiology, UEA Lead on Antibiotic
Optimizing Polymyxin Combinations Against Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria
 Infect Dis Ther (2015) 4:391 415 DOI 10.1007/s40121-015-0093-7 REVIEW Optimizing Polymyxin Combinations Against Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria Phillip J. Bergen Zackery P. Bulman Cornelia B. Landersdorfer
Infect Dis Ther (2015) 4:391 415 DOI 10.1007/s40121-015-0093-7 REVIEW Optimizing Polymyxin Combinations Against Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria Phillip J. Bergen Zackery P. Bulman Cornelia B. Landersdorfer
New treatments of multidrug-resistant Gram-negative ventilatorassociated
 Review Article Page 1 of 22 New treatments of multidrug-resistant Gram-negative ventilatorassociated pneumonia Garyphallia Poulakou 1, Styliani Lagou 1, Drosos E. Karageorgopoulos 2, George Dimopoulos
Review Article Page 1 of 22 New treatments of multidrug-resistant Gram-negative ventilatorassociated pneumonia Garyphallia Poulakou 1, Styliani Lagou 1, Drosos E. Karageorgopoulos 2, George Dimopoulos
