Histopathological liver changes in natrium fluoride administration to a population of mice NMRI type
|
|
|
- Brian Gilmore
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ORIGINAL PAPER J. Transl. Med. Res 2015;20(2):82-88 Histopathological liver changes in natrium fluoride administration to a population of mice NMRI type Violetta Băran Poesina 1, Andreea Dimcevici Poesina 2, Dumitru Dobrescu 2, Simona Negreș 3, Cornel Chirita 3, Nicolae Bacalbașa 4, Nicoleta Dimcevici-Poesina 5 Corresponding author: Violetta Bãran Poesina, MD Dental-Sinus VPB, Bucharest, Romania violetta.poesina@gmail.com 1 Dental-Sinus VPB, Bucharest, Romania 2 Catena Pharmacy, Bucharest, Romania 3 Pharmacology Department, Faculty of Pharmacy, Carol Davila University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Bucharest, Romania 4 Carol Davila University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Bucharest, Romania 5 Applied Mathematics and BiostatisticsDepartment, Faculty of Pharmacy, Carol Davila University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Bucharest, Romania ABSTRACT It has been revealed that excessive fluoride intake on long-term is associated with toxic effects and can damage a variety of organs and tissues in the human body, for example, the liver tissue. The molecular mechanisms of fluoride-induced hepato-toxicity are not well understood. The study wants to offer up-to-date insights concerning the effects of natrium fluoride on hepatic tissues when this substance is administrated to a population of mice. The study was conducted on NMRI mice descending from the pregnant females treated with 0.25 mg and 0.5 mg natrium fluoride by daily gavage, from the beginning of pregnancy until the lactation was ceased. Then, the mice, males and females, were divided in six groups, three groups descending from the pregnant females treated with 0.5 mg natrium fluoride (Groups 1A, 1B and 1C ) and three groups from the pregnant females with 0.25 mg natrium fluoride (Groups 2D, 2E and 2F). From the moment the lactation is finished until adulthood, the animals received the following treatments: homeopathic (a CH7 solution of natrium fluoride Groups A and D), allopathic-homeopathic (0.25 mg natrium fluoride administered like drinking water ad libitum and CH7 solution of natrium fluoride Group E; 0.5 mg natrium fluoride administered like drinking water ad libitum and CH7 solution of natrium fluoride Group B), and allopathic administration of natrium fluoride (0.25 mg natrium fluoride like drinking water ad libitum Group F; 0.5 mg natrium fluoride like drinking water ad libitum Group C). When the males reached adulthood, the administration of natrium fluoride was stopped and, by randomization, they were selected for euthanasia. The euthanasia was realized by cervical dislocation. The testes for the histopathological examination were preserved in a 10% formalin solution. The preparation of samples for optical microscopy was realized with Hematoxylin-Eosin staining. The results indicate that natrium fluoride administered in different doses, even in homeopathic dose or in allopathic-homeopathic dose, determined centrolobular vacuolar dystrophy of hepatic tissue, cariomegalia, granulovacuolar dystrophy, centrolobular hyperemia centrolobular degenerescences of hepatocytes and discreet centrolobular apoptosis. Copyright Celsius Publishing House Key words: natrium fluoride, histopathology, mice, hepatic tissue 82 Journal of Translational Medicine and Research, 20 (2), 2015
2 Histopathological liver changes in natrium fluoride administration to a population of mice NMRI type INTRODUCTION The administration of fluoride during human growth and development has raised numerous questions about the effects on various organs. Because the natrium fluoride is administrated from birth to adulthood in humans, for 18 years, some of the studies aim to demonstrate the effect of natrium fluoride following long-term oral administration. The exposure to natrium fluoride revealed various modifications on the liver of animals or humans. Recent studies found that the exposure at fluoride doses of 1,5 mg/kg induces the apoptosis and the increase of intracellular calcium concentration. In addition, the presence and the level of PI3K-Akt signal the liver injury caused by fluorosis (1). Several studies reveal that drinking water fluoride levels over 2.0 mg/l can cause liver damage and kidney dysfunctions in children and that the dental fluorosis was independent of damage to the liver but not the kidney. Further studies on the mechanisms and significance underlying damage to the liver without dental fluorosis in the exposed children are warranted (2). In some cases of administration of isoflurane or halothane in anesthesia for cesarean section, the serum fluoride concentrations in the mother after anesthesia were not significantly above preanesthetic levels and there was no biochemical evidence of tissues toxicity- in this study, the renal tissue. In all neonates fluoride ion concentrations in the first voided urine sample were less than 7 µmol/l, a value well below that associated with nephrotoxicity (3). The effect of oral administration of fluoride may vary depending on the dose, duration of exposure and species, and include anemia and leukopenia (4). For natrium fluoride, the doses administered are in a very large range of values, up to 120 mg, as it has beenshown by a study about a single case of acute fluoride poisoning in a man. Following the ingestion of 120 mg of sodium fluoride, multiple reactions like tetany, multiple episodes of ventricular fibrillation and an esophageal stricture were observed (5). For some substances, the detection of drugs or other types of poison in various tissues and organs may be sufficient to prove exposure (6). Tolerable Upper Intake Level for natrium fluoride is not yet defined (7). Because of the daily fluoride intake in fluoridated areas estimated to 0,20 mg/kg/day for adults and 0.11 mg/kg/day for infants, the reasonable maximum exposure (RME) estimates were above the upper tolerable intake limit (8,9). For natrium fluoride not only the presence of substance is necessary in order to diagnose exposure, but also to detect, for example, histopathological alterations of tissues. The physiologists, pathologists and hepatologists studied hepatic stellate cells over 130 years and they reached the conclusion that the cells we mentioned have an important role in hepatic injury and fibrosis. Those alterations could be appreciated with refinement methods of cell isolation and characterization (10). The signals inducing apoptosis are very varied and the same signals can induce differentiation and proliferation in other situations. However, some pathways appear to be of particular significance in the control of cell death; recent analysis of the apoptosis induced through the cell-surface Fas receptor has been especially important for immunology (11). The administration of natrium fluoride has less effect on the tissues when blackberry and quercetin are administrated because of the synergistic effects of flavonoids on all antioxidant and histological parameters (12). When administrated, flouride showed significant increased oxidative damage of hepatocytes; consistent with the increased MDA levels and decreased levels of ascorbate in tissue and free radical scavenging enzymes like catalase, superoxide dismutase, and glutathione peroxidase (13,14). The exposure of a cell culture to natrium fluoride shows a loss of mitochondrial membrane potential (delta Psi)(8). The structural unit of the liver, the hepatic lobule, is modeled on the blood flow within the liver and is commonly used for descriptive pathology and morphological diagnoses (15). The present study aims to investigate the possible histopathological changes in the liver tissue of mice, when fluoride is administered in three doses: allopathic dose (0.25 mg natrium fluoride and 0.5 mg natrium fluoride, administered ad libitum like drinking water), homeopathic dose (CH7) and allopathic - homeopathic dose. MATERIALS AND METHODS Animals and treatment The study was performed on NMRI-type mice. All researches were conducted in accordance with the European Directive 86/609/EEC/ , the European Convention on the Protection of Vertebrate Animals (2005) and the Romanian Government Ordinance No. 37/2002 regarding the protection of animals used for experimental and other scientific purposes (8,16). Journal of Translational Medicine and Research, 20 (2),
3 Violetta Bãran Poesina et al The administration is realized in three different doses: homeopathic, allopathic and allopathichomeopathic. The substances administrated are different doses of natrium fluoride: 0.25 mg natrium fluoride, 0.5 mg natrium fluoride, and CH7 homeopathic solutions. The animals for the experiments are descendants from two kinds of maternal parents: pregnant females (mothers) treated with 0.25 mg natrium fluoride and pregnant females (mothers) treated with 0.5 mg natrium fluoride, daily administered by gavage, during pregnancy and lactation. The experimental animals were classified in six groups, males and females, compared with males and females control. The descendants were divided into Groups 1A, 1B, 1C, 2D, 2E, 2F, males and females. Groups 1A, 1B, 1C are descendants from the mothers with 0.5 mg natrium fluoride allopathic administration and Groups 2D, 2E, 2F are descendants from the mothers with 0.25 mg natrium fluoride allopathic administration. Groups 1A and 2D Homeopathic administration by gavage with one channel micropipette of a CH7 dilution of a natrium fluoride solution; Groups 1B and 2E Homeopathic administration by gavage with one channel micropipette of a CH7 dilution of a natrium fluoride solution with allopathic administration of 0.5 mg natrium fluoride ad libitum (Group 1B), respectively of a CH7 dilution of a natrium fluoride solution with allopathic administration of 0.25 mg natrium fluoride ad libitum (Group 2E), males and females; Groups 1C and 2F Allopathic administration of 0.5 mg natrium fluoride ad libitum (Group 1C), respectively allopathic administration of 0.25 mg natrium fluoride ad libitum (Group 2F), males and females. Histopathologic assessment of liver When mice reached adulthood, they were selected by randomization for euthanasia. For the histopathological examination, the animals were killed by cervical dislocation, the testes from every specimen selected for the examination were taken and introduced in a 10% formalin solution. The preparation of samples for optical microscopy was realized with Hematoxylin-Eosin staining (17). RESULTS The classification of experimental groups and the doses administrated for every group are highlighted in table 1. Histopathological assessment of liver (table 2) Microscopic evaluation We observed binucleate hepatocytes, which is common in mice liver and discrete hyperemia to the control group. When the substance is administrated, we can observe that vacuolar dystrophy is common in all groups, but apoptosis, apoptotic corpse and necrosis are more common for the allopathic doses. We can observe that at the macroscopic examination, the liver is dystrophic and discolored. For group 1A, descending from pregnant females with 0,5 mg natrium fluoride daily administration by gavage, and, after birth until adulthood, with homeopathic dose (CH7), we discovered that cariomegalia, anisocytosis, vacuolar dystrophy and granular dystrophy are present. (figure 1) For group 1B, descending from pregnant females with 0,5 mg natrium fluoride daily administration by gavage, and after birth until adulthood with homeo- Table 1 - The classification of experimental groups by dosage No Groups Dose of administered natrium fluoride (males and female) 1 Control group None 2 Group 1A Homeopathic administration by gavage with one channel micropipette of a CH7 dilution of natrium fluoride solution 3 Group 1B Homeopathic administration by gavage with one channel micropipette of a CH7 dilution of natrium fluoride solution with allopathic administration of 0,5 mg natrium fluoride ad libitum 4 Group 1C Allopathic administration of 0,5 mg natrium fluoride solution ad libitum 5 Group 2D Homeopathic administration by gavage with one channel micropipette of a CH7 dilution of natrium fluoride solution 6 Group 2E Homeopathic administration by gavage with one channel micropipette of a CH7 dilution of natrium fluoride solution with allopathic administration of mg natrium fluoride ad libitum 7 Group 2F Allopathic administration of 0,5 mg natrium fluoride solution ad libitum 84 Journal of Translational Medicine and Research, 20 (2), 2015
4 Histopathological liver changes in natrium fluoride administration to a population of mice NMRI type Table 2 - Pathological aspects of liver tissue revealed at the histopathological examination for every group No Groups Pathological aspects (males and female) 1 Control group Discrete hyperemia, binucleate hepatocytes (normal), cariomegalia, without mythosis 2 Group 1A Cariomegalia, anisocitosis, vacuolar dystrophy, granular dystrophy 3 Group 1B Diffuse vacuolar dystrophy, discrete hyperemia, cariomegalia with big cell nuclei 4 Group 1C Mononucleate and binucleate hepatocytes, cariomegalia, numerous cytoplasmic granules, apoptosis, apoptotic corpse, necrosis. Macroscopically: dystrophic liver, discoloration 5 Group 2D Apoptosis, vacuolar dystrophy, apoptotic corpse, cariomegalia 6 Group 2E Vacuolar dystrophy, anisokariosys, apoptosis Macroscopically: dystrophic liver 7 Group 2F Vacuolar dystrophy, centrilobular apoptosis, anisokariosys a b Figure 1 - Granulo-vacuolare dystrophy (H- E staining 400 x). Uninucleate and binucleate hepatic cells with granules and vacuolization; the cells nuclei remains stable, are not removed by granules or vacuolization pathic- allopathic dose (CH in drinking water ad libitum), we found diffuse vacuolar dystrophy, discrete hyperemia, cariomegaliawith big cell nuclei. (figure 2 a, b) For group 1C, descending from pregnant females with 0,5 mg natrium fluoride daily administration by gavage and after birth until adulthood with allopathic dose (0.5 in drinking water ad libitum), the morphological aspects consist inmononucleate and binucleate hepatocytes, cariomegalia, numerous cytoplasmic granules, apoptosis, apoptotic corpse, necrosis. Macroscopically: dystrophic liver, discoloration. (figure 3 a,b,c) For group 2D, descending from pregnant females with 0,25 mg natrium fluoride daily administration by gavage and, after birth until adulthood, with homeopathic dose (CH7) the microscpy revealed apoptosis, vacuolar dystrophy, apoptotic corpse and cariomegalia. (figure 4) Figure 2 - (a) Cells with eucromatic nuclei, isolated cariomegalia; binucleate hepatic cells (arrow) (HE 100X). (b) Vacuolar dystrophy and apoptotic corpse. Vacuoles does not change the position of the cells nuclei (H- E staining 100X). For group 2E, descending from pregnant females with 0,25 mg natrium fluoride daily administration by gavage, and, after birth until adulthood, with homeopathic - allopathic dose (CH in drinking water Journal of Translational Medicine and Research, 20 (2),
5 Violetta Bãran Poesina et al a b c Figure 3 - (a) - liver apoptosis (H-E staining 200X), (b) - liver apoptosis (apoptotic corpse) (arrow) (H-E staining 400X), (c) - liver apoptosis (apoptotic corpse) (arrow) (H-E staining 400X) Figure 4 - Uninucleate and binucleate hepatic cells with intracitoplasmatic granules and vacuolisation (arrow). Some of cells have excentric nuclei, cariomegalia and regenerative processes (binucleate cells) (H-E staining 200X) Figure 5 - Vacuolar dystrophy and apoptotic corpse (arrow) (HE 100X) ad libitum), we found vacuolar dystrophy, anisokariosys, and apoptosis. Macroscopically: dystrophic liver. (figure 5) For group 2F, descending from pregnant females with 0,25 mg natrium fluoride daily administration by gavage, and, after birth until adulthood, with allopathic dose (0.25 in drinking water ad libitum), we found vacuolar dystrophy, centrilobular apoptosis, and anisokariosys. (figure 6) DISCUSSION Previous studies have shown that fluoride impaired liver function and produced histopathological changes (18,19,20,21). The present study aims to assess the effect of natrium fluoride administration, at different dosages on histopathological changes of the liver during all childhood of mice NMRI type until adulthood. The control group had liver tissue characterised by the presence of the binucleated cells or cariomegalia 86 Journal of Translational Medicine and Research, 20 (2), 2015
6 Histopathological liver changes in natrium fluoride administration to a population of mice NMRI type Figure 6 - Apoptosis and vacuolar dystrophy. Apoptotic corpse. (H-E staining 400X) without mithosys. However, the experimental group, exposed to sodium fluoride, demonstrated the presence of these liver changes, characterized by the difuse aspects. The histopathological aspect of the liver is different depending on every dose administrated. The present study revealed that homeopathic doses have minimum influence on the hepatic cells, including cariomegalia and vacuolisation and minimum apoptotic cells. The allopathic - homeopathic dose is augmentated by the hyperemia and centrilobular necrosis; apoptosis is also present. Anisokariosis is present for the groups with allopathic doses and allopathic - homeopathic doses. Apoptosis is typical for liver disease. It could occur at different levels, depending on various factors that produce hepatocyte injuries (at organite level or membrane). The affected liver depends on the presence of quantities of apoptotic cells. The apoptotic cells and the necrotic cells characterized two important aspects of cells death. Apoptosis is the first manifestation of the affected cell that is going to die, and various biochemical mecanisms are involved. Also, the apoptotic cells have particular histopatological aspects and the tissue examination reveals information about the health level of the liver. In the present study, the most important pathological liver changes following the natrium fluoride allopathic administration were apoptosis, the presence of apoptotic corps orcentrilobular necrosis. These results are consistent with data reported by Wang et al. in which 40-day exposure to sodium fluoride of rabbits produced hepatocyte necrosis and vacuolar degeneration (22). Other data regarding natrium fluoride administration revealed apoptosis present in other tissues, like the oral mucosal cells (was ( /- 1.81) % in fluoride group, and ( /- 1.67)% in hepatocytes, higher than those in control group (23). Also, the mean values of relative liver and kidney weights at a 100 and 150 ppm natrium fluoride in a population of mice were significantly lower than those in the control group. The mean values of BUN, creatinine, and GPT at the 150 ppm natrium fluoride dose for the experimental groups were significantly higher than those in the control (24). Other cells where apoptosis produced by natrium fluoride is detected are the hippocampal neurons. At a 40 to 80 mg/l of fluoride significantly increased level of lactate dehydrogenaseis induced, the presence of intracellular reactive oxygen species, and a percentage of apoptosis (25). In skeletal tissue the fluoride treatment inhibits osteoblasts proliferation and a significant increase of osteoblast apoptosis was observed (after 24 and 72 hours treatment, at the lowest dose of sodium fluoride mg/l). The osteoblast apoptosis was further increased in response to higher doses (26). Apoptosis produced by natrium fluoride is studied at the level of hippocampal neurons. At 40 and 80 mg/l of fluoride the neuronal apoptosis is significantly increased (25). The administration of 10 to 100 µg/kg body weight sodium fluoride on male Wistar rats aging 75 days and with a DNA study after 2 hours of the administration of substance, a genotoxic effect in multiple organs has not been revealed (27). Changes are also present at the macroscopic level: alterations of the liver, such asdystrophya and discoloration, both in males and females. The pathophysiological mechanisms revealed death receptor mediated cascade, lysosomal permeabilisation, mitochondrial dysfunction (28), as well asantiapoptotic mechanisms. The study of nano-sized tin colloid can be used to determine the detection in different tissues of agentslike tin fluoride, sodium fluoride, poloxamer-188 and polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP), mixed and labeled with (99m) TC (29). In addition, flow-cytometry could be a technique for the quantitative analysis of apoptosis (apoptotic cells as subdiploid peak ) (30-34). CONCLUSIONS The study revealed that at different doses of natrium fluoride, the morphological aspect of liver in male and in female mice is modified. These modifications are vacuolar dystrophy and granular dystrophy, cariomegalia with big cell nuclei, mononucleate and Journal of Translational Medicine and Research, 20 (2),
7 Violetta Bãran Poesina et al binucleate hepatocytes, cariomegalia, numerous cytoplasmic granules, apoptosis, apoptotic corpse, necrosis. Macroscopically: dystrophic liver, discoloration. The significant modifications are present at the allopathic dose. The presence of the apoptotic cells and apoptotic corps revealed the hepatotoxicity of natrium fluoride. In some cases, necrosis is present and indicates the next stage of cells damages. Necrosis accompanies apoptosis and indicates the level of hepatotoxicity of natrium fluoride, especially at the allopathic doses. Interestingly, the homeopathic dose also indicates a level of hepato-toxicity (with vacuolar dystrophy and granular dystrophy). Further studies are necessary regarding the changes at cellular level, and at the level of cytoplasmic organelles and cell nuclei (DNA studies). REFERENCES 1. Fan B, Yu Y, Zhang Y. PI3K-Akt1 expression and its significance in liver tissues with chronic fluorosis. 2015;8(2): Xiong X. Dose effect relationship between drinking water fluoride levels and damage to liver and kidney functions in children. 2007;103: Abboud TK, D'Onofrio L, Reyes A, Mosaad P, Zhu J, Mantilla M, et al. Isoflurane or halothane for cesarean section: comparative maternal and neonatal effects. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand Oct;33(7): Eren E1, Ozturk M, Mumcu EF, Canatan D. Fluorosis and its hematological effects. Toxicol Ind Health Nov;21(10): Abukurah AR, Moser AM Jr, Baird CL, Randall RE Jr, Setter JG, Blanke RV. Acute sodium fluoride poisoning. JAMA Nov 13;222(7): Flanagan RJ, Connally G, Evans JM. Analytical toxicology: guidelines for sample collection postmortem. Toxicol Rev. 2005;24(1): Augenstein WL, Spoerke DG, Kulig KW, Hall AH, Hall PK, Rigs BS. Fluoride ingestion in cildren: a rewiew of 87 cases. 1991; 88: Carson F. Histotechnology: A Self-Instructional Text Erdal S, Buchanan SN. A Quantitative Look at Fluorosis, Fluoride Exposure, and ntake in Children Using a Health Risk Assessment Approach. Environ. 2005;113: Friedman S. Hepatic stellate cells: Protean, multifunctional, and enigmatic cells of the liver. 2008;88: Hale AJ, Smith CA, Sutherland LC, Stoneman VEA, Longthorne VL, Culhane AC, et al. Apoptosis: molecular regulation of cell death. 1996;236: Hamza RZ, El-Shenawy NS, Ismail HA. Protective effects of blackberry and quercetin on sodium fluoride-induced oxidative stress and histological changes in the hepatic, renal, testis and brain tissue of male rat. 2015; 26(3): Raina R, Baba NA, Verma PK, Sultana M, Singh M. Hepatotoxicity Induced by Subchronic Exposure of Fluoride and Chlorpyrifos in Wistar Rats: Mitigating Effect of Ascorbic Acid. Biol Trace Elem Res Feb 12. [Epub ahead of print] 14. Anuradha CD, Kanno S, Hirano S. Oxidative damage to mitochondria is a preliminary step to caspase-3 activation in fluoride-induced apoptosis in HL-60 cells. Free Radic Biol Med Aug 1;31(3): Thoolen B, Maronpot RR, Harada T, Nyska A, Rousseaux C, Nolte T, et al. Proliferative and nonproliferative lesions of the rat and mouse hepatobiliary system. Toxicol Pathol Dec;38(7 Suppl):5S-81S. doi: / Chen J, Chen X, Yang K, Xia T, Xie H. Studies on DNA damage and apoptosis in rat brain induce by fluoride. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi Jul;36(4): [Article in Chinese] 17. Duvall E, Wyllie AH, Morris RG. Macrophage recognition of cells undergoing programmed cell death (apoptosis). Immunology Oct; 56(2): Grucka-Mamczar E, Machoy M, Tarnawski R, Birkner E, Mamczar A, Influence of long term sodium floride administration on selected parameters of rat blood serum and liver function. 1997;30(3): Kapoor V, Prasad T, Bhatia KC. Effect of dietary fluorine on histopathological changes in calves. 1993;26(2): Kessabi M, Hamliri A, Braun JP. Experimental fluorosis in sheep: alleviating effects of aluminum. Vet Hum Toxicol Aug;28(4): Atmaca N, Atmaca HT, Kanici A, Anteplioglu T. Protective effect of resveratrol on sodium fluoride-induced oxidative stress, hepatotoxicity and neurotoxicity in rats. Food Chem Toxicol Aug;70: doi: /j.fct Epub 2014 May Wang J, Zheng Z, Zhang L, Cao D, Chen K, Lu D. An experimental study for early diagnostic features in fluorosis. Fluoride ;1: He LF1, Chen JG. DNA damage, apoptosis and cell cycle changes induced by fluoride in rat oral mucosal cells and hepatocytes. World J Gastroenterol Feb 21;12(7): Hosokawa M, Asakawa H, Kaido T, Sugaya C, Tsunoda M, Itai K, et al. Fluoride in drinking water exacerbates glomerulonephritis and induces liver damage in ICR-derived glomerulonephritis mice. 2011;93(10): Zhang M, Wang A, He W, He P, Xu B, Xia T, et al. Effects of fluoride on the expression of NCAM, oxidative stress, and apoptosis in primary cultured hippocampal neurons. Toxicology Jul 17;236(3): Yan X, Feng C, Chen Q, Li W, Wang H, Lv L, et al. Effects of sodium fluoride treatment in vitro on cell proliferation, apoptosis and caspase-3 and caspase-9 mrna expression by neonatal rat osteoblasts. Arch Toxicol May;83(5): doi: /s z. 27. Leite Ade L, Santiago JF Jr, Levy FM, Maria AG, Fernandes Mda S, Salvadori DM, Ribeiro DA, Buzalaf MA. Absence of DNA damage in multiple organsblood, liver, kidney, thyroid gland and urinary bladder) after acutefluoride exposure in rats. Hum Exp Toxicol May;26(5): K Wang. Molecular mechanisms of hepatic apoptosis. Cell Death and Disease (2014) 5, e996; doi: /cddis Kim EM, Lim ST, Sohn MH, Jeong HJ. Size Control of (99m)Tc-tin Colloid Using PVP and Buffer Solution for Sentinel Lymph Node Detection. J Korean Med Sci Jun;30(6): doi: /jkms Epub 2015 May Zamai L, Falcieri E, Zauli G, Cataldi A, Vitale M. Optimal detection of apoptosis by flow cytometry depends on cell morphology. Cytometry Nov;14(8): Erlandsen SL, Magney J. Vols. Mosby-Year Book, Fomon SJ, Ekstrand J. Fluoride intake by infants. J Public Health Dent Fall;59(4): Fox J. The Mouse in Biomedical Research Greaves P. Histopathology of Preclinical Toxicity Studies: Interpretation and Relevance in Drug Safety Evaluation Journal of Translational Medicine and Research, 20 (2), 2015
R J M E Romanian Journal of Morphology & Embryology
 Rom J Morphol Embryol 2014, 55(2):343 349 ORIGINAL PAPER R J M E Romanian Journal of Morphology & Embryology http://www.rjme.ro/ Histopathological changes of renal tissue following sodium fluoride administration
Rom J Morphol Embryol 2014, 55(2):343 349 ORIGINAL PAPER R J M E Romanian Journal of Morphology & Embryology http://www.rjme.ro/ Histopathological changes of renal tissue following sodium fluoride administration
R J M E Romanian Journal of Morphology & Embryology
 Rom J Morphol Embryol 2013, 54(4):1019 1024 ORIGINAL PAPER R J M E Romanian Journal of Morphology & Embryology http://www.rjme.ro/ Testicular histopathological changes following sodium fluoride administration
Rom J Morphol Embryol 2013, 54(4):1019 1024 ORIGINAL PAPER R J M E Romanian Journal of Morphology & Embryology http://www.rjme.ro/ Testicular histopathological changes following sodium fluoride administration
FLUORIDE EFFECTS ON GLUTATHIONE PEROXIDASE AND LIPID PEROXIDATION IN RATS
 Fluoride Vol. 37 No. 1 7 12 2004 Research Report 7 FLUORIDE EFFECTS ON GLUTATHIONE PEROXIDASE AND LIPID PEROXIDATION IN RATS I Inkielewicz, a J Krechniak a,b Gdańsk, Poland SUMMARY: Eight-week old male
Fluoride Vol. 37 No. 1 7 12 2004 Research Report 7 FLUORIDE EFFECTS ON GLUTATHIONE PEROXIDASE AND LIPID PEROXIDATION IN RATS I Inkielewicz, a J Krechniak a,b Gdańsk, Poland SUMMARY: Eight-week old male
SODIUM FLUORIDE INDUCED HISTOPATHALOGICAL CHANGES IN LIVER AND KIDNEY OF ALBINO MICE
 ACPI Acta Chim. Pharm. Indica: 4(1), 2014, 58-62 ISSN 2277-288X SODIUM FLUORIDE INDUCED HISTOPATHALOGICAL CHANGES IN LIVER AND KIDNEY OF ALBINO MICE S. KHADAR BASHA * and K. JAYANTHA RAO Division Toxicology,
ACPI Acta Chim. Pharm. Indica: 4(1), 2014, 58-62 ISSN 2277-288X SODIUM FLUORIDE INDUCED HISTOPATHALOGICAL CHANGES IN LIVER AND KIDNEY OF ALBINO MICE S. KHADAR BASHA * and K. JAYANTHA RAO Division Toxicology,
HISTOLOGICAL CHANGES IN THE BRAIN OF YOUNG FLUORIDE-INTOXICATED RATS
 12 Fluoride Vol. 35 No. 1 12-21 2002 Research Report HISTOLOGICAL CHANGES IN THE BRAIN OF YOUNG FLUORIDE-INTOXICATED RATS YM Shivarajashankara, a AR Shivashankara, a P Gopalakrishna Bhat, b S Muddanna
12 Fluoride Vol. 35 No. 1 12-21 2002 Research Report HISTOLOGICAL CHANGES IN THE BRAIN OF YOUNG FLUORIDE-INTOXICATED RATS YM Shivarajashankara, a AR Shivashankara, a P Gopalakrishna Bhat, b S Muddanna
APPENDIX C: TRANSLATION OF CHINESE/FETAL BONE STUDY. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi (Chinese Journal of Preventive Medicine) Mar; 29(2):
 APPENDIX C: TRANSLATION OF CHINESE/FETAL BONE STUDY Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi (Chinese Journal of Preventive Medicine). 1995 Mar; 29(2):103-105 Relationship Between Bone Fluoride Content, Pathological
APPENDIX C: TRANSLATION OF CHINESE/FETAL BONE STUDY Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi (Chinese Journal of Preventive Medicine). 1995 Mar; 29(2):103-105 Relationship Between Bone Fluoride Content, Pathological
IMPACT OF FLUORIDE AND SUPEROXIDE DISMUTASE ON THE GOLGI APPARATUS IN RAT RIB-CAGE CHONDROCYTES
 13 13 IMPACT OF FLUORIDE AND SUPEROXIDE DISMUTASE ON THE GOLGI APPARATUS IN RAT RIB-CAGE CHONDROCYTES Yanni Yu, a Binjie Meng a Guizhou, China SUMMARY: Chondrocytes of rib-cage cartilage from Wistar rats
13 13 IMPACT OF FLUORIDE AND SUPEROXIDE DISMUTASE ON THE GOLGI APPARATUS IN RAT RIB-CAGE CHONDROCYTES Yanni Yu, a Binjie Meng a Guizhou, China SUMMARY: Chondrocytes of rib-cage cartilage from Wistar rats
EPA Health Advisory for PFOA and PFOS Drinking Water
 EPA Health Advisory for PFOA and PFOS Drinking Water David Klein, Ph.D Postdoctoral Fellow Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Brown University David_Klein@brown.edu Outline PFOA Background How did the advisory
EPA Health Advisory for PFOA and PFOS Drinking Water David Klein, Ph.D Postdoctoral Fellow Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Brown University David_Klein@brown.edu Outline PFOA Background How did the advisory
5.17 PENTHIOPYRAD (253)
 Penthiopyrad 189 5.17 PENTHIOPYRAD (253) TOXICOLOGY Penthiopyrad is the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) approved name for N-[2- (1,3-dimethylbutyl)-3-thienyl]-1-methyl-3-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxamide
Penthiopyrad 189 5.17 PENTHIOPYRAD (253) TOXICOLOGY Penthiopyrad is the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) approved name for N-[2- (1,3-dimethylbutyl)-3-thienyl]-1-methyl-3-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxamide
5.15 HEXYTHIAZOX (176)
 Hexythiazox 225 5.15 HEXYTHIAZOX (176) TOXICOLOGY Hexythiazox is the ISO approved name for (trans-5-(4-chlorophenyl)-n-cyclohexyl-4-methyl-2-oxo- 3-thiazolidine-carboxamide (CAS No. 78587-05-0). Hexythiazox
Hexythiazox 225 5.15 HEXYTHIAZOX (176) TOXICOLOGY Hexythiazox is the ISO approved name for (trans-5-(4-chlorophenyl)-n-cyclohexyl-4-methyl-2-oxo- 3-thiazolidine-carboxamide (CAS No. 78587-05-0). Hexythiazox
APOPTOSIS IN BRAIN CELLS OF OFFSPRING RATS EXPOSED TO HIGH FLUORIDE AND LOW IODINE
 173 Ge, Ning, Feng, Wang, Yan, Wang, Wang 173 APOPTOSIS IN BRAIN CELLS OF OFFSPRING RATS EXPOSED TO HIGH FLUORIDE AND LOW IODINE Yaming Ge, a,d Hongmei Ning, b Cuiping Feng, a Hongwei Wang, a Xiaoyan Yan,
173 Ge, Ning, Feng, Wang, Yan, Wang, Wang 173 APOPTOSIS IN BRAIN CELLS OF OFFSPRING RATS EXPOSED TO HIGH FLUORIDE AND LOW IODINE Yaming Ge, a,d Hongmei Ning, b Cuiping Feng, a Hongwei Wang, a Xiaoyan Yan,
COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
 The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Veterinary Medicines Evaluation Unit EMEA/MRL/114/96-FINAL June 1996 COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS EPRINOMECTIN SUMMARY REPORT
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Veterinary Medicines Evaluation Unit EMEA/MRL/114/96-FINAL June 1996 COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS EPRINOMECTIN SUMMARY REPORT
HISTOPATHOLOGY OF FLUORIDE-INDUCED HEPATOTOXICITY IN RABBITS
 34 Fluoride Vol. 34 No. 1 34-42 2000 Research Report HISTOPATHOLOGY OF FLUORIDE-INDUCED HEPATOTOXICITY IN RABBITS A Shashi, a SP Thapar b Patiala, India SUMMARY: The effect of chronic and acute exposure
34 Fluoride Vol. 34 No. 1 34-42 2000 Research Report HISTOPATHOLOGY OF FLUORIDE-INDUCED HEPATOTOXICITY IN RABBITS A Shashi, a SP Thapar b Patiala, India SUMMARY: The effect of chronic and acute exposure
Dr/ Sherein Saeid AbdElgayed, ph.d
 هللامسب Dr/ Sherein Saeid AbdElgayed, ph.d Professor of Veterinary Pathology, Cairo University, Giza, Egypt. Chairman of the Editorial Board of Arab Journal of Science & Research Publishing (AJSRP) http://www.ajsrp.com
هللامسب Dr/ Sherein Saeid AbdElgayed, ph.d Professor of Veterinary Pathology, Cairo University, Giza, Egypt. Chairman of the Editorial Board of Arab Journal of Science & Research Publishing (AJSRP) http://www.ajsrp.com
HEPATIC CELL INJURY BY ETHINYL OESTRADIOL ESTROGEN Pandey Govind a*, Pandey S.P. b and Madhuri S. c
 Research Article HEPATIC CELL INJURY BY ETHINYL OESTRADIOL ESTROGEN Pandey Govind a*, Pandey S.P. b and Madhuri S. c a* Ex-Professor & Head of Pharmacology (Pharmacy), presently Officer-In-Charge of Rinder
Research Article HEPATIC CELL INJURY BY ETHINYL OESTRADIOL ESTROGEN Pandey Govind a*, Pandey S.P. b and Madhuri S. c a* Ex-Professor & Head of Pharmacology (Pharmacy), presently Officer-In-Charge of Rinder
EFFECTS OF FLUORIDE ON LIPID PEROXIDATION IN RABBITS
 :185 189 Research report 185 EFFECTS OF FLUORIDE ON LIPID PEROXIDATION IN RABBITS M Akdogan, a G Eraslan, b F Gultekin, a F Sahindokuyucu, c D Essiz d Ankara and Isparta, Turkey SUMMARY: Twenty-one 6-month-old
:185 189 Research report 185 EFFECTS OF FLUORIDE ON LIPID PEROXIDATION IN RABBITS M Akdogan, a G Eraslan, b F Gultekin, a F Sahindokuyucu, c D Essiz d Ankara and Isparta, Turkey SUMMARY: Twenty-one 6-month-old
Impact factor: Reporter:4A1H0019 Chen Zi Hao 4A1H0023 Huang Wan ting 4A1H0039 Sue Yi Zhu 4A1H0070 Lin Guan cheng 4A1H0077 Chen Bo xuan
 Curcumin Protects Neonatal Rat Cardiomyocytes against High Glucose-Induced Apoptosis via PI3K/Akt Signalling Pathway Wei Yu,1,2 Wenliang Zha,1 Zhiqiang Ke,1 Qing Min,2 Cairong Li,1 Huirong Sun,3 and Chao
Curcumin Protects Neonatal Rat Cardiomyocytes against High Glucose-Induced Apoptosis via PI3K/Akt Signalling Pathway Wei Yu,1,2 Wenliang Zha,1 Zhiqiang Ke,1 Qing Min,2 Cairong Li,1 Huirong Sun,3 and Chao
COMPARATIVE EVALUATION OF ISOFLURANE AND SEVOFLURANE INNOCUITY ON SOME ORGANS AND TISSUES IN RAT
 RUXANDA FLAVIA COMPARATIVE EVALUATION OF ISOFLURANE AND SEVOFLURANE INNOCUITY ON SOME ORGANS AND TISSUES IN RAT (SUMMARY OF Ph.D. THESIS) SCIENTIFIC COORDINATOR: Prof. Univ. Dr. Liviu Ioan OANA Cluj-Napoca
RUXANDA FLAVIA COMPARATIVE EVALUATION OF ISOFLURANE AND SEVOFLURANE INNOCUITY ON SOME ORGANS AND TISSUES IN RAT (SUMMARY OF Ph.D. THESIS) SCIENTIFIC COORDINATOR: Prof. Univ. Dr. Liviu Ioan OANA Cluj-Napoca
Excerpts from: Fluoride in Drinking Water: A Scientific Review of EPA's Standards (National Research Council, 2006)
 Excerpts from: Fluoride in Drinking Water: A Scientific Review of EPA's Standards (National Research Council, 2006) Note 1: The page numbers for the following quotes are those shown on the pages of the
Excerpts from: Fluoride in Drinking Water: A Scientific Review of EPA's Standards (National Research Council, 2006) Note 1: The page numbers for the following quotes are those shown on the pages of the
Mechanistic Toxicology
 SECOND EDITION Mechanistic Toxicology The Molecular Basis of How Chemicals Disrupt Biological Targets URS A. BOELSTERLI CRC Press Tavlor & France Croup CRC Press is an imp^t o* :H Taylor H Francn C'r,,jpi
SECOND EDITION Mechanistic Toxicology The Molecular Basis of How Chemicals Disrupt Biological Targets URS A. BOELSTERLI CRC Press Tavlor & France Croup CRC Press is an imp^t o* :H Taylor H Francn C'r,,jpi
Alpha Lipoic Acid Snapshot Monograph
 vitamins minerals nutrients Alpha Lipoic Acid Snapshot Monograph Alpha lipoic Acid Most Frequent Reported Uses: - Antioxidant - Peripheral neuropathy - Improves insulin signaling and regulation of appetite
vitamins minerals nutrients Alpha Lipoic Acid Snapshot Monograph Alpha lipoic Acid Most Frequent Reported Uses: - Antioxidant - Peripheral neuropathy - Improves insulin signaling and regulation of appetite
Cell Adaptation, Cell Injury and Cell Death
 Cell Adaptation, Cell Injury and Cell Death Pathology:- is the study of structural and functional abnormalities that are expressed as diseases of organs and systems. Modern pathology, proposed that injury
Cell Adaptation, Cell Injury and Cell Death Pathology:- is the study of structural and functional abnormalities that are expressed as diseases of organs and systems. Modern pathology, proposed that injury
HISTOPATHOLOGY OF MYOCARDIAL DAMAGE IN EXPERIMENTAL FLUOROSIS IN RABBITS
 Fluoride Vol. 34 No. 1 43-50 2001 Research Report 43 HISTOPATHOLOGY OF MYOCARDIAL DAMAGE IN EXPERIMENTAL FLUOROSIS IN RABBITS A Shashi, a SP Thapar b Patiala, India Summary: Young albino rabbits were administered
Fluoride Vol. 34 No. 1 43-50 2001 Research Report 43 HISTOPATHOLOGY OF MYOCARDIAL DAMAGE IN EXPERIMENTAL FLUOROSIS IN RABBITS A Shashi, a SP Thapar b Patiala, India Summary: Young albino rabbits were administered
Cycloxydim CYCLOXYDIM (179)
 Cycloxydim 125 5.9 CYCLOXYDIM (179) TOXICOLOGY Cycloxydim is the ISO approved name for (5RS)-2-[(EZ)-1-(ethoxyimino)butyl]-3-hydroxy-5-[(3RS)- thian-3-yl]cyclohex-2-en-1-one (IUPAC). The CAS chemical name
Cycloxydim 125 5.9 CYCLOXYDIM (179) TOXICOLOGY Cycloxydim is the ISO approved name for (5RS)-2-[(EZ)-1-(ethoxyimino)butyl]-3-hydroxy-5-[(3RS)- thian-3-yl]cyclohex-2-en-1-one (IUPAC). The CAS chemical name
Recently Researched Effects of Individual Nutrients
 Recently Researched Effects of Individual Nutrients Alpha Lineoleic Acid (Omega 3) 1 ensures the optimal cerebral and cognitive development of the infant the presence of large quantities of EPA and DHA
Recently Researched Effects of Individual Nutrients Alpha Lineoleic Acid (Omega 3) 1 ensures the optimal cerebral and cognitive development of the infant the presence of large quantities of EPA and DHA
5.36 THIOPHANATE-METHYL (077)
 391 5.36 THIOPHANATE-METHYL (077) TOXICOLOGY is the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) approved common name for dimethyl 4,4 -(o-phenylene)bis(3-thioallophanate) (International Union
391 5.36 THIOPHANATE-METHYL (077) TOXICOLOGY is the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) approved common name for dimethyl 4,4 -(o-phenylene)bis(3-thioallophanate) (International Union
Dithianon DITHIANON (180)
 Dithianon 201 5.11 DITHIANON (180) TOXICOLOGY Dithianon (C 14 H 4 N 2 O 2 S 2 ) is the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) approved name for 5,10-dihydro-5,10-dioxonaphtho[2,3-b]-1,4-dithiine-2,3-dicarbonitrile
Dithianon 201 5.11 DITHIANON (180) TOXICOLOGY Dithianon (C 14 H 4 N 2 O 2 S 2 ) is the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) approved name for 5,10-dihydro-5,10-dioxonaphtho[2,3-b]-1,4-dithiine-2,3-dicarbonitrile
shehab Moh Tarek ... ManarHajeer
 3 shehab Moh Tarek... ManarHajeer In the previous lecture we discussed the accumulation of oxygen- derived free radicals as a mechanism of cell injury, we covered their production and their pathologic
3 shehab Moh Tarek... ManarHajeer In the previous lecture we discussed the accumulation of oxygen- derived free radicals as a mechanism of cell injury, we covered their production and their pathologic
Interpretation of the liver hypertrophy in the toxicological evaluation of veterinary medicinal products
 Provisional translation The Food Safety Commission Final decision on September 7, 2017 This English version of the Commission Decision is intended to be reference material to provide convenience for users.
Provisional translation The Food Safety Commission Final decision on September 7, 2017 This English version of the Commission Decision is intended to be reference material to provide convenience for users.
Study of the main chemical components of Ganoderma lucidum
 Study of the main chemical components of Ganoderma lucidum Yasuo Komota et al Tokyo Medical and Dental University [Purpose] As part of the means for exerting quality control on Ganoderma lucidum 50% ethanol
Study of the main chemical components of Ganoderma lucidum Yasuo Komota et al Tokyo Medical and Dental University [Purpose] As part of the means for exerting quality control on Ganoderma lucidum 50% ethanol
Targeted Chemoprevention of Progressive Marrow Failure in Patients with Fanconi Anemia using Quercetin, a Pilot study
 Targeted Chemoprevention of Progressive Marrow Failure in Patients with Fanconi Anemia using Quercetin, a Pilot study Parinda Mehta, M.D. Division of Bone Marrow Transplantation and Immune Deficiency Cincinnati
Targeted Chemoprevention of Progressive Marrow Failure in Patients with Fanconi Anemia using Quercetin, a Pilot study Parinda Mehta, M.D. Division of Bone Marrow Transplantation and Immune Deficiency Cincinnati
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Heyam Awad
 number 4 Done by Waseem Abu Obeida Corrected by Saad Al-Hayek Doctor Heyam Awad Cell injury -in the previous lectures we talked about the causes (etiology) and the mechanism (pathogenesis) of cell injury.
number 4 Done by Waseem Abu Obeida Corrected by Saad Al-Hayek Doctor Heyam Awad Cell injury -in the previous lectures we talked about the causes (etiology) and the mechanism (pathogenesis) of cell injury.
Study of the main chemical components of Ganoderma lucidum
 Study of the main chemical components of Ganoderma lucidum Yasuo Komota et al Tokyo Medical and Dental University [Purpose] As part of the means for exerting quality control on Ganoderma lucidum 50% ethanol
Study of the main chemical components of Ganoderma lucidum Yasuo Komota et al Tokyo Medical and Dental University [Purpose] As part of the means for exerting quality control on Ganoderma lucidum 50% ethanol
Ginkgo biloba extract postconditioning reduces myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury
 Ginkgo biloba extract postconditioning reduces myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury K. Ran 1, D.-L. Yang 1, Y.-T. Chang 1, K.-M. Duan 2, Y.-W. Ou 2, H.-P. Wang 3 and Z.-J. Li 1 1 Department of Anesthesiology,
Ginkgo biloba extract postconditioning reduces myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury K. Ran 1, D.-L. Yang 1, Y.-T. Chang 1, K.-M. Duan 2, Y.-W. Ou 2, H.-P. Wang 3 and Z.-J. Li 1 1 Department of Anesthesiology,
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Duraphat 5000 ppm Fluoride Toothpaste 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION 1 g of toothpaste contains 5 mg fluoride (as sodium fluoride),
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Duraphat 5000 ppm Fluoride Toothpaste 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION 1 g of toothpaste contains 5 mg fluoride (as sodium fluoride),
Folpet (Pesticides) Summary. Risk assessment report. Food Safety Commission of Japan. Conclusion in Brief
 2017 Food Safety Commission, Cabinet Office, Government of Japan doi: 10.14252/foodsafetyfscj.2017002s Food Safety 2017; Vol. 5, No. 2, 67 71 Risk assessment report Folpet (Pesticides) Summary Food Safety
2017 Food Safety Commission, Cabinet Office, Government of Japan doi: 10.14252/foodsafetyfscj.2017002s Food Safety 2017; Vol. 5, No. 2, 67 71 Risk assessment report Folpet (Pesticides) Summary Food Safety
EFFECTS OF DIFFERENT PROTEIN DIETS ON FLUORIDE INDUCED OXIDATIVE STRESS IN MICE TESTIS
 269 EFFECTS OF DIFFERENT PROTEIN DIETS ON FLUORIDE INDUCED OXIDATIVE STRESS IN MICE TESTIS NJ Chinoy, a D Mehta, DD Jhala Ahmedabad, India SUMMARY: Adult male Swiss strain mice were fed a control protein
269 EFFECTS OF DIFFERENT PROTEIN DIETS ON FLUORIDE INDUCED OXIDATIVE STRESS IN MICE TESTIS NJ Chinoy, a D Mehta, DD Jhala Ahmedabad, India SUMMARY: Adult male Swiss strain mice were fed a control protein
Assoc. Prof. Dr. Aslı Korkmaz* and Prof. Dr. Dürdane Kolankaya**
 The possible protective effects of some flavonoids that found honey by experimental ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) induced nitrosative damage in kidney of male rats Assoc. Prof. Dr. Aslı Korkmaz* and Prof.
The possible protective effects of some flavonoids that found honey by experimental ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) induced nitrosative damage in kidney of male rats Assoc. Prof. Dr. Aslı Korkmaz* and Prof.
ADVERSE EFFECTS OF FLUORIDE AND/OR ARSENIC ON THE CEREBRAL HEMISPHERE OF MICE AND RECOVERY BY SOME ANTIDOTES
 162 :162 171 Research Report ADVERSE EFFECTS OF FLUORIDE AND/OR ARSENIC ON THE CEREBRAL HEMISPHERE OF MICE AND RECOVERY BY SOME ANTIDOTES SD Shah, NJ Chinoy a Ahmedabad, India SUMMARY: The effects of oral
162 :162 171 Research Report ADVERSE EFFECTS OF FLUORIDE AND/OR ARSENIC ON THE CEREBRAL HEMISPHERE OF MICE AND RECOVERY BY SOME ANTIDOTES SD Shah, NJ Chinoy a Ahmedabad, India SUMMARY: The effects of oral
Mechanisms of Cell Injury
 Causes of Cell Injury 1- oxygen deprivation (anoxia) 2- physical agents 3- chemical agents 4- infections agents 5- immunologic reactions 6- genetic defects 7- nutritional imbalances Mechanisms of Cell
Causes of Cell Injury 1- oxygen deprivation (anoxia) 2- physical agents 3- chemical agents 4- infections agents 5- immunologic reactions 6- genetic defects 7- nutritional imbalances Mechanisms of Cell
Histopathology: Cell necrosis and cytoplasmic accumulations
 Histopathology: Cell necrosis and cytoplasmic accumulations These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Histopathology: Cell necrosis and cytoplasmic accumulations These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2012, 4(9): Research Article
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2012, 4(9):4307-4318 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Histopathological and ultrastructural changes
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2012, 4(9):4307-4318 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Histopathological and ultrastructural changes
The liver in poisoning: what can we learn from animal models?
 The liver in poisoning: what can we learn from animal models? Stephan Krähenbühl Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology University Hospital 4031 Basel/Switzerland Kraehenbuehl@uhbs.ch Outcome and causes of
The liver in poisoning: what can we learn from animal models? Stephan Krähenbühl Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology University Hospital 4031 Basel/Switzerland Kraehenbuehl@uhbs.ch Outcome and causes of
Fluoride in Drinking Water: A Scientific Review of EPA s Standards (National Research Council, March 2006)
 1 Fluoride in Drinking Water: A Scientific Review of EPA s Standards (National Research Council, March 2006) 2 Excerpts: FLUORIDE S EFFECTS ON THE BRAIN: Fluorides also increase the production of free
1 Fluoride in Drinking Water: A Scientific Review of EPA s Standards (National Research Council, March 2006) 2 Excerpts: FLUORIDE S EFFECTS ON THE BRAIN: Fluorides also increase the production of free
Keywords: Blood urea nitrogen; Creatinine clearance; ICR-derived glomerulonephritis mice; Urinary F concentrations. INTRODUCTION
 161 glomerulonephritis () mice, of the subacute administration 161 THE EFFECTS ON RENAL FUNCTION, IN INSTITUTE OF CANCER RESEARCH-DERIVED GLOMERULONEPHRITIS () MICE, OF THE SUBACUTE ADMINISTRATION OF THE
161 glomerulonephritis () mice, of the subacute administration 161 THE EFFECTS ON RENAL FUNCTION, IN INSTITUTE OF CANCER RESEARCH-DERIVED GLOMERULONEPHRITIS () MICE, OF THE SUBACUTE ADMINISTRATION OF THE
NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET
 1 PRODUCT NAME Clinpro 5000 anti-cavity toothpaste Vanilla Mint Clinpro 5000 anti-cavity toothpaste Spearmint Clinpro 5000 anti-cavity toothpaste Bubble Gum 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Thick
1 PRODUCT NAME Clinpro 5000 anti-cavity toothpaste Vanilla Mint Clinpro 5000 anti-cavity toothpaste Spearmint Clinpro 5000 anti-cavity toothpaste Bubble Gum 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Thick
6. SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION
 6. SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION Free radicals are chemical species containing one or more unpaired electrons, like hydrogen atom, most transition metal ions, nitric oxide and oxygen, with two unpaired electrons.
6. SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION Free radicals are chemical species containing one or more unpaired electrons, like hydrogen atom, most transition metal ions, nitric oxide and oxygen, with two unpaired electrons.
ENAMEL DEFECTS AND DENTAL CARIES IN 9-YEAR-OLD CHILDREN LIVING IN FLUORIDATED AND NONFLUORIDATED AREAS OF AUCKLAND, NEW ZEALAND
 244 244 ABSTRACTS DENTAL SURVEY IN AUCKLAND, NEW ZEALAND ENAMEL DEFECTS AND DENTAL CARIES IN 9-YEAR-OLD CHILDREN LIVING IN FLUORIDATED AND NONFLUORIDATED AREAS OF AUCKLAND, NEW ZEALAND OBJECTIVES: This
244 244 ABSTRACTS DENTAL SURVEY IN AUCKLAND, NEW ZEALAND ENAMEL DEFECTS AND DENTAL CARIES IN 9-YEAR-OLD CHILDREN LIVING IN FLUORIDATED AND NONFLUORIDATED AREAS OF AUCKLAND, NEW ZEALAND OBJECTIVES: This
SAFETY ASPECTS OF MIDAZOLAM
 Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1983), 16, 37S-41S Biological Pharmaceutical Research Department, F. Hoffmann-La Roche & Co Ltd, CH-4002 Basle, Switzerland 1 The LD50 in the rat and the mouse is about 1600 mg/kg
Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1983), 16, 37S-41S Biological Pharmaceutical Research Department, F. Hoffmann-La Roche & Co Ltd, CH-4002 Basle, Switzerland 1 The LD50 in the rat and the mouse is about 1600 mg/kg
The Burden of Foodborne Chemicals
 The Burden of Foodborne Chemicals Herman Gibb, Ph.D. Sciences International, Inc. WHO Consultation to Develop a Strategy for Estimating the Global Burden of Foodborne Diseases WHO Headquarters, Geneva
The Burden of Foodborne Chemicals Herman Gibb, Ph.D. Sciences International, Inc. WHO Consultation to Develop a Strategy for Estimating the Global Burden of Foodborne Diseases WHO Headquarters, Geneva
INVESTIGATION OF NEPFROPROTECTIVE EFFECT OF SILYMARIN AGAINST METHOTREXATE AND IFOSFAMIDE INDUCED TOXICITY IN RATS.
 INVESTIGATION OF NEPFROPROTECTIVE EFFECT OF SILYMARIN AGAINST METHOTREXATE AND IFOSFAMIDE INDUCED TOXICITY IN RATS. MANOHAR NAIK K*, MANODEEP CHAKRABORTY, RIYAZ AHMED, SHAHZAD HAMZA, MOHAMMED AFSAL A R.
INVESTIGATION OF NEPFROPROTECTIVE EFFECT OF SILYMARIN AGAINST METHOTREXATE AND IFOSFAMIDE INDUCED TOXICITY IN RATS. MANOHAR NAIK K*, MANODEEP CHAKRABORTY, RIYAZ AHMED, SHAHZAD HAMZA, MOHAMMED AFSAL A R.
Hepatotoxicity and ALT/AST Enzymes Activities Change in Therapeutic and Toxic Doses Consumption of Acetaminophen in Rats
 IBBJ Summer 2017, Vol 3, No 3 Original Article Hepatotoxicity and ALT/AST Enzymes Activities Change in Therapeutic and Toxic Doses Consumption of Acetaminophen in Rats Pouria jarsiah 1, Anahita Nosrati
IBBJ Summer 2017, Vol 3, No 3 Original Article Hepatotoxicity and ALT/AST Enzymes Activities Change in Therapeutic and Toxic Doses Consumption of Acetaminophen in Rats Pouria jarsiah 1, Anahita Nosrati
PREPARED BY P.DHARANI PRASAD II YEAR B.PHARM II SEM SUB:PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
 CELL INJURY UNIT I PREPARED BY P.DHARANI PRASAD II YEAR B.PHARM II SEM SUB:PATHOPHYSIOLOGY DETECTION OF CELLULAR CHANGES AFTER INJURY BY: LIGHT MICROSCOPY OR GROSS EXAMINATION DETECT CHANGES HOURS TO DAYS
CELL INJURY UNIT I PREPARED BY P.DHARANI PRASAD II YEAR B.PHARM II SEM SUB:PATHOPHYSIOLOGY DETECTION OF CELLULAR CHANGES AFTER INJURY BY: LIGHT MICROSCOPY OR GROSS EXAMINATION DETECT CHANGES HOURS TO DAYS
Fluoride & IQ Studies: The Context. Michael Conne9, Esq Fluoride Ac>on Network Sept. 6, 2014
 Fluoride & IQ Studies: The Context Michael Conne9, Esq Fluoride Ac>on Network Sept. 6, 2014 Dr. Mullenix s Predic>on A generic behavioral pattern disruption as found in this rat study can be indicative
Fluoride & IQ Studies: The Context Michael Conne9, Esq Fluoride Ac>on Network Sept. 6, 2014 Dr. Mullenix s Predic>on A generic behavioral pattern disruption as found in this rat study can be indicative
EXPOSURE TO SODIUM FLUORIDE AFFECTS THYROID FOLLICULAR CELLS IN ALBINO RATS. Vandana V. Patil and Varsha T. Dhurvey
 Volume-5, Issue-1, Jan-Mar-2015, Coden: IJPAJX-USA, Copyrights@2015, ISSN-2231-4490 Received: 11 th Oct-2014 Revised: 29 th Oct-2014 Accepted: 30 th Oct-2014 Research article EXPOSURE TO SODIUM FLUORIDE
Volume-5, Issue-1, Jan-Mar-2015, Coden: IJPAJX-USA, Copyrights@2015, ISSN-2231-4490 Received: 11 th Oct-2014 Revised: 29 th Oct-2014 Accepted: 30 th Oct-2014 Research article EXPOSURE TO SODIUM FLUORIDE
ARTICLE REVIEW Article Review on Prenatal Fluoride Exposure and Cognitive Outcomes in Children at 4 and 6 12 Years of Age in Mexico
 ARTICLE REVIEW Article Review on Prenatal Fluoride Exposure and Cognitive Outcomes in Children at 4 and 6 12 Years of Age in Mexico Article Summary The article by Bashash et al., 1 published in Environmental
ARTICLE REVIEW Article Review on Prenatal Fluoride Exposure and Cognitive Outcomes in Children at 4 and 6 12 Years of Age in Mexico Article Summary The article by Bashash et al., 1 published in Environmental
Committee for Risk Assessment RAC. Opinion. on the specific target organ toxicity of 2-benzotriazol-2-yl-4,6-di-tert-butylphenol (UV- 320)
 Committee for Risk Assessment RAC Opinion on the specific target organ toxicity of 2-benzotriazol-2-yl-4,6-di-tert-butylphenol (UV- 320) EC number: 223-346-6 CAS number: 3846-71-7 and 2-(2H-benzotriazol-2-yl)-4,6-ditertpentylphenol
Committee for Risk Assessment RAC Opinion on the specific target organ toxicity of 2-benzotriazol-2-yl-4,6-di-tert-butylphenol (UV- 320) EC number: 223-346-6 CAS number: 3846-71-7 and 2-(2H-benzotriazol-2-yl)-4,6-ditertpentylphenol
CHMP Safety Working Party s response to the PDCO regarding aluminium hydroxide contained in allergen products
 24 June 2010 EMA/CHMP/381064/2010 Human Medicines Development and Evaluation CHMP Safety Working Party s response to the PDCO regarding aluminium hydroxide contained in allergen products Question 1 Given
24 June 2010 EMA/CHMP/381064/2010 Human Medicines Development and Evaluation CHMP Safety Working Party s response to the PDCO regarding aluminium hydroxide contained in allergen products Question 1 Given
Peking University People's Hospital, Peking University Institute of Hematology
 Qian Jiang, M.D. Peking University People's Hospital, Peking University Institute of Hematology No. 11 Xizhimen South Street, Beijing, 100044, China. Phone number: 86-10-66583802 Mobile: 86-13611115100
Qian Jiang, M.D. Peking University People's Hospital, Peking University Institute of Hematology No. 11 Xizhimen South Street, Beijing, 100044, China. Phone number: 86-10-66583802 Mobile: 86-13611115100
LIST OF FIGURES AND TABLES
 ii LIST OF FIGURES AND TABLES GENERAL INTRODUCTION Fig. 1 Effect of Pb on antioxidant enzymes and cofactors leading to inactivation of enzyme activity Fig. 2 Rationale between Pb exposures among low SES
ii LIST OF FIGURES AND TABLES GENERAL INTRODUCTION Fig. 1 Effect of Pb on antioxidant enzymes and cofactors leading to inactivation of enzyme activity Fig. 2 Rationale between Pb exposures among low SES
HOW TO DEAL WITH THOSE ABNORMAL LIVER ENZYMES David C. Twedt DVM, DACVIM Colorado State University Fort Collins, CO
 HOW TO DEAL WITH THOSE ABNORMAL LIVER ENZYMES David C. Twedt DVM, DACVIM Colorado State University Fort Collins, CO The identification of abnormal liver enzymes usually indicates liver damage but rarely
HOW TO DEAL WITH THOSE ABNORMAL LIVER ENZYMES David C. Twedt DVM, DACVIM Colorado State University Fort Collins, CO The identification of abnormal liver enzymes usually indicates liver damage but rarely
DANIEL R. DOERGE U.S. Food and Drug Administration National Center for Toxicological Research Jefferson, AR
 Research support by Interagency Agreement between NTP/NIEHS and NCTR/FDA The opinions presented are not necessarily those of the U.S. FDA or NTP NCTR/FDA Research on BPA: Integrating pharmacokinetics in
Research support by Interagency Agreement between NTP/NIEHS and NCTR/FDA The opinions presented are not necessarily those of the U.S. FDA or NTP NCTR/FDA Research on BPA: Integrating pharmacokinetics in
LIVER MORPHOLOGY AND HISTOCHEMISTRY IN RATS RESULTING FROM INGESTION OF SODIUM SELENITE AND SODIUM FLUORIDE
 6 Fluoride Vol. 33 No. 1 6-16 2000 Research Report LIVER MORPHOLOGY AND HISTOCHEMISTRY IN RATS RESULTING FROM INGESTION OF SODIUM SELENITE AND SODIUM FLUORIDE L Kołodziejczyk, a A Put, b P Grzela b Szczecin,
6 Fluoride Vol. 33 No. 1 6-16 2000 Research Report LIVER MORPHOLOGY AND HISTOCHEMISTRY IN RATS RESULTING FROM INGESTION OF SODIUM SELENITE AND SODIUM FLUORIDE L Kołodziejczyk, a A Put, b P Grzela b Szczecin,
Supporting information. Precise Photodynamic Therapy of Cancer via Subcellular Dynamic Tracing of Dual-loaded Upconversion Nanophotosensitizers
 Supporting information Precise Photodynamic Therapy of Cancer via Subcellular Dynamic Tracing of Dual-loaded Upconversion Nanophotosensitizers Yulei Chang 1, Xiaodan Li 1,3, Li zhang 1,3, Lu Xia 1, Xiaomin
Supporting information Precise Photodynamic Therapy of Cancer via Subcellular Dynamic Tracing of Dual-loaded Upconversion Nanophotosensitizers Yulei Chang 1, Xiaodan Li 1,3, Li zhang 1,3, Lu Xia 1, Xiaomin
Evaluation of Chromatin Clumping and Myelination of the Spinal Cord of Pigs with Congenital Tremor
 Vet. Pathol. 12: 1-5 (1975) Evaluation of Chromatin Clumping and Myelination of the Spinal Cord of Pigs with Congenital Tremor C.H. LAMAR and D.C. VAN SICKLE School of Veterinary Medicine, Purdue University,
Vet. Pathol. 12: 1-5 (1975) Evaluation of Chromatin Clumping and Myelination of the Spinal Cord of Pigs with Congenital Tremor C.H. LAMAR and D.C. VAN SICKLE School of Veterinary Medicine, Purdue University,
ARTICLE REVIEW Article Review on Prenatal Fluoride Exposure and Cognitive Outcomes in Children at 4 and 6 12 Years of Age in Mexico
 ARTICLE REVIEW Article Review on Prenatal Fluoride Exposure and Cognitive Outcomes in Children at 4 and 6 12 Years of Age in Mexico Article Link Article Supplementary Material Article Summary The article
ARTICLE REVIEW Article Review on Prenatal Fluoride Exposure and Cognitive Outcomes in Children at 4 and 6 12 Years of Age in Mexico Article Link Article Supplementary Material Article Summary The article
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS White toothpaste containing 1.1% sodium fluoride (3)
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use 3M TM ESPE TM Clinpro TM 5000 Anti-Cavity Toothpaste safely and effectively. See full prescribing
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use 3M TM ESPE TM Clinpro TM 5000 Anti-Cavity Toothpaste safely and effectively. See full prescribing
Ph D THESIS ABSTRACT
 ALEXANDRU IOAN CUZA UNIVERSITY IAŞI FACULTY OF BIOLOGY THE STUDY OF CHANGES FOR SEVERAL BIOCHEMICAL PARAMETERS OF OXIDATIVE STRESS IN ANIMAL MODELS FOR NEUROPSYCHIATRIC DISORDERS Ph D THESIS ABSTRACT Scientific
ALEXANDRU IOAN CUZA UNIVERSITY IAŞI FACULTY OF BIOLOGY THE STUDY OF CHANGES FOR SEVERAL BIOCHEMICAL PARAMETERS OF OXIDATIVE STRESS IN ANIMAL MODELS FOR NEUROPSYCHIATRIC DISORDERS Ph D THESIS ABSTRACT Scientific
Chemical and Biochemical Mechanism Of Cell Injury.
 Chemical and Biochemical Mechanism Of Cell Injury. Professor Dr. M. Tariq Javed Dept. of Pathology Faculty of Vet. Science The University Of Agriculture Faisalabad Cell Injury When the cell is exposed
Chemical and Biochemical Mechanism Of Cell Injury. Professor Dr. M. Tariq Javed Dept. of Pathology Faculty of Vet. Science The University Of Agriculture Faisalabad Cell Injury When the cell is exposed
Pharmacy, Str. Traian Vuia 6, Bucharest, Romania 3 Farmacia Catena, Bucharest, Romania 4 Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Bucharest, Romania
 781 EXPERIMENTAL PHARMACOLOGICAL RESEARCHES REGARDING THE INFLUENCE OF SODIUM FLUORIDE IN ALLOPATHIC AND HOMEOPATHIC DOSES ON CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM S PERFORMANCES. A CORRELATION BETWEEN BEHAVIORAL RESPONSE
781 EXPERIMENTAL PHARMACOLOGICAL RESEARCHES REGARDING THE INFLUENCE OF SODIUM FLUORIDE IN ALLOPATHIC AND HOMEOPATHIC DOSES ON CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM S PERFORMANCES. A CORRELATION BETWEEN BEHAVIORAL RESPONSE
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION GENOTOXICITY. In vitro Genotoxicity Studies
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION GENOTOXICITY In vitro Genotoxicity Studies The in vitro immortalisation (IVIM) assay relies on the induction of a survival advantage by insertional activation of cellular proto-oncogenes,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION GENOTOXICITY In vitro Genotoxicity Studies The in vitro immortalisation (IVIM) assay relies on the induction of a survival advantage by insertional activation of cellular proto-oncogenes,
2. List routes of exposure in the order of most rapid response.
 Practice Test questions: 1. What are the two areas of toxicology that a regulatory toxicologist must integrate in order to determine the "safety" of any chemical? 2. List routes of exposure in the order
Practice Test questions: 1. What are the two areas of toxicology that a regulatory toxicologist must integrate in order to determine the "safety" of any chemical? 2. List routes of exposure in the order
COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
 European Medicines Agency Veterinary Medicines and Inspections EMEA/MRL/888/03-FINAL June 2004 COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS OXFENDAZOLE (Extrapolation to all ruminants) SUMMARY REPORT (4)
European Medicines Agency Veterinary Medicines and Inspections EMEA/MRL/888/03-FINAL June 2004 COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS OXFENDAZOLE (Extrapolation to all ruminants) SUMMARY REPORT (4)
Cell Injury MECHANISMS OF CELL INJURY
 Cell Injury MECHANISMS OF CELL INJURY The cellular response to injurious stimuli depends on the following factors: Type of injury, Its duration, and Its severity. Thus, low doses of toxins or a brief duration
Cell Injury MECHANISMS OF CELL INJURY The cellular response to injurious stimuli depends on the following factors: Type of injury, Its duration, and Its severity. Thus, low doses of toxins or a brief duration
Neurotoxicity induced by Fluoride in Rat Cerebral Cortex
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 5 Number 10 (2016) pp. 938-951 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2016.510.101
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 5 Number 10 (2016) pp. 938-951 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2016.510.101
UNITED STATES ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY WASHINGTON, D.C
 UNITED STATES ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY WASHINGTON, D.C. 20460 OFFICE OF PREVENTION, PESTICIDES AND TOXIC SUBSTANCES MEMORANDUM SUBJECT: Sodium Fluoride Incident Report Summary PC Code: 075202 FROM:
UNITED STATES ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY WASHINGTON, D.C. 20460 OFFICE OF PREVENTION, PESTICIDES AND TOXIC SUBSTANCES MEMORANDUM SUBJECT: Sodium Fluoride Incident Report Summary PC Code: 075202 FROM:
A Summary of the studies conducted with CV247
 A Summary of the studies conducted with CV247 Introduction Several epidemiological studies have shown that people deficient in trace elements such as selenium, copper, manganese, and vitamins, mainly C,D
A Summary of the studies conducted with CV247 Introduction Several epidemiological studies have shown that people deficient in trace elements such as selenium, copper, manganese, and vitamins, mainly C,D
Mass Histology Service
 Mass Histology Service A complete anatomical pathology laboratory www.masshistology.com Telephone: (877) 286-6004 Report on Pathology A Time Course Study of the Local Effects of Intramuscular XXXXXXX Injection
Mass Histology Service A complete anatomical pathology laboratory www.masshistology.com Telephone: (877) 286-6004 Report on Pathology A Time Course Study of the Local Effects of Intramuscular XXXXXXX Injection
COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
 The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Veterinary Medicines Evaluation Unit EMEA/MRL/488/98-FINAL July 1998 COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS DIETHYLENE GLYCOL MONOETHYL
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Veterinary Medicines Evaluation Unit EMEA/MRL/488/98-FINAL July 1998 COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS DIETHYLENE GLYCOL MONOETHYL
TOXICOPATHOLOGICAL AND FUNCTIONAL CHARACTERIZATION OF THYROID GLAND OF RAT IN FLUOROSIS
 TOXICOPATHOLOGICAL AND FUNCTIONAL CHARACTERIZATION OF THYROID GLAND OF RAT IN FLUOROSIS *Shashi A and Parveen Kumar Department of Zoology and Environmental Sciences, Punjabi University, Patiala-147002,
TOXICOPATHOLOGICAL AND FUNCTIONAL CHARACTERIZATION OF THYROID GLAND OF RAT IN FLUOROSIS *Shashi A and Parveen Kumar Department of Zoology and Environmental Sciences, Punjabi University, Patiala-147002,
CELL INJURY AND CELL DEATH
 CELL INJURY AND CELL DEATH INTRODUCTION Cell Injury is a result of the sequence of events that occur if the limits of the adaptive capability of cells are exceeded or there is no adaptive response is possible,
CELL INJURY AND CELL DEATH INTRODUCTION Cell Injury is a result of the sequence of events that occur if the limits of the adaptive capability of cells are exceeded or there is no adaptive response is possible,
Mansoura university Faculty of medicine Histology and cell Biology Department Curriculum Content And Logbook
 Mansoura university Faculty of medicine Histology and cell Biology Department Curriculum Content And Logbook For the 1 st year Medical Student s In Histology and cell Biology Mansoura university Faculty
Mansoura university Faculty of medicine Histology and cell Biology Department Curriculum Content And Logbook For the 1 st year Medical Student s In Histology and cell Biology Mansoura university Faculty
Lecture 19 Summary Gestational Diabetes and Complications of Diabetes. Gestational diabetes;
 Lecture 19 Summary Gestational Diabetes and Complications of Diabetes Gestational diabetes; - Type of diabetes that only develops during pregnancy Usually diagnosed in late pregnancy Causes high blood
Lecture 19 Summary Gestational Diabetes and Complications of Diabetes Gestational diabetes; - Type of diabetes that only develops during pregnancy Usually diagnosed in late pregnancy Causes high blood
Keywords: Apoptosis; Fluoride; ME3T3-E1 osteoblasts; Mitochondrial membrane potential; Reactive oxygen species. INTRODUCTION
 213 and mitochondrial membrane potentials 213 FLUORIDE INDUCES APOPTOSIS IN MC3T3-E1 OSTEOBLASTS BY ALTERING ROS LEVELS AND MITOCHONDRIAL MEMBRANE POTENTIALS Xiaoyan Yan, a Xiaolin Tian, a Lu Wang, a Wenli
213 and mitochondrial membrane potentials 213 FLUORIDE INDUCES APOPTOSIS IN MC3T3-E1 OSTEOBLASTS BY ALTERING ROS LEVELS AND MITOCHONDRIAL MEMBRANE POTENTIALS Xiaoyan Yan, a Xiaolin Tian, a Lu Wang, a Wenli
CALIFORNIA ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY DEPARTMENT OF PESTICIDE REGULATION MEDICAL TOXICOLOGY BRANCH SUMMARY OF TOXICOLOGY DATA FLURIDONE
 CALIFORNIA ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY DEPARTMENT OF PESTICIDE REGULATION MEDICAL TOXICOLOGY BRANCH SUMMARY OF TOXICOLOGY DATA FLURIDONE Chemical Code # 2279, Tolerance # 420 Original: 8/20/87 Revised:
CALIFORNIA ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY DEPARTMENT OF PESTICIDE REGULATION MEDICAL TOXICOLOGY BRANCH SUMMARY OF TOXICOLOGY DATA FLURIDONE Chemical Code # 2279, Tolerance # 420 Original: 8/20/87 Revised:
Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology
 Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Product Datasheet. DC-LAMP Antibody (104G4) DDX0190P-100. Unit Size: 0.1 mg. Store at -20C. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles.
 Product Datasheet DC-LAMP Antibody (104G4) DDX0190P-100 Unit Size: 0.1 mg Store at -20C. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. Publications: 18 Protocols, Publications, Related Products, Reviews, Research Tools and
Product Datasheet DC-LAMP Antibody (104G4) DDX0190P-100 Unit Size: 0.1 mg Store at -20C. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. Publications: 18 Protocols, Publications, Related Products, Reviews, Research Tools and
Non-protein nitrogenous substances (NPN)
 Non-protein nitrogenous substances (NPN) A simple, inexpensive screening test a routine urinalysis is often the first test conducted if kidney problems are suspected. A small, randomly collected urine
Non-protein nitrogenous substances (NPN) A simple, inexpensive screening test a routine urinalysis is often the first test conducted if kidney problems are suspected. A small, randomly collected urine
By Soha Mohamed Hamdy (1),Abdelkarim Mohamed Abdellatif (2) and Rania Mortada Mahmuod (1)
 BIOCHEMICAL STUDIES ON THE EFFECT OF TURMERIC ON BREAST CANCER OF RATS By Soha Mohamed Hamdy (1),Abdelkarim Mohamed Abdellatif (2) and Rania Mortada Mahmuod (1) 1) Biochemistry Div. Chemistry Dep. Faculty
BIOCHEMICAL STUDIES ON THE EFFECT OF TURMERIC ON BREAST CANCER OF RATS By Soha Mohamed Hamdy (1),Abdelkarim Mohamed Abdellatif (2) and Rania Mortada Mahmuod (1) 1) Biochemistry Div. Chemistry Dep. Faculty
Nutritional Supplementation and Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder
 Nutritional Supplementation and Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder 1,2 Anna Patten, PhD; 1,2 Brian Christie, PhD; 3 Courtney Green, PhD and 3 Jocelynn Cook, PhD MBA. 1 Division of Medical Sciences, University
Nutritional Supplementation and Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder 1,2 Anna Patten, PhD; 1,2 Brian Christie, PhD; 3 Courtney Green, PhD and 3 Jocelynn Cook, PhD MBA. 1 Division of Medical Sciences, University
Clinical significance of CD44 expression in children with hepatoblastoma
 Clinical significance of CD44 expression in children with hepatoblastoma H.-Y. Cai 1 *, B. Yu 1 *, Z.-C. Feng 2, X. Qi 1 and X.-J. Wei 1 1 Department of General Surgery, General Hospital of Beijing Military
Clinical significance of CD44 expression in children with hepatoblastoma H.-Y. Cai 1 *, B. Yu 1 *, Z.-C. Feng 2, X. Qi 1 and X.-J. Wei 1 1 Department of General Surgery, General Hospital of Beijing Military
Pathophysiology lab 2. Cellular injury and adaptation
 Pathophysiology lab 2 Cellular injury and adaptation Adaptation Cellular changes that aim to preserve cell viability and prevent cell injury. The adaptive responses include: 1. Atrophy 2. Hypertrophy 3.
Pathophysiology lab 2 Cellular injury and adaptation Adaptation Cellular changes that aim to preserve cell viability and prevent cell injury. The adaptive responses include: 1. Atrophy 2. Hypertrophy 3.
Lipoic Acid Mineral Complex
 The Metabolic Role of Lipoic Acid Mineral Complex Mitochondrial Health and Metabolic Regulation of Cellular Function in Cancer and Stroke by Dr. Frank Antonawich An Introduction to Lipoic Acid Mineral
The Metabolic Role of Lipoic Acid Mineral Complex Mitochondrial Health and Metabolic Regulation of Cellular Function in Cancer and Stroke by Dr. Frank Antonawich An Introduction to Lipoic Acid Mineral
Protects cattle & sheep against 10 clostridial diseases
 Protects cattle & sheep against 10 clostridial diseases No other vaccine does more to shield your animals against clostridial diseases. LIVER BLACK DISEASE BACTERIAL REDWATER BRAIN TETANUS PULPY KIDNEY
Protects cattle & sheep against 10 clostridial diseases No other vaccine does more to shield your animals against clostridial diseases. LIVER BLACK DISEASE BACTERIAL REDWATER BRAIN TETANUS PULPY KIDNEY
BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES GRADUATE PROGRAM SUMMER 2013
 THE OHIO STATE UNIVERSITY BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES GRADUATE PROGRAM SUMMER 2013 Edward Lloyd Briercheck PhD Candidate Elucidation of the Mechanism by which Phosphatase and Tensin Homologue Deleted on Chromosome
THE OHIO STATE UNIVERSITY BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES GRADUATE PROGRAM SUMMER 2013 Edward Lloyd Briercheck PhD Candidate Elucidation of the Mechanism by which Phosphatase and Tensin Homologue Deleted on Chromosome
Evaluation Summary. Sample Customer 4/20/2010 TFO Testing Lab
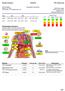 Evaluation Summary Test ph rh2 r Saliva 6.55 (6.50-6.75) 23.6 (21.5-23.5) 235 (180-220) Analysis Chart Hydration Detox Digestive Mitochondri Oxidation al Oxidation Organic Buffers Urine 6.42 (6.50-6.80)
Evaluation Summary Test ph rh2 r Saliva 6.55 (6.50-6.75) 23.6 (21.5-23.5) 235 (180-220) Analysis Chart Hydration Detox Digestive Mitochondri Oxidation al Oxidation Organic Buffers Urine 6.42 (6.50-6.80)
Threshold-Based Risk Assessment is the Same for Cancer and Non-cancer Endpoints for Non-DNA Reactive Carcinogens
 Threshold-Based Risk Assessment is the Same for Cancer and Non-cancer Endpoints for Non-DNA Reactive Carcinogens Samuel M. Cohen, MD, PhD Department of Pathology & Microbiology University of Nebraska Medical
Threshold-Based Risk Assessment is the Same for Cancer and Non-cancer Endpoints for Non-DNA Reactive Carcinogens Samuel M. Cohen, MD, PhD Department of Pathology & Microbiology University of Nebraska Medical
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Fluoride 2800 ppm Toothpaste 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION 1 g of toothpaste contains contains 2.8 mg fluoride (as sodium
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Fluoride 2800 ppm Toothpaste 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION 1 g of toothpaste contains contains 2.8 mg fluoride (as sodium
ROLE OF SOME ANTIOXIDANTS ON MERCURY CHLORIDE INDUCED SPERMATOGENESIS IN SWISS ALBINO MICE DURING PRE PUBERTAL PHASE OF LIFE
 Indian J.Sci.Res.1(2) : 19-25, 2010 ROLE OF SOME ANTIOXIDANTS ON MERCURY CHLORIDE INDUCED SPERMATOGENESIS IN SWISS ALBINO MICE DURING PRE PUBERTAL PHASE OF LIFE a1 DUGESH NANDINI SHARMA AND LATA BHATTACHARYA
Indian J.Sci.Res.1(2) : 19-25, 2010 ROLE OF SOME ANTIOXIDANTS ON MERCURY CHLORIDE INDUCED SPERMATOGENESIS IN SWISS ALBINO MICE DURING PRE PUBERTAL PHASE OF LIFE a1 DUGESH NANDINI SHARMA AND LATA BHATTACHARYA
