ijcrr Vol 04 issue 02 Category: Research Received on:25/11/11 Revised on:06/12/11 Accepted on:12/12/11
|
|
|
- Carol Malone
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
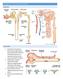
1 PROTEINURIA RENAL FUNCTION EVALUATION IN CLINICAL PRACTICE Sharan Badiger ijcrr Vol 04 issue 02 Category: Research Received on:25/11/11 Revised on:06/12/11 Accepted on:12/12/11 Professor, Department of Medicine, BLDE University s, Sri B M Patil Medical College, Bijapur, Karnataka of Corresponding Author: sharanrb@rediffmail.com ABSTRACT Patients suffering from various kidney diseases have very few clinical symptoms and signs pointing towards renal involvement. Renal functions can be assessed by microscopic and biochemical examination of urine, biochemical determinations on plasma samples and by procedures involving administration of test substances. In this article a review on proteinuria is done which is useful in day to day clinical practice. Keywords: Albumin, Globulin, Glomerular diseases, Proteinuria, Renal function INTRODUCTION A normal barrier to protein filtration begins in the glomerulus. The normal glomerular endothelial cells form a barrier and hold back cells and other particles. They are penetrated by large pores of 100nm called fenestrae that can be easily traversed by proteins. The glomerular basement traps most large proteins (>100Kda), while the foot process of epithelial cells (podocytes) cover the urinary side of the glomerular basement membrane and produce a series of narrow channels (slit diaphragm) to allow passage of small solutes and water. These slit diaphragm bridges the slits between the foot processes of the glomerular basement membrane [1]. The visceral epithelial cells are covered with negatively charged heparan sulfate proteoglycans [2]. This negative charge and size selectivity of glomerular basement membrane impedes the passage of anion molecules such as albumin, globulin and large molecular weight protein across the glomerular wall. The smaller proteins that are filtered across the glomerular basement membrane are largely reabsorbed at the proximal tubule and only small amount are excreted. PATHOPHYSIOLOGICAL CLASSIFICATION OF PROTEINURIA A) BENIGN 1. Postural Orthostatic proteinuria 2. Functional 3. Transient 4. Intermittent B) PATHOLOGICAL 1. Glomerular 2. Tubular 3. Overflow 4. Secretory A) BENIGN PROTEINURIA This is a transient proteinuria that occurs with normal renal function, bland urinary sediment, and normal blood pressure and without any significant oedema. 24 hour urine albumin is usually less than one gram. They do not indicate any significant renal disease and disappears on repeated testing. 1) Postural /Orthostatic Proteinuria 120 International Journal of Current Research and Review
2 This is seen in 3 to 5% of adolescents, especially in young males. It is characterized by increased protein excretion in the upright position and normal protein excretion during recumbency [3]. It is diagnosed by split urine protein excretion examination. In orthostatic proteinuria, the day time specimen typically has an increased concentration of protein, with night time specimen having a normal concentration usually less than 50 mg over eight hours [4]. In true glomerular disease there is reduced protein excretion in the supine position but it will not return to normal as with orthostatic proteinuria. Springberg found that long term prognosis of orthostatic proteinuria is benign in virtually all cases over many decades [5]. Data on renal biopsies on orthostatic proteinuria are confusing. Some showed minor glomerular changes [6].Posture affects urinary protein excretion, probably via an increase in glomerular capillary hydrostatic pressure and for change in permeability of the glomerular capillary walls [7]. An alternate explanation is entrapment of renal veins [8, 9]. 2) Functional Proteinuria It is a benign proteinuria due to changes in glomerular ultra filtration pressure and/or membrane permeability. It is seen in fever, exercise, cardiac failure, emotional stress and acute illness. Functional Proteinuria is usually less than 0.5 gm/day but may be as heavy as 5.0 gm/day (following marathon running). It disappears with the resolution of causative disorder [10]. Kallmeyer et al found that recent exercise can induce several gram of protein per litre of urine, sometimes together with haematuria and even casts so called jogger s nephritis [11]. Post exercise proteinuria is about 15 to 20 times the resting range of proteinuria and requires about 4 hours to regain resting value in the recovery period [12]. Poortmans et al found that proteinuria was influenced mostly by the intensity of exercise rather than its duration [13]. 3) Idiopathic Proteinuria This is seen in young healthy adults. This dipstick positive proteinuria disappears spontaneously by next clinical visit. 4) Intermittent Proteinuria This benign proteinuria is found in half of their different urine samples in absence of other renal or systemic abnormalities. B) PATHOLOGICAL PROTEINURIA This is persistent proteinuria that is detected on multiple ambulatory clinical visits. This is seen in both recumbent and upright position and usually signals a structural renal disease. 1) Glomerular Proteinuria It is the most common cause of proteinuria in clinical practice. It is characterized by a disproportionate amount of albumin in urine [14]. Due to preservation of selectivity and large concentration of albumin in blood glomerular proteinuria is 85 to 90 % albumin, accompanied by pre-albumin, transferrin and relatively low molecular weight proteins since it contains mostly albumin. They are readily detected by stick or turbidometric methods. Glomerular proteinuria ranges from few hundred mg per 24 hours to 100 gms per 24 hours. McConnell et al on evaluation of proteinuria found that urinary excretion of more than 2 gm per 24 hours is usually a result of glomerular disease [15]. In glomerular proteinuria there is increased glomerular capillary permeability to high molecular weight anionic plasma proteins. How the glomerular barrier is damaged so that it leaks more than normal remains unclear [16]. This may be due to: -Loss of fixed anionic charge (Congenital nephrotic syndrome, minimal change nephropathy) - Detachment of epithelial podocytes from basement membrane [17]. - Immune aggregation. 121 International Journal of Current Research and Review
3 - Increase in glomerular capillary pressure. The filtered protein, that reach the tubules overwhelm the limited capacity of tubular reabsorption and cause these proteins to appear in urine. Glomerular disease is classified as primary when the pathology is confined to the kidney and secondary when it is a part of multi system disorder. Glomerular proteinuria is of two types: a) Selective Proteinuria b) Non-selective Proteinuria In selective proteinuria the clearance ratio of immunoglobulin to albumin or transferrin is less than 0.10(<10%).In non-selective proteinuria the clearance ratio of immunoglobulin to albumin or transferrin is more than 0.50(>50%). GLOMERULAR PROTEINURIA -CAUSES Primary Glomerulonephropathy: - Minimal change disease - Focal segmental glomerulonephritis - Idiopathic membranous glomerulonephritis - Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis - IgA nephropathy Secondary Glomerulonephropathy: - Diabetes Mellitus - Amyloidosis - Collagen vascular disease (Eg-Lupus nephritis) - Infections - HIV - Hepatitis B and C infection - Post streptococcal - Syphilis - Malaria - Infective Endocarditis - Drugs - NSAIDS - Penicillamine - Lithium - Heroin - Heavy metals - Gastrointestinal and lung cancers - Lymphoma 2) TUBULAR PROTEINURIA Proteinuria results from the damage of proximal tubule so that normally reabsorbed protein, principally of low molecular weight pass into the urine.this usually occurs as part of the Fanconi syndrome of proximal tubular dysfunction. Tubular proteinuria usually does not exceed 2 gm per day [18, 19]. Beta 2-microglobulin is one of the many micro globulin which make up tubular proteinuria. Normal level of Beta 2- microglobulin in urine is less than 0.4 mcg/l. It can be assessed by RIA or ELISA. The urinary albumin and Beta 2-microglobulins ratio of 10 to 1 suggests the presence of Beta 2-microglobulin. Further measurement of Beta 2 lysozyme may help in distinguishing type of urinary tract infection besides diagnosis of heavy metal poisoning [20, 21].Urinary protein electrophoresis and/or immuno electrophoresis may aid in distinguishing tubular and glomerular proteinuria. TUBULAR PROTEINURIA CAUSES -Hypertensive nephrosclerosis -Tubulo interstial diseases -Fanconi syndrome -Heavy metals -Uric acid nephropathy -Acute hypersensitivity -Interstitial nephritis -Sickle cell disease -Drugs (NSAID, antibiotics) 3) OVERFLOW PROTEINURIA It is due to filtration by normal glomerulus of an abnormally large amount of low molecular weight proteins, which exceeds the capacity of the normal tubules for reabsorption. It is characterized by the presence of abnormal peak or spike on urinary electrophoresis. Most often, this is a result of the immunoglobulin over production that occurs in multiple myeloma. The resultant light change immunoglobulin fragments (Bench Jones proteins) produce a monoclonal spike in the urine electrophoresis [22, 23]. OVERFLOW PROTEINURIA CAUSES -Multiple myeloma -Myoglobinuria - Rhabdomyolysis -Lymphoproliferative disorders 4) SECRETORY PROTEINURIA It occurs due to secretion of proteins into the urine after glomerular filtration. About 20 to 30 mg/24 hours of non plasma protein is contributed by renal tubules and lower urinary tract. Mostly they are formed by Tomm-Horsfall proteins. Some secretary IgA is added by lower urinary track including the urethral glands together with trace quantity of protein of prostatic or seminal vesicular organ [24, 25]. Tomm-Horsfall protein is secreted by the 122 International Journal of Current Research and Review
4 ascending thick limb and early distal convoluted tubule into the tubular fluid. It is an easily polymerized glycoprotein. They form the major constituent of renal tubular casts [26], along with albumin and traces of many plasma proteins, including immunoglobulins [27]. In myeloma, casts contain paraproteins polymerized with Tomm-Horsfall protein, and may show a micro fibrillar structure that will stain positive with Congo red, even though no amyloid is present in renal tissue. Thus, the normal 24 hours urine protein excretion does not exceed 150 mg/dl in adults and 140 mg/m 2 in children and generally this corresponds to approximately 10 mg/dl. Microalbuminuria refers to elevated urinary albumin excretion with normal total urine proteins. This corresponds to albumin excretion rates in the range of 20 to 200 µg/min. It has been found a useful early marker of development of diabetic nephropathy. It is detected by RIA or ELISA technique. REFERENCES 1. Flanc RS, Robert MA, Strippoli GF, Chadban SJ, Kerr PG, Atkins RC. Treatment of diffuse proliferative lupus nephritis: A Meta analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am J Kidney Dis.2004; 43: Carroll MF, Temte JL. Proteinuria in adults: A diagnostic approach. American Family Physician. 2000; 62: Glassrock RJ. Postural (orthostatic) Proteinuria. N Engl J Med.1980; 18: Watt GF, Morris RW, Khank, Polaka.Urinary albumin excretion in health adult subjects: Reference value and some factors affecting their interpretation.clin Chim Acta.1988; 172: Spring Berg, Lt. Col. Peter D, Maj. Leland E Garrett, Nancy F Collins, Roscoe R Robinson. Fixed and reproducible orthostatic proteinuria: Results of a 20 year follow up study: Annals of internal medicine.1982; 97: Robinson RR. Isolated proteinuria in asymptomatic patients. J of Kidney International. 1980; 18: Wam LL, Yano S, Hiromurak, Tsukaday, Tomonos, Kawazer. Effects of posture on creatinine clearance and urinary protein excretion in patients with various renal diseases 1995; 3: Devarajan P. Mechanism of orthostatic proteinuria: Lessons from a transplant donor. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology.1993; 4: Shintaku N, Takahashi Y, Akaishi K, Sano A, Kuroda Y,Entrapment of the left renal vein in children with orthostatic proteinuria.. Pediatric Nephrology. 1990; 4: Hotter TH. Proteinuria. Kidney. 1987; 20: Kallmeyer G, Miller NM. Urinary changes in ultra-long distance marathon runners. Nephron. 1993; 64: Poortmans JR, Rampaer L, Walf JC. Renal protein excretion after exercise in man. Eur J Apply Physiol Occup Physiol. 1989; 48: Poortms JR, Labilloy D. The influence of work intensity on post exercise proteinuria. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol.1988; 57: Abuelo JG. Proteinuria: Diagnostic Principles and procedures. Ann Intern Med 1983:98; McConnell KR, Bia MJ. The Evaluation of proteinuria: An approach for the internist. Res Staff Physician.1994; Savin VJ. Mechanism of proteinuria in non inflammatory glomerular disease. American Journal of Kidney Disease.1993; 21: International Journal of Current Research and Review
5 17. Daniels BS. The role of the glomerular epithelial cell in the maintainance of the glomerular filtration barrier American Journal of Nephrology.1993; 13: Almeida AF. Clinical Approach to a Patient with Renal Disease. API textbook of Medicine 7th edition. Mumbai: The Association of Physician of India: Turner AN, Savill J, Stewart LH, Camming A. Kidney and Genitourinary Disease. Davidson s principles and practice of Medicine. 19th edition. London : Churchill Living stone; Tulkensn PM, Experimental studies on Nephrotoxicity of Aminoglycosides in low doses. Am J Med. 1986; 80 (6 B): Schardijn GHC,Statius Van Eps LW, Stout Zonnevel.Urinary B2 microglobulin urinary tract infections, Acta Clin Belg. 1980; 35: Glassrock RJ. Proteinuria. Test book of Nephrology. 3rd edition Baltimore: William Wilkins, Longo DL, Anderson KC, Plasma Cell Disorders. Harrison s Principles of Internal Medicine. 16th edition. New Delhi Mc Graw Hill Medical Publishing Division; Beinenstock J, Tomasi TB. Secretory gamma -A in normal urine. Journal of Clinical Investigation.1968; 47: Rosenman E, Boss JH.Tissue antigens in normal and pathologic urines: A review. Kidney International. 1979; 16: MC Queen EG. Composition of urinary casts. Lancet.1966; 287: Rustecki GJ, Goldsmith C, Sehreiner GE.Characterization of proteins in urinary casts. Fluorescent antibody identification of Tomm Horsfall protein in matrix and serum protein in granules.new Engl J of Med. 1971; 284: International Journal of Current Research and Review
Case Studies: Renal and Urologic Impairments Workshop
 Case Studies: Renal and Urologic Impairments Workshop Justine Lee, MD, DBIM New York Life Insurance Co. Gina Guzman, MD, DBIM, FALU, ALMI Munich Re AAIM Triennial October, 2012 The Company You Keep 1 Case
Case Studies: Renal and Urologic Impairments Workshop Justine Lee, MD, DBIM New York Life Insurance Co. Gina Guzman, MD, DBIM, FALU, ALMI Munich Re AAIM Triennial October, 2012 The Company You Keep 1 Case
Quantitative protein estimation of Urine
 Quantitative protein estimation of Urine 1 In a healthy renal and urinary tract system, the urine contains no protein or only trace amounts. The presence of increased amounts of protein in the urine can
Quantitative protein estimation of Urine 1 In a healthy renal and urinary tract system, the urine contains no protein or only trace amounts. The presence of increased amounts of protein in the urine can
Evaluation and Management of Proteinuria. Negiin Pourafshar, MD University of Virginia Division of Nephrology
 Evaluation and Management of Proteinuria Negiin Pourafshar, MD University of Virginia Division of Nephrology Case A 30-year-old man, is turned down for life insurance because of the presence of an unspecified
Evaluation and Management of Proteinuria Negiin Pourafshar, MD University of Virginia Division of Nephrology Case A 30-year-old man, is turned down for life insurance because of the presence of an unspecified
Glomerular Pathology- 1 Nephrotic Syndrome. Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin
 Glomerular Pathology- 1 Nephrotic Syndrome Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin The Nephrotic Syndrome a clinical complex resulting from glomerular disease & includes the following: (1) massive proteinuria (3.5 gm /day
Glomerular Pathology- 1 Nephrotic Syndrome Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin The Nephrotic Syndrome a clinical complex resulting from glomerular disease & includes the following: (1) massive proteinuria (3.5 gm /day
Elevated Serum Creatinine, a simplified approach
 Elevated Serum Creatinine, a simplified approach Primary Care Update Creighton University School of Medicine. April 27 th, 2018 Disclosure Slide I have no disclosures and have no conflicts with this presentation.
Elevated Serum Creatinine, a simplified approach Primary Care Update Creighton University School of Medicine. April 27 th, 2018 Disclosure Slide I have no disclosures and have no conflicts with this presentation.
Nephritic vs. Nephrotic Syndrome
 Page 1 of 18 Nephritic vs. Nephrotic Syndrome Terminology: Glomerulus: A network of blood capillaries contained within the cuplike end (Bowman s capsule) of a nephron. Glomerular filtration rate: The rate
Page 1 of 18 Nephritic vs. Nephrotic Syndrome Terminology: Glomerulus: A network of blood capillaries contained within the cuplike end (Bowman s capsule) of a nephron. Glomerular filtration rate: The rate
Disorders of the kidney. Urine analysis. Nephrotic and nephritic syndrome.
 Disorders of the kidney. Urine analysis. Nephrotic and nephritic syndrome. Azotemia and Urinary Abnormalities Disturbances in urine volume oliguria, anuria, polyuria Abnormalities of urine sediment red
Disorders of the kidney. Urine analysis. Nephrotic and nephritic syndrome. Azotemia and Urinary Abnormalities Disturbances in urine volume oliguria, anuria, polyuria Abnormalities of urine sediment red
Proteinuria. Louisiana State University
 Proteinuria W S A V A W C P, 2005 David F. Senior Louisiana State University The normal glomerulus is a highly selective barrier for filtration based on size (and on charge in the case of larger molecules).
Proteinuria W S A V A W C P, 2005 David F. Senior Louisiana State University The normal glomerulus is a highly selective barrier for filtration based on size (and on charge in the case of larger molecules).
5/10/2014. Observation, control of blood pressure. Observation, control of blood pressure and risk factors.
 Overview The Kidneys Nicola Barlow Clinical Biochemistry Department City Hospital Renal physiology Renal pathophysiology Acute kidney injury Chronic kidney disease Assessing renal function GFR Proteinuria
Overview The Kidneys Nicola Barlow Clinical Biochemistry Department City Hospital Renal physiology Renal pathophysiology Acute kidney injury Chronic kidney disease Assessing renal function GFR Proteinuria
HIHIM 409 7/26/2009. Kidney and Nephron. Fermamdo Vega, M.D. 1
 Function of the Kidneys Nephrology Fernando Vega, M.D. Seattle Healing Arts Center Remove Wastes Regulate Blood Pressure Regulate Blood Volume Regulates Electrolytes Converts Vitamin D to active form Produces
Function of the Kidneys Nephrology Fernando Vega, M.D. Seattle Healing Arts Center Remove Wastes Regulate Blood Pressure Regulate Blood Volume Regulates Electrolytes Converts Vitamin D to active form Produces
Quantitative estimation of protein in urine
 Quantitative estimation of protein in urine By sulphosalicalic acid Method BCH 472 In a healthy renal and urinary tract system, the urine contains no protein or only trace amounts. The presence of increased
Quantitative estimation of protein in urine By sulphosalicalic acid Method BCH 472 In a healthy renal and urinary tract system, the urine contains no protein or only trace amounts. The presence of increased
Glomerular pathology in systemic disease
 Glomerular pathology in systemic disease Lecture outline Lupus nephritis Diabetic nephropathy Glomerulonephritis Associated with Bacterial Endocarditis and Other Systemic Infections Henoch-Schonlein Purpura
Glomerular pathology in systemic disease Lecture outline Lupus nephritis Diabetic nephropathy Glomerulonephritis Associated with Bacterial Endocarditis and Other Systemic Infections Henoch-Schonlein Purpura
Management of New-Onset Proteinuria in the Ambulatory Care Setting. Akinlolu Ojo, MD, PhD, MBA
 Management of New-Onset Proteinuria in the Ambulatory Care Setting Akinlolu Ojo, MD, PhD, MBA Urine dipstick results Negative Trace between 15 and 30 mg/dl 1+ between 30 and 100 mg/dl 2+ between 100 and
Management of New-Onset Proteinuria in the Ambulatory Care Setting Akinlolu Ojo, MD, PhD, MBA Urine dipstick results Negative Trace between 15 and 30 mg/dl 1+ between 30 and 100 mg/dl 2+ between 100 and
Proteinuria DR. SANJAY PANDEYA MD. FRCPC.
 Proteinuria DR. SANJAY PANDEYA MD. FRCPC. Objectives Define normal and abnormal range(s) of proteinuria Evaluation of proteinuria Be aware of complications of proteinuria When to refer and when not to
Proteinuria DR. SANJAY PANDEYA MD. FRCPC. Objectives Define normal and abnormal range(s) of proteinuria Evaluation of proteinuria Be aware of complications of proteinuria When to refer and when not to
Dr Ian Roberts Oxford. Oxford Pathology Course 2010 for FRCPath Illustration-Cellular Pathology. Oxford Radcliffe NHS Trust
 Dr Ian Roberts Oxford Oxford Pathology Course 2010 for FRCPath Present the basic diagnostic features of the commonest conditions causing proteinuria & haematuria Highlight diagnostic pitfalls Nephrotic
Dr Ian Roberts Oxford Oxford Pathology Course 2010 for FRCPath Present the basic diagnostic features of the commonest conditions causing proteinuria & haematuria Highlight diagnostic pitfalls Nephrotic
Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine
 Urinary System Organs Kidney Filters blood, allowing toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions to leave the body in urine Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters
Urinary System Organs Kidney Filters blood, allowing toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions to leave the body in urine Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters
RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY
 RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY Peter McCue, M.D. Department of Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College There are no conflicts of interest. 1 Goals and Objectives! Goals Provide introduction
RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY Peter McCue, M.D. Department of Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College There are no conflicts of interest. 1 Goals and Objectives! Goals Provide introduction
Mr. I.K 58 years old
 Mr. I.K 58 years old Hospitalized because of marked pitting peripheral edema (bilateral crural and perimalleolar edema) and uncontrolled blood pressure (BP 150/100 mmhg under treatment). since age 54 years
Mr. I.K 58 years old Hospitalized because of marked pitting peripheral edema (bilateral crural and perimalleolar edema) and uncontrolled blood pressure (BP 150/100 mmhg under treatment). since age 54 years
Overview of glomerular diseases
 Overview of glomerular diseases *Endothelial cells are fenestrated each fenestra: 70-100nm in diameter Contractile, capable of proliferation, makes ECM & releases mediators *Glomerular basement membrane
Overview of glomerular diseases *Endothelial cells are fenestrated each fenestra: 70-100nm in diameter Contractile, capable of proliferation, makes ECM & releases mediators *Glomerular basement membrane
Year 2004 Paper one: Questions supplied by Megan
 QUESTION 53 Endothelial cell pathology on renal biopsy is most characteristic of which one of the following diagnoses? A. Pre-eclampsia B. Haemolytic uraemic syndrome C. Lupus nephritis D. Immunoglobulin
QUESTION 53 Endothelial cell pathology on renal biopsy is most characteristic of which one of the following diagnoses? A. Pre-eclampsia B. Haemolytic uraemic syndrome C. Lupus nephritis D. Immunoglobulin
Case Presentation Turki Al-Hussain, MD
 Case Presentation Turki Al-Hussain, MD Director, Renal Pathology Chapter Saudi Society of Nephrology & Transplantation Consultant Nephropathologist & Urological Pathologist Department of Pathology & Laboratory
Case Presentation Turki Al-Hussain, MD Director, Renal Pathology Chapter Saudi Society of Nephrology & Transplantation Consultant Nephropathologist & Urological Pathologist Department of Pathology & Laboratory
Dr P Sigwadi Paediatric Nephrology
 Dr P Sigwadi Paediatric Nephrology Prevalence - 5-15 % on a single urine sample After a series of 4 tests only 0.1% of children had persistent positive proteinuria Persistent proteinuria indicates the
Dr P Sigwadi Paediatric Nephrology Prevalence - 5-15 % on a single urine sample After a series of 4 tests only 0.1% of children had persistent positive proteinuria Persistent proteinuria indicates the
Jo Abraham MD Division of Nephrology University of Utah
 Jo Abraham MD Division of Nephrology University of Utah 68 year old male presented 3 weeks ago with a 3 month history of increasing fatigue He reported a 1 week history of increasing dyspnea with a productive
Jo Abraham MD Division of Nephrology University of Utah 68 year old male presented 3 weeks ago with a 3 month history of increasing fatigue He reported a 1 week history of increasing dyspnea with a productive
Multiple Myeloma Advances for clinical pathologists & histopathologists
 Multiple Myeloma Advances for clinical pathologists & histopathologists CME in Haematology 2014 IAPP & Dept of Pathology, BVDUMC, Pune Sunday, 4 th May 2014 Dr. M.B. Agarwal, MD, MNAMS Head, Dept of Haematology
Multiple Myeloma Advances for clinical pathologists & histopathologists CME in Haematology 2014 IAPP & Dept of Pathology, BVDUMC, Pune Sunday, 4 th May 2014 Dr. M.B. Agarwal, MD, MNAMS Head, Dept of Haematology
Anatomy/Physiology Study Guide: Unit 9 Excretory System
 Anatomy/Physiology Study Guide: Unit 9 Excretory System 1) In the space below, list the primary structures (organs) and their corresponding functions. Structures: Functions: KIDNEY 1) URETER BLADDER URETHRA
Anatomy/Physiology Study Guide: Unit 9 Excretory System 1) In the space below, list the primary structures (organs) and their corresponding functions. Structures: Functions: KIDNEY 1) URETER BLADDER URETHRA
PHGY210 Renal Physiology
 PHGY210 Renal Physiology Tomoko Takano, MD, PhD *Associate Professor of Medicine and Physiology McGill University *Nephrologist, McGill University Health Centre Lecture plan Lecture 1: Anatomy, basics
PHGY210 Renal Physiology Tomoko Takano, MD, PhD *Associate Professor of Medicine and Physiology McGill University *Nephrologist, McGill University Health Centre Lecture plan Lecture 1: Anatomy, basics
Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology
 Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
URINARY SYSTEM. Urinary System
 URINARY SYSTEM Urinary System Kidney Functions Excretion Regulation of blood volume and pressure Regulation of electrolyte and ph levels Kidney Structure Gross Anatomy Fibrous Capsule Renal Cortex Renal
URINARY SYSTEM Urinary System Kidney Functions Excretion Regulation of blood volume and pressure Regulation of electrolyte and ph levels Kidney Structure Gross Anatomy Fibrous Capsule Renal Cortex Renal
The Urinary S. (Chp. 10) & Excretion. What are the functions of the urinary system? Maintenance of water-salt and acidbase
 10.1 Urinary system The Urinary S. (Chp. 10) & Excretion 10.1 Urinary system What are the functions of the urinary system? 1. Excretion of metabolic wastes (urea, uric acid & creatinine) 1. Maintenance
10.1 Urinary system The Urinary S. (Chp. 10) & Excretion 10.1 Urinary system What are the functions of the urinary system? 1. Excretion of metabolic wastes (urea, uric acid & creatinine) 1. Maintenance
PRINCIPLE OF URINALYSIS
 PRINCIPLE OF URINALYSIS Vanngarm Gonggetyai Objective Can explain : the abnormalities detected in urine Can perform : routine urinalysis Can interprete : the results of urinalysis Examination of urine
PRINCIPLE OF URINALYSIS Vanngarm Gonggetyai Objective Can explain : the abnormalities detected in urine Can perform : routine urinalysis Can interprete : the results of urinalysis Examination of urine
Non-protein nitrogenous substances (NPN)
 Non-protein nitrogenous substances (NPN) A simple, inexpensive screening test a routine urinalysis is often the first test conducted if kidney problems are suspected. A small, randomly collected urine
Non-protein nitrogenous substances (NPN) A simple, inexpensive screening test a routine urinalysis is often the first test conducted if kidney problems are suspected. A small, randomly collected urine
Proteinuria (Protein in the Urine) Basics
 Proteinuria (Protein in the Urine) Basics OVERVIEW Proteinuria is the medical term for protein in the urine Urinary protein is detected by urine dipstick analysis, urinary protein: creatinine ratio (UP:C
Proteinuria (Protein in the Urine) Basics OVERVIEW Proteinuria is the medical term for protein in the urine Urinary protein is detected by urine dipstick analysis, urinary protein: creatinine ratio (UP:C
Running head: NEPHRON 1. The nephron the functional unit of the kidney. [Student Name] [Name of Institute] Author Note
![Running head: NEPHRON 1. The nephron the functional unit of the kidney. [Student Name] [Name of Institute] Author Note Running head: NEPHRON 1. The nephron the functional unit of the kidney. [Student Name] [Name of Institute] Author Note](/thumbs/77/75431210.jpg) Running head: NEPHRON 1 The nephron the functional unit of the kidney [Student Name] [Name of Institute] Author Note NEPHRON 2 The nephron the functional unit of the kidney The kidney is an important excretory
Running head: NEPHRON 1 The nephron the functional unit of the kidney [Student Name] [Name of Institute] Author Note NEPHRON 2 The nephron the functional unit of the kidney The kidney is an important excretory
Diabetes. Albumin. Analyte Information
 Diabetes Albumin Analyte Information -1-2014-05-02 Albumin Introduction Albumin consists of a single polypeptide chain of 585 amino acids with molecular weight of 66.5 kda. The chain is characterized by
Diabetes Albumin Analyte Information -1-2014-05-02 Albumin Introduction Albumin consists of a single polypeptide chain of 585 amino acids with molecular weight of 66.5 kda. The chain is characterized by
Renal Transporters- pathophysiology of drug - induced renal disorders. Lisa Harris, Pharmacist, John Hunter Hospital, Newcastle, 2015 November
 Renal Transporters- pathophysiology of drug - induced renal disorders Lisa Harris, Pharmacist, John Hunter Hospital, Newcastle, 2015 November Renal Failure Up to 25% of acute renal failure is drug induced
Renal Transporters- pathophysiology of drug - induced renal disorders Lisa Harris, Pharmacist, John Hunter Hospital, Newcastle, 2015 November Renal Failure Up to 25% of acute renal failure is drug induced
Interesting case seminar: Native kidneys Case Report:
 Interesting case seminar: Native kidneys Case Report: Proximal tubulopathy and light chain deposition disease presented as severe pulmonary hypertension with right-sided cardiac dysfunction and nephrotic
Interesting case seminar: Native kidneys Case Report: Proximal tubulopathy and light chain deposition disease presented as severe pulmonary hypertension with right-sided cardiac dysfunction and nephrotic
Renal Functions: Renal Functions: Renal Function: Produce Urine
 Renal Functions: Excrete metabolic waste products Reabsorb vital nutrients Regulate osmolarity: Maintain ion balance Regulate extracellular fluid volume (and thus blood pressure) Renal Functions: Regulate
Renal Functions: Excrete metabolic waste products Reabsorb vital nutrients Regulate osmolarity: Maintain ion balance Regulate extracellular fluid volume (and thus blood pressure) Renal Functions: Regulate
A clinical syndrome, composed mainly of:
 Nephritic syndrome We will discuss: 1)Nephritic syndrome: -Acute postinfectious (poststreptococcal) GN -IgA nephropathy -Hereditary nephritis 2)Rapidly progressive GN (RPGN) A clinical syndrome, composed
Nephritic syndrome We will discuss: 1)Nephritic syndrome: -Acute postinfectious (poststreptococcal) GN -IgA nephropathy -Hereditary nephritis 2)Rapidly progressive GN (RPGN) A clinical syndrome, composed
Histology Urinary system
 Histology Urinary system Urinary system Composed of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra, the urinary system plays a critical role in: 1- Blood filtration,(filtration of cellular
Histology Urinary system Urinary system Composed of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra, the urinary system plays a critical role in: 1- Blood filtration,(filtration of cellular
The functions of the kidney:
 The functions of the kidney: After reading this lecture you should be able to.. 1. List the main functions of the kidney. 2. Know the basic physiological anatomy of the kidney and the nephron 3. Describe
The functions of the kidney: After reading this lecture you should be able to.. 1. List the main functions of the kidney. 2. Know the basic physiological anatomy of the kidney and the nephron 3. Describe
Special Challenges and Co-Morbidities
 Special Challenges and Co-Morbidities Renal Disease/ Hypertension/ Diabetes in African-Americans M. Keith Rawlings, MD Medical Director Peabody Health Center AIDS Arms, Inc Dallas, TX Chair, Internal Medicine
Special Challenges and Co-Morbidities Renal Disease/ Hypertension/ Diabetes in African-Americans M. Keith Rawlings, MD Medical Director Peabody Health Center AIDS Arms, Inc Dallas, TX Chair, Internal Medicine
LECTURE 25: FILTRATION AND CLEARANCE NEPHRON FILTRATION
 LECTURE 25: FILTRATION AND CLEARANCE NEPHRON FILTRATION 1. Everything in the plasma is filtered except large proteins and red blood cells. The filtrate in Bowman s capsule is an isosmotic fluid that is
LECTURE 25: FILTRATION AND CLEARANCE NEPHRON FILTRATION 1. Everything in the plasma is filtered except large proteins and red blood cells. The filtrate in Bowman s capsule is an isosmotic fluid that is
Proteinuria Nephrotic syndrome
 Proteinuria Nephrotic syndrome Pathophysiology & management Miriam Davidovits, MD Institute of Nephrology Schneider Children s Medical Center of Israel 1 Abnormal excretion of protein into the urine is
Proteinuria Nephrotic syndrome Pathophysiology & management Miriam Davidovits, MD Institute of Nephrology Schneider Children s Medical Center of Israel 1 Abnormal excretion of protein into the urine is
PATTERNS OF RENAL INJURY
 PATTERNS OF RENAL INJURY Normal glomerulus podocyte Glomerular capillaries electron micrograph THE CLINICAL SYNDROMES 1. The Nephrotic Syndrome 2. The Acute Nephritic Syndrome 3. Rapidly Progressive Glomerulonephritis
PATTERNS OF RENAL INJURY Normal glomerulus podocyte Glomerular capillaries electron micrograph THE CLINICAL SYNDROMES 1. The Nephrotic Syndrome 2. The Acute Nephritic Syndrome 3. Rapidly Progressive Glomerulonephritis
Glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
 LECTURE NO (2) Renal Physiology Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) Faculty Of Medicine Dept.Of Physiology The glomerulus Is a tuft of capillaries enclosed within a Bowman capsule. It is supplied by an afferent
LECTURE NO (2) Renal Physiology Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) Faculty Of Medicine Dept.Of Physiology The glomerulus Is a tuft of capillaries enclosed within a Bowman capsule. It is supplied by an afferent
Proteinuria Nephrotic syndrome
 Proteinuria Nephrotic syndrome Pathophysiology & management Miriam Davidovits, MD Institute of Nephrology Schneider Children s Medical Center of Israel 1 Abnormal excretion of protein into the urine is
Proteinuria Nephrotic syndrome Pathophysiology & management Miriam Davidovits, MD Institute of Nephrology Schneider Children s Medical Center of Israel 1 Abnormal excretion of protein into the urine is
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues
 BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
Glomerular diseases mostly presenting with Nephritic syndrome
 Glomerular diseases mostly presenting with Nephritic syndrome 1 The Nephritic Syndrome Pathogenesis: proliferation of the cells in glomeruli & leukocytic infiltrate Injured capillary walls escape of RBCs
Glomerular diseases mostly presenting with Nephritic syndrome 1 The Nephritic Syndrome Pathogenesis: proliferation of the cells in glomeruli & leukocytic infiltrate Injured capillary walls escape of RBCs
RENAL SYSTEM 2 TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF NEPHRON SEGMENTS Emma Jakoi, Ph.D.
 RENAL SYSTEM 2 TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF NEPHRON SEGMENTS Emma Jakoi, Ph.D. Learning Objectives 1. Identify the region of the renal tubule in which reabsorption and secretion occur. 2. Describe the cellular
RENAL SYSTEM 2 TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF NEPHRON SEGMENTS Emma Jakoi, Ph.D. Learning Objectives 1. Identify the region of the renal tubule in which reabsorption and secretion occur. 2. Describe the cellular
Kidneys and Homeostasis
 16 The Urinary System The Urinary System OUTLINE: Eliminating Waste Components of the Urinary System Kidneys and Homeostasis Urination Urinary Tract Infections Eliminating Waste Excretion Elimination of
16 The Urinary System The Urinary System OUTLINE: Eliminating Waste Components of the Urinary System Kidneys and Homeostasis Urination Urinary Tract Infections Eliminating Waste Excretion Elimination of
Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg. Urine Casts. Microscopic Sediment Casts. Unit 2; Session 6
 Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg Unit 2; Session 6 Urine Casts Urine Casts Overview of Urinary Cast Formation Hyaline Casts Cellular Casts Granular Casts Waxy Casts Pseudo Casts Microscopic Sediment Casts
Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg Unit 2; Session 6 Urine Casts Urine Casts Overview of Urinary Cast Formation Hyaline Casts Cellular Casts Granular Casts Waxy Casts Pseudo Casts Microscopic Sediment Casts
REVIEW ARTICLE NEWER BIOMARKERS IN EARLY DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY
 JCD REVIEW ARTICLE NEWER BIOMARKERS IN EARLY DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY SAPTARSHI MUKHOPADHYAY* *FACULTY (DEPARTMENT OF MEDICINE), B R SINGH HOSPITAL (EASTERN RAILWAY), KOLKATA. INTRODUCTION renal disease. It
JCD REVIEW ARTICLE NEWER BIOMARKERS IN EARLY DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY SAPTARSHI MUKHOPADHYAY* *FACULTY (DEPARTMENT OF MEDICINE), B R SINGH HOSPITAL (EASTERN RAILWAY), KOLKATA. INTRODUCTION renal disease. It
MOLECULAR SIZE, ELECTRICAL CHARGE, AND SHAPE DETERMINE THE FILTERABILITY OF SOLUTES ACROSS THE GLOMERULAR FILTRATION BARRIER
 MOLECULAR SIZE, ELECTRICAL CHARGE, AND SHAPE DETERMINE THE FILTERABILITY OF SOLUTES ACROSS THE GLOMERULAR FILTRATION BARRIER The glomerular filtration barrier consists of three elements: (1) endothelial
MOLECULAR SIZE, ELECTRICAL CHARGE, AND SHAPE DETERMINE THE FILTERABILITY OF SOLUTES ACROSS THE GLOMERULAR FILTRATION BARRIER The glomerular filtration barrier consists of three elements: (1) endothelial
The Excretory System
 The Excretory System The excretory system The excretory system includes the skin, lungs and kidneys which all release metabolic wastes from the body. The kidneys, skin and the lungs are the principle organs
The Excretory System The excretory system The excretory system includes the skin, lungs and kidneys which all release metabolic wastes from the body. The kidneys, skin and the lungs are the principle organs
Urinary System BIO 250. Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat. Routes of Waste Elimination
 Urinary System BIO 250 Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat Routes of Waste Elimination Skin: Variable amounts of heat, salts, and water; small amounts of urea and
Urinary System BIO 250 Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat Routes of Waste Elimination Skin: Variable amounts of heat, salts, and water; small amounts of urea and
Introduction to Clinical Diagnosis Nephrology
 Introduction to Clinical Diagnosis Nephrology I. David Weiner, M.D. C. Craig and Audrae Tisher Chair in Nephrology Professor of Medicine and Physiology and Functional Genomics University of Florida College
Introduction to Clinical Diagnosis Nephrology I. David Weiner, M.D. C. Craig and Audrae Tisher Chair in Nephrology Professor of Medicine and Physiology and Functional Genomics University of Florida College
Nephrotic Syndrome. Abstract. MK Mani Chief Nephrologist, Apollo Hospital, 21, Greams Lane, Chennai
 Nephrotic Syndrome MK Mani Chief Nephrologist, Apollo Hospital, 21, Greams Lane, Chennai 600 006. 129 Abstract Much information has become available in recent times about the structure of the glomerular
Nephrotic Syndrome MK Mani Chief Nephrologist, Apollo Hospital, 21, Greams Lane, Chennai 600 006. 129 Abstract Much information has become available in recent times about the structure of the glomerular
Basic Urinary Tract Anatomy and Histology
 Basic Urinary Tract Anatomy and Histology The two kidneys are located in the retroperitoneum on either side of the vertebral bladder and the contraction of the detrusor muscle. Any mechanical barrier,
Basic Urinary Tract Anatomy and Histology The two kidneys are located in the retroperitoneum on either side of the vertebral bladder and the contraction of the detrusor muscle. Any mechanical barrier,
Nephrology - the study of the kidney. Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system
 Urinary System Nephrology - the study of the kidney Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system Functions of the Urinary System 1. Regulation
Urinary System Nephrology - the study of the kidney Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system Functions of the Urinary System 1. Regulation
2) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure.
 Class: A&P2-1 Description: Test: Excretory Test Points: 144 Test Number: 28379 Printed: 31-March-10 12:03 1) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure. Click on the Bowman's
Class: A&P2-1 Description: Test: Excretory Test Points: 144 Test Number: 28379 Printed: 31-March-10 12:03 1) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure. Click on the Bowman's
Urinary Physiology. Chapter 17 Outline. Kidney Function. Chapter 17
 Urinary Physiology Chapter 17 Chapter 17 Outline Structure and Function of the Kidney Glomerular Filtration Reabsorption of Salt and Water Renal Plasma Clearance Renal Control of Electrolyte and Acid-Base
Urinary Physiology Chapter 17 Chapter 17 Outline Structure and Function of the Kidney Glomerular Filtration Reabsorption of Salt and Water Renal Plasma Clearance Renal Control of Electrolyte and Acid-Base
Urinary system. Urinary system
 INTRODUCTION. Several organs system Produce urine and excrete it from the body Maintenance of homeostasis. Components. two kidneys, produce urine; two ureters, carry urine to single urinary bladder for
INTRODUCTION. Several organs system Produce urine and excrete it from the body Maintenance of homeostasis. Components. two kidneys, produce urine; two ureters, carry urine to single urinary bladder for
FIBRILLARY GLOMERULONEPHRITIS DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA, PITFALLS, AND DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
 FIBRILLARY GLOMERULONEPHRITIS DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA, PITFALLS, AND DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS Guillermo A. Herrera MD Louisiana State University, Shreveport Fibrils in bundles 10-20 nm d Diabetic fibrillosis
FIBRILLARY GLOMERULONEPHRITIS DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA, PITFALLS, AND DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS Guillermo A. Herrera MD Louisiana State University, Shreveport Fibrils in bundles 10-20 nm d Diabetic fibrillosis
Monoclonal Gammopathies and the Kidney. Tibor Nádasdy, MD The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH
 Monoclonal Gammopathies and the Kidney Tibor Nádasdy, MD The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH Monoclonal gammopathy of renal significance (MGRS) Biopsies at OSU (n=475) between 2007 and 2016 AL or AH
Monoclonal Gammopathies and the Kidney Tibor Nádasdy, MD The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH Monoclonal gammopathy of renal significance (MGRS) Biopsies at OSU (n=475) between 2007 and 2016 AL or AH
Collin County Community College RENAL PHYSIOLOGY
 Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 12 Urinary System 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Glomerular Filtration Filtration process that occurs in Bowman s Capsule Blood is filtered and
Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 12 Urinary System 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Glomerular Filtration Filtration process that occurs in Bowman s Capsule Blood is filtered and
Chapter 20 Diseases of the kidney:
 Chapter 20 Diseases of the kidney: 1. Which of the following is seen in Nephrotic syndrome (2000, 2004) (a) Albumin is lost in the urine, while other globulins are unaffected (b) Early hypertension (c)
Chapter 20 Diseases of the kidney: 1. Which of the following is seen in Nephrotic syndrome (2000, 2004) (a) Albumin is lost in the urine, while other globulins are unaffected (b) Early hypertension (c)
Renal Disease and PK/PD. Anjay Rastogi MD PhD Division of Nephrology
 Renal Disease and PK/PD Anjay Rastogi MD PhD Division of Nephrology Drugs and Kidneys Kidney is one of the major organ of drug elimination from the human body Renal disease and dialysis alters the pharmacokinetics
Renal Disease and PK/PD Anjay Rastogi MD PhD Division of Nephrology Drugs and Kidneys Kidney is one of the major organ of drug elimination from the human body Renal disease and dialysis alters the pharmacokinetics
Dr Ian Roberts Oxford. Oxford Pathology Course 2010 for FRCPath Illustration-Cellular Pathology. Oxford Radcliffe NHS Trust
 Dr Ian Roberts Oxford Oxford Pathology Course 2010 for FRCPath Plan of attack: Diagnostic approach to the renal biopsy Differential diagnosis of the clinical syndromes of renal disease Microscopy Step
Dr Ian Roberts Oxford Oxford Pathology Course 2010 for FRCPath Plan of attack: Diagnostic approach to the renal biopsy Differential diagnosis of the clinical syndromes of renal disease Microscopy Step
CASE 3 AN UNUSUAL CASE OF NEPHROTIC SYNDROME
 CASE 3 AN UNUSUAL CASE OF NEPHROTIC SYNDROME Dr Seethalekshmy N.V., Dr.Annie Jojo, Dr Hiran K.R., Amrita institute of Medical Sciences, Kochi, Kerala Case history 34 year old gentleman Nephrotic range
CASE 3 AN UNUSUAL CASE OF NEPHROTIC SYNDROME Dr Seethalekshmy N.V., Dr.Annie Jojo, Dr Hiran K.R., Amrita institute of Medical Sciences, Kochi, Kerala Case history 34 year old gentleman Nephrotic range
Functional morphology of kidneys Clearance
 Functional morphology of kidneys Clearance Assoc. Prof. MUDr. Markéta Bébarová, Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine, Masaryk University This presentation includes only the most important
Functional morphology of kidneys Clearance Assoc. Prof. MUDr. Markéta Bébarová, Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine, Masaryk University This presentation includes only the most important
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY WESTMEAD PRIMARY EXAM
 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY WESTMEAD PRIMARY EXAM RENAL PHYSIOLOGY - ANATOMY Glomerulus + renal tubule Each kidney has 1.3 million nephrons Cortical nephrons (85%) have shorter Loop of Henle than Juxtamedullary nephrons
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY WESTMEAD PRIMARY EXAM RENAL PHYSIOLOGY - ANATOMY Glomerulus + renal tubule Each kidney has 1.3 million nephrons Cortical nephrons (85%) have shorter Loop of Henle than Juxtamedullary nephrons
Tarek ElBaz, MD. Prof. Internal Medicine Chief, Division of Renal Medicine Al Azhar University President, ESNT
 The Kidney in Multiple Myeloma Tarek ElBaz, MD. Prof. Internal Medicine Chief, Division of Renal Medicine Al Azhar University President, ESNT Normal Cell Plasma cells produce antibodies that bind to antigens,
The Kidney in Multiple Myeloma Tarek ElBaz, MD. Prof. Internal Medicine Chief, Division of Renal Medicine Al Azhar University President, ESNT Normal Cell Plasma cells produce antibodies that bind to antigens,
Dr P Sigwadi 30 May 2012
 Dr P Sigwadi 30 May 2012 Introduction Haematuria Positive blood on urine dipstick 5 red blood cells/ microliter of urine Prevalence Gross haematuria ( macroscopic) 0.13 % Microscopic- 1.5% Haematuria +
Dr P Sigwadi 30 May 2012 Introduction Haematuria Positive blood on urine dipstick 5 red blood cells/ microliter of urine Prevalence Gross haematuria ( macroscopic) 0.13 % Microscopic- 1.5% Haematuria +
The Urinary System. BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues. Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 16 The Urinary System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 16 The Urinary System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
April 08, biology 2201 ch 11.3 excretion.notebook. Biology The Excretory System. Apr 13 9:14 PM EXCRETORY SYSTEM.
 Biology 2201 11.3 The Excretory System EXCRETORY SYSTEM 1 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid base concentrations and metabolite concentrations
Biology 2201 11.3 The Excretory System EXCRETORY SYSTEM 1 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid base concentrations and metabolite concentrations
Outline Urinary System. Urinary System and Excretion. Urine. Urinary System. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system
 Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Chapter 16 Renal will be on the Final only. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of
Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Chapter 16 Renal will be on the Final only. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of
URINARY SYSTEM CHAPTER 28 I ANATOMY OF THE URINARY SYSTEM. Student Name
 Student Name CHAPTER 28 URINARY SYSTEM L iving produces wastes. Wherever people live or work or play, wastes accumulate. To keep these areas healthy, there must be a method of disposing of these wastes
Student Name CHAPTER 28 URINARY SYSTEM L iving produces wastes. Wherever people live or work or play, wastes accumulate. To keep these areas healthy, there must be a method of disposing of these wastes
Renal Pathology 1: Glomerulus. With many thanks to Elizabeth Angus PhD for EM photographs
 Renal Pathology 1: Glomerulus With many thanks to Elizabeth Angus PhD for EM photographs Anatomy of the Kidney http://www.yalemedicalgroup.org/stw/page.asp?pageid=stw028980 The Nephron http://www.beltina.org/health-dictionary/nephron-function-kidney-definition.html
Renal Pathology 1: Glomerulus With many thanks to Elizabeth Angus PhD for EM photographs Anatomy of the Kidney http://www.yalemedicalgroup.org/stw/page.asp?pageid=stw028980 The Nephron http://www.beltina.org/health-dictionary/nephron-function-kidney-definition.html
Renal physiology D.HAMMOUDI.MD
 Renal physiology D.HAMMOUDI.MD Functions Regulating blood ionic composition Regulating blood ph Regulating blood volume Regulating blood pressure Produce calcitrol and erythropoietin Regulating blood glucose
Renal physiology D.HAMMOUDI.MD Functions Regulating blood ionic composition Regulating blood ph Regulating blood volume Regulating blood pressure Produce calcitrol and erythropoietin Regulating blood glucose
Kidney Functions Removal of toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions from the blood Regulation of blood volume, chemical composition, and ph
 The Urinary System Urinary System Organs Kidneys are major excretory organs Urinary bladder is the temporary storage reservoir for urine Ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder Urethra
The Urinary System Urinary System Organs Kidneys are major excretory organs Urinary bladder is the temporary storage reservoir for urine Ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder Urethra
Chapter 1 RENAL HAEMODYNAMICS AND GLOMERULAR FILTRATION
 3 Chapter 1 RENAL HAEMODYNAMICS AND GLOMERULAR FILTRATION David Shirley, Giovambattista Capasso and Robert Unwin The kidney has three homeostatic functions that can broadly be described as excretory, regulatory
3 Chapter 1 RENAL HAEMODYNAMICS AND GLOMERULAR FILTRATION David Shirley, Giovambattista Capasso and Robert Unwin The kidney has three homeostatic functions that can broadly be described as excretory, regulatory
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE (CKD)
 CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE (CKD) CKD implies longstanding (more than 3 months), and usually progressive, impairment in renal function. In many instances, no effective means are available to reverse the primary
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE (CKD) CKD implies longstanding (more than 3 months), and usually progressive, impairment in renal function. In many instances, no effective means are available to reverse the primary
Alterations of Renal and Urinary Tract Function
 Alterations of Renal and Urinary Tract Function Chapter 29 Urinary Tract Obstruction Urinary tract obstruction is an interference with the flow of urine at any site along the urinary tract The obstruction
Alterations of Renal and Urinary Tract Function Chapter 29 Urinary Tract Obstruction Urinary tract obstruction is an interference with the flow of urine at any site along the urinary tract The obstruction
Renal Physiology - Lectures
 Renal Physiology 2011 Lisa M. Harrison-Bernard, PhD lharris@lsuhsc.edu Renal Physiology - Lectures Physiology of Body Fluids 2. Structure & Function of the Kidneys 3. Renal Clearance & Glomerular Filtration
Renal Physiology 2011 Lisa M. Harrison-Bernard, PhD lharris@lsuhsc.edu Renal Physiology - Lectures Physiology of Body Fluids 2. Structure & Function of the Kidneys 3. Renal Clearance & Glomerular Filtration
Diabetes, Obesity and Heavy Proteinuria
 Diabetes, Obesity and Heavy Proteinuria Clinical Case 41 yo Black woman with heavy proteinuria History 2014: noted to have proteinuria on routine lab testing (1.1g/g). 1+ edema. Blood pressure has been
Diabetes, Obesity and Heavy Proteinuria Clinical Case 41 yo Black woman with heavy proteinuria History 2014: noted to have proteinuria on routine lab testing (1.1g/g). 1+ edema. Blood pressure has been
Surgical Pathology Report
 Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center Department of Pathology Shreveport, Louisiana Accession #: Collected: Received: Reported: 6/1/2012 09:18 6/2/2012 09:02 6/2/2012 Patient Name: Med. Rec.
Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center Department of Pathology Shreveport, Louisiana Accession #: Collected: Received: Reported: 6/1/2012 09:18 6/2/2012 09:02 6/2/2012 Patient Name: Med. Rec.
Excretory System-Training Handout
 Excretory System-Training Handout Karen L. Lancour National Rules Committee Chairman Life Science Excretion - Excretion is the removal of the metabolic wastes of an organism. Wastes that are removed include
Excretory System-Training Handout Karen L. Lancour National Rules Committee Chairman Life Science Excretion - Excretion is the removal of the metabolic wastes of an organism. Wastes that are removed include
PHSI2006/2906: Integrated Physiology B
 PHSI2006/2906: Integrated Physiology B TOPIC 1: RESPIRATION 1. The Mechanics of Breathing...2 2. Work of Breathing....5 3. Pulmonary Gas Exchange.. 10 4. Transport of Oxygen...16 5. Control of Respiration...20
PHSI2006/2906: Integrated Physiology B TOPIC 1: RESPIRATION 1. The Mechanics of Breathing...2 2. Work of Breathing....5 3. Pulmonary Gas Exchange.. 10 4. Transport of Oxygen...16 5. Control of Respiration...20
Lab Activity 31. Anatomy of the Urinary System. Portland Community College BI 233
 Lab Activity 31 Anatomy of the Urinary System Portland Community College BI 233 Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder: provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters: transport
Lab Activity 31 Anatomy of the Urinary System Portland Community College BI 233 Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder: provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters: transport
Chronic Kidney Disease of Uncertain Aetiology - Clinical Features. Dr. Tilak Abeysekera Consultant Nephrologist
 Chronic Kidney Disease of Uncertain Aetiology - Clinical Features Dr. Tilak Abeysekera Consultant Nephrologist Geographical Distribution Dry Zone Factors Considered for the Diagnosis of CKDu >5 years stay
Chronic Kidney Disease of Uncertain Aetiology - Clinical Features Dr. Tilak Abeysekera Consultant Nephrologist Geographical Distribution Dry Zone Factors Considered for the Diagnosis of CKDu >5 years stay
Nephron Structure inside Kidney:
 In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Problem Set #8 Solutions p. 1
 BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Problem Set #8 Solutions p. 1 1. a. Proximal tubule. b. Proximal tubule. c. Glomerular endothelial fenestrae, filtration slits between podocytes of Bowman's capsule.
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Problem Set #8 Solutions p. 1 1. a. Proximal tubule. b. Proximal tubule. c. Glomerular endothelial fenestrae, filtration slits between podocytes of Bowman's capsule.
Nephron Function and Urine Formation. Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S
 Nephron Function and Urine Formation Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S The Role of the Nephron In order for the body to properly function and maintain homeostasis, the amount of dissolved substances
Nephron Function and Urine Formation Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S The Role of the Nephron In order for the body to properly function and maintain homeostasis, the amount of dissolved substances
EXCRETION IN HUMANS 31 JULY 2013
 EXCRETION IN HUMANS 31 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss organs of excretion Look at the structure of the urinary system Look at the structure and functioning of the kidney Discuss
EXCRETION IN HUMANS 31 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss organs of excretion Look at the structure of the urinary system Look at the structure and functioning of the kidney Discuss
describe the location of the kidneys relative to the vertebral column:
 Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) list the three major functions of the urinary system: by examining Fig. 24-1, list the organs of the urinary system: describe the location
Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) list the three major functions of the urinary system: by examining Fig. 24-1, list the organs of the urinary system: describe the location
The principal functions of the kidneys
 Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
Excretion: is the removal of waste products formed by metabolism, out of the body
 Excretion in Humans Excretion: is the removal of waste products formed by metabolism, out of the body Accumulation of wastes in the cells would affect the normal functioning of the cells By getting rid
Excretion in Humans Excretion: is the removal of waste products formed by metabolism, out of the body Accumulation of wastes in the cells would affect the normal functioning of the cells By getting rid
OST Course Schedule
 OST 572 2017 Course Schedule Updated 03/06/2017 (aes) Week 1 Monday March 13, 2017 7:30-7:45 Course Syllabus /Schedule and announcements (posted on D2L) Kaufman Self Study Tuesday, March 14, 2017 1 Course
OST 572 2017 Course Schedule Updated 03/06/2017 (aes) Week 1 Monday March 13, 2017 7:30-7:45 Course Syllabus /Schedule and announcements (posted on D2L) Kaufman Self Study Tuesday, March 14, 2017 1 Course
