ENDOCRINOLOGY, DIABETES, AND METABOLISM Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Examination Blueprint
|
|
|
- Marcia Parsons
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ENDOCRINOLOGY, DIABETES, AND METABOLISM Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Examination Blueprint ABIM invites diplomates to help develop the Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism MOC exam blueprint Based on feedback from physicians that MOC assessments should better reflect what they see in practice, in 2016 the American Board of Internal Medicine (ABIM) invited all certified endocrinologists to provide ratings of the relative frequency and importance of blueprint topics in practice. This review process, which resulted in a new MOC exam blueprint, will be used on an ongoing basis to inform and update all MOC assessments created by ABIM. No matter what form ABIM s assessments ultimately take, they will need to be informed by front-line clinicians sharing their perspective on what is important to know. A sample of over 300 endocrinologists, similar to the total invited population of endocrinologists in age, gender, geographic region, and time spent in direct patient care, provided the blueprint topic ratings. The ABIM Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism Exam Committee and Board have used this feedback to update the blueprint for the MOC exam (beginning with the Fall 2016 administration). To inform how exam content should be distributed across the major blueprint content categories, ABIM considered the average respondent ratings of topic frequency and importance in each of the content categories. A second source of information was the relative frequency of patient conditions in the content categories, as seen by certified endocrinologists and documented by national health care data (described further under Content distribution below). To determine prioritization of specific exam content within each major medical content category, ABIM used the respondent ratings of topic frequency and importance to set thresholds for these parameters in the exam assembly process (described further under Detailed content outline below). Purpose of the Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism MOC exam The MOC exam is designed to evaluate whether a certified endocrinologist has maintained competence and currency in the knowledge and judgment required for practice. The exam emphasizes diagnosis and management of prevalent conditions, particularly in areas where practice has changed in recent years. As a result of the recent blueprint review by ABIM diplomates, the MOC exams will place less emphasis on rare conditions and focus more on situations in which physician intervention can have important consequences for patients. For conditions that are usually managed by other specialists, the focus will be on recognition rather than on management. Exam format The exam is composed of 240 single-best-answer multiple-choice questions, of which 40 are new questions that do not count in the examinee s score (more information on how exams are developed can be found at abim.org/about/exam-information/exam-development.aspx). Most questions describe clinical scenarios and ask about the work done (that is, tasks performed) by physicians in the course of practice: Diagnosis: making a diagnosis or identifying an underlying condition Testing: ordering tests for diagnosis, staging, or follow-up : recommending treatment or other patient care : assessing risk, determining prognosis, and applying principles from epidemiologic studies : understanding the pathophysiology of disease and basic science knowledge applicable to patient care JANUARY
2 Clinical scenarios presented take place in outpatient or inpatient settings as appropriate to a typical Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism practice. Clinical information presented may include diagnostic imaging studies, continuous glucose monitoring tracings, radiographic studies, or patient photographs. A tutorial, including examples of ABIM exam question format, can be found at abim.org/maintenance-of-certification/ exam-information/endocrinology-diabetes-metabolism/ exam-tutorial.aspx. Content distribution Listed below are the major medical content categories that define the domain for the Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism MOC exam. The relative distribution of content is expressed as a percentage of the total exam. To determine the content distribution, ABIM considered the average respondent ratings of topic frequency and importance. To cross-validate these self-reported ratings, ABIM also considered the relative frequency of conditions seen in Medicare patients by a cohort of certified endocrinologists. Informed by these data, the Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism Board Exam Committee and Board determined the content category CONTENT CATEGORY TARGET % Adrenal Disorders 9% Pituitary Disorders 9% Lipids, Obesity, and Nutrition 14% Female Reproduction 6% Male Reproduction 6% How the blueprint ratings are used to assemble the MOC exam Blueprint reviewers provided ratings of relative frequency in practice for each of the detailed content topics in the blueprint and provided ratings of the relative importance of the topics for each of the tasks described in Exam format above. In rating importance, reviewers were asked to consider factors such as the following: High risk of a significant adverse outcome Cost of care and stewardship of resources Common errors in diagnosis or management Effect on population health Effect on quality of life When failure to intervene by the physician deprives a patient of significant benefit Frequency and importance were rated on a three-point scale corresponding to low, medium, or high. The median importance ratings are reflected in the Detailed content outline below. The Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism Board Exam Committee and Board, in partnership with the physician community, have set the following parameters for selecting MOC exam questions according to the blueprint review ratings: At least 75% of exam questions will address high-importance content (indicated in green) No more than 25% of exam questions will address medium-importance content (indicated in yellow) No exam questions will address low-importance content (indicated in red) Independent of the importance and task ratings, no more than 25% of exam questions will address low-frequency content (indicated by following the topic description). Diabetes Mellitus and Hypoglycemia 26% Calcium and Bone Disorders 15% Thyroid Disorders 15% Total 100% targets shown below. The Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism MOC exam may cover other dimensions of medicine as applicable to the medical content categories, such as adolescent medicine. JANUARY
3 The content selection priorities below are applicable beginning with the Fall 2016 MOC exam and are subject to change in response to future blueprint review. Note: The same topic may appear in more than one medical content category. Detailed content outline for the Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism MOC exam High Importance: At least 75% of exam tasks Low Frequency: No more than 25% of exam questions will address topics with this designation, regardless of task or importance. ADRENAL DISORDERS (9% of exam) Diagnosis Testing GLUCOCORTICOIDS (3.5% of exam) Cushing s syndrome Management of glucocorticoid therapy Adrenal insufficiency Glucocorticoid resistance MINERALOCORTICOIDS (2% of exam) Hyperaldosteronism Hypoaldosteronism ADRENAL ANDROGENS (<2% of exam) Congenital adrenal hyperplasia ADRENAL INCIDENTALOMA (<2% of exam) Adrenal incidentaloma ADRENAL MEDULLA (<2% of exam) Pheochromocytoma Neurofibromatosis type 1 von Hippel Lindau syndrome Multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN) types 2A and 2B Familial paraganglioma syndromes Familial paragangliomapheochomocytoma syndromes JANUARY
4 tasks Low Frequency: No more than 25% of exam questions will address topics with this designation, regardless of task or importance. ADRENAL DISORDERS (9% of exam) Diagnosis Testing ADRENAL CANCER (<2% of exam) Adrenal cancer PITUITARY DISORDERS (9% of exam) Diagnosis Testing PROLACTIN (<2% of exam) Hyperprolactinemia Normoprolactinemic galactorrhea GROWTH HORMONE (<2% of exam) Acromegaly Deficiency THYROID-STIMULATING HORMONE (TSH) (<2% of exam) Thyroid-stimulating hormonesecreting adenoma Hyperplasia secondary to longstanding primary hypothyroidism Thyroid-stimulating hormone deficiency GONADOTROPINS (<2% of exam) Gonadotroph pituitary tumors Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism NONSECRETING PITUITARY TUMORS (<2% of exam) Nonsecreting pituitary tumors ADRENOCORTICOTROPIC HORMONE (ACTH) (<2% of exam) Cushing s disease ACTH deficiency JANUARY
5 tasks Low Frequency: No more than 25% of exam questions will address topics with this designation, regardless of task or importance. PITUITARY DISORDERS (9% of exam) Diagnosis Testing HYPOPITUITARISM (<2% of exam) Clinical presentation Causes Tumors Pituitary apoplexy Sheehan s syndrome Hemochromatosis Lymphocytic hypophysitis Sarcoidosis Traumatic brain injury Iatrogenic (radiation, surgery) Treatment Adjustment of growth hormone according to insulin-like growth factor 1 levels Monitoring of thyroid with free thyroxine (T4) Clinical adjustment of glucocorticoids EMPTY SELLA SYNDROME (<2% of exam) Empty sella syndrome ANTIDIURETIC HORMONE (ADH) (<2% of exam) Diabetes insipidus Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH) CRANIOPHARYNGIOMA (<2% of exam) Craniopharyngioma PITUITARY INCIDENTALOMA (<2% of exam) Pituitary incidentaloma JANUARY
6 tasks Low Frequency: No more than 25% of exam questions will address topics with this designation, regardless of task or importance. LIPIDS, OBESITY, AND NUTRITION (14% of exam) Diagnosis Testing HYPERCHOLESTEROLEMIA (<2% of exam) Primary disorders Familial hypercholesterolemia Familial defective apolipoprotein B-100 Lipoprotein (a) Elevated high-density lipoprotein cholesterol Secondary disorders HYPERTRIGLYCERIDEMIA (2% of exam) Primary disorders Familial hypertriglyceridemia Apoprotein/lipase disorders Secondary disorders Chylomicronemia MIXED HYPERLIPIDEMIA (3% of exam) Primary disorders Familial combined hyperlipidemia Familial dysbetalipoproteinemia (type III) Secondary disorders HYPOLIPIDEMIA (0% of exam) Primary disorders Secondary disorders JANUARY
7 tasks Low Frequency: No more than 25% of exam questions will address topics with this designation, regardless of task or importance. LIPIDS, OBESITY, AND NUTRITION (14% of exam) Diagnosis Testing TREATMENT OF LIPID DISORDERS (5% of exam) Diet Drugs Lifestyle Indications for treatment OBESITY AND NUTRITION (2.5% of exam) Primary disorders Secondary disorders Comorbidities Treatment of obesity Diet Drugs Lifestyle Indications for treatment FEMALE REPRODUCTION (6% of exam) Diagnosis Testing AMENORRHEA (<2% of exam) Primary Androgen insensitivity syndrome Turner syndrome Mullerian dysgenesis Congenital gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) deficiency Secondary JANUARY
8 tasks Low Frequency: No more than 25% of exam questions will address topics with this designation, regardless of task or importance. FEMALE REPRODUCTION (6% of exam) Diagnosis Testing HYPERANDROGENISM (<2% of exam) Polycystic ovary syndrome Non-polycystic ovary syndrome Hyperthecosis Ovarian tumors Adrenal tumors Nonclassic congenital adrenal hyperplasia Pregnancy-associated Anabolic steroids PREMENSTRUAL SYNDROME AND PREMENSTRUAL DYSPHORIC DISORDER (<2% of exam) Premenstrual syndrome and premenstrual dysphoric disorder ENDOCRINE CAUSES OF INFERTILITY (<2% of exam) Anovulation Age-associated infertility (diminished ovarian reserve) HORMONAL CONTRACEPTION (<2% of exam) Combined estrogen-progestin contraception Progestin-only contraception PERIMENOPAUSE AND MENOPAUSE (<2% of exam) Perimenopause Menopause Estrogen-progestin therapy SEXUAL DIFFERENTIATION (<2% of exam) Gender dysphoria Female-to-male transgender management JANUARY
9 tasks Low Frequency: No more than 25% of exam questions will address topics with this designation, regardless of task or importance. MALE REPRODUCTION (6% of exam) Diagnosis Testing HYPOGONADISM (3% of exam) Testosterone in hypogonadism Sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG)-dependent changes in testosterone Primary hypogonadism Secondary hypogonadism Genetic disorders of androgen production and action Testosterone therapy Gonadotropins INFERTILITY (<2% of exam) Causes Varicocele Cryptorchidism Klinefelter syndrome Cystic fibrosis and cystic fibrosis gene mutations Sertoli-cell-only syndrome Drug-induced infertility Obstructive azoospermia Idiopathic oligozoospermia Y-chromosome microdeletions Treatment Gonadotropins Testicular sperm extraction Intracytoplasmic sperm injection JANUARY
10 tasks Low Frequency: No more than 25% of exam questions will address topics with this designation, regardless of task or importance. MALE REPRODUCTION (6% of exam) Diagnosis Testing GYNECOMASTIA (<2% of exam) Causes Drug-induced gynecomastia Testicular tumors (Sertoli and Leydig cell tumors) Extratesticular tumors Androgen deprivation therapy for prostate cancer Hyperthyroidism Refeeding syndrome Pubertal gynecomastia Idiopathic gynecomastia Congenital and familial aromatase excess syndromes Treatment Tamoxifen Aromatase inhibitors Mammoplasty and mastectomy ERECTILE DYSFUNCTION (<2% of exam) Causes Smoking Diabetes mellitus Hypertension Hyperlipidemia Peyronie s disease Pelvic and prostate surgery Obesity JANUARY
11 tasks Low Frequency: No more than 25% of exam questions will address topics with this designation, regardless of task or importance. MALE REPRODUCTION (6% of exam) Diagnosis Testing ERECTILE DYSFUNCTION (<2% of exam) Diagnostic tests Penile duplex Doppler ultrasound Corpus cavernosography Treatment Phosphodiesterase-5 and non-specific phosphodiesterase inhibitors Prostaglandin E1, intraurethral and intracavernosal Alpha-adrenergic blockers Penis pump (penile vacuum device) Penile implant TESTOSTERONE IN AGING MEN (<2% of exam) Testosterone in aging men ABUSE OF ANDROGENS AND ANABOLIC STEROIDS (<2% of exam) Abuse of androgens and anabolic steroids SEXUAL DIFFERENTIATION (<2% of exam) Gender dysphoria Male-to-female transgender management EJACULATORY DYSFUNCTIONS (<2% of exam) Premature ejaculation Delayed ejaculation JANUARY
12 tasks Low Frequency: No more than 25% of exam questions will address topics with this designation, regardless of task or importance. DIABETES MELLITUS AND HYPOGLYCEMIA (26% of exam) Diagnosis Testing PREDIABETES (2% of exam) Impaired fasting glucose Impaired glucose tolerance Screening MONITORING GLYCEMIC CONTROL (2% of exam) Hemoglobin A1c Fructosamine, 1,5-anhydroglucitol Conventional glucose monitoring Ketone testing Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) TYPE 1 DIABETES MELLITUS (4% of exam) Ketoacidosis Recent-onset type 1 diabetes Latent autoimmune diabetes of the adult (LADA) Hyperglycemia in type 1 diabetes Hypoglycemia due to insulin management Pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS (5% of exam) Hyperosmolar nonketotic state Hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes Hypoglycemia due to oral agents and insulin management Pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes JANUARY
13 tasks Low Frequency: No more than 25% of exam questions will address topics with this designation, regardless of task or importance. DIABETES MELLITUS AND HYPOGLYCEMIA (26% of exam) Diagnosis Testing ADDITIONAL TYPES OF DIABETES (<2% of exam) Monogenic diabetes Ketosis-prone diabetes (KPD) New onset diabetes after transplant (NODAT) [posttransplant diabetes mellitus- PTDM] Pancreatic diabetes Cystic fibrosis-related diabetes Drug-induced diabetes RECOGNITION AND MANAGEMENT OF ASSOCIATED CONDITIONS (2% of exam) Hypertension Dyslipidemia Obesity Sleep apnea Fatty liver Thyroid disease Celiac disease Polycystic ovary syndrome Eating disorders Dead-in-bed syndrome PREGNANCY (<2% of exam) Gestational diabetes Pre-gestational diabetes JANUARY
14 tasks Low Frequency: No more than 25% of exam questions will address topics with this designation, regardless of task or importance. DIABETES MELLITUS AND HYPOGLYCEMIA (26% of exam) Diagnosis Testing DIABETES MELLITUS COMPLICATIONS (5% of exam) Microvascular Retinopathy Nephropathy Neuropathy Macular edema Mononeuropathies Macrovascular Coronary artery disease Heart failure Peripheral vascular disease Diabetic foot Skin disorders Lipohypertrophy Lipoatrophy Necrobiosis lipoidica Acanthosis nigricans Neuropsychiatric ISLET CELL AND PANCREAS TRANSPLANTATION (<2% of exam) Islet cell and pancreas transplantation HYPOGLYCEMIA INDEPENDENT OF DIABETES (2% of exam) Insulinoma Noninsulinoma Hypoglycemia unawareness JANUARY
15 tasks Low Frequency: No more than 25% of exam questions will address topics with this designation, regardless of task or importance. DIABETES MELLITUS AND HYPOGLYCEMIA (26% of exam) Diagnosis Testing INPATIENT DIABETES MANAGEMENT (<2% of exam) Intensive care unit Non-intensive care unit CALCIUM AND BONE DISORDERS (15% of exam) Diagnosis Testing HYPERCALCEMIA (3% of exam) Parathyroid hormone-mediated Primary hyperparathyroidism Familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia Lithium-induced Non-parathyroid hormone-mediated Hypercalcemia of malignancy Milk-alkali syndrome Sarcoidosis, tuberculosis, and other granulomatous diseases Vitamin D intoxication Post-rhabdomyolysis Adynamic bone disease Myeloma Acute adrenal insufficiency Vitamin A JANUARY
16 tasks Low Frequency: No more than 25% of exam questions will address topics with this designation, regardless of task or importance. CALCIUM AND BONE DISORDERS (15% of exam) Diagnosis Testing HYPOCALCEMIA (3% of exam) Hypoparathyroidism Parathyroid hormone (PTH) resistance Hypomagnesemia Hyperphosphatemia Celiac disease Hypocalcemia (general) OSTEOPOROSIS (4% of exam) In female In male Post-transplant and glucocorticoid-induced Renal, hepatic, and gastrointestinal disease related PAGET S DISEASE OF BONE (<2% of exam) Paget s disease of bone HYPOVITAMINOSIS D (<2% of exam) Dietary deficiency Limited sun exposure Malabsorption Liver failure Renal insufficiency Vitamin D dependent rickets type I and II Vitamin D resistant rickets Drug-induced Bone disease Nonskeletal disorders JANUARY
17 tasks Low Frequency: No more than 25% of exam questions will address topics with this designation, regardless of task or importance. CALCIUM AND BONE DISORDERS (15% of exam) Diagnosis Testing OSTEOMALACIA AND RICKETS (<2% of exam) Chronic hypophosphatemia Inhibitors of mineralization RENAL OSTEODYSTROPHY (<2% of exam) Renal osteodystrophy NEPHROLITHIASIS (<2% of exam) Nephrolithiasis OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA AND BONE DYSPLASIAS (<2% of exam) Osteogenesis imperfecta and bone dysplasias FIBROUS DYSPLASIA AND OTHER DYSPLASTIC SYNDROMES (<2% of exam) Fibrous dysplasia and other dysplastic syndromes CALCIPHYLAXIS (<2% of exam) Calciphylaxis HYPOPHOSPHATEMIA (<2% of exam) Renal losses Gastrointestinal malabsorption Internal redistribution THYROID DISORDERS (15% of exam) Diagnosis Testing HYPERTHYROIDISM (3.5% of exam) Graves disease Toxic adenoma and multinodular goiter JANUARY
18 tasks Low Frequency: No more than 25% of exam questions will address topics with this designation, regardless of task or importance. THYROID DISORDERS (15% of exam) Diagnosis Testing HYPERTHYROIDISM (3.5% of exam) Inappropriate thyroid-stimulating hormone syndromes TSH-secreting tumor Thyroid hormone resistance syndromes Artifactual TSH derangements Thyrotoxicosis with low radioactive iodine uptake Thyroiditis Factitious, accidental, and iatrogenic thyrotoxicosis Iodine-induced Struma ovarii Complicated thyrotoxicosis Subclinical hyperthyroidism HYPOTHYROIDISM (2.5% of exam) Primary Secondary Subclinical hypothyroidism Complicated hypothyroidism TSH resistance in pseudohypoparathyroidism Therapy NONTOXIC SOLITARY NODULES AND MULTINODULAR GOITER (2.5% of exam) Fine-needle aspiration/cytology interpretation Roles of ultrasound and radionuclide scanning JANUARY
19 tasks Low Frequency: No more than 25% of exam questions will address topics with this designation, regardless of task or importance. THYROID DISORDERS (15% of exam) Diagnosis Testing NONTOXIC SOLITARY NODULES AND MULTINODULAR GOITER (2.5% of exam) Treatment Surgery Levothyroxine suppression Radioactive iodine Chemotherapy and other treatments THYROID CANCER (3.5% of exam) Well differentiated epithelial cancers Hurthle cell cancer Anaplastic cancer Lymphoma Medullary cancer THYROID TEST ABNORMALITIES WITHOUT THYROID DISEASE (2.5% of exam) Euthyroid hypothyroxinemia Euthyroid hyperthyroxinemia Effect of drugs on thyroid function tests Euthyroid sick syndrome Thyroid hormone antibodies Antibody interferences with TSH measurement THYROID CHANGES IN PREGNANCY (<2% of exam) Hypothyroidism Hyperthyroidism Thyroid nodule and cancer JANUARY
Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism
 Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism Certification Examination Blueprint Purpose of the exam The exam is designed to evaluate the knowledge, diagnostic reasoning, and clinical judgment skills expected
Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism Certification Examination Blueprint Purpose of the exam The exam is designed to evaluate the knowledge, diagnostic reasoning, and clinical judgment skills expected
Table of Contents Section I Pituitary and Hypothalamus 1. Development of the Pituitary Gland 2. Divisions of the Pituitary Gland and Relationship to
 Table of Contents Section I Pituitary and Hypothalamus 1. Development of the Pituitary Gland 2. Divisions of the Pituitary Gland and Relationship to the Hypothalamus 3. Blood Supply of the Pituitary Gland
Table of Contents Section I Pituitary and Hypothalamus 1. Development of the Pituitary Gland 2. Divisions of the Pituitary Gland and Relationship to the Hypothalamus 3. Blood Supply of the Pituitary Gland
I. Provide patient care that is compassionate, appropriate and effective for the prevention and treatment of endocrinologic disorders.
 Endocrinology Curriculum Goal Endocrinology is the diagnosis and care of disorders of the endocrine system. The principal endocrine problems handled by the general internist include goiter, thyroid nodules,
Endocrinology Curriculum Goal Endocrinology is the diagnosis and care of disorders of the endocrine system. The principal endocrine problems handled by the general internist include goiter, thyroid nodules,
GASTROENTEROLOGY Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Examination Blueprint
 GASTROENTEROLOGY Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Examination Blueprint ABIM invites diplomates to help develop the Gastroenterology MOC exam blueprint Based on feedback from physicians that MOC assessments
GASTROENTEROLOGY Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Examination Blueprint ABIM invites diplomates to help develop the Gastroenterology MOC exam blueprint Based on feedback from physicians that MOC assessments
Lahey Clinic Internal Medicine Residency Program: Curriculum for Endocrinology and Metabolism
 Lahey Clinic Internal Medicine Residency Program: Curriculum for Endocrinology and Metabolism Faculty representative: Gary Cushing, MD, Department of Endocrinology Resident representative: Ajaykumar Rao,
Lahey Clinic Internal Medicine Residency Program: Curriculum for Endocrinology and Metabolism Faculty representative: Gary Cushing, MD, Department of Endocrinology Resident representative: Ajaykumar Rao,
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program. Primary Goals for Rotation. Endocrinology
 The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Endocrinology 1. GOAL: Understand the role of the pediatrician in preventing endocrine dysfunction, and in counseling and
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Endocrinology 1. GOAL: Understand the role of the pediatrician in preventing endocrine dysfunction, and in counseling and
Provide preventive counseling to parents and patients with specific endocrine conditions about:
 Endocrinology Description: The resident will become familiar with the diagnosis, management, and treatment of endocrine problems. The resident will evaluate patients with a multitude of endocrine problems,
Endocrinology Description: The resident will become familiar with the diagnosis, management, and treatment of endocrine problems. The resident will evaluate patients with a multitude of endocrine problems,
Children s Hospital & Research Center Oakland. Endocrinology
 Children s Hospital & Research Center Oakland Endocrinology 5.22 GOAL: Prevention, Counseling and Screening (Endocrine). Understand the role of the pediatrician in preventing endocrine PC, MK, dysfunction,
Children s Hospital & Research Center Oakland Endocrinology 5.22 GOAL: Prevention, Counseling and Screening (Endocrine). Understand the role of the pediatrician in preventing endocrine PC, MK, dysfunction,
CLINICAL CARDIAC ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Examination Blueprint
 CLINICAL CARDIAC ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Examination Blueprint ABIM invites diplomates to help develop the Clinical Cardiac Electrophysiology MOC exam blueprint Based on feedback
CLINICAL CARDIAC ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Examination Blueprint ABIM invites diplomates to help develop the Clinical Cardiac Electrophysiology MOC exam blueprint Based on feedback
UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN HOSPITALS AND HEALTH CENTERS. Delineation of Privileges Department of Pediatrics/Division of Endocrinology
 University of Michigan Hospitals and Health Centers UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN HOSPITALS AND HEALTH CENTERS Delineation of Privileges Department of Pediatrics/Division of Endocrinology Name: Please Print or
University of Michigan Hospitals and Health Centers UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN HOSPITALS AND HEALTH CENTERS Delineation of Privileges Department of Pediatrics/Division of Endocrinology Name: Please Print or
Chapter 20. Endocrine System Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chemical signals coordinate body functions. !
 26.1 Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chapter 20 Endocrine System! Hormones Chemical signals Secreted by endocrine glands Usually carried in the blood Cause specific changes in target cells Secretory
26.1 Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chapter 20 Endocrine System! Hormones Chemical signals Secreted by endocrine glands Usually carried in the blood Cause specific changes in target cells Secretory
Endocrine system pathology
 Endocrine system pathology Central endocrine system peripheral endocrine system: thyroid gland parathyroid gland pancreas adrenal glands Thyroid gland. the weight of normal thyroid gland is about 15 grams.
Endocrine system pathology Central endocrine system peripheral endocrine system: thyroid gland parathyroid gland pancreas adrenal glands Thyroid gland. the weight of normal thyroid gland is about 15 grams.
PITUITARY: JUST THE BASICS PART 2 THE PATIENT
 PITUITARY: JUST THE BASICS PART 2 THE PATIENT DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities none Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation none Steps taken to review and
PITUITARY: JUST THE BASICS PART 2 THE PATIENT DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities none Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation none Steps taken to review and
Endocrine part two. Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Clinical Chemistry Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy
 Endocrine part two Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Clinical Chemistry Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Cushing's disease: increased secretion of adrenocorticotropic
Endocrine part two Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Clinical Chemistry Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Cushing's disease: increased secretion of adrenocorticotropic
Chapter 12 Endocrine System (export).notebook. February 27, Mar 17 2:59 PM. Mar 17 3:09 PM. Mar 17 3:05 PM. Mar 17 3:03 PM.
 Endocrine System Hormones Chemical messengers released directly into the bloodstream Regulate: *May have wide spread effect or only affect certain tissues ** : cells with receptors that respond to specific
Endocrine System Hormones Chemical messengers released directly into the bloodstream Regulate: *May have wide spread effect or only affect certain tissues ** : cells with receptors that respond to specific
PATHOLOGY OF ENDOCRINE SYSTEM. Peerayut Sitthichaiyakul,, M.D.
 PATHOLOGY OF ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Peerayut Sitthichaiyakul,, M.D. Content Pituitary gland Anterior pituitary gland Hyperpituitarism Hypopituitarism Posteior pituitary gland Posterior pituitary syndrome Thyroid
PATHOLOGY OF ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Peerayut Sitthichaiyakul,, M.D. Content Pituitary gland Anterior pituitary gland Hyperpituitarism Hypopituitarism Posteior pituitary gland Posterior pituitary syndrome Thyroid
4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Understand the functions and disorders of the endocrine system
 4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the 4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the What are the functions of the endocrine system? What are some disorders of the endocrine system? How
4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the 4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the What are the functions of the endocrine system? What are some disorders of the endocrine system? How
Endocrinology. Endocrinology is a specialty of medicine; some would say a
 Endocrinology Endocrinology is a specialty of medicine; some would say a sub-specialty of internal medicine, which deals with the diagnosis and treatment of diseases related to hormones. Endocrinology
Endocrinology Endocrinology is a specialty of medicine; some would say a sub-specialty of internal medicine, which deals with the diagnosis and treatment of diseases related to hormones. Endocrinology
ROTATION SUMMARY ENDOCRINOLOGY
 ROTATION SUMMARY ENDOCRINOLOGY Rotation Contacts and Scheduling Details Rotation Director: Caroline Buckway, MD cbuckway@stanford.edu 650-721-1811 G313, SUMC Administrator: Ofelia Colin ofeliag@stanford.edu
ROTATION SUMMARY ENDOCRINOLOGY Rotation Contacts and Scheduling Details Rotation Director: Caroline Buckway, MD cbuckway@stanford.edu 650-721-1811 G313, SUMC Administrator: Ofelia Colin ofeliag@stanford.edu
Sexual dysfunction of chronic kidney disease. Razieh salehian.md psychiatrist
 Sexual dysfunction of chronic kidney disease Razieh salehian.md psychiatrist Disturbances in sexual function are a common feature of chronic renal failure. Sexual dysfunction is inversely associated with
Sexual dysfunction of chronic kidney disease Razieh salehian.md psychiatrist Disturbances in sexual function are a common feature of chronic renal failure. Sexual dysfunction is inversely associated with
Pediatric Endocrine Dysfunction
 Pediatric Endocrine Dysfunction Chapter 52 Debra Mercer BSN, RN, RRT Mechanisms of Hormonal Regulation The endocrine system is composed of various glands located throughout the body. These glands can synthesize
Pediatric Endocrine Dysfunction Chapter 52 Debra Mercer BSN, RN, RRT Mechanisms of Hormonal Regulation The endocrine system is composed of various glands located throughout the body. These glands can synthesize
BAPTIST HEALTH SCHOOL OF NURSING NSG 3026A: CHILDREN S HEALTH
 J 1 BAPTIST HEALTH SCHOOL OF NURSING NSG 3026A: CHILDREN S HEALTH NURSING MANAGEMENT OF ENDOCRINE DYSFUNCTION: THEORETICAL SKILLS and KNOWLEDGE, SCIENTIFIC PRINCIPLES, CRITICAL THINKING, HEALTHCARE PROMOTION,
J 1 BAPTIST HEALTH SCHOOL OF NURSING NSG 3026A: CHILDREN S HEALTH NURSING MANAGEMENT OF ENDOCRINE DYSFUNCTION: THEORETICAL SKILLS and KNOWLEDGE, SCIENTIFIC PRINCIPLES, CRITICAL THINKING, HEALTHCARE PROMOTION,
Endocrine System. Chapter 20. Endocrine Glands and Hormones. The Endocrine System. Endocrine glands
 Chapter 20 Endocrine System Endocrine Glands and Hormones The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete hormones Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times
Chapter 20 Endocrine System Endocrine Glands and Hormones The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete hormones Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times
Index. urologic.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acquired hypogonadism, prevalence of, 165 167 primary, 165 secondary, 167 Adipose tissue, as an organ, 240 241 Adrenal hyperplasia, congenital,
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acquired hypogonadism, prevalence of, 165 167 primary, 165 secondary, 167 Adipose tissue, as an organ, 240 241 Adrenal hyperplasia, congenital,
Chapter 15 ENDOCRINE AND METABOLIC IMPAIRMENT
 Chapter 15 ENDOCRINE AND METABOLIC IMPAIRMENT Introduction This chapter provides criteria used to rate permanent impairment resulting from endocrine disorders and disorders of metabolism. The endocrine
Chapter 15 ENDOCRINE AND METABOLIC IMPAIRMENT Introduction This chapter provides criteria used to rate permanent impairment resulting from endocrine disorders and disorders of metabolism. The endocrine
Chapter 26. Hormones and the Endocrine System. Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko
 Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture
Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome HEATHER BURKS, MD OU PHYSICIANS REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE SEPTEMBER 21, 2018
 Polycystic Ovary Syndrome HEATHER BURKS, MD OU PHYSICIANS REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE SEPTEMBER 21, 2018 Learning Objectives At the conclusion of this lecture, learners should: 1) Know the various diagnostic
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome HEATHER BURKS, MD OU PHYSICIANS REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE SEPTEMBER 21, 2018 Learning Objectives At the conclusion of this lecture, learners should: 1) Know the various diagnostic
Chemical Regulation. Chapter 26. Testosterone and Male Aggression: Is There a Link? THE NATURE OF CHEMICAL REGULATION
 Chapter 6 Chemical Regulation PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts and Connections, Fifth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, and Simon Testosterone and Male Aggression: Is There a Link? Among male animals,
Chapter 6 Chemical Regulation PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts and Connections, Fifth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, and Simon Testosterone and Male Aggression: Is There a Link? Among male animals,
The Endocrine System
 C H A P T E R 1 2 The Endocrine System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. List the functions of hormones. 2. Classify hormones into their major chemical categories. 3. Describe
C H A P T E R 1 2 The Endocrine System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. List the functions of hormones. 2. Classify hormones into their major chemical categories. 3. Describe
Endocrine System Notes
 Endocrine System Notes is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. - parts of the body that secrete hormones directly into the body. - parts of the body that make secretions which travel
Endocrine System Notes is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. - parts of the body that secrete hormones directly into the body. - parts of the body that make secretions which travel
The Endocrine System. Lipid-Soluble Hormones. Bio217 Sp14 Unit 5. Bio217: Pathophysiology Class Notes Professor Linda Falkow
 Bio217: Pathophysiology Class Notes Professor Linda Falkow Mechanisms of Hormonal Regulation Unit V: Endocrine System Disorders Chapter 17 Chap. 17: Mechanisms of Hormonal Regulation Chap. 18: Alterations
Bio217: Pathophysiology Class Notes Professor Linda Falkow Mechanisms of Hormonal Regulation Unit V: Endocrine System Disorders Chapter 17 Chap. 17: Mechanisms of Hormonal Regulation Chap. 18: Alterations
Pathology of the Endocrine System
 Pathology of the Endocrine System นายแพทย ดร.ณตพล ศ ภณ ฐเศรษฐก ล ภาคว ชาพยาธ ว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยนเรศวร 4 เมษายน พ.ศ. 2557 Topics Introduction Diseases of the Endocrine glands Pituitary gland
Pathology of the Endocrine System นายแพทย ดร.ณตพล ศ ภณ ฐเศรษฐก ล ภาคว ชาพยาธ ว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยนเรศวร 4 เมษายน พ.ศ. 2557 Topics Introduction Diseases of the Endocrine glands Pituitary gland
Page 1. Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System
 Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Page 1. Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System. Target Cells: Cells specialized to respond to hormones
 Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Endocrine System. Modified by M. Myers
 Endocrine System Modified by M. Myers 1 The Endocrine System 2 Endocrine Glands The endocrine system is made of glands & tissues that secrete hormones. Hormones are chemicals messengers influencing a.
Endocrine System Modified by M. Myers 1 The Endocrine System 2 Endocrine Glands The endocrine system is made of glands & tissues that secrete hormones. Hormones are chemicals messengers influencing a.
Take Home Messages in Endocrinology
 Conflict of Interest/Disclosures Take Home Messages in Endocrinology None Carolyn Becker, MD 2 Diabetes Thyroid Pituitary Adrenal Hypoglycemia Overview Diagnostic Criteria for T2DM Diabetes should be diagnosed
Conflict of Interest/Disclosures Take Home Messages in Endocrinology None Carolyn Becker, MD 2 Diabetes Thyroid Pituitary Adrenal Hypoglycemia Overview Diagnostic Criteria for T2DM Diabetes should be diagnosed
TESTOSTERONE DEFINITION
 DEFINITION A hormone that is a hydroxyl steroid ketone (C19H28O2) produced especially by the testes or made synthetically and that is responsible for inducing and maintaining male secondary sex characteristics.
DEFINITION A hormone that is a hydroxyl steroid ketone (C19H28O2) produced especially by the testes or made synthetically and that is responsible for inducing and maintaining male secondary sex characteristics.
Hormones by location
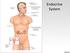 Endocrine System Hormones by location Pineal Gland: Melatonin Feeling of sleepiness Hypothalamus: Hormones that stimulate or inhibit pituitary Temp., hunger, parenting attachment, thirst Pituitary Gland:
Endocrine System Hormones by location Pineal Gland: Melatonin Feeling of sleepiness Hypothalamus: Hormones that stimulate or inhibit pituitary Temp., hunger, parenting attachment, thirst Pituitary Gland:
Overview of Reproductive Endocrinology
 Overview of Reproductive Endocrinology I have no conflicts of interest to report. Maria Yialamas, MD Female Hypothalamic--Gonadal Axis 15 4 Hormone Secretion in the Normal Menstrual Cycle LH FSH E2, Progesterone,
Overview of Reproductive Endocrinology I have no conflicts of interest to report. Maria Yialamas, MD Female Hypothalamic--Gonadal Axis 15 4 Hormone Secretion in the Normal Menstrual Cycle LH FSH E2, Progesterone,
Endocrine System. Chemical Control
 Endocrine System Chemical Control Endocrine System - the system that secretes hormones in the body - hormones can last for minutes or for hours - a major gland, once called the master gland, is the pituitary
Endocrine System Chemical Control Endocrine System - the system that secretes hormones in the body - hormones can last for minutes or for hours - a major gland, once called the master gland, is the pituitary
Diseases of thyroid & parathyroid glands (1 of 2)
 Diseases of thyroid & parathyroid glands (1 of 2) Thyroid diseases Thyrotoxicosis Hypothyroidism Thyroiditis Graves disease Goiters Neoplasms Chronic Lymphocytic (Hashimoto) Thyroiditis Subacute Granulomatous
Diseases of thyroid & parathyroid glands (1 of 2) Thyroid diseases Thyrotoxicosis Hypothyroidism Thyroiditis Graves disease Goiters Neoplasms Chronic Lymphocytic (Hashimoto) Thyroiditis Subacute Granulomatous
REFERRAL GUIDELINES ENDOCRINOLOGY
 REFERRAL GUIDELINES ENDOCRINOLOGY Referral Form: The GP Referral Template is the preferred referral tool (previously known as the Victorian Statewide Referral Form) GP Referral Template This tool is housed
REFERRAL GUIDELINES ENDOCRINOLOGY Referral Form: The GP Referral Template is the preferred referral tool (previously known as the Victorian Statewide Referral Form) GP Referral Template This tool is housed
CATEGORY Endocrine System Review. Provide labels for the following diagram CHAPTER 13 BLM
 CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.1 CATEGORY Endocrine System Review Provide labels for the following diagram. 1. 6. 2. 7. 3. 8. 4. 9. 5. 10. CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.2 OVERHEAD Glands and Their Secretions Endocrine gland
CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.1 CATEGORY Endocrine System Review Provide labels for the following diagram. 1. 6. 2. 7. 3. 8. 4. 9. 5. 10. CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.2 OVERHEAD Glands and Their Secretions Endocrine gland
Lab Guide Endocrine Section Lab Guide
 Lab Guide - 2019 Endocrine Section Lab Guide Estradiol Estradiol, Cerner Name: Estradiol Competitive test principle using a polyclonal antibody specifically directed against 17βestradiol in Roche Cobas
Lab Guide - 2019 Endocrine Section Lab Guide Estradiol Estradiol, Cerner Name: Estradiol Competitive test principle using a polyclonal antibody specifically directed against 17βestradiol in Roche Cobas
Pathology of pituitary gland. By: Shifaa Qa qa
 Pathology of pituitary gland By: Shifaa Qa qa Sella turcica Adenohypophysis (80%): - epithelial cells - acidophil, basophil, chromophobe - Somatotrophs, Mammosomatotrophs, Corticotrophs, Thyrotrophs, Gonadotrophs
Pathology of pituitary gland By: Shifaa Qa qa Sella turcica Adenohypophysis (80%): - epithelial cells - acidophil, basophil, chromophobe - Somatotrophs, Mammosomatotrophs, Corticotrophs, Thyrotrophs, Gonadotrophs
Ch 8: Endocrine Physiology
 Ch 8: Endocrine Physiology Objectives 1. Review endocrine glands of body. 2. Understand how hypothalamus controls endocrine system & sympathetic epinephrine response. 3. Learn anterior pituitary hormones
Ch 8: Endocrine Physiology Objectives 1. Review endocrine glands of body. 2. Understand how hypothalamus controls endocrine system & sympathetic epinephrine response. 3. Learn anterior pituitary hormones
Biology 30. Morinville Community High School. Unit 2: Endocrine System. Name:
 Biology 30 Morinville Community High School Unit 2: Endocrine System Name: 2 Endocrine System Unit Outline Chapter 13 text p. 434-471 Key Concept A: The endocrine system and nervous system both mediate
Biology 30 Morinville Community High School Unit 2: Endocrine System Name: 2 Endocrine System Unit Outline Chapter 13 text p. 434-471 Key Concept A: The endocrine system and nervous system both mediate
Hypogonadism 4/27/2018. Male Hypogonadism -- Definition. Epidemiology. Objectives HYPOGONADISM. Men with Hypogonadism. 95% untreated.
 Male Hypogonadism -- Definition - Low T, Low Testosterone Hypogonadism -...a clinical syndrome that results from failure of the testes to produce physiological concentrations of testosterone due to pathology
Male Hypogonadism -- Definition - Low T, Low Testosterone Hypogonadism -...a clinical syndrome that results from failure of the testes to produce physiological concentrations of testosterone due to pathology
HYPERCALCEMIA. Babak Tamizi Far MD. Assistant professor of internal medicine Al-zahra hospital, Isfahan university of medical sciences
 HYPERCALCEMIA Babak Tamizi Far MD. Assistant professor of internal medicine Al-zahra hospital, Isfahan university of medical sciences ESSENTIALS OF DIAGNOSIS Serum calcium level > 10.5 mg/dl Serum ionized
HYPERCALCEMIA Babak Tamizi Far MD. Assistant professor of internal medicine Al-zahra hospital, Isfahan university of medical sciences ESSENTIALS OF DIAGNOSIS Serum calcium level > 10.5 mg/dl Serum ionized
9.2: The Major Endocrine Organs
 9.2: The Major Endocrine Organs ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY The Major Endocrine Organs Below is a list of the major endocrine organs that we will worry about for this class We will look at hormones associated
9.2: The Major Endocrine Organs ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY The Major Endocrine Organs Below is a list of the major endocrine organs that we will worry about for this class We will look at hormones associated
Hyperandrogenism. Dr Jack Biko. MB. BCh (Wits), MMED O & G (Pret), FCOG (SA), Dip Advanced Endoscopic Surgery(Kiel, Germany)
 Hyperandrogenism Dr Jack Biko MB. BCh (Wits), MMED O & G (Pret), FCOG (SA), Dip Advanced Endoscopic Surgery(Kiel, Germany) 2012 Hyperandrogenism Excessive production of androgens Adrenal glands main source
Hyperandrogenism Dr Jack Biko MB. BCh (Wits), MMED O & G (Pret), FCOG (SA), Dip Advanced Endoscopic Surgery(Kiel, Germany) 2012 Hyperandrogenism Excessive production of androgens Adrenal glands main source
Chapter 13 worksheet
 Name: Chapter 13 worksheet The Endocrine System Please label the: hypothalamus pineal gland pituitary gland thyroid gland parathyroid gland thymus heart stomach liver adrenal glands kidneys pancreas small
Name: Chapter 13 worksheet The Endocrine System Please label the: hypothalamus pineal gland pituitary gland thyroid gland parathyroid gland thymus heart stomach liver adrenal glands kidneys pancreas small
Testosterone and other male hormones seem to be related to aggressive behavior in some species
 Testosterone and Male Aggression Testosterone and other male hormones seem to be related to aggressive behavior in some species In the fish species Oreochromis mossambicus, elevated levels have been found
Testosterone and Male Aggression Testosterone and other male hormones seem to be related to aggressive behavior in some species In the fish species Oreochromis mossambicus, elevated levels have been found
Pathophysiology of the th E d n ocr i ne S S t ys em B. Marinov, MD, PhD Endocrine system Central: Hypothalamus
 Pathophysiology of the Endocrine System B. Marinov, MD, PhD Pathophysiology Department Medical University of Plovdiv Endocrine system Central: Hypothalamus Pituitary Pineal Peripheral Thymus Thyroid Parathyroid
Pathophysiology of the Endocrine System B. Marinov, MD, PhD Pathophysiology Department Medical University of Plovdiv Endocrine system Central: Hypothalamus Pituitary Pineal Peripheral Thymus Thyroid Parathyroid
Hormones. Introduction to Endocrine Disorders. Hormone actions. Modulation of hormone levels. Modulation of hormone levels
 Introduction to Endocrine Disorders Hormones Self-regulating system (homeostasis) Affect: Growth Metabolism Reproduction Fluid and electrolyte balance Hormone actions Endocrine gland Hormone synthesis
Introduction to Endocrine Disorders Hormones Self-regulating system (homeostasis) Affect: Growth Metabolism Reproduction Fluid and electrolyte balance Hormone actions Endocrine gland Hormone synthesis
The Endocrine System. Endocrine System. 1
 The Endocrine System The Endocrine System Second-messenger system of the body Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood Hormones control several major processes Reproduction
The Endocrine System The Endocrine System Second-messenger system of the body Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood Hormones control several major processes Reproduction
Chapter 20 Endocrine System
 Chapter 20 Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times far away from the site of hormone production
Chapter 20 Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times far away from the site of hormone production
CHAPTER 12. Quick Check and Active Learning Answer Keys QUICK CHECK
 CHAPTER 12 QUICK CHECK Page 311 1. Hormones are the chemical messengers of the endocrine system. 2. Nonsteroid hormones are whole proteins, shorter chains of amino acids, or simply versions of single amino
CHAPTER 12 QUICK CHECK Page 311 1. Hormones are the chemical messengers of the endocrine system. 2. Nonsteroid hormones are whole proteins, shorter chains of amino acids, or simply versions of single amino
Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands 4/12/2016. Controlled by both nerves and hormones.
 Glands http://www.hawaiilife.com/articles/2012/03/good-news-vacation-rental-owners/ 70 Figure 10.14a gland Glands cortex Mineralocorticoids Gonadocorticoids Glucocorticoids medulla Epinephrine Norepinephrine
Glands http://www.hawaiilife.com/articles/2012/03/good-news-vacation-rental-owners/ 70 Figure 10.14a gland Glands cortex Mineralocorticoids Gonadocorticoids Glucocorticoids medulla Epinephrine Norepinephrine
The Endocrine System PART B
 9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
John Sutton, DO, FACOI, FACE, CCD. Carson Tahoe Endocrinology Carson City, NV KCOM Class of 1989
 John Sutton, DO, FACOI, FACE, CCD Carson Tahoe Endocrinology Carson City, NV KCOM Class of 1989 Gonadal Physiology and Disease 3 No Disclosures Gonadal Axis Hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal Feedback mechanisms
John Sutton, DO, FACOI, FACE, CCD Carson Tahoe Endocrinology Carson City, NV KCOM Class of 1989 Gonadal Physiology and Disease 3 No Disclosures Gonadal Axis Hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal Feedback mechanisms
Endocrine secretion cells secrete substances into the extracellular fluid
 Animal Hormones Concept 30.1 Hormones Are Chemical Messengers Endocrine secretion cells secrete substances into the extracellular fluid Exocrine secretion cells secrete substances into a duct or a body
Animal Hormones Concept 30.1 Hormones Are Chemical Messengers Endocrine secretion cells secrete substances into the extracellular fluid Exocrine secretion cells secrete substances into a duct or a body
Unit 9 - The Endocrine System 1
 Unit 9 - The Endocrine System 1 I. Unit 9: The Endocrine System A. The Endocrine System 1. Second-messenger system of the body 2. Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood 3.
Unit 9 - The Endocrine System 1 I. Unit 9: The Endocrine System A. The Endocrine System 1. Second-messenger system of the body 2. Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood 3.
Coding spotlight: diabetes provider guide to coding the diagnosis and treatment of diabetes
 Medicaid Managed Care December 2018 provider guide to coding the diagnosis and treatment of diabetes Diabetes mellitus is a chronic disorder caused by either an absolute decrease in the amount of insulin
Medicaid Managed Care December 2018 provider guide to coding the diagnosis and treatment of diabetes Diabetes mellitus is a chronic disorder caused by either an absolute decrease in the amount of insulin
Types of Hormones * OpenStax. 1 Lipid-Derived Hormones (or Lipid-soluble Hormones)
 OpenStax-CNX module: m44766 1 Types of Hormones * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will be
OpenStax-CNX module: m44766 1 Types of Hormones * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will be
Provider Bulletin December 2018 Coding spotlight: diabetes provider guide to coding the diagnosis and treatment of diabetes
 Medi-Cal Managed Care L. A. Care Provider Bulletin December 2018 provider guide to coding the diagnosis and treatment of diabetes Diabetes mellitus is a chronic disorder caused by either an absolute decrease
Medi-Cal Managed Care L. A. Care Provider Bulletin December 2018 provider guide to coding the diagnosis and treatment of diabetes Diabetes mellitus is a chronic disorder caused by either an absolute decrease
THE THYROID. Your thyroid evaluation may include the following:
 An endocrinologist is a doctor specially trained to diagnose and treat diseases affecting your glands. Glands are small organs that produce hormones, which are substances that help control various activities
An endocrinologist is a doctor specially trained to diagnose and treat diseases affecting your glands. Glands are small organs that produce hormones, which are substances that help control various activities
Kingdom of Bahrain Arabian Gulf University College of Medicine and Medical Sciences. Endocrinology. (Review) Year 5 Internal Medicine
 Kingdom of Bahrain Arabian Gulf University College of Medicine and Medical Sciences Endocrinology (Review) Year 5 Internal Medicine Presented by: Dr. Mona Arekat Prepared by: Ali Jassim Alhashli Case (1):
Kingdom of Bahrain Arabian Gulf University College of Medicine and Medical Sciences Endocrinology (Review) Year 5 Internal Medicine Presented by: Dr. Mona Arekat Prepared by: Ali Jassim Alhashli Case (1):
Endocrine Summary 1. Hormones that influence blood glucose level, and a short list of important terms:
 Endocrine Summary 1 Remember the Study Hint at the beginning of this section? Here is another example, but I ve expanded it to include Notes : Hormones that influence blood glucose level, and a short list
Endocrine Summary 1 Remember the Study Hint at the beginning of this section? Here is another example, but I ve expanded it to include Notes : Hormones that influence blood glucose level, and a short list
1. Changed level of a certain hormone Stimulation of the oxygen consumption 3. Decoupling of oxidative phosphorylation 2.
 1. How can endocrine disorders be classified? 1. Hereditary, acquired 2. Active, passive 3. Uncompensated, overcompensated 4. Primary, secondary 5.1, 4 6.1, 2, 3, 4. ENDOCRINE SYSTEM 2. Which is the MAIN
1. How can endocrine disorders be classified? 1. Hereditary, acquired 2. Active, passive 3. Uncompensated, overcompensated 4. Primary, secondary 5.1, 4 6.1, 2, 3, 4. ENDOCRINE SYSTEM 2. Which is the MAIN
Endocrine. Endocrine as it relates to the kidney. Sarah Elfering, MD University of Minnesota
 Endocrine Sarah Elfering, MD University of Minnesota Endocrine as it relates to the kidney Parathyroid gland Vitamin D Endocrine causes of HTN Adrenal adenoma PTH Bone Kidney Intestine 1, 25 OH Vitamin
Endocrine Sarah Elfering, MD University of Minnesota Endocrine as it relates to the kidney Parathyroid gland Vitamin D Endocrine causes of HTN Adrenal adenoma PTH Bone Kidney Intestine 1, 25 OH Vitamin
I. Endocrine System & Hormones Figure 1: Human Endocrine System
 I. Endocrine System & Hormones Figure 1: Human Endocrine System Endocrine System: a) Endocrine glands are ductless since they lack specific vessels for the transport of hormones throughout the body. Instead,
I. Endocrine System & Hormones Figure 1: Human Endocrine System Endocrine System: a) Endocrine glands are ductless since they lack specific vessels for the transport of hormones throughout the body. Instead,
The Endocrine System. I. Overview of the Endocrine System. II. Three Families of Hormones. III. Hormone Receptors. IV. Classes of Hormone Receptor
 The Endocrine System I. Overview of the Endocrine System A. Regulates long term metabolic processes B. Releases hormones from endocrine cells 1. Hormones are chemicals 2. Alter metabolism of cells 3. Release
The Endocrine System I. Overview of the Endocrine System A. Regulates long term metabolic processes B. Releases hormones from endocrine cells 1. Hormones are chemicals 2. Alter metabolism of cells 3. Release
Endocrine System. Chapter 18. Introduction. How Hormones Work. How Hormones Work. The Hypothalamus & Endocrine Regulation
 Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 18 The endocrine system consists of cells, tissues, & organs that secrete into the blood Hormone an organic substance secreted by a cell that has an effect on the
Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 18 The endocrine system consists of cells, tissues, & organs that secrete into the blood Hormone an organic substance secreted by a cell that has an effect on the
GUIDELINES ON. Introduction. G.R. Dohle, S. Arver, C. Bettocchi, S. Kliesch, M. Punab, W. de Ronde
 GUIDELINES ON Male Hypogonadism G.R. Dohle, S. Arver,. Bettocchi, S. Kliesch, M. Punab, W. de Ronde Introduction Male hypogonadism is a clinical syndrome caused by androgen deficiency. It may adversely
GUIDELINES ON Male Hypogonadism G.R. Dohle, S. Arver,. Bettocchi, S. Kliesch, M. Punab, W. de Ronde Introduction Male hypogonadism is a clinical syndrome caused by androgen deficiency. It may adversely
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES
 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES The endocrine system is a collection of glands that secrete hormones directly into the circulatory system to be carried toward a distant target organ. These hormones will be
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES The endocrine system is a collection of glands that secrete hormones directly into the circulatory system to be carried toward a distant target organ. These hormones will be
Endocrinology. Endocrinology. Services. Anal Fissure
 Endocrinology Endocrinology Services Anal Fissure Conditions we treat Diabetes Mellitus Diabetes Mellitus (diabetes) is diagnosed when the body s blood glucose (sugar) level is high. This happens when
Endocrinology Endocrinology Services Anal Fissure Conditions we treat Diabetes Mellitus Diabetes Mellitus (diabetes) is diagnosed when the body s blood glucose (sugar) level is high. This happens when
Endocrine System. Chapter 9
 Endocrine System Chapter 9 Endocrine Organs Hormones Chemical messengers that are released from one tissue and transported through blood to a target tissue. Chemical classification: amino acids, steroids,
Endocrine System Chapter 9 Endocrine Organs Hormones Chemical messengers that are released from one tissue and transported through blood to a target tissue. Chemical classification: amino acids, steroids,
The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System What is the system? 1. Made up of glands that produce and secrete hormones (chemical messengers) 2. Regulation of growth, metabolism, sexual development 3. Responses to stress and
The Endocrine System What is the system? 1. Made up of glands that produce and secrete hormones (chemical messengers) 2. Regulation of growth, metabolism, sexual development 3. Responses to stress and
BIO 116 Practice Assignment 1 The Endocrine System and Blood This is not a required assignment but it is recommended.
 BIO 116 Practice Assignment 1 The Endocrine System and Blood This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. 1. Match the following glands of the endocrine system with the appropriate label 1.
BIO 116 Practice Assignment 1 The Endocrine System and Blood This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. 1. Match the following glands of the endocrine system with the appropriate label 1.
The Endocrine System/Hormones
 The Endocrine System/Hormones Controls many body functions exerts control by releasing special chemical substances into the blood called hormones Hormones affect other endocrine glands or body systems
The Endocrine System/Hormones Controls many body functions exerts control by releasing special chemical substances into the blood called hormones Hormones affect other endocrine glands or body systems
Chapter 45-Hormones and the Endocrine System. Simple Hormone Pathways
 Chapter 45-Hormones and the Endocrine System Simple Hormone s Low ph in duodenum Hormones are released from an endocrine, travel through the bloodstream, and interact with the receptor or a target to cause
Chapter 45-Hormones and the Endocrine System Simple Hormone s Low ph in duodenum Hormones are released from an endocrine, travel through the bloodstream, and interact with the receptor or a target to cause
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM: AN OVERVIEW
 THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM: AN OVERVIEW Functions: 1. Reproduction 2. Growth & development 3. Maintenance of electrolytes, water and nutrient balance of the blood 4. Regulation of cell metabolism and energy
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM: AN OVERVIEW Functions: 1. Reproduction 2. Growth & development 3. Maintenance of electrolytes, water and nutrient balance of the blood 4. Regulation of cell metabolism and energy
From the editors desk
 From the editors desk Dear all, We are happy to introduce the first issue of our magazine on hormonal health. This magazine will focus on updates related to common clinical problems in diabetes, thyroid,
From the editors desk Dear all, We are happy to introduce the first issue of our magazine on hormonal health. This magazine will focus on updates related to common clinical problems in diabetes, thyroid,
Endocrine System. A gland is any organ that produces a secretion 2 types: endocrine and exocrine. Endocrine: Exocrine:
 Endocrine System Endocrine System A gland is any organ that produces a secretion 2 types: endocrine and exocrine Endocrine: Organized groups of tissue that use materials from the blood to make hormones
Endocrine System Endocrine System A gland is any organ that produces a secretion 2 types: endocrine and exocrine Endocrine: Organized groups of tissue that use materials from the blood to make hormones
Endocrine System. Chapter 24. Copyright 2012, 2007, 2003, 1999 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Endocrine System Chapter 24 1 Introduction (p. 638) Endocrine system works with nervous system to coordinate body functions Nervous system uses neural impulses Endocrine system uses hormones 2 Comparing
Endocrine System Chapter 24 1 Introduction (p. 638) Endocrine system works with nervous system to coordinate body functions Nervous system uses neural impulses Endocrine system uses hormones 2 Comparing
Lab Activity 21. Endocrine System Glucometer. Portland Community College BI 232
 Lab Activity 21 Endocrine System Glucometer Portland Community College BI 232 2 Hormone Functions ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone) Regulates the activity of the cortex of the adrenal gland TSH (thyroid
Lab Activity 21 Endocrine System Glucometer Portland Community College BI 232 2 Hormone Functions ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone) Regulates the activity of the cortex of the adrenal gland TSH (thyroid
ENDOCRINOLOGY FELLOWSHIP TRAINING PROGRAMME. CURRICULUM March Endocrinology Fellowship Committee Ministry of Health, Malaysia
 ENDOCRINOLOGY FELLOWSHIP TRAINING PROGRAMME CURRICULUM March 2008 Endocrinology Fellowship Committee Ministry of Health, Malaysia ENDOCRINOLOGY SUBSPECIALTY FELLOWSHIP TRAINING PROGRAMME KKM 1. OBJECTIVES
ENDOCRINOLOGY FELLOWSHIP TRAINING PROGRAMME CURRICULUM March 2008 Endocrinology Fellowship Committee Ministry of Health, Malaysia ENDOCRINOLOGY SUBSPECIALTY FELLOWSHIP TRAINING PROGRAMME KKM 1. OBJECTIVES
Pituitary Adenomas: Evaluation and Management. Fawn M. Wolf, MD 10/27/17
 Pituitary Adenomas: Evaluation and Management Fawn M. Wolf, MD 10/27/17 Over 18,000 pituitaries examined at autopsy: -10.6% contained adenomas (1.5-27%) -Frequency similar for men and women and across
Pituitary Adenomas: Evaluation and Management Fawn M. Wolf, MD 10/27/17 Over 18,000 pituitaries examined at autopsy: -10.6% contained adenomas (1.5-27%) -Frequency similar for men and women and across
BIOCHEMICAL TESTS FOR THE INVESTIGATION OF COMMON ENDOCRINE PROBLEMS IN THE MALE
 Authoriser: Moya O Doherty Page 1 of 7 BIOCHEMICAL TESTS FOR THE INVESTIGATION OF COMMON ENDOCRINE PROBLEMS IN THE MALE The purpose of this protocol is to describe common tests used for the investigation
Authoriser: Moya O Doherty Page 1 of 7 BIOCHEMICAL TESTS FOR THE INVESTIGATION OF COMMON ENDOCRINE PROBLEMS IN THE MALE The purpose of this protocol is to describe common tests used for the investigation
European Society of Endocrinology. ESE Recommended Curriculum of Specialisation in Clinical Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism
 European Society of Endocrinology ESE Recommended Curriculum of Specialisation in Clinical Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism Version 1.0, February 2017 This document was produced in collaboration
European Society of Endocrinology ESE Recommended Curriculum of Specialisation in Clinical Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism Version 1.0, February 2017 This document was produced in collaboration
panhypopituitarism Pattawan Wongwijitsook Maharat Nakhon Ratchasima hospital 17 Nov 2013
 panhypopituitarism Pattawan Wongwijitsook Maharat Nakhon Ratchasima hospital 17 Nov 2013 PITUITARY GLAND (HYPOPHYSIS CEREBRI) The master of endocrine glands master of endocrine glands It is a small oval
panhypopituitarism Pattawan Wongwijitsook Maharat Nakhon Ratchasima hospital 17 Nov 2013 PITUITARY GLAND (HYPOPHYSIS CEREBRI) The master of endocrine glands master of endocrine glands It is a small oval
The Endocrine System PART B
 9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
Scrub In. TSH is secreted by the pituitary and acts on the: Parathormone tends to increase the concentration of:
 Scrub In TSH is secreted by the pituitary and acts on the: a. Pancreas b. Testes c. Thymus gland d. Thyroid gland Parathormone tends to increase the concentration of: a. Calcium in the blood b. Endorphins
Scrub In TSH is secreted by the pituitary and acts on the: a. Pancreas b. Testes c. Thymus gland d. Thyroid gland Parathormone tends to increase the concentration of: a. Calcium in the blood b. Endorphins
Health Sciences Centre, Team A, Dr. L. Bohacek (Endocrine Surgery) Medical Expert
 Health Sciences Centre, Team A, Dr. L. Bohacek (Endocrine Surgery) Introduction Medical Expert This is a three month PGY 1-5 rotation in which residents gain exposure in the care and management of patients
Health Sciences Centre, Team A, Dr. L. Bohacek (Endocrine Surgery) Introduction Medical Expert This is a three month PGY 1-5 rotation in which residents gain exposure in the care and management of patients
Hypothalamus & Pituitary Gland
 Hypothalamus & Pituitary Gland Hypothalamus and Pituitary Gland The hypothalamus and pituitary gland form a unit that exerts control over the function of several endocrine glands (thyroid, adrenals, and
Hypothalamus & Pituitary Gland Hypothalamus and Pituitary Gland The hypothalamus and pituitary gland form a unit that exerts control over the function of several endocrine glands (thyroid, adrenals, and
Chapter 26 Hormones and the
 Chapter 6 Hormones and the Endocrine System Introduction In lions, the hormone testosterone promotes the development and maintenance of male traits including growth and maintenance of the mane and increased
Chapter 6 Hormones and the Endocrine System Introduction In lions, the hormone testosterone promotes the development and maintenance of male traits including growth and maintenance of the mane and increased
Regula'ng Body Func'on
 Chapter 10 Regula'ng Body Func'on Working closely with your nervous system is the endocrine system, a chemical communication system that regulate many body functions. Exocrine vs Endocrine Exocrine Glands
Chapter 10 Regula'ng Body Func'on Working closely with your nervous system is the endocrine system, a chemical communication system that regulate many body functions. Exocrine vs Endocrine Exocrine Glands
ENDOCRINOLOGY Cross setion of discipline. Zdeněk Fryšák, III. interní klinika, nefrologie, revmatologie a endokrinologie FN a LF Olomouc
 ENDOCRINOLOGY Cross setion of discipline Zdeněk Fryšák, III. interní klinika, nefrologie, revmatologie a endokrinologie FN a LF Olomouc Coordination of systems involve Nervous System» Rapid response» Short
ENDOCRINOLOGY Cross setion of discipline Zdeněk Fryšák, III. interní klinika, nefrologie, revmatologie a endokrinologie FN a LF Olomouc Coordination of systems involve Nervous System» Rapid response» Short
The Endocrine System Dr. Gary Mumaugh
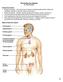 The Endocrine System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Endocrine System Endocrine system the body s second great controlling system which influences metabolic activities of cells by means of hormones Endocrine glands pituitary,
The Endocrine System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Endocrine System Endocrine system the body s second great controlling system which influences metabolic activities of cells by means of hormones Endocrine glands pituitary,
