Use of Retrospective Continuous Glucose Monitoring for Optimizing Management of Type 2 Diabetes in India
|
|
|
- Claud Warren
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 16 Journal of The Association of Physicians of India Vol. 64 April 2016 Original Article Use of Retrospective Continuous Glucose Monitoring for Optimizing Management of Type 2 Diabetes in India Viswanathan Mohan 1, Sunil Jain 2, Jothydev Kesavadev 3, Manoj Chawla 4, Abhay Mutha 5, Vijay Viswanathan 6, Banshi Saboo 7, Rajiv Kovil 8, Ambrish Mithal 9, Dharmen Punatar 10, John Shin 11 Abstract Background: Retrospective continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) studies may provide healthcare professionals (HCPs) with better understanding of glycemic patterns in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) and thereby support patient education and appropriate therapeutic interventions. Methods: Adults with T2D and A1C values between 8% and 10% were eligible for this 3-month study. Patients were scheduled for 5 visits that included baseline and a month-2 retrospective CGM study (ipro2, Medtronic) followed by data review and therapy modifications. A1C values were determined at baseline and at study end. Questionnaires were completed at each visit. HCP questionnaires assessed perception of the utility of studies; patient questionnaires assessed understanding of the importance of compliance with HCP recommendations. Indices of glycemic variability and control were calculated from CGM data retrospectively. Results: A total of 181 subjects enrolled and 148 completed the study (81.8%). There were no serious adverse device effects. Most subjects (91.2%) had >1 therapy change after review of the first ipro2 test. Mean A1C decreased from 8.6% at baseline to 8.0% at month 3 (p<0.001). Questionnaire results from patients and HCPs indicated that both groups viewed the ipro2 studies and results as acceptable and useful. CGM-based glycemic variability metrics were similar in the two ipro2 tests. Conclusion: ipro2 studies provided HCPs with insights and opportunities for initiating changes to treatment regimens and to diet and exercise behaviors, and provided patients with improved knowledge of the importance of therapy compliance. Favorable reductions in A1C suggest that ipro2 tests can facilitate optimal management of T2D. Editorial Viewpoint This study highlights theme of ipro2 system for continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) and its application in making therapeutic changes. Having results of CGM may help better counting of diabetes by more appropriate changes in regimens. However, if CGM is feasable in developing country like India remains to be seen considering factors like cost and compliance. Introduction T ype 2 diabetes (T2D) is highly prevalent in India, with over 62 million people diagnosed with diabetes and 11 million with prediabetes. 1 The disease is often poorly controlled, and there are many people for whom the diagnosis has not been confirmed. 2 Even among patients known to have T2D, many 1 Chairman and Chief Diabetologist, Dr. Mohan s Diabetes Specialities Centre and Madras Diabetes Research Foundation, Chennai, Tamil Nadu; 2 Head of the Dept., Endocrinology TOTALL Diabetes Hormone Institute, Indore, Madhya Pradesh; 3 Chairman and Chief Diabetologist, Jothydev s Diabetes Research Centre, Trivandrum, Kerala; 4 Consulting Diabetologist, Lina Diabetes Care Centre, Mumbai, Maharashtra; 5 Consultant Diabetologist, President, Diabetes Care and Research Centre, Pune, Maharashtra; 6 Head & Chief Diabetologist, M.V Hospital for Diabetes Research Centre, Chennai, Tamil Nadu; 7 Diabetologist and Metabolic Physician, Director, DIA Care Diabetes Care and Hormone Clinic, Ahmedabad, Gujarat; 8 Consulting Diabetologist, Dr. Kovil s Diabetes Care Centre, Mumbai, Maharashtra; 9 Chairman, Division of Endocrinology and Diabetes, Medanta The Medicity, Gurgaon, Haryana; 10 Consulting Diabetologist, Diab Care Centre, Mumbai, Maharashtra; 11 Director, Clinical Research Biostatistics & Bioinformatics, Medtronic MiniMed Inc., Northridge, USA Received: ; Accepted;
2 Journal of The Association of Physicians of India Vol. 64 April A B C D Fig. 1: Components of the ipro2 System. Panel A shows the ipro2 recorder attached to a subcutaneous glucose sensor (the small filament protruding from the bottom right). Panel B shows the ipro2 Smart Dock (top) and the ipro2 recorder (bottom). Panel C shows data being uploaded to a remote server from the ipro2 via the Smart Dock. Panel D shows 3 report formats available from an ipro2 study - the Daily Overlay, Overlay by Meal, and Daily Summary are unaware of the extent of their own blood glucose fluctuations and therefore, of the potential benefits from therapy modification or intensification. 3 Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) is a straightforward method of providing patients and clinicians with data regarding glucose levels. CGM data can be provided in real time, or collected unobtrusively in a recording device that is worn for several days. Data can then be retrospectively downloaded and reviewed in an office setting, where it is typically used to motivate and educate patients and guide decisions regarding therapy modifications. Figure 1 shows the ipro2 system for collection and retrospective analysis of CGM data, which includes the waterproof recording unit and subcutaneous glucose sensor (Figure 1A), the docking station for retrieving data from and recharging the battery of the recording device (Figure 1B), the user interface hosted at carelink.minimed.eu/ipro/hcp/login. jsf?bhcp=1 (Figure 1C), and the reports (Figure 1D). Compared to the earlier ipro system, the ipro2 system requires fewer startup steps, is compatible with more blood glucose meters, uses a USB connection, requires no software installation, and is compatible with electronic medical records systems. The objective of this study was to generate local India evidence to demonstrate that ipro2 studies enable healthcare professionals (HCPs) treating patients with T2D to obtain a better understanding of their patient s metabolic fluctuations and support appropriate therapeutic interventions leading to improved glycemic control. Methods Patients The study was conducted at 11 sites in India. It was approved by all institutions Ethics Committees and was registered with Clinical Trials Registry- India (CTRI/2013/03/003499). Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects prior to any studyrelated activity. Eligibility criteria included a diagnosis of T2D made at least 1 year prior to enrollment, age years, a treatment regimen including an oral antihyperglycemic medication and/or insulin, and an A1C measurement of >8.0% to < or equal to 10.0% made within 4 weeks of enrollment. The A1C values used to establish eligibility were separate from A1C values determined at the first study visit. Exclusion criteria included lack of experience with self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) and having undergone an ipro study in the past 6 months. Visit Schedule Visit 1 included A1C measurement, application of the ipro2 device, and completion of the first set of questionnaires. Visit 2 (day 3-6, 2-6 days after Visit 1) included downloading of the ipro2 data and reviewing of the ipro2 report, initiation of therapy modification(s), and completion of the second set of patient and provider questionnaires. Visit 3 (day 38-52) included application of the second ipro2 device and the third set of patient and provider questionnaires. Visit 4 occurred 3-6 days after Visit 3 (day 41-58), and included downloading of the ipro2 data and reviewing of the ipro2 report, initiation of therapy modification(s), and completion of the fourth set of patient and provider questionnaires. Visit 5 (day 78-92) included blood collection for a second A1C measurement and the fifth set of patient and provider questionnaires. Using the Reports to Guide Therapy The ipro2 reports were to be used as part of discussions between patients and their HCPs. The reports were analyzed using standardized guidelines, and treatment recommendations were generated through a combination of clinical experience and the results of the ipro2 report analysis. The suggested steps in ipro2 report analysis included sequential consideration of overnight, pre-prandial, and postprandial intervals. Potential causes for overnight hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia such as priorevening exercise were evaluated and discussed. Pre-prandial
3 18 Journal of The Association of Physicians of India Vol. 64 April 2016 Table 1: Mean change in A1C ( A1C) from visit 1 to end of study according to characteristics of subjects Characteristic Number * Change in A1C Age (Years) 18 - < (1.43) 49 - < (0.79) 55 - < (1.04) (1.01) Gender Male (1.17) Female (1.00) BMI (kg/m 2 ) < (0.88) < (0.97) < (1.12) (1.40) Duration of diabetes (yrs) < (1.36) 8 - < (0.90) 13 - < (1.08) (1.08) * Number of subjects with available A1C at Visit 1 and end of study visit; Mean change in A1C mean (SD) intervals were to be considered next, followed by postprandial intervals, with similar explorations of potential causes for observed glycemic excursions. Three different report formats (Figure 1D) provided synoptic and finegrained views of the data. The Daily Overlay plot facilitated quick review of glucose excursions and trends, the Overlay by Meal plot allowed close examination of 3 critical periods, and the Daily Summary plot helped associate patient behaviors with observed effects. Data Analysis Descriptive summaries of data are presented. CGM data were analyzed retrospectively. The mean amplitude of glycemic excursions (MAGE) was calculated according to the method of Service et al. 4 and the continuous overall net glycemic action (CONGA) was calculated according to the method of McDonnell et al. 5 Results Table 2: Reduction in A1C from baseline to end-of-study A Statistic Baseline End of Study Mean ± 8.6 ± ± ±1.11 SD Median Min. Max 5,9, , , 2.4 A1C values at baseline and at the end of the study from N=148 subjects for whom values were available at both time points Patient Enrollment and Disposition Of the 180 subjects who entered the study, 148 completed it. Of the 32 subjects who did not complete the study, 15 were withdrawn by the investigator for unknown reasons, 11 were withdrawn at their own discretion, 5 were lost to follow-up, and 1 refused to undergo study-related procedures. The mean (±SD) age of the enrolled subjects was 54.1 ± 10.1 years, their BMI was 27.1 ± 4.07 kg/m 2, mean time since diagnosis of T2D, 14.6 ± 8.1 years, and 38.7% were female. Clinically-relevant symptoms noted by HCPs included frequent hyperglycemia in 60.2% of subjects, frequent hypoglycemia in 18.2% of subjects, and erratic blood glucose levels in 48.1% of subjects. Table 1 shows the clinical characteristics of the 148 completers. A1C and Sensor Glucose Values Table 2 summarizes completers A1C values in tabular and graphic form. The 0.6 percentage point reduction in A1C values from 8.6 ±1.14% at baseline to 8.0 ± 1.06% at the end of the study was clinically and statistically significant (p<0.001). Sensor glucose (SG) values were obtained from ipro2 studies of 176 subjects who completed an initial test and from 150 who completed a second ipro2 test; the mean (±SD) SG value was ± 45.0 mg/dl in the first test and 158 ± 39 mg/dl during the second test. Improved glycemic control during the second ipro2 test was also evidenced by lower area under the curve (AUC) values for hyperglycemic excursions >180 mg/ dl. In the first ipro2 test, the mean Table 3: Mean change in A1C ( A1C) from visit 1 to end of study according to changes to treatment regimen (n=148) Type of therapy Subjects experiencing a therapy change % (n) A1C (SD) Insulin 70.9% (105) (1.19) Oral 48.0% (71) (1.14) medications Diet 67.6% (100) (1.14) Exercise 48.6% (72) (1.23) Other medication 38.5% (57) (1.28) (±SD) event AUC was mg/dl min, which decreased in the second ipro2 test to 2617± mg/dlxmin. Therapy Adjustments and Changes in A1C At least one therapy change was made in 142 (95.9%) of the completers. Among these 142, the mean A1C value decreased by 0.69±1.10 percentage points. Among the 6 (4.1%) completers who did not make a therapy change, the mean A1C value increased by 0.28±0.88 percentage points. Table 3 shows therapy adjustments and corresponding mean changes in A1C. The most frequent change was the addition of insulin; many patients also changed their treatment regimens with respect to oral medications, diet, and exercise. The largest decrease in mean A1C was among subjects who were prescribed an additional diabetes medication. Table 4 shows mean A1C changes among insulin-taking patients who experienced a change to their insulin regimen, with respect to either the quantity, timing, or type of insulin. The largest decrease in A1C was among the 35 subjects who adjusted all three aspects of their insulin regimen. CGM Data Related to Glycemic Variability Data from the two ipro2 studies allowed calculation of various parameters related to glycemic variability. Data from the first and second sets of studies were
4 Journal of The Association of Physicians of India Vol. 64 April Table 4: Mean change in A1C ( A1C) from visit 1 to end of study according to adjustments to insulin therapy regimen Type of change Quantity/ timing/ type Number A1C (%) similar with respect to the standard deviation and coefficient of variation of the SG values, MAGE values, and CONGA values using 1-, 2-, and 4-hour time windows (data not shown). Questionnaire Data from Patients Overall A1C (%) Quantity Quantity/ timing Quantity/ type Timing None Visit 1 questionnaires concerned diabetes control and selfmanagement. Regarding the most recent 3 months, 42.5% of subjects reported one or more instances of hypoglycemia (BG <70 mg/dl). Most (53.6%) subjects reported being aware of hypoglycemic events, and 40.4% reported being aware of hyperglycemic events. Only 27.6% of subjects reported checking their own blood glucose values 10 or more times in the past 30 days. The median response to a statement regarding always following their HCP s recommendation regarding their diabetes care was 6.0, indicating a high rate of compliance. Between Visits 1 and 2, the ipro2 collected and recorded glucose data. Table 5 shows questionnaire responses collected during Visit 2. Mean and median responses support the acceptability and utility of the system. Visit 3 included a brief questionnaire and application of the second ipro2 recorder. Table 6 shows questionnaire responses collected during the third visit, which indicated that patients had implemented therapy changes suggested by their HCP, that the study allowed them to better manage their diabetes than Table 5: Patient survey responses from Visit 2 (review of first ipro2 study) Characteristic Mean (SD) Median Min, Max The ipro2 was easy and comfortable to wear 6.1(0.60) 6 3,7 The ipro2 did not interfere with my daily activities 6.2(0.81) 6 1,7 As a result of the review of the ipro2 report, I am now 6.1(0.99) 6 1,7 more aware of my Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Sugar below 70 mg/dl) than before. As a result of the review of the ipro2 report, I am now 6.2(0.88) 6 1,7 more aware of my Hyperglycemia (High Blood Sugar, above 200 mg/dl) events than before The review of the ipro2 report was helpful for me to 6.2(0.76) understand my diabetes better than before 1 understand the recommendations made by my Doctor/ 6.2(0.67) 6 2,7 Health Care Professional after reviewing the ipro2 report After seeing the ipro2 report, I am more likely to follow my Doctor/Health Care Professional s recommendations regarding my diabetes care than before 6.2(0.72) 6 2,7 N=177 for each question. Responses on a scale from 1-7 were allowed, with 1 indicating strong disagreement, 4 indicating neutrality, and 7 indicating strong agreement. Table 6: Patient survey responses from visit 3 (start of second ipro2 study) Characteristic Mean (SD) Median Min, Max I implemented the therapy changes suggested by my 6.1(0.64) 6 4,7 Doctor/Health Care Professional after the ipro2 test The ipro2 evaluation allowed me to better manage my 6.1(0.78) 6 3,7 diabetes than before Information from the ipro2 reports encouraged me comply 6.2(0.68) 6 4,7 with doctor/health care professional s recommendations. Overall, the ipro2 test was beneficial for me 6.3(0.69) 6 4,7 N=151 for each question. Responses on a scale from 1-7 were allowed, with 1 indicating strong disagreement, 4 indicating neutrality, and 7 indicating strong agreement. before, that the report provided encouragement to comply with HCP recommendations, and that the ipro2 study was beneficial. Visit 4 responses indicated that patients found the second ipro2 study provided more information in managing their diabetes, and that the review was helpful for understanding their diabetes and the recommendations given by their HCP. Patient responses from Visit 5 indicated that subjects implemented therapy changes recommended after the ipro2 study, that the ipro2 study allowed them to manage their diabetes better than before, that the information in the report encouraged them to comply with treatment recommendations, that the study was beneficial overall, and that another ipro2 study in 6 months would also be valuable. Questionnaire Data from Physicians Physicians also completed questionnaires. At each patient s first visit, questionnaire responses from physicians indicated that 78.5% of the patients were unable to maintain tight diabetes control (defined as BG values mg/ dl before meals and <180 mg/dl 2 hours after meals). Increased A1C was noted for 91.7% of the patients and was seen as the most clinically significant symptom for 62.4% of patients. Physician questionnaire findings are given in Tables 7 and 8. Physicians expressed agreement with statements that the ipro2 reports were useful; that they accurately revealed hypoand hyperglycemic events; that they provided more information than SMBG alone; and that they allowed explanation of the patients diabetes and/or provided more information relevant to managing the disease than before. Most physicians felt that their patients had achieved improved glucose control. More than 80% of them would recommend another ipro2 test for the patient in 6-12 months.
5 20 Journal of The Association of Physicians of India Vol. 64 April 2016 Table 7: HCP survey responses from visit 3 and visit 5 Yes / No questions Agreement rate - visit 3 (% (n)) Agreement rate - visit 5 (% (n)) After review of the ipro2 results at the previous visit, I feel my patient has improved glucose control 53.0%(80) 53.7%(80) After review of the ipro2 results at the previous visit, I feel my patient has increased frequency of SMBG 33.8%(51) 42.3%(63) After review of the ipro2 results at the previous visit, I feel my patient has improved compliance to my 43.0%(65) 46.3%(69) recommendations After review of the ipro2 results at the previous visit, I feel my patient has no impact 5.3%(8) 4.7%(7) I would recommend another ipro2 test for this patient after 6-12 months 92.1%(139) 86.6%(129) Extent of agreement questions My patient maintained tighter diabetes control ( mg/dl before meals, < 180 mg/dl 2 hours after meals) than before Visit 3 Visit 5 Mean (SD) Median Min, Max Mean (SD) Median Min, Max 5.3(0.98) 5 2,7 5.6(1.07) 6 1.0, 7.0 This patient follows my recommendations to conduct their SMBG tests 5.9(0.96) 6 2,7 6.0(0.98) 6 1.0, 7.0 After the ipro2 tests, I feel that this patient now has a better understanding on how to manage their diabetes 5.9(0.96) 6 2,7 5.9(1.02) 6 1.0, 7.0 N=151 for Visit 3 and N=149 for Visit 5. Yes/No Questions required yes-or-no answers; Extent of Agreement Questions required responses on a scale from 1-7, with 1 indicating strong disagreement, 4 indicating neutrality, and 7 indicating strong agreement. Table 8: HCP survey responses from visit 2 and visit 4 Characteristic Mean (SD) Visit 2 (N=178) Median Min, Max Mean (SD) Visit 4 (N=151) Median Min, Max I found the information from the 6.2(0.77) 6 2,7 6.2(0.67) 6 4,7 ipro2 report useful The ipro2 report accurately 5.7(1.15) 6 2,7 5.8(1.09) 6 3,7 revealed hypoglycemic events of my patient The ipro2 report accurately 6.3(0.82) 6 2,7 6.2(0.82) 6 4,7 revealed hyperglycemic events of my patient The ipro2 test provides more 6.3(0.79) 6 2,7 6.2(0.87) 6 3,7 information than SMBG alone The 3 step methodology 6.1(0.86) 6 1,7 6.2(0.77) 6 4,7 was useful for me to make appropriate therapy recommendations for my patient The ipro2 allowed me to explain, the nature of my patient s diabetes to him/her and/or provided more information in managing this patients diabetes better than before 6.1(0.85) 6 1,7 6.1(0.73) 6 4,7 Responses on a scale from 1-7 were allowed, with 1 indicating strong disagreement, 4 indicating neutrality, and 7 indicating strong agreement. Strong agreement was indicated with a statement that patients, after the ipro2 studies, had better understanding on how to manage their diabetes (median response of 6 on a 7-point Likert scale, with 7 indicating strong agreement). Safety Data There were no reported serious adverse effects or device complaints that could have led to a serious adverse effect. Of the 7 adverse device effects there were 2 instances of itching, 2 of pain, and 1 each of a pricking sensation, irritation, and bleeding. All were at the site of device application and resolved without complications. Discussion The main finding of this study was that structured use of retrospective CGM data can help patients achieve modest but clinically significant A1C reductions within 3 months. Patients who underwent therapy changes after collaborative ipro2 reviews enjoyed larger A1C reductions than those who did not, suggesting that those therapy adjustments were guided and motivated by actionable insights from the ipro2 data. Patients and providers both found the ipro2 results acceptable and useful, and the ipro2 studies were extremely safe. Results of the current study support and extend earlier results. A recent study of 55 patients in India 6 showed that with ipro2 as a tool in the management of T2D, most patients can achieve A1C reductions and reach the goal of A1C <7.5% without any severe hypoglycemic events. A study of patients with T2D who underwent retrospective CGM studies compared to propensitymatched controls found that the CGM group had significantly more treatment modality changes, and significant improvements in the HbA1c levels at both 3 and 6 months. 7 A similar study of 38 patients with type 1 or T2D provided similar results. 8 Retrospective CGM studies have also proven useful in the context of insulin initiation in T2D, 9 gestational diabetes, 10 pre-diabetes, 11 and children with suboptimally-controlled type 1 diabetes. 12 Given the rapid improvements in performance characteristics of CGM devices, its role in diabetes management seems destined to increase. The use of CGM in developing countries like India is
6 Journal of The Association of Physicians of India Vol. 64 April still limited and there is a need for data on the use of CGM and also its acceptability to both the patients and HCPs. In this context, this study -provides data from India showing that the ipro2 studies were acceptable to both HCPs and patients and also shows their utility in controlling blood glucose levels. As was recently shown in the ICMR - INDIAB study, less than a third of patients in India are able to achieve A1C values <7%. 2 With the high prevalence and associated morbidity and cost of poorly-controlled T2D in India and other regions, expanded use of retrospective CGM studies in appropriate patients is warranted. References 1. Anjana RM, Pradeepa R, Deepa M, et al. Prevalence of diabetes and prediabetes (impaired fasting glucose and/or impaired glucose tolerance) in urban and rural India: phase I results of the Indian Council of Medical Research-INdia DIABetes (ICMR- INDIAB) study. Diabetologia 2011; 54: Unnikrishnan R, Anjana RM, Deepa M, et al. Glycemic control among individuals with self-reported diabetes in India-the ICMR- INDIAB Study. Diabetes Technol Ther 2014; 16: Strain WD, Cos X, Hirst M, et al. Time to do more: addressing clinical inertia in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2014; 105: Service FJ, Molnar GD, Rosevear JW, Ackerman E, Gatewood LC, Taylor WF. Mean amplitude of glycemic excursions, a measure of diabetic instability. Diabetes 1970; 19: McDonnell CM, Donath SM, Vidmar SI, Werther GA, Cameron FJ. A novel approach to continuous glucose analysis utilizing glycemic variation. Diabetes Technol Ther 2005; 7: Kannampilly J, Paleri A, Valsan A. The benefit of continuous glucose monitoring system(cgms-ipr02) in reducing A1C in suboptimally controlled type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Technol Ther 2014; 16:A Kim SK, Kim HJ, Kim T, et al. Effectiveness of 3-day continuous glucose monitoring for improving glucose control in type 2 diabetic patients in clinical practice. Diabetes Metabolism J 2014; 38: Cokolic M, Krajnc M, Sternad S, Rakusa M. The use of continuous glucose monitoring device: ipro2 improves long-term management of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Technol Ther 2013; 15:A57-A8. 9. Blackberry ID, Furler JS, Ginnivan LE, et al. An exploratory trial of basal and prandial insulin initiation and titration for type 2 diabetes in primary care with adjunct retrospective continuous glucose monitoring: INITIATION study. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2014; 106: Paramasivam SS, Tan ATB, Chan SP, et al. The effect of professional continuous glucose monitoring on glycaemic control and hypoglycaemia in insulin-requiring gestational diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 2014; 57:S Kesavadev J, Shankar A, Sanal G, Lally J, Krishnan G, Jothydev S. Clinical utility of CGM in pre-diabetes and its impact on modifying lifestyles. Diabetes Technol Ther 2014; 16:A Zucchini S, Scipione M, Predieri B, et al. Usefulness of CGM with ipro2 in children with T1DM and correlations between Glucose Variability and metabolic control. Pediatr Diabetes 2012; 3:118.
PDF of Trial CTRI Website URL -
 Clinical Trial Details (PDF Generation Date :- Fri, 05 Oct 2018 20:16:50 GMT) CTRI Number Last Modified On 07/08/2014 Post Graduate Thesis Type of Trial Type of Study Study Design Public Title of Study
Clinical Trial Details (PDF Generation Date :- Fri, 05 Oct 2018 20:16:50 GMT) CTRI Number Last Modified On 07/08/2014 Post Graduate Thesis Type of Trial Type of Study Study Design Public Title of Study
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Use of Freestyle Libre Pro TM Flash Glucose Monitoring System in Different Clinical Situations at a Diabetes Centre
 18 Journal of The Association of Physicians of India Vol. 65 August 217 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Use of Freestyle Libre Pro TM Flash itoring System in Different Clinical Situations at a Diabetes Centre Bangalore
18 Journal of The Association of Physicians of India Vol. 65 August 217 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Use of Freestyle Libre Pro TM Flash itoring System in Different Clinical Situations at a Diabetes Centre Bangalore
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Continuous Monitoring of Glucose in the Interstitial Fluid File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: continuous_monitoring_of_glucose_in_the_interstitial_fluid
Corporate Medical Policy Continuous Monitoring of Glucose in the Interstitial Fluid File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: continuous_monitoring_of_glucose_in_the_interstitial_fluid
Control of Glycemic Variability for Reducing Hypoglycemia Jae Hyeon Kim
 Control of Glycemic Variability for Reducing Hypoglycemia Jae Hyeon Kim Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine Conflict of interest
Control of Glycemic Variability for Reducing Hypoglycemia Jae Hyeon Kim Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine Conflict of interest
Clinical Value and Evidence of Continuous Glucose Monitoring
 Clinical Value and Evidence of Continuous Glucose Monitoring 9402313-012 Objective To review the clinical value and the recent clinical evidence for Professional and Personal CGM Key Points CGM reveals
Clinical Value and Evidence of Continuous Glucose Monitoring 9402313-012 Objective To review the clinical value and the recent clinical evidence for Professional and Personal CGM Key Points CGM reveals
Incorporating CGM Into Clinical Decision Making. Etie Moghissi, MD, FACE Clinical Associate Professor, David Geffen School of Medicine UCLA
 Incorporating CGM Into Clinical Decision Making Etie Moghissi, MD, FACE Clinical Associate Professor, David Geffen School of Medicine UCLA 1 Limitations of Current Glucose Monitoring Methods A1c Standard
Incorporating CGM Into Clinical Decision Making Etie Moghissi, MD, FACE Clinical Associate Professor, David Geffen School of Medicine UCLA 1 Limitations of Current Glucose Monitoring Methods A1c Standard
Diabetes II Insulin pumps; Continuous glucose monitoring system (CGMS) Ernest Asamoah, MD FACE FACP FRCP (Lond)
 Diabetes II Insulin pumps; Continuous glucose monitoring system (CGMS) Ernest Asamoah, MD FACE FACP FRCP (Lond) 9501366-011 20110401 Objectives Understand the need for insulin pumps and CGMS in managing
Diabetes II Insulin pumps; Continuous glucose monitoring system (CGMS) Ernest Asamoah, MD FACE FACP FRCP (Lond) 9501366-011 20110401 Objectives Understand the need for insulin pumps and CGMS in managing
REPORT INTERPRETATION
 REPORT INTERPRETATION: Interpreting ipro Professional Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Reports and Making Therapy Adjustments TARGET AUDIENCE The audience for this section is physicians, mid-level practitioners,
REPORT INTERPRETATION: Interpreting ipro Professional Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Reports and Making Therapy Adjustments TARGET AUDIENCE The audience for this section is physicians, mid-level practitioners,
Glycemic Variability:
 Glycemic Variability: Do the Differences Make a Difference? Kim L Kelly, PharmD, BCPS, FCCP Define Variability VERY LOW GLYCEMIC VARIABILITY LOW GLYCEMIC VARIABILITY HIGH GLYCEMIC VARIABILITY So what s
Glycemic Variability: Do the Differences Make a Difference? Kim L Kelly, PharmD, BCPS, FCCP Define Variability VERY LOW GLYCEMIC VARIABILITY LOW GLYCEMIC VARIABILITY HIGH GLYCEMIC VARIABILITY So what s
Advances in Diabetes Care Technologies
 1979 Advances in Diabetes Care Technologies 2015 Introduction Roughly 20% - 30% of patients with T1DM and fewer than 1% of insulin-treated patients with T2DM use an insulin pump In 2007, the US FDA estimated
1979 Advances in Diabetes Care Technologies 2015 Introduction Roughly 20% - 30% of patients with T1DM and fewer than 1% of insulin-treated patients with T2DM use an insulin pump In 2007, the US FDA estimated
CareLink. software REPORT REFERENCE GUIDE. Management Software for Diabetes
 CareLink Management Software for Diabetes software REPORT REFERENCE GUIDE How to use this guide Each type of CareLink report and its components are described in the following sections. Report data used
CareLink Management Software for Diabetes software REPORT REFERENCE GUIDE How to use this guide Each type of CareLink report and its components are described in the following sections. Report data used
Advances in Diabetes Care Technologies
 1979 Advances in Diabetes Care Technologies 2015 Introduction Insulin pump use: ~ 20% - 30% of patients with T1DM < 1% of insulin-treated patients with T2DM 2007 FDA estimates ~375,000 insulin pumps for
1979 Advances in Diabetes Care Technologies 2015 Introduction Insulin pump use: ~ 20% - 30% of patients with T1DM < 1% of insulin-treated patients with T2DM 2007 FDA estimates ~375,000 insulin pumps for
State of California Health and Human Services Agency Department of Health Care Services
 State of California Health and Human Services Agency Department of Health Care Services JENNIFER KENT Director EDMOND G. BROWN JR Governor DATE: N.L.: 03-0317 Index: Benefits TO: ALL COUNTY CALIFORNIA
State of California Health and Human Services Agency Department of Health Care Services JENNIFER KENT Director EDMOND G. BROWN JR Governor DATE: N.L.: 03-0317 Index: Benefits TO: ALL COUNTY CALIFORNIA
Report Reference Guide
 Report Reference Guide How to use this guide Each type of CareLink report and its components are described in the following sections. Report data used to generate the sample reports was from sample patient
Report Reference Guide How to use this guide Each type of CareLink report and its components are described in the following sections. Report data used to generate the sample reports was from sample patient
Today s Goals 10/6/2017. New Frontiers in Diabetes Technology. Disclosures
 New Frontiers in Diabetes Technology Marie E. McDonnell, MD Director, Brigham and Women's Diabetes Program Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes and Hypertension Brigham and Women s Hospital Today s Goals
New Frontiers in Diabetes Technology Marie E. McDonnell, MD Director, Brigham and Women's Diabetes Program Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes and Hypertension Brigham and Women s Hospital Today s Goals
Development of Optimal Kids Insulin Dosing System Formulas for Young Children with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
 DIABETES TECHNOLOGY & THERAPEUTICS Volume 14, Number 5, 2012 ª Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. DOI: 10.1089/dia.2011.0184 Development of Optimal Kids Insulin Dosing System Formulas for Young Children with Type
DIABETES TECHNOLOGY & THERAPEUTICS Volume 14, Number 5, 2012 ª Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. DOI: 10.1089/dia.2011.0184 Development of Optimal Kids Insulin Dosing System Formulas for Young Children with Type
Abbott FreeStyle Libre Pro System
 , the Professional CGM Abbott FreeStyle Libre Pro Reader Kit includes: Reader, USB cable, interactive tutorial on USB, and power adapter, user s manual, Quick Start Guide, Quick Reference Guide Kit includes:
, the Professional CGM Abbott FreeStyle Libre Pro Reader Kit includes: Reader, USB cable, interactive tutorial on USB, and power adapter, user s manual, Quick Start Guide, Quick Reference Guide Kit includes:
Abbott FreeStyle Libre Pro System
 Professional CGM Abbott FreeStyle Libre Pro Reader Kit includes: Reader, USB cable, interactive tutorial on USB, and power adapter, user s manual, Quick Start Guide, Quick Reference Guide Kit includes:
Professional CGM Abbott FreeStyle Libre Pro Reader Kit includes: Reader, USB cable, interactive tutorial on USB, and power adapter, user s manual, Quick Start Guide, Quick Reference Guide Kit includes:
Report Reference Guide. THERAPY MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE FOR DIABETES CareLink Report Reference Guide 1
 Report Reference Guide THERAPY MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE FOR DIABETES CareLink Report Reference Guide 1 How to use this guide Each type of CareLink report and its components are described in the following sections.
Report Reference Guide THERAPY MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE FOR DIABETES CareLink Report Reference Guide 1 How to use this guide Each type of CareLink report and its components are described in the following sections.
Pumps & Sensors made easy. OPADA ALZOHAILI MD FACE Endocrinology Assistant Professor Wayne State University
 Pumps & Sensors made easy OPADA ALZOHAILI MD FACE Endocrinology Assistant Professor Wayne State University DeFronzo RA. Diabetes. 2009;58:773-795. Ominous Octet Relationship of b-cell Dysfunction and Development
Pumps & Sensors made easy OPADA ALZOHAILI MD FACE Endocrinology Assistant Professor Wayne State University DeFronzo RA. Diabetes. 2009;58:773-795. Ominous Octet Relationship of b-cell Dysfunction and Development
Sponsor / Company: Sanofi Drug substance(s): Insulin Glargine. Study Identifiers: NCT
 These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert in the country of prescription. Sponsor / Company: Sanofi Drug substance(s):
These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert in the country of prescription. Sponsor / Company: Sanofi Drug substance(s):
Diabetes Management with Continuous Glucose Monitoring & Multiple Daily Injections. Aaron Michels MD
 Diabetes Management with Continuous Glucose Monitoring & Multiple Daily Injections Aaron Michels MD Outline SMBG & CGM by age group JDRF CGM Trial Sensor Augmented Insulin Pump Therapy for A1c Reduction
Diabetes Management with Continuous Glucose Monitoring & Multiple Daily Injections Aaron Michels MD Outline SMBG & CGM by age group JDRF CGM Trial Sensor Augmented Insulin Pump Therapy for A1c Reduction
Continuous Glucose Monitoring Devices Pharmacy Policy
 Line of Business: All Line of Business Effective date: August 16, 2017 Revision date: August 16, 2017 Continuous Glucose Monitoring Devices Pharmacy Policy This policy has been developed through review
Line of Business: All Line of Business Effective date: August 16, 2017 Revision date: August 16, 2017 Continuous Glucose Monitoring Devices Pharmacy Policy This policy has been developed through review
Sponsor / Company: Sanofi Drug substance(s): Insulin Glargine (HOE901) Insulin Glulisine (HMR1964)
 These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert in the country of prescription. Sponsor / Company: Sanofi Drug substance(s):
These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert in the country of prescription. Sponsor / Company: Sanofi Drug substance(s):
QUESTION 4. WHAT CLINICAL DATA ARE CURRENTLY AVAILABLE TO SUPPORT EXPANDED CGM COVERAGE BY PAYERS AS PERTAINS TO QUESTIONS 1 AND 3?
 500 1 QUESTION 4. WHAT CLINICAL DATA ARE CURRENTLY AVAILABLE TO SUPPORT EXPANDED CGM COVERAGE BY PAYERS AS PERTAINS TO QUESTIONS 1 AND 3? WHAT ADDITIONAL DATA ARE NEEDED? AACE/ACE CGM Consensus Conference:
500 1 QUESTION 4. WHAT CLINICAL DATA ARE CURRENTLY AVAILABLE TO SUPPORT EXPANDED CGM COVERAGE BY PAYERS AS PERTAINS TO QUESTIONS 1 AND 3? WHAT ADDITIONAL DATA ARE NEEDED? AACE/ACE CGM Consensus Conference:
Assessing the value of the Ambulatory Glucose Profile in clinical practice
 Assessing the value of the Ambulatory Glucose Profile in clinical practice STEPHAN MATTHAEI Abstract Glycated haemoglobin (HbA 1c) is a measure of mean blood glucose levels over time. It is not a good
Assessing the value of the Ambulatory Glucose Profile in clinical practice STEPHAN MATTHAEI Abstract Glycated haemoglobin (HbA 1c) is a measure of mean blood glucose levels over time. It is not a good
PREVENTION OF NOCTURNAL HYPOGLYCEMIA USING PREDICTIVE LOW GLUCOSE SUSPEND (PLGS)
 PREVENTION OF NOCTURNAL HYPOGLYCEMIA USING PREDICTIVE LOW GLUCOSE SUSPEND (PLGS) Pathways for Future Treatment and Management of Diabetes H. Peter Chase, MD Carousel of Hope Symposium Beverly Hilton, Beverly
PREVENTION OF NOCTURNAL HYPOGLYCEMIA USING PREDICTIVE LOW GLUCOSE SUSPEND (PLGS) Pathways for Future Treatment and Management of Diabetes H. Peter Chase, MD Carousel of Hope Symposium Beverly Hilton, Beverly
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Continuous or Intermittent Monitoring of Glucose in Interstitial Fluid Page 1 of 26 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Continuous or Intermittent Monitoring
Continuous or Intermittent Monitoring of Glucose in Interstitial Fluid Page 1 of 26 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Continuous or Intermittent Monitoring
Usefulness of Ambulatory Glucose Profile (AGP) in Diabetes Care
 C H A P T E R 41 Usefulness of Ambulatory Glucose Profile (AGP) in Diabetes Care K Chaithanya Murthy, B Ramya, E Vidya, RM Anjana, V Mohan ABSTRACT Over the past decades, several newer technologies have
C H A P T E R 41 Usefulness of Ambulatory Glucose Profile (AGP) in Diabetes Care K Chaithanya Murthy, B Ramya, E Vidya, RM Anjana, V Mohan ABSTRACT Over the past decades, several newer technologies have
OneTouch Reveal web app Report Reference Guide
 OneTouch Reveal web app Report Reference Guide Your step-by-step guide to setting up and using the OneTouch Reveal web app OneTouch Verio meter OneTouch Verio Flex meter OneTouch Verio IQ meter OneTouch
OneTouch Reveal web app Report Reference Guide Your step-by-step guide to setting up and using the OneTouch Reveal web app OneTouch Verio meter OneTouch Verio Flex meter OneTouch Verio IQ meter OneTouch
Diabetes Management: Current High Tech Innovations
 Diabetes Management: Current High Tech Innovations How Far We ve Come in the Last 40 Years William V. Tamborlane, MD Department of Pediatrics Yale School of Medicine Disclosures I am a consultant for:
Diabetes Management: Current High Tech Innovations How Far We ve Come in the Last 40 Years William V. Tamborlane, MD Department of Pediatrics Yale School of Medicine Disclosures I am a consultant for:
Making Sense of Glucose Monitoring. My Journey with Glucose Monitoring Over the Last 37 Years 8/7/2017
 HSW1 Disclosure to Participants Making Sense of Glucose Monitoring Alison B. Evert, MS, RD, CDE UW Neighborhood Clinics UW Medicine Seattle, WA Conflict of Interest (COI) and Financial Relationship Disclosures:
HSW1 Disclosure to Participants Making Sense of Glucose Monitoring Alison B. Evert, MS, RD, CDE UW Neighborhood Clinics UW Medicine Seattle, WA Conflict of Interest (COI) and Financial Relationship Disclosures:
Name of Policy: Continuous or Intermittent Monitoring of Glucose in the Interstitial Fluid
 Name of Policy: Continuous or Intermittent Monitoring of Glucose in the Interstitial Fluid Policy #: 038 Latest Review Date: December 2016 Category: DME Policy Grade: B Background/Definitions: As a general
Name of Policy: Continuous or Intermittent Monitoring of Glucose in the Interstitial Fluid Policy #: 038 Latest Review Date: December 2016 Category: DME Policy Grade: B Background/Definitions: As a general
Welcome to CareLink Pro
 Reference Guide Welcome to CareLink Pro This guide was developed to serve as a reference for obtaining patient data and reviewing CareLink Pro reports. Getting Started with CareLink Pro Adding New Patients
Reference Guide Welcome to CareLink Pro This guide was developed to serve as a reference for obtaining patient data and reviewing CareLink Pro reports. Getting Started with CareLink Pro Adding New Patients
Continuous Glucose Monitoring System
 Continuous Glucose Monitoring System Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.02.003 03/13/2001 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 4/1/2018 Section: DME Place(s)
Continuous Glucose Monitoring System Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.02.003 03/13/2001 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 4/1/2018 Section: DME Place(s)
What is a CGM? (Continuous Glucose Monitor) The Bionic Pancreas Is Coming
 The Bionic Pancreas Is Coming Montana Diabetes Professional Conference October 23, 2014 H. Peter Chase, MD Professor of Pediatrics University of Colorado Barbara Davis Center Stanford: Bruce Buckingham,
The Bionic Pancreas Is Coming Montana Diabetes Professional Conference October 23, 2014 H. Peter Chase, MD Professor of Pediatrics University of Colorado Barbara Davis Center Stanford: Bruce Buckingham,
Sponsor / Company: Sanofi Drug substance(s): insulin glargine (HOE901) According to template: QSD VERSION N 4.0 (07-JUN-2012) Page 1
 These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert in the country of prescription. Sponsor / Company: Sanofi Drug substance(s):
These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert in the country of prescription. Sponsor / Company: Sanofi Drug substance(s):
1. What s the point of a network the case for research? 2. How to use CSII effectively
 1. What s the point of a network the case for research? 2. How to use CSII effectively John Pickup King s College London Faculty of Medicine Guy s Hospital, London What should an insulin pump network do?
1. What s the point of a network the case for research? 2. How to use CSII effectively John Pickup King s College London Faculty of Medicine Guy s Hospital, London What should an insulin pump network do?
Continuous Glucose Monitoring
 Continuous Glucose Monitoring What is Continuous Glucose Monitoring? Blood glucose meters measure glucose in your blood and glucose sensors measure glucose levels in the fluid around the cells They are
Continuous Glucose Monitoring What is Continuous Glucose Monitoring? Blood glucose meters measure glucose in your blood and glucose sensors measure glucose levels in the fluid around the cells They are
Dexcom Current and Future Technology Innovations. Jorge Valdes Chief Technical Officer
 Dexcom Current and Future Technology Innovations 2015 Jorge Valdes Chief Technical Officer G5 App Sensor (Same as G4) Indicated for adults and children down to Age 2 years Tiny insertion needle (26Ga)
Dexcom Current and Future Technology Innovations 2015 Jorge Valdes Chief Technical Officer G5 App Sensor (Same as G4) Indicated for adults and children down to Age 2 years Tiny insertion needle (26Ga)
The Diamond Study: Continuous Glucose Monitoring In Patients on Mulitple Daily Insulin Injections
 8/5/217 The Diamond Study: Continuous Glucose Monitoring In Patients on Mulitple Daily Insulin Injections Richard M. Bergenstal, MD Executive Director International Diabetes Center at Park Nicollet Minneapolis,
8/5/217 The Diamond Study: Continuous Glucose Monitoring In Patients on Mulitple Daily Insulin Injections Richard M. Bergenstal, MD Executive Director International Diabetes Center at Park Nicollet Minneapolis,
Long-term effects of continuous glucose monitoring on HbA 1c levels: An audit
 Long-term effects of continuous glucose monitoring on Julie Brake Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) has become a common and useful tool in diabetes care. To understand whether a 72-hour glucose profile
Long-term effects of continuous glucose monitoring on Julie Brake Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) has become a common and useful tool in diabetes care. To understand whether a 72-hour glucose profile
Updates in Diabetes Technology
 Updates in Diabetes Technology Jessica Kirk, MSN, RN, CPN, CDE Nurse Manager, Endo ECHO No disclosures Disclosures 1 Objectives Distinguish patients appropriate for continuous glucose monitoring and insulin
Updates in Diabetes Technology Jessica Kirk, MSN, RN, CPN, CDE Nurse Manager, Endo ECHO No disclosures Disclosures 1 Objectives Distinguish patients appropriate for continuous glucose monitoring and insulin
THERAPY MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE FOR DIABETES
 THERAPY MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE FOR DIABETES Report Report Interpretation Reference Guide Guide 2009 Medtronic MiniMed. All rights reserved. 6025274-012_a CareLink Pro Report Reference Guide 0 p.2 Adherence
THERAPY MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE FOR DIABETES Report Report Interpretation Reference Guide Guide 2009 Medtronic MiniMed. All rights reserved. 6025274-012_a CareLink Pro Report Reference Guide 0 p.2 Adherence
Update on Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Technology in Diabetes. Elena Toschi, MD November 12, 2016
 Update on Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Technology in Diabetes Elena Toschi, MD November 12, 2016 Presenter Disclosure Information Elena Toschi, MD No financial disclosure Objectives: Use of CGM
Update on Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Technology in Diabetes Elena Toschi, MD November 12, 2016 Presenter Disclosure Information Elena Toschi, MD No financial disclosure Objectives: Use of CGM
Review Article. Continuous Glucose Monitoring - A Step Towards Better Diabetes Management. Ajay V Kaduskar
 Review Article Vidarbha Journal of Internal Medicine Volume 24 January 2018 Continuous Glucose Monitoring - A Step Towards Better Diabetes Management 1 Ajay V Kaduskar ABSTRACT Self-monitoring of blood
Review Article Vidarbha Journal of Internal Medicine Volume 24 January 2018 Continuous Glucose Monitoring - A Step Towards Better Diabetes Management 1 Ajay V Kaduskar ABSTRACT Self-monitoring of blood
Continuous Glucose Monitoring System
 Continuous Glucose Monitoring System Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.02.003 03/13/2001 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 04/01/2017 Section: DME Place(s)
Continuous Glucose Monitoring System Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.02.003 03/13/2001 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 04/01/2017 Section: DME Place(s)
USE OF INSULIN PUMP FOR THE 1 ST TIME IN A GOVERNMENT HOSPITAL JJ HOSPITAL, MUMBAI
 USE OF INSULIN PUMP FOR THE 1 ST TIME IN A GOVERNMENT HOSPITAL JJ HOSPITAL, MUMBAI Dr. Hemant Gupta [Associate Prof. & Unit Head, Dept of Medicine, J.J.Hospital, Mumbai] Dr. Ayaz Ahmed [lecturer] Dr. Parag
USE OF INSULIN PUMP FOR THE 1 ST TIME IN A GOVERNMENT HOSPITAL JJ HOSPITAL, MUMBAI Dr. Hemant Gupta [Associate Prof. & Unit Head, Dept of Medicine, J.J.Hospital, Mumbai] Dr. Ayaz Ahmed [lecturer] Dr. Parag
THERAPY MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE FOR DIABETES
 THERAPY MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE FOR DIABETES Report Report Interpretation Reference Guide Guide 2007 Medtronic MiniMed. All rights reserved. 6025274-0U2 120707 CareLink Pro Report Reference Guide 0 p.2 Sensor
THERAPY MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE FOR DIABETES Report Report Interpretation Reference Guide Guide 2007 Medtronic MiniMed. All rights reserved. 6025274-0U2 120707 CareLink Pro Report Reference Guide 0 p.2 Sensor
Insulin Delivery and Glucose Monitoring Methods for Diabetes Mellitus: Comparative Effectiveness
 Insulin Delivery and Glucose Monitoring Methods for Diabetes Mellitus: Comparative Effectiveness Prepared for: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) www.ahrq.gov Outline of Material Introduction
Insulin Delivery and Glucose Monitoring Methods for Diabetes Mellitus: Comparative Effectiveness Prepared for: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) www.ahrq.gov Outline of Material Introduction
GlyCulator: A Glycemic Variability Calculation Tool for Continuous Glucose Monitoring Data
 Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology Volume 5, Issue 2, March 2011 Diabetes Technology Society TECHNOLOGY REPORTS GlyCulator: A Glycemic Variability Calculation Tool for Continuous Glucose Monitoring
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology Volume 5, Issue 2, March 2011 Diabetes Technology Society TECHNOLOGY REPORTS GlyCulator: A Glycemic Variability Calculation Tool for Continuous Glucose Monitoring
Continuous Glucose Monitoring System
 Continuous Glucose Monitoring System Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.02.003 03/13/2001 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 04/01/2016 Section: DME Place(s)
Continuous Glucose Monitoring System Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.02.003 03/13/2001 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 04/01/2016 Section: DME Place(s)
OneTouch Reveal Web Application. User Manual for Healthcare Professionals Instructions for Use
 OneTouch Reveal Web Application User Manual for Healthcare Professionals Instructions for Use Contents 2 Contents Chapter 1: Introduction...4 Product Overview...4 Intended Use...4 System Requirements...
OneTouch Reveal Web Application User Manual for Healthcare Professionals Instructions for Use Contents 2 Contents Chapter 1: Introduction...4 Product Overview...4 Intended Use...4 System Requirements...
Akio Ohta, Kaori Arai, Ami Nishine, Yoshiyuki Sada, Hiroyuki Kato, Hisashi Fukuda, Shiko Asai, Yoshio Nagai, Takuyuki Katabami and Yasushi Tanaka
 Endocrine Journal 2013, 60 (2), 173-177 Or i g i n a l Comparison of daily glucose excursion by continuous glucose monitoring between type 2 diabetic patients receiving preprandial insulin aspart or postprandial
Endocrine Journal 2013, 60 (2), 173-177 Or i g i n a l Comparison of daily glucose excursion by continuous glucose monitoring between type 2 diabetic patients receiving preprandial insulin aspart or postprandial
Non-insulin treatment in Type 1 DM Sang Yong Kim
 Non-insulin treatment in Type 1 DM Sang Yong Kim Chosun University Hospital Conflict of interest disclosure None Committee of Scientific Affairs Committee of Scientific Affairs Insulin therapy is the mainstay
Non-insulin treatment in Type 1 DM Sang Yong Kim Chosun University Hospital Conflict of interest disclosure None Committee of Scientific Affairs Committee of Scientific Affairs Insulin therapy is the mainstay
Diabetes and Technology. Saturday, September 9, 2017 Aimee G sell, APRN, ANP-C, CDE
 Diabetes and Technology Saturday, September 9, 2017 Aimee G sell, APRN, ANP-C, CDE Disclosure Speaker s Bureau: Janssan Pharmaceuticals Current Technology V-Go by Valeritas Continuous Sensors (personal
Diabetes and Technology Saturday, September 9, 2017 Aimee G sell, APRN, ANP-C, CDE Disclosure Speaker s Bureau: Janssan Pharmaceuticals Current Technology V-Go by Valeritas Continuous Sensors (personal
NEW TECHNOLOGIES FOR MANAGING DIABETES ANGELA THOMPSON DNP, FNP-C, BC-ADM, CDE, FAANP
 NEW TECHNOLOGIES FOR MANAGING DIABETES ANGELA THOMPSON DNP, FNP-C, BC-ADM, CDE, FAANP No commercial support or sponsorship was received for this project I have nothing to disclose OBJECTIVES Identify at
NEW TECHNOLOGIES FOR MANAGING DIABETES ANGELA THOMPSON DNP, FNP-C, BC-ADM, CDE, FAANP No commercial support or sponsorship was received for this project I have nothing to disclose OBJECTIVES Identify at
medicines_management/correspondence/pathway-for-the-managed- Access-of-FreeStyle-Libre.
 Pathway for the Managed Access of FreeStyle Libre (Flash Glucose monitoring) for Adults and Children in the care of Trust Specialist Diabetes Clinics in Northern Ireland www.hscboard.hscni.net/download/publications/pharmacy_and_
Pathway for the Managed Access of FreeStyle Libre (Flash Glucose monitoring) for Adults and Children in the care of Trust Specialist Diabetes Clinics in Northern Ireland www.hscboard.hscni.net/download/publications/pharmacy_and_
These results are supplied for informational purposes only.
 These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert in the country of prescription Sponsor/company: sanofi-aventis ClinialTrials.gov
These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert in the country of prescription Sponsor/company: sanofi-aventis ClinialTrials.gov
Artificial Pancreas Device System (APDS)
 Medical Policy Manual Durable Medical Equipment, Policy No. 77 Artificial Pancreas Device System (APDS) Next Review: October 2019 Last Review: October 2018 Effective: November 1, 2018 IMPORTANT REMINDER
Medical Policy Manual Durable Medical Equipment, Policy No. 77 Artificial Pancreas Device System (APDS) Next Review: October 2019 Last Review: October 2018 Effective: November 1, 2018 IMPORTANT REMINDER
The MiniMed Continuous Glucose Monitoring System. JOHN J. MASTROTOTARO, Ph.D.
 DIABETES TECHNOLOGY & THERAPEUTICS Volume 2, Supplement 1, 2000 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. The MiniMed Continuous Glucose Monitoring System JOHN J. MASTROTOTARO, Ph.D. DIABETES is a major source of morbidity,
DIABETES TECHNOLOGY & THERAPEUTICS Volume 2, Supplement 1, 2000 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. The MiniMed Continuous Glucose Monitoring System JOHN J. MASTROTOTARO, Ph.D. DIABETES is a major source of morbidity,
DISCLAIMER: ECHO Nevada emphasizes patient privacy and asks participants to not share ANY Protected Health Information during ECHO clinics.
 DISCLAIMER: Video will be taken at this clinic and potentially used in Project ECHO promotional materials. By attending this clinic, you consent to have your photo taken and allow Project ECHO to use this
DISCLAIMER: Video will be taken at this clinic and potentially used in Project ECHO promotional materials. By attending this clinic, you consent to have your photo taken and allow Project ECHO to use this
Continuous Glucose Monitoring: Changing Diabetes Behavior in Real Time and Retrospectively
 Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology Volume 2, Issue 3, May 2008 Diabetes Technology Society CONTROVERSIES in Continuous Glucose Monitoring Continuous Glucose Monitoring: Changing Diabetes Behavior
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology Volume 2, Issue 3, May 2008 Diabetes Technology Society CONTROVERSIES in Continuous Glucose Monitoring Continuous Glucose Monitoring: Changing Diabetes Behavior
The importance of continuous glucose monitoring when transitioning a patient from insulin detemir to U-500R
 Diabetes Management The importance of continuous glucose monitoring when transitioning a patient from insulin detemir to U-500R Connie A Valdez* 1,2, Leah Fitzgerald 1,2 & Sarah Ziherl Hormachea 2 ABSTRACT
Diabetes Management The importance of continuous glucose monitoring when transitioning a patient from insulin detemir to U-500R Connie A Valdez* 1,2, Leah Fitzgerald 1,2 & Sarah Ziherl Hormachea 2 ABSTRACT
Presented by Dr. Bruce Perkins, MD MPH Dr. Michael Riddell, PhD
 Type 1 Diabetes and Exercise: Optimizing the Medtronic MiniMed Veo Insulin Pump and Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) for Better Glucose Control 1,2 for Healthcare Professionals Presented by Dr. Bruce
Type 1 Diabetes and Exercise: Optimizing the Medtronic MiniMed Veo Insulin Pump and Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) for Better Glucose Control 1,2 for Healthcare Professionals Presented by Dr. Bruce
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM)
 Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Date of Origin: 02/2001 Last Review Date: 07/26/2017 Effective Date: 07/26/2017 Dates Reviewed: 04/2004, 04/2005, 03/2006, 11/2006, 12/2007, 03/2008, 09/2008, 04/2009,
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Date of Origin: 02/2001 Last Review Date: 07/26/2017 Effective Date: 07/26/2017 Dates Reviewed: 04/2004, 04/2005, 03/2006, 11/2006, 12/2007, 03/2008, 09/2008, 04/2009,
POPULATION TRACKER - DREAMED USER GUIDE
 POPULATION TRACKER - DREAMED USER GUIDE November 2018 IFU-0011 05 TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION... 1 Product Description... 1 Glooko Intended Use... 1 DreaMed Intended Use...
POPULATION TRACKER - DREAMED USER GUIDE November 2018 IFU-0011 05 TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION... 1 Product Description... 1 Glooko Intended Use... 1 DreaMed Intended Use...
Sensor-augmented pump systems provide insulin delivery
 DIABETES TECHNOLOGY & THERAPEUTICS Volume 18, Number 10, 2016 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. DOI: 10.1089/dia.2016.0216 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effectiveness of Automated Insulin Management Features of the MiniMed c
DIABETES TECHNOLOGY & THERAPEUTICS Volume 18, Number 10, 2016 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. DOI: 10.1089/dia.2016.0216 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effectiveness of Automated Insulin Management Features of the MiniMed c
PEER REVIEW HISTORY ARTICLE DETAILS TITLE (PROVISIONAL)
 PEER REVIEW HISTORY BMJ Open publishes all reviews undertaken for accepted manuscripts. Reviewers are asked to complete a checklist review form (see an example) and are provided with free text boxes to
PEER REVIEW HISTORY BMJ Open publishes all reviews undertaken for accepted manuscripts. Reviewers are asked to complete a checklist review form (see an example) and are provided with free text boxes to
Designed with your patients lives in mind
 The Accu-Chek Insight diabetes therapy system Designed with your patients lives in mind With pre-filled insulin cartridge Designed for easy patient training The Accu-Chek Insight diabetes therapy system
The Accu-Chek Insight diabetes therapy system Designed with your patients lives in mind With pre-filled insulin cartridge Designed for easy patient training The Accu-Chek Insight diabetes therapy system
Figure 2.1: Glucose meter
 CHAPTER TWO: MONITORING TECHNOLOGIES 2.1 Introduction Glucose monitoring is a method of self-testing glucose (blood sugar) levels for the management of diabetes. Traditionally, it involves pricking the
CHAPTER TWO: MONITORING TECHNOLOGIES 2.1 Introduction Glucose monitoring is a method of self-testing glucose (blood sugar) levels for the management of diabetes. Traditionally, it involves pricking the
DEMYSTIFYING INSULIN THERAPY
 DEMYSTIFYING INSULIN THERAPY ASHLYN SMITH, PA-C ENDOCRINOLOGY ASSOCIATES SCOTTSDALE, AZ SECRETARY, AMERICAN SOCIETY OF ENDOCRINE PHYSICIAN ASSISTANTS ARIZONA STATE ASSOCIATION OF PHYSICIAN ASSISTANTS SPRING
DEMYSTIFYING INSULIN THERAPY ASHLYN SMITH, PA-C ENDOCRINOLOGY ASSOCIATES SCOTTSDALE, AZ SECRETARY, AMERICAN SOCIETY OF ENDOCRINE PHYSICIAN ASSISTANTS ARIZONA STATE ASSOCIATION OF PHYSICIAN ASSISTANTS SPRING
Effective Health Care Program
 Comparative Effectiveness Review Number 57 Effective Health Care Program Methods for Insulin Delivery and Glucose Monitoring: Comparative Effectiveness Executive Summary Background Diabetes mellitus is
Comparative Effectiveness Review Number 57 Effective Health Care Program Methods for Insulin Delivery and Glucose Monitoring: Comparative Effectiveness Executive Summary Background Diabetes mellitus is
Early Patient and Clinician Experiences with Continuous Glucose Monitoring
 Feature Article / Early Experiences with CGM Early Patient and Clinician Experiences with Continuous Glucose Monitoring David K. Bloomgarden, MD, FACE; Janine Freeman, RD, LD, CDE; and Elizabeth DeRobertis,
Feature Article / Early Experiences with CGM Early Patient and Clinician Experiences with Continuous Glucose Monitoring David K. Bloomgarden, MD, FACE; Janine Freeman, RD, LD, CDE; and Elizabeth DeRobertis,
Incorporating CGM Into Clinical Decision
 Incorporating CGM Into Clinical Decision Making Etie Moghissi, MD, FACE Clinical Associate Professor, David Geffen School of Medicine UCLA 1 It is Time to Think Beyond A1C HbA1c is simple to administer
Incorporating CGM Into Clinical Decision Making Etie Moghissi, MD, FACE Clinical Associate Professor, David Geffen School of Medicine UCLA 1 It is Time to Think Beyond A1C HbA1c is simple to administer
Improving Type 2 Diabetes Patient Health Outcomes with Individualized Continuing Medical Education for Primary Care
 Diabetes Ther (2016) 7:473 481 DOI 10.1007/s13300-016-0176-9 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Improving Type 2 Diabetes Patient Health Outcomes with Individualized Continuing Medical Education for Primary Care Brian
Diabetes Ther (2016) 7:473 481 DOI 10.1007/s13300-016-0176-9 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Improving Type 2 Diabetes Patient Health Outcomes with Individualized Continuing Medical Education for Primary Care Brian
nocturnal hypoglycemia percentage of Hispanics in the insulin glargine than NPH during forced patients who previously This study excluded
 Clinical Trial Design/ Primary Objective Insulin glargine Treat-to-Target Trial, Riddle et al., 2003 (23) AT.LANTUS trial, Davies et al., 2005 (24) INSIGHT trial, Gerstein et al., 2006 (25) multicenter,
Clinical Trial Design/ Primary Objective Insulin glargine Treat-to-Target Trial, Riddle et al., 2003 (23) AT.LANTUS trial, Davies et al., 2005 (24) INSIGHT trial, Gerstein et al., 2006 (25) multicenter,
Insulin Pumps and Continuous Glucose Sensors- Embracing Technology. Susan Cavalier, BS, RN, CDE Manager, Diabetes Educator Sanford Diabetes Education
 Insulin Pumps and Continuous Glucose Sensors- Embracing Technology Susan Cavalier, BS, RN, CDE Manager, Diabetes Educator Sanford Diabetes Education Diabetes Management Tools in 1974 Insulin pump history
Insulin Pumps and Continuous Glucose Sensors- Embracing Technology Susan Cavalier, BS, RN, CDE Manager, Diabetes Educator Sanford Diabetes Education Diabetes Management Tools in 1974 Insulin pump history
Insulin Pumps and Glucose Sensors in Diabetes Management
 Diabetes Update+ 2014 Congress Whistler, British Columbia Friday March 21, 2014ǀ 8:15 8:45 am Insulin Pumps and Glucose Sensors in Diabetes Management Bruce A Perkins MD MPH Division of Endocrinology Associate
Diabetes Update+ 2014 Congress Whistler, British Columbia Friday March 21, 2014ǀ 8:15 8:45 am Insulin Pumps and Glucose Sensors in Diabetes Management Bruce A Perkins MD MPH Division of Endocrinology Associate
Artificial Pancreas Device Systems. Populations Interventions Comparators Outcomes Individuals: With type 1 diabetes
 Protocol Artificial Pancreas Device Systems Medical Benefit Effective Date: 07/01/18 Next Review Date: 01/20 Preauthorization Yes Review Dates: 03/15, 03/16, 03/17, 01/18, 05/18, 01/19 Preauthorization
Protocol Artificial Pancreas Device Systems Medical Benefit Effective Date: 07/01/18 Next Review Date: 01/20 Preauthorization Yes Review Dates: 03/15, 03/16, 03/17, 01/18, 05/18, 01/19 Preauthorization
PDF of Trial CTRI Website URL -
 Clinical Trial Details (PDF Generation Date :- Tue, 16 Apr 2019 03:04:45 GMT) CTRI Number Last Modified On 29/11/2018 Post Graduate Thesis Type of Trial Type of Study Study Design Public Title of Study
Clinical Trial Details (PDF Generation Date :- Tue, 16 Apr 2019 03:04:45 GMT) CTRI Number Last Modified On 29/11/2018 Post Graduate Thesis Type of Trial Type of Study Study Design Public Title of Study
Understanding the Assessment and Progress Report
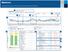 Understanding the ssessment and Progress Report ssessment and Progress 8//2-8/7/2 (7 Days) 3 7/2/2-7/27/2 (7 Days) 4 25-75% -% verage 2 4: M- 5:4 M Hyperglycemic patterns() :45 PM- :3 PM 2 3 :2 M- :5 M
Understanding the ssessment and Progress Report ssessment and Progress 8//2-8/7/2 (7 Days) 3 7/2/2-7/27/2 (7 Days) 4 25-75% -% verage 2 4: M- 5:4 M Hyperglycemic patterns() :45 PM- :3 PM 2 3 :2 M- :5 M
EVALUATION OF GLUCOSE MONITORING TECHNOLOGIES FOR COST EFFECTIVE AND QUALITY CONTROL/MANAGEMENT OF DIABETES
 EVALUATION OF GLUCOSE MONITORING TECHNOLOGIES FOR COST EFFECTIVE AND QUALITY CONTROL/MANAGEMENT OF DIABETES David P. Paul, III Monmouth University Stacy Ashworth, Leslie Salyers, Sarah Saldanha and Alberto
EVALUATION OF GLUCOSE MONITORING TECHNOLOGIES FOR COST EFFECTIVE AND QUALITY CONTROL/MANAGEMENT OF DIABETES David P. Paul, III Monmouth University Stacy Ashworth, Leslie Salyers, Sarah Saldanha and Alberto
04-Sep-17. INERTIA a failure to initiate or modify treatment in a timely manner in people whose health is likely to improve with this modification
 PROF MERLIN THOMAS DIAttitude Study INERTIA a failure to initiate or modify treatment in a timely manner in people whose health is likely to improve with this modification 13% immediately 41% of patients
PROF MERLIN THOMAS DIAttitude Study INERTIA a failure to initiate or modify treatment in a timely manner in people whose health is likely to improve with this modification 13% immediately 41% of patients
Artificial Pancreas Device Systems. Populations Interventions Comparators Outcomes. pump. pump
 Protocol Artificial Pancreas Device Systems (10130) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 04/01/18 Next Review Date: 01/19 Preauthorization Yes Review Dates: 03/15, 03/16, 03/17, 01/18 Preauthorization is required.
Protocol Artificial Pancreas Device Systems (10130) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 04/01/18 Next Review Date: 01/19 Preauthorization Yes Review Dates: 03/15, 03/16, 03/17, 01/18 Preauthorization is required.
Subjects and Methods 2017, 64 (8),
 2017, 64 (8), 827-832 Careful readings for a flash glucose monitoring system in nondiabetic Japanese subjects: individual differences and discrepancy in glucose concentrarion after glucose loading Keiko
2017, 64 (8), 827-832 Careful readings for a flash glucose monitoring system in nondiabetic Japanese subjects: individual differences and discrepancy in glucose concentrarion after glucose loading Keiko
A Simplified Indian Diabetes Risk Score for Screening for Undiagnosed Diabetic Subjects
 Original Article# A Simplified Indian Diabetes Risk Score for Screening for Undiagnosed Diabetic Subjects V Mohan*, R Deepa*, M Deepa*, S Somannavar*, M Datta** Abstract Aim : The aim of this study was
Original Article# A Simplified Indian Diabetes Risk Score for Screening for Undiagnosed Diabetic Subjects V Mohan*, R Deepa*, M Deepa*, S Somannavar*, M Datta** Abstract Aim : The aim of this study was
Efficacy/pharmacodynamics: 85 Safety: 89
 These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert in the country of prescription. Sponsor/Company: Sanofi Drug substance:
These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert in the country of prescription. Sponsor/Company: Sanofi Drug substance:
Pump Therapy - Simple, Proven, and Well Accepted
 Pump Therapy - Simple, Proven, and Well Accepted Innovating for life. Pump therapy is simple for providers and patients Healthcare Providers Simple outpatient procedure: Low burden and cost to transition
Pump Therapy - Simple, Proven, and Well Accepted Innovating for life. Pump therapy is simple for providers and patients Healthcare Providers Simple outpatient procedure: Low burden and cost to transition
USING THE MINIMED 670G SYSTEM. Instructions for the Experienced MiniMed 630G System User
 USING THE MINIMED 670G SYSTEM Instructions for the Experienced MiniMed 630G System User This is a supplemental guide. For complete instructions and safety information, please see your MiniMed 670G System
USING THE MINIMED 670G SYSTEM Instructions for the Experienced MiniMed 630G System User This is a supplemental guide. For complete instructions and safety information, please see your MiniMed 670G System
DISCLAIMER: ECHO Nevada emphasizes patient privacy and asks participants to not share ANY Protected Health Information during ECHO clinics.
 DISCLAIMER: Video will be taken at this clinic and potentially used in Project ECHO promotional materials. By attending this clinic, you consent to have your photo taken and allow Project ECHO to use this
DISCLAIMER: Video will be taken at this clinic and potentially used in Project ECHO promotional materials. By attending this clinic, you consent to have your photo taken and allow Project ECHO to use this
VIRTUAL PATIENTS DERIVED FROM THE
 VIRTUAL PATIENTS DERIVED FROM THE CARELINK DATABASE Benyamin Grosman PhD Senior Principle Scientist Medtronic Diabetes WHY VIRTUAL PATIENT MODELING? Reduce the cost of clinical trials Use models in conjunction
VIRTUAL PATIENTS DERIVED FROM THE CARELINK DATABASE Benyamin Grosman PhD Senior Principle Scientist Medtronic Diabetes WHY VIRTUAL PATIENT MODELING? Reduce the cost of clinical trials Use models in conjunction
Sanofi Diabetes Update: New evidence reinforces favorable profile of Toujeo October 2, 2018
 Sanofi Diabetes Update: New evidence reinforces favorable profile of Toujeo October 2, 2018 Background: For people with diabetes the early months of treatment with long-acting insulin are important for
Sanofi Diabetes Update: New evidence reinforces favorable profile of Toujeo October 2, 2018 Background: For people with diabetes the early months of treatment with long-acting insulin are important for
James J. Chamberlain, MD 1, Dana Dopita, RN, MSN, CDE 1, Emily Gilgen, RD, CD, CDE 1, and Annie Neuman, MPA, PA-C 1.
 604633DSTXXX10.1177/1932296815604633Journal of Diabetes Science and TechnologyChamberlain et al research-article2015 Original Article Impact of Frequent and Persistent Use of Continuous Glucose Monitoring
604633DSTXXX10.1177/1932296815604633Journal of Diabetes Science and TechnologyChamberlain et al research-article2015 Original Article Impact of Frequent and Persistent Use of Continuous Glucose Monitoring
Lessons From The Type 1 Diabetes Exchange
 Lessons From The Type 1 Diabetes Exchange Andrew Ahmann, MD Harold Schnitzer Diabetes Health Center at OHSU Presenter Disclosure Information In compliance with the accrediting board policies, the American
Lessons From The Type 1 Diabetes Exchange Andrew Ahmann, MD Harold Schnitzer Diabetes Health Center at OHSU Presenter Disclosure Information In compliance with the accrediting board policies, the American
WOULD YOU LIKE TO REDUCE THE FEAR OF HYPOGLYCAEMIA FOR YOUR PATIENTS?
 WOULD YOU LIKE TO REDUCE THE FEAR OF HYPOGLYCAEMIA FOR YOUR PATIENTS? THE ONLY SYSTEM CLINICALLY PROVEN TO REDUCE HYPOGLYCAEMIA MINIMED 640G SYSTEM WITH SMARTGUARD TECHNOLOGY 1 HYPOGLYCAEMIA IS CHALLENGING
WOULD YOU LIKE TO REDUCE THE FEAR OF HYPOGLYCAEMIA FOR YOUR PATIENTS? THE ONLY SYSTEM CLINICALLY PROVEN TO REDUCE HYPOGLYCAEMIA MINIMED 640G SYSTEM WITH SMARTGUARD TECHNOLOGY 1 HYPOGLYCAEMIA IS CHALLENGING
Clinical Study Synopsis
 Clinical Study Synopsis This Clinical Study Synopsis is provided for patients and healthcare professionals to increase the transparency of Bayer's clinical research. This document is not intended to replace
Clinical Study Synopsis This Clinical Study Synopsis is provided for patients and healthcare professionals to increase the transparency of Bayer's clinical research. This document is not intended to replace
Injecting Insulin into Out Patient Practice
 Injecting Insulin into Out Patient Practice Kathleen Colleran, MD Associate Professor UNMHSC 4/22/10 Overview Natural history of Type 2 diabetes Reasons clinicians are reluctant to start insulin therapy
Injecting Insulin into Out Patient Practice Kathleen Colleran, MD Associate Professor UNMHSC 4/22/10 Overview Natural history of Type 2 diabetes Reasons clinicians are reluctant to start insulin therapy
Advances in Diabetes Care Technologies
 Advances in Diabetes Care Technologies 1979 2015 Introduction Roughly 20% to 30% of patients with T1DM and fewer than 1% of insulin-treated patients with T2DM use an insulin pump In 2007, the U.S. FDA
Advances in Diabetes Care Technologies 1979 2015 Introduction Roughly 20% to 30% of patients with T1DM and fewer than 1% of insulin-treated patients with T2DM use an insulin pump In 2007, the U.S. FDA
Insulin Pump Therapy in children. Prof. Abdulmoein Al-Agha, FRCPCH(UK)
 Insulin Pump Therapy in children Prof. Abdulmoein Al-Agha, FRCPCH(UK) aagha@kau.edu.sa Highlights Evolution of insulin pump Pumps mimics Pancreas Goals of diabetes care What lowers HbA1c Criteria for selection
Insulin Pump Therapy in children Prof. Abdulmoein Al-Agha, FRCPCH(UK) aagha@kau.edu.sa Highlights Evolution of insulin pump Pumps mimics Pancreas Goals of diabetes care What lowers HbA1c Criteria for selection
