FIT Forum for Injection Technique
|
|
|
- Augustine Tate
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DIABETES CARE IN IRELAND FIT Forum for Injection Technique Irish Injection and Infusion Technique Recommendations 2nd Edition The Irish Injection and Infusion Technique Recommendations have been endorsed by Irish Diabetes Nurse & Midwife Diabetes Ireland TM Irish Endocrine Specialist Association Society Optimising Diabetes Care Irish Diabetes Nurse & Midwife Specialist Association
2
3 THE IRISH INJECTION AND INFUSION TECHNIQUE RECOMMENDATIONS 2nd EDITION Preface The Forum for Injection Technique (FIT) was developed to establish and promote best practice in injection technique for all involved in diabetes care. The founding members are experienced diabetes specialist nurses. The key aims are to raise awareness of existing and emerging research relating to injection technique and the impact this may have on health outcomes for those with diabetes that require subcutaneous injection therapy. FIT was established following the publication of the international New injection recommendations for patients with diabetes, (Diabetes & Metabolism 2010). These recommendations were first published in 2012 and this second edition has been updated in accordance with current research evidence. These recommendations are informed by the New Insulin Delivery Recommendations. (1) Diabetes is a serious health problem which has been described as the most challenging health issue of the 21st Century. (2) The latest research evidence in Ireland estimates prevalence of doctor diagnosed diabetes among adults is approximately 5.2% of the population. (3)The cost of diabetes care is a major burden for the Irish Health Service Executive. The Codeire study suggested 10% of the national healthcare budget is spent on treating the condition and its related complications. (4) It is estimated that almost 30% of people with diabetes use injectable therapies(5). For injectable therapies to work optimally, correct injection technique is essential and, therefore, an improvement in technique could potentially contribute to managing the cost of diabetes care. FIT is an autonomous organisation whose mission is to support people with diabetes requiring injectable therapies in achieving the best possible health outcomes, by ensuring that the correct dose is delivered to the correct injection site, using the correct technique, each and every time, whilst improving outcomes.(1) The development of FIT and the subsequent Irish Injection Technique Recommendations have been supported by BD Europe and endorsed by various bodies in Ireland including pharmaceutical companies whose therapies include subcutaneous injections of insulin and GLP-1 agonists. FIT is committed to supporting the implementation of the recommendations by all those involved in diabetes care. These recommendations will be updated at regular intervals to include new research evidence as it emerges. We therefore welcome any comments, suggestions and active participation in ensuring that the recommendations remain relevant and useful for now and the future. Sonya Browne Clinical Nurse Manager 2 Helen Burke Registered Advanced Nurse Practitioner in Diabetes Patricia Murphy Clinical Nurse Specialist Yvonne Moloney Registered Advanced Midwife Practitioner Diabetes, UL Hospitals Reference this report as: FIT Ireland 2017; The Irish Injection and Infusion Technique Recommendations 2nd Edition 3
4 THE IRISH INJECTION AND INFUSION TECHNIQUE RECOMMENDATIONS 2nd EDITION The Irish Injection and Infusion Technique Recommendations have been endorsed by Novo Nordisk Ireland fully endorse the revised Irish Injection and Infusion Technique Recommendations 2nd Edition. The full benefit for patients in utilising modern injectable therapies for treatment of diabetes is only assured by using the correct injection technique. It is important that good injection technique is understood by Healthcare Professionals and that they convey this to people with diabetes under their care. FIT is a well-established and successful initiative, which will help improve the lives of people living with diabetes. Owen Treacy, Country Manager, Novo Nordisk Ltd Sanofi is a global healthcare leader committed to discover, develop and distribute therapeutic solutions focused on patients needs. We have long been committed to improving the management of diabetes and helping to improve the quality of life of those living with diabetes. Sanofi has been involved in the development of insulin treatments for close to a century and are proud to support the FIT (Forum for Injection Technique) initiative aiming to improve current injection technique by demonstrating and sharing best practice and scientific evidence. We recognise the importance of good injection technique in ensuring people with diabetes who are using insulin therapy achieve the most benefit from their medication. We wish FIT every success and look forward to continued working with FIT in the future. Dr Hubert Bland, Medical Director, Sanofi UKI 4 DATE PUBLISHED: October 2017
5 FIT IRELAND Advances in the treatment of diabetes have led to an increase in the number of injectable therapies available. Correct technique is of paramount importance in order to ensure the benefits of injectable therapies such as insulin and GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs). The Forum for Injection Technique (FIT) provides comprehensive guidelines to improve the process and education of self-injection technique for people with diabetes. As a company committed to improving the care of patients with diabetes, Lilly Ireland welcomes the FIT initiatives that seek to ensure proper injection techniques to avoid intramuscular injections and to ensure appropriate delivery to the subcutaneous tissues as important steps in supporting diabetes care in Ireland. Deirdre Bourke, Country Lead Ireland, Eli Lilly & Company Ireland Ltd Becton Dickinson has been supporting the ground breaking and inspirational work of the Forum for Injection Technique for over 8 years. The new 2nd Edition of The Irish Injection and Infusion Technique Recommendations follows the Worldwide FITTER Congress held recently in Rome During this worldwide event, which included 183 participants from 54 countries, delegates reviewed results data from a worldwide injection technique survey and this wealth of new data provided the evidence to help formulate the best practice recommendations you will find in this Irish 2nd Edition. Our BD purpose Advancing the world of health is incredibly important to all who work at BD and BD is proud to endorse the dedicated expert work that FIT Ireland undertakes. BD welcomes the publication of the 2nd Edition of The Irish Injection and Infusion Technique Recommendations and commends the FIT Ireland Board and all the dedicated clinicians from all over Ireland for their great achievement. Stephen Barrie, Country Business Leader, Diabetes Care, BD Supported by medical technology company Becton, Dickinson U.K. Limited. ( BD and BD Logo are trademarks of Becton, Dickinson and Company BD. All rights reserved. 5
6 THE IRISH INJECTION AND INFUSION TECHNIQUE RECOMMENDATIONS 2nd EDITION KEY A Scientific Advisory Board (SAB) (FITTER,2015) led the review of available evidence and decided that for the strength of a recommendation the following scale would be used: A B C Strongly recommended Recommended Unresolved issue. For the scientific support the following scale was used At least one rigorously performed study, peer-reviewed and published At least one observational, epidemiologic or population-based study Consensus expert opinion based on extensive patient experience. Thus each recommendation is followed by both a letter and number in bold (e.g. A2). The letter indicates the weight a recommendation should have in daily practice and the number, its degree of support in the medical literature. The most relevant publications bearing on a recommendation are also cited. There are comparably few randomised clinical trials in the field of injection technique (compared, for example, with blood pressure control) so judgements such as strongly recommended versus recommended are based on a combination of the weight of clinical evidence, the implications for patient therapy and the judgement of the group of experts. These recommendations apply to the majority of people with diabetes using injectable therapy, but there will inevitably be individual exceptions for whom these recommendations must be adjusted. Acknowledgment The New Insulin and Infusion Recommendations for Patients with Diabetes: Frid AH, Kreugel G, Grassi G et al. New Insulin delivery recommendations. Mayo Clinic Proc. September 2016;91(9): informed these recommendations and we thank the editors of the Mayo Clinic for permission to use material from this article. Supported by medical technology company Becton, Dickinson U.K. Limited. ( BD and BD Logo are trademarks of Becton, Dickinson and Company BD. All rights reserved. 6 DATE PUBLISHED: October 2017
7 Contents Preface 3 Endorsements 4 KEY Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Psychology Technology Golden Rules 30 References 35 Contributors 42 Abbreviations 43 7
8 THE IRISH INJECTION AND INFUSION TECHNIQUE RECOMMENDATIONS 2nd EDITION 1.0 Anatomy and Physiology 1.1 Needle Length: 1 The 4 mm needle inserted perpendicularly is long enough to penetrate the skin and enter the subcutaneous (SC) tissue, with little risk of Intramuscular (IM) or Intradermal (ID) injection. Therefore it should be considered the safest pen needle for adults and children regardless of age, gender and Body Mass Index (BMI). (6,7,8,9,10) 2 The 4 mm needle may be used safely and effectively in all obese patients. Although 4mm is the needle of choice for these patients, a 5mm needle may be acceptable. (11,12,13,14,15,16) 3 The 4 mm needle should be inserted perpendicular to the skin (at 90 degrees to skin surface), not at an angle, regardless of whether a skin fold is raised. Fig 1 (17,18) 4 Very young children(less than 6 years old) and very thin adults (BMI<19) should use the 4 mm needle by lifting a skin fold and inserting the needle perpendicularly into it. Others may inject using the 4 mm needle without lifting a skin fold. (14,17,18,20) 5 The safest currently-available syringe needle for all patients is 6 mm in length. However, when any syringe needle is used in children (6 years and older), adolescents or slim to normal weight adults (BMI 19-25), injections should always be administered into a lifted skin fold. (8,9,14,15,19,20,21,22,23, 24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33, 34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43, 44,45,46,47,48,49) 6 Use of syringe needles in very young children (less than 6 years old) and extremely thin adults (BMI <19) is not recommended, even if they use a raised skin fold, because of the excessively high risk of Intramuscular (IM) injections. (8,9,14,15,19,20,21, 22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31, 32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41, 42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49) 7 Healthcare professionals (HCPs) should be alerted to the risks associated with using syringe or pen needles 6mm in children. (14,19,20) 8 Children still using the 5mm pen needle should inject using a lifted skin fold. But children using pen needles 5mm should be shifted to 4 mm needles if possible; and if not, should always use a lifted skin fold. (14,17,19,20) Figure 1: Insert perpendicular to the skin 8 DATE PUBLISHED: October 2017
9 STRONGLY RECOMMENDED RECOMMENDED UNRESOLVED ISSUE At least one rigorously performed study, peer-reviewed and published At least one observational, epidemiologic or population-based study. Consensus expert opinion based on extensive patient experience. 1.0 Anatomy and Physiology 1.2 Injection Site Care: 1.3 Proper Use of Pens: 9 An angled injection at 45 degrees with a 6 mm needle may be used instead of a skin fold in children older than 6 years, because the net penetration of a 45 degree injection with the 6 mm needle is approximately 4 mm. (21) 10 Avoid indenting the skin during the injection, as the needle may penetrate deeper than intended and enter the muscle. 11 Patients with tremors or other disorders which make them unable to hold a 4 mm pen needle in place may need longer needles. Figure 2: Pens should be primed 1 The site should be inspected by the patient prior to injection. Injections should then be given in a clean site using clean hands. (50,51,52) 2 The site should be cleaned when required e.g. when there is risk of infection. If alcohol is used to clean the site, the skin must be allowed to dry completely before the injection is administered. (53,54) 3 Disinfection of the site is usually not required although local decisions may be taken in a clinical setting to do so. (55,56,57,58,59) 4 Patients should never inject into sites of lipohypertrophy, inflammation, oedema, ulceration or infection, scarred or damaged tissue. (60,61, 62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69) 5 Patients should not inject through clothing. (53) 1 Pens should be primed (observing at least a drop at the needle tip) according to the manufacturer s instructions, usually before the injection in order to ensure there is unobstructed flow and to clear needle dead space. Once flow is verified, the desired dose should be dialed and the injection administered. Fig 2 (70,71) 2 Pens and cartridges are for a single patient and should never be shared between patients due to the risk of biological material from one patient being drawn into the cartridge and then injected into another person. (56,72) 3 Needles should be disposed of immediately after use instead of being left attached to the pen. This prevents the entry of air (or other contaminants) into the cartridge as well as the leakage of medication, either of which can affect dose accuracy. (72,73,74,75,76,77) 9
10 THE IRISH INJECTION AND INFUSION TECHNIQUE RECOMMENDATIONS 2nd EDITION 1.0 Anatomy and Physiology 1.3 Proper Use of Pens continued: 1.4 Proper Use of Syringes: 4 Pen needles should be used only once. (23,51,52,58,78,79, 80,81) 5 The thumb button should only be touched once the pen needle is fully inserted. After that the button should be pressed along the axis of the pen, not at an angle. (82) 6 After pushing the thumb button completely in, patients should count slowly to 10 before withdrawing the needle in order to get the full dose and prevent the leakage of medication. Fig 3 (73,74,76,83,84,85) 7 Counting past 10 may be necessary for higher doses. Counting only to 5 may be acceptable for lower doses. Patients may find the right time for themselves by trial and error, using leakage of insulin as a guide. 8 Pressure should be maintained on the thumb button until the needle is withdrawn from the skin in order to prevent aspiration of patient tissue into the cartridge. (86,87) 1 When drawing up insulin from an insulin vial, the air equivalent to the dose (or slightly greater) should be drawn up first and injected into the vial to facilitate insulin withdrawal. 2 If air bubbles are seen in the syringe, patients should tap the barrel to bring them to the surface and then remove the bubbles by pushing up the plunger. 3 Unlike pens, which have a mechanised delivery system, it is not necessary to hold the syringe needle under the skin for a count of 10 after the plunger has been depressed as the full doze has been delivered. (73,74,85) 4 Syringes should be used only once. (23,51,52,58,78,79,80,81) Figure 3: Count to 10 to allow compelte discharge from pen 10 DATE PUBLISHED: October 2017
11 STRONGLY RECOMMENDED RECOMMENDED UNRESOLVED ISSUE At least one rigorously performed study, peer-reviewed and published At least one observational, epidemiologic or population-based study. Consensus expert opinion based on extensive patient experience. 1.0 Anatomy and Physiology 1.5 Insulin Analogues and GLP-1 receptor agonists: 1.6 Human Insulin: 1 Rapid-acting insulin analogues may be given at any of the injection sites, as absorption rates do not appear to be site specific. (88,89,90,91,92) 2 Rapid-acting analogues should not be given IM although studies have shown that absorption rates are similar from subcutaneous tissue and resting muscle. Absorption from working muscle has not however been studied. Fig 4 (89,93,92) 3 Pending further studies, long acting analogues may be injected into any of the usual sites. Injecting into muscle can cause erratic glucose levels and can lead to profound hypoglycaemia. (25) 4 Pending further studies, patients using non-insulin injectable therapies should follow the recommendations already established for insulin injections with regards to needle length, site selection and site rotation. (75,94) 1 IM injections of Neutral ph suspension of crystalline insulin, protamine and zinc (NPH) and long acting insulin must be strictly avoided due to the risk of hypoglycemia. (95,96,97,98) 2 The abdomen is the preferred site for soluble human insulin (Regular), since absorption of this insulin is fastest there. (10,99,100,101,102,103) 3 The Regular/NPH mix should be given in the abdomen to increase the speed of absorption of the short-acting component of insulin in order to cover post-prandial glycemic excursions. (24) Figure 4: Rapid acting analogues should not be given IM 4 If there is risk of nocturnal hypoglycemia, NPH and NPHcontaining mixes given in the evening should be injected into the thigh or buttock as these sites have slower absorption of NPH. (104,105,106) 11
12 THE IRISH INJECTION AND INFUSION TECHNIQUE RECOMMENDATIONS 2nd EDITION 1.0 Anatomy and Physiology 1.7 Lifting a Skin Fold: 1.8 Cloudy Insulin Re-Suspension: 1 Each injection site should be examined individually and a decision made as to whether lifting a skin fold is required, taking into account the needle length used. The recommendation should be provided to the patient in writing and documented in their clinical notes. 2 The skin fold should not be squeezed so tightly that it causes skin blanching or pain. Fig 5 3 The optimal sequence should be: lift a skin fold; inject insulin slowly at a 90 degree angle to the surface of skin fold; leave the needle in the skin for a count of 10 after the plunger is fully depressed (when injecting with a pen); withdraw the needle from the skin at the same angle it was inserted; release skin fold; dispose of used needle safely in a sharps container. 12 DATE PUBLISHED: October 2017 Figure 5: Lifting a Skin Fold 1 Cloudy insulins (e.g. NPH and pre-mixed insulins) must be gently rolled and tipped until the crystals go back into suspension (solution becomes milky white). (83,107,108,109, 110,111) 2 Tipping involves one full inversion of the pen or vial and rolling is a full rotation cycle between the palms. One evidence-based method involves rolling the insulin cartridge horizontally between the palms 10 times for 5 seconds, then tipping 10 times for 10 seconds at room temperature. Fig 6, Fig 7 (112) Figure 6: Re-suspension of cloudy insulin Figure 7: Resuspension of cloudy insulin
13 STRONGLY RECOMMENDED RECOMMENDED UNRESOLVED ISSUE At least one rigorously performed study, peer-reviewed and published At least one observational, epidemiologic or population-based study. Consensus expert opinion based on extensive patient experience. 1.0 Anatomy and Physiology 1.9 Pregnant women: 3 Visually confirm that the re-suspended insulin is sufficiently mixed after each rolling and tipping, and repeat the procedure if crystal mass remains in the cartridge. (112,113) 4 Vigorous shaking should be avoided since this produces bubbles which reduce accurate dosing. Avoid exposing insulin to direct heat, light or excessive agitation. (109,110,113) 5 Store unopened insulin in a refrigerator where freezing is unlikely to occur. Fig 8 (114,115) 6 After initial use (in pen, cartridge or vial) insulin should be stored at room temperature (15-30 degrees Celsius [ C] or degrees Fahrenheit [ F]) for up to thirty days or according to manufactures recommendations and within expiry date. Pre-mix insulin pens and some of the newer insulins may vary in storage guidelines, so patients should check manufactures recommendations. (116,117) 7 If room temperatures exceed 30 C (86 F) then insulin in current use should be stored in a refrigerator. It should be allowed to warm up before injection. Insulin can be warmed by rolling it between the palms. (114,115) 1 The abdomen is a safe place for insulin administration in pregnancy. Given the thinning in abdominal fat from uterine expansion, pregnant women with diabetes (of any type) should use a 4mm/5mm pen needle. 2 First trimester: Women should be reassured that no change in insulin site or technique is needed. 3 Second trimester: Lateral parts of the abdomen can be used to inject insulin. 4 Third trimester: Insulin can be injected over the abdomen while ensuring that a skin fold is properly raised. Figure 8: Store unopened insulin in a refridgerator 13
14 THE IRISH INJECTION AND INFUSION TECHNIQUE RECOMMENDATIONS 2nd EDITION 1.0 Anatomy and Physiology 1.10 Tips for injection Education 1 Demonstrate proper injection technique to the patient and family. Then have the patient and family demonstrate proper technique back to the HCP. 2 Be sure the skin is clean and dry before injecting. Patients do not need to use a disinfectant on the skin, but if they do, they should allow it to dry completely before injecting. 3 Use needles of shorter length (4mm or shortest available), smaller diameter (highest gauge number), and the tip with the lowest penetration force to minimize pain. Use a sterile, new needle with each injection. (170) 4 Insert the needle through the skin in a smooth but not jabbing movement. The skin contains pain receptors and going through the skin too slowly or too forcefully may increase the pain. (170) 5 Inject the insulin slowly ensuring that the plunger (syringe) or thumb button (pen) has been fully depressed and all insulin has been injected. With pens the patient should count to 10 after the button has been depressed before withdrawing the needle. 6 HCPs should teach the importance of rotation and create a rotation pattern with the patient when initiating injection therapy. The message should be: Insulin will not be well-absorbed if it is always injected into the same area. It is important to move injections at least 1cm (half an inch) away from the previous injection and to use all injection sites on the body (buttocks, thighs and abdomen).(147) 7 If the same injection site is used repeatedly it may become lumpy, firm and enlarged. The insulin will not work correctly if injected into these areas. (147,202,203) 8 If pain is experienced when injecting large volumes of insulin the dose may need to be divided into two injections of a smaller volume or the concentration of insulin may need to be increased. 9 One person/one pen: insulin pens, pen cartridges and small individual vials should not be shared in order to prevent the transmission of infectious diseases. One patient/one insulin pen. (56,73,147,204,205,206,207, 208,209,210,211,212). 10 Insulin pens, pen cartridges and small individual vials should be clearly labelled with patient names/identifiers in health care facilities where common storage is used e.g. refrigerators. (213). 14 DATE PUBLISHED: October 2017
15 STRONGLY RECOMMENDED RECOMMENDED UNRESOLVED ISSUE At least one rigorously performed study, peer-reviewed and published At least one observational, epidemiologic or population-based study. Consensus expert opinion based on extensive patient experience. 2.0 Pathology 2.1 Lipohypertrophy Physical Examination For Diagnosing Lipohypertrophy (LH): The following points are helpful when performing the physical examination for LH. The examination should be performed at least once a year on all persons injecting insulin. For those found to have LH lesions, the examination should be performed even more frequently. Setting 1 Patient should be asked about abnormalities at injection sites (what, where and how long); this should guide the examination but not limit it to one area. 2 Patient must then disrobe to only underclothes. A chaperone may be needed in some cultures. 3 Room must be warm to prevent patient chilling (this ensures patient comfort but also prevents shivering and muscle tension which can interfere with the examination). 4 Light should be oblique to the skin (not overhead); the use of an examination light with an adjustable neck is ideal; light should be shined onto skin surfaces at an angle of degrees. Positioning Patient 5 Patient should be lying down on back (to relax abdominal muscles) with knees bent (to relax thigh [quadriceps] muscles). 6 If there is no table, an alternative is for the patient to be sitting, with knees bent and arms relaxed in lap. Positioning Professional 7 Hands must be washed and warmed before touching patient. 8 If no adjustable light is available, HCP can wear head lamp or use flashlight. 9 If patient is sitting HCP needs to do perform the examination seated. Technique of Physical Examination 10 Inspect site with lamp first, adjusting its angle to be able to detect any subtle risings or depressions across the surface of the skin. 11 Lipohypertrophy is usually manifested as a raised or mound-like, convex pattern with no change in skin colour or hair distribution; occasionally it can be manifested as only a shiny or hyperpigmented (especially in dark-skinned persons) area and/or an area of hair loss. 12 If detected,gain consent and mark the centre point with a skin safe pen so that area can be palpated later. 15
16 THE IRISH INJECTION AND INFUSION TECHNIQUE RECOMMENDATIONS 2nd EDITION 2.0 Pathology 2.1 Lipohypertrophy Technique for palpation 13 After hands are warmed by rubbing them together or washing in warm water, apply gel (ultrasound gel or another water-soluble lubricant for clinical use) to the injecting area and palpate with the tips of the fingers, working in towards the injecting area with light massage-like motions (forward thrusts or circular sweeps). 14 Lipohypertrophy is manifest by a change in the soft, undulating feel of the SC tissue, which is replaced by a harder, and more rubbery or less bouncy tissue. 15 Often the edges of this abnormal area are clearly demarcated and it is easy to feel the transitional zone, which appears as a step-up from the surrounding soft tissue. Measuring and Documenting the Lipohypertrophy 16 With the patient s consent and using skin safe marker pen, mark the exact position of the lesion on the patient s skin so that the patient can clearly see the extent of the lesion and avoid injecting into it. 17 Measure the distance along its largest dimension (usually the longest diameter) in mm and record in patient s chart. 18 With the patient s consent you may photograph the lesion from a distance of 1 metre without flash, using the light from an oblique source so as to reveal surface contours. 19 With the patient s consent you may use the measurements and photograph to follow progression of the lesion longterm. 20 Patient should be taught to do the visual and palpation examination monthly (using soap or hand lotion as a lubricant) and to report any change to the HCP. Role of Ultrasound in Lipohypertrophy 21 Ultrasound (US) has been used in various LH studies but its exact role has yet to be defined, either for diagnosis or management of the disorder. 22 US appears to be more sensitive and specific than clinical examination in early clinical studies, but this remains to be confirmed. 23 An US signature for LH may exist and ongoing studies are attempting to define the various image profiles of LH. 16 DATE PUBLISHED: October 2017
17 STRONGLY RECOMMENDED RECOMMENDED UNRESOLVED ISSUE At least one rigorously performed study, peer-reviewed and published At least one observational, epidemiologic or population-based study. Consensus expert opinion based on extensive patient experience. 2.0 Pathology Palpable lipohypertrophy: normal skin (fingertips close together) and lipohypertrophic tissue (fi ngertips spread apart). Photograph courtesy of Lourdes Saez-de Ibarra and Ruth Gaspar, Diabetes Nurses and Specialist Educators from La Paz Hospital, Madrid, Spain Sometimes the lipo can have the appearance of a tense, shiny area as on the leg of this 19-year old man. NB: when you see a shiny, inducted area at an injection site, SUSPECT LIPO 29 year old man said: it hurts less there. 52 year old man injected in his thigh for 25 years, began to rotate. His daily insulin requirement fell from 66 units to 30 17
18 THE IRISH INJECTION AND INFUSION TECHNIQUE RECOMMENDATIONS 2nd EDITION 2.0 Pathology 2.2 Diagnosis and Management of Lipohypertrophy: 1 Sites should be examined by the HCP at least once year or more frequently if lipohypertrophy is already present. (119,131) 2 The physical examination for lipohypertrophy is ideally performed with the patient lying down and disrobed to the underwear. But in circumstances that preclude this, examination of the patient sitting, standing or partiallyclothed is acceptable. 3 Patients should be taught to inspect their own sites and should be given training in site rotation, proper injection technique as well as in detection and prevention of lipohypertrophy. (55,57,59,63, 64,111,132,133,134,135,136,137,1 38,139,140,141,142,143,144,145, 146) 4 After obtaining patient consent, making two ink marks at opposite edges of the lipohypertrophy with a single-use skin-safe marker (at the junctions between normal and rubbery tissue) will allow the lesion to be measured or photographed and its size recorded for future assessment. (147,148,149) 5 Patients should be encouraged by education and guidance not to inject into areas of lipohypertrophy until the next examination by a HCP. Using larger injection zones and non-reuse of needles should be recommended. (141,150,151,152) 6 Switching injections from lipohypertrophy to normal tissue often requires a decrease in the dose of insulin injected. The amount of change varies from one individual to another and should be guided by frequent blood glucose measurements. Reductions often exceed 20% of their original dose; however this will be guided by the HCP. (63,64,141,150,151) 18 DATE PUBLISHED: October 2017
19 STRONGLY RECOMMENDED RECOMMENDED UNRESOLVED ISSUE At least one rigorously performed study, peer-reviewed and published At least one observational, epidemiologic or population-based study. Consensus expert opinion based on extensive patient experience. 2.0 Pathology 2.3 Injection Site Rotation: 1 Injections should be systematically rotated in such a way that they are spaced at least 1 cm (or approximate width of an adult finger) from each other in order to avoid repeat tissue trauma. (117,153,154,155) 2 Patients should be taught an easy-to-follow rotation scheme from the onset of injection therapy. This may be adjusted as needed while therapy progresses. The HCP should review the site rotation scheme with the patient at least once a year. (156) Figure 9: Injections within any quadrant should be spaced at least 1cm from each other Figure 10: Sample structured rotation plan for abdomen and thighs. Divide the injection area into quadrants or zones. Use 1 zone per week and move clockwise 3 One scheme with proven effectiveness involves dividing the injection site into quadrants (or halves when using the thighs or buttocks), using one quadrant per week and moving quadrant to quadrant in a consistent direction (e.g. clockwise). Fig 9 and Fig 10 (131,139,157,158, 159,160,161,162) 19
20 THE IRISH INJECTION AND INFUSION TECHNIQUE RECOMMENDATIONS 2nd EDITION 2.0 Pathology 2.4 Needle Reuse: 2.5 Bleeding and Bruising: 2.6 Insulin Leakage: 1 There is association between needle reuse and the presence of lipohypertrophy, although a causal relationship has not been proven. Patients should be made aware of this association (and also the association between reuse and pain or bleeding). (147) 2 Reusing insulin needles is not an optimal injection practice and patients should be discouraged from doing so. (58,69,163,164,165,166) 3 Those who are reusing needles for whatever reason including cost or availability should not be alarmed by claims of excessive morbidity from this practice. (58,60,167) 1 Patients should be reassured that local bleeding and bruising do not have adverse clinical consequences for the absorption of insulin or for overall diabetes management. Patients may be advised to avoid this site for a period of time until the bruising subsides. (168) 2 If bleeding and/or bruising are frequent or excessive, injection technique should be carefully assessed as well as the presence of a coagulopathy or the use of an anticoagulant or antiplatelet agent. Fig 11 1 Leakage at cartridge and pen needle (PN) connection: Ensure that the PN is ISOcertified compatible with the insulin pen. Position the PN along the axis of the pen before screwing or snapping it on. Pierce straight through the septum of the cartridge. 2 Dripping from the needle: Use needles which have a wider inner diameter and improved insulin flow (e.g. Extra-thin wall needles). (169) (170) Count to 10 after the plunger has been fully depressed before removing the needle from the skin. This is to allow time for forces to be transmitted through all pen parts to insulin column in cartridge. (171) 20 DATE PUBLISHED: October 2017 Figure 11: Bleeding and Bruising
21 STRONGLY RECOMMENDED RECOMMENDED UNRESOLVED ISSUE At least one rigorously performed study, peer-reviewed and published At least one observational, epidemiologic or population-based study. Consensus expert opinion based on extensive patient experience. 2.0 Pathology By trial and error, patients may learn how long they need to hold the button down and the needle under the skin in order to avoid dripping from the needle tip or backflow out of the skin. This may be less than 10 seconds. (172) Larger doses may be split to reduce the volume of insulin. (171,173) 3 Skin Leakage: Use needles with thin-wall or extra thin-wall technology. (171) (174) Count to 10 after the plunger is fully depressed before removing the needle from the skin. This allows enough time for the injected medication to spread out through the tissue planes and/or to cause the tissue to expand and stretch. (85,171,174) A small amount of skin leakage (little pearl of liquid at injection site) can be ignored. It is almost always clinically insignificant. (85) (171,174) For patients who report frequent skin leakage, a direct observation of their self-injection is important to detect possible techniquerelated issues that can be modified. (85,171,174) 21
22 THE IRISH INJECTION AND INFUSION TECHNIQUE RECOMMENDATIONS 2nd EDITION 3.0 Psychology 3.1 Role of Healthcare Professional 3.2 Therapeutic Education 1 Key tasks of the healthcare professional (HCP) include teaching patients (and other care-givers) how to inject correctly and addressing the many psychological hurdles the patient may face when injecting or infusing, especially at the initiation of treatment. (118,119) 2 The HCP must have an understanding of the anatomy of insulin delivery sites in order to help patients avoid intramuscular (IM) injections or infusions and ensure that injections and infusions are consistently given into the subcutaneous (SC) tissue, without leakage/backflow or other complications. (22,24,61,102,120) 3 The HCP must have knowledge of absorption profiles from different tissues of the injected or infused agents. (121,122) 1 The HCP should spend time exploring patient (and other care-givers ) anxieties about the injecting process and insulin itself. (119,123) 2 At the beginning of injection therapy (and at least every year thereafter) the HCP should discuss each of the essential topics and ensure that information has been fully understood. (124) 3 The essential topics include: the injection regimen the choice and management of the devices used the choice, care and selfexamination of injection sites proper injection techniques (including site rotation, injection angle and possible use of lifted skin folds) injection complications and how to avoid them optimal needle lengths safe disposal of used sharps. (118,125,126,127,128,129,130) 4 Instructions should be given in both verbal and written form and adherence checked. To see if the patient is getting what was prescribed, ask to see a needle from the latest packet given by the pharmacy. 5 Current injection practice should be assessed and observed, and injecting sites examined and palpated, if possible at each visit but at least every year. (128,129,130) 6 A quality management process should be put in place to ensure that correct injection technique is regularly practiced by the patient and is documented in the record. (128,129,130) 22 DATE PUBLISHED: October 2017
23 STRONGLY RECOMMENDED RECOMMENDED UNRESOLVED ISSUE At least one rigorously performed study, peer-reviewed and published At least one observational, epidemiologic or population-based study. Consensus expert opinion based on extensive patient experience. 3.0 Psychology 3.3 Preparing Adults and the Elderly for Injection Emotional and Psychosocial Issues 1 Show empathy by addressing the patients emotional concerns first. The HCP should explore worries and barriers to treatment and acknowledge that anxiety is normal when beginning any new medication, especially injection therapy. (124) ( ) 2 Patients, especially adolescents, should be encouraged to express their feelings about injecting, particularly their frustration, anger and struggles. 3 Patients of all ages should be reassured that this is a learning process and the health care team is there to help along the way. The message is: You are not alone, we are here to help you; we will practice together until you are comfortable giving yourself an injection. 4 With all patients it is important to explain that insulin is not a punishment or failure. Insulin is the best treatment we have for managing blood glucose. For patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (T1DM) it is the primary treatment and for patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) it is often an adjunct to oral therapy to improve blood glucose control. For patients with T2DM it is important they understand the natural progression of the disease and that insulin therapy is a part of the logical progression in its management. (123) (175) (195) 5 Managing blood glucose effectively with insulin will help prevent long-term complications. (126) (176) 6 Patients, especially adolescents, should be given as much control as possible in designing their regimen to fit their lifestyle. This could include basal bolus therapy, carbohydrate counting, having access to a structured education programme, using insulin pens and insulin pumps. 23
24 THE IRISH INJECTION AND INFUSION TECHNIQUE RECOMMENDATIONS 2nd EDITION 3.0 Psychology 3.4 Strategies for Reducing Fear, Pain and Anxiety 1 Include caregivers and family members in the planning and education of the patient and tailor the therapeutic regimen to the individual needs of the patient. 2 Have a compassionate and straight forward approach when teaching injection technique. Demonstrate the injection technique to the patient. Have the patient follow along and then demonstrate back to the educator/hcp. 3 Consider use of devices which hide the needle in case of anxiety provoked by seeing sharps. Also consider use of vibration, cold temperature or pressure to distract the nerves (gate theory) from the perception of pain. 4 Children have a lower threshold for pain. The HCP should ask about pain. For young children consider distraction techniques or play therapy (e.g. injecting a soft toy (animal or doll). Older children respond better to cognitive behavioral therapies (CBT). CBT includes relaxation training, guided imagery, graded exposure, active behavioral rehearsal, modeling and positive reinforcement as well as incentive scheduling. (175,177,178,196,97) 5 Often fear and anxiety can be significantly reduced by having the parent and child give themselves a dry injection. Often they are surprised at how painless or relatively so, the injection is. 6 In children and adolescents the use of injection ports may help reduce the initial fear of injections. (179,198,199,200,201) 7 Insulin pens with very short needles may be more acceptable to patients than the syringe and vial. This should be discussed with the patient and family when teaching injection therapy. The 4 mm pen needle is reported by patients to be less painful than longer needles. (70,72,127,176) 8 If patients occasionally experience sharp pain on injection they should be reassured that the needle may have touched a nerve ending which happens randomly and will not cause any damage. If pain persists the HCP should see the patient and evaluate the injection technique. 24 DATE PUBLISHED: October 2017
25 STRONGLY RECOMMENDED RECOMMENDED UNRESOLVED ISSUE At least one rigorously performed study, peer-reviewed and published At least one observational, epidemiologic or population-based study. Consensus expert opinion based on extensive patient experience. 3.0 Psychology 9 Keep insulin at room temperature for a more comfortable injection. Cold insulin often produces more pain. 10 If bleeding or bruising occur, reassure the patient that these do not affect the absorption of insulin or overall diabetes control. If bruising continues or haematomas develop, observe the injection technique and suggest improvements (e.g. better rotation of injection sites). 25
26 THE IRISH INJECTION AND INFUSION TECHNIQUE RECOMMENDATIONS 2nd EDITION 4.0 Technology 4.1 Needle Inner Diameter: 4.2 Insulin Infusion Sets (IIS) for Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin Infusion (CSII): 1 High flow rate needles (extrathin wall) needles have been shown to be appropriate for all injecting patients. Their obstruction, bending and breakage rates are the same as for conventional quality needles (extremely low), and they offer distinct flow advantages. Fig 12 1 Population studies suggest that CSII cannula should be changed every hours in order to minimize infusion site adverse events and potential metabolic deterioration. However these times are very patient-dependent and should be adjusted accordingly. (214,215,216,217) 2 All CSII patients should be taught to rotate infusion sites along the same principles that injecting patients are taught to rotate injection sites. (137,218) 3 Any CSII patients with unexplained glucose variability including frequent hypoglycemia/hyperglycemia should have infusion sites checked for lipohypertrophy, nodules, scarring, inflammation or other skin and SC conditions that could affect insulin flow or absorption. (137) 4 CSII patients should have their infusion sites checked frequently or at least annually for lipohypertrophy by an HCP. (216,219) 5 If lipohypertrophy is suspected, the patient should be instructed to stop infusing into these lesions and to insert the catheter into healthy tissue. (62,64,141,150,151,152) 6 Silent occlusion of insulin flow should be suspected in any patient with unexplained glucose variability, unexplained hyperglycemia, or frequent hypoglycemia/hyperglycemia. (214,219,220,221,222) 7 If silent occlusion is suspected, CSII patients should be considered for an alternative cannulae. (214,216,220,222) Figure 12: Thin walled needle & Thick walled needle 26 DATE PUBLISHED: October 2017
27 STRONGLY RECOMMENDED RECOMMENDED UNRESOLVED ISSUE At least one rigorously performed study, peer-reviewed and published At least one observational, epidemiologic or population-based study. Consensus expert opinion based on extensive patient experience. 4.0 Technology 4.3 Safety-engineered Devices: 8 All CSII patients should be considered for the shortest needle/cannula available, along the same principles as insulin injectors, to minimize the risk of IM infusion. Young children and very thin individuals (Body Mass Index <19) may need to insert into a lifted skin fold to avoid IM insertion. (222) 9 The smallest diameter needle/ cannula should be considered in CSII patients to reduce pain and the occurrence of insertion failure. (222) 10 Angled insertion sets should be considered in CSII patients who experience infusion site complications with 90 degree infusion sets. (222) 11 All CSII patients who experience a hypersensitivity reaction to cannula material or adhesive should be considered for alternative options (alternative sets, tapes or skin barriers). 12 CSII patients who are lean, muscular or active and have a high probability of the cannula or tubing being dislodged may benefit from angled (30-45 degree) insertion. (223) 13 CSII patients who have difficulty inserting their infusion set manually for any reason should insert their infusion sets with the assistance of a mechanical insertion device. (223) 14 CSII patients who become pregnant may require adjustments to their infusion sets, site locations and frequency of site changes. Figure 13: Safety-engineered pen needle Needlestick Injuries/Blood-borne Infection Risk 1 Safety-engineered devices play a critical role in protecting injectors, pump users and downstream workers. Nurses and other healthcare workers at risk must receive appropriate education and training in how to minimize risk by following optimal techniques, using available safety-engineered devices and wearing protective clothing (e.g., gloves). (224) 2 Safety-engineered devices should be considered first-line choice if injections are given by a third party. Pen and syringes with needles used in these settings should have protective mechanisms for all sharp ends of the delivery device. Fig 13 (225,226,227,228,229,230,231, 232,233,234) 27
28 THE IRISH INJECTION AND INFUSION TECHNIQUE RECOMMENDATIONS 2nd EDITION 4.0 Technology 4.3 Safety-engineered Devices continued: 3 The use of safety-engineered devices should be considered for certain autonomous home-injecting patients with diabetes (e.g. those known to be seropositive for Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV), Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) and Hepatitis C Virus (HCV), children injecting at school). (225,235,236,237) 4 Patients with small children at home and/or sub-optimal sharps disposal options should also consider using safety-engineered devices. (226,227,229,230,231,238) 5 HCPs should be involved in the trialing and choice of safety-engineered devices used in their health care setting. Evaluation prior to adoption should include key specialists (e.g. experienced end users, infection control and occupational health). (231,239) 28 DATE PUBLISHED: October Healthcare settings where insulin pens are used must follow a strict one-patient / one-pen policy. (240) 7 The optimal safety-engineered device should provide protection for patients, caregivers and all others who may come in contact with the sharp device. (226,227,228,229,230,231, 232,233,234) 8 Manufacturers should investigate all reported needlestick injuries (NSI) to determine if they are related to a device failure. 9 To minimize the risk of NSI through a skin-fold, the use of shorter needles (e.g. 4 and 5 mm pen needles; 6mm insulin syringe) without a skin fold is recommended. (8,16,48,241) 10 If a lifted skin fold is used, the patient should ensure that finger and thumb are approximately 2.5cm (1 inch) apart and should make the injection in the center of the fold thus minimizing throughskinfold NSI risk. (241) 11 NSI awareness campaigns must be carried out regularly and should include all persons in potential contact with medical sharps. (226,227,228,229,242,243) 12 Needle recapping should not be done and manufacturers should design sharps protection mechanisms which make recapping impossible. Fig 14 (226,227,229,230,231) Figure 14: Safety-engineered syringe
29 STRONGLY RECOMMENDED RECOMMENDED UNRESOLVED ISSUE At least one rigorously performed study, peer-reviewed and published At least one observational, epidemiologic or population-based study. Consensus expert opinion based on extensive patient experience. 4.0 Technology 13 Hospitals must encourage reporting of NSI and near misses and establish a no blame culture. Central review of all NSI/near misses must take place regularly to allow for policy change and assess educational needs. (226,227,229,230,231) 14 Review and appraisal of the effectiveness of education and training and of adherence to guidelines must be performed at regular intervals. A reporting system for violations must be put in place. (225,226,227,228,229,230, 231,232,233,234) 15 Attention must be paid to proper use of safety-engineered devices. If they are not activated, because of user inattention or lack of training, they provide no additional risk reduction over conventional (non-safety) devices. (225,226, 227,228,229,230,231,232,233,2 34) 16 Sharps containers must be easily accessible at the point of care beside the patient, prior to the injection or infusion. Containers should bear the warning, Needles can seriously damage the health of others. Please ensure safe disposal or similar. (226,227,229,230,231,238) 17 While HBV vaccination should be population-wide, the minimum standard is its mandatory offering by the employer to all workers exposed to sharps. Vaccination status should be reviewed annually at employee s performance assessment. (244) 18 First aid information what to do in the event of a NSI should be readily available in all health care facilities. 19 All workers in possible contact with sharps should be aware of local safety and disposal regulations. Legal and societal consequences of non-adherence should be reviewed. (245) 20 Safe disposal should be taught to patients, care-givers and all others who may come in contact with the sharp device from the beginning of injection or infusion therapy and reinforced throughout. (246) 21 Potential adverse events of NSIs should be emphasized to the patients family, caregivers and service providers (e.g. rubbish collectors and cleaners). 22 Under no circumstance should sharps material be disposed of into the public rubbish system. 29
If you inject diabetes medication, you should know how important correct injection technique is for effectively managing your diabetes.
 Insulin injection technique best practices Expert recommendations on injecting insulin with pen and insulin syringe needles If you inject diabetes medication, you should know how important correct injection
Insulin injection technique best practices Expert recommendations on injecting insulin with pen and insulin syringe needles If you inject diabetes medication, you should know how important correct injection
Safe and Gentle Injection of Insulin. Guide for correct injection technique. Englische Ausgabe
 Safe and Gentle Injection of Insulin Guide for correct injection technique Englische Ausgabe Insulin injection basics 1 Insulin has to be injected into the subcutaneous fat layer 3 Rotate the injection
Safe and Gentle Injection of Insulin Guide for correct injection technique Englische Ausgabe Insulin injection basics 1 Insulin has to be injected into the subcutaneous fat layer 3 Rotate the injection
Injection technique for different needle lengths
 Injection technique for different needle lengths Use the correct technique to better manage your diabetes 1 Why it s important to use the shortest needles available Reduce your risk of injecting into the
Injection technique for different needle lengths Use the correct technique to better manage your diabetes 1 Why it s important to use the shortest needles available Reduce your risk of injecting into the
Acknowledgement goes to WHO for use of their hand washing technique
 How to administer third party insulin injections safely with a pen device, safety pen needle and syringe 1 Hand washing It takes at least 15 seconds to wash your hands. This is about how long it takes
How to administer third party insulin injections safely with a pen device, safety pen needle and syringe 1 Hand washing It takes at least 15 seconds to wash your hands. This is about how long it takes
INSULIN INJECTION KNOW-HOW
 0-1- INSULIN INJECTION KNOW-HOW Learning how to Congratulations for making the move to insulin therapy. It won t be long before you start enjoying better blood sugar control, more energy, and a host of
0-1- INSULIN INJECTION KNOW-HOW Learning how to Congratulations for making the move to insulin therapy. It won t be long before you start enjoying better blood sugar control, more energy, and a host of
Things you need to know about injections
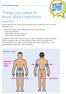 www.trend-uk.org Things you need to know about injections Injection sites: You can see from the picture below the best sites for injecting insulin or GLP-1 medications are: Back of the upper arms (difficult
www.trend-uk.org Things you need to know about injections Injection sites: You can see from the picture below the best sites for injecting insulin or GLP-1 medications are: Back of the upper arms (difficult
BEST 4 Diabetes. Optimisation of insulin module
 BEST 4 Diabetes Optimisation of insulin module Confidence and competence Where would you rate yourself? Why do all of our patient not achieve optimal blood glucose control? Insulin Therapy Goals and Purpose
BEST 4 Diabetes Optimisation of insulin module Confidence and competence Where would you rate yourself? Why do all of our patient not achieve optimal blood glucose control? Insulin Therapy Goals and Purpose
Gentle and safe injections. Tips and tricks for injecting insulin.
 Gentle and safe injections. Tips and tricks for injecting insulin. Freedom. Confidence. With mylife. Gentle and safe injections The correct injection technique The insulin is injected into the subcutaneous
Gentle and safe injections. Tips and tricks for injecting insulin. Freedom. Confidence. With mylife. Gentle and safe injections The correct injection technique The insulin is injected into the subcutaneous
BEST 4 Diabetes. Optimisation of insulin module
 BEST 4 Diabetes Optimisation of insulin module Confidence and competence Where would you rate yourself? Why do all of our patient not achieve optimal blood glucose control? Insulin Therapy Goals and Purpose
BEST 4 Diabetes Optimisation of insulin module Confidence and competence Where would you rate yourself? Why do all of our patient not achieve optimal blood glucose control? Insulin Therapy Goals and Purpose
Patient Information Publications Warren Grant Magnuson Clinical Center National Institutes of Health
 Warren Grant Magnuson Clinical Center National Institutes of Health What is a subcutaneous injection? A subcutaneous injection is given in the fatty layer of tissue just under the skin. A subcutaneous
Warren Grant Magnuson Clinical Center National Institutes of Health What is a subcutaneous injection? A subcutaneous injection is given in the fatty layer of tissue just under the skin. A subcutaneous
KEEPING SAFE WITH INSULIN THERAPY
 KEEPING SAFE WITH INSULIN THERAPY kk WHY IS THIS LEAFLET FOR YOU? Insulin treatment improves the quality of life in many people and saves the lives of others. It is used to lower blood glucose levels.
KEEPING SAFE WITH INSULIN THERAPY kk WHY IS THIS LEAFLET FOR YOU? Insulin treatment improves the quality of life in many people and saves the lives of others. It is used to lower blood glucose levels.
PLEASE READ THIS USER MANUAL BEFORE USE
 USER MANUAL Humalog 200 units/ml KwikPen, solution for injection in a pre-filled pen insulin lispro PLEASE READ THIS USER MANUAL BEFORE USE USE ONLY IN THIS PEN, OR SEVERE OVERDOSE CAN RESULT Read the
USER MANUAL Humalog 200 units/ml KwikPen, solution for injection in a pre-filled pen insulin lispro PLEASE READ THIS USER MANUAL BEFORE USE USE ONLY IN THIS PEN, OR SEVERE OVERDOSE CAN RESULT Read the
Gentle and safe injections. Tips and tricks for injecting insulin.
 Gentle and safe injections. Tips and tricks for injecting insulin. More freedom. More confidence. With mylife. Gentle and safe injections The correct injection technique The insulin is injected into the
Gentle and safe injections. Tips and tricks for injecting insulin. More freedom. More confidence. With mylife. Gentle and safe injections The correct injection technique The insulin is injected into the
Insulin Delivery System and Self Monitoring Blood Sugar (SMBG ) Leyden V. Florido, RN, MAN
 Insulin Delivery System and Self Monitoring Blood Sugar (SMBG ) Leyden V. Florido, RN, MAN Management of Diabetes Mellitus Pharmacological Glucose Lowering Agents/Oral Antidiabetes Drug/Oral Hypogycemic
Insulin Delivery System and Self Monitoring Blood Sugar (SMBG ) Leyden V. Florido, RN, MAN Management of Diabetes Mellitus Pharmacological Glucose Lowering Agents/Oral Antidiabetes Drug/Oral Hypogycemic
For use only with Lilly 3 ml insulin cartridges (100 units/ml). Do not use other brands of insulin cartridges.
 MS9662 MS9663 HumaPen LUXURA INSULIN DELIVERY DEVICE INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE For use only with Lilly 3 ml insulin cartridges (100 units/ml). Do not use other brands of insulin cartridges. Your HumaPen LUXURA
MS9662 MS9663 HumaPen LUXURA INSULIN DELIVERY DEVICE INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE For use only with Lilly 3 ml insulin cartridges (100 units/ml). Do not use other brands of insulin cartridges. Your HumaPen LUXURA
For use only with Lilly 3 ml insulin cartridges (100 units/ml). Do not use other brands of insulin cartridges.
 MS9673 HumaPen LUXURA HD INSULIN DELIVERY DEVICE INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE For use only with Lilly 3 ml insulin cartridges (100 units/ml). Do not use other brands of insulin cartridges. The colour of your HumaPen
MS9673 HumaPen LUXURA HD INSULIN DELIVERY DEVICE INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE For use only with Lilly 3 ml insulin cartridges (100 units/ml). Do not use other brands of insulin cartridges. The colour of your HumaPen
Instructions for Use HEMLIBRA (hem-lee-bruh) (emicizumab-kxwh) injection, for subcutaneous use
 Instructions for Use HEMLIBRA (hem-lee-bruh) (emicizumab-kxwh) injection, for subcutaneous use Be sure that you read, understand, and follow the Instructions for Use before injecting HEMLIBRA. Your healthcare
Instructions for Use HEMLIBRA (hem-lee-bruh) (emicizumab-kxwh) injection, for subcutaneous use Be sure that you read, understand, and follow the Instructions for Use before injecting HEMLIBRA. Your healthcare
HumaPen LUXURA HD INSULIN DELIVERY DEVICE INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
 1 HumaPen LUXURA HD INSULIN DELIVERY DEVICE INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE For use only with Lilly 3 ml insulin cartridges (100 units/ml). Do not use other brands of insulin cartridges. The color of your HumaPen
1 HumaPen LUXURA HD INSULIN DELIVERY DEVICE INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE For use only with Lilly 3 ml insulin cartridges (100 units/ml). Do not use other brands of insulin cartridges. The color of your HumaPen
Policy for the safe administration of Insulin
 Policy for the safe administration of Insulin This is a working document and any changes that become necessary to this policy must be Notified in writing to the Medicine Management Group via the Chief
Policy for the safe administration of Insulin This is a working document and any changes that become necessary to this policy must be Notified in writing to the Medicine Management Group via the Chief
The Advantages of Short Pen Needles. Insulin injection with pen needles
 Clinical Evidence Folder The Advantages of Short Pen Needles Insulin injection with pen needles 1. Introduction 3 2. Utilization of Shorter Pen Needles 4 2.1. Injection Sites 4 2.2. Injection Site and
Clinical Evidence Folder The Advantages of Short Pen Needles Insulin injection with pen needles 1. Introduction 3 2. Utilization of Shorter Pen Needles 4 2.1. Injection Sites 4 2.2. Injection Site and
1 Before You Begin. Injection Instructions. Safety Tips. Disposing of Used Syringes, Needles, and Supplies. Having Someone Help You With Injections
 Injection Instructions (Logo) FUZEON (R) enfuvirtide 1 Before You Begin This is a step-by-step guide to injecting FUZEON (enfuvirtide) that helps remind you about what you learned at your healthcare provider
Injection Instructions (Logo) FUZEON (R) enfuvirtide 1 Before You Begin This is a step-by-step guide to injecting FUZEON (enfuvirtide) that helps remind you about what you learned at your healthcare provider
Best Practice Guideline to support Correct Injection Technique in Diabetes Care
 Best Practice Guideline to support Correct Injection Technique in Diabetes Care B e s t P r a c t i c e i n D i a b e t e s C a r e PAGE 2 Contents Introduction Our Supporters Endorsements SECTION 1. THE
Best Practice Guideline to support Correct Injection Technique in Diabetes Care B e s t P r a c t i c e i n D i a b e t e s C a r e PAGE 2 Contents Introduction Our Supporters Endorsements SECTION 1. THE
HumaPen SAVVIO INSULIN DELIVERY DEVICE INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
 HumaPen SAVVIO INSULIN DELIVERY DEVICE INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE For Single Patient Use Only www.lilly.ca INTRODUCTION HumaPen SAVVIO is designed for ease of use. You can give yourself multiple doses from one
HumaPen SAVVIO INSULIN DELIVERY DEVICE INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE For Single Patient Use Only www.lilly.ca INTRODUCTION HumaPen SAVVIO is designed for ease of use. You can give yourself multiple doses from one
Correct Site Rotation
 Injection Techniques Questionnaire (ITQ) WorldWide Results 2014-2015 Correct Site Rotation BACKGROUND Correct Rotation = at least 1 cm between successive injections Lipohypertrophy and Observed Correct
Injection Techniques Questionnaire (ITQ) WorldWide Results 2014-2015 Correct Site Rotation BACKGROUND Correct Rotation = at least 1 cm between successive injections Lipohypertrophy and Observed Correct
Instructions for Use Enbrel (en-brel) (etanercept) for injection, for subcutaneous use Multiple-dose Vial
 Instructions for Use Enbrel (en-brel) (etanercept) for injection, for subcutaneous use Multiple-dose Vial How do I prepare and give an injection with Enbrel multiple-dose vial? A multiple-dose vial contains
Instructions for Use Enbrel (en-brel) (etanercept) for injection, for subcutaneous use Multiple-dose Vial How do I prepare and give an injection with Enbrel multiple-dose vial? A multiple-dose vial contains
PATIENT INFORMATION. D iabetes. What You Need to Know About. Insulin
 PATIENT INFORMATION Medicine To Treat: D iabetes What You Need to Know About Insulin INTRODUCTION The insulin preparations currently available in Singapore are mostly from human origin; pork or bovine
PATIENT INFORMATION Medicine To Treat: D iabetes What You Need to Know About Insulin INTRODUCTION The insulin preparations currently available in Singapore are mostly from human origin; pork or bovine
insulin and injections
 insulin and injections Insulin is a hormone made by the beta cells in the pancreas. Insulin allows sugar to go from the bloodstream into the body s cells and be used for energy. Insulin lowers blood sugar.
insulin and injections Insulin is a hormone made by the beta cells in the pancreas. Insulin allows sugar to go from the bloodstream into the body s cells and be used for energy. Insulin lowers blood sugar.
STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE TO SELF-INFUSION. Subcutaneous Administration of GAMMAGARD LIQUID
 STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE TO SELF-INFUSION Subcutaneous Administration of GAMMAGARD LIQUID This handy guide will help you manage your subcutaneous administration of GAMMAGARD LIQUID. If you have questions on
STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE TO SELF-INFUSION Subcutaneous Administration of GAMMAGARD LIQUID This handy guide will help you manage your subcutaneous administration of GAMMAGARD LIQUID. If you have questions on
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE
 SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE TITLE: ISSUED FOR: Nursing DATE: REVIEWED: PAGES: RESPONSIBILITY: RN, LPN 07/81 9/10 1 of 5 PURPOSE: 1. To maintain aseptic technique in preparing and administering
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE TITLE: ISSUED FOR: Nursing DATE: REVIEWED: PAGES: RESPONSIBILITY: RN, LPN 07/81 9/10 1 of 5 PURPOSE: 1. To maintain aseptic technique in preparing and administering
Instructions for Use Enbrel (en-brel) (etanercept) injection, for subcutaneous use Single-dose Prefilled Syringe
 Instructions for Use Enbrel (en-brel) (etanercept) injection, for subcutaneous use Single-dose Prefilled Syringe How do I prepare and give an injection with Enbrel Single-dose Prefilled Syringe? There
Instructions for Use Enbrel (en-brel) (etanercept) injection, for subcutaneous use Single-dose Prefilled Syringe How do I prepare and give an injection with Enbrel Single-dose Prefilled Syringe? There
Instructions for Use. Welcome!
 Instructions for Use Welcome! The AMJEVITA SureClick autoinjector is a single-use prefilled autoinjector. Consult your doctor if you have any questions about your dose. Your doctor has prescribed AMJEVITA
Instructions for Use Welcome! The AMJEVITA SureClick autoinjector is a single-use prefilled autoinjector. Consult your doctor if you have any questions about your dose. Your doctor has prescribed AMJEVITA
Insulin Basic facts. Patient Education Patient Care Services. What is insulin? What types of insulin are there? Basal Insulin
 Patient Education Insulin Basic facts Insulin is a protein made by the pancreas that allows your cells to use glucose for energy. There are different types of insulin: Basal long-acting insulin that controls
Patient Education Insulin Basic facts Insulin is a protein made by the pancreas that allows your cells to use glucose for energy. There are different types of insulin: Basal long-acting insulin that controls
DO NOT TRANSFER TO A SYRINGE SEVERE OVERDOSE CAN RESULT
 HP8824 Instructions for Use ENTUZITY KwikPen (insulin injection, human biosynthetic) 500 units/ml, 3 ml pen www.lilly.ca IMPORTANT Know your dose of ENTUZITY insulin. The Pen delivers your dose in insulin
HP8824 Instructions for Use ENTUZITY KwikPen (insulin injection, human biosynthetic) 500 units/ml, 3 ml pen www.lilly.ca IMPORTANT Know your dose of ENTUZITY insulin. The Pen delivers your dose in insulin
BD Nano 4mm Pen Needles
 BD Nano mm Pen Needles Preferred by patients₉ Less effort to inject medication for people with hand strength issues₉* BD's smallest, thinnest pen needle was rated as less painful and easier to insert₉
BD Nano mm Pen Needles Preferred by patients₉ Less effort to inject medication for people with hand strength issues₉* BD's smallest, thinnest pen needle was rated as less painful and easier to insert₉
Patient Education Pharmacy Services
 Patient Education This handout details the types of insulin. It also covers how to store, mix and inject insulin. What is insulin? Insulin is made by the pancreas and acts as a key to move glucose (sugar)
Patient Education This handout details the types of insulin. It also covers how to store, mix and inject insulin. What is insulin? Insulin is made by the pancreas and acts as a key to move glucose (sugar)
PEN USER MANUAL Byetta 5 micrograms solution for injection in pre-filled pen (exenatide)
 PEN USER MANUAL Byetta 5 micrograms solution for injection in pre-filled pen (exenatide) Section 1. WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT YOUR BYETTA PEN Read this section completely before you begin. Then, move
PEN USER MANUAL Byetta 5 micrograms solution for injection in pre-filled pen (exenatide) Section 1. WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT YOUR BYETTA PEN Read this section completely before you begin. Then, move
SymlinPen (SĬM-lĭnPen) 120 (pramlintide acetate) Pen-Injector
 SYMLIN (pramlintide acetate) injection for subcutaneous use 4 SymlinPen (SĬM-lĭnPen) 120 (pramlintide acetate) Pen-Injector Read the Medication Guide and these Instructions for Use before you start using
SYMLIN (pramlintide acetate) injection for subcutaneous use 4 SymlinPen (SĬM-lĭnPen) 120 (pramlintide acetate) Pen-Injector Read the Medication Guide and these Instructions for Use before you start using
PLEASE READ THESE INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE USE
 Instructions for use KwikPen ABASAGLAR 100 units/ml solution for injection in a pre-filled pen Insulin glargine PLEASE READ THESE INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE USE Read the instructions for use before you start
Instructions for use KwikPen ABASAGLAR 100 units/ml solution for injection in a pre-filled pen Insulin glargine PLEASE READ THESE INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE USE Read the instructions for use before you start
Lilly. Disposable Insulin Delivery Device User Manual
 1 PV 3734 AMP Lilly Disposable Insulin Delivery Device User Manual Instructions for Use Read and follow all of these instructions carefully. If you do not follow these instructions completely, you may
1 PV 3734 AMP Lilly Disposable Insulin Delivery Device User Manual Instructions for Use Read and follow all of these instructions carefully. If you do not follow these instructions completely, you may
How to Use ENBREL : Vial Adapter Method
 How to Use ENBREL : Vial Adapter Method SETTING UP FOR AN INJECTION Select a clean, well-lit, flat working surface, such as a table. Take the ENBREL dose tray out of the refrigerator and place it on your
How to Use ENBREL : Vial Adapter Method SETTING UP FOR AN INJECTION Select a clean, well-lit, flat working surface, such as a table. Take the ENBREL dose tray out of the refrigerator and place it on your
Cap Clip Rubber Seal Plunger Pen Body Dose Window
 Instructions for Use Humalog 100 units/ml Junior KwikPen, solution for injection in a pre-filled pen insulin lispro PLEASE READ THESE INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE USE Read the Instructions for Use before you start
Instructions for Use Humalog 100 units/ml Junior KwikPen, solution for injection in a pre-filled pen insulin lispro PLEASE READ THESE INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE USE Read the Instructions for Use before you start
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE TYMLOS (tim lows ) (abaloparatide) injection, for subcutaneous use
 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE TYMLOS (tim lows ) (abaloparatide) injection, for subcutaneous use Instructions for Use Read and follow this Instructions for Use so that you inject TYMLOS pen the right way. Call
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE TYMLOS (tim lows ) (abaloparatide) injection, for subcutaneous use Instructions for Use Read and follow this Instructions for Use so that you inject TYMLOS pen the right way. Call
NovoPen Echo User guide
 NovoPen Echo User guide Read this user guide carefully before you use your NovoPen Echo for insulin delivery the first time Find a quick guide at the back of this manual NovoPen Echo Pen Insulin window
NovoPen Echo User guide Read this user guide carefully before you use your NovoPen Echo for insulin delivery the first time Find a quick guide at the back of this manual NovoPen Echo Pen Insulin window
Giving Medicine by Subcutaneous Injection
 Giving Medicine by Subcutaneous Injection A subcutaneous injection, also called a sub Q or SQ shot, is one that is given into the layers of skin and fat on top of the muscle. Follow these steps for giving
Giving Medicine by Subcutaneous Injection A subcutaneous injection, also called a sub Q or SQ shot, is one that is given into the layers of skin and fat on top of the muscle. Follow these steps for giving
Important Safety Information for Adlyxin (lixisenatide) injection
 A GLP-1 receptor agonist (RA) Adlyxin (lixisenatide) injection 20 mcg Information To Help Answer Patients Questions This booklet contains information about Adlyxin to help you answer patients questions
A GLP-1 receptor agonist (RA) Adlyxin (lixisenatide) injection 20 mcg Information To Help Answer Patients Questions This booklet contains information about Adlyxin to help you answer patients questions
SELF-INJECTION GUIDE
 SELF-INJECTION GUIDE (asfotase alfa) 40 mg/ml solution for injection 18 mg/0.45 ml 28 mg/0.7 ml 40 mg/1 ml 100 mg/ml solution for injection 80 mg/0.8 ml asfotase alfa Introduction Contents This Self-Injection
SELF-INJECTION GUIDE (asfotase alfa) 40 mg/ml solution for injection 18 mg/0.45 ml 28 mg/0.7 ml 40 mg/1 ml 100 mg/ml solution for injection 80 mg/0.8 ml asfotase alfa Introduction Contents This Self-Injection
Patient Information. Preventing and treating blood clots
 Patient Information Preventing and treating blood clots 1_Clexane_Patient_Booklet_AW05.indd 1 8/04/2016 11:26 a The information provided in this document is for patients prescribed CLEXANE, and should
Patient Information Preventing and treating blood clots 1_Clexane_Patient_Booklet_AW05.indd 1 8/04/2016 11:26 a The information provided in this document is for patients prescribed CLEXANE, and should
Instructions for Use Enbrel (en-brel) (etanercept) Single-use Prefilled SureClick Autoinjector
 Instructions for Use Enbrel (en-brel) (etanercept) Single-use Prefilled SureClick Autoinjector How do I prepare and give an injection with Enbrel Single-use Prefilled SureClick Autoinjector? This section
Instructions for Use Enbrel (en-brel) (etanercept) Single-use Prefilled SureClick Autoinjector How do I prepare and give an injection with Enbrel Single-use Prefilled SureClick Autoinjector? This section
Instructions for Use. BASAGLAR KwikPen. insulin glargine injection (100 units/ml, 3 ml pen)
 Instructions for Use BASAGLAR KwikPen insulin glargine injection (100 units/ml, 3 ml pen) 1 Read the Instructions for Use before you start using BASAGLAR and each time you get another BASAGLAR KwikPen.
Instructions for Use BASAGLAR KwikPen insulin glargine injection (100 units/ml, 3 ml pen) 1 Read the Instructions for Use before you start using BASAGLAR and each time you get another BASAGLAR KwikPen.
Instructions For Use PRALUENT (PRAHL-u-ent) (alirocumab) Injection, for Subcutaneous Injection Single-Dose Pre-Filled Syringe (75 mg/ml)
 Instructions For Use PRALUENT (PRAHL-u-ent) (alirocumab) Injection, for Subcutaneous Injection Single-Dose Pre-Filled Syringe (75 mg/ml) Important Information The device is a single-dose pre-filled syringe.
Instructions For Use PRALUENT (PRAHL-u-ent) (alirocumab) Injection, for Subcutaneous Injection Single-Dose Pre-Filled Syringe (75 mg/ml) Important Information The device is a single-dose pre-filled syringe.
IMPORTANT: PLEASE READ. Don t
 PATIENT/CAREGIVER INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE - ORENCIA (ABATACEPT) PREFILLED SYRINGE WITH BD ULTRASAFE PASSIVE TM NEEDLE GUARD WITH FLANGE EXTENDERS Getting started with ORENCIA therapy Did you receive self-injection
PATIENT/CAREGIVER INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE - ORENCIA (ABATACEPT) PREFILLED SYRINGE WITH BD ULTRASAFE PASSIVE TM NEEDLE GUARD WITH FLANGE EXTENDERS Getting started with ORENCIA therapy Did you receive self-injection
MICAFUNGIN MIXING
 1 1-800-862-2731 MICAFUNGIN MIXING Drug Name: MICAFUNGIN Volume and Rate: over 1 hour Schedule: KEY POINTS: FLUSHING: Saline Micafungin Saline Heparin 1. Always wash your hands with an antibacterial soap
1 1-800-862-2731 MICAFUNGIN MIXING Drug Name: MICAFUNGIN Volume and Rate: over 1 hour Schedule: KEY POINTS: FLUSHING: Saline Micafungin Saline Heparin 1. Always wash your hands with an antibacterial soap
User Manual Important: First read the Medication Guide that comes inside your FORTEO carton.
 FORTEO (for-tay-o) teriparatide (rdna origin) injection 1 User Manual Important: First read the Medication Guide that comes inside your FORTEO carton. Before you use your new FORTEO delivery device, please
FORTEO (for-tay-o) teriparatide (rdna origin) injection 1 User Manual Important: First read the Medication Guide that comes inside your FORTEO carton. Before you use your new FORTEO delivery device, please
SCIG INFUSIONS A PRACTICAL GUIDE FOR PATIENTS
 PRIMARY IMMUNODEFICIENCIES SCIG INFUSIONS: A PRACTICAL GUIDE FOR PATIENTS SCIG INFUSIONS A PRACTICAL GUIDE FOR PATIENTS 1 PRIMARY IMMUNODEFICIENCIES ABBREVIATIONS IG IVIG PID SCIG Immunoglobulin Intravenous
PRIMARY IMMUNODEFICIENCIES SCIG INFUSIONS: A PRACTICAL GUIDE FOR PATIENTS SCIG INFUSIONS A PRACTICAL GUIDE FOR PATIENTS 1 PRIMARY IMMUNODEFICIENCIES ABBREVIATIONS IG IVIG PID SCIG Immunoglobulin Intravenous
Instructions for Use. HUMALOG KwikPen. insulin lispro injection (rdna origin) 100 units/ml, 3 ml pen
 1 Instructions for Use HUMALOG KwikPen insulin lispro injection (rdna origin) 100 units/ml, 3 ml pen Read the Instructions for Use before you start taking HUMALOG and each time you get another KwikPen.
1 Instructions for Use HUMALOG KwikPen insulin lispro injection (rdna origin) 100 units/ml, 3 ml pen Read the Instructions for Use before you start taking HUMALOG and each time you get another KwikPen.
Normal Immunoglobulin (Human) 16%, solution for subcutaneous administration.
 Normal Immunoglobulin (Human) 16%, solution for subcutaneous administration. Consumer Medicine Information What is in this leaflet This leaflet answers some common questions about. It does not contain
Normal Immunoglobulin (Human) 16%, solution for subcutaneous administration. Consumer Medicine Information What is in this leaflet This leaflet answers some common questions about. It does not contain
HUMULIN 70/30 KwikPen
 1 Instructions for Use HUMULIN 70/30 KwikPen (70% human insulin isophane suspension 30% human insulin injection [rdna origin]) 100 units/ml, 3 ml pen Read the Instructions for Use before you start taking
1 Instructions for Use HUMULIN 70/30 KwikPen (70% human insulin isophane suspension 30% human insulin injection [rdna origin]) 100 units/ml, 3 ml pen Read the Instructions for Use before you start taking
Many people use a combination of the standard 17mm cannula and the shorter 13mm cannula length depending where on their body they are inserting.
 There are many types of infusion sets available through AMSL Diabetes. Our infusion sets are obtained through Animas and are all manufactured by UnoMedical which has a worldwide reputation for producing
There are many types of infusion sets available through AMSL Diabetes. Our infusion sets are obtained through Animas and are all manufactured by UnoMedical which has a worldwide reputation for producing
Do not re use needles. If you do you might not get your dose (underdosing) or get too much (overdosing) as the needle could block.
 What are the ingredients in TOUJEO? Active ingredient: insulin glargine Inactive ingredients: zinc, m cresol, glycerol and water for injection Hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide may be added to adjust
What are the ingredients in TOUJEO? Active ingredient: insulin glargine Inactive ingredients: zinc, m cresol, glycerol and water for injection Hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide may be added to adjust
Logic. Owner s Guide. Blood Glucose Monitor
 Owner s Guide Logic Blood Glucose Monitor TM You will notice these symbols on your vials of test strips and control solution as well as the label on the back of your BD Logic TM Blood Glucose Monitor.
Owner s Guide Logic Blood Glucose Monitor TM You will notice these symbols on your vials of test strips and control solution as well as the label on the back of your BD Logic TM Blood Glucose Monitor.
The Enbrel SureClick autoinjector is a single-dose prefilled autoinjector. It contains one 50 mg dose of Enbrel.
 Instructions for Use Welcome! The Enbrel SureClick autoinjector is a single-dose prefilled autoinjector. It contains one 50 mg dose of Enbrel. Your healthcare provider has prescribed Enbrel SureClick autoinjector
Instructions for Use Welcome! The Enbrel SureClick autoinjector is a single-dose prefilled autoinjector. It contains one 50 mg dose of Enbrel. Your healthcare provider has prescribed Enbrel SureClick autoinjector
TRANSCRIPT for Lantus SoloSTAR pen injection for your patients
 TRANSCRIPT for Lantus SoloSTAR pen injection for your patients SUPER: Prescription Lantus is a long-acting insulin used to treat adults with type 2 diabetes and adults and pediatric patients (children
TRANSCRIPT for Lantus SoloSTAR pen injection for your patients SUPER: Prescription Lantus is a long-acting insulin used to treat adults with type 2 diabetes and adults and pediatric patients (children
HOW TO USE... 5mg. Pocket Guide
 HOW TO USE... Pocket Guide 4 ZOMACTON [somatropin (rdna origin)] for Injection Supplies ZOMACTON 5 mg (powder) Preparation syringe Syringe and injection needle Diluent (liquid) Diluent (liquid) contains
HOW TO USE... Pocket Guide 4 ZOMACTON [somatropin (rdna origin)] for Injection Supplies ZOMACTON 5 mg (powder) Preparation syringe Syringe and injection needle Diluent (liquid) Diluent (liquid) contains
Injection Technique (I.T.), Glycemic Variability, and Lipohypertrophy. Why I.T. All Matters
 Injection Technique (I.T.), Glycemic Variability, and Lipohypertrophy Why I.T. All Matters Larry Hirsch, MD Vice-President, Global Medical Affairs BD Diabetes Care Seoul, South Korea KDA-ICDM 29 September
Injection Technique (I.T.), Glycemic Variability, and Lipohypertrophy Why I.T. All Matters Larry Hirsch, MD Vice-President, Global Medical Affairs BD Diabetes Care Seoul, South Korea KDA-ICDM 29 September
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE. EMGALITY TM (em-gal-it-ē) (galcanezumab-gnlm)
 1 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE EMGALITY TM (em-gal-it-ē) (galcanezumab-gnlm) injection, for subcutaneous use Prefilled Pen For subcutaneous injection only. Before you use the EMGALITY prefilled pen (Pen), read
1 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE EMGALITY TM (em-gal-it-ē) (galcanezumab-gnlm) injection, for subcutaneous use Prefilled Pen For subcutaneous injection only. Before you use the EMGALITY prefilled pen (Pen), read
I n s t r u c t i o n M a n u a l
 I n s t r u c t i o n M a n u a l TABLE OF CONTENTS 2.5THE STARTER KIT...4 3.USING THE INJEX SYSTEM...5 3.1 PREPARING THE INJECTOR...5 1. INTRODUCTION TO THE INJEX TM SYSTEM...1 1.1PRODUCT DESCRIPTION...1
I n s t r u c t i o n M a n u a l TABLE OF CONTENTS 2.5THE STARTER KIT...4 3.USING THE INJEX SYSTEM...5 3.1 PREPARING THE INJECTOR...5 1. INTRODUCTION TO THE INJEX TM SYSTEM...1 1.1PRODUCT DESCRIPTION...1
EVER Pharma D-mine Pen Pen injector for Apomorphine 10 mg/ml
 EVER Pharma D-mine Pen Pen injector for Apomorphine 10 mg/ml Instructions for Use with Dacepton 3 ml Cartridges Apomorphine hydrochloride hemihydrate solution for injection Subcutaneous Use TABLE OF CONTENTS
EVER Pharma D-mine Pen Pen injector for Apomorphine 10 mg/ml Instructions for Use with Dacepton 3 ml Cartridges Apomorphine hydrochloride hemihydrate solution for injection Subcutaneous Use TABLE OF CONTENTS
MYALEPT (MAI-uh-lept) (metreleptin) for injection for subcutaneous use
 .3 mg per vial _ A healthcare provider should show you how to inject MYALEPT before you use it for the first time. A healthcare provider should also watch you inject your MYALEPT dose the first time you
.3 mg per vial _ A healthcare provider should show you how to inject MYALEPT before you use it for the first time. A healthcare provider should also watch you inject your MYALEPT dose the first time you
EVOGAM. Information for patients Evogam 2014 NZ Patient Brochure Update v11
 EVOGAM Information for patients 11881 Evogam 2014 NZ Patient Brochure Update v11 Information for patients and caregivers about EVOGAM This booklet is designed to help you follow the training you will have
EVOGAM Information for patients 11881 Evogam 2014 NZ Patient Brochure Update v11 Information for patients and caregivers about EVOGAM This booklet is designed to help you follow the training you will have
Living Well Successfully managing diabetes
 Living Well Successfully managing diabetes with 4mm Pen Needles Helping all people live healthy lives Our most comfortable injection experience ever Successfully managing diabetes with BD Micro-Fine +
Living Well Successfully managing diabetes with 4mm Pen Needles Helping all people live healthy lives Our most comfortable injection experience ever Successfully managing diabetes with BD Micro-Fine +
Vial. A healthcare provider should show you how to inject MYALEPT before you use it for
 MYALEPT (metreleptin) for injection Instructions for Use MYALEPT (MAI-uh-lept) (metreleptin) for injection Vial A healthcare provider should show you how to inject MYALEPT before you use it for 8 Do not
MYALEPT (metreleptin) for injection Instructions for Use MYALEPT (MAI-uh-lept) (metreleptin) for injection Vial A healthcare provider should show you how to inject MYALEPT before you use it for 8 Do not
Vancouver Neuropituitary Program
 Step 4: Give the Injection 1. Clean the injection site skin with an alcohol swab; let it air dry. 2. Hold the skin around the injection site in the manner described above. 3. Insert the IM needle into
Step 4: Give the Injection 1. Clean the injection site skin with an alcohol swab; let it air dry. 2. Hold the skin around the injection site in the manner described above. 3. Insert the IM needle into
GET TO KNOW YOUR PEN. Needle cap. Rubber seal. Insulin scale. Pen cap. Cartridge holder Plunger. Insulin name. Dose window Dose. pointer.
 GET TO KNOW YOUR PEN You ve taken an important step by adding Toujeo (insulin glargine injection) U-3 to your diabetes treatment plan. Toujeo is a long-acting insulin used to treat adults with type and
GET TO KNOW YOUR PEN You ve taken an important step by adding Toujeo (insulin glargine injection) U-3 to your diabetes treatment plan. Toujeo is a long-acting insulin used to treat adults with type and
PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET MEDICINE TO TREAT: DIABETES. Insulin
 PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET MEDICINE TO TREAT: DIABETES Insulin This medicine has been proven to be safe and effective, but it can cause serious injury if a mistake happens while taking it. This means
PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET MEDICINE TO TREAT: DIABETES Insulin This medicine has been proven to be safe and effective, but it can cause serious injury if a mistake happens while taking it. This means
To provide nursing staff with guidelines for the safe and appropriate administration of insulin.
 SUBJECT: ADMINISTRATION OF INSULIN This cancels NP 513 dated 3/1/07 1. PURPOSE: COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL NURSING POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SECTION - Medications POLICY NUMBER: 513 Effective Date: June
SUBJECT: ADMINISTRATION OF INSULIN This cancels NP 513 dated 3/1/07 1. PURPOSE: COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL NURSING POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SECTION - Medications POLICY NUMBER: 513 Effective Date: June
READ THIS FOR SAFE AND EFFECTIVE USE OF YOUR MEDICINE PATIENT MEDICATION INFORMATION. AIM-oh-vig Pr AIMOVIG (erenumab injection)
 READ THIS FOR SAFE AND EFFECTIVE USE OF YOUR MEDICINE PATIENT MEDICATION INFORMATION AIM-oh-vig Pr AIMOVIG (erenumab injection) Single-Use Pre-filled SureClick Autoinjector Read this carefully before you
READ THIS FOR SAFE AND EFFECTIVE USE OF YOUR MEDICINE PATIENT MEDICATION INFORMATION AIM-oh-vig Pr AIMOVIG (erenumab injection) Single-Use Pre-filled SureClick Autoinjector Read this carefully before you
The Enbrel SureClick autoinjector is a single-dose prefilled autoinjector. It contains one 50 mg dose of Enbrel.
 Instructions for Use Welcome! The Enbrel SureClick autoinjector is a single-dose prefilled autoinjector. It contains one 50 mg dose of Enbrel. Your healthcare provider has prescribed Enbrel SureClick autoinjector
Instructions for Use Welcome! The Enbrel SureClick autoinjector is a single-dose prefilled autoinjector. It contains one 50 mg dose of Enbrel. Your healthcare provider has prescribed Enbrel SureClick autoinjector
For use only with INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
 TM For use only with INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE IMPORTANT NOTICE: Please read this safety information first. 1. Follistim Pen is a precision device. It is very important that you read and follow all directions
TM For use only with INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE IMPORTANT NOTICE: Please read this safety information first. 1. Follistim Pen is a precision device. It is very important that you read and follow all directions
PART III: CONSUMER INFORMATION
 PART III: CONSUMER INFORMATION Pr Norditropin NordiFlex Somatropin for injection This leaflet is Part III of a three-part "Product Monograph" published when Norditropin was approved for sale in Canada
PART III: CONSUMER INFORMATION Pr Norditropin NordiFlex Somatropin for injection This leaflet is Part III of a three-part "Product Monograph" published when Norditropin was approved for sale in Canada
Stretching. Knees: Rotate your knees in a circle, keeping them together and bending down slightly.
 Stretching Stretching the Major Muscle Groups Static Stretches Hamstrings: Hang down and try to reach your toes; don t push it. Keep legs and back straight. Just go down to a comfortable level for your
Stretching Stretching the Major Muscle Groups Static Stretches Hamstrings: Hang down and try to reach your toes; don t push it. Keep legs and back straight. Just go down to a comfortable level for your
Home Care Services HomeMed MedEQUIP Michigan Visiting Care Michigan Visiting Nurses Wheelchair Seating Service PROCEDURE
 UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN HOSPITALS AND HEALTH CENTERS UMHHC-HCS: 253.054 First Approved Date: 3/2010 Home Care Services HomeMed MedEQUIP Michigan Visiting Care Michigan Visiting Nurses Wheelchair Seating
UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN HOSPITALS AND HEALTH CENTERS UMHHC-HCS: 253.054 First Approved Date: 3/2010 Home Care Services HomeMed MedEQUIP Michigan Visiting Care Michigan Visiting Nurses Wheelchair Seating
MODULE 2 THE LABORATORY RAT
 University Animal Care Committee LABORATORY ANIMAL BIOMETHODOLOGY WORKSHOP MODULE 2 THE LABORATORY RAT SUBSTANCE ADMINISTRATION AND BLOOD COLLECTION Substance Administration: Subcutaneous injection Intramuscular
University Animal Care Committee LABORATORY ANIMAL BIOMETHODOLOGY WORKSHOP MODULE 2 THE LABORATORY RAT SUBSTANCE ADMINISTRATION AND BLOOD COLLECTION Substance Administration: Subcutaneous injection Intramuscular
How to use your Pergoveris pre-filled pen
 How to use your Pergoveris pre-filled pen Information in this user guide is based on the European product information for Pergoveris. It is not country specific and may vary from country to country. Please
How to use your Pergoveris pre-filled pen Information in this user guide is based on the European product information for Pergoveris. It is not country specific and may vary from country to country. Please
I can show you how I give my. child insulin
 Our Journey with Diabetes Si usted desea esta información en español, por favor pídasela a su enfermero o doctor. I can show you how I give my What should I know about insulin syringes? Insulin must be
Our Journey with Diabetes Si usted desea esta información en español, por favor pídasela a su enfermero o doctor. I can show you how I give my What should I know about insulin syringes? Insulin must be
Package leaflet: Information for the user
 Package leaflet: Information for the user Aimovig 70 mg solution for injection in pre-filled pen erenumab This medicine is subject to additional monitoring. This will allow quick identification of new
Package leaflet: Information for the user Aimovig 70 mg solution for injection in pre-filled pen erenumab This medicine is subject to additional monitoring. This will allow quick identification of new
My Doctor Says I Need to Inject Insulin In Special Sites... Which Ones Should I Use? Getting Started. Site Selection
 My Doctor Says I Need to Inject Insulin In Special Sites... Which Ones Should I Use? Getting Started Site Selection You need to know where to inject insulin so that your injections will be easier, safer
My Doctor Says I Need to Inject Insulin In Special Sites... Which Ones Should I Use? Getting Started Site Selection You need to know where to inject insulin so that your injections will be easier, safer
Important Safety Instructions 1-2. Maintenance 3. Features 4. Assembly Parts List 5. Assembly Instructions 6-9. Console Operation 10
 Important Safety Instructions 1-2 Maintenance 3 Features 4 Assembly Parts List 5 Assembly Instructions 6-9 Console Operation 10 Moving Machine 12 Exercise Instructions 13-18 Exploded Drawing 19 Parts List
Important Safety Instructions 1-2 Maintenance 3 Features 4 Assembly Parts List 5 Assembly Instructions 6-9 Console Operation 10 Moving Machine 12 Exercise Instructions 13-18 Exploded Drawing 19 Parts List
Standard operating procedures for preparation and administration of intramuscular injections. No Action Rationale
 Standard operating procedures for preparation and administration of intramuscular injections Preparation Overview No Action Rationale 1 Collect and check all equipment 2 Check that the packaging of all
Standard operating procedures for preparation and administration of intramuscular injections Preparation Overview No Action Rationale 1 Collect and check all equipment 2 Check that the packaging of all
PIEDMONT ACCESS TO HEALTH SERVICES, INC.
 PIEDMONT ACCESS TO HEALTH SERVICES, INC. Policy Number: 01-10-039 SUBJECT: I. M. Injections EFFECTIVE DATE: 3/2010 REVIEWED/REVISED: 7/21/2011, 07/27/2012, 10/7/2013, 10/27/2014, 05/16/2016 POLICY: I.
PIEDMONT ACCESS TO HEALTH SERVICES, INC. Policy Number: 01-10-039 SUBJECT: I. M. Injections EFFECTIVE DATE: 3/2010 REVIEWED/REVISED: 7/21/2011, 07/27/2012, 10/7/2013, 10/27/2014, 05/16/2016 POLICY: I.
What do you need to know before you go home?
 What do you need to know before you go home? What is Insulin Types of Insulin Injection Sites How to Inject Insulin Correctly Low Blood Sugar and Treatment Sick Day Management After leaving the Hospital:
What do you need to know before you go home? What is Insulin Types of Insulin Injection Sites How to Inject Insulin Correctly Low Blood Sugar and Treatment Sick Day Management After leaving the Hospital:
Stratis INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE. Needle-free Injection System. 0.5mL volume (+/-5%)
 Stratis Needle-free Injection System INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE 0.5mL volume (+/-5%) Stratis English Symbols Glossary (Note: All symbols are derived from ISO 15223-1, Medical Devices - Symbols to be used with
Stratis Needle-free Injection System INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE 0.5mL volume (+/-5%) Stratis English Symbols Glossary (Note: All symbols are derived from ISO 15223-1, Medical Devices - Symbols to be used with
DBA Design Effectiveness Awards SoloSTAR. A disposable pen injector for insulin
 DBA Design Effectiveness Awards 2009 SoloSTAR A disposable pen injector for insulin Category: Sub category: Client company: Design consultancy: Product Consumer Sanofi Aventis GmbH DCA Design International
DBA Design Effectiveness Awards 2009 SoloSTAR A disposable pen injector for insulin Category: Sub category: Client company: Design consultancy: Product Consumer Sanofi Aventis GmbH DCA Design International
Inspection Window. Syringe Body
 Guide to Parts Before use Instructions for Use UDENYCA (yoo-den-i-kah) (pegfilgrastim-cbqv) Injection Single-Dose Prefilled Syringe Inspection Window Needle Cap Needle Label Plunger Plunger Head Needle
Guide to Parts Before use Instructions for Use UDENYCA (yoo-den-i-kah) (pegfilgrastim-cbqv) Injection Single-Dose Prefilled Syringe Inspection Window Needle Cap Needle Label Plunger Plunger Head Needle
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE HUMIRA 40 MG/0.8 ML, 20 MG/0.4 ML AND 10 MG/0.2 ML SINGLE-USE PREFILLED SYRINGE
 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE HUMIRA (Hu-MARE-ah) (adalimumab) 40 MG/0.8 ML, 20 MG/0.4 ML AND 10 MG/0.2 ML SINGLE-USE PREFILLED SYRINGE Do not try to inject HUMIRA yourself until you have been shown the right way
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE HUMIRA (Hu-MARE-ah) (adalimumab) 40 MG/0.8 ML, 20 MG/0.4 ML AND 10 MG/0.2 ML SINGLE-USE PREFILLED SYRINGE Do not try to inject HUMIRA yourself until you have been shown the right way
TYPe 1 DIABeTeS. A short guide for parents and children. from the outset.
 TYPe 1 DIABeTeS A short guide for parents and children A guide that will allow you to get to know type 1 diabetes and deal with it with peace of mind from the outset. Contents Glycaemic control 04 What
TYPe 1 DIABeTeS A short guide for parents and children A guide that will allow you to get to know type 1 diabetes and deal with it with peace of mind from the outset. Contents Glycaemic control 04 What
ARROW EZ-IO Intraosseous Vascular Access System Procedure Template
 ARROW EZ-IO Intraosseous Vascular Access System Procedure Template PURPOSE To provide procedural guidance for establishment of intraosseous vascular access using the ARROW EZ-IO Intraosseous Vascular Access
ARROW EZ-IO Intraosseous Vascular Access System Procedure Template PURPOSE To provide procedural guidance for establishment of intraosseous vascular access using the ARROW EZ-IO Intraosseous Vascular Access
A STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE FOR HEALTHCARE PROFESSIONALS TO USING THE ENBREL 50MG PRE-FILLED PEN MYCLIC
 1. ENBREL (etanercept) SmPC and Patient Information Leaflet. Available at: www.ema.europa.eu. A STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE FOR HEALTHCARE PROFESSIONALS TO USING THE ENBREL 50MG PRE-FILLED PEN MYCLIC Step 1: Preparing
1. ENBREL (etanercept) SmPC and Patient Information Leaflet. Available at: www.ema.europa.eu. A STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE FOR HEALTHCARE PROFESSIONALS TO USING THE ENBREL 50MG PRE-FILLED PEN MYCLIC Step 1: Preparing
H1N1 Vaccine Administration Manual for Paramedics
 H1N1 Vaccine Administration Manual for Paramedics TABLE OF CONTENTS I. Introduction II. Policy and Procedure for Administering Medications A. Intradermal B. Intramuscular C. Subcutaneous III. Pictorial
H1N1 Vaccine Administration Manual for Paramedics TABLE OF CONTENTS I. Introduction II. Policy and Procedure for Administering Medications A. Intradermal B. Intramuscular C. Subcutaneous III. Pictorial
Instructions for Use. For use with. 10 mg vial
 Instructions for Use For use with 10 mg vial Table of Contents Parts of the ZOMA-Jet 10... 1 Supplies you will need to mix a ZOMACTON 10 mg Vial... 2 Mix a ZOMACTON 10 mg vial... 3 Reset the ZOMA-Jet 10...
Instructions for Use For use with 10 mg vial Table of Contents Parts of the ZOMA-Jet 10... 1 Supplies you will need to mix a ZOMACTON 10 mg Vial... 2 Mix a ZOMACTON 10 mg vial... 3 Reset the ZOMA-Jet 10...
