The Advantages of Short Pen Needles. Insulin injection with pen needles
|
|
|
- Elvin Beasley
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Clinical Evidence Folder The Advantages of Short Pen Needles Insulin injection with pen needles
2 1. Introduction 3 2. Utilization of Shorter Pen Needles Injection Sites Injection Site and Angle Skin Fold ( Pinch Up ) Skin and Subcutaneous Thickness Aspects associated with Shorter Pen Needles Efficacy of Shorter Pen Needles Safety: Adverse Events and Leakage Safety: Adverse Events, Hypo- and Hyperglycemia Risk: BMI and Obesity Risk: Intramuscular Injections Risk: Lipohypertrophy Risk: Pediatrics Efficiency of Shorter Pen Needles Patients Experiences With Shorter Pen Needles Pain Definition and Outcomes Preferences Definition and Outcomes Compliance Definition and Outcomes Preventive Strategies Training Conclusion 30 Bibliography/Literature 31 2
3 1. Introduction Diabetes mellitus is a major health problem that has become a global epidemic, especially in modern Western and Asian countries. The prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus is increasing because of the growing number of overweight and obese individuals. Recent studies have shown that 30 % of all diabetic patients are treated with insulin. [Hauner et al. 2007] For patients and healthcare professionals, effective diabetes mangement is essential for successful therapy. The insulin injection technique has a significant effect on glycemic control, safety and tolerability. Several types of pen needles are currently available for insulin injection. Traditionally, most patients with diabetes mellitus used long pen needles with 8 to 12.7 mm length. Over the past few years, science has focused on shorter pen needles. Nowadays, shorter-length pen needles (4 mm and 5 mm) are considered standard for injection technique. This scientific folder covers the utilization of shorter pen needles in terms of injection sites, injection angles, skin preparation and associated topics such as efficacy, safety, patient satisfaction and preferences. Furthermore, it advises healthcare professionals on the best practice for their patients. All the mentioned factors play a major role in the efficiency of insulin doses and make clinical training especially valuable. All information in this folder is obtained from recently published studies in order to give a comprehensive overview of the performance and safety of short length pen needles. 3
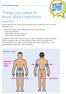
4 2. Utilization of Shorter Pen Needles 2.1. Injection Sites 29 % 88 % 59 % Preferred injection sites (for children, adolescents and adults, multiple answers were possible) [De Coninck et al. 2010] Definition The term injection site is used to describe the preferred body sites for needle placement and injection. Outcomes Most patients used the following four injections sites [Hirsch et al. 2014]: abdomen, thighs, upper arms, buttocks. 16 % In general, the abdomen and the thighs are the preferred body areas to inject insulin. [Kreugel et al. 2010] A multinational survey of children, adolescents and adults allowed multiple answers and found the following: the abdomen (with 88 %) was the most frequently used injection site for insulin administration, followed by the thighs with 59 %, the arms with 29 %, and the buttocks with 16 %. [De Coninck et al. 2010] Surveys on pediatric populations confirmed these results. In a pediatric population of 40 children and adolescents, the preferred injection sites were the abdomen with 55 % and the thighs with 25 %. The buttocks were less frequently used with only 12.5 %. The arm was only preferred by 7.5 % of all children and adolescents because of the potential risk of intramuscular injections in the arm due to the short distance between the skin and the muscle and the technically difficult procedure of forming a lifted skin fold. [Marran et al. 2014] 4
5 7.5 % 55 % 25 % 12.5 % An accurate injection technique for subcutaneous insulin administration is important for improved glucose control. The correct procedure includes the preferred injection sites, the injection angle, skin folds (pinch up) and skin conditions. Preferred injection sites (pediatric populations) [Marran et al. 2014] A second trial on pediatric patients showed that the abdomen is the overall preferred injection site. Interestingly, differentiating between preschool children (aged between 2 and 6 years old) and older children and adolescents showed that the arm was used as frequently as the abdomen in preschool children. [Lo Presti et al. 2012] To reduce discomfort and adverse effects, the rotation of injection sites is recommended. [Kreugel et al. 2010] Several patients chose their injection site based on pain (12 %). 21 % of patients stated to have injected into the same site for an entire day or even a few days. One third of patients stated not to have a specific injection routine. A clinically important aspect for injection procedure is the injection zone. In case of abdominal injections, 82 % of patients prefer large injection zones such as a postcard or a playing-card format. This can be clinically supported because the risk of lipohypertrophy seems to be more frequent in patients using smaller injection zones. 91 % of patients rotate within the same site and 93 % rotate from the left to the right side of their body. [De Coninck et al. 2010] Procedure notes The site of injection should be inspected by the patient prior to injection. Injections should be administrated in a clean site using clean hands. The site should be disinfected when found to be unclean or there is a risk of infection (e.g. in hospitals and nursing rooms). Disinfection of the site is not necessary outside the institutional setting. [Frid et al. 2010] For children or adolescents, arms should only be used for injections if a skin fold can be pinched. This usually requires injection by a third person. [Frid et al. 2010] If slim adults prefer injection into the limbs or abdomens, even 4 and 5 mm pen needles may require the use of a skin fold to prevent intramuscular injections. [Frid et al. 2010] The best way to preserve normal tissue is to properly and consistently rotate injection sites: dividing injection site into quadrants, using one quadrant per week and moving clockwise. Injections within the quadrant should be spaced at least 1 cm apart to avoid the repetition of a tissue trauma. [Frid et al. 2010] 5
6 2.2. Injection Site and Angle Definition The injection angle is the angle at which the needle is inserted into the human body. Different injection sites require different angles. Also, the length of the needle influences the injection angle. Outcomes Although the literature disagrees on this topic, several recommendations can be given: Buttocks A clear recommendation for different needle lengths cannot be given for the injection site at the buttocks because there is not enough clinical data for a final evaluation. In comparison to the abdomen, arms, and thighs, the buttocks are much less frequently used. [Grassi et al. 2014, Marran et al. 2014] ThighS The recommended angle for adult patients using pen needles of 4 or 5 mm is 90 degrees to the skin surface without lifting a skin fold. [Lo Presti et al. 2012, Kreugel et al. 2011, Gibney et al. 2010, Birkebaek et al. 2008] For longer pen needle lengths (6 to 12 mm), the recommended angle is 90 degrees with a lifted skin fold. [De Coninck et al. 2010, Gibney et al. 2010] For children, thigh insertions should be done at 90 degrees with a skin fold. [Lo Presti et al. 2012, De Coninck et al. 2010] De Coninck et al. recommend a lifted skin fold regardless of needle length for slim or normal weight children and adults. [De Coninck et al. 2010] If just 8 mm pen needles are available for children, they should be used with a skin fold and injected at 45 degrees. [Frid et al. 2010] Abdomen The recommended angle for adult patients using pen needles with a length of 4 or 5 mm is 90 degrees to the skin surface without lifting a skin fold. [Grassi et al. 2014, Hirsch et al. 2014, Lo Presti et al. 2012, Kreugel et al. 2011, Gibney et al. 2010, Frid et al. 2010, Hirsch et al. 2010, Birkebaek et al. 2008] The same applies to 6 mm pen needles which should be injected at an angle of 90 degrees without a pinched skin fold in adults. [Frid et al. 2010] 8 mm, 10 mm and 12 mm pen needles can be used at 90 degrees to the skin surface with a pinched skin fold. [Kreugel et al. 2011, Gibney et al. 2010, Hirsch et al. 2010] For children, 4 mm, 5 mm, 6 mm, 10 mm and 12 mm pen needles can be used at 90 degrees with a skin fold. [Lo Presti et al. 2012, Hirsch et al. 2014, Frid et al. 2010] 6
7 The choice of the injection angle 45 or 90 degrees is influenced by the injection site and the needle length. It is not recommended to insert 4 mm pen needles at a 45-degree angle [Hirsch et al. 2014] For children and adolescents 6 mm pen needles may be used at an angle of 45 degrees instead of a skin fold. [Frid et al. 2010] If just 8 mm pen needles are available for children, the needles should be used with a skin fold and injected at a 45-degree angle. [Frid et al. 2010] Arm For adults the recommended angle for pen needles of 4 to 12 mm lengths is 90 degrees with a pinched skin fold. [De Coninck et al. 2010] Alternatively, 4 mm pen needles can be applied at 90 degrees without a skin fold according to the anatomical conditions. [Gibney et al. 2010] In children the recommended angle for all pen needle lengths is 90 degrees with a pinched skin fold. [Lo Presti et al. 2012, De Coninck et al. 2010] If just 8 mm pen needles are available for children, the needles should be used with a skin fold and injected at 45 degrees. [Frid et al. 2010] Recommendations for 4 mm pen needles are not consistent: One recommendation states that in many children and adolescents an insertion at 90 degrees without a lifted skin fold is possible. [Frid et al. 2010] Procedure notes 4 mm pen needles cannot be inserted at 45 degree because of the physical characteristics of the needle length and hub. [Hirsch et al. 2014] Avoid denting the skin while injecting children and adolescents; there is a possibility that the needle may penetrate deeper skin structures such as muscle tissue. [Frid et al. 2010] Currently valid injection guidelines for adults recommend the use of needles with shorter lengths; there is no medical reason for recommending pen needles > 8 mm. [Frid et al. 2010] If adults prefer needles 8 mm, they should lift a skin fold or inject at a 45-degree angle. [Sim et al. 2014, Frid et al. 2010] Patients should rotate injection sites within specific body areas. [Kreugel et al. 2011] Abdomen and thighs are the most recommended injection sites. [Kreugel et al. 2011] 7
8 2.3. Skin Fold ( Pinch Up ) Definition For subcutaneous injection, a skin fold ( pinch up ) can be created between the thumb and the index finger (possibly with the addition of the middle finger). Outcomes Skin folds are used when the presumed distance between skin surface and muscle is less than the length of the needle. Lifting skin folds in the abdomen and thighs is relatively easy. A skin fold is more difficult to do in the buttocks (where it is rarely needed) and virtually impossible to perform properly on the arm. A proper skin fold is made with the thumb and index finger. Lifting skin with the whole hand poses the risk of lifting muscle tissue and of causing an intramuscular injection. [Frid et al. 2010] A detailed description of injections with or without skin folds for the different injection sites is given in table 1. In a pediatric population of 40 children and adolescents, who predominantely use 8 mm needles, only 5 % do not use skin folds. [Marran et al. 2014] A multinational survey of type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus patients describes their experience with skin folds. Patients who make a skin fold were asked when they release the skin fold. Most (54 %) said they release it before the injection is finished or right after the injection, instead of holding it for at least five more seconds after the injection has been given. Approximately 20 % of patients use their entire hand to lift a skin fold. [De Coninck et al. 2010] In a trial on pediatric patients (n = 101) with type 1 diabetes, the children were divided into three groups according to age: 2 to 6, 7 to 13, and 14 to 17 year olds. Most of the children in the youngest group were using 4 mm pen needles, most in the oldest group were using 6 mm needles. In the middle group, 4, 5 and 6 mm needles were used equally. All raised a skin fold. The authors recommend the use of a skin fold for 2 to 6 year old children. Furthermore, the most preferable pen needle for all children appears to be the 4 mm pen needle. [Lo Presti et al. 2012] 8
9 Children/very thin persons Adults Size 4 mm, 5 mm 6 mm 8 mm 10 to 12 mm 4 to 6 mm 8 to 12 mm ABDOMEN with PU 90 or without PU 45 THIGHS BUTTOCKS with PU 90 with PU 90 with PU 45 not recommended without PU 90 with PU 90 ARM with PU 90 with PU 90 with PU 45 not recommended with PU 90 Table 1 The upper arm is not recommended, since you would need a second person for the pinch up. *PU = pinch up In a multinational survey of 4,352 patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus 3.6 % of patients use 12.7 mm needles 1.8 % use 12 mm needles 1.6 % use 10 mm needles 48.6 % use 8 mm needles 15.8 % use 6 mm needles 21.6 % use 5 mm needles 7.0 % of patients do not know what length of needle they use. More than one quarter of thigh injections (27.1 %) were administered without a lifted skin fold and 76 % were administered at an angle of 90 degrees. Only 49 % of subjects who inject into the arm pinch a skin fold. Of those, 66 % inject directly at a 90-degree angle. 55 % of subjects who inject into their buttocks use a pinched-up skin fold; 26 % of all injections into the buttocks are given at an angle of 45 degrees. [De Coninck et al. 2010] Procedure notes For 4 mm pen needles skin folds are not required. [Bergenstal et al. 2015, Grassi et al. 2014, Frid et al. 2010, Hirsch et al. 2010] Very thin or very young children may need a skin fold when using a 4 mm pen needle. [Bergenstal et al. 2015] For 5 and 6 mm pen needles skin folds are generally not required for adults and obese patients. [Frid et al. 2010] When injecting into the limbs or slim abdomen, 6 mm pen needles should be used either with a skin fold or at a 45-degree angle. [Frid et al. 2010] Patients using pen needles 8 mm should pinch a skin fold or inject at 45 degrees to avoid intramuscular injections. [Bergenstal et al. 2015, Frid et al. 2010] 9
10 2.4. Skin and Subcutaneous Thickness The thickness of epidermis and dermis at different injection sites is relatively constant across ages, ethnic groups, BMI and gender. It is 1.9 to 2.4 mm on the average and rarely > 3 mm. The thickness of subcutaneous tissue in adults, however, varies depending on gender, body site and BMI. Epidermis Dermis Subcutaneous tissue Muscle Skin thickness = mm The thickness of skin is relatively constant [Grassi et al. 2014, Frid et al. 2010] Definition The skin consists of epidermis, dermis and subcutaneous tissue. The skin thickness is made up of the superficial skin (epidermis) and the dermis. The subcutaneous fat layer describes the thickness of the subcutaneous tissue only. Consequently, the distance from the epidermis to the muscle tissue includes the skin thickness and the subcutaneous fat thickness. [Sim et al. 2014] The subcutaneous tissue is the ideal site for the administration of insulin, because blood flow through this fatty layer is slow and predictable. Whereas the flow in the dermis is slow but variable, and blood flow in the muscle is faster and irregular depending on the muscle activity. Outcomes In general, the skin thickness of different populations in adults with diabetes mellitus has comparable dimensions. [Hirsch et al. 2014, Hofman et al. 2010] Gibney et al. explored the skin thickness of adult diabetes mellitus patients and found mean values of 2.2 mm at the arms, 1.99 mm at the thighs, 2.2 mm at the abdomen, and 2.4 mm on the buttocks. Comparable data could be observed by Sim et al. This working group found a skin thickness of 2 mm on the upper arm and 2.29 mm at the abdomen. However, skin thickness on thighs and buttocks was not evaluated. The skin thickness among children is slightly lower than in adults and increases with age. The subcutaneous tissue dimensions are comparable in pediatric patients until puberty, as well. After puberty, the subcutaneous fat tissue mass of girls increases while in boys the mass decreases slightly. [Frid et al. 2010] Marran et al. measured the skin thickness of children and adolescents and found mean values of 1.34 mm at the arm, 1.47 mm at the thighs, 1.65 mm at the abdomen, and 1.79 mm on the buttocks. Furthermore, obese patients' skin dimensions are similar to those of normal-weight and thin patients. [Frid et al. 2010] According to Hofman et al., the thigh skin thickness in adult males is greater than in females (approximately 10 %). 10
11 10.8 mm arm 13.9 mm abdomen 10.4 mm thighs 15.4 mm buttocks Subcutaneous thickness of adults at different injection sites (mean values) [Gibney et al. 2010] The thickness of epidermis and dermis at different injection sites is relatively constant across ages, ethnic groups, BMI and gender. It is 1.9 to 2.4 mm on average and rarely > 3 mm at injection sites for insulin. The thickness of subcutaneous tissue in adults, however, varies depending on gender, body site and BMI. [Grassi et al. 2014, Frid et al. 2010] For example, a clinical study on 341 adult diabetes mellitus patients explored the distance from the epidermis to the muscle tissue. The median distance from skin surface to muscle tissue is 10.9 mm at the thighs 12 mm at the arms 14.7 mm at the abdomen and 16.9 mm on the buttocks. The absolute minimum distance is at the thigh with 2.8 mm. The absolute minimum distance at the arm, the abdomen and the buttocks was < 5 mm. [Hirsch et al. 2014] In another study, the subcutaneous thickness of adults at different body sites for injections showed mean values of 10.8 mm at the arms 10.4 mm at the thighs 13.9 mm at the abdomen and 15.4 mm on the buttocks. [Gibney et al. 2010] Procedure notes In general, the subcutaneous thickness increased across injection sites in adults and pediatric patients in the following order: arms, thighs, abdomen and buttocks [Marran et al. 2014] Several factors affect the subcutaneous fat thickness BMI: thickness is higher in patients with a higher BMI [Sim et al. 2014] Gender: thickness is higher in females [Sim et al. 2014, Hofman et al. 2010] A categorizing scheme of the distances from the skin surface to the muscle tissue in < 4 mm and > 6 mm showed: The majority of distances were > 6 mm (abdomen 67.9 %, thigh 84.9 %) No patients had a skin surface to muscle fascia distance at the thigh < 4 mm No adults had a skin surface to muscle fascia distance at the abdomen < 4 mm [Birkebaek et al. 2008] In a clinical trial, the average subcutaneous thickness at the upper arm is 5.50 ± 2.68 mm and at the abdomen ± 6.54 mm. [Sim et al. 2014] 11
12 3. Aspects Associated With Shorter Pen Needles 3.1. Efficacy of Shorter P Which one is more efficacious Definition Similar to long needles, the efficacy of shorter pen needles depends on a proper injection technique and correct glycemic control. Outcome Generally, 4 mm pen needles can substantially reduce the risk of inadvertent intramuscular injection if the correct injection technique is used. [Hirsch et al. 2014] Studies have confirmed equal efficacy as well as safety of and tolerability to shorter pen needles for obese patients. [Frid et al. 2010] 12
13 en Needles 4 mm 12 mm? a A questionnaire put to 346 diabetes mellitus patients, who had switched to 4 mm pen needles, showed improved glucose control. Three months after having switched, patients reported mean reductions in HbA 1c of 0.58 %, in fasting blood glucose of 14 mg/dl (0.78 mmol/l) and in total daily insulin dose of 2.0 IU. Several randomized, controlled studies and surveys have evaluated glycemic control with pen needles of different lengths: No differences in glycemic control were observed between the 32 Gauge 4 mm and the 31 Gauge 8 mm or 29 Gauge 12.7 mm pen needles in obese patients with diabetes mellitus (randomized, controlled trial on 274 patients). Mean HbA 1c levels were slightly lower when 4 mm pen needles were used: % and % versus the 8 mm and 12.7 mm pen needles, within the equivalence margins. [Bergenstal et al. 2015] No significant differences in the average fructosamine level and HbA 1c level showed between the 33 Gauge 4 mm and the 32 Gauge 4 mm pen needles (randomized, controlled trial on 87 patients). [Valentini et al. 2015] Similar HbA 1c equivalence criteria were evaluated for 31 Gauge 4 mm versus 8 mm and 29 Gauge 4 mm versus 12.7 mm pen needles (randomized, controlled trial on 274 patients). [Strock et al. 2013] A subgroup analysis showed equivalent glycemic control for the above named needle sizes in obese and non-obese patients. [Hirsch et al. 2012] No changes were observed with respect to HbA 1c, serum fructosamine, 1.5-anhydroglucitol, and no hypoglycemic events could be observed between 5 mm and 8 mm pen needles (both 31 Gauge; randomized crossover trial on 130 patients). [Kreugel et al. 2011] Equivalent glycemic control was found with a 32 Gauge 4 mm and a 32 Gauge 6 mm pen needle (randomized crossover trial on 41 patients). [Miwa et al. 2012] A questionnaire put to 346 diabetes mellitus patients, who had switched to 4 mm pen needles, showed improved glucose control. Three months after having switched, patients reported mean reductions in HbA 1c of 0.58 %, in fasting blood glucose of 14 mg/dl (0.78 mmol/l) and in a total daily insulin dose of 2.0 IU. [Grassi et al. 2014] The 32 Gauge 4 mm pen needle provided equivalent glycemic control to the 31 Gauge 5 mm and 8 mm pen needles (randomized crossover trial on 173 patients). [Hirsch et al. 2010] 13
14 3.2. Safety: Adverse Events and Leakage 80 % Reported leakage without skin fold [Hirsch et al. 2010] Definition Insulin always should be injected in the subcutaneous tissue without adverse effects. An important adverse event is the leakage of medication which can affect therapy accuracy. Outcome The persistent use of 8 mm and 12.7 mm pen needles appears to be based on habit and clinical inertia without any evidence of superior reduction of leakage or backflow from the skin. [Hirsch et al. 2014] Currently, there is no consistent evidence of an increase in insulin leakage in patient populations using shorter needles of 4, 5, or 6 mm in length. Insulin leakage from the skin with 4 mm pen needles is equivalent to that of injecting with longer, wider-diameter needles. [Frid et al. 2010] The equivalence of shorter and longer pen needles is based on several clinical trials: There was no significant difference in reported leakage rates between the 32 Gauge 4 mm and the 31 Gauge 8 mm or 29 Gauge 12.7 mm pen needles, with differences ranging from 4.1 % to 4.3 % of injections. Leakage volumes were significantly larger with the 12.7 mm than with the 8 mm and 4 mm pen needles. Injections reported to have leaked had a significantly greater mean insulin dose than injections without reported leakage from the pen needles. [Bergenstal et al. 2015] No difference in insulin leakage was observed between the 33 Gauge 4 mm and the 32 Gauge 4 mm pen needles (risk excess: 17 %). The subgroup analysis confirmed this risk excess in patients administering higher insulin doses. [Valentini et al. 2015] Leakage from the skin was significantly reduced with extra-thin wall 32 Gauge 4 mm, 31 Gauge 5 mm and 31 Gauge 8 mm pen needles in comparison to conventional pen needles with 32 Gauge 4 to 8 mm, 31 Gauge 4.5 to 6 mm and 31 Gauge 8 mm pen needles. [Aronson et al. 2013] The explored pen needles (32 Gauge 4 mm, 31 Gauge 5 mm and 8 mm pen needles) reported similar injection site leakage. 58 % of the leakage was observed when using 5 and 8 mm pen needles. [Hirsch et al. 2010] 14
15 20 % Reported leakage with skin fold [Hirsch et al. 2010] A subgroup analysis showed fewer total leakage events when using the 4 mm pen needle in obese and non-obese patients. [Hirsch et al. 2012] A comparison of 5 mm and 8 mm (each of 31 Gauge) pen needles showed less insulin leakage with the 8 mm pen needle. There was no correlation (for both needle lengths) between insulin leakage from the skin and parameters such as BMI, waist-to-hip ratio, HbA 1c, the total amount of daily administered insulin, or the injection site. [Kreugel et al. 2011] In a crossover study on adult diabetes patients, insulin leakage was rare and no significant differences could be observed between 4 mm and 6 mm (each of 32 Gauge) pen needles. Nevertheless, leakage was numerically higher in the 4 mm pen needle group. [Miwa et al. 2012] The incidence of leakage differs considerably between different clinical trials. In a population of 259 patients (122 children/adolescents and 137 adults), adults showed more often insulin leakage than younger subjects (70 % leakage in adults and only 56 % leakage in children or adolescents; significant difference). The volume of substance given (200, 400, or 600 µl) did not affect the occurrence of leakage. Leakage was more likely to occur with vertical injections (65 % for vertical and 59 % for angled injections; significant difference) and with thigh injections (66 % to thigh and 58 % to abdomen; significant difference). In general, the amount of leakage recorded in each case was minimal. [Hofman et al. 2010] A comparison of 32 Gauge 4 mm, 31 Gauge 5 mm and 8 mm pen needles showed that nearly all leakage reports were with injections at 90 degrees. Moreover, about 20 % of events reported with 4 mm and 5 mm pen needles were with lifted skin folds, and 80 % without skin folds. [Hirsch et al. 2010] A survey of 4,352 insulin-injecting type 1 and type 2 diabetes patients described a rate of nearly 43 % of patients with insulin leakage from their pen needles after injection. There was no relationship detected between the time that the needle was kept under the skin and the degree of leakage from the site. [De Coninck et al. 2010] 15
16 3.3. Safety: Adverse Events, Hypo-/Hyperglycemia Blood glucose level mg/dl Blood glucose level mmol/l Definition Hyperglycemia is defined as an excessively high blood glucose level and hypoglycemia is described as an excessively low blood glucose level. The corresponding blood glucose level for hyperglycemia is > 400 mg/dl, and < 50 mg/dl for hypoglycemia. [Bergenstal et al. 2015] Outcomes In diabetes mellitus patients, hyperglycemia is usually caused by low insulin levels. While there are many reasons, hypoglycemia can be provoked by intramuscular injections. [Hirsch et al. 2014] Bergenstal et al. explored three pen needle sizes (4 mm, 8 mm, and 12.7 mm) in a randomized crossover study and found that the most frequently reported adverse events were hyperglycemia, hypoglycemia, and upper respiratory tract infections. Hyperglycemic and hypoglycemic adverse events (per 1,000 patient days) did not differ between the pen needles under evaluation. [Bergenstal et al. 2015] In a further comparison of 32 Gauge 4 mm, 31 Gauge 5 mm and 8 mm pen needles, hypo- and hyperglycemic adverse events were infrequent and did not differ between the different needle sizes. [Hirsch et al. 2010] These results were confirmed by Kreugel et al. In their comparison, 5 mm and 8 mm (each of 31 Gauge) pen needles showed no difference in hypoglycemic events. [Kreugel et al. 2011] No significant difference in hypoglycemia events was observed between the 33 Gauge 4 mm and the 32 Gauge 4 mm pen needles. The study shows that there was a trend towards higher risk when using 32 Gauge needles. [Valentini et al. 2015] The comparison of extra-thin-wall pen needles (32 Gauge 4 mm, 31 Gauge 5 mm and 31 Gauge 8 mm) with conventional pen needles (32 Gauge 4 to 8 mm, 31 Gauge 4.5 to 6 mm and 31 Gauge 8 mm) showed that the most frequent adverse events were hypoglycemia (8.3 % of patients using the extra-thin pen needles and 6 % with the usual pen needles) and hyperglycemia (2.9 % with extra-thin pen needles and 4.1 % with usual pen needles; no significant difference). [Aronson et al. 2013] 16
17 3.4. Risk: BMI and Obesity Underweight Normal weight Overweight Obese (Class I) Obese (Class II) Obese (Class III) < > 40 Definition The prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus is increasing because of the growing number of overweight and obese individuals. The success of insulin therapy should be the concern of both physicians and healthcare professionals as well as of patients with diabetes mellitus. Connected with this is the question of whether obesity and a higher BMI influence therapy success. Furthermore, there was no relationship between HbA 1c level and BMI on children with type 1 diabetes and the use of 4 mm, 5 mm, and 6 mm pen needles. [Lo Presti et al. 2012] A head-to-head comparison of obese (35.0 ± 4.9 kg/m 2 ) and non-obese patients (25.9 ± 2.3 kg/m 2 ) with different pen needle lengths (4 mm, 5 mm and 8 mm) found more leakage events in patients with BMI > 30 for all lengths. [Hirsch et al. 2012] Outcomes Anatomically, obese patients have similar skin dimensions to normal weight and thin patients. [Frid et al. 2010] It is also known that there is an inverse risk of intramuscular injection with an increasing BMI. Patients with a lower BMI score of < 25 have a higher risk of intramuscular injection than obese patients at any injection site and regardless of needle length. [Hirsch et al. 2014] Bergenstal et al. evaluated adult diabetes mellitus patients with a BMI of 30 or greater (mean BMI: 37) using three different pen needle sizes (4 mm, 8 mm, and 12.7 mm) and found no interaction between BMI and leakage rates. [Bergenstal et al. 2015] 17
18 3.5. Risk: Intramuscular Injections 5 mm 6 mm Pen needle length and injection angle have an important influence on inadvertent intramuscular injections. <2% >5% Risk of intramuscular injection depending on needle length and injection angle [Gibney et al. 2010] Definition The risk of hypoglycemia is increased by intramuscular injections. These are defined as injections of a substance directly into muscle tissue. In general, intramuscular injections increase insulin absorption and lead to a fall in plasma glucose during muscle exercise. Outcomes In general, longer needles increase the risk of inadvertent intramuscular injection. [Frid et al. 2010] On the other hand, the risk is substantially reduced with a 45-degree insertion angle. [Hirsch et al. 2014] A clinical trial on 388 adults with diabetes mellitus (type 1 and type 2) in the US measured needle length and calculated injection tissue depth. The injections were carried out using pen needles of different lengths at 45- and 90-degree angles without lifted skin folds. The results show that more than 98 % of 90-degree insertions with a 5 mm needle are placed in the subcutaneous tissue. Pen needles of 6 mm and 8 mm length have proportionately more injections into muscle (> 5 % and 15 %, respectively). A 12.7 mm pen needle inserted at 90 degrees is intramuscular in 45 % of the cases and even with a 45-degree injection angle, 21 % of injections are still in the muscle. These data support the use of shorter needle lengths. [Gibney et al. 2010] Additionally, the skin thickness and the thickness of the subcutaneous fat are important factors to consider when choosing a pen needle length and an injection method. The risk of inadvertent intramuscular injection is generally higher if the needle length is longer than skin and subcutaneous fat thickness. [Sim et al. 2014] Therefore, the risk of intramuscular injection is inversely related to the BMI. For a BMI < 25, a 2 to 4 fold greater risk can be observed in comparison to obese patients at any injection site. The estimated risk of intramuscular injections is higher in men than in women, regardless of needle length (men have a 2 to 4 fold higher risk than women). For example, the risk of intramuscular injection at the thigh is estimated to be 40.2 % for men and 13.8 % in women when using an 8 mm pen needle. [Hirsch et al. 2014] The intramuscular injection risk with 4 mm pen needles is < 1 % in women and < 5 % in men across all injection sites. [Hirsch et al. 2014] An important reason is that women have significantly more subcutaneous adipose tissue (approximately 5 mm) than men. [Hirsch et al. 2014] A comparison of adults and children showed that children had a higher risk of intramuscular injection (5.5 %) than adults (1.3 %). [Hofman et al. 2010] Lo Presti et al. confirmed these results and found that the youngest group of patients has the highest risk. For patients between 2 and 6 years (no pinch up), 20.2 % intramuscular injections occurred when using a 4 mm needles, with a two-fold increase with 5 mm needles and a three-fold increase with 6 mm pen needles. [Lo Presti et al. 2012] 18
19 8 mm 12.7 mm 12.7 mm 15% 45% 21% A survey of pediatric patients (40 children and adolescents) estimated the risk of intramuscular injection at the different injection sites. The risk of intramuscular injection is reduced if a 4 mm pen needle is used, but not completely eliminated. Nonetheless, the risk of intramuscular injection was greater with longer needles. [Marran et al. 2014] Hofman et al. explored the ideal injection techniques using 5 mm needles on 259 patients (122 children or adolescents and 137 adults). There was a significant correlation between age and the likelihood of an intramuscular injection. Intramuscular injection was much less frequent in adults. Despite the relatively small number of intramuscular injections, the results showed a difference in the incidence of intramuscular injections in children and adolescents depending on their gender. In pre-pubertal boys, the site made no difference, but angled and skin-fold injections appeared to reduce intramuscular incidence. Among girls, no intramuscular deposition was recorded when the skin was pinched or the injection was applied to the thigh. [Hofman et al. 2010] The risk of intramuscular injections varies in correlation with the injection angle and the needle length at each injection site. The risk of intramuscular injection is particularly high at the thighs and lowest on the buttocks. The risk at the arm and abdomen can be classified as intermediate. [Hirsch et al. 2014] A clinical trial on 156 type 2 diabetes mellitus patients explored the risk of intramuscular injection based on needle length and body mass index (with 90-degree insertion in the abdomen and upper arm without skin folds). The risk of intramuscular injection in the abdomen was: 1.9 % for 4 mm 5.1 % for 5 mm 12.8 % for 6 mm and 28.8 % for 8 mm pen needles. The risk of intramuscular injection in the upper arm was: 3.2 % for 4 mm 20.5 % for 5 mm 35.3 % for 6 mm and 58.9 % for 8 mm pen needles. Furthermore, these results show that the risk of intramuscular injection increases with longer needles in both the abdomen and upper arm. [Sim et al. 2014] Other authors confirmed the results and concluded that 4 mm and 5 mm pen needles reduce intramuscular insulin injections without increasing the backflow of insulin to the skin surface. [Gibney et al. 2010, Birkenbaek et al. 2008] 19
20 3.6. Risk: Lipohypertrophy 45.8 % 35.7 % Ways of identifying lipohypertrophies [Grassi et al. 2014] Definition Lipohypertrophy appears as swelling and or hardening subcutaneous tissue at injection sites. A higher frequency of lipohypertrophy is recognized in patients who use a pen needle several times or repeatedly inject in restricted areas. [Ji et al. 2017] Outcomes In contrast to healthy skin, lipohypertrophic skin cannot be pinched tightly together. In some patients the lesion can be hard or scar like. Lipohypertrophy is common. A questionnaire put to 346 diabetes mellitus patients found lipohypertrophy in 35.7 % by visual inspection and 45.8 % by palpation. The chance of detecting lipohypertrophy was 48.7 % if visual and touch evaluation were combined. [Grassi et al. 2014] A comparable overall risk of lipohypertrophy in approx. 50 % of patients was found by a second survey of children, adolescents and adults. Abdominal lipohypertrophy was more frequent when two smaller sized injection zones were used, and the reuse of needles increased the risk as well. [De Corninck et al. 2010] Recently published surveys have highlighted lipohypertrophy as the most common complication resulting from insulin injection. The 2016 Worldwide Injection Technique Questionnaire Study of 13,000 patients from 42 countries supports an association between the presence of lipohypertrophy and the use of older, less purified insulin formulations, failure to rotate sites, use of small injecting zones, repeated injection into the same location and reuse of needles. Injections into the lipohypertrophic tissue may also worsen hypertrophy. Therefore, insulin absorption is probably delayed. With respect to this topic, patients should not inject into the lipohypertrophic area until it returns to normal (which takes months to years). [Frid et al. 2016] 20
21 3.7. Risk: Pediatrics 2-6 years 7-13 years years high risk level low Definition Children and their parents are often apprehensive at the beginning of insulin therapy. This apprehension is mostly related to an earlier experience of pain and the negative impact of injections. Outcomes Fear and anxiety can negatively influence the success of insulin therapy. [Frid et al. 2010] For children and adolescents, the use of a 4 mm, 5 mm or 6 mm pen needle is recommended, especially for slim patients. Pediatric patients who inject into the limbs may need to lift a skin fold, especially when using a 5 mm or 6 mm pen needle. There is no medical reason for recommending needles longer than 6 mm for children and adolescents. [Frid et al. 2010] Marran et al. stated that 4 mm pen needles reduced (but did not eliminate) the risk of intramuscular injection. 4 mm pen needles are preferable for children with a lower BMI. [Marran et al. 2014] Hofman et al. concluded that 8 mm needles have an unacceptable rate of intramuscular injections. Even 6 mm pen needles have a high rate of intramuscular injections when inserted at 90 degrees. In this study, no intramuscular injections were reported with an angled insertion. [Hofman et al. 2010] A comparison of children aged 2 to 6, 7 to 13, and 14 to 17 years old showed that the youngest group is at greatest risk of intramuscular injections. Interestingly, some children do not insert the needle fully if they feel the procedure to be painful. This impaired technique increases the risk of intradermal injections with a 4 mm pen needle. Children and their parents should be trained in the proper injection technique, including needle insertion to its full length. [Lo Presti et al. 2012] 21
22 4. Efficiency of Shorter Pen Needles 4. Efficiency of Shorte Which one is more efficient Definition The success of glycemic control depends on adjustments in the insulin dose, as the daily insulin dose calculation has to reflect individual patient conditions. In their clinical trial, Bergenstal et al. described a range of 6 to 350 IU, with the largest single dose being 100 IU. [Bergenstal et al. 2015] Outcomes No differences in insulin doses were found between the 32 Gauge 4 mm and the 31 Gauge 8 mm or 29 Gauge 12.7 mm pen needles in obese patients with diabetes mellitus (randomized, controlled trial on 274 patients). [Bergenstal et al. 2015] Furthermore, the daily insulin dose remained unchanged and did not differ between the 33 Gauge 4 mm and the 32 Gauge 4 mm pen needles (randomized, controlled trial on 87 patients). [Valentini et al. 2015] A questionnaire put to 259 follow-up patients who switched to a 4 mm pen needle showed no significant differences in total insulin doses after a period of three months. [Grassi et al. 2014] 22
23 r Pen Needles 4 mm 12 mm? A questionnaire put to 259 follow-up patients who switched to a 4 mm pen needle showed no significant differences in total insulin doses after a period of three months. [Grassi et al. 2014] The comparison of 4 mm, 5 mm and 8 mm pen needles did not show a substantial change in insulin doses. Only 21 of 163 patients reported any change in insulin dosage, and only 13 patients reported dose changes > 10 %. [Hirsch et al. 2010] A randomized crossover trial on 130 patients could not find any changes in insulin doses but the dose was slightly higher with 8 mm pen needles. [Kreugel et al. 2011] Extra-thin pen needles are able to reduce the time needed to deliver medication by 52 % to 60 % in comparison to regular pen needles. [Aronson et al. 2013] 23
24 5. Patients Experiences With Shorter Pen Needles 5.1. Pain Definition and For pain intensity measurement, the VAS (Visual Analog Scale) is a unidimensional measurement instrument which is used widely. Two scales are available: VAS 100 and VAS 150. Definition The perception of pain in injection therapy can be influenced by several factors and patient conditions: These include needle length and diameter, and injection technique. Furthermore, pain perception differs between adults and children. For pain intensity measurement, the VAS (Visual Analog Scale) is an unidimensional instrument which is used widely. Two ranges are available: VAS 100 and VAS 150. The VAS 100 ranges between 0 (no pain) and 100 (worst possible pain). The VAS 150 ranges from -75 (much less painful) to 75 (much more painful) and is centered at 0 (as painful as previous needle). Outcome In general, most injections are not painful, except in the infrequent event that the needle comes into direct contact with nerve endings. Some patients, however, are exceptionally sensitive. [Frid et al. 2010] Children in particular experience more discomfort than adults. The injection angle or site of injection seems to have no bearing on whether the subject feels pain or not. In addition, abdominal injections are less painful than those applied to the thighs. [Hofman et al. 2010] 24
25 Outcomes Bergenstal mm vs. 12 mm: Bergenstal mm vs. 8 mm: Nagai mm vs. 5 mm: Hirsch mm vs. 5 mm: (BMI > 30) Hirsch mm vs. 5 mm: (BMI < 30) Miwa mm vs. 6 mm: Hirsch mm vs. 8 mm: Hirsch mm vs. 5 mm: much less painful as painful as much more previous needle painful Table 2 Summarized results on a visual analog scale VAS 150 Randomized, controlled trials and comparative studies evaluated pain perception by using pen needles with different lengths. The results support the assumption that shorter pen needles reduce pain sensations. The detailed findings can be summarized as follows: Relative injection pain can be assessed using a 150 visual analog scale, which compares injection pain perceived by patients at the end of one period with that in the previous period. Visual analog scale scores range from -75 (much less painful) to 75 (much more painful), with 0 (scale midpoint) meaning as painful as the previous needle. Bergenstal et al. found that the average pain scores with 4 mm pen needles were significantly lower than with 8 mm, and 12.7 mm needles (4 mm versus 8 mm: and 4 mm versus 12.7 mm: -30.8; VAS 150; randomized crossover study; n = 274). [Bergenstal et al. 2015] Nagai et al. evaluated a 32 Gauge 4 mm (straight wall) needle, a thinner micro-tapered 33 Gauge tip and a 28 Gauge 5 mm needle. The patients perceived less pain with the 32 Gauge 4 mm needle (mean VAS score was -14.5; VAS 150; randomized crossover study; n = 84). [Nagai et al. 2013] A 32 Gauge 4 mm pen needle was reported to be less painful than the 31 Gauge 5 mm and 8 mm pen needles (VAS was 11.9 less for the 4 mm versus 5 mm and 23.3 less for 4 mm versus 8 mm; VAS 150; randomized crossover trial on 173 patients). [Hirsch et al. 2010] A subgroup analysis showed a significant reduction in relative pain for the 4 mm versus 8 mm in obese and non-obese patients. Pain reduction was also observed for patients with a BMI 30 (in the 4 and 5 mm pen needle group). The VAS pain difference was not significant for subjects with a BMI < 30. [Hirsch et al. 2012] A clinical trial on 41 diabetes mellitus patients confirmed the above named publications: the 32 Gauge 4 mm pen needle was perceived as being significantly less painful and rated as significantly more favourable than the 32 Gauge 6 mm pen needle (average VAS score for comparative pain was mm; VAS 150; randomized crossover trial). [Miwa et al. 2012] Table 2 shows the above summarized results on a visual analog scale VAS 150. When comparing the results of Bergenstal et al and Hirsch 2010 the perceived pain generally seems to be influenced by the applied needle lengths. In the Bergenstal study where 4 mm, 8 mm and 12.7 mm pen needles were applied, the 4 mm versus 8 mm scored much lower compared to the study of Hirsch et al. where the 8 mm pen needle was the longest needle length used next to 4 mm and 5 mm needle lengths. The pain of an 8 mm pen needle seems to be worse when there is no longer needle alternative but only shorter ones. 25
26 5.1. Pain Definition and Outcomes Kursat mm: 14.6 (BMI overall) Kursat mm: 14.1 (BMI 25-30) Kursat mm: 15.1 (BMI 20-25) Kursat mm: 17.3 (BMI > 30) Kursat mm: 28.3 (BMI & BMI 25-30) Kursat mm: 31.8 (BMI > 30) Kursat mm: 28.7 (BMI overall) Kreugel mm: 7 Kreugel mm: 9 0 no pain worst possible pain Table 3 Summarized pain scores on a visual analog scale VAS 100 As an alternative to the 150 visual analog scale for assessing pain, a visual analog scale VAS 100 can also be used, where 0 is no pain and 100 is worst possible pain. In 130 insulin-treated type 1 and type 2 diabetes patients, pain perception was low for both needles (5 mm and 8 mm). A significant difference could not be observed (each of 31 Gauge; randomized crossover trial on 130 patients). [Kreugel et al. 2011] Also, pain measurement with 4 mm and 8 mm pen needles on 296 diabetes mellitus patients showed higher pain scores with the longer needle (VAS 100). Furthermore, pain perception increases with the age of the patients (for both needle lengths) and with a rising BMI. [Kursat et al. 2013] Table 3 shows the pain scores on the visual analog scale VAS 100 for the above studies. Procedure notes A series of recommendations and tips can be given to reduce pain sensations [Frid et al. 2010]: Keep insulin which is in use at room temperature. Inject only when alcohol from disinfection has fully dried. Avoid injecting at hair roots. Use shorter and thinner needles. Use a new needle for each injection. Insert the needle in a quick dart-like movement, inject slowly; massaging the site before or after injection may speed up absorption. 26
27 5.2. Preferences Definition and Outcomes? 12 mm 4 mm Which one is preferred Definition Understanding patients' preferences for different insulin therapy attributes may improve patients' satisfaction and medication adherence. Today, the overall patient preference for insulin therapy is low due to inconvenience, the possibility of pain during injection and other adverse effects. Outcomes In recent years, there has been a shift towards shorter pen needles not only as the result of decisions made by healthcare professionals but also due to patients preferences. Several publications explored patients preferences in clinical trials. In a randomized crossover study on 274 diabetes mellitus patients, significantly more patients preferred the 4 mm pen needle versus the 12.7 mm pen needle. Although more patients preferred the 4 mm needle to the 8 mm needle, this difference was not significant. [Bergenstal et al. 2015] Approximately 2/3 of patients preferred the 4 mm pen needle in a second randomized crossover study on 173 patients. [Hirsch et al. 2010] A survey of 259 diabetes mellitus patients showed high levels of satisfaction after switching to a 4 mm pen needle. [Grassi et al. 2014] Furthermore, the overall preference of extra-thin-wall pen needles was 68.2 % versus 11.6 % for conventional needles. The satisfaction parameters Insertion ease and Convenience also favored the extra-thin-wall pen needles (63.6 % versus 6.1 % and 36.4 % versus 4 % respectively). [Aronson et al. 2013] Also, the comparison of a 4 mm (straight wall) versus a thinner micro-tapered 5 mm needle favored the 4 mm needle in the parameters Usability and Visual impression. [Nagai et al. 2013] A crossover study on adult diabetes patients favored the 4 mm over a 6 mm pen needle in the outcome parameter Visual impression. Similar ratings were found for needle stability. [Miwa et al. 2012] A clear patient preference was not observed in all study trials. No specific preference could be found between a 33 Gauge 4 mm and the 32 Gauge 4 mm pen needle. There was a general trend towards the 33 Gauge needle for the parameters Pain during needle insertion, Pain during injection, Ease of needle insertion and Global satisfaction. [Valentini et al. 2015] Moreover, there was no significant difference in patients' preferences in a clinical trial of 130 insulin-treated type 1 and type 2 diabetes patients (5 mm versus 8 mm): 46 % of patients preferring the 5 mm needle, 41 % the 8 mm needle, and 13 % did not prefer a particular needle length. [Kreugel et al. 2011] 27
28 5.3. Compliance Definition and Outcomes Compliance outcome parameters are rarely explored in clinical trials. Definition Compliance means the voluntary cooperation and adherence of the patient to the therapy regime. Outcomes Compliance outcome parameters are rarely explored in clinical trials. Only three clinical trials evaluated compliance-related outcome parameters, such as ease of use, ease of insertion and needle anxiety. A randomized comparison of a 33 Gauge and 32 Gauge 4 mm pen needle favored the 33 Gauge needle with regard to the parameters: pain during needle insertion, pain during injection, ease of needle insertion, and global satisfaction. [Valentini et al. 2015] In the future, more clinical data on patient-related outcome parameter such as patients' compliance or patients' satisfaction are needed to understand the patients' preferences and to increase the acceptance of therapy regimes. These qualitative outcome parameters help to increase the cooperation between healthcare professionals and patients. A randomized crossover study compared three pen needle sizes (4 mm, 8 mm, and 12.7 mm) and showed significantly superior ease of use, ease of insertion, and needle anxiety in the 4 mm group in comparison to 8 mm or 12.7 mm pen needles. [Bergenstal et al. 2015] In a crossover study on adult diabetes patients, a 4 mm pen needle was rated as superior on the outcome parameter ease of use (in comparison to a 6 mm pen needle). [Miwa et al. 2012] 28
29 6.1. Training 6. Preventive Strategies Like the outcome parameter Compliance, the implementation of training programs is effective in increasing the performance and safety of insulin therapy. However, available data on this topic is rare. Frid et al. stated in their injection recommendations that education and training are needed for proper and effective use of pen needles. [Frid et al. 2010] A multicentered questionnaire asked (in a yes or no fashion) if patients had actually been instructed on the injection technique by an educator. It varied hugely between different countries. [De Coninck et al. 2010] Only one questionnaire answered by 346 diabetes mellitus patients aimed at evaluating the effects of an educational program for injection techniques. Switching to a 4 mm pen needle showed improved glucose control and greater satisfaction with the insulin therapy when training programs were in place. [Grassi et al. 2014] Another survey (the Swansdown Survey) found that the greatest educational need is detectable in older patients who had been injecting insulin for over ten years and who used outdated practices. [Grassi et al. 2014] In order to improve the quality of insulin therapy, clinical projects where an educational program must be attended are desirable. Another key aspect is the interaction of educational programs and patient compliance. Especially the question as to whether training can increase patient compliance is worthy of further investigation. 29
If you inject diabetes medication, you should know how important correct injection technique is for effectively managing your diabetes.
 Insulin injection technique best practices Expert recommendations on injecting insulin with pen and insulin syringe needles If you inject diabetes medication, you should know how important correct injection
Insulin injection technique best practices Expert recommendations on injecting insulin with pen and insulin syringe needles If you inject diabetes medication, you should know how important correct injection
BD Nano 4mm Pen Needles
 BD Nano mm Pen Needles Preferred by patients₉ Less effort to inject medication for people with hand strength issues₉* BD's smallest, thinnest pen needle was rated as less painful and easier to insert₉
BD Nano mm Pen Needles Preferred by patients₉ Less effort to inject medication for people with hand strength issues₉* BD's smallest, thinnest pen needle was rated as less painful and easier to insert₉
Injection Technique (I.T.), Glycemic Variability, and Lipohypertrophy. Why I.T. All Matters
 Injection Technique (I.T.), Glycemic Variability, and Lipohypertrophy Why I.T. All Matters Larry Hirsch, MD Vice-President, Global Medical Affairs BD Diabetes Care Seoul, South Korea KDA-ICDM 29 September
Injection Technique (I.T.), Glycemic Variability, and Lipohypertrophy Why I.T. All Matters Larry Hirsch, MD Vice-President, Global Medical Affairs BD Diabetes Care Seoul, South Korea KDA-ICDM 29 September
INSULIN INJECTION KNOW-HOW
 0-1- INSULIN INJECTION KNOW-HOW Learning how to Congratulations for making the move to insulin therapy. It won t be long before you start enjoying better blood sugar control, more energy, and a host of
0-1- INSULIN INJECTION KNOW-HOW Learning how to Congratulations for making the move to insulin therapy. It won t be long before you start enjoying better blood sugar control, more energy, and a host of
Safe and Gentle Injection of Insulin. Guide for correct injection technique. Englische Ausgabe
 Safe and Gentle Injection of Insulin Guide for correct injection technique Englische Ausgabe Insulin injection basics 1 Insulin has to be injected into the subcutaneous fat layer 3 Rotate the injection
Safe and Gentle Injection of Insulin Guide for correct injection technique Englische Ausgabe Insulin injection basics 1 Insulin has to be injected into the subcutaneous fat layer 3 Rotate the injection
Correct Site Rotation
 Injection Techniques Questionnaire (ITQ) WorldWide Results 2014-2015 Correct Site Rotation BACKGROUND Correct Rotation = at least 1 cm between successive injections Lipohypertrophy and Observed Correct
Injection Techniques Questionnaire (ITQ) WorldWide Results 2014-2015 Correct Site Rotation BACKGROUND Correct Rotation = at least 1 cm between successive injections Lipohypertrophy and Observed Correct
Injection technique for different needle lengths
 Injection technique for different needle lengths Use the correct technique to better manage your diabetes 1 Why it s important to use the shortest needles available Reduce your risk of injecting into the
Injection technique for different needle lengths Use the correct technique to better manage your diabetes 1 Why it s important to use the shortest needles available Reduce your risk of injecting into the
Living Well Successfully managing diabetes
 Living Well Successfully managing diabetes with 4mm Pen Needles Helping all people live healthy lives Our most comfortable injection experience ever Successfully managing diabetes with BD Micro-Fine +
Living Well Successfully managing diabetes with 4mm Pen Needles Helping all people live healthy lives Our most comfortable injection experience ever Successfully managing diabetes with BD Micro-Fine +
Gentle and safe injections. Tips and tricks for injecting insulin.
 Gentle and safe injections. Tips and tricks for injecting insulin. Freedom. Confidence. With mylife. Gentle and safe injections The correct injection technique The insulin is injected into the subcutaneous
Gentle and safe injections. Tips and tricks for injecting insulin. Freedom. Confidence. With mylife. Gentle and safe injections The correct injection technique The insulin is injected into the subcutaneous
Things you need to know about injections
 www.trend-uk.org Things you need to know about injections Injection sites: You can see from the picture below the best sites for injecting insulin or GLP-1 medications are: Back of the upper arms (difficult
www.trend-uk.org Things you need to know about injections Injection sites: You can see from the picture below the best sites for injecting insulin or GLP-1 medications are: Back of the upper arms (difficult
Gentle and safe injections. Tips and tricks for injecting insulin.
 Gentle and safe injections. Tips and tricks for injecting insulin. More freedom. More confidence. With mylife. Gentle and safe injections The correct injection technique The insulin is injected into the
Gentle and safe injections. Tips and tricks for injecting insulin. More freedom. More confidence. With mylife. Gentle and safe injections The correct injection technique The insulin is injected into the
Enjoy brilliance. mylife Clickfine DiamondTip more comfort with the perfect tip.
 Enjoy brilliance. mylife Clickfine DiamondTip more comfort with the perfect tip. 6-bevel needle tip for a smoother injection 1,2 Thin wall technology for a faster flux of medication Special silicone surface
Enjoy brilliance. mylife Clickfine DiamondTip more comfort with the perfect tip. 6-bevel needle tip for a smoother injection 1,2 Thin wall technology for a faster flux of medication Special silicone surface
Defining the ideal injection techniques when using 5-mm needles in children and adults
 Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online June 28, 2010 Defining the ideal injection techniques when using 5-mm needles in children and adults Paul Leslie Hofman MD 1, José Guilherme Behrensdorf
Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online June 28, 2010 Defining the ideal injection techniques when using 5-mm needles in children and adults Paul Leslie Hofman MD 1, José Guilherme Behrensdorf
Patient Education Pharmacy Services
 Patient Education This handout details the types of insulin. It also covers how to store, mix and inject insulin. What is insulin? Insulin is made by the pancreas and acts as a key to move glucose (sugar)
Patient Education This handout details the types of insulin. It also covers how to store, mix and inject insulin. What is insulin? Insulin is made by the pancreas and acts as a key to move glucose (sugar)
Injection Techniques Questionnaire (ITQ) WorldWide Results Needle Gauge
 Injection Techniques Questionnaire (ITQ) WorldWide Results 2014-2015 Needle Gauge BACKGROUND All needles are at least twice as long as the skin is thick More than twice as long 31G =.26mm Surface = 1
Injection Techniques Questionnaire (ITQ) WorldWide Results 2014-2015 Needle Gauge BACKGROUND All needles are at least twice as long as the skin is thick More than twice as long 31G =.26mm Surface = 1
Insulin Basic facts. Patient Education Patient Care Services. What is insulin? What types of insulin are there? Basal Insulin
 Patient Education Insulin Basic facts Insulin is a protein made by the pancreas that allows your cells to use glucose for energy. There are different types of insulin: Basal long-acting insulin that controls
Patient Education Insulin Basic facts Insulin is a protein made by the pancreas that allows your cells to use glucose for energy. There are different types of insulin: Basal long-acting insulin that controls
Enjoy brilliance. mylife Clickfine DiamondTip more comfort with the perfect tip.
 Enjoy brilliance. mylife Clickfine DiamondTip more comfort with the perfect tip. 6-bevel needle tip for a smoother injection 1,2 Thin wall technology for a faster flux of medication Special silicone surface
Enjoy brilliance. mylife Clickfine DiamondTip more comfort with the perfect tip. 6-bevel needle tip for a smoother injection 1,2 Thin wall technology for a faster flux of medication Special silicone surface
Many people use a combination of the standard 17mm cannula and the shorter 13mm cannula length depending where on their body they are inserting.
 There are many types of infusion sets available through AMSL Diabetes. Our infusion sets are obtained through Animas and are all manufactured by UnoMedical which has a worldwide reputation for producing
There are many types of infusion sets available through AMSL Diabetes. Our infusion sets are obtained through Animas and are all manufactured by UnoMedical which has a worldwide reputation for producing
Lessons learned from working with international injection technique guidelines
 Lessons learned from working with international injection technique guidelines Anders Frid, MD, PhD Clinic of Endocrinology, Skåne University Hospital, Malmö Oslo 23rd March 2012 INJECTION TECHNIQUE IS
Lessons learned from working with international injection technique guidelines Anders Frid, MD, PhD Clinic of Endocrinology, Skåne University Hospital, Malmö Oslo 23rd March 2012 INJECTION TECHNIQUE IS
ASSESSMENT AND CARE Monitor for the following and remove catheter if there is: redness, pain, swelling, firm tissue, exudates, bleeding or leakage.
 POLICY An Indwelling subcutaneous catheter may be inserted when an infant requires regular subcutaneous injections (At least one subcutaneous injection per day). SUPPORTIVE DATA In the NICU medications
POLICY An Indwelling subcutaneous catheter may be inserted when an infant requires regular subcutaneous injections (At least one subcutaneous injection per day). SUPPORTIVE DATA In the NICU medications
Evaluation of the Use of PenNeedle 32G Taper in Children being Treated with Growth Hormone
 Clin Pediatr Endocrinol 2008; 17(1), 1-7 Copyright 2008 by The Japanese Society for Pediatric Endocrinology Original Article Evaluation of the Use of PenNeedle 32G Taper in Children being Treated with
Clin Pediatr Endocrinol 2008; 17(1), 1-7 Copyright 2008 by The Japanese Society for Pediatric Endocrinology Original Article Evaluation of the Use of PenNeedle 32G Taper in Children being Treated with
Patient Information Publications Warren Grant Magnuson Clinical Center National Institutes of Health
 Warren Grant Magnuson Clinical Center National Institutes of Health What is a subcutaneous injection? A subcutaneous injection is given in the fatty layer of tissue just under the skin. A subcutaneous
Warren Grant Magnuson Clinical Center National Institutes of Health What is a subcutaneous injection? A subcutaneous injection is given in the fatty layer of tissue just under the skin. A subcutaneous
Insulin Delivery System and Self Monitoring Blood Sugar (SMBG ) Leyden V. Florido, RN, MAN
 Insulin Delivery System and Self Monitoring Blood Sugar (SMBG ) Leyden V. Florido, RN, MAN Management of Diabetes Mellitus Pharmacological Glucose Lowering Agents/Oral Antidiabetes Drug/Oral Hypogycemic
Insulin Delivery System and Self Monitoring Blood Sugar (SMBG ) Leyden V. Florido, RN, MAN Management of Diabetes Mellitus Pharmacological Glucose Lowering Agents/Oral Antidiabetes Drug/Oral Hypogycemic
Policy for the safe administration of Insulin
 Policy for the safe administration of Insulin This is a working document and any changes that become necessary to this policy must be Notified in writing to the Medicine Management Group via the Chief
Policy for the safe administration of Insulin This is a working document and any changes that become necessary to this policy must be Notified in writing to the Medicine Management Group via the Chief
BEST 4 Diabetes. Optimisation of insulin module
 BEST 4 Diabetes Optimisation of insulin module Confidence and competence Where would you rate yourself? Why do all of our patient not achieve optimal blood glucose control? Insulin Therapy Goals and Purpose
BEST 4 Diabetes Optimisation of insulin module Confidence and competence Where would you rate yourself? Why do all of our patient not achieve optimal blood glucose control? Insulin Therapy Goals and Purpose
Sponsor / Company: Sanofi Drug substance(s): Insulin Glargine. Study Identifiers: NCT
 These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert in the country of prescription. Sponsor / Company: Sanofi Drug substance(s):
These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert in the country of prescription. Sponsor / Company: Sanofi Drug substance(s):
SCIG INFUSIONS A PRACTICAL GUIDE FOR PATIENTS
 PRIMARY IMMUNODEFICIENCIES SCIG INFUSIONS: A PRACTICAL GUIDE FOR PATIENTS SCIG INFUSIONS A PRACTICAL GUIDE FOR PATIENTS 1 PRIMARY IMMUNODEFICIENCIES ABBREVIATIONS IG IVIG PID SCIG Immunoglobulin Intravenous
PRIMARY IMMUNODEFICIENCIES SCIG INFUSIONS: A PRACTICAL GUIDE FOR PATIENTS SCIG INFUSIONS A PRACTICAL GUIDE FOR PATIENTS 1 PRIMARY IMMUNODEFICIENCIES ABBREVIATIONS IG IVIG PID SCIG Immunoglobulin Intravenous
Overview of the FITNESSGRAM Body Composition Standards
 body composition Body composition refers to the division of total body weight (mass) into components, most commonly fat mass and fat-free mass. The proportion of total body weight that is fat (referred
body composition Body composition refers to the division of total body weight (mass) into components, most commonly fat mass and fat-free mass. The proportion of total body weight that is fat (referred
PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET MEDICINE TO TREAT: DIABETES. Insulin
 PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET MEDICINE TO TREAT: DIABETES Insulin This medicine has been proven to be safe and effective, but it can cause serious injury if a mistake happens while taking it. This means
PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET MEDICINE TO TREAT: DIABETES Insulin This medicine has been proven to be safe and effective, but it can cause serious injury if a mistake happens while taking it. This means
BEST 4 Diabetes. Optimisation of insulin module
 BEST 4 Diabetes Optimisation of insulin module Confidence and competence Where would you rate yourself? Why do all of our patient not achieve optimal blood glucose control? Insulin Therapy Goals and Purpose
BEST 4 Diabetes Optimisation of insulin module Confidence and competence Where would you rate yourself? Why do all of our patient not achieve optimal blood glucose control? Insulin Therapy Goals and Purpose
Glatopa is prescription medicine used for the treatment of people with relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis (MS).
 PATIENT INFORMATION Glatopa (gluh-toh-puh) (Glatiramer Acetate Injection) for Subcutaneous Use Read this Patient Information before you start using Glatopa and each time you get a refill. There may be
PATIENT INFORMATION Glatopa (gluh-toh-puh) (Glatiramer Acetate Injection) for Subcutaneous Use Read this Patient Information before you start using Glatopa and each time you get a refill. There may be
Hamdiye Arda Sürücü 1*, Hatice Okur Arslan 2
 Journal of Caring Sciences 2018; 7 (2): 67-74 doi:10.15171/jcs.2018.011 http:// journals.tbzmed.ac.ir/ JCS Original Article in Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes: Prevalence and Risk Factors Hamdiye Arda
Journal of Caring Sciences 2018; 7 (2): 67-74 doi:10.15171/jcs.2018.011 http:// journals.tbzmed.ac.ir/ JCS Original Article in Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes: Prevalence and Risk Factors Hamdiye Arda
How to Use ENBREL : Vial Adapter Method
 How to Use ENBREL : Vial Adapter Method SETTING UP FOR AN INJECTION Select a clean, well-lit, flat working surface, such as a table. Take the ENBREL dose tray out of the refrigerator and place it on your
How to Use ENBREL : Vial Adapter Method SETTING UP FOR AN INJECTION Select a clean, well-lit, flat working surface, such as a table. Take the ENBREL dose tray out of the refrigerator and place it on your
Patient Information. Preventing and treating blood clots
 Patient Information Preventing and treating blood clots 1_Clexane_Patient_Booklet_AW05.indd 1 8/04/2016 11:26 a The information provided in this document is for patients prescribed CLEXANE, and should
Patient Information Preventing and treating blood clots 1_Clexane_Patient_Booklet_AW05.indd 1 8/04/2016 11:26 a The information provided in this document is for patients prescribed CLEXANE, and should
PATIENT INFORMATION. D iabetes. What You Need to Know About. Insulin
 PATIENT INFORMATION Medicine To Treat: D iabetes What You Need to Know About Insulin INTRODUCTION The insulin preparations currently available in Singapore are mostly from human origin; pork or bovine
PATIENT INFORMATION Medicine To Treat: D iabetes What You Need to Know About Insulin INTRODUCTION The insulin preparations currently available in Singapore are mostly from human origin; pork or bovine
Sponsor / Company: Sanofi Drug substance(s): HOE901-U300 (insulin glargine) According to template: QSD VERSION N 4.0 (07-JUN-2012) Page 1
 These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert in the country of prescription. Sponsor / Company: Sanofi Drug substance(s):
These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert in the country of prescription. Sponsor / Company: Sanofi Drug substance(s):
Instructions for Use Enbrel (en-brel) (etanercept) injection, for subcutaneous use Single-dose Prefilled Syringe
 Instructions for Use Enbrel (en-brel) (etanercept) injection, for subcutaneous use Single-dose Prefilled Syringe How do I prepare and give an injection with Enbrel Single-dose Prefilled Syringe? There
Instructions for Use Enbrel (en-brel) (etanercept) injection, for subcutaneous use Single-dose Prefilled Syringe How do I prepare and give an injection with Enbrel Single-dose Prefilled Syringe? There
SELF-INJECTION GUIDE
 SELF-INJECTION GUIDE (asfotase alfa) 40 mg/ml solution for injection 18 mg/0.45 ml 28 mg/0.7 ml 40 mg/1 ml 100 mg/ml solution for injection 80 mg/0.8 ml asfotase alfa Introduction Contents This Self-Injection
SELF-INJECTION GUIDE (asfotase alfa) 40 mg/ml solution for injection 18 mg/0.45 ml 28 mg/0.7 ml 40 mg/1 ml 100 mg/ml solution for injection 80 mg/0.8 ml asfotase alfa Introduction Contents This Self-Injection
Gillian Kreugel, M.S.C., Joost C. Keers, Ph.D., Michiel N. Kerstens, M.D., Ph.D., and Bruce H.R. Wolffenbuttel, M.D., Ph.D.
 DIABETES TECHNOLOGY & THERAPEUTICS Volume 13, Number 7, 2011 ª Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. DOI: 10.1089/dia.2011.0010 Randomized Trial on the Influence of the Length of Two Insulin Pen Needles on Glycemic Control
DIABETES TECHNOLOGY & THERAPEUTICS Volume 13, Number 7, 2011 ª Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. DOI: 10.1089/dia.2011.0010 Randomized Trial on the Influence of the Length of Two Insulin Pen Needles on Glycemic Control
Your guide to diabetes management
 Your guide to diabetes management Injecting insulin and making healthy lifestyle choices Understanding insulin therapy How do I inject insulin? In general, there are two ways you can inject insulin. Talk
Your guide to diabetes management Injecting insulin and making healthy lifestyle choices Understanding insulin therapy How do I inject insulin? In general, there are two ways you can inject insulin. Talk
Efficacy/pharmacodynamics: 85 Safety: 89
 These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert in the country of prescription. Sponsor/Company: Sanofi Drug substance:
These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert in the country of prescription. Sponsor/Company: Sanofi Drug substance:
I can show you how I give my. child insulin
 Our Journey with Diabetes Si usted desea esta información en español, por favor pídasela a su enfermero o doctor. I can show you how I give my What should I know about insulin syringes? Insulin must be
Our Journey with Diabetes Si usted desea esta información en español, por favor pídasela a su enfermero o doctor. I can show you how I give my What should I know about insulin syringes? Insulin must be
Xultophy 100/3.6. (insulin degludec, liraglutide) New Product Slideshow
 Xultophy 100/3.6 (insulin degludec, liraglutide) New Product Slideshow Introduction Brand name: Xultophy Generic name: Insulin degludec, liraglutide Pharmacological class: Human insulin analog + glucagon-like
Xultophy 100/3.6 (insulin degludec, liraglutide) New Product Slideshow Introduction Brand name: Xultophy Generic name: Insulin degludec, liraglutide Pharmacological class: Human insulin analog + glucagon-like
Self-Injection Instructions for Injectable Gold
 Self-Injection Instructions for Injectable Gold A Guide for Patients Mary Pack Arthritis Centre 895 West 10th Avenue Vancouver BC V5Z 1L7 Tel: 604-875-4021 What to Have Ready Ampoule of medication Sterile
Self-Injection Instructions for Injectable Gold A Guide for Patients Mary Pack Arthritis Centre 895 West 10th Avenue Vancouver BC V5Z 1L7 Tel: 604-875-4021 What to Have Ready Ampoule of medication Sterile
Arterial Puncture Wrist
 U.S. Toll Free 866-GOLIMBS Venipuncture Arterial Puncture Wrist Part No: KKM99 Radial artery puncture is a common approach for blood collection and artery catheterization, and this simulator provides realistic
U.S. Toll Free 866-GOLIMBS Venipuncture Arterial Puncture Wrist Part No: KKM99 Radial artery puncture is a common approach for blood collection and artery catheterization, and this simulator provides realistic
Frequency of Lipohypertrophy and Associated Risk Factors in Young Patients with Type 1 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study
 Diabetes Ther (2016) 7:259 267 DOI 10.1007/s13300-016-0161-3 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Frequency of Lipohypertrophy and Associated Risk Factors in Young Patients with Type 1 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study Ayman
Diabetes Ther (2016) 7:259 267 DOI 10.1007/s13300-016-0161-3 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Frequency of Lipohypertrophy and Associated Risk Factors in Young Patients with Type 1 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study Ayman
Instructions for Use Enbrel (en-brel) (etanercept) for injection, for subcutaneous use Multiple-dose Vial
 Instructions for Use Enbrel (en-brel) (etanercept) for injection, for subcutaneous use Multiple-dose Vial How do I prepare and give an injection with Enbrel multiple-dose vial? A multiple-dose vial contains
Instructions for Use Enbrel (en-brel) (etanercept) for injection, for subcutaneous use Multiple-dose Vial How do I prepare and give an injection with Enbrel multiple-dose vial? A multiple-dose vial contains
Presentation Menu. Walk-in Slide. Full Presentation. Access. Site. Needle. Flush. Comfort. Monitor. Removing the EZ-IO catheter.
 Presentation Menu Walk-in Slide Full Presentation Access Site Needle Flush Comfort Monitor Removing the EZ-IO catheter Clinical Support Explore. Discover. Examine. Vidacare Workshop Programmes www.vidacare.com
Presentation Menu Walk-in Slide Full Presentation Access Site Needle Flush Comfort Monitor Removing the EZ-IO catheter Clinical Support Explore. Discover. Examine. Vidacare Workshop Programmes www.vidacare.com
Lecture 6 Fitness Fitness 1. What is Fitness? 2. Cardiorespiratory Fitness 3. Muscular Fitness 4. Flexibility 5. Body Composition
 Lecture 6 Fitness 1 Fitness 1. What is Fitness? 2. Cardiorespiratory Fitness 3. Muscular Fitness 4. Flexibility 5. Body Composition 2 1 Americans (on average) are not a healthy bunch 3 Sitting is the new
Lecture 6 Fitness 1 Fitness 1. What is Fitness? 2. Cardiorespiratory Fitness 3. Muscular Fitness 4. Flexibility 5. Body Composition 2 1 Americans (on average) are not a healthy bunch 3 Sitting is the new
FIT Forum for Injection Technique
 DIABETES CARE IN IRELAND FIT Forum for Injection Technique Irish Injection and Infusion Technique Recommendations 2nd Edition The Irish Injection and Infusion Technique Recommendations have been endorsed
DIABETES CARE IN IRELAND FIT Forum for Injection Technique Irish Injection and Infusion Technique Recommendations 2nd Edition The Irish Injection and Infusion Technique Recommendations have been endorsed
insulin and injections
 insulin and injections Insulin is a hormone made by the beta cells in the pancreas. Insulin allows sugar to go from the bloodstream into the body s cells and be used for energy. Insulin lowers blood sugar.
insulin and injections Insulin is a hormone made by the beta cells in the pancreas. Insulin allows sugar to go from the bloodstream into the body s cells and be used for energy. Insulin lowers blood sugar.
Methotrexate Injections
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Methotrexate Injections Steps to follow Your provider has prescribed that you receive methotrexate by injection. This handout explains the drug, its side effects, drug interactions,
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Methotrexate Injections Steps to follow Your provider has prescribed that you receive methotrexate by injection. This handout explains the drug, its side effects, drug interactions,
INJECTABLE THERAPIES IN DIABETES. Barbara Ann McKee Diabetes Specialist Nurse
 INJECTABLE THERAPIES IN DIABETES Barbara Ann McKee Diabetes Specialist Nurse 1 Aims of the session Describe the different injectable agents for diabetes and when they would be used. Describe some common
INJECTABLE THERAPIES IN DIABETES Barbara Ann McKee Diabetes Specialist Nurse 1 Aims of the session Describe the different injectable agents for diabetes and when they would be used. Describe some common
My Doctor Says I Need to Inject Insulin In Special Sites... Which Ones Should I Use? Getting Started. Site Selection
 My Doctor Says I Need to Inject Insulin In Special Sites... Which Ones Should I Use? Getting Started Site Selection You need to know where to inject insulin so that your injections will be easier, safer
My Doctor Says I Need to Inject Insulin In Special Sites... Which Ones Should I Use? Getting Started Site Selection You need to know where to inject insulin so that your injections will be easier, safer
Workshop 4 Making the complex simple
 Workshop 4 Making the complex simple Goal of workshop Insulin commencement making the complex simple Ensure participants are confident with Selecting and using devices Troubleshooting injection issues
Workshop 4 Making the complex simple Goal of workshop Insulin commencement making the complex simple Ensure participants are confident with Selecting and using devices Troubleshooting injection issues
Acknowledgement goes to WHO for use of their hand washing technique
 How to administer third party insulin injections safely with a pen device, safety pen needle and syringe 1 Hand washing It takes at least 15 seconds to wash your hands. This is about how long it takes
How to administer third party insulin injections safely with a pen device, safety pen needle and syringe 1 Hand washing It takes at least 15 seconds to wash your hands. This is about how long it takes
BUTTONHOLE CANNULATION
 BUTTONHOLE CANNULATION What is a Buttonhole? Technique in which an AV fistula is cannulated in the exact same spot, at the same angle and at the same depth of penetration every time. Benefits Reduction
BUTTONHOLE CANNULATION What is a Buttonhole? Technique in which an AV fistula is cannulated in the exact same spot, at the same angle and at the same depth of penetration every time. Benefits Reduction
The Tumescent Technique TUMESCENT TECHNIQUE. by itself We strongly recommend that you consult with one of our nutrition and
 procedures. Body sculpting can be performed on virtually any area of the body. If there is a body area of concern not mentioned, please ask specifically about these areas at the time of consultation. The
procedures. Body sculpting can be performed on virtually any area of the body. If there is a body area of concern not mentioned, please ask specifically about these areas at the time of consultation. The
Inspection Window. Syringe Body
 Guide to Parts Before use Instructions for Use UDENYCA (yoo-den-i-kah) (pegfilgrastim-cbqv) Injection Single-Dose Prefilled Syringe Inspection Window Needle Cap Needle Label Plunger Plunger Head Needle
Guide to Parts Before use Instructions for Use UDENYCA (yoo-den-i-kah) (pegfilgrastim-cbqv) Injection Single-Dose Prefilled Syringe Inspection Window Needle Cap Needle Label Plunger Plunger Head Needle
Diabetes, sugar. Greenville Veterinary Clinic LLC 409 E. Jamestown Rd. Greenville, PA (724)
 Greenville Veterinary Clinic LLC 409 E. Jamestown Rd. Greenville, PA 16125 (724) 588-5260 Feline diabetes mellitus Diabetes, sugar AffectedAnimals: Most diabetic cats are older than 10 years of age when
Greenville Veterinary Clinic LLC 409 E. Jamestown Rd. Greenville, PA 16125 (724) 588-5260 Feline diabetes mellitus Diabetes, sugar AffectedAnimals: Most diabetic cats are older than 10 years of age when
ASSESSING BODY COMPOSITION
 ALL ABOUT EXERCISE ASSESSING BODY COMPOSITION BODY MASS INDEX Body Mass Index (BMI) is a number calculated from a person s height and weight. BMI is an indicator of total body fat and is used to screen
ALL ABOUT EXERCISE ASSESSING BODY COMPOSITION BODY MASS INDEX Body Mass Index (BMI) is a number calculated from a person s height and weight. BMI is an indicator of total body fat and is used to screen
Package leaflet: Information for the user
 Package leaflet: Information for the user Aimovig 70 mg solution for injection in pre-filled pen erenumab This medicine is subject to additional monitoring. This will allow quick identification of new
Package leaflet: Information for the user Aimovig 70 mg solution for injection in pre-filled pen erenumab This medicine is subject to additional monitoring. This will allow quick identification of new
Parental Overview Document of FITNESSGRAM Assessment in Georgia
 F I T N E S S G R A M R e f e r e n c e G u i d e P a g e 1 Parental Overview Document of FITNESSGRAM Assessment in Georgia The FITNESSGRAM Reference Guide is intended to provide answers to some common
F I T N E S S G R A M R e f e r e n c e G u i d e P a g e 1 Parental Overview Document of FITNESSGRAM Assessment in Georgia The FITNESSGRAM Reference Guide is intended to provide answers to some common
PEN USER MANUAL Byetta 5 micrograms solution for injection in pre-filled pen (exenatide)
 PEN USER MANUAL Byetta 5 micrograms solution for injection in pre-filled pen (exenatide) Section 1. WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT YOUR BYETTA PEN Read this section completely before you begin. Then, move
PEN USER MANUAL Byetta 5 micrograms solution for injection in pre-filled pen (exenatide) Section 1. WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT YOUR BYETTA PEN Read this section completely before you begin. Then, move
4/16/2014. w w w. I C A o r g
 w w w. I C A 2 0 1 4. o r g Obesity and Mortality Sam Gutterman, FSA, FCAS, MAAA, CERA, HonFIA April 2014 1 Agenda Obesity where are we now Mortality how bad is it and a paradox Health it can get worse
w w w. I C A 2 0 1 4. o r g Obesity and Mortality Sam Gutterman, FSA, FCAS, MAAA, CERA, HonFIA April 2014 1 Agenda Obesity where are we now Mortality how bad is it and a paradox Health it can get worse
Dermatological complications of insulin therapy in children with type 1 diabetes
 in children with type 1 diabetes Hilde E van Munster, MSc 2 Cathelijne PM van de Sande 2 Paul G Voorhoeve, MD, PhD 2,3 Janiëlle AEM van Alfen-van der Velden, MD, PhD 1,2 1 Department of Pediatric Endocrinology,
in children with type 1 diabetes Hilde E van Munster, MSc 2 Cathelijne PM van de Sande 2 Paul G Voorhoeve, MD, PhD 2,3 Janiëlle AEM van Alfen-van der Velden, MD, PhD 1,2 1 Department of Pediatric Endocrinology,
Obesity and mortality
 Obesity and mortality Sam Gutterman, FSA, FCAS, CERA, MAAA, HonFIA INTERNATIONAL MORTALITY AND LONGEVITY SYMPOSIUM 2014 15-17 September 2014, Birmingham Agenda Obesity where are we now Mortality how bad
Obesity and mortality Sam Gutterman, FSA, FCAS, CERA, MAAA, HonFIA INTERNATIONAL MORTALITY AND LONGEVITY SYMPOSIUM 2014 15-17 September 2014, Birmingham Agenda Obesity where are we now Mortality how bad
TRANSCRIPT for Lantus SoloSTAR pen injection for your patients
 TRANSCRIPT for Lantus SoloSTAR pen injection for your patients SUPER: Prescription Lantus is a long-acting insulin used to treat adults with type 2 diabetes and adults and pediatric patients (children
TRANSCRIPT for Lantus SoloSTAR pen injection for your patients SUPER: Prescription Lantus is a long-acting insulin used to treat adults with type 2 diabetes and adults and pediatric patients (children
TAKING THE OUT OF INSULIN DELIVERY
 G N I T S TAKING THE OUT OF INSULIN DELIVERY PHOTO: THINKSTOCK Nearly a century after its discovery, most insulin is still delivered via a needle, which many people with diabetes find painful and inconvenient.
G N I T S TAKING THE OUT OF INSULIN DELIVERY PHOTO: THINKSTOCK Nearly a century after its discovery, most insulin is still delivered via a needle, which many people with diabetes find painful and inconvenient.
The Enbrel SureClick autoinjector is a single-dose prefilled autoinjector. It contains one 50 mg dose of Enbrel.
 Instructions for Use Welcome! The Enbrel SureClick autoinjector is a single-dose prefilled autoinjector. It contains one 50 mg dose of Enbrel. Your healthcare provider has prescribed Enbrel SureClick autoinjector
Instructions for Use Welcome! The Enbrel SureClick autoinjector is a single-dose prefilled autoinjector. It contains one 50 mg dose of Enbrel. Your healthcare provider has prescribed Enbrel SureClick autoinjector
WHEN YOUR PANCREAS IS NOT A HAPPY CAMPER A PRESENTATION ON DIABETES MANAGEMENT IN THE CAMP SETTING AMANDA COSCHI, BSCN, RN, CDE
 WHEN YOUR PANCREAS IS NOT A HAPPY CAMPER A PRESENTATION ON DIABETES MANAGEMENT IN THE CAMP SETTING AMANDA COSCHI, BSCN, RN, CDE MAY 5, 2018 OBJECTIVES Strong understanding of diabetes and its management
WHEN YOUR PANCREAS IS NOT A HAPPY CAMPER A PRESENTATION ON DIABETES MANAGEMENT IN THE CAMP SETTING AMANDA COSCHI, BSCN, RN, CDE MAY 5, 2018 OBJECTIVES Strong understanding of diabetes and its management
Evaluation of AVF and AVG
 Evaluation of AVF and AVG 2013 Nephrology Nursing Symposium Albuquerque Vascular Access Leading cause of hospitalization in the ESRD population Annual cost approaching $1.5 billion (USRDS, 2004) Current
Evaluation of AVF and AVG 2013 Nephrology Nursing Symposium Albuquerque Vascular Access Leading cause of hospitalization in the ESRD population Annual cost approaching $1.5 billion (USRDS, 2004) Current
Vernell Kea RN, CCTN May 23, 2012.
 Insulin Teaching and Administration for Newly Diagnosed Adolescent Patients Vernell Kea RN, CCTN May 23, 2012. Insulin Teaching and Administration for Newly Diagnosed Adolescent Patients Overview of Diabetes
Insulin Teaching and Administration for Newly Diagnosed Adolescent Patients Vernell Kea RN, CCTN May 23, 2012. Insulin Teaching and Administration for Newly Diagnosed Adolescent Patients Overview of Diabetes
H1N1 Vaccine Administration Manual for Paramedics
 H1N1 Vaccine Administration Manual for Paramedics TABLE OF CONTENTS I. Introduction II. Policy and Procedure for Administering Medications A. Intradermal B. Intramuscular C. Subcutaneous III. Pictorial
H1N1 Vaccine Administration Manual for Paramedics TABLE OF CONTENTS I. Introduction II. Policy and Procedure for Administering Medications A. Intradermal B. Intramuscular C. Subcutaneous III. Pictorial
A quick guide to diabetes for people changing from tablets to insulin (type 2 diabetes) Diabetes and Endocrinology Patient Information Leaflet
 A quick guide to diabetes for people changing from tablets to insulin (type 2 diabetes) Diabetes and Endocrinology Patient Information Leaflet What is diabetes? Diabetes is a condition where the amount
A quick guide to diabetes for people changing from tablets to insulin (type 2 diabetes) Diabetes and Endocrinology Patient Information Leaflet What is diabetes? Diabetes is a condition where the amount
Presuming all the above symptoms are not present, pain is more likely to be mechanical and caused by a sprain, strain or poor posture.
 Page 1 of 8 View this article online at: patient.info/health/back-pain-exercises Back Pain Exercises Back pain is very common but in most cases is not caused by a serious problem. Most cases of back pain
Page 1 of 8 View this article online at: patient.info/health/back-pain-exercises Back Pain Exercises Back pain is very common but in most cases is not caused by a serious problem. Most cases of back pain
The TRUE Guide to Diabetes Care
 monitor track manage A TRUEinsight Guide manage The TRUE Guide to Diabetes Care Important Questions and Informative Answers for People With Diabetes A Guide to Diabetes Care You ve been diagnosed with
monitor track manage A TRUEinsight Guide manage The TRUE Guide to Diabetes Care Important Questions and Informative Answers for People With Diabetes A Guide to Diabetes Care You ve been diagnosed with
IMPORTANT: PLEASE READ. Don t
 PATIENT/CAREGIVER INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE - ORENCIA (ABATACEPT) PREFILLED SYRINGE WITH BD ULTRASAFE PASSIVE TM NEEDLE GUARD WITH FLANGE EXTENDERS Getting started with ORENCIA therapy Did you receive self-injection
PATIENT/CAREGIVER INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE - ORENCIA (ABATACEPT) PREFILLED SYRINGE WITH BD ULTRASAFE PASSIVE TM NEEDLE GUARD WITH FLANGE EXTENDERS Getting started with ORENCIA therapy Did you receive self-injection
Injection Impact Survey Executive Summary
 All rights reserved. Injection Impact Survey Executive Summary Prepared for the American Association of Diabetes Educators Presented by Harris Interactive Public Relations Research Team w w w. h a r r
All rights reserved. Injection Impact Survey Executive Summary Prepared for the American Association of Diabetes Educators Presented by Harris Interactive Public Relations Research Team w w w. h a r r
Title: EZ-IO. Effective Date: January SOG Number: EMS Rescinds:
 S O G Title: EZ-IO Effective Date: January 2010 SOG Number: EMS - 25 Rescinds: Scope: Providers Authorized are AIC s in the following certifications EMT-I and EMT-P who have been trained and cleared by
S O G Title: EZ-IO Effective Date: January 2010 SOG Number: EMS - 25 Rescinds: Scope: Providers Authorized are AIC s in the following certifications EMT-I and EMT-P who have been trained and cleared by
Intramuscular injections
 Intramuscular injections BENEFITS OF TREATMENT WITH INJECTION With injections of subcutaneous and intramuscular injection is possible to: - the administration of drugs to patients with impaired consciousness
Intramuscular injections BENEFITS OF TREATMENT WITH INJECTION With injections of subcutaneous and intramuscular injection is possible to: - the administration of drugs to patients with impaired consciousness
ANGIOPLASTY AND STENTING
 ANGIOPLASTY AND STENTING What is angioplasty and stenting? During an angioplasty, your vascular surgeon inflates a small balloon inside a narrowed blood vessel. This balloon helps to widen your blood vessel
ANGIOPLASTY AND STENTING What is angioplasty and stenting? During an angioplasty, your vascular surgeon inflates a small balloon inside a narrowed blood vessel. This balloon helps to widen your blood vessel
Placename CCG. Policies for the Commissioning of Healthcare
 Placename CCG Policies for the Commissioning of Healthcare Policy for the funding of insulin pumps and continuous glucose monitoring devices for patients with diabetes 1 Introduction 1.1 This document
Placename CCG Policies for the Commissioning of Healthcare Policy for the funding of insulin pumps and continuous glucose monitoring devices for patients with diabetes 1 Introduction 1.1 This document
Shockwave therapy for cellulite
 Shockwave therapy for cellulite Dr Markus Steinert Abstract A suitable treatment for cellulite has been sought for many years. This paper discusses the use of shockwaves to treat cellulite. It was demonstrated
Shockwave therapy for cellulite Dr Markus Steinert Abstract A suitable treatment for cellulite has been sought for many years. This paper discusses the use of shockwaves to treat cellulite. It was demonstrated
Ig Therapy: One Size Does Not Fit All
 Ig Therapy: One Size Does Not Fit All Carla Duff, CPNP, MSN, IgCN Advanced Registered Nurse Practitioner University of South Florida Division of Allergy, Immunology, and Rheumatology 1 Objectives Understand
Ig Therapy: One Size Does Not Fit All Carla Duff, CPNP, MSN, IgCN Advanced Registered Nurse Practitioner University of South Florida Division of Allergy, Immunology, and Rheumatology 1 Objectives Understand
INSTRUCTIONS FOR PREPARING AND GIVING AN INJECTION OF ENBREL POWDER
 INSTRUCTIONS FOR PREPARING AND GIVING AN INJECTION OF ENBREL POWDER Introduction The following instructions explain how to prepare and inject Enbrel powder for injection. Please read the instructions carefully
INSTRUCTIONS FOR PREPARING AND GIVING AN INJECTION OF ENBREL POWDER Introduction The following instructions explain how to prepare and inject Enbrel powder for injection. Please read the instructions carefully
HOW TO USE YOUR LANTUS SOLOSTAR PEN
 HOW TO USE YOUR LANTUS SOLOSTAR PEN A STEP BY STEP GUIDE TO USING YOUR LANTUS SOLOSTAR PEN This quick reference guide is a short version of the instruction leaflet. It is designed to help make it easier
HOW TO USE YOUR LANTUS SOLOSTAR PEN A STEP BY STEP GUIDE TO USING YOUR LANTUS SOLOSTAR PEN This quick reference guide is a short version of the instruction leaflet. It is designed to help make it easier
What are the assessments? Why is aerobic capacity important?
 What are the assessments? Aerobic Capacity- The PACER or the One-Mile Run Body Composition- Height/Weight Abdominal Strength - Curl-Up Upper Body Strength - Push-Up Flexibility - Back-Saver Sit and Reach
What are the assessments? Aerobic Capacity- The PACER or the One-Mile Run Body Composition- Height/Weight Abdominal Strength - Curl-Up Upper Body Strength - Push-Up Flexibility - Back-Saver Sit and Reach
Injection Techniques Questionnaire (ITQ) WorldWide Results Insulin Usage
 Injection Techniques Questionnaire (ITQ) WorldWide Results 2014-2015 Insulin Usage BACKGROUND Lipohypertrophy in Diabetes or How much does a lipo cost? Dr. Treichel, Magdeburg Studies * have shown that
Injection Techniques Questionnaire (ITQ) WorldWide Results 2014-2015 Insulin Usage BACKGROUND Lipohypertrophy in Diabetes or How much does a lipo cost? Dr. Treichel, Magdeburg Studies * have shown that
Fitness A complete approach to Health. Creating Balance
 Fitness A complete approach to Health Creating Balance Fitness Learning Outcomes Phase 1 1. Explain the difference between Fat body weight and Lean body weight and the importance of balance. 2. Categorize
Fitness A complete approach to Health Creating Balance Fitness Learning Outcomes Phase 1 1. Explain the difference between Fat body weight and Lean body weight and the importance of balance. 2. Categorize
INJECTION TECHNIQUE IS IT IMPORTANT? Anders Frid, MD, PhD, T.I.T.AN Athens
 INJECTION TECHNIQUE IS IT IMPORTANT? Anders Frid, MD, PhD, T.I.T.AN Athens Injection Technique: What Do We Know and What Do We Want to Know? What about insulin absorption? Are modern insulin analogues
INJECTION TECHNIQUE IS IT IMPORTANT? Anders Frid, MD, PhD, T.I.T.AN Athens Injection Technique: What Do We Know and What Do We Want to Know? What about insulin absorption? Are modern insulin analogues
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
 Comfort Injects 50 Comfort-in INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE English user manual 1 Introduction Thank you for choosing the Comfort in Needle free Injection system, developed with your comfort and convenience in
Comfort Injects 50 Comfort-in INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE English user manual 1 Introduction Thank you for choosing the Comfort in Needle free Injection system, developed with your comfort and convenience in
Obesity Management in Patients with Diabetes Jamy D. Ard, MD Sunday, February 11, :15 a.m. 11:00 a.m.
 Obesity Management in Patients with Diabetes Jamy D. Ard, MD Sunday, February 11, 2018 10:15 a.m. 11:00 a.m. Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is closely associated with obesity, primarily through the link
Obesity Management in Patients with Diabetes Jamy D. Ard, MD Sunday, February 11, 2018 10:15 a.m. 11:00 a.m. Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is closely associated with obesity, primarily through the link
Next steps for success.
 Next steps for success. More tips for using CGM* training course. The Animas Vibe System is approved for persons age 2 and older. *Continuous Glucose Monitoring Important Safety Information The Animas
Next steps for success. More tips for using CGM* training course. The Animas Vibe System is approved for persons age 2 and older. *Continuous Glucose Monitoring Important Safety Information The Animas
DIABETES - FACT SHEET
 DIABETES - FACT SHEET What is diabetes? Diabetes mellitus, often shortened to diabetes, is a chronic condition that affects the body's ability to control blood sugar level and use energy from food. In
DIABETES - FACT SHEET What is diabetes? Diabetes mellitus, often shortened to diabetes, is a chronic condition that affects the body's ability to control blood sugar level and use energy from food. In
9.Pediatric Procedures
 9.Pediatric Procedures A. Introduction 1. Pediatric blood collection may be by skin puncture or venipuncture. 2. Skill in pediatric phlebotomy is gained by knowledge of special collection equipment, observation
9.Pediatric Procedures A. Introduction 1. Pediatric blood collection may be by skin puncture or venipuncture. 2. Skill in pediatric phlebotomy is gained by knowledge of special collection equipment, observation
Copyright 2010 Informa UK Limited Not for Sale or Commercial Distribution
 Current Medical Research & Opinion Vol. 26, No. 6, 2010, 1519 1530 0300-7995 Article 5499/481203 doi:10.1185/03007995.2010.481203 All rights reserved: reproduction in whole or part not permitted Original
Current Medical Research & Opinion Vol. 26, No. 6, 2010, 1519 1530 0300-7995 Article 5499/481203 doi:10.1185/03007995.2010.481203 All rights reserved: reproduction in whole or part not permitted Original
A Fact Sheet for Parents and Carers Insulin and Diabetes
 A Fact Sheet for Parents and Carers Insulin and Diabetes In type 1 diabetes the body stops producing insulin. Insulin therapy is essential in the treatment of type 1 diabetes, together with a healthy eating
A Fact Sheet for Parents and Carers Insulin and Diabetes In type 1 diabetes the body stops producing insulin. Insulin therapy is essential in the treatment of type 1 diabetes, together with a healthy eating
Clinical Study Synopsis
 Clinical Study Synopsis This Clinical Study Synopsis is provided for patients and healthcare professionals to increase the transparency of Bayer's clinical research. This document is not intended to replace
Clinical Study Synopsis This Clinical Study Synopsis is provided for patients and healthcare professionals to increase the transparency of Bayer's clinical research. This document is not intended to replace
