The Current Environment of CGM Technologies. Barry H. Ginsberg, M.D., Ph.D.
|
|
|
- Corey Melton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology Volume 1, Issue 1, January 2007 Diabetes Technology Society SYMPOSIUM The Current Environment of CGM Technologies Introduction Barry H., M.D., Ph.D. This presentation discusses the technology involved in continuous blood glucose monitoring, focusing on the various classes of sensors. It also includes some potential uses for continuous glucose data now and in the future. Overview of CGM Technology Direct versus Indirect Measurement Direct glucose measurements measure a specific property of glucose, which must be distinguished from any similar properties in other molecules. Measurable properties of glucose include measures of its spectral, chemical, and competitive binding profiles. Indirect measurements of glucose measure its effect on other properties. For example, glucose seems to change the resistance of the skin to a radio frequency signal so the Pendra device measures glucose via radio frequency impedance. The Orsense device measures Rouleax formation, a stacking of red blood cells in small blood vessels, in response to glucose. The Glucon device indirectly measures glucose by looking at the sound created by tissue expansion when heated rapidly by light. Direct measurements tend to be more predictable than indirect ones because the signal being measured is usually unique and interferences more predictable. With indirect measurements, the signal is often not unique; there are many chemicals and other substances within the body that may produce the same signal. For example, glucose affects the refractive index of the eye and this effect can be measured indirectly. However, every optically active chemical in the body that goes through a blood vessel also has the potential to change the refractive index of the eye. Implantable Sensors Implantable sensors are still years away because of issues relating to biocompatibility and the risks inherent to surgical placement of these devices in blood vessels. Most of these sensors are glucose oxidase based; however, others are based on competitive binding or spectral properties. Glucose Oxidase Glucose oxidase-based sensor technology depends on the reaction of glucose with oxygen in the presence of glucose oxidase to create gluconic acid. The glucose oxidase enzyme is regenerated after it reduces oxygen to hydrogen peroxide. In most sensor systems, the hydrogen peroxide is then oxidized specifically by a hydrogen peroxide electrode causing the movement of electrons which can be measured. Measurement of glucose through glucose oxidation is highly specific in that virtually nothing cross-reacts with glucose oxidase. However, there are potential interferences with the electrode. The limitation of using this method in an implantable sensor is that the reaction requires one oxygen molecule for each glucose molecule. Glucose is present in the body at vast molar excess over oxygen so oxygen is the limiting reagent, not glucose, and a simple glucose oxidase sensor implanted in the body would measure oxygen levels not glucose levels. To prevent this, implantable sensors must somehow give oxygen an advantage over glucose. The DexCom implantable device does this by using a GORE membrane; blood vessels grow right into the membrane, providing the necessary oxygen supply. The device transmits its glucose measurements to an external radio frequency receiver. Tests show that 96% and 97% of its readings fall within the Author Affiliation: BD Medical Diabetes Care, Franklin Lakes, New Jersey Abbreviations: (AGP) ambulatory glucose profile, (CGM) continuous glucose monitoring, (S4MS) Sensors for Medicine and Science, (FDA) Food and Drug Administration, (ROC) receiver operating characteristic, (SMBG) self-monitoring of blood glucose Keywords: continuous, diabetes, glucose, hypoglycemia, monitor, noninvasive Corresponding Author: Barry H., M.D., Ph.D., BD Medical Diabetes Care, 1 Becton Drive, Franklin Lakes, New Jersey 07417; address barry_ginsberg@bd.com J Diabetes Sci Technol 2007;1(1):
2 Clarke Error Grid A & B Zones, respectively, after it has been calibrated and compared to self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) and YSI analysis. A brief note on measuring accuracy: Traditionally, having 95% of readings in the A & B Zones of an Error Grid was considered an acceptable level of accuracy for a continuous blood glucose monitoring device. As devices have become more accurate this may need to be reconsidered. Measurements in the extremes of the B Zone readings are often very inaccurate (i.e. a reading of 170 with a reference value of 71 is a B on the Clarke Error Grid). My personal belief is that while having 95% of readings within the A & B Zones is an acceptable level of accuracy, 85-90% of those readings should be in the A Zone. Competitive Binding There is a clever technology from Sensors for Medicine and Science (S4MS) which uses glucose binding to quench fluorescence from a reporter molecule. The sensor capsule shines a light against the fluorescent binding molecule, which sends a signal back to a detector. When glucose is bound to the molecule the fluorescent signal is decreased, so as glucose levels increase the measured fluorescence decreases. The resulting glucose calculations are transmitted to a radio frequency receiver. Spectral The Animas implantable device uses spectroscopy to measure glucose. A miniaturized sensor is implanted in a blood vessel where it detects small changes in glucose levels. A larger device, which houses a laser generator and performs signal analysis, is located within a closed compartment under the skin. Its infrared laser signal is transmitted to and then returned from the miniaturized sensor in the blood vessel for data processing. Needle Sensors The needle sensor from Medtronic was the first needle sensor available on market. Based on glucose oxidase, it is currently in its second generation with the CGMS Gold system, which utilizes a three-day sensor. The sensor reads interstitial glucose every five minutes, maintains up to 10 days worth of data, and can be downloaded by the healthcare professional. The overall error is approximately 15% when evaluated by independent investigators. Currently, the system is indicated for adjunctive use, which means it cannot be used to make clinical decisions about insulin dose. The patient or healthcare provider must perform a test with a blood glucose meter to evaluate the glucose value used when taking a mealtime insulin dose. The Medtronic Guardian RT device is a wireless system that uses a three-day sensor and displays glucose values every five minutes. It also features high and low threshold alarms. Medtronics recently introduced a version of this system that combines the Guardian RT glucose sensor with an insulin pump. The FreeStyle Navigator from Abbott Diabetes Care uses glucose oxidase but not oxygen to detect interstitial glucose levels. The electrode has a long carbon chain that holds both glucose oxidase and an osmium mediator, called a wired enzyme. After glucose has reduced the glucose oxidase the enzyme passes its electrons to the osmium mediator rather than oxygen. The mediator then passes the electrons to the electrode for measurement. This is very interesting because it avoids using oxygen and thus the requirement for a limiting membrane on the sensor. This could ultimately lead to a much more accurate system. The FreeStyle Navigator device is wireless and utilizes a 5-day sensor. The initial calibration period is 10 hours. Early data show inaccuracies to be in the 11-13% range when the system is used in a clinical setting and 14-17% when used by patients. The FreeStyle Navigator system has not received Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval. The Isense system uses a 7-day glucose oxidase electrode. The device has a reported inaccuracy rate of approximately 17%. The GlucoDay S device from A.Menarini Diagnostics uses microdialysis to measure glucose. A microdialysis tube is inserted into the abdominal wall and connects a micropump to a biosensor. The micropump pumps a perfusion solution through the tube; as the fluid flows through the tube under the patient s skin it picks up glucose through the dialysis membrane and is transported to the biosensor and is there measured for glucose content. Glucose levels are measured every three minutes for 48 hours, the duration of the sensor s intended use in-clinic. Real-time blood glucose readings are shown on the monitor and can be downloaded to a computer for analysis. The device also features a programmable alarm. An independent measurement of accuracy showed that the device had an inaccuracy of approximately 13%. Noninvasive Transcutaneous Sensors There are a number of transcutaneous methods to measure glucose: reverse iontophoresis; intercellular fluid sampling; and measurement of dermal characteristics such as photoacoustics, radio frequency impedance, and refractive index. 118
3 Iontophoresis The first continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) device to receive FDA approval was the GlucoWatch. Although its process is often described as reverse iontophoresis, it actually measures bulk flow of glucose across a membrane. The device utilizes an electrical charge to pull sodium and chloride out of the patient s skin; glucose is passively pulled along with the water of hydration of the salts. The extracted solution is then oxidized and measured for glucose content. Overall the device has an error rate of approximately 17-20%. The sensor measures glucose levels every ten minutes but only has a 12-hour half-life so it must be changed twice per day. Also, it causes significant skin irritation. It is approved for sale in the US. There are other devices in development that use transcutaneous methodology, such as the SpectRx system. This device creates a small hole in the skin, places a cap on the puncture, and then draws up small amounts of fluid over the next three days, measuring the amount of glucose in the fluid. In a similar fashion, Bayer Diagnostics is working on a device that uses sonic force to disrupt the skin. Intercellular fluid from the wound would then be collected and measured for glucose. Photoacoustics The Glucon device uses an interesting methodology called photoacoustics. This involves applying laser light to the skin above a blood vessel, causing a small but rapid increase in temperature in the blood vessel and making a soft popping sound. The device listens to the pop and determines glucose levels from the acoustic characteristics of the sound. Unlike the other systems, which measure interstitial glucose, the Glucon actually measures blood glucose. The device is not yet approved by the FDA and is not for sale in the US. Using Continuous Data Today and Tomorrow Understanding the Past Reviewing glucose trend data from continuous glucose monitoring provides patients with an opportunity to identify patterns of poor control and then determine ways to improve their control. Unfortunately, patterns are not always easily identified and often there are no apparent patterns. Several years ago, Drs. Roger Mazze and David Rodbard developed a method of glucose data analysis called the ambulatory glucose profile. The method was never widely adopted because most patients were not testing at the necessary high frequency. Now, with continuous monitoring, patients can gather enough data points to utilize the method. Essentially, the ambulatory glucose profile (AGP) provides a mean value across the day. All of the values from multiple days are shown on a single time scale from midnight to midnight. The average for each period is shown along with a standard deviation. As shown in Figure 1, the mean value is represented by the orange line and the standard deviation around it is shaded in blue. The profile in this example shows relatively small standard deviation variability from midnight to noon. Fine-tuning control during times of lower variability (green area) can be achieved through pharmacologic therapy adjustment. However, periods of extreme variability (red area) may also require lifestyle interventions. With the availability of CGM data, the AGP can be a valuable tool for evaluating glycemic control. Light Scattering The GlucoLight device is a non-invasive sensor that uses mscatter (microscatter) to measure the scatter of light from cells to determine glucose levels in interstitial fluid. Like the Glucon device, the GlucoLight system is not yet approved by the FDA. Summary There are a wide variety of continuous devices available now and in the near future. These systems have limited static accuracy (approximately 15-20%) compared with traditional blood glucose meters; however, they offer much more information about the patient s glucose trends. The key is to learn how to use these systems properly. Figure 1. Analysis of Ambulatory Glucose Profile 119
4 The Present The availability of CGM data not only allows for more effective pattern recognition and therapeutic intervention, it also provides information for planning daily insulin dosages. Patients who take insulin calculate their dosage using a general formula based on their food intake and current blood glucose level. Can patients use CGM devices to make this calculation? First, it is important to note that none of the CGM devices currently available have FDA approval for replacement of SMBG; they cannot be used to calculate a dose without SMGM confirmation. However, for the sake of discussion, we will look at the differences between SMBG and CGM data in terms of calculating a bolus insulin dose. We know that the accuracy of most CGM devices is in the 14-20% error range whereas the error range for SMBG meters is 5-7%. This means that if a patient had a blood glucose level of 50 mg/dl, a typical SMBG device would have a 95% confidence range of mg/dl but a CGM device would have a larger range of mg/dl. Assuming the patient has an insulin sensitivity factor of 30, calculating the bolus dose using the SMBG device could result in a dosage that is off by up to one quarter of a unit. Using the CGM data would result in a dosage that is off by up to three quarters of a unit. In the lower glucose ranges, these differences are not particularly significant; however when glucose is extremely elevated the error rates become quite significant. For example, if the true glucose is 400 mg/dl, the SMBG device could read mg/dl while the CGM device could show mg/dl. The error in dosage using SMBG would be approximately 2 units off compared to an error of approximately 5 units using CGM. However, it is important to remember that the other component of monitoring is the trend in glucose level. Knowing glucose trends is so important that it compensates for any differences in accuracy. Glucose values change rapidly over time. Data from the GlucoWatch shows that glucose changes at a rate of approximately +1 mg/dl/min to -1 mg/dl/min in 50% of the readings. Glucose may change as much as +2 mg/dl/ min to -2 mg/dl/min in 90% of the readings. In some instances, the maximum rate of change can be as high as 5 mg/dl per minute. With such variability, it is much more valuable for a patient to know the trend in their glucose level than to know their current level. With the trend, they can predict what their blood sugar will be after the minutes it takes for injected insulin to have an Figure 2. Profile of patient glucose variability. effect. This is one primary advantage of CGM technology over traditional SMBG. Figure 2 shows data from a patient whose pre-breakfast glucose was 125 mg/dl. However, his glucose was approximately 225 mg/dl by the time his insulin started working. Had the patient known where his glucose would eventually be, he would have increased his dosage accordingly. Because his pre-lunch glucose was now 200 mg/dl, he added a correctional dose to his usual bolus. However, by the time the insulin started working, his glucose had already dropped to 75 mg/dl. In short, the ability to calculate insulin dosages based on future glucose levels provides a much safer and more effective way of achieving glycemic control. The Future Some key issues to consider when looking to the future of continuous glucose monitoring relate to how we can better predict hypoglycemia or adjust basal insulin rates. There is also the question of when a closed-loop system will finally be available. Trade-Off Between Sensitivity and Specificity There are a lot of predictive algorithms currently available; some are much more complicated than others. However, in every algorithm, the focus is on sensitivity and specificity. Sensitivity refers to how well the device predicts hypoglycemia while specificity refers to its ability to detect hypoglycemia. Sensitivity and specificity are measured using Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curves. This method was developed in the 1950 s as a by-product of research on interpreting radio signals contaminated by noise. 120
5 Within the context of hypoglycemia predictions, ROC curves allow us to look at the trade-off between sensitivity and specificity. Are patients willing to be bothered with false alarms (sensitivity) if the device detects 100% of actual hypoglycemic events (specificity)? If a patient is hypoglycemic every third night, is he willing to be woken up three or four times per night in order to pick up that one event? This is a question that each individual must decide. Adjusting Basal Insulin Rates A key concern with CGM is that patients will begin micro-adjusting their basal rates. With continuous sensors, patients will see their glucose every few minutes and may chose to take small bursts of insulin to lower elevated blood glucose between meals. Although they will be instructed to confirm glucose levels with SMBG before making any adjustments, they will need better algorithms and training about how to make insulin adjustments without overcorrecting. Conclusion Currently available continuous glucose monitoring systems lack the accuracy of blood glucose monitoring. However, the benefit of having glucose trend data makes them more useful than blood glucose monitoring for making decisions about insulin therapy. They also can be used for preventing hypoglycemia; however, sensitivity and specificity must be considered. 121
Monitoring of Blood Glucose Level
 University of Zagreb Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Computing Biomedical instrumentation Monitoring of Blood Glucose Level Biomedical instrumentation 1/17 Outline Introduction Principles of Blood
University of Zagreb Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Computing Biomedical instrumentation Monitoring of Blood Glucose Level Biomedical instrumentation 1/17 Outline Introduction Principles of Blood
Diabetes II Insulin pumps; Continuous glucose monitoring system (CGMS) Ernest Asamoah, MD FACE FACP FRCP (Lond)
 Diabetes II Insulin pumps; Continuous glucose monitoring system (CGMS) Ernest Asamoah, MD FACE FACP FRCP (Lond) 9501366-011 20110401 Objectives Understand the need for insulin pumps and CGMS in managing
Diabetes II Insulin pumps; Continuous glucose monitoring system (CGMS) Ernest Asamoah, MD FACE FACP FRCP (Lond) 9501366-011 20110401 Objectives Understand the need for insulin pumps and CGMS in managing
1. Continuous Glucose Monitoring
 1. Continuous Glucose Monitoring 1. Physiology of interstitial fluid glucose 2. Comparison of CGM and self-monitored blood glucose (SMBG) data 3. Insulin dosing indication in BGM vs. CGM & the FDA 4. Protection
1. Continuous Glucose Monitoring 1. Physiology of interstitial fluid glucose 2. Comparison of CGM and self-monitored blood glucose (SMBG) data 3. Insulin dosing indication in BGM vs. CGM & the FDA 4. Protection
Figure 2.1: Glucose meter
 CHAPTER TWO: MONITORING TECHNOLOGIES 2.1 Introduction Glucose monitoring is a method of self-testing glucose (blood sugar) levels for the management of diabetes. Traditionally, it involves pricking the
CHAPTER TWO: MONITORING TECHNOLOGIES 2.1 Introduction Glucose monitoring is a method of self-testing glucose (blood sugar) levels for the management of diabetes. Traditionally, it involves pricking the
NEW TECHNOLOGIES FOR MANAGING DIABETES ANGELA THOMPSON DNP, FNP-C, BC-ADM, CDE, FAANP
 NEW TECHNOLOGIES FOR MANAGING DIABETES ANGELA THOMPSON DNP, FNP-C, BC-ADM, CDE, FAANP No commercial support or sponsorship was received for this project I have nothing to disclose OBJECTIVES Identify at
NEW TECHNOLOGIES FOR MANAGING DIABETES ANGELA THOMPSON DNP, FNP-C, BC-ADM, CDE, FAANP No commercial support or sponsorship was received for this project I have nothing to disclose OBJECTIVES Identify at
FAQs for HCP segment New Instructions for Dexcom G5 Mobile Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) System Non-Adjunctive Indication
 FAQs for HCP segment New Instructions for Dexcom G5 Mobile Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) System Non-Adjunctive Indication Q1. The Dexcom G5 Mobile System is the first CGM System to receive FDA approval
FAQs for HCP segment New Instructions for Dexcom G5 Mobile Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) System Non-Adjunctive Indication Q1. The Dexcom G5 Mobile System is the first CGM System to receive FDA approval
Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring: From Application to Evaluation
 Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring: From Application to Evaluation Gary Scheiner MS, CDE Owner/Director, Integrated Diabetes Services 333 E. Lancaster Ave., Suite 24 Wynnewood, PA 1996 (877) 735-3648
Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring: From Application to Evaluation Gary Scheiner MS, CDE Owner/Director, Integrated Diabetes Services 333 E. Lancaster Ave., Suite 24 Wynnewood, PA 1996 (877) 735-3648
ssociation of Children s Diabetes Clinicians Clinicians Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Training for Healthcare Professionals and Patients
 ssociation of Children s Diabetes Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Training for Healthcare Professionals and Patients 1 ssociation of Children s Diabetes Contents Chapter Page no. STEP 1...3 Getting
ssociation of Children s Diabetes Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Training for Healthcare Professionals and Patients 1 ssociation of Children s Diabetes Contents Chapter Page no. STEP 1...3 Getting
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Continuous Monitoring of Glucose in the Interstitial Fluid File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: continuous_monitoring_of_glucose_in_the_interstitial_fluid
Corporate Medical Policy Continuous Monitoring of Glucose in the Interstitial Fluid File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: continuous_monitoring_of_glucose_in_the_interstitial_fluid
Making the Most of Continuous Glucose Monitoring
 Making the Most of Continuous Glucose Monitoring Gary Scheiner MS, CDE Owner & Clinical Director Integrated Diabetes Services LLC Wynnewood, PA AADE 2014 Diabetes Educator of the Year gary@integrateddiabetes.com
Making the Most of Continuous Glucose Monitoring Gary Scheiner MS, CDE Owner & Clinical Director Integrated Diabetes Services LLC Wynnewood, PA AADE 2014 Diabetes Educator of the Year gary@integrateddiabetes.com
Today s Goals 10/6/2017. New Frontiers in Diabetes Technology. Disclosures
 New Frontiers in Diabetes Technology Marie E. McDonnell, MD Director, Brigham and Women's Diabetes Program Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes and Hypertension Brigham and Women s Hospital Today s Goals
New Frontiers in Diabetes Technology Marie E. McDonnell, MD Director, Brigham and Women's Diabetes Program Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes and Hypertension Brigham and Women s Hospital Today s Goals
Subject Index. Breastfeeding, self-monitoring of blood glucose 56
 Subject Index Animas Vibe 86, 130 Artificial pancreas clinical studies inpatient studies 175 180 outpatient studies outcome assessment 182, 183 technology 180, 181 telemedicine 182 components glucose sensor
Subject Index Animas Vibe 86, 130 Artificial pancreas clinical studies inpatient studies 175 180 outpatient studies outcome assessment 182, 183 technology 180, 181 telemedicine 182 components glucose sensor
Agreement between Glucose Trends Derived from Three Simultaneously Worn Continuous Glucose Sensors
 Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology Volume 2, Issue 5, September 2008 Diabetes Technology Society ORIGINAL ARTICLES Agreement between Glucose Trends Derived from Three Simultaneously Worn Continuous
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology Volume 2, Issue 5, September 2008 Diabetes Technology Society ORIGINAL ARTICLES Agreement between Glucose Trends Derived from Three Simultaneously Worn Continuous
Continuous Glucose Monitors for Diabetes Management
 Continuous Glucose Monitors for Diabetes Management Ryan Huang, DO PGY II, Sonia Garcia-Jayne, DO PGY II Mandeep Gill, DO PGY I, Justin Leeka, DO, PGY I, Catherine Nguyen OMS IV Family Medicine Residency,
Continuous Glucose Monitors for Diabetes Management Ryan Huang, DO PGY II, Sonia Garcia-Jayne, DO PGY II Mandeep Gill, DO PGY I, Justin Leeka, DO, PGY I, Catherine Nguyen OMS IV Family Medicine Residency,
Quick Reference Guide
 FLASH GLUCOSE MONITORING SYSTEM Quick Reference Guide IMPORTANT USER INFORMATION Before you use your System, review all the product instructions and the Interactive Tutorial. The Quick Reference Guide
FLASH GLUCOSE MONITORING SYSTEM Quick Reference Guide IMPORTANT USER INFORMATION Before you use your System, review all the product instructions and the Interactive Tutorial. The Quick Reference Guide
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Dexcom G6 Training for Healthcare Professionals and Patients
 ssociation of Children s Diabetes Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Dexcom G6 Training for Healthcare Professionals and Patients 1 ssociation of Children s Diabetes Contents Chapter Page no. Chapter
ssociation of Children s Diabetes Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Dexcom G6 Training for Healthcare Professionals and Patients 1 ssociation of Children s Diabetes Contents Chapter Page no. Chapter
Quick Reference Guide
 FLASH GLUCOSE MONITORING SYSTEM Quick Reference Guide IMPORTANT USER INFORMATION Before you use your System, review all the product instructions and the Interactive Tutorial. The Quick Reference Guide
FLASH GLUCOSE MONITORING SYSTEM Quick Reference Guide IMPORTANT USER INFORMATION Before you use your System, review all the product instructions and the Interactive Tutorial. The Quick Reference Guide
TABLE OF CONTENTS. HLC102A - Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM): Technologies and Global Markets
 TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1 STUDY GOALS AND OBJECTIVES 1 REASONS FOR DOING THIS STUDY 1 CONTRIBUTIONS TO THE STUDY AND INTENDED AUDIENCE 1 SCOPE AND FORMAT 1 METHODOLOGY AND INFORMATION
TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1 STUDY GOALS AND OBJECTIVES 1 REASONS FOR DOING THIS STUDY 1 CONTRIBUTIONS TO THE STUDY AND INTENDED AUDIENCE 1 SCOPE AND FORMAT 1 METHODOLOGY AND INFORMATION
RELEASED. Clearing your active insulin
 To clear all your settings: 1. Make sure the pump is not connected to your body. 2. Go to the Manage Settings screen. Menu > Utilities > Manage Settings 3. Simultaneously press and hold and until the Manage
To clear all your settings: 1. Make sure the pump is not connected to your body. 2. Go to the Manage Settings screen. Menu > Utilities > Manage Settings 3. Simultaneously press and hold and until the Manage
INSPIRED BY GIVE HIM MORE. The MiniMed 670G system is the world s first insulin delivery system that automatically adapts to your child s needs.
 INSPIRED BY GIVE HIM MORE. The MiniMed 670G system is the world s first insulin delivery system that automatically adapts to your child s needs. * NOW APPROVED FOR AGES 7 AND UP. Waterproof to a depth
INSPIRED BY GIVE HIM MORE. The MiniMed 670G system is the world s first insulin delivery system that automatically adapts to your child s needs. * NOW APPROVED FOR AGES 7 AND UP. Waterproof to a depth
Continuous Glucose Monitoring
 Continuous Glucose Monitoring Information about fully-subsidised continuous glucose monitoring for children and young people with type 1 diabetes Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) can help in managing
Continuous Glucose Monitoring Information about fully-subsidised continuous glucose monitoring for children and young people with type 1 diabetes Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) can help in managing
Updates in Diabetes Technology
 Updates in Diabetes Technology Jessica Kirk, MSN, RN, CPN, CDE Nurse Manager, Endo ECHO No disclosures Disclosures 1 Objectives Distinguish patients appropriate for continuous glucose monitoring and insulin
Updates in Diabetes Technology Jessica Kirk, MSN, RN, CPN, CDE Nurse Manager, Endo ECHO No disclosures Disclosures 1 Objectives Distinguish patients appropriate for continuous glucose monitoring and insulin
Diabetes Technology Update. Sarah Konigsberg, MD Diabetes & Endocrine Assoc. April 7, 2018
 Diabetes Technology Update Sarah Konigsberg, MD Diabetes & Endocrine Assoc. April 7, 2018 Disclosures None No future technologies are FDA approved Continuous Glucose Monitors Continuous Glucose Monitors
Diabetes Technology Update Sarah Konigsberg, MD Diabetes & Endocrine Assoc. April 7, 2018 Disclosures None No future technologies are FDA approved Continuous Glucose Monitors Continuous Glucose Monitors
INSPIRED BY GIVE HER MORE. The MiniMed 670G system is the world s first insulin delivery system that automatically adapts to your child s needs.
 INSPIRED BY GIVE HER MORE. The MiniMed 670G system is the world s first insulin delivery system that automatically adapts to your child s needs. * NOW APPROVED FOR AGES 7 AND UP. MORE TIME HERE TO USING
INSPIRED BY GIVE HER MORE. The MiniMed 670G system is the world s first insulin delivery system that automatically adapts to your child s needs. * NOW APPROVED FOR AGES 7 AND UP. MORE TIME HERE TO USING
Quick Reference Guide
 FLASH GLUCOSE MONITORING SYSTEM Quick Reference Guide FreeStyle LibreLink app A FreeStyle Libre product IMPORTANT USER INFORMATION Before you use your System, review all the product instructions and the
FLASH GLUCOSE MONITORING SYSTEM Quick Reference Guide FreeStyle LibreLink app A FreeStyle Libre product IMPORTANT USER INFORMATION Before you use your System, review all the product instructions and the
When Will CGM Replace SMBG? Roy W. Beck, MD, PhD. JAEB Center for Health Research Tampa, Florida
 When Will CGM Replace SMBG? Roy W. Beck, MD, PhD JAEB Center for Health Research Tampa, Florida Financial Disclosures Dr. Beck does not have any personal conflicts of interest His employer, the JAEB Center
When Will CGM Replace SMBG? Roy W. Beck, MD, PhD JAEB Center for Health Research Tampa, Florida Financial Disclosures Dr. Beck does not have any personal conflicts of interest His employer, the JAEB Center
Usefulness of Ambulatory Glucose Profile (AGP) in Diabetes Care
 C H A P T E R 41 Usefulness of Ambulatory Glucose Profile (AGP) in Diabetes Care K Chaithanya Murthy, B Ramya, E Vidya, RM Anjana, V Mohan ABSTRACT Over the past decades, several newer technologies have
C H A P T E R 41 Usefulness of Ambulatory Glucose Profile (AGP) in Diabetes Care K Chaithanya Murthy, B Ramya, E Vidya, RM Anjana, V Mohan ABSTRACT Over the past decades, several newer technologies have
DIABETES TECHNOLOGY: WHERE ARE WE NOW AND WHERE ARE WE GOING? Presented by: Tom Brobson
 DIABETES TECHNOLOGY: WHERE ARE WE NOW AND WHERE ARE WE GOING? Presented by: Tom Brobson March 3 rd, 2018 Who is this guy? Accelerating Progress 1 Oh that guy! Accelerating Progress 2 STATE OF T1D CARE
DIABETES TECHNOLOGY: WHERE ARE WE NOW AND WHERE ARE WE GOING? Presented by: Tom Brobson March 3 rd, 2018 Who is this guy? Accelerating Progress 1 Oh that guy! Accelerating Progress 2 STATE OF T1D CARE
First steps for success.
 First steps for success. Getting to know continuous glucose monitoring (CGM). The Animas Vibe System is approved for persons age 2 and older. Important Safety Information The Animas Vibe Insulin Pump and
First steps for success. Getting to know continuous glucose monitoring (CGM). The Animas Vibe System is approved for persons age 2 and older. Important Safety Information The Animas Vibe Insulin Pump and
Next steps for success.
 Next steps for success. More tips for using CGM* training course. The Animas Vibe System is approved for persons age 2 and older. *Continuous Glucose Monitoring Important Safety Information The Animas
Next steps for success. More tips for using CGM* training course. The Animas Vibe System is approved for persons age 2 and older. *Continuous Glucose Monitoring Important Safety Information The Animas
EVALUATION OF GLUCOSE MONITORING TECHNOLOGIES FOR COST EFFECTIVE AND QUALITY CONTROL/MANAGEMENT OF DIABETES
 EVALUATION OF GLUCOSE MONITORING TECHNOLOGIES FOR COST EFFECTIVE AND QUALITY CONTROL/MANAGEMENT OF DIABETES David P. Paul, III Monmouth University Stacy Ashworth, Leslie Salyers, Sarah Saldanha and Alberto
EVALUATION OF GLUCOSE MONITORING TECHNOLOGIES FOR COST EFFECTIVE AND QUALITY CONTROL/MANAGEMENT OF DIABETES David P. Paul, III Monmouth University Stacy Ashworth, Leslie Salyers, Sarah Saldanha and Alberto
MEDICAL POLICY Continuous Glucose Monitoring Systems and Insulin Pumps
 POLICY: PG0177 ORIGINAL EFFECTIVE: 12/01/08 LAST REVIEW: 05/24/18 MEDICAL POLICY Continuous Glucose Monitoring Systems and Insulin Pumps GUIDELINES This policy does not certify benefits or authorization
POLICY: PG0177 ORIGINAL EFFECTIVE: 12/01/08 LAST REVIEW: 05/24/18 MEDICAL POLICY Continuous Glucose Monitoring Systems and Insulin Pumps GUIDELINES This policy does not certify benefits or authorization
Biosensor and its electrochemical transducer
 YINAN TANG Background Biosensor and its electrochemical transducer Simple, inexpensive, accurate and sensitive platform Inherent miniaturization for both the detector and control instrumentation Application
YINAN TANG Background Biosensor and its electrochemical transducer Simple, inexpensive, accurate and sensitive platform Inherent miniaturization for both the detector and control instrumentation Application
Continuous Glucose Monitoring
 Continuous Glucose Monitoring What is Continuous Glucose Monitoring? Blood glucose meters measure glucose in your blood and glucose sensors measure glucose levels in the fluid around the cells They are
Continuous Glucose Monitoring What is Continuous Glucose Monitoring? Blood glucose meters measure glucose in your blood and glucose sensors measure glucose levels in the fluid around the cells They are
Continuous Glucose Monitoring: Changing Diabetes Behavior in Real Time and Retrospectively
 Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology Volume 2, Issue 3, May 2008 Diabetes Technology Society CONTROVERSIES in Continuous Glucose Monitoring Continuous Glucose Monitoring: Changing Diabetes Behavior
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology Volume 2, Issue 3, May 2008 Diabetes Technology Society CONTROVERSIES in Continuous Glucose Monitoring Continuous Glucose Monitoring: Changing Diabetes Behavior
FreeStyle Lite A Blood Glucose Meter That Requires No Coding
 Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology Volume 2, Issue 4, July 2008 Diabetes Technology Society SYMPOSIUM Shridhara, Ph.D. Abstract Background: Abbott Diabetes Care introduced the FreeStyle Lite blood
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology Volume 2, Issue 4, July 2008 Diabetes Technology Society SYMPOSIUM Shridhara, Ph.D. Abstract Background: Abbott Diabetes Care introduced the FreeStyle Lite blood
Report Reference Guide
 Report Reference Guide How to use this guide Each type of CareLink report and its components are described in the following sections. Report data used to generate the sample reports was from sample patient
Report Reference Guide How to use this guide Each type of CareLink report and its components are described in the following sections. Report data used to generate the sample reports was from sample patient
INSULIN INITIATION AND INTENSIFICATION WITH A FOCUS ON HYPOGLYCEMIA REDUCTION
 INSULIN INITIATION AND INTENSIFICATION WITH A FOCUS ON HYPOGLYCEMIA REDUCTION Jaiwant Rangi, MD, FACE Nov 10 th 2018 DISCLOSURES Speaker Novo Nordisk Sanofi-Aventis Boheringer Ingleheim Merck Abbvie Abbott
INSULIN INITIATION AND INTENSIFICATION WITH A FOCUS ON HYPOGLYCEMIA REDUCTION Jaiwant Rangi, MD, FACE Nov 10 th 2018 DISCLOSURES Speaker Novo Nordisk Sanofi-Aventis Boheringer Ingleheim Merck Abbvie Abbott
Does Technology helps adolescents with type 1 diabetes in fasting Ramadan?
 Does Technology helps adolescents with type 1 diabetes in fasting Ramadan? Abdulmoein Al-Agha, FRCPCH Professor of Paediatric Endocrinology, King Abdulaziz University Hospital, http://aagha.kau.edu.sa
Does Technology helps adolescents with type 1 diabetes in fasting Ramadan? Abdulmoein Al-Agha, FRCPCH Professor of Paediatric Endocrinology, King Abdulaziz University Hospital, http://aagha.kau.edu.sa
Advances Towards the Bionic Pancreas.
 Advances Towards the Bionic Pancreas. Ron Brazg MD, FACE Rainier Clinical Research Center Renton, WA DISCLOSURES Rainier Clinical Research Center is an independent research facility not directly affiliated
Advances Towards the Bionic Pancreas. Ron Brazg MD, FACE Rainier Clinical Research Center Renton, WA DISCLOSURES Rainier Clinical Research Center is an independent research facility not directly affiliated
CareLink. software REPORT REFERENCE GUIDE. Management Software for Diabetes
 CareLink Management Software for Diabetes software REPORT REFERENCE GUIDE How to use this guide Each type of CareLink report and its components are described in the following sections. Report data used
CareLink Management Software for Diabetes software REPORT REFERENCE GUIDE How to use this guide Each type of CareLink report and its components are described in the following sections. Report data used
CONTINUOUS OR INTERMITTENT GLUCOSE MONITORING IN INTERSTITIAL FLUID
 FLUID Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent
FLUID Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent
QUESTION 4. WHAT CLINICAL DATA ARE CURRENTLY AVAILABLE TO SUPPORT EXPANDED CGM COVERAGE BY PAYERS AS PERTAINS TO QUESTIONS 1 AND 3?
 500 1 QUESTION 4. WHAT CLINICAL DATA ARE CURRENTLY AVAILABLE TO SUPPORT EXPANDED CGM COVERAGE BY PAYERS AS PERTAINS TO QUESTIONS 1 AND 3? WHAT ADDITIONAL DATA ARE NEEDED? AACE/ACE CGM Consensus Conference:
500 1 QUESTION 4. WHAT CLINICAL DATA ARE CURRENTLY AVAILABLE TO SUPPORT EXPANDED CGM COVERAGE BY PAYERS AS PERTAINS TO QUESTIONS 1 AND 3? WHAT ADDITIONAL DATA ARE NEEDED? AACE/ACE CGM Consensus Conference:
Abbott FreeStyle Libre Pro System
 Professional CGM Abbott FreeStyle Libre Pro Reader Kit includes: Reader, USB cable, interactive tutorial on USB, and power adapter, user s manual, Quick Start Guide, Quick Reference Guide Kit includes:
Professional CGM Abbott FreeStyle Libre Pro Reader Kit includes: Reader, USB cable, interactive tutorial on USB, and power adapter, user s manual, Quick Start Guide, Quick Reference Guide Kit includes:
Abbott FreeStyle Libre Pro System
 , the Professional CGM Abbott FreeStyle Libre Pro Reader Kit includes: Reader, USB cable, interactive tutorial on USB, and power adapter, user s manual, Quick Start Guide, Quick Reference Guide Kit includes:
, the Professional CGM Abbott FreeStyle Libre Pro Reader Kit includes: Reader, USB cable, interactive tutorial on USB, and power adapter, user s manual, Quick Start Guide, Quick Reference Guide Kit includes:
Information Overload! CGM, Navigating for Success. Presented by: Kathi Milton RD, CDE and Amy Foreman RN, CDE
 Information Overload! CGM, Navigating for Success Presented by: Kathi Milton RD, CDE and Amy Foreman RN, CDE CGM-What is it? Continuous Glucose Monitor: a device that provides measurement of glucose data,
Information Overload! CGM, Navigating for Success Presented by: Kathi Milton RD, CDE and Amy Foreman RN, CDE CGM-What is it? Continuous Glucose Monitor: a device that provides measurement of glucose data,
REPORT INTERPRETATION
 REPORT INTERPRETATION: Interpreting ipro Professional Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Reports and Making Therapy Adjustments TARGET AUDIENCE The audience for this section is physicians, mid-level practitioners,
REPORT INTERPRETATION: Interpreting ipro Professional Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Reports and Making Therapy Adjustments TARGET AUDIENCE The audience for this section is physicians, mid-level practitioners,
GlucoMen LX PLUS blood glucose and blood ketone meter. Accuracy Evaluation to New ISO 15197:2013, with Technical and Specification Data
 GlucoMen LX PLUS: Accuracy Evaluations to ISO 15197:2013 with Technical and Specification Data GlucoMen LX PLUS blood glucose and blood ketone meter Accuracy Evaluation to New ISO 15197:2013, with Technical
GlucoMen LX PLUS: Accuracy Evaluations to ISO 15197:2013 with Technical and Specification Data GlucoMen LX PLUS blood glucose and blood ketone meter Accuracy Evaluation to New ISO 15197:2013, with Technical
Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems enable
 DIA-2014-0375-ver9-Wang_1P.3d 05/05/15 2:45pm Page 1 DIABETES TECHNOLOGY & THERAPEUTICS Volume 17, Number 8, 2015 ª Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. DOI: 10.1089/dia.2014.0375 DIA-2014-0375-ver9-Wang_1P Type: original-article
DIA-2014-0375-ver9-Wang_1P.3d 05/05/15 2:45pm Page 1 DIABETES TECHNOLOGY & THERAPEUTICS Volume 17, Number 8, 2015 ª Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. DOI: 10.1089/dia.2014.0375 DIA-2014-0375-ver9-Wang_1P Type: original-article
Advances in Diabetes Care Technologies
 1979 Advances in Diabetes Care Technologies 2015 Introduction Roughly 20% - 30% of patients with T1DM and fewer than 1% of insulin-treated patients with T2DM use an insulin pump In 2007, the US FDA estimated
1979 Advances in Diabetes Care Technologies 2015 Introduction Roughly 20% - 30% of patients with T1DM and fewer than 1% of insulin-treated patients with T2DM use an insulin pump In 2007, the US FDA estimated
MEDICAL POLICY Continuous Glucose Monitoring Systems and Insulin Pumps
 POLICY: PG0177 ORIGINAL EFFECTIVE: 12/01/08 LAST REVIEW: 02/13/18 MEDICAL POLICY Continuous Glucose Monitoring Systems and Insulin Pumps GUIDELINES This policy does not certify benefits or authorization
POLICY: PG0177 ORIGINAL EFFECTIVE: 12/01/08 LAST REVIEW: 02/13/18 MEDICAL POLICY Continuous Glucose Monitoring Systems and Insulin Pumps GUIDELINES This policy does not certify benefits or authorization
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM)
 Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Background Info A1c Average glucose levels over previous 2-3 months Currently remains gold standard for determining control Indicator of risk for development of complications
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Background Info A1c Average glucose levels over previous 2-3 months Currently remains gold standard for determining control Indicator of risk for development of complications
Report Reference Guide. THERAPY MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE FOR DIABETES CareLink Report Reference Guide 1
 Report Reference Guide THERAPY MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE FOR DIABETES CareLink Report Reference Guide 1 How to use this guide Each type of CareLink report and its components are described in the following sections.
Report Reference Guide THERAPY MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE FOR DIABETES CareLink Report Reference Guide 1 How to use this guide Each type of CareLink report and its components are described in the following sections.
Use of Continuous Glucose Monitoring in the Detection and Prevention of Hypoglycemia
 Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology Volume 1, Issue 1, January 2007 Diabetes Technology Society SYMPOSIUM Use of Continuous Glucose Monitoring in the Detection and Prevention of Hypoglycemia Howard
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology Volume 1, Issue 1, January 2007 Diabetes Technology Society SYMPOSIUM Use of Continuous Glucose Monitoring in the Detection and Prevention of Hypoglycemia Howard
Diabetes Management with Continuous Glucose Monitoring & Multiple Daily Injections. Aaron Michels MD
 Diabetes Management with Continuous Glucose Monitoring & Multiple Daily Injections Aaron Michels MD Outline SMBG & CGM by age group JDRF CGM Trial Sensor Augmented Insulin Pump Therapy for A1c Reduction
Diabetes Management with Continuous Glucose Monitoring & Multiple Daily Injections Aaron Michels MD Outline SMBG & CGM by age group JDRF CGM Trial Sensor Augmented Insulin Pump Therapy for A1c Reduction
The Realities of Technology in Type 1 Diabetes
 The Realities of Technology in Type 1 Diabetes May 6, 2017 Rosanna Fiallo-scharer, MD Margaret Frederick, RN Disclosures I have no conflicts of interest to disclose I will discuss some unapproved treatments
The Realities of Technology in Type 1 Diabetes May 6, 2017 Rosanna Fiallo-scharer, MD Margaret Frederick, RN Disclosures I have no conflicts of interest to disclose I will discuss some unapproved treatments
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM)
 Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Date of Origin: 02/2001 Last Review Date: 07/26/2017 Effective Date: 07/26/2017 Dates Reviewed: 04/2004, 04/2005, 03/2006, 11/2006, 12/2007, 03/2008, 09/2008, 04/2009,
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Date of Origin: 02/2001 Last Review Date: 07/26/2017 Effective Date: 07/26/2017 Dates Reviewed: 04/2004, 04/2005, 03/2006, 11/2006, 12/2007, 03/2008, 09/2008, 04/2009,
Current Glucometers. Junior s s Glucose Log. All have advantages and disadvantages Answer 2
 Diabetes Dilemmas: Using Technology To Solve Clinical Conundrums Stephen E. Gitelman, MD UCSF A teenager with type 1 diabetes for 5 years comes into your office for a follow- up visit. You want to review
Diabetes Dilemmas: Using Technology To Solve Clinical Conundrums Stephen E. Gitelman, MD UCSF A teenager with type 1 diabetes for 5 years comes into your office for a follow- up visit. You want to review
Incorporating CGM Into Clinical Decision Making. Etie Moghissi, MD, FACE Clinical Associate Professor, David Geffen School of Medicine UCLA
 Incorporating CGM Into Clinical Decision Making Etie Moghissi, MD, FACE Clinical Associate Professor, David Geffen School of Medicine UCLA 1 Limitations of Current Glucose Monitoring Methods A1c Standard
Incorporating CGM Into Clinical Decision Making Etie Moghissi, MD, FACE Clinical Associate Professor, David Geffen School of Medicine UCLA 1 Limitations of Current Glucose Monitoring Methods A1c Standard
Approved by: Integrated Health Quality Management Subcommittee Effective Date: Department of Origin: Integrated Healthcare Services.
 Reference #: MC/L008 Page: 1 of 8 PRODUCT APPLICATION: PreferredOne Community Health Plan (PCHP) PreferredOne Administrative Services, Inc. (PAS) ERISA PreferredOne Administrative Services, Inc. (PAS)
Reference #: MC/L008 Page: 1 of 8 PRODUCT APPLICATION: PreferredOne Community Health Plan (PCHP) PreferredOne Administrative Services, Inc. (PAS) ERISA PreferredOne Administrative Services, Inc. (PAS)
Early Patient and Clinician Experiences with Continuous Glucose Monitoring
 Feature Article / Early Experiences with CGM Early Patient and Clinician Experiences with Continuous Glucose Monitoring David K. Bloomgarden, MD, FACE; Janine Freeman, RD, LD, CDE; and Elizabeth DeRobertis,
Feature Article / Early Experiences with CGM Early Patient and Clinician Experiences with Continuous Glucose Monitoring David K. Bloomgarden, MD, FACE; Janine Freeman, RD, LD, CDE; and Elizabeth DeRobertis,
MEDICAL POLICY Continuous Glucose Monitoring Systems and Insulin Pumps
 POLICY: PG0177 ORIGINAL EFFECTIVE: 12/01/08 LAST REVIEW: 07/10/18 MEDICAL POLICY Continuous Glucose Monitoring Systems and Insulin Pumps GUIDELINES This policy does not certify benefits or authorization
POLICY: PG0177 ORIGINAL EFFECTIVE: 12/01/08 LAST REVIEW: 07/10/18 MEDICAL POLICY Continuous Glucose Monitoring Systems and Insulin Pumps GUIDELINES This policy does not certify benefits or authorization
Objectives. Glucose Monitoring Today. Tracking Glucose ISO Standards. Continuous Glucose Monitoring & Diabetes Management 3/7/2015
 Objectives Continuous Glucose Monitoring & Diabetes Management Tomas C. Walker, DNP, APRN, CDE Director, Clinical Projects Dexcom, Inc. San Diego, CA 1. Review current limitations of SMBG 2. Understand
Objectives Continuous Glucose Monitoring & Diabetes Management Tomas C. Walker, DNP, APRN, CDE Director, Clinical Projects Dexcom, Inc. San Diego, CA 1. Review current limitations of SMBG 2. Understand
Noninvasive Glucose Monitors to 2022
 Noninvasive Glucose Monitors to 2022 Devices, Technologies, Players and Prospects Report Prospectus Greystone Research associates N o n i n v a s i v e G l u c o s e M o n i t o r s t o 2 0 2 2 Greystone
Noninvasive Glucose Monitors to 2022 Devices, Technologies, Players and Prospects Report Prospectus Greystone Research associates N o n i n v a s i v e G l u c o s e M o n i t o r s t o 2 0 2 2 Greystone
Noninvasive Glucose Monitors Devices, Technologies, Players and Prospects
 Report Prospectus Noninvasive Glucose Monitors Devices, Technologies, Players and Prospects 1 Improving Diabetes Management For diabetes patients, glucose monitoring is a way of life, a several-times-per-day
Report Prospectus Noninvasive Glucose Monitors Devices, Technologies, Players and Prospects 1 Improving Diabetes Management For diabetes patients, glucose monitoring is a way of life, a several-times-per-day
Understanding the CareLinkTM Sensor Meter Overview Report: Page 1
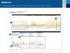 Understanding the CareLinkTM Sensor Meter Overview Report: Page 1 Sensor & Meter Overview (1 of 3) 4-Hour Glucose Sensor Overlay - Readings & Averages (mg/dl) 1 Glucose Sensor Overlay Bedtime to Wake-Up
Understanding the CareLinkTM Sensor Meter Overview Report: Page 1 Sensor & Meter Overview (1 of 3) 4-Hour Glucose Sensor Overlay - Readings & Averages (mg/dl) 1 Glucose Sensor Overlay Bedtime to Wake-Up
Receiver and App Setup
 Continuous Glucose Monitoring System Receiver and App Setup For training videos visit dexcom.com/medicare Overview Your Dexcom G5 Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) System is made up of: Transmitter (Sensor
Continuous Glucose Monitoring System Receiver and App Setup For training videos visit dexcom.com/medicare Overview Your Dexcom G5 Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) System is made up of: Transmitter (Sensor
Continuous Glucose Monitoring System. Receiver Setup
 Continuous Glucose Monitoring System Receiver Setup Overview Your Dexcom G5 Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) System is made up of: Receiver What do I do with it? Review your readings. Set and receive
Continuous Glucose Monitoring System Receiver Setup Overview Your Dexcom G5 Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) System is made up of: Receiver What do I do with it? Review your readings. Set and receive
Advances in Diabetes Care Technologies
 1979 Advances in Diabetes Care Technologies 2015 Introduction Insulin pump use: ~ 20% - 30% of patients with T1DM < 1% of insulin-treated patients with T2DM 2007 FDA estimates ~375,000 insulin pumps for
1979 Advances in Diabetes Care Technologies 2015 Introduction Insulin pump use: ~ 20% - 30% of patients with T1DM < 1% of insulin-treated patients with T2DM 2007 FDA estimates ~375,000 insulin pumps for
POPULATION TRACKER - DREAMED USER GUIDE
 POPULATION TRACKER - DREAMED USER GUIDE November 2018 IFU-0011 05 TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION... 1 Product Description... 1 Glooko Intended Use... 1 DreaMed Intended Use...
POPULATION TRACKER - DREAMED USER GUIDE November 2018 IFU-0011 05 TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION... 1 Product Description... 1 Glooko Intended Use... 1 DreaMed Intended Use...
Quick Reference Guide. Sensor Smart Transmitter Mobile App
 Quick Reference Guide Sensor Smart Transmitter Mobile App Refer to the Eversense CGM User Guide for more detailed information. For a Spanish version of the User Guide and Quick Reference Guide, please
Quick Reference Guide Sensor Smart Transmitter Mobile App Refer to the Eversense CGM User Guide for more detailed information. For a Spanish version of the User Guide and Quick Reference Guide, please
Clinical Value and Evidence of Continuous Glucose Monitoring
 Clinical Value and Evidence of Continuous Glucose Monitoring 9402313-012 Objective To review the clinical value and the recent clinical evidence for Professional and Personal CGM Key Points CGM reveals
Clinical Value and Evidence of Continuous Glucose Monitoring 9402313-012 Objective To review the clinical value and the recent clinical evidence for Professional and Personal CGM Key Points CGM reveals
WHAT CAN I DO TO REDUCE MY RISK OF DEVELOPING THE COMPLICATIONS OF TYPE 1 DIABETES?
 Christian In better control with his pump since 2012 WHAT CAN I DO TO REDUCE MY RISK OF DEVELOPING THE COMPLICATIONS OF TYPE 1 DIABETES? Many people with Type 1 diabetes worry about potential long-term
Christian In better control with his pump since 2012 WHAT CAN I DO TO REDUCE MY RISK OF DEVELOPING THE COMPLICATIONS OF TYPE 1 DIABETES? Many people with Type 1 diabetes worry about potential long-term
Diabetes Devices Workshop Angela Aldrich, PharmD, PhC April Mott, PharmD, PhC, BCPS Presbyterian Medical Group 28 January 2018
 Diabetes Devices Workshop Angela Aldrich, PharmD, PhC April Mott, PharmD, PhC, BCPS Presbyterian Medical Group 28 January 2018 Pumps & Sensors & Meters, Oh My! A Tale of Two Meters Technology for glucometers
Diabetes Devices Workshop Angela Aldrich, PharmD, PhC April Mott, PharmD, PhC, BCPS Presbyterian Medical Group 28 January 2018 Pumps & Sensors & Meters, Oh My! A Tale of Two Meters Technology for glucometers
Comparing the use of SMBG vs. CGM data to Optimize Glucose Control in T2DM
 Comparing the use of SMBG vs. CGM data to Optimize Glucose Control in T2DM For the first time using CGM to assess glucose control achieved in both groups Richard M. Bergenstal, MD International Diabetes
Comparing the use of SMBG vs. CGM data to Optimize Glucose Control in T2DM For the first time using CGM to assess glucose control achieved in both groups Richard M. Bergenstal, MD International Diabetes
CGM Therapy Expert Program
 CGM Therapy Expert Program PROGRAM OVERVIEW The Medtronic-Bayer CGM Therapy Expert Program is designed to update healthcare professionals on the most current scientific and technical information regarding
CGM Therapy Expert Program PROGRAM OVERVIEW The Medtronic-Bayer CGM Therapy Expert Program is designed to update healthcare professionals on the most current scientific and technical information regarding
OneTouch Reveal Web Application. User Manual for Healthcare Professionals Instructions for Use
 OneTouch Reveal Web Application User Manual for Healthcare Professionals Instructions for Use Contents 2 Contents Chapter 1: Introduction...4 Product Overview...4 Intended Use...4 System Requirements...
OneTouch Reveal Web Application User Manual for Healthcare Professionals Instructions for Use Contents 2 Contents Chapter 1: Introduction...4 Product Overview...4 Intended Use...4 System Requirements...
Non-Invasive Glucose Monitoring. Kevin Walls April 12, :30 PM-7:30 PM.
 Non-Invasive Glucose Monitoring Kevin Walls April 12, 2018 6:30 PM-7:30 PM. Technology is evolving Technology is evolving at such a rapid rate it s hard to keep up. Imagine living a healthier life without
Non-Invasive Glucose Monitoring Kevin Walls April 12, 2018 6:30 PM-7:30 PM. Technology is evolving Technology is evolving at such a rapid rate it s hard to keep up. Imagine living a healthier life without
The Growing Future of Diabetes: Insulin Pump Therapy in Type 1 and 2 Diabetes
 The Growing Future of Diabetes: Insulin Pump Therapy in Type 1 and 2 Diabetes Sarah Dombrowski, PharmD, BCACP Pennsylvania Pharmacists Association 10/20/18 1 Objectives At the completion of this activity,
The Growing Future of Diabetes: Insulin Pump Therapy in Type 1 and 2 Diabetes Sarah Dombrowski, PharmD, BCACP Pennsylvania Pharmacists Association 10/20/18 1 Objectives At the completion of this activity,
People with type 1 diabetes and Do It Yourself (DIY) technology solutions ABOUT THIS POSITION STATEMENT
 Position Statement People with type 1 diabetes and Do It Yourself (DIY) technology solutions ABOUT THIS POSITION STATEMENT Diabetes Australia believes that people with diabetes should have choice and access
Position Statement People with type 1 diabetes and Do It Yourself (DIY) technology solutions ABOUT THIS POSITION STATEMENT Diabetes Australia believes that people with diabetes should have choice and access
THERAPY MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE FOR DIABETES
 THERAPY MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE FOR DIABETES Report Report Interpretation Reference Guide Guide 2009 Medtronic MiniMed. All rights reserved. 6025274-012_a CareLink Pro Report Reference Guide 0 p.2 Adherence
THERAPY MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE FOR DIABETES Report Report Interpretation Reference Guide Guide 2009 Medtronic MiniMed. All rights reserved. 6025274-012_a CareLink Pro Report Reference Guide 0 p.2 Adherence
Seven Simple Steps to Start. Your Dexcom G4 PLATINUM System
 Seven Simple Steps to Start Your Dexcom G4 PLATINUM System Receiver Sensor Applicator Transmitter Sensor Remove transmitter from tray and wait 10 minutes Do Not Throw Away Battery life ~ 6 months Charging
Seven Simple Steps to Start Your Dexcom G4 PLATINUM System Receiver Sensor Applicator Transmitter Sensor Remove transmitter from tray and wait 10 minutes Do Not Throw Away Battery life ~ 6 months Charging
- Non-invasive - Mobile; collect data continuously at anywhere and any time - Used outside clinical setting
 Background Advances in medical technologies are increasing remote patient monitoring programs. These technologies enable healthcare professionals to monitor the health status of patients outside clinical
Background Advances in medical technologies are increasing remote patient monitoring programs. These technologies enable healthcare professionals to monitor the health status of patients outside clinical
Animas Vibe System World-class insulin pumping meets world-class CGM*
 Animas Vibe System World-class insulin pumping meets world-class CGM* Fully integrated with Dexcom G4 PLATINUM CGM* *Continuous glucose monitoring. My Animas pump has really put me in the driver s seat
Animas Vibe System World-class insulin pumping meets world-class CGM* Fully integrated with Dexcom G4 PLATINUM CGM* *Continuous glucose monitoring. My Animas pump has really put me in the driver s seat
Understanding the CareLink TM Therapy Management Dashboard Report
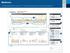 3 2 1 5 6 7 4 1 This is a great place to start recognizing trends. In this example you may see plenty of events that result in a low glucose trend. A low glucose is identified as a value less than 70mg/dL.
3 2 1 5 6 7 4 1 This is a great place to start recognizing trends. In this example you may see plenty of events that result in a low glucose trend. A low glucose is identified as a value less than 70mg/dL.
Since the discovery of insulin, the management of type 1 diabetes
 SPECIAL Clinical FEATURE Review Realistic Expectations and Practical Use of Continuous Glucose Monitoring for the Endocrinologist Irl B. Hirsch University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, Washington
SPECIAL Clinical FEATURE Review Realistic Expectations and Practical Use of Continuous Glucose Monitoring for the Endocrinologist Irl B. Hirsch University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, Washington
GLOOKO DREAMED FOR ANDROID USER GUIDE
 GLOOKO DREAMED FOR ANDROID USER GUIDE November 2018 IFU-0017 02 TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION... 2 Product Description... 2 Glooko Intended Use... 2 Dreamed Intended Use... 2
GLOOKO DREAMED FOR ANDROID USER GUIDE November 2018 IFU-0017 02 TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION... 2 Product Description... 2 Glooko Intended Use... 2 Dreamed Intended Use... 2
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM)/Real-Time Flash Glucose Scanning (FGS) Training for Healthcare Professionals and Patients
 ssociation of Children s Diabetes Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM)/Real-Time Flash Glucose Scanning (FGS) Training for Healthcare Professionals and Patients 1 ssociation of Children s Diabetes Contents
ssociation of Children s Diabetes Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM)/Real-Time Flash Glucose Scanning (FGS) Training for Healthcare Professionals and Patients 1 ssociation of Children s Diabetes Contents
Diabetes and Technology. Saturday, September 9, 2017 Aimee G sell, APRN, ANP-C, CDE
 Diabetes and Technology Saturday, September 9, 2017 Aimee G sell, APRN, ANP-C, CDE Disclosure Speaker s Bureau: Janssan Pharmaceuticals Current Technology V-Go by Valeritas Continuous Sensors (personal
Diabetes and Technology Saturday, September 9, 2017 Aimee G sell, APRN, ANP-C, CDE Disclosure Speaker s Bureau: Janssan Pharmaceuticals Current Technology V-Go by Valeritas Continuous Sensors (personal
Case Study. Patient Profile. Baseline Report - Daily Patterns. Insights
 Case Study Patient Profile Sex/Age: Female, 48 years old Disease diagnosis: Type 2 for past 13 years, coronary artery disease for 3 years, complains of severe tiredness HbA1c: 9.0% Diabetes medication
Case Study Patient Profile Sex/Age: Female, 48 years old Disease diagnosis: Type 2 for past 13 years, coronary artery disease for 3 years, complains of severe tiredness HbA1c: 9.0% Diabetes medication
Bern Harrison, B.A., Cheryl Leazenby, B.S., and Solveig Halldorsdottir, Ph.D.
 Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology Volume 5, Issue 4, July 2011 Diabetes Technology Society TECHNOLOGY REPORTS Accuracy of the CONTOUR Blood Glucose Monitoring System Bern, B.A., Cheryl Leazenby,
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology Volume 5, Issue 4, July 2011 Diabetes Technology Society TECHNOLOGY REPORTS Accuracy of the CONTOUR Blood Glucose Monitoring System Bern, B.A., Cheryl Leazenby,
Interpretation of Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Data
 Interpretation of Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Data Sherri Horvat, BSN, RN, CDE Blood Glucose Manager, Animas Corporation A Johnson & Johnson Diabetes Care Company Overview of CGM Continuous glucose
Interpretation of Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Data Sherri Horvat, BSN, RN, CDE Blood Glucose Manager, Animas Corporation A Johnson & Johnson Diabetes Care Company Overview of CGM Continuous glucose
Diabetes through my eyes. Rick Mauseth, M.D. W.A.D.E. April 2013
 Diabetes through my eyes Rick Mauseth, M.D. W.A.D.E. April 2013 Ant hills Total Available Glucose utilized Two drops of urine in test tube Add 10 drops of water Added tablet Foamed and got hot Compared
Diabetes through my eyes Rick Mauseth, M.D. W.A.D.E. April 2013 Ant hills Total Available Glucose utilized Two drops of urine in test tube Add 10 drops of water Added tablet Foamed and got hot Compared
Welcome to CareLink Pro
 Reference Guide Welcome to CareLink Pro This guide was developed to serve as a reference for obtaining patient data and reviewing CareLink Pro reports. Getting Started with CareLink Pro Adding New Patients
Reference Guide Welcome to CareLink Pro This guide was developed to serve as a reference for obtaining patient data and reviewing CareLink Pro reports. Getting Started with CareLink Pro Adding New Patients
THERAPY MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE FOR DIABETES
 THERAPY MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE FOR DIABETES Report Report Interpretation Reference Guide Guide 2007 Medtronic MiniMed. All rights reserved. 6025274-0U2 120707 CareLink Pro Report Reference Guide 0 p.2 Sensor
THERAPY MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE FOR DIABETES Report Report Interpretation Reference Guide Guide 2007 Medtronic MiniMed. All rights reserved. 6025274-0U2 120707 CareLink Pro Report Reference Guide 0 p.2 Sensor
Glucometers Gastrostomy Tubes Nasogastric Tubes Insulin pumps Continuous Glucose monitoring system Closed Loop Smart phones/tablets
 Devices Glucometers Gastrostomy Tubes Nasogastric Tubes Insulin pumps Continuous Glucose monitoring system Closed Loop Smart phones/tablets Accuracy Glucometers The ISO (International Organization for
Devices Glucometers Gastrostomy Tubes Nasogastric Tubes Insulin pumps Continuous Glucose monitoring system Closed Loop Smart phones/tablets Accuracy Glucometers The ISO (International Organization for
Continuous or Intermittent Monitoring of Glucose in Interstitial Fluid. Original Policy Date
 MP 1.01.15 Continuous or Intermittent Monitoring of Glucose in Interstitial Fluid Medical Policy Section Durable Medical Equipment Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed
MP 1.01.15 Continuous or Intermittent Monitoring of Glucose in Interstitial Fluid Medical Policy Section Durable Medical Equipment Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed
Diabetes Technology Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin Infusion Therapy And Continuous Glucose Monitoring In Adults: An Endocrine Society Clinical
 Diabetes Technology Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin Infusion Therapy And Continuous Glucose Monitoring In Adults: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline Task Force Members Anne Peters, MD (Chair)
Diabetes Technology Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin Infusion Therapy And Continuous Glucose Monitoring In Adults: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline Task Force Members Anne Peters, MD (Chair)
NDSS Helpline
 Continuous GLUCOSE MONITORING A guide to using CGM for children and young people with type 1 diabetes NDSS Helpline 1300 136 588 ndss.com.au The National Diabetes Services Scheme is an initiative of the
Continuous GLUCOSE MONITORING A guide to using CGM for children and young people with type 1 diabetes NDSS Helpline 1300 136 588 ndss.com.au The National Diabetes Services Scheme is an initiative of the
Pumps & Sensors made easy. OPADA ALZOHAILI MD FACE Endocrinology Assistant Professor Wayne State University
 Pumps & Sensors made easy OPADA ALZOHAILI MD FACE Endocrinology Assistant Professor Wayne State University DeFronzo RA. Diabetes. 2009;58:773-795. Ominous Octet Relationship of b-cell Dysfunction and Development
Pumps & Sensors made easy OPADA ALZOHAILI MD FACE Endocrinology Assistant Professor Wayne State University DeFronzo RA. Diabetes. 2009;58:773-795. Ominous Octet Relationship of b-cell Dysfunction and Development
