ANTI-DIABETIC EFFECT OF THUNBERGIA LAURIFOLIA LINN. AQUEOUS EXTRACT
|
|
|
- Darleen Washington
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ANTI-DIABETIC EFFECT OF THUNBERGIA LAURIFOLIA LINN. AQUEOUS EXTRACT S Aritajat, S Wutteerapol and K Saenphet Department of Biology, Faculty of Science, Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai, Thailand Abstract. Several kinds of medicinal plants have been used to treat diabetes mellitus. In the present study, Thunbergia laurifolia Linn. (purple flower strain) were tested for hypoglycemic activity in rats. The effects on the reproductive system and the histology of the pancreas were also investigated. The hypoglycemic properties of the aqueous extract from the leaves (6 mg/ml/day) were evaluated in normoglycemic and alloxan-induced diabetic rats. The results showed that high blood glucose levels of diabetic rats were associated with severe destruction of β-cells (insulin-secreting cells) in the islet of Langerhans. The 15-day-treatment of T. laurifolia extract decreased levels of blood glucose in diabetic rats. The recovery of some β-cells was found in diabetic rats treated with the extract, although not completely normal. Whether T. laurifolia leaf contains insulin-like substance(s) which directly act as hypoglycemic agents, or contains substances that induce the regenerative process of β-cells remains to be further investigated. Alteration of the reproductive system was also observed in diabetic rats, but it was not improved by treatment with T. laurifolia extract. INTRODUCTION Diabetes mellitus is generally acknowledged to be due to insulin deficiency (Type I) which results from pathologic changes in pancreatic β-cells, or due to insulin insensitivity (Type II). Elevation of glucose blood level and a greatly increased risk of reproductive malfunction are common symptoms in diabetic patients (Jiang, 1996). At present, a large number of Thai people is affected by diabetes mellitus. Since the cost of imported anti-diabetic drugs is relatively high, traditional herbal medicine has become an alternative, affordable choice for diabetes treatment. Many plant species have been recommended for curing diabetes and some of them have proven hypoglycemic activity, for instance; Enicostemma littorale Blume (Maroo et al, 22), Gymnema inodorum, Stevia rebaudiana and Tinospora crispa, (Saenphet et al, 22; Pongchaidecha et al, 2; Anulukanapakorn et al, 1999). In Thailand, various kinds of medicinal plants have been used widely, as recommended by traditional physicians. Nevertheless, most plants have been used without scientific evidence to support their safety and effectiveness. The use of medicinal plants for diabetes treatment has also been popular among Thai people. Due to the high cost of synthetic drugs for curing diabetes, the attempt to develop Thai medicinal plants into modern herbal products with reliable quality and efficacy is of interest. Correspondence: S Aritajat, Department of Biology, Faculty of Science, Chiang Mai University, Chaing Mai 52, Thailand. salkaats@chiangmai.ac.th Thunbergia laurifolia Linn. has also been recommended by Thai traditional healers for treating diabetes. It is a climbing plant with smooth opposed leaves along the stem. The leaves are 8-1 cm long and 4-5 cm broad, broad-based, narrowing to a pointed tip, usually with scalloped lobes towards the base. The purple flowers are trumpet-shaped and produced during November-January. The seed pod is cone-shaped, 1 cm long, with a round base. In Thailand, it is called Rang Juad, Yaw Kaew, Kob Sha Nang, Gum Lung Chang Puak, or Krua Nan Nae in the North. Generally, this plant could be used for various purposes, including anti-toxicity, antiinflammatory, and in the treatment of pneumonia (Utogapachn, 1976). According to Thai traditional medicine, a mixture of the root or leaf of T. laurifolia with water rinsed from rice can be effectively used as a detoxifying agent. The antidotal activity of T. laurifolia against insecticides has been confirmed by scientific research (Tejasen and Thongthapp, 198). Nevertheless, reports of its anti-diabetic activity are still insufficient. Due to its popular use as a detoxifying and antidiabetic herb, T. laurifolia was selected in the present study for investigation of its hypoglycemic effect. A single dose of aqueous extract from dried leaves was administered to alloxan-induced diabetic rats. At the end of the treatment period, the levels of blood glucose and reproductive alteration of the rats were examined. The results of this primary research would provide valuable information for intensive studies of the effective concentration of the extract and the toxicity of this plant, to develop effective natural products for treating diabetes. Vol 35 (Suppl 2) 24 53
2 SOUTHEAST ASIAN J TROP MED PUBLIC HEALTH MATERIALS AND METHODS Plant materials The leaves of T. laurifolia were collected, washed, and sliced. The slices were dried at 3-4 C for 2 hours. The extract, at a concentration of 6 mg/ml, was prepared by extracting a 6-g-portion of the slices in a 1 liter beaker containing 1 ml of distilled water. After extraction at 3-4 C for 2 hours, the filtrate of 6 mg/ml extract was obtained. Animal preparation Male Wistar rats (Rattus norvegicus) weighing between 1-15 g were purchased from the National Laboratory Animal Center, Salaya, Nakhon Pathom, Thailand. They were allowed to acclimate in the departmental animal facility for at least one week prior to the day of the experiment. They had access to water and a standard pellet diet (C.P. No.82). The study room was maintained at approximately 25 ± 2 C. The photoperiod was 12-hour light and dark. Diabetes was induced by intraperitoneal injection of alloxan (4 mg/ml) once daily, for 2 days. Seven days post-injection, blood glucose concentrations were assayed by enzymatic (glucose oxidase) determination using a commercial test kit (Sigma, No. 51). Rats with blood glucose concentrations of 25 mg/ml or higher were counted as diabetic rats. Experimental design Rats were randomized into 4 groups (1 each); 1) normal rats that received distilled water 1 ml/day, 2) normal rats that received 6 mg/ ml/day of T. laurifolia extract, 3) diabetic rats that received distilled water 1 ml/day, 4) diabetic rats that received 6 mg/ ml/day of T. laurifolia extract. They were treated for 15 days. At the end of the treatment period, the rats were sacrificed to measure blood glucose, the weights of the testes and seminal vesicle, and the density of the sperm in the epididymis. The histology of the pancreas and testes was also investigated. Histology Tissue sections (5 µm) of pancreas and testes were routinely processed for paraffin-embedding. The sections of testes were stained with hematoxylin, while those of the pancreas were stained by Gomori method (Grimstone and Skaer, 1972). Morphological examination was conducted under a light microscope. Pancreatic β-cells were stained light blue, while α-cells were stained red. Statistical methods Means and standard deviations were calculated. The significant difference was analyzed by Student s t -test. RESULTS Blood glucose levels and histology of pancreas As shown in Table 1, the blood glucose levels of the control group of normoglycemic rats were relatively low ( mg/1ml.). There was a trend of decreased blood glucose levels in the normoglycemic rats that received T. laurifolia extract (6 mg/ml/day) for 15 days, although significant differences were not found between pre- and posttreatment periods, or between groups (Table 1, Fig 1). The blood glucose levels of the diabetic rats were markedly higher than the normoglycemic rats. The diabetic rats that had received T. laurifolia extract had significantly lower blood glucose levels compared with those that received distilled water. Nevertheless, the blood glucose levels of this group were not as low as those of the normoglycemic rats (Table 1, Fig 1). Histological study of pancreas revealed that endocrine tissues in both groups of normoglycemic rats formed the islets of Langerhans, which were scattered throughout the pancreatic tissues. They accounted for about 1% of all pancreatic tissues. β-cells (insulinsecreting cells) were found in the central region of the islets, while α cells (glucagon-secreting cells) were found at the peripheral region (Fig 2 A and B). Severe destruction of β-cells was found in the diabetic rats. Only a small area of islets of Langerhans were present and both β- and α cells could rarely be seen. Pyknotic nuclei were detected in some β-cells (Fig 2C). The islets of Langerhans of the diabetic rats treated with T. laurifolia extract were larger than the untreated group and more β-cells were also found (Fig 2 D). The numbers of islets of Langerhans in the normoglycemic groups were, however, higher than those of treated and untreated diabetic groups. Reproductive system Significant differences in testicular weights were not found between groups (Table 1, Fig 3). Nevertheless, the diabetic rats in both groups showed a significantly lower weight of seminal vesicle and lower density of sperm compared with the rats in the normoglycemic groups. Treatment of the diabetic rats with T. laurifolia extract did not give better results for sperm density or weight of seminal vesicle than the untreated diabetic rats (Table 1, Fig 4 and 5). Testicular morphology, including germ cells of normal control rats, were practically normal (Fig 6A). In diabetic rats, most seminiferous tubules showed a loose arrangement due to reduction in diameter and 54 Vol 35 (Suppl 2) 24
3 ANTI-DIABETIC EFFECT OF T. LAURIFOLIA Table 1 Effect of aqueous extract of Thunbergia laurifolia Linn. on blood glucose levels and reproductive systems of diabetic rats. Group Blood glucose Blood glucose Weight of Weight of Sperm density level prior to level after testes seminal vesicle treatment treatment (mg/1 ml) (mg/1 ml) (mg/g BW) (mg/g BW) ( 1 5 cells/ml) Normal control ± 1.78 a 6.3 ± a ± 1.23 a 2. ±.48 a 39.7 ± 3.46 a rats (1 ml / day distilled water) Normal rats ±67.84 a 92.8 ± a ± 5.4 a 1.67 ±.72 a ± 8.74 b (6 mg/ml/day T. laurifolia extract) Diabetic rats 1,16.83 ± b ± b ± 4.4 a.64 ±.3 b 1.59 ± 7.68 c (1 ml/ day distilled water) Diabetic rats 1, ± b ± b 16.7 ± 4.4 a.68 ±.35 b 5.37 ± 3.81 c (6 mg/ml/day T. laurifolia extract) Results are expressed as means ± SD; a, b, c indicate significant differences between groups (p <.1) 2, Blood glucose (mg/1 ml blood) 1,8 1,6 1,4 1,2 1, Before treatment After treatment 2 Fig 1- Effect of aqueous extract of Thunbergia laurifolia Linn. on blood glucose levels of normal and diabetic rats (means ± SD): TL = Thunbergia laurifolia Linn. extract. atrophy of the tubules (Fig 6B). Spermatogenesis was noticeably disturbed. All kinds of germ cells were markedly degenerated and vacuolization of some germ cells was observed. Sertoli and Leydig cells also showed degeneration. The lumen of some tubules contained sloughed debris (Fig 6B). The alteration of testicular morphology was not improved by treatment with T. laurifolia extract. The histological aspects of this group were similar to those of untreated diabetic rats (Fig 6C). Vol 35 (Suppl 2) 24 55
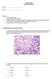
4 SOUTHEAST ASIAN J TROP MED PUBLIC HEALTH Fig 2- The pancreatic tissue of rat:(x225): A. untreated normoglycemic group; B. normo-glycemic group treated with T. laurifolia Linn. extract. Notice the normal size of islet of Langerhans (I) in both groups; C. untreated diabetic group showing degeneration of the islet of Langerhans; D. diabetic group treated with T. laurifolia Linn. extract. Notice the recovery of islet of Langerhans. DISCUSSION The decrease in the blood glucose levels of the diabetic rats treated with T. laurifolia extract was significantly higher (p<.1) than the other groups (Table 1). This clearly indicated the hypoglycemic activity of this plant. This result was similar to reports of some medicinal plants that have proven effect in lowering blood glucose, for instance, chloroform extract of garlic (Tewit et al, 1996), aqueous extract of Gymnema inodorum, Stevia rebaudiana, and Tinospora crispa, (Anulukanapakorn, 1999; Pongchaidecha et al, 2; Saenphet et al, 22). Extracts from the root of Helicteres isora were also found to decrease the levels of glucose, triglycerides, and insulin in mice (Chakrabarti et al, 22). It was noted that the destruction accounting for 9% of insulin-secreting β-cells of the islets of Langerhans was caused by alloxan; hence, high blood glucose levels were detected. When compared with the untreated diabetic rats, the higher numbers of islets of Langerhans found in the diabetic rats treated with extract of T. laurifolia were associated with lower levels of blood glucose. The extract might aid in the recovery of β-cells to secrete insulin; the blood glucose level, therefore, was lower after treatment. Nevertheless, the recovery of β-cells was marginally observed. High levels of serum insulin and low levels of blood glucose were reported in the diabetic rats that were trained to exercise (Laileard et al, 1996). The authors suggest that exercise could induce the recovery of β-cells in diabetic rats. The recovery of β-cells found in this study (Fig 2 C, D), which was associated with low blood glucose levels was likely induced by the extract of T. laurifolia. The blood glucose levels of the diabetic rats treated with the extract of T. laurifolia, however, was not as low as that of the normoglycemic 56 Vol 35 (Suppl 2) 24
5 ANTI-DIABETIC EFFECT OF T. LAURIFOLIA Testicular weight (mg/g BW) Weight of seminal vesicle (mg/g BW) Sperm density (x1 5 cells/ml) Fig 3- Effect of aqueous extract of Thunbergia laurifolia Linn. on testicular weights of normal and diabetic rats (means ± SD): TL = Thunbergia laurifolia Linn. extract ** ** Fig 4- Effect of aqueous extract of Thunbergia laurifolia Linn. on the weights of seminal vesicles of normal and diabetic rats (means ± SD): TL = Thunbergia laurifolia Linn. extract ** Fig 5- Effect of aqueous extract of Thunbergia laurifolia Linn. on epididymal sperm density of normal and diabetic rats (means ± SD): TL = Thunbergia laurifolia Linn. extract. rats. This might be due to the short period of treatment (15 days). Further study with longer periods of treatment might give better results in lowering blood glucose levels. Whether T. laurifolia leaf contains insulin-like substance(s), which act directly as hypoglycemic agents or contains substances which ** ** could induce the regenerative process of β-cells remains to be further investigated. Our results suggest T. laurifolia as a new plant for the treatment of diabetes. It would be interesting and useful to study in detail its hypoglycemic mechanism. The alterations in the reproductive organs of the diabetic rats were not surprising. Most diabetic patients report disturbances in sexual function (Jiang, 1996). Decreased levels of serum lutinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) were detected in the diabetic rats (Feng et al, 21). Since testosterone synthesis is regulated by gonadotropins (Shetty et al, 1996), the regression of Ledig cells (testosteronesecreting cells) found in this study was likely due to the deprivation of those gonadotropins. The high blood sugar levels might cause the abnormal homeostatic regulatory systems of the diabetic rats, and the anterior pituitary gland, which produces gonadotropins, might also be a sensitive target. As a consequence of malfunction of the pituitary-gonadal axis, the destruction of germ cells, a decrease in size of the seminiferous tubules and of the seminal vesicles were evident. The lack of alteration in testicular weight, however, is difficult to explain in view of the histologic finding. Since testes are composed of many kinds of tissue, the destruction of some seminiferous tubules might not affect the total weight of the testes. Although T. laurifolia extract appeared to have hypoglycemic effect, the function of the reproductive system was not reversible when the extract was given to diabetic rats for 15 days. Appropriate treatment duration with this plant may exert an improvement in the reproductive system deteriorated by diabetes, and further investigation is required. REFERENCES Anulukanapakorn K, Pancharoen O, Baniddhi J. Hypoglycemic effect of Tinospora crispa (Linn.) Mier ex Hook f. & Thoms (Menispermaceae) in rats. J Dept Med Sci 1999;41: Chakrabarti R, Vikramadithyan RK, Mullangi R, et al, Antidiabetic and hypolipidemic activity of Helicteres isora in animal model. J Ethnopharmacol 22;81: Feng SL, Li SH, Wang Y, Chen CC, Gao, B. Effect of ligustrum fruit extract on reproduction in experimental diabetic rats. 21. Asian J Androl 21;3:71-3. Grimstone AV, Skaer RJ. A guidebook to microscopical methods. London: Cambridge University Press, Vol 35 (Suppl 2) 24 57
6 SOUTHEAST ASIAN J TROP MED PUBLIC HEALTH Fig 6- Cross section of rat testis (x2),: A. normoglycemic group showing normal histology of the seminiferous tubules (S) with various stages of spermatogenesis. Notice the great number of sperm (SP) and Leydig cells (L); B. diabetic group showing degeneration and vacuolization (V) of germ cells. Notice the smaller size of seminiferous tubules (S) compared to A, the disappearance of sperm and the regression of Leydig cells (L); C. diabetic group treated with aqueous extract of Thunbergia laurifolia Linn., the histologic aspects are similar to B. Jiang GY. Practical diabetes. 1 st ed. Beijing: People s Health Publishing House, Laileard N, Pongchaidecha A, Boonnayathap U, et al. Effects of exercise and diabetic condition on gastrointestinal transit and glucose homeostasis in rats. Thai J Physiol Sci 1996;9: Maroo J, Vasu VT, Aalinkeel R, Gupta S. Glucose lowering effect of aqueous extract of Enicostemma littorale Blume in diabetes: a possible mechanism of action. J Ethnophamacol 22;81: Pongchaidecha A, Lailerd N, Pornsinthusate A, et al. Effect of Stevia rebaudiana on glucose homeostasis in insulin-deficient diabetic rats. Chiang Mai, Thailand: The 2nd National Seminar on Pharmaceutical Biotechnology, June 21-23, 2. Saenphat S, Seanphet K, Wutteeraphon S. Effect of aqueous extracts from Gymnema inodorum Dince on pancreatic ultrastructural changes of diabetic capillaries J Electron Micros Soc Thai 22;16: 236. Shetty J, Marathe GK, Ramaswamy S, et al. Pituitary gonadotrophins regulate spermatogonial differentiation and proliferation in the rat. J Bio Sci 1996;21: Tejasen P, Thongthapp S. The study of the insecticide antitoxicity of Thunbergia laurifolia L. Chiang Mai Med Bull 198;19: Tewit S, Patumery S, Kasantikul V. Effect of garlic extract on serum insulin, serum lipid profiles and cardiovascular functions in induced diabetic rats. Thai J Physiol Sci 1996;91:73. Utogapachn C. Medicinal plants and tropical diseases. Bangkok: Phrapittaya International, Vol 35 (Suppl 2) 24
INTRODUCTION MATERIALS AND METHODS
 SPERM DENSITY AND ULTRASTRUCTURE OF SERTOLI CELLS IN MALE RATS TREATED WITH KAEMPFERIA PARVIFLORA WALL. EX BAKER EXTRACT Paiwan Sudwan 1,2, Kanokporn Saenphet 1, Supap Saenphet 1 and Chalobol Wongsawad
SPERM DENSITY AND ULTRASTRUCTURE OF SERTOLI CELLS IN MALE RATS TREATED WITH KAEMPFERIA PARVIFLORA WALL. EX BAKER EXTRACT Paiwan Sudwan 1,2, Kanokporn Saenphet 1, Supap Saenphet 1 and Chalobol Wongsawad
A. K. EYONG AND V. B. BRAIDE
 GLOBAL JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES VOL 8, NO. 1&2, 2009: 23-30 COPYRIGHT BACHUDO SCIENCE CO. LTD PRINTED IN NIGERIA. ISSN 1596-2911 www.globaljournalseries.com; Email: info@globaljournalseries.com EFFECTS
GLOBAL JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES VOL 8, NO. 1&2, 2009: 23-30 COPYRIGHT BACHUDO SCIENCE CO. LTD PRINTED IN NIGERIA. ISSN 1596-2911 www.globaljournalseries.com; Email: info@globaljournalseries.com EFFECTS
Endocrine Glands System. Agha Zohaib Khan
 Endocrine Glands System Agha Zohaib Khan Introduction Endocrine means secreting internally. Indeed, the endocrine system is made up of glands whose secretions enter the blood stream. Hence these glands
Endocrine Glands System Agha Zohaib Khan Introduction Endocrine means secreting internally. Indeed, the endocrine system is made up of glands whose secretions enter the blood stream. Hence these glands
Anatomy & Physiology Revealed Instructions. 1. From the Module dropdown menu, chose the 12. Digestive system.
 #10 - Objectives: Examine the histology of selected body organs using Anatomy & Physiology Revealed software and microscope slides. Be able to identify each organ and the specific structures indicated
#10 - Objectives: Examine the histology of selected body organs using Anatomy & Physiology Revealed software and microscope slides. Be able to identify each organ and the specific structures indicated
Hormones of brain-testicular axis
 (Hormone Function) Hormones of brain-testicular axis anterior pituitary drives changes during puberty controlled by GnRH from hypothalamus begins to secrete FSH, LH LH targets interstitial endocrinocytes
(Hormone Function) Hormones of brain-testicular axis anterior pituitary drives changes during puberty controlled by GnRH from hypothalamus begins to secrete FSH, LH LH targets interstitial endocrinocytes
Human Physiology 6.6- Hormones, Homeostasis, and Reproduction
 Human Physiology 6.6- Hormones, Homeostasis, and Reproduction Essential idea: Hormones are used when signals need to be widely distributed. Application: William Harvey s investigation of sexual reproduction
Human Physiology 6.6- Hormones, Homeostasis, and Reproduction Essential idea: Hormones are used when signals need to be widely distributed. Application: William Harvey s investigation of sexual reproduction
Refer to the figure below, a diagram of a renal tubule, to answer the following questions.
 1. The digestion and utilization of which nutrient creates the greatest need for osmoregulation by the kidneys? a. protein b. starch c. fat d. oil e. cellulose 2. Which of the following is true of urea?
1. The digestion and utilization of which nutrient creates the greatest need for osmoregulation by the kidneys? a. protein b. starch c. fat d. oil e. cellulose 2. Which of the following is true of urea?
Chapter 14 Reproduction Review Assignment
 Date: Mark: _/45 Chapter 14 Reproduction Review Assignment Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Use the diagram above to answer the next question.
Date: Mark: _/45 Chapter 14 Reproduction Review Assignment Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Use the diagram above to answer the next question.
Efferent Ducts and Epididymis
 increase) the secretion of each of the androgen regulated proteins. Regulation of spermatogenesis is therefore an extremely complex cascade of cell-cell interactions with the Leydig cells supporting germ
increase) the secretion of each of the androgen regulated proteins. Regulation of spermatogenesis is therefore an extremely complex cascade of cell-cell interactions with the Leydig cells supporting germ
Mohammad Sha ban. Basheq Jehad. Hamzah Nakhleh
 11 Mohammad Sha ban Basheq Jehad Hamzah Nakhleh Physiology of the reproductive system In physiology, we are concerned with the mechanisms in which the system functions, and how the system responds to different
11 Mohammad Sha ban Basheq Jehad Hamzah Nakhleh Physiology of the reproductive system In physiology, we are concerned with the mechanisms in which the system functions, and how the system responds to different
Male Reproductive System
 Male Reproductive System organs that function in: gamete and hormone production not all in abdominal cavity paired testicles = controlled by LH & FSH duct systems accessory glands Testis: Gross Histology
Male Reproductive System organs that function in: gamete and hormone production not all in abdominal cavity paired testicles = controlled by LH & FSH duct systems accessory glands Testis: Gross Histology
Hormonal Control of Male Sexual Function
 Hormonal Control of Male Sexual Function A majority of the control of sexual functions in the male (and the female) begins with secretions of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) by the hypothalamus.
Hormonal Control of Male Sexual Function A majority of the control of sexual functions in the male (and the female) begins with secretions of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) by the hypothalamus.
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM. Mr. Erick Santizo
 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Mr. Erick Santizo DO HORMONES ONLY DEAL WITH SEX? -Hormones: are chemical substances which are produced by animals and plants to regulate the organism s activities. They are produced in
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Mr. Erick Santizo DO HORMONES ONLY DEAL WITH SEX? -Hormones: are chemical substances which are produced by animals and plants to regulate the organism s activities. They are produced in
REPRODUCCIÓN. La idea fija. Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 REPRODUCCIÓN La idea fija How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development, birth
REPRODUCCIÓN La idea fija How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development, birth
Adapted from Preg. & Part., Senger
 MALE ENDOCRINOLOGY AND SPERMATOGENESIS (Chapter 10) AVS 222 (Instructor: Dr. Amin Ahmadzadeh) I. MALE ENDOCRINOLOGY (Figure10-1 to 10-3) A. Glands and their respective hormones 1) Hypothalamic hormone:
MALE ENDOCRINOLOGY AND SPERMATOGENESIS (Chapter 10) AVS 222 (Instructor: Dr. Amin Ahmadzadeh) I. MALE ENDOCRINOLOGY (Figure10-1 to 10-3) A. Glands and their respective hormones 1) Hypothalamic hormone:
Endocrine System. Chapter 20. Endocrine Glands and Hormones. The Endocrine System. Endocrine glands
 Chapter 20 Endocrine System Endocrine Glands and Hormones The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete hormones Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times
Chapter 20 Endocrine System Endocrine Glands and Hormones The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete hormones Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times
Summary: Endocrinology 4
 Mammlian Physiology 2 Page 1 Summary: Endocrinology 4 January-12-11 21:06 Notes by Yingzhou Edward Pan Pathophysiology of the adrenal cortex Pancreas, Insulin and Diabetes Growth Hormones in males and
Mammlian Physiology 2 Page 1 Summary: Endocrinology 4 January-12-11 21:06 Notes by Yingzhou Edward Pan Pathophysiology of the adrenal cortex Pancreas, Insulin and Diabetes Growth Hormones in males and
SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development,
SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development,
Robert Wadlow and his father
 Robert Wadlow and his father 1 Robert Wadlow Wadlow reached 8 ft 11.1 in (2.72 m) in height and weighed 485 lb (220 kg) at his death at age 22. Born in Illinois. His great size and his continued growth
Robert Wadlow and his father 1 Robert Wadlow Wadlow reached 8 ft 11.1 in (2.72 m) in height and weighed 485 lb (220 kg) at his death at age 22. Born in Illinois. His great size and his continued growth
Endocrine System. Endocrine vs. Exocrine. Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Endocrine System Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Endocrine vs. Exocrine Endocrine glands secrete their products called hormones into body fluids (the internal environment) Exocrine glands secrete their
Endocrine System Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Endocrine vs. Exocrine Endocrine glands secrete their products called hormones into body fluids (the internal environment) Exocrine glands secrete their
Testicular Toxicity: Evaluation During Drug Development Guidance for Industry
 Testicular Toxicity: Evaluation During Drug Development Guidance for Industry DRAFT GUIDANCE This guidance document is being distributed for comment purposes only. Comments and suggestions regarding this
Testicular Toxicity: Evaluation During Drug Development Guidance for Industry DRAFT GUIDANCE This guidance document is being distributed for comment purposes only. Comments and suggestions regarding this
REPRODUCTIVE ENDOCRINOLOGY OF THE MALE
 Reproductive Biotechnologies Andrology I REPRODUCTIVE ENDOCRINOLOGY OF THE MALE Prof. Alberto Contri REPRODUCTIVE ENDOCRINOLOGY OF THE MALE SPERMATOGENESIS AND REPRODUCTIVE BEHAVIOR RELATED TO THE ACTIVITY
Reproductive Biotechnologies Andrology I REPRODUCTIVE ENDOCRINOLOGY OF THE MALE Prof. Alberto Contri REPRODUCTIVE ENDOCRINOLOGY OF THE MALE SPERMATOGENESIS AND REPRODUCTIVE BEHAVIOR RELATED TO THE ACTIVITY
Endocrine system release hormones to regulates physiological process e.g growth, reproduction, metabolism, mentrual cycle, development of secondary
 Endocrine system release hormones to regulates physiological process e.g growth, reproduction, metabolism, mentrual cycle, development of secondary sexual characteristics Consists of endocrine glands which
Endocrine system release hormones to regulates physiological process e.g growth, reproduction, metabolism, mentrual cycle, development of secondary sexual characteristics Consists of endocrine glands which
Endocrine System. Chemical Control
 Endocrine System Chemical Control Endocrine System - the system that secretes hormones in the body - hormones can last for minutes or for hours - a major gland, once called the master gland, is the pituitary
Endocrine System Chemical Control Endocrine System - the system that secretes hormones in the body - hormones can last for minutes or for hours - a major gland, once called the master gland, is the pituitary
Chapter 12 Endocrine System (export).notebook. February 27, Mar 17 2:59 PM. Mar 17 3:09 PM. Mar 17 3:05 PM. Mar 17 3:03 PM.
 Endocrine System Hormones Chemical messengers released directly into the bloodstream Regulate: *May have wide spread effect or only affect certain tissues ** : cells with receptors that respond to specific
Endocrine System Hormones Chemical messengers released directly into the bloodstream Regulate: *May have wide spread effect or only affect certain tissues ** : cells with receptors that respond to specific
Type 1 Diabetes 2/23/2015. Endocrine System Hormones. Living with Type 1 Diabetes
 Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Living with Type 1 Diabetes Type 1 Diabetes results from the autoimmune destruction of the insulin- producing beta-cells in the pancreas. The lack of insulin leads to
Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Living with Type 1 Diabetes Type 1 Diabetes results from the autoimmune destruction of the insulin- producing beta-cells in the pancreas. The lack of insulin leads to
Hypothalamus & Pituitary Gland
 Hypothalamus & Pituitary Gland Hypothalamus and Pituitary Gland The hypothalamus and pituitary gland form a unit that exerts control over the function of several endocrine glands (thyroid, adrenals, and
Hypothalamus & Pituitary Gland Hypothalamus and Pituitary Gland The hypothalamus and pituitary gland form a unit that exerts control over the function of several endocrine glands (thyroid, adrenals, and
Chemical Regulation. Chapter 26. Testosterone and Male Aggression: Is There a Link? THE NATURE OF CHEMICAL REGULATION
 Chapter 6 Chemical Regulation PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts and Connections, Fifth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, and Simon Testosterone and Male Aggression: Is There a Link? Among male animals,
Chapter 6 Chemical Regulation PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts and Connections, Fifth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, and Simon Testosterone and Male Aggression: Is There a Link? Among male animals,
Histology of Male Reproductive system (1)
 Histology of Male Reproductive system (1) Prof. Dr. Malak A. Al-yawer Learning Objectives At the end of this lecture, the medical student will be able to: State the organization of the testis Define seminiferous
Histology of Male Reproductive system (1) Prof. Dr. Malak A. Al-yawer Learning Objectives At the end of this lecture, the medical student will be able to: State the organization of the testis Define seminiferous
Endocrine System Hormones & Homeostasis. Regents Biology
 Endocrine System Hormones & Homeostasis 2009-2010 Homeostasis Homeostasis maintaining internal balance in the body organism must keep internal conditions stable even if environment changes also called
Endocrine System Hormones & Homeostasis 2009-2010 Homeostasis Homeostasis maintaining internal balance in the body organism must keep internal conditions stable even if environment changes also called
Control of Glucose Metabolism
 Glucose Metabolism Control of Glucose Metabolism The pancreas is both an exocrine and endocrine gland. It secretes digestive enzymes into the duodenum (exocrine) and 3 specific hormones into the bloodstream
Glucose Metabolism Control of Glucose Metabolism The pancreas is both an exocrine and endocrine gland. It secretes digestive enzymes into the duodenum (exocrine) and 3 specific hormones into the bloodstream
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 11 The Human Endocrine System. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 11-1 through 11-18. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 11-1. Given a hormone, identify
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 11 The Human Endocrine System. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 11-1 through 11-18. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 11-1. Given a hormone, identify
Pharmacologyonline 1: (2009) HYPOGLYCEMIC EFFECT OF PHOEBE LA CEOLATA O ALLOXA -I DUCED DIABETIC MICE
 HYPOGLYCEMIC EFFECT OF PHOEBE LA CEOLATA O ALLOXA -I DUCED DIABETIC MICE SEMWAL DK 1 *, RAWAT U 1, SEMWAL R 2, SINGH K 3, SINGH R 3, SAINI B 3, KRISHAN P 3, SINGH M 4 1 Department of Chemistry, University
HYPOGLYCEMIC EFFECT OF PHOEBE LA CEOLATA O ALLOXA -I DUCED DIABETIC MICE SEMWAL DK 1 *, RAWAT U 1, SEMWAL R 2, SINGH K 3, SINGH R 3, SAINI B 3, KRISHAN P 3, SINGH M 4 1 Department of Chemistry, University
NOTES 11.5: ENDOCRINE SYSTEM. Pages
 NOTES 11.5: ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Pages 1031-1042 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Communication system that controls metabolism, growth, and development with hormones Maintains homeostasis Hormones: chemical messengers released
NOTES 11.5: ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Pages 1031-1042 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Communication system that controls metabolism, growth, and development with hormones Maintains homeostasis Hormones: chemical messengers released
Reproductive Endocrinology. Isabel Hwang Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Hong Kong Hong Kong May2007
 Reproductive Endocrinology Isabel Hwang Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Hong Kong Hong Kong May2007 isabelss@hkucc.hku.hk A 3-hormone chain of command controls reproduction with
Reproductive Endocrinology Isabel Hwang Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Hong Kong Hong Kong May2007 isabelss@hkucc.hku.hk A 3-hormone chain of command controls reproduction with
Reproductive Hormones
 Reproductive Hormones Male gonads: testes produce male sex cells! sperm Female gonads: ovaries produce female sex cells! ovum The union of male and female sex cells during fertilization produces a zygote
Reproductive Hormones Male gonads: testes produce male sex cells! sperm Female gonads: ovaries produce female sex cells! ovum The union of male and female sex cells during fertilization produces a zygote
6. The diagram below represents an interaction between parts of an organism.
 Endocrine Review 1. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. Each arrow in the diagram represents a different hormone released by the pituitary
Endocrine Review 1. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. Each arrow in the diagram represents a different hormone released by the pituitary
Endocrine System. Chapter 18. Introduction. How Hormones Work. How Hormones Work. The Hypothalamus & Endocrine Regulation
 Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 18 The endocrine system consists of cells, tissues, & organs that secrete into the blood Hormone an organic substance secreted by a cell that has an effect on the
Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 18 The endocrine system consists of cells, tissues, & organs that secrete into the blood Hormone an organic substance secreted by a cell that has an effect on the
Chapter 21. Human Endocrine System
 Chapter 21 Human Endocrine System Endocrine System Consist of endocrine glands that secrete hormones which regulate a wide range of activities in humans Hormones- are secreted by glands and diffuse directly
Chapter 21 Human Endocrine System Endocrine System Consist of endocrine glands that secrete hormones which regulate a wide range of activities in humans Hormones- are secreted by glands and diffuse directly
1. The diagram below represents the homeostatic control of body temperature. What does the part labelled X represent? D. Hypothalamus (Total 1 mark)
 1. The diagram below represents the homeostatic control of body temperature. What does the part labelled X represent? A. Heart B. Kidney C. Pituitary D. Hypothalamus 2. What is the sequence of operations
1. The diagram below represents the homeostatic control of body temperature. What does the part labelled X represent? A. Heart B. Kidney C. Pituitary D. Hypothalamus 2. What is the sequence of operations
Biology of Reproduction-Biol 326
 Biology of Reproduction-Biol 326 READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY. ANSWER ALL THE QUESTIONS ON THE ANSWER SHEET. THE ANSWER ON THE ANSWER SHEET IS YOUR OFFICIAL ANSWER REGARDLESS OF WHAT YOU MARK ON THE
Biology of Reproduction-Biol 326 READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY. ANSWER ALL THE QUESTIONS ON THE ANSWER SHEET. THE ANSWER ON THE ANSWER SHEET IS YOUR OFFICIAL ANSWER REGARDLESS OF WHAT YOU MARK ON THE
Chapter 20. Endocrine System Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chemical signals coordinate body functions. !
 26.1 Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chapter 20 Endocrine System! Hormones Chemical signals Secreted by endocrine glands Usually carried in the blood Cause specific changes in target cells Secretory
26.1 Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chapter 20 Endocrine System! Hormones Chemical signals Secreted by endocrine glands Usually carried in the blood Cause specific changes in target cells Secretory
1. To describe the gross structure of the pituitary gland and be able to identify the pars nervosa, pars intermedia and pars distalis.
 ENDOCRINE Objectives 1. To describe the gross structure of the pituitary gland and be able to identify the pars nervosa, pars intermedia and pars distalis. 2. Identify and describe the histological features
ENDOCRINE Objectives 1. To describe the gross structure of the pituitary gland and be able to identify the pars nervosa, pars intermedia and pars distalis. 2. Identify and describe the histological features
Male reproduction. Cross section of Human Testis ผศ.ดร.พญ.ส ว ฒณ ค ปต ว ฒ ภาคว ชาสร รว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร ศ ร ราชพยาบาล 1. Aims
 Aims Male reproduction Male reproductive structure Spermatogenesis ส ว ฒณ ค ปต ว ฒ ห อง 216 โทร: 7578 Hypothalamo-pituitary-testicular axis Male sex hormone action Male reproductive structure Male reproductive
Aims Male reproduction Male reproductive structure Spermatogenesis ส ว ฒณ ค ปต ว ฒ ห อง 216 โทร: 7578 Hypothalamo-pituitary-testicular axis Male sex hormone action Male reproductive structure Male reproductive
REPRODUCTION The diagram below shows a section through seminiferous tubules in a testis.
 1. The diagram below shows a section through seminiferous tubules in a testis. Which cell produces testosterone? 2. A function of the interstitial cells in the testes is to produce A sperm B testosterone
1. The diagram below shows a section through seminiferous tubules in a testis. Which cell produces testosterone? 2. A function of the interstitial cells in the testes is to produce A sperm B testosterone
Chapter 20 Endocrine System
 Chapter 20 Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times far away from the site of hormone production
Chapter 20 Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times far away from the site of hormone production
Male Reproductive System
 21-1 21-2 Reproductive System Male Reproductive System Genital Tract In males the testes, held outside the body in the scrotum (optimum temp of about 35 0 C), produce sperm. Sperm mature in coiled tubes
21-1 21-2 Reproductive System Male Reproductive System Genital Tract In males the testes, held outside the body in the scrotum (optimum temp of about 35 0 C), produce sperm. Sperm mature in coiled tubes
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.45 - ENDOCRINE SYSTEM.
 !! www.clutchprep.com Chemical signals allow cells to communicate with each other Pheromones chemical signals released to the environment to communicate with other organisms Autocrine signaling self-signaling,
!! www.clutchprep.com Chemical signals allow cells to communicate with each other Pheromones chemical signals released to the environment to communicate with other organisms Autocrine signaling self-signaling,
Effects of Ablation of the Submaxillary Gland in Guinea Pigs IV. Cause of deterioration of the tubules in the testes
 1961 475 Effects of Ablation of the Submaxillary Gland in Guinea Pigs IV. Cause of deterioration of the tubules in the testes Kazuo Suzuki Received August 1, 1960 Shakujii Institute, Tokyo Medical College,
1961 475 Effects of Ablation of the Submaxillary Gland in Guinea Pigs IV. Cause of deterioration of the tubules in the testes Kazuo Suzuki Received August 1, 1960 Shakujii Institute, Tokyo Medical College,
Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE
 Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE I. FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY (Fig. 28.1) A. Testes: glands which produce male gametes, as well as glands producing testosterone 2. Seminiferous tubules (Fig.28.3; 28.5) a.
Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE I. FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY (Fig. 28.1) A. Testes: glands which produce male gametes, as well as glands producing testosterone 2. Seminiferous tubules (Fig.28.3; 28.5) a.
Male Reproduction Organs. 1. Testes 2. Epididymis 3. Vas deferens 4. Urethra 5. Penis 6. Prostate 7. Seminal vesicles 8. Bulbourethral glands
 Outline Terminology Human Reproduction Biol 105 Lecture Packet 21 Chapter 17 I. Male Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Sperm development II. Female Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Egg development
Outline Terminology Human Reproduction Biol 105 Lecture Packet 21 Chapter 17 I. Male Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Sperm development II. Female Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Egg development
Chapter 45-Hormones and the Endocrine System. Simple Hormone Pathways
 Chapter 45-Hormones and the Endocrine System Simple Hormone s Low ph in duodenum Hormones are released from an endocrine, travel through the bloodstream, and interact with the receptor or a target to cause
Chapter 45-Hormones and the Endocrine System Simple Hormone s Low ph in duodenum Hormones are released from an endocrine, travel through the bloodstream, and interact with the receptor or a target to cause
Endocrine System. A system that consists of glands that transmit chemical messengers throughout the body.
 Endocrine System A system that consists of glands that transmit chemical messengers throughout the body. HORMONES: chemical that circulates throughout the blood stream and influence the activity of distant
Endocrine System A system that consists of glands that transmit chemical messengers throughout the body. HORMONES: chemical that circulates throughout the blood stream and influence the activity of distant
THE EFFECTS OF REPEATED INJECTIONS OF CHORIONIC GONADOTROPIN ON THE TESTES OF THE LEOPARD FROG (RANA PIPIENS SCHREBER)
 THE EFFECTS OF REPEATED INJECTIONS OF CHORIONIC GONADOTROPIN ON THE TESTES OF THE LEOPARD FROG (RANA PIPIENS SCHREBER) ROBERT P. McCOURT Department of Zoology and Entomology, The Ohio State University,
THE EFFECTS OF REPEATED INJECTIONS OF CHORIONIC GONADOTROPIN ON THE TESTES OF THE LEOPARD FROG (RANA PIPIENS SCHREBER) ROBERT P. McCOURT Department of Zoology and Entomology, The Ohio State University,
Module 2 Endocrine System
 Module 2 Endocrine System Student Name: 1 Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Lesson 4 Lesson 5 Total Marks Total Possible Marks 10 8 14 21 16 69 Your Mark Teacher Comments: 2 (10 marks) Lesson 1: Structure and
Module 2 Endocrine System Student Name: 1 Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Lesson 4 Lesson 5 Total Marks Total Possible Marks 10 8 14 21 16 69 Your Mark Teacher Comments: 2 (10 marks) Lesson 1: Structure and
5 15/3/2012. Malik Al-Momani
 5 15/3/2012 Malik Al-Momani بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Spermatogenesis Note : Please refer to slides so see photos. Quick Revision : - Testis is divided by septum into testicular lobules, inside the lobules
5 15/3/2012 Malik Al-Momani بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Spermatogenesis Note : Please refer to slides so see photos. Quick Revision : - Testis is divided by septum into testicular lobules, inside the lobules
Ch. 39 Endocrine System
 Ch. 39 Endocrine System The Endocrine System The endocrine system is made up of glands that release their products into the bloodstream These products deliver messages throughout the body Hormones Hormones
Ch. 39 Endocrine System The Endocrine System The endocrine system is made up of glands that release their products into the bloodstream These products deliver messages throughout the body Hormones Hormones
CHAPTER 12. Quick Check and Active Learning Answer Keys QUICK CHECK
 CHAPTER 12 QUICK CHECK Page 311 1. Hormones are the chemical messengers of the endocrine system. 2. Nonsteroid hormones are whole proteins, shorter chains of amino acids, or simply versions of single amino
CHAPTER 12 QUICK CHECK Page 311 1. Hormones are the chemical messengers of the endocrine system. 2. Nonsteroid hormones are whole proteins, shorter chains of amino acids, or simply versions of single amino
Effect of Coriandrum sativum, a common herbal medicine, on endocrine and reproductive organ structure and function
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Alternative Medicine Volume 7 Number 2 Effect of Coriandrum sativum, a common herbal medicine, on endocrine and reproductive organ structure and function E Al Suhaimi
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Alternative Medicine Volume 7 Number 2 Effect of Coriandrum sativum, a common herbal medicine, on endocrine and reproductive organ structure and function E Al Suhaimi
Module J ENDOCRINE SYSTEM. Learning Outcome
 Module J ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Topic from HAPS Guidelines General functions of the endocrine system Chemical classification of hormones & mechanism of hormone actions at receptors. Control of hormone secretion
Module J ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Topic from HAPS Guidelines General functions of the endocrine system Chemical classification of hormones & mechanism of hormone actions at receptors. Control of hormone secretion
Hormones. BIT 230 Walsh Chapter 8
 Hormones BIT 230 Walsh Chapter 8 Hormones Regulatory molecules Affect all areas of metabolism Endocrine- hormones travel via the bloodstream to its target cell: true hormone Modern definition- any regulatory
Hormones BIT 230 Walsh Chapter 8 Hormones Regulatory molecules Affect all areas of metabolism Endocrine- hormones travel via the bloodstream to its target cell: true hormone Modern definition- any regulatory
10.7 The Reproductive Hormones
 10.7 The Reproductive Hormones December 10, 2013. Website survey?? QUESTION: Who is more complicated: men or women? The Female Reproductive System ovaries: produce gametes (eggs) produce estrogen (steroid
10.7 The Reproductive Hormones December 10, 2013. Website survey?? QUESTION: Who is more complicated: men or women? The Female Reproductive System ovaries: produce gametes (eggs) produce estrogen (steroid
ANTI-DIABETIC ACTIVITY OF HELICTERES ISORA ROOT
 ANTI-DIABETIC ACTIVITY OF HELICTERES ISORA ROOT Sama Venkatesh *1, G.Dayananda Reddy 1, B.Madhava Reddy 1, M.Lakshman 2. 1 Department of Pharmacognosy, G.Pulla Reddy College of Pharmacy, Mehdipatnam, Hyderabad
ANTI-DIABETIC ACTIVITY OF HELICTERES ISORA ROOT Sama Venkatesh *1, G.Dayananda Reddy 1, B.Madhava Reddy 1, M.Lakshman 2. 1 Department of Pharmacognosy, G.Pulla Reddy College of Pharmacy, Mehdipatnam, Hyderabad
Anatomy and Physiology. The Endocrine System
 Anatomy and Physiology The Endocrine System The endocrine system includes anything that secretes hormones directly into body fluids. Endocrine glands include: the thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, kidney,
Anatomy and Physiology The Endocrine System The endocrine system includes anything that secretes hormones directly into body fluids. Endocrine glands include: the thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, kidney,
Male Reproductive System
 Male Reproductive System Constitution of male reproductive system Genital gland ----testis Genital ducts epididymis / ductus deferens / urinary duct Accessory sex glands Penis prostate gland Seminal vesicle
Male Reproductive System Constitution of male reproductive system Genital gland ----testis Genital ducts epididymis / ductus deferens / urinary duct Accessory sex glands Penis prostate gland Seminal vesicle
NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 September 11, 2017 Control Mechanisms 2: Endocrine Control
 NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 September 11, 2017 Control Mechanisms 2: Endocrine Control Hormones are chemical messengers that are secreted into the blood by endocrine cells or specialized neurons.
NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 September 11, 2017 Control Mechanisms 2: Endocrine Control Hormones are chemical messengers that are secreted into the blood by endocrine cells or specialized neurons.
Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands 4/12/2016. Controlled by both nerves and hormones.
 Glands http://www.hawaiilife.com/articles/2012/03/good-news-vacation-rental-owners/ 70 Figure 10.14a gland Glands cortex Mineralocorticoids Gonadocorticoids Glucocorticoids medulla Epinephrine Norepinephrine
Glands http://www.hawaiilife.com/articles/2012/03/good-news-vacation-rental-owners/ 70 Figure 10.14a gland Glands cortex Mineralocorticoids Gonadocorticoids Glucocorticoids medulla Epinephrine Norepinephrine
Research Article. The effects of zinc supplement on fertility in male mice
 Available online wwwjocprcom Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 216, 8(1):66-7 Research Article ISSN : 975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 The effects of zinc supplement on fertility in male mice
Available online wwwjocprcom Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 216, 8(1):66-7 Research Article ISSN : 975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 The effects of zinc supplement on fertility in male mice
Grade XI. Biology. (Important Questions) #GrowWithGreen
 Grade XI Biology (Important Questions) #GrowWithGreen Questions 1. Use the following information to answer the question (a) Identify the family shown in the floral diagram given. Also, give its floral
Grade XI Biology (Important Questions) #GrowWithGreen Questions 1. Use the following information to answer the question (a) Identify the family shown in the floral diagram given. Also, give its floral
Ch45: Endocrine System
 Ch45: Endocrine System Endocrine System Homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. Function = coordinate and control the body with hormones to maintain homeostasis Works with
Ch45: Endocrine System Endocrine System Homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. Function = coordinate and control the body with hormones to maintain homeostasis Works with
HORMONES AND CELL SIGNALLING
 HORMONES AND CELL SIGNALLING TYPES OF CELL JUNCTIONS CHEMICAL SIGNALS AND MODES OF ACTION Endocrine system produces chemical messages = hormones that are transported from endocrine gland to target cell
HORMONES AND CELL SIGNALLING TYPES OF CELL JUNCTIONS CHEMICAL SIGNALS AND MODES OF ACTION Endocrine system produces chemical messages = hormones that are transported from endocrine gland to target cell
Chapter 18: Endocrine Glands
 Chapter 18: Endocrine Glands I. Functions of the Endocrine System A. List and describe the eight major functions of the endocrine system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Page 1 of 19 C II. Pituitary Gland and
Chapter 18: Endocrine Glands I. Functions of the Endocrine System A. List and describe the eight major functions of the endocrine system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Page 1 of 19 C II. Pituitary Gland and
Biology 30. Morinville Community High School. Unit 2: Endocrine System. Name:
 Biology 30 Morinville Community High School Unit 2: Endocrine System Name: 2 Endocrine System Unit Outline Chapter 13 text p. 434-471 Key Concept A: The endocrine system and nervous system both mediate
Biology 30 Morinville Community High School Unit 2: Endocrine System Name: 2 Endocrine System Unit Outline Chapter 13 text p. 434-471 Key Concept A: The endocrine system and nervous system both mediate
Endocrine System WHO IS IN CONTROL?
 Endocrine System WHO IS IN CONTROL? Objectives Explain how the endocrine and nervous system work together to regulate bodily functions Describe the basic anatomy of the endocrine system Describe the functions
Endocrine System WHO IS IN CONTROL? Objectives Explain how the endocrine and nervous system work together to regulate bodily functions Describe the basic anatomy of the endocrine system Describe the functions
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM The male reproductive system consists of primary sex organs (testes) and secondary or accessory sex organs. The secondary organs consist of a series of genital ducts (ductules
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM The male reproductive system consists of primary sex organs (testes) and secondary or accessory sex organs. The secondary organs consist of a series of genital ducts (ductules
Sick Call Screener Course. Endocrine System (2.11)
 Sick Call Screener Course Endocrine System (2.11) 2.9-2-1 Enabling Objectives 1.58 Utilize the knowledge of endocrine system anatomy while assessing a patient with a endocrine complaint 1.59 Utilize the
Sick Call Screener Course Endocrine System (2.11) 2.9-2-1 Enabling Objectives 1.58 Utilize the knowledge of endocrine system anatomy while assessing a patient with a endocrine complaint 1.59 Utilize the
Endocrine System Notes
 Endocrine System Notes is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. - parts of the body that secrete hormones directly into the body. - parts of the body that make secretions which travel
Endocrine System Notes is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. - parts of the body that secrete hormones directly into the body. - parts of the body that make secretions which travel
Reproductive System Purpose General Structures Male Structures Functions Female Anatomy Structures Functions Clinical Applications
 The Reproductive System: Male, Ch 23 Outline of class lecture After studying the male reproductive system you should be able to: 1. Define the purpose of reproduction and identify the general organs of
The Reproductive System: Male, Ch 23 Outline of class lecture After studying the male reproductive system you should be able to: 1. Define the purpose of reproduction and identify the general organs of
Outline. Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation
 Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
Homeostasis Through Chemistry. The Endocrine System Topic 6.6
 Homeostasis Through Chemistry The Endocrine System Topic 6.6 Comparing NS & ES Animals have two systems of internal communication and regulation The nervous system Response time: Fast, quick Signals: electrical
Homeostasis Through Chemistry The Endocrine System Topic 6.6 Comparing NS & ES Animals have two systems of internal communication and regulation The nervous system Response time: Fast, quick Signals: electrical
ENDOCRINOLOGY. Dr.AZZA SAJID ALKINANY 2 nd STAGE
 ENDOCRINOLOGY Dr.AZZA SAJID ALKINANY 2 nd STAGE THE RELATIONSHIP AMONG THE HYPOTHALMUS,POSTERIOR PITUITARY AND TARGET TISSUES. The posterior pituitary does not produce its own hormones, but stores and
ENDOCRINOLOGY Dr.AZZA SAJID ALKINANY 2 nd STAGE THE RELATIONSHIP AMONG THE HYPOTHALMUS,POSTERIOR PITUITARY AND TARGET TISSUES. The posterior pituitary does not produce its own hormones, but stores and
Evaluation of antifertility efficacy of Carica papaya seed extract through histological indices in Male Albino Rats
 International Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Sciences 2013, Sep., Vol. 4 (3) ISSN: 0976-9390 IJCPS Evaluation of antifertility efficacy of Carica papaya seed extract through histological indices
International Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Sciences 2013, Sep., Vol. 4 (3) ISSN: 0976-9390 IJCPS Evaluation of antifertility efficacy of Carica papaya seed extract through histological indices
-The process by which organisms maintain, control, and coordinate their internal environment with a constantly changing external environment
 -The process by which organisms maintain, control, and coordinate their internal environment with a constantly changing external environment -It is all of the activities that help to maintain an organism
-The process by which organisms maintain, control, and coordinate their internal environment with a constantly changing external environment -It is all of the activities that help to maintain an organism
Lab Exercise Endocrine System
 Lab Exercise Endocrine System Name Date Materials: Human torso model Compound light microscope Prepared slides of the pituitary gland, pineal gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, thymus gland, adrenal
Lab Exercise Endocrine System Name Date Materials: Human torso model Compound light microscope Prepared slides of the pituitary gland, pineal gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, thymus gland, adrenal
Cell Divisions. The autosomes represent the whole body. * Male Sex Chromosomes: XY * Female Sex Chromosomes: XX
 Cell Divisions Each Cell (including gonads) has 46 chromosomes (23 pairs of chromosomes: 22 pairs of autosomes, 1 pair of sex chromosomes) which are located in the nucleus). The autosomes represent the
Cell Divisions Each Cell (including gonads) has 46 chromosomes (23 pairs of chromosomes: 22 pairs of autosomes, 1 pair of sex chromosomes) which are located in the nucleus). The autosomes represent the
Endocrine System. Chapter 24. Copyright 2012, 2007, 2003, 1999 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Endocrine System Chapter 24 1 Introduction (p. 638) Endocrine system works with nervous system to coordinate body functions Nervous system uses neural impulses Endocrine system uses hormones 2 Comparing
Endocrine System Chapter 24 1 Introduction (p. 638) Endocrine system works with nervous system to coordinate body functions Nervous system uses neural impulses Endocrine system uses hormones 2 Comparing
The Endocrine System 2
 The Endocrine System 2 Continuing on from the previous instalment, we will now look at the adrenal glands, the pancreas and the gonads as parts of the endocrine system. Adrenal Glands The adrenal glands
The Endocrine System 2 Continuing on from the previous instalment, we will now look at the adrenal glands, the pancreas and the gonads as parts of the endocrine system. Adrenal Glands The adrenal glands
Testosterone and other male hormones seem to be related to aggressive behavior in some species
 Testosterone and Male Aggression Testosterone and other male hormones seem to be related to aggressive behavior in some species In the fish species Oreochromis mossambicus, elevated levels have been found
Testosterone and Male Aggression Testosterone and other male hormones seem to be related to aggressive behavior in some species In the fish species Oreochromis mossambicus, elevated levels have been found
Effect of excess (within tolerable range) and excessive iodine for different durations on functional status of testis with possible mechanism
 Section III. Chapter 4 Effect of excess (within tolerable range) and excessive iodine for different durations on functional status of testis with possible mechanism Introduction Thyroid hormones regulate
Section III. Chapter 4 Effect of excess (within tolerable range) and excessive iodine for different durations on functional status of testis with possible mechanism Introduction Thyroid hormones regulate
Glandular Epithelium. Dr. Hersh Abdul Ham-Karim BVM&S, PG Dip, MSc and PhD
 Glandular Epithelium Dr. Hersh Abdul Ham-Karim BVM&S, PG Dip, MSc and PhD Glandular Epithelium Groups of surface cells differentiate, proliferate, and penetrate underlying connective tissue. Their main
Glandular Epithelium Dr. Hersh Abdul Ham-Karim BVM&S, PG Dip, MSc and PhD Glandular Epithelium Groups of surface cells differentiate, proliferate, and penetrate underlying connective tissue. Their main
IN normal male fowls, four developmental stages of spermatogenetic activity
 Development of the Testis Tubule in the Fowl By GAMAL A. R. KAMAR (From the Animal Production Department, Faculty of Agriculture, Cairo University, Giza, Egypt) With three plates (figs. 1-3) SUMMARY Three
Development of the Testis Tubule in the Fowl By GAMAL A. R. KAMAR (From the Animal Production Department, Faculty of Agriculture, Cairo University, Giza, Egypt) With three plates (figs. 1-3) SUMMARY Three
Research Article. The effects of titanium oxide nanoparticles on testis tissue and spermatogenesis in mice
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2016, 8(4):1014-1018 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 The effects of titanium oxide nanoparticles on
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2016, 8(4):1014-1018 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 The effects of titanium oxide nanoparticles on
9.3 Stress Response and Blood Sugar
 9.3 Stress Response and Blood Sugar Regulate Stress Response Regulate Blood Sugar Stress Response Involves hormone pathways that regulate metabolism, heart, rate and breathing The Adrenal Glands a pair
9.3 Stress Response and Blood Sugar Regulate Stress Response Regulate Blood Sugar Stress Response Involves hormone pathways that regulate metabolism, heart, rate and breathing The Adrenal Glands a pair
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required
To General Embryology Dr: Azza Zaki
 Introduction To General Embryology The Human Development is a continuous process that begins when an ovum from a female is fertilized by a sperm from a male. Cell division, growth and differentiation transform
Introduction To General Embryology The Human Development is a continuous process that begins when an ovum from a female is fertilized by a sperm from a male. Cell division, growth and differentiation transform
I PU Biology Chemical Coordination
 I PU Biology Chemical Coordination Questions carrying 1 Mark each. 1. Define hormone. 2. Mention the name of the neurosecretorycells,which secrete the hormone in the hypothalamus. 3. Which of the endocrine
I PU Biology Chemical Coordination Questions carrying 1 Mark each. 1. Define hormone. 2. Mention the name of the neurosecretorycells,which secrete the hormone in the hypothalamus. 3. Which of the endocrine
Lowers Blood Sugar Naturally
 Lowers Blood Sugar Naturally Scientific Studies Have Proven That These Eleven Natural Ingradients Normalise Blood Sugar Momordica charantia Gymnema sylvestre Pterocarpus marsupium Salacia Reticulata Curcuma
Lowers Blood Sugar Naturally Scientific Studies Have Proven That These Eleven Natural Ingradients Normalise Blood Sugar Momordica charantia Gymnema sylvestre Pterocarpus marsupium Salacia Reticulata Curcuma
Chapter 8.2 The Endocrine System
 Major Endocrine Organs Hypothalamus Pineal Gland Pituitary Gland Thyroid Gland Thymus Gland Adrenal Glands Pancreas Ovaries (Female) Testis (Male) Chapter 8.2 The Endocrine System The endocrine system
Major Endocrine Organs Hypothalamus Pineal Gland Pituitary Gland Thyroid Gland Thymus Gland Adrenal Glands Pancreas Ovaries (Female) Testis (Male) Chapter 8.2 The Endocrine System The endocrine system
Human Anatomy, First Edition. Endocrine System. Chapter 20 Lecture Outline: Endocrine System. McKinley & O'Loughlin
 Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 20 Lecture Outline: Endocrine System 1 Endocrine System Endocrine system and the nervous system often work together to bring about homeostasis.
Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 20 Lecture Outline: Endocrine System 1 Endocrine System Endocrine system and the nervous system often work together to bring about homeostasis.
Unit 4 Homeostasis. The term homeostasis refers to the body s attempt. Your body systems must to maintain a stable internal environment -
 Unit 4 Homeostasis The term homeostasis refers to the body s attempt Your body systems must to maintain a stable internal environment - The body is trying to maintain, through a series of monitored adjustments.
Unit 4 Homeostasis The term homeostasis refers to the body s attempt Your body systems must to maintain a stable internal environment - The body is trying to maintain, through a series of monitored adjustments.
