Addition of a Nitric Oxide Inhibitor to a More Biocompatible Peritoneal Dialysis Solution in a Rat Model of Chronic Renal Failure
|
|
|
- Steven McGee
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis, Vol. 26, 2010 Marijke de Graaff, 1 Anniek Vlijm, 1 Machteld M. Zweers, 1 Annemieke M. Coester, 1 Fréderic Vandemaele, 2 Dirk G. Struijk, 1,3 Raymond T. Krediet 1 Addition of a Nitric Oxide Inhibitor to a More Biocompatible Peritoneal Dialysis Solution in a Rat Model of Chronic Renal Failure Biocompatible dialysis solutions have been developed to preserve peritoneal membrane morphology and function. Compared with a conventional solution, a combination of glycerol, amino acids, and dextrose in a bicarbonate/lactate buffer (GLAD) led to less peritoneal fibrosis and fewer vessels in a chronic peritoneal exposure model in the rat. However, no concomitant reduction in small-solute transport was observed. We hypothesized that this result could be attributable to peritoneal vasodilation induced by vasoactive substances such as nitric oxide. The aim of the present study was to investigate whether fast transport of small solutes and proteins induced by exposure to GLAD could be influenced by N γ -methyl-l-arginine acetate (L-NMMA), an inhibitor of NO. These investigations used our rat model of long-term peritoneal exposure with chronic renal failure. All rats underwent peritoneal catheter implantation and a 70% nephrectomy. Thereafter, the rats were allocated to 3 groups: 16 weeks of peritoneal exposure to GLAD and L-NMMA, to GLAD only, or to buffer (bicarbonate/lactate without any osmotic agent). Afterward, a standard peritoneal permeability analysis adjusted for the rat was performed. Subsequently, the rats were euthanized, and tissue samples were obtained for morphometric determinations. No effect of L-MNNA on the transport of small solutes and proteins was From: 1 Division of Nephrology, Department of Medicine, Academic Medical Center, University of Amsterdam, Amsterdam, Netherlands; 2 Baxter R&D, Nivelles, Belgium; and 3 Dianet Foundation Amsterdam Utrecht, Netherlands. found. Also, no effect on morphology was found. Our findings make it unlikely that NO is directly involved, being more in favor of a direct effect of amino acids on peritoneal transport. Key words Amino acids, glycerol, peritoneal exposure model, nitric oxide, NO Introduction Long-term peritoneal dialysis (PD) can lead to morphologic and functional alterations of the peritoneum (1). These alterations are probably caused by chronic exposure to bioincompatible dialysis solutions. Extremely high concentrations of glucose and the presence of glucose degradation products are among the most important culprits (2). We developed a long-term peritoneal exposure model in Wistar rats, with and without chronic renal failure, in which such alterations could be induced and alternative solutions tested (3,4). A recent study showed that, compared with a conventional dialysis solution, a mixture of osmotic agents and bicarbonate/lactate buffer [glycerol 1.4%, amino acids 0.5%, dextrose 1.1% (GLAD)] used in a peritoneal exposure model in rats with renal failure resulted in a reduced number of peritoneal vessels (5). However, transport of small solutes was not reduced. We hypothesized that these unexpected findings might be attributable to vasodilation. Dilation of peritoneal vessels can be caused by exposure to amino acids or by upregulation of endothelial NO synthase (enos). A study in stable PD patients exposed to an amino acid based solution (as compared with a glucose-based solution) showed
2 8 Effects of NO on the Peritoneal Membrane higher peritoneal blood flow and higher mass transfer area coefficients (MTACs) of small solutes. This effect was independent of vasodilating prostaglandins, and it was also unlikely to be mediated by NO (6). On the other hand, uremic rats have showed increased expression of enos and a beneficial effect of NOS inhibition by N γ -nitro-l-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME) on permeability changes during peritonitis (7,8). Production of NO can be inhibited by L-arginine analogs (9) such as L-NAME and N γ -monomethyl-larginine (L-NMMA). The latter is able to inhibit both constitutive and inducible NO synthase (10). The aim of the present study was to investigate whether fast transport of small solutes and proteins induced by exposure to GLAD could be influenced by L-NMMA in our rat model of chronic peritoneal exposure with renal failure. Materials and methods Male Wistar rats (Harlan CBP, Zeist, Netherlands) with a body weight of g were divided into 3 groups: Experimental group: exposure to GLAD with L- NMMA Positive control group: exposure to GLAD only Negative control group: exposure to buffer only (bicarbonate/lactate solution without any osmotic agent) All dialysis solutions were provided by Baxter, Nivelles, Belgium. The rats were housed one to a cage under standardized conditions. All rats underwent catheter implantation and a one-step 70% nephrectomy as previously described (4,5). After the 70% nephrectomy, the animals received a nephroprotective diet to avoid premature mortality from uremia during the period of investigation. For 16 weeks, all rats received daily infusions of the designated study solution. Before instillation, all PD fluids were preheated to 37 C and heparinized (5 IU/ ml). The rats received 6 ml/100 g body weight dialysis fluid intraperitoneally until their body weight exceeded 420 g. Thereafter, the infusion volume was set at 20 ml dialysis fluid daily. To monitor renal function, blood samples were drawn under isofluran anesthesia every 2 weeks by tail vein puncture. In the GLAD L-NMMA group, L-MNNA (1 mg/kg body weight) was added to the GLAD solution and administered intraperitoneally. After the experimental period of 16 weeks, a standard peritoneal permeability analysis adjusted for the rat (SPARa) was performed (11). The rats were kept in metabolic cages for a 24-hour urine collection the day before the SPARa to allow residual renal function to be calculated. The SPARa is a modification of the human standard peritoneal permeability analysis (12) that uses dextran 70 (Hyskon: Medisan Pharmaceuticals AB, Uppsala, Sweden) as a volume marker. Every SPARa was performed in a 4-hour dwell with 3.86% Physioneal solution (Baxter Healthcare, Dublin, Ireland). After the SPARa, omental tissue was obtained for morphometric analysis. To judge the extent and distribution pattern of fibrosis, the omentum was stained with pico sirius red (Edward Gurr, BDH brand VWR International, West Chester, PA, U.S.A.). The scoring was classified as follows: 0 = normal presence of fibrous tissue (compared with tissues from untreated rats from other studies), 1 = mild fibrosis, 2 = moderate excess, 3 = severe deposition of fibrosis. Platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule 1 antibody (goat anti-rat CD31: Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA, U.S.A.) was used to count the number of vessels per microscopic field in the rat omental tissue. The vessel density was scored using computeraided morphometrics. Peritoneal transport (urea and creatinine) was expressed as dialysate-to-plasma (D/P) ratios and MTACs. Glucose absorption was calculated as the difference between the glucose in the dialysate at the start of the SPARa and the glucose in the dialysate at the end of the SPARa relative to the instilled quantity of glucose. Peritoneal function parameters and fluid kinetics such as net ultrafiltration rate, lymphatic absorption rate, transcapillary ultrafiltration rate, and free water transport were calculated as previously described (12 14). Albumin, immunoglobulin G, and fibrinogen concentrations in plasma and dialysate were measured by ELISA. Statistical analyses were performed using the SPSS software package (version 16.0: SPSS, Chicago, IL, U.S.A.). An analysis of variance with a Bonferroni correction was used to compare the study groups. Results Not all animals completed the study. Nephrectomy complications and catheter problems were the reasons for dropout in 32%. After the SPARa, 3 animals were excluded because they had signs of peritonitis on
3 de Graaff et al. 9 morphology examination of peritoneal tissues. At the end of the experimental period, 24 rats could be analyzed. Severity of kidney failure after 16 weeks was comparable in the 3 groups. Creatinine clearances were 2.5 ± 0.6 ml/min (mean ± standard deviation) for the GLAD L-NMMA group, 2.3 ± 0.5 ml/min for the GLAD group, and 2.3 ± 1.1 ml/min for the buffer group. Table I summarizes the parameters of peritoneal solute and fluid transport. Solute transport was higher in both GLAD groups than in the buffer group. The difference reached significance for the GLAD group for D/P urea and D/P albumin. Both GLAD groups showed significantly higher glucose absorption. We observed no differences between the GLAD L-NMMA and GLAD groups, meaning that no effect on peritoneal solute transport parameters of L-NMMA was observed. The GLAD L-NMMA and GLAD groups both showed reduced sodium sieving, but this reduction was not reflected in the amount of free water transport. Table II shows the semiquantitative scoring of fibrosis and vessels. All groups showed similar fibrotic changes in the omental tissue and a similar number of vessels per microscopic field, without any effect of L-NMMA. Discussion The addition of L-NMMA to a GLAD dialysis solution had no effect on peritoneal function and morphology. The present study therefore failed to solve the discrepancy between the reduction in the number of peritoneal vessels (5) and the unaltered solute transport rates with exposure to GLAD as compared with exposure to a conventional dialysis solution. Three possible explanations for the absence of an effect of L-NMMA should be considered: First, the dose of L-NMMA used in the study could have been too low. However, the same dose of L- NMMA administered intravenously to patients with septic shock caused an increase in blood pressure (15). It could therefore be expected that L-NMMA applied locally might inhibit NO synthesis in the peritoneal cavity. Second, it is possible that L-NMMA has an effect only immediately after administration. In our study design, L-NMMA was administered daily for 16 weeks. After those 16 weeks, the rats did not receive L-NMMA on the specific day of the peritoneal function test. Third, it may be that NO is uninvolved in stable, noninfected PD. Observations in a rabbit model of PD support this idea. The addition of L-arginine, the substrate of NO synthesis, had no more effect on peritoneal transport parameters than did the inhibitor L-NMMA (16). Addition of the NO donor nitroprusside in the same rabbit model increased peritoneal albumin clearance 86%. An exchange with a 1.1% amino-acid solution and one with TABLE I Peritoneal transport parameters measured during a standard peritoneal permeability analysis adjusted for the rat a GLAD L-NMMA GLAD Buffer Variable (n=9) (n=7) (n=8) D/P urea 0.78± ±0.09 b 0.69±0.06 D/P creatinine 0.58± ± ±0.10 MTAC urea 0.20± ± ±0.02 MTAC creatinine 0.12± ± ±0.03 Glucose absorption (%) 72±3 b 69±4 b 62±6 Net ultrafiltration rate (μl/min) 46±15 51±15 44±12 Lymphatic absorption rate (μl/min) 31±8 31±17 28±12 Transcapillary ultrafiltration rate (μl/min) 79±12 83±14 73±10 Maximal dip D/P sodium 0.10±0.02 b 0.10±0.02 b 0.14±0.04 Free water transport (ml at 60 min.) 3.1± ± ±0.6 D/P albumin ( 10 3 ) 12.4± ±5.9 b 8.6±1.7 D/P immunoglobulin G ( 10 3 ) 9.2± ± ±1.2 D/P fibrinogen ( 10 3 ) 4.6± ± ±2.5 a Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation. b p < 0.05 versus buffer. GLAD = glycerol, amino acids, and dextrose in a bicarbonate/lactate buffer; L-NMMA = N γ -methyl-l-arginine acetate; D/P = dialysate-to-plasma ratio; MTAC = mass transfer area coefficient.
4 10 Effects of NO on the Peritoneal Membrane TABLE II Quantification of fibrosis and number of blood vessels in omental tissue a GLAD L-NMMA GLAD Buffer Variable (n=9) (n=7) (n=8) Submesothelial area 1.7± ± ±0.8 Intersegmental area 1.2± ± ±0.5 Perivascular area 1.3± ± ±0.5 Overall fibrotic score 4.2± ± ±1.3 Vessels per microscopic field (n) 22±3 21±8 16±3 a Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation. No significant differences were observed. GLAD = glycerol, amino acids, and dextrose in a bicarbonate/lactate buffer; L-NMMA = N γ -methyl-larginine acetate. nitroprusside increased small-solute transport in PD patients to some extent, but only nitroprusside doubled peritoneal protein clearances (17). Kinetic modeling in the same study showed that the major effect of nitroprusside is on the large-pore radius, a parameter that amino acids hardly influence. Conclusions It can be concluded that the absence of a decrease in small-solute transport is most likely attributable to the vasodilating effects of the amino acids present in GLAD. No indication is present that transport would be induced by inflammation leading to induction of NO synthase. These results support further investigations in humans. Acknowledgments The authors acknowledge Agnes G. Zegwaard, Charlotte P. Peters, and Deirisa Lopes Barreto for their participation in the experiment, and Jos B. Mulder for his assistance in the histology analyses. References 1 De Vriese AS, Mortier S, Lameire NH. What happens to the peritoneal membrane in long-term peritoneal dialysis? Perit Dial Int 2001;21(Suppl 3):S Davies SJ, Phillips L, Naish PF, Russell GI. Peritoneal glucose exposure and changes in membrane solute transport with time on peritoneal dialysis. J Am Soc Nephrol 2001;12: Zweers MM, Splint LJ, Krediet RT, Struijk DG. Ultrastructure of basement membranes of peritoneal capillaries in a chronic peritoneal infusion model in the rat. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2001;16: Vrtovsnik F, Coester A, Lopes Barreto D, et al. The induction of chronic kidney failure in a long-term peritoneal exposure model in the rat: effects on functional and structural peritoneal alterations. Perit Dial Int 2010;[in press]. 5 de Graaff M, Zegwaard AH, Zweers MM, et al. The effects of a dialysis solution with a combination of glycerol/amino acids/dextrose on the peritoneal membrane in chronic renal failure. Perit Dial Int 2010;30: Douma CE, de Waart DR, Struijk DG, Krediet RT. Effect of amino acid based dialysate on peritoneal blood flow and permeability in stable CAPD patients: a potential role for nitric oxide? Clin Nephrol 1996;45: Combet S, Ferrier ML, Landschoot van M, et al. Chronic uremia induces permeability changes, increased nitric oxide synthase expression, and structural modifications in the peritoneum. J Am Soc Nephrol 2001;12: Ferrier ML, Combet S, Landschoot van M, et al. Inhibition of nitric oxide synthase reverses changes in peritoneal permeability in a rat model of acute peritonitis. Kidney Int 2001;60: Gross SS, Stuehr DJ, Aisaka K, Jaffe EA, Levi R, Griffith OW. Macrophage and endothelial cell nitric oxide synthesis: cell-type selective inhibition by NGaminoarginine, NG-nitroarginine and NGmethylarginine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1990;170: Lambert LE, Whitten JP, Baron BM, Cheng HC, Doherty NS, McDonald IA. Nitric oxide synthesis in the CNS endothelium and macrophages differs in its sensitivity to inhibition by arginine analogues. Life Sci 1991;48: Zweers MM, Splint LJ, Krediet RT, Struijk DG. Effect of fluid supplementation and modality on peritoneal permeability characteristics in a rat peritoneal dialysis model. Perit Dial Int 2001;21: Smit W, van Dijk P, Langedijk MJ, et al. Peritoneal function and assessment of reference values using a 3.86% glucose solution. Perit Dial Int 2003;23: Smit W, Struijk DG, Ho-dac-Pannekeet MM, Krediet RT. Quantification of free water transport in peritoneal dialysis. Kidney Int 2004;66: Zweers MM, Imholz AL, Struijk DG, Krediet RT. Correction of sodium sieving for diffusion from the circulation. Adv Perit Dial 1999;15: Petros A, Bennett D, Vallance P. Effect of nitric oxide synthase inhibitors on hypotension in patients with septic shock. Lancet 1991;338: Douma CE, Zweers MM, de Waart DR, van der Wardt AB, Krediet RT, Struijk DG. Substrate and
5 de Graaff et al. 11 inhibitor for nitric oxide synthase during peritoneal dialysis in rabbits. Perit Dial Int 1999;19(Suppl 2):S Douma CE, Imholz AL, Struijk DG, Krediet RT. Similarities and differences between the effect of amino acids and nitroprusside on peritoneal permeability during CAPD. Blood Purif 1998;16: Corresponding author: Marijke de Graaff, Academic Medical Center, Division of Nephrology, Department of Medicine, Room A01-132, PO Box 22660, Amsterdam 1100 DD Netherlands.
The relationship between effluent potassium due to cellular release, free water transport and CA125 in peritoneal dialysis patients
 NDT Plus (2008) 1 [Suppl 4]: iv41 iv45 doi: 10.1093/ndtplus/sfn123 The relationship between effluent potassium due to cellular release, free water transport and CA125 in peritoneal dialysis patients Annemieke
NDT Plus (2008) 1 [Suppl 4]: iv41 iv45 doi: 10.1093/ndtplus/sfn123 The relationship between effluent potassium due to cellular release, free water transport and CA125 in peritoneal dialysis patients Annemieke
Free-water transport in fast transport status: A comparison between CAPD peritonitis and long-term PD
 Kidney International, Vol. 65 (2004), pp. 298 303 Free-water transport in fast transport status: A comparison between CAPD peritonitis and long-term PD WATSKE SMIT, NICOLE VAN DEN BERG, NATALIE SCHOUTEN,
Kidney International, Vol. 65 (2004), pp. 298 303 Free-water transport in fast transport status: A comparison between CAPD peritonitis and long-term PD WATSKE SMIT, NICOLE VAN DEN BERG, NATALIE SCHOUTEN,
Free water transport: Clinical implications. Sodium sieving during short very hypertonic dialysis exchanges
 Free water transport: Clinical implications Raymond T Krediet, MD,PhD University of Amsterdam Sodium sieving during short very hypertonic dialysis exchanges Nolph KD et al. Ann Int Med 1969;70:931-947
Free water transport: Clinical implications Raymond T Krediet, MD,PhD University of Amsterdam Sodium sieving during short very hypertonic dialysis exchanges Nolph KD et al. Ann Int Med 1969;70:931-947
Analysis of fluid transport pathways and their determinants in peritoneal dialysis patients with ultrafiltration failure
 original article http://www.kidney-international.org & 26 International Society of Nephrology Analysis of fluid transport pathways and their determinants in peritoneal dialysis patients with ultrafiltration
original article http://www.kidney-international.org & 26 International Society of Nephrology Analysis of fluid transport pathways and their determinants in peritoneal dialysis patients with ultrafiltration
Free water transport, small pore transport and the osmotic pressure gradient
 Nephrol Dial Transplant (2008) 23: 2350 2355 doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfm768 Advance Access publication 5 November 2007 Original Article Free water transport, small pore transport and the osmotic pressure gradient
Nephrol Dial Transplant (2008) 23: 2350 2355 doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfm768 Advance Access publication 5 November 2007 Original Article Free water transport, small pore transport and the osmotic pressure gradient
3/21/2017. Solute Clearance and Adequacy Targets in Peritoneal Dialysis. Peritoneal Membrane. Peritoneal Membrane
 3/21/2017 Solute Clearance and Adequacy Targets in Peritoneal Dialysis Steven Guest MD Director, Medical Consulting Services Baxter Healthcare Corporation Deerfield, IL, USA Peritoneal Membrane Image courtesy
3/21/2017 Solute Clearance and Adequacy Targets in Peritoneal Dialysis Steven Guest MD Director, Medical Consulting Services Baxter Healthcare Corporation Deerfield, IL, USA Peritoneal Membrane Image courtesy
How to evaluate the peritoneal membrane?
 How to evaluate the peritoneal membrane? B. Bammens Brussels, May 12 2016 BELGIUM How to evaluate a hemodialyzer? How to evaluate a hemodialyzer? How to evaluate a hemodialyzer? From: Robert W. Schrier
How to evaluate the peritoneal membrane? B. Bammens Brussels, May 12 2016 BELGIUM How to evaluate a hemodialyzer? How to evaluate a hemodialyzer? How to evaluate a hemodialyzer? From: Robert W. Schrier
PART ONE. Peritoneal Kinetics and Anatomy
 PART ONE Peritoneal Kinetics and Anatomy Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis, Vol. 20, 2004 Ewa E. Kaczmarek, Alicja E. Grzegorzewska Two Years on Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis Does It Change Peritoneal
PART ONE Peritoneal Kinetics and Anatomy Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis, Vol. 20, 2004 Ewa E. Kaczmarek, Alicja E. Grzegorzewska Two Years on Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis Does It Change Peritoneal
Objectives. Peritoneal Dialysis vs. Hemodialysis 02/27/2018. Peritoneal Dialysis Prescription and Adequacy Monitoring
 Peritoneal Dialysis Prescription and Adequacy Monitoring Christine B. Sethna, MD, EdM Division Director, Pediatric Nephrology Cohen Children s Medical Center Associate Professor Hofstra Northwell School
Peritoneal Dialysis Prescription and Adequacy Monitoring Christine B. Sethna, MD, EdM Division Director, Pediatric Nephrology Cohen Children s Medical Center Associate Professor Hofstra Northwell School
Physiology of Blood Purification: Dialysis & Apheresis. Outline. Solute Removal Mechanisms in RRT
 Physiology of Blood Purification: Dialysis & Apheresis Jordan M. Symons, MD University of Washington School of Medicine Seattle Children s Hospital Outline Physical principles of mass transfer Hemodialysis
Physiology of Blood Purification: Dialysis & Apheresis Jordan M. Symons, MD University of Washington School of Medicine Seattle Children s Hospital Outline Physical principles of mass transfer Hemodialysis
Strategies to Preserve the Peritoneal Membrane. Reusz GS Ist Dept of Pediatrics Semmelweis University, Budapest
 Strategies to Preserve the Peritoneal Membrane Reusz GS Ist Dept of Pediatrics Semmelweis University, Budapest Outline 1. Structure of the peritoneal membrane 2. Mechanisms of peritoneal injury 3. Signs
Strategies to Preserve the Peritoneal Membrane Reusz GS Ist Dept of Pediatrics Semmelweis University, Budapest Outline 1. Structure of the peritoneal membrane 2. Mechanisms of peritoneal injury 3. Signs
What is a PET? Although there are many types of pets, we will be discussing the Peritoneal Equilibration Test
 1 2 3 What is a PET? Although there are many types of pets, we will be discussing the Peritoneal Equilibration Test 4 Background information about the PET 1983 Dr. Twardowski and colleagues began measuring
1 2 3 What is a PET? Although there are many types of pets, we will be discussing the Peritoneal Equilibration Test 4 Background information about the PET 1983 Dr. Twardowski and colleagues began measuring
Ultrafiltration failure (UFF) is an important cause of
 Peritoneal Dialysis International, Vol. 32, pp. 537 544 doi: 10.3747/pdi.2011.00175 0896-8608/12 $3.00 +.00 Copyright 2012 International Society for Peritoneal Dialysis TWO-IN-ONE PROTOCOL: SIMULTANEOUS
Peritoneal Dialysis International, Vol. 32, pp. 537 544 doi: 10.3747/pdi.2011.00175 0896-8608/12 $3.00 +.00 Copyright 2012 International Society for Peritoneal Dialysis TWO-IN-ONE PROTOCOL: SIMULTANEOUS
Automated peritoneal dialysis (APD) has become
 Peritoneal Dialysis International, Vol. 32, pp. 605 611 doi: 10.3747/pdi.2011.00166 0896-8608/12 $3.00 +.00 Copyright 2012 International Society for Peritoneal Dialysis TIME COURSE OF PERITONEAL FUNCTION
Peritoneal Dialysis International, Vol. 32, pp. 605 611 doi: 10.3747/pdi.2011.00166 0896-8608/12 $3.00 +.00 Copyright 2012 International Society for Peritoneal Dialysis TIME COURSE OF PERITONEAL FUNCTION
2016 Annual Dialysis Conference Michelle Hofmann RN, BSN, CNN Renal Clinical Educator - Home
 Fluid Management 2016 Annual Dialysis Conference Michelle Hofmann RN, BSN, CNN Renal Clinical Educator - Home Objectives Define euvolemia Determine factors which contribute to fluid imbalance Discuss strategies
Fluid Management 2016 Annual Dialysis Conference Michelle Hofmann RN, BSN, CNN Renal Clinical Educator - Home Objectives Define euvolemia Determine factors which contribute to fluid imbalance Discuss strategies
Benefits of switching from a conventional to a low-gdp bicarbonate/lactate-buffered dialysis solution in a rat model
 Kidney International, Vol. 67 (2005), pp. 1559 1565 Benefits of switching from a conventional to a low-gdp bicarbonate/lactate-buffered dialysis solution in a rat model SISKA MORTIER, DIRK FAICT, NORBERT
Kidney International, Vol. 67 (2005), pp. 1559 1565 Benefits of switching from a conventional to a low-gdp bicarbonate/lactate-buffered dialysis solution in a rat model SISKA MORTIER, DIRK FAICT, NORBERT
Peritoneal dialysis fluid-induced changes of the peritoneal membrane are reversible after peritoneal rest in rats
 Nephrol Dial Transplant (2005) 20: 189 193 doi:10.1093/ndt/gfh559 Advance Access publication 30 November 2004 Brief Report Peritoneal dialysis fluid-induced changes of the peritoneal membrane are reversible
Nephrol Dial Transplant (2005) 20: 189 193 doi:10.1093/ndt/gfh559 Advance Access publication 30 November 2004 Brief Report Peritoneal dialysis fluid-induced changes of the peritoneal membrane are reversible
Chapter 2 Peritoneal Equilibration Testing and Application
 Chapter 2 Peritoneal Equilibration Testing and Application Francisco J. Cano Case Presentation FW, a recently diagnosed patient with CKD Stage 5, is a 6-year-old boy who has been recommended to initiate
Chapter 2 Peritoneal Equilibration Testing and Application Francisco J. Cano Case Presentation FW, a recently diagnosed patient with CKD Stage 5, is a 6-year-old boy who has been recommended to initiate
PERITONEAL EQUILIBRATION TEST. AR. Merrikhi. MD. Isfahan University of Medical Sciences
 PERITONEAL EQUILIBRATION TEST AR. Merrikhi. MD. Isfahan University of Medical Sciences INTRODUCTION The peritoneal equilibration test (PET) is a semiquantitative assessment of peritoneal membrane transport
PERITONEAL EQUILIBRATION TEST AR. Merrikhi. MD. Isfahan University of Medical Sciences INTRODUCTION The peritoneal equilibration test (PET) is a semiquantitative assessment of peritoneal membrane transport
PART FOUR. Metabolism and Nutrition
 PART FOUR Metabolism and Nutrition Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis, Vol. 22, 2006 Costas Fourtounas, Eirini Savidaki, Marilena Roumelioti, Periklis Dousdampanis, Andreas Hardalias, Pantelitsa Kalliakmani,
PART FOUR Metabolism and Nutrition Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis, Vol. 22, 2006 Costas Fourtounas, Eirini Savidaki, Marilena Roumelioti, Periklis Dousdampanis, Andreas Hardalias, Pantelitsa Kalliakmani,
Ana Paula Bernardo. CHP Hospital de Santo António ICBAS/ Universidade do Porto
 Ana Paula Bernardo CHP Hospital de Santo António ICBAS/ Universidade do Porto Clinical relevance of hyperphosphatemia Phosphate handling in dialysis patients Phosphate kinetics in PD peritoneal phosphate
Ana Paula Bernardo CHP Hospital de Santo António ICBAS/ Universidade do Porto Clinical relevance of hyperphosphatemia Phosphate handling in dialysis patients Phosphate kinetics in PD peritoneal phosphate
Peritoneal Transport: From Basics to Bedside
 Review Article Peritoneal Transport: From Basics to Bedside Tao Wang, Bengt Lindholm 1 Comprehensive understanding of peritoneal solute and fluid transport is of clinical significance to nephrologists
Review Article Peritoneal Transport: From Basics to Bedside Tao Wang, Bengt Lindholm 1 Comprehensive understanding of peritoneal solute and fluid transport is of clinical significance to nephrologists
Hyaluronan Influence on Diffusive Permeability of the Peritoneum In Vitro
 Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis, Vol. 24, 2008 Teresa Grzelak, Beata Szary, Krystyna Czyzewska Hyaluronan Influence on Diffusive Permeability of the Peritoneum In Vitro Hyaluronan (HA), an essential component
Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis, Vol. 24, 2008 Teresa Grzelak, Beata Szary, Krystyna Czyzewska Hyaluronan Influence on Diffusive Permeability of the Peritoneum In Vitro Hyaluronan (HA), an essential component
Failure to obtain adequate rates of ultrafiltration (UF) is
 Page 1 of 6 Peritoneal Dialysis International Peritoneal Dialysis International, inpress www.pdiconnect.com 0896-8608/16 $3.00 +.00 Copyright 2016 International Society for Peritoneal Dialysis ANALYSIS
Page 1 of 6 Peritoneal Dialysis International Peritoneal Dialysis International, inpress www.pdiconnect.com 0896-8608/16 $3.00 +.00 Copyright 2016 International Society for Peritoneal Dialysis ANALYSIS
Drug Use in Dialysis
 (Last Updated: 08/22/2018) Created by: Socco, Samantha Drug Use in Dialysis Drambarean, B. (2017). Drug Use in Dialysis. Lecture presented at PHAR 503 Lecture in UIC College of Pharmacy, Chicago. DIALYSIS
(Last Updated: 08/22/2018) Created by: Socco, Samantha Drug Use in Dialysis Drambarean, B. (2017). Drug Use in Dialysis. Lecture presented at PHAR 503 Lecture in UIC College of Pharmacy, Chicago. DIALYSIS
Sequential peritoneal equilibration test: a new method for assessment and modelling of peritoneal transport
 Nephrol Dial Transplant (2013) 28: 447 454 doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfs592 Sequential peritoneal equilibration test: a new method for assessment and modelling of peritoneal transport Magda Galach 1, Stefan Antosiewicz
Nephrol Dial Transplant (2013) 28: 447 454 doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfs592 Sequential peritoneal equilibration test: a new method for assessment and modelling of peritoneal transport Magda Galach 1, Stefan Antosiewicz
Adequacy of automated peritoneal dialysis with and without manual daytime exchange: A randomized controlled trial
 http://www.kidney-international.org & 2006 International Society of Nephrology original article Adequacy of automated peritoneal dialysis with and without manual daytime exchange: A randomized controlled
http://www.kidney-international.org & 2006 International Society of Nephrology original article Adequacy of automated peritoneal dialysis with and without manual daytime exchange: A randomized controlled
Early Estimation of High Peritoneal Permeability Can Predict Poor Prognosis for Technique Survival in Patients on Peritoneal Dialysis
 Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis, Vol. 22, 2006 Hidetomo Nakamoto, 1,2 Hirokazu Imai, 2 Hideki Kawanishi, 2 Masahiko Nakamoto, 2 Jun Minakuchi, 2 Shinichi Kumon, 2 Syuichi Watanabe, 2 Yoshhiko Shiohira,
Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis, Vol. 22, 2006 Hidetomo Nakamoto, 1,2 Hirokazu Imai, 2 Hideki Kawanishi, 2 Masahiko Nakamoto, 2 Jun Minakuchi, 2 Shinichi Kumon, 2 Syuichi Watanabe, 2 Yoshhiko Shiohira,
The low ph of conventional peritoneal dialysis (PD) solutions,
 Peritoneal Dialysis International, Vol. 29, pp. 158 162 Printed in Canada. All rights reserved. 0896-8608/09 $3.00 +.00 Copyright 2009 International Society for Peritoneal Dialysis EFFECTS OF IONIZED SODIUM
Peritoneal Dialysis International, Vol. 29, pp. 158 162 Printed in Canada. All rights reserved. 0896-8608/09 $3.00 +.00 Copyright 2009 International Society for Peritoneal Dialysis EFFECTS OF IONIZED SODIUM
The peritoneal equilibration test (PET) was developed THE SHORT PET IN PEDIATRICS. Bradley A. Warady and Janelle Jennings
 Peritoneal Dialysis International, Vol. 27, pp. 441 445 Printed in Canada. All rights reserved. 0896-8608/07 $3.00 +.00 Copyright 2007 International Society for Peritoneal Dialysis THE SHORT PET IN PEDIATRICS
Peritoneal Dialysis International, Vol. 27, pp. 441 445 Printed in Canada. All rights reserved. 0896-8608/07 $3.00 +.00 Copyright 2007 International Society for Peritoneal Dialysis THE SHORT PET IN PEDIATRICS
Peritoneal Dialysis Prescriptions: A Primer for Nurses
 Peritoneal Dialysis Prescriptions: A Primer for Nurses A Primer ABCs of PD R x Betty Kelman RN-EC MEd CNeph (C) Toronto General Hospital University Health Network Toronto, Ontario, Canada A moment to remember
Peritoneal Dialysis Prescriptions: A Primer for Nurses A Primer ABCs of PD R x Betty Kelman RN-EC MEd CNeph (C) Toronto General Hospital University Health Network Toronto, Ontario, Canada A moment to remember
A Case of Encapsulating Peritoneal Sclerosis Suspected to Result from the Use of Icodextrin Peritoneal Solution
 Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis, Vol. 25, 2009 Hideki Kawanishi, Sadanori Shintaku, Masayuki Shishida, Misaki Morrishi, Shinichiro Tsuchiya, Kiyohiko Dohi A Case of Encapsulating Peritoneal Sclerosis Suspected
Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis, Vol. 25, 2009 Hideki Kawanishi, Sadanori Shintaku, Masayuki Shishida, Misaki Morrishi, Shinichiro Tsuchiya, Kiyohiko Dohi A Case of Encapsulating Peritoneal Sclerosis Suspected
02/21/2017. Assessment of the Peritoneal Membrane: Practice Workshop. Objectives. Review of Physiology. Marina Villano, MSN, RN, CNN
 Assessment of the Peritoneal Membrane: Practice Workshop Marina Villano, MSN, RN, CNN marina.villano@fmc-na.com Objectives Briefly review normal peritoneal physiology including the three pore model. Compare
Assessment of the Peritoneal Membrane: Practice Workshop Marina Villano, MSN, RN, CNN marina.villano@fmc-na.com Objectives Briefly review normal peritoneal physiology including the three pore model. Compare
Volume Management 2/25/2017. Disclosures statement: Objectives. To discuss evaluation of hypervolemia in peritoneal dialysis patients
 Volume Management Sagar Nigwekar MD, MMSc Massachusetts General Hospital E-mail: snigwekar@mgh.harvard.edu March 14, 2017 Disclosures statement: Consultant: Allena, Becker Professional Education Grant
Volume Management Sagar Nigwekar MD, MMSc Massachusetts General Hospital E-mail: snigwekar@mgh.harvard.edu March 14, 2017 Disclosures statement: Consultant: Allena, Becker Professional Education Grant
PD prescribing for all. QUESTION: Which approach? One size fits all or haute couture? (1) or (2)? The patient 18/03/2014.
 PD prescribing for all Pr Max Dratwa Honorary consultant, Nephrology-Dialysis CHU Brugmann Université Libre de Bruxelles BSN 22 March 2014 QUESTION: Which approach? One size fits all or haute couture?
PD prescribing for all Pr Max Dratwa Honorary consultant, Nephrology-Dialysis CHU Brugmann Université Libre de Bruxelles BSN 22 March 2014 QUESTION: Which approach? One size fits all or haute couture?
Encapsulating peritoneal sclerosis (EPS) is a lifethreatening
 Peritoneal Dialysis International, Vol. 30, pp. 163 169 doi: 10.3747/pdi.2009.00022 0896-8608/10 $3.00 +.00 Copyright 2010 International Society for Peritoneal Dialysis ORIGINAL ARTICLES EARLY DIAGNOSTIC
Peritoneal Dialysis International, Vol. 30, pp. 163 169 doi: 10.3747/pdi.2009.00022 0896-8608/10 $3.00 +.00 Copyright 2010 International Society for Peritoneal Dialysis ORIGINAL ARTICLES EARLY DIAGNOSTIC
Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis, Vol. 29, 2013
 Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis, Vol. 29, 2013 Takeyuki Hiramatsu, 1 Takahiro Hayasaki, 1 Akinori Hobo, 1 Shinji Furuta, 1 Koki Kabu, 2 Yukio Tonozuka, 2 Yoshiyasu Iida 1 Icodextrin Eliminates Phosphate
Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis, Vol. 29, 2013 Takeyuki Hiramatsu, 1 Takahiro Hayasaki, 1 Akinori Hobo, 1 Shinji Furuta, 1 Koki Kabu, 2 Yukio Tonozuka, 2 Yoshiyasu Iida 1 Icodextrin Eliminates Phosphate
Renal Self Learning Package INTRODUCTION TO PERITONEAL DIALYSIS
 Renal Self Learning Package INTRODUCTION TO PERITONEAL DIALYSIS St George Hospital Renal Department, reviewed 2017 St George Hospital Renal Department RENAL SELF LEARNING PACKAGE INTRODUCTION TO PERITONEAL
Renal Self Learning Package INTRODUCTION TO PERITONEAL DIALYSIS St George Hospital Renal Department, reviewed 2017 St George Hospital Renal Department RENAL SELF LEARNING PACKAGE INTRODUCTION TO PERITONEAL
Peritoneal Dialysis Solutions. Cristina Lage Medical Affairs and Information
 Peritoneal Dialysis Solutions Cristina Lage Medical Affairs and Information 1 Standard, single-chambered FME PD solutions - composition * Electrolytes to maintain balance Sodium 134-140 mmol/l Potassium
Peritoneal Dialysis Solutions Cristina Lage Medical Affairs and Information 1 Standard, single-chambered FME PD solutions - composition * Electrolytes to maintain balance Sodium 134-140 mmol/l Potassium
The CARI Guidelines Caring for Australians with Renal Impairment. Peritoneal transport and ultrafiltration GUIDELINES
 Date written: January 2004 Final submission: May 2004 Peritoneal transport and ultrafiltration GUIDELINES No recommendations possible based on Level I or II evidence SUGGESTIONS FOR CLINICAL CARE (Suggestions
Date written: January 2004 Final submission: May 2004 Peritoneal transport and ultrafiltration GUIDELINES No recommendations possible based on Level I or II evidence SUGGESTIONS FOR CLINICAL CARE (Suggestions
What Does Peritoneal Thickness in Peritoneal Dialysis Patients Tell Us?
 Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis, Vol. 23, 2007 Soner Duman, 1 Suha Sureyya Ozbek, 2 Ebru Sevinc Gunay, 1 Devrim Bozkurt, 1 Gulay Asci, 1 Savas Sipahi, 1 Fatih Kirçelli, 1 Muhittin Ertilav, 1 Mehmet Özkahya,
Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis, Vol. 23, 2007 Soner Duman, 1 Suha Sureyya Ozbek, 2 Ebru Sevinc Gunay, 1 Devrim Bozkurt, 1 Gulay Asci, 1 Savas Sipahi, 1 Fatih Kirçelli, 1 Muhittin Ertilav, 1 Mehmet Özkahya,
Spontaneous VEGF Production by Cultured Peritoneal Mesothelial Cells from Patients on Peritoneal Dialysis Long-term peritoneal dialysis (PD) may
 Spontaneous VEGF Production by Cultured Peritoneal Mesothelial Cells from Patients on Peritoneal Dialysis Long-term peritoneal dialysis (PD) may result in increased peritoneal vascularization secondary
Spontaneous VEGF Production by Cultured Peritoneal Mesothelial Cells from Patients on Peritoneal Dialysis Long-term peritoneal dialysis (PD) may result in increased peritoneal vascularization secondary
PART ONE. Peritoneal Kinetics and Anatomy
 PART ONE Peritoneal Kinetics and Anatomy Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis, Vol. 22, 2006 Paul A. Fein, Irfan Fazil, Muhammad A. Rafiq, Teresa Schloth, Betty Matza, Jyotiprakas Chattopadhyay, Morrell M.
PART ONE Peritoneal Kinetics and Anatomy Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis, Vol. 22, 2006 Paul A. Fein, Irfan Fazil, Muhammad A. Rafiq, Teresa Schloth, Betty Matza, Jyotiprakas Chattopadhyay, Morrell M.
Gambrosol Trio, clinical studies 91 Glitazone, malnutrition-inflammationatherosclerosis
 Subject Index Acidosis, see Metabolic acidosis Activated carbon, sorbents 337 Adipokines adipose tissue and systemic inflammation 169 functions 167 169 prospects for study in renal patients 171 Adiponectin,
Subject Index Acidosis, see Metabolic acidosis Activated carbon, sorbents 337 Adipokines adipose tissue and systemic inflammation 169 functions 167 169 prospects for study in renal patients 171 Adiponectin,
Acid-base profile in patients on PD
 Kidney International, Vol. 6, Supplement 88 (23), pp. S26 S36 Acid-base profile in patients on PD SALIM MUJAIS Renal Division, Baxter Healthcare Corporation, McGaw Park, Illinois Acid-base profile in patients
Kidney International, Vol. 6, Supplement 88 (23), pp. S26 S36 Acid-base profile in patients on PD SALIM MUJAIS Renal Division, Baxter Healthcare Corporation, McGaw Park, Illinois Acid-base profile in patients
PERITONEAL DIALYSIS PRESCRIPTION MANAGEMENT QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE
 PERITONEAL DIALYSIS PRESCRIPTION MANAGEMENT QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE This quick reference guide will help serve as a reference tool for clinicians setting a patient s Peritoneal Dialysis (PD) prescription.
PERITONEAL DIALYSIS PRESCRIPTION MANAGEMENT QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE This quick reference guide will help serve as a reference tool for clinicians setting a patient s Peritoneal Dialysis (PD) prescription.
LLL Session - Nutritional support in renal disease
 ESPEN Congress Leipzig 2013 LLL Session - Nutritional support in renal disease Peritoneal dialysis D. Teta (CH) Nutrition Support in Patients undergoing Peritoneal Dialysis (PD) Congress ESPEN, Leipzig
ESPEN Congress Leipzig 2013 LLL Session - Nutritional support in renal disease Peritoneal dialysis D. Teta (CH) Nutrition Support in Patients undergoing Peritoneal Dialysis (PD) Congress ESPEN, Leipzig
You can sleep while I dialyze
 You can sleep while I dialyze Nocturnal Peritoneal Dialysis Dr. Suneet Singh Medical Director, PD, VGH Division of Nephrology University of British Columbia Acknowledgements Melissa Etheridge You can sleep
You can sleep while I dialyze Nocturnal Peritoneal Dialysis Dr. Suneet Singh Medical Director, PD, VGH Division of Nephrology University of British Columbia Acknowledgements Melissa Etheridge You can sleep
Glucose sparing in peritoneal dialysis: Implications and metrics
 http://www.kidney-international.org & 26 International Society of Nephrology Glucose sparing in peritoneal dialysis: Implications and metrics C Holmes 1 and S Mujais 1 1 Renal Division, Baxter Healthcare
http://www.kidney-international.org & 26 International Society of Nephrology Glucose sparing in peritoneal dialysis: Implications and metrics C Holmes 1 and S Mujais 1 1 Renal Division, Baxter Healthcare
No increase in small-solute transport in peritoneal dialysis patients treated without hypertonic glucose for fifty-four months
 Pagniez et al. BMC Nephrology (2017) 18:278 DOI 10.1186/s12882-017-0690-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE No increase in small-solute transport in peritoneal dialysis patients treated without hypertonic glucose for fifty-four
Pagniez et al. BMC Nephrology (2017) 18:278 DOI 10.1186/s12882-017-0690-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE No increase in small-solute transport in peritoneal dialysis patients treated without hypertonic glucose for fifty-four
Renal Disease and PK/PD. Anjay Rastogi MD PhD Division of Nephrology
 Renal Disease and PK/PD Anjay Rastogi MD PhD Division of Nephrology Drugs and Kidneys Kidney is one of the major organ of drug elimination from the human body Renal disease and dialysis alters the pharmacokinetics
Renal Disease and PK/PD Anjay Rastogi MD PhD Division of Nephrology Drugs and Kidneys Kidney is one of the major organ of drug elimination from the human body Renal disease and dialysis alters the pharmacokinetics
The Physiology of Peritoneal Dialysis As Related To Drug Removal
 The Physiology of Peritoneal Dialysis As Related To Drug Removal Thomas A. Golper, MD, FACP, FASN Vanderbilt University Medical Center Nashville, TN thomas.golper@vanderbilt.edu Clearance By Dialysis Clearance
The Physiology of Peritoneal Dialysis As Related To Drug Removal Thomas A. Golper, MD, FACP, FASN Vanderbilt University Medical Center Nashville, TN thomas.golper@vanderbilt.edu Clearance By Dialysis Clearance
Maintaining Peritoneal Dialysis Adequacy: The Process of Incremental Prescription
 Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis, Vol. 34, 2018 Susie Q. Lew Maintaining Peritoneal Dialysis Adequacy: The Process of Incremental Prescription Urea kinetics (weekly Kt/V) greater than 1.7 generally define
Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis, Vol. 34, 2018 Susie Q. Lew Maintaining Peritoneal Dialysis Adequacy: The Process of Incremental Prescription Urea kinetics (weekly Kt/V) greater than 1.7 generally define
Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis and Automated Peritoneal Dialysis: What, Who, Why, and How? Review and Case Study
 Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis, Vol. 33, 2017 Kunal Malhotra, Ramesh Khanna Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis and Automated Peritoneal Dialysis: What, Who, Why, and How? Review and Case Study
Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis, Vol. 33, 2017 Kunal Malhotra, Ramesh Khanna Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis and Automated Peritoneal Dialysis: What, Who, Why, and How? Review and Case Study
ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY AND RENAL REPLACEMENT THERAPY IN CHILDREN. Bashir Admani KPA Precongress 24/4/2018
 ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY AND RENAL REPLACEMENT THERAPY IN CHILDREN Bashir Admani KPA Precongress 24/4/2018 Case presentation SP 11month old Presenting complaint: bloody diarrhea, lethargy On exam: dehydration,
ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY AND RENAL REPLACEMENT THERAPY IN CHILDREN Bashir Admani KPA Precongress 24/4/2018 Case presentation SP 11month old Presenting complaint: bloody diarrhea, lethargy On exam: dehydration,
HDx THERAPY. Enabled by. Making possible personal.
 HDx THERAPY Enabled by Making possible personal. THE NEXT HORIZON IN DIALYSIS IS CLOSER THAN YOU THINK PHOSPHATE UREA HDx BY THERANOVA EXPANDS YOUR RENAL POSSIBILITIES The new HDx therapy (expanded HD)
HDx THERAPY Enabled by Making possible personal. THE NEXT HORIZON IN DIALYSIS IS CLOSER THAN YOU THINK PHOSPHATE UREA HDx BY THERANOVA EXPANDS YOUR RENAL POSSIBILITIES The new HDx therapy (expanded HD)
Peritoneal transport testing
 THOROUGH CRITICAL APPRAISAL www.sin-italy.org/jnonline www.jnephrol.com Peritoneal transport testing Vincenzo La Milia Nephrology and Dialysis Department, A. Manzoni Hospital, Lecco - Italy Ab s t r a
THOROUGH CRITICAL APPRAISAL www.sin-italy.org/jnonline www.jnephrol.com Peritoneal transport testing Vincenzo La Milia Nephrology and Dialysis Department, A. Manzoni Hospital, Lecco - Italy Ab s t r a
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues
 BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
MOLECULAR SIZE, ELECTRICAL CHARGE, AND SHAPE DETERMINE THE FILTERABILITY OF SOLUTES ACROSS THE GLOMERULAR FILTRATION BARRIER
 MOLECULAR SIZE, ELECTRICAL CHARGE, AND SHAPE DETERMINE THE FILTERABILITY OF SOLUTES ACROSS THE GLOMERULAR FILTRATION BARRIER The glomerular filtration barrier consists of three elements: (1) endothelial
MOLECULAR SIZE, ELECTRICAL CHARGE, AND SHAPE DETERMINE THE FILTERABILITY OF SOLUTES ACROSS THE GLOMERULAR FILTRATION BARRIER The glomerular filtration barrier consists of three elements: (1) endothelial
End-Stage Renal Disease. Anna Vinnikova, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Division of Nephrology
 End-Stage Renal Disease Anna Vinnikova, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Division of Nephrology ESRD : Life with renal replacement therapy CASE: 18 month old male with HUS develops ESRD PD complicated
End-Stage Renal Disease Anna Vinnikova, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Division of Nephrology ESRD : Life with renal replacement therapy CASE: 18 month old male with HUS develops ESRD PD complicated
The CARI Guidelines Caring for Australians with Renal Impairment. Monitoring patients on peritoneal dialysis GUIDELINES
 Date written: August 2004 Final submission: July 2005 Monitoring patients on peritoneal dialysis GUIDELINES No recommendations possible based on Level I or II evidence SUGGESTIONS FOR CLINICAL CARE (Suggestions
Date written: August 2004 Final submission: July 2005 Monitoring patients on peritoneal dialysis GUIDELINES No recommendations possible based on Level I or II evidence SUGGESTIONS FOR CLINICAL CARE (Suggestions
Glucose and Mannitol Have Different Effects on Peritoneal Morphology in Chronically Dialyzed Rats
 Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis, Vol. 19, 2003 Arkadiusz Styszynski, Beata Kwiatkowska, Katarzyna Wieczorowska Tobis, Andrzej Breborowicz, Dimitrios G. Oreopoulos 1 Glucose and Mannitol Have Different
Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis, Vol. 19, 2003 Arkadiusz Styszynski, Beata Kwiatkowska, Katarzyna Wieczorowska Tobis, Andrzej Breborowicz, Dimitrios G. Oreopoulos 1 Glucose and Mannitol Have Different
ad e quate adjective \ˈa-di-kwət\
 PD Prescriptions and Adequacy Monitoring: The Basics Fundamentals of Dialysis in Children Seattle, Washington February 27th, 2016 Colin White Steve Alexander Brad Warady Alicia Neu Franz Schaefer Bruce
PD Prescriptions and Adequacy Monitoring: The Basics Fundamentals of Dialysis in Children Seattle, Washington February 27th, 2016 Colin White Steve Alexander Brad Warady Alicia Neu Franz Schaefer Bruce
Excretory System Workbook
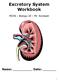 Excretory System Workbook MCHS Biology 20 Mr. Korotash Name: Date: 1 Study the diagram above. Name the structures and indicate their functions by completing the following table: Structure 1. Function 2.
Excretory System Workbook MCHS Biology 20 Mr. Korotash Name: Date: 1 Study the diagram above. Name the structures and indicate their functions by completing the following table: Structure 1. Function 2.
Renal Replacement Therapies
 Renal Replacement Therapies M I H Á L Y T A P O L Y A I, M D, F A S N, F A C P A s s o c i a t e P r o f e s s o r D e p a r t m e n t o f N e p h r o l o g y L o u i s i a n a S t a t e U n i v e r s
Renal Replacement Therapies M I H Á L Y T A P O L Y A I, M D, F A S N, F A C P A s s o c i a t e P r o f e s s o r D e p a r t m e n t o f N e p h r o l o g y L o u i s i a n a S t a t e U n i v e r s
The CARI Guidelines Caring for Australians with Renal Impairment. Mode of dialysis at initiation GUIDELINES
 Date written: September 2004 Final submission: February 2005 Mode of dialysis at initiation GUIDELINES No recommendations possible based on Level I or II evidence SUGGESTIONS FOR CLINICAL CARE (Suggestions
Date written: September 2004 Final submission: February 2005 Mode of dialysis at initiation GUIDELINES No recommendations possible based on Level I or II evidence SUGGESTIONS FOR CLINICAL CARE (Suggestions
Initial Approach 2/5/2016. Case 1. Case 2. ? Volume Overload = Ultrafiltration Failure
 Case 1 Shweta Bansal, MBBS, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Director, Home Dialysis Program University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio San Antonio, TX, USA 35 y/m with ESRD sec to FSGS
Case 1 Shweta Bansal, MBBS, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Director, Home Dialysis Program University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio San Antonio, TX, USA 35 y/m with ESRD sec to FSGS
Peritoneal water transport characteristics of diabetic patients undergoing peritoneal dialysis: a longitudinal study
 American Journal of Nephrology. 2017; 46(1): 47-54 Peritoneal water transport characteristics of diabetic patients undergoing peritoneal dialysis: a longitudinal study Ana Fernandes, a Roi Ribera-Sanchez,b
American Journal of Nephrology. 2017; 46(1): 47-54 Peritoneal water transport characteristics of diabetic patients undergoing peritoneal dialysis: a longitudinal study Ana Fernandes, a Roi Ribera-Sanchez,b
Proceedings of the ISPD 2006 The 11th Congress of the ISPD /07 $ MAXIMIZING THE SUCCESS OF PERITONEAL DIALYSIS IN HIGH TRANSPORTERS
 Proceedings of the ISPD 2006 The 11th Congress of the ISPD 0896-8608/07 $3.00 +.00 August 25 29, 2006, Hong Kong Copyright 2007 International Society for Peritoneal Dialysis Peritoneal Dialysis International,
Proceedings of the ISPD 2006 The 11th Congress of the ISPD 0896-8608/07 $3.00 +.00 August 25 29, 2006, Hong Kong Copyright 2007 International Society for Peritoneal Dialysis Peritoneal Dialysis International,
Ch 17 Physiology of the Kidneys
 Ch 17 Physiology of the Kidneys Review Anatomy on your own SLOs List and describe the 4 major functions of the kidneys. List and explain the 4 processes of the urinary system. Diagram the filtration barriers
Ch 17 Physiology of the Kidneys Review Anatomy on your own SLOs List and describe the 4 major functions of the kidneys. List and explain the 4 processes of the urinary system. Diagram the filtration barriers
Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis, Vol. 23, 2007
 Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis, Vol. 23, 2007 Antonios H. Tzamaloukas, 1,2 Aideloje Onime, 1,2 Dominic S.C. Raj, 2 Glen H. Murata, 1 Dorothy J. VanderJagt, 3 Karen S. Servilla 1,2 Computation of the Dose
Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis, Vol. 23, 2007 Antonios H. Tzamaloukas, 1,2 Aideloje Onime, 1,2 Dominic S.C. Raj, 2 Glen H. Murata, 1 Dorothy J. VanderJagt, 3 Karen S. Servilla 1,2 Computation of the Dose
Jacek Waniewski, 1 Stefan Antosiewicz, 2 Daniel Baczynski, 2 Jan Poleszczuk, 1 Mauro Pietribiasi, 1 Bengt Lindholm, 3 and Zofia Wankowicz 2
 Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine Volume 216, Article ID 824294, 1 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/216/824294 Research Article Peritoneal Fluid Transport rather than Peritoneal Solute Transport
Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine Volume 216, Article ID 824294, 1 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/216/824294 Research Article Peritoneal Fluid Transport rather than Peritoneal Solute Transport
Brief communication (Original)
 Asian Biomedicine Vol. 8 No. 1 February 2014; 67-73 DOI: 10.5372/1905-7415.0801.263 Brief communication (Original) Long-term clinical effects of treatment by daytime ambulatory peritoneal dialysis with
Asian Biomedicine Vol. 8 No. 1 February 2014; 67-73 DOI: 10.5372/1905-7415.0801.263 Brief communication (Original) Long-term clinical effects of treatment by daytime ambulatory peritoneal dialysis with
From Peritoneal Dialysis to Hemodialysis How could we improve the transition? Th Lobbedez CHU de Caen Self Dialysis Meeting 22 May 2014
 From Peritoneal Dialysis to Hemodialysis How could we improve the transition? Th Lobbedez CHU de Caen Self Dialysis Meeting 22 May 2014 Deux grands principes concernant la DP La dialyse péritonéale doit
From Peritoneal Dialysis to Hemodialysis How could we improve the transition? Th Lobbedez CHU de Caen Self Dialysis Meeting 22 May 2014 Deux grands principes concernant la DP La dialyse péritonéale doit
The Effect of Residual Renal Function at the Initiation of Dialysis on Patient Survival
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2009.24.1.55 The Effect of Residual Renal Function at the Initiation of Dialysis on Patient Survival Seoung Gu Kim 1 and Nam Ho Kim 2 Department of Internal Medicine,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2009.24.1.55 The Effect of Residual Renal Function at the Initiation of Dialysis on Patient Survival Seoung Gu Kim 1 and Nam Ho Kim 2 Department of Internal Medicine,
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Stages. CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE Treatment Options. Incident counts & adjusted rates, by primary diagnosis Figure 2.
 Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Stages Stage 1 GFR > 90 (evidence of renal disease) Stage 2 GFR 60-89 Stage 3 GFR 30-59 Stage 4 GFR 15-29 Stage 5 GFR
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Stages Stage 1 GFR > 90 (evidence of renal disease) Stage 2 GFR 60-89 Stage 3 GFR 30-59 Stage 4 GFR 15-29 Stage 5 GFR
Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis, Vol. 27, 2011
 Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis, Vol. 27, 2011 Eriko Kojima, Tsutomu Inoue, Keita Sueyoshi, Takahiko Sato, Masahiro Tsuda, Tomohiro Kikuta, Yusuke Watanabe, Hiroshi Takane, Tsuneo Takenaka, Hiromichi Suzuki
Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis, Vol. 27, 2011 Eriko Kojima, Tsutomu Inoue, Keita Sueyoshi, Takahiko Sato, Masahiro Tsuda, Tomohiro Kikuta, Yusuke Watanabe, Hiroshi Takane, Tsuneo Takenaka, Hiromichi Suzuki
Cell-Derived Inflammatory Mediators
 Cell-Derived Inflammatory Mediators Introduction about chemical mediators in inflammation Mediators may be Cellular mediators cell-produced or cell-secreted derived from circulating inactive precursors,
Cell-Derived Inflammatory Mediators Introduction about chemical mediators in inflammation Mediators may be Cellular mediators cell-produced or cell-secreted derived from circulating inactive precursors,
Prof. Andrzej Wiecek Department of Nephrology, Endocrinology and Metabolic Diseases Medical University of Silesia Katowice, Poland.
 What could be the role of renal denervation in chronic kidney disease? Andrzej Wiecek, Katowice, Poland Chairs: Peter J. Blankestijn, Utrecht, The Netherlands Jonathan Moss, Glasgow, UK Prof. Andrzej Wiecek
What could be the role of renal denervation in chronic kidney disease? Andrzej Wiecek, Katowice, Poland Chairs: Peter J. Blankestijn, Utrecht, The Netherlands Jonathan Moss, Glasgow, UK Prof. Andrzej Wiecek
Time trends in initiation and dose of dialysis in end-stage renal disease patients in The Netherlands
 Nephrol Dial Transplant (2003) 18: 552 558 Original Article Time trends in initiation and dose of dialysis in end-stage renal disease patients in The Netherlands Fabian Termorshuizen 1, Johanna C. Korevaar
Nephrol Dial Transplant (2003) 18: 552 558 Original Article Time trends in initiation and dose of dialysis in end-stage renal disease patients in The Netherlands Fabian Termorshuizen 1, Johanna C. Korevaar
PERITONEAL DIALYSIS PRESCRIPTION MANAGEMENT GUIDE
 PERITONEAL DIALYSIS PRESCRIPTION MANAGEMENT GUIDE TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction.... 3 SECTION 1: FUNDAMENTALS OF THE PRESCRIPTION.... 4 Getting Started: Patient Pathway to First Prescription.... 5 Volume
PERITONEAL DIALYSIS PRESCRIPTION MANAGEMENT GUIDE TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction.... 3 SECTION 1: FUNDAMENTALS OF THE PRESCRIPTION.... 4 Getting Started: Patient Pathway to First Prescription.... 5 Volume
St George & Sutherland Hospitals PERITONEAL DIALYSIS UNIT RENAL DEPARTMENT Workplace Instruction (Renal_SGH_WPI_097)
 PERITONEAL DIALYSIS (PD) PERITONEAL EQUILIBRATION TEST (PET) Cross references NSW Health PD2007_036 - Infection Control Policy SGH-TSH CLIN027 - Aseptic Technique - Competency and Education Requirements
PERITONEAL DIALYSIS (PD) PERITONEAL EQUILIBRATION TEST (PET) Cross references NSW Health PD2007_036 - Infection Control Policy SGH-TSH CLIN027 - Aseptic Technique - Competency and Education Requirements
Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index, home hemodialysis outcomes 131
 Subject Index Aksys PHD system 113 Anemia, home outcomes 111, 172, 173 Automated peritoneal dialysis dialysis comparison 17, 18 selection factors 18, 19 telemedicine system 19 21 Blood pressure -peritoneal
Subject Index Aksys PHD system 113 Anemia, home outcomes 111, 172, 173 Automated peritoneal dialysis dialysis comparison 17, 18 selection factors 18, 19 telemedicine system 19 21 Blood pressure -peritoneal
Ch 19: The Kidneys. Functional unit of kidneys:?? Developed by John Gallagher, MS, DVM
 Ch 19: The Kidneys Homeostatic regulation of ECF volume and BP Osmolarity 290 mosm Ion balance Na+ and K+, etc. ph (acid-base balance Excretion of wastes & foreign substances Hormone production EPO Renin
Ch 19: The Kidneys Homeostatic regulation of ECF volume and BP Osmolarity 290 mosm Ion balance Na+ and K+, etc. ph (acid-base balance Excretion of wastes & foreign substances Hormone production EPO Renin
Vincenzo La Milia 1, Giuseppe Pontoriero 1, Giovambattista Virga 2 and Francesco Locatelli 1
 Nephrol Dial Transplant (2015) 30: 1741 1746 doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfv275 Advance Access publication 16 July 2015 Ionic conductivity of peritoneal dialysate: a new, easy and fast method of assessing peritoneal
Nephrol Dial Transplant (2015) 30: 1741 1746 doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfv275 Advance Access publication 16 July 2015 Ionic conductivity of peritoneal dialysate: a new, easy and fast method of assessing peritoneal
Managing Acid Base and Electrolyte Disturbances with RRT
 Managing Acid Base and Electrolyte Disturbances with RRT John R Prowle MA MSc MD MRCP FFICM Consultant in Intensive Care & Renal Medicine RRT for Regulation of Acid-base and Electrolyte Acid base load
Managing Acid Base and Electrolyte Disturbances with RRT John R Prowle MA MSc MD MRCP FFICM Consultant in Intensive Care & Renal Medicine RRT for Regulation of Acid-base and Electrolyte Acid base load
Encapsulating Peritoneal Sclerosis (EPS)
 Encapsulating Peritoneal Sclerosis (EPS) Joni H. Hansson 1 Scott F. Cameron 1 Zenon Protopapas 1 Rajnish Mehrotra 2 1 Hospital of Saint Raphael/Yale University, New Haven, CT 2 Harbor-UCLA Medical Center,
Encapsulating Peritoneal Sclerosis (EPS) Joni H. Hansson 1 Scott F. Cameron 1 Zenon Protopapas 1 Rajnish Mehrotra 2 1 Hospital of Saint Raphael/Yale University, New Haven, CT 2 Harbor-UCLA Medical Center,
Imad Ahmed MD. Renal Associates of West Michigan
 Imad Ahmed MD Renal Associates of West Michigan ESRD Facts: - Medicare funded program - Cost - Significant mortality and morbidity - Reduced quality of life - Shrinking donor pool ESRD CAUSES - DM - Hypertension
Imad Ahmed MD Renal Associates of West Michigan ESRD Facts: - Medicare funded program - Cost - Significant mortality and morbidity - Reduced quality of life - Shrinking donor pool ESRD CAUSES - DM - Hypertension
The principal functions of the kidneys
 Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
The functions of the kidney:
 The functions of the kidney: After reading this lecture you should be able to.. 1. List the main functions of the kidney. 2. Know the basic physiological anatomy of the kidney and the nephron 3. Describe
The functions of the kidney: After reading this lecture you should be able to.. 1. List the main functions of the kidney. 2. Know the basic physiological anatomy of the kidney and the nephron 3. Describe
Chapter 2 End-Stage Renal Disease: Scope and Trends
 Chapter 2 End-Stage Renal Disease: Scope and Trends Chapter 2 End-Stage Renal Disease: Scope and Trends END-STAGE RENAL DISEASE DEFINED The primary functions of the kidney are to remove waste products
Chapter 2 End-Stage Renal Disease: Scope and Trends Chapter 2 End-Stage Renal Disease: Scope and Trends END-STAGE RENAL DISEASE DEFINED The primary functions of the kidney are to remove waste products
The greatest benefit of peritoneal dialysis (PD) is the
 Peritoneal Dialysis International, Vol. 26, pp. 150 154 Printed in Canada. All rights reserved. 0896-8608/06 $3.00 +.00 Copyright 2006 International Society for Peritoneal Dialysis COMBINATION THERAPY
Peritoneal Dialysis International, Vol. 26, pp. 150 154 Printed in Canada. All rights reserved. 0896-8608/06 $3.00 +.00 Copyright 2006 International Society for Peritoneal Dialysis COMBINATION THERAPY
RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY
 RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY Peter McCue, M.D. Department of Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College There are no conflicts of interest. 1 Goals and Objectives! Goals Provide introduction
RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY Peter McCue, M.D. Department of Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College There are no conflicts of interest. 1 Goals and Objectives! Goals Provide introduction
THERAPEUTIC INTERVENTIONS TO PRESERVE RESIDUAL KIDNEY FUNCTION. Rajnish Mehrotra Harborview Medical Center University of Washington, Seattle
 THERAPEUTIC INTERVENTIONS TO PRESERVE RESIDUAL KIDNEY FUNCTION Rajnish Mehrotra Harborview Medical Center University of Washington, Seattle 1 2 Outline of Presentation Refinements in our understanding
THERAPEUTIC INTERVENTIONS TO PRESERVE RESIDUAL KIDNEY FUNCTION Rajnish Mehrotra Harborview Medical Center University of Washington, Seattle 1 2 Outline of Presentation Refinements in our understanding
Making possible personal.
 Making possible personal. HDX THERAPY, ENABLED BY THE THERANOVA DIALYZER HDF PERFORMANCE AND BEYOND AS SIMPLE AS HD The THERANOVA dialyzer, featuring an innovative membrane, effectively targets large middle
Making possible personal. HDX THERAPY, ENABLED BY THE THERANOVA DIALYZER HDF PERFORMANCE AND BEYOND AS SIMPLE AS HD The THERANOVA dialyzer, featuring an innovative membrane, effectively targets large middle
PD In Acute Kidney Injury. February 7 th -9 th, 2013
 PD In Acute Kidney Injury February 7 th -9 th, 2013 Objectives PD as a viable initial therapy PD in AKI PD versus dhd PD versus CVVHD Why not PD first PD for AKI Early days (1970 s) PD was the option of
PD In Acute Kidney Injury February 7 th -9 th, 2013 Objectives PD as a viable initial therapy PD in AKI PD versus dhd PD versus CVVHD Why not PD first PD for AKI Early days (1970 s) PD was the option of
I. FILL IN THE BLANKS
 1 BHARAT SEVAK SAMAJ NATIONAL DEVELOPMENT AGENCY, PROMOTED BY GOVERNMENT OF INDIA CENTRAL BOARD OF EXAMINATIONS BSS NATIONAL VOCATIONAL EDUCATION MISSION AHE025-BSS DIPLOMA IN DIALYSIS TECHNOLOGY TWO YEARS
1 BHARAT SEVAK SAMAJ NATIONAL DEVELOPMENT AGENCY, PROMOTED BY GOVERNMENT OF INDIA CENTRAL BOARD OF EXAMINATIONS BSS NATIONAL VOCATIONAL EDUCATION MISSION AHE025-BSS DIPLOMA IN DIALYSIS TECHNOLOGY TWO YEARS
Successful long-term peritoneal dialysis (PD) requires
 Proceedings of the ISPD 2001 The IXth Congress of the ISPD June 26 29, 2001, Montréal, Canada Peritoneal Dialysis International, Vol. 21 (2001), Supplement 3 0896-8608/01 $3.00 +.00 Copyright 2001 International
Proceedings of the ISPD 2001 The IXth Congress of the ISPD June 26 29, 2001, Montréal, Canada Peritoneal Dialysis International, Vol. 21 (2001), Supplement 3 0896-8608/01 $3.00 +.00 Copyright 2001 International
Future Perspectives in Peritoneal Dialysis
 Future Perspectives in Peritoneal Dialysis Dialysis Initiatives Nefrologen Meeting September 21, 2017 Joanne M. Bargman MD FRCPC Director, Peritoneal Dialysis Program University Health Network Professor
Future Perspectives in Peritoneal Dialysis Dialysis Initiatives Nefrologen Meeting September 21, 2017 Joanne M. Bargman MD FRCPC Director, Peritoneal Dialysis Program University Health Network Professor
The transport barrier in intraperitoneal therapy
 Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 288: F433 F442, 2005; doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00313.2004. The transport barrier in intraperitoneal therapy Michael F. Flessner Division of Nephrology, Department of Medicine, University
Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 288: F433 F442, 2005; doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00313.2004. The transport barrier in intraperitoneal therapy Michael F. Flessner Division of Nephrology, Department of Medicine, University
