Diabetic Foot Infection
|
|
|
- Rodney Hubbard
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Diabetic Foot Infection How I do it? Saritphat Orrapin, MD, FRCS (Thailand) Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Division, Department of Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, Center of Excellence for Diabetic foot care (TU-CDC) Thammasat University Hospital
2 Center of Excellence for Diabetic foot care TU-CDC Committee (Multidisciplinary team) Endocrinologist Vascular Surgeon APN Dr. Thipaporn Tarawanich Dr. Boonying Siribumrungwong Phunyada Napunnaphat Dr. Pimjai Anthanon Dr. Theotphum Benyakorn Saowaluck Triwiroj Dr. Kanoklada Srikua Arpaporn Kuthongkul Dermatologist Dr. Saritphat Orrapin Dr. Patcha Pongjareon Orthopedic Surgeon and Podologist Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Dr. Natetaya Nimpitak Dr. Sirunya Parjareon Dr. Chayanin Angthong Dr. Marut Arunakul
3 Diabetes mellitus (DM) Global registry (International diabetes federation, IDF) : 415 Million DM patients 2050: 643 Million DM patients Thailand registry : 5 Million DM patients 1. International Diabetes Federation. DF Diabetes Atlas Aekplakorn W. Thai National Health Examination. Survey (NHES V), National Health Examination Survey Office, Health System Research Institute 2016
4 Diabetic foot ulcer (DFU) DFU 1 in 4 of DM (25%) 1 DFU vs non-dfu 3 years Mortality rate: 31.9% VS 12.0% 2 Most common cause of death: Coronary artery disease (CAD) Ankle brachial index (ABI): correlate negatively with the severity of CAD 3 DFU with amputation 5 years Mortality rate: 46% 4 one amputation every 7 min could be directly attributed to diabetes 5 1.Boulton AJ, Diabetes care Junrungsee S. Diabetic Medicine Benyakorn T. Int J Low Extrem Wounds Nouvong A, Rutherford's Vascular surgery Carinci F, Acta Diabetol..2016
5 Etiologies of DFU Peripheral arterial disease (PAD) Atherosclerosis 1,2 Peripheral neuropathy 1,2 Foot deformity Repetitive trauma Chronic ulcer Poor vascular supply Delay wound healing Chronic ulcer Hyperglycemia Oxidative stress Chronic ulcer 1.. Dosluoglu HH., Rutherford's Vascular surgery Orrapin S et al. Applied Vascular Surgery Vol 4: Clinical practice in Vascular surgery Armstrong DG, N Engl J Med 2017
6 Etiologies of Diabetic foot infection (DFI) Peripheral arterial disease (PAD) Atherosclerosis Peripheral neuropathy Poor vascular supply (Poor capillary flow) Poor local wound immune system DFI 1,2 Hyperglycemia Poor systemic immune system DFI 1,2 1.. Nouvong A, Rutherford's Vascular surgery Orrapin S et al. Applied Vascular Surgery Vol 4: Clinical practice in Vascular surgery Armstrong DG, N Engl J Med 2017
7 Orrapin S et al. Applied Vascular Surgery Vol 4: Clinical practice in Vascular surgery 2017.
8 Peripheral arterial disease (PAD) PAD: closed associated with DFU DM = major atherosclerotic risk factor - increases risk of symptomatic PAD 1-2 Prevalence of PAD in DM: %. 3 1% increase in Hb A1c = increased 28% risk of PAD in DM. 4 DM + PAD = increased risk of DFI + high morbidity/mortality. 5 Poor control of atherosclerotic risk factor in Thai DM population. 6 Hb A1c ; glycated hemoglobin 1. Norgren L, J Vasc Surg Tendera M, European heart journal Rhee SY, Diabetes research and clinical practice Dosluoglu HH, Rutherford's Vascular surgery. Philadelphia: Elsevier; Britton KA, Vascular medicine (London, England) Orrapin S, AVD 2015
9 DM + PAD (Neuroischemic ulcer)
10 DM foot Diabetic foot infection (DFI): soft tissue or bone infection below the malleoli 1,2 1. Fassil W et al. Am Fam Physician Lipsky BA et al. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2016.
11 Definition of DFI Infection of soft tissue or bone at below malleoli in DFU patients 1 1. Soft tissue infection 2. Osteomyelitis Presence of local +/- systemic signs and symptoms of inflammation 2 DFI - 60% of all cause of lower extremity amputation 3 1. Nouvong A, Rutherford's Vascular surgery Lipsky BA, Diabetes/metabolism research and reviews Peters EJ, Medical Clinics of North America. 2013
12 DFI Local sign 2 of the following: 1 1. Local swelling or induration 2. Erythema >0.5 cm around the wound 3. Local tenderness or pain 4. Local warmth 5. Purulent discharge Systemic sign (SIRS) 2 of the following: 1 1. Temperature > 38 C or < 36 C 2. Heart rate > 90 beats/min 3. Respiratory rate >20 breaths/min or PaCO 2 < 32 mmhg 4. WBC >12 000/mm 3 or < 4000/mm 3, or >10% immature (band) forms Excluded: other causes of skin inflammation - gout, fracture, trauma, venous thrombosis, etc. SIRS: systemic inflammatory response syndrome, WBC; white blood cell count 1. Lipsky BA. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2016
13 DFU Callus formation Foot deformities
14 DFI Erythema Purulent discharge Local swelling
15 The classification systems: Presence and Severity of DFI by IDSA with PEDIS classification (Infection part) by IWGDF 1,2 Infective Clinical classification No local and systemic signs of infection Skin or subcutaneous tissue infection - Erythema extends > 0.5, <2 cm around rim of wound Deep structure than skin and subcutaneous tissues (Bone, Joint, Tendon or Muscle) or Erythema extending 2 cm from the wound margin Local sign + SIRS ( 2 sign of systemic inflammation) IWGDF/IDSA classification 1 (uninfected) 2 (mild infection) - Superficial Soft tissue infection 3 (moderate infection) - Deep Soft tissue infection (Myositis) - Osteomyelitis 4 (severe infection) IDSA; Infectious Diseases Society of America IWGDF; International Working Group on the Diabetic Foot 1. Schaper NC. Diabetes Metab Res Rev Lipsky BA. Clin Infect Dis 2012
16 IWGDF/IDSA classification High IWGDF/IDSA 1,2 Long hospital stay Poor prognosis Amputation prediction 1. Wukich DK, Diabetes care Lipsky BA. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2016
17 Other classification 1. Meggitt-Wegner Ulcer Classification Score 1 2. The University of Texas Health Science Center San Antonio Diabetic Wound Classification System 2 3. Etc. 1. Wagner FW Jr. The diabetic foot. Orthopedics Lavery LA, J Foot Ankle Surg 1996
18 Meggitt-Wegner Ulcer Classification Score 1 Grade Lesion 1 Superficial diabetic ulcer (partial or full thickness) 2 Ulcer extension to ligament, tendon, joint capsule, or deep fascia 3 Deep ulcer with abscess, osteomyelitis, or joint sepsis 4 Gangrene localized to portion of forefoot or heel 5 Extensive gangrenous involvement of the entire foot 1. Wagner FW Jr. The diabetic foot. Orthopedics 1987
19 The University of Texas Health Science Center San Antonio Diabetic Wound Classification System 1 Grade 0 I II III A Pre- or post ulcerative lesion completely epithelialized Superficial wound, not involving tendon, capsule, capsule or bone Wound penetrating to tendon or capsule Wound penetrating to bone B Pre- or post ulcerative lesion, completely epithelialized with infection Superficial wound, not involving tendon, capsule, or bone with infection Wound penetrating to tendon or capsule with infection Wound penetrating to bone or joint with infection C Pre- or post ulcerative lesion, completely epithelialized with ischemia Superficial wound. not involving tendon, capsule, or bone with ischemia Wound penetrating to tendon or capsule with ischemia Wound penetrating to bone or joint with ischemia D Pre- or post ulcerative lesion, completely epithelialized with infection and ischemia Superficial wound, not involving tendon, capsule, or bone with infection and ischemia Wound penetrating to tendon or capsule with infection and ischemia Wound penetrating to bone or joint with infection and ischemia 1. Lavery LA, J Foot Ankle Surg 1996
20 Diabetic Wound Classification System Outcomes deteriorated with increasing grade and stage of wounds 1 Combination tools with additional clinical information: accurate interpretations 2 Need of further studies assessing reliability and accuracy of all systems 3 1. Armstrong DG, Diabetes Care Santema, Int Wound J Monteiro-Soares M, Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2014
21 Osteomyelitis (OM) High risk OM wound 1. Ulcer lies over a bony prominence 2. Sausage toe (indurated and redness toes) 3. Large ulcers (area >2 cm 2 ) 4. Unresponsive to adequate treatment Bony prominence Sausage toe Large ulcers 1. Lipsky BA. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2016
22 Osteomyelitis (OM) Probe-to-bone test 1 Blunt sterile metal probe inserted through bone Hard and Gritty 7.2 time of OM For all infected open wound: 1 Probe-to-bone test Low risk OM: negative test rules out diagnosis High risk OM: positive test largely diagnostic Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR): suggest of OM in suspected patients 1,2,3 > 70 mm/h (77% sensitivity and 77%specificity) 1. Lipsky BA. Diabetes Metab Res Rev Uzun GThe Tohoku journal of experimental medicine Papanas, Int J Low Extrem Wounds 2013
23 Osteomyelitis (OM) Definite diagnosis: Bone sample: positive results on histological (microbiological) examinations Equivocal diagnosis or Determining causative pathogen s antibiotic susceptibility: for unresponsive for ordinary treatment (Empirical antibiotic) Probable diagnosis Combination of diagnostic tests: Probe-to-bone Serum inflammatory markers Plain X-ray: all case of Non-superficial DFI MRI Radionuclide scanning 1. Lipsky BA. Diabetes Metab Res Rev Armstrong DG, N Engl J Med 2017
24 Osteomyelitis (OM) Plain X-ray: all Non-superficial DFI 54% sensitivity and 68% specificity Typical feature of OM in DFI Loss of bone cortex with bony erosion Trabecular bone destruction or marrow radiolucency Bone sclerosis, Periosteal reaction or elevation Presence of sequestrum: devitalized bone Presence of involucrum: bone growth outside previously existing bone Presence of cloacae: opening in the involucrum or cortex Presence of evidence of a sinus tract from the bone to the soft tissue 1. Lipsky BA. Diabetes Metab Res Rev Hingorani A, Journal of vascular surgery. 2016
25 Osteomyelitis (OM) MRI: best imaging for OM diagnosis 90% sensitivity and 85% specificity MRI is not available or contraindicated white blood cell-labelled radionuclide scan, single-photon emission computed tomography and computed tomography (SPECT/CT) fluorine-18-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (PET) scans 1. Dinh T, Int J Low Extreme Lipsky BA. Diabetes Metab Res Rev Hingorani A, Journal of vascular surgery. 2016
26 Assessing severity Vital signs and Physical examination Basic blood tests Debride wound Probe assess depth and extent of infection Assess arterial perfusion further vascular assessment (ABI, TBI, TCOM) Angiogram Revascularization 1. Lipsky BA. Diabetes Metab Res Rev Armstrong DG, N Engl J Med 2017
27 Characteristics suggesting a more serious diabetic foot infection Wound Wound Penetrates to subcutaneous tissues (e.g. fascia, tendon, muscle, joint and bone) Cellulitis Local signs Extensive (>2 cm), distant from ulceration or rapidly progressive Severe inflammation or induration, crepitus, bullae, discoloration, necrosis or gangrene, ecchymoses or petechiae and new anaesthesia 1. Lipsky BA. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2016
28 Extensive (>2 cm) VS Necrosis or gangrene Penetrates subcutaneous tissues
29 Characteristics suggesting a more serious diabetic foot infection Systemic (hospitalization) Presentation Systemic signs Laboratory tests Acute onset/worsening or rapidly progressive Fever, chills, hypotension, confusion and volume depletion Leukocytosis, very high CRP/ESR, severe/worsening hyperglycemia, acidosis, AKI and electrolyte abnormalities Complicating features Current treatment Presence of a foreign body (accidentally or surgically implanted), puncture wound, deep abscess, arterial or venous insufficiency, lymphedema, immunosuppressive illness or treatment Progression on appropriate antibiotic and supportive therapy 1. Lipsky BA. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2016
30 Microbiological considerations Tissue specimen: For Causative microorganisms + antibiotic sensitivity Do not swab culture Send collected specimens to microbiology laboratory promptly + sterile transport containers 1. Lipsky BA. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2016
31 Management Select specific antibiotic agents for 1-2 weeks for treatment Based on causative pathogens antibiotic susceptibilities clinical severity efficacy and costs Moderated and Severe infection: Parenteral therapy initially Switch to oral therapy when infection responding 1. Lipsky BA. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2016
32 Empiric antibiotic regimen Severity Factors Pathogen Empirical antibiotic regimen Mild No complicating features GPC Pen, 1 st Ceph ß-lactam allergy or intolerance GPC Clindamycin; FQ; T/S; macrolide; doxy Recent antibiotic exposure GPC + GNR ß-L-ase-1; T/S; FQ High risk for MRSA a MRSA Linezolid; T/S; doxy; macrolide; FQ a high local prevalence of MRSA, recent stay in healthcare institution, recent antibiotic therapy or known MRSA colonization b high local prevalence of Pseudomonas infections, warm climate or frequent exposure of the foot to water.
33 Severity Factors Pathogen Empirical antibiotic regimen Moderate and severe No complicating features GPC + GNR ß-L-ase 1; second/third gen ceph Recent antibiotics GPC + GNR ß-L-ase 2; third gen ceph, group 1 carbapenem (depends on prior therapy; seek advice) Macerated ulcer and warm climate Ischemic limb/necrosis/gas forming GNR + Pseudomonas GPC + GNR + Anaerobes ß-L-ase 2; S-S pen+ceftazidime, S-S pen+cipro, group 2 carbapenem ß-L-ase 1 or 2; group 1 or 2 carbapenem; second/ third gen ceph+clindamycin or metronidazole MRSA risk factors a MRSA Consider addition of, or substituting with, glycopeptides; linezolid; daptomycin; fusidic acid; T/S (±rif)*; doxycycline; FQ Risk factors for ESBL Carbapenems, FQ, aminoglycoside and colistin resistant GNR b a high local prevalence of MRSA, recent stay in healthcare institution, recent antibiotic therapy or known MRSA colonization b high local prevalence of Pseudomonas infections, warm climate or frequent exposure of the foot to water.
34 Management Consult surgical specialist Moderate DFI Severe DFI 1. Lipsky BA. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2016
35 Management Urgent surgical intervention Deep abscesses Compartment syndrome Necrotizing soft tissue infections Procedure: minor debridement or drainage to extensive resections, major amputation. 1. Lipsky BA. Diabetes Metab Res Rev Armstrong DG, N Engl J Med 2017
36 Management Non-urgent infections Initial surgical intervention: limited to incision and drainage If non responding - further resection Major amputation 1. Non-viable limb 2. Potentially life-threatening infection 3. Functionally useless 1. Lipsky BA. Diabetes Metab Res Rev Armstrong DG, N Engl J Med 2017
37 Dorsum incision metatarsal head to base at medial border of 2 nd metatarsal bone lateral border of 4 th metatarsal bone Skin bridge (fullthickness skin bridge) > 2 cm > 2 cm Plantar incision Imaginary line from 2 nd toe to mid calcaneal bone Avoid weight-bearing surface 1. Rerkasem K, Vascular Surgery Orrapin S, Prevention and Management of The Diabetic foot Orrapin S et al. Applied Vascular Surgery Vol 4: Clinical practice in Vascular surgery 2017
38 Medial incision: first metatarsal head - navicular tuberosity mid imaginary line from plantar heel to medial malleolus Lateral incision: fifth metatarsal base - Achilles tendon and fibula 1. Rerkasem K, Vascular Surgery Orrapin S, Prevention and Management of The Diabetic foot Orrapin S et al. Applied Vascular Surgery Vol 4: Clinical practice in Vascular surgery 2017
39
40 Management OM Considering orthopedic surgical intervention 1. Spreading soft tissue infection 2. Destroyed soft tissue envelope 3. Progressive bone destruction on X-ray 4. Bone protruding through the ulcer For resection OM: no more than 1 week of antibiotic therapy For non-resection OM: 6 weeks of antibiotic 1. Lipsky BA. Diabetes Metab Res Rev Armstrong DG, N Engl J Med 2017
41 Surgical treatment VS Antibiotic treatment Nonsurgical approach with antibiotic therapy can be successful in selected cases No ischemia (CLI) 2 2. No necrotizing soft tissue infections 2 Similar outcomes: healing rates, time to healing, and short-term complications 2 1. José Luis Lázaro-Martínez, Diabetes Care Mesut Mutluoglu, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017
42 Management PAD Revascularization 1,2 Endovascular VS Open bypass Critical limb ischemia (Severe PAD) 2,3 Resting Ankle pressure < mmhg Toe pressure < 50 mmhg TCOM <30 mmhg PVR: flat or barely pulsatile 1. Lipsky BA. Diabetes Metab Res Rev Bianchi C, Rutherford's Vascular surgery Hopf, Wound Rep Reg 2006
43 Take home message 1. Diagnosis of soft tissue infection VS osteomyelitis 2. Control blood sugar and co-morbid condition (esp. Cardiac disease) 3. Assessing severity and Eradicated infection Antibiotic Limited debridement and amputation 4. Microbiologic consideration tissue specimen culture 5. Evaluation vascular supply and revascularization as indicated 6. Off-loading technique Total Contact Cast (TCC) or other instrument Surgery
44 Center of Excellence for Diabetic foot care TU-CDC Committee (Multidisciplinary team) Endocrinologist Vascular Surgeon APN Dr. Thipaporn Tarawanich Dr. Boonying Siribumrungwong Phunyada Napunnaphat Dr. Pimjai Anthanon Dr. Theotphum Benyakorn Saowaluck Triwiroj Dr. Kanoklada Srikua Arpaporn Kuthongkul Dermatologist Dr. Saritphat Orrapin Dr. Patcha Pongjareon Orthopedic Surgeon and Podologist Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Dr. Natetaya Nimpitak Dr. Sirunya Parjareon Dr. Chayanin Angthong Dr. Marut Arunakul
45 1. Lipsky BA. Diabetes Metab Res Rev Armstrong DG, N Engl J Med 2017
Bone and Joint Infections in Diabetics: Diagnosis and Management of Diabetic Foot and Other Common Lower Extremity Infections
 Bone and Joint Infections in Diabetics: Diagnosis and Management of Diabetic Foot and Other Common Lower Extremity Infections Objectives How do you to diagnose, classify and manage DFI? How do you diagnose
Bone and Joint Infections in Diabetics: Diagnosis and Management of Diabetic Foot and Other Common Lower Extremity Infections Objectives How do you to diagnose, classify and manage DFI? How do you diagnose
Definitions and criteria
 Several disciplines are involved in the management of diabetic foot disease and having a common vocabulary is essential for clear communication. Thus, based on a review of the literature, the IWGDF has
Several disciplines are involved in the management of diabetic foot disease and having a common vocabulary is essential for clear communication. Thus, based on a review of the literature, the IWGDF has
1 of :19
 1 of 8 3-12-2012 12:19 Diabetic foot ulcer classification system for research purposes Introduction Aims of the ulcer research classification system Definitions and categorisation for the ulcer research
1 of 8 3-12-2012 12:19 Diabetic foot ulcer classification system for research purposes Introduction Aims of the ulcer research classification system Definitions and categorisation for the ulcer research
Antimicrobial Guidelines for the Empirical Management of Diabetic Foot Infections
 Antimicrobial Guidelines for the Empirical Management of Diabetic Foot Infections Version 7.2 PAGL Inclusion Approved at January 2017 PGC APPROVED BY: TRUST REFERENCE: B3/2017 AWP REF: UHL Policies and
Antimicrobial Guidelines for the Empirical Management of Diabetic Foot Infections Version 7.2 PAGL Inclusion Approved at January 2017 PGC APPROVED BY: TRUST REFERENCE: B3/2017 AWP REF: UHL Policies and
Foot infections are now among the most
 Article Progress in a pedestrian problem: A review of the revised Infectious Diseases Society of America diabetic foot infection guidelines Benjamin A Lipsky This article was first published in The Diabetic
Article Progress in a pedestrian problem: A review of the revised Infectious Diseases Society of America diabetic foot infection guidelines Benjamin A Lipsky This article was first published in The Diabetic
Wounds and Infections: Wound Management From the ID Physician Standpoint. Alena Klochko, MD Orlando VA Medical Center Infectious Disease Department
 Wounds and Infections: Wound Management From the ID Physician Standpoint Alena Klochko, MD Orlando VA Medical Center Infectious Disease Department Objectives Distinguish between colonization, critical
Wounds and Infections: Wound Management From the ID Physician Standpoint Alena Klochko, MD Orlando VA Medical Center Infectious Disease Department Objectives Distinguish between colonization, critical
Diabetic Foot Ulcers. Alex Khan APRN ACNS-BC MSN CWCN CFCN WCN-C. Advanced Practice Nurse / Adult Clinical Nurse Specialist
 Diabetic Foot Ulcers Alex Khan APRN ACNS-BC MSN CWCN CFCN WCN-C Advanced Practice Nurse / Adult Clinical Nurse Specialist Organization of Wound Care Nurses www.woundcarenurses.org Objectives Identify Diabetic/Neuropathic
Diabetic Foot Ulcers Alex Khan APRN ACNS-BC MSN CWCN CFCN WCN-C Advanced Practice Nurse / Adult Clinical Nurse Specialist Organization of Wound Care Nurses www.woundcarenurses.org Objectives Identify Diabetic/Neuropathic
Fighting Infection in Diabetes
 I have no disclosures Fighting Infection in Diabetes Emily Abdoler, MD Division of Infectious Diseases GomerBlog. http://gomerblog.com/2018/02/nystatin-statin/ Does DM Increase Risk of Infections? Diabetic
I have no disclosures Fighting Infection in Diabetes Emily Abdoler, MD Division of Infectious Diseases GomerBlog. http://gomerblog.com/2018/02/nystatin-statin/ Does DM Increase Risk of Infections? Diabetic
My Diabetic Patient Has No Pulses; What Should I Do?
 Emily Malgor, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery University of Oklahoma, Oklahoma City My Diabetic Patient Has No Pulses; What Should I Do? There are no disclosures. Background Diabetes affects 387 million
Emily Malgor, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery University of Oklahoma, Oklahoma City My Diabetic Patient Has No Pulses; What Should I Do? There are no disclosures. Background Diabetes affects 387 million
Foot infections in persons with diabetes are
 DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF DIABETIC FOOT INFECTION * James S. Tan, MD, MACP, FCCP ABSTRACT According to the American Diabetes Association, approximately 82 000 nontraumatic lower-limb amputations were
DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF DIABETIC FOOT INFECTION * James S. Tan, MD, MACP, FCCP ABSTRACT According to the American Diabetes Association, approximately 82 000 nontraumatic lower-limb amputations were
Updated Guidelines for Managing Diabetic Foot Infections
 Updated Guidelines for Managing Diabetic Foot Infections Benjamin A. Lipsky, MD, FACP, FIDSA, FRCP Emeritus Professor, University of Washington Visiting Professor, University of Geneva Visiting Professor,
Updated Guidelines for Managing Diabetic Foot Infections Benjamin A. Lipsky, MD, FACP, FIDSA, FRCP Emeritus Professor, University of Washington Visiting Professor, University of Geneva Visiting Professor,
Limb Salvage in Diabetic Ischemic Foot. Kritaya Kritayakirana, MD, FACS Assistant Professor Chulalongkorn University April 30, 2017
 Limb Salvage in Diabetic Ischemic Foot Kritaya Kritayakirana, MD, FACS Assistant Professor Chulalongkorn University April 30, 2017 Case Male 67 years old Underlying DM, HTN, TVD Present with gangrene
Limb Salvage in Diabetic Ischemic Foot Kritaya Kritayakirana, MD, FACS Assistant Professor Chulalongkorn University April 30, 2017 Case Male 67 years old Underlying DM, HTN, TVD Present with gangrene
I have no financial interests to disclose in regards to this lecture.
 Evaluation and Treatment of Diabetic Foot Ulcerations John M. Giurini, D.P.M. Associate Professor in Surgery Harvard Medical School Disclosure Statement I have no financial interests to disclose in regards
Evaluation and Treatment of Diabetic Foot Ulcerations John M. Giurini, D.P.M. Associate Professor in Surgery Harvard Medical School Disclosure Statement I have no financial interests to disclose in regards
Diabetic Foot Ulcer Treatment and Prevention
 Diabetic Foot Ulcer Treatment and Prevention Alexander Reyzelman DPM, FACFAS Associate Professor California School of Podiatric Medicine at Samuel Merritt University Diabetic Foot Ulcers One of the most
Diabetic Foot Ulcer Treatment and Prevention Alexander Reyzelman DPM, FACFAS Associate Professor California School of Podiatric Medicine at Samuel Merritt University Diabetic Foot Ulcers One of the most
Expert opinion on the management of infections in the diabetic foot
 DIABETES/METABOLISM RESEARCH AND REVIEWS Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2012; 28(Suppl 1): 163 178. Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com).2248 REVIEW ARTICLE Expert opinion on the management
DIABETES/METABOLISM RESEARCH AND REVIEWS Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2012; 28(Suppl 1): 163 178. Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com).2248 REVIEW ARTICLE Expert opinion on the management
Will it heal? How to assess the probability of wound healing
 Will it heal? How to assess the probability of wound healing Richard F. Neville, M.D. Professor of Surgery Chief, Division of Vascular Surgery George Washington University Limb center case 69 yr old male
Will it heal? How to assess the probability of wound healing Richard F. Neville, M.D. Professor of Surgery Chief, Division of Vascular Surgery George Washington University Limb center case 69 yr old male
Prof Oluwadiya KS FMCS (Orthop) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon / Associate Professor Division of Orthopaedics and Traumatology Department of Surgery
 Prof Oluwadiya KS FMCS (Orthop) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon / Associate Professor Division of Orthopaedics and Traumatology Department of Surgery College of Health Sciences Ladoke Akintola University
Prof Oluwadiya KS FMCS (Orthop) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon / Associate Professor Division of Orthopaedics and Traumatology Department of Surgery College of Health Sciences Ladoke Akintola University
Introduction. Epidemiology Pathophysiology Classification Treatment
 Diabetic Foot Introduction Epidemiology Pathophysiology Classification Treatment Epidemiology DM largest cause of neuropathy in N.A. 1 million DM patients in Canada Half don t know Foot ulcerations is
Diabetic Foot Introduction Epidemiology Pathophysiology Classification Treatment Epidemiology DM largest cause of neuropathy in N.A. 1 million DM patients in Canada Half don t know Foot ulcerations is
CHAPTER 16 LOWER EXTREMITY. Amanda K Silva, MD and Warren Ellsworth, MD, FACS
 CHAPTER 16 LOWER EXTREMITY Amanda K Silva, MD and Warren Ellsworth, MD, FACS The plastic and reconstructive surgeon is often called upon to treat many wound problems of the lower extremity. These include
CHAPTER 16 LOWER EXTREMITY Amanda K Silva, MD and Warren Ellsworth, MD, FACS The plastic and reconstructive surgeon is often called upon to treat many wound problems of the lower extremity. These include
EVALUATION OF THE VASCULAR STATUS OF DIABETIC WOUNDS Travis Littman, MD NorthWest Surgical Specialists
 EVALUATION OF THE VASCULAR STATUS OF DIABETIC WOUNDS Travis Littman, MD NorthWest Surgical Specialists Nothing To Disclosure DISCLOSURES I have no outside conflicts of interest, financial incentives, or
EVALUATION OF THE VASCULAR STATUS OF DIABETIC WOUNDS Travis Littman, MD NorthWest Surgical Specialists Nothing To Disclosure DISCLOSURES I have no outside conflicts of interest, financial incentives, or
Wound Jeopardy: Name That Wound Session 142 Saturday, September 10 th 2011
 Initial Wound Care Consult History Physical Examination Detailed examination of the wound Photographs Cultures Procedures TCOM ABI Debridement Management Decisions A Detailed History and Physical (wound)
Initial Wound Care Consult History Physical Examination Detailed examination of the wound Photographs Cultures Procedures TCOM ABI Debridement Management Decisions A Detailed History and Physical (wound)
Wound Classification. Overview
 Overview Jeffrey A. Niezgoda, MD FACHM, MAPWCA, CHWS Review of Initial Wound Care Consultation Rational for Classification Wound Appearance Wound Etiology Management Algorithms Initial Wound Care Consult
Overview Jeffrey A. Niezgoda, MD FACHM, MAPWCA, CHWS Review of Initial Wound Care Consultation Rational for Classification Wound Appearance Wound Etiology Management Algorithms Initial Wound Care Consult
-> Education -> Excellence
 Quality Conference 5/2557 Extravasations: Event -> Education -> Excellence รศ.นพ. รว ศ เร องตระก ล สาขาว ชาก มารศ ลยศาสตร ภาควชาศลยศาสตร Extravasations: Event 1. Thrombophlebitis - superficial vein 2.
Quality Conference 5/2557 Extravasations: Event -> Education -> Excellence รศ.นพ. รว ศ เร องตระก ล สาขาว ชาก มารศ ลยศาสตร ภาควชาศลยศาสตร Extravasations: Event 1. Thrombophlebitis - superficial vein 2.
PATHWAY #4 DIABETIC FOOT DISORDERS VOLUME 45, NUMBER 5, SEPTEMBER/OCTOBER 2006 S 29
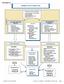 PATHWAY #4 DIABETIC FOOT DISORDERS VOLUME 45, NUMBER 5, SEPTEMBER/OCTOBER 2006 S 29 be present. Hospitalization is required to treat the infection as well as systemic sequelae. Patients with poor vascular
PATHWAY #4 DIABETIC FOOT DISORDERS VOLUME 45, NUMBER 5, SEPTEMBER/OCTOBER 2006 S 29 be present. Hospitalization is required to treat the infection as well as systemic sequelae. Patients with poor vascular
L APPROCCIO AL TRATTAMENTO DEL PIEDE DIABETICO INFETTO
 L APPROCCIO AL TRATTAMENTO DEL PIEDE DIABETICO INFETTO Dott.ssa Fabrizia Toscanella Resp. Centro Prevenzione e Cura del Piede Diabetico Villa Tiberia Hospital, Roma LA CLINICA NEL DIABETE: INCONTRO TRA
L APPROCCIO AL TRATTAMENTO DEL PIEDE DIABETICO INFETTO Dott.ssa Fabrizia Toscanella Resp. Centro Prevenzione e Cura del Piede Diabetico Villa Tiberia Hospital, Roma LA CLINICA NEL DIABETE: INCONTRO TRA
Arterial Studies And The Diabetic Foot Patient
 Arterial Studies And The Patient George L. Berdejo, BA, RVT, FSVU gberdejo@wphospital.org Disclosures I have nothing to disclose! Diabetes mellitus continues to grow in global prevalence and to consume
Arterial Studies And The Patient George L. Berdejo, BA, RVT, FSVU gberdejo@wphospital.org Disclosures I have nothing to disclose! Diabetes mellitus continues to grow in global prevalence and to consume
CLI Therapy- LINCed Multi disciplinary discussions on CLI
 CLI Therapy- LINCed Multi disciplinary discussions on CLI Critical limb ischemia and managing the infected wound Michiel Schreve North West Clinics Alkmaar, The Netherlands Disclosure Speaker name: Michiel
CLI Therapy- LINCed Multi disciplinary discussions on CLI Critical limb ischemia and managing the infected wound Michiel Schreve North West Clinics Alkmaar, The Netherlands Disclosure Speaker name: Michiel
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript J Diabetes Metab. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2014 July 07.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Diabetes Metab. 2013 November 1; 4(9): 310. doi:10.4172/2155-6156.1000310. Foreign Body with Gas Gangrene in an Elderly Patient
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Diabetes Metab. 2013 November 1; 4(9): 310. doi:10.4172/2155-6156.1000310. Foreign Body with Gas Gangrene in an Elderly Patient
AIM OF MASTERCLASS. Overview of the diabetic foot disease. Modern approach to management
 AIM OF MASTERCLASS Overview of the diabetic foot disease Modern approach to management DIABETIC FOOT DISEASE THROUGHOUT THE WORLD, THERE IS AN AMPUTATION EVERY 20 SECONDS MOST OF THESE AMPUTATIONS ARE
AIM OF MASTERCLASS Overview of the diabetic foot disease Modern approach to management DIABETIC FOOT DISEASE THROUGHOUT THE WORLD, THERE IS AN AMPUTATION EVERY 20 SECONDS MOST OF THESE AMPUTATIONS ARE
Jack W. Hutter DPM, FACFAS, C.ped
 Jack W. Hutter DPM, FACFAS, C.ped First Described in 1883 as osteoarthropathy seen in cases of syphilis The typical presentation of the rocker bottom foot As imaging techniques improved the extent of severity
Jack W. Hutter DPM, FACFAS, C.ped First Described in 1883 as osteoarthropathy seen in cases of syphilis The typical presentation of the rocker bottom foot As imaging techniques improved the extent of severity
Aetiology Macroangiopathy occurs mainly distally ie Popliteal artery There is arterial wall calcification Microangiopathy is less common
 DIABETIC FOOT Facts 5% of the population is diabetic 12% of diabetic admissions are with foot problems 1/3rd of diabetic foot ulcerations are neuropathic, 1/3rd are ischaemic and 1/3 are of a mixed in
DIABETIC FOOT Facts 5% of the population is diabetic 12% of diabetic admissions are with foot problems 1/3rd of diabetic foot ulcerations are neuropathic, 1/3rd are ischaemic and 1/3 are of a mixed in
Practical Point in Holistic Diabetic Foot Care 3 March 2016
 Diabetic Foot Ulcer : Vascular Management Practical Point in Holistic Diabetic Foot Care 3 March 2016 Supapong Arworn, MD Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Department of Surgery, Chiang Mai
Diabetic Foot Ulcer : Vascular Management Practical Point in Holistic Diabetic Foot Care 3 March 2016 Supapong Arworn, MD Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Department of Surgery, Chiang Mai
Total Contact Cast System
 Total Contact Cast System Instructions for Use Products Included in Cutimed Off-Loader Select kit Qty Cutimed Cavity Sterile 1 ea. Cutisorb Cotton Gauze 2" x 2" 4 ea. Delta-Lite Conformable Fiberglass
Total Contact Cast System Instructions for Use Products Included in Cutimed Off-Loader Select kit Qty Cutimed Cavity Sterile 1 ea. Cutisorb Cotton Gauze 2" x 2" 4 ea. Delta-Lite Conformable Fiberglass
Diabetic Neuropathic Arthropathy (Charcot) Kiwon Young M.D. ( 양기원 ) Eulji Hospital Dept of Orthopaedic Foot & Ankle Clinic Seoul, KOREA
 Diabetic Neuropathic Arthropathy (Charcot) Kiwon Young M.D. ( 양기원 ) Eulji Hospital Dept of Orthopaedic Foot & Ankle Clinic Seoul, KOREA Charcot 1. What is it? (definition) & Who gets it? (epidemiology
Diabetic Neuropathic Arthropathy (Charcot) Kiwon Young M.D. ( 양기원 ) Eulji Hospital Dept of Orthopaedic Foot & Ankle Clinic Seoul, KOREA Charcot 1. What is it? (definition) & Who gets it? (epidemiology
DIABETIC FOOT ULCER CLASSIFICATION SYSTEMS. A Review of the Literature
 A Review of the Literature Red Yellow Black (RYB) Breakdown (prominent in nursing literature) For this classification I didn t manage to find further information (yet) R: red wounds that exhibit pale pink
A Review of the Literature Red Yellow Black (RYB) Breakdown (prominent in nursing literature) For this classification I didn t manage to find further information (yet) R: red wounds that exhibit pale pink
Acknowledgements. No tengo conflictos de interés que revelar. I have no conflicts of interest to disclose. Michael S. Conte. David G.
 No tengo conflictos de interés que revelar I have no conflicts of interest to disclose. Critical Limb Ischemia : The Need for a New System to Define Disease Burden and Stratify Amputation Risk and Need
No tengo conflictos de interés que revelar I have no conflicts of interest to disclose. Critical Limb Ischemia : The Need for a New System to Define Disease Burden and Stratify Amputation Risk and Need
Transmetatarsal amputation in an at-risk diabetic population: a retrospective study
 The Journal of Diabetic Foot Complications Transmetatarsal amputation in an at-risk diabetic population: a retrospective study Authors: Merribeth Bruntz, DPM, MS* 1,2, Heather Young, MD 3,4, Robert W.
The Journal of Diabetic Foot Complications Transmetatarsal amputation in an at-risk diabetic population: a retrospective study Authors: Merribeth Bruntz, DPM, MS* 1,2, Heather Young, MD 3,4, Robert W.
ULCERS 1/12/ million diabetics in the US (2012) Reamputation Rate 26.7% at 1 year 48.3% at 3 years 60.7% at 5 years
 Jay Christensen D.P.M Advanced Foot and Ankle of Wisconsin 2-4% of the population at any given time will have ulcers 0.06-0.20% of the total population Average age of patients 70 years increased as more
Jay Christensen D.P.M Advanced Foot and Ankle of Wisconsin 2-4% of the population at any given time will have ulcers 0.06-0.20% of the total population Average age of patients 70 years increased as more
Objectives. Define classes of uncomplicated skin and soft tissue infection (SSTI) that drive empiric antimicrobial selection
 Objectives Define classes of uncomplicated skin and soft tissue infection (SSTI) that drive empiric antimicrobial selection Purulent SSTI Non-purulent SSTI Recognize conditions that suggest complications
Objectives Define classes of uncomplicated skin and soft tissue infection (SSTI) that drive empiric antimicrobial selection Purulent SSTI Non-purulent SSTI Recognize conditions that suggest complications
Diabetic Foot Infections
 PL Detail-Document #320509 This PL Detail-Document gives subscribers additional insight related to the Recommendations published in PHARMACIST S LETTER / PRESCRIBER S LETTER May 2016 Diabetic Foot Infections
PL Detail-Document #320509 This PL Detail-Document gives subscribers additional insight related to the Recommendations published in PHARMACIST S LETTER / PRESCRIBER S LETTER May 2016 Diabetic Foot Infections
Multidisciplinary approach to BTK Y. Gouëffic, MD, PhD
 Multidisciplinary approach to BTK Y. Gouëffic, MD, PhD Department of vascular surgery, University Hospital of Nantes, France Response to the increased demand of hospital care Population is aging Diabetes
Multidisciplinary approach to BTK Y. Gouëffic, MD, PhD Department of vascular surgery, University Hospital of Nantes, France Response to the increased demand of hospital care Population is aging Diabetes
Increased pressures at
 Surgical Off-loading of Plantar Hallux Ulcerations These approaches can be used to treat DFUs. By Adam R. Johnson, DPM Increased pressures at the plantar aspect of the hallux leading to chronic hyperkeratosis
Surgical Off-loading of Plantar Hallux Ulcerations These approaches can be used to treat DFUs. By Adam R. Johnson, DPM Increased pressures at the plantar aspect of the hallux leading to chronic hyperkeratosis
Diabetes Mellitus and the Associated Complications
 Understanding and the complications relating to the disease can assist the fitter to better serve patients. and the Associated Complications Released January, 2011 Total: 25.8 million people, or 8.3% of
Understanding and the complications relating to the disease can assist the fitter to better serve patients. and the Associated Complications Released January, 2011 Total: 25.8 million people, or 8.3% of
The Great Debate: Offloading Diabetic Foot Ulcers: TCC vs. CAM Walkers Gregory A Bohn, MD MAPWCA, ABPM/UHMS
 The Great Debate: Offloading Diabetic Foot Ulcers: TCC vs. CAM Walkers Gregory A Bohn, MD MAPWCA, ABPM/UHMS Department of Surgery Central Michigan School of Medicine Tawas, Michigan Disclosures Medical/Scientific
The Great Debate: Offloading Diabetic Foot Ulcers: TCC vs. CAM Walkers Gregory A Bohn, MD MAPWCA, ABPM/UHMS Department of Surgery Central Michigan School of Medicine Tawas, Michigan Disclosures Medical/Scientific
DISCLOSURE STATEMENT 10/8/ BASIC OF ELEMENTS OF LIMB SALVAGE MANAGEMENT
 LI MB SALVAGE MANAGEMENT October 11, 2018 DISCLOSURE STATEMENT My opinions do not represent the VA s opinions in regards to product preference No specific proprietary data from the VA has been included
LI MB SALVAGE MANAGEMENT October 11, 2018 DISCLOSURE STATEMENT My opinions do not represent the VA s opinions in regards to product preference No specific proprietary data from the VA has been included
OSTEOMYELITIS. If it occurs in adults, then the axial skeleton is the usual site.
 OSTEOMYELITIS Introduction Osteomyelitis is an acute or chronic inflammatory process of the bone and its structures secondary to infection with pyogenic organisms. Pathophysiology Osteomyelitis may be
OSTEOMYELITIS Introduction Osteomyelitis is an acute or chronic inflammatory process of the bone and its structures secondary to infection with pyogenic organisms. Pathophysiology Osteomyelitis may be
Wound Care Evaluation by Kris Dalseg MS PT CWS CLT
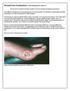 Wound Care Evaluation by Kris Dalseg MS PT CWS CLT This document is intended to describe a standard wound care evaluation for healthcare practitioners. In healthcare, all aspects of our treatment have
Wound Care Evaluation by Kris Dalseg MS PT CWS CLT This document is intended to describe a standard wound care evaluation for healthcare practitioners. In healthcare, all aspects of our treatment have
Practical guidelines on the management and prevention of the diabetic foot 2011
 DIABETES/METABOLISM RESEARCH AND REVIEWS Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2012; 28(Suppl 1): 225 231. Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com).2253 IWGDF GUIDELINES Practical guidelines
DIABETES/METABOLISM RESEARCH AND REVIEWS Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2012; 28(Suppl 1): 225 231. Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com).2253 IWGDF GUIDELINES Practical guidelines
Validation and Clinical Utility of the SVS WIfI Threatened Limb Classification
 Validation and Clinical Utility of the SVS WIfI Threatened Limb Classification PRESENTED BY: 11 th Houston Aortic Symposium 15 February 2018 Joseph L. Mills, Sr., M.D. Reid Endowed Professor of Surgery
Validation and Clinical Utility of the SVS WIfI Threatened Limb Classification PRESENTED BY: 11 th Houston Aortic Symposium 15 February 2018 Joseph L. Mills, Sr., M.D. Reid Endowed Professor of Surgery
PUT YOUR BEST FOOT FORWARD
 PUT YOUR BEST FOOT FORWARD Bala Ramanan, MBBS 1 st year vascular surgery fellow Introduction The epidemic of diabetes and ageing of our population ensures critical limb ischemia will continue to grow.
PUT YOUR BEST FOOT FORWARD Bala Ramanan, MBBS 1 st year vascular surgery fellow Introduction The epidemic of diabetes and ageing of our population ensures critical limb ischemia will continue to grow.
General surgery department of SGMU Lecturer ass. Khilgiyaev R.H. Anaerobic infection. Gas gangrene
 Anaerobic infection Gas gangrene Anaerobic bacteria Anaerobic bacteria are the most numerous inhabitants of the normal gastrointestinal tract, including the mouth Bacteroides fragilis and Clostridium The
Anaerobic infection Gas gangrene Anaerobic bacteria Anaerobic bacteria are the most numerous inhabitants of the normal gastrointestinal tract, including the mouth Bacteroides fragilis and Clostridium The
Topics. Musculoskeletal Infection Extremities. Detection of Infection. Role of Imaging in Extremity Infection. Detection of Infection
 Topics Musculoskeletal Infection Extremities Nuttaya Pattamapaspong M.D. Department of Radiology, Faculty of Medicine, Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai, Thailand Role of imaging in extremity infection
Topics Musculoskeletal Infection Extremities Nuttaya Pattamapaspong M.D. Department of Radiology, Faculty of Medicine, Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai, Thailand Role of imaging in extremity infection
STANDARD TREATMENT GUIDELINES. The Diabetic foot. Prevention and management in India. Quick Reference Guide (Draft) January 2016
 STANDARD TREATMENT GUIDELINES The Diabetic foot Prevention and management in India Quick Reference Guide (Draft) January 2016 Ministry of Health & Family Welfare Government of India TABLE OF CONTENTS-
STANDARD TREATMENT GUIDELINES The Diabetic foot Prevention and management in India Quick Reference Guide (Draft) January 2016 Ministry of Health & Family Welfare Government of India TABLE OF CONTENTS-
2012 Infectious Diseases Society of America Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Diabetic Foot Infections a
 IDSA GUIDELINES 2012 Infectious Diseases Society of America Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Diabetic Foot Infections a Benjamin A. Lipsky, 1 Anthony R. Berendt, 2 Paul B.
IDSA GUIDELINES 2012 Infectious Diseases Society of America Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Diabetic Foot Infections a Benjamin A. Lipsky, 1 Anthony R. Berendt, 2 Paul B.
Multisciplinary Team and Diabetic Foot Syndrome
 Multisciplinary Team and Diabetic Foot Syndrome Giacomo Clerici MD Roberto Ferraresi MD Amputation Prevention Centre Humanitas Hospitals Group Milan and Bergamo giacomoclerici@me.com Twitter @diabeticfoot1
Multisciplinary Team and Diabetic Foot Syndrome Giacomo Clerici MD Roberto Ferraresi MD Amputation Prevention Centre Humanitas Hospitals Group Milan and Bergamo giacomoclerici@me.com Twitter @diabeticfoot1
Clasificación WIFI: Finalmente hablaremos el mismo idioma! WIfI: Wound, Ischemia, foot Infection The SVS Threatened Limb Classification
 Clasificación WIFI: Finalmente hablaremos el mismo idioma! WIfI: Wound, Ischemia, foot Infection The SVS Threatened Limb Classification Joseph L. Mills, Sr., M.D. Professor of Surgery, Chief, Vascular
Clasificación WIFI: Finalmente hablaremos el mismo idioma! WIfI: Wound, Ischemia, foot Infection The SVS Threatened Limb Classification Joseph L. Mills, Sr., M.D. Professor of Surgery, Chief, Vascular
VASCULAR DISEASE: THREE THINGS YOU SHOULD KNOW JAMES A.M. SMITH, D.O. KANSAS VASCULAR MEDICINE, P.A. WICHITA, KANSAS
 VASCULAR DISEASE: THREE THINGS YOU SHOULD KNOW JAMES A.M. SMITH, D.O. KANSAS VASCULAR MEDICINE, P.A. WICHITA, KANSAS KANSAS ASSOCIATION OF OSTEOPATHIC MEDICINE ANNUAL CME CONVENTION APRIL 13, 2018 THREE
VASCULAR DISEASE: THREE THINGS YOU SHOULD KNOW JAMES A.M. SMITH, D.O. KANSAS VASCULAR MEDICINE, P.A. WICHITA, KANSAS KANSAS ASSOCIATION OF OSTEOPATHIC MEDICINE ANNUAL CME CONVENTION APRIL 13, 2018 THREE
DIABETIC FOOT RISK CLASSIFICATION IN A TERTIARY CARE TEACHING HOSPITAL OF PESHAWAR
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE DIABETIC FOOT RISK CLASSIFICATION IN A TERTIARY CARE TEACHING HOSPITAL OF PESHAWAR Ghulam Shabbier, Said Amin, Ishaq Khattak, Sadeeq-ur-Rehman Department of Medicine Khyber Teaching Hospital
ORIGINAL ARTICLE DIABETIC FOOT RISK CLASSIFICATION IN A TERTIARY CARE TEACHING HOSPITAL OF PESHAWAR Ghulam Shabbier, Said Amin, Ishaq Khattak, Sadeeq-ur-Rehman Department of Medicine Khyber Teaching Hospital
Diabetic Foot Ulcers (DFUs) Mehr Ali Rahimi Endocrinologist Associate Proffessor of Kermansha University of Medical Scinces
 بسم الله الرحمن الرحیم Diabetic Foot Ulcers (DFUs) Mehr Ali Rahimi Endocrinologist Associate Proffessor of Kermansha University of Medical Scinces ١ Case ۵۶ year old woman with DM٢ admitted with a diabetesrelated
بسم الله الرحمن الرحیم Diabetic Foot Ulcers (DFUs) Mehr Ali Rahimi Endocrinologist Associate Proffessor of Kermansha University of Medical Scinces ١ Case ۵۶ year old woman with DM٢ admitted with a diabetesrelated
Case 1. July 14, th week wound gel 3 cm x 2.5 cm = 7.5 cm². May 25, st wound gel on 290 days PI treatment 4 cm x 2.4 cm = 9.
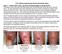 2.5% Sodium Hyaluronate Wound Gel Study Cases Case 1 Patient with Lower Leg Ulcer Not Responding to Compression This patient was a 50-year old male patient with nonhealing right lower leg since January
2.5% Sodium Hyaluronate Wound Gel Study Cases Case 1 Patient with Lower Leg Ulcer Not Responding to Compression This patient was a 50-year old male patient with nonhealing right lower leg since January
National Clinical Conference 2018 Baltimore, MD
 National Clinical Conference 2018 Baltimore, MD No relevant financial relationships to disclose Wound Care Referral The patient has been maximized from a vascular standpoint. She has no other options.
National Clinical Conference 2018 Baltimore, MD No relevant financial relationships to disclose Wound Care Referral The patient has been maximized from a vascular standpoint. She has no other options.
Rochester Patient Safety C. difficile Prevention Collaborative: Long Term Care Antimicrobial Stewardship (funded by NYSDOH)
 Rochester Patient Safety C. difficile Prevention Collaborative: Long Term Care Antimicrobial Stewardship (funded by NYSDOH) Clinical Practice Guideline* for the Diagnosis and Management of Acute Bacterial
Rochester Patient Safety C. difficile Prevention Collaborative: Long Term Care Antimicrobial Stewardship (funded by NYSDOH) Clinical Practice Guideline* for the Diagnosis and Management of Acute Bacterial
Management Of The Diabetic foot
 Management Of The Diabetic foot Aims, Pathways, Treatments Nikki Coates 12/1/18 Diabetic foot pathology Neuropathy Foot deformity Vascular disease Sensory neuropathy Limited Joint Mobility Smoking Autonomic
Management Of The Diabetic foot Aims, Pathways, Treatments Nikki Coates 12/1/18 Diabetic foot pathology Neuropathy Foot deformity Vascular disease Sensory neuropathy Limited Joint Mobility Smoking Autonomic
Root Cause Analysis for nontraumatic
 Root Cause Analysis for nontraumatic amputations 2016 (Full Data) Date Richard Leigh and Stella Vig, Co-Chairs London SCN Footcare Network October 2015 Outline of London RCA 2016 London Hospitals invited
Root Cause Analysis for nontraumatic amputations 2016 (Full Data) Date Richard Leigh and Stella Vig, Co-Chairs London SCN Footcare Network October 2015 Outline of London RCA 2016 London Hospitals invited
Nanogen Aktiv. Naz Wahab MD, FAAFP, FAPWCA Nexderma
 Nanogen Aktiv Naz Wahab MD, FAAFP, FAPWCA Nexderma Patient BM 75 y.o female with a history of Type 2 Diabetes, HTN, Hypercholesterolemia, Renal insufficiency, Chronic back Pain, who had undergone a L3-L4
Nanogen Aktiv Naz Wahab MD, FAAFP, FAPWCA Nexderma Patient BM 75 y.o female with a history of Type 2 Diabetes, HTN, Hypercholesterolemia, Renal insufficiency, Chronic back Pain, who had undergone a L3-L4
DIABETIC ULCERS V PRESSURE ULCERS SO, WHAT DO YOU CALL IT?
 DIABETIC ULCERS V PRESSURE ULCERS SO, WHAT DO YOU CALL IT? Arthur Stone, DPM Mary Sieggreen, MSN,CNS,NP,CVN Faculty Disclosure Dr. Stone has listed an affiliation with: Advisory Board Member..FXI, Inc.
DIABETIC ULCERS V PRESSURE ULCERS SO, WHAT DO YOU CALL IT? Arthur Stone, DPM Mary Sieggreen, MSN,CNS,NP,CVN Faculty Disclosure Dr. Stone has listed an affiliation with: Advisory Board Member..FXI, Inc.
Clinical assessment of diabetic foot in 5 minutes
 Clinical assessment of diabetic foot in 5 minutes Assoc. Prof. N. Tentolouris, MD 1 st Department of Propaedeutic Internal Medicine Medical School Laiko General Hospital Leading Innovative Vascular Education
Clinical assessment of diabetic foot in 5 minutes Assoc. Prof. N. Tentolouris, MD 1 st Department of Propaedeutic Internal Medicine Medical School Laiko General Hospital Leading Innovative Vascular Education
The distinguishing traits of CLI: what makes it so different? Roberto Ferraresi Cardiovascular CathLab
 The distinguishing traits of CLI: what makes it so different? Roberto Ferraresi Cardiovascular CathLab Potential conflicts of interest Roberto Ferraresi, MD I have the following potential conflicts of
The distinguishing traits of CLI: what makes it so different? Roberto Ferraresi Cardiovascular CathLab Potential conflicts of interest Roberto Ferraresi, MD I have the following potential conflicts of
Practical Point in Diabetic Foot Care 3-4 July 2017
 Diabetic Foot Ulcer : Role of Vascular Surgeon Practical Point in Diabetic Foot Care 3-4 July 2017 Supapong Arworn, MD Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Department of Surgery, Chiang Mai University
Diabetic Foot Ulcer : Role of Vascular Surgeon Practical Point in Diabetic Foot Care 3-4 July 2017 Supapong Arworn, MD Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Department of Surgery, Chiang Mai University
Concepts of Total Contact Cast(TCC) Negative Pressure Wound Therapy(NPWT)
 Concepts of Total Contact Cast(TCC) & Negative Pressure Wound Therapy(NPWT) Chungnam National University Hospital Orthopaedic Surgery Chan Kang Total Contact Cast TTC on DM foot ulcer Risk classification
Concepts of Total Contact Cast(TCC) & Negative Pressure Wound Therapy(NPWT) Chungnam National University Hospital Orthopaedic Surgery Chan Kang Total Contact Cast TTC on DM foot ulcer Risk classification
Diabetic/Neuropathic Foot Ulcer Assessment Guide South West Regional Wound Care Program Last Updated April 7,
 Developed in collaboration with the Wound Care Champions, Wound Care Specialists, Enterostomal Nurses, and South West Regional Wound Care Program (SWRWCP) members from Long Term Care Homes, Hospitals,
Developed in collaboration with the Wound Care Champions, Wound Care Specialists, Enterostomal Nurses, and South West Regional Wound Care Program (SWRWCP) members from Long Term Care Homes, Hospitals,
Treatment of infection
 Clinica Ortopedica e Traumatologica Università degli Studi di Pavia Fondazione IRCCS Policlinico San Matteo Chairman: Prof. F. Benazzo Goals: - Healing of infection - Healing of fracture - Try to keep
Clinica Ortopedica e Traumatologica Università degli Studi di Pavia Fondazione IRCCS Policlinico San Matteo Chairman: Prof. F. Benazzo Goals: - Healing of infection - Healing of fracture - Try to keep
Fluorescent Angiography: Practical uses in the Clinical Setting
 Fluorescent Angiography: Practical uses in the Clinical Setting Charles Andersen MD, FACS, MAPWCA Chief Vascular/Endovascular/ Limb Preservation Surgery Service (Emeritus) Chief of Wound Care Service Madigan
Fluorescent Angiography: Practical uses in the Clinical Setting Charles Andersen MD, FACS, MAPWCA Chief Vascular/Endovascular/ Limb Preservation Surgery Service (Emeritus) Chief of Wound Care Service Madigan
GLOBAL VASCULAR GUIDELINES: A NEW PATHWAY FOR LIMB SALVAGE
 GLOBAL VASCULAR GUIDELINES: A NEW PATHWAY FOR LIMB SALVAGE Michael S. Conte MD Professor and Chief, Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Co-Director, Center for Limb Preservation Co-Director, Heart and Vascular
GLOBAL VASCULAR GUIDELINES: A NEW PATHWAY FOR LIMB SALVAGE Michael S. Conte MD Professor and Chief, Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Co-Director, Center for Limb Preservation Co-Director, Heart and Vascular
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abscess, with diabetic foot ulcers, 472 Achilles tendon, in calcanectomy, for osteomyelitis, 473, 483 in calcaneus anatomy, 477 478 in Syme
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abscess, with diabetic foot ulcers, 472 Achilles tendon, in calcanectomy, for osteomyelitis, 473, 483 in calcaneus anatomy, 477 478 in Syme
Due to Perimed s commitment to continuous improvement of our products, all specifications are subject to change without notice.
 A summary Disclaimer The information contained in this document is intended to provide general information only. It is not intended to be, nor does it constitute, medical advice. Under no circumstances
A summary Disclaimer The information contained in this document is intended to provide general information only. It is not intended to be, nor does it constitute, medical advice. Under no circumstances
Advanced Clinical Solutions. Pressure Ulcer. Carilex Medical Group 1
 Advanced Clinical Solutions Pressure Ulcer Carilex Medical Group 1 Advanced Clinical Solutions Contents About Pressure Ulcer! 2 Stages of Pressure Ulcer! 5 Reference! 7 Carilex Medical Group 1 About Pressure
Advanced Clinical Solutions Pressure Ulcer Carilex Medical Group 1 Advanced Clinical Solutions Contents About Pressure Ulcer! 2 Stages of Pressure Ulcer! 5 Reference! 7 Carilex Medical Group 1 About Pressure
Assessment and Management of Wounds In Diabetes. Maria Mousley Northamptonshire NHS Foundation Trust
 Assessment and Management of Wounds In Diabetes Maria Mousley Northamptonshire NHS Foundation Trust Background At least 61000 people with diabetes in England have a foot ulcer at any given time There are
Assessment and Management of Wounds In Diabetes Maria Mousley Northamptonshire NHS Foundation Trust Background At least 61000 people with diabetes in England have a foot ulcer at any given time There are
Indian Journal of Basic & Applied Medical Research; December 2011: Issue-1, Vol.-1, P
 Original article: Analysis of the Risk Factors, Presentation and Predictors of Outcome in Patients Presenting with Diabetic Foot Ulcers at Tertiary Care Hospital in Karnataka Sarita Kanth Associate Professor,
Original article: Analysis of the Risk Factors, Presentation and Predictors of Outcome in Patients Presenting with Diabetic Foot Ulcers at Tertiary Care Hospital in Karnataka Sarita Kanth Associate Professor,
The Diabetic Foot Screen and Management Foundation Series of Modules for Primary Care
 The Diabetic Foot Screen and Management Foundation Series of Modules for Primary Care Anita Murray - Senior Podiatrist Diabetes, SCH Learning Outcomes Knowledge of the Model of Care For The Diabetic Foot
The Diabetic Foot Screen and Management Foundation Series of Modules for Primary Care Anita Murray - Senior Podiatrist Diabetes, SCH Learning Outcomes Knowledge of the Model of Care For The Diabetic Foot
Diabetic Foot Ulcers. Care for Patients in All Settings
 Diabetic Foot Ulcers Care for Patients in All Settings Summary This quality standard focuses on care for people who have developed or are at risk of developing a diabetic foot ulcer. The scope of the standard
Diabetic Foot Ulcers Care for Patients in All Settings Summary This quality standard focuses on care for people who have developed or are at risk of developing a diabetic foot ulcer. The scope of the standard
Diabetic foot ulcer and poor compliance: How would you treat?
 Jessica Farnsworth, MD Department of Family Medicine, University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha Paul Paulman, MD University of Nebraska College of Medicine, Department of Family Medicine, Omaha Diabetic
Jessica Farnsworth, MD Department of Family Medicine, University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha Paul Paulman, MD University of Nebraska College of Medicine, Department of Family Medicine, Omaha Diabetic
Address: Left Leg. other: Nails: thick yellow brittle fungus abnormal thick yellow brittle fungus abnormal
 South West Regional Wound Care Toolkit: Interdisciplinary Lower Leg Assessment Form Instructions for use: Competent/ Proficient/ Expert level HCP to complete if lower leg ulcer present or risk of ulcer
South West Regional Wound Care Toolkit: Interdisciplinary Lower Leg Assessment Form Instructions for use: Competent/ Proficient/ Expert level HCP to complete if lower leg ulcer present or risk of ulcer
Global Vascular Guideline on the Management of Chronic Limb Threatening Ischemia -a new foundation for evidence-based care
 Global Vascular Guideline on the Management of Chronic Limb Threatening Ischemia -a new foundation for evidence-based care Michael S. Conte MD Professor and Chief, Division of Vascular and Endovascular
Global Vascular Guideline on the Management of Chronic Limb Threatening Ischemia -a new foundation for evidence-based care Michael S. Conte MD Professor and Chief, Division of Vascular and Endovascular
Diabetic Feet. Juanita Muller
 Diabetic Feet Juanita Muller Mr RR 69 year old male CHARCOT ARTHROPATHY Diabetic Feet Callus Acute injury and ulceration Infection Osteomylitis Chronic ulceration Ischaemic necrosis Charcot s arthropathy
Diabetic Feet Juanita Muller Mr RR 69 year old male CHARCOT ARTHROPATHY Diabetic Feet Callus Acute injury and ulceration Infection Osteomylitis Chronic ulceration Ischaemic necrosis Charcot s arthropathy
Treat the whole patient, not just the hole in the patient! 3/21/2017 CAN YOU CONNECT THE DOTS?? PHILOSOPHY OBJECTIVES
 CAN YOU CONNECT THE DOTS?? Boone Hospital Wound Healing Center Kimberly Jamison, MD, FACP, FAPWCA, PCWC Kim Mitchell, RN, BSN OBJECTIVES Describe the basic concepts of chronic wound care to ensure an optimal
CAN YOU CONNECT THE DOTS?? Boone Hospital Wound Healing Center Kimberly Jamison, MD, FACP, FAPWCA, PCWC Kim Mitchell, RN, BSN OBJECTIVES Describe the basic concepts of chronic wound care to ensure an optimal
Acute and Chronic WOUND ASSESSMENT. Wound Assessment OBJECTIVES ITEMS TO CONSIDER
 WOUND ASSESSMENT Acute and Chronic OBJECTIVES Discuss classification systems and testing methods for pressure ulcers, venous, arterial and diabetic wounds List at least five items to be assessed and documented
WOUND ASSESSMENT Acute and Chronic OBJECTIVES Discuss classification systems and testing methods for pressure ulcers, venous, arterial and diabetic wounds List at least five items to be assessed and documented
Hyperbarics in Diabetic Wound Care. Aurel Mihai, MD & Brian Kline, MD
 Hyperbarics in Diabetic Wound Care Aurel Mihai, MD & Brian Kline, MD Presentation Outline The Scope of the Problem Important Definitions Standard Wound Care Hyperbaric Oxygen as an Adjunct Diabetic Foot
Hyperbarics in Diabetic Wound Care Aurel Mihai, MD & Brian Kline, MD Presentation Outline The Scope of the Problem Important Definitions Standard Wound Care Hyperbaric Oxygen as an Adjunct Diabetic Foot
Statistics on DM and DFU risk
 Disclosure NOTHING Statistics on DM and DFU risk National Institute of Diabetes Digestive & Kidney Diseases: As of September 2011 an estimated 16 million Americans are known to have diabetes, with many
Disclosure NOTHING Statistics on DM and DFU risk National Institute of Diabetes Digestive & Kidney Diseases: As of September 2011 an estimated 16 million Americans are known to have diabetes, with many
Off Loading, TCC, Shoe 을지의대을지병원 족부정형외과 이경태
 Off Loading, TCC, Shoe 을지의대을지병원 족부정형외과 이경태 DMF Protocol VIPS approach V : Vascular I : infection P : Pressure off S : specific wound care Ulcer/Pressure off& Biomechanics PVD vs Peripheral neuropathy NP
Off Loading, TCC, Shoe 을지의대을지병원 족부정형외과 이경태 DMF Protocol VIPS approach V : Vascular I : infection P : Pressure off S : specific wound care Ulcer/Pressure off& Biomechanics PVD vs Peripheral neuropathy NP
Front line management of the Diabetic Foot
 Front line management of the Diabetic Foot n o ti e b a i D + s te k o Sm = g in p Am a t u Sam Fratesi MD Smoking + diabetes = amputation Almost 2 million Canadians have diabetes In amputated diabetics
Front line management of the Diabetic Foot n o ti e b a i D + s te k o Sm = g in p Am a t u Sam Fratesi MD Smoking + diabetes = amputation Almost 2 million Canadians have diabetes In amputated diabetics
of :07
 he diabetic foot ulcer - management and outcomes of 6 3-12-2012 11:07 The diabetic foot ulcer - management and outcomes Impaired perfusion Infection Extent and depth Condition of the ulcer Site Sensation
he diabetic foot ulcer - management and outcomes of 6 3-12-2012 11:07 The diabetic foot ulcer - management and outcomes Impaired perfusion Infection Extent and depth Condition of the ulcer Site Sensation
Surgical Treatment of the Infected Diabetic Foot
 SUPPLEMENT ARTICLE Surgical Treatment of the Infected Diabetic Foot Jeff G. van Baal Diabetic Foot Unit, Department of Surgery, Twenteborg Hospital, Almelo, The Netherlands Foot infections are common in
SUPPLEMENT ARTICLE Surgical Treatment of the Infected Diabetic Foot Jeff G. van Baal Diabetic Foot Unit, Department of Surgery, Twenteborg Hospital, Almelo, The Netherlands Foot infections are common in
Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery University of South Florida School of Medicine Tampa, Florida
 Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery University of South Florida School of Medicine Tampa, Florida Appearance: oearly < 3 mo. olate > 3 mo.. Extent: Szilagyi Classification: Grade I: infection
Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery University of South Florida School of Medicine Tampa, Florida Appearance: oearly < 3 mo. olate > 3 mo.. Extent: Szilagyi Classification: Grade I: infection
Frank K. Galbraith D.P.M. Dr. Frank Galbraith
 Frank K. Galbraith D.P.M. Dr. Frank Galbraith Ingrown Toenails Paronychia (infected toenail) Onychomycosis (fungal nails) From improper trimming, leaving nail sharp corners Curved nails Thick (Hypertrophic)
Frank K. Galbraith D.P.M. Dr. Frank Galbraith Ingrown Toenails Paronychia (infected toenail) Onychomycosis (fungal nails) From improper trimming, leaving nail sharp corners Curved nails Thick (Hypertrophic)
ESPID New Bone and Joint Infection Guidelines
 ESPID New Bone and Joint Infection Guidelines Theoklis Zaoutis, MD, MSCE Professor of Pediatrics and Epidemiology Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania Chief, Division of Infectious
ESPID New Bone and Joint Infection Guidelines Theoklis Zaoutis, MD, MSCE Professor of Pediatrics and Epidemiology Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania Chief, Division of Infectious
PSEUDO-CELLULITIS - ALL THAT S RED IS NOT INFECTION
 JAN 18 2018 ASP ECHO CLINIC CHARLES KRASNER, M.D. PSEUDO-CELLULITIS - ALL THAT S RED IS NOT INFECTION FIRST HOSPITALIZATION: 62 YEAR OLD MALE ADMITTED WITH DIAGNOSIS OF CELLULITIS Hx of AODM, Morbid Obesity,
JAN 18 2018 ASP ECHO CLINIC CHARLES KRASNER, M.D. PSEUDO-CELLULITIS - ALL THAT S RED IS NOT INFECTION FIRST HOSPITALIZATION: 62 YEAR OLD MALE ADMITTED WITH DIAGNOSIS OF CELLULITIS Hx of AODM, Morbid Obesity,
Diabetic Foot Complications
 Diabetic Foot Complications Podiatry Specialty Clinic YKHC Bethel, Alaska August 1-3, 2017 Charles C. Edwards, DPM Alaska Native Tribal Health Consortium Peripheral Neuropathy Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
Diabetic Foot Complications Podiatry Specialty Clinic YKHC Bethel, Alaska August 1-3, 2017 Charles C. Edwards, DPM Alaska Native Tribal Health Consortium Peripheral Neuropathy Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
Service Development Tool for the Assessment of Provision of Services for Patients with Diabetes Related Foot Problems
 Division of Medicine & Community Services Service Development Tool for the Assessment of Provision of Services for Patients with Diabetes Related Foot Problems Graham Holt Advanced Practitioner / Podiatrist
Division of Medicine & Community Services Service Development Tool for the Assessment of Provision of Services for Patients with Diabetes Related Foot Problems Graham Holt Advanced Practitioner / Podiatrist
