Lectin histochemical study on the kidney of normal and streptozotocin-induced diabetic hamsters
|
|
|
- Jeffery Robertson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Histol Histopath (1993) 8: Histology and Histopathology Lectin histochemical study on the kidney of normal and streptozotocin-induced diabetic hamsters J.I. ~guirrelp*, J.-S. ~ anl, S. Itagakil and K. Doil IDepartment of Biomedical Science, Faculty of Agriculture, The University of Tokyo, Bunkyo, Tokyo, Japan and 2Scientific Research Commission of Buenos Aires Province (C.I.C.), Argentina Summary. Lectin histochernical characteristics of the kidney of normal and streptozotocin (SZ)-induced diabetic APA harnsters were investigated. Paraffin sections of the kidney of animals killed at 1 and 3 rnonths after SZ-injection were stained with the following 10 lectins: PNA, BPA, DBA, SBA, GSA-1, GSA-11, MPA, WGA, UEA-1 and Con A. Renal lectin binding characteristics of normal APA harnsters differed in sorne aspects from those in other species reported previously. In the kidney of SZ-induced diabetic APA hamsters, binding activities of sorne lectins increased in the affected Bowman's capsules and glorneruli as well as in degenerated epithelial cells of uriniferous tubules. Among thern, GSA-11 in particular exhibited strong binding activity to the degenerated epithelial cells of Bowman's capsules, dista1 convoluted tubules and collecting ducts. Key words: APA hamster, Diabetes, Kidney, Lectin histochemistry, Streptozotocin lntroduction Syrian harnsters of the APA strain, which has been rnaintained as a closed colony by random breeding in our laboratory, are known to develop spontaneous mesangial thickening in the renal glomeruli from an early age (Han et al., 1992a). They also develop focal and segmental glome~losclerosis (FSG) after 6 rnonths of age (Doi et al., 1987). Recently, Han et al. (1990) reported that streptozotocin (SZ)-induced diabetic APA hamsters developed glornemlar lipidosis and FSG within a short period, and they described histopathological, ultrastructural and morphornetric characteristics of the renal lesions (Han et al., 1992b; Han and Doi, 1992). On the other hand, reports of lectin histochemistry of the kidney in either normal or diabetic Syrian hamsters Offprint requests to: Dr. K. Doi, Department of Biomedical Science, Faculty of Agriculture, The University of Tokyo, Yayoi 1-1-1, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113, Japan are scarce, although those in other laboratory animal species have been reported, and lectin histochernical changes are seen in diabetic kidneys (Watanabe et al., ; Holthofer, 1983; Schulte and Spicer, 1983; Hawthorne et al., 1986; Yonezawa et al., 1986; Henninger et al., 1987; Kizaki et al., 1989). To detect changes of glycoprotein cornponent in the Syrian hamster kidney, in this study we tried to clarify the lectin binding characteristics of the kidney in normal and SZinduced diabetic APA hamsters. Materials and methods Twenty 2-rnonth-old male Syrian hamsters of the APA strain were injected intraperitoneally with 40 mglkg b.w. of SZ (Lot No. 78F-0517, Sigma) dissolved in 0.1M citrate buffer (ph 4.5) according to the rnethod of Han et al. (1990). Six age-rnatched rnale APA harnsters received citrate buffer alone and served as controls. Blood glucose levels were colourimetrically measured on blood samples collected from each animal by orbital sinus puncture at 2-week intervals. Anirnals were killed by exsanguination under ether anaesthesia at 1 and 3 months after SZ-injection (MAI), respectively. Kidneys were fixed in 10% neutralbuffered formalin and 2 pm-paraffin sections were stained with haematoxylin and eosin (HE) or periodic acid-schiff (PAS). For lectin histochemistry, sections were also stained with Arachis hypogaea agglutinin (PNA), Bauhinia purpurea agglutinin (BPA), Dolichos biflorus agglutinin (DBA), Glycine max agglutinin (SBA), Griffonia simplicifolia agglutinin (GSA)-1, GSA-11, Maclura pomifera agglutinin (MPA), Triticum vulgaris agglutinin (WGA) and Ulex europeaus agglutinin (UEA)-1 (horseradish peroxidase (HRP) conjugated form, E-Y laboratories, San Mateo, CA) as reported before (Itagaki et al., 1988) and with Canavalia ensiformis (Con A) (Sigma, USA) according to the method of Bernhard and Avrameas (1971). Briefly, after blocking of endogenous peroxidase, sections were incubated with 0.1 % bovine
2 serum albumin in phosphate buffer saline (PBS) for 30 min and sequently with a solution containing pglml lectin-hrp conjugate in PBS overnight at 4 "C. 3,3'diaminobenzidine was used as HRP substrate and counterstain was carried out by haematoxylin. For ConA, instead of lectin-hrp conjugate solution, sections were incubated with unconjugated Con A (50 yglml PBS) overnight at 4 "C and with HRP (25 yglml in PBS) lhr at room temperature. Some sections were digested with 0.15% trypsin (Merck) in PBS for 30 min at 37 "C before lectin staining. Histochemical control staining was also carried out as reported before (Itagaki et al., 1988). Results Changes in blood glucose levels Diabetes developed in SZ-injected animals on and after 2 weeks (blood glucose levels: >350 mgldl) while no significant change in blood glucose leve1 was recorded in control ones. Histological findings of the kidney of control animal Control animals developed slight expansion of mesangial area of spontaneous nature in the renal glomeruli at 3 MAI (Fig. 1 a). Lectin histochemical findings of the kidney of control animal Lectin reactivities of the kidney at 3 MAI are summarized in Table l. The lectin binding characteristics were almost common to animals killed at 1 and 3 MAI, and trypsin pretreatment had little enhancing effects on the lectin stainability. Renal corpuscle: The epithelia of Bowman's capsules were always stained with WGA, DBA, GSA-1 (Fig. lb),sba and MPA and only sometimes with PNA and BPA. GSA-1 (Fig. lb), MPA and BPA bound weakly or moderately to some of the capillary loops but no lectins had binding sites in the mesangium. Proximal convoluted tubule: WGA, GSA-1 (Fig. lb), Table 1. Lectin reacitivy in each segment of nephron in APA hamsters. WG A UEA-I DBA GSA-I GSA-II PN A SBA MPA BPA ConA Renal corpuscle P. BOW. 1-2 O O O O v. Bow o o o O Cap.3 O O O O 0-2 O O O O O Mes.4 O O O O O O O O O O O Proximal tubules Conv. B.B.5 m.= 6.6. Loop of Henle Desc.8 A.B. Asc.9 A.B. Cyt. Collecting Ducts Cort" A.B. c yt. Med.12 A.B. c yt l: Parietal layer of Bowman's capsule; 2: Visceral layer; 3: Capillary loops; 4: Mesangium; 5: Brush border of proximal convoluted tubule cells; 6: Cytoplasm; 7: Straight portion; Descending loop of Henle; Ascending loop of Henle; lo: Apical border; 11: Cortical collecting ducts; 12: Medullary collecting ducts. Numbers indicate staining intensity on a subjective scale from 0. unreactive, to 4, most reactive. A 0-1, 0-2, 0-3 or 0-4 indicate heterogeneity in staining, with a subpopulation of cells being unstained and the remainder varying in reactivity from 1-4. ': Binding to each lectin was seen as a granular pattem.
3 SBA (Fig. lc), MPA and BPA uniformly stained bmsh borders of epithelial cells, to which GSA-11 (Fig. Id), PNA and Con A showed heterogeneous stainability. In addition, al1 lectins except for UEA-1 exhibited granular staining pattern within the cytoplasm of epithelial cells. Straight proximal tubule: Al1 lectins except for UEA-1 and DBA bound moderately to both the brush border and cytoplasm of some epithelial cells. Descending loop of Henle: A11 lectins except for Con A and GSA-11 uniformly bound to the apical border of epithelial cells, while no lectins had binding sites in their cytoplasm. Ascending loop of Henle: Al1 lectins exhibited binding activities with varying intensity to the apical border of epithelial cells. WGA, DBA and SBA bound weakly but constantly to the cytoplasm of al1 epithelial cells, but Fig. 1. A kidney of control APA hamster at 3 MAI. Except for a, al1 are lectin histochemically stained. a. Slight expansion of mesangial atea. PAS x 600. b. Epithelia of Bowman's oapsule. proximal and distal convoluted tubules (arrowhead) and cortical collecting..,e..... ducts (arrow).- '4,.. r7! a...' ' S.t... i!?' :f. 2 are posjtjve for -.,-2.:- s ' % y i$t:*,?# GSA-1.~ ,. -.. '3 +!? :' ' c. Epithelia of :.*.. " 5:. - proximal (arrow- 8,: '! 1 I' i, ;. :~... head) and distal ",' \, ( a, ' ',. Lb... ' '.: '. '. ;-, -, -. are positive for.'..:. a :'. '.r.,..;.= "'SBA.xl25..%.. " -.. '\,. 1.: :.... -: d. GSA-ll.! '.,..,, * ;'!;.'e- ;,-O-..m\ e reactivity to.. ',.*.' v. y epithelia : e.... proximal and.- Lb"..... e -.'J. I. A '., ~,.. : ii..,\. J - ' I *--.a.% 'i -,....S I ; tubules (arrow) ' '..". ' distal tubules is.:... vely variable, : and no positive reaction is seen,j 4 * ld'. ' * in this case. x 125.
4 UEA-1, GSA-11, PNA and BPA only bound sporadically to the epithelial cell cytoplasm. Distal convoluted tubule and cortical collecting duct: DBA, UEA-1, WGA and SBA (Fig. lc) bound strongly to the apical border and moderately or strongly to the cytoplasm of epithelial cells. On the other hand, GSA-1 (Fig. lb), GSA-11 (Fig. Id), PNA (Fig. le), MPA and BPA bound to the apical border andlor cytoplasm of epithelial cells with varying intensity. Medullary collecting duct: Al1 lectins bound to epithelial cells with varying pattem (Fig. lf). Among them, WGA and UEA-1 bound moderately or strongly to both the apical border and cytoplasm of epithelial cells. Histological findings of the kidney of diabetic animal Lesions in the uriniferous tubules were characterized by marked vacuolization of epithelial cells in the proximal convoluted tubules and by necrosis and desquamation of epithelial cells in the dista1 convoluted tubules and collecting ducts (Fig. 2a). On the other hand, lesions in the renal glomeruli were characterized by FSG showing segmental expasion of mesangial area with lipid droplets and foam cells at 3 MAI (Fig. 2b). In this connection, mild expansion of mesangial area was already observed in some glomeruli in the juxtamedullary cortex at 1 MAI. Lectin histochemical findings of the kidney of diabetic animal Lectin reactivities in the kidney of diabetic animals at 3 MAI are shown in Table 2. Apart from an increase in the intensity of lectin reactivity at 3 MAI, the lectin binding characteristics were almost common to hamsters killed at 1 and 3 MAI. Renal corpuscle: DBA and GSA-1 (Fig. 2c) reactivities to parietal epithelial cells became stronger, and GSA-11 bound strongly to both the parietal and visceral epithelial cells at 3 MAI (Fig. 2d). GSA-1 (Fig. 2c), GSA-11, PNA, SBA, MPA, BPA and Con A exhibited granular stainability in the mesangium and foam cells, especially at 3 MAI. Proximal convoluted tubule: The cytoplasm of degenerated epithelial cells was granularly stained with al1 lectins except for UEA-1, and their stainabilities increased at 3 MAI. Straight proximal tubule: Lectin binding characteristics of epithelial cells in diabetic animals did not differ from Table 2. Lectin reactivity in each segment of nephron in 3 MAI SZ-induced diabetic APA hamsters. WG A U EA- I DBA GSA-I GSA-II PN A SEA MPA BPA ConA Renal cotpuscle 1 P. BOW. 1-2 O V. BOW. 1-3 O O O- 1 O Cap. O O O 0-3 O O O O Mes. O O O Proximal tubules Conv. 6.b. c yt Str. B.B. Loop of Henle Desc.A.6. Asc.A.6. Distal tubules A.B. Cdlecting ducts Cort. A.B O CYt O- 1 Med. A.B O O 0-3 O CH l: See the footnotes in Table 1 about abbreviation of each site. Numbers indicate staining intensity on a subjective scale from 0, unreactive, to 4, most reactive. A 0-1, 0-2, 0.3 or 0-4 indicate heterogeneity in staining, with a subpopulation of cells being unstained and the remainder varying in reactivity from 1-4. ': Binding to each lectin was seen as granular to vacuolar pattem.
5 those in control ones. Descending and ascending loop of Henle: There was no significant difference in the lectin reactivity of epithelial cells between diabetic and control animals. Dista1 convoluted tubule: PNA showed strong binding activity to the apical border of epithelial cells at 3 MAI (Fig. 2e). In addition, SBA and MPA bound to the apical border and PNA (Fig. 2e), GSA-11 (Fig. 2d), SBA and MPA to the cytoplasm of degenerated epithelial cells, respective1 y. Cortical collecting duct: The binding activity of GSA-11 to the cytoplasm of degenerated epithelial cells increased at 3 MAI (Fig. 2d). Medullary collecting duct: The cytoplasm of epithelial cells was moderately or strongly stained with PNA (Fig. 20, SBA and MPA at 3 MAI. iig. 2. A idstney of SZktducacl dtabetk APA hamta at 3 w. Except foraendb, a11 are IieGtin - h- iiy stalned. a. Necmts ln &&alconvokitedtutnlle sfntheha f-d). HE x 150. area with llpm dcpkts and foam cells. x 600, a Cytopiasm of f m cells sh<mrs gmnular stalnabiitty for m-i (m-1, d W c lmduw tubbenal owakrsd -a
6 Discussian In the present study, we clarified the lectin binding characteristics of the kidney of normal and SZ-induced diabetic APA hamsters, of which histological and histopathological findings were the same as those previously reported by Han et al. (1992b). Except for WGA stainability, lectin binding characteristics of the normal APA hamsters were almost similar to those of normal rats (Le Hir and Dubach, 1982; Murata et al., 1983). Namely, WGA bound to neither glomerular capillary loops nor mesangium in APA hamsters. Holthofer (1983) reported that SBA had affinity to the proximal tubule epithelial cells in humans, pigs and rats while SBA receptors were found preferentially in the distal tubule epithelial cells in mice, rats, guinea pigs and rabbits. SBA stainability in APA hamsters was similar to that in the latter animal species. In addition, UEA-1 was considered to be a marker of distal tubule epithelial cells in APA hamsters as reported in rabbits, guinea pigs and pigs by Holthofer (1983). Thus APA hamsters shared many lectin binding characteristics in the kidney with other animal species, and this suggests that the main nephron functions are basically the same in al1 animal species though there are some structural differences among them. As to the changes in lectin binding activities of the kidney of diabetic animals, Hawthorne et al. (1986) reported an accumulation of WGA-positive substance in the glomerular basement membrane and mesangium in diabetic rats. In addition, Yonezawa et al. (1986) reported that GSA-1 A4 had binding sites in the sclerotic areas of glomeruli in diabetic mice. In the kidney of diabetic APA hamsters, as compared with control ones, the lectin reactivity generally increased especially at 3 MAI, and granular deposition, positive for many lectins, was observed in the thickened mesangium, foam cells and degenerated epithelial cells of the proximal convoluted tubule. This suggests that glycocompounds accumulated in such affected renal structures as mentioned above probably due to long-lasting hyperlipidemia as well as hyperglycemia as reported in SZ-injected APA hamsters by Han et al. (1992b). Furthermore, GSA-11 bound strongly to the degenerated parietal cells of Bowman's capsules and it increased its reactivity to the degenerated epithelial cells in the distal convoluted tubules and collecting ducts in diabetic APA hamsters at 3 MAI. Such a change in GSA-11 stainability has not been reported in other diabetic models, and GSA-11 may be useful as an indicator of the development of lesions in the distal tubule epithelia in the case of SZ-induced diabetic APA hamsters. References Bernhard W. and Avrameas S. (1971). Ultrastructural visualization of cellular carbohydrate components by means of Concanavalin A. Exp. Cell Res. 64, Doi K., Yamamoto T., lsegawa N,, Doi C. and Mitsuoka T. (1987). Agerelated non-neoplastic lesions in the heart and kidneys of Syrian hamsters of the APA strain. Lab. Anim. 21, Han J.-S. and Doi K. (1992). Morphometric study on the renal glomeruli of streptozotocin (SZ)-induced diabetic APA hamsters. Histol. Histopath. 7, Han J.-S., Norimatsu M., Sugawara Y. and Doi K. (1990). Acute toxicity of streptozotocin in Syrian hamsters of the APA strain. J. Toxicol. Pathol. 3, Han J.-S., Norimatsu M., ltagaki S. and Doi K. (1992a). Early development of spontaneous glomerular lesion in Syrian hamsters of APA strain. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 54, Han J.-S., Sugawara Y. and Doi K. (1992b). Rapid induction of glomerular lipidosis in APA hamsters by streptozotocin. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 73, Hawthorne G., MacLellan J.R., Mythen M., Alberti K. and Turner G. (1986). Studies on glomerular basement membrane in experimental diabetes using lectin histochemistry in Wistar rats. Diabetologia Henninger R.A., Mayfield R.K., Hawey J.N., Ge Z.-H. and Sens D.A. (1987). Lectin detection of renal glycogen in rats with short-term streptozotocin-diabetes. Diabetologia 30, Holthofer H. (1983). Lectin binding sites in kidney. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 31, ltagaki S., Honjo K., Doi K. and Mitsuoka T. (1988). Histochemical characteristics of glycoproteins in the bile duct system of mice immunized with swine serum. Histochemistry 90, Kizaki T., Takeda Z., Watanabe M., Hanioka K. and ltoh H. (1989). Histochemical analysis of changes in lectin binding in murine glomerular lesions. Acta Pathol. Jpn. 39, Le Hir M. and Dubach U.C. (1982). The cellular specificity of lectin binding in the kidney. l. A light microscopical study in the rat. Histochemistry 74, Murata F., Tsuyama S., Suzuki S., Hamada H., Ozawa M. and Muramatsu T. (1983). Distribution of glycocongutates in the kidney studied by use of labeled lectins. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 31, Schulte B.A. and Spicer S.S. (1983). Histochemical evaluation of mouse and rat kidneys with lectin-horseradish peroxidase conjugates. Am. J. Anat. 168, Watanabe M., Muramatsu T., Shirate H. and Ugai K. (1981). Discrete distnbution of binding sites for Dolichos biflorus agglutinin (DBA) and Peanut agglutinin (PNA) in mouse organ tissues. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 29, Yonezawa S., Shibata M., Shimizu T., Nakamura T. and Sato E. (1986). Griffonia simplicifolia 1-A4 staining of mice glomerular tufts and its alterations in diabetic mice. Acta Pathol. Jpn. 36, Accepted November 20, 1992
Morphometric study on the renal glomeruli of streptozotocin (SZ)-induced diabetic APA hamsters
 Histol Histopath (1 992) 7: 549-554 Histology and Histopathology Morphometric study on the renal glomeruli of streptozotocin (SZ)-induced diabetic APA hamsters J.-S. Han and K.Doi Department of Biomedical
Histol Histopath (1 992) 7: 549-554 Histology and Histopathology Morphometric study on the renal glomeruli of streptozotocin (SZ)-induced diabetic APA hamsters J.-S. Han and K.Doi Department of Biomedical
LABORATORY EXERCISES FOR THE URINARY SYSTEM
 LABORATORY EXERCISES FOR THE URINARY SYSTEM cortex Medulla DEMO SLIDE BOX 172 (450-E001-H-76). Kidney, horse. the inner medulla medullary rays, Uriniferous tubules expand both the cortex and medulla corticomedullary
LABORATORY EXERCISES FOR THE URINARY SYSTEM cortex Medulla DEMO SLIDE BOX 172 (450-E001-H-76). Kidney, horse. the inner medulla medullary rays, Uriniferous tubules expand both the cortex and medulla corticomedullary
Urinary System Laboratory
 Urinary System Laboratory 1 Adrenal gland Organs of The Urinary System Renal artery and vein Kidney Ureter Urinary bladder Figure 26.1 2 Urethra Functions of the urinary system organs: Urethra expels urine
Urinary System Laboratory 1 Adrenal gland Organs of The Urinary System Renal artery and vein Kidney Ureter Urinary bladder Figure 26.1 2 Urethra Functions of the urinary system organs: Urethra expels urine
Histochemical Detection of Glycoconjugates in the Male Reproductive System of the Horse
 J. Vet. Sci. (2003), 4(1), 21-28 J O U R N A L O F Veterinary Science Histochemical Detection of Glycoconjugates in the Male Reproductive System of the Horse Tae-young Ha, Mee-jung Ahn, Yong-duk Lee, Jae-hyuk
J. Vet. Sci. (2003), 4(1), 21-28 J O U R N A L O F Veterinary Science Histochemical Detection of Glycoconjugates in the Male Reproductive System of the Horse Tae-young Ha, Mee-jung Ahn, Yong-duk Lee, Jae-hyuk
Urinary System. Dr. Ahmed Maher Dr. Ahmed Manhal
 Urinary System Dr. Ahmed Maher Dr. Ahmed Manhal Presentation Map Kidney (cortex & medulla). Nephron. Duct system. Juxtaglomerular apparatus. Ureter, bladder & urethra. Definition & General Structure The
Urinary System Dr. Ahmed Maher Dr. Ahmed Manhal Presentation Map Kidney (cortex & medulla). Nephron. Duct system. Juxtaglomerular apparatus. Ureter, bladder & urethra. Definition & General Structure The
RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY
 RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY Peter McCue, M.D. Department of Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College There are no conflicts of interest. 1 Goals and Objectives! Goals Provide introduction
RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY Peter McCue, M.D. Department of Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College There are no conflicts of interest. 1 Goals and Objectives! Goals Provide introduction
PHGY210 Renal Physiology
 PHGY210 Renal Physiology Tomoko Takano, MD, PhD *Associate Professor of Medicine and Physiology McGill University *Nephrologist, McGill University Health Centre Lecture plan Lecture 1: Anatomy, basics
PHGY210 Renal Physiology Tomoko Takano, MD, PhD *Associate Professor of Medicine and Physiology McGill University *Nephrologist, McGill University Health Centre Lecture plan Lecture 1: Anatomy, basics
Urinary system. Urinary system
 INTRODUCTION. Several organs system Produce urine and excrete it from the body Maintenance of homeostasis. Components. two kidneys, produce urine; two ureters, carry urine to single urinary bladder for
INTRODUCTION. Several organs system Produce urine and excrete it from the body Maintenance of homeostasis. Components. two kidneys, produce urine; two ureters, carry urine to single urinary bladder for
Histology Urinary system
 Histology Urinary system Urinary system Composed of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra, the urinary system plays a critical role in: 1- Blood filtration,(filtration of cellular
Histology Urinary system Urinary system Composed of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra, the urinary system plays a critical role in: 1- Blood filtration,(filtration of cellular
Lab Activity 31. Anatomy of the Urinary System. Portland Community College BI 233
 Lab Activity 31 Anatomy of the Urinary System Portland Community College BI 233 Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder: provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters: transport
Lab Activity 31 Anatomy of the Urinary System Portland Community College BI 233 Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder: provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters: transport
Chapter 23. The Nephron. (functional unit of the kidney
 Chapter 23 The Nephron (functional unit of the kidney Renal capsule The Nephron Renal cortex Nephron Collecting duct Efferent arteriole Afferent arteriole (a) Renal corpuscle: Glomerular capsule Glomerulus
Chapter 23 The Nephron (functional unit of the kidney Renal capsule The Nephron Renal cortex Nephron Collecting duct Efferent arteriole Afferent arteriole (a) Renal corpuscle: Glomerular capsule Glomerulus
Kidney Functions Removal of toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions from the blood Regulation of blood volume, chemical composition, and ph
 The Urinary System Urinary System Organs Kidneys are major excretory organs Urinary bladder is the temporary storage reservoir for urine Ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder Urethra
The Urinary System Urinary System Organs Kidneys are major excretory organs Urinary bladder is the temporary storage reservoir for urine Ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder Urethra
Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine
 Urinary System Organs Kidney Filters blood, allowing toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions to leave the body in urine Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters
Urinary System Organs Kidney Filters blood, allowing toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions to leave the body in urine Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters
Frontal section of human kidney. (Scheme).
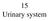 15 Urinary system 15-001 Kidney Cortex Medulla Papilla renalis Medial Lateral Medullary ray Labyrinth Columna renalis Pelvis renalis Calix renalis Ureter Capsula fibrosa Lobus renalis Columna renalis 15-01.
15 Urinary system 15-001 Kidney Cortex Medulla Papilla renalis Medial Lateral Medullary ray Labyrinth Columna renalis Pelvis renalis Calix renalis Ureter Capsula fibrosa Lobus renalis Columna renalis 15-01.
URINARY SYSTEM. These organs lie posterior or inferior to the. (membrane).
 URINARY SYSTEM I. INTRODUCTION Each kidney is made up of about a million tiny tubules called nephrons. Each nephron individually filters the blood and makes urine and it does the job completely, from start
URINARY SYSTEM I. INTRODUCTION Each kidney is made up of about a million tiny tubules called nephrons. Each nephron individually filters the blood and makes urine and it does the job completely, from start
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY DR.CHARUSHILA RUKADIKAR ASSISTANT PROFESSOR PHYSIOLOGY
 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY DR.CHARUSHILA RUKADIKAR ASSISTANT PROFESSOR PHYSIOLOGY GROSS ANATOMY Location *Bean-shaped *Retroperitoneal *At level of T12 L1 vertebrae. *The right kidney lies slightly inferior to left
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY DR.CHARUSHILA RUKADIKAR ASSISTANT PROFESSOR PHYSIOLOGY GROSS ANATOMY Location *Bean-shaped *Retroperitoneal *At level of T12 L1 vertebrae. *The right kidney lies slightly inferior to left
Human Urogenital System 26-1
 Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
CHAPTER 25 URINARY. Urinary system. Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1. functions
 CHAPTER 25 URINARY Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1 fluid waste elimination secretion of wastes control blood volume and BP control blood ph electrolyte levels RBC levels hormone production
CHAPTER 25 URINARY Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1 fluid waste elimination secretion of wastes control blood volume and BP control blood ph electrolyte levels RBC levels hormone production
Histology / First stage The Urinary System: Introduction. Kidneys
 The Urinary System: Introduction The urinary system consists of the paired kidneys and ureters, the bladder, and the urethra. This system helps maintain homeostasis by a complex combination of processes
The Urinary System: Introduction The urinary system consists of the paired kidneys and ureters, the bladder, and the urethra. This system helps maintain homeostasis by a complex combination of processes
THE RENAL / URINARY SYSTEM
 1 THE RENAL / URINARY SYSTEM Definition/Description: The Renal/Urinary system is the body system, which plays a vital role in the maintenance of homeostasis by the following processes: 1. Production of
1 THE RENAL / URINARY SYSTEM Definition/Description: The Renal/Urinary system is the body system, which plays a vital role in the maintenance of homeostasis by the following processes: 1. Production of
Kidney Structure. Renal Lobe = renal pyramid & overlying cortex. Renal Lobule = medullary ray & surrounding cortical labryinth.
 Kidney Structure Capsule Hilum ureter renal pelvis major and minor calyxes renal and vein segmental arteries interlobar arteries arcuate arteries interlobular arteries Medulla renal pyramids cortical/renal
Kidney Structure Capsule Hilum ureter renal pelvis major and minor calyxes renal and vein segmental arteries interlobar arteries arcuate arteries interlobular arteries Medulla renal pyramids cortical/renal
Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology
 Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Nephron Function and Urine Formation. Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S
 Nephron Function and Urine Formation Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S The Role of the Nephron In order for the body to properly function and maintain homeostasis, the amount of dissolved substances
Nephron Function and Urine Formation Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S The Role of the Nephron In order for the body to properly function and maintain homeostasis, the amount of dissolved substances
H I S T O L O G Y O F T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M
 SCPA 602- Anatomical Basis For Pathological Study H I S T O L O G Y O F T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M S O M P H O N G N A R K P I N I T, M. D. D E P A R T M E N T O F P A T H O B I O L O G Y F A C U
SCPA 602- Anatomical Basis For Pathological Study H I S T O L O G Y O F T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M S O M P H O N G N A R K P I N I T, M. D. D E P A R T M E N T O F P A T H O B I O L O G Y F A C U
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra
 Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Kidney Function Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Endocrine functions regulates
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Kidney Function Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Endocrine functions regulates
Lectin-histochemical and -cytochemical study of periodic acid Schiff-Positive lysosome granules as a histological feature of the female mouse kidney
 Histol Histopathol (2002) 17: 1017-1024 http://www.hh.um.es Histology and Histopathology Cellular and Molecular Biology Lectin-histochemical and -cytochemical study of periodic acid Schiff-Positive lysosome
Histol Histopathol (2002) 17: 1017-1024 http://www.hh.um.es Histology and Histopathology Cellular and Molecular Biology Lectin-histochemical and -cytochemical study of periodic acid Schiff-Positive lysosome
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra
 Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Kidney Function Endocrine functions regulates
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Kidney Function Endocrine functions regulates
19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY ROLE OF THE URINARY SYSTEM THE URINARY SYSTEM. Components and function. V BS 122 Physiology II 151 Class of 2011
 19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY THE URINARY SYSTEM Components and function The urinary system is composed of two kidneys, the functionally filtering apparatus, which connect through two tubular structures called
19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY THE URINARY SYSTEM Components and function The urinary system is composed of two kidneys, the functionally filtering apparatus, which connect through two tubular structures called
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015
 RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
Urinary System and Fluid Balance. Urine Production
 Urinary System and Fluid Balance Name Pd Date Urine Production The three processes critical to the formation of urine are filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Match these terms with the correct statement
Urinary System and Fluid Balance Name Pd Date Urine Production The three processes critical to the formation of urine are filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Match these terms with the correct statement
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues
 BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
Histology Urinary system
 Histology Urinary system By the end of the topic the learner should be able to: Describe the histological structure of the kidney. Illustrate the ultrastructure of the blood renal barrier. Illustrate the
Histology Urinary system By the end of the topic the learner should be able to: Describe the histological structure of the kidney. Illustrate the ultrastructure of the blood renal barrier. Illustrate the
AP2, Lab 7 - THE URINARY SYSTEM
 AP2, Lab 7 - THE URINARY SYSTEM I. SYSTEM COMPONENTS (Figs. 25.1 25.4) KIDNEYS Each kidney contains approx. 1,000,000 tubular NEPHRONS which produce FILTRATE from the plasma and then add to or take from
AP2, Lab 7 - THE URINARY SYSTEM I. SYSTEM COMPONENTS (Figs. 25.1 25.4) KIDNEYS Each kidney contains approx. 1,000,000 tubular NEPHRONS which produce FILTRATE from the plasma and then add to or take from
A lectin histochemical study of the thoracic respiratory air sacs of the fowl
 Onderstepoort Journal of Veterinary Research, 72:175 180 (2005) A lectin histochemical study of the thoracic respiratory air sacs of the fowl A.J. BEZUIDENHOUT Department of Biomedical Sciences, College
Onderstepoort Journal of Veterinary Research, 72:175 180 (2005) A lectin histochemical study of the thoracic respiratory air sacs of the fowl A.J. BEZUIDENHOUT Department of Biomedical Sciences, College
Lectin Cytochemistry of the Rabbit Conjunctiva and Lacrimal Sac
 LABORATORY INVESTIGATIONS Lectin Cytochemistry of the Rabbit Conjunctiva and Lacrimal Sac Seiji Maeda, Makoto Ishikawa, Tohru Abe and Shozo Sakuragi Department of Ophthalmology, Akita University School
LABORATORY INVESTIGATIONS Lectin Cytochemistry of the Rabbit Conjunctiva and Lacrimal Sac Seiji Maeda, Makoto Ishikawa, Tohru Abe and Shozo Sakuragi Department of Ophthalmology, Akita University School
Histopathology: Hypertension and diabetes in the kidney These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features.
 Histopathology: Hypertension and diabetes in the kidney These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need
Histopathology: Hypertension and diabetes in the kidney These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need
Histology and Histochemical Distribution of Goblet Cells in the Descending Colonic Epithelium of the Swamp Buffalo (Bubalus bubalis)
 Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 43 : 63-68 (2009) Histology and Histochemical Distribution of Goblet Cells in the Descending Colonic Epithelium of the Swamp Buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) Pakawadee Pongket 1 *, Maleewan
Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 43 : 63-68 (2009) Histology and Histochemical Distribution of Goblet Cells in the Descending Colonic Epithelium of the Swamp Buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) Pakawadee Pongket 1 *, Maleewan
Carbohydrates and mucins. Dr Phil Bryant, Wales, UK
 Carbohydrates and mucins Dr Phil Bryant, Wales, UK Carbohydrates Provide cells with energy by converting to glucose Excess glucose stored in liver and muscle as glycogen Residual unstored glycogen is turned
Carbohydrates and mucins Dr Phil Bryant, Wales, UK Carbohydrates Provide cells with energy by converting to glucose Excess glucose stored in liver and muscle as glycogen Residual unstored glycogen is turned
Figure 26.1 An Introduction to the Urinary System
 Chapter 26 Figure 26.1 An Introduction to the Urinary System Components of the Urinary System Kidney Produces urine Ureter Transports urine toward the urinary bladder Urinary Bladder Temporarily stores
Chapter 26 Figure 26.1 An Introduction to the Urinary System Components of the Urinary System Kidney Produces urine Ureter Transports urine toward the urinary bladder Urinary Bladder Temporarily stores
Basic Urinary Tract Anatomy and Histology
 Basic Urinary Tract Anatomy and Histology The two kidneys are located in the retroperitoneum on either side of the vertebral bladder and the contraction of the detrusor muscle. Any mechanical barrier,
Basic Urinary Tract Anatomy and Histology The two kidneys are located in the retroperitoneum on either side of the vertebral bladder and the contraction of the detrusor muscle. Any mechanical barrier,
The functions of the kidney:
 The functions of the kidney: After reading this lecture you should be able to.. 1. List the main functions of the kidney. 2. Know the basic physiological anatomy of the kidney and the nephron 3. Describe
The functions of the kidney: After reading this lecture you should be able to.. 1. List the main functions of the kidney. 2. Know the basic physiological anatomy of the kidney and the nephron 3. Describe
Surgical Pathology Report
 Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center Department of Pathology Shreveport, Louisiana Accession #: Collected: Received: Reported: 6/1/2012 09:18 6/2/2012 09:02 6/2/2012 Patient Name: Med. Rec.
Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center Department of Pathology Shreveport, Louisiana Accession #: Collected: Received: Reported: 6/1/2012 09:18 6/2/2012 09:02 6/2/2012 Patient Name: Med. Rec.
sfigure 1: Detection of L-fucose in normal mouse renal cortex using the plant lectin LTL
 sfigure 1: Detection of L-fucose in normal mouse renal cortex using the plant lectin LTL LTL staining Negative control Fluorescence microscopy of normal (CL-11 +/+ ) mouse renal tissue after staining with
sfigure 1: Detection of L-fucose in normal mouse renal cortex using the plant lectin LTL LTL staining Negative control Fluorescence microscopy of normal (CL-11 +/+ ) mouse renal tissue after staining with
Six different peroxidase conjugated lectins were purchased. 10% buffered formalin, embedded in paraffin, and
 J Clin Pathol 1986;39:736-741 Study of childhood renal tumours using peroxidase conjugated lectins S KUMAR, T CARR, HB MARSDEN, PH MORRIS-JONES From the Christie Hospital and Holt Radium Institute, Manchester
J Clin Pathol 1986;39:736-741 Study of childhood renal tumours using peroxidase conjugated lectins S KUMAR, T CARR, HB MARSDEN, PH MORRIS-JONES From the Christie Hospital and Holt Radium Institute, Manchester
Questions? Homework due in lab 6. PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!)
 Questions? Homework due in lab 6 PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!) Part 3 Variations in Urine Formation Composition varies Fluid volume Solute concentration Variations in Urine Formation
Questions? Homework due in lab 6 PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!) Part 3 Variations in Urine Formation Composition varies Fluid volume Solute concentration Variations in Urine Formation
Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia. 1987, 32
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) The Effect of Glomerulonephritis on -A Special Reference to the Glomeru Aortic Intima- Ohi, Junji Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia. 1987, 32 Issue Date
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) The Effect of Glomerulonephritis on -A Special Reference to the Glomeru Aortic Intima- Ohi, Junji Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia. 1987, 32 Issue Date
Interesting case seminar: Native kidneys Case Report:
 Interesting case seminar: Native kidneys Case Report: Proximal tubulopathy and light chain deposition disease presented as severe pulmonary hypertension with right-sided cardiac dysfunction and nephrotic
Interesting case seminar: Native kidneys Case Report: Proximal tubulopathy and light chain deposition disease presented as severe pulmonary hypertension with right-sided cardiac dysfunction and nephrotic
You will find the kidney animation linked on my blog: mskjcrowley.wordpress.com
 Name: SBI4U Nephron Quest To do this task you will need; this worksheet, something to write on, something to write with and the kidney flash movie. You will find the kidney animation linked on my blog:
Name: SBI4U Nephron Quest To do this task you will need; this worksheet, something to write on, something to write with and the kidney flash movie. You will find the kidney animation linked on my blog:
Lectin-peroxidase conjugates in histopathology of gastrointestinal mucosa
 Lectin-peroxidase conjugates in histopathology of gastrointestinal mucosa W. D. KUHLMANN, P. PESCHKE, K. WURSTER Laboratory of Experimental Medicine and Immunocytochemistry, Institut für Nuklearmedizin,
Lectin-peroxidase conjugates in histopathology of gastrointestinal mucosa W. D. KUHLMANN, P. PESCHKE, K. WURSTER Laboratory of Experimental Medicine and Immunocytochemistry, Institut für Nuklearmedizin,
Light and electron microscopical studies of focal glomerular sclerosis
 J. clin. Path., 1971, 24, 846-850 Light and electron microscopical studies of focal glomerular sclerosis A. H. NAGI, F. ALEXANDER, AND R. LANNIGAN From the Department of Pathology, Queen's University of
J. clin. Path., 1971, 24, 846-850 Light and electron microscopical studies of focal glomerular sclerosis A. H. NAGI, F. ALEXANDER, AND R. LANNIGAN From the Department of Pathology, Queen's University of
INVESTIGATION OF THE ULTRAFINE STRUCTURE OF THE KIDNEY BY MEANS OF SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPE
 THE KURUME MEDICAL JOURNAL 1975 Vol.22, No.3, P.135-141 INVESTIGATION OF THE ULTRAFINE STRUCTURE OF THE KIDNEY BY MEANS OF SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPE I. THE GLOMERULUS SHINSHI NODA Department of Urology,
THE KURUME MEDICAL JOURNAL 1975 Vol.22, No.3, P.135-141 INVESTIGATION OF THE ULTRAFINE STRUCTURE OF THE KIDNEY BY MEANS OF SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPE I. THE GLOMERULUS SHINSHI NODA Department of Urology,
Differentiation of Renal Tubular Epithelium in Renal Transplantation Cytology
 Differentiation of Renal Tubular Epithelium in Renal Transplantation Cytology G. BERRY SCHUMANN, M.D., LAWRENCE J. PALMIERI, B.S., C.T.(ASCP), AND DAVID B. JONES, M.D. Schumann, G. Berry, Palmieri, Lawrence
Differentiation of Renal Tubular Epithelium in Renal Transplantation Cytology G. BERRY SCHUMANN, M.D., LAWRENCE J. PALMIERI, B.S., C.T.(ASCP), AND DAVID B. JONES, M.D. Schumann, G. Berry, Palmieri, Lawrence
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY WESTMEAD PRIMARY EXAM
 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY WESTMEAD PRIMARY EXAM RENAL PHYSIOLOGY - ANATOMY Glomerulus + renal tubule Each kidney has 1.3 million nephrons Cortical nephrons (85%) have shorter Loop of Henle than Juxtamedullary nephrons
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY WESTMEAD PRIMARY EXAM RENAL PHYSIOLOGY - ANATOMY Glomerulus + renal tubule Each kidney has 1.3 million nephrons Cortical nephrons (85%) have shorter Loop of Henle than Juxtamedullary nephrons
Lectin-binding sites in the epithelium of normal human appendix vermiformis and in acute appendicitis
 Histol Histopathol (1 995) 10: 61-70 Histology and Histopathology Lectin-binding sites in the epithelium of normal human appendix vermiformis and in acute appendicitis U. Brinckl, R. Bosbachl, M. Korabiowskal,
Histol Histopathol (1 995) 10: 61-70 Histology and Histopathology Lectin-binding sites in the epithelium of normal human appendix vermiformis and in acute appendicitis U. Brinckl, R. Bosbachl, M. Korabiowskal,
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.44 - OSMOREGULATION AND EXCRETION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com Osmoregulation regulation of solute balance and water loss to maintain homeostasis of water content Excretion process of eliminating waste from the body, like nitrogenous waste Kidney
!! www.clutchprep.com Osmoregulation regulation of solute balance and water loss to maintain homeostasis of water content Excretion process of eliminating waste from the body, like nitrogenous waste Kidney
Renal Pathology 1: Glomerulus. With many thanks to Elizabeth Angus PhD for EM photographs
 Renal Pathology 1: Glomerulus With many thanks to Elizabeth Angus PhD for EM photographs Anatomy of the Kidney http://www.yalemedicalgroup.org/stw/page.asp?pageid=stw028980 The Nephron http://www.beltina.org/health-dictionary/nephron-function-kidney-definition.html
Renal Pathology 1: Glomerulus With many thanks to Elizabeth Angus PhD for EM photographs Anatomy of the Kidney http://www.yalemedicalgroup.org/stw/page.asp?pageid=stw028980 The Nephron http://www.beltina.org/health-dictionary/nephron-function-kidney-definition.html
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 23: The Urinary System, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 23: The Urinary System, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 23: The Urinary System, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system
Osmoregulation and the Excretory System
 Honors Biology Study Guide Chapter 25.4 25.10 Name Osmoregulation and the Excretory System FUNCTIONS OF THE EXCRETORY SYSTEM OSMOREGULATION Freshwater: Marine: Land Animals: Sources of Nitrogenous Wastes?
Honors Biology Study Guide Chapter 25.4 25.10 Name Osmoregulation and the Excretory System FUNCTIONS OF THE EXCRETORY SYSTEM OSMOREGULATION Freshwater: Marine: Land Animals: Sources of Nitrogenous Wastes?
A. Incorrect! The urinary system is involved in the regulation of blood ph. B. Correct! The urinary system is involved in the synthesis of vitamin D.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 22: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system is not correct? Question #01 (A) The urinary system
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 22: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system is not correct? Question #01 (A) The urinary system
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY, HOMEOSTASIS OF FLUID COMPARTMENTS (1)
 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY, HOMEOSTASIS OF FLUID COMPARTMENTS (1) Dr. Attila Nagy 2017 Functional roles of the kidney 1.Homeostasis of fluid compartments (isosmia, isovolemia, isoionia, isohydria,) 2. Elimination
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY, HOMEOSTASIS OF FLUID COMPARTMENTS (1) Dr. Attila Nagy 2017 Functional roles of the kidney 1.Homeostasis of fluid compartments (isosmia, isovolemia, isoionia, isohydria,) 2. Elimination
PLATES 24 TO 26. (Received for publication, December 4, 1935)
 Published Online: 1 March, 1936 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.63.3.303 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on January 19, 2019 THE VISCERAL LESIONS PRODUCED IN MICE BY THE SALIVARY GLAND VIRUS OF MICE*
Published Online: 1 March, 1936 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.63.3.303 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on January 19, 2019 THE VISCERAL LESIONS PRODUCED IN MICE BY THE SALIVARY GLAND VIRUS OF MICE*
Urinary Anatomy. Lab 40. Kidneys. Nephrons. Renal Corpuscle
 Urinary Anatomy Lab 40. Urinary Anatomy and Kidney Dissection Kidneys: filters blood, produces urine Ureters: convey urine to bladder Bladder: holding tank Urethra: carries urine to the outside for elimination
Urinary Anatomy Lab 40. Urinary Anatomy and Kidney Dissection Kidneys: filters blood, produces urine Ureters: convey urine to bladder Bladder: holding tank Urethra: carries urine to the outside for elimination
Urinary System BIO 250. Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat. Routes of Waste Elimination
 Urinary System BIO 250 Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat Routes of Waste Elimination Skin: Variable amounts of heat, salts, and water; small amounts of urea and
Urinary System BIO 250 Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat Routes of Waste Elimination Skin: Variable amounts of heat, salts, and water; small amounts of urea and
Excretory Lecture Test Questions Set 1
 Excretory Lecture Test Questions Set 1 1. The separation and ejection of metabolic wastes, usually in aqueous solution, is: a. reabsorption b. secretion c. filtration d. excretion e. endocrinology 2. Besides
Excretory Lecture Test Questions Set 1 1. The separation and ejection of metabolic wastes, usually in aqueous solution, is: a. reabsorption b. secretion c. filtration d. excretion e. endocrinology 2. Besides
Human Physiology - Problem Drill 17: The Kidneys and Nephronal Physiology
 Human Physiology - Problem Drill 17: The Kidneys and Nephronal Physiology Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
Human Physiology - Problem Drill 17: The Kidneys and Nephronal Physiology Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 6, No 4, 2017,
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 6, No 4, 2017, 2706 2711 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) COMPARATIVE MICROANATOMICAL FEATURES OF THE RENAL CORTEX IN EMU (Dromaius novaehollandiae)
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 6, No 4, 2017, 2706 2711 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) COMPARATIVE MICROANATOMICAL FEATURES OF THE RENAL CORTEX IN EMU (Dromaius novaehollandiae)
Ageing of the human oviduct: lectin histochemistry
 Histol Histopathol (2001) 16: 21-28 001: 10.14670/HH-16.21 http://www.ehu.es/histol-histopathol Histology and Histopathology Cellular and Molecular Biology Ageing of the human oviduct: lectin histochemistry
Histol Histopathol (2001) 16: 21-28 001: 10.14670/HH-16.21 http://www.ehu.es/histol-histopathol Histology and Histopathology Cellular and Molecular Biology Ageing of the human oviduct: lectin histochemistry
R. B. MARSHALL Department of Veterinary Pathology and Public Health, Massey University, Palmerston North, New Zealand
 THE ROUTE OF ENTRY OF LEPTOSPIRES INTO THE KIDNEY TUBULE R. B. MARSHALL Department of Veterinary Pathology and Public Health, Massey University, Palmerston North, New Zealand PLATES X and XI IT has been
THE ROUTE OF ENTRY OF LEPTOSPIRES INTO THE KIDNEY TUBULE R. B. MARSHALL Department of Veterinary Pathology and Public Health, Massey University, Palmerston North, New Zealand PLATES X and XI IT has been
Use of lectin histochemistry in pancreatic cancer
 J Clin Pathol 1988;41:324-328 Use of lectin histochemistry in pancreatic cancer C K CHING, R BLACK, T HELLIWELL, A SAVAGE, H BARR, J M RHODES From the Departments of Medicine and Histopathology, The University
J Clin Pathol 1988;41:324-328 Use of lectin histochemistry in pancreatic cancer C K CHING, R BLACK, T HELLIWELL, A SAVAGE, H BARR, J M RHODES From the Departments of Medicine and Histopathology, The University
Running head: NEPHRON 1. The nephron the functional unit of the kidney. [Student Name] [Name of Institute] Author Note
![Running head: NEPHRON 1. The nephron the functional unit of the kidney. [Student Name] [Name of Institute] Author Note Running head: NEPHRON 1. The nephron the functional unit of the kidney. [Student Name] [Name of Institute] Author Note](/thumbs/77/75431210.jpg) Running head: NEPHRON 1 The nephron the functional unit of the kidney [Student Name] [Name of Institute] Author Note NEPHRON 2 The nephron the functional unit of the kidney The kidney is an important excretory
Running head: NEPHRON 1 The nephron the functional unit of the kidney [Student Name] [Name of Institute] Author Note NEPHRON 2 The nephron the functional unit of the kidney The kidney is an important excretory
General Anatomy of Urinary System
 General Anatomy of Urinary System URINARY SYSTEM ORGANS Kidneys (2) Ureters (2) Urinary bladder Urethra KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Control blood volume and composition KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Filter blood plasma, eliminate
General Anatomy of Urinary System URINARY SYSTEM ORGANS Kidneys (2) Ureters (2) Urinary bladder Urethra KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Control blood volume and composition KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Filter blood plasma, eliminate
Unit #4 Waste and Excretion. The Kidneys
 Unit #4 Waste and Excretion The Kidneys Renal Hilus (Hilus) the doorway of the kidney Ureter leaves this region blood and lymphatic vessels enter and exit here Renal Capsule (Capsule) smooth fibrous tissue
Unit #4 Waste and Excretion The Kidneys Renal Hilus (Hilus) the doorway of the kidney Ureter leaves this region blood and lymphatic vessels enter and exit here Renal Capsule (Capsule) smooth fibrous tissue
Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings. Dr. Nabil Khouri
 Dr. Nabil Khouri Objectives: General objectives: - to identify the kidney s structures, function and location - to analyze the relationship between microscopic structure and function Specific objectives:
Dr. Nabil Khouri Objectives: General objectives: - to identify the kidney s structures, function and location - to analyze the relationship between microscopic structure and function Specific objectives:
CHAPTER 2. Primary Glomerulonephritis
 2nd Report of the PRIMARY GLOMERULONEPHRITIS CHAPTER 2 Primary Glomerulonephritis Sunita Bavanandan Lee Han Wei Lim Soo Kun 21 PRIMARY GLOMERULONEPHRITIS 2nd Report of the 2.1 Introduction This chapter
2nd Report of the PRIMARY GLOMERULONEPHRITIS CHAPTER 2 Primary Glomerulonephritis Sunita Bavanandan Lee Han Wei Lim Soo Kun 21 PRIMARY GLOMERULONEPHRITIS 2nd Report of the 2.1 Introduction This chapter
Immunofluorescent localization of Tamm-Horsfall mucoprotein in human kidney
 J. clin. Path. (1969), 22,334-339 Immunofluorescent localization of Tamm-Horsfall mucoprotein in human kidney J. K. McKENZIE1 AND E. G. McQUEEN From the Wellcome Medical Research Institute, Department
J. clin. Path. (1969), 22,334-339 Immunofluorescent localization of Tamm-Horsfall mucoprotein in human kidney J. K. McKENZIE1 AND E. G. McQUEEN From the Wellcome Medical Research Institute, Department
Chapter 26: Urinary System By: Eddie Tribiana and Piers Frieden
 Chapter 26: Urinary System By: Eddie Tribiana and Piers Frieden The urinary system is important because it performs vital excretory functions Takes blood from renal arteries into the kidney to filtrate
Chapter 26: Urinary System By: Eddie Tribiana and Piers Frieden The urinary system is important because it performs vital excretory functions Takes blood from renal arteries into the kidney to filtrate
The principal functions of the kidneys
 Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
Urinary System VASTACCESS, INC.
 Urinary System www.vastaccess.com 2 Urinary Tract Kidney Ureter Urinary Bladder Urethra Prostate (male) Membranous (male) Spongy (male) 3 Kidney Relations Suprarenal (Adrenal) Glands Liver Duodenum Transverse
Urinary System www.vastaccess.com 2 Urinary Tract Kidney Ureter Urinary Bladder Urethra Prostate (male) Membranous (male) Spongy (male) 3 Kidney Relations Suprarenal (Adrenal) Glands Liver Duodenum Transverse
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2
 BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 16 Urinary System 1 The Kidneys Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Functions of Urinary system o The Kidneys:
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 16 Urinary System 1 The Kidneys Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Functions of Urinary system o The Kidneys:
16 Effect of cell surface N-linked oligosaccharide chains on the compaction of preimplantation mouse embryos
 16 Effect of cell surface N-linked oligosaccharide chains on the compaction of preimplantation mouse embryos H.Hayashi, N.Minami, M.Yamada and K.Utsumi Department of Animal science, College of Agriculture,
16 Effect of cell surface N-linked oligosaccharide chains on the compaction of preimplantation mouse embryos H.Hayashi, N.Minami, M.Yamada and K.Utsumi Department of Animal science, College of Agriculture,
Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion.
 The Kidney Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion. The kidney has 6 roles in the maintenance of homeostasis. 6 Main Functions 1. Ion Balance
The Kidney Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion. The kidney has 6 roles in the maintenance of homeostasis. 6 Main Functions 1. Ion Balance
Basic Functions of the Kidneys
 Dr. Adelina Vlad Basic Functions of the Kidneys Eliminate plasma METABOLIC WASTE PRODUCTS and FOREIGN COMPOUNDS The kidney are the primary means for eliminating metabolic waste products (urea, creatinine,
Dr. Adelina Vlad Basic Functions of the Kidneys Eliminate plasma METABOLIC WASTE PRODUCTS and FOREIGN COMPOUNDS The kidney are the primary means for eliminating metabolic waste products (urea, creatinine,
Anatomy/Physiology Study Guide: Unit 9 Excretory System
 Anatomy/Physiology Study Guide: Unit 9 Excretory System 1) In the space below, list the primary structures (organs) and their corresponding functions. Structures: Functions: KIDNEY 1) URETER BLADDER URETHRA
Anatomy/Physiology Study Guide: Unit 9 Excretory System 1) In the space below, list the primary structures (organs) and their corresponding functions. Structures: Functions: KIDNEY 1) URETER BLADDER URETHRA
Distribution of fibronectin in normal and diseased
 J Clin Pathol 1980;33:1021-1028 Distribution of fibronectin in normal and diseased human kidneys AJ DIXON, J BURNS, MS DUNNILL, AND JO'D McGEE From the Department ofpathology, University of Oxford, John
J Clin Pathol 1980;33:1021-1028 Distribution of fibronectin in normal and diseased human kidneys AJ DIXON, J BURNS, MS DUNNILL, AND JO'D McGEE From the Department ofpathology, University of Oxford, John
H. M. Carleton, Lecturer in Histology, University of Oxford. (From the Department of Physiology.) INTRODUCTORY.
 Note on the Comparative Effects on Tissues of Isotonic Saline and Distilled Water when used as Solvents for Mercuric Chloride and Formol in Histological Fixation. By H. M. Carleton, Lecturer in Histology,
Note on the Comparative Effects on Tissues of Isotonic Saline and Distilled Water when used as Solvents for Mercuric Chloride and Formol in Histological Fixation. By H. M. Carleton, Lecturer in Histology,
2) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure.
 Class: A&P2-1 Description: Test: Excretory Test Points: 144 Test Number: 28379 Printed: 31-March-10 12:03 1) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure. Click on the Bowman's
Class: A&P2-1 Description: Test: Excretory Test Points: 144 Test Number: 28379 Printed: 31-March-10 12:03 1) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure. Click on the Bowman's
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY, HOMEOSTASIS OF FLUID COMPARTMENTS (1)
 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY, HOMEOSTASIS OF FLUID COMPARTMENTS (1) Dr. Attila Nagy 2017 Functional role of the kidney 1.Homeostasis of fluid compartments (isosmia, isovolemia, isoionia, isohydria,) 2. Elimination
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY, HOMEOSTASIS OF FLUID COMPARTMENTS (1) Dr. Attila Nagy 2017 Functional role of the kidney 1.Homeostasis of fluid compartments (isosmia, isovolemia, isoionia, isohydria,) 2. Elimination
Renal System Physiology
 M58_MARI0000_00_SE_EX09.qxd 7/18/11 2:37 PM Page 399 E X E R C I S E 9 Renal System Physiology Advance Preparation/Comments 1. Prior to the lab, suggest to the students that they become familiar with the
M58_MARI0000_00_SE_EX09.qxd 7/18/11 2:37 PM Page 399 E X E R C I S E 9 Renal System Physiology Advance Preparation/Comments 1. Prior to the lab, suggest to the students that they become familiar with the
Osmoregulation regulates solute concentrations and balances the gain and loss of water
 Ch 44 Osmoregulation & Excretion Osmoregulation regulates solute concentrations and balances the gain and loss of water Freshwater animals show adaptations that reduce water uptake and conserve solutes
Ch 44 Osmoregulation & Excretion Osmoregulation regulates solute concentrations and balances the gain and loss of water Freshwater animals show adaptations that reduce water uptake and conserve solutes
URINARY SYSTEM CHAPTER 28 I ANATOMY OF THE URINARY SYSTEM. Student Name
 Student Name CHAPTER 28 URINARY SYSTEM L iving produces wastes. Wherever people live or work or play, wastes accumulate. To keep these areas healthy, there must be a method of disposing of these wastes
Student Name CHAPTER 28 URINARY SYSTEM L iving produces wastes. Wherever people live or work or play, wastes accumulate. To keep these areas healthy, there must be a method of disposing of these wastes
Renal System and Excretion
 Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
Na + Transport 1 and 2 Linda Costanzo, Ph.D.
 Na + Transport 1 and 2 Linda Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. The terminology applied to single nephron function, including the meaning of TF/P
Na + Transport 1 and 2 Linda Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. The terminology applied to single nephron function, including the meaning of TF/P
Question 1: Solution 1: Question 2: Question 3: Question 4: Class X The Excretory System Biology
 A. MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE: (select the most appropriate option in each case) Book Name: Selina Concise Question 1: Excretion primarily involves (a) removal of all byproducts during catabolism (b) removal
A. MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE: (select the most appropriate option in each case) Book Name: Selina Concise Question 1: Excretion primarily involves (a) removal of all byproducts during catabolism (b) removal
Urinary System. BSC 2086 A & P 2 Professor Tcherina Duncombe Palm Beach State College
 Urinary System BSC 2086 A & P 2 Professor Tcherina Duncombe Palm Beach State College Filter plasma, separate and eliminate wastes Functions Regulate blood volume and pressure Regulate osmolarity of body
Urinary System BSC 2086 A & P 2 Professor Tcherina Duncombe Palm Beach State College Filter plasma, separate and eliminate wastes Functions Regulate blood volume and pressure Regulate osmolarity of body
S.N.KANSAGRA SCHOOL BIOLOGY DEPARTMENT. 1. Fibrous connective tissue covering the kidneys.
 Name Q1. Name the following: S.N.KANSAGRA SCHOOL Date 1. Fibrous connective tissue covering the kidneys. 2. The deep notch present on the inner surface of the kidney. 3. The peripheral dark reddish brown
Name Q1. Name the following: S.N.KANSAGRA SCHOOL Date 1. Fibrous connective tissue covering the kidneys. 2. The deep notch present on the inner surface of the kidney. 3. The peripheral dark reddish brown
The excretory system
 Key Words The excretory system haemoglobin Convoluted tubule Loop of Henle nephron ureter/-s sweat glands Bowman s capsule Glomerulus cholesterol Bladder Excretion is the removal of the waste products
Key Words The excretory system haemoglobin Convoluted tubule Loop of Henle nephron ureter/-s sweat glands Bowman s capsule Glomerulus cholesterol Bladder Excretion is the removal of the waste products
organs of the urinary system
 organs of the urinary system Kidneys (2) bean-shaped, fist-sized organ where urine is formed. Lie on either sides of the vertebral column, in a depression beneath peritoneum and protected by lower ribs
organs of the urinary system Kidneys (2) bean-shaped, fist-sized organ where urine is formed. Lie on either sides of the vertebral column, in a depression beneath peritoneum and protected by lower ribs
HISTOLOGY OF THE URINARY SYSTEM
 HISTOLOGY OF THE URINARY SYSTEM The Urinary System Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder & urethra Urine flows from each kidney, down its ureter to the bladder and to the outside via the urethra Filter the
HISTOLOGY OF THE URINARY SYSTEM The Urinary System Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder & urethra Urine flows from each kidney, down its ureter to the bladder and to the outside via the urethra Filter the
The Urinary S. (Chp. 10) & Excretion. What are the functions of the urinary system? Maintenance of water-salt and acidbase
 10.1 Urinary system The Urinary S. (Chp. 10) & Excretion 10.1 Urinary system What are the functions of the urinary system? 1. Excretion of metabolic wastes (urea, uric acid & creatinine) 1. Maintenance
10.1 Urinary system The Urinary S. (Chp. 10) & Excretion 10.1 Urinary system What are the functions of the urinary system? 1. Excretion of metabolic wastes (urea, uric acid & creatinine) 1. Maintenance
WJEC. BY4 Kidney Questions
 NAME: OPTION GROUP WJEC BY4 Kidney Questions Question Book 2 (Legacy Qs from Jan 2000 to June 2014) Question Number(s) Due Date & Pass Mark Homework Mark Resist Question number(s) Resist Due Date & Pass
NAME: OPTION GROUP WJEC BY4 Kidney Questions Question Book 2 (Legacy Qs from Jan 2000 to June 2014) Question Number(s) Due Date & Pass Mark Homework Mark Resist Question number(s) Resist Due Date & Pass
