Diabetic retinopathy and visual impairment in disaster prone coastal population of Bangladesh
|
|
|
- Melinda Davidson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Diabetic retinopathy and visual impairment in disaster prone coastal population of Bangladesh M. Abu Sayeed 1, AH Syedur Rahman 2, Md. Hazrat Ali 2, Mir Masudur Rhaman 1, J Ashraful Haq 1 and Akhter Banu 3 Original Article 1 Department of Community Medicine, Ibrahim Medical College (IMC), Dhaka; 2 Department of Ophthalmology, Bangladesh Institute of Research and Rehabilitation in Diabetes and Endocrine Metabolic Disorders (BIRDEM); 3 Institute of Nutrition and Food Science (INFS), University of Dhaka Abstract Background and objective Disaster prone coastal population has least accessibility to health care and very little is known about the prevalence of diabetes, diabetic retinopathy (DR) and visual impairment. This study addressed the prevalence of visual impairment and DR and risk factors related to DR among population residing in disaster prone areas of Bangladesh. Methods: Thirty-two coastal communities in six coastal districts were purposively selected. All coastal people of age 18 years or more were considered eligible. Investigations included clinical history, anthropometry (height, weight, waist- and hip-girth), blood pressure and fasting blood glucose (FBG). The participants with hyperglycemia (FBG 5.6mmol/l) were undertaken for eye examination. Visual acuity was measured bilaterally using the Snellen chart. An Early treatment diabetic retinopathy study (ETDRS) cut out chart with E Optotypes was used. Results: A total of 7567 participants volunteered and 1540 had hyperglycemia (FBG 5.6mmol/l). Of the hyperglycemic participants, 1214 (91.7%) participated for complete eye examination. Visual impairment of any type was found in 14.1%, any type cataract in 27.8% and any type DR in 18%. The participants of advancing age of higher social class and higher central obesity had excess risk for developing DR. The participants with known family history of diabetes also had greater risk. Compared with the group having FBG mmol/l those having FBG >6.9mmol/l had significant risk for DR (OR 3.11, 95%CI ). Conclusion: The study concludes that visual impairment and cataract of any type is almost comparable with other coastal populations. The coastal people had higher prevalence of DR compared to rural population from other areas of Bangladesh and it was also higher than global estimate. The persons with higher age from higher social class with higher central obesity had excess risk for DR. The risk of DR increased with increasing hyperglycemia. Further study may be undertaken to confirm these findings. IMC J Med Sci 2016; 10(1): Introduction Of the alarming trend of non-communicable diseases (NCD), type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is common throughout the world and more alarming in the south-east Asian region [1]. A global estimate of diabetes in the year 2000 was 171 million. This figure is likely to be more than double (366 million) by 2030; and most significant Address for Correspondence: Prof. M. Abu Sayeed, Department of Community Medicine, Ibrahim Medical College, 122 Kazi Nazrul Islam Avenue, Shahbag, Dhaka sayeed@imc.ac.bd
2 Sayeed MA et al. IMC J Med Sci 2016; 10(1): increase will occur in the developing countries [1]. T2DM affects elderly people in the developed countries, whereas, in the developing and least developing countries, younger people are more affected [2]. We have the same experience in Bangladesh [3]. Additionally, the prevalence of micro-vascular complications is common in these populations [4-6]. Of the micro-vascular sequels, diabetic retinopathy (DR) was found to be the most disabling complications as it results into loss of vision. A community based study in Sri Lanka reported that more than one-fourth (27.4%) of the diabetic patients had DR [7]. This report indicates that the most diabetic people are prone to develop DR and eventually blindness. For Bangladesh, several population based studies reported the increasing trend of T2DM [8-10]; but there was no community based study on DR. This study addressed the prevalence and risk of DR at the community level in a disaster prone coastal population of Bangladesh. Material and methods The study protocol was approved by the Ethical Review Committee of the Diabetic Association of Bangladesh (BADAS). Study area and population. A disaster prone population of coastal area was purposively selected. A total of 32 geographical sites [18 secondary schools, 5 primary schools, 5 Madrasahs (religious schools) including 4 Union Councils] were selected purposively in six coastal districts of Barisal, Borguna, Vola, Pirojpur, Potuakhali and Jhalokathi. The study areas were reported elsewhere [11] and is shown in Fig 1 and 2. The investigations at community level started on 17 th September 2013 and ended on 12 th May At the start, we made contact with the teachers and the students of the selected institutions. We discussed the proposed study with them informing the objectives and the investigation procedure in detail. All parents, guardians, neighbors and relatives of the students and teachers were invited to participate. All villagers of age 18 years or more were considered eligible. The students and teachers volunteered to inform the villagers about the study. Additionally, volunteers prepared the list of the interested participants. Informed consent was taken from each participant and was advised to attend the investigation site in the next morning with an overnight fast the algorithm of the study is shown in Fig Fig.1: Map of Bangladesh showing the location of six coastal districts included in the study [11] Note: 1 Barisal, 2 Pirojpur, 3 Jhalokhati, 4 Patuakhali, 5 Barguna, 6 Bhola 4 Interviewing, measurement of anthropometry and blood pressure: In the morning, the participant was interviewed about occupation, education, income, illness (present or past) and medication. Interview on family-history included diabetes, hypertension (HTN), stroke, coronary heart diseases (CHD), peripheral vascular disease (PVD), foot-ulcer and leg amputation. The anthropometric measurements were height, weight, waist- and hip-girth. Body mass index (BMI = weight in kg / height in met sq.) and waist-to-hip ratio (WHR = waist / hip) were calculated. Blood pressure was measured after 10 min rest with standard cuff, fitted with mercury sphygmomanometer. A mean of the two measures was accepted. 6
3 12 IMC J Med Sci 2016; 10(1): Sayeed MA et al. Barisal Pirojpur Jhalokhati Patuakhali Barguna Bhola Fig.2: Map showing the study sites in each coastal district. Each Dot ( ) indicates location of study site [11] Collection of blood sample: Taking an aseptic measure five ml of fasting blood sample was collected for estimation of fasting blood glucose (FBG mmol/l) and lipids (total cholesterol [Tchol], triglycerides [TG], low-density lipoprotein [LDL] and high-density lipoproteins [HDL]). Finally, biochemical tests were carried out in BIRDEM laboratory. Plasma glucose was measured by glucose oxidase-peroxidase method using Technicon M-II auto-analyzer. To reduce the cost, a randomized sample was drawn (n=225) for the estimation of T-chol, TG and HDL by autoanalyzer (Hitachi-704) using enzymatic method. The coefficient of variation (CV) was allowed 5%. While collecting blood sample a drop of blood was taken on a hemo-glucotest strip (One Touch select sample, Lifescan) for rapid assessment of FBG [12]. We used ADA and WHO diagnostic criteria for hyperglycemia and predicting diabetes [13,14]. The participants, who showed FBG 5.6 mmol/l, were referred to ophthalmologist for eye examination (Fig 3). The participants presented with eye complaints, irrespective of glycemic status, were also referred. Eye examinations: This included visual acuity test and fundoscopy by a two-member team of the ophthalmologists. Both ophthalmologists had the experience of eye examination in the department of ophthalmology at BIRDEM hospital. It may be noted that BIRDEM, a national referral center for endocrine disorders, where these ophthalmologists examine about 100 diabetic patients daily for the diagnosis of DR.
4 Sayeed MA et al. IMC J Med Sci 2016; 10(1): Eligible Participants ( 18y) N = Enrolled Participants: N=7567 FBG<5.6mmol/l N=6027 FBG 5.6 mmol/l N = 1540 Eye Examination 1412 Impaired Visual acuity Mild impaired (6/9 6/12) Moderate impaired (6/18 6/36) Severe impaired ( 6/60) Cataract Hyper-Mature cataract Early & Mature cataract Fig-3: Algorithm of the study Retinopathy Mild retinopathy (Pre-proliferative / background) Moderate to severe retinopathy (Proliferative) Maculopathy Visual acuity was measured bilaterally using the Snellen chart. An early treatment diabetic retinopathy study (ETDRS) cut out chart with E Optotypes was used [15]. Torch light and pinhole were also used [16]. The cause of visual impairment (cataract, refractive error and retinopathy) was identified [16, 17]. Then the pupil was dilated by using 1% Tropicamide and the fundus was examined with direct ophthalmoscope [18]. Diabetic retinopathy (DR) was diagnosed and classified according to classification of DR and diabetic macular edema [19]. The study findings on DR have been modified for easy presentation: (a) Pre-proliferative microaneurysms with or without intraretinal hemorrhages; (b) proliferative neovascularization with or without Vitreous/preretinal hemorrhage; (c) Diabetic macular edema (maculopathy) any thickening or lipid exudates in the macula [20]. Statistical analyses The prevalence rates of cataract, impaired visual acuity and diabetic retinopathy according to sex, family history and social class were given in percentages with 95% confidence interval (CI). The biophysical characteristics were shown in mean with standard deviation. We used unpaired t- test for comparison of characteristics between participants with and without retinopathy. For assessment of risk odds ratio (OR) with 95% CI were used. SPSS version 20 was used for all analyzing qualitative and quantitative data. Less than 0.05 was considered significant. Results According to eligibility criteria (age 18y), as mentioned above, a total of 11,850 were found eligible (Fig 3). Of them, 7567 (63.85%) took part in the investigation. The prevalence of hyperglycemia (FBG 5.6 mmol/l) was found in 1540 (20.4%). Of them, 1412 (91.7%) volunteered eye examination. The prevalence (with CI) of cataract, impaired visual acuity and diabetic retinopathy was 27.8 ( ), 14.1 ( ) and 17.9 ( ), respectively (Table 1). The prevalence of DR according to sex, social class and family history were shown in table 2. The prevalence of DR was significantly higher among those who had known diabetic member in their first degree relatives than those who had no known diabetic member in their families. Regarding social class, the affluent participants had
5 14 IMC J Med Sci 2016; 10(1): Sayeed MA et al. significantly higher DR than their non-affluent counterparts. Compared with the women the men had higher frequency though not significant. Table-1: Prevalence [% (95% CI*)] of cataract, impaired visual acuity and retinopathy (n=1412) Cataract n % (95% CI) a. No Cataract ( ) b. Cataract Early + Mature ( ) Hyper-mature ( ) Total cataract ( ) Visual acuity a. Normal (6/6) ( ) b. Impaired Mild (6/9-6/12) ( ) Moderate (6/18-6/36) ( ) Severe (=>6/60) ( ) Total impaired ( ) Diabetic Retinopathy a. Absent ( ) b. Present Mild (pre-proliferative ( ) / background) Moderate to severe ( ) (proliferative) Maculopathy ( ) (macular edema) Total diabetic retinopathy ( ) CI* - confidence interval Table-2: Prevalence [% (95% CI*)] of retinopathy according to sex, family history (n=1412) and social class (n=1377) Variables n % (95% CI*) Sex (n: men/women= 585/827) Men ( ) Women ( ) Family history of diabetes (n: Absent/Present= 833/579) Absent (or not known) ( ) Present ( ) Social class (n: Non affluent/affluent= 480/897) Non affluent (poor) ( ) Affluent (middle and rich) ( ) CI* - confidence interval Table-3: Comparison of characteristics between participants with and without retinopathy No retinopathy n=617 Retinopathy n=145 Characteristics Mean SD Mean SD p Age (y) BMI WHR WHTR SBP (mmhg) DBP (mmhg) FBG (mmol/l) Chol (mg/dl)* TG (mg/dl)* HDL (mg/dl)* LDL (mg/dl)* SD standard deviation; p after unpaired t-test; * - a randomized sample size (n = 225) Table-4: Prevalence (%) and Risk factors estimated for retinopathy Risk variables % OR 95% p CI*) Sex Women Men Social class Poor Middle + Rich Family history of diabetes Absent or not known Present Glycemic status(fbg, mmol/l) NFG (<5.6) IFG ( ) DM (>6.9) Age quartile (y) Quartile 1 (<30) Quartile 2 (<31 40) Quartile 3 (<41 55) Quartile 4 (>55) BMI quartile Quartile 1 (<19.5) Quartile 2 (< ) Quartile 3 (< ) Quartile 4 (>24.8) WHR quartile Quartile 1 (<0.81) Quartile 2 (< ) Quartile 3 (< ) Quartile 4 (>0.93) OR odds ratio *CI confidence interval
6 Sayeed MA et al. IMC J Med Sci 2016; 10(1): Table 3 showed the comparisons of biophysical characteristics between participants with and without DR. The participants with DR had significantly higher age (p<0.001), higher central obesity (WHR p<0.001; and WHtR p=0.01), higher fasting FBG (p<0.001). Interestingly, there was no significant difference in general obesity (BMI p=0.917). Even more interesting is that the participants with DR had significantly lower total cholesterol (p=0.03) and lower low-density lipoprotein (LDL p=0.047). The risk factors related to DR was shown in Table 4. Compared with the non-affluent, the affluent participants had higher risk (OR 1.54, 95% CI, ). Likewise, the participants from known diabetic family had greater risk (OR 1.52, CI, ) than their counterparts having no known diabetes in their families. The participants with diabetes had excess risk (OR 3.11, CI, ) than those with normal (NFG) or impaired fasting glucose (IFG). For an increasing age, higher the quartiles greater is the risk. Similarly, higher is the central obesity (WHR) more is the risk (Table 4); whereas, general obesity (BMI) was found to have no effect on DR. Discussion This is the first study, which addressed the prevalence of DR and visual impairment in a coastal population. Some socio-demographic and biophysical risk factors were also assessed. Two important aspects of the study are worth mentioning. Firstly, the study population has least access to health care services and diagnostic facilities. Secondly, the study areas are mostly inaccessible due to inconvenient communication and precarious weather condition. We had some advantages. We could refer the persons with cataract to nearby centers for surgery organized and maintained by Fred Hollow Foundation. The local people especially teachers and students were very much cordial. They actively and sincerely volunteered the study in every step (carrying message to the villagers from house to house and making list of the participants and taking them to the investigation site. There are few published studies on the prevalence of visual impairment and cataract among coastal population for comparisons. Patil S et al reported very high prevalence of impaired visual acuity (33.0%) and cataract (82.4%) in Sindhudurg district on the western coastal strip of India [21]. They reported high prevalence among coastal population may be due to higher age group (>50y) they studied. So far available a population based study of Bangladesh showed that overall prevalence of DR was 5.4% among the rural people of age 30 years or older [22]. Our study demonstrated that compared with the rural people of other areas of Bangladesh, the coastal people had increased prevalence of DR. An estimated global prevalence of any DR was found 6.96% (95CI, ) [23]. Thus, the global estimate also indicates that the coastal people are more susceptible for developing DR. A Singapore Eye Study among the migrant Indians (age >40y) reported that the prevalence of DR was 10.5% (95% CI, ) [24]. This finding also showed that our study population bears greater risk for DR. With regard to risk factors, we found persons with advancing age, higher class with family history of diabetes had excess risk for DR. These findings are consistent with other studies [20 23]. In contrast, the Singapore study [24] observed that lower income and living in smaller houses were associated with vision threatening DR. An interesting finding was that the level of total cholesterol and LDL-cholesterol was found significantly lower in those who had no DR than those who had. The findings indicate that these lipid fractions appear to be protective against DR. The explanation is not known. We had some limitations. The sampling technique was a purposive one. We could not include dietary habit (salt, fruits and vegetables), physical activities and housing status. We could not afford two important but relevant investigations like hemoglobin A1c and stereoscopic digital photography. Conclusion We conclude that the prevalence of visual impairment and cataract is comparable with other studies; whereas, the prevalence of DR among the
7 16 IMC J Med Sci 2016; 10(1): Sayeed MA et al. coastal people was higher than that of the rural Bangladeshis and also higher than global estimates and Indian migrants. The persons with higher age from higher social class with higher central obesity had excess risk for both diabetes and DR. Further study may be undertaken to confirm the study findings and if found consistent then the coastal people need an urgent Eye Care facilities for the prevention of visual impairment and blindness. Acknowledgements We are grateful to Fred Hollow Foundation (FHF) for their financial support. We are indebted to Prof AH Syedur Rahman, Department of Ophthalmology, BIRDEM for his initiative to communicate to FHF. We deeply acknowledge him posthumously with all our deepest respect. We appreciate the cooperation extended by the Ibrahim Medical College and the Department of Ophthalmology, BSMMU, Dhaka. We are grateful and obliged to the teachers, students and all participants of coastal area for their cordial and pleasant hospitality. References 1. Wild S, Roglic G, Green A, Sicree R, King H: Global Prevalence of Diabetes: Estimates for the year 2000 and projections for Diabetes Care 2004; 27: World Health Organization: Guidelines for the prevention, management and care of diabetes mellitus. EMRO Technical publications series 32, Geneva Khanam PA, Mahtab H, Ahmed AU, Sayeed MA, Azad Khan AK. In Bangladesh diabetes starts earlier now than 10 years back: a BIRDEM study. Ibrahim Med Coll J 2008; 2(1): Sayeed MA, Khanam PA, Choudhury RI, Mahtab H, Azad Khan AK. Retinopathy and nephropathy are the most prevalent complications among diabetic subjects in Bangladesh. Diabetologia 2005; 48(Suppl 1): Abs-944 (P: A343). 5. Khan S, Khanam P, Latif Z, Mahtab H, Azad Khan AK, Banu A, Sayeed MA. Nephropathy was the most frequent complication among people with diabetes after a 10-year follow up (p243, Abs). Diabetes UK, Diabetic Medicine 2006; 23[suppl-4]: Sayeed MA, Khanam PA, Mahtab H and Azad Khan AK. Microvascular complications among diabetic subjects predominate in the long-term follow up: 15-year retrospective study. Diab Res Clin Pract 2000; 50: S Katulanda P, Priyanga Ranasinghe P and Jayawardena R. Prevalence of retinopathy among adults with self-reported diabetes mellitus: the Sri Lanka diabetes and Cardiovascular Study. BMC Ophthalmol 2014; 14: 100. doi: / Sayeed MA, Mahtab H, Khanam PA, Latif ZA, Banu A and Azad Khan AK. Prevalence of diabetes and impaired fasting glucose in urban population of Bangladesh. Bangladesh Med Res Counc Bull 2007; 33(1): Sayeed MA, Rhaman MM, Fayezunnessa N, Khanam PA, Begum T, Mahtab H and Banu A. Childhood diabetes in a Bangladeshi population. Journal of Diabetes Mellitus 2013; 3(1): Rahim MA, Hussain A, Azad Khan AK, Sayeed MA, Keramat Ali SM, Vaaler S. Rising prevalence of type 2 diabetes in rural Bangladesh: a population based study. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2007; 77(2): Sayeed MA, Syedur Rahman AH, Hazrat Ali M, Subrina Afrin, Masudur Rhaman M, Mainul Hasan Chowdhury M and Banu A. Prevalence of hypertension in people living in coastal areas of Bangladesh. Ibrahim Med Coll J 2015; 9(1): Florkowski C, Budgen C, Kendall D, Lunt H and Moore MP. Comparison of blood glucose meters in a New Zealand diabetes centre. Ann Clin Biochem 2009; 46: Gabir MM, Hanson RL, Dabelea D, Imperatore G, Roumain J, Bennett PH and Knowler WC. The 1997 American Diabetes Association and 1999 World Health Organization criteria for hyperglycemia in the diagnosis and prediction of diabetes. Diabetes Care 2000; 23(8):
8 Sayeed MA et al. IMC J Med Sci 2016; 10(1): American Diabetes Association. Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes Diabetes Care 2011; 34(Suppl 1): S11 S Focal photocoagulation treatment of diabetic macular edema. Relationship of treatment effect to fluorescein angiographic and other retinal characteristics at baseline: ETDRS report no. 19. Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study Research Group. Arch Ophthalmol 1995; 113: Neena J, Rachel J, Praveen V, Murthy GV. Rapid assessment of avoidable blindness in India. PLOS One 2008; 3: e Prajna NV, Venkataswamy G. Cataract blindness-the Indian Experience. Bull World Health Organ 2007; 79: Klein R, Klein BEK, Moss SE, Davis MD, Demets DL. The Wisconsin epidemiologic study of diabetic retinopathy-x. Four year incidence and progression of diabetic retinopathy, when age at diagnosis is 30 years or more. Arch Ophthalmol 1989; 107: Wilkinson CP, Ferris FL, 3rd, Klein RE, et al. Proposed international clinical diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema disease severity scales. Ophthalmology 2003; 110: Ciulla TA, Amador AG, Zinman B. Diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema: pathophysiology, screening, and novel therapies. Diabetes Care 2003; 26(9): Patil S, Gogate P, Vora S, Ainapure S, Hingane RN, Kulkarni AN, Shammanna BR. Prevalence, causes of blindness, visual impairment and cataract surgical services in Sindhudurg district on the western coastal strip of India. Indian J Ophthalmol 2014; 62(2): Akhter A, Fatema K, Ahmed SF, Afroz A, Ali L, Hussain A. Prevalence and associated risk indicators of retinopathy in a rural Bangladeshi population with and without diabetes. Ophthalmic Epidemiol 2013; 20(4): Yau JW, Rogers SL, Kawasaki R, Lamoureux EL, Kowalski JW, Bek T, et al, Meta- Analysis for Eye Disease (META-EYE) Study Group. Global prevalence and major risk factors of diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes Care 2012; 35(3): Zheng Y, Lamoureux EL, Lavanya R, Wu R, Ikram MK, Wang JJ, Mitchell P et al. Prevalence and risk factors of diabetic retinopathy in migrant Indians in an urbanized society in Asia: the Singapore Indian eye study. Ophthalmology 2012; 119(10):
UNDERNUTRITION AND ADIPOSITY IN CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENTS: A NUTRITION PARADOX IN BANGLADESH
 Original Article UNDERNUTRITION AND ADIPOSITY IN CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENTS: A NUTRITION PARADOX IN BANGLADESH M. Abu Sayeed 1, Mir Masudur Rhaman 1, Akhter Banu 2 and Hajera Mahtab 3 1 Department of Community
Original Article UNDERNUTRITION AND ADIPOSITY IN CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENTS: A NUTRITION PARADOX IN BANGLADESH M. Abu Sayeed 1, Mir Masudur Rhaman 1, Akhter Banu 2 and Hajera Mahtab 3 1 Department of Community
Diabetic Management beyond traditional risk factors and LDL-C control: Can we improve macro and microvascular risks?
 Retinopathy Diabetes has a negative effect on eyes in many ways, increasing the risk of cataracts for example, but the most common and serious ocular complication of diabetes is retinopathy. Diabetic retinopathy
Retinopathy Diabetes has a negative effect on eyes in many ways, increasing the risk of cataracts for example, but the most common and serious ocular complication of diabetes is retinopathy. Diabetic retinopathy
Abstract. Introduction. Original paper. Comparison of screening for diabetic retinopathy by non-specialists and specialists
 Comparison of screening for diabetic retinopathy by non-specialists and specialists Effectiveness of screening for diabetic retinopathy by nonspecialist doctors: the importance of physician-ophthalmologist
Comparison of screening for diabetic retinopathy by non-specialists and specialists Effectiveness of screening for diabetic retinopathy by nonspecialist doctors: the importance of physician-ophthalmologist
Retinopathy in a diabetic population
 Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2007), Vol. 5, No. 2, Issue 18, 204-209 Retinopathy in a diabetic population Shrestha S 1, Malla OK 2, Karki DB 3, Byanju RN 4 2 Fellow of NAMS, 3 Professor, NAMS,
Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2007), Vol. 5, No. 2, Issue 18, 204-209 Retinopathy in a diabetic population Shrestha S 1, Malla OK 2, Karki DB 3, Byanju RN 4 2 Fellow of NAMS, 3 Professor, NAMS,
JMSCR Vol. 03 Issue 08 Page August 2015
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v3i8.05 Study of Prevalence of Diabetic Retinopathy in Already Confirmed Diabetic Patients Who Were
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v3i8.05 Study of Prevalence of Diabetic Retinopathy in Already Confirmed Diabetic Patients Who Were
Association of Thyroid Hormone Levels Among Type 2 Diabetic Patients Attending a Tertiary Care Hospital
 Bangladesh Med Res Counc Bull 2016; 42:90-94 Association of Thyroid Hormone Levels Among Type 2 Diabetic Patients Attending a Tertiary Care Hospital Abstract Khan NZ 1, Muttalib MA 2, Sultana GS 3 1 Department
Bangladesh Med Res Counc Bull 2016; 42:90-94 Association of Thyroid Hormone Levels Among Type 2 Diabetic Patients Attending a Tertiary Care Hospital Abstract Khan NZ 1, Muttalib MA 2, Sultana GS 3 1 Department
THE PREVALENCE OF CAUSES FOR DIABETIC RETINOPATHY USING MATHEMATICAL MODELS
 International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology (IJARET) Volume 9, Issue 6, November-December 2018, pp. 167 171, Article ID: IJARET_09_06_017 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijaret/issues.asp?jtype=ijaret&vtype=9&itype=6
International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology (IJARET) Volume 9, Issue 6, November-December 2018, pp. 167 171, Article ID: IJARET_09_06_017 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijaret/issues.asp?jtype=ijaret&vtype=9&itype=6
Prevalence of diabetic retinopathy in diabetics of rural population belonging to Ramanagara and Chikkaballapura districts of Karnataka
 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 5, Issue 3, March 215 1 ISSN 225-3153 Prevalence of diabetic retinopathy in diabetics of rural population belonging to Ramanagara and
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 5, Issue 3, March 215 1 ISSN 225-3153 Prevalence of diabetic retinopathy in diabetics of rural population belonging to Ramanagara and
Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients
 Chattagram Maa-O-Shishu Hospital Medical College Journal DOI: 10.11566/cmosh.2013.1201.4 Original Article Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients Siddiqui SRA 1 Rahman MZ 2 * Alam ASMT 1
Chattagram Maa-O-Shishu Hospital Medical College Journal DOI: 10.11566/cmosh.2013.1201.4 Original Article Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients Siddiqui SRA 1 Rahman MZ 2 * Alam ASMT 1
Asian Journal of Medical and Biological Research ISSN (Print) (Online)
 , 152-157; doi: 10.3329/ajmbr.v3i2.33562 Asian Journal of Medical and Biological Research ISSN 2411-4472 (Print) 2412-5571 (Online) www.ebupress.com/journal/ajmbr Article Impact of type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
, 152-157; doi: 10.3329/ajmbr.v3i2.33562 Asian Journal of Medical and Biological Research ISSN 2411-4472 (Print) 2412-5571 (Online) www.ebupress.com/journal/ajmbr Article Impact of type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
RANZCO Screening and Referral Pathway for Diabetic Retinopathy #
 RANZCO Screening and Referral Pathway for Diabetic Retinopathy # Patient Presents a. Screen for Diabetic Retinopathy every 2 years b. Begin screening at diagnosis of Diabetes * Clinical Modifi ers Yearly
RANZCO Screening and Referral Pathway for Diabetic Retinopathy # Patient Presents a. Screen for Diabetic Retinopathy every 2 years b. Begin screening at diagnosis of Diabetes * Clinical Modifi ers Yearly
Diabetic retinopathy (DR) was first PROCEEDINGS DIABETIC RETINOPATHY * Ronald Klein, MD, MPH ABSTRACT
 DIABETIC RETINOPATHY * Ronald Klein, MD, MPH ABSTRACT Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is characterized by the development of retinal microaneurysms, hemorrhages, deposits of leaked lipoproteins (hard exudates),
DIABETIC RETINOPATHY * Ronald Klein, MD, MPH ABSTRACT Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is characterized by the development of retinal microaneurysms, hemorrhages, deposits of leaked lipoproteins (hard exudates),
FREQUENCY OF DIABETIC RETINOPATHY IN A TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL USING DIGITAL RETINAL IMAGING TECHNOLOGY
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE FREQUENCY OF DIABETIC RETINOPATHY IN A TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL USING DIGITAL RETINAL IMAGING TECHNOLOGY INTRODUCTION As more and more people are being affected with diabetes and with poor
ORIGINAL ARTICLE FREQUENCY OF DIABETIC RETINOPATHY IN A TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL USING DIGITAL RETINAL IMAGING TECHNOLOGY INTRODUCTION As more and more people are being affected with diabetes and with poor
Study of correlation of severity of diabetic retinopathy with levels of haemogloelbin A1c in patients with type II Diabetes Mellitus
 Original article: Study of correlation of severity of diabetic retinopathy with levels of haemogloelbin A1c in patients with type II Diabetes Mellitus 1Dr Apoorva*, 2 Dr Sabhia Jan 1Senior Resident, 2
Original article: Study of correlation of severity of diabetic retinopathy with levels of haemogloelbin A1c in patients with type II Diabetes Mellitus 1Dr Apoorva*, 2 Dr Sabhia Jan 1Senior Resident, 2
Longitudinal study of a cohort of people with diabetes screened by the Exeter Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Programme
 (2002) 16, 140 145 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 1470-269X/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/eye CLINICAL STUDY Longitudinal study of a cohort of people with diabetes screened by the Exeter Diabetic
(2002) 16, 140 145 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 1470-269X/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/eye CLINICAL STUDY Longitudinal study of a cohort of people with diabetes screened by the Exeter Diabetic
A review of socio-economic factors affecting for diabetes
 A review of socio-economic factors affecting for diabetes Abstract MWASM Weerasinghe 1 Diabetes is one of the principal healthcare challenge in worldwide and diabetes is a serious complex condition which
A review of socio-economic factors affecting for diabetes Abstract MWASM Weerasinghe 1 Diabetes is one of the principal healthcare challenge in worldwide and diabetes is a serious complex condition which
Blood Pressure, Lipids, and Obesity Are Associated With Retinopathy
 Epidemiology/Health Services/Psychosocial Research O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Blood Pressure, Lipids, and Obesity Are Associated With Retinopathy The Hoorn Study HENDRIK A. VAN LEIDEN, MD 1,2 JACQUELINE
Epidemiology/Health Services/Psychosocial Research O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Blood Pressure, Lipids, and Obesity Are Associated With Retinopathy The Hoorn Study HENDRIK A. VAN LEIDEN, MD 1,2 JACQUELINE
Use of Eye Care Services among Type 2 Diabetic Patients in Laguna
 Original Article Philippine Journal of OPHTHALMOLOGY Use of Eye Care Services among Type 2 Diabetic Patients in Laguna Glenn Carandang, MD, MPH, 1,2, Maria Victoria Rondaris, MD, MPH, 3, and Genejane Adarlo,
Original Article Philippine Journal of OPHTHALMOLOGY Use of Eye Care Services among Type 2 Diabetic Patients in Laguna Glenn Carandang, MD, MPH, 1,2, Maria Victoria Rondaris, MD, MPH, 3, and Genejane Adarlo,
DIABETIC RETINOPATHY AMONG TYPE 2 DIABETIC PATIENTS PRESENTING WITH MICROALBUMINURIA
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE DIABETIC RETINOPATHY AMONG TYPE 2 DIABETIC PATIENTS PRESENTING WITH MICROALBUMINURIA Arshad Hussain 1, Iqbal Wahid 2, Danish Ali Khan 3 ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION: Diabetes mellitus is becoming
ORIGINAL ARTICLE DIABETIC RETINOPATHY AMONG TYPE 2 DIABETIC PATIENTS PRESENTING WITH MICROALBUMINURIA Arshad Hussain 1, Iqbal Wahid 2, Danish Ali Khan 3 ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION: Diabetes mellitus is becoming
Diagnosis and treatment of diabetic retinopathy. Blake Cooper MD Ophthalmologist Vitreoretinal Surgeon Retina Associates Kansas City
 Diagnosis and treatment of diabetic retinopathy Blake Cooper MD Ophthalmologist Vitreoretinal Surgeon Retina Associates Kansas City Disclosures Consulted for Novo Nordisk 2017,2018. Will be discussing
Diagnosis and treatment of diabetic retinopathy Blake Cooper MD Ophthalmologist Vitreoretinal Surgeon Retina Associates Kansas City Disclosures Consulted for Novo Nordisk 2017,2018. Will be discussing
DIABETES PREVALENCE: A COMPARISON BETWEEN URBAN AND RURAL AREAS OF BANGLADESH
 E S Scholars www.setscholars.org T Knowledge is Power September 2012 Volume 1, Issue 4 Article #10 IRJALS Research Paper ISSN: 1839-8499 DIABETES PREVALENCE: A COMPARISON BETWEEN URBAN AND RURAL AREAS
E S Scholars www.setscholars.org T Knowledge is Power September 2012 Volume 1, Issue 4 Article #10 IRJALS Research Paper ISSN: 1839-8499 DIABETES PREVALENCE: A COMPARISON BETWEEN URBAN AND RURAL AREAS
Awareness of Diabetic Retinopathy in Rural Population in South Tamil Nadu
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/336 Awareness of Diabetic Retinopathy in Rural Population in South Tamil Nadu N Sharmila 1, K Kavitha 1, S Ganapathy
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/336 Awareness of Diabetic Retinopathy in Rural Population in South Tamil Nadu N Sharmila 1, K Kavitha 1, S Ganapathy
Diabetic Retinopathy
 Diabetic Retinopathy Overview This presentation covers the following topics: Definitions Epidemiology of diabetic retinopathy Evidence for public health approaches Screening for diabetic retinopathy Health
Diabetic Retinopathy Overview This presentation covers the following topics: Definitions Epidemiology of diabetic retinopathy Evidence for public health approaches Screening for diabetic retinopathy Health
CHAPTER 3 DIABETES MELLITUS, OBESITY, HYPERTENSION AND DYSLIPIDEMIA IN ADULT CENTRAL KERALA POPULATION
 CHAPTER 3 DIABETES MELLITUS, OBESITY, HYPERTENSION AND DYSLIPIDEMIA IN ADULT CENTRAL KERALA POPULATION 3.1 BACKGROUND Diabetes mellitus (DM) and impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) have reached epidemic proportions
CHAPTER 3 DIABETES MELLITUS, OBESITY, HYPERTENSION AND DYSLIPIDEMIA IN ADULT CENTRAL KERALA POPULATION 3.1 BACKGROUND Diabetes mellitus (DM) and impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) have reached epidemic proportions
RISK FACTORS FOR DIABETIC RETINOPATHY PROGRESSION
 2015 ILEX PUBLISHING HOUSE, Bucharest, Roumania http://www.jrdiabet.ro Rom J Diabetes Nutr Metab Dis. 22(2):159-165 doi: 10.1515/rjdnmd-2015-0020 RISK FACTORS FOR DIABETIC RETINOPATHY PROGRESSION Mónika
2015 ILEX PUBLISHING HOUSE, Bucharest, Roumania http://www.jrdiabet.ro Rom J Diabetes Nutr Metab Dis. 22(2):159-165 doi: 10.1515/rjdnmd-2015-0020 RISK FACTORS FOR DIABETIC RETINOPATHY PROGRESSION Mónika
Original Article Retinopathy in Type 2 DM Pak Armed Forces Med J 2015; 65(1):63-7
 Original Article Retinopathy in Type 2 DM Pak Armed Forces Med J 2015; 65(1):63-7 FREQUENCY OF RETINOPATHY IN NEWLY DIAGNOSED PATIENTS OF TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS (DM) Kumail Abbas Khan, Sultan Mehmood
Original Article Retinopathy in Type 2 DM Pak Armed Forces Med J 2015; 65(1):63-7 FREQUENCY OF RETINOPATHY IN NEWLY DIAGNOSED PATIENTS OF TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS (DM) Kumail Abbas Khan, Sultan Mehmood
Diabetes Care 24: , 2001
 Pathophysiology/Complications O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Prevalence and Significance of Retinopathy in Subjects With Type 1 Diabetes of Less Than 5 Years Duration Screened for the Diabetes Control and
Pathophysiology/Complications O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Prevalence and Significance of Retinopathy in Subjects With Type 1 Diabetes of Less Than 5 Years Duration Screened for the Diabetes Control and
A pilot Study of 25-Hydroxy Vitamin D in Egyptian Diabetic Patients with Diabetic Retinopathy
 A pilot Study of 25-Hydroxy Vitamin D in Egyptian Diabetic Patients with Diabetic Retinopathy El-Orabi HA 1, Halawa MR 1, Abd El-Salam MM 1, Eliewa TF 2 and Sherif NSE 1 Internal Medicine and Endocrinology
A pilot Study of 25-Hydroxy Vitamin D in Egyptian Diabetic Patients with Diabetic Retinopathy El-Orabi HA 1, Halawa MR 1, Abd El-Salam MM 1, Eliewa TF 2 and Sherif NSE 1 Internal Medicine and Endocrinology
Clinical biomicroscopy versus fluorescein angiography: Effectiveness and sensitivity in detecting diabetic retinopathy
 European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 17 no. 1, 2007 / pp. 84-88 Clinical biomicroscopy versus fluorescein angiography: Effectiveness and sensitivity in detecting diabetic retinopathy S.S. KHALAF, M.D.
European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 17 no. 1, 2007 / pp. 84-88 Clinical biomicroscopy versus fluorescein angiography: Effectiveness and sensitivity in detecting diabetic retinopathy S.S. KHALAF, M.D.
Diabetes Research Unit, Department of Clinical Medicine Faculty of Medicine, University of Colombo, Colombo, Sri Lanka. 2
 International Journal of Technical Research and Applications e-issn: 2320-8163, IDENTIFICATION OF RISK FACTORS FOR SELECTED NON COMMUNICABLE DISEASES AMONG PUBLIC SECTOR OFFICE EMPLOYEES, SRI LANKA. A.K.S.H.
International Journal of Technical Research and Applications e-issn: 2320-8163, IDENTIFICATION OF RISK FACTORS FOR SELECTED NON COMMUNICABLE DISEASES AMONG PUBLIC SECTOR OFFICE EMPLOYEES, SRI LANKA. A.K.S.H.
Plasma fibrinogen level, BMI and lipid profile in type 2 diabetes mellitus with hypertension
 World Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences ISSN (Print): 2321-3310; ISSN (Online): 2321-3086 Published by Atom and Cell Publishers All Rights Reserved Available online at: http://www.wjpsonline.org/ Original
World Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences ISSN (Print): 2321-3310; ISSN (Online): 2321-3086 Published by Atom and Cell Publishers All Rights Reserved Available online at: http://www.wjpsonline.org/ Original
Diabetic Retinopathy. Barry Emara MD FRCS(C) Giovanni Caboto Club October 3, 2012
 Diabetic Retinopathy Barry Emara MD FRCS(C) Giovanni Caboto Club October 3, 2012 Outline Statistics Anatomy Categories Assessment Management Risk factors What do you need to do? Objectives Summarize the
Diabetic Retinopathy Barry Emara MD FRCS(C) Giovanni Caboto Club October 3, 2012 Outline Statistics Anatomy Categories Assessment Management Risk factors What do you need to do? Objectives Summarize the
Diabetic and the Eye: An Introduction
 Diabetic and the Eye: An Introduction Lawrence Iu FRCSEd (Ophth), FCOphthHK, FHKAM (Ophthalmology) Department of Ophthalmology, Grantham Hospital & Queen Mary Hospital Background Diabetes mellitus (DM)
Diabetic and the Eye: An Introduction Lawrence Iu FRCSEd (Ophth), FCOphthHK, FHKAM (Ophthalmology) Department of Ophthalmology, Grantham Hospital & Queen Mary Hospital Background Diabetes mellitus (DM)
Lipid Profile, Glycaemic and Anthropometric Status of Students of a Private Medical College in Dhaka City
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Lipid Profile, Glycaemic and Anthropometric Status of Students of a Private Medical College in Dhaka City *R Yeasmin1, S Parveen2, N Nahar1, K Begum1, F Akhter3, M Aziz3, F Islam3, T Eyaub3
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Lipid Profile, Glycaemic and Anthropometric Status of Students of a Private Medical College in Dhaka City *R Yeasmin1, S Parveen2, N Nahar1, K Begum1, F Akhter3, M Aziz3, F Islam3, T Eyaub3
FACTORS ASSOCIATED WITH DIABETIC RETINOPATHY AMONG TYPE 2 DIABETIC PATIENTS: A HOSPITAL BASED CASE-CONTROL STUDY
 Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health FACTORS ASSOCIATED WITH DIABETIC RETINOPATHY AMONG TYPE 2 DIABETIC PATIENTS: A HOSPITAL BASED CASE-CONTROL STUDY Wisit Chaveepojnkamjorn 1, Pornpana Somjit 2, Suthee
Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health FACTORS ASSOCIATED WITH DIABETIC RETINOPATHY AMONG TYPE 2 DIABETIC PATIENTS: A HOSPITAL BASED CASE-CONTROL STUDY Wisit Chaveepojnkamjorn 1, Pornpana Somjit 2, Suthee
Diabetic Retinopathy Screening in Hong Kong. Dr. Rita Gangwani M.S, FRCS (Ophth), FCOphth(HK), FHKAM Eye Institute, The University of Hong Kong
 Diabetic Retinopathy Screening in Hong Kong Dr. Rita Gangwani M.S, FRCS (Ophth), FCOphth(HK), FHKAM Eye Institute, The University of Hong Kong Co-Investigators Prof. David Wong Prof. Sarah McGhee Dr. Wico
Diabetic Retinopathy Screening in Hong Kong Dr. Rita Gangwani M.S, FRCS (Ophth), FCOphth(HK), FHKAM Eye Institute, The University of Hong Kong Co-Investigators Prof. David Wong Prof. Sarah McGhee Dr. Wico
Prevalence of diabetes and impaired fasting glucose in Uygur children of Xinjiang, China
 Prevalence of diabetes and impaired fasting glucose in Uygur children of Xinjiang, China J. Zhang 1, Y.T. Ma 1, X. Xie 1, Y.N. Yang 1, F. Liu 2, X.M. Li 1, Z.Y. Fu 1, X. Ma 1, B.D. Chen 2, Y.Y. Zheng 1,
Prevalence of diabetes and impaired fasting glucose in Uygur children of Xinjiang, China J. Zhang 1, Y.T. Ma 1, X. Xie 1, Y.N. Yang 1, F. Liu 2, X.M. Li 1, Z.Y. Fu 1, X. Ma 1, B.D. Chen 2, Y.Y. Zheng 1,
A CROSS SECTIONAL STUDY OF RELATIONSHIP OF OBESITY INDICES WITH BLOOD PRESSURE AND BLOOD GLUCOSE LEVEL IN YOUNG ADULT MEDICAL STUDENTS
 Original Article A CROSS SECTIONAL STUDY OF RELATIONSHIP OF OBESITY INDICES WITH BLOOD PRESSURE AND BLOOD GLUCOSE LEVEL IN YOUNG ADULT MEDICAL STUDENTS Renu Lohitashwa, Parwati Patil ABSTRACT Overweight
Original Article A CROSS SECTIONAL STUDY OF RELATIONSHIP OF OBESITY INDICES WITH BLOOD PRESSURE AND BLOOD GLUCOSE LEVEL IN YOUNG ADULT MEDICAL STUDENTS Renu Lohitashwa, Parwati Patil ABSTRACT Overweight
Diabetes Management and Considerations for the Indian Culture
 Diabetes Management and Considerations for the Indian Culture Ramachandra G. Naik, MD Senior Medical Director Worldwide Clinical Affairs Johnson & Johnson Diabetes Solutions Companies September 24, 2015
Diabetes Management and Considerations for the Indian Culture Ramachandra G. Naik, MD Senior Medical Director Worldwide Clinical Affairs Johnson & Johnson Diabetes Solutions Companies September 24, 2015
A Study on Identification of Socioeconomic Variables Associated with Non-Communicable Diseases Among Bangladeshi Adults
 American Journal of Biomedical Science and Engineering 2018; 4(3): 24-29 http://www.aascit.org/journal/ajbse ISSN: 2381-103X (Print); ISSN: 2381-1048 (Online) A Study on Identification of Socioeconomic
American Journal of Biomedical Science and Engineering 2018; 4(3): 24-29 http://www.aascit.org/journal/ajbse ISSN: 2381-103X (Print); ISSN: 2381-1048 (Online) A Study on Identification of Socioeconomic
Fundus Fluorescein Angiography in Diabetic Retinopathy: Correlation of Angiographic Findings to the Clinical Maculopathy Abstract: Purpose:
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 2 Ver. XII (Feb. 2016), PP 80-88 www.iosrjournals.org Fundus Fluorescein Angiography in Diabetic
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 2 Ver. XII (Feb. 2016), PP 80-88 www.iosrjournals.org Fundus Fluorescein Angiography in Diabetic
DIABETES MEASURES GROUP OVERVIEW
 2014 PQRS OPTIONS F MEASURES GROUPS: DIABETES MEASURES GROUP OVERVIEW 2014 PQRS MEASURES IN DIABETES MEASURES GROUP: #1. Diabetes: Hemoglobin A1c Poor Control #2. Diabetes: Low Density Lipoprotein (LDL-C)
2014 PQRS OPTIONS F MEASURES GROUPS: DIABETES MEASURES GROUP OVERVIEW 2014 PQRS MEASURES IN DIABETES MEASURES GROUP: #1. Diabetes: Hemoglobin A1c Poor Control #2. Diabetes: Low Density Lipoprotein (LDL-C)
Diabetic Learning Event: Diabetic Eye Screening and Retinopathy- Samantha Mann & Mark Frost
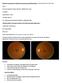 Diabetic Learning Event: Diabetic Eye Screening and Retinopathy- Samantha Mann & Mark Frost Case 1 : 63 yr-old Caucasian woman with type-2 Diabetes for 8 years Ex-smoker Hypertension- 5 years FH: father
Diabetic Learning Event: Diabetic Eye Screening and Retinopathy- Samantha Mann & Mark Frost Case 1 : 63 yr-old Caucasian woman with type-2 Diabetes for 8 years Ex-smoker Hypertension- 5 years FH: father
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Study on Prevalence of Pre-Diabetes in Urban Area of Mumbai and Its Association with Various
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Study on Prevalence of Pre-Diabetes in Urban Area of Mumbai and Its Association with Various
Diabetic retinopathy is a retinal vascular abnormality; due to chronic
 Original Article Associated factors of diabetic retinopathy in patients that referred to teaching hospitals in Babol Seyed Ahmad Rasoulinejad (MD) *1 Karimollah Hajian-Tilaki (PhD) 2 Elnaz Mehdipour (MD)
Original Article Associated factors of diabetic retinopathy in patients that referred to teaching hospitals in Babol Seyed Ahmad Rasoulinejad (MD) *1 Karimollah Hajian-Tilaki (PhD) 2 Elnaz Mehdipour (MD)
INTRODUCTION AND SYMPTOMS
 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION AND SYMPTOMS Introduction of Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is a potentially blinding complication of diabetes. It is defined as presence of one or more definite
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION AND SYMPTOMS Introduction of Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is a potentially blinding complication of diabetes. It is defined as presence of one or more definite
Serum Retinol-binding Protein 4 Levels in Patients with Diabetic Retinopathy
 The Journal of International Medical Research 2010; 38: 95 99 Serum Retinol-binding Protein 4 Levels in Patients with Diabetic Retinopathy Z-Z LI 1, X-Z LU 2, J-B LIU 1 AND L CHEN 1 1 Department of Endocrinology,
The Journal of International Medical Research 2010; 38: 95 99 Serum Retinol-binding Protein 4 Levels in Patients with Diabetic Retinopathy Z-Z LI 1, X-Z LU 2, J-B LIU 1 AND L CHEN 1 1 Department of Endocrinology,
Abdominal volume index and conicity index in predicting metabolic abnormalities in young women of different socioeconomic class
 Research Article Abdominal volume index and conicity index in predicting metabolic abnormalities in young women of different socioeconomic class Vikram Gowda, Kripa Mariyam Philip Department of Physiology,
Research Article Abdominal volume index and conicity index in predicting metabolic abnormalities in young women of different socioeconomic class Vikram Gowda, Kripa Mariyam Philip Department of Physiology,
Prediction of Cardiovascular Disease in suburban population of 3 municipalities in Nepal
 Prediction of Cardiovascular Disease in suburban population of 3 municipalities in Nepal Koju R, Gurung R, Pant P, Humagain S, Yogol CM, Koju A, Manandhar K, Karmacharya B, Bedi TRS Address for Correspondence:
Prediction of Cardiovascular Disease in suburban population of 3 municipalities in Nepal Koju R, Gurung R, Pant P, Humagain S, Yogol CM, Koju A, Manandhar K, Karmacharya B, Bedi TRS Address for Correspondence:
Unraveling the concealed and calculated cardiovascular risks in diabetes
 15 P B Fernando Memorial Oration 2015 Unraveling the concealed and calculated cardiovascular risks in diabetes Weerarathna T P 1 Journal of the Ceylon College of Physicians, 2016, 47, 15-19 Abstract Cardiovascular
15 P B Fernando Memorial Oration 2015 Unraveling the concealed and calculated cardiovascular risks in diabetes Weerarathna T P 1 Journal of the Ceylon College of Physicians, 2016, 47, 15-19 Abstract Cardiovascular
JMSCR Vol 04 Issue 12 Page December 2016
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i12.97 Prevalence of various stages of Diabetic
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i12.97 Prevalence of various stages of Diabetic
Original Article Coronary artery disease in a rural population of Bangladesh: is dyslipidemia or adiposity a significant risk?
 Original Article Coronary artery disease in a rural population of Bangladesh: is dyslipidemia or adiposity a significant risk? Sajal Krishna Banerjee 1, Chaudhury Meshkat Ahmed 1, Mir Masudur Rhaman 2,
Original Article Coronary artery disease in a rural population of Bangladesh: is dyslipidemia or adiposity a significant risk? Sajal Krishna Banerjee 1, Chaudhury Meshkat Ahmed 1, Mir Masudur Rhaman 2,
Population Based Assessment of Diabetes and Diabetic Retinopathy in South Kerala- Project Trinetra: An Interim Report
 36 Kerala Journal of Ophthalmology Vol. XXI, No. 1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Population Based Assessment of Diabetes and Diabetic Retinopathy in South Kerala- Project Trinetra: An Interim Report Dr. Manoj Soman
36 Kerala Journal of Ophthalmology Vol. XXI, No. 1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Population Based Assessment of Diabetes and Diabetic Retinopathy in South Kerala- Project Trinetra: An Interim Report Dr. Manoj Soman
Eyes on Diabetics: How to Avoid Blindness in Diabetic Patient
 Eyes on Diabetics: How to Avoid Blindness in Diabetic Patient Rova Virgana FK Unpad Pusat Mata Nasional RS Mata Cicendo Bandung Eye Center (Hospital and Clinic) PIT IDI Jabar 2018 Keys Facts from WHO
Eyes on Diabetics: How to Avoid Blindness in Diabetic Patient Rova Virgana FK Unpad Pusat Mata Nasional RS Mata Cicendo Bandung Eye Center (Hospital and Clinic) PIT IDI Jabar 2018 Keys Facts from WHO
Alarming Frequency of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM) Attending a Tertiary Care Hospital in Bangladesh
 JCD ORIGINAL ARTICLE Alarming Frequency of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM) Attending a Tertiary Care Hospital in Bangladesh Nusrat-Sultana, Hasanat MA, Sharmin-Jahan, Mashfiqul-Hasan, Sandesh-Panthi,
JCD ORIGINAL ARTICLE Alarming Frequency of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM) Attending a Tertiary Care Hospital in Bangladesh Nusrat-Sultana, Hasanat MA, Sharmin-Jahan, Mashfiqul-Hasan, Sandesh-Panthi,
Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME)
 Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) 1 Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) Sadrina T. Shaw OMT I Student July 26, 2014 Advisor: Dr. Uwaydat Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) 2
Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) 1 Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) Sadrina T. Shaw OMT I Student July 26, 2014 Advisor: Dr. Uwaydat Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) 2
Speaker Disclosure Statement. " Dr. Tim Maillet and Dr. Vladimir Kozousek have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
 Speaker Disclosure Statement Dr. Tim Maillet and Dr. Vladimir Kozousek have no conflicts of interest to disclose. Diabetes Morbidity Diabetes doubles the risk of stroke. Diabetes quadruples the risk of
Speaker Disclosure Statement Dr. Tim Maillet and Dr. Vladimir Kozousek have no conflicts of interest to disclose. Diabetes Morbidity Diabetes doubles the risk of stroke. Diabetes quadruples the risk of
Study of 189 Cases of Diabetic Retinopathy at CMC Larkana
 Original Article Study of 189 Cases of Diabetic Retinopathy at CMC Larkana Shahid Jamal Siddiqui, Sayed Imtiaz Ali Shah, Abdul Qadir Shaikh, Mohammed Yousuf Depar, Safder Ali Abbassi Pak J Ophthalmol 2007,
Original Article Study of 189 Cases of Diabetic Retinopathy at CMC Larkana Shahid Jamal Siddiqui, Sayed Imtiaz Ali Shah, Abdul Qadir Shaikh, Mohammed Yousuf Depar, Safder Ali Abbassi Pak J Ophthalmol 2007,
Use of eye care services by people with diabetes: the Melbourne Visual Impairment Project
 410 Department of Ophthalmology, University of Melbourne, Melbourne, Australia C A McCarty C W Lloyd-Smith P M Livingston Y L Stanislavsky H R Taylor Victorian WorkCover Authority, Melbourne, Australia
410 Department of Ophthalmology, University of Melbourne, Melbourne, Australia C A McCarty C W Lloyd-Smith P M Livingston Y L Stanislavsky H R Taylor Victorian WorkCover Authority, Melbourne, Australia
Original Article. Akshar V Soni 1*, Ashok Kumar Meena 2 1 PG Resident (3 rd year), 2 Professor & Head, Department of Ophthalmology,
 International Journal of Medical Research Professionals Original Article A One Year Cross Sectional Study for Evaluation of in of Essential Hypertension with High Serum Lipids among Attending Eye OPD,
International Journal of Medical Research Professionals Original Article A One Year Cross Sectional Study for Evaluation of in of Essential Hypertension with High Serum Lipids among Attending Eye OPD,
Prevalence and risk factors associated with retinopathy in diabetic patients at Parirenyatwa Hospital outpatients clinic in Harare, Zimbabwe
 Prevalence and risk factors associated with retinopathy in diabetic patients at Parirenyatwa Hospital outpatients clinic in Harare, Zimbabwe To cite: Machingura PI, Macheka B, Mukona M, Mateveke K, Okwanga
Prevalence and risk factors associated with retinopathy in diabetic patients at Parirenyatwa Hospital outpatients clinic in Harare, Zimbabwe To cite: Machingura PI, Macheka B, Mukona M, Mateveke K, Okwanga
Diabetes mellitus is diagnosed and characterized by chronic hyperglycemia. The effects of
 Focused Issue of This Month Early Diagnosis of Diabetes Mellitus Hyun Shik Son, MD Department of Internal Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine E - mail : sonhys@gmail.com J Korean
Focused Issue of This Month Early Diagnosis of Diabetes Mellitus Hyun Shik Son, MD Department of Internal Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine E - mail : sonhys@gmail.com J Korean
Diabetes and Hypertension
 Diabetes and Hypertension M.Nakhjvani,M.D Tehran University of Medical Sciences 20-8-96 Hypertension Common DM comorbidity Prevalence depends on diabetes type, age, BMI, ethnicity Major risk factor for
Diabetes and Hypertension M.Nakhjvani,M.D Tehran University of Medical Sciences 20-8-96 Hypertension Common DM comorbidity Prevalence depends on diabetes type, age, BMI, ethnicity Major risk factor for
Metabolic Syndrome Update The Metabolic Syndrome: Overview. Global Cardiometabolic Risk
 Metabolic Syndrome Update 21 Marc Cornier, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Division of Endocrinology, Metabolism & Diabetes University of Colorado Denver Denver Health Medical Center The Metabolic
Metabolic Syndrome Update 21 Marc Cornier, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Division of Endocrinology, Metabolism & Diabetes University of Colorado Denver Denver Health Medical Center The Metabolic
Diabesity A Public Health Crisis: AOA Evidence Based Translation to Care Series
 Diabesity A Public Health Crisis: AOA Evidence Based Translation to Care Series Joseph J. Pizzimenti, OD, FAAO Associate Professor Nova Southeastern University The Eye Care Institute pizzimen@nova.edu
Diabesity A Public Health Crisis: AOA Evidence Based Translation to Care Series Joseph J. Pizzimenti, OD, FAAO Associate Professor Nova Southeastern University The Eye Care Institute pizzimen@nova.edu
A screening approach in the primary care setting
 Emerging Treatments and Technologies O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Two-Field Photography Can Identify Patients With Vision-Threatening Diabetic Retinopathy A screening approach in the primary care setting
Emerging Treatments and Technologies O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Two-Field Photography Can Identify Patients With Vision-Threatening Diabetic Retinopathy A screening approach in the primary care setting
300 Biomed Environ Sci, 2018; 31(4):
 300 Biomed Environ Sci, 2018; 31(4): 300-305 Letter to the Editor Combined Influence of Insulin Resistance and Inflammatory Biomarkers on Type 2 Diabetes: A Population-based Prospective Cohort Study of
300 Biomed Environ Sci, 2018; 31(4): 300-305 Letter to the Editor Combined Influence of Insulin Resistance and Inflammatory Biomarkers on Type 2 Diabetes: A Population-based Prospective Cohort Study of
Epidemiology of Diabetes, Impaired Glucose Homeostasis and Cardiovascular Risk. Eberhard Standl
 Epidemiology of Diabetes, Impaired Glucose Homeostasis and Cardiovascular Risk Eberhard Standl European Heart House Sophia Antipolis Thursday, June 17, 2010 IDF Diabetes Atlas 2009: Global Numbers Still
Epidemiology of Diabetes, Impaired Glucose Homeostasis and Cardiovascular Risk Eberhard Standl European Heart House Sophia Antipolis Thursday, June 17, 2010 IDF Diabetes Atlas 2009: Global Numbers Still
PART 1: GENERAL RETINAL ANATOMY
 PART 1: GENERAL RETINAL ANATOMY General Anatomy At Ora Serrata At Optic Nerve Head Fundoscopic View Of Normal Retina What Is So Special About Diabetic Retinopathy? The WHO definition of blindness is
PART 1: GENERAL RETINAL ANATOMY General Anatomy At Ora Serrata At Optic Nerve Head Fundoscopic View Of Normal Retina What Is So Special About Diabetic Retinopathy? The WHO definition of blindness is
Diabetic retinopathy is the
 ORIGINAL ARTICLES Digital Retinal Imaging in a Residencybased Patient-centered Medical Home Robert Newman, MD; Doyle M. Cummings, PharmD; Lisa Doherty, MD, MPH; Nick R. Patel, MD BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES:
ORIGINAL ARTICLES Digital Retinal Imaging in a Residencybased Patient-centered Medical Home Robert Newman, MD; Doyle M. Cummings, PharmD; Lisa Doherty, MD, MPH; Nick R. Patel, MD BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES:
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 48, No. 2, by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN /06/$32.
 Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 48, No. 2, 2006 2006 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/06/$32.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2006.03.043
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 48, No. 2, 2006 2006 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/06/$32.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2006.03.043
Longitudinal Studies of Incidence and Progression of Diabetic Retinopathy Assessed by Retinal Photography in Pima Indians
 Epidemiology/Health Services/Psychosocial Research O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Longitudinal Studies of Incidence and Progression of Diabetic Retinopathy Assessed by Retinal Photography in Pima Indians
Epidemiology/Health Services/Psychosocial Research O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Longitudinal Studies of Incidence and Progression of Diabetic Retinopathy Assessed by Retinal Photography in Pima Indians
Impact of Physical Activity on Metabolic Change in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients
 2012 International Conference on Life Science and Engineering IPCBEE vol.45 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore DOI: 10.7763/IPCBEE. 2012. V45. 14 Impact of Physical Activity on Metabolic Change in Type
2012 International Conference on Life Science and Engineering IPCBEE vol.45 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore DOI: 10.7763/IPCBEE. 2012. V45. 14 Impact of Physical Activity on Metabolic Change in Type
Metabolic Syndrome in Asians
 Metabolic Syndrome in Asians Alka Kanaya, MD Asst. Professor of Medicine, UCSF Asian CV Symposium, November 17, 2007 The Metabolic Syndrome Also known as: Syndrome X Insulin Resistance Syndrome The Deadly
Metabolic Syndrome in Asians Alka Kanaya, MD Asst. Professor of Medicine, UCSF Asian CV Symposium, November 17, 2007 The Metabolic Syndrome Also known as: Syndrome X Insulin Resistance Syndrome The Deadly
Diabetic Retinopatathy
 Diabetic Retinopatathy Jay M. Haynie, OD, FAAO Financial Disclosure I have received honoraria or am on the advisory board for the following companies: Carl Zeiss Meditec Arctic DX Macula Risk Advanced
Diabetic Retinopatathy Jay M. Haynie, OD, FAAO Financial Disclosure I have received honoraria or am on the advisory board for the following companies: Carl Zeiss Meditec Arctic DX Macula Risk Advanced
Review of key findings from the Singapore Malay Eye Study (SiMES-1)
 Singapore Med J 2012; 53(2) : 82 Review of key findings from the Singapore Malay Eye Study (SiMES-1) Rosman M 1,2, FRCSE, FAMS, Zheng Y 2, MD, Lamoureux E 2,3, PhD, Saw SM 1,2,4, MBBS, PhD, Aung T 1,2,5,
Singapore Med J 2012; 53(2) : 82 Review of key findings from the Singapore Malay Eye Study (SiMES-1) Rosman M 1,2, FRCSE, FAMS, Zheng Y 2, MD, Lamoureux E 2,3, PhD, Saw SM 1,2,4, MBBS, PhD, Aung T 1,2,5,
Prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus among Non-Bahraini Workers Registered in Primary Health Care in Bahrain
 Prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus among Non-Bahraini Workers Page 1 of 10 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.25, No.1, March 2003 Prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus among Non-Bahraini Workers Registered in Primary
Prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus among Non-Bahraini Workers Page 1 of 10 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.25, No.1, March 2003 Prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus among Non-Bahraini Workers Registered in Primary
6/10/2016. Hui-Chun Hsu
 Hui-Chun Hsu PhD, RN, CDE Chief, Department of Diabetes Management Lee s Endocrinology Clinic Pingtung, Taiwan Disclosure to Participants Conflict of Interest (COI) and Financial Relationship Disclosures:
Hui-Chun Hsu PhD, RN, CDE Chief, Department of Diabetes Management Lee s Endocrinology Clinic Pingtung, Taiwan Disclosure to Participants Conflict of Interest (COI) and Financial Relationship Disclosures:
Awareness of diabetic retinopathy in Egyptian diabetic patients attending Kasr Al-Ainy outpatient clinic: A cross-sectional study
 Awareness of diabetic retinopathy in Egyptian diabetic patients attending Kasr Al-Ainy outpatient clinic: A cross-sectional study Marwa Mostafa Ahmed (1) Mayssa Ibrahim Ali () Hala Mohamed El-Mofty (3)
Awareness of diabetic retinopathy in Egyptian diabetic patients attending Kasr Al-Ainy outpatient clinic: A cross-sectional study Marwa Mostafa Ahmed (1) Mayssa Ibrahim Ali () Hala Mohamed El-Mofty (3)
Subclinical Diabetic Macular Edema Study
 Diabetic Retinopathy Clinical Research Network Subclinical Diabetic Macular Edema Study Version 2.0 March 21, 2006 Subclinical DME Protocol v2 0 3-21-06.doc Table of Contents Chapter 1. Background Information
Diabetic Retinopathy Clinical Research Network Subclinical Diabetic Macular Edema Study Version 2.0 March 21, 2006 Subclinical DME Protocol v2 0 3-21-06.doc Table of Contents Chapter 1. Background Information
CLINICAL SCIENCES. Results After Lens Extraction in Patients With Diabetic Retinopathy. Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study Report Number 25
 CLINICAL SCIENCES Results After Lens Extraction in Patients With Diabetic Retinopathy Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study Report Number 25 Emily Y. Chew, MD; William E. Benson, MD; Nancy A. Remaley,
CLINICAL SCIENCES Results After Lens Extraction in Patients With Diabetic Retinopathy Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study Report Number 25 Emily Y. Chew, MD; William E. Benson, MD; Nancy A. Remaley,
Fasting Glucose, Obesity, and Metabolic Syndrome as Predictors of Type 2 Diabetes: The Cooper Center Longitudinal Study
 Fasting Glucose, Obesity, and Metabolic Syndrome as Predictors of Type 2 Diabetes: The Cooper Center Longitudinal Study Laura F. DeFina, MD,* Gloria Lena Vega, PhD,Þ David Leonard, PhD,Þ and Scott M. Grundy,
Fasting Glucose, Obesity, and Metabolic Syndrome as Predictors of Type 2 Diabetes: The Cooper Center Longitudinal Study Laura F. DeFina, MD,* Gloria Lena Vega, PhD,Þ David Leonard, PhD,Þ and Scott M. Grundy,
Sight Threatening Diabetic Retinopathy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
 Original Article Sight Threatening Diabetic Retinopathy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Mohammad Memon, Sajjad Ali Surhio, Shahzad Memon, Noor Bakht Nizamani, Khalid Iqbal. Talpur Pak J Ophthalmol 2014, Vol.
Original Article Sight Threatening Diabetic Retinopathy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Mohammad Memon, Sajjad Ali Surhio, Shahzad Memon, Noor Bakht Nizamani, Khalid Iqbal. Talpur Pak J Ophthalmol 2014, Vol.
The Natural History of Diabetic Retinopathy and How Primary Care Makes A Difference
 The Natural History of Diabetic Retinopathy and How Primary Care Makes A Difference We will discuss - How exactly does blood sugar control affect retinopathy? - What are other factors that we measure in
The Natural History of Diabetic Retinopathy and How Primary Care Makes A Difference We will discuss - How exactly does blood sugar control affect retinopathy? - What are other factors that we measure in
Prevalence and associations of overweight among adult women in Sri Lanka: a national survey
 Prevalence and associations of overweight among adult women in Sri Lanka Prevalence and associations of overweight among adult women in Sri Lanka: a national survey Renuka Jayatissa 1, S M Moazzem Hossain
Prevalence and associations of overweight among adult women in Sri Lanka Prevalence and associations of overweight among adult women in Sri Lanka: a national survey Renuka Jayatissa 1, S M Moazzem Hossain
An individual with undiagnosed diabetes is someone whose diabetes has not. Undiagnosed diabetes: Does it matter? Research Recherche
 Undiagnosed diabetes: Does it matter? Research Recherche Dr. Young is Professor and Head, and Dr. Mustard is Associate Professor, Department of Community Health Sciences, University of Manitoba, Winnipeg,
Undiagnosed diabetes: Does it matter? Research Recherche Dr. Young is Professor and Head, and Dr. Mustard is Associate Professor, Department of Community Health Sciences, University of Manitoba, Winnipeg,
Figure S1. Comparison of fasting plasma lipoprotein levels between males (n=108) and females (n=130). Box plots represent the quartiles distribution
 Figure S1. Comparison of fasting plasma lipoprotein levels between males (n=108) and females (n=130). Box plots represent the quartiles distribution of A: total cholesterol (TC); B: low-density lipoprotein
Figure S1. Comparison of fasting plasma lipoprotein levels between males (n=108) and females (n=130). Box plots represent the quartiles distribution of A: total cholesterol (TC); B: low-density lipoprotein
Clinical Care Performance. Financial Year 2012 to 2018
 Clinical Care Performance Financial Year 2012 to 2018 SHP Clinical Care Performance Diabetes Mellitus Hyperlipidemia Hypertension Diabetes Mellitus Find out how our patients are doing for: HbA1C HbA1c
Clinical Care Performance Financial Year 2012 to 2018 SHP Clinical Care Performance Diabetes Mellitus Hyperlipidemia Hypertension Diabetes Mellitus Find out how our patients are doing for: HbA1C HbA1c
Common Causes of Vision Loss
 Common Causes of Vision Loss Learning Objectives To identify the most common causes of vision loss in the United States To differentiate the most common forms of agerelated macular degeneration and diabetic
Common Causes of Vision Loss Learning Objectives To identify the most common causes of vision loss in the United States To differentiate the most common forms of agerelated macular degeneration and diabetic
To identify the risk factors for high prevalence of diabetes and impaired glucose tolerance in Indian rural population
 CMYK 19 ORIGINAL ARTICLE To identify the risk factors for high prevalence of diabetes and impaired glucose tolerance in Indian rural population Sudha S. Deo 1, Avinash Zantye 2, Rajashree Mokal 3, Shilpa
CMYK 19 ORIGINAL ARTICLE To identify the risk factors for high prevalence of diabetes and impaired glucose tolerance in Indian rural population Sudha S. Deo 1, Avinash Zantye 2, Rajashree Mokal 3, Shilpa
Treatment of Diabetic Macular Edema without Intravitreal injections
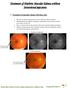 Treatment of Diabetic Macular Edema without Intravitreal injections 1. Treatment of macular edema with laser only This 60 year old female presented on 02-01-2007 for retinal evaluation. She had proliferative
Treatment of Diabetic Macular Edema without Intravitreal injections 1. Treatment of macular edema with laser only This 60 year old female presented on 02-01-2007 for retinal evaluation. She had proliferative
Correlation between fasting insulin and blood pressure in obese and non-obese middle aged Indian diabetic adults
 Volume: 2, Issue: 5, 241-245 May 2015 www.allsubjectjournal.com e-issn: 2349-4182 p-issn: 2349-5979 Impact Factor: 3.762 Raja Reddy P Assistant professor, Department of Physiology, Sri Devaraj Urs Medical
Volume: 2, Issue: 5, 241-245 May 2015 www.allsubjectjournal.com e-issn: 2349-4182 p-issn: 2349-5979 Impact Factor: 3.762 Raja Reddy P Assistant professor, Department of Physiology, Sri Devaraj Urs Medical
DIABETIC RETINOPATHY
 DIABETIC RETINOPATHY C. L. B. Canny, MD FRCSC Diabetic retinopathy is the most serious eye manifestation of diabetes and is responsible for most of the blindness caused by diabetes. Diabetic retinopathy
DIABETIC RETINOPATHY C. L. B. Canny, MD FRCSC Diabetic retinopathy is the most serious eye manifestation of diabetes and is responsible for most of the blindness caused by diabetes. Diabetic retinopathy
The investigation of serum lipids and prevalence of dyslipidemia in urban adult population of Warangal district, Andhra Pradesh, India
 eissn: 09748369, www.biolmedonline.com The investigation of serum lipids and prevalence of dyslipidemia in urban adult population of Warangal district, Andhra Pradesh, India M Estari, AS Reddy, T Bikshapathi,
eissn: 09748369, www.biolmedonline.com The investigation of serum lipids and prevalence of dyslipidemia in urban adult population of Warangal district, Andhra Pradesh, India M Estari, AS Reddy, T Bikshapathi,
Modelling Reduction of Coronary Heart Disease Risk among people with Diabetes
 Modelling Reduction of Coronary Heart Disease Risk among people with Diabetes Katherine Baldock Catherine Chittleborough Patrick Phillips Anne Taylor August 2007 Acknowledgements This project was made
Modelling Reduction of Coronary Heart Disease Risk among people with Diabetes Katherine Baldock Catherine Chittleborough Patrick Phillips Anne Taylor August 2007 Acknowledgements This project was made
Janice Lazear, DNP, FNP-C, CDE DIAGNOSIS AND CLASSIFICATION OF DIABETES
 Janice Lazear, DNP, FNP-C, CDE DIAGNOSIS AND CLASSIFICATION OF DIABETES Objectives u At conclusion of the lecture the participant will be able to: 1. Differentiate between the classifications of diabetes
Janice Lazear, DNP, FNP-C, CDE DIAGNOSIS AND CLASSIFICATION OF DIABETES Objectives u At conclusion of the lecture the participant will be able to: 1. Differentiate between the classifications of diabetes
Percentiles Distribution of CVD Risk Factors in Elderly of Asian Indian Origin: The Santiniketan Longitudinal Study on Aging
 Percentiles Distribution of CVD Risk Factors in Elderly of Asian Indian Origin: The Santiniketan Longitudinal Study on Aging Tamashree Dutta 1, Arnab Ghosh 2 Biomedical research Laboratory, Department
Percentiles Distribution of CVD Risk Factors in Elderly of Asian Indian Origin: The Santiniketan Longitudinal Study on Aging Tamashree Dutta 1, Arnab Ghosh 2 Biomedical research Laboratory, Department
Diabetic Retinopathy
 Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetes can be classified into type 1 diabetes mellitus and type 2 diabetes mellitus, formerly known as insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, and non-insulin diabetes mellitus, respectively.
Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetes can be classified into type 1 diabetes mellitus and type 2 diabetes mellitus, formerly known as insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, and non-insulin diabetes mellitus, respectively.
Andrew J. Barkmeier, MD; Benjamin P. Nicholson, MA; Levent Akduman, MD
 c l i n i c a l s c i e n c e Effectiveness of Laser Photocoagulation in Clinically Significant Macular Edema With Focal Versus Diffuse Parafoveal Thickening on Optical Coherence Tomography Andrew J. Barkmeier,
c l i n i c a l s c i e n c e Effectiveness of Laser Photocoagulation in Clinically Significant Macular Edema With Focal Versus Diffuse Parafoveal Thickening on Optical Coherence Tomography Andrew J. Barkmeier,
Diabetes mellitus: A risk factor affecting visual outcome in branch retinal vein occlusion
 European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 13 no. 7, 2003 / pp. 648-652 Diabetes mellitus: A risk factor affecting visual outcome in branch retinal vein occlusion J. SWART 1,2, J.W. REICHERT-THOEN 1, M.S.
European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 13 no. 7, 2003 / pp. 648-652 Diabetes mellitus: A risk factor affecting visual outcome in branch retinal vein occlusion J. SWART 1,2, J.W. REICHERT-THOEN 1, M.S.
