RANZCO Screening and Referral Pathway for Diabetic Retinopathy #
|
|
|
- Grace Jacobs
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 RANZCO Screening and Referral Pathway for Diabetic Retinopathy # Patient Presents a. Screen for Diabetic Retinopathy every 2 years b. Begin screening at diagnosis of Diabetes * Clinical Modifi ers Yearly screening for Diabetic Retinopathy should be undertaken routinely for patients in the following groups: 1. Duration of diabetes greater than 15 years 2. Poor Glycaemic control (HbA1c > 8% or 64 mmol/mol) 3. Systemic Disease a. Poorly controlled hypertension, blood lipids b. Other diabetic complications (Cardiac disease, cerebrovascular Disease, Renal disease) c. Foot Ulcers (Neuropathy, Peripheral Vascular Disease) 4. Indigenous or from a Non-English speaking background Clinical Assessment a. Clinical History b. Clinical Modifiers * of risk of progression of Diabetic Retinopathy c. Best Corrected Visual Acuity d. Digital Fundus Photography (Non-mydriatic acceptable) Grade Visual Acuity a. 6/9 or worse (unexplained by other pathology): refer to b. Better than 6/9: continue to Grade Image Quality Grade Image Quality a. Inadequate for accurate grading Diabetic Retinopathy: i repeat imaging with dilated pupils. ii If still inadequate: refer to b. Adequate for grading Diabetic Retinopathy Abbreviations: DR Diabetic Retinopathy Hb Haemorrhages Hex Hard exudates IRMA Intraretinal microvascular abnormality MA Microaneurysms NPDR Non-proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy NVD Neovascularisation at disc NVE Neovascularisation elsewhere PDR Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy VB Venous beading Grade Diabetic Retinopathy No Diabetic Retinopathy i. Clinical Modifiers * Present: Repeat screening in 1 year ii. Clinical Modifiers * Absent: Repeat screening in 2 years Communication Communicate the results of Diabetic Retinopathy Screening to the patient and all physicians involved in their care (General Practitioner, Endocrinologist, ) within 2 weeks Grade Diabetic Maculopathy Grade NPDR (risk of PDR) Pregnancy Examination in First Trimester. Action: Routine referral to No Diabetic Maculopathy Non-Centre Involving (Vision Threatening) Definition: MA, Hb, Hex, Thickening within 2 disc diameters of the foveal centre. within 12 weeks Centre Involving (Vision Aff ecting) Definition: MA, Hb, Hex, Thickening within 500 microns (1/3 disc diameter) of the foveal centre. within 4 weeks Mild NPDR Definition: MA only. One year risk PDR: 1-5% Action: repeat screening in 1 year Moderate NPDR Definition: MA + Hb + VB (less than severe NPDR). One year risk of PDR: 12-26% Action: i. Comprehensive Eye and Fundus Examination required ii. Refer to Recommended within 12 weeks iii. Monitoring of Retinopathy coordinated with Severe NPDR Definition: 20 MA + Hb in each quadrant of fundus, VB in 2 quadrants, IRMA in 1 quadrants (4:2:1 rule). One year risk of PDR: 50% Recommended within 4 weeks Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (PDR) Definition: NVD, NVE, Iris Neovascularisation, Vitreous haemorrhage or Pre-retinal haemorrhage. within 1 week Sudden Severe Visual Loss Definition: Vitreous haemorrhage, Retinal Detachment, Rubeotic Glaucoma same day This chart should be read in conjunction with the accompanying document: Clinical Notes for Screening and Referral Pathway for Diabetic Retinopathy. # In New Zealand, a national screening service is in place, free for patients. RANZCO recommends that patients should be referred on to the local service provider, where one is available. The RANZCO Diabetic Retinopathy Screening and Referral Pathway can be used as default where no screening service is available.
2 Clinical Notes for RANZCO Screening and Referral Pathway for Diabetic Retinopathy in Australia This document should accompany the RANZCO Screening and Referral Pathway for Diabetic Retinopathy in Australia chart. 1. Patient Presentation a. All patients with diabetes should undergo screening for diabetic retinopathy at the time of diagnosis of diabetes and then every 2 years if no retinopathy is present (NHMRC 2008, Guideline 4, pg 72). b. Children with Type 1 Diabetes should begin screening for diabetic retinopathy when they reach puberty (NHMRC 2008, Guideline 5, pg 72). c. Pregnant women with a history of diabetes should be screened for the presence of diabetic retinopathy in the first trimester of pregnancy (NHMRC 2008, Guideline 10, pg 72). d. Pregnant women who develop gestational diabetes do not require screening for diabetic retinopathy. e. Recognise and record the source of referral for the patient having diabetic retinopathy screening. f. Patients with diabetes who present opportunistically for optometric review should be screened for diabetic retinopathy and the results of the screening examination communicated to their caring physician in the same way as a patient who is referred specifically for diabetic retinopathy screening. g. Patients already under the care of an ophthalmologist for management of diabetic eye disease do not require repeat screening, provided they are taking part in a regular programme of monitoring and treatment. 2. Screening Examination a. Collect appropriate demographic data i. Source of referral (contact details) ii. Contact details for all caring physicians (General Practitioner, Endocrinologist, ) iii. Date of most recent screening examination for diabetic retinopathy (i.e. interval since last diabetic retinopathy screening examination) (Failure to attend for diabetic retinopathy screening examinations is a risk for vision loss Diabet Med Jul;33(7): doi: /dme Epub 2015 Oct 6. Screening attendance, age group and diabetic retinopathy level at first screen. Scanlon PH1, Stratton IM1, Leese GP2, Bachmann MO3, Land M4, Jones C5, Page 1
3 Ferguson B6; Four Nations Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Study Group.) b. History i. Diabetes duration, medications, control ii. Vascular risk factors: Hypertension, Lipids, Smoking iii. Systemic Disease and complications of Diabetes 1. Cardiovascular 2. Cerebrovascular 3. Renal 4. Neuropathy iv. Past Ocular History 1. Diabetic Retinopathy Treatment 2. Other v. Clinical Modifiers : Risks for progression of Diabetic Retinopathy Patients at higher risk of progression of diabetic retinopathy should be examined yearly if there is no evidence of diabetic retinopathy. (NHMRC 2008, Guideline 6, pg 72) 1. Duration of diabetes greater than 15 years 2. Poor Glycaemic control (HbA1c > 8% or 64 mmol/mol) 3. Systemic Disease a. Poorly controlled hypertension, blood lipids b. Other diabetic complications (Cardiac disease, cerebrovascular Disease, Renal disease) c. Foot Ulcers (Neuropathy, Peripheral Vascular Disease) 4. Pregnancy 5. Indigenous, Non-English speaking c. Assessment of Visual Acuity i. Best corrected visual acuity ii. (Pinhole vision is acceptable) iii. Recent or rapid deterioration in visual acuity should prompt referral even if vision is > 6/9 d. Digital Fundus Photography is the expected standard for fundus examination i. Pupil Dilatation 1. Increases the sensitivity and specificity of detection of diabetic retinopathy 2. Is Not mandatory if a high quality image is obtainable with a non-mydriatic camera or Ultra-Wide Field (UWF) camera (Ophthalmology 2016;123: Identification of Diabetic Retinopathy and Ungradable Image Rate with Ultrawide Field Page 2
4 Imaging in a National Teleophthalmology Program Paolo S. Silva, MD, et al) (Ultra-wide-field imaging in diabetic retinopathy; an overview Khalil Ghasemi Falavarjani et al, Journal of Current Ophthalmology 28 (2016) 57-60) 3. Is Mandatory if a high quality image cannot be obtained with a non-mydriatic camera or UWF camera ii. Recommended images 1. UWF Image 2. Two 45 degree fundus images should be captured: a. Centred on the macula b. Nasal fundus, showing at least 3 disc diameters of the nasal fundus from the edge of the optic disc (this is the standard for the English NDS programme and the NZ programme) iii. OCT Assessment of the macula aids the detection of diabetic macular oedema. However, its use in diabetic retinopathy screening programmes is not yet validated and therefore OCT imaging is not mandatory or recommended as part of a screening examination. 3. Grading of Diabetic Retinopathy a. Should be undertaken by the optometrist who is conducting the screening examination. The screener will therefore also be responsible for determining: i. Screening interval (i.e. interval until the patient should return for the next diabetic retinopathy screening examination) ii. Referral for ophthalmologist review, if required. b. Grading of diabetic retinopathy has 3 elements: i. Visual Acuity ii. Image Quality iii. Severity of Diabetic Retinopathy c. It is recommended that all professionals involved in the screening and grading of diabetic retinopathy should be familiar with the epidemiology and clinical features of diabetic retinopathy. This could involve completion of an on-line diabetic retinopathy grading course (eg University of Melbourne Course). 4. Grading of Visual Acuity a. Referral is recommended if visual acuity is less than 6/9. Substantial centre-involving diabetic macular oedema can be present despite normal vision. Page 3
5 b. If visual acuity has fallen recently, referral should also be considered. 5. Grading of Image Quality a. The image should be of sufficient clarity and field to allow reliable detection of diabetic retinopathy. The small retinal vessels should be visible. b. The images should cover an adequate area of the fundus (two 45 deg images as detailed earlier) 6. Grading of Diabetic Retinopathy a. Grading is based upon the International Clinical Diabetic Retinopathy and Diabetic Macular Oedema Severity Scale. (Proposed International Clinical Diabetic Retinopathy and Diabetic Macular Edema Disease Severity Scales. C. P. Wilkinson et al. Ophthalmology 2003;110: ) b. Grading should focus separately on the two aspects of diabetic retinopathy that cause most vision loss i. Diabetic Macular Oedema ii. Non-proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy and the risk of Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy. iii. Patients assessed to have Moderate Non-proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy should: 1. Have a comprehensive ophthalmic examination including dilated examination of the fundus. a. Many patients with diabetic retinopathy will have changes that are outside the 45 degrees of a standard single field non-mydriatic retinal camera i. 8-15% have retinopathy only present outside this zone ii. 27% with proliferative diabetic retinopathy have neovascularisation outside this zone iii. (Diabetic retinopathy as detected using ophthalmoscopy, a nonmydriatic camera and a standard fundus camera. Klein R, Klein BE, Neider MW, Hubbard LD, Meuer SM, Brothers RJ. Ophthalmology Apr;92(4):485-91) 2. Routine referral to an ophthalmologist with an interest in the management of diabetic retinopathy is recommended, but not mandatory 3. A collaborative regimen of monitoring of patients with moderate non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy could be Page 4
6 established between the screening optometrist and the ophthalmologist. 7. Communication of Results of Screening Examination for Diabetic Retinopathy a. The result of diabetic retinopathy screening should be communicated, in a timely fashion, to the patient, and the patients caring physicians (General Practitioner, Endocrinologist and ). b. The development/presence of diabetic retinopathy is an important finding, with implications for the risk of vision loss, and for the risk of systemic diseases related to diabetes including myocardial infarction, stroke and renal disease (Diabetes Care Jul;30(7): Epub 2007 Mar 26. Diabetic retinopathy and the risk of coronary heart disease: the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study. Cheung N1, Wang JJ, Klein R, Couper DJ, Sharrett AR, Wong TY.) c. This allows appropriate steps to be taken to improve diabetes management (blood glucose control) and the management of other vascular risk factors in order to slow the progression of diabetic retinopathy and the development and progression of other vascular complications of diabetes including myocardial infarction, stroke, renal disease and foot disease. Page 5
FRANZCO, MD, MBBS. Royal Darwin Hospital
 Diabetes and Eye By Dr. Nishantha Wijesinghe FRANZCO, MD, MBBS Consultant Ophthalmologist Royal Darwin Hospital 98% of Diabetics do not need to suffer from severe visual loss Yet Diabetic eye disease is
Diabetes and Eye By Dr. Nishantha Wijesinghe FRANZCO, MD, MBBS Consultant Ophthalmologist Royal Darwin Hospital 98% of Diabetics do not need to suffer from severe visual loss Yet Diabetic eye disease is
Diabetic and the Eye: An Introduction
 Diabetic and the Eye: An Introduction Lawrence Iu FRCSEd (Ophth), FCOphthHK, FHKAM (Ophthalmology) Department of Ophthalmology, Grantham Hospital & Queen Mary Hospital Background Diabetes mellitus (DM)
Diabetic and the Eye: An Introduction Lawrence Iu FRCSEd (Ophth), FCOphthHK, FHKAM (Ophthalmology) Department of Ophthalmology, Grantham Hospital & Queen Mary Hospital Background Diabetes mellitus (DM)
INTRODUCTION AND SYMPTOMS
 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION AND SYMPTOMS Introduction of Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is a potentially blinding complication of diabetes. It is defined as presence of one or more definite
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION AND SYMPTOMS Introduction of Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is a potentially blinding complication of diabetes. It is defined as presence of one or more definite
Diabetic Retinopathy. Barry Emara MD FRCS(C) Giovanni Caboto Club October 3, 2012
 Diabetic Retinopathy Barry Emara MD FRCS(C) Giovanni Caboto Club October 3, 2012 Outline Statistics Anatomy Categories Assessment Management Risk factors What do you need to do? Objectives Summarize the
Diabetic Retinopathy Barry Emara MD FRCS(C) Giovanni Caboto Club October 3, 2012 Outline Statistics Anatomy Categories Assessment Management Risk factors What do you need to do? Objectives Summarize the
DR Screening In Singapore: Achievements & Future Challenges
 DR Screening In Singapore: Achievements & Future Challenges Ecosse Lamoureux Director, Population Research Platform Singapore Eye Research Institute (SERI) Background About 600,000 of Singaporeans aged
DR Screening In Singapore: Achievements & Future Challenges Ecosse Lamoureux Director, Population Research Platform Singapore Eye Research Institute (SERI) Background About 600,000 of Singaporeans aged
National Diabetes Retinal Screening Grading System and Referral Guidelines
 National Diabetes Retinal Screening Grading System and Referral Guidelines 2006 Citation: Ministry of Health. 2006. National Diabetes Retinal Screening Grading System and Referral Guidelines 2006. Wellington:
National Diabetes Retinal Screening Grading System and Referral Guidelines 2006 Citation: Ministry of Health. 2006. National Diabetes Retinal Screening Grading System and Referral Guidelines 2006. Wellington:
Diabetic Retinopathy Screening in Hong Kong. Dr. Rita Gangwani M.S, FRCS (Ophth), FCOphth(HK), FHKAM Eye Institute, The University of Hong Kong
 Diabetic Retinopathy Screening in Hong Kong Dr. Rita Gangwani M.S, FRCS (Ophth), FCOphth(HK), FHKAM Eye Institute, The University of Hong Kong Co-Investigators Prof. David Wong Prof. Sarah McGhee Dr. Wico
Diabetic Retinopathy Screening in Hong Kong Dr. Rita Gangwani M.S, FRCS (Ophth), FCOphth(HK), FHKAM Eye Institute, The University of Hong Kong Co-Investigators Prof. David Wong Prof. Sarah McGhee Dr. Wico
Diabetes and Eye Health more than meets the eye Vision Initiative - in association with PSA
 Diabetes and Eye Health more than meets the eye Vision Initiative - in association with PSA Vision 2020 Australia Vision Initiative RANZCO & OAA (Vic) Proud members of Vision 2020 Australia Outline Vision
Diabetes and Eye Health more than meets the eye Vision Initiative - in association with PSA Vision 2020 Australia Vision Initiative RANZCO & OAA (Vic) Proud members of Vision 2020 Australia Outline Vision
Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME)
 Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) 1 Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) Sadrina T. Shaw OMT I Student July 26, 2014 Advisor: Dr. Uwaydat Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) 2
Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) 1 Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) Sadrina T. Shaw OMT I Student July 26, 2014 Advisor: Dr. Uwaydat Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) 2
Medical Retina 2011 Nicholas Lee
 Medical Retina 2011 Nicholas Lee 1 Diabetic Retinopathy Epidemiology 1000 registered blind each year 2% diabetics registered as blind (8% of all Blind Registrations) 42% with Mild Background DR will progress
Medical Retina 2011 Nicholas Lee 1 Diabetic Retinopathy Epidemiology 1000 registered blind each year 2% diabetics registered as blind (8% of all Blind Registrations) 42% with Mild Background DR will progress
DIABETIC RETINOPATHY
 DIABETIC RETINOPATHY C. L. B. Canny, MD FRCSC Diabetic retinopathy is the most serious eye manifestation of diabetes and is responsible for most of the blindness caused by diabetes. Diabetic retinopathy
DIABETIC RETINOPATHY C. L. B. Canny, MD FRCSC Diabetic retinopathy is the most serious eye manifestation of diabetes and is responsible for most of the blindness caused by diabetes. Diabetic retinopathy
PART 1: GENERAL RETINAL ANATOMY
 PART 1: GENERAL RETINAL ANATOMY General Anatomy At Ora Serrata At Optic Nerve Head Fundoscopic View Of Normal Retina What Is So Special About Diabetic Retinopathy? The WHO definition of blindness is
PART 1: GENERAL RETINAL ANATOMY General Anatomy At Ora Serrata At Optic Nerve Head Fundoscopic View Of Normal Retina What Is So Special About Diabetic Retinopathy? The WHO definition of blindness is
Diabetic Retinopathy
 Diabetic Retinopathy Overview This presentation covers the following topics: Definitions Epidemiology of diabetic retinopathy Evidence for public health approaches Screening for diabetic retinopathy Health
Diabetic Retinopathy Overview This presentation covers the following topics: Definitions Epidemiology of diabetic retinopathy Evidence for public health approaches Screening for diabetic retinopathy Health
FREQUENCY OF DIABETIC RETINOPATHY IN A TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL USING DIGITAL RETINAL IMAGING TECHNOLOGY
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE FREQUENCY OF DIABETIC RETINOPATHY IN A TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL USING DIGITAL RETINAL IMAGING TECHNOLOGY INTRODUCTION As more and more people are being affected with diabetes and with poor
ORIGINAL ARTICLE FREQUENCY OF DIABETIC RETINOPATHY IN A TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL USING DIGITAL RETINAL IMAGING TECHNOLOGY INTRODUCTION As more and more people are being affected with diabetes and with poor
Diagnosis and treatment of diabetic retinopathy. Blake Cooper MD Ophthalmologist Vitreoretinal Surgeon Retina Associates Kansas City
 Diagnosis and treatment of diabetic retinopathy Blake Cooper MD Ophthalmologist Vitreoretinal Surgeon Retina Associates Kansas City Disclosures Consulted for Novo Nordisk 2017,2018. Will be discussing
Diagnosis and treatment of diabetic retinopathy Blake Cooper MD Ophthalmologist Vitreoretinal Surgeon Retina Associates Kansas City Disclosures Consulted for Novo Nordisk 2017,2018. Will be discussing
EyePACS Grading System (Part 3): Detecting Proliferative (Neovascular) Diabetic Retinopathy. George Bresnick MD MPA Jorge Cuadros OD PhD
 EyePACS Grading System (Part 3): Detecting Proliferative (Neovascular) Diabetic Retinopathy George Bresnick MD MPA Jorge Cuadros OD PhD Anatomy of the eye: 3 Normal Retina Retinal Arcades Macula Optic
EyePACS Grading System (Part 3): Detecting Proliferative (Neovascular) Diabetic Retinopathy George Bresnick MD MPA Jorge Cuadros OD PhD Anatomy of the eye: 3 Normal Retina Retinal Arcades Macula Optic
Sponsored by. Shared care and referral pathways. Part 2: diabetes screening leading from the front
 CET CONTINUING Sponsored by 1 CET POINT Shared care and referral pathways Part 2: diabetes screening leading from the front Chris Steele, BSc (Hons), FCOptom, DCLP, DipOC, DipTp(IP), FBCLA The alarming
CET CONTINUING Sponsored by 1 CET POINT Shared care and referral pathways Part 2: diabetes screening leading from the front Chris Steele, BSc (Hons), FCOptom, DCLP, DipOC, DipTp(IP), FBCLA The alarming
One-Field of View vs. Two-Fields of View; Is a Macula Centered Photograph Adequate for Diabetic Retinopathy Screening? -
 International Journal of Ophthalmology & Vision Research Research Article One-Field of View vs. Two-Fields of View; Is a Macula Centered Photograph Adequate for Diabetic Retinopathy Screening? - Mirriam
International Journal of Ophthalmology & Vision Research Research Article One-Field of View vs. Two-Fields of View; Is a Macula Centered Photograph Adequate for Diabetic Retinopathy Screening? - Mirriam
The Human Eye. Cornea Iris. Pupil. Lens. Retina
 The Retina Thin layer of light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye (the film of the camera). Light rays are focused on the retina then transmitted to the brain. The macula is the very small area in
The Retina Thin layer of light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye (the film of the camera). Light rays are focused on the retina then transmitted to the brain. The macula is the very small area in
Diabetic Retinopathy
 Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetes can be classified into type 1 diabetes mellitus and type 2 diabetes mellitus, formerly known as insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, and non-insulin diabetes mellitus, respectively.
Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetes can be classified into type 1 diabetes mellitus and type 2 diabetes mellitus, formerly known as insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, and non-insulin diabetes mellitus, respectively.
Jay M. Haynie, O.D.; F.A.A.O. Olympia Tacoma Renton Kennewick Washington
 Jay M. Haynie, O.D.; F.A.A.O. Olympia Tacoma Renton Kennewick Washington I Jay M. Haynie, OD, FAAO have received honoraria from the following companies: Reichert Technologies Notal Vision Carl Zeiss Meditec
Jay M. Haynie, O.D.; F.A.A.O. Olympia Tacoma Renton Kennewick Washington I Jay M. Haynie, OD, FAAO have received honoraria from the following companies: Reichert Technologies Notal Vision Carl Zeiss Meditec
Management of diabetic eye disease: an overview
 Peter Blows Photographic screening for diabetic eye disease can identify patients who will benefit from laser treatment. BOTSWANA MANAGEMENT Management of diabetic eye disease: an overview Laser for DR
Peter Blows Photographic screening for diabetic eye disease can identify patients who will benefit from laser treatment. BOTSWANA MANAGEMENT Management of diabetic eye disease: an overview Laser for DR
Slide notes: The major chronic complications of diabetes mellitus are described here. Among these, microvascular complications have an important
 1 2 The major chronic complications of diabetes mellitus are described here. Among these, microvascular complications have an important role. They comprise microangiopathy, diabetic retinopathy, diabetic
1 2 The major chronic complications of diabetes mellitus are described here. Among these, microvascular complications have an important role. They comprise microangiopathy, diabetic retinopathy, diabetic
Diabetic Management beyond traditional risk factors and LDL-C control: Can we improve macro and microvascular risks?
 Retinopathy Diabetes has a negative effect on eyes in many ways, increasing the risk of cataracts for example, but the most common and serious ocular complication of diabetes is retinopathy. Diabetic retinopathy
Retinopathy Diabetes has a negative effect on eyes in many ways, increasing the risk of cataracts for example, but the most common and serious ocular complication of diabetes is retinopathy. Diabetic retinopathy
Central Mersey Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Programme. Referring patients for Diabetic Retinopathy Screening
 Central Mersey Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Programme Referring patients for Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Information for GPs in Halton & St Helens, Knowsley and Warrington PCT Version: June 2008 Review
Central Mersey Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Programme Referring patients for Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Information for GPs in Halton & St Helens, Knowsley and Warrington PCT Version: June 2008 Review
Telemedicine Diagnostic Challenges for Diabetic Retinopathy
 Telemedicine Diagnostic Challenges for Diabetic Retinopathy Ingrid Zimmer-Galler, M.D. Johns Hopkins Office of Telemedicine Financial Disclosures None 1 Telemedicine Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Performed
Telemedicine Diagnostic Challenges for Diabetic Retinopathy Ingrid Zimmer-Galler, M.D. Johns Hopkins Office of Telemedicine Financial Disclosures None 1 Telemedicine Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Performed
Diabetic Retinopatathy
 Diabetic Retinopatathy Jay M. Haynie, OD, FAAO Financial Disclosure I have received honoraria or am on the advisory board for the following companies: Carl Zeiss Meditec Arctic DX Macula Risk Advanced
Diabetic Retinopatathy Jay M. Haynie, OD, FAAO Financial Disclosure I have received honoraria or am on the advisory board for the following companies: Carl Zeiss Meditec Arctic DX Macula Risk Advanced
Use of Eye Care Services among Type 2 Diabetic Patients in Laguna
 Original Article Philippine Journal of OPHTHALMOLOGY Use of Eye Care Services among Type 2 Diabetic Patients in Laguna Glenn Carandang, MD, MPH, 1,2, Maria Victoria Rondaris, MD, MPH, 3, and Genejane Adarlo,
Original Article Philippine Journal of OPHTHALMOLOGY Use of Eye Care Services among Type 2 Diabetic Patients in Laguna Glenn Carandang, MD, MPH, 1,2, Maria Victoria Rondaris, MD, MPH, 3, and Genejane Adarlo,
Longitudinal study of a cohort of people with diabetes screened by the Exeter Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Programme
 (2002) 16, 140 145 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 1470-269X/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/eye CLINICAL STUDY Longitudinal study of a cohort of people with diabetes screened by the Exeter Diabetic
(2002) 16, 140 145 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 1470-269X/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/eye CLINICAL STUDY Longitudinal study of a cohort of people with diabetes screened by the Exeter Diabetic
Abstract. Introduction. Original paper. Comparison of screening for diabetic retinopathy by non-specialists and specialists
 Comparison of screening for diabetic retinopathy by non-specialists and specialists Effectiveness of screening for diabetic retinopathy by nonspecialist doctors: the importance of physician-ophthalmologist
Comparison of screening for diabetic retinopathy by non-specialists and specialists Effectiveness of screening for diabetic retinopathy by nonspecialist doctors: the importance of physician-ophthalmologist
Use of eye care services by people with diabetes: the Melbourne Visual Impairment Project
 410 Department of Ophthalmology, University of Melbourne, Melbourne, Australia C A McCarty C W Lloyd-Smith P M Livingston Y L Stanislavsky H R Taylor Victorian WorkCover Authority, Melbourne, Australia
410 Department of Ophthalmology, University of Melbourne, Melbourne, Australia C A McCarty C W Lloyd-Smith P M Livingston Y L Stanislavsky H R Taylor Victorian WorkCover Authority, Melbourne, Australia
Fundus Fluorescein Angiography in Diabetic Retinopathy: Correlation of Angiographic Findings to the Clinical Maculopathy Abstract: Purpose:
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 2 Ver. XII (Feb. 2016), PP 80-88 www.iosrjournals.org Fundus Fluorescein Angiography in Diabetic
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 2 Ver. XII (Feb. 2016), PP 80-88 www.iosrjournals.org Fundus Fluorescein Angiography in Diabetic
Mild NPDR. Moderate NPDR. Severe NPDR
 Diabetic retinopathy Diabetic retinopathy is the most common cause of blindness in adults aged 35-65 years-old. Hyperglycaemia is thought to cause increased retinal blood flow and abnormal metabolism in
Diabetic retinopathy Diabetic retinopathy is the most common cause of blindness in adults aged 35-65 years-old. Hyperglycaemia is thought to cause increased retinal blood flow and abnormal metabolism in
Dr Dianne Sharp Ophthalmologist Retina Specialists, Parnell Greenlane Clinical Centre
 Dr Dianne Sharp Ophthalmologist Retina Specialists, Parnell Greenlane Clinical Centre 11:00-11:55 WS #115: The Revolution in Macular Degeneration Management 12:05-13:00 WS #127: The Revolution in Macular
Dr Dianne Sharp Ophthalmologist Retina Specialists, Parnell Greenlane Clinical Centre 11:00-11:55 WS #115: The Revolution in Macular Degeneration Management 12:05-13:00 WS #127: The Revolution in Macular
Marcus Gonzales, OD, FAAO Cedar Springs Eye Clinic
 Marcus Gonzales, OD, FAAO Cedar Springs Eye Clinic 25.6 million adults 11.3% of the adult population 10.9 million adults 65 years and older 26.9% of this age population 79 million people are Pre-diabetic!!
Marcus Gonzales, OD, FAAO Cedar Springs Eye Clinic 25.6 million adults 11.3% of the adult population 10.9 million adults 65 years and older 26.9% of this age population 79 million people are Pre-diabetic!!
A screening approach in the primary care setting
 Emerging Treatments and Technologies O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Two-Field Photography Can Identify Patients With Vision-Threatening Diabetic Retinopathy A screening approach in the primary care setting
Emerging Treatments and Technologies O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Two-Field Photography Can Identify Patients With Vision-Threatening Diabetic Retinopathy A screening approach in the primary care setting
Diabetic Retinopathy
 Diabetic Retinopathy Secretary for Quality of Care Anne L. Coleman, MD, PhD Academy Staff Nicholas P. Emptage, MAE Doris Mizuiri Shannon Kealey, MLS Flora C. Lum, MD Medical Editor: Design: Approved by:
Diabetic Retinopathy Secretary for Quality of Care Anne L. Coleman, MD, PhD Academy Staff Nicholas P. Emptage, MAE Doris Mizuiri Shannon Kealey, MLS Flora C. Lum, MD Medical Editor: Design: Approved by:
EyePACS Grading System (Part 2): Detecting Presence and Severity of Background (Non-Proliferative) Diabetic Retinopathy Lesion
 EyePACS Grading System (Part 2): Detecting Presence and Severity of Background (Non-Proliferative) Diabetic Retinopathy Lesion George Bresnick MD MPA Jorge Cuadros OD PhD Anatomy of the eye: 3 Normal Retina
EyePACS Grading System (Part 2): Detecting Presence and Severity of Background (Non-Proliferative) Diabetic Retinopathy Lesion George Bresnick MD MPA Jorge Cuadros OD PhD Anatomy of the eye: 3 Normal Retina
Diabetic retinopathy
 research Daniel Ting Jonathon Ng Nigel Morlet Joshua Yuen Antony Clark Hugh Taylor Jill Keefe David Preen Diabetic retinopathy Screening and management by Australian GPs Aim To describe current diabetic
research Daniel Ting Jonathon Ng Nigel Morlet Joshua Yuen Antony Clark Hugh Taylor Jill Keefe David Preen Diabetic retinopathy Screening and management by Australian GPs Aim To describe current diabetic
 measure of your overall performance. An isolated glucose test is helpful to let you know what your sugar level is at one moment, but it doesn t tell you whether or not your diabetes is under adequate control
measure of your overall performance. An isolated glucose test is helpful to let you know what your sugar level is at one moment, but it doesn t tell you whether or not your diabetes is under adequate control
Eyes on Diabetics: How to Avoid Blindness in Diabetic Patient
 Eyes on Diabetics: How to Avoid Blindness in Diabetic Patient Rova Virgana FK Unpad Pusat Mata Nasional RS Mata Cicendo Bandung Eye Center (Hospital and Clinic) PIT IDI Jabar 2018 Keys Facts from WHO
Eyes on Diabetics: How to Avoid Blindness in Diabetic Patient Rova Virgana FK Unpad Pusat Mata Nasional RS Mata Cicendo Bandung Eye Center (Hospital and Clinic) PIT IDI Jabar 2018 Keys Facts from WHO
Diabetes Retinopathy Extension Dataset
 For reference only Do Not Use For more information contact: cdsis@nhs.net Diabetes Retinopathy Extension Dataset March 2006 National Clinical Dataset Development Programme (NCDDP) Support Team Information
For reference only Do Not Use For more information contact: cdsis@nhs.net Diabetes Retinopathy Extension Dataset March 2006 National Clinical Dataset Development Programme (NCDDP) Support Team Information
MANAGING DIABETIC RETINOPATHY. <Your Hospital Name> <Your Logo>
 MANAGING DIABETIC RETINOPATHY It s difficult living with Diabetes Mellitus. Ask any diabetic... Their lives are centered around meal plans, glucose levels, and insulin
MANAGING DIABETIC RETINOPATHY It s difficult living with Diabetes Mellitus. Ask any diabetic... Their lives are centered around meal plans, glucose levels, and insulin
Widefield Retinal Imaging with Auto Fluorescence Technology in the Optometric Practice
 Widefield Retinal Imaging with Auto Fluorescence Technology in the Optometric Practice This course will define ultra-widefield retinal imaging and autofluorescence for the attendee. Will show how it is
Widefield Retinal Imaging with Auto Fluorescence Technology in the Optometric Practice This course will define ultra-widefield retinal imaging and autofluorescence for the attendee. Will show how it is
The College of Optometrists - Learning outcomes for the Professional Certificate in Medical Retina
 Learning outcomes for the Professional Certificate in Medical Retina, incorporating diabetic retinopathy screening and age related macular degeneration The professional certificate is a prerequisite to
Learning outcomes for the Professional Certificate in Medical Retina, incorporating diabetic retinopathy screening and age related macular degeneration The professional certificate is a prerequisite to
Diabetic Retinopathy A Presentation for the Public
 Diabetic Retinopathy A Presentation for the Public Ray M. Balyeat, MD The Eye Institute Tulsa, Oklahoma The Healthy Eye Light rays enter the eye through the cornea, pupil and lens. These light rays are
Diabetic Retinopathy A Presentation for the Public Ray M. Balyeat, MD The Eye Institute Tulsa, Oklahoma The Healthy Eye Light rays enter the eye through the cornea, pupil and lens. These light rays are
DIABETIC RETINOPATHY (DR) PREFERRED PRACTICE PATTERNS (PPP) Philippines 2016
 DIABETIC RETINOPATHY (DR) PREFERRED PRACTICE PATTERNS (PPP) Philippines 2016 The Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) Preferred Practice Patterns (PPP) Philippines: 2016 was prepared by the VitreoRetina Society of
DIABETIC RETINOPATHY (DR) PREFERRED PRACTICE PATTERNS (PPP) Philippines 2016 The Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) Preferred Practice Patterns (PPP) Philippines: 2016 was prepared by the VitreoRetina Society of
Outline. Preventing & Treating Diabetes Related Blindness. Eye Care Center Doctors. Justin Kanoff, MD. Eye Care Center of Northern Colorado
 Outline Preventing & Treating Diabetes Related Blindness Justin Kanoff, MD Eye Care Center of Northern Colorado 303 974 4302 Introduction to Eye Care Center of Northern Colorado How the eye works Eye problems
Outline Preventing & Treating Diabetes Related Blindness Justin Kanoff, MD Eye Care Center of Northern Colorado 303 974 4302 Introduction to Eye Care Center of Northern Colorado How the eye works Eye problems
Diabesity A Public Health Crisis: AOA Evidence Based Translation to Care Series
 Diabesity A Public Health Crisis: AOA Evidence Based Translation to Care Series Joseph J. Pizzimenti, OD, FAAO Associate Professor Nova Southeastern University The Eye Care Institute pizzimen@nova.edu
Diabesity A Public Health Crisis: AOA Evidence Based Translation to Care Series Joseph J. Pizzimenti, OD, FAAO Associate Professor Nova Southeastern University The Eye Care Institute pizzimen@nova.edu
Optical Coherence Tomography in Diabetic Retinopathy. Mrs Samantha Mann Consultant Ophthalmologist Clinical Lead of SEL-DESP
 Optical Coherence Tomography in Diabetic Retinopathy Mrs Samantha Mann Consultant Ophthalmologist Clinical Lead of SEL-DESP Content OCT imaging Retinal layers OCT features in Diabetes Some NON DR features
Optical Coherence Tomography in Diabetic Retinopathy Mrs Samantha Mann Consultant Ophthalmologist Clinical Lead of SEL-DESP Content OCT imaging Retinal layers OCT features in Diabetes Some NON DR features
MAGNITUDE OF DIABETIC EYE DISEASE IN INDIA
 Dear Doctor This booklet contains information about your role as a physician in preventing blindness in your diabetic patients. You are the first point of contact for your diabetic patients. You see them
Dear Doctor This booklet contains information about your role as a physician in preventing blindness in your diabetic patients. You are the first point of contact for your diabetic patients. You see them
For details on measurement and recording of visual acuity, refer to Annex 1. VISION INTERPRETING RESULTS ABSTRACT
 management update on functional decline in older adults 2012 Unit No. 5 VISION Dr Au Eong Kah Guan, Ms Yulianti, Ms Fifiana ABSTRACT Among Singaporean adults of Chinese origin aged 40 to 79 years old,
management update on functional decline in older adults 2012 Unit No. 5 VISION Dr Au Eong Kah Guan, Ms Yulianti, Ms Fifiana ABSTRACT Among Singaporean adults of Chinese origin aged 40 to 79 years old,
Perspectives on Screening for Diabetic Retinopathy. Dr. Dan Samaha, Optometrist, MSc Clinical Lecturer School of Optometry, Université de Montréal
 Perspectives on Screening for Diabetic Retinopathy 1 Dr. Dan Samaha, Optometrist, MSc Clinical Lecturer School of Optometry, Université de Montréal Current standards 2 According to the Canadian Diabetes
Perspectives on Screening for Diabetic Retinopathy 1 Dr. Dan Samaha, Optometrist, MSc Clinical Lecturer School of Optometry, Université de Montréal Current standards 2 According to the Canadian Diabetes
Microaneurysms in the development of diabetic retinopathy (UKPDS 42)
 Diabetologia (1999) 42: 1107±1112 Ó Springer-Verlag 1999 Microaneurysms in the development of diabetic retinopathy (UKPDS 42) E.M. Kohner 1, I. M. Stratton 2, S. J. Aldington 3, R. C. Turner 2, D. R. Matthews
Diabetologia (1999) 42: 1107±1112 Ó Springer-Verlag 1999 Microaneurysms in the development of diabetic retinopathy (UKPDS 42) E.M. Kohner 1, I. M. Stratton 2, S. J. Aldington 3, R. C. Turner 2, D. R. Matthews
Clinical biomicroscopy versus fluorescein angiography: Effectiveness and sensitivity in detecting diabetic retinopathy
 European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 17 no. 1, 2007 / pp. 84-88 Clinical biomicroscopy versus fluorescein angiography: Effectiveness and sensitivity in detecting diabetic retinopathy S.S. KHALAF, M.D.
European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 17 no. 1, 2007 / pp. 84-88 Clinical biomicroscopy versus fluorescein angiography: Effectiveness and sensitivity in detecting diabetic retinopathy S.S. KHALAF, M.D.
D iabetic retinopathy is the leading cause of blindness in
 920 EXTENDED REPORT Effect of mydriasis and different field strategies on digital image screening of diabetic eye disease H Murgatroyd, A Ellingford, A Cox, M Binnie, J D Ellis, C J MacEwen, G P Leese...
920 EXTENDED REPORT Effect of mydriasis and different field strategies on digital image screening of diabetic eye disease H Murgatroyd, A Ellingford, A Cox, M Binnie, J D Ellis, C J MacEwen, G P Leese...
Diabetic Eye Disease Visual Recognition & Interpretation of Clinical Signs
 + Diabetic Eye Disease Visual Recognition & Interpretation of Clinical Signs Quiz created by CLEARVIEW Training Jane Macnaughton MCOptom & Peter Chapman MCOptom FBDO + CET Accreditation C 19106 2 CET Points
+ Diabetic Eye Disease Visual Recognition & Interpretation of Clinical Signs Quiz created by CLEARVIEW Training Jane Macnaughton MCOptom & Peter Chapman MCOptom FBDO + CET Accreditation C 19106 2 CET Points
ZEISS AngioPlex OCT Angiography. Clinical Case Reports
 Clinical Case Reports Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (PDR) Case Report 969 PROLIFERATIVE DIABETIC RETINOPATHY 1 1-year-old diabetic female presents for follow-up of proliferative diabetic retinopathy
Clinical Case Reports Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (PDR) Case Report 969 PROLIFERATIVE DIABETIC RETINOPATHY 1 1-year-old diabetic female presents for follow-up of proliferative diabetic retinopathy
Proposed International Clinical Diabetic Retinopathy and Diabetic Macular Edema Disease Severity Scales
 Proposed International Clinical Diabetic Retinopathy and Diabetic Macular Edema Disease Severity Scales C. P. Wilkinson, MD, 1 Frederick L. Ferris, III, MD, 2 Ronald E. Klein, MD, MPH, 3 Paul P. Lee, MD,
Proposed International Clinical Diabetic Retinopathy and Diabetic Macular Edema Disease Severity Scales C. P. Wilkinson, MD, 1 Frederick L. Ferris, III, MD, 2 Ronald E. Klein, MD, MPH, 3 Paul P. Lee, MD,
This is the author s accepted version, converted from Word format.
 Archived at the Flinders Academic Commons: http://dspace.flinders.edu.au/dspace/ This is the author s accepted version, converted from Word format. The original can be found at: http://www.nature.com/eye/journal/v20/n2/pdf/6701834a.pdf
Archived at the Flinders Academic Commons: http://dspace.flinders.edu.au/dspace/ This is the author s accepted version, converted from Word format. The original can be found at: http://www.nature.com/eye/journal/v20/n2/pdf/6701834a.pdf
Retinal Vein Occlusion (RVO) Treatment pathway- Northeast England. Retinal Vein Occlusion (RVO) with Macular oedema (MO)
 Retinal Vein Occlusion (RVO) Treatment pathway- Northeast England (Royal Victoria Infirmary, Sunderland Eye Infirmary, James Cook University Hospital, Darlington Memorial Hospital, University Hospital
Retinal Vein Occlusion (RVO) Treatment pathway- Northeast England (Royal Victoria Infirmary, Sunderland Eye Infirmary, James Cook University Hospital, Darlington Memorial Hospital, University Hospital
Amber Priority. Image Library
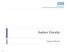 Amber Priority Image Library Amber flag Diabetic Maculopathy (M1) Pre-proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (R2) Old, treated and now inactive DR (R1/M0/P1or R0/M0/P1) Where only partial or incomplete images
Amber Priority Image Library Amber flag Diabetic Maculopathy (M1) Pre-proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (R2) Old, treated and now inactive DR (R1/M0/P1or R0/M0/P1) Where only partial or incomplete images
The economic impact of diabetic macular oedema in Australia
 The economic impact of diabetic macular oedema in Australia Bayer Australia Ltd APRIL 2015 Report prepared by: Deloitte Access Economics Pty Ltd With special thanks to: Ms Julie Heraghty, Macular Disease
The economic impact of diabetic macular oedema in Australia Bayer Australia Ltd APRIL 2015 Report prepared by: Deloitte Access Economics Pty Ltd With special thanks to: Ms Julie Heraghty, Macular Disease
Speaker Disclosure Statement. " Dr. Tim Maillet and Dr. Vladimir Kozousek have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
 Speaker Disclosure Statement Dr. Tim Maillet and Dr. Vladimir Kozousek have no conflicts of interest to disclose. Diabetes Morbidity Diabetes doubles the risk of stroke. Diabetes quadruples the risk of
Speaker Disclosure Statement Dr. Tim Maillet and Dr. Vladimir Kozousek have no conflicts of interest to disclose. Diabetes Morbidity Diabetes doubles the risk of stroke. Diabetes quadruples the risk of
Diabetes Care 24: , 2001
 Pathophysiology/Complications O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Prevalence and Significance of Retinopathy in Subjects With Type 1 Diabetes of Less Than 5 Years Duration Screened for the Diabetes Control and
Pathophysiology/Complications O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Prevalence and Significance of Retinopathy in Subjects With Type 1 Diabetes of Less Than 5 Years Duration Screened for the Diabetes Control and
Case Report Inherent Challenges in Managing Long Standing Refractory Diabetic Macular Edema
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC OPHTHALMOLOGY Case Report Inherent Challenges in Managing Long Standing Refractory Diabetic Macular Edema V Swetha E Jeganathan 1,2 * and Karen Madill 3 1 Department of Ophthalmology,
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC OPHTHALMOLOGY Case Report Inherent Challenges in Managing Long Standing Refractory Diabetic Macular Edema V Swetha E Jeganathan 1,2 * and Karen Madill 3 1 Department of Ophthalmology,
Is OCT-A Needed As An Investigative Tool During The Management Of Diabetic Macular Edema
 Is OCT-A Needed As An Investigative Tool During The Management Of Diabetic Macular Edema Ayman M Khattab MD, FRCS Professor of Ophthalmology Cairo University Diabetic Macular Edema (DME) Diabetic macular
Is OCT-A Needed As An Investigative Tool During The Management Of Diabetic Macular Edema Ayman M Khattab MD, FRCS Professor of Ophthalmology Cairo University Diabetic Macular Edema (DME) Diabetic macular
Diabetes Complications. Rezvan Salehidoost, M.D., Endocrinologist
 Diabetes Complications Rezvan Salehidoost, M.D., Endocrinologist Different Diabetes Complications Macro vascular Micro vascular Infections Macro vascular Complications Macro-vascular Complications Ischemic
Diabetes Complications Rezvan Salehidoost, M.D., Endocrinologist Different Diabetes Complications Macro vascular Micro vascular Infections Macro vascular Complications Macro-vascular Complications Ischemic
7.1 Grading Diabetic Retinopathy
 Chapter 7 DIABETIC RETINOPATHYGRADING -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- A consistent approach to the
Chapter 7 DIABETIC RETINOPATHYGRADING -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- A consistent approach to the
Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies
 Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies Ophthalmology Retinal Imaging Examination Survey Years: 2005 to 2006 SAS Transport File: OPXRET_D.XPT December 2008 NHANES 2005 2006 Data Documentation Exam Component:
Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies Ophthalmology Retinal Imaging Examination Survey Years: 2005 to 2006 SAS Transport File: OPXRET_D.XPT December 2008 NHANES 2005 2006 Data Documentation Exam Component:
Clinical Trials in Diabetic Retinopathy. Harry W. Flynn Jr., M.D. Nidhi Relhan Batra, M.D.
 1 Clinical Trials in Diabetic Retinopathy 2018 Harry W. Flynn Jr., M.D. Nidhi Relhan Batra, M.D. Bascom Palmer Eye Institute 900 N.W. 17th Street Miami, FL 33136 Phone: (305) 326-6118 Fax: (305) 326-6417
1 Clinical Trials in Diabetic Retinopathy 2018 Harry W. Flynn Jr., M.D. Nidhi Relhan Batra, M.D. Bascom Palmer Eye Institute 900 N.W. 17th Street Miami, FL 33136 Phone: (305) 326-6118 Fax: (305) 326-6417
Diabetic Retinopathy WHAT IS DIABETIC RETINOPATHY? WHAT CAUSES DIABETIC RETINOPATHY? WHAT ARE THE STAGES OF DIABETIC RETINOPATHY?
 Diabetic Retinopathy WHAT IS DIABETIC RETINOPATHY? Diabetic retinopathy affects 8 million Americans with diabetes. A leading cause of blindness in American adults, it is caused by damage to the small blood
Diabetic Retinopathy WHAT IS DIABETIC RETINOPATHY? Diabetic retinopathy affects 8 million Americans with diabetes. A leading cause of blindness in American adults, it is caused by damage to the small blood
Diabetic Retinal Screening, Grading, Monitoring and Referral Guidance. Objective
 Diabetic Retinal Screening, Grading, Monitoring and Referral Guidance. Objective The Diabetic Retinal Grading, Monitoring and Referral Guidance 2015 updates all previous guidelines And outlines the key
Diabetic Retinal Screening, Grading, Monitoring and Referral Guidance. Objective The Diabetic Retinal Grading, Monitoring and Referral Guidance 2015 updates all previous guidelines And outlines the key
OCT Assessment of the Vitreoretinal Relationship in CSME
 December 2007 Sonia Rani John et al. - IFIS 375 ORIGINAL ARTICLE OCT Assessment of the Vitreoretinal Relationship in CSME Dr. Manoj S. DNB FRCS, Dr. Unnikrishnan Nair MS DO FRCS, Dr. Gargi Sathish MS Introduction
December 2007 Sonia Rani John et al. - IFIS 375 ORIGINAL ARTICLE OCT Assessment of the Vitreoretinal Relationship in CSME Dr. Manoj S. DNB FRCS, Dr. Unnikrishnan Nair MS DO FRCS, Dr. Gargi Sathish MS Introduction
Diabetic Retinopathy in Primary Care
 Diabetic Retinopathy in Primary Care Epidemiology Diabetes is one of the most serious challenges to health care world rld-wide. According to recent projections it will affect 239 million people e by 2010-
Diabetic Retinopathy in Primary Care Epidemiology Diabetes is one of the most serious challenges to health care world rld-wide. According to recent projections it will affect 239 million people e by 2010-
Study of 189 Cases of Diabetic Retinopathy at CMC Larkana
 Original Article Study of 189 Cases of Diabetic Retinopathy at CMC Larkana Shahid Jamal Siddiqui, Sayed Imtiaz Ali Shah, Abdul Qadir Shaikh, Mohammed Yousuf Depar, Safder Ali Abbassi Pak J Ophthalmol 2007,
Original Article Study of 189 Cases of Diabetic Retinopathy at CMC Larkana Shahid Jamal Siddiqui, Sayed Imtiaz Ali Shah, Abdul Qadir Shaikh, Mohammed Yousuf Depar, Safder Ali Abbassi Pak J Ophthalmol 2007,
A Patient s Guide to Diabetic Retinopathy
 Diabetic Retinopathy A Patient s Guide to Diabetic Retinopathy 840 Walnut Street, Philadelphia PA 19107 www.willseye.org Diabetic Retinopathy 1. Definition Diabetic retinopathy is a complication of diabetes
Diabetic Retinopathy A Patient s Guide to Diabetic Retinopathy 840 Walnut Street, Philadelphia PA 19107 www.willseye.org Diabetic Retinopathy 1. Definition Diabetic retinopathy is a complication of diabetes
Front Line Diabetic Retinopathy What Not to Miss and Why
 Front Line Diabetic Retinopathy What Not to Miss and Why David M Brown MD FACS Clinical Professor of Ophthalmology Blanton Eye Institute, Houston Methodist Hospital Baylor College of Medicine Retina Consultants
Front Line Diabetic Retinopathy What Not to Miss and Why David M Brown MD FACS Clinical Professor of Ophthalmology Blanton Eye Institute, Houston Methodist Hospital Baylor College of Medicine Retina Consultants
Champlain LHIN. Estimated that 55,563 people over age 18 live with diabetes
 Champlain LHIN Estimated that 55,563 people over age 18 live with diabetes Healthy, caring communities supported by health services of choice that achieve results- today and for the future Impact of Diabetes
Champlain LHIN Estimated that 55,563 people over age 18 live with diabetes Healthy, caring communities supported by health services of choice that achieve results- today and for the future Impact of Diabetes
Facts About Diabetic Eye Disease
 Facts About Diabetic Eye Disease Points to Remember 1. Diabetic eye disease comprises a group of eye conditions that affect people with diabetes. These conditions include diabetic retinopathy, diabetic
Facts About Diabetic Eye Disease Points to Remember 1. Diabetic eye disease comprises a group of eye conditions that affect people with diabetes. These conditions include diabetic retinopathy, diabetic
Review. Diabetic retinopathy: global prevalence, major risk factors, screening practices and public health challenges: a review ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION
 bs_bs_banner Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology 2016; 44: 260 277 doi: 10.1111/ceo.12696 Review Diabetic retinopathy: global prevalence, major risk factors, screening practices and public health challenges:
bs_bs_banner Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology 2016; 44: 260 277 doi: 10.1111/ceo.12696 Review Diabetic retinopathy: global prevalence, major risk factors, screening practices and public health challenges:
Diabetic Retinopathy Clinical Research Network
 Diabetic Retinopathy Clinical Research Network Peripheral Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) Lesions on Ultrawide-field Fundus Images and Risk of DR Worsening Over Time Version 4.0 July 21, 2017 peripheral dr lesions
Diabetic Retinopathy Clinical Research Network Peripheral Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) Lesions on Ultrawide-field Fundus Images and Risk of DR Worsening Over Time Version 4.0 July 21, 2017 peripheral dr lesions
The Potential For Teleophthalmology in the Patient-Centered Medical Home Model
 The Potential For Teleophthalmology in the Patient-Centered Medical Home Model Christina Sheppler, PhD Legacy Research Institute Devers Eye Institute NRTRC Telemedicine Conference March 26, 2014 Disclosures
The Potential For Teleophthalmology in the Patient-Centered Medical Home Model Christina Sheppler, PhD Legacy Research Institute Devers Eye Institute NRTRC Telemedicine Conference March 26, 2014 Disclosures
OUR EYES & HOW WE SEE
 OUR EYES & HOW WE SEE UNDERSTAND MORE ABOUT OUR EYES & HOW WE SEE Our Eyes & How We See The eye is our visual gateway to the world. Within it, an array of delicate components labour away to give us the
OUR EYES & HOW WE SEE UNDERSTAND MORE ABOUT OUR EYES & HOW WE SEE Our Eyes & How We See The eye is our visual gateway to the world. Within it, an array of delicate components labour away to give us the
Serious Eye diseases, New treatments. Mr. M. Usman Saeed MBBS, FRCS, FRCOphth Consultant Ophthalmologist
 Serious Eye diseases, New treatments Mr. M. Usman Saeed MBBS, FRCS, FRCOphth Consultant Ophthalmologist 5 major causes of loss of vision Cataracts Glaucoma Macular degeneration Retinal Vein occlusions
Serious Eye diseases, New treatments Mr. M. Usman Saeed MBBS, FRCS, FRCOphth Consultant Ophthalmologist 5 major causes of loss of vision Cataracts Glaucoma Macular degeneration Retinal Vein occlusions
Diabetic Eye Screening
 Diabetic Eye Screening Lorraine Lockwood Engagement Manager Health Intelligence Classification: Internal / Public 26/10/16 Who we are (EDESP) formed on 1 st April 2016 Who should be screened? All patients
Diabetic Eye Screening Lorraine Lockwood Engagement Manager Health Intelligence Classification: Internal / Public 26/10/16 Who we are (EDESP) formed on 1 st April 2016 Who should be screened? All patients
Diabetic retinopathy (DR) was first PROCEEDINGS DIABETIC RETINOPATHY * Ronald Klein, MD, MPH ABSTRACT
 DIABETIC RETINOPATHY * Ronald Klein, MD, MPH ABSTRACT Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is characterized by the development of retinal microaneurysms, hemorrhages, deposits of leaked lipoproteins (hard exudates),
DIABETIC RETINOPATHY * Ronald Klein, MD, MPH ABSTRACT Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is characterized by the development of retinal microaneurysms, hemorrhages, deposits of leaked lipoproteins (hard exudates),
Population base eye screening in Scotland. Challenges of equity and coverage. Graham Leese University of Dundee
 Population base eye screening in Scotland. Challenges of equity and coverage Graham Leese University of Dundee Edinburgh July 16 th 2018 NUMBER OF PATIENTS RECEIVING LASER IN TAYSIDE 300 250 200 Number
Population base eye screening in Scotland. Challenges of equity and coverage Graham Leese University of Dundee Edinburgh July 16 th 2018 NUMBER OF PATIENTS RECEIVING LASER IN TAYSIDE 300 250 200 Number
Diabetic Retinopathy: Managing the Extremes. J. Michael Jumper, MD West Coast Retina
 Diabetic Retinopathy: Managing the Extremes J. Michael Jumper, MD West Coast Retina Case 1: EC 65 y.o. HM No vision complaints Meds: Glyburide Metformin Pioglitazone Va: 20/20 OU 20/20 Case 2: HS 68 y.o.
Diabetic Retinopathy: Managing the Extremes J. Michael Jumper, MD West Coast Retina Case 1: EC 65 y.o. HM No vision complaints Meds: Glyburide Metformin Pioglitazone Va: 20/20 OU 20/20 Case 2: HS 68 y.o.
Year 2 MBChB Clinical Skills Session Ophthalmoscopy. Reviewed & ratified by: Mr M Batterbury Consultant Ophthalmologist
 Year 2 MBChB Clinical Skills Session Ophthalmoscopy Reviewed & ratified by: o Mr M Batterbury Consultant Ophthalmologist Learning objectives o To understand the anatomy and physiology of the external and
Year 2 MBChB Clinical Skills Session Ophthalmoscopy Reviewed & ratified by: o Mr M Batterbury Consultant Ophthalmologist Learning objectives o To understand the anatomy and physiology of the external and
Subclinical Diabetic Macular Edema Study
 Diabetic Retinopathy Clinical Research Network Subclinical Diabetic Macular Edema Study Version 2.0 March 21, 2006 Subclinical DME Protocol v2 0 3-21-06.doc Table of Contents Chapter 1. Background Information
Diabetic Retinopathy Clinical Research Network Subclinical Diabetic Macular Edema Study Version 2.0 March 21, 2006 Subclinical DME Protocol v2 0 3-21-06.doc Table of Contents Chapter 1. Background Information
Central venous occlusion
 Central venous occlusion Central venous occlusion (right eye) There are dark haemorrhages at the macula and all over the retina. Choroidal haemangioma A choroidal haemangioma has salmon pink colour. There
Central venous occlusion Central venous occlusion (right eye) There are dark haemorrhages at the macula and all over the retina. Choroidal haemangioma A choroidal haemangioma has salmon pink colour. There
CLINICAL SCIENCES. Computer Classification of Nonproliferative Diabetic Retinopathy. is characterized by structural
 CLINICAL SCIENCES Computer Classification of Nonproliferative Diabetic Retinopathy Samuel C. Lee, PhD; Elisa T. Lee, PhD; Yiming Wang, MS; Ronald Klein, MD; Ronald M. Kingsley, MD; Ann Warn, MD Objective:
CLINICAL SCIENCES Computer Classification of Nonproliferative Diabetic Retinopathy Samuel C. Lee, PhD; Elisa T. Lee, PhD; Yiming Wang, MS; Ronald Klein, MD; Ronald M. Kingsley, MD; Ann Warn, MD Objective:
10/8/13. the diabetes epidemic: strategies for saving sight. financial disclo$ure. unlabeled-investigative use disclosure
 10/8/13 ASORN 2013 Annual Meeting New Orleans, LA the diabetes epidemic: strategies for saving sight Kate Goldblum, CNP financial disclo$ure I have no financial interests relevant to my presentation. unlabeled-investigative
10/8/13 ASORN 2013 Annual Meeting New Orleans, LA the diabetes epidemic: strategies for saving sight Kate Goldblum, CNP financial disclo$ure I have no financial interests relevant to my presentation. unlabeled-investigative
DR as a Biomarker for Systemic Vascular Complications
 DR as a Biomarker for Systemic Vascular Complications Lihteh Wu MD Asociados de Mácula, Vítreo y Retina de Costa Rica San José, Costa Rica LW65@cornell.edu Disclosures Dr Wu has received lecture fees from
DR as a Biomarker for Systemic Vascular Complications Lihteh Wu MD Asociados de Mácula, Vítreo y Retina de Costa Rica San José, Costa Rica LW65@cornell.edu Disclosures Dr Wu has received lecture fees from
Variation associated with measurement of retinal vessel diameters at different points in the pulse cycle
 57 SCIENTIFIC REPORT Variation associated with measurement of retinal vessel diameters at different points in the pulse cycle M D Knudtson, B E K Klein, R Klein, T Y Wong, L D Hubbard, K E Lee, S M Meuer,
57 SCIENTIFIC REPORT Variation associated with measurement of retinal vessel diameters at different points in the pulse cycle M D Knudtson, B E K Klein, R Klein, T Y Wong, L D Hubbard, K E Lee, S M Meuer,
DIABETIC RETINOPATHY
 THE UK GUIDE DIABETIC RETINOPATHY Everything you need to know about diabetic retinopathy Jaheed Khan BSc (Hons) MBBS MD FRCOphth Fellow of the Royal College of Ophthalmologists Association for Research
THE UK GUIDE DIABETIC RETINOPATHY Everything you need to know about diabetic retinopathy Jaheed Khan BSc (Hons) MBBS MD FRCOphth Fellow of the Royal College of Ophthalmologists Association for Research
VISUAL PROGNOSIS OF PROLIFERATING DIABETIC
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1963) 47, 611. VISUAL PROGNOSIS OF PROLIFERATING DIABETIC RETINOPATHY* BY WILLIAM PARKES BEETHAM From the Harvard Medical School, the Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary, and the New
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1963) 47, 611. VISUAL PROGNOSIS OF PROLIFERATING DIABETIC RETINOPATHY* BY WILLIAM PARKES BEETHAM From the Harvard Medical School, the Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary, and the New
A COMPLETE GUIDE TO THE CLARUS 500 ULTRA-WIDEFIELD RETINAL CAMERA
 A COMPLETE GUIDE TO THE CLARUS 500 ULTRA-WIDEFIELD RETINAL CAMERA BY DANIEL EPSHTIEN, OD Originally published on newgradoptometry.com Ultra-widefield retinal imaging has had a contentious path to acceptance
A COMPLETE GUIDE TO THE CLARUS 500 ULTRA-WIDEFIELD RETINAL CAMERA BY DANIEL EPSHTIEN, OD Originally published on newgradoptometry.com Ultra-widefield retinal imaging has had a contentious path to acceptance
DIABETIC EYE DISEASE: STRENGTHENING SERVICES TO PREVENT BLINDNESS LONDON SCHOOL OF HYGIENE & TROPICAL MEDICINE
 DIABETIC EYE DISEASE: STRENGTHENING SERVICES TO PREVENT BLINDNESS LONDON SCHOOL OF HYGIENE & TROPICAL MEDICINE LONDON. SCHOOLef HYGIENE l?l &TROPICAL ~ MEDICINE GLOSSARY A Acute extraocular muscle palsy
DIABETIC EYE DISEASE: STRENGTHENING SERVICES TO PREVENT BLINDNESS LONDON SCHOOL OF HYGIENE & TROPICAL MEDICINE LONDON. SCHOOLef HYGIENE l?l &TROPICAL ~ MEDICINE GLOSSARY A Acute extraocular muscle palsy
