Angiographic suites equipped with flat panel detector CT
|
|
|
- Maude Malone
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ORIGINAL RESEARCH INTERVENTIONAL Exploring the Value of Using Color-Coded Quantitative DSA Evaluation on Bilateral Common Carotid Arteries in Predicting the Reliability of Intra-Ascending Aorta Flat Detector CT CBV Maps Q. Zhang, R. Xu, Q. Sun, H. Zhang, J. Mao, T. Shan, W. Pan, Y. Deuerling-Zheng, M. Kowarschik, and J. Beilner ABSTRACT BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Cerebral blood volume, acquired with flat panel detector CT by injecting contrast medium into the ascending aorta, enabled real-time acquisition of brain functional information with remarkable reduction of contrast medium usage comparing to an intravenous injection approach. However, individual vasculature and flow variations cause inhomogeneous contrast medium distribution and unexpected asymmetric perfusion for certain patients even without cerebral circulatory disorders. This work aimed at testing the feasibility of using color-coded quantitative DSA to predict the reliability of flat panel detector CT based CBV maps by injecting contrast medium into the ascending aorta by exploring the correlation between measurements of color-coded quantitative DSA and the symmetry of CBV maps. MATERIALS AND METHODS: For 12 patients without perfusion-related cerebral abnormities, color-coded quantitative DSA at the aortic arch and flat panel detector CT based CBV maps by injecting contrast medium into the ascending aorta were acquired. In color-coded quantitative DSA, ROIs were defined on the bilateral common carotid arteries. Time-density curves were extracted, and area under the curve values were calculated. To evaluate brain perfusion symmetry, we defined ROIs on the anterior and middle cerebral artery territories in CBV maps, and quantitative CBV values were extracted. RESULTS: Eight patients demonstrated good perfusion symmetry with relative CBV of , and their relative area under the curve was found to be For the other 4 patients, CBV from the left hemisphere was significantly lower than that from the right with relative CBV of This asymmetric perfusion was confirmed by the color-coded quantitative DSA with relative area under the curve values of CONCLUSIONS: This preliminary study showed good correlation between relative area under the curve from color-coded quantitative DSA and relative CBV from CBV maps. Color-coded quantitative DSA potentially helped sort out patients whose vascular anatomy could support reliable CBV acquisitions of flat detector CT by injecting contrast medium into the ascending aorta. ABBREVIATIONS: AUC area under the curve; CCA common carotid artery; CCQ-DSA color-coded quantitative DSA; CM contrast medium; FPCT flat panel detector CT; IA-FPCT-CBV intra-ascending aorta CM injection to acquire FPCT CBV maps; rauc relative AUC; rcbv relative CBV; TDC time-density curve Received July 21, 2014; accepted after revision October 21. From the Beijing PLA Military General Hospital (Q.Z., R.X., H.Z., J.M., T.S., W.P.), Affiliated Bayi Brain Hospital, Beijing, China; Healthcare Sector (Q.S., J.B.), Siemens Ltd China, Beijing, China; and Siemens AG (Y.D.-Z., M.K.), Erlangen, Germany. Please address correspondence to Qiang Zhang, MD, Beijing PLA Military General Hospital, Affiliated Bayi Brain Hospital, No. 5, Nanmencang, Dongcheng District, Beijing, , China; vivien-sun1226@hotmail.com; and Ruxiang Xu, MD, Beijing PLA Military General Hospital, Affiliated Bayi Brain Hospital, No. 5, Nanmencang, Dongcheng District, Beijing, , China; xuruxiang_bjjz@hotmail.com Angiographic suites equipped with flat panel detector CT (FPCT) for clinical imaging practice have been increasingly accepted during neurointerventions. This technique offers significant advantages in patient management because the patient does not have to be transferred between different clinical units for diagnosis and treatment, improving clinical workflow and increasing patient safety. 1-3 Continuous development in imaging technology has led to significant improvement of image acquisition and postprocessing tools in FPCT. Recently, an important brain perfusion parameter, CBV (milliliter/1000 milliliter), can be acquired by using FPCT. It has been suggested that a color-coded CBV map, which displays hemodynamic information in the capillary level of the entire brain parenchyma, provides a measurement of regional CBV variations and information on suspected ischemia, which is of great value for patients with acute ischemic stroke. 4,5 The CBV value measured with this technique has been validated in a number of clinical studies, proving that the CBV maps generated from FPCT correlated well with CT perfusion maps from multisection CT, which were regarded as ground truth. 6-9 This technique offered the possibility of obtaining functional information and assessing the viability of the brain tissue during interventional procedures Zhang May
2 Table 1: Patient diagnostic and treatment information Patient No. Age (yr) Sex DSA Diagnosis Treatment 1 35 Female Left internal carotid artery aneurysm Stent-assisted coiling 2 49 Male Left internal carotid artery aneurysm Medication 3 46 Male Sagittal sinus thrombus Medication 4 43 Male Sellar mass 5 54 Female Subarachnoid hemorrhage Medication 6 47 Male Further investigation needed Medication 7 50 Male Mild stenosis on right vertebral artery 8 49 Male Further investigation needed 9 37 Male Further investigation needed Medication Male Hemorrhage on left occipital lobe Medication Female Further investigation needed Female Glomus jugulare tumor Medication lumbar puncture the reliability of IA-FPCT-CBV on a patient-specific basis before the acquisition. MATERIALS AND METHODS Patient Selection From January 2013 to November 2013, CCQ-DSA at the aortic arch and IA- FPCT-CBV were acquired for 12 patients (8 men, 4 women; mean age, years) without perfusion-related cerebral abnormities. Detailed diagnostic and treatment information of each patient is listed in Table 1. This study was approved by the hospital ethics committee. Advancements in protocols of contrast medium (CM) injection and image acquisition have been further investigated to achieve an optimized whole-brain CBV map acquisition pipeline by using FPCT A number of studies have demonstrated the feasibility of obtaining CBV maps via intravenous CM injection by using FPCT. However, with this injection protocol, the CM will be diluted during the transit, thus only a small portion of the injected CM contributed to the formation of CBV maps. In contrast, intra-arterial administration has become an attractive method to increase the CM delivery and efficiency and may provide a viable approach for reducing the amount of CM used during FPCT CBV imaging. The feasibility and clinical value of intra-ascending aorta CM injection to acquire FPCT CBV maps (IA-FPCT-CBV) have been tested and confirmed; this approach enabled remarkably reduced CM usage relative to the intravenous CM injection protocol (350 mg I/mL; total amount, 96 ml; 20% diluted versus ml, nondiluted) by using FPCT. Moreover, the reliability of this intra-arterial injection approach has also been validated against conventional CT perfusion imaging with intravenous CM injection. 15 However, nonuniform CM distribution could be observed for a number of patients even without cerebral circulatory disorders, causing unexpected asymmetric perfusion in 2 hemispheres, mainly in the territories of the anterior and middle cerebral arteries. 15,16 A possible explanation for nonuniform distribution could be patients individual vasculature variations at the aortic arch, high blood flow speed, and the limited length of the ascending aorta. Currently, color-coded quantitative digital subtraction angiography (CCQ-DSA) could be generated from a conventional DSA sequence at no additional radiation exposure or CM use, which enhanced the recognition of hemodynamic and morphologic findings. This technique provides a means to display temporal information of contrasted blood flow and attenuation for the duration of the DSA acquisition in a single colorcoded image. Moreover, this image allowed the creation of a time-density curve (TDC) of a CM bolus in user-defined regions, from which quantitative blood flow information could be also extracted This work aimed at exploring the correlation between measurement of CCQ-DSA on the main feeding arteries and symmetry of CBV maps and testing the feasibility of using CCQ-DSA to predict CCQ-DSA and CBV Map Generation All patients received intravenous sedation and local anesthesia. The Seldinger technique was used to place a 5F sheath into the right femoral artery, and a 5F pigtail catheter was inserted and located at the ascending aorta. A routine conventional DSA sequence (7.5 frames/s) at the aortic arch was then acquired by using a rotational FPCT system (Artis zeego; Siemens, Erlangen, Germany). Thirty milliliters of nondiluted CM (350 mg I/mL) was injected by a power injector (600 psi, Avidia; Imaxeon, Silverwater, New South Wales, Australia) through the pigtail catheter at an injection rate of 15 ml/s. With a commercially available postprocessing software (syngo iflow; Siemens), this DSA sequence was converted to a CCQ-DSA image, which quantitatively showed the blood flow dynamics. In addition, a CBV map was acquired by using the same FPCT system. Twenty milliliters of CM diluted by 76 ml of saline to a total volume of 96 ml was injected with a rate of 6 ml/s during 16 seconds. The generation of the CBV map consisted of two 3D image-acquisition steps, including a mask run followed by a fill run. To ensure maximum brain tissue and intravascular contrast enhancement, we started the fill run with an 8-second x-ray delay. During the 3D image acquisition, the C-arm rotated for 200 in 8 seconds, with an angle increment of 0.5. A total of 397 projection images were generated with an x-ray dose of 0.36 Gy/frame. The reconstruction was performed by using commercially available software (syngo DynaPBV Neuro; Siemens). The fully automatic reconstruction algorithm has been extensively described in detail in another work. 20 Quantitative Evaluation The CCQ-DSA and CBV imaging results were quantitatively reviewed by 2 experienced neuroradiologists, respectively. On the basis of the DSA sequence (Fig 1A), rectangular ROIs were defined on symmetric bilateral common carotid arteries (CCAs) on the generated CCQ-DSA image. The ROIs were placed approximately 8 10 cm away from the aortic arch, with their sizes approximately 0.02 cm 2. This selected ROI area could completely cover the artery cross-sections in the radial direction for a short distance, thus having minimal influence from superimposing vessels (Fig 1B). The corresponding TDCs, determined by the number and intensity of colored pixels inside the ROI, were extracted (Fig 1C). The area under curve (AUC) could be calculated from AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 36: May
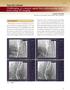
3 FIG 1. As an example, in patient 5, a conventional DSA sequence at 5 time instances shows the course of CM passing through the aortic arch and its major branching arteries (A). In the generated CCQ-DSA image, ROIs are defined on bilateral CCAs as red (ROI-R) and green (ROI-L) rectangles (B). Corresponding TDCs were extracted from the defined ROI, showing good correlation between the 2 curves (C). On the CBV maps (D), 3 planes were selected (upper panel). The lower panel corresponded to the above planes (left, plane 1; middle, plane 2; right, plane 3), with ROIs defined in pairs (ROI-R on the right hemisphere and ROI-L on the left hemisphere) on each plane covering characteristic anatomic structures to examine rcbv on 2 hemispheres: the frontal and parietal lobes in plane 1; frontal lobe and basal ganglia region in plane 2; and temporal lobe in plane Zhang May
4 the TDC, indicating the amount of contrasted blood flowing through the selected ROI during the image acquisition. The AUC of the TDC on the right CCA was regarded as the baseline and was set as reference value 1, and the AUC of the TDC on the left CCA was calculated relative to it. Next, the ratio between the AUC extracted from 2 CCAs, called relative AUC (rauc), was then obtained by 1) rauc AUC _left CCA /AUC _right CCA, where AUC _left CCA and AUC _right CCA were the areas calculated under the TDC profile from the ROI on the left and the right CCA, respectively. To evaluate the symmetry of brain perfusion, we selected 3 anatomically characteristic planes crossing the frontal, parietal, and temporal lobes and basal ganglia regions. Circular ROIs with an area of approximately 3.0 cm 2 were manually defined on axial planes to cover the anterior and middle cerebral artery territories of both hemispheres, with major vessels excluded (Fig 1D). A spatially averaged CBV value in the ROI was extracted, and relative CBV (rcbv) values were then calculated by 2) rcbv CBV _left hemisphere /CBV _right hemisphere, Table 2: From the CCQ-DSA images, AUC values calculated for TDCs extracted from ROIs on bilateral CCAs and the AUC ratio between left and right sides Patient No. AUC-ROI-R (Reference) AUC-ROI-L rauc Note: R indicates right; L, left. where CBV _left hemisphere and CBV _right hemisphere were the mean CBV values extracted from the ROIs on the left and the right hemispheres, respectively. Thus, perfusion symmetry (1.0 for perfect symmetry) in different anatomic regions could be quantitatively examined. RESULTS IA-FPCT-CBV was technically successful, and all the resulting image quality was adequate for evaluation. No adverse physiologic changes caused by CBV map acquisitions were detected for any patient. From the CCQ-DSA images, AUC values for bilateral CCA were extracted from the TDC and are summarized in Table 2. Quantitative CBV evaluation results are listed in Table 3. For patients 1 7 and 12, CCQ-DSA evaluation showed rauc values of From CBV maps, rcbv was found to be An exemplary case (patient 5) was shown in Fig 1. There was good correlation between the profiles of the TDC extracted from the 2 ROIs, including the wash-in, wash-out phase; pulsatile flow pattern; peak intensity; and duration of contrast enhancement. On the generated CBV maps, correspondence on the perfusion level on 2 hemispheres was visually evident. Quantitative CBV evaluation was performed in 3 planes in the ROIs defined at the frontal, parietal, and temporal lobes and basal ganglia; this evaluation also showed excellent perfusion symmetry for each pair of ROIs. In 4 patients (patients 8 11), inhomogeneous CM distribution on bilateral CCAs, with an rauc value of could be observed. Table 3 shows that CBV from the left hemisphere was significantly lower than that from the right hemisphere in certain regions for these patients with an rcbv of Imaging results of patient 11 are shown as an exemplary case (Fig 2). Differences could be easily detected for TDC comparison. Although the shape of 2 TDCs remained similar, the magnitude was much lower for the curve from the left CCA, resulting in an AUC deviation of 24%. Large CBV variations in multiple regions on 2 hemispheres could be also detected by visual inspection on the CBV Table 3: Quantitative CBV measurement and perfusion symmetry of patients Patient No. Planes Plane 1 ROI1-R ROI1-L rcbv ROI2-R ROI2-L rcbv Plane 2 ROI1-R ROI1-L rcbv ROI2-R ROI2-L rcbv Plane 3 ROI1-R ROI1-L rcbv rcbv with most asymmetry a 0.77 a 0.76 a 0.70 a 0.90 a Significant asymmetric perfusion was detected. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 36: May
5 FIG 2. As an example, in patient 11, conventional DSA sequence at 5 time instances shows the course of CM passing through the aortic arch and its major branching arteries (A). In the generated CCQ-DSA image, ROIs were defined on bilateral CCAs (B). Corresponding TDCs were extracted from the defined ROIs, showing large deviations in magnitude between the 2 curves (C). CBV maps evidently show low perfusion levels in plane 1 (lower panel, left) in the parietal lobe, in plane 2 (lower panel, middle) in both the frontal lobe and basal ganglia region, and in plane 3 (lower panel, right) in the temporal lobe (D). 964 Zhang May
6 FIG 3. Linear regression analysis shows that rauc and rcbv with the most asymmetry have approximately a linear relationship. map. The CBV value in the left hemisphere was significantly lower than that from the right hemisphere with the maximum CBV deviation close to 30%. Specifically, a low perfusion level was mainly detected in plane 1 in the parietal lobe (ROI2), in plane 2 in both the frontal lobe (ROI1) and basal ganglia region (ROI2), and in plane 3 in the temporal lobe (ROI1). Asymmetric perfusion between 2 hemispheres may only appear in some regions. For each patient, the rcbv with the largest deviation from the perfect symmetry through all the examined regions was used and scatterplots were created against the rauc. In Fig 3, the relationships between rauc and rcbv were quantified by linear logistic regression. There was no point lying far from the cluster of data points or far from the regression line, and the high correlation (R ) indicated an approximate linear relationship between rauc and rcbv. DISCUSSION It has been previously confirmed that CBV maps acquired with FPCT could obtain functional information of the entire brain immediately in the angiographic suite for patients undergoing diagnostic angiography or endovascular treatment. Compared with CT- and FPCT-based perfusion imaging by using an intravenous injection protocol, the IA-FPCT-CBV technique not only enabled real-time monitoring of the brain function, assessments of perfusion parameters during an intervention, and direct evaluation of the treatment outcome but also achieved significant reduction of CM dose, thus potentially minimizing the CM-induced side effects. The major challenge of this intra-arterial injection protocol was the unexpected asymmetry of perfusion for certain patients between the left/right hemispheres shown on the generated CBV map, which may be caused by nonuniform CM distribution. In fact, for those patients who showed perfusion asymmetry, it could sometimes be observed that a slightly larger portion of CM from the catheter tip flowed through the ostium of the brachiocephalic trunk and then fed into the right CCA and thus the right hemisphere. Due to the high complexity of the blood flow and CM distributions during transit, it is challenging for the clinicians to visually detect and analyze parameters such as AUC on a conventional monochromatic DSA sequence; this challenge may be an important indicator for physiologic variations. The use of CCQ-DSA with parametric color-coding not only allowed easier visual evaluation but also enabled quantification and estimation of the blood supply to the brain. In our study, the feasibility of determining CBV symmetry before the acquisition on the basis of CCQ-DSA assessment was investigated. With CCQ-DSA, measurement of the AUC of the TDC in ROIs placed on symmetric CCAs was immediate and quantitative. The CCQ-DSA was generated from the routinely acquired DSA sequence on the aortic arch; thus, no additional CM and x-ray dose was needed. The presented results showed that on the CBV maps, there were no significant differences in CBV values from characteristic regions on the left and right hemispheres for 8 patients. For the other 4 patients, the CBV value was higher on the right hemisphere in 1 examined region. The same tendency was observed in the AUC measurements of the TDC extracted from bilateral CCAs. We have shown that there is an almost linear relationship between rauc and rcbv with the most asymmetry, proving that for a specific patient, the use of CCQ-DSA was feasible for predicting whether a reliable IA-FPCT-CBV map could be generated that correctly reflected the perfusion level without inherent bias induced by an intra-arterial injection protocol. Therefore, the combination of CCQ-DSA could help to sort out patients who are/are not suitable for undergoing IA-FPCT- CBV acquisitions. For those patients who have shown a large discrepancy of AUC values on the bilateral CCAs, an intravenous injection protocol is suggested, or other advanced intra-arterial injection protocols enabling uniform CM distribution need to be further investigated and developed. The restrictions and limitations of this study should be also mentioned. First, a complete bolus transport consisting of wash-in and wash-out through defined ROIs on CCAs should be included during image acquisition to ensure a correct AUC calculation and comparison. Therefore, the DSA acquisition time has to be long enough, typically 8 10 seconds. Besides, due to the high flow rate in the CCA, the DSA acquisition frame rate of 7.5 frames/s is suggested to make sure that major flow characteristics are well-captured. Second, the CCQ-DSA image is based on the subtraction of a sequence of angiographic images; thus, any patient motion will cause degradation of image quality and subsequent inaccuracies in the quantification results. Therefore, the patient must be well-stabilized to minimize motion-induced artifacts during image acquisition. Third, the catheter position should be carefully controlled with the tip close to the aortic valve. Otherwise, different CM transport distances may bring deviations across patients. Fourth, current available technology of angiographic systems allows only CBV measurement. However, it has been previously demonstrated that cerebral blood flow and cerebral perfusion reserve have also been valuable parameters for achieving comprehensive evaluation on the brain functional changes. Fifth, the number of patients recruited into this study is small; hence, the feasibility of this method was only demonstrated preliminarily. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 36: May
7 CONCLUSIONS IA-FPCT-CBV map acquisition could allow whole-brain perfusion imaging directly in the angiographic suite, but with significantly less CM compared with an intravenous-injection protocol. This preliminary study showed good correlation between the AUC of the TDC at the CCA from CCQ-DSA images and measurements on CBV maps. CCQ-DSA evaluation may be applied before the CBV acquisition in clinics, to help decide whether patients are suitable for undergoing IA-FPCT-CBV acquisitions. Disclosures: Qi Sun OTHER RELATIONSHIPS: employee of Siemens, China. Yu Deuerling-Zheng OTHER RELATIONSHIPS: employee of Siemens. Markus Kowarschik OTHER RELATIONSHIPS: employee of Siemens. Janina Beilner OTHER RELATIONSHIPS: employee of Siemens, China. REFERENCES 1. Kalender W, Kyriakou Y. Flat-detector CT (FD-CT). Eur Radiol 2007;17: Fahrig R, Fox S, Lownie S, et al. Use of a C-arm system to generate true 3-D computed rotational angiograms: preliminary in vitro and in vivo results. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1997;l18: Akpek S, Brunner T, Benndorf G, et al. Three-dimensional imaging and cone beam volume CT in C-arm angiography with flat panel detector. Diagn Interv Radiol 2005;11: Ahmed AS, Zellerhoff M, Strother CM, et al. C-arm CT measurement of cerebral blood volume: an experimental study in canines. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2009;30: Bley T, Strother CM, Pulfer KA, et al. C-arm CT measurement of cerebral blood volume in ischemic stroke: an experimental study in canines. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2010;31: Struffert T, Deuerling-Zheng Y, Kloska S, et al. Flat detector CT in the evaluation of brain parenchyma, intracranial vasculature, and cerebral blood volume: a pilot study in patients with acute symptoms of cerebral ischemia. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2010;31: Struffert T, Deuerling-Zheng Y, Engelhorn T, et al. Feasibility of cerebral blood volume mapping by flat panel detector CT in the angiography suite: first experience in patients with acute middle cerebral artery occlusions. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2012;33: Fiorella D, Turk A, Chaudry I, et al. A prospective, multicenter pilot study investigating the utility of flat detector derived parenchymal blood volume maps to estimate cerebral blood volume in stroke patients. J Neurointerv Surg 2014;6: Struffert T, Deuerling-Zheng Y, Kloska S, et al. Cerebral blood volume imaging by flat detector computed tomography in comparison to conventional multislice perfusion CT. Eur Radiol 2011;21: Lin CJ, Yu M, Hung SC, et al. In-room assessment of cerebral blood volume for guidance during intra-arterial thrombolytic therapy. Interv Neuroradiol 2012;18: Fieselmann A, Ganguly A, Deuerling-Zheng Y, et al. Automatic measurement of contrast bolus distribution in carotid arteries using a C-arm angiography system to support interventional perfusion imaging. In: Proceedings of SPIE Medical Imaging 2011: Visualization, Image-Guided Procedures, and Modeling, Orlando, Florida. March 1, 2011;7964:79641W 12. Klostranec JM, Ehtiati T, Rao S, et al. Comparison of aortic arch and intravenous contrast injection techniques for C-arm cone beam CT. Acad Radiol 2013;20: Yasuda R, Royalty K, Pulfer K, et al. C-arm CT measurement of cerebral blood volume using intra-arterial injection of contrast medium: an experimental study in canines. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2012;33: Ganguly A, Fieselmann A, Marks M, et al. Cerebral CT perfusion using an interventional C-arm imaging system: cerebral blood flow measurements. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2011;32: Zhang Q, Wang B, Han J, et al. Feasibility study of perfusion imaging using flat detector CT with an intra-arterial injection protocol compared to conventional multi-slice perfusion CT with an intravenous injection protocol. Interv Neuroradiol 2013;19: Itokawa H, Moriya M, Fujimoto M, et al. Assessment of C-arm cerebral blood volume maps obtained through aortic arch injection with 50% and 30% diluted contrast medium. In: Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the American Society of Neuroradiology, San Diego, California. May 18 23, 2013: Strother CM, Bender F, Deuerling-Zheng Y, et al. Parametric color coding of digital subtraction angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2010;31: Lin CJ, Hung SC, Guo WY, et al. Monitoring peri-therapeutic cerebral circulation time: a feasibility study using color-coded quantitative DSA in patients with steno-occlusive arterial disease. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2012;33: Struffert T, Ott S, Kowarschik M, et al. Measurement of quantifiable parameters by time-density curves in the elastase-induced aneurysm model: first results in the comparison of a flow diverter and a conventional aneurysm stent. Eur Radiol 2013;23: Zellerhoff M, Deuerling-Zheng Y, Strother CM, et al. Measurement of cerebral blood volume using angiographic C-arm systems. In: Proceedings of SPIE Medical Imaging 2009: Biomedical Applications in Molecular, Structural, and Functional Imaging, Orlando, Florida. February 27, 2009;7262:72620H 966 Zhang May
There is good evidence for the use of color in tasks that. Parametric Color Coding of Digital Subtraction Angiography ORIGINAL RESEARCH
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH C.M. Strother F. Bender Y. Deuerling-Zheng K. Royalty K.A. Pulfer J. Baumgart M. Zellerhoff B. Aagaard-Kienitz D.B. Niemann M.L. Lindstrom Parametric Color Coding of Digital Subtraction
ORIGINAL RESEARCH C.M. Strother F. Bender Y. Deuerling-Zheng K. Royalty K.A. Pulfer J. Baumgart M. Zellerhoff B. Aagaard-Kienitz D.B. Niemann M.L. Lindstrom Parametric Color Coding of Digital Subtraction
Flat detector CT (FD-CT) equipped angiographic systems are
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH INTERVENTIONAL Dynamic Angiography and Perfusion Imaging Using Flat Detector CT in the Angiography Suite: A Pilot Study in Patients with Acute Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusions T. Struffert,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH INTERVENTIONAL Dynamic Angiography and Perfusion Imaging Using Flat Detector CT in the Angiography Suite: A Pilot Study in Patients with Acute Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusions T. Struffert,
Modifi ed CT perfusion contrast injection protocols for improved CBF quantifi cation with lower temporal sampling
 Investigations and research Modifi ed CT perfusion contrast injection protocols for improved CBF quantifi cation with lower temporal sampling J. Wang Z. Ying V. Yao L. Ciancibello S. Premraj S. Pohlman
Investigations and research Modifi ed CT perfusion contrast injection protocols for improved CBF quantifi cation with lower temporal sampling J. Wang Z. Ying V. Yao L. Ciancibello S. Premraj S. Pohlman
Making the difference with Live Image Guidance
 AneurysmFlow Interventional X-ray Making the difference with Live Image Guidance Enhance insight into cerebral aneurysm flow Key benefits Visualizes blood flow patterns in the parent vessel and aneurysm
AneurysmFlow Interventional X-ray Making the difference with Live Image Guidance Enhance insight into cerebral aneurysm flow Key benefits Visualizes blood flow patterns in the parent vessel and aneurysm
Making the difference with Live Image Guidance
 AneurysmFlow Interventional X-ray Making the difference with Live Image Guidance Enhance insight into cerebral aneurysm flow Key benefits Visualizes blood flow patterns in the parent vessel and aneurysm
AneurysmFlow Interventional X-ray Making the difference with Live Image Guidance Enhance insight into cerebral aneurysm flow Key benefits Visualizes blood flow patterns in the parent vessel and aneurysm
Combined Anatomical and Functional Imaging with Revolution * CT
 GE Healthcare Case studies Combined Anatomical and Functional Imaging with Revolution * CT Jean-Louis Sablayrolles, M.D. Centre Cardiologique du Nord, Saint-Denis, France Case 1 Whole Brain Perfusion and
GE Healthcare Case studies Combined Anatomical and Functional Imaging with Revolution * CT Jean-Louis Sablayrolles, M.D. Centre Cardiologique du Nord, Saint-Denis, France Case 1 Whole Brain Perfusion and
Lung Perfusion Analysis New Pathways in Lung Imaging. Case Study Brochure PLA 309 Hospital
 Lung Perfusion Analysis New Pathways in Lung Imaging Case Study Brochure PLA 309 Hospital http://www.toshibamedicalsystems.com Toshiba Medical Systems Corporation 2012 all rights reserved. Design and specifications
Lung Perfusion Analysis New Pathways in Lung Imaging Case Study Brochure PLA 309 Hospital http://www.toshibamedicalsystems.com Toshiba Medical Systems Corporation 2012 all rights reserved. Design and specifications
1Pulse sequences for non CE MRA
 MRI: Principles and Applications, Friday, 8.30 9.20 am Pulse sequences for non CE MRA S. I. Gonçalves, PhD Radiology Department University Hospital Coimbra Autumn Semester, 2011 1 Magnetic resonance angiography
MRI: Principles and Applications, Friday, 8.30 9.20 am Pulse sequences for non CE MRA S. I. Gonçalves, PhD Radiology Department University Hospital Coimbra Autumn Semester, 2011 1 Magnetic resonance angiography
Published August 16, 2012 as /ajnr.A3243
 Published August 16, 2012 as 10.3174/ajnr.A3243 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Y. Shinohara M. Sakamoto H. Takeuchi T. Uno T. Watanabe T. Kaminou T. Ogawa Subarachnoid Hyperattenuation on Flat Panel Detector Based
Published August 16, 2012 as 10.3174/ajnr.A3243 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Y. Shinohara M. Sakamoto H. Takeuchi T. Uno T. Watanabe T. Kaminou T. Ogawa Subarachnoid Hyperattenuation on Flat Panel Detector Based
Automatic Ascending Aorta Detection in CTA Datasets
 Automatic Ascending Aorta Detection in CTA Datasets Stefan C. Saur 1, Caroline Kühnel 2, Tobias Boskamp 2, Gábor Székely 1, Philippe Cattin 1,3 1 Computer Vision Laboratory, ETH Zurich, 8092 Zurich, Switzerland
Automatic Ascending Aorta Detection in CTA Datasets Stefan C. Saur 1, Caroline Kühnel 2, Tobias Boskamp 2, Gábor Székely 1, Philippe Cattin 1,3 1 Computer Vision Laboratory, ETH Zurich, 8092 Zurich, Switzerland
Spontaneous Recanalization after Complete Occlusion of the Common Carotid Artery with Subsequent Embolic Ischemic Stroke
 Original Contribution Spontaneous Recanalization after Complete Occlusion of the Common Carotid Artery with Subsequent Embolic Ischemic Stroke Abstract Introduction: Acute carotid artery occlusion carries
Original Contribution Spontaneous Recanalization after Complete Occlusion of the Common Carotid Artery with Subsequent Embolic Ischemic Stroke Abstract Introduction: Acute carotid artery occlusion carries
Detectability of unruptured intracranial aneurysms on thinslice non-contrast-enhanced CT
 Detectability of unruptured intracranial aneurysms on thinslice non-contrast-enhanced CT Poster No.: C-9 Congress: ECR 5 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Nakadate, Y. Iwasa, M. Kishino, U. Tateishi;
Detectability of unruptured intracranial aneurysms on thinslice non-contrast-enhanced CT Poster No.: C-9 Congress: ECR 5 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Nakadate, Y. Iwasa, M. Kishino, U. Tateishi;
A P ilots tudy inevaluationof DysfunctionalHem odialysisvascular A ccessu sings yngoiflow
 A P ilots tudy inevaluationof DysfunctionalHem odialysisvascular A ccessu sings yngoiflow R u Yu T AN,Fu ChiehT S AI,T zet eccho N G,ApporvaGO GN A,KianGuanL EE,S uh ChienP AN G,AliciaHuiyingO ng,chiehs
A P ilots tudy inevaluationof DysfunctionalHem odialysisvascular A ccessu sings yngoiflow R u Yu T AN,Fu ChiehT S AI,T zet eccho N G,ApporvaGO GN A,KianGuanL EE,S uh ChienP AN G,AliciaHuiyingO ng,chiehs
Place for Interventional Radiology in Acute Stroke
 Place for Interventional Radiology in Acute Stroke Dr Lakmalie Paranahewa MBBS, MD(Radiology), FRCR Consultant Interventional Radiologist Asiri Group of Hospitals Objectives Imaging in Stroke Neurovascular
Place for Interventional Radiology in Acute Stroke Dr Lakmalie Paranahewa MBBS, MD(Radiology), FRCR Consultant Interventional Radiologist Asiri Group of Hospitals Objectives Imaging in Stroke Neurovascular
Whole brain CT perfusion maps with paradoxical low mean transit time to predict infarct core
 Whole brain CT perfusion maps with paradoxical low mean transit time to predict infarct core Poster No.: B-292 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Topic: Neuro Authors: S. Chakraborty, M. E. Ahmad,
Whole brain CT perfusion maps with paradoxical low mean transit time to predict infarct core Poster No.: B-292 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Topic: Neuro Authors: S. Chakraborty, M. E. Ahmad,
Case Report 1. CTA head. (c) Tele3D Advantage, LLC
 Case Report 1 CTA head 1 History 82 YEAR OLD woman with signs and symptoms of increased intra cranial pressure in setting of SAH. CT Brain was performed followed by CT Angiography of head. 2 CT brain Extensive
Case Report 1 CTA head 1 History 82 YEAR OLD woman with signs and symptoms of increased intra cranial pressure in setting of SAH. CT Brain was performed followed by CT Angiography of head. 2 CT brain Extensive
MEDICAL POLICY EFFECTIVE DATE: 12/18/08 REVISED DATE: 12/17/09, 03/17/11, 05/19/11, 05/24/12, 05/23/13, 05/22/14
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: CT (COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY) PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: CT (COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY) PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical
STROKE - IMAGING. Dr RAJASEKHAR REDDY 2nd Yr P.G. RADIODIAGNOSIS KIMS,Narkatpalli.
 STROKE - IMAGING Dr RAJASEKHAR REDDY 2nd Yr P.G. RADIODIAGNOSIS KIMS,Narkatpalli. STROKE Describes a clinical event that consists of sudden onset of neurological symptoms Types Infarction - occlusion of
STROKE - IMAGING Dr RAJASEKHAR REDDY 2nd Yr P.G. RADIODIAGNOSIS KIMS,Narkatpalli. STROKE Describes a clinical event that consists of sudden onset of neurological symptoms Types Infarction - occlusion of
Flat detector equipped C-arm angiographic systems used in the
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH INTERVENTIONAL C-Arm Flat Detector CT Parenchymal Blood Volume Thresholds for Identification of Infarcted Parenchyma in the Neurointerventional Suite M. Kamran and J.V. Byrne ABSTRACT
ORIGINAL RESEARCH INTERVENTIONAL C-Arm Flat Detector CT Parenchymal Blood Volume Thresholds for Identification of Infarcted Parenchyma in the Neurointerventional Suite M. Kamran and J.V. Byrne ABSTRACT
Anatomic Evaluation of the Circle of Willis: MR Angiography versus Intraarterial Digital Subtraction Angiography
 Anatomic Evaluation of the Circle of Willis: MR Angiography versus Intraarterial Digital Subtraction Angiography K. W. Stock, S. Wetzel, E. Kirsch, G. Bongartz, W. Steinbrich, and E. W. Radue PURPOSE:
Anatomic Evaluation of the Circle of Willis: MR Angiography versus Intraarterial Digital Subtraction Angiography K. W. Stock, S. Wetzel, E. Kirsch, G. Bongartz, W. Steinbrich, and E. W. Radue PURPOSE:
Index. average stress 146. see ACIS
 Index ACIS (autonomous catheter insertion system) 156, 237 39, 241 49 acute stroke treatment 59, 69, 71 anatomical model 88 aneurismal clipping treatment 106, 110 aneurysm 2 3, 26, 47 50, 52 55, 67 68,
Index ACIS (autonomous catheter insertion system) 156, 237 39, 241 49 acute stroke treatment 59, 69, 71 anatomical model 88 aneurismal clipping treatment 106, 110 aneurysm 2 3, 26, 47 50, 52 55, 67 68,
MR Imaging with the CCSVI or Haacke protocol
 MR Imaging with the CCSVI or Haacke protocol Reports from the Haacke protocol are often made available to the patients. The report consists of four major components: 1. anatomical images of major neck
MR Imaging with the CCSVI or Haacke protocol Reports from the Haacke protocol are often made available to the patients. The report consists of four major components: 1. anatomical images of major neck
Blunt Carotid Injury- CT Angiography is Adequate For Screening. Kelly Knudson, M.D. UCHSC April 3, 2006
 Blunt Carotid Injury- CT Angiography is Adequate For Screening Kelly Knudson, M.D. UCHSC April 3, 2006 CT Angiography vs Digital Subtraction Angiography Blunt carotid injury screening is one of the very
Blunt Carotid Injury- CT Angiography is Adequate For Screening Kelly Knudson, M.D. UCHSC April 3, 2006 CT Angiography vs Digital Subtraction Angiography Blunt carotid injury screening is one of the very
Evaluation and treatment of intracranial aneurysms using Dual Energy CT Angiography (DECTA) and rotational Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA).
 Evaluation and treatment of intracranial aneurysms using Dual Energy CT Angiography (DECTA) and rotational Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA). L. Testaverde, G. Pelle, A. Saltarelli, P. Rabuffi, M.
Evaluation and treatment of intracranial aneurysms using Dual Energy CT Angiography (DECTA) and rotational Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA). L. Testaverde, G. Pelle, A. Saltarelli, P. Rabuffi, M.
Role of Three-Dimensional Rotational Angiography in the Treatment of Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas
 Open Access Case Report DOI: 10.7759/cureus.1932 Role of Three-Dimensional Rotational Angiography in the Treatment of Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Yigit Ozpeynirci 1, Bernd Schmitz 2, Melanie Schick
Open Access Case Report DOI: 10.7759/cureus.1932 Role of Three-Dimensional Rotational Angiography in the Treatment of Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Yigit Ozpeynirci 1, Bernd Schmitz 2, Melanie Schick
B-Flow, Power Doppler and Color Doppler Ultrasound in the Assessment of Carotid Stenosis: Comparison with 64-MD-CT Angiography
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 2, March: 805-809, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net B-Flow, Power Doppler and Color Doppler Ultrasound in the Assessment of Carotid Stenosis: Comparison with
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 2, March: 805-809, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net B-Flow, Power Doppler and Color Doppler Ultrasound in the Assessment of Carotid Stenosis: Comparison with
Imaging of Moya Moya Disease
 Abstract Imaging of Moya Moya Disease Pages with reference to book, From 181 To 185 Rashid Ahmed, Hurnera Ahsan ( Liaquat National Hospital, Karachi. ) Moya Moya disease is a rare disease causing occlusion
Abstract Imaging of Moya Moya Disease Pages with reference to book, From 181 To 185 Rashid Ahmed, Hurnera Ahsan ( Liaquat National Hospital, Karachi. ) Moya Moya disease is a rare disease causing occlusion
On Call Guide to CT Perfusion. Updated: March 2011
 On Call Guide to CT Perfusion Updated: March 2011 CT Stroke Protocol 1. Non contrast CT brain 2. CT perfusion: contrast 40cc bolus dynamic imaging at 8 slice levels ~ 60 sec creates perfusion color maps
On Call Guide to CT Perfusion Updated: March 2011 CT Stroke Protocol 1. Non contrast CT brain 2. CT perfusion: contrast 40cc bolus dynamic imaging at 8 slice levels ~ 60 sec creates perfusion color maps
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING. James Chen (MS IV)
 HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
Dynamic 3D MR Angiography of Intra- and Extracranial Vascular Malformations at 3T: A Technical Note
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:630 634, March 2005 Technical Note Dynamic 3D MR Angiography of Intra- and Extracranial Vascular Malformations at 3T: A Technical Note S. Ziyeh, R. Strecker, A. Berlis, J. Weber,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:630 634, March 2005 Technical Note Dynamic 3D MR Angiography of Intra- and Extracranial Vascular Malformations at 3T: A Technical Note S. Ziyeh, R. Strecker, A. Berlis, J. Weber,
Non-Invasive Follow-up Evaluation of Post-Embolized AVM with Time-Resolved MRA: A Case Report
 Non-Invasive Follow-up Evaluation of Post-Embolized AVM with Time-Resolved MRA: A Case Report Yong Woon Shim, MD 1 Tae-Sub Chung, MD 1 Won-Suk Kang, MD 1 Jin-Yang Joo, MD 2 Ralph Strecker, MD 3 Juergen
Non-Invasive Follow-up Evaluation of Post-Embolized AVM with Time-Resolved MRA: A Case Report Yong Woon Shim, MD 1 Tae-Sub Chung, MD 1 Won-Suk Kang, MD 1 Jin-Yang Joo, MD 2 Ralph Strecker, MD 3 Juergen
Cardiac Computed Tomography
 Cardiac Computed Tomography Authored and approved by Koen Nieman Stephan Achenbach Francesca Pugliese Bernard Cosyns Patrizio Lancellotti Anastasia Kitsiou Contents CARDIAC COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY Page 1.
Cardiac Computed Tomography Authored and approved by Koen Nieman Stephan Achenbach Francesca Pugliese Bernard Cosyns Patrizio Lancellotti Anastasia Kitsiou Contents CARDIAC COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY Page 1.
Applicable Neuroradiology
 For the Clinical Neurology Clerkship LSU Medical School New Orleans Amy W Voigt, MD Clerkship Director Introduction The field of Radiology first developed following the discovery of X-Rays by Wilhelm Roentgen
For the Clinical Neurology Clerkship LSU Medical School New Orleans Amy W Voigt, MD Clerkship Director Introduction The field of Radiology first developed following the discovery of X-Rays by Wilhelm Roentgen
PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3
 PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3 The Basics Arteries: Carry blood away from the heart toward tissues. They typically have thicker vessels walls to handle increased pressure. Contain internal and external elastic
PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3 The Basics Arteries: Carry blood away from the heart toward tissues. They typically have thicker vessels walls to handle increased pressure. Contain internal and external elastic
Mechanical Thrombectomy of Large Vessel Occlusions Using Stent Retriever Devices
 Mechanical Thrombectomy of Large Vessel Occlusions Using Stent Retriever Devices Joey English MD, PhD Medical Director, Neurointerventional Services California Pacific Medical Center Hospitals, San Francisco,
Mechanical Thrombectomy of Large Vessel Occlusions Using Stent Retriever Devices Joey English MD, PhD Medical Director, Neurointerventional Services California Pacific Medical Center Hospitals, San Francisco,
Overview
 Overview Tutorial Script 1 Script for the Virtual Stroke Lab Tutorial Overview http://www.ilstu.edu Background and Vocabulary This podcast provides an overview of The Virtual Stroke Lab, a free virtual
Overview Tutorial Script 1 Script for the Virtual Stroke Lab Tutorial Overview http://www.ilstu.edu Background and Vocabulary This podcast provides an overview of The Virtual Stroke Lab, a free virtual
What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)?
 American Society of Neuroradiology What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall
American Society of Neuroradiology What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall
[(PHY-3a) Initials of MD reviewing films] [(PHY-3b) Initials of 2 nd opinion MD]
![[(PHY-3a) Initials of MD reviewing films] [(PHY-3b) Initials of 2 nd opinion MD] [(PHY-3a) Initials of MD reviewing films] [(PHY-3b) Initials of 2 nd opinion MD]](/thumbs/89/98619893.jpg) 2015 PHYSICIAN SIGN-OFF (1) STUDY NO (PHY-1) CASE, PER PHYSICIAN REVIEW 1=yes 2=no [strictly meets case definition] (PHY-1a) CASE, IN PHYSICIAN S OPINION 1=yes 2=no (PHY-2) (PHY-3) [based on all available
2015 PHYSICIAN SIGN-OFF (1) STUDY NO (PHY-1) CASE, PER PHYSICIAN REVIEW 1=yes 2=no [strictly meets case definition] (PHY-1a) CASE, IN PHYSICIAN S OPINION 1=yes 2=no (PHY-2) (PHY-3) [based on all available
Posterior Cerebral Artery Aneurysms with Common Carotid Artery Occlusion: A Report of Two Cases
 Journal of Neuroendovascular Therapy 2017; 11: 371 375 Online March 3, 2017 DOI: 10.5797/jnet.cr.2016-0114 Posterior Cerebral Artery Aneurysms with Common Carotid Artery Occlusion: A Report of Two Cases
Journal of Neuroendovascular Therapy 2017; 11: 371 375 Online March 3, 2017 DOI: 10.5797/jnet.cr.2016-0114 Posterior Cerebral Artery Aneurysms with Common Carotid Artery Occlusion: A Report of Two Cases
The learning curve associated with intracranial angioplasty and stenting: analysis from a single center
 Original Article Page 1 of 7 The learning curve associated with intracranial angioplasty and stenting: analysis from a single center Peiquan Zhou, Guang Zhang, Zhiyong Ji, Shancai Xu, Huaizhang Shi Department
Original Article Page 1 of 7 The learning curve associated with intracranial angioplasty and stenting: analysis from a single center Peiquan Zhou, Guang Zhang, Zhiyong Ji, Shancai Xu, Huaizhang Shi Department
Feasibility of a New C-arm angiography (DYNA-CT) based three-dimensional algorithm in combination with myocardial perfusion assessment
 Feasibility of a New C-arm angiography (DYNA-CT) based three-dimensional algorithm in combination with myocardial perfusion assessment H. Rittger*, A.M.Sinha, J. Rieber±, G. Lauritsch+, J. Brachmann *Universitätsklinik
Feasibility of a New C-arm angiography (DYNA-CT) based three-dimensional algorithm in combination with myocardial perfusion assessment H. Rittger*, A.M.Sinha, J. Rieber±, G. Lauritsch+, J. Brachmann *Universitätsklinik
X ray Based Imaging in Neurovascular Intervention Requirements and Challenges
 University of Massachusetts X ray Based Imaging in Neurovascular Intervention Requirements and Challenges Division Neuroimaging and Intervention & The New England Center for Stroke Research Departments
University of Massachusetts X ray Based Imaging in Neurovascular Intervention Requirements and Challenges Division Neuroimaging and Intervention & The New England Center for Stroke Research Departments
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript J Am Coll Radiol. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2013 June 24.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Am Coll Radiol. 2010 January ; 7(1): 73 76. doi:10.1016/j.jacr.2009.06.015. Cerebral Aneurysms Janet C. Miller, DPhil, Joshua A.
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Am Coll Radiol. 2010 January ; 7(1): 73 76. doi:10.1016/j.jacr.2009.06.015. Cerebral Aneurysms Janet C. Miller, DPhil, Joshua A.
SAMPLE EDITION PELVIC AND LOWER EXTREMITY ARTERIES WITH ENDOVASCULAR REVASCULARIZATION. Cardiovascular Illustrations and Guidelines
 Cardiovascular Illustrations and Guidelines PELVIC AND LOWER EXTREMITY ARTERIES WITH ENDOVASCULAR REVASCULARIZATION ANGIOPLASTY INTRAVASCULAR STENT PLACEMENT ATHERECTOMY For Fem-Pop Territory Angioplasty
Cardiovascular Illustrations and Guidelines PELVIC AND LOWER EXTREMITY ARTERIES WITH ENDOVASCULAR REVASCULARIZATION ANGIOPLASTY INTRAVASCULAR STENT PLACEMENT ATHERECTOMY For Fem-Pop Territory Angioplasty
Computed tomographic pulmonary angiography procedures: Contrast media dilution from the venous to the systemic circulation
 Computed tomographic pulmonary angiography procedures: Contrast media dilution from the venous to the systemic circulation Petter Bugge Askeland Project thesis at the Faculty of Medicine UNIVERSITETET
Computed tomographic pulmonary angiography procedures: Contrast media dilution from the venous to the systemic circulation Petter Bugge Askeland Project thesis at the Faculty of Medicine UNIVERSITETET
Coronary angiography and PCI
 Coronary arteries Coronary angiography and PCI Samo Granda, Franjo Naji Department of Cardiology Clinical department of internal medicine University clinical centre Maribor Coronary arteries Atherosclerosis
Coronary arteries Coronary angiography and PCI Samo Granda, Franjo Naji Department of Cardiology Clinical department of internal medicine University clinical centre Maribor Coronary arteries Atherosclerosis
Postoperative Assessment of Extracranial Intracranial Bypass by Time- Resolved 3D Contrast-Enhanced MR Angiography Using Parallel Imaging
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2243 2247, October 2005 Postoperative Assessment of Extracranial Intracranial Bypass by Time- Resolved 3D Contrast-Enhanced MR Angiography Using Parallel Imaging Kazuhiro Tsuchiya,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2243 2247, October 2005 Postoperative Assessment of Extracranial Intracranial Bypass by Time- Resolved 3D Contrast-Enhanced MR Angiography Using Parallel Imaging Kazuhiro Tsuchiya,
Diagnosis of Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion with Transcranial Color-Coded Real-Time Sonography
 Diagnosis of Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion with Transcranial Color-Coded Real-Time Sonography Kazumi Kimura, Yoichiro Hashimoto, Teruyuki Hirano, Makoto Uchino, and Masayuki Ando PURPOSE: To determine
Diagnosis of Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion with Transcranial Color-Coded Real-Time Sonography Kazumi Kimura, Yoichiro Hashimoto, Teruyuki Hirano, Makoto Uchino, and Masayuki Ando PURPOSE: To determine
Radiographic myelography and postmyelographic CT using
 Published December 7, 2007 as 10.3174/ajnr.A0853 ORIGINAL RESEARCH J.-H. Buhk E. Elolf D. Jacob H.-H. Rustenbeck A. Mohr M. Knauth A Comparison of Angiographic CT and Multisection CT in Lumbar Myelographic
Published December 7, 2007 as 10.3174/ajnr.A0853 ORIGINAL RESEARCH J.-H. Buhk E. Elolf D. Jacob H.-H. Rustenbeck A. Mohr M. Knauth A Comparison of Angiographic CT and Multisection CT in Lumbar Myelographic
MR Advance Techniques. Vascular Imaging. Class II
 MR Advance Techniques Vascular Imaging Class II 1 Vascular Imaging There are several methods that can be used to evaluate the cardiovascular systems with the use of MRI. MRI will aloud to evaluate morphology
MR Advance Techniques Vascular Imaging Class II 1 Vascular Imaging There are several methods that can be used to evaluate the cardiovascular systems with the use of MRI. MRI will aloud to evaluate morphology
Vascular. Experiences Using an Angiography System with a Inch FPD - CT-Like Imaging of the Neck and Abdomen - 1.
 Vascular Experiences Using an Angiography System with a 17 17 Inch FPD - CT-Like Imaging of the Neck and Abdomen - Department of Radiology, University Hospital, Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine
Vascular Experiences Using an Angiography System with a 17 17 Inch FPD - CT-Like Imaging of the Neck and Abdomen - Department of Radiology, University Hospital, Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine
The potential role of quantitative digital subtraction angiography in evaluating type B chronic aortic dissection during TEVAR: preliminary results
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 516-522 The potential role of quantitative digital subtraction angiography in evaluating type B chronic aortic dissection during TEVAR:
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 516-522 The potential role of quantitative digital subtraction angiography in evaluating type B chronic aortic dissection during TEVAR:
CT perfusion in Moyamoya disease
 CT perfusion in Moyamoya disease Poster No.: C-1726 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: K. C. Lam, C. P. Tsang, K. K. Wong, R. LEE ; HK, Hong Kong/HK Keywords: Hemodynamics / Flow dynamics,
CT perfusion in Moyamoya disease Poster No.: C-1726 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: K. C. Lam, C. P. Tsang, K. K. Wong, R. LEE ; HK, Hong Kong/HK Keywords: Hemodynamics / Flow dynamics,
Assessment of Vasospasm and Delayed Cerebral Ischemia after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Current concepts and Value of CT Perfusion and CT Angiography
 Assessment of Vasospasm and Delayed Cerebral Ischemia after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Current concepts and Value of CT Perfusion and CT Angiography Poster No.: C-2563 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational
Assessment of Vasospasm and Delayed Cerebral Ischemia after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Current concepts and Value of CT Perfusion and CT Angiography Poster No.: C-2563 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational
Comparison of Five Major Recent Endovascular Treatment Trials
 Comparison of Five Major Recent Endovascular Treatment Trials Sample size 500 # sites 70 (100 planned) 316 (500 planned) 196 (833 estimated) 206 (690 planned) 16 10 22 39 4 Treatment contrasts Baseline
Comparison of Five Major Recent Endovascular Treatment Trials Sample size 500 # sites 70 (100 planned) 316 (500 planned) 196 (833 estimated) 206 (690 planned) 16 10 22 39 4 Treatment contrasts Baseline
Neuro-Vascular Intervention AAPC Regional Conference Springfield, MA
 Neuro-Vascular Intervention AAPC Regional Conference Springfield, MA October 8, 2010 1 Presented by: David Zielske, MD,CIRCC, CPC H, CCC, CCS, RCC General Recommendations for Physician Dictations State
Neuro-Vascular Intervention AAPC Regional Conference Springfield, MA October 8, 2010 1 Presented by: David Zielske, MD,CIRCC, CPC H, CCC, CCS, RCC General Recommendations for Physician Dictations State
Subtraction Helical CT Angiography of Intra- and Extracranial Vessels: Technical Considerations and Preliminary Experience
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:451 455, March 2003 Subtraction Helical CT Angiography of Intra- and Extracranial Vessels: Technical Considerations and Preliminary Experience Vijayam K. Jayakrishnan, Philip M.
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:451 455, March 2003 Subtraction Helical CT Angiography of Intra- and Extracranial Vessels: Technical Considerations and Preliminary Experience Vijayam K. Jayakrishnan, Philip M.
Experimental Assessment of Infarct Lesion Growth in Mice using Time-Resolved T2* MR Image Sequences
 Experimental Assessment of Infarct Lesion Growth in Mice using Time-Resolved T2* MR Image Sequences Nils Daniel Forkert 1, Dennis Säring 1, Andrea Eisenbeis 2, Frank Leypoldt 3, Jens Fiehler 2, Heinz Handels
Experimental Assessment of Infarct Lesion Growth in Mice using Time-Resolved T2* MR Image Sequences Nils Daniel Forkert 1, Dennis Säring 1, Andrea Eisenbeis 2, Frank Leypoldt 3, Jens Fiehler 2, Heinz Handels
Imaging Strategies for Endovascular Cardiovascular Procedures and Percutaneous Aortic Valves. Roy K Greenberg, MD
 Imaging Strategies for Endovascular Cardiovascular Procedures and Percutaneous Aortic Valves Roy K Greenberg, MD Disclosure Research support Cook Inc, Boston Scientific, W.L.Gore, Cordis, Vascutek, Terarecon
Imaging Strategies for Endovascular Cardiovascular Procedures and Percutaneous Aortic Valves Roy K Greenberg, MD Disclosure Research support Cook Inc, Boston Scientific, W.L.Gore, Cordis, Vascutek, Terarecon
The standard examination to evaluate for a source of subarachnoid
 Published April 11, 2013 as 10.3174/ajnr.A3478 ORIGINAL RESEARCH INTERVENTIONAL Use of CT Angiography and Digital Subtraction Angiography in Patients with Ruptured Cerebral Aneurysm: Evaluation of a Large
Published April 11, 2013 as 10.3174/ajnr.A3478 ORIGINAL RESEARCH INTERVENTIONAL Use of CT Angiography and Digital Subtraction Angiography in Patients with Ruptured Cerebral Aneurysm: Evaluation of a Large
A New Trend in Vascular Imaging: the Arterial Spin Labeling (ASL) Sequence
 A New Trend in Vascular Imaging: the Arterial Spin Labeling (ASL) Sequence Poster No.: C-1347 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Hodel, A. GUILLONNET, M. Rodallec, S. GERBER, R. 1
A New Trend in Vascular Imaging: the Arterial Spin Labeling (ASL) Sequence Poster No.: C-1347 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Hodel, A. GUILLONNET, M. Rodallec, S. GERBER, R. 1
Hemodynamic patterns of status epilepticus detected by susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI)
 Hemodynamic patterns of status epilepticus detected by susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI) Poster No.: C-1086 Congress: ECR 014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. AELLEN, E. Abela, R. Kottke, E. Springer,
Hemodynamic patterns of status epilepticus detected by susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI) Poster No.: C-1086 Congress: ECR 014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. AELLEN, E. Abela, R. Kottke, E. Springer,
Siemens Healthineers Erlangen, August 27, Siemens Healthineers presents imaging for complex, minimally invasive procedures
 Press Siemens Healthineers Erlangen, August 27, 2016 ESC 2016 in Rome: Exhibition 4, Booth N200 Siemens Healthineers presents imaging for complex, minimally invasive procedures Integrated imaging portfolio
Press Siemens Healthineers Erlangen, August 27, 2016 ESC 2016 in Rome: Exhibition 4, Booth N200 Siemens Healthineers presents imaging for complex, minimally invasive procedures Integrated imaging portfolio
TEACHING CASE # 5. Reocclusion Of Transverse And Sigmoid Venous Sinuses Mechanical and Chemical Thrombectomy
 TEACHING CASE # 5 Reocclusion Of Transverse And Sigmoid Venous Sinuses Mechanical and Chemical Thrombectomy CASE PRESENTATION 22M with right transverse and sigmoid venous sinuses occlusion s/p transvenous
TEACHING CASE # 5 Reocclusion Of Transverse And Sigmoid Venous Sinuses Mechanical and Chemical Thrombectomy CASE PRESENTATION 22M with right transverse and sigmoid venous sinuses occlusion s/p transvenous
ICAS is a viable treatment option in the case of symptomatic
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH M.-N. Psychogios P. Schramm J.-H. Buhk A. Xyda K. Gröschel K. Jung M. Knauth Angiographic CT after Intravenous Contrast Agent Application: A Noninvasive Follow-Up Tool after Intracranial
ORIGINAL RESEARCH M.-N. Psychogios P. Schramm J.-H. Buhk A. Xyda K. Gröschel K. Jung M. Knauth Angiographic CT after Intravenous Contrast Agent Application: A Noninvasive Follow-Up Tool after Intracranial
Methods. Yahya Paksoy, Bülent Oğuz Genç, and Emine Genç. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24: , August 2003
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1364 1368, August 2003 Retrograde Flow in the Left Inferior Petrosal Sinus and Blood Steal of the Cavernous Sinus Associated with Central Vein Stenosis: MR Angiographic Findings
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1364 1368, August 2003 Retrograde Flow in the Left Inferior Petrosal Sinus and Blood Steal of the Cavernous Sinus Associated with Central Vein Stenosis: MR Angiographic Findings
Developing a Statistical Method of Quantifying Vascular Response after Radiotherapy Co-supervised by Dr. Glenn Bauman and Dr.
 6 Week Project Developing a Statistical Method of Quantifying Vascular Response after Radiotherapy Co-supervised by Dr. Glenn Bauman and Dr. Slav Yartsev Michal Stankiewicz April 9, 2013 Medical Biophysics,
6 Week Project Developing a Statistical Method of Quantifying Vascular Response after Radiotherapy Co-supervised by Dr. Glenn Bauman and Dr. Slav Yartsev Michal Stankiewicz April 9, 2013 Medical Biophysics,
Challenging of contrast agent-free endovascular treatment using 3D imaging
 AC17-0010 Challenging of contrast agent-free endovascular treatment using 3D imaging Amane Kozuki Department of Cardiology, Osaka Saiseikai Nakatsu Hospital Introduction With advances in devices and techniques,
AC17-0010 Challenging of contrast agent-free endovascular treatment using 3D imaging Amane Kozuki Department of Cardiology, Osaka Saiseikai Nakatsu Hospital Introduction With advances in devices and techniques,
Volumetric Perfusion CT Using Prototype 256 Detector Row CT Scanner: Preliminary Study with Healthy Porcine Model V
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2536 2541, November/December 2005 Technical Note Volumetric Perfusion CT Using Prototype 256 Detector Row CT Scanner: Preliminary Study with Healthy Porcine Model V Shinichiro
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2536 2541, November/December 2005 Technical Note Volumetric Perfusion CT Using Prototype 256 Detector Row CT Scanner: Preliminary Study with Healthy Porcine Model V Shinichiro
Imaging of Cerebrovascular Disease
 Imaging of Cerebrovascular Disease A Practical Guide Val M. Runge, MD Editor-in-Chief of Investigative Radiology Institute for Diagnostic, Interventional, and Pediatric Radiology Inselspital, University
Imaging of Cerebrovascular Disease A Practical Guide Val M. Runge, MD Editor-in-Chief of Investigative Radiology Institute for Diagnostic, Interventional, and Pediatric Radiology Inselspital, University
IMAGING IN ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE
 IMAGING IN ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE Timo Krings MD, PhD, FRCP (C) Professor of Radiology & Surgery Braley Chair of Neuroradiology, Chief and Program Director of Diagnostic and Interventional Neuroradiology;
IMAGING IN ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE Timo Krings MD, PhD, FRCP (C) Professor of Radiology & Surgery Braley Chair of Neuroradiology, Chief and Program Director of Diagnostic and Interventional Neuroradiology;
Utility of Variable Helical Pitch CT Scanning Technique for CT Angiography of Aortoiliac and Lower Extremity Arteries
 Utility of Variable Helical Pitch CT Scanning Technique for CT Angiography of Aortoiliac and Lower Extremity Arteries Poster No.: C-0863 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A. Nakamoto,
Utility of Variable Helical Pitch CT Scanning Technique for CT Angiography of Aortoiliac and Lower Extremity Arteries Poster No.: C-0863 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A. Nakamoto,
Pipeline Embolization Device
 Pipeline Embolization Device The power to redefine aneurysm treatment. REDEFINE The Pipeline device redefines treatment for large or giant wide-necked aneurysms by reconstructing the parent artery and
Pipeline Embolization Device The power to redefine aneurysm treatment. REDEFINE The Pipeline device redefines treatment for large or giant wide-necked aneurysms by reconstructing the parent artery and
CT angiography techniques. Boot camp
 CT angiography techniques Boot camp Overview Basic concepts Contrast administration arterial opacification Time scan acquisition during the arterial phase Protocol examples Helical non-gated CTA Pulmonary
CT angiography techniques Boot camp Overview Basic concepts Contrast administration arterial opacification Time scan acquisition during the arterial phase Protocol examples Helical non-gated CTA Pulmonary
Carotid artery stenting for long CTO and pseudo occlusion of carotid artery -2 case reports-
 Carotid artery stenting for long CTO and pseudo occlusion of carotid artery -2 case reports- Katsutoshi Takayama, MD, Ph.D Department of Radiology and Interventional Neuroradiology Ishinkai Yao General
Carotid artery stenting for long CTO and pseudo occlusion of carotid artery -2 case reports- Katsutoshi Takayama, MD, Ph.D Department of Radiology and Interventional Neuroradiology Ishinkai Yao General
Cerebral angiography, using the attenuation effects of x-ray
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH C.J. Lin S.C. Hung W.Y. Guo F.C. Chang C.B. Luo J. Beilner M. Kowarschik W.F. Chu C.Y. Chang Monitoring Peri-Therapeutic Cerebral Circulation Time: A Feasibility Study Using Color-Coded
ORIGINAL RESEARCH C.J. Lin S.C. Hung W.Y. Guo F.C. Chang C.B. Luo J. Beilner M. Kowarschik W.F. Chu C.Y. Chang Monitoring Peri-Therapeutic Cerebral Circulation Time: A Feasibility Study Using Color-Coded
SVD+ Dynamic Volume CT:
 SVD+ Dynamic Volume CT: Delay Insensitive Brain Perfusion Analysis Erin Angel, PhD Manager, CT Clinical Science Toshiba America Medical Systems, Inc. SVD+ Dynamic Volume CT: Delay Insensitive Brain Perfusion
SVD+ Dynamic Volume CT: Delay Insensitive Brain Perfusion Analysis Erin Angel, PhD Manager, CT Clinical Science Toshiba America Medical Systems, Inc. SVD+ Dynamic Volume CT: Delay Insensitive Brain Perfusion
Arterial Map of the Thorax, Abdomen and Pelvis 2017 Edition
 Arterial Map of the Thorax, Abdomen and Pelvis Angiography 75605 (-26) Aortography, thoracic 75625 (-26) Aortography, abdominal by serialography 75630 (-26) Aortography, abdominal + bilat iliofemoral 75705
Arterial Map of the Thorax, Abdomen and Pelvis Angiography 75605 (-26) Aortography, thoracic 75625 (-26) Aortography, abdominal by serialography 75630 (-26) Aortography, abdominal + bilat iliofemoral 75705
JlntSocPlastination, Vol4:16-22,
 JlntSocPlastination, Vol4:16-22, 1990 16 SECTIONAL ANATOMY: STANDARDIZED METHODOLOGY Alexander Lane, Coordinator of Anatomy and Physiology, Triton College, Visiting Associate Professor, University of Illinois
JlntSocPlastination, Vol4:16-22, 1990 16 SECTIONAL ANATOMY: STANDARDIZED METHODOLOGY Alexander Lane, Coordinator of Anatomy and Physiology, Triton College, Visiting Associate Professor, University of Illinois
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 14. Ischemia and Infarction II
 14. Ischemia and Infarction II Lacunar infarcts are small deep parenchymal lesions involving the basal ganglia, internal capsule, thalamus, and brainstem. The vascular supply of these areas includes the
14. Ischemia and Infarction II Lacunar infarcts are small deep parenchymal lesions involving the basal ganglia, internal capsule, thalamus, and brainstem. The vascular supply of these areas includes the
Ultrasound. Computed tomography. Case studies. Utility of IQon Spectral CT in. cardiac imaging
 Ultrasound Computed tomography Case studies Utility of IQon Spectral CT in cardiac imaging Cardiac imaging is a challenging procedure where it is necessary to image a motion-free heart. This requires a
Ultrasound Computed tomography Case studies Utility of IQon Spectral CT in cardiac imaging Cardiac imaging is a challenging procedure where it is necessary to image a motion-free heart. This requires a
ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE. Current Treatment Approaches for Acute Ischemic Stroke
 ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE Current Treatment Approaches for Acute Ischemic Stroke EARLY MANAGEMENT OF ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE Rapid identification of a stroke Immediate EMS transport to nearest stroke center
ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE Current Treatment Approaches for Acute Ischemic Stroke EARLY MANAGEMENT OF ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE Rapid identification of a stroke Immediate EMS transport to nearest stroke center
Pre-and Post Procedure Non-Invasive Evaluation of the Patient with Carotid Disease
 Pre-and Post Procedure Non-Invasive Evaluation of the Patient with Carotid Disease Michael R. Jaff, D.O., F.A.C.P., F.A.C.C. Assistant Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Director, Vascular Medicine
Pre-and Post Procedure Non-Invasive Evaluation of the Patient with Carotid Disease Michael R. Jaff, D.O., F.A.C.P., F.A.C.C. Assistant Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Director, Vascular Medicine
The variation of carotid origin, the divergent orientation of common carotid (frequent posterior and left to right direction of right common as
 1 Introduction The access to the common carotid during carotid stenting is very challenging and is responsible of a significant number of embolic complications in the ipsilateral but also in the contralateral
1 Introduction The access to the common carotid during carotid stenting is very challenging and is responsible of a significant number of embolic complications in the ipsilateral but also in the contralateral
CT perfusion scans are widely applied to assess ischemia (low
 Published April 17, 2014 as 10.3174/ajnr.A3935 ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Early Basal Ganglia Hyperperfusion on CT Perfusion in Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Marker of Irreversible Damage? V. Shahi, J.E. Fugate,
Published April 17, 2014 as 10.3174/ajnr.A3935 ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Early Basal Ganglia Hyperperfusion on CT Perfusion in Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Marker of Irreversible Damage? V. Shahi, J.E. Fugate,
2013 Coding Changes. Diagnostic Radiology. Nuclear Medicine
 2013 Coding Changes The principal coding changes affecting Radiologists in 2013 occur in the Interventional Radiology Section of the AMA/CPT Manual. As in the past, we continue to see the Relative Update
2013 Coding Changes The principal coding changes affecting Radiologists in 2013 occur in the Interventional Radiology Section of the AMA/CPT Manual. As in the past, we continue to see the Relative Update
Disclosures. CREST Trial: Summary. Lecture Outline 4/16/2015. Cervical Atherosclerotic Disease
 Disclosures Your Patient Has Carotid Bulb Stenosis and a Tandem Intracranial Stenosis: How Do SAMMPRIS and Other Evidence Inform Your Treatment? UCSF Vascular Symposium 2015 Steven W. Hetts, MD Associate
Disclosures Your Patient Has Carotid Bulb Stenosis and a Tandem Intracranial Stenosis: How Do SAMMPRIS and Other Evidence Inform Your Treatment? UCSF Vascular Symposium 2015 Steven W. Hetts, MD Associate
Speed, Comfort and Quality with NeuroDrive
 Speed, Comfort and Quality with NeuroDrive Echelon Oval provides a broad range of capabilities supporting fast, accurate diagnosis of brain conditions and injuries. From anatomical depiction to vascular
Speed, Comfort and Quality with NeuroDrive Echelon Oval provides a broad range of capabilities supporting fast, accurate diagnosis of brain conditions and injuries. From anatomical depiction to vascular
CTP is an imaging technique commonly used in conjunction. Radiation Doses of Cerebral Blood Volume Measurements Using C-Arm CT: A Phantom Study
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH PATIENT SAFETY Radiation Doses of Cerebral Blood Volume Measurements Using C-Arm CT: A Phantom Study W.F. Chu, C.J. Lin, W.S. Chen, S.C. Hung, C.F. Chiu, T.H. Wu, and W.Y. Guo ABSTRACT
ORIGINAL RESEARCH PATIENT SAFETY Radiation Doses of Cerebral Blood Volume Measurements Using C-Arm CT: A Phantom Study W.F. Chu, C.J. Lin, W.S. Chen, S.C. Hung, C.F. Chiu, T.H. Wu, and W.Y. Guo ABSTRACT
CT angiography (CTA) becomes more and more important
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH B.F. Tomandl T. Hammen E. Klotz H. Ditt B. Stemper M. Lell Bone-Subtraction CT Angiography for the Evaluation of Intracranial Aneurysms PURPOSE: CT angiography (CTA) has been established
ORIGINAL RESEARCH B.F. Tomandl T. Hammen E. Klotz H. Ditt B. Stemper M. Lell Bone-Subtraction CT Angiography for the Evaluation of Intracranial Aneurysms PURPOSE: CT angiography (CTA) has been established
How to perform DSA-based Cerebral Aneurysm Flow measurements
 How to perform DSA-based Cerebral Aneurysm Flow measurements Poster No.: C-1919 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: D. Ruijters, N. Benachour, T. Grünhagen, F. van Nijnatten, O. 1 3 2
How to perform DSA-based Cerebral Aneurysm Flow measurements Poster No.: C-1919 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: D. Ruijters, N. Benachour, T. Grünhagen, F. van Nijnatten, O. 1 3 2
Validation of CT Perfusion Imaging Against Invasive Angiography and FFR on a 320-MDCT Scanner
 Validation of CT Perfusion Imaging Against Invasive Angiography and FFR on a 320-MDCT Scanner Zhen Qian, Gustavo Vasquez, Sarah Rinehart, Parag Joshi, Eric Krivitsky, Anna Kalynych, Dimitri Karmpaliotis,
Validation of CT Perfusion Imaging Against Invasive Angiography and FFR on a 320-MDCT Scanner Zhen Qian, Gustavo Vasquez, Sarah Rinehart, Parag Joshi, Eric Krivitsky, Anna Kalynych, Dimitri Karmpaliotis,
Length Measurements of the Aorta After Endovascular Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair
 Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 18, 481 486 (1999) Article No. ejvs.1999.0882 Length Measurements of the Aorta After Endovascular Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair J. J. Wever, J. D. Blankensteijn, I. A. M. J.
Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 18, 481 486 (1999) Article No. ejvs.1999.0882 Length Measurements of the Aorta After Endovascular Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair J. J. Wever, J. D. Blankensteijn, I. A. M. J.
X-Ray & CT Physics / Clinical CT
 Computed Tomography-Basic Principles and Good Practice X-Ray & CT Physics / Clinical CT INSTRUCTORS: Dane Franklin, MBA, RT (R) (CT) Office hours will be Tuesdays from 5pm to 6pm CLASSROOM: TIME: REQUIRED
Computed Tomography-Basic Principles and Good Practice X-Ray & CT Physics / Clinical CT INSTRUCTORS: Dane Franklin, MBA, RT (R) (CT) Office hours will be Tuesdays from 5pm to 6pm CLASSROOM: TIME: REQUIRED
Vascular CT Protocols
 Vascular CT Protocols V 1D: Chest and abdominal CT angiogram (aortic dissection protocol) V 1T: Chest CT angiogram (aortic trauma protocol) V 2: Abdominal and pelvis CT angiogram (aortic aneurysm protocol)
Vascular CT Protocols V 1D: Chest and abdominal CT angiogram (aortic dissection protocol) V 1T: Chest CT angiogram (aortic trauma protocol) V 2: Abdominal and pelvis CT angiogram (aortic aneurysm protocol)
Cardiac Imaging Tests
 Cardiac Imaging Tests http://www.medpagetoday.com/upload/2010/11/15/23347.jpg Standard imaging tests include echocardiography, chest x-ray, CT, MRI, and various radionuclide techniques. Standard CT and
Cardiac Imaging Tests http://www.medpagetoday.com/upload/2010/11/15/23347.jpg Standard imaging tests include echocardiography, chest x-ray, CT, MRI, and various radionuclide techniques. Standard CT and
The goal of cerebral aneurysm treatments, whether
 J Neurosurg 117:29 36, 2012 Optimized angiographic computed tomography with intravenous contrast injection: an alternative to conventional angiography in the follow-up of clipped aneurysms? Clinical article
J Neurosurg 117:29 36, 2012 Optimized angiographic computed tomography with intravenous contrast injection: an alternative to conventional angiography in the follow-up of clipped aneurysms? Clinical article
Advanced Neuroimaging for Acute Stroke
 Advanced Neuroimaging for Acute Stroke E. Bradshaw Bunney, MD, FACEP Professor Department Of Emergency Medicine University of Illinois at Chicago Swedish American Belvidere Hospital Disclosures FERNE Board
Advanced Neuroimaging for Acute Stroke E. Bradshaw Bunney, MD, FACEP Professor Department Of Emergency Medicine University of Illinois at Chicago Swedish American Belvidere Hospital Disclosures FERNE Board
Carotid Imaging. Dr Andrew Farrall. Consultant Neuroradiologist
 20121123 SSCA http://www.neuroimage.co.uk/network Andrew Farrall Carotid Imaging Dr Andrew Farrall Consultant Neuroradiologist SFC Brain Imaging Research Centre (www.sbirc.ed.ac.uk), SINAPSE Collaboration
20121123 SSCA http://www.neuroimage.co.uk/network Andrew Farrall Carotid Imaging Dr Andrew Farrall Consultant Neuroradiologist SFC Brain Imaging Research Centre (www.sbirc.ed.ac.uk), SINAPSE Collaboration
