PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3
|
|
|
- Dorothy Wilkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3 The Basics Arteries: Carry blood away from the heart toward tissues. They typically have thicker vessels walls to handle increased pressure. Contain internal and external elastic lamina that allow stretch and recoil (the reason you can feel a pulse clinically). On models, arteries are colored red if they carry oxygenated blood and blue if they carry deoxygenated blood. Veins: Carry blood back to the heart from tissues. They have thinner vessels walls designed to collapse and one way valves. They lack elastic lamina. Compression of veins by muscle contraction helps move blood. On models, veins are blue if the carry deoxygenated blood and red if they carry oxygenated blood. 1
2 Elements of the Cardiovascular System found in the head and neck region are the arteries and veins that supply the region Major Arteries Superior Temporal Internal Carotid External Carotid Common carotid Vertebral Subclavian Brachiocephalic Trunk Major Veins Superior sagittal Sinus Transverse Sinus Sigmoid Sinus Temporal External Jugular Internal Jugular Vertebral Brachiocephalics Overview of Arterial Blood flow patterns 2
3 Major Arteries of the Head and Neck Distribution of Major Arteries of the Head and Neck External Carotid Superficial Temporal Internal Carotid Vertebral Common Carotid Subclavian Branches that supply external head area Upper/Lower jaw, chewing muscles, teeth, nasal cavity, and Dura Mater Muscles of the anterior portion of the face Parotid Salivary glands and most of the superior aspects of the scalp Posterior aspects of the scalp Brain and internal aspects of the skull Spinal cord in cervical region and Brain Supplies the External and Internal Carotids Gives raise to Vertebral and supplies arms 3
4 Distribution of Major Arteries of the Head and Neck Anterior cerebral Middle cerebral Basilar Posterior cerebral Circle of Willis (IC) supply most of the cerebral hemisphere except the occipital lobes (IC) Supply most of the lateral surface of the cerebral hemispheres Formed by union of the L&R vertebral, Cranial meninges and cerebrum Terminal branch of the basilar, supply interior aspect of cerebral hemispheres and occipital lobe An anastomosis for the two vertebral and internalcarotid arteries. Gives rise to numerous small branches that supply the brain. Important source of collateral circulation in the event of gradual obstructions. Basic Blood patterns for Veins 4
5 Major Veins of the Head and neck Region Venous Blood flow from the Brain 5
6 Areas drained by the Major Veins of the Head and Neck Superior Sagittal Sinus Transverse Sinus Sigmoid Sinus Temporal Vein Drains all CSF and passes blood on to Transverse Sinuses posterior Passes blood along to Sigmoid Sinuses Passes blood along to the Internal Jugular Drains Parotid Salivary glands and most of the superior aspects of the scalp. Passes blood along to External Jugular. Drains posterior aspects of the scalp. Passes blood along to External Jugular. Drains Muscles of the anterior portion of the face. Passes blood to the Internal Jugular Drains Upper/Lower jaw, chewing muscles, teeth, nasal cavity, and Dura Mater. Passes blood to the External Jugular Areas drained by the Major Veins of the Head and Neck External Jugular Internal Jugular Brachiocephalic Passes blood to the Brachiocephalic. Passes blood to the Brachiocephalic Both Brachiocephalic veins come together to form the Super Vena Cava. 6
7 Clinical Concerns Occlusions: Obstruction of blood flow, result from thrombi, thrombophlebitis, or tumors. Cerebral contusions: brain trauma in which the pia is striped for the brain surface allowing blood to enter the subarachnoid space. Cerebral Lacerations: Damage that results in ruptured blood vessels allowing bleeding into the brain and subarachnoid space, causing intracranial pressure and cerebral compression. Ischemic Stroke: Impaired cerebral blood flow with development of neurological deficits. Most common causes are spontaneous cerebrovascular accidents such as embolism, thrombosis, hemorrhage, subarachnoid hemorrhage. Clinical Concerns Hemorrhagic Stroke: Follows the rupture of an artery usually caused by an aneurysm. Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA): Neurological symptoms resulting from temporary ischemia. The symptoms of staggering, dizziness, light-headedness, fainting, and parasthesias last a few minutes, but can persist for up to an hour. 7
Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14
 Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14 14. Identify (on cadaver specimens, models and diagrams) and name the principal arteries and veins of the CNS: Why is it important to understand blood supply
Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14 14. Identify (on cadaver specimens, models and diagrams) and name the principal arteries and veins of the CNS: Why is it important to understand blood supply
OBJECTIVES. At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: List the cerebral arteries.
 DR JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: List the cerebral arteries. Describe the cerebral arterial supply regarding the origin, distribution and branches.
DR JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: List the cerebral arteries. Describe the cerebral arterial supply regarding the origin, distribution and branches.
HEAD/NECK VESSELS. Objectives
 Objectives Arterial Supply to Head and Neck Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain Common carotid arteries Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain External carotid arteries Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain External
Objectives Arterial Supply to Head and Neck Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain Common carotid arteries Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain External carotid arteries Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain External
Veins of the Face and the Neck
 Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
YOU MUST BRING GLOVES FOR THIS ACTIVITY
 ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
Vascular Disorders. Nervous System Disorders (Part B-1) Module 8 -Chapter 14. Cerebrovascular disease S/S 1/9/2013
 Nervous System Disorders (Part B-1) Module 8 -Chapter 14 Overview ACUTE NEUROLOGIC DISORDERS Vascular Disorders Infections/Inflammation/Toxins Metabolic, Endocrinologic, Nutritional, Toxic Neoplastic Traumatic
Nervous System Disorders (Part B-1) Module 8 -Chapter 14 Overview ACUTE NEUROLOGIC DISORDERS Vascular Disorders Infections/Inflammation/Toxins Metabolic, Endocrinologic, Nutritional, Toxic Neoplastic Traumatic
Blood Supply. Allen Chung, class of 2013
 Blood Supply Allen Chung, class of 2013 Objectives Understand the importance of the cerebral circulation. Understand stroke and the types of vascular problems that cause it. Understand ischemic penumbra
Blood Supply Allen Chung, class of 2013 Objectives Understand the importance of the cerebral circulation. Understand stroke and the types of vascular problems that cause it. Understand ischemic penumbra
The dura is sensitive to stretching, which produces the sensation of headache.
 Dural Nerve Supply Branches of the trigeminal, vagus, and first three cervical nerves and branches from the sympathetic system pass to the dura. Numerous sensory endings are in the dura. The dura is sensitive
Dural Nerve Supply Branches of the trigeminal, vagus, and first three cervical nerves and branches from the sympathetic system pass to the dura. Numerous sensory endings are in the dura. The dura is sensitive
Lab Activity 25. Blood Vessels & Circulation. Portland Community College BI 232
 Lab Activity 25 Blood Vessels & Circulation Portland Community College BI 232 Artery and Vein Histology Walls have 3 layers: Tunica intima Tunica media Tunica externa 2 Tunica Intima Is the innermost layer
Lab Activity 25 Blood Vessels & Circulation Portland Community College BI 232 Artery and Vein Histology Walls have 3 layers: Tunica intima Tunica media Tunica externa 2 Tunica Intima Is the innermost layer
VESSELS: GROSS ANATOMY
 ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
TRANSVERSE SECTION PLANE Scalp 2. Cranium. 13. Superior sagittal sinus
 TRANSVERSE SECTION PLANE 1 1. Scalp 2. Cranium 3. Superior sagittal sinus 4. Dura mater 5. Falx cerebri 6. Frontal lobes of the cerebrum 7. Middle meningeal artery 8. Cortex, grey matter 9. Cerebral vessels
TRANSVERSE SECTION PLANE 1 1. Scalp 2. Cranium 3. Superior sagittal sinus 4. Dura mater 5. Falx cerebri 6. Frontal lobes of the cerebrum 7. Middle meningeal artery 8. Cortex, grey matter 9. Cerebral vessels
Brain ميهاربا لض اف دمح ا د The Meninges 1- Dura Mater of the Brain endosteal layer does not extend meningeal layer falx cerebri tentorium cerebelli
 .احمد د فاضل ابراهيم Lecture 15 Brain The Meninges Three protective membranes or meninges surround the brain in the skull: the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater 1- Dura Mater of the Brain
.احمد د فاضل ابراهيم Lecture 15 Brain The Meninges Three protective membranes or meninges surround the brain in the skull: the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater 1- Dura Mater of the Brain
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING. James Chen (MS IV)
 HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
Bio& 242, Unit 3/ Lab 4 Blood Vessels, Lymphatic System and Blood Pressure G. Blevins/ G. Brady Summer 2009
 Bio& 242, Unit 3/ Lab 4 Blood Vessels, Lymphatic System and Blood Pressure G. Blevins/ G. Brady Summer 2009 Major Arteries and for arteries and veins with common names your answer must include either artery
Bio& 242, Unit 3/ Lab 4 Blood Vessels, Lymphatic System and Blood Pressure G. Blevins/ G. Brady Summer 2009 Major Arteries and for arteries and veins with common names your answer must include either artery
M555 Medical Neuroscience Blood Flow in CNS Meninges Blood Brain Barrier CSF
 M555 Medical Neuroscience Blood Flow in CNS Meninges Blood Brain Barrier CSF Arterial Blood Flow to CNS approximately % of what goes wrong within the skull that produces neurological deficits is vascular
M555 Medical Neuroscience Blood Flow in CNS Meninges Blood Brain Barrier CSF Arterial Blood Flow to CNS approximately % of what goes wrong within the skull that produces neurological deficits is vascular
THE VESSELS OF BLOOD CIRCULATION
 THE VESSELS OF BLOOD CIRCULATION scientistcindy.com /the-vessels-of-blood-circulation.html NOTE: You should familiarize yourself with the anatomy of the heart and have a good understanding of the flow
THE VESSELS OF BLOOD CIRCULATION scientistcindy.com /the-vessels-of-blood-circulation.html NOTE: You should familiarize yourself with the anatomy of the heart and have a good understanding of the flow
Unit #3: Dry Lab A. David A. Morton, Ph.D.
 Unit #3: Dry Lab A David A. Morton, Ph.D. Skull Intracranial Hemorrhage Pg. 26 Epidural Hematoma Pg. 26 Skull Pg. 26 Subdural Hematoma Pg. 26 Subdural Hematoma Pg. 26 Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Pg. 26 Subarachnoid
Unit #3: Dry Lab A David A. Morton, Ph.D. Skull Intracranial Hemorrhage Pg. 26 Epidural Hematoma Pg. 26 Skull Pg. 26 Subdural Hematoma Pg. 26 Subdural Hematoma Pg. 26 Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Pg. 26 Subarachnoid
3 Circulatory Pathways
 40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
Blood Supply of the CNS
 Blood Supply of the CNS Lecture Objectives Describe the four arteries supplying the CNS. Follow up each artery to its destination. Describe the circle of Willis and its branches. Discuss the principle
Blood Supply of the CNS Lecture Objectives Describe the four arteries supplying the CNS. Follow up each artery to its destination. Describe the circle of Willis and its branches. Discuss the principle
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes
 Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes Blood Supply to the Brain MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. LEARNING OBJECTIVES After study of the assigned learning
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes Blood Supply to the Brain MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. LEARNING OBJECTIVES After study of the assigned learning
Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD
 Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD Boston Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School None Disclosures Conventional US Anterior fontanelle
Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD Boston Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School None Disclosures Conventional US Anterior fontanelle
Superior View of the Skull (Norma Verticalis) Anteriorly the frontal bone articulates with the two parietal bones AT THE CORONAL SUTURE
 Superior View of the Skull (Norma Verticalis) Anteriorly the frontal bone articulates with the two parietal bones AT THE CORONAL SUTURE 1 The two parietal bones articulate in the midline AT THE SAGITTAL
Superior View of the Skull (Norma Verticalis) Anteriorly the frontal bone articulates with the two parietal bones AT THE CORONAL SUTURE 1 The two parietal bones articulate in the midline AT THE SAGITTAL
Medical Review Guidelines Magnetic Resonance Angiography
 Medical Review Guidelines Magnetic Resonance Angiography Medical Guideline Number: MRG2001-05 Effective Date: 2/13/01 Revised Date: 2/14/2006 OHCA Reference OAC 317:30-5-24. Radiology. (f) Magnetic Resonance
Medical Review Guidelines Magnetic Resonance Angiography Medical Guideline Number: MRG2001-05 Effective Date: 2/13/01 Revised Date: 2/14/2006 OHCA Reference OAC 317:30-5-24. Radiology. (f) Magnetic Resonance
Classical CNS Disease Patterns
 Classical CNS Disease Patterns Inflammatory Traumatic In response to the trauma of having his head bashed in GM would have experienced some of these features. NOT TWO LITTLE PEENY WEENY I CM LACERATIONS.
Classical CNS Disease Patterns Inflammatory Traumatic In response to the trauma of having his head bashed in GM would have experienced some of these features. NOT TWO LITTLE PEENY WEENY I CM LACERATIONS.
Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus
 Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF
 Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF Lecture Objectives Describe the arrangement of the meninges and their relationship to brain and spinal cord. Explain the occurrence of epidural, subdural and subarachnoid
Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF Lecture Objectives Describe the arrangement of the meninges and their relationship to brain and spinal cord. Explain the occurrence of epidural, subdural and subarachnoid
CARDIOVASCULAR DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD
 CARDIOVASCULAR DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD 18 Systemic Circulation Figure 19.19 Pulmonary Circulation Figure 19.18b 1. Thyroid gland 2. Trachea 3. Brachiocephalic 4. Common carotid 5. Internal jugular 6. Superior
CARDIOVASCULAR DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD 18 Systemic Circulation Figure 19.19 Pulmonary Circulation Figure 19.18b 1. Thyroid gland 2. Trachea 3. Brachiocephalic 4. Common carotid 5. Internal jugular 6. Superior
What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)?
 American Society of Neuroradiology What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall
American Society of Neuroradiology What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Understand how the brain is organized, protected, and supplied
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Understand how the brain is organized, protected, and supplied
Blood Supply. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Blood Supply Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Review Sessions with Dr. Riedl Tuesdays 4-5pm in MCB 3-146 (the main lab room) The first exam is coming soon!
Blood Supply Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Review Sessions with Dr. Riedl Tuesdays 4-5pm in MCB 3-146 (the main lab room) The first exam is coming soon!
Lab Photo Review Sheet
 9 8 0. Posterior Median Sulcus. Central Canal. Dorsal (Posterior) Horn. Ventral (Anterior) Horn. Grey Matter. White Matter. Anterior Median Fissure 8. Ventral (Anterior) Root (ramus) 9. Dorsal (Posterior)
9 8 0. Posterior Median Sulcus. Central Canal. Dorsal (Posterior) Horn. Ventral (Anterior) Horn. Grey Matter. White Matter. Anterior Median Fissure 8. Ventral (Anterior) Root (ramus) 9. Dorsal (Posterior)
PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA
 PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Outline Anatomical Structure and Boundaries Foramina and Communications with other spaces and cavities Contents Pterygopalatine Ganglion Especial emphasis on certain arteries and
PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Outline Anatomical Structure and Boundaries Foramina and Communications with other spaces and cavities Contents Pterygopalatine Ganglion Especial emphasis on certain arteries and
Cranial cavity. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Cranial cavity Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology The Meninges The brain in the skull is surrounded by three membranes or meninges: 1-DURA MATER 2-ARACHNOID MATER 3-PIA MATER
Cranial cavity Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology The Meninges The brain in the skull is surrounded by three membranes or meninges: 1-DURA MATER 2-ARACHNOID MATER 3-PIA MATER
Cranial Cavity REFERENCES: OBJECTIVES OSTEOLOGY. Stephen A. Gudas, PT, PhD
 Stephen A. Gudas, PT, PhD Cranial Cavity REFERENCES: Moore and Agur, Essential Clinical Anatomy (ECA), 3rd ed., pp. 496 498; 500 507; 512 514 Grant s Atlas 12 th ed., Figs 7.6; 7.19 7.30. Grant s Dissector
Stephen A. Gudas, PT, PhD Cranial Cavity REFERENCES: Moore and Agur, Essential Clinical Anatomy (ECA), 3rd ed., pp. 496 498; 500 507; 512 514 Grant s Atlas 12 th ed., Figs 7.6; 7.19 7.30. Grant s Dissector
Meninges and Ventricles
 Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
Tutorials. By Dr Sharon Truter
 Tutorials By Dr Sharon Truter To the Tutorials By Dr Sharon Truter What to expect from the Tutorials What to expect from these tutorials Outlines, structure, guided reading, explanations, mnemonics Begin
Tutorials By Dr Sharon Truter To the Tutorials By Dr Sharon Truter What to expect from the Tutorials What to expect from these tutorials Outlines, structure, guided reading, explanations, mnemonics Begin
Health Sciences 1110 Module 8 Nervous System Part II LAB 8. Watch the Brain Surgery video and answer the questions on your worksheet.
 Health Sciences 1110 Module 8 Nervous System Part II LAB 8 Watch the Brain Surgery video and answer the questions on your worksheet. Interactive Physiology o Open Internet Explorer and go to the Health
Health Sciences 1110 Module 8 Nervous System Part II LAB 8 Watch the Brain Surgery video and answer the questions on your worksheet. Interactive Physiology o Open Internet Explorer and go to the Health
The Cardiovascular System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Cardiovascular System 11PART B The Heart: Cardiac Output Cardiac output (CO) Amount of blood pumped
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Cardiovascular System 11PART B The Heart: Cardiac Output Cardiac output (CO) Amount of blood pumped
Cerebral hemisphere. Parietal Frontal Occipital Temporal
 Cerebral hemisphere Sulcus / Fissure Central Precental gyrus Postcentral gyrus Lateral (cerebral) Parieto-occipital Cerebral cortex Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Temporal lobe Insula Amygdala Hippocampus
Cerebral hemisphere Sulcus / Fissure Central Precental gyrus Postcentral gyrus Lateral (cerebral) Parieto-occipital Cerebral cortex Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Temporal lobe Insula Amygdala Hippocampus
Breathing. Heart Rate
 Breathing Heart Rate Inspiration Expiration (Pressos not Stretched) Heart Rate increases with inspiration (Pressos Stretched) Heart Rate decreases with expiration Upside Down (Pressos Stretched) HR Decreases
Breathing Heart Rate Inspiration Expiration (Pressos not Stretched) Heart Rate increases with inspiration (Pressos Stretched) Heart Rate decreases with expiration Upside Down (Pressos Stretched) HR Decreases
Brain Injuries. Presented By Dr. Said Said Elshama
 Brain Injuries Presented By Dr. Said Said Elshama Types of head injuries 1- Scalp injuries 2- Skull injuries 3- Intra Cranial injuries ( Brain ) Anatomical structure of meninges Intra- Cranial Injuries
Brain Injuries Presented By Dr. Said Said Elshama Types of head injuries 1- Scalp injuries 2- Skull injuries 3- Intra Cranial injuries ( Brain ) Anatomical structure of meninges Intra- Cranial Injuries
Cranial cavity. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Cranial cavity Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Cerebrum Cerebral hemispheres The Meninges The brain in the skull is surrounded by three membranes or meninges: 1-THE DURA
Cranial cavity Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Cerebrum Cerebral hemispheres The Meninges The brain in the skull is surrounded by three membranes or meninges: 1-THE DURA
For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER
 GROSS ANATOMY EXAMINATION May 15, 2000 For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER 1. Pain associated with an infection limited to the middle
GROSS ANATOMY EXAMINATION May 15, 2000 For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER 1. Pain associated with an infection limited to the middle
2. capillaries - allow exchange of materials between blood and tissue fluid
 Chapter 19 - Vascular System A. categories and general functions: 1. arteries - carry blood away from heart 2. capillaries - allow exchange of materials between blood and tissue fluid 3. veins - return
Chapter 19 - Vascular System A. categories and general functions: 1. arteries - carry blood away from heart 2. capillaries - allow exchange of materials between blood and tissue fluid 3. veins - return
Cardiovascular system:
 Cardiovascular system: Mediastinum: The mediastinum: lies between the right and left pleura and lungs. It extends from the sternum in front to the vertebral column behind, and from the root of the neck
Cardiovascular system: Mediastinum: The mediastinum: lies between the right and left pleura and lungs. It extends from the sternum in front to the vertebral column behind, and from the root of the neck
Arterial Map of the Thorax, Abdomen and Pelvis 2017 Edition
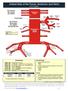 Arterial Map of the Thorax, Abdomen and Pelvis Angiography 75605 (-26) Aortography, thoracic 75625 (-26) Aortography, abdominal by serialography 75630 (-26) Aortography, abdominal + bilat iliofemoral 75705
Arterial Map of the Thorax, Abdomen and Pelvis Angiography 75605 (-26) Aortography, thoracic 75625 (-26) Aortography, abdominal by serialography 75630 (-26) Aortography, abdominal + bilat iliofemoral 75705
Stroke. Understanding. Professor Richard Iain Lindley
 Understanding Stroke Professor Richard Iain Lindley Published by Family Doctor Publications Limited in association with the British Medical Association IMPORTANT This book is intended not as a substitute
Understanding Stroke Professor Richard Iain Lindley Published by Family Doctor Publications Limited in association with the British Medical Association IMPORTANT This book is intended not as a substitute
Unit 18: Cranial Cavity and Contents
 Unit 18: Cranial Cavity and Contents Dissection Instructions: The calvaria is to be removed without damage to the dura mater which is attached to the inner surface of the calvaria. Cut through the outer
Unit 18: Cranial Cavity and Contents Dissection Instructions: The calvaria is to be removed without damage to the dura mater which is attached to the inner surface of the calvaria. Cut through the outer
Cerebrovascular Disorders. Blood, Brain, and Energy. Blood Supply to the Brain 2/14/11
 Cerebrovascular Disorders Blood, Brain, and Energy 20% of body s oxygen usage No oxygen/glucose reserves Hypoxia - reduced oxygen Anoxia - Absence of oxygen supply Cell death can occur in as little as
Cerebrovascular Disorders Blood, Brain, and Energy 20% of body s oxygen usage No oxygen/glucose reserves Hypoxia - reduced oxygen Anoxia - Absence of oxygen supply Cell death can occur in as little as
Traumatic Brain Injury TBI Presented by Bill Masten
 1 2 Cerebrum two hemispheres and four lobes. Cerebellum (little brain) coordinates the back and forth ballet of motion. It judges the timing of every movement precisely. Brainstem coordinates the bodies
1 2 Cerebrum two hemispheres and four lobes. Cerebellum (little brain) coordinates the back and forth ballet of motion. It judges the timing of every movement precisely. Brainstem coordinates the bodies
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Endovascular Therapies for Extracranial Vertebral Artery Disease File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: endovascular_therapies_for_extracranial_vertebral_artery_disease
Corporate Medical Policy Endovascular Therapies for Extracranial Vertebral Artery Disease File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: endovascular_therapies_for_extracranial_vertebral_artery_disease
Anatomy of Pituitary Gland
 Anatomy of Pituitary Gland Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives At the end of the lecture,
Anatomy of Pituitary Gland Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives At the end of the lecture,
Artery 1 Head and Thoracic Arteries. Arrange the parts in the order blood flows through them.
 Artery 1 Head and Thoracic Arteries 1. Given the following parts of the aorta: 1. abdominal aorta 2. aortic arch 3. ascending aorta 4. thoracic aorta Arrange the parts in the order blood flows through
Artery 1 Head and Thoracic Arteries 1. Given the following parts of the aorta: 1. abdominal aorta 2. aortic arch 3. ascending aorta 4. thoracic aorta Arrange the parts in the order blood flows through
Anatomy and Physiology, Spring 2015 Exam II: Form A April 9, Name Student Number
 Anatomy and Physiology, Spring 2015 Exam II: Form A April 9, 2015 Name Student Number For Questions 1 2 refer to the following table. 1 Ventricular pressure is greater than aortic 6 AV valve is open 2
Anatomy and Physiology, Spring 2015 Exam II: Form A April 9, 2015 Name Student Number For Questions 1 2 refer to the following table. 1 Ventricular pressure is greater than aortic 6 AV valve is open 2
The Nervous System. PowerPoint Lecture Slides C H A P T E R 7. Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College C H A P T E R 7 The Nervous System NERVOUS SYSTEM OVERVIEW Essential Question: What are the primary functions
PowerPoint Lecture Slides Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College C H A P T E R 7 The Nervous System NERVOUS SYSTEM OVERVIEW Essential Question: What are the primary functions
Neuropathology lecture series. III. Neuropathology of Cerebrovascular Disease. Physiology of cerebral blood flow
 Neuropathology lecture series III. Neuropathology of Cerebrovascular Disease Physiology of cerebral blood flow Brain makes up only 2% of body weight Percentage of cardiac output: 15-20% Percentage of O
Neuropathology lecture series III. Neuropathology of Cerebrovascular Disease Physiology of cerebral blood flow Brain makes up only 2% of body weight Percentage of cardiac output: 15-20% Percentage of O
Ventricles, CSF & Meninges. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Ventricles, CSF & Meninges Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Coffee Hour Thursday (Sept 14) 8:30-9:30am Surdyk s Café in Northrop Auditorium Stop by for a minute or an
Ventricles, CSF & Meninges Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Coffee Hour Thursday (Sept 14) 8:30-9:30am Surdyk s Café in Northrop Auditorium Stop by for a minute or an
For Emergency Doctors. Dr Suzanne Smallbane November 2011
 For Emergency Doctors Dr Suzanne Smallbane November 2011 A: Orbit B: Sphenoid Sinus C: Temporal Lobe D: EAC E: Mastoid air cells F: Cerebellar hemisphere A: Frontal lobe B: Frontal bone C: Dorsum sellae
For Emergency Doctors Dr Suzanne Smallbane November 2011 A: Orbit B: Sphenoid Sinus C: Temporal Lobe D: EAC E: Mastoid air cells F: Cerebellar hemisphere A: Frontal lobe B: Frontal bone C: Dorsum sellae
ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES
 ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES LABORATORY OBJECTIVES: 1. Histology: Identify structures indicated on three different slides or images of nervous system tissue. These images
ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES LABORATORY OBJECTIVES: 1. Histology: Identify structures indicated on three different slides or images of nervous system tissue. These images
CMS Limitations Guide MRA Radiology Services
 CMS Limitations Guide MRA Radiology Services Starting July 1, 2008, CMS has placed numerous medical necessity limits on tests and procedures. This reference guide provides you with all of the latest changes.
CMS Limitations Guide MRA Radiology Services Starting July 1, 2008, CMS has placed numerous medical necessity limits on tests and procedures. This reference guide provides you with all of the latest changes.
REVIEW/PREVIEW OF HEAD AND NECK ANATOMY FOR ENT EXAM
 REVIEW/PREVIEW OF HEAD AND NECK ANATOMY FOR ENT EXAM - 2017 PALPATE CAROTID ARTERY: AT LEVEL OF CAROTID BIFURCATION VERTEBRAL LEVEL C4 Sternocleidomastoid Muscle INTERNAL CAROTID EXTERNAL CAROTID COMMON
REVIEW/PREVIEW OF HEAD AND NECK ANATOMY FOR ENT EXAM - 2017 PALPATE CAROTID ARTERY: AT LEVEL OF CAROTID BIFURCATION VERTEBRAL LEVEL C4 Sternocleidomastoid Muscle INTERNAL CAROTID EXTERNAL CAROTID COMMON
History of revascularization
 History of revascularization Author (year) Kredel, 1942 Woringer& Kunlin, 1963 Donaghy& Yasargil, 1968 Loughheed 1971 Kikuchini & Karasawa1973 Karasawa, 1977 Story, 1978 Sundt, 1982 EC/IC bypass study
History of revascularization Author (year) Kredel, 1942 Woringer& Kunlin, 1963 Donaghy& Yasargil, 1968 Loughheed 1971 Kikuchini & Karasawa1973 Karasawa, 1977 Story, 1978 Sundt, 1982 EC/IC bypass study
The Nervous System PART C. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7 PART C Protection of the Central Nervous System Scalp and skin Skull and vertebral
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7 PART C Protection of the Central Nervous System Scalp and skin Skull and vertebral
Head Trauma Inservice (October)
 John Tramell - Head Trauma Inservice, October 2005.doc Page 1 Head Trauma Inservice (October) Head trauma is the leading cause of death in trauma patients. Having a basic understanding of the anatomy and
John Tramell - Head Trauma Inservice, October 2005.doc Page 1 Head Trauma Inservice (October) Head trauma is the leading cause of death in trauma patients. Having a basic understanding of the anatomy and
General Anatomy p. 1 Organization of the Human Body p. 1 Skeleton of the Human Body p. 4 Ossification of the Bones p. 6 Bone Structure p. 8 Joints p.
 General Anatomy p. 1 Organization of the Human Body p. 1 Skeleton of the Human Body p. 4 Ossification of the Bones p. 6 Bone Structure p. 8 Joints p. 10 Principal Joints (Immovable) p. 12 Synovial Joints
General Anatomy p. 1 Organization of the Human Body p. 1 Skeleton of the Human Body p. 4 Ossification of the Bones p. 6 Bone Structure p. 8 Joints p. 10 Principal Joints (Immovable) p. 12 Synovial Joints
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM CARDIAC SYSTEM TWO TYPES OF CIRCULATION Systemic system delivers blood to ALL body cells and carries away waste. The red blood cells use hemoglobin to carry oxygen to the cells Pulmonary
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM CARDIAC SYSTEM TWO TYPES OF CIRCULATION Systemic system delivers blood to ALL body cells and carries away waste. The red blood cells use hemoglobin to carry oxygen to the cells Pulmonary
REVIEW SHEET Anatomy of Blood Vessels
 REVIEW SHEET Anatomy of Blood Vessels Name LabTime/Date Microscopic Structure of the Blood Vessels 1. Cross-sectional views of an aftery of a vein are shown here. ldentify each; on the lines to the sides,
REVIEW SHEET Anatomy of Blood Vessels Name LabTime/Date Microscopic Structure of the Blood Vessels 1. Cross-sectional views of an aftery of a vein are shown here. ldentify each; on the lines to the sides,
SKULL AS A WHOLE + ANTERIOR CRANIAL FOSSA
 SKULL AS A WHOLE + ANTERIOR CRANIAL FOSSA LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture, the student should be able to know: Parts of skeleton (axial and appendicular) Parts of skull Sutures of skull
SKULL AS A WHOLE + ANTERIOR CRANIAL FOSSA LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture, the student should be able to know: Parts of skeleton (axial and appendicular) Parts of skull Sutures of skull
C h a p t e r PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas
 C h a p t e r 15 The Nervous System: The Brain and Cranial Nerves PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing
C h a p t e r 15 The Nervous System: The Brain and Cranial Nerves PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing
NEURO IMAGING 2. Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity
 NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
Contents. Page 1. Homework 11 Chapter Blood Vessels Due: Week 6 Lec 11
 Page 1 Homework 11 Chapter 18-19 Blood Vessels Due: Week 6 Lec 11 Contents When printing, make sure that you specify the page range that you want to print out! Learning objectives for Lecture 11:...pg
Page 1 Homework 11 Chapter 18-19 Blood Vessels Due: Week 6 Lec 11 Contents When printing, make sure that you specify the page range that you want to print out! Learning objectives for Lecture 11:...pg
IV. Cerebrovascular diseases
 IV. Cerebrovascular diseases - Cerebrovascular disease denotes brain disorders caused by pathologic processes involving the blood vessels. - The three main pathogenic mechanisms are: 1. Thrombotic occlusion
IV. Cerebrovascular diseases - Cerebrovascular disease denotes brain disorders caused by pathologic processes involving the blood vessels. - The three main pathogenic mechanisms are: 1. Thrombotic occlusion
Copy Right- Hongqi ZHANG-Department of Anatomy-Fudan University. Systematic Anatomy. Angiology Part 4. Veins. Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 )
 Systematic Anatomy Angiology Part 4 Veins Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 General introduction of the veins Vessel which return the blood back to atrium No pulsation,veneous blood, metabolic
Systematic Anatomy Angiology Part 4 Veins Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 General introduction of the veins Vessel which return the blood back to atrium No pulsation,veneous blood, metabolic
HEART HEALTH WEEK 2 SUPPLEMENT. A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease ATHEROSCLEROSIS. Fatty deposits can narrow and harden the artery
 WEEK 2 SUPPLEMENT HEART HEALTH A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease ATHEROSCLEROSIS FIGURE 1 Atherosclerosis is an inflammatory process where cholesterol is deposited in the wall of arteries and
WEEK 2 SUPPLEMENT HEART HEALTH A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease ATHEROSCLEROSIS FIGURE 1 Atherosclerosis is an inflammatory process where cholesterol is deposited in the wall of arteries and
Occlusion of All Four Extracranial Vessels With Minimal Clinical Symptomatology. Case Report
 Occlusion of All Four Extracranial Vessels With Minimal Clinical Symptomatology. Case Report BY JIRI J. VITEK, M.D., JAMES H. HALSEY, JR., M.D., AND HOLT A. McDOWELL, M.D. Abstract: Occlusion of All Four
Occlusion of All Four Extracranial Vessels With Minimal Clinical Symptomatology. Case Report BY JIRI J. VITEK, M.D., JAMES H. HALSEY, JR., M.D., AND HOLT A. McDOWELL, M.D. Abstract: Occlusion of All Four
3-Deep fascia: is absent (except over the parotid gland & buccopharngeal fascia covering the buccinator muscle)
 The Face 1-Skin of the Face The skin of the face is: Elastic Vascular (bleed profusely however heal rapidly) Rich in sweat and sebaceous glands (can cause acne in adults) It is connected to the underlying
The Face 1-Skin of the Face The skin of the face is: Elastic Vascular (bleed profusely however heal rapidly) Rich in sweat and sebaceous glands (can cause acne in adults) It is connected to the underlying
Chapter 15 Neurological Emergencies Stroke (1 of 2) Stroke (2 of 2) Seizures Altered Mental Status (AMS) Brain Structure and Function
 1 Chapter 15 Neurological Emergencies 2 Stroke (1 of 2) Stroke is the leading cause of death in the United States. After heart disease and cancer It is common in geriatric patients. More than women have
1 Chapter 15 Neurological Emergencies 2 Stroke (1 of 2) Stroke is the leading cause of death in the United States. After heart disease and cancer It is common in geriatric patients. More than women have
The CNS Part II pg
 The CNS Part II pg. 455-474 Protection of the Brain Objectives Describe how the meninges, cerebrospinal fluid, and the blood brain barrier protect the CNS. Explain how Cerebrospinal fluid is formed, and
The CNS Part II pg. 455-474 Protection of the Brain Objectives Describe how the meninges, cerebrospinal fluid, and the blood brain barrier protect the CNS. Explain how Cerebrospinal fluid is formed, and
Chapter 15 Neurological Emergencies Stroke (1 of 2) Stroke (2 of 2) Seizures Altered Mental Status (AMS)
 1 2 3 4 5 Chapter 15 Neurological Emergencies Stroke (1 of 2) Stroke is the leading cause of death in the United States. After heart disease and cancer It is common in geriatric patients. More than women
1 2 3 4 5 Chapter 15 Neurological Emergencies Stroke (1 of 2) Stroke is the leading cause of death in the United States. After heart disease and cancer It is common in geriatric patients. More than women
CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services
 CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services Starting October 1, 2015, CMS will update their existing medical necessity limitations on tests and procedures to correspond to ICD-10 codes. This limitations
CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services Starting October 1, 2015, CMS will update their existing medical necessity limitations on tests and procedures to correspond to ICD-10 codes. This limitations
The Neck the lower margin of the mandible above the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle
 The Neck is the region of the body that lies between the lower margin of the mandible above and the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle below Nerves of the neck Cervical Plexus Is formed
The Neck is the region of the body that lies between the lower margin of the mandible above and the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle below Nerves of the neck Cervical Plexus Is formed
ANASTAMOSIS FOR BRAIN STEM ISCHEMIA/Khodadad et al.
 ANASTAMOSIS FOR BRAIN STEM ISCHEMIA/Khodadad et al. visualization of the posterior inferior cerebellar artery. The patient, now 11 months post-operative, has shown further neurological improvement since
ANASTAMOSIS FOR BRAIN STEM ISCHEMIA/Khodadad et al. visualization of the posterior inferior cerebellar artery. The patient, now 11 months post-operative, has shown further neurological improvement since
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
Spasm of the extracranial internal carotid artery resulting from blunt trauma demonstrated by angiography
 Spasm of the extracranial internal carotid artery resulting from blunt trauma demonstrated by angiography Case report ELISHA S. GURDJIAN, M.D., BLAISE AUDET, M.D., RENATO W. SIBAYAN, M.D., AND LLYWELLYN
Spasm of the extracranial internal carotid artery resulting from blunt trauma demonstrated by angiography Case report ELISHA S. GURDJIAN, M.D., BLAISE AUDET, M.D., RENATO W. SIBAYAN, M.D., AND LLYWELLYN
10/14/2018 Dr. Shatarat
 2018 Objectives To discuss mediastina and its boundaries To discuss and explain the contents of the superior mediastinum To describe the great veins of the superior mediastinum To describe the Arch of
2018 Objectives To discuss mediastina and its boundaries To discuss and explain the contents of the superior mediastinum To describe the great veins of the superior mediastinum To describe the Arch of
Central Nervous System (CNS) -> brain and spinal cord. Major Divisions of the nervous system:
 Central Nervous System (CNS) -> brain and spinal cord Major Divisions of the nervous system: Afferent (sensory input) -> cell bodies outside of the central nervous system (CNS), carry info into the CNS
Central Nervous System (CNS) -> brain and spinal cord Major Divisions of the nervous system: Afferent (sensory input) -> cell bodies outside of the central nervous system (CNS), carry info into the CNS
b. The groove between the two crests is called 2. The neural folds move toward each other & the fuse to create a
 Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
Figure ) The specific chamber of the heart that is indicated by letter A is called the. Diff: 1 Page Ref: 364
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Short Answer Figure 11.1 Using Figure 11.1, identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label.
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Short Answer Figure 11.1 Using Figure 11.1, identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label.
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins
 Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
Cerebrovascular Disease
 Neuropathology lecture series Cerebrovascular Disease Physiology of cerebral blood flow Brain makes up only 2% of body weight Percentage of cardiac output: 15-20% Percentage of O 2 consumption (resting):
Neuropathology lecture series Cerebrovascular Disease Physiology of cerebral blood flow Brain makes up only 2% of body weight Percentage of cardiac output: 15-20% Percentage of O 2 consumption (resting):
The NIHSS score is 4 (considering 2 pts for the ataxia involving upper and lower limbs.
 Neuroscience case 5 1. Speech comprehension, ability to speak, and word use were normal in Mr. Washburn, indicating that aphasia (cortical language problem) was not involved. However, he did have a problem
Neuroscience case 5 1. Speech comprehension, ability to speak, and word use were normal in Mr. Washburn, indicating that aphasia (cortical language problem) was not involved. However, he did have a problem
Vascular Malformations of the Brain. William A. Cox, M.D. Forensic Pathologist/Neuropathologist. September 8, 2014
 Vascular Malformations of the Brain William A. Cox, M.D. Forensic Pathologist/Neuropathologist September 8, 2014 Vascular malformations of the brain are classified into four principal groups: arteriovenous
Vascular Malformations of the Brain William A. Cox, M.D. Forensic Pathologist/Neuropathologist September 8, 2014 Vascular malformations of the brain are classified into four principal groups: arteriovenous
Ministry of Health. BC Chronic Disease and Selected Procedure Case Definitions. Chronic Disease Information Working Group. Date Created: June 29, 2015
 Ministry of Health BC Chronic Disease and Selected Procedure Case Definitions Author: Chronic Disease Information Working Group Date Created: June 29, 2015 Last Updated: February 01, 2018 Version: Email:
Ministry of Health BC Chronic Disease and Selected Procedure Case Definitions Author: Chronic Disease Information Working Group Date Created: June 29, 2015 Last Updated: February 01, 2018 Version: Email:
Tikrit University College of Dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y.
 Lec [3]/The scalp The scalp extends from the supraorbital margins anteriorly to the nuchal lines at the back of the skull and down to the temporal lines at the sides. The forehead, from eyebrows to hairline,
Lec [3]/The scalp The scalp extends from the supraorbital margins anteriorly to the nuchal lines at the back of the skull and down to the temporal lines at the sides. The forehead, from eyebrows to hairline,
The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels Outline PART 1: BLOOD VESSEL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
 The Cardiovascular System: Blood s Outline PART 1: BLOOD VESSEL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION A. The three major types of blood vessels are, capillaries, and. (p. 699; Fig. 19.1) 1. Arteries carry blood away
The Cardiovascular System: Blood s Outline PART 1: BLOOD VESSEL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION A. The three major types of blood vessels are, capillaries, and. (p. 699; Fig. 19.1) 1. Arteries carry blood away
Emergency Department Stroke Registry Indicator Specifications 2018 Report Year (07/01/2017 to 06/30/2018 Discharge Dates)
 2018 Report Year (07/01/2017 to 06/30/2018 Discharge Dates) Summary of Changes I62.9 added to hemorrhagic stroke ICD-10-CM diagnosis code list (table 3) Measure Description Methodology Rationale Measurement
2018 Report Year (07/01/2017 to 06/30/2018 Discharge Dates) Summary of Changes I62.9 added to hemorrhagic stroke ICD-10-CM diagnosis code list (table 3) Measure Description Methodology Rationale Measurement
