Nostril Asymmetry A Microform of Cleft Lip and Palate? Department of Orthodontics, School of Dentistry, Showa University.
|
|
|
- Sylvia Butler
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Review J. Showa Univ. Dent. Soc. 7: , 1987 Nostril Asymmetry A Microform of Cleft Lip and Palate? Department of Orthodontics, School of Dentistry, Showa University Tat SUO FUKUHARA In the last 20 years, studies in experimental teratology have approached the problems of cleft lip and/or cleft palate (CLP) from various directions. Laboratory studies with experimental animals have indicated that these defects can be caused by some chemical agents and X-radiation administered at critical periods during prenatal development. However, such experiments have not proven that the cause of these defects are entirely exogenic. There is no doubt that drugs, radiation and environmental pollutants can possibly cause birth defects in individual cases. Statistically, however, they do not seem to have contributed to much of an increase. On the other hand, the great advances in genetics and embryology in the past years have not brought about a noticeable decrease either. If most of the birth defects are the result of natural genetic variation, one might speculate that there are no obvious ways to eradicate them. Murakami, Nishimura and other researchers have studied this area thoroughly, using X-radiation, maternal hypoxia, trypan-blue injection, etc. Their findings show that CLP may be hereditary in man and in certain strains of experimental animals. Fraser et al. have administered standard doses of cortisone for 11 days after insemination of some specific strain (A/Jax) and have demonstrated cleft palate in 100 per cent; other crossbred groups indicated different results. This is significant evidence of the importance of genetic background. However, Larsson has stated that environmental factors can be considered to play a prominent role in the etiology of isolated cleft palate. Etoh and his collaborators have reported an induction method of CLP in cultured rat embryos by localized administration of tunicamycin (TM), they have suggested that this TM appears to primarily affect the growth of the medial nasal process which prevents its fusion with the lateral nasal process. In spite of these laboratory studies, however, through long clinical experience, we have numerous cases which strongly imply genetic etiology for human cleft lip and/or cleft palate. The most controversial questions regard the origin and manifestation of these defects in certain families where the defects appear in every generation. However, other instances present sporadic manifestation. The same is true in the data from population surveys (Table 1). The different ratios of incidence among these various populations might be explained as follows: (1) racial differences which might result in variations in the "lethal" effects of these congenital defects; (2) cultural differences in handling defective infants, as in some races where, it is believed, an infant born with any defect is put to death immediately; (3) possible population differences of gene distributions and gene expressivity; (4) environmental differences which may affect the development of the embryo. The latter two are extremely important in the clinical study of human genetics, genetic prognosis, and genetic counseling. Population surveys provide the materials for determining gene frequencies; on the other hand, data for determining expressivity of genes which may be responsible for these defects in certain given families are not yet available. 1. Genetic Relation between Cleft Lip and Cleft Palate In spite of the general agreement that cleft lip, cleft palate, uvula bifida, anencephaly, spina bifida, etc. are classified as "status dysraphicus," the genetic relations of each to the other differ in certain ways. When the proband had a cleft lip, with or without a cleft palate, the same conditions
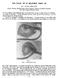
2 Table 1 Incidence of cleft lip and/or cleft palate. Table 2 Association of types of abnormalities between propositi and their relatives. were observed in the relatives, but extremely few cases of isolate cleft palate were found, and vice versa, the difference being statistically significant (Table 2). Fogh-Andersen also states that cleft lip, with or without cleft palate, is genetically independent of isolated cleft palate: the former is a characteristic of recessive or conditioned dominant inheritance; the latter is inherited as a dominant characteristic with a low rate of manifestation. It is presumed that soft tissue anomaly may be associated with bone cleft or deformity ; on the other hand, that cleft or deformity in the bony structure is not always associated with obvious soft tissue defects. In the past series of the author's studies, the ordinary P-A cephalography did not clearly demonstrate the defects in their images, since the image of the nasal floor where the defect may exist, is almost parallel to the eye-ear plane to which the radiation is oriented. However, laminographic X-ray technique was employed to detect the possible carrier status which may be revealed in the bony structures, premaxilla, nasal septum, and nasal shelf. Figure 1 indicates unoperated nose of the cleft patients taken at random from our files. Asymmetry of the nostrils is clearly illustrated in the cleft lip, unilateral cleft lip and palate patients other than the isolated cleft palate. This implies that inner and/or outer nasal structures will be coincidentally affected in the dysjunctioning process of the lip, alveolus and palate. Figure 2 illustrates a mother of a CLP daughter and a son with spina bifida. She had plastic surgery for a deviated nose before marriage. The nostril present severe asymmetry; the right nostril is drooping than the left. The soft tissue deformity is well coordinated with the images of the nasal septum and shelves which strongly indicates the bone deformities by her P-A X-ray. In Fig. 3 the mother of the CLP daughter shows that the left nostril is drooping and the image of the nasal shelf in the X-ray implies an opened or irregularly formed nasal shelf. The upper left lateral incisor is extremely large in the mesiodistal dimension of the crown and decalcificated at the neck. Figure 4a illustrates a non-operated male whose notches in the philtrum and lip indicate an almost transitional to the cleft condition. The X-ray shows that the level of the border of the shelves is not even. Figure 4b shows a pit closed to the left nostril and a trace of the lower lip fistulas. Figure 5 is a young female orthodontic patient. The upper right lateral incisor is congenitally missing which leaves a space in the frontal segment. Occlusal X-ray endorses a congenital missing lateral incisor and an uneven level of the shelves and asymmetry in the nostrils. Careful observation on her right philtrum may implicate that a subtle but traceable line could be a "mini-cleft" such as the case in Fig. 4a.
3 Fig. 1. Variations of unoperated nostril contours found in the cleft patients. Fig. 2. Mother of a CLP daughter and a son with spina vifida (asymmetry : +2). Deviation in the nasal septum and uneven shelves are illustrated in the laminographic X-ray. 2. Diagnosis of Visible and Non-visible Carrier Status of Cleft Palate There are some eccentric contours in the shape of the nostrils, philtrum, irregular formations and rotation or occasional absence of the maxillary lateral incisors. Some individuals may also show visible associated congenital defects, such as polydactyly, syndactyly, clubfoot, hernia, malformations of the ear, etc. The variations in expressivity and resulting sporadic penetrances may be due to an exogenic sensitivity characteristic of these genetic syndromes, as suggested by experiments with animals. As one may expect, CLP shows a wide range of variants in the anatomy, as well as in Fig. 3. Mother of a CLP daughter (asymmetry : +3). Deviation in the nasal septum and uneven shelves are illustrated in the laminographic X-ray. Malformation in the maxillary lateral incisor. the physiology. The laminographic X-ray technique or CT scanning reveals subtle, otherwise invisible, traces of CLP deformities which have been concealed behind a thick veil of the soft tissues.
4 Fig. 4a. A male with a notch in the upper lip and philtrum (Non-operated, transitional type) (Arrow head). Fig. 4b. A male with a pit in the philtrum and lower lip fistulas (Arrow head). Fig. 5. A young orthodontic patient with missing maxillary lateral incisor. Nostril deformity is clear and a trace of "mini-cleft" in the left philtrum (Arrow head). 3. Discussion In the study of the pathogenesis of congenital deformities, consideration must be given to the wide range of transitional and continuous variants of these defects. For example, in the genetic study of dwarfism of the maxillary lateral incisors, the congenitally missing teeth must be treated as being in the same category. Therefore, asymmetry in the nostrils should also be considered in the genealogic study, as a "forme
5 145 Fig. 6. A sample used in Pashayan's study. Asymmetry of the nostril contour will not be illustrated only taking the measurements of its length and the width. fruste" or microform in CLP, like other characteristics : the dwarfed or congenital missing maxillary lateral incisors, lower lip fistula, incomplete notch or trace in the philtrum. These microforms may have resulted from the undergrowth of the areas at the embryological stage or indulgent activity of the gene or genes and/or through the interaction of teratogenic agents. Pashayan and Fraser concluded that nostril asymmetry is not a microform of the CLP using experimental subjects of 50 parents (25 male, and 25 female) of children with cleft lip, with or without cleft palate, and 50 subjects drawn from the hospital staff and others. Measurements of nostril length and width were taken on the photograph to the nearest 0.5 mm. The control group has longer and narrower nostrils than the experimental group but the difference is not statistically significant (Fig. 6). Pashayan states in the paper that "perhaps Fukuhara's findings resulted from a selection of cases in which a near relative had a visible microform of cleft lip." However, there would be a methodological problem that asymmetry of the nostril contour can not be evaluated by only measuring the length and width. Asymmetry of the nostril may be evaluated by comparison of the contour or form of the nostril as a whole, and may be figured by other means than simple measuring the length and width of the nostril. Mills et al. also found no appreciable difference between the frequency of asymmetrical nostrils in a control population compared to the relatives of parents with CLP. These two studies are using 50 to 100 families as samples but the incidence of the microform will be small as the CLP incidence, so that typical asymmetry cases as illustrated in the present paper will not be presented in the sample sizes. A manifestation can not be observed in all the families of the clefts, while the frequencies of other traits, incomplete notch in the philtrum as an example, will be very few in the cleft syndrome. Conclusively, however, these results can not deny the implication that nostril asymmetry would be one of the rudimentary manifestations for cleft formation especially in the unilateral cases, and Pashayan's statement concludes contrarily that nostril asymmetry has a close relation with another visible microform of the cleft syndrome. Woolf and his collaborators have stated that "in some families cleft lip with or without cleft palate, and isolated cleft palate are strongly heritable through the action of a dominant single gene, less heritable in others through the interaction of polygenes and non-genetic factors, and may appear in others a phenocopy through the action of teratogenic agents." The extent and subtlety of these transitional variations require further study upon determination of the etiology whether these were products of recessive or dominant genes affected as exogents in the prenatal environment or entirely an exogenic product since only customary morphological methods were used for the diagnosis of these congenital defects. P-A laminography will be a tool in the diagnosis of non-visible irregularities in nasopalatal bone structures presumed to be connected with congenital CLP deformities, however, the X-ray image is not very clear. It is presumed that 3-D reconstruction of C-T scanning can prove the relation between unilateral bone deformity and asymmetry nostrils in the near future. References 1) Etoh, K., Figueroa, A., Tamura, K. & Pratt, R.M.: Induction of cleft lip in cultured rat embryo by localized administration of tunicamycine. J. Embryol. Exp. Morphol., 64: 1-9, ) Fogh-Andersen, P.: Inheritance of Harelip and Cleft Palate. Copenhagen, 1943, Ejnar Munksgaards Forlag. 3) Fogh-Andersen, P.: Inheritance pattern for cleft lip and cleft palate, In: Pruzansky, S.
6 (ed.): Congenital anomalies of the face and associated structures, Springfield, 1961, Charles C. Thomas. 4) Fraser, F.C., Faubstat, T.D., & Kalter, H.: The experimental production of congenital defects with particular reference to cleft palate, Neo-natal Studies, 2: 43-58, ) Fukuhara, T. & Saito, S.: Possible carrier status of hereditary cleft palate with cleft lip: Report of cases. Bull. Tokyo Med. Dent. Univ., 10: , ) Fukuhara, T.: New method and approach to the genetics of cleft lip and cleft palate. J. Dent. Res., 44 (Part 2-Suppl.): Jan.-Feb., ) Mills, L.F., Niswander, J.D., Mazaheri, M. & Brunelle, J.A.: Minor oral and facial defects in relatives of oral cleft patients. Angle Orthod., 38: , ) Murakami, U.: Studies on mechanisms manifesting congenital anomalies. Jpn. J. Hum. Genet., 8: , ) Murakami, U., Kameyama, Y. & Nogami, H.: Skeletal malformation in the mouse fetus caused by maternal hypoxia during early stages of pregnancy. Ann. Rep. Res. Inst. Environ. Med., 14: 53-60, ) Nishimura, H., Tanimura, T. & Suzuki, M.: Effects of thailomide administered to pregnant mice upon the development of their offspring. Acta Med. Univ. Kioto, 38: , ) Niswander, J.D.: Laminographic X-ray studies in families with cleft lip and cleft palate. Arch. Oral Biol., 13: , ) Pashayan, H. & Fraser, F.C.: Nostril asymmetry not a microform of cleft lip. Cleft Palate J., 8: , ) Tolarova, M.: Microforms of cleft lip and/or cleft palate. Acta Chir. Plast. (Praha), 11: , ) Tolarova, M., Havlova, Z. & Ruzickova, J.: The distribution of characters considered to be microforms of cleft lip and/or palate in a population of normal year old subjects. Act. Chir. Plast, 9: 1-14, ) Weinberger, T.W.: Cleft microform : report of case. J. Den. Child., March-April: , ) Woolf, C.M., Woolf, R.M. & Broadbent, B.S.: Lateral incisor anomalies. Microforms of cleft lip and palate? Plast. Reconstr. Surg., 35, , (Received August 10, 1987)
Dr.ALI AL BAZZAZ PLASTIC SURGON CLEFT LIP AND PALATE
 Dr.ALI AL BAZZAZ PLASTIC SURGON CLEFT LIP AND PALATE Cleft lip (cheiloschisis) and cleft palate (palatoschisis), which can also occur together as cleft lip and palate, are variations of a type of clefting
Dr.ALI AL BAZZAZ PLASTIC SURGON CLEFT LIP AND PALATE Cleft lip (cheiloschisis) and cleft palate (palatoschisis), which can also occur together as cleft lip and palate, are variations of a type of clefting
Abnormal Morphology of the Soft Palate: I. The Prevalence of Cleft Uvula
 Abnormal Morphology of the Soft Palate: I. The Prevalence of Cleft Uvula LAWRENCE H. MESKIN, D.D.S., M.S.D. ROBERT J. GORLIN, D.D.S., M.S. ROBERT J. ISAACSON, D.D.S., Ph.D. Minneapolis, Minnesota Isolated
Abnormal Morphology of the Soft Palate: I. The Prevalence of Cleft Uvula LAWRENCE H. MESKIN, D.D.S., M.S.D. ROBERT J. GORLIN, D.D.S., M.S. ROBERT J. ISAACSON, D.D.S., Ph.D. Minneapolis, Minnesota Isolated
OF THE LIP AND PALATE. By T. D. FOSTER, M.D.S., F.D.S., D.Orth.R.C.S. School of Dental Surgery, University of Birmingham
 MAXILLARY DEFORMITIES IN REPAIRED CLEFTS OF THE LIP AND PALATE By T. D. FOSTER, M.D.S., F.D.S., D.Orth.R.C.S. School of Dental Surgery, University of Birmingham IN patients with repaired clefts of the
MAXILLARY DEFORMITIES IN REPAIRED CLEFTS OF THE LIP AND PALATE By T. D. FOSTER, M.D.S., F.D.S., D.Orth.R.C.S. School of Dental Surgery, University of Birmingham IN patients with repaired clefts of the
Oblique lip-alveolar banding in patients with cleft lip and palate
 Oblique lip-alveolar banding in patients with cleft lip and palate Sharan Naidoo *,a Kurt-W Bütow a,b a Facial Cleft Deformity Clinic, Department of Maxillofacial and Oral Surgery, University of Pretoria
Oblique lip-alveolar banding in patients with cleft lip and palate Sharan Naidoo *,a Kurt-W Bütow a,b a Facial Cleft Deformity Clinic, Department of Maxillofacial and Oral Surgery, University of Pretoria
Remember from the first year embryology Trilaminar disc has 3 layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm
 Development of face Remember from the first year embryology Trilaminar disc has 3 layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm The ectoderm forms the neural groove, then tube The neural tube lies in the mesoderm
Development of face Remember from the first year embryology Trilaminar disc has 3 layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm The ectoderm forms the neural groove, then tube The neural tube lies in the mesoderm
Figure 1. Basic anatomy of the palate
 CHAPTER 10 CLEFT LIP AND PALATE Chen Yan, MD and Sanjay Naran, MD I. ANATOMY AND DEFINITIONS A. Cleft Lip (CL) alone, Cleft Lip with Cleft Palate (CLP), and Cleft Palate (CP) alone 1. CL alone and CLP
CHAPTER 10 CLEFT LIP AND PALATE Chen Yan, MD and Sanjay Naran, MD I. ANATOMY AND DEFINITIONS A. Cleft Lip (CL) alone, Cleft Lip with Cleft Palate (CLP), and Cleft Palate (CP) alone 1. CL alone and CLP
An Anterior Tooth Size Comparison in Unilateral and Bilateral Congenitally Absent Maxillary Lateral Incisors
 An Anterior Tooth Size Comparison in Unilateral and Bilateral Congenitally Absent Maxillary Lateral Incisors Abstract The purpose of this study is to compare the anterior tooth size width in patients with
An Anterior Tooth Size Comparison in Unilateral and Bilateral Congenitally Absent Maxillary Lateral Incisors Abstract The purpose of this study is to compare the anterior tooth size width in patients with
Epidemiological Aspects of Cleft Lip and Palate in Iran
 ORIGINAL REPORT Epidemiological Aspects of Cleft Lip and Palate in Iran Alireza Karimee Yazdee 1, Babak Saedi 1, Amir Arvin Sazegar 1, and Parvin Mehdipour 2 1 Department of Otolaryngology, School of Medicine,
ORIGINAL REPORT Epidemiological Aspects of Cleft Lip and Palate in Iran Alireza Karimee Yazdee 1, Babak Saedi 1, Amir Arvin Sazegar 1, and Parvin Mehdipour 2 1 Department of Otolaryngology, School of Medicine,
Cleft Lip and Palate: The Effects on Speech and Resonance
 Ann W. Kummer, PhD, CCC-SLP Cincinnati Children s Cleft lip and/or palate can have a negative impact on both speech and resonance. The following is a summary of normal anatomy, the types and causes of
Ann W. Kummer, PhD, CCC-SLP Cincinnati Children s Cleft lip and/or palate can have a negative impact on both speech and resonance. The following is a summary of normal anatomy, the types and causes of
Postnatal Growth. The study of growth in growing children is for two reasons : -For health and nutrition assessment
 Growth of The Soft Tissues Postnatal Growth Postnatal growth is defined as the first 20 years of growth after birth krogman 1972 The study of growth in growing children is for two reasons : -For health
Growth of The Soft Tissues Postnatal Growth Postnatal growth is defined as the first 20 years of growth after birth krogman 1972 The study of growth in growing children is for two reasons : -For health
ofunusual and Occult Clefts of the Palate JOHN MARQUIS CONVERSE, MD. SIDNEY L. HOROWITZ, D.D.S. MELVIN H. BECKER M.D, New York New York-4:11
 TheUse oftomographyin: the Diagnosis ofunusual and Occult Clefts of the Palate JOHN MARQUIS CONVERSE, MD. SIDNEY L. HOROWITZ, D.D.S. MELVIN H. BECKER M.D, New York New York-4:11 The ma or1ty of patients
TheUse oftomographyin: the Diagnosis ofunusual and Occult Clefts of the Palate JOHN MARQUIS CONVERSE, MD. SIDNEY L. HOROWITZ, D.D.S. MELVIN H. BECKER M.D, New York New York-4:11 The ma or1ty of patients
Original Research. Figure 1: (a) Unilateral complete cleft of the lip and palate, (b) unilateral complete skeletal cleft with a Simonart s band.
 Received: 14 th August 2015 Accepted: 19 th November 2015 Conflicts of Interest: None Source of Support: Nil Original Research Simonart s Bands and Facial Growth in Unilateral Cleft Lip and Palate Patients:
Received: 14 th August 2015 Accepted: 19 th November 2015 Conflicts of Interest: None Source of Support: Nil Original Research Simonart s Bands and Facial Growth in Unilateral Cleft Lip and Palate Patients:
Plastic Surgeon, Middlesbrough General Hospital, Stockton Children's Hospital, Newcastle Regional Hospital Board
 THE NASAL TIP IN BILATERAL HARE LIP By J. POTTER, F.R.C.S.Ed. Plastic Surgeon, Middlesbrough General Hospital, Stockton Children's Hospital, Newcastle Regional Hospital Board IN the problem of the bilateral
THE NASAL TIP IN BILATERAL HARE LIP By J. POTTER, F.R.C.S.Ed. Plastic Surgeon, Middlesbrough General Hospital, Stockton Children's Hospital, Newcastle Regional Hospital Board IN the problem of the bilateral
LATERAL CEPHALOMETRIC EVALUATION IN CLEFT PALATE PATIENTS
 POLSKI PRZEGLĄD CHIRURGICZNY 2009, 81, 1, 23 27 10.2478/v10035-009-0004-2 LATERAL CEPHALOMETRIC EVALUATION IN CLEFT PALATE PATIENTS PRADEEP JAIN, ANAND AGARWAL, ARVIND SRIVASTAVA Department of Plastic
POLSKI PRZEGLĄD CHIRURGICZNY 2009, 81, 1, 23 27 10.2478/v10035-009-0004-2 LATERAL CEPHALOMETRIC EVALUATION IN CLEFT PALATE PATIENTS PRADEEP JAIN, ANAND AGARWAL, ARVIND SRIVASTAVA Department of Plastic
Prenatal Diagnosis of Cleft Lip
 Commentary Prenatal Diagnosis of Cleft Lip What the Sonologist Needs to Tell the Surgeon John. Mulliken, MD, eryl R. enacerraf, MD Division of Plastic Surgery, Children s Hospital (J..M.) Department of
Commentary Prenatal Diagnosis of Cleft Lip What the Sonologist Needs to Tell the Surgeon John. Mulliken, MD, eryl R. enacerraf, MD Division of Plastic Surgery, Children s Hospital (J..M.) Department of
A REVIEW OF CLASSIFICATION SYSTEMS FOR CLEFT LIP AND PALATE PATIENTS- I. MORPHOLOGICAL CLASSIFICATIONS
 Review Article A REVIEW OF CLASSIFICATION SYSTEMS FOR CLEFT LIP AND PALATE PATIENTS- I. MORPHOLOGICAL CLASSIFICATIONS Syed Nasir Shah, Mariya Khalid, Muhammad Sartaj Khan Department of Prosthodontics,
Review Article A REVIEW OF CLASSIFICATION SYSTEMS FOR CLEFT LIP AND PALATE PATIENTS- I. MORPHOLOGICAL CLASSIFICATIONS Syed Nasir Shah, Mariya Khalid, Muhammad Sartaj Khan Department of Prosthodontics,
Cephalometric Analysis
 Cephalometric Analysis of Maxillary and Mandibular Growth and Dento-Alveolar Change Part III In two previous articles in the PCSO Bulletin s Faculty Files, we discussed the benefits and limitations of
Cephalometric Analysis of Maxillary and Mandibular Growth and Dento-Alveolar Change Part III In two previous articles in the PCSO Bulletin s Faculty Files, we discussed the benefits and limitations of
EVALUATION AND MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WITH CLEFT LIP AND PALATE
 EVALUATION AND MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WITH CLEFT LIP AND PALATE DEFINING TERMS PRIMARY PALATE- Structures anterior to the incisive foramen Includes the nose, lip alveolus, and hard palate back to the incisive
EVALUATION AND MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WITH CLEFT LIP AND PALATE DEFINING TERMS PRIMARY PALATE- Structures anterior to the incisive foramen Includes the nose, lip alveolus, and hard palate back to the incisive
Elements of Dysmorphology I. Krzysztof Szczałuba
 Elements of Dysmorphology I Krzysztof Szczałuba 9.05.2016 Common definitions (1) Dysmorphology: recognition and study of birth defects (congenital malformations) and syndromes [David Smith, 1960] Malformation:
Elements of Dysmorphology I Krzysztof Szczałuba 9.05.2016 Common definitions (1) Dysmorphology: recognition and study of birth defects (congenital malformations) and syndromes [David Smith, 1960] Malformation:
The study of hereditary traits
 Hereditary traits The study of hereditary traits Traits determined by phenotypic expression of one or several genes, ± interaction with environment factors; The weight of hereditary factors in phenotype
Hereditary traits The study of hereditary traits Traits determined by phenotypic expression of one or several genes, ± interaction with environment factors; The weight of hereditary factors in phenotype
DENTAL MANAGEMENT OF CLEFT LIP AND PALATE. J Harewood DDS MA MS
 DENTAL MANAGEMENT OF CLEFT LIP AND PALATE J Harewood DDS MA MS CLEFT LIP/PALATE: INCIDENCE Cleft lip and/or palate 1:1000 Varies with race Japan: 20: 10 000 Western Europe: 12: 10 000 USA: 10.2:10 000
DENTAL MANAGEMENT OF CLEFT LIP AND PALATE J Harewood DDS MA MS CLEFT LIP/PALATE: INCIDENCE Cleft lip and/or palate 1:1000 Varies with race Japan: 20: 10 000 Western Europe: 12: 10 000 USA: 10.2:10 000
Vancouver, B.C., Canada
 THE "ALAR SHIFT" REVISITED By THEODORE F. WILKIE, B.A., M.D., F.R.C.S.(C), F.A.C.S. Vancouver, B.C., Canada IN the hands of many plastic surgeons certain procedures have an evanescent history. Usually
THE "ALAR SHIFT" REVISITED By THEODORE F. WILKIE, B.A., M.D., F.R.C.S.(C), F.A.C.S. Vancouver, B.C., Canada IN the hands of many plastic surgeons certain procedures have an evanescent history. Usually
ONE out of every eight hundred children in the United States is born with
 REPAIR OF THE CLEFT LIP ROBIN ANDERSON, M.D. Department of Plastic Surgery ONE out of every eight hundred children in the United States is born with a cleft lip, a cleft palate, or both. Within this group
REPAIR OF THE CLEFT LIP ROBIN ANDERSON, M.D. Department of Plastic Surgery ONE out of every eight hundred children in the United States is born with a cleft lip, a cleft palate, or both. Within this group
Evaluation for Severe Physically Handicapping Malocclusion. August 23, 2012
 Evaluation for Severe Physically Handicapping Malocclusion August 23, 2012 Presenters: Office of Health Insurance Programs Division of OHIP Operations Lee Perry, DDS, MBA, Medicaid Dental Director Gulam
Evaluation for Severe Physically Handicapping Malocclusion August 23, 2012 Presenters: Office of Health Insurance Programs Division of OHIP Operations Lee Perry, DDS, MBA, Medicaid Dental Director Gulam
BONE GRAFTING IN TREATMENT OF CLEFT LIP AND PALATE 337
 PRIMARY BONE GRAFTING IN THE TREATMENT OF CLEFT LIP AND PALATE WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO ALVEOLAR COLLAPSE By FRANK ROBINSON, F.R.C.S., and BARRIE WOOD, L.D.S. Burns and Plastic Surgery Unit, Booth Hall
PRIMARY BONE GRAFTING IN THE TREATMENT OF CLEFT LIP AND PALATE WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO ALVEOLAR COLLAPSE By FRANK ROBINSON, F.R.C.S., and BARRIE WOOD, L.D.S. Burns and Plastic Surgery Unit, Booth Hall
Pitfalls in counselling: the craniosynostoses
 J7 Med Genet 1991; 28: 117-121 Pitfalls in counselling: the craniosynostoses Romana Marini, Karen Temple, Lyn Chitty, Sally Genet, Michael Baraitser Abstract We describe three families to highlight the
J7 Med Genet 1991; 28: 117-121 Pitfalls in counselling: the craniosynostoses Romana Marini, Karen Temple, Lyn Chitty, Sally Genet, Michael Baraitser Abstract We describe three families to highlight the
THE KING AND THE SCRATCHED DIAMOND
 BIRTH DEFECTS 1 THE KING AND THE SCRATCHED DIAMOND Once there was a king who had a beautiful, large pure diamond. There was no other diamond like it in the world. One day, it became deeply scratched. The
BIRTH DEFECTS 1 THE KING AND THE SCRATCHED DIAMOND Once there was a king who had a beautiful, large pure diamond. There was no other diamond like it in the world. One day, it became deeply scratched. The
Cleidocranial Dysplasia
 BRIEF REPORTS Cleidocranial Dysplasia Anita Sharma Rohtash Yadav Kuldip Ahlawat Cleidocranial dysplasia (CCD), is characterized by short stature, typical facial features and variable degree of pan-skeletal
BRIEF REPORTS Cleidocranial Dysplasia Anita Sharma Rohtash Yadav Kuldip Ahlawat Cleidocranial dysplasia (CCD), is characterized by short stature, typical facial features and variable degree of pan-skeletal
William F. Walsh, M.D. Katharine D. Wenstrom, M.D. In the early weeks of fetal development, parts of the lip or palate (the roof of the
 John B. Pietsch, M.D. William F. Walsh, M.D. Katharine D. Wenstrom, M.D. Cleft Lip and Palate What are Cleft Lip and Cleft Palate? In the early weeks of fetal development, parts of the lip or palate (the
John B. Pietsch, M.D. William F. Walsh, M.D. Katharine D. Wenstrom, M.D. Cleft Lip and Palate What are Cleft Lip and Cleft Palate? In the early weeks of fetal development, parts of the lip or palate (the
Proboscis lateralis: report of two cases
 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2003) 56, 704 708 CASE REPORT Proboscis lateralis: report of two cases Lütfi Eroğlu a, *, Osman Ata Uysal b a Faculty of Medicine, Department of Plastic and
The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2003) 56, 704 708 CASE REPORT Proboscis lateralis: report of two cases Lütfi Eroğlu a, *, Osman Ata Uysal b a Faculty of Medicine, Department of Plastic and
Postgraduate Medical School, University of London
 THE COMPARATIVE ANATOMY OF CLEFT LIP AND PALATE Part I Classification of Cleft Lip and Palate in Dogs By JAMES CALNAN, F.R.C.S., M.R.C.P. Postgraduate Medical School, University of London IN the veterinary
THE COMPARATIVE ANATOMY OF CLEFT LIP AND PALATE Part I Classification of Cleft Lip and Palate in Dogs By JAMES CALNAN, F.R.C.S., M.R.C.P. Postgraduate Medical School, University of London IN the veterinary
Sensitivity of a Method for the Analysis of Facial Mobility. II. Interlandmark Separation
 Sensitivity of a Method for the Analysis of Facial Mobility. II. Interlandmark Separation CARROLL-ANN TROTMAN, B.D.S., M.A., M.S. JULIAN J. FARAWAY, PH.D. Objective: This study demonstrates a method of
Sensitivity of a Method for the Analysis of Facial Mobility. II. Interlandmark Separation CARROLL-ANN TROTMAN, B.D.S., M.A., M.S. JULIAN J. FARAWAY, PH.D. Objective: This study demonstrates a method of
ASSESSMENT OF MAXILLARY FIRST MOLAR ROTATION IN SKELETAL CLASS II, AND THEIR COMPARISON WITH CLASS I AND CLASS III SUBJECTS
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE ASSESSMENT OF MAXILLARY FIRST MOLAR ROTATION IN SKELETAL CLASS II, AND THEIR COMPARISON WITH CLASS I AND CLASS III SUBJECTS ABSTRACT FARHAT AMIN, BDS, MCPS, FCPS Mesial rotation of maxillary
ORIGINAL ARTICLE ASSESSMENT OF MAXILLARY FIRST MOLAR ROTATION IN SKELETAL CLASS II, AND THEIR COMPARISON WITH CLASS I AND CLASS III SUBJECTS ABSTRACT FARHAT AMIN, BDS, MCPS, FCPS Mesial rotation of maxillary
Chapter 2. Material and methods
 Chapter 2 Material and methods Material and methods Summary This chapter describes the subjects and methods being used in this study. Between 1986 and 1997 9 expeditions were undertaken in remote areas
Chapter 2 Material and methods Material and methods Summary This chapter describes the subjects and methods being used in this study. Between 1986 and 1997 9 expeditions were undertaken in remote areas
Speech/Resonance Disorders due to Clefts and Craniofacial Anomalies
 Speech/Resonance Disorders due to Clefts and Craniofacial Anomalies Ann W. Kummer, PhD, CCC-SLP Cincinnati Children s Hospital Medical Center Royalties: Financial Disclosures Book: Kummer, AW. Cleft Palate
Speech/Resonance Disorders due to Clefts and Craniofacial Anomalies Ann W. Kummer, PhD, CCC-SLP Cincinnati Children s Hospital Medical Center Royalties: Financial Disclosures Book: Kummer, AW. Cleft Palate
Finite Element Modeling of Complete Unilateral Cleft and Palate using MIMICS
 I J C T A, 9(37) 2016, pp. 257-262 International Science Press Finite Element Modeling of Complete Unilateral Cleft and Palate using MIMICS (Maxillary dimensional changes in a Finite element model of a
I J C T A, 9(37) 2016, pp. 257-262 International Science Press Finite Element Modeling of Complete Unilateral Cleft and Palate using MIMICS (Maxillary dimensional changes in a Finite element model of a
MULTIFACTORIAL DISEASES. MG L-10 July 7 th 2014
 MULTIFACTORIAL DISEASES MG L-10 July 7 th 2014 Genetic Diseases Unifactorial Chromosomal Multifactorial AD Numerical AR Structural X-linked Microdeletions Mitochondrial Spectrum of Alterations in DNA Sequence
MULTIFACTORIAL DISEASES MG L-10 July 7 th 2014 Genetic Diseases Unifactorial Chromosomal Multifactorial AD Numerical AR Structural X-linked Microdeletions Mitochondrial Spectrum of Alterations in DNA Sequence
G l o s s a r y. The lack of closure of a normal body orifice or. passage
 A P P E N D I XE G l o s s a r y Allergic rhinitis Swelling of the membrane in the nasal chamber due to allergic reactions; the condition may obstruct breathing Alveolar ridge The bony arches of the maxilla
A P P E N D I XE G l o s s a r y Allergic rhinitis Swelling of the membrane in the nasal chamber due to allergic reactions; the condition may obstruct breathing Alveolar ridge The bony arches of the maxilla
Upper Triangular Flap Method for Primary Repairs of Incomplete Unilateral Cleft Lip Patients. Minor to Two-Thirds Way Defects
 HEAD AND NECK SURGERY Upper Triangular Flap Method for Primary Repairs of Incomplete Unilateral Cleft Lip Patients Minor to Two-Thirds Way Defects Kyung S. Koh, MD, PhD,* Tae Suk Oh, MD,* and Jin Woo Song,
HEAD AND NECK SURGERY Upper Triangular Flap Method for Primary Repairs of Incomplete Unilateral Cleft Lip Patients Minor to Two-Thirds Way Defects Kyung S. Koh, MD, PhD,* Tae Suk Oh, MD,* and Jin Woo Song,
Height- Weight Growth of Cleft Children,
 Height- Weight Growth of Cleft Children, Birth to Six Years DENNIS N. RANALLI, D.D.S.* MOHAMMAD MAZAHERI, D.D.S., M.Sc. Lancaster, Pennsylvania 17602 In 1960 the Toronto Research Institute of the Hospital
Height- Weight Growth of Cleft Children, Birth to Six Years DENNIS N. RANALLI, D.D.S.* MOHAMMAD MAZAHERI, D.D.S., M.Sc. Lancaster, Pennsylvania 17602 In 1960 the Toronto Research Institute of the Hospital
 Evaluation of the maxillary morphological changes following distraction in CLP patients decrease in the Ul to NF except for Case 6. me [35] instance,血e small maxillary advancement of 2.4 mm and maxillary
Evaluation of the maxillary morphological changes following distraction in CLP patients decrease in the Ul to NF except for Case 6. me [35] instance,血e small maxillary advancement of 2.4 mm and maxillary
A REVIEW OF CLASSIFICATION SYSTEMS FOR CLEFTLIP AND PALATE PATIENTS II. EMBRYOLOGICAL CLASSIFICATIONS
 eview Article JKCD June 0, Vol., No. A EVIEW OF CASSIFICATION SYSTEMS FO CEFTIP AND PAATE PATIENTS II. EMBYOOGICA CASSIFICATIONS Syed Nasir Shah, Mariya Khalid, Muhammad Sartaj Khan Department of Prosthodontics
eview Article JKCD June 0, Vol., No. A EVIEW OF CASSIFICATION SYSTEMS FO CEFTIP AND PAATE PATIENTS II. EMBYOOGICA CASSIFICATIONS Syed Nasir Shah, Mariya Khalid, Muhammad Sartaj Khan Department of Prosthodontics
Developing Facial Symmetry Using an Intraoral Device: A Case Report
 Developing Facial Symmetry Using an Intraoral Device: A Case Report by Theodore R. Belfor, D.D.S.; and G. Dave Singh, D.D.Sc., Ph.D., B.D.S. Dr. Theodore Belfor graduated from New York University College
Developing Facial Symmetry Using an Intraoral Device: A Case Report by Theodore R. Belfor, D.D.S.; and G. Dave Singh, D.D.Sc., Ph.D., B.D.S. Dr. Theodore Belfor graduated from New York University College
Quintuplets with Clefts: Follow-up at 5 Years. Y erucham ZirsermaAn, D.M.D. Icana Brin, D.M.D. Dan Mancer, M.D.
 Quintuplets with Clefts: Follow-up at 5 Years Y erucham ZirsermaAn, D.M.D. Icana Brin, D.M.D. Dan Mancer, M.D. Follow-up observations are presented of a set of quintuplets at 5 years of age. Three of the
Quintuplets with Clefts: Follow-up at 5 Years Y erucham ZirsermaAn, D.M.D. Icana Brin, D.M.D. Dan Mancer, M.D. Follow-up observations are presented of a set of quintuplets at 5 years of age. Three of the
Dental Research Journal
 Dental Research Journal Case Report Binder s syndrome: Report of two cases Hitesh Vij 1, Puneet Batra 2, Partha Sadhu 3, Ruchieka Vij 1 1 Departments of Oral Pathology and Microbiology and 2 Orthodontics,
Dental Research Journal Case Report Binder s syndrome: Report of two cases Hitesh Vij 1, Puneet Batra 2, Partha Sadhu 3, Ruchieka Vij 1 1 Departments of Oral Pathology and Microbiology and 2 Orthodontics,
APPROACH TO A DYSMORPHIC INDIVIDUAL. Denise LM Goh
 APPROACH TO A DYSMORPHIC INDIVIDUAL Denise LM Goh Contents The dysmorphic child Incidence of congenital anomalies Suspicion for diagnosis Approach to the dysmorphic child Problem analysis history hysical
APPROACH TO A DYSMORPHIC INDIVIDUAL Denise LM Goh Contents The dysmorphic child Incidence of congenital anomalies Suspicion for diagnosis Approach to the dysmorphic child Problem analysis history hysical
Basic Training. ISUOG Basic Training Examining the Upper Lip, Face & Profile
 ISUOG Examining the Upper Lip, Face & Profile Learning objectives At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Describe how to obtain the 3 planes required to assess the anatomy of the fetal face Recognise
ISUOG Examining the Upper Lip, Face & Profile Learning objectives At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Describe how to obtain the 3 planes required to assess the anatomy of the fetal face Recognise
Rotation-Advancement Principle. in Cleft Lip Closure. D. RALPH MILLARD, JR., M.D., F.A.C.S. Miami, Florida
 Rotation-Advancement Principle in Cleft Lip Closure D. RALPH MILLARD, JR., M.D., F.A.C.S. Miami, Florida Correction of prealveolar, alveolar, and postalveolar clefts poses a fivefold project: natural appearance,
Rotation-Advancement Principle in Cleft Lip Closure D. RALPH MILLARD, JR., M.D., F.A.C.S. Miami, Florida Correction of prealveolar, alveolar, and postalveolar clefts poses a fivefold project: natural appearance,
THE PREVALENCE OF HYPODONTIA IN CHILDREN WITH CLEFT AND NONRELATED CONTROLS
 THE PREVALENCE OF HYPODONTIA IN CHILDREN WITH CLEFT AND NONRELATED CONTROLS Claudia COREGA, Alin SERBANESCU, Mihai COREGA, Mihaela BACIUT University of Medicine and Pharmacy Iuliu Hatieganu Cluj-Napoca,
THE PREVALENCE OF HYPODONTIA IN CHILDREN WITH CLEFT AND NONRELATED CONTROLS Claudia COREGA, Alin SERBANESCU, Mihai COREGA, Mihaela BACIUT University of Medicine and Pharmacy Iuliu Hatieganu Cluj-Napoca,
The Prevention of Maxillary Collapse in
 The Prevention of Maxillary Collapse in Congenital Lip and Palate Cases CHARLES E. HUGH H. JEROME E. HORTON, M.D. CRAWFORD, M.D. ADAMSON, M.D. SAMUEL BUXTON, D.D.S. REUBEN COOPER, M.S. JACK KANTER, D.D.S.
The Prevention of Maxillary Collapse in Congenital Lip and Palate Cases CHARLES E. HUGH H. JEROME E. HORTON, M.D. CRAWFORD, M.D. ADAMSON, M.D. SAMUEL BUXTON, D.D.S. REUBEN COOPER, M.S. JACK KANTER, D.D.S.
Typical Cleft Hand. Windblown Hand. Congenital, Developmental Arrest. Congenital, Failure of Differentiation. Longitudinal (vs.
 Typical Cleft Hand Congenital, Developmental Arrest Longitudinal (vs. Transverse) Central Deficiency (vs. Preaxial, Postaxial, Phocomelia) Windblown Hand Congenital, Failure of Differentiation Contracture
Typical Cleft Hand Congenital, Developmental Arrest Longitudinal (vs. Transverse) Central Deficiency (vs. Preaxial, Postaxial, Phocomelia) Windblown Hand Congenital, Failure of Differentiation Contracture
What ASE orthodontists must (?) know about genetics
 Genetics Request from the ASE President 2013-2014 What ASE orthodontists must (?) know about genetics Carine CARELS, DDS, PhD professor of orthodontics OCB research group leader Radboudumc Department of
Genetics Request from the ASE President 2013-2014 What ASE orthodontists must (?) know about genetics Carine CARELS, DDS, PhD professor of orthodontics OCB research group leader Radboudumc Department of
MedStar Health considers Septoplasty-Rhinoplasty medically necessary for the following indications:
 MedStar Health, Inc. POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL MP.038.MH Septoplasty-Rhinoplasty This policy applies to the following lines of business: MedStar Employee (Select) MedStar MA DSNP CSNP MedStar CareFirst
MedStar Health, Inc. POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL MP.038.MH Septoplasty-Rhinoplasty This policy applies to the following lines of business: MedStar Employee (Select) MedStar MA DSNP CSNP MedStar CareFirst
22q11 deletion syndrome Report from observation charts
 Orofacial function of persons having 22q11 deletion syndrome Report from observation charts The survey comprises 147 observation charts. Synonyms: CATCH 22, Di George syndrome, Velocardiofacial syndrome
Orofacial function of persons having 22q11 deletion syndrome Report from observation charts The survey comprises 147 observation charts. Synonyms: CATCH 22, Di George syndrome, Velocardiofacial syndrome
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Rhinologic Computed Tomographic Evaluation in Patients With Cleft Lip and Palate
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Rhinologic Computed Tomographic Evaluation in Patients With Cleft Lip and Palate Hideaki Suzuki, MD, PhD; Tai Yamaguchi, DDS, PhD; Masayuki Furukawa, MD, PhD Objective: To investigate
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Rhinologic Computed Tomographic Evaluation in Patients With Cleft Lip and Palate Hideaki Suzuki, MD, PhD; Tai Yamaguchi, DDS, PhD; Masayuki Furukawa, MD, PhD Objective: To investigate
Chronology of Deciduous Teeth Eruption in Children With Cleft Lip and Palate
 Chronology of Deciduous Teeth Eruption in Children With Cleft Lip and Palate CRISTIANE DUQUE GISELE DA SILVA DALBEN ANDREZA MARIA FÁBIO ARANHA CLEIDE FELíCIO DE CARVALHO CARRARA, M.SC. MARCIA RIBEIRO GOMIDE,
Chronology of Deciduous Teeth Eruption in Children With Cleft Lip and Palate CRISTIANE DUQUE GISELE DA SILVA DALBEN ANDREZA MARIA FÁBIO ARANHA CLEIDE FELíCIO DE CARVALHO CARRARA, M.SC. MARCIA RIBEIRO GOMIDE,
Dentofacial analysis in North Indian females
 Available online at www.ijpab.com ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 1 (3): 28-33 (2013) Research Article International Journal of Pure & Applied Bioscience Dentofacial analysis in North Indian
Available online at www.ijpab.com ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 1 (3): 28-33 (2013) Research Article International Journal of Pure & Applied Bioscience Dentofacial analysis in North Indian
CLEFT LIP and PALATE. Sahlgrenska University Hospital Göteborg, Sweden. Information about Cleft Lip and Palate. English version
 CLEFT LIP and PALATE Sahlgrenska University Hospital Göteborg, Sweden Information about Cleft Lip and Palate English version 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS page What are cleft lip and palate? 3 Which children can
CLEFT LIP and PALATE Sahlgrenska University Hospital Göteborg, Sweden Information about Cleft Lip and Palate English version 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS page What are cleft lip and palate? 3 Which children can
PAPAIN IN THE TR EA TM EN T O F BILA TER A L CLEFT PALATES
 Die T ydskrif van die T.V.S.A. PAPAIN IN THE TR EA TM EN T O F BILA TER A L CLEFT PALATES C. J. D reyer,* G. G avron" ami P. Ci eaton-jones* HE incidence of clefts of the lip and T palate in South Africa
Die T ydskrif van die T.V.S.A. PAPAIN IN THE TR EA TM EN T O F BILA TER A L CLEFT PALATES C. J. D reyer,* G. G avron" ami P. Ci eaton-jones* HE incidence of clefts of the lip and T palate in South Africa
Sex-linked Cleft Palate* Report of a Family and Review of 77 Kindreds
 J. med. Genet. (I966). 3, I7. Sex-linked Cleft Palate* Report of a Family and Review of 77 Kindreds E. DAVID WEINSTEINt and MAIMON M. COHEN+ From the Department of Human Genetics, University of Michigan,
J. med. Genet. (I966). 3, I7. Sex-linked Cleft Palate* Report of a Family and Review of 77 Kindreds E. DAVID WEINSTEINt and MAIMON M. COHEN+ From the Department of Human Genetics, University of Michigan,
Embryo#1. Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb باشق جهاد. 0 P a g e
 Embryo#1 Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb باشق جهاد 0 P a g e Before you start, it is important to link what you learn in gross anatomy with developmental stages discussed in embryology. Cells that form organs
Embryo#1 Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb باشق جهاد 0 P a g e Before you start, it is important to link what you learn in gross anatomy with developmental stages discussed in embryology. Cells that form organs
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY GR. T. POPA - IASI FACULTY OF DENTAL MEDICINE
 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY GR. T. POPA - IASI FACULTY OF DENTAL MEDICINE ABSTRACT CONTRIBUTIONS OF THREE-DIMENSIONAL IMAGING TO THE DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF CLEFT LIP AND PALATE PhD ADVISOR,
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY GR. T. POPA - IASI FACULTY OF DENTAL MEDICINE ABSTRACT CONTRIBUTIONS OF THREE-DIMENSIONAL IMAGING TO THE DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF CLEFT LIP AND PALATE PhD ADVISOR,
What is Hemifacial Microsomia? By Pravin K. Patel, MD and Bruce S. Bauer, MD Children s Memorial Hospital, Chicago, IL
 What is Hemifacial Microsomia? By Pravin K. Patel, MD and Bruce S. Bauer, MD Children s Memorial Hospital, Chicago, IL 773-880-4094 Early in the child s embryonic development the structures destined to
What is Hemifacial Microsomia? By Pravin K. Patel, MD and Bruce S. Bauer, MD Children s Memorial Hospital, Chicago, IL 773-880-4094 Early in the child s embryonic development the structures destined to
Cervical Vertebral Anomalies in Cleft Lip and Palate. ANDREW SanpHAm, B.D.S., F.D.S.R.C.S., D.ORrtH.
 Cervical Vertebral Anomalies in Cleft Lip and Palate ANDREW SanpHAm, B.D.S., F.D.S.R.C.S., D.ORrtH. A survey was made of the upper cervical vertebrae in children with cleft lip and palate in order to determine
Cervical Vertebral Anomalies in Cleft Lip and Palate ANDREW SanpHAm, B.D.S., F.D.S.R.C.S., D.ORrtH. A survey was made of the upper cervical vertebrae in children with cleft lip and palate in order to determine
Cairo Dental Journal (24) Number (I), 77:84 January, Haitham Sayed Attia 3, Mohamed Saied Hamed 1 and Monteser El Koutobey 2
 Cairo Dental Journal (24) Number (I), 77:84 January, 2008 Anthropometric Analysis of cases of Unilateral Cleft Lip Versus cases of Complete Unilateral Cleft Lip and Palate Haitham Sayed Attia 3, Mohamed
Cairo Dental Journal (24) Number (I), 77:84 January, 2008 Anthropometric Analysis of cases of Unilateral Cleft Lip Versus cases of Complete Unilateral Cleft Lip and Palate Haitham Sayed Attia 3, Mohamed
ORAL AND CRANIOFACIAL CHARACTERISTICS OF UNTREATED ADULT UNILATERAL CLEFT LIP AND PALATE INDIVIDUALS
 Short Communication ORAL AND CRANIOFACIAL CHARACTERISTICS OF UNTREATED ADULT UNILATERAL CLEFT LIP AND PALATE INDIVIDUALS M. S. Ravi Professor, Dept. of Orthodontics, A. B. Shetty Memorial Institute of
Short Communication ORAL AND CRANIOFACIAL CHARACTERISTICS OF UNTREATED ADULT UNILATERAL CLEFT LIP AND PALATE INDIVIDUALS M. S. Ravi Professor, Dept. of Orthodontics, A. B. Shetty Memorial Institute of
Dr. N. Retnakumari. MDS, M.Phil, Dr. Manuja Vargheese, Dr. Madhu.S, Dr. Divya. S
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 12, Issue 5 (Nov.- Dec. 2013), PP 11-15 A new approach in Presurgical Infant Orthopedics using an Active
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 12, Issue 5 (Nov.- Dec. 2013), PP 11-15 A new approach in Presurgical Infant Orthopedics using an Active
SEMI- ANNUAL FELLOWSHIP REPORT June 2015 to December 2015
 SEMI- ANNUAL FELLOWSHIP REPORT June 2015 to December 2015 Submitted by, Dr.Arun Ramaiah., Resident fellow, St.Thomas Cleft and Craniofacial centre. Letter to CCI To start with I would like to thank Cleft
SEMI- ANNUAL FELLOWSHIP REPORT June 2015 to December 2015 Submitted by, Dr.Arun Ramaiah., Resident fellow, St.Thomas Cleft and Craniofacial centre. Letter to CCI To start with I would like to thank Cleft
Scientific Forum. Nostrilplasty: Raising, Lowering, Widening, and Symmetry Correction of the Alar Rim
 Nostrilplasty: Raising, Lowering, Widening, and Symmetry Correction of the lar Rim Richard Ellenbogen, MD; and Greg azell, MD ackground: lthough the alar rim has frequently been neglected in correction
Nostrilplasty: Raising, Lowering, Widening, and Symmetry Correction of the lar Rim Richard Ellenbogen, MD; and Greg azell, MD ackground: lthough the alar rim has frequently been neglected in correction
APPENDIX A. MEDICAID ORTHODONTIC INITIAL ASSESSMENT FORM (IAF) You will need this scoresheet and a disposable ruler (or a Boley Gauge)
 APPENDIX A MEDICAID ORTHODONTIC INITIAL ASSESSMENT FORM (IAF) You will need this scoresheet and a disposable ruler (or a Boley Gauge) Name: _ I. D. Number: Conditions: 1. Cleft palate deformities 2. Deep
APPENDIX A MEDICAID ORTHODONTIC INITIAL ASSESSMENT FORM (IAF) You will need this scoresheet and a disposable ruler (or a Boley Gauge) Name: _ I. D. Number: Conditions: 1. Cleft palate deformities 2. Deep
Orthodontic Morphological Evaluation of Treacher Collins Syndrome
 Cong. Anorn., 39: 243-253,1999 Original Orthodontic Morphological Evaluation of Treacher Collins Syndrome Sachio UMEMURA Department of Orthodontics, Ohu University School of Dentistry, 31-1 Misumido Tomita,
Cong. Anorn., 39: 243-253,1999 Original Orthodontic Morphological Evaluation of Treacher Collins Syndrome Sachio UMEMURA Department of Orthodontics, Ohu University School of Dentistry, 31-1 Misumido Tomita,
Fetal Medicine. Case Presentations. Dr Ermos Nicolaou Fetal Medicine Unit Chris Hani Baragwanath Hospital. October 2003
 Case Presentations Dr Ermos Nicolaou Fetal Medicine Unit Chris Hani Baragwanath Hospital October 2003 Case 1 Ms A M 22year old P0 G1 Referred from Sebokeng Hospital at 36w for polyhydramnios On Ultrasound:
Case Presentations Dr Ermos Nicolaou Fetal Medicine Unit Chris Hani Baragwanath Hospital October 2003 Case 1 Ms A M 22year old P0 G1 Referred from Sebokeng Hospital at 36w for polyhydramnios On Ultrasound:
Spectrum of Cranio-facial anomalies during 2 Ultrasound. trimester on
 Spectrum of Cranio-facial anomalies during 2 Ultrasound nd trimester on Poster No.: C-0378 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: K. Dave, S. Solanki; Ahmedabad/IN Keywords: Obstetrics (Pregnancy
Spectrum of Cranio-facial anomalies during 2 Ultrasound nd trimester on Poster No.: C-0378 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: K. Dave, S. Solanki; Ahmedabad/IN Keywords: Obstetrics (Pregnancy
T HERE is an unusual and interesting variety of craniosynostosis in
 SURGICAL TREATMENT OF CONGENITAL ANOMALIES OF THE CORONAL AND METOPIC SUTURES TECHNICAL NOTE DONALD D. MATSON, M.D. Neurosurgical Service, The Children's Medical Center, and Deparlment of Surgery, Itarvard
SURGICAL TREATMENT OF CONGENITAL ANOMALIES OF THE CORONAL AND METOPIC SUTURES TECHNICAL NOTE DONALD D. MATSON, M.D. Neurosurgical Service, The Children's Medical Center, and Deparlment of Surgery, Itarvard
Cleft-Craniofacial Center
 Cleft-Craniofacial Center A Pioneering T eam 2 Welcome to the Cleft-Craniofacial Center at Children s Hospital of Pittsburgh The Cleft-Craniofacial Center at Children s Hospital of Pittsburgh has been
Cleft-Craniofacial Center A Pioneering T eam 2 Welcome to the Cleft-Craniofacial Center at Children s Hospital of Pittsburgh The Cleft-Craniofacial Center at Children s Hospital of Pittsburgh has been
(i) Family 1. The male proband (1.III-1) from European descent was referred at
 1 Supplementary Note Clinical descriptions of families (i) Family 1. The male proband (1.III-1) from European descent was referred at age 14 because of scoliosis. He had normal development. Physical evaluation
1 Supplementary Note Clinical descriptions of families (i) Family 1. The male proband (1.III-1) from European descent was referred at age 14 because of scoliosis. He had normal development. Physical evaluation
Modified Intraoral Repositioning Appliance in Complete Bilateral Cleft Lip and Palate
 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-1096 CASE REPORT IJCPD Modified Intraoral Repositioning Appliance in Complete Bilateral Cleft Lip and Palate 1 Pradeep Raghav, 2 NK Ahuja, 3 Subhash Gahlawat 1 Professor, Department
10.5005/jp-journals-10005-1096 CASE REPORT IJCPD Modified Intraoral Repositioning Appliance in Complete Bilateral Cleft Lip and Palate 1 Pradeep Raghav, 2 NK Ahuja, 3 Subhash Gahlawat 1 Professor, Department
Genetic counselling in PGD
 Genetic counselling in PGD Sérgio Castedo Serviço de Genética Faculdade de Medicina do Porto scastedo@netcabo.pt Disclosure of interests Sérgio Castedo is the CEO of GDPN, a private genetics diagnostic
Genetic counselling in PGD Sérgio Castedo Serviço de Genética Faculdade de Medicina do Porto scastedo@netcabo.pt Disclosure of interests Sérgio Castedo is the CEO of GDPN, a private genetics diagnostic
SURGICAL TREATMENT OF MANDIBULAR ASYMMETRY By MARIAN GORSKI, M.D., 1 and IRENA HALINA TARCZYNSKA, M.D. Maxillo-Facial Clinic, Warsaw Medical Academy
 SURGICL TRETMENT OF MNDIULR SYMMETRY y MRIN GORSKI, M.D., 1 and IREN HLIN TRCZYNSK, M.D. Maxillo-Facial Clinic, Warsaw Medical cademy UNILTERL mandibular deformities may be due to either overgrowth or
SURGICL TRETMENT OF MNDIULR SYMMETRY y MRIN GORSKI, M.D., 1 and IREN HLIN TRCZYNSK, M.D. Maxillo-Facial Clinic, Warsaw Medical cademy UNILTERL mandibular deformities may be due to either overgrowth or
Pharyngeal Apparatus. Pouches Endoderm Grooves Ectoderm Arch Neural Crest Somitomeres Aortic Arch - Vessel
 Pharyngeal Apparatus Pouches Endoderm Grooves Ectoderm Arch Neural Crest Somitomeres Aortic Arch - Vessel Segmental Organization Humans: Arch 1-4 prominent Arch 5 absent Arch 6 - transient First Arch Face
Pharyngeal Apparatus Pouches Endoderm Grooves Ectoderm Arch Neural Crest Somitomeres Aortic Arch - Vessel Segmental Organization Humans: Arch 1-4 prominent Arch 5 absent Arch 6 - transient First Arch Face
I have no disclosures
 I have no disclosures Provide an overview of the spectrum of congenital upper extremity anomalies Describe the key imaging findings of these abnormalities Discuss the important clinical features of these
I have no disclosures Provide an overview of the spectrum of congenital upper extremity anomalies Describe the key imaging findings of these abnormalities Discuss the important clinical features of these
Attachment G. Orthodontic Criteria Index Form Comprehensive D8080. ABBREVIATIONS CRITERIA for Permanent Dentition YES NO
 First Review IL HFS Dental Program Models Second Review Ortho cad Attachment G Orthodontic Criteria Index Form Comprehensive D8080 Ceph Film X-Rays Photos Narrative Patient Name: DOB: ABBREVIATIONS CRITERIA
First Review IL HFS Dental Program Models Second Review Ortho cad Attachment G Orthodontic Criteria Index Form Comprehensive D8080 Ceph Film X-Rays Photos Narrative Patient Name: DOB: ABBREVIATIONS CRITERIA
ORTHODONTIC INITIAL ASSESSMENT FORM (OIAF) w/ INSTRUCTIONS
 Use the accompanying Tip Sheet and How to Score the Orthodontic Initial Assessment Form for guidance in completion of the assessment form. You will need this score sheet and a disposable ruler (or a Boley
Use the accompanying Tip Sheet and How to Score the Orthodontic Initial Assessment Form for guidance in completion of the assessment form. You will need this score sheet and a disposable ruler (or a Boley
ORTHOGNATHIC SURGERY
 Status Active Medical and Behavioral Health Policy Section: Surgery Policy Number: IV-16 Effective Date: 10/22/2014 Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Minnesota medical policies do not imply that members should
Status Active Medical and Behavioral Health Policy Section: Surgery Policy Number: IV-16 Effective Date: 10/22/2014 Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Minnesota medical policies do not imply that members should
clefting in France. I Epidemiology and frequency in
 Journal of Medical Genetics, 1982, 19, 8-15 An epidemiological and genetic study of facial clefting in France. I Epidemiology and frequency in relatives' C BONAITI*t, M L BRIARD*, J FEINGOLD*t, B PAVY+,
Journal of Medical Genetics, 1982, 19, 8-15 An epidemiological and genetic study of facial clefting in France. I Epidemiology and frequency in relatives' C BONAITI*t, M L BRIARD*, J FEINGOLD*t, B PAVY+,
IJCMR 553. ORIGINAL RESEARCH Different Population- Different Analysis A Cephalometric Study. Sachin Singh 1, Jayesh Rahalkar 2 ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION
 IJCMR 553 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Different Population- Different Analysis A Cephalometric Study Sachin Singh 1, Jayesh Rahalkar 2 ABSTRACT Introduction: Cephalometric norms derived for Caucasian population
IJCMR 553 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Different Population- Different Analysis A Cephalometric Study Sachin Singh 1, Jayesh Rahalkar 2 ABSTRACT Introduction: Cephalometric norms derived for Caucasian population
UCL Repair: Emphasis on Muscle Dissection and Reconstruction
 UCL Repair: Emphasis on Muscle Dissection and Reconstruction Unilateral cleft lip repair is performed using rotation-advancement technique. Markings are made on columella base, redlines, Cupid s bow on
UCL Repair: Emphasis on Muscle Dissection and Reconstruction Unilateral cleft lip repair is performed using rotation-advancement technique. Markings are made on columella base, redlines, Cupid s bow on
Single Gene (Monogenic) Disorders. Mendelian Inheritance: Definitions. Mendelian Inheritance: Definitions
 Single Gene (Monogenic) Disorders Mendelian Inheritance: Definitions A genetic locus is a specific position or location on a chromosome. Frequently, locus is used to refer to a specific gene. Alleles are
Single Gene (Monogenic) Disorders Mendelian Inheritance: Definitions A genetic locus is a specific position or location on a chromosome. Frequently, locus is used to refer to a specific gene. Alleles are
Unilateral Cleft Lip Repair by using White-skin-roll Flap from Cleft Side of Lip
 Unilateral Cleft Lip Repair by using White-skin-roll Flap from Cleft Side of Lip Background: With all due consideration to the restoration of function, post-operative aesthetic appearance of the cleft
Unilateral Cleft Lip Repair by using White-skin-roll Flap from Cleft Side of Lip Background: With all due consideration to the restoration of function, post-operative aesthetic appearance of the cleft
Unilateral Cleft Palate, a case report.
 Original Article Published on 29-09-05 Yaşar Göyenç* Hakan Gürcan Gürel** Author s affiliations: * PhD, Professor ** DDS, Research Assistant Department of Orthodontics, Faculty of Dentistry, Selcuk University,
Original Article Published on 29-09-05 Yaşar Göyenç* Hakan Gürcan Gürel** Author s affiliations: * PhD, Professor ** DDS, Research Assistant Department of Orthodontics, Faculty of Dentistry, Selcuk University,
Effects of Early and Late Cheiloplasty on Posterior Part of Maxillary Dental Arch Development in Infants
 Research Article Effects of Early and Late Cheiloplasty on Posterior Part of Maxillary Dental Arch Development in Infants Radovan Malina (contact author), Department of Biology and Ecology, Matej Bel University,
Research Article Effects of Early and Late Cheiloplasty on Posterior Part of Maxillary Dental Arch Development in Infants Radovan Malina (contact author), Department of Biology and Ecology, Matej Bel University,
OTITIS MEDIA IN NONSYNDROMIC OROFACIAL CLEFT FAMILIES. Teresa Alexandra Ruegg. B.A. Biology, California State University: Northridge, 2010
 OTITIS MEDIA IN NONSYNDROMIC OROFACIAL CLEFT FAMILIES by Teresa Alexandra Ruegg B.A. Biology, California State University: Northridge, 2010 Submitted to the Graduate Faculty of Human Genetics Genetic Counseling
OTITIS MEDIA IN NONSYNDROMIC OROFACIAL CLEFT FAMILIES by Teresa Alexandra Ruegg B.A. Biology, California State University: Northridge, 2010 Submitted to the Graduate Faculty of Human Genetics Genetic Counseling
Page 1 of 6 Initials Revision American Society of Plastic Surgeons
 Plastic Surgery & Dermatology Associates (PSDA) CLEFT LIP AND/OR PALATE ASSOCIATED NOSE / RHINOPLASTY SURGERY INFORMATION SHEET AND INFORMED CONSENT Instructions This is an informed consent document that
Plastic Surgery & Dermatology Associates (PSDA) CLEFT LIP AND/OR PALATE ASSOCIATED NOSE / RHINOPLASTY SURGERY INFORMATION SHEET AND INFORMED CONSENT Instructions This is an informed consent document that
Treatment of Hemifacial Microsomia: A Case Report
 Iran J Ortho. 2015 June; 10(1):e4931. Published online 2015 June 13. doi: 10.17795/ijo-4931 Case Report Treatment of Hemifacial Microsomia: A Case Report Mohsen Shirazi, 1 Elahe Soltanmohamadi Borujeni,
Iran J Ortho. 2015 June; 10(1):e4931. Published online 2015 June 13. doi: 10.17795/ijo-4931 Case Report Treatment of Hemifacial Microsomia: A Case Report Mohsen Shirazi, 1 Elahe Soltanmohamadi Borujeni,
Complications in single gene analysis
 Complications in single gene analysis A. Lethals In chickens creeper X creeper 2/3 creeper : 1/3 normal But: 1/4th of the eggs never hatched and were found to have grossly deformed chicks Legend: C'C'
Complications in single gene analysis A. Lethals In chickens creeper X creeper 2/3 creeper : 1/3 normal But: 1/4th of the eggs never hatched and were found to have grossly deformed chicks Legend: C'C'
Tooth Maturation in Cleft Lip, Cleft Palate, or Both. HaAnNELoRE T. Loevy, C.D., PH.D. Howarbp Apuss, D.D.S.
 Tooth Maturation in Cleft Lip, Cleft Palate, or Both HaAnNELoRE T. Loevy, C.D., PH.D. Howarbp Apuss, D.D.S. The relation between chronologic age and the development of permanent teeth in patients with
Tooth Maturation in Cleft Lip, Cleft Palate, or Both HaAnNELoRE T. Loevy, C.D., PH.D. Howarbp Apuss, D.D.S. The relation between chronologic age and the development of permanent teeth in patients with
FACIAL FORM AS A SUBCLINICAL PHENOTYPE OF NONSYNDROMIC OROFACIAL CLEFTING: AN ANTHROPOMETRIC ANALYSIS. Suman Gorantla. DMD, Boston University, 2007
 FACIAL FORM AS A SUBCLINICAL PHENOTYPE OF NONSYNDROMIC OROFACIAL CLEFTING: AN ANTHROPOMETRIC ANALYSIS by Suman Gorantla DMD, Boston University, 2007 MPH, East Tennessee State University, 2005 Submitted
FACIAL FORM AS A SUBCLINICAL PHENOTYPE OF NONSYNDROMIC OROFACIAL CLEFTING: AN ANTHROPOMETRIC ANALYSIS by Suman Gorantla DMD, Boston University, 2007 MPH, East Tennessee State University, 2005 Submitted
Three-dimensional assessment of the alveolar bone defect in unilateral cleft lip and palate patients
 Three-dimensional assessment of the alveolar bone defect in unilateral cleft lip and palate patients Poster No.: C-2009 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: D. Haba, Y. Deçolli, A. Nemtoi,
Three-dimensional assessment of the alveolar bone defect in unilateral cleft lip and palate patients Poster No.: C-2009 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: D. Haba, Y. Deçolli, A. Nemtoi,
Faravareh Khordadpoor (PhD in molecular genetics) 1- Tehran Medical Genetics Laboratory 2- Science and research branch, Islamic Azad University
 Faravareh Khordadpoor (PhD in molecular genetics) 1- Tehran Medical Genetics Laboratory 2- Science and research branch, Islamic Azad University 1395 21 مشاوره ژنتیک و نقش آن در پیش گیری از معلولیت ها 20
Faravareh Khordadpoor (PhD in molecular genetics) 1- Tehran Medical Genetics Laboratory 2- Science and research branch, Islamic Azad University 1395 21 مشاوره ژنتیک و نقش آن در پیش گیری از معلولیت ها 20
Case Report Prosthodontic Rehabilitation Alternative of Patients with Cleft Lip and Palate (CLP): Two Cases Report
 International Dentistry Volume 2009, Article ID 515790, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2009/515790 Case Report Prosthodontic Rehabilitation Alternative of Patients with Cleft Lip and Palate (CLP): Two Cases Report
International Dentistry Volume 2009, Article ID 515790, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2009/515790 Case Report Prosthodontic Rehabilitation Alternative of Patients with Cleft Lip and Palate (CLP): Two Cases Report
