A REVIEW OF CLASSIFICATION SYSTEMS FOR CLEFTLIP AND PALATE PATIENTS II. EMBRYOLOGICAL CLASSIFICATIONS
|
|
|
- Philippa Weaver
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
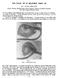
1 eview Article JKCD June 0, Vol., No. A EVIEW OF CASSIFICATION SYSTEMS FO CEFTIP AND PAATE PATIENTS II. EMBYOOGICA CASSIFICATIONS Syed Nasir Shah, Mariya Khalid, Muhammad Sartaj Khan Department of Prosthodontics Sardar Begum Dental College and Hospital, Gandhara University, Academy Town, Peshawar, Pakistan ABSTACT The second and final article of this series describes the embryological classifications of cleft lip and palate patients, their usage and deficiencies. INTODUCTION This article has described classification systems based on the embryological features. The structures contributing to the formation of face are the frontonasal prominence, maxillary prominence and mandibular prominence. The frontonasal prominence forms forehead, bridge of nose, medial and lateral nasal prominence. The maxillary prominence forms cheeks and lateral portion of upper lip and the mandibular prominence forms the lower lip. The medial nasal prominence forms the philtrum of the upper lip, crest and tip of nose whereas the lateral nasal prominence forms the alae of nose. During the fifth week of intrauterine life, nasal placodes invaginate to form nasal pits. The prominence on the outer edge of pits is the lateral nasal prominences and those on the inner edge are the medial nasal prominences. During following two weeks, maxillary prominences grow medially, compressing medial nasal prominence towards midline. Hence, upper lip is formed by two medial nasal prominences and two maxillary prominences. Cleft deformities of lips is due to partial or complete lack of fusion of the maxillary prominence with the medial nasal prominence on one or both sides. The two medial nasal prominences merge not only at the surface but also at a deeper level and form a structure known as intermaxillary segment. Inter- Correspondence: Dr. Syed Nasir Shah Head Department of Prosthodontics Sardar Begum Dental College and Hospital, Gandhara University, Academy Town, Peshawar, Pakistan syedshah@live.com maxillary segment is responsible for the formation of philtrum of upper lip, jaw component which carries four incisors and palatal component which forms triangular primary palate. During the sixth week of development, palatine shelves appear as two shelves like outgrowths from the maxillary prominence directing obliquely downward on each side of tongue. In the seventh week, palatine shelves ascend to attain horizontal position above the tongue and fuse forming secondary palate. Anteriorly, the shelves fuse with triangular primary palate. The incisive foramen is the midline landmark between primary and secondary palates. The incisive foramen is the dividing landmark between the anterior and posterior cleft deformities in all embryological classifications. The previous article of this series described the morphological classifications of cleft lip and palate. This article has described some of the more wellknown embryological classifications.. KENAHAN STIPED Y CASSIFICATION: Kernahan proposed this classification in. This system provides graphic classification scheme using Y-configuration as shown in figure. Areas and - ip (It represents the fusion line between the maxillary prominence and medial nasal prominence at lip level). Areas and Alveolus (It represents the fusion line between the maxillary prominence and intermaxillary segment).
2 JKCD June 0, Vol., No. incisive papilla Fig. : Kernahan striped Y classification Areas and Primary Palate (It represents the fusion line between the primary and secondary palate and lies anterior to the incisive foramen). Areas and - Hard palate (It represents the fusion line between palatine shelves of the hard palate posterior to the incisive foramen). Area - Soft palate The small circle represents incisive papilla. In order to show the cleft, stippling of the appropriate areas is done on the above diagram. EXAMPES:. Clefts of the soft palate will be represented by the following diagram.. eft Cleft lip will be represented by the following diagram.. MODIFIED STIPED-Y ESAHY CASSIFICATION: Elsahy modified Kernahan Striped Y classification in by recording more details as shown in Figure 0 Fig. : Modified striped-y Elshay classification Triangle represents the fusion line between the at nostril floor level on right side while triangle represents the fusion line between the on the left side at the nostril floor level. Square represents the fusion line between the at upper lip level on the right side while square represents the fusion line between the at upper lip level on the left side. Square represents the right alveolus while square represents the left alveolus (fusion line between the maxillary prominence and intermaxillary segment). Square and represents the fusion line between primary and secondary hard palate (which lies anterior to the incisive foramen) on the right and left side respectively. Squares and 0 represents the fusion line between palatine shelves of hard palate and lies posterior to the incisive foramen. Square represents the soft palate. Circle represents the posterior pharyngeal wall. Circle represents the pre-maxilla. This classification has following advantages over original striped-y.. It gives information about the degree of cleft lip. For example, if there is unilateral complete cleft lip(involving lip and nostril floor) stippling will include the triangle and square on that side (incase of bilateral cleft lip, the respective areas
3 will be stippled on both sides). If the cleft lip is incomplete i.e. it does not include nostril floor, then the stippling will include square or only(if bilateral, then squares on both sides). Examples: 0 ight Complete cleft lip 0 eft Incomplete Cleft lip Bilateral complete cleft lip. It can indicate the collapse of the alveolar arch. For example, if there is collapse of the lateral maxillary segment, squares and or and (depending upon the side) will be shaded black instead of stippled. Example: Collapse of ight maxillary segment will be shown as follows: 0. It represents hard and soft palate separately. Squares and 0 represents hard palate and are bordered by lines (to distinguish it from soft palate) whereas square represents soft palate and is bordered by a single line.. It indicates displacement of palatal segments. If there is displacement of the palatal segment towards the right, an X can be drawn over the arrow on the right side, if displacement is towards left, then X will be drawn on the left. Example: Displacement of palatal segments towards the left will be represented by following diagram. 0 JKCD June 0, Vol., No. 0. It gives information about the state of velopharygeal closure. As, circle represents the posterior pharyngeal wall, if there is a good velopharyngeal closure, a line is drawn on the dots to join circle with square. If there is no velopharyngeal closure, no line is drawn. Thus, the length of the line drawn between circle and square indicates the degree of velopharyngeal closure. Examples: 0 Complete velopharyngeal closure. It indicates the presence or absence of protruding pre-maxilla and the degree of protrusion. If there is protrusion of pre-maxilla, a line is drawn along the dots in the direction of arrow towards circle number. The length of line drawn will indicate the degree of pre-maxillary protrusion. Example: The following diagram shows presence and degree of pre-maxillary protrusion.. FIEDMAN S CASSIFICATION: In, Friedman combined Elsahy and millard s classification by using numbers in each segment of the diagram to represent severity of the condition as shown in figure. Triangles and - Nostril arch. Triangles and - Nasal floor (fusion line be- X 0 Incomplete velopharyngeal closure
4 JKCD June 0, Vol., No. STEP I: This step includes the depiction of the deformity of the nasal arches (triangles and )and nasal floors (triangles and ). In each triangular space, the defect is recorded in the following manner. 0 = Cleft microform (e.g; notching) = Mild deformity (i.e; some actual tissue deficiency) tween the maxillary prominence and medial nasal = Moderate deformity prominence at nostril floor level). = Severe deformity IGHT EFT POABIUM STEP II: Fig. : Friedman s classification Square and - ip (fusion line between the at the upper lip level). Squares and - Alveolus (fusion line between the maxillary prominence and intermaxillary segment). Squares and 0-Primary palate (fusion line between the primary palate and secondary palate and is present anterior to the incisive foramen). Square - Hard palate (fusion line between the two palatine shelves of hard palate). Square - Soft palate. 0 Circle - Velopharyngeal valve. Circle and - Prolabium. There are eight steps to record clinical findings and to represent them in this diagram. NOSTI ACH NASA FOO IP AVEOUS PE-INCISIVE TIGONE HAD PAATE SOFT PAATE VEOPHAYNGEA VAVE FUNCTION It includes the depiction of the amount of prolabium or pre-maxillary protrusion on one or both sides (semi circles and ). 0 = No protrusion = Mild protrusion (< p ) = Moderate protrusion (> p,<0 p ) = Severe protrusion(>0p ) STEP III: This step depicts the upper lip deformity. = Cleft microform a = Congenital scar in usual cleft position (subcutaneous cleft) b = Notch in the vermillion border = / cleft lip (cleft in vertical dimension) = /cleft lip (cleft in vertical dimension) = Complete cleft lip STEP IV: It shows the defect in the alveolus. = Cleft microform
5 JKCD June 0, Vol., No. a = Submucous cleft b = Notch = Partial cleft = Complete cleft a = Absence of maxillary arch collapse b = Presence of maxillary arch collapse STEP V: It represents the pre-incisive foramena ltrigones. = Partial cleft STEP VIII: It represents velopharyngeal valve dysfunction 0 = No impairment = Mild impairment = Moderate impairment = Severe impairment EXAMPE: A months old child has bilateral complete cleft lip and palate. Patient has a severe nasal deformity, marked pre maxillary protrusion, complete cleft lip, alveolus, primary and secondary palate as well as complete cleft in soft palate. Assessment of the = Complete cleft velopharyngeal valve dysfunction cannot be made until X= Not rated. STEP VI: It describes the anatomy of the hard palate the child is - years of age. The child s deformity will be represented by following diagram. IGHT EFT POABIUM NOSTI ACH = Posterior / cleft NASA FOO IP AVEOUS = Posterior / cleft PE-INCISIVE 0 TIGONE = Complete cleft HAD PAATE. STEP VII: It indicates a defect in the soft palate or velum including uvula. = Cleft microform of uvula a = Hypoplasia of musculus uvulae b = Septate uvula c = Bifid uvula = Submucous cleft of velum a = Occult b = Overt = Posterior /of velum = Posterior / of velum = Complete cleft of velum. 0 DISCUSSION SOFT PAATE VEOPHAYNGEA VAVE FUNCTION Kernahan and Stark in were for the first time struck by the idea of the importance of classification based on embryology unlike previous classifications based on morphological features. They took the incisive foramen or papilla as the dividing point between the primary and secondary palate. This classification divided clefts into three groups: clefts of primary palate, clefts of secondary palate and clefts of both primary and secondary palate. Kernahan in converted his previous embryologically based classification of from descriptive format into symbolic representation (known as Striped Y ). It gained more popularity than previous one because of its self explanatory and easy de-
6 lineation. However, there were some shortcomings, i.e. the degree of cleft lip cannot be properly shown, premaxillary protrusion, alveolar arch collapse and velopharyngeal incompetence cannot be depicted. Elsahy in modified Kernahan s Striped Y classification by including more details. His classification described degree of cleft lip, collapse of the alveolar arch, displacement of palatal segments, state of velopha-ryngeal closure, absence or presence of protruding premaxilla and degree of pre-maxillary protrusion. Millard in further modified the Elsahy striped Y by adding inverted triangles atop the upright triangular segments and to stand for the right and left aspects of the nasal arch. This revised classification received considerable fame amongst surgeons. Until, when attempts were being made all over the world to present a classification system which fully describes the cleft lip and palate condition, no one highlighted the importance of severity of cleft which is a very important factor in predicting prognosis of patient. Friedman et al in was the first one to describe the severity of the anatomical and functional deformity by further modifying Millard s striped Y and introducing a number in each diagrammatic segment. Though Harkins et al gave importance to severity of cleft but his classification also did not fully explain the condition of cleft. Drawback of Fried-man s classification is that some features need subjective interpretation like deformity of nose, velopharyngeal incompetence so different clinicians may give different severity score to the same patient which may create confusion among clinicians. Schwartz et al in presented a system which was also based on Kernahan Striped Y and classified clefts using three digits, one for the left side of the Y, another for the right side and a third for the base of Y. Posadaset al 0 in 00 proposed an embryological classification in which he incorporated elements related to palate, lip, and nose that described their complexity from a surgical perspective. Different classifications of cleft lip and palate have been proposed since, but attempt has never been made to gather them under one article. For easy understanding of the reader, this series has classified Classifications of cleft lip and palate for the first time and has also described in detail some of the more famous and easily applicable classifications. The first article described morphological classifications in which different cleft conditions were classified on the basis JKCD June 0, Vol., No. of morphology whereas second article describes classification based on embryology. Most of the embryological classifications use Striped Y initially proposed by Kernahan. Striped Y gives true depiction of the fusion lines of the orona-salembryological structures pertaining to cleft lip and palate and makes representation of cleft condition of patient very easy. Upper two limbs of Y represent fusion line of primary palate with secondary palate and lower limb of Y represent fusion line of two palatine shelves of hard palate. These fusion lines are the sites where the cleft can appear. This article has described embryologic classification systems of cleft lip and palate which are easy to use and at the same time fully explains condition of cleft. Most of the embryologic classifications have graphic representation which makes their use easier. EFEENCES. Sadler TW. angman s Medical Embryology. th ed. Chapel Hill: ippincott Williams and Wilkins; Hodgkinson PD, Brown S, Duncan D, Grant C, Mc Naughton A, Thomas P et al. Management of children with cleft lip and palate: a review describing the application of multidisciplinary team working in this condition based upon the experiences of a regional cleft lip and palate centre in the United Kingdom. Fetal and Maternal Medicine eview 00; : -.. Kernahan DA. The Striped Y-a symbolic classification for cleft lip and palate. Plastreconstrsurg ; : -0.. Elsahy NI. The modified striped Y-a systematic classification for cleft lip and palate. Cleft Palate J. ; 0: -0.. Friedman HI, Sayetta B, Coston GN, Hussey J. Symbolic representation of cleft lip and palate. Cleft Palate Craniofacial J. ; : -.. Kernahan DA, Stark B. A new classification for cleft lip and cleft palate. Plastic reconstrsurg ; ():.. Millard D. Jr Cleft Craft.Vol. Boston: ittle, Brown;.. Harkins CS, Berlin A, Harding, ongacre J, Snodgrasse M. Proposed morphological classification of congenital cleft lip and cleft palate. Cleft Palate Bull 0; 0-.. Schwartz S, Kapala JT, ajchgot H, oberts G. Accurate and systematic numerical recording system for the identification of various types of lip and maxillary clefts. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. ; 0: Posadas M, Alvarado V, Behar JM.A new approach to classify cleft lip and palate. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 00; (): -0.
A REVIEW OF CLASSIFICATION SYSTEMS FOR CLEFT LIP AND PALATE PATIENTS- I. MORPHOLOGICAL CLASSIFICATIONS
 Review Article A REVIEW OF CLASSIFICATION SYSTEMS FOR CLEFT LIP AND PALATE PATIENTS- I. MORPHOLOGICAL CLASSIFICATIONS Syed Nasir Shah, Mariya Khalid, Muhammad Sartaj Khan Department of Prosthodontics,
Review Article A REVIEW OF CLASSIFICATION SYSTEMS FOR CLEFT LIP AND PALATE PATIENTS- I. MORPHOLOGICAL CLASSIFICATIONS Syed Nasir Shah, Mariya Khalid, Muhammad Sartaj Khan Department of Prosthodontics,
Remember from the first year embryology Trilaminar disc has 3 layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm
 Development of face Remember from the first year embryology Trilaminar disc has 3 layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm The ectoderm forms the neural groove, then tube The neural tube lies in the mesoderm
Development of face Remember from the first year embryology Trilaminar disc has 3 layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm The ectoderm forms the neural groove, then tube The neural tube lies in the mesoderm
Cleft Lip and Palate: The Effects on Speech and Resonance
 Ann W. Kummer, PhD, CCC-SLP Cincinnati Children s Cleft lip and/or palate can have a negative impact on both speech and resonance. The following is a summary of normal anatomy, the types and causes of
Ann W. Kummer, PhD, CCC-SLP Cincinnati Children s Cleft lip and/or palate can have a negative impact on both speech and resonance. The following is a summary of normal anatomy, the types and causes of
Dr.ALI AL BAZZAZ PLASTIC SURGON CLEFT LIP AND PALATE
 Dr.ALI AL BAZZAZ PLASTIC SURGON CLEFT LIP AND PALATE Cleft lip (cheiloschisis) and cleft palate (palatoschisis), which can also occur together as cleft lip and palate, are variations of a type of clefting
Dr.ALI AL BAZZAZ PLASTIC SURGON CLEFT LIP AND PALATE Cleft lip (cheiloschisis) and cleft palate (palatoschisis), which can also occur together as cleft lip and palate, are variations of a type of clefting
NEUROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM
 LECTURE 4 SKULL NEUROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM CRANIUM NEUROCRANIUM (protective case around brain) VISCEROCRANIUM (skeleton of face) NASOMAXILLARY COMPLEX MANDIBLE (DESMOCRANIUM)
LECTURE 4 SKULL NEUROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM CRANIUM NEUROCRANIUM (protective case around brain) VISCEROCRANIUM (skeleton of face) NASOMAXILLARY COMPLEX MANDIBLE (DESMOCRANIUM)
Embryo#1. Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb باشق جهاد. 0 P a g e
 Embryo#1 Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb باشق جهاد 0 P a g e Before you start, it is important to link what you learn in gross anatomy with developmental stages discussed in embryology. Cells that form organs
Embryo#1 Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb باشق جهاد 0 P a g e Before you start, it is important to link what you learn in gross anatomy with developmental stages discussed in embryology. Cells that form organs
Figure 1. Basic anatomy of the palate
 CHAPTER 10 CLEFT LIP AND PALATE Chen Yan, MD and Sanjay Naran, MD I. ANATOMY AND DEFINITIONS A. Cleft Lip (CL) alone, Cleft Lip with Cleft Palate (CLP), and Cleft Palate (CP) alone 1. CL alone and CLP
CHAPTER 10 CLEFT LIP AND PALATE Chen Yan, MD and Sanjay Naran, MD I. ANATOMY AND DEFINITIONS A. Cleft Lip (CL) alone, Cleft Lip with Cleft Palate (CLP), and Cleft Palate (CP) alone 1. CL alone and CLP
Rotation-Advancement Principle. in Cleft Lip Closure. D. RALPH MILLARD, JR., M.D., F.A.C.S. Miami, Florida
 Rotation-Advancement Principle in Cleft Lip Closure D. RALPH MILLARD, JR., M.D., F.A.C.S. Miami, Florida Correction of prealveolar, alveolar, and postalveolar clefts poses a fivefold project: natural appearance,
Rotation-Advancement Principle in Cleft Lip Closure D. RALPH MILLARD, JR., M.D., F.A.C.S. Miami, Florida Correction of prealveolar, alveolar, and postalveolar clefts poses a fivefold project: natural appearance,
CLEFT PALATE & MISARTICULATION
 CLEFT PALATE & MISARTICULATION INTRODUCTION o Between the 6th and 12th weeks of fetal gestation,the left and right sides of the face and facial skeleton fuse in the midddle. When they do fail to do so,
CLEFT PALATE & MISARTICULATION INTRODUCTION o Between the 6th and 12th weeks of fetal gestation,the left and right sides of the face and facial skeleton fuse in the midddle. When they do fail to do so,
04 Development of the Face and Neck. Development of the Face Development of the neck
 04 Development of the Face and Neck Development of the Face Development of the neck Development of the face Overview of facial development The fourth week ~ the twelfth week of prenatal development Between
04 Development of the Face and Neck Development of the Face Development of the neck Development of the face Overview of facial development The fourth week ~ the twelfth week of prenatal development Between
Pharyngeal Apparatus. Pouches Endoderm Grooves Ectoderm Arch Neural Crest Somitomeres Aortic Arch - Vessel
 Pharyngeal Apparatus Pouches Endoderm Grooves Ectoderm Arch Neural Crest Somitomeres Aortic Arch - Vessel Segmental Organization Humans: Arch 1-4 prominent Arch 5 absent Arch 6 - transient First Arch Face
Pharyngeal Apparatus Pouches Endoderm Grooves Ectoderm Arch Neural Crest Somitomeres Aortic Arch - Vessel Segmental Organization Humans: Arch 1-4 prominent Arch 5 absent Arch 6 - transient First Arch Face
Postnatal Growth. The study of growth in growing children is for two reasons : -For health and nutrition assessment
 Growth of The Soft Tissues Postnatal Growth Postnatal growth is defined as the first 20 years of growth after birth krogman 1972 The study of growth in growing children is for two reasons : -For health
Growth of The Soft Tissues Postnatal Growth Postnatal growth is defined as the first 20 years of growth after birth krogman 1972 The study of growth in growing children is for two reasons : -For health
Speech/Resonance Disorders due to Clefts and Craniofacial Anomalies
 Speech/Resonance Disorders due to Clefts and Craniofacial Anomalies Ann W. Kummer, PhD, CCC-SLP Cincinnati Children s Hospital Medical Center Royalties: Financial Disclosures Book: Kummer, AW. Cleft Palate
Speech/Resonance Disorders due to Clefts and Craniofacial Anomalies Ann W. Kummer, PhD, CCC-SLP Cincinnati Children s Hospital Medical Center Royalties: Financial Disclosures Book: Kummer, AW. Cleft Palate
DENTAL MANAGEMENT OF CLEFT LIP AND PALATE. J Harewood DDS MA MS
 DENTAL MANAGEMENT OF CLEFT LIP AND PALATE J Harewood DDS MA MS CLEFT LIP/PALATE: INCIDENCE Cleft lip and/or palate 1:1000 Varies with race Japan: 20: 10 000 Western Europe: 12: 10 000 USA: 10.2:10 000
DENTAL MANAGEMENT OF CLEFT LIP AND PALATE J Harewood DDS MA MS CLEFT LIP/PALATE: INCIDENCE Cleft lip and/or palate 1:1000 Varies with race Japan: 20: 10 000 Western Europe: 12: 10 000 USA: 10.2:10 000
EVALUATION AND MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WITH CLEFT LIP AND PALATE
 EVALUATION AND MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WITH CLEFT LIP AND PALATE DEFINING TERMS PRIMARY PALATE- Structures anterior to the incisive foramen Includes the nose, lip alveolus, and hard palate back to the incisive
EVALUATION AND MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WITH CLEFT LIP AND PALATE DEFINING TERMS PRIMARY PALATE- Structures anterior to the incisive foramen Includes the nose, lip alveolus, and hard palate back to the incisive
The Advantages of Two Stages in Repair. of Bilateral Cleft Lip. VICTOR SPINA, M.D. Sado Paulo, Brazil
 The Advantages of Two Stages in Repair of Bilateral Cleft Lip VICTOR SPINA, M.D. Sado Paulo, Brazil The suggestion of using two stages for the surgical correction of complete bilateral clefts of the lip
The Advantages of Two Stages in Repair of Bilateral Cleft Lip VICTOR SPINA, M.D. Sado Paulo, Brazil The suggestion of using two stages for the surgical correction of complete bilateral clefts of the lip
G l o s s a r y. The lack of closure of a normal body orifice or. passage
 A P P E N D I XE G l o s s a r y Allergic rhinitis Swelling of the membrane in the nasal chamber due to allergic reactions; the condition may obstruct breathing Alveolar ridge The bony arches of the maxilla
A P P E N D I XE G l o s s a r y Allergic rhinitis Swelling of the membrane in the nasal chamber due to allergic reactions; the condition may obstruct breathing Alveolar ridge The bony arches of the maxilla
Trigeminal Nerve (V)
 Trigeminal Nerve (V) Lecture Objectives Discuss briefly how the face is developed. Follow up the course of trigeminal nerve from its point of central connections, exit and down to its target areas. Describe
Trigeminal Nerve (V) Lecture Objectives Discuss briefly how the face is developed. Follow up the course of trigeminal nerve from its point of central connections, exit and down to its target areas. Describe
Prenatal Diagnosis of Cleft Lip
 Commentary Prenatal Diagnosis of Cleft Lip What the Sonologist Needs to Tell the Surgeon John. Mulliken, MD, eryl R. enacerraf, MD Division of Plastic Surgery, Children s Hospital (J..M.) Department of
Commentary Prenatal Diagnosis of Cleft Lip What the Sonologist Needs to Tell the Surgeon John. Mulliken, MD, eryl R. enacerraf, MD Division of Plastic Surgery, Children s Hospital (J..M.) Department of
Essentials in Head and Neck Embryology. Part 3 Development of the head, face, and oral cavity
 Essentials in Head and Neck Embryology Part 3 Development of the head, face, and oral cavity Outline General overview of prenatal development Embryonic period phase 1 Formation of bilaminar disk Formation
Essentials in Head and Neck Embryology Part 3 Development of the head, face, and oral cavity Outline General overview of prenatal development Embryonic period phase 1 Formation of bilaminar disk Formation
Upper arch. 1Prosthodontics. Dr.Bassam Ali Al-Turaihi. Basic anatomy & & landmark of denture & mouth
 1Prosthodontics Lecture 2 Dr.Bassam Ali Al-Turaihi Basic anatomy & & landmark of denture & mouth Upper arch Palatine process of maxilla: it form the anterior three quarter of the hard palate. Horizontal
1Prosthodontics Lecture 2 Dr.Bassam Ali Al-Turaihi Basic anatomy & & landmark of denture & mouth Upper arch Palatine process of maxilla: it form the anterior three quarter of the hard palate. Horizontal
Dr.Sepideh Falah-kooshki
 Dr.Sepideh Falah-kooshki MAXILLA Premaxillary/median palatal suture (radiolucent). Incisive fossa and foramen (radiolucent). Nasal passages (radiolucent). Nasal septum (radiopaque). Anterior nasal spine
Dr.Sepideh Falah-kooshki MAXILLA Premaxillary/median palatal suture (radiolucent). Incisive fossa and foramen (radiolucent). Nasal passages (radiolucent). Nasal septum (radiopaque). Anterior nasal spine
OPERATIVE CORRECTION BY OSTEOTOMY OF RECESSED MALAR MAXILLARY COMPOUND IN A CASE OF OXYCEPHALY
 OPERATIVE CORRECTION BY OSTEOTOMY OF RECESSED MALAR MAXILLARY COMPOUND IN A CASE OF OXYCEPHALY By Sir HAROLD GILLIES, C.B.E., F.R.C.S., and STEWART H. HARRISON, F.R.C.S., L.D.S., R.C.S. From the Plastic
OPERATIVE CORRECTION BY OSTEOTOMY OF RECESSED MALAR MAXILLARY COMPOUND IN A CASE OF OXYCEPHALY By Sir HAROLD GILLIES, C.B.E., F.R.C.S., and STEWART H. HARRISON, F.R.C.S., L.D.S., R.C.S. From the Plastic
Jan 24: Cleft Lip/Cleft Palate (updated 08/06) Jan 24: Cleft Lip/Cleft Palate (updated 08/06) Preceptor: ; Vacation Scott
 Jan 24: Cleft Lip/Cleft Palate (updated 08/06) Preceptor: ; Vacation Scott 1. (Amy) Discuss the incidence, causes and genetic aspects of cleft lips and palates (CL and CP). Cleft lip/palate deformities
Jan 24: Cleft Lip/Cleft Palate (updated 08/06) Preceptor: ; Vacation Scott 1. (Amy) Discuss the incidence, causes and genetic aspects of cleft lips and palates (CL and CP). Cleft lip/palate deformities
Head and Neck Development and Malformations
 Head and Neck Development and Malformations Yang Chai, DDS, PhD Professor George and MaryLou Boone Chair Ostrow School of Dentistry of USC ychai@usc.edu C D E A. B Learning Objectives - Learn cranial neural
Head and Neck Development and Malformations Yang Chai, DDS, PhD Professor George and MaryLou Boone Chair Ostrow School of Dentistry of USC ychai@usc.edu C D E A. B Learning Objectives - Learn cranial neural
CLEFT LIP and PALATE. Sahlgrenska University Hospital Göteborg, Sweden. Information about Cleft Lip and Palate. English version
 CLEFT LIP and PALATE Sahlgrenska University Hospital Göteborg, Sweden Information about Cleft Lip and Palate English version 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS page What are cleft lip and palate? 3 Which children can
CLEFT LIP and PALATE Sahlgrenska University Hospital Göteborg, Sweden Information about Cleft Lip and Palate English version 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS page What are cleft lip and palate? 3 Which children can
3. The Jaw and Related Structures
 Overview and objectives of this dissection 3. The Jaw and Related Structures The goal of this dissection is to observe the muscles of jaw raising. You will also have the opportunity to observe several
Overview and objectives of this dissection 3. The Jaw and Related Structures The goal of this dissection is to observe the muscles of jaw raising. You will also have the opportunity to observe several
The Role of the Lip Adhesion Procedure. in Cleft Lip Repair*
 The Role of the Lip Adhesion Procedure in Cleft Lip Repair* RALPH HAMILTON, M.D. WILLIAM P. GRAHAM, III, M.D. PETER RANDALL, M.D. Philadelphia, Pa. 19104 Introduction A lip adhesion procedure utilizing
The Role of the Lip Adhesion Procedure in Cleft Lip Repair* RALPH HAMILTON, M.D. WILLIAM P. GRAHAM, III, M.D. PETER RANDALL, M.D. Philadelphia, Pa. 19104 Introduction A lip adhesion procedure utilizing
Page 2 of 5 9th weeks of gestation, as the palatal shelves change from a vertical to horizontal position and fuse. The tongue must migrate away from t
 Page 1 of 5 TITLE: Cleft Lip and Palate SOURCE: UTMB Dept. of Otolaryngology Grand Rounds DATE: January 28, 1998 RESIDENT PHYSICIAN: Greg Young, M.D. FACULTY: Ronald Deskin, M.D. SERIES EDITOR: Francis
Page 1 of 5 TITLE: Cleft Lip and Palate SOURCE: UTMB Dept. of Otolaryngology Grand Rounds DATE: January 28, 1998 RESIDENT PHYSICIAN: Greg Young, M.D. FACULTY: Ronald Deskin, M.D. SERIES EDITOR: Francis
A TECHNIQUE FOR ONE STAGE REPAIR OF COMPLETE PALATAL CLEFT
 A TECHNIQUE FOR ONE STAGE REPAIR OF COMPLETE PALATAL CLEFT Pages with reference to book, From 105 To 107 Iftikhar Ahmad, M. Rafiq Khan, Abdullah Jan, Abdur Rasheed ( Department of E.N.T. and Head and Neck
A TECHNIQUE FOR ONE STAGE REPAIR OF COMPLETE PALATAL CLEFT Pages with reference to book, From 105 To 107 Iftikhar Ahmad, M. Rafiq Khan, Abdullah Jan, Abdur Rasheed ( Department of E.N.T. and Head and Neck
Subdivided into Vestibule & Oral cavity proper
 Extends from the lips to the oropharyngeal isthmus The oropharyngeal isthmus: Is the junction of mouth and pharynx. Is bounded: Above by the soft palate and the palatoglossal folds Below by the dorsum
Extends from the lips to the oropharyngeal isthmus The oropharyngeal isthmus: Is the junction of mouth and pharynx. Is bounded: Above by the soft palate and the palatoglossal folds Below by the dorsum
Arrangement of the artificial teeth:
 Lecture Prosthodontic Dr. Osama Arrangement of the artificial teeth: It s the placement of the teeth on a denture with definite objective in mind or it s the setting of teeth on temporary bases. Rules
Lecture Prosthodontic Dr. Osama Arrangement of the artificial teeth: It s the placement of the teeth on a denture with definite objective in mind or it s the setting of teeth on temporary bases. Rules
Original Research. Figure 1: (a) Unilateral complete cleft of the lip and palate, (b) unilateral complete skeletal cleft with a Simonart s band.
 Received: 14 th August 2015 Accepted: 19 th November 2015 Conflicts of Interest: None Source of Support: Nil Original Research Simonart s Bands and Facial Growth in Unilateral Cleft Lip and Palate Patients:
Received: 14 th August 2015 Accepted: 19 th November 2015 Conflicts of Interest: None Source of Support: Nil Original Research Simonart s Bands and Facial Growth in Unilateral Cleft Lip and Palate Patients:
TRANSCRIPT OF NARRATION FOR DEVELOPMENT OF THE FACE
 TRANSCRIPT OF NARRATION FOR DEVELOPMENT OF THE FACE Slide 1 (introduction) In this lecture, I ll be addressing two separate but interrelated topics. First, I ll be summarizing some of the most fundamental
TRANSCRIPT OF NARRATION FOR DEVELOPMENT OF THE FACE Slide 1 (introduction) In this lecture, I ll be addressing two separate but interrelated topics. First, I ll be summarizing some of the most fundamental
Cairo Dental Journal (24) Number (I), 77:84 January, Haitham Sayed Attia 3, Mohamed Saied Hamed 1 and Monteser El Koutobey 2
 Cairo Dental Journal (24) Number (I), 77:84 January, 2008 Anthropometric Analysis of cases of Unilateral Cleft Lip Versus cases of Complete Unilateral Cleft Lip and Palate Haitham Sayed Attia 3, Mohamed
Cairo Dental Journal (24) Number (I), 77:84 January, 2008 Anthropometric Analysis of cases of Unilateral Cleft Lip Versus cases of Complete Unilateral Cleft Lip and Palate Haitham Sayed Attia 3, Mohamed
SEMI- ANNUAL FELLOWSHIP REPORT June 2015 to December 2015
 SEMI- ANNUAL FELLOWSHIP REPORT June 2015 to December 2015 Submitted by, Dr.Arun Ramaiah., Resident fellow, St.Thomas Cleft and Craniofacial centre. Letter to CCI To start with I would like to thank Cleft
SEMI- ANNUAL FELLOWSHIP REPORT June 2015 to December 2015 Submitted by, Dr.Arun Ramaiah., Resident fellow, St.Thomas Cleft and Craniofacial centre. Letter to CCI To start with I would like to thank Cleft
Respiratory System Embryology
 Respiratory System Embryology Development of the nose and Palate Development of the nose At the end of the fourth week, facial prominences consisting primarily of neural crest-derived mesenchyme and formed
Respiratory System Embryology Development of the nose and Palate Development of the nose At the end of the fourth week, facial prominences consisting primarily of neural crest-derived mesenchyme and formed
It has been proposed that partially edentulous maxillectomy
 CLASSICAL ARTICLE Basic principles of obturator design for partially edentulous patients. Part II: Design principles Mohamed A. Aramany, DMD, MS* Eye and Ear Hospital of Pittsburgh and University of Pittsburgh,
CLASSICAL ARTICLE Basic principles of obturator design for partially edentulous patients. Part II: Design principles Mohamed A. Aramany, DMD, MS* Eye and Ear Hospital of Pittsburgh and University of Pittsburgh,
ORTHODONTIC INITIAL ASSESSMENT FORM (OIAF) w/ INSTRUCTIONS
 Use the accompanying Tip Sheet and How to Score the Orthodontic Initial Assessment Form for guidance in completion of the assessment form. You will need this score sheet and a disposable ruler (or a Boley
Use the accompanying Tip Sheet and How to Score the Orthodontic Initial Assessment Form for guidance in completion of the assessment form. You will need this score sheet and a disposable ruler (or a Boley
Oral cavity landmarks
 By: Dr. Ahmed Rabah Oral cavity landmarks The knowledge of oral anatomy and physiology will help the operator and provides enough landmarks to act as positive guide during denture construction. This subject
By: Dr. Ahmed Rabah Oral cavity landmarks The knowledge of oral anatomy and physiology will help the operator and provides enough landmarks to act as positive guide during denture construction. This subject
APPENDIX A. MEDICAID ORTHODONTIC INITIAL ASSESSMENT FORM (IAF) You will need this scoresheet and a disposable ruler (or a Boley Gauge)
 APPENDIX A MEDICAID ORTHODONTIC INITIAL ASSESSMENT FORM (IAF) You will need this scoresheet and a disposable ruler (or a Boley Gauge) Name: _ I. D. Number: Conditions: 1. Cleft palate deformities 2. Deep
APPENDIX A MEDICAID ORTHODONTIC INITIAL ASSESSMENT FORM (IAF) You will need this scoresheet and a disposable ruler (or a Boley Gauge) Name: _ I. D. Number: Conditions: 1. Cleft palate deformities 2. Deep
Lips and labial mucosa
 Lips and labial mucosa External portion of the lips: the vermilion border and the skin Vermilion border : the exposed red portion of the lip, covered by mucous membrane, no mucous glands Boundary: the
Lips and labial mucosa External portion of the lips: the vermilion border and the skin Vermilion border : the exposed red portion of the lip, covered by mucous membrane, no mucous glands Boundary: the
By SIDNEY KAHN, M.D., and JOSEPH WINSTEN, M.D. From the Plastic Surgical Service of Dr Arthur 3?. Barsky, Mount Sinai Hospital, New York City
 SURGICAL APPROACHES TO THE BILATERAL CLEFT LIP PROBLEM By SIDNEY KAHN, M.D., and JOSEPH WINSTEN, M.D. From the Plastic Surgical Service of Dr Arthur 3?. Barsky, Mount Sinai Hospital, New York City INTRODUCTION
SURGICAL APPROACHES TO THE BILATERAL CLEFT LIP PROBLEM By SIDNEY KAHN, M.D., and JOSEPH WINSTEN, M.D. From the Plastic Surgical Service of Dr Arthur 3?. Barsky, Mount Sinai Hospital, New York City INTRODUCTION
Plastic Surgeon, Middlesbrough General Hospital, Stockton Children's Hospital, Newcastle Regional Hospital Board
 THE NASAL TIP IN BILATERAL HARE LIP By J. POTTER, F.R.C.S.Ed. Plastic Surgeon, Middlesbrough General Hospital, Stockton Children's Hospital, Newcastle Regional Hospital Board IN the problem of the bilateral
THE NASAL TIP IN BILATERAL HARE LIP By J. POTTER, F.R.C.S.Ed. Plastic Surgeon, Middlesbrough General Hospital, Stockton Children's Hospital, Newcastle Regional Hospital Board IN the problem of the bilateral
Postgraduate Medical School, University of London
 THE COMPARATIVE ANATOMY OF CLEFT LIP AND PALATE Part I Classification of Cleft Lip and Palate in Dogs By JAMES CALNAN, F.R.C.S., M.R.C.P. Postgraduate Medical School, University of London IN the veterinary
THE COMPARATIVE ANATOMY OF CLEFT LIP AND PALATE Part I Classification of Cleft Lip and Palate in Dogs By JAMES CALNAN, F.R.C.S., M.R.C.P. Postgraduate Medical School, University of London IN the veterinary
Morphological variations of soft palate and influence of age on it: A digital cephalometric study
 Original Research Article Morphological variations of soft palate and influence of age on it: A digital cephalometric study C. Vani 1*, T. Vinila Lakshmi 2, V. Dheeraj Roy 3 1 Professor, 2 Post graduate
Original Research Article Morphological variations of soft palate and influence of age on it: A digital cephalometric study C. Vani 1*, T. Vinila Lakshmi 2, V. Dheeraj Roy 3 1 Professor, 2 Post graduate
6610 NE 181st Street, Suite #1, Kenmore, WA
 660 NE 8st Street, Suite #, Kenmore, WA 9808 www.northshoredentalacademy.com.08.900 READ CHAPTER The Professional Dental Assistant (p.-9) No Key Terms Recall Questions:,,,, and 6 CLASS SYLLABUS DAY READ
660 NE 8st Street, Suite #, Kenmore, WA 9808 www.northshoredentalacademy.com.08.900 READ CHAPTER The Professional Dental Assistant (p.-9) No Key Terms Recall Questions:,,,, and 6 CLASS SYLLABUS DAY READ
AVADENT-WAGNER EZ GUIDE PROTOCOL
 APPOINTMENT A. Final Impressions 1 APPOINTMENT 2 APPOINTMENT 3 D. Seat Wagner EZ Guide Try-In B. Papillameter Measurement E. Refine Anterior Teeth C. Tooth Mould Selection F. Interocclusal Record G. Deliver
APPOINTMENT A. Final Impressions 1 APPOINTMENT 2 APPOINTMENT 3 D. Seat Wagner EZ Guide Try-In B. Papillameter Measurement E. Refine Anterior Teeth C. Tooth Mould Selection F. Interocclusal Record G. Deliver
Trigeminal nerve. Slide in bold and please go back to see the pictures, if I skipped any part of record that because it wasn t clear to me
 Trigeminal nerve Slide in bold and please go back to see the pictures, if I skipped any part of record that because it wasn t clear to me Hala nsour 2/26/2018 P a g e 1 this lecture contain two topics
Trigeminal nerve Slide in bold and please go back to see the pictures, if I skipped any part of record that because it wasn t clear to me Hala nsour 2/26/2018 P a g e 1 this lecture contain two topics
Oblique lip-alveolar banding in patients with cleft lip and palate
 Oblique lip-alveolar banding in patients with cleft lip and palate Sharan Naidoo *,a Kurt-W Bütow a,b a Facial Cleft Deformity Clinic, Department of Maxillofacial and Oral Surgery, University of Pretoria
Oblique lip-alveolar banding in patients with cleft lip and palate Sharan Naidoo *,a Kurt-W Bütow a,b a Facial Cleft Deformity Clinic, Department of Maxillofacial and Oral Surgery, University of Pretoria
Introduction. Images supplied. SUBJECT IMAGES (Victor Vinnetou) TARGET IMAGES (Mbuyisa Makhubu)
 Victor Vinnetou and Mbuyisa Makhubu facial comparison case, compiled by Dr T Houlton, School of Anatomical Sciences, University of the Witwatersrand (3 June 2016) Introduction There currently exists an
Victor Vinnetou and Mbuyisa Makhubu facial comparison case, compiled by Dr T Houlton, School of Anatomical Sciences, University of the Witwatersrand (3 June 2016) Introduction There currently exists an
Dental Morphology and Vocabulary
 Dental Morphology and Vocabulary Palate Palate Palate 1 2 Hard Palate Rugae Hard Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate 4 Palate Hard Palate Soft Palate Maxillary Arch (Maxilla) (Uppers)
Dental Morphology and Vocabulary Palate Palate Palate 1 2 Hard Palate Rugae Hard Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate 4 Palate Hard Palate Soft Palate Maxillary Arch (Maxilla) (Uppers)
William F. Walsh, M.D. Katharine D. Wenstrom, M.D. In the early weeks of fetal development, parts of the lip or palate (the roof of the
 John B. Pietsch, M.D. William F. Walsh, M.D. Katharine D. Wenstrom, M.D. Cleft Lip and Palate What are Cleft Lip and Cleft Palate? In the early weeks of fetal development, parts of the lip or palate (the
John B. Pietsch, M.D. William F. Walsh, M.D. Katharine D. Wenstrom, M.D. Cleft Lip and Palate What are Cleft Lip and Cleft Palate? In the early weeks of fetal development, parts of the lip or palate (the
Chapter 66: Cleft Lip and Palate. Rober W. Seibert, Robert M. Bumsted. a. Missing, malformed, and supernumerary teeth
 Chapter 66: Cleft Lip and Palate Rober W. Seibert, Robert M. Bumsted Cleft lip and palate deformities are common congenital disorders whose management requires a long-term comprehensive program of care
Chapter 66: Cleft Lip and Palate Rober W. Seibert, Robert M. Bumsted Cleft lip and palate deformities are common congenital disorders whose management requires a long-term comprehensive program of care
Bones Ethmoid bone Inferior nasal concha Lacrimal bone Maxilla Nasal bone Palatine bone Vomer Zygomatic bone Mandible
 splanchnocranium - Consists of part of skull that is derived from branchial arches - The facial bones are the bones of the anterior and lower human skull Bones Ethmoid bone Inferior nasal concha Lacrimal
splanchnocranium - Consists of part of skull that is derived from branchial arches - The facial bones are the bones of the anterior and lower human skull Bones Ethmoid bone Inferior nasal concha Lacrimal
Nagri D et al. Linear occlusion and Neutral Zone recording for severely resorbed ridges
 Doi:10.21276/ledent.2018.02.01.02 Case Report LINEAR OCCLUSION AND NEUTRAL ZONE RECORDING USING TISSUE CONDITIONER REPORT OF A SEVERELY RESORBED RIDGE Divya Nagri, 1Ashish Kakkar, 2Neeraj Mittal, 3Lovely
Doi:10.21276/ledent.2018.02.01.02 Case Report LINEAR OCCLUSION AND NEUTRAL ZONE RECORDING USING TISSUE CONDITIONER REPORT OF A SEVERELY RESORBED RIDGE Divya Nagri, 1Ashish Kakkar, 2Neeraj Mittal, 3Lovely
Jaw relations and jaw relation records
 Lecture 11 Prosthodontics Dr. Osama Jaw relations and jaw relation records Jaw relations can be classified into 3 categories 1-Orientation jaw relation 2-Vertical jaw relation 3-Horizontal jaw relation
Lecture 11 Prosthodontics Dr. Osama Jaw relations and jaw relation records Jaw relations can be classified into 3 categories 1-Orientation jaw relation 2-Vertical jaw relation 3-Horizontal jaw relation
Vancouver, B.C., Canada
 THE "ALAR SHIFT" REVISITED By THEODORE F. WILKIE, B.A., M.D., F.R.C.S.(C), F.A.C.S. Vancouver, B.C., Canada IN the hands of many plastic surgeons certain procedures have an evanescent history. Usually
THE "ALAR SHIFT" REVISITED By THEODORE F. WILKIE, B.A., M.D., F.R.C.S.(C), F.A.C.S. Vancouver, B.C., Canada IN the hands of many plastic surgeons certain procedures have an evanescent history. Usually
45 SECONDARY LZ CORRECTION
 45 SECONDARY LZ CORRECTION AFTER ROTATION AND ADVANCEMENT NOT ENOUGH ROTATION MOST COMMON COMPLAINT BY SURGEONS USING THE ROTATIONADVANCEMENT METHOD HAS BEEN SHORTNESS OF THE VERTICAL HEIGHT OF THE LIP
45 SECONDARY LZ CORRECTION AFTER ROTATION AND ADVANCEMENT NOT ENOUGH ROTATION MOST COMMON COMPLAINT BY SURGEONS USING THE ROTATIONADVANCEMENT METHOD HAS BEEN SHORTNESS OF THE VERTICAL HEIGHT OF THE LIP
REVIEW OF CLINICAL EMBRYOLOGY OF HEAD AND NECK
 REVIEW OF CLINICAL EMBRYOLOGY OF HEAD AND NECK OUTLINE - EMBRYOLOGY UNDERLYING CLINICAL CONDITIONS I. EARLY DEVELOPMENT OF FACE: CLEFT LIP, CLEFT PALATE, OBSTRUCTED NASOLACRIMAL DUCT II. BRANCHIAL ARCHES
REVIEW OF CLINICAL EMBRYOLOGY OF HEAD AND NECK OUTLINE - EMBRYOLOGY UNDERLYING CLINICAL CONDITIONS I. EARLY DEVELOPMENT OF FACE: CLEFT LIP, CLEFT PALATE, OBSTRUCTED NASOLACRIMAL DUCT II. BRANCHIAL ARCHES
Development of the nasal cavity :
 Development of the nasal cavity : several processes contribute to the development of the nose, the nose consists of 2 cavities separated by a septum, and the nasal cavity is separated from the oral cavity
Development of the nasal cavity : several processes contribute to the development of the nose, the nose consists of 2 cavities separated by a septum, and the nasal cavity is separated from the oral cavity
Upper Triangular Flap Method for Primary Repairs of Incomplete Unilateral Cleft Lip Patients. Minor to Two-Thirds Way Defects
 HEAD AND NECK SURGERY Upper Triangular Flap Method for Primary Repairs of Incomplete Unilateral Cleft Lip Patients Minor to Two-Thirds Way Defects Kyung S. Koh, MD, PhD,* Tae Suk Oh, MD,* and Jin Woo Song,
HEAD AND NECK SURGERY Upper Triangular Flap Method for Primary Repairs of Incomplete Unilateral Cleft Lip Patients Minor to Two-Thirds Way Defects Kyung S. Koh, MD, PhD,* Tae Suk Oh, MD,* and Jin Woo Song,
UCL Repair: Emphasis on Muscle Dissection and Reconstruction
 UCL Repair: Emphasis on Muscle Dissection and Reconstruction Unilateral cleft lip repair is performed using rotation-advancement technique. Markings are made on columella base, redlines, Cupid s bow on
UCL Repair: Emphasis on Muscle Dissection and Reconstruction Unilateral cleft lip repair is performed using rotation-advancement technique. Markings are made on columella base, redlines, Cupid s bow on
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section. REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton 1 POINT EACH. THE SKULL MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The major components of the axial skeleton include the 7. The
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton 1 POINT EACH. THE SKULL MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The major components of the axial skeleton include the 7. The
Dr.Mikulás Krisztina. Fabrication of the trial denture, and the try in procedure
 Dr.Mikulás Krisztina Fabrication of the trial denture, and the try in procedure the correct shape for the labial, buccal and palatal surfaces Adjusting the upper record rim Before starting adjustment-upper
Dr.Mikulás Krisztina Fabrication of the trial denture, and the try in procedure the correct shape for the labial, buccal and palatal surfaces Adjusting the upper record rim Before starting adjustment-upper
Anatomy of Oral Cavity DR. MAAN AL-ABBASI
 Anatomy of Oral Cavity DR. MAAN AL-ABBASI By the end of this lecture you should be able to: 1. Differentiate different parts of the oral cavity 2. Describe the blood and nerve supply of mucosa and muscles
Anatomy of Oral Cavity DR. MAAN AL-ABBASI By the end of this lecture you should be able to: 1. Differentiate different parts of the oral cavity 2. Describe the blood and nerve supply of mucosa and muscles
AVADENT-WAGNER EZ GUIDE PROTOCOL
 APPOINTMENT 1 APPOINTMENT 2 APPOINTMENT 3 A. Final Impressions D. Seat Try-In B. Papillameter Measurement E. Refine Anterior Teeth C. Tooth Mould Selection F. Interocclusal Record G. Deliver Final Dentures
APPOINTMENT 1 APPOINTMENT 2 APPOINTMENT 3 A. Final Impressions D. Seat Try-In B. Papillameter Measurement E. Refine Anterior Teeth C. Tooth Mould Selection F. Interocclusal Record G. Deliver Final Dentures
Def. - the process of exchanging information and ideas
 What is communication Def. - the process of exchanging information and ideas All living things communicate. Acquiring Human Communication Humans communicate in many ways What is a communication disorder?
What is communication Def. - the process of exchanging information and ideas All living things communicate. Acquiring Human Communication Humans communicate in many ways What is a communication disorder?
Figure (2-6): Labial frenum and labial notch.
 The anatomy of the edentulous ridge in the maxilla and mandible is very important for the design of a complete denture. The consistency of the mucosa and architecture of the underlying bone is different
The anatomy of the edentulous ridge in the maxilla and mandible is very important for the design of a complete denture. The consistency of the mucosa and architecture of the underlying bone is different
Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development. Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L.
 Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L. Dennis Proximal contact areas Contact areas are on the mesial and
Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L. Dennis Proximal contact areas Contact areas are on the mesial and
A Study of Classification Systems for Maxillectomy Defects
 A Study of Classification Systems for Maxillectomy Defects Zubair Durrani FFDRCS, FRCS, FRCS (OMFS)* Syed Ghazanfar Hassan FFDRCS** Shomaila Ameer Alam BDS*** * Associate Professor & Consultant Oral and
A Study of Classification Systems for Maxillectomy Defects Zubair Durrani FFDRCS, FRCS, FRCS (OMFS)* Syed Ghazanfar Hassan FFDRCS** Shomaila Ameer Alam BDS*** * Associate Professor & Consultant Oral and
OF THE LIP AND PALATE. By T. D. FOSTER, M.D.S., F.D.S., D.Orth.R.C.S. School of Dental Surgery, University of Birmingham
 MAXILLARY DEFORMITIES IN REPAIRED CLEFTS OF THE LIP AND PALATE By T. D. FOSTER, M.D.S., F.D.S., D.Orth.R.C.S. School of Dental Surgery, University of Birmingham IN patients with repaired clefts of the
MAXILLARY DEFORMITIES IN REPAIRED CLEFTS OF THE LIP AND PALATE By T. D. FOSTER, M.D.S., F.D.S., D.Orth.R.C.S. School of Dental Surgery, University of Birmingham IN patients with repaired clefts of the
CLINICAL NOTE. Long-Term Results in the Bilateral Cleft Lip Repair by Mulliken s Method
 CLINICAL NOTE Long-Term Results in the Bilateral Cleft Lip Repair by Mulliken s Method Seok-Kwun Kim, MD, PhD, Myung-Hoon Kim, MD, Yong-Seok Kwon, MD, and Keun-Cheol Lee, MD, PhD Purpose: To evaluate long-term
CLINICAL NOTE Long-Term Results in the Bilateral Cleft Lip Repair by Mulliken s Method Seok-Kwun Kim, MD, PhD, Myung-Hoon Kim, MD, Yong-Seok Kwon, MD, and Keun-Cheol Lee, MD, PhD Purpose: To evaluate long-term
Elements of Dysmorphology I. Krzysztof Szczałuba
 Elements of Dysmorphology I Krzysztof Szczałuba 9.05.2016 Common definitions (1) Dysmorphology: recognition and study of birth defects (congenital malformations) and syndromes [David Smith, 1960] Malformation:
Elements of Dysmorphology I Krzysztof Szczałuba 9.05.2016 Common definitions (1) Dysmorphology: recognition and study of birth defects (congenital malformations) and syndromes [David Smith, 1960] Malformation:
Chapter 7. Skeletal System
 Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Skull A. The skull is made up of 22 bones: 8 cranial bones, 13 facial bones, and the mandible. B. The Cranium encloses and protects the brain, provides attachments for muscles,
Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Skull A. The skull is made up of 22 bones: 8 cranial bones, 13 facial bones, and the mandible. B. The Cranium encloses and protects the brain, provides attachments for muscles,
AXIAL SKELETON SKULL
 AXIAL SKELETON SKULL CRANIAL BONES (8 total flat bones w/ 2 paired) 1. Frontal forms forehead & upper portion of eyesocket (orbital) 2. Parietal paired bones; form superior & lateral walls of cranium 3.
AXIAL SKELETON SKULL CRANIAL BONES (8 total flat bones w/ 2 paired) 1. Frontal forms forehead & upper portion of eyesocket (orbital) 2. Parietal paired bones; form superior & lateral walls of cranium 3.
CLASSIFICATIONS. Established in 1994 as a subcommittee of the. Prosthodontic Care Committee
 CLASSIFICATIONS Established in 1994 as a subcommittee of the Prosthodontic Care Committee Committee Members Thomas J. McGarry, DDS, Chair Arthur Nimmo, DDS James F. Skiba, DDS Christopher R. Smith, DDS
CLASSIFICATIONS Established in 1994 as a subcommittee of the Prosthodontic Care Committee Committee Members Thomas J. McGarry, DDS, Chair Arthur Nimmo, DDS James F. Skiba, DDS Christopher R. Smith, DDS
LATERAL CEPHALOMETRIC EVALUATION IN CLEFT PALATE PATIENTS
 POLSKI PRZEGLĄD CHIRURGICZNY 2009, 81, 1, 23 27 10.2478/v10035-009-0004-2 LATERAL CEPHALOMETRIC EVALUATION IN CLEFT PALATE PATIENTS PRADEEP JAIN, ANAND AGARWAL, ARVIND SRIVASTAVA Department of Plastic
POLSKI PRZEGLĄD CHIRURGICZNY 2009, 81, 1, 23 27 10.2478/v10035-009-0004-2 LATERAL CEPHALOMETRIC EVALUATION IN CLEFT PALATE PATIENTS PRADEEP JAIN, ANAND AGARWAL, ARVIND SRIVASTAVA Department of Plastic
Infratemporal fossa: Tikrit University college of Dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck Anatomy 2 nd y.
 Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
The Prevention of Maxillary Collapse in
 The Prevention of Maxillary Collapse in Congenital Lip and Palate Cases CHARLES E. HUGH H. JEROME E. HORTON, M.D. CRAWFORD, M.D. ADAMSON, M.D. SAMUEL BUXTON, D.D.S. REUBEN COOPER, M.S. JACK KANTER, D.D.S.
The Prevention of Maxillary Collapse in Congenital Lip and Palate Cases CHARLES E. HUGH H. JEROME E. HORTON, M.D. CRAWFORD, M.D. ADAMSON, M.D. SAMUEL BUXTON, D.D.S. REUBEN COOPER, M.S. JACK KANTER, D.D.S.
Samantha W. Chou, D.M.D N. Southport Ave. Chicago, Illinois Phone: Fax:
 Samantha W. Chou, D.M.D. 2325 N. Southport Ave. Chicago, Illinois 60614 Phone: 312-608-6881 Fax: 773-296-0601 Samanthawchou@gmail.com What is our role as the dentist? "We live in a culture in which people
Samantha W. Chou, D.M.D. 2325 N. Southport Ave. Chicago, Illinois 60614 Phone: 312-608-6881 Fax: 773-296-0601 Samanthawchou@gmail.com What is our role as the dentist? "We live in a culture in which people
Surgical Treatment of the Nasal-Maxillary Complex in Adolescents With Cleft Lip and Palate
 Surgical Treatment of the Nasal-Maxillary Complex in Adolescents With Cleft Lip and Palate Fernando D. Burstein MD, FACS, FAAP Atlanta, Georgia, USA Rather than treating nasal, maxillary, and soft tissue
Surgical Treatment of the Nasal-Maxillary Complex in Adolescents With Cleft Lip and Palate Fernando D. Burstein MD, FACS, FAAP Atlanta, Georgia, USA Rather than treating nasal, maxillary, and soft tissue
ONE out of every eight hundred children in the United States is born with
 REPAIR OF THE CLEFT LIP ROBIN ANDERSON, M.D. Department of Plastic Surgery ONE out of every eight hundred children in the United States is born with a cleft lip, a cleft palate, or both. Within this group
REPAIR OF THE CLEFT LIP ROBIN ANDERSON, M.D. Department of Plastic Surgery ONE out of every eight hundred children in the United States is born with a cleft lip, a cleft palate, or both. Within this group
BONE GRAFTING IN TREATMENT OF CLEFT LIP AND PALATE 337
 PRIMARY BONE GRAFTING IN THE TREATMENT OF CLEFT LIP AND PALATE WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO ALVEOLAR COLLAPSE By FRANK ROBINSON, F.R.C.S., and BARRIE WOOD, L.D.S. Burns and Plastic Surgery Unit, Booth Hall
PRIMARY BONE GRAFTING IN THE TREATMENT OF CLEFT LIP AND PALATE WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO ALVEOLAR COLLAPSE By FRANK ROBINSON, F.R.C.S., and BARRIE WOOD, L.D.S. Burns and Plastic Surgery Unit, Booth Hall
-Ibrahim Al-Naser. -Dr Al- Muhtaseb. 1 P a g e
 -1 -Ibrahim Al-Naser - -Dr Al- Muhtaseb 1 P a g e The Digestive System The doctor started the lecture by talking about the class rules. The GI system is an organ system, it is divided into: The Alimentary
-1 -Ibrahim Al-Naser - -Dr Al- Muhtaseb 1 P a g e The Digestive System The doctor started the lecture by talking about the class rules. The GI system is an organ system, it is divided into: The Alimentary
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol.4/ Issue 47/ June 11, 2015 Page 8176
 CORRECTION OF ALVEOLAR ARCH MALALIGNMENT AFTER TOTAL CORRECTION IN UNILATERAL AND BILATERAL GR III CLEFTS T. Mohana Rao 1, D. Mukunda Reddy 2, R. Srikanth 3, N. Rambabu 4, R. Parvathi 5 HOWTOCITETHISARTICLE:
CORRECTION OF ALVEOLAR ARCH MALALIGNMENT AFTER TOTAL CORRECTION IN UNILATERAL AND BILATERAL GR III CLEFTS T. Mohana Rao 1, D. Mukunda Reddy 2, R. Srikanth 3, N. Rambabu 4, R. Parvathi 5 HOWTOCITETHISARTICLE:
TRAUMA TO THE FACE AND MOUTH
 Dr.Yahya A. Ali 3/10/2012 F.I.C.M.S TRAUMA TO THE FACE AND MOUTH Bailey & Love s 25 th edition Injuries to the orofacial region are common, but the majority are relatively minor in nature. A few are major
Dr.Yahya A. Ali 3/10/2012 F.I.C.M.S TRAUMA TO THE FACE AND MOUTH Bailey & Love s 25 th edition Injuries to the orofacial region are common, but the majority are relatively minor in nature. A few are major
PH-04A: Clinical Photography Production Checklist With A Small Camera
 PH-04A: Clinical Photography Production Checklist With A Small Camera Operator Name Total 0-49, Passing 39 Your Score Patient Name Date of Series Instructions: Evaluate your Series of photographs first.
PH-04A: Clinical Photography Production Checklist With A Small Camera Operator Name Total 0-49, Passing 39 Your Score Patient Name Date of Series Instructions: Evaluate your Series of photographs first.
Finite Element Modeling of Complete Unilateral Cleft and Palate using MIMICS
 I J C T A, 9(37) 2016, pp. 257-262 International Science Press Finite Element Modeling of Complete Unilateral Cleft and Palate using MIMICS (Maxillary dimensional changes in a Finite element model of a
I J C T A, 9(37) 2016, pp. 257-262 International Science Press Finite Element Modeling of Complete Unilateral Cleft and Palate using MIMICS (Maxillary dimensional changes in a Finite element model of a
Introduction to Occlusion and Mechanics of Mandibular Movement
 Introduction to Occlusion and Mechanics of Mandibular Movement Dr. Pauline Hayes Garrett Department of Endodontics, Prosthodontics, and Operative Dentistry University of Maryland, Baltimore Assigned reading
Introduction to Occlusion and Mechanics of Mandibular Movement Dr. Pauline Hayes Garrett Department of Endodontics, Prosthodontics, and Operative Dentistry University of Maryland, Baltimore Assigned reading
By DONALD WINSTOCK, M.B., F.D.S. St Bartholomew's Hospital and The Middlesex Hospital, London
 ALVEOLAR OSTECTOMY AND MENTOPLASTY IN THE TREATMENT OF MANDIBULAR PROGNATHISM By DONALD WINSTOCK, M.B., F.D.S. St Bartholomew's Hospital and The Middlesex Hospital, London THERE are basically two groups
ALVEOLAR OSTECTOMY AND MENTOPLASTY IN THE TREATMENT OF MANDIBULAR PROGNATHISM By DONALD WINSTOCK, M.B., F.D.S. St Bartholomew's Hospital and The Middlesex Hospital, London THERE are basically two groups
Sensitivity of a Method for the Analysis of Facial Mobility. II. Interlandmark Separation
 Sensitivity of a Method for the Analysis of Facial Mobility. II. Interlandmark Separation CARROLL-ANN TROTMAN, B.D.S., M.A., M.S. JULIAN J. FARAWAY, PH.D. Objective: This study demonstrates a method of
Sensitivity of a Method for the Analysis of Facial Mobility. II. Interlandmark Separation CARROLL-ANN TROTMAN, B.D.S., M.A., M.S. JULIAN J. FARAWAY, PH.D. Objective: This study demonstrates a method of
Class II. Bilateral Cleft Lip and Palate. Clinician: Dr. Mike Mayhew, Boone, NC Patient: R.S. Cleft Lip and Palate.
 Bilateral Cleft Lip and Palate Clinician: Dr. Mike Mayhew, Boone, NC Patient: R.S. Class II Cleft Lip and Palate Pretreatment Diagnosis Class II dolichofacial female, age 22 years 11 months, presented
Bilateral Cleft Lip and Palate Clinician: Dr. Mike Mayhew, Boone, NC Patient: R.S. Class II Cleft Lip and Palate Pretreatment Diagnosis Class II dolichofacial female, age 22 years 11 months, presented
Trigeminal Nerve Worksheets, Distributions Page 1
 Trigeminal Nerve Worksheet #1 Distribution by Nerve Dr. Darren Hoffmann Dental Gross Anatomy, Spring 2013 We have drawn out each of the branches of CN V in lecture and you have an idea now for their basic
Trigeminal Nerve Worksheet #1 Distribution by Nerve Dr. Darren Hoffmann Dental Gross Anatomy, Spring 2013 We have drawn out each of the branches of CN V in lecture and you have an idea now for their basic
Anatomy and Physiology. Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull
 Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 DRO Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull Name: Period: Bones of the Human Skull Bones of the Cranium: Frontal bone: forms the forehead and the
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 DRO Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull Name: Period: Bones of the Human Skull Bones of the Cranium: Frontal bone: forms the forehead and the
/TLv/ A classification of the edentulous jaws. Trauma; Preprosthetic Surgery. iiiii!iii!iii! ] BASAL
![/TLv/ A classification of the edentulous jaws. Trauma; Preprosthetic Surgery. iiiii!iii!iii! ] BASAL /TLv/ A classification of the edentulous jaws. Trauma; Preprosthetic Surgery. iiiii!iii!iii! ] BASAL](/thumbs/72/66558540.jpg) Trauma; Preprosthetic Surgery A classification of the edentulous jaws J. I. awood ~ and R. A. Howell 2 ~Maxillofacial Unit, Royal Infirmary, hester, UK, 2Liverpool Dental Hospital, Liverpool, UK J. L awood
Trauma; Preprosthetic Surgery A classification of the edentulous jaws J. I. awood ~ and R. A. Howell 2 ~Maxillofacial Unit, Royal Infirmary, hester, UK, 2Liverpool Dental Hospital, Liverpool, UK J. L awood
IMPRESSION MAKING (IN COMPLETE DENTURES)
 IMPRESSION MAKING (IN COMPLETE DENTURES) DR ZURYATI AB GHANI BDS (WALES), Grad Dip Clin Dent (Adelaide), Doctor in Clinical Dentistry (prosthodontics), Adelaide, FRACDS 17.06.2007 Impressions An impression
IMPRESSION MAKING (IN COMPLETE DENTURES) DR ZURYATI AB GHANI BDS (WALES), Grad Dip Clin Dent (Adelaide), Doctor in Clinical Dentistry (prosthodontics), Adelaide, FRACDS 17.06.2007 Impressions An impression
DEVELOPING ANALOGUE/SUBTITUTE FOR THE MANDIBULAR DENTURE BEARING AREA. Dr Muhammad Rizwan Memon FCPS Assistant Professor
 DEVELOPING ANALOGUE/SUBTITUTE FOR THE MANDIBULAR DENTURE BEARING AREA Dr Muhammad Rizwan Memon FCPS Assistant Professor Crest of Residual Ridge Buccal Shelf Shape of supporting structure Mylohyoid Ridge
DEVELOPING ANALOGUE/SUBTITUTE FOR THE MANDIBULAR DENTURE BEARING AREA Dr Muhammad Rizwan Memon FCPS Assistant Professor Crest of Residual Ridge Buccal Shelf Shape of supporting structure Mylohyoid Ridge
Acoustic Analysis of Nasal and Oral Speech of Normal versus Cleft Lip and Palate Asharani Neelakanth 1 Mrs. Umarani K. 2
 IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 3, Issue 05, 2015 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Acoustic Analysis of Nasal and Oral Speech of Normal versus Cleft Lip and Palate Asharani
IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 3, Issue 05, 2015 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Acoustic Analysis of Nasal and Oral Speech of Normal versus Cleft Lip and Palate Asharani
Skeletal system. Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi. E. mail:
 Skeletal system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Functions of Bone and The Skeletal System Support: The skeleton serves as the structural framework
Skeletal system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Functions of Bone and The Skeletal System Support: The skeleton serves as the structural framework
