Review Article Mutations in Sodium Channel Gene SCN9A and the Pain Perception Disorders
|
|
|
- Daniel Powers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Advances in Anesthesiology Volume 2015, Article ID , 6 pages Review Article Mutations in Sodium Channel Gene SCN9A and the Pain Perception Disorders Danica MarkoviT, 1 Radmilo JankoviT, 1,2 and Ines VeselinoviT 1 1 Center for Anesthesiology and Reanimatology, Clinical Center Niš, Bulevar Dr. Zorana Djindjića 48, Niš, Serbia 2 Department for Anesthesia and Intensive Care, School of Medicine, University of Niš, Bulevar Dr. Zorana Djindjića 81, Niš, Serbia Correspondence should be addressed to Danica Marković; danica-amm@medfak.ni.ac.rs Received 29 September 2014; Accepted 8 February 2015 Academic Editor: Sorin J. Brull Copyright 2015 Danica Marković et al. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Voltage-gated sodium channels (NaV) play a crucial role in development and propagation of action potentials in neurons and muscle cells. NaV1.7 channels take a special place in modern science since it is believed that they contribute to nerve hyperexcitability. Mutations of the gene SCN9A, which codes the α subunit of NaV1.7 channels, are associated with pain perception disorders (primary erythermalgia, congenital analgesia, and paroxysmal pain disorder). It is considered that the SCN9A gene mutations may cause variations in sensitivity to pain, from complete insensitivity to extreme sensitivity. Further research of the SCN9A gene polymorphism influence on pain sensitivity is essential for the understanding of the pathophysiology of pain and the development of the appropriate targeted pain treatment. 1. Introduction Pain is the unpleasant physical or emotional feeling which occurs due to current or threatening tissue damage. Surgical stimulation is the most common predictable cause of pain and the duty of anesthesiologist is to provide an adequate amount of appropriate anesthetics in order to alleviate pain. Researches indicate that mild to extreme sensation of pain occurs in 30 70% of patients in postoperative period, which indicates that the pain treatment is not yet adequately developed. It is necessary to develop targeted pain therapy in order to relieve the postoperative recovery and reduce the total number of hospital days. Genetic researches enable the discovery of mutations which cause pain disorders. Diseases like primary erythromelalgia, paroxysmal pain disorder, and congenital analgesia may serve as adequate research models (Table 1). The causes of different pain perception in the general population may be investigated on these disease models. Targeting of the genes responsible for excessive perception of pain will enable the development of the targeted pain therapy and accurately determine the proper dosage [1]. 2. Sodium Channel Structure and Function Voltage-gated sodium channels (NaV) play a key role in occurrence and propagation of action potentials in neurons and muscle cells. They allow the increase of sodium permeability through the cell membrane during the depolarisation phase. Nine isoforms of NaV channels differ in amino acid sequences and in a variety of physiological and pharmacological properties. Their activation has three states: deactivated (closed), activated (opened), and inactivated (closed) [1, 2]. NaV channels are large complexes of glycoproteins responsiblefortheinitialphaseofactionpotentialinexcitable cells. They consist of one α subunit and one or more β subunits. Subunit α is a large transmembrane protein of approximately 260 kda with about 2000 amino acid residues. It is built out of four homologous domains (DI DIV) which contain specific voltage sensors. Each homologous domain is built out of six transmembrane segments (S1 S6). Four domains conjoin inside the membrane and form a pore permeable for sodium. Sodium passes through these pores down the concentration gradient during the propagation of
2 2 Advances in Anesthesiology Table 1: Pain disorders and their characteristics. Disorder IEM PEPD CIP Inheritance AD AD AR Channel function Increased Increased Absent Symptoms Most frequent SNPs Painful feet and hands (burning) as the response to heat and movement F1449V, L858F, L858H A863P, S241T, N395K, I136V, V1316A, G616R, G856D, I848T, I234T, and F216S Burning in rectal, ocular, and mandibular region, skin redness M1627K No pain feeling at all S459X, I767X, W897X, M899I, and M932L action potential. Every α subunit is associated with one or more β subunits (β1 β4) which represent transmembrane proteins with one extracellular IgG loop and one intracellular Cend.Thisconnectionaffectsthetotalnumberofthese channels on the cell surface, the sensitivity to voltage changes, the kinetics of α subunits, and the connections with other signaling molecules and cytoskeleton molecules. Mutations of the genes which code the α subunit created nine genes in total during the evolution in mammals. These genes code active channels and differ in tissue specificity and biophysical properties. Mutation of these genes causes substitution of a single amino acid and is associated with various diseases. Some of them are pain sensitivity disorders, epilepsy, various types of paralysis, ataxia, arrhythmia, muscle tissue diseases, tremor, dystonia, and so forth. It is considered that they are also responsible for some psychiatric diseases [3 6]. 3. NaV1.7 Channels ChannelsNaV1.7arealsocalledthevoltage-gatedsodium channel type IV α subunit. They are coded by the SCN9A gene and are highly expressed in sensory neurons of the dorsal roots, trigeminal ganglion, and sympathetic neurons ganglia, mainly in the nociceptors [2]. They are built out of 1977 amino acids (approximately 225 kda) [6]. Immunohistochemical studies have shown that NaV1.7 is also present on the distal neurite ends, close to the impulse trigger zone. These channels show the possibility of depolarization even on minor stimuli and their biophysical function is to conduct stimuli which are below threshold. Theyarecharacterizedbyslowinactivationandslowrecovery from inactivation. This allows them to answer to small depolarization stimuli and to amplify generation potentials onnerveendings.scientistsbelievethattheroleofnav1.7is to contribute to nerve hyperexcitability [2, 6 8]. 4. The Genetic Basis of NaV1.7 SCN9A gene is coding the α subunit of NaV1.7 and is primarily expressed in neurons of the dorsal root ganglia, sympathetic neurons ganglia, Swann cells, and neuroendocrine cells [9]. It is located on the 2q24.3 chromosome and consists of 26 exons [6, 10]. Subunits α are coded by the SCN1A-SCN5A and SCN8A- SCN11A genes, while subunits β are coded by the SCN1B- SCN4B genes [6]. Channel activity and function are regulated depending on which β subunit is associated with the α domain [3 5]. Researchers have shown thatmutationsin the gene SCN9A are also associated with diseases whose base lies in the disorders of pain perception. This includes primary erythermalgia, congenital analgesia, and paroxysmal pain disorder. According to this, scientists have concluded that the SCN9A gene mutation can cause variations in the sensitivity to pain from complete insensitivity to extreme sensitivity [9]. 5. Primary Erythermalgia and SCN9A Gene Mutation Primary (inherited) erythromelalgia (IEM) is an autosomal dominant disease and represents a rare neurovascular disorder. It is characterized by the appearance of extreme neuropathicpainintheformofburningintheextremities as the response to heat or movement. Most patients feel the first symptoms in the early childhood (5-6 years); however, in some families symptoms can appear not earlier than in the old age. It is considered that the onset of symptoms depends on gene splicing as well as mutual combination of exons [11]. This disorder is highly resistant to therapy. Cooling of extremities relieves pain in the early stages; however, the later stages of the disease require the use of anesthetics [11]. Two reports describe the partial relief of pain in the patients with IEM using lidocaine and mexiletine [12, 13]. The other study conducted by Legroux-Crespel et al. describes the relief of pain in the patients with IEM with oral administration of mexiletine [14, 15]. It has been shown that it comes to the resistance to the anesthetic infusions after a while in somepatients,aswellastheresistancetotheanesthetic creams (mexiletine, fentanyl, and lidocaine) [11]. Davis and Sandoroni have shown that in the case of patients with IEM, lidocaine relieves pain in only 55% of cases [13]. It is well known that in the basis of IEM lies a genetic mutation. However, there are numerous mutations which have to be considered and a great number of researches have been conducted with the aim of detecting the specific cause as well as finding a targeted and effective disease treatment [16]. The genetic basis of IEM is found on the second chromosome as it was observed as the existence of recombinations in the genetic region between D2S2370 and D2S1776, which can be found on 2q Yang et al. have revealed the connection between this syndrome and the 5.98cM region on the chromosome 2q24.2-q24.3. Further sequencing on
3 Advances in Anesthesiology 3 the selected candidate genes has defined the first missense mutations on the SCN9A gene (I848T, L858F) [1, 6]. To date, 19 mutations associated with IEM have been found, including 18 missense mutations which cause substitution of one amino acid and one in-frame deletion. The penetration of IEM mutations is almost 100% and they all move the activation of NaV1.7 in the direction of hyperpolarization and slow deactivation [6, 17]. The most important mutations in current genetic research are F1449V, L858F, L858H A863P, S241T, N395K, I136V, V1316A, G616R, G856D, I848T, I234T, and F216S [4, 6, 11, 14, 16, 18 23]. MutationsI848TandL858HarelocatedintheS4-S5 linker region of the domain II (DIIS4-S5) on the gene SCN9A. The mutated channels have shown a few differences in comparison with the wild type channel NaV1.7. Both mutations shift the voltage dependence of activation. All of the changes that have been found increase excitability of spinal sensory neurons which express NaV1.7 [7]. Rush et al. have demonstrated that the L858H mutation makes the neurons of dorsal root ganglia (GDK) hyperexcitable, while it makes the sympathetic ganglia neurons hypoexcitable [23]. Yang et al. have shown that there is also a mutation I848T which is linked to IEM [1]. Cummins et al. have shown that these mutations affect the biophysical properties on these channels because both of these mutations cause a significant shift of hyperpolarization in the V 1/2 channel activation [7]. F1449VandA853Pmutationsresultedinalowerthreshold of triggering the action potential in the GDK and in a greater intensity of responses to stimuli compared to controls [14]. Mutation N395K, located on the S6 segment of domain I, is associated with a very serious form of IEM. The mentioned mutation is located on the gene segment which is responsible for the transcription of the locus which binds local anesthetic. Therefore, it directly affects the interaction of local anesthetic with the channel by reducing their sensitivity to the local anesthetic. This has been proved on HEK293 cells. Mutation F216S on the same gene was inserted in the HEK293 cell line by transfection, but this mutation is (unlike previous) located outside of the locus which binds local anesthetic. This has proved that this mutation, unlike N395K, affects the voltage dependent characteristics of the channel but does not affect the interaction with local anesthetics. The explanation of this phenomenon is that the channels with the mutation N395K have a disturbed inactivation and this reduces the number of channels which bind a local anesthetic (lidocaine in this case). Other scientists explain this phenomenon by the fact that this mutation impacts the direct interaction of lidocaine with the channel in inactive state [16]. The effects of S241T mutations are reducing the time to achieve the peak of action potential, slow deactivation, and an increased sensitivity of the channels to low stimuli. Serine (S) and threonine (T) are amino acids with similar biochemical characteristics because of the presence of reactive OH group in the side chains. Therefore, it is expected that the protein will retain its basic function due to the substitution S241T. However, Serine on the position 241 in S4-S5 linker region is a potential place for the binding of phosphorus, which is a part ofaproteinkinasecmolecule.ser-241ishighlyconserved residua in DI S4-S5 linker region in all of the membrane channels of vertebrates. Any change in this residue, even with a biochemically similar amino acid, causes changes in the porosityofthechannelanditsfunction.also,thesidechain of threonine is larger than the side chain of Serine and that also has the effect on the changing of the channel function [4]. Ahn et al. have identified the mutation on the SCN9A gene, which results in the substitution of Isoleucine with threonine (I234T). Cells with this mutation show a shift in the voltage dependent activation, rapid reach of the peak, slower deactivation, and an increased response to depolarization [18]. Further researches continue in the group of patients with IEM, in the group of patients with insufficient manifested symptoms of IEM, and in the group of patients with combined symptoms of IEM. In such patients the mutation 4894G>A, A1632T, on the gene for NaV1.7 has been observed [17]. 6. Paroxysmal Pain Disorder and Mutations on the SCN9A Gene Paroxysmal extreme pain disorder (PEPD) is a rare disorder which is characterized with the episodes of pain in the form of burning in rectal, ocular, and mandibular region associated with autoimmune manifestations in the form of skin redness. It is described that the first symptoms of disease occur in the neonatal period or in the early childhood and that they retain through their lives [24]. Allofthe10knownmissensemutationsoftheNaV1.7 onthegenescn9awhichhaveimpactontheoccurrence of PEPD cause the changes in channel closing (inactivation). Reduced inactivation of these channels causes prolonged action potential and repetitive firing. The most frequent mutation is M1627K [2, 17, 25]. 7. Congenital Analgesia and Mutations on SCN9A Gene Congenital insensitivity to pain (CIP) represents an extremely rare disorder in which a person cannot feel the pain. The genetic basis of this disorder also lies in the mutations of the SCN9A gene [2]. Some of these mutations are S459X, I767X, W897X, M899I, and M932L [10, 26 28]. Research conducted by Yuan et al. included the analysis of the sequences of the candidate genes. Two heterozygous mutations (M899I and M932L) in the gene SCN9A were found and it is considered that they are responsible for the onset of this disease. However, a recently discovered, nonsynonymous polymorphism on one nucleotide (single nucleotide polymorphism, SNP) c.3312g>t, inside of exon 16 ofthegenescn9a,resultsinthev1104laminoacidsubstitution in the human NaV1.7. This SNP has been present in those who have a decreased sensitivity to pain as well as in healthy family members. Due to the fact that this SNP is present in the genome of 6.5% of the healthy Chinese population, it is
4 4 Advances in Anesthesiology assumed that this mutation may be responsible for the variation in the sensitivity of pain in the general population [26]. 8. Link between the Pain Perception Disorders and Mutations on the Gene SCN9A Mutation A1632T was found in the patients with a combination of symptoms that characterize both disorders, IEM and PEPD. Eberhardt et al. have implemented the mutated DNA (previously extracted from lymphocytes and epithelial cells of oral mucosa) by transfection into the HEK 293 cells (human embryonic kidney 293 cells) and provoke the T/E/D/K/V substitutions of amino acids on the A1632 residue. They observed the consequential effect on the conductivity of the cell membrane. All the exons as well as the border parts between the exons and introns on the SCN9A gene were amplified by the PCR technique, using genetically specific intronic primers. Mutations A1632D/E/K/T were implemented in the splicing variants of the gene NaV1.7 and then the gene was introduced by transfection into the HEK 293 cells. After the establishment of the stable cell culture, which level of action potential is needed to cause the cell excitation was examined. Mutations T/D/E (substitution of alanine by threonine/aspartame/glutamic acid) on the position 1632 cause a significant shift of the fast inactivation, while the substitution of alanine by valine and lysine does not modify the fast inactivation.thesedataindicatethatthesizeandthepossible conformation changes in the protein as well as mutation of the gene may lead to the changes in the conduction of the action potential and in the perception of pain [17]. Some mutations, like A1632E, change the function of NaV1.7channel.Thisisreflectedinthecombinationoftwo out of three previously mentioned syndromes. This suggests thatfurtherresearchofthemutationsonthisgenecould answer the question: what intensity of pain do patients actuallyfeelinthepresenceofstimulation[2]. 9. Application of Research in Anesthesiology Studies conducted on the SCN9A gene indicate that the changesinthenav1.7proteinstructureplaythekeyrole in the occurrence of pain and suggest that the IEM, PEPD, and CIP may serve as disease models for the future research about appropriate targeted pain therapy [16]. It is evident that patients respond differently to current treatment strategies, so it is almost impossible for the clinician to assume the reaction of the individual and the specific dose to be applied. Drugs that inhibit voltage-gated sodium channels are being used in the treatment of pain, and this includes local anesthetics and Nav-blocking anticonvulsants [29]. The importance of Nav receptors in pain treatment is proved in studies [30, 31]. New drugs are being discovered, and they should be more specific, since it has been proved that gene mutations have a consequence of different level of drug-receptor binging [32]. Duan et al. investigated if the polymorphism 3312G>T on the gene SCN9A is responsible for the intensity of pain perception variability in the general population. The study included patients of years of age that were subjected to pancreatectomy operations with general anesthesia (0.05 mg/kg Midazolam, 2 mg/kg Propofol, 0.5 μg/kg Sufentanil, and 0.6 mg/kg Rocuronium for the induction of anesthesia, inhalation of 1% Sevoflurane, and infusion of μg/kg/min Remifentanil, 6 10 mg/kg/h Propofol, and 0.2 mg/kg Rocuronium for the maintenance of anesthesia). 40 mg of parecoxib sodium and 2 mg of tropisetron hydrochloride were given intravenously fifteen minutes before incision for the alleviation of postoperative pain and prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting. Immediately after surgery it has been enabled for patients to receive 0.5 μg/ml Sufentanil and 5 mg/ml Tramadol in controlled infusion.ithasbeenstatisticallyprovedthatthepatients homozygous for the allele 3312G had a greater need for postoperative analgesia than those who were heterozygous for 3312T allele. This research demonstrated that the reduction in the sensitivity to postoperative pain is linked to SNP SCN9A3312G>T. The patients carriers of the SCN9A3312T allele had lower sensitivity to similar operative stimuli and required a lower level of analgesia than those who carried the 3312G allele [9]. A comprehensive study conducted by Reimanna et al. indicated the importance of the R1150W SNP on the SCN9A gene for the increased pain perception in the patients with osteoarthritis, patients after lumbar discectomy, amputees with phantom pain, pain-assessed people with sciatica, and patients with pancreatitis. Genotypisation proved that there exists a significant correlation between greater pain perception and A allele, which is less common in general population. The result was confirmed in a group of healthy women who were exposed to noxious stimuli [33]. This result was confirmed by Valdes et al. on the patients suffering from osteoarthritis [34]. However, Holliday et al. have denied these studies with the claims that this mutation is not connected with the greater pain perception, and this was explained by the fact that their sample was heterogenous. The authors also point out that more comprehensive and more specific studies arerequiredinthefuture[35]. When it comes to the treatment of chronic pain, there are demands which clinicians can rarely follow, because the accurate target therapy based on genetic testing is needed. Theile and Cummins have showed, based on the research conductedonstablytransfectedhumanembrionickidney cells, that the most effective therapy in the case of IEM is Lidocaine, Aspirin, Mexiletine, and Gabapentin, while, in the case of PEPD, the most effective therapy is Carbamazepine, Riluzole, Anandamide, and Lacosamide [36]. Drugs which block sodium channels, such as local anesthetics (Lidocaine), anticonvulsants (Carbamazepine, Phenytoin), and tricyclic antidepressants (Imipramine), were only partially successful in the case of IEM. Mutations V1316A, I848T,andI136VonthegeneSCN9Ashowedahigher resistance to Lidocaine when compared to wild type channels in the experiment conducted by Wu et al. An alternative to Lidocaine could be Mexiletine, since it showed more efficiency than Lidocaine, especially in patients with I848T mutation [6, 37]. It has also been shown that Mexiletine is an adequate replacement for Lidocaine in the case of L858F mutation [38].
5 Advances in Anesthesiology Conclusion Treatment of pain disorders has not proved to be successful in long-term application. Modern researches in pharmacogenomics suggest that further understanding of NaV1.7 channel function and pharmacology will be crucial for understanding of the pathophysiology of pain and for the development of the appropriate targeted pain treatment. Pain perception disorders are very rare; however, the findings suggest that there is a high possibility that the allelic differences in the SCN9A gene affect the pain perception in general population. Therefore, it will be possible to apply targeted therapy in everyday clinical practice, especially in intensive care units, in patients with normal pain threshold. In this way it would be possible to facilitate postoperative course, to avoid unwanted effects of pain treatment, and to reduce the number of postoperative hospital days. Conflict of Interests The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper. References [1] Y. Yang, Y. Wang, S. Lietal., MutationsinSCN9A, encoding a sodium channel alpha subunit, in patients with primary erythermalgia, Medical Genetics, vol. 41, no. 3, pp , [2] M.Estacion,S.D.Dib-Hajj,P.J.Benkeetal., NaV1.7gain-offunction mutations as a continuum: a1632e displays physiological changes associated with erythromelalgia and paroxysmal extreme pain disorder mutations and produces symptoms of both disorders, The Neuroscience, vol. 28, no. 43, pp , [3] C. J. Laedermann, N. Syam, M. Pertin, I. Decosterd, and H. Abriel, β1- and β3-voltage-gated sodium channel subunits modulate cell surface expression and glycosylation of Nav1.7 in HEK293 cells, Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience, vol. 7, pp. 1 12, [4]A.Lampert,S.D.Dib-Hajj,L.Tyrrell,andS.G.Waxman, Size matters: erythromelalgia mutation S241T in Nav1.7 alters channel gating, TheJournalofBiologicalChemistry, vol. 281, no. 47, pp , [5] M. H. Meisler and J. A. Kearney, Sodium channel mutations in epilepsy and other neurological disorders, The Clinical Investigation,vol.115,no.8,pp ,2005. [6] M.-T. Wu, P.-Y. Huang, C.-T. Yen, C.-C. Chen, and M.-J. Lee, A novel SCN9A mutation responsible for primary erythromelalgiaandisresistanttothetreatmentofsodiumchannelblockers, PLoS ONE,vol.8,no.1,ArticleIDe55212,2013. [7] T. R. Cummins, S. D. Dib-Hajj, and S. G. Waxman, Electrophysiological properties of mutant Na v 1.7sodiumchannelsina painful inherited neuropathy, The Neuroscience,vol. 24,no.38,pp ,2004. [8]J.P.H.DrenthandS.G.Waxman, Mutationsinsodiumchannel gene SCN9A cause a spectrum of human genetic pain disorders, The Clinical Investigation, vol. 117, no. 12, pp , [9] G. Duan, G. Xiang, X. Zhang, R. Yuan, H. Zhan, and D. Qi, A single-nucleotide polymorphism in SCN9A may decrease postoperative pain sensitivity in the general population, Anesthesiology,vol.118,no.2,pp ,2013. [10] J. J. Cox, F. Reimann, A. K. Nicholas et al., An SCN9A channelopathy causes congenital inability to experience pain, Nature,vol.444,no.7121,pp ,2006. [11] J.-S. Choi, X. Cheng, E. Foster et al., Alternative splicing may contribute to time-dependent manifestation of inherited erythromelalgia, Brain,vol.133,no.6,pp ,2010. [12] S. M. Kuhnert, W. J. Phillips, and M. D. P. Davis, Lidocaine and mexiletine therapy for erythromelalgia, Archives of Dermatology,vol.135,no.12,pp ,1999. [13] M. D. Davis and P. Sandoroni, Lidocaine patch for pain of erytromelalgia, Archives of Dermatology,vol.138,no.1,pp.17 19, [14] S. D. Dib-Hajj, A. M. Rush, T. R. Cummins et al., Gain-offunction mutation in Nav1.7 in familial erythromelalgia induces bursting of sensory neurons, Brain, vol. 128, no. 8, pp , [15] E.Legroux-Crespel,B.Sassolas,G.Guillet,I.Kupfer,D.Dupre, and L. Misery, Treatment of familial erythermalgia with the association of lidocaine and mexiletine, Annales de DermatologieetdeVénéréologie,vol.130,no.4,pp ,2003. [16] P. L. Sheets, J. O. Jackson II, S. G. Waxman, S. D. Dib-hajj, and T. R. Cummins, A Nav 1.7 channel mutation associated with hereditary erythromelalgia contributes to neuronal hyperexcitability and displays reduced lidocaine sensitivity, Journal of Physiology,vol.581,no.3,pp ,2007. [17] M. Eberhardt, J. Nakajima, A. B. Klinger et al., Inherited pain sodium channel nav1.7 A1632T mutation causes erythromelalgia due to a shift of fast inactivation, TheJournalofBiological Chemistry, vol. 289, no. 4, pp , [18] H.-S.Ahn,S.D.Dib-Hajj,J.J.Coxetal., AnewNav1.7sodium channel mutation I234T in a child with severe pain, European Pain,vol.14,no.9,pp ,2010. [19] C. Han, A. M. Rush, S. D. Dib-Hajj et al., Sporadic onset of erythermalgia: a gain-of-function mutation in Nav1.7, Annals of Neurology,vol.59,no.3,pp ,2006. [20] T. P. Harty, S. D. Dib-Hajj, L. Tyrrell et al., Nav1.7 mutant A863P in erythromelalgia: effects of altered activation and steady-state inactivation on excitability of nociceptive dorsal root ganglion neurons, Neuroscience, vol. 26, no. 48, pp , [21] X. Cheng, S. D. Dib-Hajj, L. Tyrrell, and S. G. Waxman, Mutation I136V alters electrophysiological properties of the NaV1.7 channel in a family with onset of erythromelalgia in the second decade, Molecular Pain,vol.4,article1,2008. [22] J. G. J. Hoeijmakers, C. Han, I. S. J. Merkies et al., Small nerve fibres, small hands and small feet: a new syndrome of pain, dysautonomia and acromesomelia in a kindred with a novel NaV1.7 mutation, Brain, vol. 135, no. 2,pp , [23] A. M. Rush, S. D. Dib-Hajj, S. Liu, T. R. Cummins, J. A. Black, and S. G. Waxman, A single sodium channel mutation produces hyper- or hypoexcitability in different types of neurons, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,vol.103,no.21,pp ,2006. [24] C. R. Fertleman, C. D. Ferrie, J. Aicardi et al., Paroxysmal extreme pain disorder (previously familial rectal pain syndrome), Neurology, vol. 69, no. 6, pp , [25]S.D.Dib-Hajj,M.Estacion,B.W.Jareckietal., Paroxysmal extreme pain disorder M1627K mutation in human Nav 1.7 renders DRG neurons hyperexcitable, Molecular Pain, vol. 4, article 37, 2008.
6 6 Advances in Anesthesiology [26] R. Yuan, X. Zhang, Q. Deng et al., Two novel SCN9A gene heterozygous mutations may cause partial deletion of pain perception, Pain Medicine,vol.12,no.10, pp ,2011. [27] F. B. J. Young, A life without pain? Hedonists take note, Clinical Genetics,vol.73,no.1,pp.31 33,2008. [28]Y.P.Goldberg,J.Macfarlane,M.L.Macdonaldetal., Lossof-function mutations in the Nav1.7 gene underlie congenital indifference to pain in multiple human populations, Clinical Genetics,vol.71,no.4,pp ,2007. [29] J. J. Clare, Targeting voltage-gated sodium channels for pain therapy, ExpertOpiniononInvestigationalDrugs,vol.19,no.1, pp.45 62,2010. [30] I.T.Strickland,J.C.Martindale,P.L.Woodhams,A.J.Reeve, I. P. Chessell, and D. S. McQueen, Changes in the expression of NaV1.7, NaV1.8 and NaV1.9 in a distinct population of dorsal root ganglia innervating the rat knee joint in a model of chronic inflammatory joint pain, European Pain, vol.12,no. 5, pp , [31] W. Wang, J. Gu, Y.-Q. Li, and Y.-X. Tao, Are voltage-gated sodium channels on the dorsal root ganglion involved in the development of neuropathic pain? Molecular Pain, vol. 7, article 16, [32] J. R. Walkera, P. A. Novicka, W. H. Parsonsa et al., Marked difference in saxitoxin and tetrodotoxin affinity for the human nociceptive voltage-gated sodium channel (Nav1.7), Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, vol. 109, no. 44, pp , [33] F.Reimanna,J.J.Cox,I.Belferetal., Painperceptionisaltered by a nucleotide polymorphism in SCN9A, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, vol.107,no.11,pp ,2010. [34] A.M.Valdes,N.K.Arden,F.L.Vaughnetal., RoleoftheNa v 1.7 R1150W amino acid change in susceptibility to symptomatic knee osteoarthritis and multiple regional pain, Arthritis Care &Research,vol.63,no.3,pp ,2011. [35] K. L. Holliday, W. Thomson, T. Neogi et al., The nonsynonymous SNP, R1150W, in SCN9A is not associated with chronic widespread pain susceptibility, Molecular Pain, vol. 8, article 72, [36] J. W. Theile and T. R. Cummins, Inhibition of Navβ4 peptidemediated resurgent sodium currents in Nav1.7 channels by carbamazepine, riluzole, and anandamide, Molecular Pharmacology,vol.80,no.4,pp ,2011. [37] D. M. Kullmann and S. G. Waxman, Neurological channelopathies: new insights into disease mechanisms and ion channel function, Physiology, vol. 588, no. 11, pp , [38] R. Cregg, J. J. Cox, D. L. H. Bennett, J. N. Wood, and R. Werehausen, Mexiletine as a treatment for primary erythromelalgia: normalization of biophysical properties of mutant L858F Nav1.7 sodium channels, British Pharmacology, vol. 171, no. 19, pp , 2014.
7 MEDIATORS of INFLAMMATION The Scientific World Journal Gastroenterology Research and Practice Diabetes Research International Endocrinology Immunology Research Disease Markers Submit your manuscripts at BioMed Research International PPAR Research Obesity Ophthalmology Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Stem Cells International Oncology Parkinson s Disease Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine AIDS Behavioural Neurology Research and Treatment Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity
A case of inherited erythromelalgia.
 A case of inherited erythromelalgia. Steven P Novella; Fuki M Hisama; Sulayman D Dib-Hajj; Stephen G Waxman Summary and Case Summary Background: A 15-year-old boy presented with recurrent episodes of erythema
A case of inherited erythromelalgia. Steven P Novella; Fuki M Hisama; Sulayman D Dib-Hajj; Stephen G Waxman Summary and Case Summary Background: A 15-year-old boy presented with recurrent episodes of erythema
Inherited erythromelalgia mutations in Na v 1.7
 Inherited erythromelalgia mutations in Na v 1.7 I II III IV A863P N F216S S241T N395K L1 I848T L858F L858H L2 F1449V L3 C Mutation V 1/2 Activation V 1/2 Inactivation Slow Inactivation Deactivation Ramp
Inherited erythromelalgia mutations in Na v 1.7 I II III IV A863P N F216S S241T N395K L1 I848T L858F L858H L2 F1449V L3 C Mutation V 1/2 Activation V 1/2 Inactivation Slow Inactivation Deactivation Ramp
Putative low penetrance or susceptibility variants: sodium channel genes in painful neuropathy as an example
 Putative low penetrance or susceptibility variants: sodium channel genes in painful neuropathy as an example Carl Fratter 1 Kate Sergeant 1, Julie C Evans 1, Anneke Seller 1, David Bennett 2 1 Oxford Medical
Putative low penetrance or susceptibility variants: sodium channel genes in painful neuropathy as an example Carl Fratter 1 Kate Sergeant 1, Julie C Evans 1, Anneke Seller 1, David Bennett 2 1 Oxford Medical
Mutations in sodium-channel gene SCN9A cause a spectrum of human genetic pain disorders
 Mutations in sodium-channel gene SCN9A cause a spectrum of human genetic pain disorders Joost P.H. Drenth, Stephen G. Waxman J Clin Invest. 2007;117(12):3603-3609. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci33297. Science
Mutations in sodium-channel gene SCN9A cause a spectrum of human genetic pain disorders Joost P.H. Drenth, Stephen G. Waxman J Clin Invest. 2007;117(12):3603-3609. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci33297. Science
Local Anesthetics. Xiaoping Du Room E417 MSB Department of Pharmacology Phone (312) ;
 Local Anesthetics Xiaoping Du Room E417 MSB Department of Pharmacology Phone (312)355 0237; Email: xdu@uic.edu Summary: Local anesthetics are drugs used to prevent or relieve pain in the specific regions
Local Anesthetics Xiaoping Du Room E417 MSB Department of Pharmacology Phone (312)355 0237; Email: xdu@uic.edu Summary: Local anesthetics are drugs used to prevent or relieve pain in the specific regions
A case of inherited erythromelalgia
 A case of inherited erythromelalgia Steven P Novella, Fuki M Hisama, Sulayman D Dib-Hajj and Stephen G Waxman* CASE STUDY SUMMARY Background A 15-year-old boy presented with recurrent episodes of erythema
A case of inherited erythromelalgia Steven P Novella, Fuki M Hisama, Sulayman D Dib-Hajj and Stephen G Waxman* CASE STUDY SUMMARY Background A 15-year-old boy presented with recurrent episodes of erythema
Paroxysmal extreme pain disorder mutations within the D3/S4 S5 linker of Nav1.7 cause moderate destabilization of fast inactivation
 J Physiol 586.17 (2008) pp 4137 4153 4137 Paroxysmal extreme pain disorder mutations within the D3/S4 S5 linker of Nav1.7 cause moderate destabilization of fast inactivation Brian W. Jarecki, Patrick L.
J Physiol 586.17 (2008) pp 4137 4153 4137 Paroxysmal extreme pain disorder mutations within the D3/S4 S5 linker of Nav1.7 cause moderate destabilization of fast inactivation Brian W. Jarecki, Patrick L.
A Novel Na v 1.7 Mutation Producing Carbamazepine-Responsive Erythromelalgia
 A Novel Na v 1.7 Mutation Producing Carbamazepine-Responsive Erythromelalgia Tanya Z. Fischer, MD, PhD, 1 3 Elaine S. Gilmore, MD, PhD, 2 4 Mark Estacion, PhD, 1 3 Emmanuella Eastman, BS, 1 3 Sean Taylor,
A Novel Na v 1.7 Mutation Producing Carbamazepine-Responsive Erythromelalgia Tanya Z. Fischer, MD, PhD, 1 3 Elaine S. Gilmore, MD, PhD, 2 4 Mark Estacion, PhD, 1 3 Emmanuella Eastman, BS, 1 3 Sean Taylor,
Cellular/Molecular The Journal of Neuroscience, November 29, (48):
 12566 The Journal of Neuroscience, November 29, 2006 26(48):12566 12575 Cellular/Molecular Na v 1.7 Mutant A863P in Erythromelalgia: Effects of Altered Activation and Steady-State Inactivation on Excitability
12566 The Journal of Neuroscience, November 29, 2006 26(48):12566 12575 Cellular/Molecular Na v 1.7 Mutant A863P in Erythromelalgia: Effects of Altered Activation and Steady-State Inactivation on Excitability
Voltage Gated Ion Channels
 Voltage Gated Ion Channels The Machines That Make It Possible... Topics I Introduction Electrochemical Gradients Passive Membrane Properties Action Potential Voltage-Gated Ion Channels Ligand-Gated Ion
Voltage Gated Ion Channels The Machines That Make It Possible... Topics I Introduction Electrochemical Gradients Passive Membrane Properties Action Potential Voltage-Gated Ion Channels Ligand-Gated Ion
Neurological channelopathies: new insights into disease mechanisms and ion channel function
 Neurologicalchannelopathies:newinsightsintodiseasemechanismsand ionchannelfunction DimitriMKullmann 1 andstephengwaxman 2 1 InstituteofNeurology,UniversityCollegeLondon,London,UK 2 DepartmentofNeurology,YaleUniversitySchoolofMedicine,NewHaven,
Neurologicalchannelopathies:newinsightsintodiseasemechanismsand ionchannelfunction DimitriMKullmann 1 andstephengwaxman 2 1 InstituteofNeurology,UniversityCollegeLondon,London,UK 2 DepartmentofNeurology,YaleUniversitySchoolofMedicine,NewHaven,
Seizure: the clinical manifestation of an abnormal and excessive excitation and synchronization of a population of cortical
 Are There Sharing Mechanisms of Epilepsy, Migraine and Neuropathic Pain? Chin-Wei Huang, MD, PhD Department of Neurology, NCKUH Basic mechanisms underlying seizures and epilepsy Seizure: the clinical manifestation
Are There Sharing Mechanisms of Epilepsy, Migraine and Neuropathic Pain? Chin-Wei Huang, MD, PhD Department of Neurology, NCKUH Basic mechanisms underlying seizures and epilepsy Seizure: the clinical manifestation
Research Article Clinical Outcome of a Novel Anti-CD6 Biologic Itolizumab in Patients of Psoriasis with Comorbid Conditions
 Dermatology Research and Practice Volume 2, Article ID 13326, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/.1155/2/13326 Research Article Clinical Outcome of a Novel Anti-CD6 Biologic Itolizumab in Patients of Psoriasis
Dermatology Research and Practice Volume 2, Article ID 13326, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/.1155/2/13326 Research Article Clinical Outcome of a Novel Anti-CD6 Biologic Itolizumab in Patients of Psoriasis
Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels: Therapeutic Targets for Painpme_719. Sulayman D. Dib-Hajj, PhD, Joel A. Black, PhD, and Stephen G.
 1260..1269 PAIN MEDICINE Volume 10 Number 7 2009 Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels: Therapeutic Targets for Painpme_719 Sulayman D. Dib-Hajj, PhD, Joel A. Black, PhD, and Stephen G. Waxman, MD, PhD Department
1260..1269 PAIN MEDICINE Volume 10 Number 7 2009 Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels: Therapeutic Targets for Painpme_719 Sulayman D. Dib-Hajj, PhD, Joel A. Black, PhD, and Stephen G. Waxman, MD, PhD Department
Brian Kahan, D.O. FAAPMR, DABPM, DAOCRM, FIPP Center for Pain Medicine and Physiatric Rehabilitation 2002 Medical Parkway Suite 150 Annapolis, MD
 Brian Kahan, D.O. FAAPMR, DABPM, DAOCRM, FIPP Center for Pain Medicine and Physiatric Rehabilitation 2002 Medical Parkway Suite 150 Annapolis, MD 1630 Main Street Suite 215 Chester, MD 410-571-9000 www.4-no-pain.com
Brian Kahan, D.O. FAAPMR, DABPM, DAOCRM, FIPP Center for Pain Medicine and Physiatric Rehabilitation 2002 Medical Parkway Suite 150 Annapolis, MD 1630 Main Street Suite 215 Chester, MD 410-571-9000 www.4-no-pain.com
Neurophysiology of Nerve Impulses
 M52_MARI0000_00_SE_EX03.qxd 8/22/11 2:47 PM Page 358 3 E X E R C I S E Neurophysiology of Nerve Impulses Advance Preparation/Comments Consider doing a short introductory presentation with the following
M52_MARI0000_00_SE_EX03.qxd 8/22/11 2:47 PM Page 358 3 E X E R C I S E Neurophysiology of Nerve Impulses Advance Preparation/Comments Consider doing a short introductory presentation with the following
Clinical Spectrum and Genetic Mechanism of GLUT1-DS. Yasushi ITO (Tokyo Women s Medical University, Japan)
 Clinical Spectrum and Genetic Mechanism of GLUT1-DS Yasushi ITO (Tokyo Women s Medical University, Japan) Glucose transporter type 1 (GLUT1) deficiency syndrome Mutation in the SLC2A1 / GLUT1 gene Deficiency
Clinical Spectrum and Genetic Mechanism of GLUT1-DS Yasushi ITO (Tokyo Women s Medical University, Japan) Glucose transporter type 1 (GLUT1) deficiency syndrome Mutation in the SLC2A1 / GLUT1 gene Deficiency
Research Article Subcutaneous Single Injection Digital Block with Epinephrine
 Anesthesiology Research and Practice Volume 2012, Article ID 487650, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/487650 Research Article Subcutaneous Single Injection Digital Block with Epinephrine Motoki Sonohata, 1 Satomi
Anesthesiology Research and Practice Volume 2012, Article ID 487650, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/487650 Research Article Subcutaneous Single Injection Digital Block with Epinephrine Motoki Sonohata, 1 Satomi
Case presentations from diagnostic exome sequencing results in ion channels M. Koko, U. Hedrich, H. Lerche DASNE meeting 2017, Eisenach
 Case presentations from diagnostic exome sequencing results in ion channels M. Koko, U. Hedrich, H. Lerche DASNE meeting 2017, Eisenach CASE 1: Clinical picture Patient s presentation: 38 year old jewish
Case presentations from diagnostic exome sequencing results in ion channels M. Koko, U. Hedrich, H. Lerche DASNE meeting 2017, Eisenach CASE 1: Clinical picture Patient s presentation: 38 year old jewish
JULY 21, Genetics 101: SCN1A. Katie Angione, MS CGC Certified Genetic Counselor CHCO Neurology
 JULY 21, 2018 Genetics 101: SCN1A Katie Angione, MS CGC Certified Genetic Counselor CHCO Neurology Disclosures: I have no financial interests or relationships to disclose. Objectives 1. Review genetic
JULY 21, 2018 Genetics 101: SCN1A Katie Angione, MS CGC Certified Genetic Counselor CHCO Neurology Disclosures: I have no financial interests or relationships to disclose. Objectives 1. Review genetic
2/7/16. Ion channel properties
 The Wellcome Trust - Biomedical Vacation Scholarships provide promising undergraduates with hands-on experience of research during the summer vacation, with the aim of encouraging them to consider a career
The Wellcome Trust - Biomedical Vacation Scholarships provide promising undergraduates with hands-on experience of research during the summer vacation, with the aim of encouraging them to consider a career
TMC9 as a novel mechanosensitive ion channel
 TMC9 as a novel mechanosensitive ion channel Mechanical forces play numerous roles in physiology. When an object contacts our skin, it exerts a force that is encoded as touch or pain depending on its intensity.
TMC9 as a novel mechanosensitive ion channel Mechanical forces play numerous roles in physiology. When an object contacts our skin, it exerts a force that is encoded as touch or pain depending on its intensity.
Brain Advance Access published July 22, doi: /brain/aws187 Brain 2012: Page 1 of 16 1
 Brain Advance Access published July 22, 2012 doi:10.1093/brain/aws187 Brain 2012: Page 1 of 16 1 BRAIN A JOURNAL OF NEUROLOGY Functional profiles of SCN9A variants in dorsal root ganglion neurons and superior
Brain Advance Access published July 22, 2012 doi:10.1093/brain/aws187 Brain 2012: Page 1 of 16 1 BRAIN A JOURNAL OF NEUROLOGY Functional profiles of SCN9A variants in dorsal root ganglion neurons and superior
Tumor suppressor genes D R. S H O S S E I N I - A S L
 Tumor suppressor genes 1 D R. S H O S S E I N I - A S L What is a Tumor Suppressor Gene? 2 A tumor suppressor gene is a type of cancer gene that is created by loss-of function mutations. In contrast to
Tumor suppressor genes 1 D R. S H O S S E I N I - A S L What is a Tumor Suppressor Gene? 2 A tumor suppressor gene is a type of cancer gene that is created by loss-of function mutations. In contrast to
The Pain Pathway. dorsal root ganglion. primary afferent nociceptor. TRP: Transient Receptor Potential
 Presented by Issel Anne L. Lim 1 st Year PhD Candidate Biomedical Engineering Johns Hopkins University 580.427/580.633 Ca Signals in Biological Systems Outline The Pain Pathway TRP: Transient Receptor
Presented by Issel Anne L. Lim 1 st Year PhD Candidate Biomedical Engineering Johns Hopkins University 580.427/580.633 Ca Signals in Biological Systems Outline The Pain Pathway TRP: Transient Receptor
Case Report Congenital Insensitivity to Pain: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
 Case Reports in Neurological Medicine, Article ID 141953, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/141953 Case Report Congenital Insensitivity to Pain: A Case Report and Review of the Literature Leema Reddy
Case Reports in Neurological Medicine, Article ID 141953, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/141953 Case Report Congenital Insensitivity to Pain: A Case Report and Review of the Literature Leema Reddy
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Intravenous Anesthetics for the Treatment of Chronic Pain File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: intravenous_anesthetics_for_the_treatment_of_chronic_pain
Corporate Medical Policy Intravenous Anesthetics for the Treatment of Chronic Pain File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: intravenous_anesthetics_for_the_treatment_of_chronic_pain
Pathophysiology of Pain
 Pathophysiology of Pain Wound Inflammatory response Chemical mediators Activity in Pain Path PAIN http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s2/chapter08.html Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University
Pathophysiology of Pain Wound Inflammatory response Chemical mediators Activity in Pain Path PAIN http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s2/chapter08.html Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University
211MDS Pain theories
 211MDS Pain theories Definition In 1986, the International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP) defined pain as a sensory and emotional experience associated with real or potential injuries, or described
211MDS Pain theories Definition In 1986, the International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP) defined pain as a sensory and emotional experience associated with real or potential injuries, or described
Multiple Mechanisms for Pain - How Can We Improve the Chances of Success?
 Multiple Mechanisms for Pain - How Can We Improve the Chances of Success? Ann Hayes October 2017 What are the different types of pain? Neuropathic Diabetic neuropathy, PHN, sciatica Caused by damage to
Multiple Mechanisms for Pain - How Can We Improve the Chances of Success? Ann Hayes October 2017 What are the different types of pain? Neuropathic Diabetic neuropathy, PHN, sciatica Caused by damage to
currents in Nav1.7 channels by carbamazepine, riluzole and anandamide
 Molecular Pharmacology This article has Fast not been Forward. copyedited Published and formatted. The on final July version 25, 2011 may differ as doi:10.1124/mol.111.072751 from this version. TITLE PAGE
Molecular Pharmacology This article has Fast not been Forward. copyedited Published and formatted. The on final July version 25, 2011 may differ as doi:10.1124/mol.111.072751 from this version. TITLE PAGE
Epileptogenesis: A Clinician s Perspective
 Epileptogenesis: A Clinician s Perspective Samuel F Berkovic Epilepsy Research Centre, University of Melbourne Austin Health Epileptogenesis The process of development and sustaining the propensity to
Epileptogenesis: A Clinician s Perspective Samuel F Berkovic Epilepsy Research Centre, University of Melbourne Austin Health Epileptogenesis The process of development and sustaining the propensity to
Chapter 25. General Anesthetics
 Chapter 25 1. Introduction General anesthetics: 1. Analgesia 2. Amnesia 3. Loss of consciousness 4. Inhibition of sensory and autonomic reflexes 5. Skeletal muscle relaxation An ideal anesthetic: 1. A
Chapter 25 1. Introduction General anesthetics: 1. Analgesia 2. Amnesia 3. Loss of consciousness 4. Inhibition of sensory and autonomic reflexes 5. Skeletal muscle relaxation An ideal anesthetic: 1. A
Research Article The Need for Improved Management of Painful Diabetic Neuropathy in Primary Care
 Pain Research and Management Volume 2016, Article ID 1974863, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1974863 Research Article The Need for Improved Management of Painful Diabetic Neuropathy in Primary
Pain Research and Management Volume 2016, Article ID 1974863, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1974863 Research Article The Need for Improved Management of Painful Diabetic Neuropathy in Primary
Clinical Study IVIG Effects on Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate in Children
 International Pediatrics, Article ID 981465, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/981465 Clinical Study IVIG Effects on Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate in Children Farhad Salehzadeh, Ahmadvand Noshin,
International Pediatrics, Article ID 981465, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/981465 Clinical Study IVIG Effects on Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate in Children Farhad Salehzadeh, Ahmadvand Noshin,
Insulin Resistance. Biol 405 Molecular Medicine
 Insulin Resistance Biol 405 Molecular Medicine Insulin resistance: a subnormal biological response to insulin. Defects of either insulin secretion or insulin action can cause diabetes mellitus. Insulin-dependent
Insulin Resistance Biol 405 Molecular Medicine Insulin resistance: a subnormal biological response to insulin. Defects of either insulin secretion or insulin action can cause diabetes mellitus. Insulin-dependent
Research Article Hb A1c Separation by High Performance Liquid Chromatography in Hemoglobinopathies
 Scientifica Volume 2016, Article ID 2698362, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/2698362 Research Article Hb A1c Separation by High Performance Liquid Chromatography in Hemoglobinopathies Vani Chandrashekar
Scientifica Volume 2016, Article ID 2698362, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/2698362 Research Article Hb A1c Separation by High Performance Liquid Chromatography in Hemoglobinopathies Vani Chandrashekar
Medications for the Treatment of Neuropathic Pain
 Medications for the Treatment of Neuropathic Pain February 23, 2011 Jinny Tavee, MD Associate Professor Neurological Institute Cleveland Clinic Foundation Neuropathic Pain Pain, paresthesias, and sensory
Medications for the Treatment of Neuropathic Pain February 23, 2011 Jinny Tavee, MD Associate Professor Neurological Institute Cleveland Clinic Foundation Neuropathic Pain Pain, paresthesias, and sensory
Pathophysiology of Pain. Ramon Go MD Assistant Professor Anesthesiology and Pain medicine NYP-CUMC
 Pathophysiology of Pain Ramon Go MD Assistant Professor Anesthesiology and Pain medicine NYP-CUMC Learning Objectives Anatomic pathway of nociception Discuss the multiple target sites of pharmacological
Pathophysiology of Pain Ramon Go MD Assistant Professor Anesthesiology and Pain medicine NYP-CUMC Learning Objectives Anatomic pathway of nociception Discuss the multiple target sites of pharmacological
180 Days EAE: Protection persists during maintained admin. of phenytoin
 CAP area (mvmsec) 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0 1.1 Clinical score 180 Days EAE: Protection persists during maintained admin. of phenytoin Control EAE EAE Phen Cont EAE EAE Phen 0.8 0.7 0.6 Contr
CAP area (mvmsec) 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0 1.1 Clinical score 180 Days EAE: Protection persists during maintained admin. of phenytoin Control EAE EAE Phen Cont EAE EAE Phen 0.8 0.7 0.6 Contr
2/7/16. Neurons maintain a negative membrane potential. Membrane potential. Ion conductances determine the membrane potential
 Neurons maintain a negative membrane potential. V Ion channels are key regulators of membrane potential. Low Na + 2mM High K + 125mM Low Ca + (10-7 ) Low Cl - (5mM) Membrane potential. V ENa= RT/nF ln[na+]o/[na+]in
Neurons maintain a negative membrane potential. V Ion channels are key regulators of membrane potential. Low Na + 2mM High K + 125mM Low Ca + (10-7 ) Low Cl - (5mM) Membrane potential. V ENa= RT/nF ln[na+]o/[na+]in
Pain Management Clinic ISIC
 Pain Management Clinic ISIC Let us rebuild a pain free life Pain is one of the commonest symptoms in patients attending OPDs of various hospitals and clinics. Chronic pain is any pain that has persisted
Pain Management Clinic ISIC Let us rebuild a pain free life Pain is one of the commonest symptoms in patients attending OPDs of various hospitals and clinics. Chronic pain is any pain that has persisted
Cellular Neurobiology BIPN140. 1st Midterm Exam October 18 th, Tuesday Material covered: Lectures 1-6 & Reading
 Cellular Neurobiology BIPN140 1st Midterm Exam October 18 th, Tuesday Material covered: Lectures 1-6 & Reading Review session October 17 th 3500 Pacitic Hall, 6-8 pm (access code is 127895) Come with questions!
Cellular Neurobiology BIPN140 1st Midterm Exam October 18 th, Tuesday Material covered: Lectures 1-6 & Reading Review session October 17 th 3500 Pacitic Hall, 6-8 pm (access code is 127895) Come with questions!
A rare variant in MYH6 confers high risk of sick sinus syndrome. Hilma Hólm ESC Congress 2011 Paris, France
 A rare variant in MYH6 confers high risk of sick sinus syndrome Hilma Hólm ESC Congress 2011 Paris, France Disclosures I am an employee of decode genetics, Reykjavik, Iceland. Sick sinus syndrome SSS is
A rare variant in MYH6 confers high risk of sick sinus syndrome Hilma Hólm ESC Congress 2011 Paris, France Disclosures I am an employee of decode genetics, Reykjavik, Iceland. Sick sinus syndrome SSS is
Case Report Bilateral Distal Femoral Nailing in a Rare Symmetrical Periprosthetic Knee Fracture
 Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 745083, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/745083 Case Report Bilateral Distal Femoral Nailing in a Rare Symmetrical Periprosthetic Knee Fracture Marcos Carvalho,
Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 745083, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/745083 Case Report Bilateral Distal Femoral Nailing in a Rare Symmetrical Periprosthetic Knee Fracture Marcos Carvalho,
Novel Methods to Identify Pain Targets : Genomic/Genetic Approaches
 Novel Methods to Identify Pain Targets : Genomic/Genetic Approaches Luda Diatchenko, MD, PhD Canada Excellence Research Chair in Human Pain Genetics Alan Edwards Centre for Research on Pain, McGill University,
Novel Methods to Identify Pain Targets : Genomic/Genetic Approaches Luda Diatchenko, MD, PhD Canada Excellence Research Chair in Human Pain Genetics Alan Edwards Centre for Research on Pain, McGill University,
Nerve. (2) Duration of the stimulus A certain period can give response. The Strength - Duration Curve
 Nerve Neuron (nerve cell) is the structural unit of nervous system. Nerve is formed of large numbers of nerve fibers. Types of nerve fibers Myelinated nerve fibers Covered by myelin sheath interrupted
Nerve Neuron (nerve cell) is the structural unit of nervous system. Nerve is formed of large numbers of nerve fibers. Types of nerve fibers Myelinated nerve fibers Covered by myelin sheath interrupted
CHAPTER 4 PAIN AND ITS MANAGEMENT
 CHAPTER 4 PAIN AND ITS MANAGEMENT Pain Definition: An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described in terms of such damage. Types of Pain
CHAPTER 4 PAIN AND ITS MANAGEMENT Pain Definition: An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described in terms of such damage. Types of Pain
Genetics of Sudden Cardiac Death. Geoffrey Pitt Ion Channel Research Unit Duke University. Disclosures: Grant funding from Medtronic.
 Genetics of Sudden Cardiac Death Geoffrey Pitt Ion Channel Research Unit Duke University Disclosures: Grant funding from Medtronic Duke U N I V E R S I T Y Sudden Cardiac Death High incidence 50-100 per
Genetics of Sudden Cardiac Death Geoffrey Pitt Ion Channel Research Unit Duke University Disclosures: Grant funding from Medtronic Duke U N I V E R S I T Y Sudden Cardiac Death High incidence 50-100 per
Conference Paper Antithrombotic Therapy in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndromes: Biological Markers and Personalized Medicine
 Conference Papers in Medicine, Article ID 719, pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/13/719 Conference Paper Antithrombotic Therapy in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndromes: Biological Markers and Personalized
Conference Papers in Medicine, Article ID 719, pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/13/719 Conference Paper Antithrombotic Therapy in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndromes: Biological Markers and Personalized
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (January 2018) Vol. 70 (12), Page
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (January 2018) Vol. 70 (12), Page 2172-2177 Blockage of HCN Channels with ZD7288 Attenuates Mechanical Hypersensitivity in Rats Model of Diabetic Neuropathy Hussain
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (January 2018) Vol. 70 (12), Page 2172-2177 Blockage of HCN Channels with ZD7288 Attenuates Mechanical Hypersensitivity in Rats Model of Diabetic Neuropathy Hussain
Research Article Reduction of Pain and Edema of the Legs by Walking Wearing Elastic Stockings
 International Vascular Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 648074, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/648074 Research Article Reduction of Pain and Edema of the Legs by Walking Wearing Elastic Stockings
International Vascular Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 648074, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/648074 Research Article Reduction of Pain and Edema of the Legs by Walking Wearing Elastic Stockings
Case Report A Rare Case of Near Complete Regression of a Large Cervical Disc Herniation without Any Intervention Demonstrated on MRI
 Case Reports in Radiology, Article ID 832765, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/832765 Case Report A Rare Case of Near Complete Regression of a Large Cervical Disc Herniation without Any Intervention
Case Reports in Radiology, Article ID 832765, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/832765 Case Report A Rare Case of Near Complete Regression of a Large Cervical Disc Herniation without Any Intervention
HLA and antigen presentation. Department of Immunology Charles University, 2nd Medical School University Hospital Motol
 HLA and antigen presentation Department of Immunology Charles University, 2nd Medical School University Hospital Motol MHC in adaptive immunity Characteristics Specificity Innate For structures shared
HLA and antigen presentation Department of Immunology Charles University, 2nd Medical School University Hospital Motol MHC in adaptive immunity Characteristics Specificity Innate For structures shared
Lina AL-Lawama and Tasneem Montaj. Abdullah Nimer. Loai Zghoul
 2 Lina AL-Lawama and Tasneem Montaj Abdullah Nimer Loai Zghoul At the end of this sheet you should be able to understand the general characteristics of action potential and some of its clinical applications
2 Lina AL-Lawama and Tasneem Montaj Abdullah Nimer Loai Zghoul At the end of this sheet you should be able to understand the general characteristics of action potential and some of its clinical applications
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION. (Please activate your clickers--question next slide)
 MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION (Please activate your clickers--question next slide) From Science, 3/12/2010: Pain s in the genes : Subtle changes to a certain gene seem to determine how sensitive people
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION (Please activate your clickers--question next slide) From Science, 3/12/2010: Pain s in the genes : Subtle changes to a certain gene seem to determine how sensitive people
Spinal Cord Injury Pain. Michael Massey, DO CentraCare Health St Cloud, MN 11/07/2018
 Spinal Cord Injury Pain Michael Massey, DO CentraCare Health St Cloud, MN 11/07/2018 Objectives At the conclusion of this session, participants should be able to: 1. Understand the difference between nociceptive
Spinal Cord Injury Pain Michael Massey, DO CentraCare Health St Cloud, MN 11/07/2018 Objectives At the conclusion of this session, participants should be able to: 1. Understand the difference between nociceptive
Acute Pain NETP: SEPTEMBER 2013 COHORT
 Acute Pain NETP: SEPTEMBER 2013 COHORT Pain & Suffering an unpleasant sensory & emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described in terms of such damage International
Acute Pain NETP: SEPTEMBER 2013 COHORT Pain & Suffering an unpleasant sensory & emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described in terms of such damage International
Case Report Pseudothrombocytopenia due to Platelet Clumping: A Case Report and Brief Review of the Literature
 Case Reports in Hematology Volume 2016, Article ID 3036476, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3036476 Case Report Pseudothrombocytopenia due to Platelet Clumping: A Case Report and Brief Review of
Case Reports in Hematology Volume 2016, Article ID 3036476, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3036476 Case Report Pseudothrombocytopenia due to Platelet Clumping: A Case Report and Brief Review of
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION. (Please activate your clickers)
 MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION (Please activate your clickers) Membrane structure Lipid bilayer: hydrophobic fatty acid interior Phosphate + hydrophilic group exterior Membrane structure Proteins incorporated
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION (Please activate your clickers) Membrane structure Lipid bilayer: hydrophobic fatty acid interior Phosphate + hydrophilic group exterior Membrane structure Proteins incorporated
2018 Learning Outcomes
 I. Pain Physiology and Anatomy (20%) A. Describe the basic anatomy of the nervous system. B. Describe the physiological mechanisms of neuronal function (eg- action potentials). C. Review the nociceptive
I. Pain Physiology and Anatomy (20%) A. Describe the basic anatomy of the nervous system. B. Describe the physiological mechanisms of neuronal function (eg- action potentials). C. Review the nociceptive
Refractory Status Epilepticus in Children: What are the Options?
 Refractory Status Epilepticus in Children: What are the Options? Weng Man Lam, PharmD, BCPS, BCPPS PICU Clinical Pharmacy Specialist Memorial Hermann Texas Medical Center November 11, 2017 Objectives 1.
Refractory Status Epilepticus in Children: What are the Options? Weng Man Lam, PharmD, BCPS, BCPPS PICU Clinical Pharmacy Specialist Memorial Hermann Texas Medical Center November 11, 2017 Objectives 1.
Research Article Predictive Factors for Medical Consultation for Sore Throat in Adults with Recurrent Pharyngotonsillitis
 International Otolaryngology Volume 2016, Article ID 6095689, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6095689 Research Article Predictive Factors for Medical Consultation for Sore Throat in Adults with
International Otolaryngology Volume 2016, Article ID 6095689, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6095689 Research Article Predictive Factors for Medical Consultation for Sore Throat in Adults with
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier
 Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name Genetic Causes of Hypothyroidism 1. Loss of function mutations in TSHR cause thyroid
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name Genetic Causes of Hypothyroidism 1. Loss of function mutations in TSHR cause thyroid
Case Report Pediatric Transepiphyseal Seperation and Dislocation of the Femoral Head
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 703850, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/703850 Case Report Pediatric Transepiphyseal Seperation and Dislocation of the Femoral Head Mehmet Elmadag,
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 703850, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/703850 Case Report Pediatric Transepiphyseal Seperation and Dislocation of the Femoral Head Mehmet Elmadag,
Name: Answer Key. Question 1.
 2007 7.013 Problem Set 6 Due before 5 PM on FRIDAY, April 27, 2007. Turn answers in to the box outside of 68-120. PLEASE WRITE YOUR ANSWERS ON THIS PRINTOUT. Question 1. 1a. This is a diagram showing changes
2007 7.013 Problem Set 6 Due before 5 PM on FRIDAY, April 27, 2007. Turn answers in to the box outside of 68-120. PLEASE WRITE YOUR ANSWERS ON THIS PRINTOUT. Question 1. 1a. This is a diagram showing changes
BIOL2005 WORKSHEET 2008
 BIOL2005 WORKSHEET 2008 Answer all 6 questions in the space provided using additional sheets where necessary. Hand your completed answers in to the Biology office by 3 p.m. Friday 8th February. 1. Your
BIOL2005 WORKSHEET 2008 Answer all 6 questions in the space provided using additional sheets where necessary. Hand your completed answers in to the Biology office by 3 p.m. Friday 8th February. 1. Your
Physiology of the nerve
 Physiology of the nerve Objectives Transmembrane potential Action potential Relative and absolute refractory period The all-or-none law Hoorweg Weiss curve Du Bois Reymond principle Types of nerve fibres
Physiology of the nerve Objectives Transmembrane potential Action potential Relative and absolute refractory period The all-or-none law Hoorweg Weiss curve Du Bois Reymond principle Types of nerve fibres
別紙 No. 掲載雑誌名 ISSN Impact Factor (2016) 1 Acs Nano Acta Biomaterialia Acta Crystallographica Section D-Structural
 別紙 1 Acs Nano 1936-0851 13.942 2 Acta Biomaterialia 1742-7061 6.319 3 Acta Crystallographica Section D-Structural Biology 0907-4449 2.114 4 Acta Neuropathologica 0001-6322 12.213 5 Acta Ophthalmologica
別紙 1 Acs Nano 1936-0851 13.942 2 Acta Biomaterialia 1742-7061 6.319 3 Acta Crystallographica Section D-Structural Biology 0907-4449 2.114 4 Acta Neuropathologica 0001-6322 12.213 5 Acta Ophthalmologica
Case Report Asymptomatic Pulmonary Vein Stenosis: Hemodynamic Adaptation and Successful Ablation
 Case Reports in Cardiology Volume 2016, Article ID 4979182, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/4979182 Case Report Asymptomatic Pulmonary Vein Stenosis: Hemodynamic Adaptation and Successful Ablation
Case Reports in Cardiology Volume 2016, Article ID 4979182, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/4979182 Case Report Asymptomatic Pulmonary Vein Stenosis: Hemodynamic Adaptation and Successful Ablation
Clinical Study Incidence of Retinopathy of Prematurity in Extremely Premature Infants
 ISRN Pediatrics, Article ID 134347, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/134347 Clinical Study Incidence of Retinopathy of Prematurity in Extremely Premature Infants Alparslan Fahin, Muhammed Fahin,
ISRN Pediatrics, Article ID 134347, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/134347 Clinical Study Incidence of Retinopathy of Prematurity in Extremely Premature Infants Alparslan Fahin, Muhammed Fahin,
Special Issue on Pain and Itch
 Special Issue on Pain and Itch Title: Recent Progress in Understanding the Mechanisms of Pain and Itch Guest Editor of the Special Issue: Ru-Rong Ji, PhD Chronic pain is a major health problem world-wide.
Special Issue on Pain and Itch Title: Recent Progress in Understanding the Mechanisms of Pain and Itch Guest Editor of the Special Issue: Ru-Rong Ji, PhD Chronic pain is a major health problem world-wide.
Computational Systems Biology: Biology X
 Bud Mishra Room 1002, 715 Broadway, Courant Institute, NYU, New York, USA L#4:(October-0-4-2010) Cancer and Signals 1 2 1 2 Evidence in Favor Somatic mutations, Aneuploidy, Copy-number changes and LOH
Bud Mishra Room 1002, 715 Broadway, Courant Institute, NYU, New York, USA L#4:(October-0-4-2010) Cancer and Signals 1 2 1 2 Evidence in Favor Somatic mutations, Aneuploidy, Copy-number changes and LOH
Ingredient Efficacy Evaluation
 Ingredient Efficacy Evaluation Thousands of physicians nationwide trust LidoPro ointment for safe, effective, and convenient pain management. LidoPro contains ingredients that deliver anti-inflammatory
Ingredient Efficacy Evaluation Thousands of physicians nationwide trust LidoPro ointment for safe, effective, and convenient pain management. LidoPro contains ingredients that deliver anti-inflammatory
CHAPTER 4 PAIN AND ITS MANAGEMENT
 CHAPTER 4 PAIN AND ITS MANAGEMENT Pain Definition: An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described in terms of such damage. Types of Pain
CHAPTER 4 PAIN AND ITS MANAGEMENT Pain Definition: An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described in terms of such damage. Types of Pain
Bear: Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain 3e
 Bear: Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain 3e Chapter 03: The Neuronal Membrane at Rest Introduction Action potential in the nervous system Action potential vs. resting potential Slide 1 Slide 2 Cytosolic
Bear: Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain 3e Chapter 03: The Neuronal Membrane at Rest Introduction Action potential in the nervous system Action potential vs. resting potential Slide 1 Slide 2 Cytosolic
Materials and Methods
 Anesthesiology 2007; 107:495 501 Copyright 2007, the American Society of Anesthesiologists, Inc. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Differential Contribution of Sodium Channel Subtypes to Action Potential
Anesthesiology 2007; 107:495 501 Copyright 2007, the American Society of Anesthesiologists, Inc. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Differential Contribution of Sodium Channel Subtypes to Action Potential
Charlie Taylor, PhD CpTaylor Consulting Chelsea, MI, USA
 Contribution of Calcium Channel α 2 δ Binding Sites to the Pharmacology of Gabapentin and Pregabalin Charlie Taylor, PhD CpTaylor Consulting Chelsea, MI, USA Disclosure Information Charlie Taylor, PhD
Contribution of Calcium Channel α 2 δ Binding Sites to the Pharmacology of Gabapentin and Pregabalin Charlie Taylor, PhD CpTaylor Consulting Chelsea, MI, USA Disclosure Information Charlie Taylor, PhD
Baris Beytullah Koc, 1 Martijn Schotanus, 1 Bob Jong, 2 and Pieter Tilman Introduction. 2. Case Presentation
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 7898090, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/7898090 Case Report The Role of Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI in a Child with Sport-Induced Avascular
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 7898090, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/7898090 Case Report The Role of Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI in a Child with Sport-Induced Avascular
Ionchannels and channelopaties in the heart
 Ionchannels and channelopaties in the heart Csatorna müködés Több betegség Drugok kapcsolodása csat.hoz Sejtekbe ioncsat.expresszios módszerek, bemutatása Viktória Szőts Action of membrane transport protein
Ionchannels and channelopaties in the heart Csatorna müködés Több betegség Drugok kapcsolodása csat.hoz Sejtekbe ioncsat.expresszios módszerek, bemutatása Viktória Szőts Action of membrane transport protein
The importance of pharmacogenetics in the treatment of epilepsy
 The importance of pharmacogenetics in the treatment of epilepsy Öner Süzer and Esat Eşkazan İstanbul University, Cerrahpaşa Faculty of Medicine, Department of Pharmacology and Clinical Pharmacology Introduction
The importance of pharmacogenetics in the treatment of epilepsy Öner Süzer and Esat Eşkazan İstanbul University, Cerrahpaşa Faculty of Medicine, Department of Pharmacology and Clinical Pharmacology Introduction
Eisuke Nomura, Hisatada Hiraoka, and Hiroya Sakai. 1. Introduction. 2. Case Report
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 1026861, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1026861 Case Report Spontaneous Recurrent Hemarthrosis of the Knee: A Report of Two Cases with a Source
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 1026861, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1026861 Case Report Spontaneous Recurrent Hemarthrosis of the Knee: A Report of Two Cases with a Source
Case Report Double-Layered Lateral Meniscus in an 8-Year-Old Child: Report of a Rare Case
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 5263248, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5263248 Case Report Double-Layered Lateral Meniscus in an 8-Year-Old Child: Report of a Rare Case Susumu
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 5263248, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5263248 Case Report Double-Layered Lateral Meniscus in an 8-Year-Old Child: Report of a Rare Case Susumu
Clinical Neurophysiology
 Clinical Neurophysiology 2013 Dept. of Neurology Basic and clinical Neurophysiology Basic neurophysiology Identify mechanisms that make the nervous system work Molecules, cells, groups of cells, functional
Clinical Neurophysiology 2013 Dept. of Neurology Basic and clinical Neurophysiology Basic neurophysiology Identify mechanisms that make the nervous system work Molecules, cells, groups of cells, functional
Outline. Neuron Structure. Week 4 - Nervous System. The Nervous System: Neurons and Synapses
 Outline Week 4 - The Nervous System: Neurons and Synapses Neurons Neuron structures Types of neurons Electrical activity of neurons Depolarization, repolarization, hyperpolarization Synapses Release of
Outline Week 4 - The Nervous System: Neurons and Synapses Neurons Neuron structures Types of neurons Electrical activity of neurons Depolarization, repolarization, hyperpolarization Synapses Release of
Lacosamide (Vimpat) for partial-onset epilepsy monotherapy. December 2011
 Lacosamide (Vimpat) for partial-onset epilepsy monotherapy This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search. It is not intended to be a
Lacosamide (Vimpat) for partial-onset epilepsy monotherapy This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search. It is not intended to be a
By the end of this lecture the students will be able to:
 UNIT VII: PAIN Objectives: By the end of this lecture the students will be able to: Review the concept of somatosensory pathway. Describe the function of Nociceptors in response to pain information. Describe
UNIT VII: PAIN Objectives: By the end of this lecture the students will be able to: Review the concept of somatosensory pathway. Describe the function of Nociceptors in response to pain information. Describe
NEURONS Chapter Neurons: specialized cells of the nervous system 2. Nerves: bundles of neuron axons 3. Nervous systems
 NEURONS Chapter 12 Figure 12.1 Neuronal and hormonal signaling both convey information over long distances 1. Nervous system A. nervous tissue B. conducts electrical impulses C. rapid communication 2.
NEURONS Chapter 12 Figure 12.1 Neuronal and hormonal signaling both convey information over long distances 1. Nervous system A. nervous tissue B. conducts electrical impulses C. rapid communication 2.
Supplemental material to this article can be found at:
 Supplemental material to this article can be found at: http://jpet.aspetjournals.org/content/suppl/2008/03/31/jpet.107.133413.dc1 0022-3565/08/3261-89 99$20.00 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL
Supplemental material to this article can be found at: http://jpet.aspetjournals.org/content/suppl/2008/03/31/jpet.107.133413.dc1 0022-3565/08/3261-89 99$20.00 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL
MRC-Holland MLPA. Description version 14; 28 September 2016
 SALSA MLPA probemix P279-B3 CACNA1A Lot B3-0816. As compared to version B2 (lot B2-1012), one reference probe has been replaced and the length of several probes has been adjusted. Voltage-dependent calcium
SALSA MLPA probemix P279-B3 CACNA1A Lot B3-0816. As compared to version B2 (lot B2-1012), one reference probe has been replaced and the length of several probes has been adjusted. Voltage-dependent calcium
Research Article Relationship between Pain and Medial Meniscal Extrusion in Knee Osteoarthritis
 Advances in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 210972, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/210972 Research Article Relationship between Pain and Medial Meniscal Extrusion in Knee Osteoarthritis Hiroaki
Advances in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 210972, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/210972 Research Article Relationship between Pain and Medial Meniscal Extrusion in Knee Osteoarthritis Hiroaki
Case Report Multiple Giant Cell Tumors of Tendon Sheath Found within a Single Digit of a 9-Year-Old
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 1834740, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1834740 Case Report Multiple Giant Cell Tumors of Tendon Sheath Found within a Single Digit of a 9-Year-Old
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 1834740, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1834740 Case Report Multiple Giant Cell Tumors of Tendon Sheath Found within a Single Digit of a 9-Year-Old
ANC: Section 1. Block AP - 1 J.Thomas.Mortimer &Narendra Bhadra.
 ANC: Section 1. Block AP - 1 J.Thomas.Mortimer &Narendra Bhadra. Introduction In some clinical applications, it is desirable to arrest or block propagating action potentials and eliminate the possibility
ANC: Section 1. Block AP - 1 J.Thomas.Mortimer &Narendra Bhadra. Introduction In some clinical applications, it is desirable to arrest or block propagating action potentials and eliminate the possibility
1.7 exon 5 increases the impact of the painful PEPD mutant channel I1461T
 Research paper Channels 3:4, 261-269; July/August 2009; 2009 Landes Bioscience Research Paper Alternative splicing 1.7 exon 5 increases the impact of the painful PEPD mutant channel I1461T Brian W. Jarecki,
Research paper Channels 3:4, 261-269; July/August 2009; 2009 Landes Bioscience Research Paper Alternative splicing 1.7 exon 5 increases the impact of the painful PEPD mutant channel I1461T Brian W. Jarecki,
Biology 2C03: Genetics What is a Gene?
 Biology 2C03: Genetics What is a Gene? September 9 th, 2013 Model Organisms - E. coli - Yeast - Worms - Arabodopsis - Fruitflie - Mouse What is a Gene? - Define, recognize, describe and apply Mendel s
Biology 2C03: Genetics What is a Gene? September 9 th, 2013 Model Organisms - E. coli - Yeast - Worms - Arabodopsis - Fruitflie - Mouse What is a Gene? - Define, recognize, describe and apply Mendel s
Functional insights from genetic channelopathies Stephanie Schorge
 Functional Insights From Genetic Channelopathies Dr. 1 Royal Society University Research Fellow Department of Clinical and Experimental Epilepsy Aims of channelopathies lecture Describe channelopathies
Functional Insights From Genetic Channelopathies Dr. 1 Royal Society University Research Fellow Department of Clinical and Experimental Epilepsy Aims of channelopathies lecture Describe channelopathies
HLA and antigen presentation. Department of Immunology Charles University, 2nd Medical School University Hospital Motol
 HLA and antigen presentation Department of Immunology Charles University, 2nd Medical School University Hospital Motol MHC in adaptive immunity Characteristics Specificity Innate For structures shared
HLA and antigen presentation Department of Immunology Charles University, 2nd Medical School University Hospital Motol MHC in adaptive immunity Characteristics Specificity Innate For structures shared
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier
 Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name Choroideremia OMIM number for disease 303100 Disease alternative names please
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name Choroideremia OMIM number for disease 303100 Disease alternative names please
Cell Membrane and Transport
 Cell Membrane and Transport 29/06/2015 11:08 AM Describe the Characteristics of the phospholipid Bilayer. The Phospholipid bilayer is made up of a double layer of membrane lipids that have a hydrophobic
Cell Membrane and Transport 29/06/2015 11:08 AM Describe the Characteristics of the phospholipid Bilayer. The Phospholipid bilayer is made up of a double layer of membrane lipids that have a hydrophobic
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
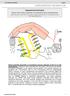 doi: 1.138/nature588 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplemental Information Sensory neuron sodium channel Na v 1.8 is essential for pain at cold temperatures Katharina Zimmermann*, Andreas Leffler*, Alexandru
doi: 1.138/nature588 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplemental Information Sensory neuron sodium channel Na v 1.8 is essential for pain at cold temperatures Katharina Zimmermann*, Andreas Leffler*, Alexandru
