TMC9 as a novel mechanosensitive ion channel
|
|
|
- Neil Carr
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 TMC9 as a novel mechanosensitive ion channel Mechanical forces play numerous roles in physiology. When an object contacts our skin, it exerts a force that is encoded as touch or pain depending on its intensity. Likewise, sound waves physically move cell processes in the inner ear, enabling us to hear. Forces intrinsic to the human body are also important. For instance, blood pressure is tightly regulated by mechanosensitive feedback processes. Mechanotransduction, the conversion of mechanical stimuli into electrochemical signals, is ubiquitous, but the molecular players are vastly unknown. Because mechanotransduction can be exquisitely fast, it is believed to be mediated by ion channels rather than second messengers (Corey and Hudspeth, 1979). Mechanosensitive ion channels (MSCs) are thought to rapidly transform mechanical deformations of the plasma membrane into electric currents. However, very few MSCs have been identified, precluding a precise investigation of the physiology and pathophysiology of the different mechanotransduction processes. Through a previous screen of candidate genes, the laboratory of Dr. Sharif-Naeini isolated TMC9 as a putative MSC. TMC9 is well conserved amongst mammals and is present in several tissues, but its function is unknown. For my honours project, I joined the laboratory to investigate the role of TMC9 in mechanotransduction. The first part of my project aimed at determining whether TMC9 formed a MSC in heterologous systems. I performed electrophysiological experiments with Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells transfected with a control plasmid or a plasmid expressing TMC9. Mechanosensitive currents were elicited by applying pulses of negative pressure through the recording electrode while recording in the cell-attached patch clamp configuration. Overexpressing TMC9 in CHO cells substantially increased the mechanosensitive currents. To determine whether this was due to TMC9 forming a channel or simply modulating the activity of endogenous channels, I broke down
2 the patch recordings into two categories: active and silent patches. Active patches had at least one active MSC, while silent patches had none. There was a higher percentage of active patches and the currents in the active patches were significantly enhanced in cells overexpressing TMC9, suggesting a higher channel density at the plasma membrane. I then measured the activation threshold, single-channel conductance, reversal potential and calcium permeability of the mechanosensitive ion channels in control and TMC9-transfected cells. Similar results for both groups suggest that expressing TMC9 enhanced the number of mechanosensitive ion channels that are endogenously expressed by CHO cells. To confirm that TMC9 indeed forms an ion conduction channel, our laboratory purified it and reconstituted it in artificial lipid bilayers. Recordings from those bilayers demonstrated that TMC9 forms an ion conducting pore, and is therefore a novel ion channel. This first set of experiments demonstrated that TMC9 can form a mechanosensitive channel, but its physiological role remained unknown. Thus, I next investigated the contribution of TMC9 to different mechanotransduction processes. Somatosensation, which comprises bodily sensations such as touch, pain and proprioception, relies heavily on mechanotransduction. The neurons involved in somatosensation are located in dorsal root ganglia (DRG), which sit adjacent to the spinal cord. DRG neurons send one axon to the periphery to sense the external environment and another one to the central nervous system to convey information. Piezo2, one of the few MSCs known to date, is expressed by a subset of DRG neurons and has been found to be the main transducer of light-touch (Ranade et al., 2014). However, the channels mediating pain mechanotransduction remain elusive. Previous recordings from painsensing DRG neurons (nociceptors) unveiled that they possess high threshold, low conductance MSCs, but their genetic identity is unknown (Cho et al., 2002; Drew et al., 2002; Sharif-Naeini,
3 2015). Interestingly, TMC9 overexpression in CHO cells induced the expression of MSCs with similar activation threshold and conductance. Moreover, TMC9 is endogenously expressed in DRG neurons. We thus asked whether TMC9 could be involved in the transduction of painful mechanical stimuli. I recorded mechanosensitive currents from dissociated nociceptors that were treated with mock or TMC9-targetting sirna. Knocking down TMC9 significantly reduced the mechanosensitive currents. Moreover, the percentage of active patches and the currents in the active patches were smaller. Overall, TMC9 appears to be an important player in nociceptive mechanotransduction. Because those experiments were performed in vitro, further in vivo experiments are needed to assert that TMC9 is involved in our ability to sense mechanical pain. Nonetheless, identifying the MSCs responsible for pain transduction in vivo would have important implications for pathological pain conditions. For instance, the sensitization of MSCs has been implicated in osteoarthritis, a degenerative joint disease characterized by painful movements (McDougall, 2006; Sharif-Naeini, 2015). In addition to pain-inducing stimuli being more painful in osteoarthritis, stimuli that normally do not elicit painful responses are now painful, a condition named allodynia. This allodynia can be explained by the sensitized MSCs getting activated by innocuous movements. Knowing the identity of the channels would greatly help investigate the contribution of MSCs to osteoarthritis and other diseases with similar underlying pathophysiology. Moreover, it would provide an interesting therapeutic target to treat such pathologies. My honours project in Dr. Sharif-Naeini has been very exciting and productive. Before engaging in graduate studies at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, I am conducting a summer research project funded by an NSERC award in Dr. Sharif-Naeini s laboratory. In addition to analyzing the role of TMC9 in more physiological conditions to cogently show that the channel
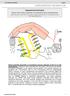
4 is important in vivo, I plan to decipher the precise mechanism by which the channel transduces mechanical forces into electric currents using site-directed mutagenesis. Figure legend Model for the role of TMC9 in the transduction of painful mechanical stimuli. In the periphery, a nociceptor innervates the skin with free nerve endings. When a painful mechanical stimulus is sensed by the nerve terminals, the tension in the membrane increases, forcing TMC9 to open and flux cations (red box). This flow of positive charges can be measured electrophysiologically, with typical square-shaped single channel openings shown on the right. When the stimulus is strong enough, an action potential is generated and reaches the cell body of the nociceptor, which sits in a dorsal root ganglion. The electrical signal is then propagated to the dorsal horn of the spinal cord, where it is processed and sent to the brain. References Cho H, Shin J, Shin CY, Lee SY, Oh U (2002) Mechanosensitive ion channels in cultured sensory neurons of neonatal rats. The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience 22: Corey DP, Hudspeth AJ (1979) Response latency of vertebrate hair cells. Biophysical journal 26: Drew LJ, Wood JN, Cesare P (2002) Distinct mechanosensitive properties of capsaicin-sensitive and - insensitive sensory neurons. The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience 22:Rc228. McDougall JJ (2006) Arthritis and pain. Neurogenic origin of joint pain. Arthritis research & therapy 8:220. Ranade SS, Woo SH, Dubin AE, Moshourab RA, Wetzel C, Petrus M, Mathur J, Begay V, Coste B, Mainquist J, Wilson AJ, Francisco AG, Reddy K, Qiu Z, Wood JN, Lewin GR, Patapoutian A (2014) Piezo2 is the major transducer of mechanical forces for touch sensation in mice. Nature 516: Sharif-Naeini R (2015) Contribution of mechanosensitive ion channels to somatosensation. Progress in molecular biology and translational science 131:53-71.
5 Na Ca Tension Na Ca Painful stimulus 1 pa 250 ms To brain Skin Dorsal root ganglion Spinal cord
Coding of Sensory Information
 Coding of Sensory Information 22 November, 2016 Touqeer Ahmed PhD Atta-ur-Rahman School of Applied Biosciences National University of Sciences and Technology Sensory Systems Mediate Four Attributes of
Coding of Sensory Information 22 November, 2016 Touqeer Ahmed PhD Atta-ur-Rahman School of Applied Biosciences National University of Sciences and Technology Sensory Systems Mediate Four Attributes of
CHAPTER 10 THE SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 10 THE SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM 10.1. SOMATOSENSORY MODALITIES "Somatosensory" is really a catch-all term to designate senses other than vision, hearing, balance, taste and smell. Receptors that could
CHAPTER 10 THE SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM 10.1. SOMATOSENSORY MODALITIES "Somatosensory" is really a catch-all term to designate senses other than vision, hearing, balance, taste and smell. Receptors that could
Somatosensation. Recording somatosensory responses. Receptive field response to pressure
 Somatosensation Mechanoreceptors that respond to touch/pressure on the surface of the body. Sensory nerve responds propotional to pressure 4 types of mechanoreceptors: Meissner corpuscles & Merkel discs
Somatosensation Mechanoreceptors that respond to touch/pressure on the surface of the body. Sensory nerve responds propotional to pressure 4 types of mechanoreceptors: Meissner corpuscles & Merkel discs
Neurobiology Biomed 509 Sensory transduction References: Luo , ( ), , M4.1, M6.2
 Neurobiology Biomed 509 Sensory transduction References: Luo 4.1 4.8, (4.9 4.23), 6.22 6.24, M4.1, M6.2 I. Transduction The role of sensory systems is to convert external energy into electrical signals
Neurobiology Biomed 509 Sensory transduction References: Luo 4.1 4.8, (4.9 4.23), 6.22 6.24, M4.1, M6.2 I. Transduction The role of sensory systems is to convert external energy into electrical signals
PAIN MANAGEMENT in the CANINE PATIENT
 PAIN MANAGEMENT in the CANINE PATIENT Laurie Edge-Hughes, BScPT, MAnimSt (Animal Physio), CAFCI, CCRT Part 1: Laurie Edge-Hughes, BScPT, MAnimSt (Animal Physio), CAFCI, CCRT 1 Pain is the most common reason
PAIN MANAGEMENT in the CANINE PATIENT Laurie Edge-Hughes, BScPT, MAnimSt (Animal Physio), CAFCI, CCRT Part 1: Laurie Edge-Hughes, BScPT, MAnimSt (Animal Physio), CAFCI, CCRT 1 Pain is the most common reason
Somatic Sensation (MCB160 Lecture by Mu-ming Poo, Friday March 9, 2007)
 Somatic Sensation (MCB160 Lecture by Mu-ming Poo, Friday March 9, 2007) Introduction Adrian s work on sensory coding Spinal cord and dorsal root ganglia Four somatic sense modalities Touch Mechanoreceptors
Somatic Sensation (MCB160 Lecture by Mu-ming Poo, Friday March 9, 2007) Introduction Adrian s work on sensory coding Spinal cord and dorsal root ganglia Four somatic sense modalities Touch Mechanoreceptors
Psychophysical laws. Legge di Fechner: I=K*log(S/S 0 )
 Psychophysical laws Legge di Weber: ΔS=K*S Legge di Fechner: I=K*log(S/S 0 ) Sensory receptors Vision Smell Taste Touch Thermal senses Pain Hearing Balance Proprioception Sensory receptors Table 21-1 Classification
Psychophysical laws Legge di Weber: ΔS=K*S Legge di Fechner: I=K*log(S/S 0 ) Sensory receptors Vision Smell Taste Touch Thermal senses Pain Hearing Balance Proprioception Sensory receptors Table 21-1 Classification
35-2 The Nervous System Slide 1 of 38
 1 of 38 35-2 The Nervous System The nervous system controls and coordinates functions throughout the body and responds to internal and external stimuli. 2 of 38 Neurons Neurons The messages carried by
1 of 38 35-2 The Nervous System The nervous system controls and coordinates functions throughout the body and responds to internal and external stimuli. 2 of 38 Neurons Neurons The messages carried by
Sensory coding and somatosensory system
 Sensory coding and somatosensory system Sensation and perception Perception is the internal construction of sensation. Perception depends on the individual experience. Three common steps in all senses
Sensory coding and somatosensory system Sensation and perception Perception is the internal construction of sensation. Perception depends on the individual experience. Three common steps in all senses
Notes: Nervous System
 Notes: Nervous System KEY CONCEPT #1 The and the provide the means by which organ systems. The body s communication systems help maintain homeostasis. A stimulus is. Responses. The nervous and endocrine
Notes: Nervous System KEY CONCEPT #1 The and the provide the means by which organ systems. The body s communication systems help maintain homeostasis. A stimulus is. Responses. The nervous and endocrine
Chapter 6. Gathering information; the sensory systems
 Chapter 6 Gathering information; the sensory systems Gathering information the sensory systems The parts of the nervous system that receive and process information are termed sensory systems. There are
Chapter 6 Gathering information; the sensory systems Gathering information the sensory systems The parts of the nervous system that receive and process information are termed sensory systems. There are
211MDS Pain theories
 211MDS Pain theories Definition In 1986, the International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP) defined pain as a sensory and emotional experience associated with real or potential injuries, or described
211MDS Pain theories Definition In 1986, the International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP) defined pain as a sensory and emotional experience associated with real or potential injuries, or described
Somatosensory System. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Somatosensory System Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Dr. Riedl s review session this week: Tuesday (Oct 10) 4-5pm in MCB 3-146B 2 Sensory Systems Sensory
Somatosensory System Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Dr. Riedl s review session this week: Tuesday (Oct 10) 4-5pm in MCB 3-146B 2 Sensory Systems Sensory
Somatosensory modalities!
 Somatosensory modalities! The somatosensory system codes five major sensory modalities:! 1. Discriminative touch! 2. Proprioception (body position and motion)! 3. Nociception (pain and itch)! 4. Temperature!
Somatosensory modalities! The somatosensory system codes five major sensory modalities:! 1. Discriminative touch! 2. Proprioception (body position and motion)! 3. Nociception (pain and itch)! 4. Temperature!
NEURONS Chapter Neurons: specialized cells of the nervous system 2. Nerves: bundles of neuron axons 3. Nervous systems
 NEURONS Chapter 12 Figure 12.1 Neuronal and hormonal signaling both convey information over long distances 1. Nervous system A. nervous tissue B. conducts electrical impulses C. rapid communication 2.
NEURONS Chapter 12 Figure 12.1 Neuronal and hormonal signaling both convey information over long distances 1. Nervous system A. nervous tissue B. conducts electrical impulses C. rapid communication 2.
The Pain Pathway. dorsal root ganglion. primary afferent nociceptor. TRP: Transient Receptor Potential
 Presented by Issel Anne L. Lim 1 st Year PhD Candidate Biomedical Engineering Johns Hopkins University 580.427/580.633 Ca Signals in Biological Systems Outline The Pain Pathway TRP: Transient Receptor
Presented by Issel Anne L. Lim 1 st Year PhD Candidate Biomedical Engineering Johns Hopkins University 580.427/580.633 Ca Signals in Biological Systems Outline The Pain Pathway TRP: Transient Receptor
TABLE OF CONTINENTS. PSYC1002 Notes. Neuroscience.2. Cognitive Processes Learning and Motivation. 37. Perception Mental Abilities..
 TABLE OF CONTINENTS Neuroscience.2 Cognitive Processes...21 Learning and Motivation. 37 Perception.....54 Mental Abilities.. 83 Abnormal Psychology....103 1 Topic 1: Neuroscience Outline 1. Gross anatomy
TABLE OF CONTINENTS Neuroscience.2 Cognitive Processes...21 Learning and Motivation. 37 Perception.....54 Mental Abilities.. 83 Abnormal Psychology....103 1 Topic 1: Neuroscience Outline 1. Gross anatomy
Cellular Bioelectricity
 ELEC ENG 3BB3: Cellular Bioelectricity Notes for Lecture 24 Thursday, March 6, 2014 8. NEURAL ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY We will look at: Structure of the nervous system Sensory transducers and neurons Neural coding
ELEC ENG 3BB3: Cellular Bioelectricity Notes for Lecture 24 Thursday, March 6, 2014 8. NEURAL ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY We will look at: Structure of the nervous system Sensory transducers and neurons Neural coding
LESSON 3.3 WORKBOOK. Why does applying pressure relieve pain? Workbook. Postsynaptic potentials
 Depolarize to decrease the resting membrane potential. Decreasing membrane potential means that the membrane potential is becoming more positive. Excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSP) graded postsynaptic
Depolarize to decrease the resting membrane potential. Decreasing membrane potential means that the membrane potential is becoming more positive. Excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSP) graded postsynaptic
Pathophysiology of Pain
 Pathophysiology of Pain Wound Inflammatory response Chemical mediators Activity in Pain Path PAIN http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s2/chapter08.html Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University
Pathophysiology of Pain Wound Inflammatory response Chemical mediators Activity in Pain Path PAIN http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s2/chapter08.html Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University
Chapter 17 Nervous System
 Chapter 17 Nervous System 1 The Nervous System Two Anatomical Divisions Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain and Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Two Types of Cells Neurons Transmit nerve impulses
Chapter 17 Nervous System 1 The Nervous System Two Anatomical Divisions Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain and Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Two Types of Cells Neurons Transmit nerve impulses
SMELL 2
 SENSORY SYSTEMS 1 SMELL 2 TASTE 3 HEARING 4 TOUCH EQUILIBRIUM 5 PAIN 6 OTHER SENSES 7 HOW DO SENSORY CELLS CONVERT STIMULI INTO ACTION POTENTIALS? HOW DO SENSORY SYSTEMS DETECT CHEMICAL STIMULI? HOW DO
SENSORY SYSTEMS 1 SMELL 2 TASTE 3 HEARING 4 TOUCH EQUILIBRIUM 5 PAIN 6 OTHER SENSES 7 HOW DO SENSORY CELLS CONVERT STIMULI INTO ACTION POTENTIALS? HOW DO SENSORY SYSTEMS DETECT CHEMICAL STIMULI? HOW DO
Bi/CNS/NB 150: Neuroscience. November 11, 2015 SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM. Ralph Adolphs
 Bi/CNS/NB 150: Neuroscience November 11, 2015 SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM Ralph Adolphs 1 Menu for today Touch -peripheral -central -plasticity Pain 2 Sherrington (1948): senses classified as --teloreceptive
Bi/CNS/NB 150: Neuroscience November 11, 2015 SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM Ralph Adolphs 1 Menu for today Touch -peripheral -central -plasticity Pain 2 Sherrington (1948): senses classified as --teloreceptive
LESSON 3.3 WORKBOOK. Why does applying pressure relieve pain?
 Postsynaptic potentials small changes in voltage (membrane potential) due to the binding of neurotransmitter. Receptor-gated ion channels ion channels that open or close in response to the binding of a
Postsynaptic potentials small changes in voltage (membrane potential) due to the binding of neurotransmitter. Receptor-gated ion channels ion channels that open or close in response to the binding of a
Function of the Nervous System
 Nervous System Function of the Nervous System Receive sensory information, interpret it, and send out appropriate commands to form a response Composed of neurons (functional unit of the nervous system)
Nervous System Function of the Nervous System Receive sensory information, interpret it, and send out appropriate commands to form a response Composed of neurons (functional unit of the nervous system)
Receptors and Neurotransmitters: It Sounds Greek to Me. Agenda. What We Know About Pain 9/7/2012
 Receptors and Neurotransmitters: It Sounds Greek to Me Cathy Carlson, PhD, RN Northern Illinois University Agenda We will be going through this lecture on basic pain physiology using analogies, mnemonics,
Receptors and Neurotransmitters: It Sounds Greek to Me Cathy Carlson, PhD, RN Northern Illinois University Agenda We will be going through this lecture on basic pain physiology using analogies, mnemonics,
Seizure: the clinical manifestation of an abnormal and excessive excitation and synchronization of a population of cortical
 Are There Sharing Mechanisms of Epilepsy, Migraine and Neuropathic Pain? Chin-Wei Huang, MD, PhD Department of Neurology, NCKUH Basic mechanisms underlying seizures and epilepsy Seizure: the clinical manifestation
Are There Sharing Mechanisms of Epilepsy, Migraine and Neuropathic Pain? Chin-Wei Huang, MD, PhD Department of Neurology, NCKUH Basic mechanisms underlying seizures and epilepsy Seizure: the clinical manifestation
Nervous System. 2. Receives information from the environment from CNS to organs and glands. 1. Relays messages, processes info, analyzes data
 Nervous System 1. Relays messages, processes info, analyzes data 2. Receives information from the environment from CNS to organs and glands 3. Transmits impulses from CNS to muscles and glands 4. Transmits
Nervous System 1. Relays messages, processes info, analyzes data 2. Receives information from the environment from CNS to organs and glands 3. Transmits impulses from CNS to muscles and glands 4. Transmits
PHGY Physiology. SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Sensory Receptors. Martin Paré
 PHGY 212 - Physiology SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Sensory Receptors Martin Paré Assistant Professor of Physiology & Psychology pare@biomed.queensu.ca http://brain.phgy.queensu.ca/pare Sensory Systems Question:
PHGY 212 - Physiology SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Sensory Receptors Martin Paré Assistant Professor of Physiology & Psychology pare@biomed.queensu.ca http://brain.phgy.queensu.ca/pare Sensory Systems Question:
Excitation-Contraction Coupling & Reflexes, Proprioception and Movement. PSK 4U Unit 4, Day 4
 Excitation-Contraction Coupling & Reflexes, Proprioception and Movement PSK 4U Unit 4, Day 4 Excitation-Contraction Coupling Muscles work by converting electrical and chemical energy into mechanical energy!
Excitation-Contraction Coupling & Reflexes, Proprioception and Movement PSK 4U Unit 4, Day 4 Excitation-Contraction Coupling Muscles work by converting electrical and chemical energy into mechanical energy!
How can we go about studying the neuronal processes involved in sensation and perception?
 How can we go about studying the neuronal processes involved in sensation and perception? quantified sensory input sensory coding psychophysi cs neuronal activity decoding, decision making percept, behavior
How can we go about studying the neuronal processes involved in sensation and perception? quantified sensory input sensory coding psychophysi cs neuronal activity decoding, decision making percept, behavior
Introduction to some interesting research questions: Molecular biology of the primary afferent nociceptor
 Introduction to some interesting research questions: Molecular biology of the primary afferent nociceptor NOCICEPTORS ARE NOT IDENTICAL PEPTIDE SubP/CGRP Trk A NON-PEPTIDE IB4 P2X 3 c-ret Snider and McMahon
Introduction to some interesting research questions: Molecular biology of the primary afferent nociceptor NOCICEPTORS ARE NOT IDENTICAL PEPTIDE SubP/CGRP Trk A NON-PEPTIDE IB4 P2X 3 c-ret Snider and McMahon
SENSATION & PERCEPTION
 SENSATION & PERCEPTION Sensation and perception result from a symphony of sensory receptors and the neurons those receptors communicate with. The receptors and neurons fire in different combinations and
SENSATION & PERCEPTION Sensation and perception result from a symphony of sensory receptors and the neurons those receptors communicate with. The receptors and neurons fire in different combinations and
Axon Nerve impulse. Axoplasm Receptor. Axomembrane Stimuli. Schwann cell Effector. Myelin Cell body
 Nervous System Review 1. Explain a reflex arc. 2. Know the structure, function and location of a sensory neuron, interneuron, and motor neuron 3. What is (a) Neuron Axon Nerve impulse Axoplasm Receptor
Nervous System Review 1. Explain a reflex arc. 2. Know the structure, function and location of a sensory neuron, interneuron, and motor neuron 3. What is (a) Neuron Axon Nerve impulse Axoplasm Receptor
Animal Physiology Study Guide
 Animal Physiology Study Guide 1. Which of the following are an example of passive transport? 2. Which active transport? 3. How can you tell? 1. Which of the following are an example of passive transport?
Animal Physiology Study Guide 1. Which of the following are an example of passive transport? 2. Which active transport? 3. How can you tell? 1. Which of the following are an example of passive transport?
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF NEURONS. AP Biology Chapter 48
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF NEURONS AP Biology Chapter 48 Objectives Describe the different types of neurons Describe the structure and function of dendrites, axons, a synapse, types of ion channels, and
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF NEURONS AP Biology Chapter 48 Objectives Describe the different types of neurons Describe the structure and function of dendrites, axons, a synapse, types of ion channels, and
Mechanism of Pain Production
 Mechanism of Pain Production Pain conducting nerve fibers are small myelinated (A-delta) or unmyelinated nerve fibers (C-fibers). Cell bodies are in the dorsal root ganglia (DRG) or sensory ganglia of
Mechanism of Pain Production Pain conducting nerve fibers are small myelinated (A-delta) or unmyelinated nerve fibers (C-fibers). Cell bodies are in the dorsal root ganglia (DRG) or sensory ganglia of
Sensation Chapter 46
 Sensation Chapter 46 Natasha McDougal and Kaleb Hood Background and Purpose Nerve impulses occur because of a change in action potential Graded potentials in the dendrites and cell body can have either
Sensation Chapter 46 Natasha McDougal and Kaleb Hood Background and Purpose Nerve impulses occur because of a change in action potential Graded potentials in the dendrites and cell body can have either
Outline. Animals: Nervous system. Neuron and connection of neurons. Key Concepts:
 Animals: Nervous system Neuron and connection of neurons Outline 1. Key concepts 2. An Overview and Evolution 3. Human Nervous System 4. The Neurons 5. The Electrical Signals 6. Communication between Neurons
Animals: Nervous system Neuron and connection of neurons Outline 1. Key concepts 2. An Overview and Evolution 3. Human Nervous System 4. The Neurons 5. The Electrical Signals 6. Communication between Neurons
Pharmacology of Pain Transmission and Modulation
 Pharmacology of Pain Transmission and Modulation 2 Jürg Schliessbach and Konrad Maurer Nociceptive Nerve Fibers Pain is transmitted to the central nervous system via thinly myelinated Aδ and unmyelinated
Pharmacology of Pain Transmission and Modulation 2 Jürg Schliessbach and Konrad Maurer Nociceptive Nerve Fibers Pain is transmitted to the central nervous system via thinly myelinated Aδ and unmyelinated
Module H NERVOUS SYSTEM
 Module H NERVOUS SYSTEM Topic from General functions of the nervous system Organization of the nervous system from both anatomical & functional perspectives Gross & microscopic anatomy of nervous tissue
Module H NERVOUS SYSTEM Topic from General functions of the nervous system Organization of the nervous system from both anatomical & functional perspectives Gross & microscopic anatomy of nervous tissue
MYOFASCIAL PAIN. Dr. Janet Travell ( ) credited with bringing MTrPs to the attention of healthcare providers.
 Myofascial Trigger Points background info Laurie Edge-Hughes BScPT, MAnimSt (Animal Physio), CAFCI, CCRT History lesson Dr. Janet Travell (1901 1997) credited with bringing MTrPs to the attention of healthcare
Myofascial Trigger Points background info Laurie Edge-Hughes BScPT, MAnimSt (Animal Physio), CAFCI, CCRT History lesson Dr. Janet Travell (1901 1997) credited with bringing MTrPs to the attention of healthcare
Carlson (7e) PowerPoint Lecture Outline Chapter 7: Audition, the Body Senses, and the Chemical Senses
 Carlson (7e) PowerPoint Lecture Outline Chapter 7: Audition, the Body Senses, and the Chemical Senses This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited
Carlson (7e) PowerPoint Lecture Outline Chapter 7: Audition, the Body Senses, and the Chemical Senses This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited
Quantitative Electrophysiology
 ECE 795: Quantitative Electrophysiology Notes for Lecture #10 Wednesday, November 22, 2006 14. FUNDAMENTALS OF FUNCTIONAL ELECTRICAL STIMULATION (FES) We will look at: Design issues for FES Subthreshold
ECE 795: Quantitative Electrophysiology Notes for Lecture #10 Wednesday, November 22, 2006 14. FUNDAMENTALS OF FUNCTIONAL ELECTRICAL STIMULATION (FES) We will look at: Design issues for FES Subthreshold
What is the effect on the hair cell if the stereocilia are bent away from the kinocilium?
 CASE 44 A 53-year-old man presents to his primary care physician with complaints of feeling like the room is spinning, dizziness, decreased hearing, ringing in the ears, and fullness in both ears. He states
CASE 44 A 53-year-old man presents to his primary care physician with complaints of feeling like the room is spinning, dizziness, decreased hearing, ringing in the ears, and fullness in both ears. He states
Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences
 Spinal Cord I Lecture Outline and Objectives CNS/Head and Neck Sequence TOPIC: FACULTY: THE SPINAL CORD AND SPINAL NERVES, Part I Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences LECTURE: Monday,
Spinal Cord I Lecture Outline and Objectives CNS/Head and Neck Sequence TOPIC: FACULTY: THE SPINAL CORD AND SPINAL NERVES, Part I Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences LECTURE: Monday,
Physiology Unit 2 SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY
 Physiology Unit 2 SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY In Physiology Today Sensory System Sensory information Conscious sensations Unconscious sensations Sensory processing Transferring stimulus energy into a graded potential
Physiology Unit 2 SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY In Physiology Today Sensory System Sensory information Conscious sensations Unconscious sensations Sensory processing Transferring stimulus energy into a graded potential
THE HISTORY OF NEUROSCIENCE
 THE HISTORY OF NEUROSCIENCE BIOLOGICAL ASPECTS OF BEHAVIOR: THE NEURON & NEURAL COMMUNICATION NERVOUS SYSTEM Combined activity of the brain, spinal cord & other nerve fibers Acts as an information processing
THE HISTORY OF NEUROSCIENCE BIOLOGICAL ASPECTS OF BEHAVIOR: THE NEURON & NEURAL COMMUNICATION NERVOUS SYSTEM Combined activity of the brain, spinal cord & other nerve fibers Acts as an information processing
Applied Neuroscience. Conclusion of Science Honors Program Spring 2017
 Applied Neuroscience Conclusion of Science Honors Program Spring 2017 Review Circle whichever is greater, A or B. If A = B, circle both: I. A. permeability of a neuronal membrane to Na + during the rise
Applied Neuroscience Conclusion of Science Honors Program Spring 2017 Review Circle whichever is greater, A or B. If A = B, circle both: I. A. permeability of a neuronal membrane to Na + during the rise
Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System
 15 Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to Sensory Pathways and
15 Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to Sensory Pathways and
Skin types: hairy and glabrous (e.g. back vs. palm of hand)
 Lecture 19 revised 03/10 The Somatic Sensory System Skin- the largest sensory organ we have Also protects from evaporation, infection. Skin types: hairy and glabrous (e.g. back vs. palm of hand) 2 major
Lecture 19 revised 03/10 The Somatic Sensory System Skin- the largest sensory organ we have Also protects from evaporation, infection. Skin types: hairy and glabrous (e.g. back vs. palm of hand) 2 major
Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
 Chapter 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Chapter 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Nervous System. Chapter Structure of the Nervous System. Neurons
 33.1 Structure of the Neurons Neurons are specialized nerve cells that help you gather information about your environment, interpret the information, and react to it. Neurons consist of three main regions:
33.1 Structure of the Neurons Neurons are specialized nerve cells that help you gather information about your environment, interpret the information, and react to it. Neurons consist of three main regions:
Implantable Microelectronic Devices
 ECE 8803/4803 Implantable Microelectronic Devices Fall - 2015 Maysam Ghovanloo (mgh@gatech.edu) School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology 2015 Maysam Ghovanloo 1 Outline
ECE 8803/4803 Implantable Microelectronic Devices Fall - 2015 Maysam Ghovanloo (mgh@gatech.edu) School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology 2015 Maysam Ghovanloo 1 Outline
READ THIS PAGE BEFORE YOU BEGIN THE EXAM.
 BIPN 100B MAMMALIAN PHYSIOLOGY 1 - Fall 2009 Page 1 First midterm exam Name ID number General Instructions: READ THIS PAGE BEFORE YOU BEGIN THE EXAM. 1. Write your name on every page. (5 points off for
BIPN 100B MAMMALIAN PHYSIOLOGY 1 - Fall 2009 Page 1 First midterm exam Name ID number General Instructions: READ THIS PAGE BEFORE YOU BEGIN THE EXAM. 1. Write your name on every page. (5 points off for
Sample Lab Report 1 from 1. Measuring and Manipulating Passive Membrane Properties
 Sample Lab Report 1 from http://www.bio365l.net 1 Abstract Measuring and Manipulating Passive Membrane Properties Biological membranes exhibit the properties of capacitance and resistance, which allow
Sample Lab Report 1 from http://www.bio365l.net 1 Abstract Measuring and Manipulating Passive Membrane Properties Biological membranes exhibit the properties of capacitance and resistance, which allow
Neurons Chapter 7 2/19/2016. Learning Objectives. Cells of the Nervous System. Cells of the Nervous System. Cells of the Nervous System
 Learning Objectives Neurons Chapter 7 Identify and describe the functions of the two main divisions of the nervous system. Differentiate between a neuron and neuroglial cells in terms of structure and
Learning Objectives Neurons Chapter 7 Identify and describe the functions of the two main divisions of the nervous system. Differentiate between a neuron and neuroglial cells in terms of structure and
Chapter 11 Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Chapter Outline
 Chapter 11 Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Chapter Outline Module 11.1 Overview of the Nervous System (Figures 11.1-11.3) A. The nervous system controls our perception and experience
Chapter 11 Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Chapter Outline Module 11.1 Overview of the Nervous System (Figures 11.1-11.3) A. The nervous system controls our perception and experience
Thursday, January 22, Nerve impulse
 Nerve impulse Transmembrane Potential caused by ions moving through cell membrane at different rates Two main ions of concern Na + - Sodium K + - potassium Cell membrane not freely permeable therefore
Nerve impulse Transmembrane Potential caused by ions moving through cell membrane at different rates Two main ions of concern Na + - Sodium K + - potassium Cell membrane not freely permeable therefore
The Somatosensory System
 The Somatosensory System Reading: BCP Chapter 12 cerebrovortex.com Divisions of the Somatosensory System Somatosensory System Exteroceptive External stimuli Proprioceptive Body position Interoceptive Body
The Somatosensory System Reading: BCP Chapter 12 cerebrovortex.com Divisions of the Somatosensory System Somatosensory System Exteroceptive External stimuli Proprioceptive Body position Interoceptive Body
9.01 Midterm Examination NAME October 27, 2003
 9.01 - Neuroscience & Behavior, Fall 2003 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Instructor: Professor Gerald Schneider 9.01 Midterm Examination NAME 1) Karl Wernicke, in the 1870s, formulated a model of
9.01 - Neuroscience & Behavior, Fall 2003 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Instructor: Professor Gerald Schneider 9.01 Midterm Examination NAME 1) Karl Wernicke, in the 1870s, formulated a model of
Special Senses. Mechanoreception Electroreception Chemoreception Others
 Special Senses Mechanoreception Electroreception Chemoreception Others Recall our receptor types Chemically regulated: Respond to particular chemicals Voltage regulated: respond to changing membrane potential
Special Senses Mechanoreception Electroreception Chemoreception Others Recall our receptor types Chemically regulated: Respond to particular chemicals Voltage regulated: respond to changing membrane potential
Chapter 7 Nerve Cells and Electrical Signaling
 Chapter 7 Nerve Cells and Electrical Signaling 7.1. Overview of the Nervous System (Figure 7.1) 7.2. Cells of the Nervous System o Neurons are excitable cells which can generate action potentials o 90%
Chapter 7 Nerve Cells and Electrical Signaling 7.1. Overview of the Nervous System (Figure 7.1) 7.2. Cells of the Nervous System o Neurons are excitable cells which can generate action potentials o 90%
What is pain?: An unpleasant sensation. What is an unpleasant sensation?: Pain. - Aristotle.
 What is pain?: An unpleasant sensation. What is an unpleasant sensation?: Pain. - Aristotle. Nociception The detection of tissue damage or impending tissue damage, but There can be tissue damage without
What is pain?: An unpleasant sensation. What is an unpleasant sensation?: Pain. - Aristotle. Nociception The detection of tissue damage or impending tissue damage, but There can be tissue damage without
LESSON 3.2 WORKBOOK How do our neurons communicate with each other?
 LESSON 3.2 WORKBOOK How do our neurons communicate with each other? This lesson introduces you to how one neuron communicates with another neuron during the process of synaptic transmission. In this lesson
LESSON 3.2 WORKBOOK How do our neurons communicate with each other? This lesson introduces you to how one neuron communicates with another neuron during the process of synaptic transmission. In this lesson
Chapter 34 The Nervous System:
 Chapter 34 The Nervous System: 3.5 Learning Objectives 3.5.3 Responses in the human 1. The nervous system: two-part division into the CNS and the PNS. 2. Neurons, name 3 types, give structure and function
Chapter 34 The Nervous System: 3.5 Learning Objectives 3.5.3 Responses in the human 1. The nervous system: two-part division into the CNS and the PNS. 2. Neurons, name 3 types, give structure and function
COGS 107B Week 2. Hyun Ji Friday 4:00-4:50pm
 COGS 107B Week 2 Hyun Ji Friday 4:00-4:50pm Lecture 3: Proprioception Principles: The Neuron Doctrine and The Law of Dynamic Polarization Proprioception Joint-protecting reflexes (ex. Knee jerk reflex)
COGS 107B Week 2 Hyun Ji Friday 4:00-4:50pm Lecture 3: Proprioception Principles: The Neuron Doctrine and The Law of Dynamic Polarization Proprioception Joint-protecting reflexes (ex. Knee jerk reflex)
Somatic Sensory System I. Background
 Somatic Sensory System I. Background A. Differences between somatic senses and other senses 1. Receptors are distributed throughout the body as opposed to being concentrated at small, specialized locations
Somatic Sensory System I. Background A. Differences between somatic senses and other senses 1. Receptors are distributed throughout the body as opposed to being concentrated at small, specialized locations
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 1.138/nature588 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplemental Information Sensory neuron sodium channel Na v 1.8 is essential for pain at cold temperatures Katharina Zimmermann*, Andreas Leffler*, Alexandru
doi: 1.138/nature588 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplemental Information Sensory neuron sodium channel Na v 1.8 is essential for pain at cold temperatures Katharina Zimmermann*, Andreas Leffler*, Alexandru
Omar Sami. Muhammad Abid. Muhammad khatatbeh
 10 Omar Sami Muhammad Abid Muhammad khatatbeh Let s shock the world In this lecture we are going to cover topics said in previous lectures and then start with the nerve cells (neurons) and the synapses
10 Omar Sami Muhammad Abid Muhammad khatatbeh Let s shock the world In this lecture we are going to cover topics said in previous lectures and then start with the nerve cells (neurons) and the synapses
Page 1. Neurons Transmit Signal via Action Potentials: neuron At rest, neurons maintain an electrical difference across
 Chapter 33: The Nervous System and the Senses Neurons: Specialized excitable cells that allow for communication throughout the body via electrical impulses Neuron Anatomy / Function: 1) Dendrites: Receive
Chapter 33: The Nervous System and the Senses Neurons: Specialized excitable cells that allow for communication throughout the body via electrical impulses Neuron Anatomy / Function: 1) Dendrites: Receive
PHGY 210,2,4 - Physiology SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY. Martin Paré
 PHGY 210,2,4 - Physiology SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Martin Paré Associate Professor of Physiology & Psychology pare@biomed.queensu.ca http://brain.phgy.queensu.ca/pare PHGY 210,2,4 - Physiology SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY
PHGY 210,2,4 - Physiology SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Martin Paré Associate Professor of Physiology & Psychology pare@biomed.queensu.ca http://brain.phgy.queensu.ca/pare PHGY 210,2,4 - Physiology SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY
Cochlear anatomy, function and pathology I. Professor Dave Furness Keele University
 Cochlear anatomy, function and pathology I Professor Dave Furness Keele University d.n.furness@keele.ac.uk Aims and objectives of these lectures Introduction to gross anatomy of the cochlea Focus (1) on
Cochlear anatomy, function and pathology I Professor Dave Furness Keele University d.n.furness@keele.ac.uk Aims and objectives of these lectures Introduction to gross anatomy of the cochlea Focus (1) on
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Functions of the Nervous System nervous system stimulus response Neuron structure and function neurons nerve impulses dendrite
 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Functions of the Nervous System The nervous system is a network of communication used by body parts to maintain homeostasis and bodily functions. The nervous system gathers information
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Functions of the Nervous System The nervous system is a network of communication used by body parts to maintain homeostasis and bodily functions. The nervous system gathers information
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (January 2018) Vol. 70 (12), Page
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (January 2018) Vol. 70 (12), Page 2172-2177 Blockage of HCN Channels with ZD7288 Attenuates Mechanical Hypersensitivity in Rats Model of Diabetic Neuropathy Hussain
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (January 2018) Vol. 70 (12), Page 2172-2177 Blockage of HCN Channels with ZD7288 Attenuates Mechanical Hypersensitivity in Rats Model of Diabetic Neuropathy Hussain
The Nervous System. Nerves, nerves everywhere!
 The Nervous System Nerves, nerves everywhere! Purpose of the Nervous System The information intake and response system of the body. Coordinates all body functions, voluntary and involuntary! Responds to
The Nervous System Nerves, nerves everywhere! Purpose of the Nervous System The information intake and response system of the body. Coordinates all body functions, voluntary and involuntary! Responds to
Sensory Pathways & Somatic Nervous System. Chapter 15
 Sensory Pathways & Somatic Nervous System Chapter 15 How Does Brain Differentiate Sensations? Pain impulses make brain aware of injuries and infections. Impulses from eye, ear, nose and tongue make brain
Sensory Pathways & Somatic Nervous System Chapter 15 How Does Brain Differentiate Sensations? Pain impulses make brain aware of injuries and infections. Impulses from eye, ear, nose and tongue make brain
Portions from Chapter 6 CHAPTER 7. The Nervous System: Neurons and Synapses. Chapter 7 Outline. and Supporting Cells
 CHAPTER 7 The Nervous System: Neurons and Synapses Chapter 7 Outline Neurons and Supporting Cells Activity in Axons The Synapse Acetylcholine as a Neurotransmitter Monoamines as Neurotransmitters Other
CHAPTER 7 The Nervous System: Neurons and Synapses Chapter 7 Outline Neurons and Supporting Cells Activity in Axons The Synapse Acetylcholine as a Neurotransmitter Monoamines as Neurotransmitters Other
The Function of Nervous Tissue *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46531 1 The Function of Nervous Tissue * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section,
OpenStax-CNX module: m46531 1 The Function of Nervous Tissue * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section,
There Are 5 Different Types Of Sensory Receptors* *Note: Not all are touch (somatic) receptors.
 1 First, a bit of information relating to receptors: From sensory organ to sensory organ, receptors work in fundamentally the same way A receptor is always the dendrite of a sensory neuron or a specialized
1 First, a bit of information relating to receptors: From sensory organ to sensory organ, receptors work in fundamentally the same way A receptor is always the dendrite of a sensory neuron or a specialized
Learning Modules - Medical Gross Anatomy Nervous System Overview - Page 1 of 14
 Nervous System Overview - Page 1 of 14 Overview of the Nervous System Every minute of every day, your nervous system is sending and receiving countless messages about what is happening both inside and
Nervous System Overview - Page 1 of 14 Overview of the Nervous System Every minute of every day, your nervous system is sending and receiving countless messages about what is happening both inside and
EE 791 Lecture 2 Jan 19, 2015
 EE 791 Lecture 2 Jan 19, 2015 Action Potential Conduction And Neural Organization EE 791-Lecture 2 1 Core-conductor model: In the core-conductor model we approximate an axon or a segment of a dendrite
EE 791 Lecture 2 Jan 19, 2015 Action Potential Conduction And Neural Organization EE 791-Lecture 2 1 Core-conductor model: In the core-conductor model we approximate an axon or a segment of a dendrite
-Detect heat or cold and help maintain body temperature
 Sensory Receptors -Transduce stimulus energy and transmit signals to the central nervous system -Reception occurs when a receptor detectd a stimulus -Perception occurs in the brain as this information
Sensory Receptors -Transduce stimulus energy and transmit signals to the central nervous system -Reception occurs when a receptor detectd a stimulus -Perception occurs in the brain as this information
Nervous System. Made of two parts. Central Peripheral
 Nervous System Made of two parts Central Peripheral The Central Nervous System is made of the brain and the spinal cord. The Central Nervous System controls everything in the body. A system that controls
Nervous System Made of two parts Central Peripheral The Central Nervous System is made of the brain and the spinal cord. The Central Nervous System controls everything in the body. A system that controls
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM. Homeostasis Strand
 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Homeostasis Strand Introduction In general, a nervous system has three overlapping functions : 1. Sensory input conduction of signals from sensory receptors to integration centres 2.
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Homeostasis Strand Introduction In general, a nervous system has three overlapping functions : 1. Sensory input conduction of signals from sensory receptors to integration centres 2.
The lowest level of stimulation that a person can detect. absolute threshold. Adapting one's current understandings to incorporate new information.
 absolute threshold The lowest level of stimulation that a person can detect accommodation Adapting one's current understandings to incorporate new information. acuity Sharp perception or vision audition
absolute threshold The lowest level of stimulation that a person can detect accommodation Adapting one's current understandings to incorporate new information. acuity Sharp perception or vision audition
Bioscience in the 21st century
 Bioscience in the 21st century Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Dr. Michael Burger Outline: 1. Why neuroscience? 2. The neuron 3. Action potentials 4. Synapses 5. Organization of the nervous system 6.
Bioscience in the 21st century Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Dr. Michael Burger Outline: 1. Why neuroscience? 2. The neuron 3. Action potentials 4. Synapses 5. Organization of the nervous system 6.
The Nervous System. Anatomy of a Neuron
 The Nervous System Chapter 38.1-38.5 Anatomy of a Neuron I. Dendrites II. Cell Body III. Axon Synaptic terminal 1 Neuron Connections dendrites cell body terminal cell body cell body terminals dendrites
The Nervous System Chapter 38.1-38.5 Anatomy of a Neuron I. Dendrites II. Cell Body III. Axon Synaptic terminal 1 Neuron Connections dendrites cell body terminal cell body cell body terminals dendrites
Cell Membrane and Transport
 Cell Membrane and Transport 29/06/2015 11:08 AM Describe the Characteristics of the phospholipid Bilayer. The Phospholipid bilayer is made up of a double layer of membrane lipids that have a hydrophobic
Cell Membrane and Transport 29/06/2015 11:08 AM Describe the Characteristics of the phospholipid Bilayer. The Phospholipid bilayer is made up of a double layer of membrane lipids that have a hydrophobic
Outline. Neuron Structure. Week 4 - Nervous System. The Nervous System: Neurons and Synapses
 Outline Week 4 - The Nervous System: Neurons and Synapses Neurons Neuron structures Types of neurons Electrical activity of neurons Depolarization, repolarization, hyperpolarization Synapses Release of
Outline Week 4 - The Nervous System: Neurons and Synapses Neurons Neuron structures Types of neurons Electrical activity of neurons Depolarization, repolarization, hyperpolarization Synapses Release of
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial
 Pain Pathways Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Pain Pathways MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. NCC3. Genetically determined circuits are the foundation
Pain Pathways Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Pain Pathways MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. NCC3. Genetically determined circuits are the foundation
What it Takes to be a Pain
 What it Takes to be a Pain Pain Pathways and the Neurophysiology of pain Dennis S. Pacl, MD, FACP, FAChPM Austin Palliative Care/ Hospice Austin A Definition of Pain complex constellation of unpleasant
What it Takes to be a Pain Pain Pathways and the Neurophysiology of pain Dennis S. Pacl, MD, FACP, FAChPM Austin Palliative Care/ Hospice Austin A Definition of Pain complex constellation of unpleasant
Chapter 7. Objectives
 Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
Chapter 7. The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement
 Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
The How of Tactile Sensation
 The How of Tactile Sensation http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s2/chapter02.html Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University at Buffalo Objectives 1. Understand how sensory stimuli are encoded
The How of Tactile Sensation http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s2/chapter02.html Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University at Buffalo Objectives 1. Understand how sensory stimuli are encoded
SENSORY NERVOUS SYSTEM & SENSORY RECEPTORS. Dr. Ayisha Qureshi Professor MBBS, MPhil
 SENSORY NERVOUS SYSTEM & SENSORY RECEPTORS Dr. Ayisha Qureshi Professor MBBS, MPhil Sensory Deprivation Tank Is the world really as we perceive it? Is the world really as we perceive it? NO. The world
SENSORY NERVOUS SYSTEM & SENSORY RECEPTORS Dr. Ayisha Qureshi Professor MBBS, MPhil Sensory Deprivation Tank Is the world really as we perceive it? Is the world really as we perceive it? NO. The world
Biological Psychology
 Unit 3a Defini,ons Biological Psychology = a branch of psychology concerned with the links between biology and behavior. Some biological psychologists call themselves behavioral neuroscientists, neuropsychologists,
Unit 3a Defini,ons Biological Psychology = a branch of psychology concerned with the links between biology and behavior. Some biological psychologists call themselves behavioral neuroscientists, neuropsychologists,
By the end of this lecture the students will be able to:
 UNIT VII: PAIN Objectives: By the end of this lecture the students will be able to: Review the concept of somatosensory pathway. Describe the function of Nociceptors in response to pain information. Describe
UNIT VII: PAIN Objectives: By the end of this lecture the students will be able to: Review the concept of somatosensory pathway. Describe the function of Nociceptors in response to pain information. Describe
