Neuromuscular Control During the Bench Press Movement in an Elite Disabled and Able-Bodied Athlete
|
|
|
- Rosa Fitzgerald
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal of Human Kinetics volume 60/2017, DOI: /hukin Section IV Behavioural Sciences in Sport - adaptive sports Neuromuscular Control During the Bench Press Movement in an Elite Disabled and Able-Bodied Athlete by Artur Gołaś 1, Anna Zwierzchowska 1, Adam Maszczyk 1, Michał Wilk 1, Petr Stastny 2, Adam Zając 1 The disabled population varies significantly in regard to physical fitness, what is conditioned by the damage to the locomotor system. Recently there has been an increased emphasis on the role of competitive sport in enhancing health and the quality of life of individuals with disability. One of the sport disciplines of Paralympics is the flat bench press. The bench press is one of the most popular resistance exercises used for the upper body in healthy individuals. It is used not only by powerlifters, but also by athletes in most strength-speed oriented sport disciplines. The objective of the study was to compare neuromuscular control for various external loads (from 60 to 100% ) during the flat bench press performed by an elite able-bodied athlete and an athlete with lower limb disability. The research project is a case study of two elite bench press athletes with similar sport results: an able-bodied athlete (M.W., age 34 years, body mass 103 kg, body height 1.72 m, in the flat bench press 200 kg) and a disabled athlete (M.T., age 31 years, body mass 92 kg, body height 1.70 m, in the flat bench press 190 kg). The activity was recorded for four muscles: pectoralis major (PM), anterior deltoid (AD), as well as for the lateral and long heads of the triceps brachii (TBlat and TBlong). The T-test revealed statistically significant differences between peak activity of all the considered muscles (AD with p = 0.001; PM with p = 0.001; TBlat with p = and TBlong with p = 0.002) between the 2 athletes. The analysis of peak activity differences of M.W and M.T. in relation to the load revealed statistically significant differences for load changes between: 60 to 100% (p = 0.007), 70 to 100% (p = 0.016) and 80 to 100% (p = 0.032). The flat bench press performed without legs resting firmly on the ground leads to the increased engagement of upper body muscles and to their greater activation. Isolated initial positions can be used to generate greater engagement of muscle groups during the bench press exercise and evoke their higher activation. Key words: bench press, muscle activity, internal structure, disabled athletes. Introduction The disabled population varies significantly in regard to physical fitness, what is conditioned by the damage to the locomotor system. There are disabled individuals that move and function independently, as well as those that are affected by total disability and are entirely dependent on others. A major type of damage to the locomotor system includes spinal cord injuries (SCI), cerebral palsy and amputations. The development of medical sciences and technological advances have led to the extension of life expectancy and better quality of life in people with locomotor system dysfunctions, equalizing their occupational and sporting opportunities with these of the healthy population (DeJong et al., 1991). Recently the disabled population has attracted much attention of researchers from different fields of science (Franceschini et al., 2012). The locomotor disability leads to a number of posttraumatic problems, both early and delayed, which stimulate the search for new methods of improving the life of disabled subjects. 1 - The Jerzy Kukuczka Academy of Physical Education in Katowice. 2 - Charles University in Prague. Authors submitted their contribution to the article to the editorial board. Accepted for printing in the Journal of Human Kinetics vol. 60/2017 in December 2017.
2 210 Neuromuscular Control During the Bench Press Movement in Sport and physical activity are widely accepted as necessary components of health. One of the many alternative forms of rehabilitation of the disabled includes competitive sports. Recently there has been an increased emphasis on the role of competitive sport in enhancing health and the quality of life of individuals with disability (Goldberg, 1995). One of the sport disciplines of Paralympics is the flat bench press. The bench press is an often recommended exercise for individuals with paraplegia, amputations and other locomotors dysfunctions. It is characterized by short-term, high intensity efforts which require significant development of muscular strength of the uppers limbs and trunk. Paralympic powerlifters participate in the bench press, which consists of athletes lowering a barbell to the chest, holding it motionless, and then pressing it upwards to full arm extension. Athletes are given three attempts, with the winning athlete lifting the largest amount of weight (IPC 2015; Willick et al., 2016). Data regarding injuries for para-athletes participating in powerlifting are scarce (Athanasopoulos et al., 2009; Reynolds et al., 1994). The bench press is one of the most popular resistance exercises used for the upper body in the healthy population. It is used not only by powerlifters, but also by athletes in most strength-speed oriented sport disciplines (Tillar and Ettema, 2013). In competitive bench pressing the result is represented by the maximal weight that can be lowered to the chest and lifted (pushed up) to the full extension of the elbow joints (Tillar and Ettema, 2009). The competitive bench press is connected with a very reproducible movement technique, which is perfected for many years of training. Various methods are used in bench pressing to improve the lifting technique which includes grip width, angle and bench, inclination angle variation. Dumbbells and an unstable surface are used to improve balance and coordination. The internal structure of the bench press exercise has been analysed and described extensively in the literature (Golas et al., 2016; Maszczyk et al., 2016; Sakamoto and Sinclair, 2012; Stastny et al., 2017). However, no studies have considered the analysis of muscular activity during the bench press movement in elite abledbody and disabled athletes. Therefore, the objective of the study was to compare neuromuscular control for various external loads (from 60 to 100% ) during the flat bench press performed by an elite able-bodied athlete and an athlete with lower limb disability. Methods Participants The research project is a case study of two elite bench press athletes with similar sport results: an able-bodied athlete (M.W., age 34 years, body mass 103 kg, body height 1.72 m, in the flat bench press of 200 kg) and a disabled athlete (M.T., age 31 years, body mass 92 kg, body height 1.70 m, in the flat bench press of 190 kg). The individual with lower limb disability performed the task according to the IPF (International Powerlifting Federation) regulations concerning the lift (bench press), used during international competitions for the disabled. The participants did not perform any additional resistance exercises for 72 hours prior to testing to avoid fatigue. The subjects were informed verbally and in writing about the procedures and possible risks of the tests and provided written consent before they were included in the study. The study received the approval of the Bioethics Committee at the Academy of Physical Education in Katowice, Poland. Procedures The measurements were performed in the Laboratory of Muscular Strength and Power at the Academy of Physical Education in Katowice. There were two sessions of the experiment. Session 1 was aimed at determination of one repetition maximum during the flat bench press (). Session 2 consisted of performing the flat bench press exercise with increasing loads (60-100% ). The procedure consisted of performing individual attempts of the flat bench press with an increasing load (from 60 to 100% ) with 5 min rest periods between attempts. A standardized warm-up protocol was used for each session, including a general warm-up (5 min), using a hand cycle ergometer (heart rate of around 130 bpm) and performing several lower and upper body resistance exercises. The specific part of the warm-up consisted of three bench press sets with the load adjusted accordingly to perform 15, 10 and 5 repetitions. Journal of Human Kinetics - volume 60/2017
3 by Artur Gołaś et al. 211 The determination of was performed according to the protocol by Tillaar and Saeterbakken (2014). The percentage of the load was calculated based on the self-reported values by the participants. The self-reported was set according to the provided information regarding maximal lifts performed in the previous three months. The rest periods between sets were 5 minutes to avoid potential effects of fatigue. When the self-reported was successful, a trial with an additional load of kg was performed. When the initial trial was unsuccessful, the weight was decreased by kg. A total of two to three trials were performed per participant. Participants were instructed to maintain the head, shoulder blades and buttocks in contact with the bench at all time. Two experienced spotters assisted the athletes in the preload phases. Electromyography An eight-channel Noraxon TeleMyo 2400 system (Noraxon USA Inc., Scottsdale, AZ; 1500Hz) was used for recording and analysis of biopotentials from the muscles. The activity was recorded for four muscles: pectoralis major (PM), anterior deltoid (AD), as well as for the lateral and long heads of the triceps brachii (TBlat and TBlong). Before placing the gel coated selfadhesive electrodes (Dri-Stick Silver circular semg Electrodes AE-131, NeuroDyne Medical, USA), the skin was shaved, abraded and washed with alcohol. The electrodes (11 mm contact diameter and a 2 cm center-to-center distance) were placed along the presumed direction of the underlying muscle fiber according to the recommendations by SENIAM (Hermens et al., 2000). The EMG signals were sampled at a rate of 1000 Hz. Signals were band pass filtered with a cut off frequency of 8 and 450 Hz, after which the root-mean-square (RMS) was calculated. All the electrodes were located on the right side of the participant, regardless of whether this was the dominant side or not. The grounding electrode was placed on the connection with the triceps brachii muscle. Video recording was used for identification of the beginning and completion of the movement. After completion of all the tests in a single day, 2-3 s evaluations of static bench press movements were performed in order to normalize electromyographic records according to the SENIAM procedure. The analysis was based on peak activity during the bench press (both from the eccentric and concentric phases). Table 1 Changes in peak muscle activity (%) of four muscles during the bench press with different loads (60%, 70%, 80%, 90% and 100% ). Muscle/load 60% 70% 80% DISABLED ATHLETE 90% 100% AD PM Tblat TBlong ABLE-BODIED ATHLETE AD PM Tblat TBlong Editorial Committee of Journal of Human Kinetics
4 212 Neuromuscular Control During the Bench Press Movement in Peak muscle activity differences in the able-bodied and disabled athlete in relation to load changes Load values (%) 60 vs vs vs vs * 70 vs vs vs * 80 vs vs * 90 vs. 100 p Table 2 * p < Statistical Analysis The data were processed using Statistica software and presented as means with standard deviations. The Shapiro-Wilk, as well as Levene and Mauchly s tests were used in order to verify the normality, homogeneity and sphericity of the sample s data variances, respectively. The statistical analysis was aimed at determining the differences in muscle peak activity between the 2 participants using the T-test (Maszczyk et al., 2012, 2014, 2016; Przednowek et al., 2016). The statistical significance was set at p < Results Changes in peak muscle activity of four chosen muscles for analysis (AD, PM, TBlat, TBlong) during the bench press with different loads (60, 70, 80, 90 and 100% ) are presented in Table 1. The T-test revealed statistically significant differences between peak activity of all the considered muscles (AD with p = 0.001; PM with p = 0.001; TBlat with p = and TBlong with p = 0.002) between the 2 athletes. The analysis of peak activity differences of M.W and M.T. in relation to particular loads revealed statistically significant differences for load changes between: 60 to 100% (p = 0.007), 70 to 100 % (p = 0.016) and 80 to 100% (p = 0.032) (Table 2). For the athlete with disability, the increase in the load from 70 to 100% led to an increase in activity of all the analysed muscles (for AD by 49%, for PM by 44%, for TBlat by 46% and for TBlong by 37%). In the able-bodied athlete, a similar increase in the load caused higher activity in the anterior deltoid and the long head of the triceps brachii (by 71% and 40%, respectively), while decreases in activity of the pectoralis major (PM) and lateral head of the triceps brachii were observed (TBlat; by 1% and 18%, respectively). Discussion Resistance exercises elicit a combination of neural and muscular responses and adaptations (Kay et al., 2000). Workout variety increases motivation and long term adaptation, while avoiding monotony and overtraining (Crewther et al., 2005). Increased muscular activation resulting from training is most often ascribed to a combination of greater recruitment (the number of fibers involved in a muscle action) and higher rate coding (the frequency at which the motor units are stimulated; Enoka and Fuglevand, 2001; Enoka and Duchateau, 2015). The results of our research indicate Journal of Human Kinetics - volume 60/2017
5 by Artur Gołaś et al. 213 statistically significant differences between the disabled and able-body athletes in peak activity of all muscles (AD, PM, TBlat, TBlong). Analysis of peak activity differences in relation to the lifted load revealed significant differences for load changes between: 60 to 100%, 70 to 100 % and 80 to 100%. For the able-bodied athlete our results are in accordance with the literature which indicates that an increase in the load during the standard bar bench press causes greater peak activation of the triceps brachii and anterior deltoid without significant increases in PM activation (Maszczyk et al., 2016; Saeterbakken et al., 2017). However, for the athlete with disability, higher loads caused increased activity of all the studied muscles, yet there is no relevant data in the literature in this regard (Stastny et al., 2017). These differences are most noticeable when changing to maximum loads. Changes in EMG activity between the able-bodied and disabled athlete during the bench press movement are most likely related to tonic muscle control (Welsch et al., 2005). To perform a motor task the CNS activates particular muscle groups in a pre-determined sequence. However, activation of prime movers in a particular exercises is not always identical during changes of the external load (Stastny et al., 2016). Brennecke et al. (2009) suggest alternative principles of muscular activation during the same and progressive loads which have not been yet precisely explained. The first principle relates to minimal energy expenditure. The second principle is based on the prediction of external forces such as gravity, while the third one consists of muscle synergy between particular parts of the body. The recruitment of motor units and its firing frequency are controlled by central command of the CNS, and may be regulated by reciprocal feedback (Nichols et al., 1999). For the athlete with lower limb disability, the change in the load from 70 to 100% led to an increase in activity of all the analysed muscles (for AD by 49%, for PM by 44%, for TBlat by 46% and for TBlong by 37%). In the able-bodied athlete, a comparable increase in the load caused higher activity in the anterior deltoid and the long head of the triceps brachii (TBlong by 71% and 40%, respectively), while a decrease in the activity of the pectoralis major (PM) and the lateral head of the triceps brachii (TBlat; by 1% and 18%, respectively). For the athlete with lower limb disability, with a limited kinaesthetic sense and proprioception in this area, a compensation of deficits occurred, by increased synchronization of motor units and greater involvement of particular muscle groups during the bench press movement. The lack of support and lower limb muscle activation evoked greater muscle activation in the disabled athlete and a substantial stretch of the pectoralis major muscle. This could have been generated by a more flat lying position compared to the able-bodied athlete, which can result from reduced muscle tone in the back muscles. This difference in the lying position between the able bodied and disabled athletes at the elite level consequently led to a different movement structure during the flat bench press. A methodological limitation of the study is the lack of possibilities for evaluation of the external structure of the movement (forces and movement torques), and small sample size (case study) which substantially reduces the opportunity for generalization. Future research in this area should concentrate on the analysis of the internal and external structure (Krol and Golas, 2017) of the bench press movement between ablebodied and disabled athletes. Conclusion The flat bench press performed without legs resting firmly on the ground leads to the increased engagement of upper body muscles and their higher activation. Future research should concentrate on larger groups of subjects with various lower limb disabilities (amputations, palsies at various degrees). When evaluating muscle activity in disabled subjects during the bench press movement, both sides of the body should be analysed to determine possible asymmetry. Practical implications Isolated initial positions can be used to generate greater engagement of muscle groups during the bench press exercise and evoke their higher activation. Editorial Committee of Journal of Human Kinetics
6 214 Neuromuscular Control During the Bench Press Movement in Acknowledgement This work was supported by the grant PROGRESS Q41, PRIMUS 17/MED05, and Ministry of Science and Higher Education of Poland under grant NRSA and N RSA , as well as by Statutory Research of Academy of Physical Education in Katowice in the years research head - dr hab. Adam Maszczyk associate professor. References Athanasopoulos S, Mandalidis D, Tsakoniti A, Athanasopoulos I, Strimpakos N, Papadopoulos E, Pyrros DG, Parisis C, Kapreli E. The 2004 Paralympic Games: physiotherapy services in the paralympic village polyclinic. Open Sports Med J, 2009; 3: 1 8 Brennecke A, Guimarães TM, Leone R, Cadarci M, Mochizuki L, Simão R, Amadio AC, Serrão JC. Neuromuscular activity during bench press exercise performed with and without the preexhaustion method. J Strength Cond Res, 2009; 23(7): Crewther B, Cronin J, Keogh J. Possible stimuli for strength and power adaptation - Acute mechanical responses. Sports Med, 2005; 35: DeJong G, Batavia AI. Toward a health services research capacity in spinal cord injury. Paraplegia, 1991; 29: Enoka RM, Duchateau J. Inappropriate interpretation of surface EMG signals and muscle fiber characteristics impedes understanding of the control of neuromuscular function. J Appl Physiol, 2015; 119: Enoka RM, Fuglevand AJ. Motor unit physiology: some unresolved issues. Muscle Nerve, 2001; 24: 4 17 Franceschini M, Pagliacci MC, Russo T, Felzani G, Aito S, Marini C. Occurrence and predictors of employment after traumatic spinal cord injuries: the GISEM study. Spinal Cord, 2012; 50(3): Golas A, Maszczyk A, Zajac A, Mikolajec K, Stastny P. Optimizing Post Activation Potentiation for Explosive Activities in Competitive Sports. J Hum Kinet, 2016; 52 (1): Goldberg B. Sports and Exercise for Children with Chronic Health Conditions. Champaign, Illinois: Human Kinetics, Hermens HJ, Freriks B, Disselhorst-Klug C, Rau G. Development of recommendations for SEMG sensors and sensor placement procedures. J Elect Kin, 2000; 10(5): Kay D, Clair Gibson A, Mitchell MJ, Lambert MI, Noakes TD. Different neuromuscular recruitment patterns during eccentric, concentric and isometric contractions. J Electromyogr Kinesiol, 2000; 10: Krol H, Golas A. Effect of Barbell Weight on the Structure of the Flat Bench Press. J Strength Cond Res, 2017; 31(5): Maszczyk A, Gołaś A, Czuba M, Krol H, Wilk M, Stastny P, Goodwin J, Kostrzewa M, Zajac A. Emg analysis and modelling of flat bench press using artificial neural networks. South African Journal for Research in Sport, Physical Education and Recreation, 2016; 38(1): Maszczyk A, Gołaś A, Pietraszewski P, Roczniok R, Zajac A, Stanula A. Application of Neural and Regression Models in Sports Results Prediction. Procedia Social and Behavioral Sciences, 2014; 117: Maszczyk A, Roczniok R, Waśkiewicz Z, Czuba M, Mikołajec K, Zajac A, Stanula A. Application of regression and neural models to predict competitive swimming performance. Percept Mot Skills, 2012; 114(2): Nichols TR, Cope TC, Abelew TA. Rapid Spinal mechanism of motor control. Exerc Sport Sci Rev, 1999; 27: Przednowek K, Iskra J, Maszczyk A, Nawrocka M. Regression shrinkage and neural models in predicting the results of 400-metres hurdles races. Biol Sport, 2016; 33(4): Reynolds J, Stirk A, Thomas A, Geary F. Paralympics Barcelona Br J Sports Med, 1994; 28: Saeterbakken AH, Mo DA, Scott S, Andersen V. The effects of bench press variations in competitive athletes on muscle activity and performance. J Hum Kinet, 2017; 57: Sakamoto A, Sinclair PJ. Muscle activations under varying lifting speeds and intensities during bench press. Eur J Appl Physiol, 2012; 112(3): Journal of Human Kinetics - volume 60/2017
7 by Artur Gołaś et al. 215 Stastny P, Gołaś A, Blazek D, Maszczyk A, Wilk M, Pietraszewski P, Petr M, Uhlir P, Zajac A. A systematic review of surface electromyography analyses of the bench press movement task. PLoS ONE, 2017; 12(2): e Stastny P, Tufano JJ, Golas A, Petr M. Strengthening the Gluteus Medius Using Various Bodyweight and Resistance Exercises. Strength & Conditioning Journal, 2016; 38: Tillaar R, Ettema G. A comparison of successful and unsuccessful attempts in maximal bench pressing. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise, 2009; 41(11): Tillaar R, Ettema G. Comparison of muscle activity in concentric and counter movement maximum bench press. J Hum Kinet, 2013; 38(1): Tillaar R, Saeterbakken A. Effect of fatigue upon performance and electromyographic activity in 6-RM bench Press. J Hum Kinet, 2014; 40(1): Welsch EA, Bird MJ, Mayhew JL. Electromyographic activity of the pectoralis major and anterior deltoid muscles during three upper-body lifts. J Strength Cond Res, 2005; 19(2): Willick SE, Cushman DM, Blauwet CA, Emery C, Webborn N, Derman W, Schwellnus M, Stomphorst J, Van de Vliet P. The epidemiology of injuries in powerlifting at the London 2012 Paralympic Games: An analysis of 1411 athlete-days. Scand J Med Sci Sports, 2016; 26(10): Corresponding author: Artur Gołaś Ph.D. Department of Sports Training Jerzy Kukuczka Academy of Physical Education in Katowice, Mikolowska 72A, Katowice, Poland. a.golas@awf.katowice.pl Editorial Committee of Journal of Human Kinetics
CHANGES IN BAR VELOCITY AND MUSCULAR ACTIVITY DURING THE BENCH PRESS IN RELATION TO THE LOAD LIFTED
 Central European Journal of Sport Sciences and Medicine Vol. 11, No. 3/2015: 95 101 DOI: 10.18276/cej.2015.3-11 CHANGES IN BAR VELOCITY AND MUSCULAR ACTIVITY DURING THE BENCH PRESS IN RELATION TO THE LOAD
Central European Journal of Sport Sciences and Medicine Vol. 11, No. 3/2015: 95 101 DOI: 10.18276/cej.2015.3-11 CHANGES IN BAR VELOCITY AND MUSCULAR ACTIVITY DURING THE BENCH PRESS IN RELATION TO THE LOAD
Muscular activity patterns of female and male athletes during the flat bench press
 Original Muscular Paper activity patterns of female and male athletes https://doi.org/10.5114/biolsport.2018.74193 Muscular activity patterns of female and male athletes during the flat bench press AUTHORS:
Original Muscular Paper activity patterns of female and male athletes https://doi.org/10.5114/biolsport.2018.74193 Muscular activity patterns of female and male athletes during the flat bench press AUTHORS:
A Comparison of Muscle Activity in Concentric and Counter Movement Maximum Bench Press
 Journal of Human Kinetics volume 38/2013, 63-71 DOI: 1478/hukin-2013-0046 63 Section I Kinesiology A Comparison of Muscle Activity in Concentric and Counter Movement Maximum Bench Press by Roland van den
Journal of Human Kinetics volume 38/2013, 63-71 DOI: 1478/hukin-2013-0046 63 Section I Kinesiology A Comparison of Muscle Activity in Concentric and Counter Movement Maximum Bench Press by Roland van den
The Effects of Bench Press Variations in Competitive Athletes on Muscle Activity and Performance
 Journal of Human Kinetics volume 57/2017, 61-71 DOI: 10.1515/hukin-2017-0047 61 Section I Kinesiology The Effects of Bench Press Variations in Competitive Athletes on Muscle Activity and Performance by
Journal of Human Kinetics volume 57/2017, 61-71 DOI: 10.1515/hukin-2017-0047 61 Section I Kinesiology The Effects of Bench Press Variations in Competitive Athletes on Muscle Activity and Performance by
A comparison of muscle activity and 1-RM strength of three chest-press exercises with different stability requirements
 Journal of Sports Sciences, March 1st 2011; 29(5): 533 538 A comparison of muscle activity and 1-RM strength of three chest-press exercises with different stability requirements ATLE H. SAETERBAKKEN 1,
Journal of Sports Sciences, March 1st 2011; 29(5): 533 538 A comparison of muscle activity and 1-RM strength of three chest-press exercises with different stability requirements ATLE H. SAETERBAKKEN 1,
Effect of Fatigue Upon Performance and Electromyographic Activity in 6-RM Bench Press
 Journal of Human Kinetics volume 40/2014, 57-65 DOI: 10.2478/hukin-2014-0007 57 Section I Kinesiology Effect of Fatigue Upon Performance and Electromyographic Activity in 6-RM Bench Press by Roland van
Journal of Human Kinetics volume 40/2014, 57-65 DOI: 10.2478/hukin-2014-0007 57 Section I Kinesiology Effect of Fatigue Upon Performance and Electromyographic Activity in 6-RM Bench Press by Roland van
Original research papers
 Original research papers Pol. J. Sport Tourism 2017, 24, 79-85 79 movement features WhiCh describe the flat BenCh Press HENRYK KRÓL 1, BARTŁOMIEJ GARBACIAK 2 1 Jerzy Kukuczka Academy of Physical Education
Original research papers Pol. J. Sport Tourism 2017, 24, 79-85 79 movement features WhiCh describe the flat BenCh Press HENRYK KRÓL 1, BARTŁOMIEJ GARBACIAK 2 1 Jerzy Kukuczka Academy of Physical Education
Original Article Activation of pectoralis major and deltoid during bench press and pullover exercises until the concentric failure
 Journal of Physical Education and Sport (JPES), 17(4), Art 294, pp. 2588-2592, 2017 online ISSN: 2247-806X; p-issn: 2247 8051; ISSN - L = 2247-8051 JPES Original Article Activation of pectoralis major
Journal of Physical Education and Sport (JPES), 17(4), Art 294, pp. 2588-2592, 2017 online ISSN: 2247-806X; p-issn: 2247 8051; ISSN - L = 2247-8051 JPES Original Article Activation of pectoralis major
Powerlifting. English for THE GAMES
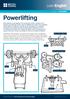 English for THE GAMES Powerlifting When athletes come together from around the world to compete in the Olympic and Paralympic Games, they are fulfilling their dreams and competing at the highest level.
English for THE GAMES Powerlifting When athletes come together from around the world to compete in the Olympic and Paralympic Games, they are fulfilling their dreams and competing at the highest level.
Acute Effects of Dropsets Among Different Resistance Training Methods in Upper Body Performance
 Journal of Human Kinetics volume 34/2012, 105-111 DOI: 10.2478/v10078-012-0069-6 105 Section III Sports Training Acute Effects of Dropsets Among Different Resistance Training Methods in Upper Body Performance
Journal of Human Kinetics volume 34/2012, 105-111 DOI: 10.2478/v10078-012-0069-6 105 Section III Sports Training Acute Effects of Dropsets Among Different Resistance Training Methods in Upper Body Performance
Resistance training is incorporated into training
 AN ELECTROMYOGRAPHY ANALYSIS OF 3 MUSCLES SURROUNDING THE SHOULDER JOINT DURING THE PERFORMANCE OF A CHEST PRESS EXERCISE AT SEVERAL ANGLES ARTHUR A. TREBS, 1 JASON P. BRANDENBURG, 2 AND WILLIAM A. PITNEY
AN ELECTROMYOGRAPHY ANALYSIS OF 3 MUSCLES SURROUNDING THE SHOULDER JOINT DURING THE PERFORMANCE OF A CHEST PRESS EXERCISE AT SEVERAL ANGLES ARTHUR A. TREBS, 1 JASON P. BRANDENBURG, 2 AND WILLIAM A. PITNEY
Training the Shoulder for Racquet Sports Michael Barnes, MEd, CSCS
 Training the Shoulder for Racquet Sports Michael Barnes, MEd, CSCS Many sport movements involve accelerating an implement, such as a ball, bat or racquet, or transferring force from the ground to the hands.
Training the Shoulder for Racquet Sports Michael Barnes, MEd, CSCS Many sport movements involve accelerating an implement, such as a ball, bat or racquet, or transferring force from the ground to the hands.
Shoulders above the rest?
 Exclusive ACE Sponsored Research Shoulders above the rest? BY SAMANTHA SWEENEY, M.S., JOHN P. PORCARI, PH.D., CLAYTON CAMIC, PH.D., ATTILA KOVACS, PH.D., AND CARL FOSTER, PH.D. The shoulders the deltoids
Exclusive ACE Sponsored Research Shoulders above the rest? BY SAMANTHA SWEENEY, M.S., JOHN P. PORCARI, PH.D., CLAYTON CAMIC, PH.D., ATTILA KOVACS, PH.D., AND CARL FOSTER, PH.D. The shoulders the deltoids
Original Article. Resistance training acute session: pectoralis major, latissimus dorsi and triceps brachii electromyographic activity
 Journal of Physical Education and Sport (JPES), 18(2), Art 95, pp. 648-653, 2018 online ISSN: 2247-806X; p-issn: 2247 8051; ISSN - L = 2247-8051 JPES Original Article Resistance training acute session:
Journal of Physical Education and Sport (JPES), 18(2), Art 95, pp. 648-653, 2018 online ISSN: 2247-806X; p-issn: 2247 8051; ISSN - L = 2247-8051 JPES Original Article Resistance training acute session:
The bench press is a ubiquitous strength-training
 Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 25, 19(), 587 591 25 National Strength & Conditioning Association THE INFLUENCE OF GRIP WIDTH AND FOREARM PRONATION/SUPINATION ON UPPER-BODY MYOELECTRIC ACTIVITY
Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 25, 19(), 587 591 25 National Strength & Conditioning Association THE INFLUENCE OF GRIP WIDTH AND FOREARM PRONATION/SUPINATION ON UPPER-BODY MYOELECTRIC ACTIVITY
Chapter 14 Training Muscles to Become Stronger
 Chapter 14 Training Muscles to Become Stronger Slide Show developed by: Richard C. Krejci, Ph.D. Professor of Public Health Columbia College 11.22.11 Objectives 1. Describe the following four methods to
Chapter 14 Training Muscles to Become Stronger Slide Show developed by: Richard C. Krejci, Ph.D. Professor of Public Health Columbia College 11.22.11 Objectives 1. Describe the following four methods to
Strength and conditioning specialists are continually
 THE INFLUENCE OF BAR DIAMETER ON NEUROMUSCULAR STRENGTH AND ACTIVATION: INFERENCES FROM AN ISOMETRIC UNILATERAL BENCH PRESS DOUGLAS FIORANELLI AND C. MATTHEW LEE Exercise Physiology Laboratory, Department
THE INFLUENCE OF BAR DIAMETER ON NEUROMUSCULAR STRENGTH AND ACTIVATION: INFERENCES FROM AN ISOMETRIC UNILATERAL BENCH PRESS DOUGLAS FIORANELLI AND C. MATTHEW LEE Exercise Physiology Laboratory, Department
differentiate between the various types of muscle contractions; describe the factors that influence strength development;
 CHAPTER 6 Muscles at Work After completing this chapter you should be able to: differentiate between the various types of muscle contractions; describe the factors that influence strength development;
CHAPTER 6 Muscles at Work After completing this chapter you should be able to: differentiate between the various types of muscle contractions; describe the factors that influence strength development;
Muscle Activation in strength training exercises with and without using the clip-on device Gripper
 Muscle Activation in strength training exercises with and without using the clip-on device Gripper Contract research for Actiweight AS by The Norwegian School of Sport Sciences 2016 Responsible: Tron Krosshaug,
Muscle Activation in strength training exercises with and without using the clip-on device Gripper Contract research for Actiweight AS by The Norwegian School of Sport Sciences 2016 Responsible: Tron Krosshaug,
D: there are no strength gains typically at this early stage in training
 Name: KIN 410 Final Motor Control (B) units 6, + FALL 2016 1. Place your name at the top of this page of questions, and on the answer sheet. 2. Both question and answer sheets must be turned in. 3. Read
Name: KIN 410 Final Motor Control (B) units 6, + FALL 2016 1. Place your name at the top of this page of questions, and on the answer sheet. 2. Both question and answer sheets must be turned in. 3. Read
Author: Max Schmarzo Draft. Purpose
 Author: Max Schmarzo Draft Purpose The purpose of this paper is to introduce the concepts of accessible strength and strength ceiling and its relationship with muscular force in regards to both the structural
Author: Max Schmarzo Draft Purpose The purpose of this paper is to introduce the concepts of accessible strength and strength ceiling and its relationship with muscular force in regards to both the structural
MENTOR METHOD OF TRAINING
 MENTOR METHOD OF TRAINING When trying to improve performance on the field of play or on the court, whatever your sport, it is important that you understand where it all begins. For an athlete there are
MENTOR METHOD OF TRAINING When trying to improve performance on the field of play or on the court, whatever your sport, it is important that you understand where it all begins. For an athlete there are
Chapter 4. Muscular Strength and Endurance KIN 217 3/28/18 1
 Chapter 4 Muscular Strength and Endurance KIN 217 1 Functions of Muscle Tissues Functions: provide stability and postural tone, allow purposeful movement, heat production. Muscle mass constitutes: 40 to
Chapter 4 Muscular Strength and Endurance KIN 217 1 Functions of Muscle Tissues Functions: provide stability and postural tone, allow purposeful movement, heat production. Muscle mass constitutes: 40 to
Effects of Acute Stretching on Resistance Training Performance
 9 Effects of Acute Stretching on Resistance Training Performance Shaun J. Marek, Jon M. Wolfarth, Luke J. Dettinger, Darin C. Kelley University of Wisconsin at Eau Claire, WI ABSTRACT Abstract. Marek,
9 Effects of Acute Stretching on Resistance Training Performance Shaun J. Marek, Jon M. Wolfarth, Luke J. Dettinger, Darin C. Kelley University of Wisconsin at Eau Claire, WI ABSTRACT Abstract. Marek,
ISOMETRIC SQUAT FORCE OUTPUT AND MUSCLE ACTIVITY IN STABLE AND UNSTABLE CONDITIONS
 Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 2006, 20(4), 915-918 i^j 2006 National Strength & Conditioning Association ISOMETRIC SQUAT FORCE OUTPUT AND MUSCLE ACTIVITY IN STABLE AND UNSTABLE CONDITIONS
Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 2006, 20(4), 915-918 i^j 2006 National Strength & Conditioning Association ISOMETRIC SQUAT FORCE OUTPUT AND MUSCLE ACTIVITY IN STABLE AND UNSTABLE CONDITIONS
Influence of Exercise Order on Electromyographic Activity During Upper Body Resistance Training
 Journal of Human Kinetics volume 44/2014, 203-209 DOI: 10.2478/hukin-2014-0127 203 Section III Sports Training Influence of Exercise Order on Electromyographic Activity During Upper Body Resistance Training
Journal of Human Kinetics volume 44/2014, 203-209 DOI: 10.2478/hukin-2014-0127 203 Section III Sports Training Influence of Exercise Order on Electromyographic Activity During Upper Body Resistance Training
Traditional free-weight exercises provide constant
 COMPARISON OF KINEMATICS AND MUSCLE ACTIVATION IN FREE-WEIGHT BACK SQUAT WITH AND WITHOUT ELASTIC BANDS ATLE H. SAETERBAKKEN, 1 VIDAR ANDERSEN, 1 AND ROLAND VAN DEN TILLAAR 2 1 Department of Teacher Education
COMPARISON OF KINEMATICS AND MUSCLE ACTIVATION IN FREE-WEIGHT BACK SQUAT WITH AND WITHOUT ELASTIC BANDS ATLE H. SAETERBAKKEN, 1 VIDAR ANDERSEN, 1 AND ROLAND VAN DEN TILLAAR 2 1 Department of Teacher Education
Chapter 20: Muscular Fitness and Assessment
 Chapter 20: Muscular Fitness and Assessment American College of Sports Medicine. (2010). ACSM's resource manual for guidelines for exercise testing and prescription (6th ed.). New York: Lippincott, Williams
Chapter 20: Muscular Fitness and Assessment American College of Sports Medicine. (2010). ACSM's resource manual for guidelines for exercise testing and prescription (6th ed.). New York: Lippincott, Williams
OPTION 4 Improving Performance How do athletes train for improved performance? Strength Training
 OPTION 4 Improving Performance How do athletes train for improved performance? Strength Training 1. strength training! The main goal of strength training is to increase the maximum force that a particular
OPTION 4 Improving Performance How do athletes train for improved performance? Strength Training 1. strength training! The main goal of strength training is to increase the maximum force that a particular
Maximising Fitness for Teenage Boys
 www.tdrfitness.com Maximising Fitness for Teenage Boys Toni Reinikainen B.Sci(Sp.Ex.Sci) Level 1 ASCA Children are not Small Adults Lack of Knowledge? At the age of 4 Ugly Parent Syndrome Peak Height
www.tdrfitness.com Maximising Fitness for Teenage Boys Toni Reinikainen B.Sci(Sp.Ex.Sci) Level 1 ASCA Children are not Small Adults Lack of Knowledge? At the age of 4 Ugly Parent Syndrome Peak Height
Whole Body Strength Men
 Whole Body Strength Men Whole Body Strength for Men Introduction This exercise routine is created for men and women with the goal of strengthening their overall body. Included in this workout are a range
Whole Body Strength Men Whole Body Strength for Men Introduction This exercise routine is created for men and women with the goal of strengthening their overall body. Included in this workout are a range
Supplements are to be used to improve performance in the gym and to enhance health on a day to day basis.
 Workout Plans: - 3 Days per week weight training with 20 mins PWO SSC Cardio - 2 Days per week conditioning/hiit training - 2 Rest Day per week Nutrition Plans: Diet should consist of a lower carbohydrate
Workout Plans: - 3 Days per week weight training with 20 mins PWO SSC Cardio - 2 Days per week conditioning/hiit training - 2 Rest Day per week Nutrition Plans: Diet should consist of a lower carbohydrate
Poor squat technique increases the risk of an acute or chronic low back or knee injury. A few key technique points are listed below:
 1. 1 3. 2 The cornerstone exercise of any effective strength training program designed for sports with lower body demands is the squat. Successful squat training not only reduces the risk of injury, but
1. 1 3. 2 The cornerstone exercise of any effective strength training program designed for sports with lower body demands is the squat. Successful squat training not only reduces the risk of injury, but
Activation of Selected Core Muscles during Pressing
 fa International Journal of Kinesiology & Sports Science ISSN 2202-946X Vol. 3 No. 4; October 2015 Australian International Academic Centre, Australia Flourishing Creativity & Literacy Activation of Selected
fa International Journal of Kinesiology & Sports Science ISSN 2202-946X Vol. 3 No. 4; October 2015 Australian International Academic Centre, Australia Flourishing Creativity & Literacy Activation of Selected
Evaluation of muscle activity on different surfaces
 International Research Journal of Applied and Basic Sciences 214 Available online at www.irjabs.com ISSN 2251-838X / Vol, 8 (6): 692-696 Science Explorer Publications Evaluation of muscle activity on different
International Research Journal of Applied and Basic Sciences 214 Available online at www.irjabs.com ISSN 2251-838X / Vol, 8 (6): 692-696 Science Explorer Publications Evaluation of muscle activity on different
Repetition Maximum Continuum
 Parts of a Lifting Program Before putting weight on the bar, the athlete needs to know some of the basic terms used in weight training. Repetition or rep refers to the number of times you perform a movement
Parts of a Lifting Program Before putting weight on the bar, the athlete needs to know some of the basic terms used in weight training. Repetition or rep refers to the number of times you perform a movement
Discuss the training tradition and how it has influenced preparation for athletes.
 MOVEMENT BASED PHILOSOPHY AN APPROACH TO PROGRAM DESIGN LEARNING OBJECTIVES Discuss the training tradition and how it has influenced preparation for athletes. Introduce the key concepts behind movement
MOVEMENT BASED PHILOSOPHY AN APPROACH TO PROGRAM DESIGN LEARNING OBJECTIVES Discuss the training tradition and how it has influenced preparation for athletes. Introduce the key concepts behind movement
CSEP-Certified Certified Personal Trainer (CSEP-CPT) CPT) Musculoskeletal Prescription
 CSEP-Certified Certified Personal Trainer (CSEP-CPT) CPT) Musculoskeletal Prescription 1 Exercise Prescription for Improving Muscular Strength & Endurance Key Concepts: 4.17 4.18 2 Key Training Principles
CSEP-Certified Certified Personal Trainer (CSEP-CPT) CPT) Musculoskeletal Prescription 1 Exercise Prescription for Improving Muscular Strength & Endurance Key Concepts: 4.17 4.18 2 Key Training Principles
Strength and conditioning? Chapter 4 Training Techniques. Weight gain (24yr, 73kg, 177cm, takes 18% protein) Guidelines.
 Strength and conditioning? Chapter 4 Training Techniques Minimise the probability of injury Maximise performance Athletic Training Spring 2014 Jihong Park Guidelines Safety: environment, technique, nutrition
Strength and conditioning? Chapter 4 Training Techniques Minimise the probability of injury Maximise performance Athletic Training Spring 2014 Jihong Park Guidelines Safety: environment, technique, nutrition
ELECTROMYOGRAPHIC COMPARISON OF BARBELL DEADLIFT, HEX BAR ACCEPTED DEADLIFT AND HIP THRUST EXERCISES: A CROSS-OVER STUDY
 Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research Publish Ahead of Print DOI: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000001826 ELECTROMYOGRAPHIC COMPARISON OF BARBELL DEADLIFT, HEX BAR DEADLIFT AND HIP THRUST EXERCISES: A CROSS-OVER
Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research Publish Ahead of Print DOI: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000001826 ELECTROMYOGRAPHIC COMPARISON OF BARBELL DEADLIFT, HEX BAR DEADLIFT AND HIP THRUST EXERCISES: A CROSS-OVER
CSEP-Certified Certified Personal Trainer (CSEP-CPT) CPT) Musculoskeletal Fitness Theory
 CSEP-Certified Certified Personal Trainer (CSEP-CPT) CPT) Musculoskeletal Fitness Theory 1 Basic Anatomy Key Concepts: 3.23-3.25 3.25 2 Force & Levers 1 st class» seesaw» muscles that extend neck R F AF
CSEP-Certified Certified Personal Trainer (CSEP-CPT) CPT) Musculoskeletal Fitness Theory 1 Basic Anatomy Key Concepts: 3.23-3.25 3.25 2 Force & Levers 1 st class» seesaw» muscles that extend neck R F AF
Rugby is a physically demanding game with multiple
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE TRENDS in Sport Sciences 2016; 4(23): 185-191 ISSN 2299-9590 The differences in shoulder muscle activity between injured and uninjured rugby players during player- and bag-tackling PETR
ORIGINAL ARTICLE TRENDS in Sport Sciences 2016; 4(23): 185-191 ISSN 2299-9590 The differences in shoulder muscle activity between injured and uninjured rugby players during player- and bag-tackling PETR
Products: Deep Freeze Power In Motion Turbo Recovery Body Wash Gel
 Our line of products works within a synergistic and defined partnership. The unique balance focuses on injury prevention, pain management and total well-being. Deep Freeze is committed to making a difference
Our line of products works within a synergistic and defined partnership. The unique balance focuses on injury prevention, pain management and total well-being. Deep Freeze is committed to making a difference
CAN TRAINING IMPROVE YOUR ABILITY TO CO-CONTRACT? Jordan Yurchevich. St. Francis Xavier University. October 9, 2006
 CAN TRAINING IMPROVE YOUR ABILITY TO CO-CONTRACT? Jordan Yurchevich 200306793 St. Francis Xavier University October 9, 2006 1 Introduction The aim of the present study is to determine whether or not training
CAN TRAINING IMPROVE YOUR ABILITY TO CO-CONTRACT? Jordan Yurchevich 200306793 St. Francis Xavier University October 9, 2006 1 Introduction The aim of the present study is to determine whether or not training
Neither Stretching nor Postactivation Potentiation Affect Maximal Force and Rate of Force Production during Seven One-Minute Trials
 Neither Stretching nor Postactivation Potentiation Affect Maximal Force and Rate of Force Production during Seven One-Minute Trials David M. Bazett-Jones Faculty Sponsors: Jeffery M. McBride & M. R. McGuigan
Neither Stretching nor Postactivation Potentiation Affect Maximal Force and Rate of Force Production during Seven One-Minute Trials David M. Bazett-Jones Faculty Sponsors: Jeffery M. McBride & M. R. McGuigan
APF PowerPoint: Unit 1
 APF PowerPoint: Unit 1 BASIC DEFINITIONS Repetition one complete movement of an exercise. Repetition consists of concentric and eccentric muscle actions. Set group of repetitions performed continuously
APF PowerPoint: Unit 1 BASIC DEFINITIONS Repetition one complete movement of an exercise. Repetition consists of concentric and eccentric muscle actions. Set group of repetitions performed continuously
Understanding the program
 Live Fit Fat Loss Workshop 13 Understanding the program Theory The idea behind completing full-body workouts is that, in general, they are more energy-expensive compared to a typical body part split routine.
Live Fit Fat Loss Workshop 13 Understanding the program Theory The idea behind completing full-body workouts is that, in general, they are more energy-expensive compared to a typical body part split routine.
Chapter 8: Muscular Strength & Endurance. ACE Personal Trainer Manual Third Edition
 Chapter 8: Muscular Strength & Endurance ACE Personal Trainer Manual Third Edition Introduction Muscles are unique in their ability to relax, contract, and produce force. In addition, this metabolically
Chapter 8: Muscular Strength & Endurance ACE Personal Trainer Manual Third Edition Introduction Muscles are unique in their ability to relax, contract, and produce force. In addition, this metabolically
Mathias Method By Ryan Mathias Strength to Change the World
 Mathias Method By Ryan Mathias Strength to Change the World Level 4- Becoming Explosive This is a program for those who already have built a significant amount of strength and are ready to put that strength
Mathias Method By Ryan Mathias Strength to Change the World Level 4- Becoming Explosive This is a program for those who already have built a significant amount of strength and are ready to put that strength
Common injuries in athletes with impairment: do we need different prevention strategies in Paralympic athletes to Olympic athletes?
 Common injuries in athletes with impairment: do we need different prevention strategies in Paralympic athletes to Olympic athletes? Nick Webborn Clinical Professor (Sport & Exercise Medicine) Centre for
Common injuries in athletes with impairment: do we need different prevention strategies in Paralympic athletes to Olympic athletes? Nick Webborn Clinical Professor (Sport & Exercise Medicine) Centre for
CHAPTER 4: The musculo-skeletal system. Practice questions - text book pages QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS. Answers
 CHAPTER 4: The musculo-skeletal system Practice questions - text book pages 64-66 1) A prime mover of hip flexion is the: a. rectus femoris. b. Iliopsoas. c. vastus muscles. d. gluteus maximus. b. Key
CHAPTER 4: The musculo-skeletal system Practice questions - text book pages 64-66 1) A prime mover of hip flexion is the: a. rectus femoris. b. Iliopsoas. c. vastus muscles. d. gluteus maximus. b. Key
Physical Fitness Profiles Among National Powerlifters With Disabilities
 Jurnal Media Ilmu Keolahragaan Indonesia Volume 3. Edisi 1. Juli 2013. ISSN: 2088-6802 Artikel Penelitian http://journal.unnes.ac.id/nju/index.php/miki Physical Fitness Profiles Among National Powerlifters
Jurnal Media Ilmu Keolahragaan Indonesia Volume 3. Edisi 1. Juli 2013. ISSN: 2088-6802 Artikel Penelitian http://journal.unnes.ac.id/nju/index.php/miki Physical Fitness Profiles Among National Powerlifters
GOLFERS TEN PROGRAM 1. SELF STRETCHING OF THE SHOULDER CAPSULE
 GOLFERS TEN PROGRAM 1. SELF STRETCHING OF THE SHOULDER CAPSULE POSTERIOR CAPSULAR STRETCH Bring your arm across your chest toward the opposite shoulder. With the opposite arm grasp your arm at your elbow.
GOLFERS TEN PROGRAM 1. SELF STRETCHING OF THE SHOULDER CAPSULE POSTERIOR CAPSULAR STRETCH Bring your arm across your chest toward the opposite shoulder. With the opposite arm grasp your arm at your elbow.
6. Increased fat mass 2. Decreased anaerobic capacity
 The Importance of Resistance Training for the Aging Competitive Swimmer Peter Reaburn PhD Introduction Research has consistently shown that competitive swim performance decreases with increasing age. This
The Importance of Resistance Training for the Aging Competitive Swimmer Peter Reaburn PhD Introduction Research has consistently shown that competitive swim performance decreases with increasing age. This
DEVELOPING EXPLOSIVE POWER
 DEVELOPING EXPLOSIVE POWER Dr. Adam Storey Lead Strength & Conditioning Specialist for Athletics NZ OVERVIEW How Strong is Strong Enough? Strength spectrum & strength in a sporting context. Explosive Strength
DEVELOPING EXPLOSIVE POWER Dr. Adam Storey Lead Strength & Conditioning Specialist for Athletics NZ OVERVIEW How Strong is Strong Enough? Strength spectrum & strength in a sporting context. Explosive Strength
Increasing Explosive Power of the Shoulder in Volleyball Players
 National Strength & Conditioning Association Volume 25, Number 6, page 7 11 Increasing Explosive Power of the Shoulder in Volleyball Players Cedric Dupuis Claire Tourny-Chollet CETAPS, University of Sports
National Strength & Conditioning Association Volume 25, Number 6, page 7 11 Increasing Explosive Power of the Shoulder in Volleyball Players Cedric Dupuis Claire Tourny-Chollet CETAPS, University of Sports
chapter Exercise Technique for Alternative Modes and Nontraditional Implement Training
 chapter 16 Exercise Technique for Alternative Modes and Nontraditional Implement Training Chapter Objectives Understand the basic guidelines for performing resistance exercise with alternative modes and
chapter 16 Exercise Technique for Alternative Modes and Nontraditional Implement Training Chapter Objectives Understand the basic guidelines for performing resistance exercise with alternative modes and
Strength / Plate Loaded / Purestrength. Sport performance.
 Strength / Plate Loaded / Purestrength Sport performance. 162 163 STRENGTH Strength / Plate Loaded / Purestrength 164 165 STRENGTH Strength / Plate Loaded / Purestrength 166 STRENGTH Discover more about
Strength / Plate Loaded / Purestrength Sport performance. 162 163 STRENGTH Strength / Plate Loaded / Purestrength 164 165 STRENGTH Strength / Plate Loaded / Purestrength 166 STRENGTH Discover more about
ANALYSIS OF MUSCLE ACTIVITY DURING THE BENCH PRESS EXERCISE PERFORMED WITH THE PRE-ACTIVATION METHOD ON STABLE AND UNSTABLE SURFACES
 Pirauá, A.L.T. et al.: ANALYSIS OF MUSCLE ACTIVITY DURING THE BENCH... Kinesiology 49(2017)2:161-168 ANALYSIS OF MUSCLE ACTIVITY DURING THE BENCH PRESS EXERCISE PERFORMED WITH THE PRE-ACTIVATION METHOD
Pirauá, A.L.T. et al.: ANALYSIS OF MUSCLE ACTIVITY DURING THE BENCH... Kinesiology 49(2017)2:161-168 ANALYSIS OF MUSCLE ACTIVITY DURING THE BENCH PRESS EXERCISE PERFORMED WITH THE PRE-ACTIVATION METHOD
Strength Training for the Average Collegiate or H.S. Athlete: A Return to Push-Ups & Sit-Ups
 Strength Training for the Average Collegiate or H.S. Athlete: A Return to Push-Ups & Sit-Ups Tim Bacon October 2006 10 Problems with Traditional College Weight Training Programs 1. Too short, intensive
Strength Training for the Average Collegiate or H.S. Athlete: A Return to Push-Ups & Sit-Ups Tim Bacon October 2006 10 Problems with Traditional College Weight Training Programs 1. Too short, intensive
Effects of whole-body vibration applied to lower extremity muscles during decline bench press exercise
 J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact 2016; 16(3):204-210 Journal of Musculoskeletal and Neuronal Interactions Original Article Effects of whole-body vibration applied to lower extremity muscles during decline
J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact 2016; 16(3):204-210 Journal of Musculoskeletal and Neuronal Interactions Original Article Effects of whole-body vibration applied to lower extremity muscles during decline
Section III: Concept 11: Muscular Fitness
 Section III: Concept 11: Muscular Fitness ١ Health Benefits of Muscular Fitness Include muscular strength and ٢ endurance Promote many health benefits Avoiding back problems Reducing risks of injury Reducing
Section III: Concept 11: Muscular Fitness ١ Health Benefits of Muscular Fitness Include muscular strength and ٢ endurance Promote many health benefits Avoiding back problems Reducing risks of injury Reducing
GK Jane Division of Physical Education, University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa
 ISO-INERTIAL MEASUREMENT OF MUSCULAR STRENGTH: AN ASSESSMENT ALTERNATIVE GK Jane Division of Physical Education, University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa INTRODUCTION Success in many
ISO-INERTIAL MEASUREMENT OF MUSCULAR STRENGTH: AN ASSESSMENT ALTERNATIVE GK Jane Division of Physical Education, University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa INTRODUCTION Success in many
Swiss Ball Twists w/ Dumbell
 Swiss Ball Twists w/ Dumbell Starting Position: Lower back on swiss ball, feet facing forward, shoulder width apart. Movement: Hold dumbbell vertically with arms straight. Rotate through hips until the
Swiss Ball Twists w/ Dumbell Starting Position: Lower back on swiss ball, feet facing forward, shoulder width apart. Movement: Hold dumbbell vertically with arms straight. Rotate through hips until the
P3 Week One - M-W-F Workout Routine:
 P3 Week One - M-W-F Workout Routine: P3 Week One - M-W-F Workout Routine: Circuit Training Exercises Side Deltoid Raise w/ band Triceps Extensions Ball Pushups: Ball Squat: (hold dumbbells on your side
P3 Week One - M-W-F Workout Routine: P3 Week One - M-W-F Workout Routine: Circuit Training Exercises Side Deltoid Raise w/ band Triceps Extensions Ball Pushups: Ball Squat: (hold dumbbells on your side
TRAINING IN SPORTS. Key Points :
 TRAINING IN SPORTS Key Points : Strength Definition, Types and Methods of Improving Strength Isometric, Isotonic and Isokinetic. Endurance Definition, Types and Methods of Develop Endurance Continuous
TRAINING IN SPORTS Key Points : Strength Definition, Types and Methods of Improving Strength Isometric, Isotonic and Isokinetic. Endurance Definition, Types and Methods of Develop Endurance Continuous
The Golfers Ten Program. 1. Self Stretching of the Shoulder Capsule
 The Golfers Ten Program 1. Self Stretching of the Shoulder Capsule A. Posterior capsular stretch Bring your arm across your chest toward the opposite shoulder. With the opposite arm grasp your arm at your
The Golfers Ten Program 1. Self Stretching of the Shoulder Capsule A. Posterior capsular stretch Bring your arm across your chest toward the opposite shoulder. With the opposite arm grasp your arm at your
CANADIAN PHYSICAL PERFORMANCE EXCHANGE FITNESS STANDARD FOR TYPE 1 WILDLAND FIRE FIGHTERS (WFX-FIT) SIX WEEK TRAINING PROGRAM
 CANADIAN PHYSICAL PERFORMANCE EXCHANGE FITNESS STANDARD FOR TYPE 1 WILDLAND FIRE FIGHTERS () SIX WEEK TRAINING PROGRAM SIX WEEK TRAINING PROGRAM FOR THE TYPE 1 WILDLAND FIRE FIGHTER NATIONAL EXCHANGE FITNESS
CANADIAN PHYSICAL PERFORMANCE EXCHANGE FITNESS STANDARD FOR TYPE 1 WILDLAND FIRE FIGHTERS () SIX WEEK TRAINING PROGRAM SIX WEEK TRAINING PROGRAM FOR THE TYPE 1 WILDLAND FIRE FIGHTER NATIONAL EXCHANGE FITNESS
MUSCLE. Report. Volume 7 Issue 5. The latest Scientific Discoveries in the Fields of Resistance Exercise, Nutrition and Supplementation.
 MUSCLE Report Volume 7 Issue 5 The latest Scientific Discoveries in the Fields of Resistance Exercise, Nutrition and Supplementation. IEMG Muscle Report Volume 7 Issue 5 Are you training your muscles or
MUSCLE Report Volume 7 Issue 5 The latest Scientific Discoveries in the Fields of Resistance Exercise, Nutrition and Supplementation. IEMG Muscle Report Volume 7 Issue 5 Are you training your muscles or
Fitness Intro. Freshmen PE
 Fitness Intro Freshmen PE Physical Fitness Are you able to get through your day easily without tiring? Does your body respond quickly when it needs to? Are you mentally alert in class? Do you feel good
Fitness Intro Freshmen PE Physical Fitness Are you able to get through your day easily without tiring? Does your body respond quickly when it needs to? Are you mentally alert in class? Do you feel good
Original research papers
 Original research papers Pol. J. Sport Tourism 2017, 24, 139-144 139 KINETIC AND KINEMATIC CHARACTERISTICS AS THE BASIS FOR EVALUATING TAKE-OFF IN BACKWARD ACROBATIC JUMPS HENRYK KRÓL 1, MAŁGORZATA KLYSZCZ-MORCINIEC
Original research papers Pol. J. Sport Tourism 2017, 24, 139-144 139 KINETIC AND KINEMATIC CHARACTERISTICS AS THE BASIS FOR EVALUATING TAKE-OFF IN BACKWARD ACROBATIC JUMPS HENRYK KRÓL 1, MAŁGORZATA KLYSZCZ-MORCINIEC
THE GREAT EIGHT. Australian Institute of Fitness 1 / 13
 THE GREAT EIGHT Australian Institute of Fitness 1 / 13 ABOUT THE GREAT EIGHT Exercises that is! Eight GREAT exercises. By now you should have opened your Master Trainer elog Book (see Welcome section)
THE GREAT EIGHT Australian Institute of Fitness 1 / 13 ABOUT THE GREAT EIGHT Exercises that is! Eight GREAT exercises. By now you should have opened your Master Trainer elog Book (see Welcome section)
Fitness Intro. Freshmen PE
 Fitness Intro Freshmen PE Physical Fitness Are you able to get through your day easily without tiring? Does your body respond quickly when it needs to? Are you mentally alert in class? Do you feel good
Fitness Intro Freshmen PE Physical Fitness Are you able to get through your day easily without tiring? Does your body respond quickly when it needs to? Are you mentally alert in class? Do you feel good
2011 EliteSoccerPower.com
 Developing Power for Soccer By Mike Grafstein B.Ph.Ed, RMT, YCS As may or may not know soccer is now a game of power and speed and players of all ages need to train that way. With that in mind I have put
Developing Power for Soccer By Mike Grafstein B.Ph.Ed, RMT, YCS As may or may not know soccer is now a game of power and speed and players of all ages need to train that way. With that in mind I have put
Strength / PLATE LOADED/ PURESTRENGTH. Sport performance. STRENGTH
 Sport performance. 196 197 Express your strength. 198 199 Discover more about Purestrength www.technogym.com/purestrength 200 201 Purestrength BODY PRINT SYSTEM The special high-density upholstery filling
Sport performance. 196 197 Express your strength. 198 199 Discover more about Purestrength www.technogym.com/purestrength 200 201 Purestrength BODY PRINT SYSTEM The special high-density upholstery filling
Muscular Analysis of Upper Extremity Exercises McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved. 8-1
 Muscular Analysis of Upper Extremity Exercises 2007 McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved. 8-1 Muscular Analysis of Upper Extremity Exercises Upper extremity - often one of body's weakest areas
Muscular Analysis of Upper Extremity Exercises 2007 McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved. 8-1 Muscular Analysis of Upper Extremity Exercises Upper extremity - often one of body's weakest areas
Mathias Method By Ryan Mathias Strength to Change the World
 Mathias Method By Ryan Mathias Strength to Change the World Level 4- Becoming Explosive This is a program for those who already have built a significant amount of strength and are ready to put that strength
Mathias Method By Ryan Mathias Strength to Change the World Level 4- Becoming Explosive This is a program for those who already have built a significant amount of strength and are ready to put that strength
Lesson #3. Muscular Strength and Endurance
 Lesson #3 Muscular Strength and Endurance MILO OF CROTONA LEGENDARY USE OF THE OVERLOAD PRINCIPLE The Story of Milo This famous athlete increased his strength by lifting a small calf several times a week.
Lesson #3 Muscular Strength and Endurance MILO OF CROTONA LEGENDARY USE OF THE OVERLOAD PRINCIPLE The Story of Milo This famous athlete increased his strength by lifting a small calf several times a week.
Effect of Static Stretching or Foam Rolling on Hamstrings Range of Motion and Strength
 Southern Illinois University Carbondale OpenSIUC Research Papers Graduate School Summer 8-10-2017 Effect of Static Stretching or Foam Rolling on Hamstrings Range of Motion and Strength Grant Wiseman Southern
Southern Illinois University Carbondale OpenSIUC Research Papers Graduate School Summer 8-10-2017 Effect of Static Stretching or Foam Rolling on Hamstrings Range of Motion and Strength Grant Wiseman Southern
POWERLIFTING RULE INTERPRETATIONS
 19-1 POWERLIFTING RULE INTERPRETATIONS SECTION A - GENERAL RULES A-1. A-2. A-3. A-4. A-5. A-6. A-7. A-8. A-9. A-10. A-11. In cases not covered by these interpretations, USA Powerlifting Rules will govern.
19-1 POWERLIFTING RULE INTERPRETATIONS SECTION A - GENERAL RULES A-1. A-2. A-3. A-4. A-5. A-6. A-7. A-8. A-9. A-10. A-11. In cases not covered by these interpretations, USA Powerlifting Rules will govern.
Station 1 Push Ups (1 Minute) Age Record (year of birth) GIRLS 12 years years
 Station 1 Push Ups (1 Minute) 18 26 13 15 15 22 9 11 12 18 5 7 9 14 3 3 20 20 23 24 30 33 15 15 15 14 13 13 2. Start by lying flat on board with hands under chest 3. On Go, Push up to fully extend arms
Station 1 Push Ups (1 Minute) 18 26 13 15 15 22 9 11 12 18 5 7 9 14 3 3 20 20 23 24 30 33 15 15 15 14 13 13 2. Start by lying flat on board with hands under chest 3. On Go, Push up to fully extend arms
WTC I Term 2 Notes/Assessments
 WTC I Term 2 Notes/Assessments Muscle Identification The human body consists of many muscles and muscle groups. We will focus on a select few that are most prevalent when training. The muscular system
WTC I Term 2 Notes/Assessments Muscle Identification The human body consists of many muscles and muscle groups. We will focus on a select few that are most prevalent when training. The muscular system
Benefits of Weight bearing increased awareness of the involved side decreased fear improved symmetry regulation of muscle tone
 From the information we have gathered during our Evaluation, the Clinical Reasoning we used to identify key problem areas and the Goals Established with functional outcomes we now have enough information
From the information we have gathered during our Evaluation, the Clinical Reasoning we used to identify key problem areas and the Goals Established with functional outcomes we now have enough information
Modelling analysis and prediction of women javelin throw results in the years
 Original Modelling Paper analysis and prediction of sports results DOI: 10.5604/20831862.1189201 Biol. Sport 2015;32:345-350 Modelling analysis and prediction of women javelin results in the years 1946
Original Modelling Paper analysis and prediction of sports results DOI: 10.5604/20831862.1189201 Biol. Sport 2015;32:345-350 Modelling analysis and prediction of women javelin results in the years 1946
Advance Resistance Training for Health & Fitness Professionals
 s EDUCATION WORKSHOPS Advance Resistance Training for Health & Fitness Professionals with B.App.Sc (Physio), Dip.Ed (P.E.) CONTENTS Topic Page 1. Introduction 3 2. Muscle Physiology & Training Implications
s EDUCATION WORKSHOPS Advance Resistance Training for Health & Fitness Professionals with B.App.Sc (Physio), Dip.Ed (P.E.) CONTENTS Topic Page 1. Introduction 3 2. Muscle Physiology & Training Implications
Swimmers Scapular Re-Education Program
 Swimmers Scapular Re-Education Program INCORRECT ante tilt and anterior humerus CORRECT Power Square Position This muscle re-education program is designed to improve dynamic control of the shoulder blades
Swimmers Scapular Re-Education Program INCORRECT ante tilt and anterior humerus CORRECT Power Square Position This muscle re-education program is designed to improve dynamic control of the shoulder blades
EMG SIGNAL ANALYSIS OF SELECTED MUSCLES DURING SHOTS AND PASSES IN BASKETBALL
 9 Faculty of Physical Education and Physiotherapy, Opole University of Technology, Poland Paweł Pakosz EMG SIGNAL ANALYSIS OF SELECTED MUSCLES DURING SHOTS AND PASSES IN BASKETBALL ABSTRACT During testing,
9 Faculty of Physical Education and Physiotherapy, Opole University of Technology, Poland Paweł Pakosz EMG SIGNAL ANALYSIS OF SELECTED MUSCLES DURING SHOTS AND PASSES IN BASKETBALL ABSTRACT During testing,
Total Body Exercises for Volleyball
 Total Body Exercises for Volleyball By Dennis Jackson, CSCS Strength-and-Power-for-Volleyball.com You strength training should include total body exercises such as deadlifts and power cleans. Total body
Total Body Exercises for Volleyball By Dennis Jackson, CSCS Strength-and-Power-for-Volleyball.com You strength training should include total body exercises such as deadlifts and power cleans. Total body
BARBELL HIP THRUST. Eckert, RM 1 and Snarr, RL 1,2
 Eckert, RM and Snarr, RL. Barbell hip thrust. J Sport Human Perf 2014;2(2):1-9. DOI: 10.12922/jshp.0037.2014 1 SHORT REPORT BARBELL HIP THRUST OPEN ACCESS Eckert, RM 1 and Snarr, RL 1,2 1 School of Nutrition
Eckert, RM and Snarr, RL. Barbell hip thrust. J Sport Human Perf 2014;2(2):1-9. DOI: 10.12922/jshp.0037.2014 1 SHORT REPORT BARBELL HIP THRUST OPEN ACCESS Eckert, RM 1 and Snarr, RL 1,2 1 School of Nutrition
The Golf Swing Speed Challenge (103) - First 3 Weeks
 103 The Golf Swing Speed Challenge (103) - First 3 Weeks In the first three weeks of this elite program you're going to be predominantly doing two things 1. Improving your flexibility through a range of
103 The Golf Swing Speed Challenge (103) - First 3 Weeks In the first three weeks of this elite program you're going to be predominantly doing two things 1. Improving your flexibility through a range of
WEIGHT LIFTING PROGRESSION ACROMIOPLASTY WITH DISTAL CLAVICLE RESECTION, ROTATOR CUFF REPAIR (POST OPERATIVE)
 WEIGHT LIFTING PROGRESSION ACROMIOPLASTY WITH DISTAL CLAVICLE RESECTION, ROTATOR CUFF REPAIR (POST OPERATIVE) A. CONTRAINDICATED EXERCISES FOR PHASE I- (ILLUSTRATED BELOW) - Front Raises, lateral raises,
WEIGHT LIFTING PROGRESSION ACROMIOPLASTY WITH DISTAL CLAVICLE RESECTION, ROTATOR CUFF REPAIR (POST OPERATIVE) A. CONTRAINDICATED EXERCISES FOR PHASE I- (ILLUSTRATED BELOW) - Front Raises, lateral raises,
Upper Body Exercises
 Lesson Upper Body Exercises Arms & Shoulders By Carone Fitness Anterior (Front) Of Arm Although arms are sometimes focused on too much, they still are an important part of a balanced strength training
Lesson Upper Body Exercises Arms & Shoulders By Carone Fitness Anterior (Front) Of Arm Although arms are sometimes focused on too much, they still are an important part of a balanced strength training
STAR Research Journal
 STAR Research Journal Available online at www.starresearchjournal.com (Star International Journal) PHYSICAL EDUCATION Star. Phy. Edn. 04 (2013) EFFECT OF PLYOMETRIC AND CIRCUIT TRAINING ON LEG STRENGTH,
STAR Research Journal Available online at www.starresearchjournal.com (Star International Journal) PHYSICAL EDUCATION Star. Phy. Edn. 04 (2013) EFFECT OF PLYOMETRIC AND CIRCUIT TRAINING ON LEG STRENGTH,
What Factors Determine Vertical Jumping Height?
 What Factors Determine Vertical Jumping Height? L. Oddsson University College of Physical Education and Department of Physiology Ill, Karolinska Institute, Stockholm. Sweden. INTRODUCTION The ability to
What Factors Determine Vertical Jumping Height? L. Oddsson University College of Physical Education and Department of Physiology Ill, Karolinska Institute, Stockholm. Sweden. INTRODUCTION The ability to
BACHELOR THESIS. Muscle activity in m.pectoralis major during bench press variations in healthy young males. Adam Sahlén
 Bachelor's programme in Exercise Biomedicine, 180 credits BACHELOR THESIS Muscle activity in m.pectoralis major during bench press variations in healthy young males Adam Sahlén Bachelor thesis in Exercise
Bachelor's programme in Exercise Biomedicine, 180 credits BACHELOR THESIS Muscle activity in m.pectoralis major during bench press variations in healthy young males Adam Sahlén Bachelor thesis in Exercise
SITES OF FAILURE IN MUSCLE FATIGUE
 of 4 SITES OF FAILURE IN MUSCLE FATIGUE Li-Qun Zhang -4 and William Z. Rymer,2,4 Sensory Motor Performance Program, Rehabilitation Institute of Chicago Departments of 2 Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation,
of 4 SITES OF FAILURE IN MUSCLE FATIGUE Li-Qun Zhang -4 and William Z. Rymer,2,4 Sensory Motor Performance Program, Rehabilitation Institute of Chicago Departments of 2 Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation,
Core deconditioning Smoking Outpatient Phase 1 ROM Other
 whereby the ball does not stay properly centered in the shoulder socket during shoulder movement. This condition may be associated with impingement of the rotator cuff on the acromion bone and coracoacromial
whereby the ball does not stay properly centered in the shoulder socket during shoulder movement. This condition may be associated with impingement of the rotator cuff on the acromion bone and coracoacromial
Available online at Pelagia Research Library. European Journal of Experimental Biology, 2014, 4(1):
 Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Experimental Biology, 2014, 4(1):595-599 ISSN: 2248 9215 CODEN (USA): EJEBAU Investigation of effects of imagery training on changes
Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Experimental Biology, 2014, 4(1):595-599 ISSN: 2248 9215 CODEN (USA): EJEBAU Investigation of effects of imagery training on changes
Push-up exercises are very popular in upperbody DYNAMIC AND ELECTROMYOGRAPHICAL ANALYSIS IN VARIANTS OF PUSH-UP EXERCISE
 Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 2005, 19(1), 146 151 2005 National Strength & Conditioning Association DYNAMIC AND ELECTROMYOGRAPHICAL ANALYSIS IN VARIANTS OF PUSH-UP EXERCISE MARINA K.
Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 2005, 19(1), 146 151 2005 National Strength & Conditioning Association DYNAMIC AND ELECTROMYOGRAPHICAL ANALYSIS IN VARIANTS OF PUSH-UP EXERCISE MARINA K.
