Acute effect of resistance exercise performed at different intensities on urine loss in older women
|
|
|
- Mitchell Campbell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 original paper Acute effect of resistance exercise performed at different intensities on urine loss in older women doi: Enaiane Cristina Menezes 1, Janeisa Franck Virtuoso 2, André Luiz Demantova Gurjão 3, Giovana Zarpellon Mazo 1 1 Santa Catarina State University, Florianópolis, SC, Brazil 2 Federal University of Santa Catarina, Araranguá, SC, Brazil 3 Federal University of São Francisco Valley, Petrolina, PE, Brazil Physiotherapy Quarterly (formerly Fizjoterapia) 2018, 26 (2), University School of Physical Education in Wrocław Abstract Introduction. To evaluate the acute effect of resistance exercise performed at different intensities (moderate and vigorous) on urine loss in older women with mixed and stress urinary incontinence. Methods. The total of 16 older women with urinary incontinence underwent 2 sessions of resistance exercises involving different muscle groups. In a balanced crossover design, 1 of the 2 exercise intensities (12 or 6 repetitions maximum, RM) was applied in each session. The pad test was used to assess urine loss in the 2 sessions, with a weight increase of 2 g as the criterion. Differences in the pad test results between the sessions were compared with the use of the Wilcoxon test. Results. The mean pad weight was 0.69 ± 0.94 g at the intensity of 12RM and 0.50 ± 0.53 g at 6RM. In accordance with the cut-off adopted (2 g), only 2 of the 16 women lost urine. No significant difference in the pad test results (p = 0.975) was observed between the 2 resistance exercise intensities. Conclusions. Resistance exercise performed at different intensities (moderate and vigorous) did not cause urine loss in older women with urinary incontinence. Key words: older adults, urinary incontinence, weight lifting Introduction Leakage of urine during physical activities, particularly high-impact exercise, has been reported in the literature [1, 2]. The prevalence of urine loss can reach up to 67% among young athletes, who report to leak urine during their activities [1]. This fact might be explained by pelvic floor muscle weakness in situations of increased intra-abdominal pressure [3]. Furthermore, Shaw et al. [4] reported a progressive increase in intra-abdominal pressure with more intense exercises. According to Da Roza [5], this type of exercise requires an increase in the contraction strength of the pelvic floor muscles to close the urogenital hiatus and to maintain urinary continence. In an attempt to understand what occurs in pelvic floor muscles immediately after resistance (squatting) or strenuous aerobic exercise (jumping jacks, vertical jumps, and running up and down the stairs), Ree et al. [6] observed that the maximal voluntary contraction pressure was reduced by 24.4% immediately after exercise in women with stress urinary incontinence (UI). Furthermore, exercise could stretch and overload the pelvic floor muscles [3]. According to Nygaard et al. [7], the impact of physical exercise on UI is not well established in the literature and there might be risk factors or protective factors of this disorder. Knowledge of the effects of exercise on urine loss is even more sparse with reference to the elderly female population. Although it is known that UI is associated with decreased mobility [8] and that older women performing physical exercise have better pelvic floor muscle function than their sedentary peers [9], it is necessary to determine whether older women with UI lose urine when performing resistance exercise at different intensities (moderate and vigorous). Therefore, the objective of this study was to evaluate the acute effect of resistance exercise performed at different intensities (moderate and vigorous) on urine loss in older women with mixed and stress UI. Subjects and methods Study design and participants This was a crossover study in which 22 older women ( 60 years old) living in the metropolitan region of Florianópolis, SC, Brazil, were recruited intentionally. The criterion of inclusion was the presence of stress and/or mixed UI (urine loss at least once a month). Older women who only had urge incontinence or pelvic organ prolapse and who withdrew from the intervention because of external factors (travel and other social commitments) were excluded. The final sample consisted of 16 participants. Instruments and data collection The International Continence Society defines UI as any involuntary loss of urine [10]. Thus, the examined women were asked the following question: During the past year, did you lose urine (unintentionally into your panties) at least once a month? If affirmative, the presence of UI symptoms was identified and the participants were interviewed to determine the type and frequency of urine loss. Correspondence address: Enaiane Cristina Menezes, Universidade do Estado de Santa Catarina Centro de Ciências da Saúde e do Esporte Laboratório de Gerontologia, Rua Pascoal Simone, 358, Coqueiros, Florianópolis, SC, Brazil, enaianemenezes@gmail.com Received: Accepted: Citation: Menezes EC, Virtuoso JF, Demantova Gurjão AL, Mazo GZ. Acute effect of resistance exercise performed at different intensities on urine loss in older women. Physiotherapy Quarterly. 2018;26(2):23 27; doi:
2 E.C. Menezes, J.F. Virtuoso, A.L. Demantova Gurjão, G.Z. Mazo Physiotherapy Quarterly (formerly Fizjoterapia) 2018, 26 (2) The type of UI was verified by asking the following questions: (a) Do you lose urine on coughing, sneezing, exercising or lifting? (b) Do you lose urine before reaching the toilet after feeling a strong urge to urinate or without noticing? An affirmative answer to question (a) was defined as stress UI and to question (b) as urge UI. Mixed UI was determined in cases of an affirmative answer to both questions. For the participants characterization, sociodemographic data (age, marital status, education level, and current occupation) were obtained by interview. The pad test was used to assess urine loss during resistance exercises. Each pad was weighed on precision scales before use and placed in the perineal region near the external urethral meatus. The participants were then asked to drink 500 ml of water and to rest for 30 minutes. After this period, the subjects underwent the resistance exercise session. At the end of exercise, the pad was removed and weighed again. The difference between the initial and final weight of 2 g was defined as urine loss during exercise [11]. On the day of the pad test application, the women were asked not to consume certain foods, such as citric fruit, caffeine, or tea. Experimental design Figure 1 shows the experimental protocol, which was divided into 7 steps: (1) Familiarization: The objective of this step was to familiarize the participants with the execution of the range of motion, breathing, and adequate pace of movement of each exercise. A metronome set at the speed of 34 bpm was used to control the pace of movement. The participants were asked to complete one phase of the exercise (concentric or eccentric) at each metronome beep. With respect to breathing, the women were instructed to inspire during the eccentric phase and expire during the concentric phase of the exercise. This step had a duration of 2 4 sessions. (2) Determination of load reproducibility at 12RM (moderate intensity): Repetition maximum (RM) tests were performed to define the loads of each participant for the different resistance exercises (fly, horizontal leg press, lat pull down, adductor machine, triceps pulley, and biceps pulley) in the target zone of 12RM, in accordance with Gurjão et al. [12]. For the target zone of 12RM, the participants were asked to perform the maximum number of repetitions possible with a load subjectively defined by the researcher (trial and error). If the number of repetitions exceeded 15RM, 1 kg was added for each 2 excess repetitions. If the number of repetitions was less than 10RM, the load was adjusted by trial and error. During the test, the maximum of 2 attempts of load definition were made for each exercise, with a resting interval of 10 minutes between the attempts. The participants were asked to perform the repetitions at the speed of 2 seconds for the concentric phase and 2 seconds for the eccentric phase, using a metronome. The tests were repeated after a minimum period of 48 hours, which allowed to avoid errors in the definition of training loads and to verify reproducibility. For the exercises performed at the intensity of 12RM, the intra-class correlation coefficients (ICC) were higher than 0.90 (Table 1). This step had a duration of 2 4 sessions. (3) Determination of load reproducibility at 6RM (vigorous intensity): This step had the same objective and used the same procedures as those adopted for the target zone of 12RM. The difference in the definition of training loads in the target zone of 6RM was that if the number of repetitions exceeded 10RM, 1 kg was added for each 2 excess repetitions. The ICC values were higher than 0.70 (Table 1). This step had a duration of 2 4 sessions. (4) Randomization of the participants: Before the interventions, the women participating in the study were ran- Exercise Table 1. Intra-class correlation coefficients (ICC) for load reproducibility ICC Fly 12RM Leg press 12RM Lat pull down 12RM Adductor 12RM Triceps 12RM Biceps 12RM Fly 6RM Leg press 6RM Lat pull down 6RM Adductor 6RM Triceps 6RM Biceps 6RM RM repetition maximum 24 F familiarization, RM repetition maximum, D12RM/RP12RM determination and reproducibility of the 12 RM load, D6RM/RP6RM determination and reproducibility of the 6RM load, R randomization, In1 intervention 1, W washout period (crossover design), In2 intervention 2 Figure 1. Steps of the experimental protocol
3 Physiotherapy Quarterly (formerly Fizjoterapia) 2018, 26 (2) E.C. Menezes, J.F. Virtuoso, A.L. Demantova Gurjão, G.Z. Mazo domized with regard to the intensity of resistance exercise, i.e., if a subject was randomized to the vigorous intensity (6RM), her first intervention was performed at this intensity and the second at the moderate intensity (12RM) and vice versa. (5) Intervention 1: The objective of this step was to evaluate urine loss (pad test) of the participants during the resistance exercise session (acute effect) in accordance with the intensity (12RM or 6RM) selected for the first intervention. This step had a duration of 1 session. For the moderate intensity, the participants performed 3 sets in the zone of 12RM with the load defined in the test, with a resting interval of 60 seconds between the sets and the speed of 2 seconds for the concentric phase and 2 seconds for the eccentric phase. For the vigorous intensity, the women performed 3 sets in the zone of 6RM with the load defined in the test, with a resting interval of 60 seconds between the sets and the speed of 2 seconds for the concentric phase and 2 seconds for the eccentric phase. The resistance exercises were performed in the following sequence: fly, horizontal leg press, lat pull down, adductor machine, triceps pulley, biceps pulley, and abdominal crunch. The adequate loads defined in steps 2 and 3 allowed fatigue (technical failure) to occur close to the target zone. Abdominal crunch was the only exercise not applied in steps 2 and 3. For both intensities, 3 sets of 10RM without loads were performed. This step had a duration of 1 session. (6) Washout period (crossover design): The objective of this step was to avoid a carryover effect in which the first session of resistance exercise interferes with the second session. A washout period of 4 7 days between one intervention and the other, performed at different intensities (12RM or 6RM), was adopted. (7) Intervention 2: This step had the same objective and used the same procedures as those applied in intervention 1, except that the participants performed the resistance exercise session with a different intensity (12RM or 6RM) than in intervention 1. This step had a duration of 1 session. The participants were recruited in accordance with the inclusion criteria by an external researcher. The researcher responsible for the load determinations and training sessions was unaware of the severity of urine loss symptoms. Data analysis Santa Catarina State University, under protocol number The study was registered in the Brazilian Registry of Clinical Trials UTN: U Informed consent Informed consent has been obtained from all individuals included in this study. Results The mean age of the participants (n = 16) was ± 6.45 years. Regarding sociodemographic data, 37.5% (n = 6) of the women had complete elementary education, 43.8% (n = 7) were married, and 68.8% (n = 11) were retired. Mixed UI was present in 87.5% (n = 14) of the women and stress UI in 12.5% (n = 2). The mean number of sessions in the process of the study (from familiarization to intervention 2) was ± As can be seen in Table 2, a significant difference between the exercise intensities (12RM and 6RM) performed by the older women with UI was observed for all resistance exercises. The mean urine loss (pad test result) during the exercise session was 0.69 ± 0.94 g for the moderate intensity (12RM) and 0.50 ± 0.53 g for the vigorous intensity (6RM). With the consideration of the cut-off adopted (2 g), among the 16 older women studied, only 1 lost urine at the intensity of 12RM (4.09 g) and another at the intensity of 6RM Table 2. Comparison of loads between different intensities (12RM and 6RM) of resistance exercise (n = 16) Exercise 12RM Load 6RM p value Fly ± ± 3.55 < Leg press ± ± 7.44 < Lat pull down ± ± 5.09 < Adductor ± ± 4.78 < Triceps ± ± 5.11 < Biceps ± ± 3.71 < Values are presented as mean ± standard deviation RM repetition maximum The data were stored and analysed with the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS, IBM), version The categorical variables are reported as simple frequency and percentage, and measures of position and dispersion were used for numerical variables. The distribution of the data was verified by the Shapiro-Wilk test. The ICC was used to verify the test-retest reproducibility of the loads applied at the intensities of 12RM and 6RM. For inferential analysis, the Wilcoxon test allowed to evaluate differences in the pad test results between the 12RM and 6RM intensities. The paired t-test was used to verify differences between the loads applied at the intensities of 12RM and 6RM. The level of significance of p < 0.05 was adopted for all tests. Ethical approval The research related to human use has been complied with Resolution 466/2012 of the National Health Council, has followed the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki, and has been approved by the Ethics in Research Committee of the ULA upper limit of agreement; LLA lower limit of agreement Figure 2. Pad test results for the intensities of 12RM and 6RM (n = 16) 25
4 E.C. Menezes, J.F. Virtuoso, A.L. Demantova Gurjão, G.Z. Mazo Physiotherapy Quarterly (formerly Fizjoterapia) 2018, 26 (2) 26 Z Wilcoxon test; p level of significance Figure 3. Comparison of urine loss at different exercise intensities (n = 16) (2.20 g). In addition, Figure 2 illustrates the agreement between pad weights at the 2 exercise intensities. No significant difference (p = 0.486) in mean pad weights was observed at the exercise intensities tested (Figure 3), thus proving the null hypothesis of this experiment that resistance exercise at different intensities does not cause urine loss in older women with UI. Discussion In the presented study, urine loss during resistance exercise was observed in only 2 older women with UI (1 at the intensity of 12RM and 1 at the intensity of 6RM). Although we did not use a vaginal transducer to measure intra-abdominal pressure during exercise at different intensities, these findings suggest that resistance exercise provides indirect protection, preventing urine loss in women with UI. The impact of physical exercise on the pelvic floor has been described as a risk factor for the development of UI in research on the prevalence of urine loss in female athletes [1, 2, 13]. In a study of Da Roza et al. [13], 72.7% of female trampolinists reported urine loss during exercise. Ree et al. [6], submitting women to resistance and strenuous aerobic exercise, observed the mean urine loss in the pad test of 3.8 g. Scientific evidence of the impact of different exercise intensities is needed for the population of older women because UI is a multifactorial phenomenon and physical exercise remains a behavioural and modifiable factor of this condition [14]. Stress UI, a disorder affecting all older women of this study, occurs in situations of increased intra-abdominal pressure [10]. According to Shaw et al. [4], the intra-abdominal pressure rises with increasing intensity of the activity; for example, walking at an inclination of 7% results in an intra-abdominal pressure of 35 cm H 2 O compared with 66.5 cm H 2 O for running and 41.6 cm H 2 O for cycling. In this case, strenuous exercise can lead to overload and weakening of the pelvic floor muscles [3], as well as muscle fatigue immediately after the activity [6]. In addition to an increase of intra-abdominal pressure in certain physical activities, this rise can also be caused by obesity [15]. In this respect, waist circumference has been shown to be an important risk factor for the development of UI [8, 16]. Intervention studies have demonstrated a decrease of up to 47% in episodes of urine loss with a reduction in body weight [17]. This discussion on the increase in intra-abdominal pressure is in accordance with the theoretical model proposed by Nygaard et al. [7], in which exercise can affect the pelvic floor differently, acting on this structure in a bidirectional manner (positive and negative). Thus, the benefits of exercise or physical activity on the pelvic floor are limited. However, these authors stated that the activities could reduce body weight and increase muscle strength, and in this way contribute to the reduction of UI symptoms [7]. In the elderly population, resistance exercise has been reported to be beneficial for physical [18, 19] and psychological health [20], as well as to reduce physical disabilities [21]. High-intensity exercises (> 70% 1RM) lead to greater gains in muscle strength [22] and bone mass in older adults [18]. In the present study, lower mean pad weights during exercise were observed for the higher intensity (6RM). In addition to the acute effect on urine loss, some clinical trials [23] applying a 3-month intervention program consisting of exercises to strengthen the pelvic floor, lower limb, abdominal muscles, latissimus dorsi, and rhomboid muscles demonstrated significant improvement of UI, reducing the frequency of urine loss and curing these symptoms. Another important aspect is that UI not only impacts on the social life of older women [24] but also is related to lower handgrip strength and slower gait speed [25]. Taken together, the findings suggest that resistance exercise could be an accessible tool to improve the symptoms of urine loss, as well as other physical aspects relevant to the health of older women. Limitations Physical exercise is known to cause an increase in intraabdominal pressure. However, this study did not apply vaginal transducers to measure the number of pressure peaks caused by the different exercises in the sessions. In addition, the use of medications such as diuretics and sedatives was not controlled in this study. Conclusions In the present study, resistance exercise performed at different intensities (moderate and vigorous) did not cause urine loss in most of the older women with UI. Although resistance exercise can increase intra-abdominal pressure as documented in the health literature, women with UI in the presented study did not suffer from acute effects of increased intra-abdominal pressure in the pelvic floor caused by exercise. Further research should investigate the intra-abdominal pressure that resistance exercise can exert on the structures of the pelvic floor in older women using devices such as vaginal transducers. In addition, experimental designs exploring the long-term effects of resistance exercise in the elderly female population with UI are needed. Disclosure statement No author has any financial interest or received any financial benefit from this research. Conflict of interest The authors state no conflict of interest.
5 Physiotherapy Quarterly (formerly Fizjoterapia) 2018, 26 (2) E.C. Menezes, J.F. Virtuoso, A.L. Demantova Gurjão, G.Z. Mazo References 1. Nygaard IE, Thompson FL, Svengalis SL, Albright JP. Urinary incontinence in elite nulliparous athletes. Obstet Gynecol. 1994;84(2): ; doi: / (95) Thyssen HH, Clevin L, Olesen S, Lose G. Urinary incontinence in elite female athletes and dancers. Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct. 2002;13(1):15 17; doi: /s Bø K. Urinary incontinence, pelvic floor dysfunction, exercise and sport. Sports Med. 2004;34(7): ; doi: / Shaw JM, Hamad NM, Coleman TJ, Egger MJ, Hsu Y, Hitchcock R, et al. Intra-abdominal pressures during activity in women using an intra-vaginal pressure transducer. J Sports Sci. 2014;32(12): ; doi: / Da Roza T. Urinary incontinence in young nulliparous women: the effects of different levels of physical activity (thesis). Porto: Universidade do Porto; Ree ML, Nygaard I, Bø K. Muscular fatigue in the pelvic floor muscles after strenuous physical activity. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2007;86(7): ; doi: / Nygaard I, Shaw J, Egger MJ. Exploring the association between lifetime physical activity and pelvic floor disorders: study and design challenges. Contemp Clin Trials. 2012;33(4): ; doi: /j.cct Bresee C, Dubina ED, Khan AA, Sevilla C, Grant D, Eilber KS, et al. Prevalence and correlates of urinary incontinence among older community-dwelling women. Female Pelvic Med Reconstr Surg. 2014;20(6): ; doi: /SPV Virtuoso JF, Mazo GZ, Menezes EC. Urinary incontinence and perineal muscle function in physically active and sedentary elderly women. Braz J Phys Ther. 2011;15(4): ; doi: /S Haylen BT, de Ridder D, Freeman RM, Swift SE, Berghmans B, Lee J, et al. An International Urogynecological Association (IUGA)/International Continence Society (ICS) joint report on the terminology for female pelvic floor dysfunction. Neurourol Urodyn. 2010;29:4 20; doi: /nau Ghoniem G, Stanford E, Kenton K, Achtari C, Goldberg R, Mascarenhas T, et al. Evaluation and outcome measures in the treatment of female urinary stress incontinence: International Urogynecological Association (IUGA) guidelines for research and clinical practice. Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct. 2008;19(1):5 33; doi: / s Gurjão AL, Gobbi LT, Carneiro NH, Gonçalves R, Ferreira de Moura R, Cyrino ES, et al. Effect of strength training on rate of force development in older women. Res Q Exerc Sport. 2012;83(2): ; doi: / Da Roza T, Brandão S, Mascarenhas T, Jorge RN, Duarte JA. Volume of training and the ranking level are associated with the leakage of urine in young female trampolinists. Clin J Sport Med. 2015;25(3): ; doi: /JSM Grewar H, McLean L. The integrated continence system: a manual therapy approach to the treatment of stress urinary incontinence. Man Ther. 2008;13(5): ; doi: /j.math Dursun M, Otunctemur A, Ozbek E, Sahin S, Besiroglu H, Koklu I. Stress urinary incontinence and visceral adipose index: a new risk parameter. Int Urol Nephrol. 2014;46(12): ; doi: /s Devore EE, Minassian VA, Grodstein F. Factors associated with persistent urinary incontinence. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2013;209(2):145.e1 145.e6; doi: /j. ajog Wing RR, West DS, Grady D, Creasman JM, Richter HE, Myers D, et al. Effect of weight loss on urinary incontinence in overweight and obese women: results at 12 and 18 months. J Urol. 2010;184(3): ; doi: /j.juro Karabulut M, Bemben DA, Sherk VD, Anderson MA, Abe T, Bemben MG. Effects of high-intensity resistance training and low-intensity resistance training with vascular restriction on bone markers in older men. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2011;111(8): ; doi: /s Cadore EL, Pinto RS, Bottaro M, Izquierdo M. Strength and endurance training prescription in healthy and frail elderly. Aging Dis. 2014;5(3): ; doi: / AD Singh NA, Stavrinos TM, Scarbek Y, Galambos G, Liber C, Fiatarone Singh MA. A randomized controlled trial of high versus low intensity weight training versus general practitioner care for clinical depression in older adults. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2005;60(6): ; doi: /gerona/ Liu C, Latham N. Can progressive resistance strength training reduce physical disability in older adults? A meta-analysis study. Disabil Rehabil. 2011;33(2):87 97; doi: / Raymond MJ, Bramley-Tzerefos RE, Jeffs KJ, Winter A, Holland AE. Systematic review of high-intensity progressive resistance strength training of the lower limb compared with other intensities of strength training in older adults. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2013;94(8): ; doi: /j.apmr Kim H, Yoshida H, Suzuki T. The effects of multidimensional exercise treatment on community-dwelling elderly Japanese women with stress, urge, and mixed urinary incontinence: a randomized controlled trial. Int J Nurs Stud. 2011;48(10): ; doi: /j.ijnurstu Elbiss MH, Osman N, Hammad FT. Social impact and healthcare-seeking behavior among women with urinary incontinence in the United Arab Emirates. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2013;122(2): ; doi: /j.ijgo Kim H, Yoshida H, Hu X, Saito K, Yoshida Y, Kim M, et al. Association between self-reported urinary incontinence and musculoskeletal conditions in community-dwelling elderly women: a cross-sectional study. Neurourol Urodyn. 2015;34(4): ; doi: /nau
Prevalence of Stress Urinary Incontinence in Elite Female Endurance Athletes
 Journal of Human Kinetics volume 44/2014, 91-96 DOI: 10.2478/hukin-2014-0114 91 Section II Exercise Physiology & Sports Medicine Prevalence of Stress Urinary Incontinence in Elite Female Endurance Athletes
Journal of Human Kinetics volume 44/2014, 91-96 DOI: 10.2478/hukin-2014-0114 91 Section II Exercise Physiology & Sports Medicine Prevalence of Stress Urinary Incontinence in Elite Female Endurance Athletes
Using Physiotherapy to Manage Urinary Incontinence in Women
 Using Physiotherapy to Manage Urinary Incontinence in Women Bladder control problems are common, and affect people of all ages, genders and backgrounds. These problems are referred to as urinary incontinence
Using Physiotherapy to Manage Urinary Incontinence in Women Bladder control problems are common, and affect people of all ages, genders and backgrounds. These problems are referred to as urinary incontinence
Risks and Considerations Exercising with Pelvic Floor Dysfunction
 Risks and Considerations Exercising with Pelvic Floor Dysfunction Maeve Whelan MSc SMISCP Specialist Chartered Physiotherapist Milltown Physiotherapy Acknowledgement Taryn Hallam PT THE PROBLEM 1 in 7
Risks and Considerations Exercising with Pelvic Floor Dysfunction Maeve Whelan MSc SMISCP Specialist Chartered Physiotherapist Milltown Physiotherapy Acknowledgement Taryn Hallam PT THE PROBLEM 1 in 7
CONSERVATIVE MANAGEMENT OF URINARY INCONTINENCE IN WOMEN. Riette Vosloo Physiotherapist in Women s s Health
 CONSERVATIVE MANAGEMENT OF URINARY INCONTINENCE IN WOMEN Riette Vosloo Physiotherapist in Women s s Health CONSERVATIVE TREATMENT Any therapy that does not involve Pharmacologic intervention or Surgical
CONSERVATIVE MANAGEMENT OF URINARY INCONTINENCE IN WOMEN Riette Vosloo Physiotherapist in Women s s Health CONSERVATIVE TREATMENT Any therapy that does not involve Pharmacologic intervention or Surgical
The development of a questionnaire to measure the severity of symptoms and the quality of life before and after surgery for stress incontinence
 BJOG: an International Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology November 2003, Vol. 110, pp. 983 988 The development of a questionnaire to measure the severity of symptoms and the quality of life before and
BJOG: an International Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology November 2003, Vol. 110, pp. 983 988 The development of a questionnaire to measure the severity of symptoms and the quality of life before and
Promoting pelvic floor safe exercise
 How to find out more Promoting safe exercise To find out more visit www.continence.org.nz or call 0800 650 659. You will find: further information about the, including how to identify and exercise these
How to find out more Promoting safe exercise To find out more visit www.continence.org.nz or call 0800 650 659. You will find: further information about the, including how to identify and exercise these
This file was dowloaded from the institutional repository Brage NIH - brage.bibsys.no/nih
 This file was dowloaded from the institutional repository Brage NIH - brage.bibsys.no/nih Roza, T. D., Araujo, M. P., Viana, R., Viana, S., Jorge, R. N., Bø, K., Mascarenhas, T. (2012). Pelvic floor muscle
This file was dowloaded from the institutional repository Brage NIH - brage.bibsys.no/nih Roza, T. D., Araujo, M. P., Viana, R., Viana, S., Jorge, R. N., Bø, K., Mascarenhas, T. (2012). Pelvic floor muscle
Look Good Feel Good. after pregnancy. Physiotherapy advice and exercises for new mums
 Look Good Feel Good after pregnancy Physiotherapy advice and exercises for new mums How to exercise after pregnancy with physiotherapy Bowel Tail Bone Uterus Bladder Pubic Bone Pelvic Floor Muscles Urethra
Look Good Feel Good after pregnancy Physiotherapy advice and exercises for new mums How to exercise after pregnancy with physiotherapy Bowel Tail Bone Uterus Bladder Pubic Bone Pelvic Floor Muscles Urethra
IMPROVING URINARY INCONTINENCE
 IMPROVING URINARY INCONTINENCE INFORMATION FOR OLDER ADULTS, FAMILIES, AND CAREGIVERS READ THIS PAMPHLET TO LEARN: What Urinary Incontinence is. How to Manage Urinary Incontinence. What Pelvic Floor Exercises
IMPROVING URINARY INCONTINENCE INFORMATION FOR OLDER ADULTS, FAMILIES, AND CAREGIVERS READ THIS PAMPHLET TO LEARN: What Urinary Incontinence is. How to Manage Urinary Incontinence. What Pelvic Floor Exercises
Treatment Outcomes of Tension-free Vaginal Tape Insertion
 Are the Treatment Outcomes of Tension-free Vaginal Tape Insertion the Same for Patients with Stress Urinary Incontinence with or without Intrinsic Sphincter Deficiency? A Retrospective Study in Hong Kong
Are the Treatment Outcomes of Tension-free Vaginal Tape Insertion the Same for Patients with Stress Urinary Incontinence with or without Intrinsic Sphincter Deficiency? A Retrospective Study in Hong Kong
Who s in Charge of your Exercise? You or Your Pelvic Floor?
 Who s in Charge of your Exercise? You or Your Pelvic Floor? Ingrid Nygaard, MD, MS Professor University of Utah Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Exercise is good for you. Factors Considered At
Who s in Charge of your Exercise? You or Your Pelvic Floor? Ingrid Nygaard, MD, MS Professor University of Utah Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Exercise is good for you. Factors Considered At
Promoting pelvic floor safe exercise
 Promoting pelvic floor safe exercise Did you know that almost every exercise your client does affects their pelvic floor? Some exercises can actually harm these muscles, leading to bladder or bowel control
Promoting pelvic floor safe exercise Did you know that almost every exercise your client does affects their pelvic floor? Some exercises can actually harm these muscles, leading to bladder or bowel control
Toning your pelvic floor WELCOME
 Toning your pelvic floor WELCOME Introductions Amelia Samuels, Physiotherapist, Active Rehabilitation Physiotherapy Supporting the Continence Foundation of Australia Continence Foundation of Australia
Toning your pelvic floor WELCOME Introductions Amelia Samuels, Physiotherapist, Active Rehabilitation Physiotherapy Supporting the Continence Foundation of Australia Continence Foundation of Australia
Northwest Rehabilitation Associates, Inc.
 Pelvic Health Patient Intake Form Name: Date: Please answer the following questions as honestly and thoroughly as you can. Your responses will help us better understand your condition and provide the best
Pelvic Health Patient Intake Form Name: Date: Please answer the following questions as honestly and thoroughly as you can. Your responses will help us better understand your condition and provide the best
Pelvic Floor Insufficiency
 Pelvic Floor Insufficiency JEANET TE BURNEY, PT, MSPT, CMPT, RYT BOULDER COMMUNITY HEALTH OUTPATIENT REHABILITATION SERVICES 303-415-4400 Objectives Review the function of the pelvic floor muscles Discuss
Pelvic Floor Insufficiency JEANET TE BURNEY, PT, MSPT, CMPT, RYT BOULDER COMMUNITY HEALTH OUTPATIENT REHABILITATION SERVICES 303-415-4400 Objectives Review the function of the pelvic floor muscles Discuss
leisure or sport skills living activities and other activities with vigor Ø Physical fitness: ability of the body to respond to physical demands
 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Ø Discuss benefits and guidelines of physical activity and exercise Ø Explain the components of health-related fitness Ø Explain how to improve health through moderate physical activity
LEARNING OBJECTIVES Ø Discuss benefits and guidelines of physical activity and exercise Ø Explain the components of health-related fitness Ø Explain how to improve health through moderate physical activity
Comparison of pelvic floor muscle strength in competition-level athletes and untrained women
 Comparison of pelvic floor muscle strength in competition-level athletes and untrained women Ingunn Ludviksdottir 1, Hildur Hardardottir 2,3, Thorgerdur Sigurdardottir 2,4, Gudmundur F. Ulfarsson 5 SUMMARY
Comparison of pelvic floor muscle strength in competition-level athletes and untrained women Ingunn Ludviksdottir 1, Hildur Hardardottir 2,3, Thorgerdur Sigurdardottir 2,4, Gudmundur F. Ulfarsson 5 SUMMARY
INCONTINENCE. Continence and Pelvic Floor Rehabilitation TYPES OF INCONTINENCE STRESS INCONTINENCE STRESS INCONTINENCE STRESS INCONTINENCE 11/08/2015
 INCONTINENCE Continence and Pelvic Floor Rehabilitation Dr Irmina Nahon PhD Pelvic Floor Physiotherapist www.nahonpfed.com.au Defined as the accidental and inappropriate passage of urine or faeces (ICI
INCONTINENCE Continence and Pelvic Floor Rehabilitation Dr Irmina Nahon PhD Pelvic Floor Physiotherapist www.nahonpfed.com.au Defined as the accidental and inappropriate passage of urine or faeces (ICI
Urinary Incontinence and Sport: First and Preliminary Experience With a Combined Pelvic Floor Rehabilitation Program in Three Female Athletes
 Health Care for Women International, 31:435 443, 2010 Copyright Taylor & Francis Group, LLC ISSN: 0739-9332 print / 1096-4665 online DOI: 10.1080/07399330903324254 Urinary Incontinence and Sport: First
Health Care for Women International, 31:435 443, 2010 Copyright Taylor & Francis Group, LLC ISSN: 0739-9332 print / 1096-4665 online DOI: 10.1080/07399330903324254 Urinary Incontinence and Sport: First
OPTION 4 Improving Performance How do athletes train for improved performance? Strength Training
 OPTION 4 Improving Performance How do athletes train for improved performance? Strength Training 1. strength training! The main goal of strength training is to increase the maximum force that a particular
OPTION 4 Improving Performance How do athletes train for improved performance? Strength Training 1. strength training! The main goal of strength training is to increase the maximum force that a particular
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Screening of Immediate Post Partum Females for Urinary Incontinence Ami Vishal Mehta 1, Zarna
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Screening of Immediate Post Partum Females for Urinary Incontinence Ami Vishal Mehta 1, Zarna
Pelvic Floor Exercises
 Directorate of Women, Children and Surgical Services Burton and District Urogynaecology Centre A Nationally Accredited Urogynaecology Unit Pelvic Floor Exercises You have been given this leaflet because
Directorate of Women, Children and Surgical Services Burton and District Urogynaecology Centre A Nationally Accredited Urogynaecology Unit Pelvic Floor Exercises You have been given this leaflet because
Influence of exercise order on upper body maximum and submaximal strength gains in trained men
 Eastern Illinois University The Keep Faculty Research and Creative Activity Kinesiology & Sports Studies September 2013 Influence of exercise order on upper body maximum and submaximal strength gains in
Eastern Illinois University The Keep Faculty Research and Creative Activity Kinesiology & Sports Studies September 2013 Influence of exercise order on upper body maximum and submaximal strength gains in
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP)
 CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) FOCUSED QUESTION What is the effect of retraining diaphragmatic, deep abdominal, and pelvic floor muscle (PFM) coordinated function in a graded, multi-stage, supervised
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) FOCUSED QUESTION What is the effect of retraining diaphragmatic, deep abdominal, and pelvic floor muscle (PFM) coordinated function in a graded, multi-stage, supervised
Promoting Continence with Physiotherapy
 A Common problem for Men and women Promoting Continence with Physiotherapy This leaflet contains information about physiotherapy advice and treatment for anyone with bladder and bowel problems. This may
A Common problem for Men and women Promoting Continence with Physiotherapy This leaflet contains information about physiotherapy advice and treatment for anyone with bladder and bowel problems. This may
Dynamic rehabilitative ultrasound for pelvic floor disorders Introduction in techniques and hands-on-workshop
 Dynamic rehabilitative ultrasound for pelvic floor disorders Introduction in techniques and hands-on-workshop Bärbel Junginger, B.Sc. /physiotherapist, manualtherapist (IFOMPT) Kaven Baessler, MD, PhD
Dynamic rehabilitative ultrasound for pelvic floor disorders Introduction in techniques and hands-on-workshop Bärbel Junginger, B.Sc. /physiotherapist, manualtherapist (IFOMPT) Kaven Baessler, MD, PhD
Incontinence: Risks, Causes and Care
 Welcome To Incontinence: Risks, Causes and Care Presented by Kamal Masaki, MD Professor and Chair Department of Geriatric Medicine John A. Burns School of Medicine, UH Manoa September 5, 2018 10:00 11:00
Welcome To Incontinence: Risks, Causes and Care Presented by Kamal Masaki, MD Professor and Chair Department of Geriatric Medicine John A. Burns School of Medicine, UH Manoa September 5, 2018 10:00 11:00
Pelvic Floor Muscle Training Concept
 Intervention published in Trials 2015 Nov 17;16(1):524 as additional file 1 Pelvic Floor Muscle Training Concept for Women Suffering from Stress Urinary Incontinence Helena Luginbuehl 1,2, Corinne Lehmann
Intervention published in Trials 2015 Nov 17;16(1):524 as additional file 1 Pelvic Floor Muscle Training Concept for Women Suffering from Stress Urinary Incontinence Helena Luginbuehl 1,2, Corinne Lehmann
Adult women s experiences of urinary incontinence: a systematic review of qualitative evidence protocol
 Adult women s experiences of urinary incontinence: a systematic review of qualitative evidence protocol Adilson Mendes 1 Luiza Hoga 1 Bruna Gonçalves 1 Pamela Silva 1 Priscilla Pereira 1 1. School of Nursing,
Adult women s experiences of urinary incontinence: a systematic review of qualitative evidence protocol Adilson Mendes 1 Luiza Hoga 1 Bruna Gonçalves 1 Pamela Silva 1 Priscilla Pereira 1 1. School of Nursing,
Fitness A complete approach to Health. Creating Balance
 Fitness A complete approach to Health Creating Balance Fitness Learning Outcomes Phase 1 1. Explain the difference between Fat body weight and Lean body weight and the importance of balance. 2. Categorize
Fitness A complete approach to Health Creating Balance Fitness Learning Outcomes Phase 1 1. Explain the difference between Fat body weight and Lean body weight and the importance of balance. 2. Categorize
PREVENTING URINARY INCONTINENCE through PELVIC FLOOR REHABILITATION in DISABLED ELDERLY
 PREVENTING URINARY INCONTINENCE through PELVIC FLOOR REHABILITATION in DISABLED ELDERLY Paolo DI BENEDETTO Lecturer, Tor Vergata University, Rome, Italy Former Director of Rehabilitation Department Institute
PREVENTING URINARY INCONTINENCE through PELVIC FLOOR REHABILITATION in DISABLED ELDERLY Paolo DI BENEDETTO Lecturer, Tor Vergata University, Rome, Italy Former Director of Rehabilitation Department Institute
INTERNATIONAL UROGYNAECOLOGICAL ASSOCIATION (IUGA) JOINT REPORT ON THE TERMINOLOGY FOR SURGICAL PROCEDURES TO
 AN AMERICAN UROGYNECOLOGIC SOCIETY (AUGS) / INTERNATIONAL UROGYNAECOLOGICAL ASSOCIATION (IUGA) JOINT REPORT ON THE TERMINOLOGY FOR SURGICAL PROCEDURES TO TREAT PELVIC ORGAN PROLAPSE NEED FOR A WORKING
AN AMERICAN UROGYNECOLOGIC SOCIETY (AUGS) / INTERNATIONAL UROGYNAECOLOGICAL ASSOCIATION (IUGA) JOINT REPORT ON THE TERMINOLOGY FOR SURGICAL PROCEDURES TO TREAT PELVIC ORGAN PROLAPSE NEED FOR A WORKING
Aetiology 1998 Bump & Norton Theoretical model
 Kate Lough MSc MCSP Handout IUGA Nice 2015 Physiotherapy and the Provision of Pelvic Floor Muscle Training and Lifestyle Intervention in the Conservative Management of Pelvic Organ Prolapse an evidence
Kate Lough MSc MCSP Handout IUGA Nice 2015 Physiotherapy and the Provision of Pelvic Floor Muscle Training and Lifestyle Intervention in the Conservative Management of Pelvic Organ Prolapse an evidence
The diagnostic strength of the 24-h pad test for self-reported symptoms of urinary incontinence in pregnancy and after childbirth
 Int Urogynecol J (8) 19:525 53 DOI.7/s192-7-472-z ORIGINAL ARTICLE The diagnostic strength of the 24-h pad test for self-reported symptoms of urinary incontinence in pregnancy and after childbirth Jacobus
Int Urogynecol J (8) 19:525 53 DOI.7/s192-7-472-z ORIGINAL ARTICLE The diagnostic strength of the 24-h pad test for self-reported symptoms of urinary incontinence in pregnancy and after childbirth Jacobus
Perineometer as a strength assessment & training tool for pelvic floor muscles in stress urinary incontinent elderly women
 Original article: Perineometer as a strength assessment & training tool for pelvic floor muscles in stress urinary incontinent elderly women Dr. Shwetanjali Gandhe, Dr. Shyam Ganvir 1MPT student, Dept.
Original article: Perineometer as a strength assessment & training tool for pelvic floor muscles in stress urinary incontinent elderly women Dr. Shwetanjali Gandhe, Dr. Shyam Ganvir 1MPT student, Dept.
Pelvic floor weakness
 Information leaflet for patients Pelvic floor weakness Physiotherapy department You have been referred to this department for treatment and advice because you have one or more of the following symptoms:
Information leaflet for patients Pelvic floor weakness Physiotherapy department You have been referred to this department for treatment and advice because you have one or more of the following symptoms:
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Judith A. Thompson & Peter B. O Sullivan & N. Kathryn Briffa & Patricia Neumann
 Int Urogynecol J (2007) 18:779 786 DOI 10.1007/s00192-006-0225-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of transperineal and transabdominal ultrasound in the assessment of voluntary pelvic floor muscle contractions
Int Urogynecol J (2007) 18:779 786 DOI 10.1007/s00192-006-0225-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of transperineal and transabdominal ultrasound in the assessment of voluntary pelvic floor muscle contractions
Urodynamic findings in women with insensible incontinence
 bs_bs_banner International Journal of Urology (2013) 20, 429 433 doi: 10.1111/j.1442-2042.2012.03146.x Original Article: Clinical Investigation Urodynamic findings in women with insensible Benjamin M Brucker,
bs_bs_banner International Journal of Urology (2013) 20, 429 433 doi: 10.1111/j.1442-2042.2012.03146.x Original Article: Clinical Investigation Urodynamic findings in women with insensible Benjamin M Brucker,
Molecular-level benefits of stabilizing blood glucose levels. Copyright 2015 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved.
 Fitness Chapter 6 No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education. 1 What Is Fitness? Physical fitness: ability of the body to respond to physical demands Skill-related
Fitness Chapter 6 No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education. 1 What Is Fitness? Physical fitness: ability of the body to respond to physical demands Skill-related
Stress. incontinence FACTS, ADVICE, AND EXERCISES.
 Stress incontinence FACTS, ADVICE, AND EXERCISES Facts about incontinence Urinary incontinence is a common problem; one in every four women has problems with some form of leakage. Incontinence can be anything
Stress incontinence FACTS, ADVICE, AND EXERCISES Facts about incontinence Urinary incontinence is a common problem; one in every four women has problems with some form of leakage. Incontinence can be anything
The Pelvic Floor Muscles - a Guide for Women
 The Pelvic Floor Muscles - a Guide for Women This booklet is supported by WWWWW Wellbeing of Women Registered Charity No. 239281 www.wellbeingofwomen.org.uk Introduction Up to a third of all women experience
The Pelvic Floor Muscles - a Guide for Women This booklet is supported by WWWWW Wellbeing of Women Registered Charity No. 239281 www.wellbeingofwomen.org.uk Introduction Up to a third of all women experience
Pelvic Floor Exercises: a guide for women
 Approvals: Gynae Guidelines Group: Jul 2018 O&G SDU: Jul 2018 Clinical Guidelines Subgroup: not required BMV: Sep 2018 Equality Impact Assessment: Oct 2018 Patient Experience Group: February 2019 Division
Approvals: Gynae Guidelines Group: Jul 2018 O&G SDU: Jul 2018 Clinical Guidelines Subgroup: not required BMV: Sep 2018 Equality Impact Assessment: Oct 2018 Patient Experience Group: February 2019 Division
Table of Contents. Part 1
 2 Table of Contents Part 1 PHYSICAL TRAINING FOR MEMBERS OF THE SOUTH AFRICAN NATIONAL DEFENCE FORCE... 4 MANUAL ON PHYSICAL TRAINING IN THE SANDF... 4 Introduction... 4 AIm... 4 What is fitness?... 4
2 Table of Contents Part 1 PHYSICAL TRAINING FOR MEMBERS OF THE SOUTH AFRICAN NATIONAL DEFENCE FORCE... 4 MANUAL ON PHYSICAL TRAINING IN THE SANDF... 4 Introduction... 4 AIm... 4 What is fitness?... 4
Efficacy of Adding Active Technique as Biofeedback to Pelvic Floor Muscles Training on Cure of Female Stress Urinary Incontinence- A Systematic Review
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 1, March: 289-294, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Efficacy of Adding Active Technique as Biofeedback to Pelvic Floor Muscles Training on Cure of Female Stress
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 1, March: 289-294, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Efficacy of Adding Active Technique as Biofeedback to Pelvic Floor Muscles Training on Cure of Female Stress
The urethral support system during pregnancy and after childbirth Wijma, Jacobus
 University of Groningen The urethral support system during pregnancy and after childbirth Wijma, Jacobus IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish
University of Groningen The urethral support system during pregnancy and after childbirth Wijma, Jacobus IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish
LIFETIME FITNESS HEALTHY NUTRITION. UNIT 3 Lesson 4 LEAN BODY COMPOSITION
 LIFETIME FITNESS HEALTHY NUTRITION MUSCULAR STRENGTH AEROBIC ENDURANCE UNIT 3 Lesson 4 FLEXIBILITY MUSCULAR ENDURANCE LEAN BODY COMPOSITION Created by Derek G. Becher B.P.E., B. Ed., AFLCA Resistance Trainer
LIFETIME FITNESS HEALTHY NUTRITION MUSCULAR STRENGTH AEROBIC ENDURANCE UNIT 3 Lesson 4 FLEXIBILITY MUSCULAR ENDURANCE LEAN BODY COMPOSITION Created by Derek G. Becher B.P.E., B. Ed., AFLCA Resistance Trainer
Pelvic Floor Exercises
 Pelvic Floor Exercises Information for patients, relatives and carers For more information, please contact: Women s Health Physiotherapy Department The York Hospital Wigginton Road, York, YO31 8HE Tel:
Pelvic Floor Exercises Information for patients, relatives and carers For more information, please contact: Women s Health Physiotherapy Department The York Hospital Wigginton Road, York, YO31 8HE Tel:
Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercises
 INFORMATION FOR WOMEN OF ALL AGES Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercises How to exercise and strengthen your pelvic floor muscles ASSOCIATION OF CHARTERED PHYSIOTHERAPISTS IN WOMEN S HEALTH This leaflet is supported
INFORMATION FOR WOMEN OF ALL AGES Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercises How to exercise and strengthen your pelvic floor muscles ASSOCIATION OF CHARTERED PHYSIOTHERAPISTS IN WOMEN S HEALTH This leaflet is supported
The Reliability of Four Different Methods. of Calculating Quadriceps Peak Torque Angle- Specific Torques at 30, 60, and 75
 The Reliability of Four Different Methods. of Calculating Quadriceps Peak Torque Angle- Specific Torques at 30, 60, and 75 By: Brent L. Arnold and David H. Perrin * Arnold, B.A., & Perrin, D.H. (1993).
The Reliability of Four Different Methods. of Calculating Quadriceps Peak Torque Angle- Specific Torques at 30, 60, and 75 By: Brent L. Arnold and David H. Perrin * Arnold, B.A., & Perrin, D.H. (1993).
Chapter 14 Training Muscles to Become Stronger
 Chapter 14 Training Muscles to Become Stronger Slide Show developed by: Richard C. Krejci, Ph.D. Professor of Public Health Columbia College 11.22.11 Objectives 1. Describe the following four methods to
Chapter 14 Training Muscles to Become Stronger Slide Show developed by: Richard C. Krejci, Ph.D. Professor of Public Health Columbia College 11.22.11 Objectives 1. Describe the following four methods to
Pelvic Support Problems
 AP012, April 2010 ACOG publications are protected by copyright and all rights are reserved. ACOG publications may not be reproduced in any form or by any means without written permission from the copyright
AP012, April 2010 ACOG publications are protected by copyright and all rights are reserved. ACOG publications may not be reproduced in any form or by any means without written permission from the copyright
Training a Wayward Bladder
 D. James Ballard, PT, DPT, GCS The University of Utah, Dept. of Physical Therapy Training a Wayward Bladder Agenda 1. Discuss urinary incontinence 2. Review pelvic floor and lower urinary tract functional
D. James Ballard, PT, DPT, GCS The University of Utah, Dept. of Physical Therapy Training a Wayward Bladder Agenda 1. Discuss urinary incontinence 2. Review pelvic floor and lower urinary tract functional
KS4 Physical Education
 KS4 Physical Education Methods of Training These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates that the slide contains activities created
KS4 Physical Education Methods of Training These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates that the slide contains activities created
Oxford Pelvic Floor Services A guide to the pelvic floor muscles Information for women
 Oxford Pelvic Floor Services A guide to the pelvic floor muscles Information for women Introduction Many women suffer from weakness of their pelvic floor muscles. Common symptoms include: leaking urine
Oxford Pelvic Floor Services A guide to the pelvic floor muscles Information for women Introduction Many women suffer from weakness of their pelvic floor muscles. Common symptoms include: leaking urine
 Fluid Resistance Strength and Cardio Exercise Equipment GET TWICE THE RESULTS IN HALF THE TIME! Rehab ~ Sports Performance ~ Fitness ~ Active Aging AeroStrength Hydraulic Exercise Equipment saves time
Fluid Resistance Strength and Cardio Exercise Equipment GET TWICE THE RESULTS IN HALF THE TIME! Rehab ~ Sports Performance ~ Fitness ~ Active Aging AeroStrength Hydraulic Exercise Equipment saves time
Urinary incontinence is a common and debilitating
 Female Urology Using the Vibrance Kegel Device With Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercise for Stress Urinary Incontinence: A Randomized Controlled Pilot Study Teng Aik Ong, Su Yen Khong, Keng Lim Ng, Jesse Ron
Female Urology Using the Vibrance Kegel Device With Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercise for Stress Urinary Incontinence: A Randomized Controlled Pilot Study Teng Aik Ong, Su Yen Khong, Keng Lim Ng, Jesse Ron
Oxford Pelvic Floor Services A guide to the pelvic floor muscles. Information for men
 Oxford Pelvic Floor Services A guide to the pelvic floor muscles Information for men Introduction Many men suffer from weakness of their pelvic floor muscles. Common symptoms include: leaking urine with
Oxford Pelvic Floor Services A guide to the pelvic floor muscles Information for men Introduction Many men suffer from weakness of their pelvic floor muscles. Common symptoms include: leaking urine with
Rehabilitation, Core Stability & Personal Training using the Swiss Ball
 s EDUCATION WORKSHOPS Rehabilitation, Core Stability & Personal Training using the Swiss Ball with B.App.Sc (Physio), Dip.Ed (P.E.) CONTENTS Topic Page 1. Introduction 2. Core Stability Basics 3 3. Core
s EDUCATION WORKSHOPS Rehabilitation, Core Stability & Personal Training using the Swiss Ball with B.App.Sc (Physio), Dip.Ed (P.E.) CONTENTS Topic Page 1. Introduction 2. Core Stability Basics 3 3. Core
URINARY INCONTINENCE AMONG OBESE WOMEN: A CROSS- SECTIONAL STUDY
 WORLD JOURNAL OF PHARMACY AND PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES Aisha et al. SJIF Impact Factor 6.647 Volume 6, Issue 9, 1384-1391 Research Article ISSN 2278 4357 URINARY INCONTINENCE AMONG OBESE WOMEN: A CROSS-
WORLD JOURNAL OF PHARMACY AND PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES Aisha et al. SJIF Impact Factor 6.647 Volume 6, Issue 9, 1384-1391 Research Article ISSN 2278 4357 URINARY INCONTINENCE AMONG OBESE WOMEN: A CROSS-
Running head: CROSSFIT VS. TRADITIONAL EXERCISE BIERHAUS 1
 Running head: CROSSFIT VS. TRADITIONAL EXERCISE BIERHAUS 1 Comparison of Metabolic Equivalent of Task and Heart Rate Levels of an Adult with Intellectual Disability Participating in Crossfit and Traditional
Running head: CROSSFIT VS. TRADITIONAL EXERCISE BIERHAUS 1 Comparison of Metabolic Equivalent of Task and Heart Rate Levels of an Adult with Intellectual Disability Participating in Crossfit and Traditional
Pelvic floor exercises for women
 Pelvic floor exercises for women The Continence Service Patient Information Leaflet Introduction Do any of these sound like you? I always leak urine when I do exercises. I cross my legs when I sneeze.
Pelvic floor exercises for women The Continence Service Patient Information Leaflet Introduction Do any of these sound like you? I always leak urine when I do exercises. I cross my legs when I sneeze.
Bill Landry BScPT, BScH, MCPA, CAFCI Family Physiotherapy Centre of London
 Bill Landry BScPT, BScH, MCPA, CAFCI blandry@fpclondon.com Family Physiotherapy Centre of London Objectives To describe the scope of post-prostatectomy incontinence To describe what s been done To provide
Bill Landry BScPT, BScH, MCPA, CAFCI blandry@fpclondon.com Family Physiotherapy Centre of London Objectives To describe the scope of post-prostatectomy incontinence To describe what s been done To provide
CHAPTER 15: KINESIOLOGY OF FITNESS AND EXERCISE
 CHAPTER 15: KINESIOLOGY OF FITNESS AND EXERCISE KINESIOLOGY Scientific Basis of Human Motion, 12th edition Hamilton, Weimar & Luttgens Presentation Created by TK Koesterer, Ph.D., ATC Humboldt State University
CHAPTER 15: KINESIOLOGY OF FITNESS AND EXERCISE KINESIOLOGY Scientific Basis of Human Motion, 12th edition Hamilton, Weimar & Luttgens Presentation Created by TK Koesterer, Ph.D., ATC Humboldt State University
17 th European congress of Physical Rehabilitation Medicine. 38th SIMFER congress
 17 th European congress of Physical Rehabilitation Medicine 38th SIMFER congress European Rehabilitation: Quality, Evidence, Efficacy and Effectiveness Venice, May 23 27 2010 THE PHYSIATRIST AND URO-GYNECOLOGICAL
17 th European congress of Physical Rehabilitation Medicine 38th SIMFER congress European Rehabilitation: Quality, Evidence, Efficacy and Effectiveness Venice, May 23 27 2010 THE PHYSIATRIST AND URO-GYNECOLOGICAL
Uterus (Womb) Rectum. Another problem could be the sensation of something coming down at the birth canal or back passage (prolapse).
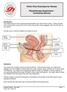 Pelvic Floor Exercises for Women Physiotherapy Department Continence Service Introduction This leaflet tells you how to exercise and strengthen your pelvic floor muscles. These muscles form a broad sling
Pelvic Floor Exercises for Women Physiotherapy Department Continence Service Introduction This leaflet tells you how to exercise and strengthen your pelvic floor muscles. These muscles form a broad sling
Patient Information Incontinence & Prolapse Self-help
 Patient Information Incontinence & Prolapse Self-help Urogynaecology Introduction This leaflet is produced as a self-help guide for women of East and North Herts that are experiencing issues with continence.
Patient Information Incontinence & Prolapse Self-help Urogynaecology Introduction This leaflet is produced as a self-help guide for women of East and North Herts that are experiencing issues with continence.
Pelvic floor exercises for women. An information guide
 TO PROVIDE THE VERY BEST CARE FOR EACH PATIENT ON EVERY OCCASION Pelvic floor exercises for women An information guide Pelvic Floor Exercises for Women This leaflet will provide you with information about
TO PROVIDE THE VERY BEST CARE FOR EACH PATIENT ON EVERY OCCASION Pelvic floor exercises for women An information guide Pelvic Floor Exercises for Women This leaflet will provide you with information about
Physical fitness : ability of the body to respond to physical. Skill-related fitness : ability to perform specific leisure or sport
 Chapter 6: Fitness What Is Fitness? Physical fitness : ability of the body to respond to physical demands Skill-related fitness : ability to perform specific leisure or sport skills Health-related fitness:
Chapter 6: Fitness What Is Fitness? Physical fitness : ability of the body to respond to physical demands Skill-related fitness : ability to perform specific leisure or sport skills Health-related fitness:
Urinary Incontinence
 Urinary Incontinence Q: What is urinary incontinence (UI)? A: UI is also known as loss of bladder control or urinary leakage. UI is when urine leaks out before you can get to a bathroom. If you have UI,
Urinary Incontinence Q: What is urinary incontinence (UI)? A: UI is also known as loss of bladder control or urinary leakage. UI is when urine leaks out before you can get to a bathroom. If you have UI,
Pelvic floor function in elite nulliparous athletes
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2007; 30: 81 85 Published online 14 May 2007 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.4027 Pelvic floor function in elite nulliparous athletes J. A.
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2007; 30: 81 85 Published online 14 May 2007 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.4027 Pelvic floor function in elite nulliparous athletes J. A.
Five for Life Student Portfolio
 Five for Life Student Series 1, Student Edition Table of Contents Student Essential Question: How do my current behaviors and fitness affect my health now and in the future? Over the course of this portfolio,
Five for Life Student Series 1, Student Edition Table of Contents Student Essential Question: How do my current behaviors and fitness affect my health now and in the future? Over the course of this portfolio,
Compassionate and effective management
 IMPACT OF STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE ON QUALITY OF LIFE * Paul Abrams, MD, FRCS ABSTRACT Evaluating the impact of stress urinary incontinence (SUI) on quality of life (QOL) is of paramount importance,
IMPACT OF STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE ON QUALITY OF LIFE * Paul Abrams, MD, FRCS ABSTRACT Evaluating the impact of stress urinary incontinence (SUI) on quality of life (QOL) is of paramount importance,
Maximising Fitness for Teenage Boys
 www.tdrfitness.com Maximising Fitness for Teenage Boys Toni Reinikainen B.Sci(Sp.Ex.Sci) Level 1 ASCA Children are not Small Adults Lack of Knowledge? At the age of 4 Ugly Parent Syndrome Peak Height
www.tdrfitness.com Maximising Fitness for Teenage Boys Toni Reinikainen B.Sci(Sp.Ex.Sci) Level 1 ASCA Children are not Small Adults Lack of Knowledge? At the age of 4 Ugly Parent Syndrome Peak Height
Lecture 6 Fitness Fitness 1. What is Fitness? 2. Cardiorespiratory Fitness 3. Muscular Fitness 4. Flexibility 5. Body Composition
 Lecture 6 Fitness 1 Fitness 1. What is Fitness? 2. Cardiorespiratory Fitness 3. Muscular Fitness 4. Flexibility 5. Body Composition 2 1 Americans (on average) are not a healthy bunch 3 Sitting is the new
Lecture 6 Fitness 1 Fitness 1. What is Fitness? 2. Cardiorespiratory Fitness 3. Muscular Fitness 4. Flexibility 5. Body Composition 2 1 Americans (on average) are not a healthy bunch 3 Sitting is the new
Fitness Intro. Freshmen PE
 Fitness Intro Freshmen PE Physical Fitness Are you able to get through your day easily without tiring? Does your body respond quickly when it needs to? Are you mentally alert in class? Do you feel good
Fitness Intro Freshmen PE Physical Fitness Are you able to get through your day easily without tiring? Does your body respond quickly when it needs to? Are you mentally alert in class? Do you feel good
Post Natal Exercises
 York Teaching Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Post Natal Exercises Taking care of yourself For more information, please contact: Women s Health Physiotherapy Scarborough Hospital: 01723 342259 Woodlands
York Teaching Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Post Natal Exercises Taking care of yourself For more information, please contact: Women s Health Physiotherapy Scarborough Hospital: 01723 342259 Woodlands
Year 7 End of Year Exam Revision
 Year 7 End of Year Exam Revision Physical Education https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=el1_enlemka Starter Video The Exam The exam you will sit is out of 40 marks. 25 of these are multiple choice, 7 are short
Year 7 End of Year Exam Revision Physical Education https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=el1_enlemka Starter Video The Exam The exam you will sit is out of 40 marks. 25 of these are multiple choice, 7 are short
Fitness and Wellness 12th Edition Hoeger TEST BANK Full download at:
 Fitness and Wellness 12th Edition Hoeger TEST BANK Full download at: https://testbankreal.com/download/fitness-wellness-12th-edition-hoeger-testbank/ Fitness and Wellness 12th Edition Hoeger SOLUTIONS
Fitness and Wellness 12th Edition Hoeger TEST BANK Full download at: https://testbankreal.com/download/fitness-wellness-12th-edition-hoeger-testbank/ Fitness and Wellness 12th Edition Hoeger SOLUTIONS
FITNESS WEIGHT TRAINING PRINCIPLES TERMS
 FITNESS WEIGHT TRAINING- is the use of progressive resistance exercises to improve performance in a sport or activity. Weight lifting is a sport that can be recreational or competitive for both men and
FITNESS WEIGHT TRAINING- is the use of progressive resistance exercises to improve performance in a sport or activity. Weight lifting is a sport that can be recreational or competitive for both men and
Beginner and advanced exercises. utilizing a stability ball. Professionally managed by:
 Beginner and advanced exercises utilizing a stability ball Professionally managed by: Mission: The National Institute for Fitness and Sport is committed to enhancing human health, physical fitness and
Beginner and advanced exercises utilizing a stability ball Professionally managed by: Mission: The National Institute for Fitness and Sport is committed to enhancing human health, physical fitness and
A Stress Urinary Incontinence fact sheet for
 A Stress Urinary Incontinence fact sheet for women and teenagers What is Stress Urinary Incontinence? Get to know your gusset - the science bit Stress urinary incontinence (SUI) is defined as a sudden
A Stress Urinary Incontinence fact sheet for women and teenagers What is Stress Urinary Incontinence? Get to know your gusset - the science bit Stress urinary incontinence (SUI) is defined as a sudden
Portfolio 601/5840/2. Focus Awards Level 3 Diploma In Fitness Instructing and Personal Training (RQF)
 Portfolio Focus Awards Level 3 Diploma In Fitness Instructing and Personal Training (RQF) 601/5840/2 1 Assessment Plan Assessor name: Learner name: Date and timings of planned assessment Unit/s and/or
Portfolio Focus Awards Level 3 Diploma In Fitness Instructing and Personal Training (RQF) 601/5840/2 1 Assessment Plan Assessor name: Learner name: Date and timings of planned assessment Unit/s and/or
Diagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Incontinence. Urinary Incontinence
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Incontinence Leslee L. Subak, MD Professor Obstetrics, Gynecology & RS Epidemiology, Urology University of California, San Francisco Urinary Incontinence Common - 25%
Diagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Incontinence Leslee L. Subak, MD Professor Obstetrics, Gynecology & RS Epidemiology, Urology University of California, San Francisco Urinary Incontinence Common - 25%
Obesity and smoking: Are they modulators of cough intravesical peak pressure in stress urinary incontinence?
 Neurourology International Braz J Urol Vol 37 (4): 528-533, July - August, 2011 Obesity and smoking: Are they modulators of cough intravesical peak pressure in stress urinary incontinence? Paulo Emilio
Neurourology International Braz J Urol Vol 37 (4): 528-533, July - August, 2011 Obesity and smoking: Are they modulators of cough intravesical peak pressure in stress urinary incontinence? Paulo Emilio
The degree of bother and healthcare seeking behaviour in women with symptoms of pelvic organ prolapse from a developing gulf country
 Hammad et al. BMC Women's Health (2018) 18:77 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12905-018-0570-8 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The degree of bother and healthcare seeking behaviour in women with symptoms of pelvic
Hammad et al. BMC Women's Health (2018) 18:77 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12905-018-0570-8 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The degree of bother and healthcare seeking behaviour in women with symptoms of pelvic
POSTPARTUM CORE/PELVIC FLOOR STRENGTHENING AND RETURN TO SPORT CHELSEA HOLT, PT, DPT CU SPORTS MEDICINE AND PERFORMANCE CENTER BOULDER, CO
 POSTPARTUM CORE/PELVIC FLOOR STRENGTHENING AND RETURN TO SPORT CHELSEA HOLT, PT, DPT CU SPORTS MEDICINE AND PERFORMANCE CENTER BOULDER, CO OBJECTIVES Present and describe musculoskeletal issues present
POSTPARTUM CORE/PELVIC FLOOR STRENGTHENING AND RETURN TO SPORT CHELSEA HOLT, PT, DPT CU SPORTS MEDICINE AND PERFORMANCE CENTER BOULDER, CO OBJECTIVES Present and describe musculoskeletal issues present
Intramachine and intermachine reproducibility of concentric performance: A study of the Con-Trex MJ and the Cybex Norm dynamometers
 Isokinetics and Exercise Science 12 (4) 91 97 91 IOS Press Intramachine and intermachine reproducibility of concentric performance: A study of the Con-Trex MJ and the Cybex Norm dynamometers C. Bardis
Isokinetics and Exercise Science 12 (4) 91 97 91 IOS Press Intramachine and intermachine reproducibility of concentric performance: A study of the Con-Trex MJ and the Cybex Norm dynamometers C. Bardis
APF PowerPoint: Unit 1
 APF PowerPoint: Unit 1 BASIC DEFINITIONS Repetition one complete movement of an exercise. Repetition consists of concentric and eccentric muscle actions. Set group of repetitions performed continuously
APF PowerPoint: Unit 1 BASIC DEFINITIONS Repetition one complete movement of an exercise. Repetition consists of concentric and eccentric muscle actions. Set group of repetitions performed continuously
A non-invasive, safe and effective treatment that improves pelvic floor muscle contraction and diminishes urine loss in pelvic floor disorders 1
 A non-invasive, safe and effective treatment that improves pelvic floor muscle contraction and diminishes urine loss in pelvic floor disorders 1 INNOVO INNOVO has changed my life for the better. I no longer
A non-invasive, safe and effective treatment that improves pelvic floor muscle contraction and diminishes urine loss in pelvic floor disorders 1 INNOVO INNOVO has changed my life for the better. I no longer
Use of pessary in the treatment of pelvic floor dysfunctions: a systematic review
 review paper Use of pessary in the treatment of pelvic floor dysfunctions: a systematic review doi: https://doi.org/10.5114/pq.2018.74704 Physiotherapy Quarterly (formerly Fizjoterapia) 2018, 26 (1), 1
review paper Use of pessary in the treatment of pelvic floor dysfunctions: a systematic review doi: https://doi.org/10.5114/pq.2018.74704 Physiotherapy Quarterly (formerly Fizjoterapia) 2018, 26 (1), 1
restore the pelvic floor
 restore the pelvic floor A non-invasive, safe, and effective treatment that improves pelvic floor muscle contraction and diminishes urine loss in pelvic floor disorders 1 has changed my life for the better.
restore the pelvic floor A non-invasive, safe, and effective treatment that improves pelvic floor muscle contraction and diminishes urine loss in pelvic floor disorders 1 has changed my life for the better.
Pelvic floor exercises for women. Information for patients Continence Service
 Pelvic floor exercises for women Information for patients Continence Service page 2 of 8 Why do I need to do pelvic floor exercises? Many women experience pelvic floor problems at some time during their
Pelvic floor exercises for women Information for patients Continence Service page 2 of 8 Why do I need to do pelvic floor exercises? Many women experience pelvic floor problems at some time during their
Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms: Lifestyle Advice, Bladder Training and Pelvic Floor Exercises
 MALE LUTS/CUP_11_11 Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms: Lifestyle Advice, Bladder Training and Pelvic Floor Exercises Lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) include the need to pass water very frequently (frequency)
MALE LUTS/CUP_11_11 Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms: Lifestyle Advice, Bladder Training and Pelvic Floor Exercises Lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) include the need to pass water very frequently (frequency)
LH12 INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES: There are TWO sections on this paper: Section A (25 Questions) and Section B (5 Questions)
 LH12 UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON SCHOOL OF SPORT AND BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES BSC (HONS) SPORT REHABILITATION SEMESTER TWO EXAMINATION 2015/2016 INJURY PREVENTION & FUNCTIONAL REHABILITATION MODULE NO. SRB 5006 Date:
LH12 UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON SCHOOL OF SPORT AND BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES BSC (HONS) SPORT REHABILITATION SEMESTER TWO EXAMINATION 2015/2016 INJURY PREVENTION & FUNCTIONAL REHABILITATION MODULE NO. SRB 5006 Date:
The causes of OA of the knee are multiple and include aging (wear and tear), obesity, and previous knee trauma or surgery. OA affects usually the
 The Arthritic Knee The causes of OA of the knee are multiple and include aging (wear and tear), obesity, and previous knee trauma or surgery. OA affects usually the medial compartment of the knee, and
The Arthritic Knee The causes of OA of the knee are multiple and include aging (wear and tear), obesity, and previous knee trauma or surgery. OA affects usually the medial compartment of the knee, and
Biological theory for the construct of intrinsic capacity to be used in clinical settings Matteo Cesari, MD, PhD
 Biological theory for the construct of intrinsic capacity to be used in clinical settings Matteo Cesari, MD, PhD World Health Organization Geneva (Switzerland) December 1, 2016 World Health Organization.
Biological theory for the construct of intrinsic capacity to be used in clinical settings Matteo Cesari, MD, PhD World Health Organization Geneva (Switzerland) December 1, 2016 World Health Organization.
EXERCISE AS MEDICINE. Dr Prue Cormie Post Doctoral Research Fellow Vario Health Institute
 EXERCISE AS MEDICINE Dr Prue Cormie Post Doctoral Research Fellow Vario Health Institute p.cormie@ecu.edu.au IMPACT OF CHRONIC DISEASE Preventable, non-communicable chronic diseases are currently responsible
EXERCISE AS MEDICINE Dr Prue Cormie Post Doctoral Research Fellow Vario Health Institute p.cormie@ecu.edu.au IMPACT OF CHRONIC DISEASE Preventable, non-communicable chronic diseases are currently responsible
When Laughing is No Longer Funny Managing Transient Urinary Incontinence in Hospitalized Elderly Women
 When Laughing is No Longer Funny Managing Transient Urinary Incontinence in Hospitalized Elderly Women Grace Umejei, BSN, RN, CWOC. Texas Health Presbyterian Hospital Dallas NICHE Online Connect Webinars
When Laughing is No Longer Funny Managing Transient Urinary Incontinence in Hospitalized Elderly Women Grace Umejei, BSN, RN, CWOC. Texas Health Presbyterian Hospital Dallas NICHE Online Connect Webinars
STAR Research Journal
 STAR Research Journal Available online at www.starresearchjournal.com (Star International Journal) PHYSICAL EDUCATION Star. Phy. Edn. 04 (2013) EFFECT OF PLYOMETRIC AND CIRCUIT TRAINING ON LEG STRENGTH,
STAR Research Journal Available online at www.starresearchjournal.com (Star International Journal) PHYSICAL EDUCATION Star. Phy. Edn. 04 (2013) EFFECT OF PLYOMETRIC AND CIRCUIT TRAINING ON LEG STRENGTH,
