Pelvic Floor Muscle Training Concept
|
|
|
- Emerald McCarthy
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Intervention published in Trials 2015 Nov 17;16(1):524 as additional file 1 Pelvic Floor Muscle Training Concept for Women Suffering from Stress Urinary Incontinence Helena Luginbuehl 1,2, Corinne Lehmann 3, Jean-Pierre Baeyens 2, Annette Kuhn 4, Lorenz Radlinger 1 1 Bern University of Applied Sciences, Health, Discipline of Physiotherapy, Switzerland 2 Vrije Universiteit Brussel, Faculty of Physical Education and Physiotherapy, Belgium 3 Bern University Hospital and University of Bern, Department of Physiotherapy, Switzerland 4 Women s Hospital, Urogynaecology, Bern University Hospital and University of Bern, Switzerland PFMT Concept (Version 2) - Page 1
2 PFMT Concept (Version 2) - Page 2
3 Introduction To date, the focus of research on pelvic floor muscle (PFM) function has been on the concentric and isometric muscle action that leads to the lift and squeeze but so far no light has been shed on the eccentric or eccentric-concentric type of contraction and the related involuntary or reflexive power. Power has to be interpreted as mechanical power (P(t) = F x v power equals force times velocity) in the sense of rate of force development in the here described context of training. It can be assumed that the impact loading on the PFM evoked by coughing, running, jumping or any abrupt rise in intra-abdominal pressure provokes involuntary muscle reactivity. Based on the literature review presented in the study protocol the main deficit of an insufficient and incontinent PFM is the lower maximal force and the lower power compared to sufficient PFM. Consequently, the special attribute of the standardized therapy plan for the experimental group introduced here aims at power with voluntary and in contrast to the control group as well as involuntary reactive strength with reflexive PFM contractions as a characteristic of a physiological unconscious and not perceived functioning of PFM during daily life activities or activities with short but intensive impacts (jumps, running, coughing etc.). Although conventional therapy programs finally also focus on the power, however, fast voluntary PFM contractions are applied only. That means this program of the control group is carried out without the above mentioned involuntary reactive contractions. Both programs are based on the latest position stand paper of the American College of Sports Medicine (ACSM) [1, 2], PFM concepts [3, 4], and strength training concepts [1, 2, 5-7]. However, even in these references the training methods vary within a certain range (e.g. repetitions: 8-12; rest intervals: 1-2 minutes, velocity: slow to moderate, etc.). This lack in standardization of training regimens is well known [8]. Therefore, within in these methodological ranges training programs presented her are precisely standardized for the control and experimental group separately and following the references and training principles and methods. The planned progression of training for strength, power and hypertrophy is shown in Table 1. Table 1. Time schedule and progression phases of training for, strength, hypertrophy and power for experimental and control group (compiled following [1-3, 5-7]) Week Training Frequency 1-5 Motor learning + power Motor learning 6-9 Strength + hypertrophy Strength + hypertrophy + power Power Strength + hypertrophy + power 45 (plus 3 personal physiotherapy consultations) 12 (plus 2 personal physiotherapy consultations) 21 (plus 4 personal physiotherapy consultations) PFMT Concept (Version 2) - Page 3
4 Respected training principles Training procedures for, strength, hypertrophy and power training phases will follow the below mentioned training principles for both groups. Variation / periodization. Changes of a therapy program over time allow for the training stimulus remain to be effective and challenging. The here used classical periodization is characterized by the intention to carry out the fundamental aspects (, strength, hypertrophy, power) to prepare distinct abilities. [1] Table 1 shows a 16 weeks lasting training program with a total number of 78 training sessions with additional 9 personal consultations (= physiotherapy sessions) for both groups. Motor learning and phases are comparable for both groups, however the main difference between the programs is the applied type of muscle action (control group (CON): isometric, concentric; experimental group (EXP): isometric, concentric, eccentric und eccentric-concentric) and speed of movement (CON: voluntary slow to moderate (to explosive) [3, 5]; EXP: explosive, reactive, reflexive; for details see tables for weekly training below). Muscle action and velocity of muscle action. All training adaptations are specific to the stimulus applied. The relevant factors are the muscle actions involved (CON: concentric; EXP: concentric, eccentric-concentric), the speed of movement (CON: slow moderate fast; EXP: explosive reactive) and the muscle groups trained (CON: PFM; EXP: PFM). The supra-maximal eccentric actions are known to produce an additional benefit in terms of force generation compared to concentric or isometric contractions. The recommendations of the ACSM [1] do not bring up the idea of involuntary eccentricconcentric, reactive strength training with maximal explosive contraction velocities as Schmidtbleicher and Güllich [7] propose. However, ACSM recommends jumps with fast repetition velocity for maximal progression in jump performance. This idea will be introduced into the training program of the experimental group aiming on the reactive activation of PFM. The program of the control group uses slow to moderate to fast voluntary contractions instead. Loads during jumps and running are described as a trigger for incontinence. Loading. Due to the fact that no external weights are possible it is not possible to carry out a 1 repetition maximum (1RM) like recommended. Therefore it is quite difficult to describe the loading of PFM strength training. Voluntary (and involuntary) contractions of the PFM will be performed in relation to maximal voluntary contraction (MVC). The patients will be familiarized with this maximal loading and submaximal loads will be estimated and performed in relation to 100%MVC. [1] Volume. One to three sets per exercise are recommended to be used by novice individuals. For progression long term studies indicated multiple sets and a systematic variation of volume over time. [1] Exercise selection. This training program focusses on the voluntary and involuntary PFM contraction. Involuntary PFM contraction will be performed by running or jumping on the spot. [1] Rest periods. The range of rest periods will be 30 seconds to 120 seconds because the exercises used are with low complexity. [1] Frequency. Besides 9 personal physiotherapy consultations both groups will train 3 times a week (week 1-5 3x/week, 3x/day; week x/week, 1x/day = 78 home training sessions) for 16 weeks to be comparable in training frequency. [1] PFMT Concept (Version 2) - Page 4
5 Basic Therapy The basic therapy will be performed in both groups equally during the 9 intended physiotherapy sessions. Basic therapy represents the usual physiotherapy session contents in the presence of a physiotherapist and patient. Both groups will receive the basic therapy during 9 physiotherapy sessions which homogeneously distributed take place in the weeks 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, and 16. First, the home exercises and training methods will be instructed, supervised and controlled by the physiotherapist at the 9 physiotherapy sessions only, which is best practice and sufficient [9]. This procedure should also grant a high and sustained adherence over time [10, 11]. Second, each patient will receive the necessary proper basic information and instruction [12] and will be taught to perform a correct voluntary PFM contraction. Basic therapy additionally includes: information regarding anatomical, (patho-)physiological aspects of SUI [13-15], performing an isolated PFM contraction [16], postural control, breathing, and PFM contraction with continuous breathing [17], exercising pre-contraction [18], fluid intake [19], micturition and defecation behavior [20], co-contraction [21] of PFM and M. abdominus transversus [22] during intra-abdominal pressure increase. The 9 personal therapy consultations will not be included into the total amount of 78 therapy units (= 100% of all therapy units). Third, life style interventions for pelvic floor dysfunction will additionally be given during the therapy and follow-up period following the recommendations of Chiarelli [23]. Therapy plan According to the above discussed training principles and basic therapy a detailed and standardized training program is carried out in the following for each week of training including a short description of the related physiotherapy session 1-9 (aims, basic therapy) and the separate home exercise program for each group with aims of training, exercises used, relevant muscle action type and contraction velocity, description of loading, number of repetitions, volume, duration of rest, training frequency per day/week, and body position applied. PFMT Concept (Version 2) - Page 5
6 1 st week of exercise program 1 st Physiotherapy session The patient is able to perform a correct isolated maximal voluntary pelvic floor muscle (PFM) contraction (squeeze around pelvic openings and inward (cranial) lift [24, 25]. Basic therapy: Make an anamnesis and explain the function of the pelvic floor [13-15]. Teach isolated PFM contractions [16] and the home exercise program corresponding to the randomized groups (see below). Muscle action: concentric-isometric, explosive Repetitions: 3x 2-3 seconds hold Position: supine Muscle action: concentric, slow ) Volume: 1 - Position: sitting on a armchair 2 nd week of exercise program 2 nd Physiotherapy session Control and improvement of the home exercise program. Patient knows the interaction between diaphragm and PFM. The patient is able to prevent an interruption of breathing while contracting PFM [17]. Basic therapy: Teach the patient to concentrate on breathing. The patient contracts PFM and counts loudly with continuous breathing to five. Teach the home exercise program corresponding to the randomized groups (see below). Muscle action: concentric-isometric, explosive Repetitions: 4x 2-3s hold Position: sitting upright (chair without arm) Repetitions: 3 Position: sitting upright Muscle action: concentric, slow to moderate Volume: 1 - Position: supine Muscle action: concentric, slow to moderate Volume: 1 - Position: sitting upright (chair without arm) PFMT Concept (Version 2) - Page 6
7 3 rd week of exercise program Muscle action: concentric-isometric, explosive Repetitions: 5x 4s hold Volume: 5 Position: sitting upright (chair without arm) Repetitions: 5 Volume: 5 Position: sitting upright Muscle action: concentric, slow to moderate Position: supine Muscle action: concentric, slow to moderate Position: sitting upright (chair without arm) 4 th week of exercise program 3 th Physiotherapy Session Control and improvement of the home exercise program. The patient is able to perform adequate trunk stabilization in functional positions and movements [17]. Basic therapy: Exercise the correct posture in sitting, standing and lifting. Let feel the difference to inadequate trunk stabilization. Teach the home exercise program corresponding to the randomized groups (see below). Muscle action: concentric-isometric, explosive Repetitions: 4x 2-3s hold Volume: 6 Repetitions: 5 Muscle action: concentric, slow to moderate Position: sitting upright Muscle action: concentric, slow to moderate 2 minutes PFMT Concept (Version 2) - Page 7
8 5 th week of exercise program Muscle action: concentric-isometric, explosive Repetitions: 5x 3-4s hold Volume: 6 Repetitions: 3 Volume: 5 Muscle action: concentric, moderate Muscle action: concentric, moderate Position: standing in a squat position 6 th week of exercise program 4 th Physiotherapy session Control and improvement of the home exercise program. The patient is able to contract PFM against increased intra-abdominal pressure. Basic therapy: Training of voluntary contraction immediately before coughing or lifting something (The «Knack» = voluntary PFM pre-contraction) [18]. Teach the exercise program corresponding to the randomized groups (see below). Loading: 60-85% of MVC Repetitions: 1x 5s hold Position: sitting on the floor + power Exercises: running on the spot with co-contraction Muscle action: concentric-isometric, reactive Time: 15s Position: sitting on the floor PFMT Concept (Version 2) - Page 8
9 7 th week of exercise program Loading: 60-85% of MVC 15s x 5s Position: lying on the floor in a bridging position + power Exercises: running on the spot with co-contraction Muscle action: concentric-isometric, reactive Time: 15s Position: lying on the floor in a bridging position 8 th week of exercise program 5 th Physiotherapy session Control and improvement of the home exercise program. The patient should be able to create and evaluate a micturition-protocol [19]. Basic therapy: Demonstrate an example of a micturition-protocol. Teach that the micturition and the defecation [20] take place without pressing. Teach the home exercise program corresponding to the randomized groups (see below). Repetitions: 3 Volume: 5 x 5s Position: lying on forearms and knees + power Exercises: running on the spot with co-contraction Muscle action: concentric-isometric, reactive Time: 15s Position: lying on forearms and knees PFMT Concept (Version 2) - Page 9
10 9 th week of exercise program Loading: maximal: % of MVC Repetitions: 4 Volume: 5 x 5s Position: lying on hands and knees + power Exercises: running on the spot with co-contraction Muscle action: concentric-isometric, reactive Time: 15s Position: lying on hands And knees 10 th week of exercise program 6 th Physiotherapy session Control and improvement of the home exercise program. The patient is able to interpret her micturition-protocol. Basic therapy: Evaluate and discuss the micturition-protocol. Teach the home exercise program corresponding to the randomized groups (see below). power (voluntary) Loading: % Position: squat position x 5s Position: sitting on the floor with legs crossed Exercises: running on the spot (no co-contraction) Muscle action: reactive Time: 15s Position: sitting on the floor with legs crossed PFMT Concept (Version 2) - Page 10
11 11 th week of exercise program power (voluntary) Loading: %, squat position x 5s Exercises: squat jumps 12 th week of exercise program 7 th Physiotherapy session Control and improvement of the home exercise program. The patient is able to contract isolated transversus abdominus muscle [22, 26]. Basic therapy: Training of voluntary contraction of lower abdominal muscles as the patient would like to zip too tight pants. Important: no movements within the spine region and breathing should be performed. Teach the home exercise program corresponding to the randomized groups (see below). power (voluntary) Loading: % Volume: 4, squat position x 8s in a straddle position Exercises: squat jumps Volume: 4 in a straddle position PFMT Concept (Version 2) - Page 11
12 13 th week of exercise program power (voluntary) Exercises: squat jump, squat position x 5s Position: single leg standing (left and right) Exercises: counter movement jump Position: single leg standing (left and right) 14 th week of exercise program 8 th Physiotherapy session Control and improvement of the home exercise program. The patient is able to contract PFM and transversus abdominus muscle in a co-contraction simultaneously. Basic therapy: Training of PFM and transversus abdominus muscle co-contraction combined with coughing or other exhaling maneuvers [21]. Teach the home exercise program corresponding to the randomized groups (see below). Exercises: counter movement jumps x 10s, squat position power Exercises: drop jump Muscle action: concentric-isometric, fast x (5s + 3x fast) Position: sitting upright PFMT Concept (Version 2) - Page 12
13 15 th week of exercise program Exercises: counter movement jump Volume: 4 x 10s, squat position Exercises: drop jump Volume: 4 power Muscle action: concentric-isometric, fast x (10s + 3x fast) Position: single leg standing (left and right) 16 th week of exercise program 9 th Physiotherapy session Control and improvement of the home exercise program. All open questions of the patient relating to SUI and behavior should be resolved. The patient will be informed about the next steps after this training period. Basic therapy: Give the patient an opportunity to ask questions. Explain the next steps. Exercises: counter movement jump Volume: 5 x 10s, squat position power Exercises: drop jump Muscle action: concentric-isometric, fast x (10s + 3x fast) Volume: 5 Position: single leg standing (left and right) PFMT Concept (Version 2) - Page 13
14 17 th week until 6 months follow-up After the intervention phase the patients receive an information sheet and instruction about the necessary and following home exercise program between the end of therapy and the 6 months followup. Generally patients should continue performing PFM exercises for years after completing their physiotherapy education sessions [27]. Both groups continue their training as described below. Exercises: counter movement jump Repetitions: 6 Volume: 4 x 10s, squat position power Exercises: drop jump Muscle action: concentric-isometric, fast Repetitions: 5 x (10s + 3x fast) Position: single leg standing (left and right) Further information Take care while you are lifting up something: Don t forget the pre-contraction of the pelvic floor muscle! Drink at least 1½ liter per day and prefer water. 5-6x micturition per day and 0-1x per night are okay. Be mindful on the correct posture while sitting, standing and lifting. PFMT Concept (Version 2) - Page 14
15 References 1. American College of Sports Medicine: American College of Sports Medicine position stand. Progression models in resistance training for healthy adults. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2009, 41(3): Kraemer WJ, Adams K, Cafarelli E, Dudley GA, Dooly C, Feigenbaum MS, Fleck SJ, Franklin B, Fry AC, Hoffman JR, Newton RU, Potteiger J, Stone MH, Ratamess NA, Triplett-McBride T; American College of Sports Medicine: American College of Sports Medicine position stand. Progression models in resistance training for healthy adults. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2002, 34(2): Bo K, Morkved S: Motor Learning. In: Bo K, Berghmans B, Morkved S, van Kampen M Eds. Evidence Based Physical Therapy for the Pelvic Floor Bridging Science and Clinical Practice. Edinburgh, Churchill Livingstone 2007, p Winstein CJ: Knowledge of results and - implications for physical therapy. Phys Ther 1991, 71(2): Bo K, Aschehoug A: Strength Training. In: Bo K, Berghmans B, Morkved S, van Kampen M Eds. Evidence Based Physical Therapy for the Pelvic Floor Bridging Science and Clinical Practice. Edinburgh, Churchill Livingstone 2007, p Kraemer WJ, Ratamess NA: Fundamentals of resistance training: progression and exercise prescription. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2004, 36(4): Schmidtbleicher D, Güllich A: Dimensionen des Kraftverhaltens. Orthopädische Praxis 1999, 35(11): Dumoulin C, Glazener C, Jenkinson D: Determining the optimal pelvic floor muscle training regimen for women with stress urinary incontinence. Neurourol Urodyn 2011, 30(5): Felicíssimo MF, Carneiro MM, Saleme CS, Pinto RZ, da Fonseca AM, da Silva-Filho AL: Intensive supervised versus unsupervised pelvic floor muscle training for the treatment of stress urinary incontinence: a randomized comparative trial. Int Urogynecol J (7): Borello-France D, Burgio KL, Goode PS, Ye W, Weidner AC, Lukacz ES, Jelovsek JE, Bradley CS, Schaffer J, Hsu Y, Kenton K, Spino C: Pelvic Floor Disorders Network. Adherence to behavioral interventions for stress incontinence: rates, barriers, and predictors. Phys Ther 2013, 93(6): Alewijnse D, Mesters I: Strategies to enhance adherence and reduce drop out in conservative treatment. In: Bo K, Berghmans B, Morkved S, van Kampen M Eds. Evidence Based Physical Therapy for the Pelvic Floor Bridging Science and Clinical Practice. Edinburgh, Churchill Livingstone 2007, p Bo K: Pelvic floor muscle training in treatment of female stress urinary incontinence, pelvic organ prolapse and sexual dysfunction. World J Urol 2012, 30(4): Ashton-Miller JA, Howard D, DeLancey JO: The functional anatomy of the female pelvic floor. In: Bo K, Berghmans B, Morkved S, van Kampen M Eds. Evidence Based Physical Therapy for the Pelvic Floor Bridging Science and Clinical Practice. Edinburgh, Churchill Livingstone 2007, p Vodusek DB: Neuroanatomy and neurophysiology of pelvic floor muscles. In: Bo K, Berghmans B, Morkved S, van Kampen M Eds. Evidence Based Physical Therapy for the Pelvic Floor Bridging Science and Clinical Practice. Edinburgh, Churchill Livingstone 2007, p Ashton-Miller JA, Howard D, DeLancey JO: The functional anatomy of the female pelvic floor and stress continence control system. Scand J Urol Nephrol Suppl 2001, (207): Bo K, Larsen S, Oseid S, Kvarstein B, Hagen R, Jorgensen J: Knowledge about and ability to correct pelvic floor muscle exercises in women with urinary stress incontinence. Neurourol Urodyn 1988, 7(3): Hodges P, Sapsford R, Pengel L: Postural and respiratory functions of the pelvic floor muscles. Neurourol Urodyn 2007, 26(3): Miller JM, Perucchini D, Carchidi LT, DeLancey JO, Ashton-Miller J: Pelvic floor muscle contraction during a cough and decreased vesical neck mobility. Obstet Gynecol 2001, 97(2): Stay K, Dwyer PL, Rosamilia A: Women overestimate daytime urinary frequency: the importance of the bladder diary. J Urol 2009, 181(5): Lubowski DZ, Swash M, Nicholls RJ, Henry MM: Increase in pudendal nerve terminal motor latency with defaecation straining. Br J Surg 1988, 75(11): Sapsford R, Hodges P, Richardson C, Cooper D, Markwell S, Jull G: Co activation of the abdominal and pelvic floor muscles during voluntary exercises. Neurourol Urodyn 2001, 20(1): Bo K, Mørkved S, Frawley H, Sherburn M: Evidence for benefit of transversus abdominis training alone or in combination with pelvic floor muscle training to treat female urinary incontinence: a systematic review. Neurourol Urodyn 2009, 28(5): Chiarelli P: Lifestyle interventions of pelvic floor dysfunctions. In: Bo K, Berghmans B, Morkved S, van Kampen M Eds. Evidence Based Physical Therapy for the Pelvic Floor Bridging Science and Clinical Practice. Edinburgh, Churchill Livingstone 2007, p Henderson JW, Wang S, Egger MJ, Masters M, Nygaard I: Can women correctly contract their pelvic floor muscles without formal instruction? Female Pelvic Med Reconstr Surg 2013, 19(1): Kegel AH: Progressive resistance exercise in the functional restoration of the perineal muscles. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1948, 56(2): Bo K, Sherburn M, Allen T: Transabdominal ultrasound measurement of pelvic floor muscle activity when activated directly or via a transversus abdominis muscle contraction. Neurourol Urodyn 2003, 22(6): Simard C, Tu le M: Long-term efficacy of pelvic floor muscle rehabilitation for older women with urinary incontinence. J Obstet Gynaecol Can 2010, 32(12): PFMT Concept (Version 2) - Page 15
Dynamic rehabilitative ultrasound for pelvic floor disorders Introduction in techniques and hands-on-workshop
 Dynamic rehabilitative ultrasound for pelvic floor disorders Introduction in techniques and hands-on-workshop Bärbel Junginger, B.Sc. /physiotherapist, manualtherapist (IFOMPT) Kaven Baessler, MD, PhD
Dynamic rehabilitative ultrasound for pelvic floor disorders Introduction in techniques and hands-on-workshop Bärbel Junginger, B.Sc. /physiotherapist, manualtherapist (IFOMPT) Kaven Baessler, MD, PhD
Pelvic Floor Exercise. Brigi0e Fung Physiotherapist
 Pelvic Floor Exercise Brigi0e Fung Physiotherapist Treatment for urinary incontinence Pelvic floor muscle exercise (Kegel, 1948) Bladder retraining Behaviour modification Treatment for urinary incontinence
Pelvic Floor Exercise Brigi0e Fung Physiotherapist Treatment for urinary incontinence Pelvic floor muscle exercise (Kegel, 1948) Bladder retraining Behaviour modification Treatment for urinary incontinence
The pelvic floor muscles (PFM) form
 Correlation of Digital Palpation and Transabdominal Ultrasound for Assessment of Pelvic Floor Muscle Contraction Amir Massoud Arab, PT, PhD 1 ; Roxana Bazaz Behbahani, PT, BSc 2 ; Leila Lorestani, PT,
Correlation of Digital Palpation and Transabdominal Ultrasound for Assessment of Pelvic Floor Muscle Contraction Amir Massoud Arab, PT, PhD 1 ; Roxana Bazaz Behbahani, PT, BSc 2 ; Leila Lorestani, PT,
Risks and Considerations Exercising with Pelvic Floor Dysfunction
 Risks and Considerations Exercising with Pelvic Floor Dysfunction Maeve Whelan MSc SMISCP Specialist Chartered Physiotherapist Milltown Physiotherapy Acknowledgement Taryn Hallam PT THE PROBLEM 1 in 7
Risks and Considerations Exercising with Pelvic Floor Dysfunction Maeve Whelan MSc SMISCP Specialist Chartered Physiotherapist Milltown Physiotherapy Acknowledgement Taryn Hallam PT THE PROBLEM 1 in 7
Bill Landry BScPT, BScH, MCPA, CAFCI Family Physiotherapy Centre of London
 Bill Landry BScPT, BScH, MCPA, CAFCI blandry@fpclondon.com Family Physiotherapy Centre of London Objectives To describe the scope of post-prostatectomy incontinence To describe what s been done To provide
Bill Landry BScPT, BScH, MCPA, CAFCI blandry@fpclondon.com Family Physiotherapy Centre of London Objectives To describe the scope of post-prostatectomy incontinence To describe what s been done To provide
Effect of PFMT: Kegel, LA, USA Pelvic floor rehabilitation. Problems with systematic reviews / meta-analysis 15/10/2013
 Exercise programs for the pelvic floor evidence for an optimal program? ICS Barcelona PT-Roundtable 2013 Kari Bø Professor, PhD PT, Exercise Scientist Affiliations to disclose: Enter Organisation/relationship
Exercise programs for the pelvic floor evidence for an optimal program? ICS Barcelona PT-Roundtable 2013 Kari Bø Professor, PhD PT, Exercise Scientist Affiliations to disclose: Enter Organisation/relationship
Aetiology 1998 Bump & Norton Theoretical model
 Kate Lough MSc MCSP Handout IUGA Nice 2015 Physiotherapy and the Provision of Pelvic Floor Muscle Training and Lifestyle Intervention in the Conservative Management of Pelvic Organ Prolapse an evidence
Kate Lough MSc MCSP Handout IUGA Nice 2015 Physiotherapy and the Provision of Pelvic Floor Muscle Training and Lifestyle Intervention in the Conservative Management of Pelvic Organ Prolapse an evidence
Effect of Abdominal Versus Pelvic Floor Muscles Exercises on Vaginal and Leak Point Pressures in Mild Stress Urinary Incontinence in Obese Women
 Effect of Abdominal Versus Pelvic Floor Muscles Exercises on Vaginal and Leak Point Pressures in Mild Stress Urinary Incontinence in Obese Women 1 Dalia M. Kamel 1 Ali A. Thabet 2 Sayed A. Tantawy and
Effect of Abdominal Versus Pelvic Floor Muscles Exercises on Vaginal and Leak Point Pressures in Mild Stress Urinary Incontinence in Obese Women 1 Dalia M. Kamel 1 Ali A. Thabet 2 Sayed A. Tantawy and
The adaptations to resistance training are largely
 INFLUENCE OF SUPERVISION RATIO ON MUSCLE ADAPTATIONS TO RESISTANCE TRAINING IN NONTRAINED SUBJECTS PAULO GENTIL AND MARTIM BOTTARO College of Physical Education, University of Brasilia, Brasilia, Brazil
INFLUENCE OF SUPERVISION RATIO ON MUSCLE ADAPTATIONS TO RESISTANCE TRAINING IN NONTRAINED SUBJECTS PAULO GENTIL AND MARTIM BOTTARO College of Physical Education, University of Brasilia, Brasilia, Brazil
This file was dowloaded from the institutional repository Brage NIH - brage.bibsys.no/nih
 This file was dowloaded from the institutional repository Brage NIH - brage.bibsys.no/nih Bø, Kari (2012). Pelvic floor muscle training in treatment of female stress urinary incontinence, pelvic organ
This file was dowloaded from the institutional repository Brage NIH - brage.bibsys.no/nih Bø, Kari (2012). Pelvic floor muscle training in treatment of female stress urinary incontinence, pelvic organ
The Pelvic Floor Muscles - a Guide for Women
 The Pelvic Floor Muscles - a Guide for Women This booklet is supported by WWWWW Wellbeing of Women Registered Charity No. 239281 www.wellbeingofwomen.org.uk Introduction Up to a third of all women experience
The Pelvic Floor Muscles - a Guide for Women This booklet is supported by WWWWW Wellbeing of Women Registered Charity No. 239281 www.wellbeingofwomen.org.uk Introduction Up to a third of all women experience
Pelvic Floor and More.. Urinary Continence. Urinary Incontinence. Normal Bladder Function
 Pelvic Floor and More.. Jo Pitts Women s and Men s Health Physiotherapist Milton Keynes University Hospital Women s and Men s Health Physiotherapy at MKUH Pregnancy-related back and pelvic girdle pain
Pelvic Floor and More.. Jo Pitts Women s and Men s Health Physiotherapist Milton Keynes University Hospital Women s and Men s Health Physiotherapy at MKUH Pregnancy-related back and pelvic girdle pain
A Bearinger, SPT; B Cobb, SPT; L Shank, SPT; M Gevontmakher, SPT
 What goes up must come down? An analysis of the Periform Plus intravaginal sensor with indicator using simultaneous Ultrasound imaging and Surface Electromyography in healthy continent women. A Bearinger,
What goes up must come down? An analysis of the Periform Plus intravaginal sensor with indicator using simultaneous Ultrasound imaging and Surface Electromyography in healthy continent women. A Bearinger,
Effects of Combined Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercises in Patient with Urinary Incontinence
 MACROJOURNALS The Journal of MacroTrends in Health and Medicine Effects of Combined Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercises in Patient with Urinary Incontinence Vjollca Ndreu*, Fatjona Kamberi*, Enkeleda Sinaj*,
MACROJOURNALS The Journal of MacroTrends in Health and Medicine Effects of Combined Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercises in Patient with Urinary Incontinence Vjollca Ndreu*, Fatjona Kamberi*, Enkeleda Sinaj*,
Promoting pelvic floor safe exercise
 Promoting pelvic floor safe exercise Did you know that almost every exercise your client does affects their pelvic floor? Some exercises can actually harm these muscles, leading to bladder or bowel control
Promoting pelvic floor safe exercise Did you know that almost every exercise your client does affects their pelvic floor? Some exercises can actually harm these muscles, leading to bladder or bowel control
Promoting pelvic floor safe exercise
 How to find out more Promoting safe exercise To find out more visit www.continence.org.nz or call 0800 650 659. You will find: further information about the, including how to identify and exercise these
How to find out more Promoting safe exercise To find out more visit www.continence.org.nz or call 0800 650 659. You will find: further information about the, including how to identify and exercise these
Sportlyzer s Core Exercises
 Sportlyzer s Core Exercises Core training exercises are as important part of your training schedule as your endurance training. You need it to support your everyday running and improve your racing results.
Sportlyzer s Core Exercises Core training exercises are as important part of your training schedule as your endurance training. You need it to support your everyday running and improve your racing results.
TEST-RETEST RELIABILITY OF PELVIC FLOOR MUSCLE CONTRACTION. Ingeborg Hoff BRÆKKEN, PhD student, Msci, PT, Manual therapist 1
 TEST-RETEST RELIABILITY OF PELVIC FLOOR MUSCLE CONTRACTION MEASURED BY 4D ULTRASOUND Ingeborg Hoff BRÆKKEN, PhD student, Msci, PT, Manual therapist 1 Memona MAJIDA, Consultant gynaecologist 2 Marie Ellström
TEST-RETEST RELIABILITY OF PELVIC FLOOR MUSCLE CONTRACTION MEASURED BY 4D ULTRASOUND Ingeborg Hoff BRÆKKEN, PhD student, Msci, PT, Manual therapist 1 Memona MAJIDA, Consultant gynaecologist 2 Marie Ellström
Training a Wayward Bladder
 D. James Ballard, PT, DPT, GCS The University of Utah, Dept. of Physical Therapy Training a Wayward Bladder Agenda 1. Discuss urinary incontinence 2. Review pelvic floor and lower urinary tract functional
D. James Ballard, PT, DPT, GCS The University of Utah, Dept. of Physical Therapy Training a Wayward Bladder Agenda 1. Discuss urinary incontinence 2. Review pelvic floor and lower urinary tract functional
Perineometer as a strength assessment & training tool for pelvic floor muscles in stress urinary incontinent elderly women
 Original article: Perineometer as a strength assessment & training tool for pelvic floor muscles in stress urinary incontinent elderly women Dr. Shwetanjali Gandhe, Dr. Shyam Ganvir 1MPT student, Dept.
Original article: Perineometer as a strength assessment & training tool for pelvic floor muscles in stress urinary incontinent elderly women Dr. Shwetanjali Gandhe, Dr. Shyam Ganvir 1MPT student, Dept.
PREVENTING URINARY INCONTINENCE through PELVIC FLOOR REHABILITATION in DISABLED ELDERLY
 PREVENTING URINARY INCONTINENCE through PELVIC FLOOR REHABILITATION in DISABLED ELDERLY Paolo DI BENEDETTO Lecturer, Tor Vergata University, Rome, Italy Former Director of Rehabilitation Department Institute
PREVENTING URINARY INCONTINENCE through PELVIC FLOOR REHABILITATION in DISABLED ELDERLY Paolo DI BENEDETTO Lecturer, Tor Vergata University, Rome, Italy Former Director of Rehabilitation Department Institute
Determining the Optimal Pelvic Floor Muscle Training Regimen for Women with Stress Urinary Incontinence
 Neurourology and Urodynamics 30:746 753 (2011) Determining the Optimal Pelvic Floor Muscle Training Regimen for Women with Stress Urinary Incontinence Chantale Dumoulin, 1 Cathryn Glazener, 2 and David
Neurourology and Urodynamics 30:746 753 (2011) Determining the Optimal Pelvic Floor Muscle Training Regimen for Women with Stress Urinary Incontinence Chantale Dumoulin, 1 Cathryn Glazener, 2 and David
Toning your pelvic floor WELCOME
 Toning your pelvic floor WELCOME Introductions Amelia Samuels, Physiotherapist, Active Rehabilitation Physiotherapy Supporting the Continence Foundation of Australia Continence Foundation of Australia
Toning your pelvic floor WELCOME Introductions Amelia Samuels, Physiotherapist, Active Rehabilitation Physiotherapy Supporting the Continence Foundation of Australia Continence Foundation of Australia
Over Active Pelvic Floor
 Over Active Pelvic Floor Maeve Whelan SMISCP Specialist Chartered Physiotherapist, Women s Health Background The concept of an overactive pelvic floor (OAPF) is relatively new in pelvic floor rehabilitation.
Over Active Pelvic Floor Maeve Whelan SMISCP Specialist Chartered Physiotherapist, Women s Health Background The concept of an overactive pelvic floor (OAPF) is relatively new in pelvic floor rehabilitation.
This file was dowloaded from the institutional repository Brage NIH - brage.bibsys.no/nih
 This file was dowloaded from the institutional repository Brage NIH - brage.bibsys.no/nih Bø, K., Hilde, G., Stær-Jensen, J., Brækken, I. H. (2011). Can the Paula method facilitate co-contraction of the
This file was dowloaded from the institutional repository Brage NIH - brage.bibsys.no/nih Bø, K., Hilde, G., Stær-Jensen, J., Brækken, I. H. (2011). Can the Paula method facilitate co-contraction of the
Initial management of stress urinary incontinence: pelvic floor muscle training and duloxetine
 DOI: 1.1111/j.1471-528.6.878.x www.blackwellpublishing.com/bjog Review article Initial management of stress urinary incontinence: pelvic floor muscle training and duloxetine RM Freeman Urogynaecology Unit,
DOI: 1.1111/j.1471-528.6.878.x www.blackwellpublishing.com/bjog Review article Initial management of stress urinary incontinence: pelvic floor muscle training and duloxetine RM Freeman Urogynaecology Unit,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Judith A. Thompson & Peter B. O Sullivan & N. Kathryn Briffa & Patricia Neumann
 Int Urogynecol J (2007) 18:779 786 DOI 10.1007/s00192-006-0225-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of transperineal and transabdominal ultrasound in the assessment of voluntary pelvic floor muscle contractions
Int Urogynecol J (2007) 18:779 786 DOI 10.1007/s00192-006-0225-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of transperineal and transabdominal ultrasound in the assessment of voluntary pelvic floor muscle contractions
The diagnostic strength of the 24-h pad test for self-reported symptoms of urinary incontinence in pregnancy and after childbirth
 Int Urogynecol J (8) 19:525 53 DOI.7/s192-7-472-z ORIGINAL ARTICLE The diagnostic strength of the 24-h pad test for self-reported symptoms of urinary incontinence in pregnancy and after childbirth Jacobus
Int Urogynecol J (8) 19:525 53 DOI.7/s192-7-472-z ORIGINAL ARTICLE The diagnostic strength of the 24-h pad test for self-reported symptoms of urinary incontinence in pregnancy and after childbirth Jacobus
POSTPARTUM CORE/PELVIC FLOOR STRENGTHENING AND RETURN TO SPORT CHELSEA HOLT, PT, DPT CU SPORTS MEDICINE AND PERFORMANCE CENTER BOULDER, CO
 POSTPARTUM CORE/PELVIC FLOOR STRENGTHENING AND RETURN TO SPORT CHELSEA HOLT, PT, DPT CU SPORTS MEDICINE AND PERFORMANCE CENTER BOULDER, CO OBJECTIVES Present and describe musculoskeletal issues present
POSTPARTUM CORE/PELVIC FLOOR STRENGTHENING AND RETURN TO SPORT CHELSEA HOLT, PT, DPT CU SPORTS MEDICINE AND PERFORMANCE CENTER BOULDER, CO OBJECTIVES Present and describe musculoskeletal issues present
Pelvic Floor Exercises
 Pelvic Floor Exercises Information for patients, relatives and carers For more information, please contact: Women s Health Physiotherapy Department The York Hospital Wigginton Road, York, YO31 8HE Tel:
Pelvic Floor Exercises Information for patients, relatives and carers For more information, please contact: Women s Health Physiotherapy Department The York Hospital Wigginton Road, York, YO31 8HE Tel:
Pregnancy related pelvic floor dysfunction- suggested teaching presentation for Midwives
 Pregnancy related pelvic floor dysfunction- suggested teaching presentation for Midwives 1 Aims of this self assessment competency To equip Midwives with the knowledge and skills to teach pelvic floor
Pregnancy related pelvic floor dysfunction- suggested teaching presentation for Midwives 1 Aims of this self assessment competency To equip Midwives with the knowledge and skills to teach pelvic floor
Physiotherapy in the Context of Vesicovaginal Fistula. Jessica L. McKinney, PT, MS 20 March 2017
 Physiotherapy in the Context of Vesicovaginal Fistula Jessica L. McKinney, PT, MS 20 March 2017 Disclosures Renovia, Inc: strategic consultant Training centers to report the types of physiotherapy available
Physiotherapy in the Context of Vesicovaginal Fistula Jessica L. McKinney, PT, MS 20 March 2017 Disclosures Renovia, Inc: strategic consultant Training centers to report the types of physiotherapy available
Introduction Owner of Physiotherapy and Pilates Evolved in Ferrymead, Christchurch
 Pre and Postnatal Exercise Utilising Pilates Concepts By Kate Bonner Physiotherapist and Owner of Physiotherapy and Pilates Evolved 1063 Ferry Road, Ferrymead, Christchurch Introduction Owner of Physiotherapy
Pre and Postnatal Exercise Utilising Pilates Concepts By Kate Bonner Physiotherapist and Owner of Physiotherapy and Pilates Evolved 1063 Ferry Road, Ferrymead, Christchurch Introduction Owner of Physiotherapy
Pilates for Chronic Low Back Pain
 Pilates for Chronic Low Back Pain Julianne Bettencourt March 23, 2015 Course Year: 2014 Integrated Fitness, Visalia, CA Abstract Low back pain is an injury that affects thousands of people every day and
Pilates for Chronic Low Back Pain Julianne Bettencourt March 23, 2015 Course Year: 2014 Integrated Fitness, Visalia, CA Abstract Low back pain is an injury that affects thousands of people every day and
Information on Physical Therapy For Urogynecologic Problems
 Information on Physical Therapy For Urogynecologic Problems You have scheduled an appointment for evaluation and treatment of a urogynecologic problem. Following, you will find a pelvic floor questionnaire
Information on Physical Therapy For Urogynecologic Problems You have scheduled an appointment for evaluation and treatment of a urogynecologic problem. Following, you will find a pelvic floor questionnaire
Pelvic floor muscle training is effective in treatment of female stress urinary incontinence, but how does it work?
 Int Urogynecol J (2004) 15: 76 84 DOI 10.1007/s00192-004-1125-0 REVIEW ARTICLE Kari Bø Pelvic floor muscle training is effective in treatment of female stress urinary incontinence, but how does it work?
Int Urogynecol J (2004) 15: 76 84 DOI 10.1007/s00192-004-1125-0 REVIEW ARTICLE Kari Bø Pelvic floor muscle training is effective in treatment of female stress urinary incontinence, but how does it work?
Core exercises. Abdominal Ball Passing
 Abdominal Ball Passing Start with ball in hands, tighten abdominal muscle to stabilize spine and lift legs up to grasp ball. Pass ball to feet. Lower legs down while keeping your abdominal muscles tight
Abdominal Ball Passing Start with ball in hands, tighten abdominal muscle to stabilize spine and lift legs up to grasp ball. Pass ball to feet. Lower legs down while keeping your abdominal muscles tight
Using Physiotherapy to Manage Urinary Incontinence in Women
 Using Physiotherapy to Manage Urinary Incontinence in Women Bladder control problems are common, and affect people of all ages, genders and backgrounds. These problems are referred to as urinary incontinence
Using Physiotherapy to Manage Urinary Incontinence in Women Bladder control problems are common, and affect people of all ages, genders and backgrounds. These problems are referred to as urinary incontinence
Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercises
 INFORMATION FOR WOMEN OF ALL AGES Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercises How to exercise and strengthen your pelvic floor muscles ASSOCIATION OF CHARTERED PHYSIOTHERAPISTS IN WOMEN S HEALTH This leaflet is supported
INFORMATION FOR WOMEN OF ALL AGES Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercises How to exercise and strengthen your pelvic floor muscles ASSOCIATION OF CHARTERED PHYSIOTHERAPISTS IN WOMEN S HEALTH This leaflet is supported
Pelvic floor weakness
 Information leaflet for patients Pelvic floor weakness Physiotherapy department You have been referred to this department for treatment and advice because you have one or more of the following symptoms:
Information leaflet for patients Pelvic floor weakness Physiotherapy department You have been referred to this department for treatment and advice because you have one or more of the following symptoms:
The urethral support system during pregnancy and after childbirth Wijma, Jacobus
 University of Groningen The urethral support system during pregnancy and after childbirth Wijma, Jacobus IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish
University of Groningen The urethral support system during pregnancy and after childbirth Wijma, Jacobus IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish
CHRONIC PAIN AND WOMEN S HEALTH NEWSLETTER
 INCONTINENCE INCONTINENCE CHRONIC PAIN AND WOMEN S HEALTH NEWSLETTER BLADDER CONTROL INCONTINENCE Do any of these scenarios sound familiar? Allergy season is in full swing and you are not only dealing
INCONTINENCE INCONTINENCE CHRONIC PAIN AND WOMEN S HEALTH NEWSLETTER BLADDER CONTROL INCONTINENCE Do any of these scenarios sound familiar? Allergy season is in full swing and you are not only dealing
CLARE ETP PROGRAMME. Sets - This is the completion of the prescribed number of reps without rest
 Programme Objective: Strength Development & Core Development Glossary Reps - Also written as repetition. This refers to the completion of one single lift/exercise Sets - This is the completion of the prescribed
Programme Objective: Strength Development & Core Development Glossary Reps - Also written as repetition. This refers to the completion of one single lift/exercise Sets - This is the completion of the prescribed
The theory and practice of getting fitter and stronger
 The theory and practice of getting fitter and stronger David Docherty, PhD, Professor Emeritus School of Exercise Science, Physical and Health Education University of Victoria All the presentations are
The theory and practice of getting fitter and stronger David Docherty, PhD, Professor Emeritus School of Exercise Science, Physical and Health Education University of Victoria All the presentations are
Physical Therapy Treatment for Pelvic Floor Disorders: Interventions and Home Programs
 Physical Therapy Treatment for Pelvic Floor Disorders: Interventions and Home Programs T INA M A LLEN, PT PRPC BCB - PMD U N I V E R S I T Y O F W A S H I N G T O N M E D I C A L C E N T E R H E R M A
Physical Therapy Treatment for Pelvic Floor Disorders: Interventions and Home Programs T INA M A LLEN, PT PRPC BCB - PMD U N I V E R S I T Y O F W A S H I N G T O N M E D I C A L C E N T E R H E R M A
CONSERVATIVE MANAGEMENT OF URINARY INCONTINENCE IN WOMEN. Riette Vosloo Physiotherapist in Women s s Health
 CONSERVATIVE MANAGEMENT OF URINARY INCONTINENCE IN WOMEN Riette Vosloo Physiotherapist in Women s s Health CONSERVATIVE TREATMENT Any therapy that does not involve Pharmacologic intervention or Surgical
CONSERVATIVE MANAGEMENT OF URINARY INCONTINENCE IN WOMEN Riette Vosloo Physiotherapist in Women s s Health CONSERVATIVE TREATMENT Any therapy that does not involve Pharmacologic intervention or Surgical
Pelvic Floor Exercises
 Pelvic Floor Exercises Physiotherapy Department Patient information leaflet Up to a third of women experience a problem with their pelvic floor muscles at some point during their life. The muscles can
Pelvic Floor Exercises Physiotherapy Department Patient information leaflet Up to a third of women experience a problem with their pelvic floor muscles at some point during their life. The muscles can
ARTICLE IN PRESS. Manual Therapy
 Manual Therapy xxx (2010) 1 7 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Manual Therapy journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/math Original Article An alternative for urinary incontinence: Retraining diaphragmatic,
Manual Therapy xxx (2010) 1 7 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Manual Therapy journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/math Original Article An alternative for urinary incontinence: Retraining diaphragmatic,
THE ROLE OF THE MID-TORSO IN SPEED DEVELOPMENT
 THE ROLE OF THE MID-TORSO IN SPEED DEVELOPMENT The mid-torso is made up of 4 major muscle groups: 1. Rectus Abdominus Origin Base of sternum and bottom ribs Insertion Pubis bone (as part of the pelvis)
THE ROLE OF THE MID-TORSO IN SPEED DEVELOPMENT The mid-torso is made up of 4 major muscle groups: 1. Rectus Abdominus Origin Base of sternum and bottom ribs Insertion Pubis bone (as part of the pelvis)
Neither Stretching nor Postactivation Potentiation Affect Maximal Force and Rate of Force Production during Seven One-Minute Trials
 Neither Stretching nor Postactivation Potentiation Affect Maximal Force and Rate of Force Production during Seven One-Minute Trials David M. Bazett-Jones Faculty Sponsors: Jeffery M. McBride & M. R. McGuigan
Neither Stretching nor Postactivation Potentiation Affect Maximal Force and Rate of Force Production during Seven One-Minute Trials David M. Bazett-Jones Faculty Sponsors: Jeffery M. McBride & M. R. McGuigan
Pelvic Floor Exercises
 Directorate of Women, Children and Surgical Services Burton and District Urogynaecology Centre A Nationally Accredited Urogynaecology Unit Pelvic Floor Exercises You have been given this leaflet because
Directorate of Women, Children and Surgical Services Burton and District Urogynaecology Centre A Nationally Accredited Urogynaecology Unit Pelvic Floor Exercises You have been given this leaflet because
POWER AND THE PELVIS
 POWER AND THE PELVIS HOW TO PREPARE FOR ACTIVITY AND SUPPORT YOUR PELVIS BREE RUTTEN, B.Sc.P.T. PELVIC FLOOR FUNCTION: Support your pelvic organs to prevent prolapse Help to keep bladder and bowel closed
POWER AND THE PELVIS HOW TO PREPARE FOR ACTIVITY AND SUPPORT YOUR PELVIS BREE RUTTEN, B.Sc.P.T. PELVIC FLOOR FUNCTION: Support your pelvic organs to prevent prolapse Help to keep bladder and bowel closed
Changes in muscle activity of the abdominal muscles according to exercise method and speed during dead bug exercise
 Original Article https://doi.org/10.14474/ptrs.2017.6.1.1 pissn 2287-7576 eissn 2287-7584 Phys Ther Rehabil Sci 2017, 6 (1), 1-6 www.jptrs.org Changes in muscle activity of the abdominal muscles according
Original Article https://doi.org/10.14474/ptrs.2017.6.1.1 pissn 2287-7576 eissn 2287-7584 Phys Ther Rehabil Sci 2017, 6 (1), 1-6 www.jptrs.org Changes in muscle activity of the abdominal muscles according
Speed Development 2011
 Speed Development 2011 Chris Korfist Fundamental movement principles a/k/a Warm-up Stiff Spine Hip hinge Squat Fixed pelvis Medial support Frontal support Hip hinge Continued Ankle movement Ankle rocker
Speed Development 2011 Chris Korfist Fundamental movement principles a/k/a Warm-up Stiff Spine Hip hinge Squat Fixed pelvis Medial support Frontal support Hip hinge Continued Ankle movement Ankle rocker
Part A: Running. Max 5 mins. Slow run forwards 5m and return x 2. Hip out x 2. Hip in x 2. Heel Flicks x 2
 Part A: Running. Max 5 mins. Slow run forwards 5m and return x 2 Jog straight to the 20m line. Make sure you keep your upper body straight. Your hip, knee and foot are aligned. Do not let your knee buckle
Part A: Running. Max 5 mins. Slow run forwards 5m and return x 2 Jog straight to the 20m line. Make sure you keep your upper body straight. Your hip, knee and foot are aligned. Do not let your knee buckle
Letter from the SAUGA President
 Volume3, Issue 1 February 2016 Letter from the SAUGA President Things are hotting up in Cape Town literally and figuratively!! The IUGA meeting Cape Town August 2016 now has an exciting academic programme
Volume3, Issue 1 February 2016 Letter from the SAUGA President Things are hotting up in Cape Town literally and figuratively!! The IUGA meeting Cape Town August 2016 now has an exciting academic programme
Constriction of the levator hiatus during instruction of pelvic floor or transversus abdominis contraction: a 4D ultrasound study
 DOI 10.1007/s00192-008-0719-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Constriction of the levator hiatus during instruction of pelvic floor or transversus abdominis contraction: a 4D ultrasound study Kari Bø & Ingeborg H. Brækken
DOI 10.1007/s00192-008-0719-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Constriction of the levator hiatus during instruction of pelvic floor or transversus abdominis contraction: a 4D ultrasound study Kari Bø & Ingeborg H. Brækken
Pelvic Girdle Pain in Pregnancy
 CHFT If you have any comments about this leaflet or the service you have received you can contact : Assistant Therapy Services Co-ordinator Rehabilitation Department Calderdale Royal Hospital Salterhebble
CHFT If you have any comments about this leaflet or the service you have received you can contact : Assistant Therapy Services Co-ordinator Rehabilitation Department Calderdale Royal Hospital Salterhebble
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP)
 CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) FOCUSED QUESTION What is the effect of retraining diaphragmatic, deep abdominal, and pelvic floor muscle (PFM) coordinated function in a graded, multi-stage, supervised
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) FOCUSED QUESTION What is the effect of retraining diaphragmatic, deep abdominal, and pelvic floor muscle (PFM) coordinated function in a graded, multi-stage, supervised
Speed Development Chris Korfist
 Speed Development 2011 Chris Korfist Fundamental movement Stiff Spine Hip hinge Squat Fixed pelvis Medial support Frontal support Hip hinge principles a/k/a Warm-up Continued Ankle movement Ankle rocker
Speed Development 2011 Chris Korfist Fundamental movement Stiff Spine Hip hinge Squat Fixed pelvis Medial support Frontal support Hip hinge principles a/k/a Warm-up Continued Ankle movement Ankle rocker
Pelvic floor muscle activity during jumps in continent and incontinent women: an exploratory study
 Pelvic floor muscle activity during jumps in continent and incontinent women: an exploratory study Helene Moser, Monika Leitner, Patric Eichelberger, Annette Kuhn, Jean-Pierre Baeyens & Lorenz Radlinger
Pelvic floor muscle activity during jumps in continent and incontinent women: an exploratory study Helene Moser, Monika Leitner, Patric Eichelberger, Annette Kuhn, Jean-Pierre Baeyens & Lorenz Radlinger
Copyright Cardiff University
 This exercise programme has been developed by physiotherapists specifically for people with movement disorders. Exercise is not without its risks and this or any other exercise programme has potential
This exercise programme has been developed by physiotherapists specifically for people with movement disorders. Exercise is not without its risks and this or any other exercise programme has potential
5/29/2015. Objectives. Functions of the PFM. Various phases of PFM. Evaluation of the PFM
 The Physical Therapist s Approach to the Female Pelvic Floor Musculature Examination and Treatment. Presented By: Evelyne Burtis, DPT Objectives Core and pelvic floor muscles (PFM) Functions of the PFM
The Physical Therapist s Approach to the Female Pelvic Floor Musculature Examination and Treatment. Presented By: Evelyne Burtis, DPT Objectives Core and pelvic floor muscles (PFM) Functions of the PFM
This file was dowloaded from the institutional repository Brage NIH - brage.bibsys.no/nih
 This file was dowloaded from the institutional repository Brage NIH - brage.bibsys.no/nih Bø, K., Majida, M., Engh, M. E. (2012). Does a ring pessary in situ influence the pelvic floor muscle function
This file was dowloaded from the institutional repository Brage NIH - brage.bibsys.no/nih Bø, K., Majida, M., Engh, M. E. (2012). Does a ring pessary in situ influence the pelvic floor muscle function
Pre - Operative Rehabilitation Program for Patellar Instability
 Pre - Operative Rehabilitation Program for Patellar Instability This protocol is designed to assist you with your preparation for surgery and should be followed under the direction of a physiotherapist
Pre - Operative Rehabilitation Program for Patellar Instability This protocol is designed to assist you with your preparation for surgery and should be followed under the direction of a physiotherapist
The effectiveness of pelvic floor exercises on symptoms in females with stress urinary incontinence
 Medical Communication Biosci. Biotech. Res. Comm. 11(4): 681-686 (2018) The effectiveness of pelvic floor exercises on symptoms in females with stress urinary incontinence Nitesh Malhotra 1 * and Aksh
Medical Communication Biosci. Biotech. Res. Comm. 11(4): 681-686 (2018) The effectiveness of pelvic floor exercises on symptoms in females with stress urinary incontinence Nitesh Malhotra 1 * and Aksh
URINARY INCONTINENCE AMONG OBESE WOMEN: A CROSS- SECTIONAL STUDY
 WORLD JOURNAL OF PHARMACY AND PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES Aisha et al. SJIF Impact Factor 6.647 Volume 6, Issue 9, 1384-1391 Research Article ISSN 2278 4357 URINARY INCONTINENCE AMONG OBESE WOMEN: A CROSS-
WORLD JOURNAL OF PHARMACY AND PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES Aisha et al. SJIF Impact Factor 6.647 Volume 6, Issue 9, 1384-1391 Research Article ISSN 2278 4357 URINARY INCONTINENCE AMONG OBESE WOMEN: A CROSS-
17 th European congress of Physical Rehabilitation Medicine. 38th SIMFER congress
 17 th European congress of Physical Rehabilitation Medicine 38th SIMFER congress European Rehabilitation: Quality, Evidence, Efficacy and Effectiveness Venice, May 23 27 2010 THE PHYSIATRIST AND URO-GYNECOLOGICAL
17 th European congress of Physical Rehabilitation Medicine 38th SIMFER congress European Rehabilitation: Quality, Evidence, Efficacy and Effectiveness Venice, May 23 27 2010 THE PHYSIATRIST AND URO-GYNECOLOGICAL
Pelvic floor exercises for women. Information for patients Continence Service
 Pelvic floor exercises for women Information for patients Continence Service page 2 of 8 Why do I need to do pelvic floor exercises? Many women experience pelvic floor problems at some time during their
Pelvic floor exercises for women Information for patients Continence Service page 2 of 8 Why do I need to do pelvic floor exercises? Many women experience pelvic floor problems at some time during their
Training Philosophy. There are numerous views on core conditioning.
 Abs Lab Presented by Helen Vanderburg BKin, ACE, CanFitPro, Yoga and Pilates 2005 IDEA Instructor of the Year 2006/ 1996 CanFitPro Presenter of the Year Nautilus and BOSU Fitness Education Team Introduction
Abs Lab Presented by Helen Vanderburg BKin, ACE, CanFitPro, Yoga and Pilates 2005 IDEA Instructor of the Year 2006/ 1996 CanFitPro Presenter of the Year Nautilus and BOSU Fitness Education Team Introduction
Uterus (Womb) Rectum. Another problem could be the sensation of something coming down at the birth canal or back passage (prolapse).
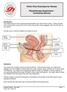 Pelvic Floor Exercises for Women Physiotherapy Department Continence Service Introduction This leaflet tells you how to exercise and strengthen your pelvic floor muscles. These muscles form a broad sling
Pelvic Floor Exercises for Women Physiotherapy Department Continence Service Introduction This leaflet tells you how to exercise and strengthen your pelvic floor muscles. These muscles form a broad sling
Thera-Band /Hand Weight Exercises
 Thera-Band /Hand Weight Exercises Created by: Kate Blanchette, BSc.N, RN ACSM Exercise Specialist Certified Trevor Harris, Certified Kinesiologist GENERAL INFORMATION Technique Tips Posture stand or sit
Thera-Band /Hand Weight Exercises Created by: Kate Blanchette, BSc.N, RN ACSM Exercise Specialist Certified Trevor Harris, Certified Kinesiologist GENERAL INFORMATION Technique Tips Posture stand or sit
Look Good Feel Good. after pregnancy. Physiotherapy advice and exercises for new mums
 Look Good Feel Good after pregnancy Physiotherapy advice and exercises for new mums How to exercise after pregnancy with physiotherapy Bowel Tail Bone Uterus Bladder Pubic Bone Pelvic Floor Muscles Urethra
Look Good Feel Good after pregnancy Physiotherapy advice and exercises for new mums How to exercise after pregnancy with physiotherapy Bowel Tail Bone Uterus Bladder Pubic Bone Pelvic Floor Muscles Urethra
Physiotherapy Following Your Spinal Discectomy
 Physiotherapy Following Your Spinal Discectomy Patient information How to contact us Physiotherapy Department Watford General Hospital West Hertfordshire Hospitals NHS Trust Vicarage Road, Watford, Hertfordshire,
Physiotherapy Following Your Spinal Discectomy Patient information How to contact us Physiotherapy Department Watford General Hospital West Hertfordshire Hospitals NHS Trust Vicarage Road, Watford, Hertfordshire,
Pelvic Floor Dysfunction (PFD) Interdisciplinary Treatment and Referral Consideration for Physician Assistants
 Pelvic Floor Dysfunction (PFD) Interdisciplinary Treatment and Referral Consideration for Physician Assistants Gerry Keenan, MMS, PA C Tammy Roehling, PT, DPT Learner Objectives 1. Recreate the pelvic
Pelvic Floor Dysfunction (PFD) Interdisciplinary Treatment and Referral Consideration for Physician Assistants Gerry Keenan, MMS, PA C Tammy Roehling, PT, DPT Learner Objectives 1. Recreate the pelvic
Lumbar decompression or discectomy
 Information and exercises Lumbar decompression or discectomy Introduction A lumbar decompression or discectomy is done to relieve pressure on the nerves in order to relieve pain and altered sensation.
Information and exercises Lumbar decompression or discectomy Introduction A lumbar decompression or discectomy is done to relieve pressure on the nerves in order to relieve pain and altered sensation.
PELVIC PHYSIOTHERAPY EDUCATION GUIDELINE
 PELVIC PHYSIOTHERAPY EDUCATION GUIDELINE Initiated at the International Continence Society (ICS) Annual Meeting in San Francisco 2009 Initially Adopted by the ICS Physiotherapy Committee September 2010
PELVIC PHYSIOTHERAPY EDUCATION GUIDELINE Initiated at the International Continence Society (ICS) Annual Meeting in San Francisco 2009 Initially Adopted by the ICS Physiotherapy Committee September 2010
GOTIMETRAINING. P O S T N A T A L EXERCISES BY RAYMOND ELLIOTT T R A N S F O R M Y O U R L I F E 0-3 WEEKS POST NATAL
 P O S T N A T A L EXERCISES BY RAYMOND ELLIOTT VOLUME I JULY 2016 SAFE EXERCIES FOR: 0-3 WEEKS POST NATAL 3-8 WEEKS POST NATAL 8-12 WEEK POST NATAL 12-16 WEEKS POST NATAL ES 5.50 IT 5.00 FR 8.00 GB 5.00
P O S T N A T A L EXERCISES BY RAYMOND ELLIOTT VOLUME I JULY 2016 SAFE EXERCIES FOR: 0-3 WEEKS POST NATAL 3-8 WEEKS POST NATAL 8-12 WEEK POST NATAL 12-16 WEEKS POST NATAL ES 5.50 IT 5.00 FR 8.00 GB 5.00
CORE STABILITY & LOW BACK PAIN. Tim Ellis, Physiotherapist BA(Hons) BSc(Hons) MHlthSc(Hons) APA
 CORE STABILITY & LOW BACK PAIN Tim Ellis, Physiotherapist BA(Hons) BSc(Hons) MHlthSc(Hons) APA 1 Core Stability & Low Back Pain In this 8 page ebook, our Principal Physiotherapist, Tim Ellis, explains
CORE STABILITY & LOW BACK PAIN Tim Ellis, Physiotherapist BA(Hons) BSc(Hons) MHlthSc(Hons) APA 1 Core Stability & Low Back Pain In this 8 page ebook, our Principal Physiotherapist, Tim Ellis, explains
Jay R. Hoffman, Ph.D., FACSM, CSCS*D. Peer Reviewed Scientific Publications (since 2000)
 Jay R. Hoffman, Ph.D., FACSM, CSCS*D EDUCATION Ph.D. University of Connecticut M.S. B.S. Queens College St. Johns University Academic Rank Professor, Department Chair Courses Taught HES 302 Assessment
Jay R. Hoffman, Ph.D., FACSM, CSCS*D EDUCATION Ph.D. University of Connecticut M.S. B.S. Queens College St. Johns University Academic Rank Professor, Department Chair Courses Taught HES 302 Assessment
Pelvic Floor Exercises
 Pelvic Floor Exercises Physiotherapy - Woman s Health Providing a range of NHS services in Gateshead, South Tyneside and Sunderland. 2 Introduction Physiotherapists, doctors and nurses know that exercising
Pelvic Floor Exercises Physiotherapy - Woman s Health Providing a range of NHS services in Gateshead, South Tyneside and Sunderland. 2 Introduction Physiotherapists, doctors and nurses know that exercising
Core Exercises. 1. Side Plank Lift
 Core Exercises Core strength exercises strengthen your core muscles, including your abdominal muscles, back muscles and the muscles around the pelvis. Strong core muscles make it easier to do many physical
Core Exercises Core strength exercises strengthen your core muscles, including your abdominal muscles, back muscles and the muscles around the pelvis. Strong core muscles make it easier to do many physical
IMPROVING URINARY INCONTINENCE
 IMPROVING URINARY INCONTINENCE INFORMATION FOR OLDER ADULTS, FAMILIES, AND CAREGIVERS READ THIS PAMPHLET TO LEARN: What Urinary Incontinence is. How to Manage Urinary Incontinence. What Pelvic Floor Exercises
IMPROVING URINARY INCONTINENCE INFORMATION FOR OLDER ADULTS, FAMILIES, AND CAREGIVERS READ THIS PAMPHLET TO LEARN: What Urinary Incontinence is. How to Manage Urinary Incontinence. What Pelvic Floor Exercises
Core Stability Exercises
 Core Stability Exercises Static Floor Exercises The plank Hold a straight body position, supported on elbows and toes. Brace the abdominals and set the low back in the neutral position. Hold this position
Core Stability Exercises Static Floor Exercises The plank Hold a straight body position, supported on elbows and toes. Brace the abdominals and set the low back in the neutral position. Hold this position
Levator Plate Upward Lift on Dynamic Sonography and Levator Muscle Strength
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Levator Plate Upward Lift on Dynamic Sonography and Levator Muscle Strength Ghazaleh Rostaminia, MD, Jennifer Peck, PhD, Lieschen Quiroz, MD, S. Abbas Shobeiri, MD Received December 4,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Levator Plate Upward Lift on Dynamic Sonography and Levator Muscle Strength Ghazaleh Rostaminia, MD, Jennifer Peck, PhD, Lieschen Quiroz, MD, S. Abbas Shobeiri, MD Received December 4,
Physiotherapy. Hip Conditioning Program
 Physiotherapy This is a general hip conditioning program designed to provide you with a wide variety of exercises and strategies to manage your symptoms. Improved hip strength, flexibility and stability
Physiotherapy This is a general hip conditioning program designed to provide you with a wide variety of exercises and strategies to manage your symptoms. Improved hip strength, flexibility and stability
Efficacy of Adding Active Technique as Biofeedback to Pelvic Floor Muscles Training on Cure of Female Stress Urinary Incontinence- A Systematic Review
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 1, March: 289-294, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Efficacy of Adding Active Technique as Biofeedback to Pelvic Floor Muscles Training on Cure of Female Stress
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 1, March: 289-294, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Efficacy of Adding Active Technique as Biofeedback to Pelvic Floor Muscles Training on Cure of Female Stress
NATURAL DEVELOPMENT AND TRAINABILITY OF PLYOMETRIC ABILITY DURING CHILDHOOD BY KIRSTY QUERL SPORT SCIENTIST STRENGTH AND CONDITIONING COACH
 NATURAL DEVELOPMENT AND TRAINABILITY OF PLYOMETRIC ABILITY DURING CHILDHOOD BY KIRSTY QUERL SPORT SCIENTIST STRENGTH AND CONDITIONING COACH The truth... Youth are not as active as they used to be, Decline
NATURAL DEVELOPMENT AND TRAINABILITY OF PLYOMETRIC ABILITY DURING CHILDHOOD BY KIRSTY QUERL SPORT SCIENTIST STRENGTH AND CONDITIONING COACH The truth... Youth are not as active as they used to be, Decline
Rehabilitation, Core Stability & Personal Training using the Swiss Ball
 s EDUCATION WORKSHOPS Rehabilitation, Core Stability & Personal Training using the Swiss Ball with B.App.Sc (Physio), Dip.Ed (P.E.) CONTENTS Topic Page 1. Introduction 2. Core Stability Basics 3 3. Core
s EDUCATION WORKSHOPS Rehabilitation, Core Stability & Personal Training using the Swiss Ball with B.App.Sc (Physio), Dip.Ed (P.E.) CONTENTS Topic Page 1. Introduction 2. Core Stability Basics 3 3. Core
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Effect of Pelvic Floor Muscle Training Based on Severity of Incontinence on Dr. Zarna Ronak
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Effect of Pelvic Floor Muscle Training Based on Severity of Incontinence on Dr. Zarna Ronak
Patient Information EXERCISE FOR OSTEOPOROSIS
 EXERCISE FOR OSTEOPOROSIS What is Osteoporosis? Osteoporosis is decreased bone density, or weak bones. It can lead to brittle bones, which increases your chance of fractures, particularly if you have had
EXERCISE FOR OSTEOPOROSIS What is Osteoporosis? Osteoporosis is decreased bone density, or weak bones. It can lead to brittle bones, which increases your chance of fractures, particularly if you have had
Pilates by Numb3rs. Experience Pilates Limited 2004
 Pilates by Numb3rs On first sight there is a lot to remember, but we will go through each of these so no need to panic! The following exercises are vital to all Pilates moves and allow you to feel the
Pilates by Numb3rs On first sight there is a lot to remember, but we will go through each of these so no need to panic! The following exercises are vital to all Pilates moves and allow you to feel the
Technique. Lesson. By Carone Fitness. Technique
 Lesson By Carone Fitness Introduction The most important part of strength training is technique. Many exercisers focus too much on how much weight they can lift or how many repetitions they can perform.
Lesson By Carone Fitness Introduction The most important part of strength training is technique. Many exercisers focus too much on how much weight they can lift or how many repetitions they can perform.
ACL Injury Prevention Program Exercises
 Prac ce these exercises on your own and with your team. Always warm up before any exercise or playing. Get blood circula ng to your muscles and joint before you start your exercises, game or prac ce. Stretch.
Prac ce these exercises on your own and with your team. Always warm up before any exercise or playing. Get blood circula ng to your muscles and joint before you start your exercises, game or prac ce. Stretch.
THE COMPLETE GUIDE TO PILATES EXERCISES
 THE COMPLETE GUIDE TO PILATES EXERCISES By Beenax Healthy living. Healthy you. INTRODUCTION Pilates (or the Pilates method) is a series of about 500 exercises inspired by calisthenics, yoga and ballet.
THE COMPLETE GUIDE TO PILATES EXERCISES By Beenax Healthy living. Healthy you. INTRODUCTION Pilates (or the Pilates method) is a series of about 500 exercises inspired by calisthenics, yoga and ballet.
A Cross-Sectional Comparison of Different Resistance Training Techniques in the Squat Exercise
 A Cross-Sectional Comparison of Different Resistance Training Techniques in the Squat Exercise Alison Egan Faculty Sponsor: Mike McGuigan, Department of Exercise and Sport Science ABSTRACT The purpose
A Cross-Sectional Comparison of Different Resistance Training Techniques in the Squat Exercise Alison Egan Faculty Sponsor: Mike McGuigan, Department of Exercise and Sport Science ABSTRACT The purpose
Pelvic floor exercises for women. An information guide
 TO PROVIDE THE VERY BEST CARE FOR EACH PATIENT ON EVERY OCCASION Pelvic floor exercises for women An information guide Pelvic Floor Exercises for Women This leaflet will provide you with information about
TO PROVIDE THE VERY BEST CARE FOR EACH PATIENT ON EVERY OCCASION Pelvic floor exercises for women An information guide Pelvic Floor Exercises for Women This leaflet will provide you with information about
Snow Angels on Foam Roll
 Thoracic Mobilization on Foam Roll Lie on your back with a foam roller positioned horizontally across your mid back, and arms crossed in front of your body. Bend your knees so your feet are resting flat
Thoracic Mobilization on Foam Roll Lie on your back with a foam roller positioned horizontally across your mid back, and arms crossed in front of your body. Bend your knees so your feet are resting flat
Not a Laughing Matter
 Not a Laughing Matter How to Incorporate Pelvic Health Rehabilitation into your STAR program Nancy Corvigno MSPT PRPC Certified Star Clinician STAR Program at Griffin Hospital Survivorship Training and
Not a Laughing Matter How to Incorporate Pelvic Health Rehabilitation into your STAR program Nancy Corvigno MSPT PRPC Certified Star Clinician STAR Program at Griffin Hospital Survivorship Training and
BACK SPASM. Explanation. Causes. Symptoms
 BACK SPASM Explanation A back spasm occurs when the muscles of the back involuntarily contract due to injury in the musculature of the back or inflammation in the structural spine region within the discs
BACK SPASM Explanation A back spasm occurs when the muscles of the back involuntarily contract due to injury in the musculature of the back or inflammation in the structural spine region within the discs
