Henderson, G. (Gary); Barnes, C. A. (Christopher); Portas, M. D. (Matthew)
|
|
|
- Kimberly Morton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 TeesRep - Teesside's Research Repository Factors associated with increased propensity for hamstring injury in English Premier League soccer players Item type Authors Article Henderson, G. (Gary); Barnes, C. A. (Christopher); Portas, M. D. (Matthew) Citation Henderson, G., Barnes, C. A. and Portas, M. D. (2010) 'Factors associated with increased propensity for hamstring injury in English Premier League soccer players', Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport, 13 (4), pp DOI Publisher Journal Additional Link Rights /j.jsams Elsevier Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport Author can archive post-print (ie final draft postrefereeing). For full details see [Accessed 01/10/2010] Downloaded 2-Jul :26:36 Link to item TeesRep - Teesside University's Research Repository -
2 This full text version, available on TeesRep, is the post-print (final version prior to publication) of: Henderson, G., Barnes, C. A. and Portas, M. D. (2010) 'Factors associated with increased propensity for hamstring injury in English Premier League soccer players', Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport, 13 (4), pp For details regarding the final published version please click on the following DOI link: When citing this source, please use the final published version as above. This document was downloaded from Please do not use this version for citation purposes. All items in TeesRep are protected by copyright, with all rights reserved, unless otherwise indicated. TeesRep: Teesside University's Research Repository
3 Factors associated with increased propensity for hamstring injury in English Premier League soccer players. Running Head: Hamstring Injury in Soccer Gary Henderson 1, Christopher A Barnes 2 and Matthew D Portas School of Social Sciences and Law, University of Teesside, Middlesbrough, UK 2. Sport Science Department, Middlesbrough Football Club, Middlesbrough, UK Corresponding Author: Mr Christopher A Barnes Head of Sports Science Middlesbrough AFC Training Headquarters Rockliffe Park Hurworth Place Nr. Darlington DL2 2DU chris.barnes@mfc.co.uk Tel: Fax:
4 ABSTRACT The aim of this study was to concurrently model the influence of a number of physical and performance parameters on subsequent incidence of hamstring injury in a squad of English 5 Premier League soccer players. Thirty six healthy, male, elite, professional soccer players (age 22.6 ± 5.2 years, height 1.81 ± 0.08 m, mass 75.8 ± 9.4 kg, lean mass 69.0 ± 8.0 kg) were assessed during the first week of pre-season training for anthropometry, flexibility, lower limb strength and power, speed and agility. Over the 45 weeks of the subsequent competitive season all hamstring injuries were diagnosed and recorded. Multiple logistic regression analysis 10 was performed to link individual physical and performance capabilities with propensity to sustain a hamstring injury. A model containing age, lean mass, non-counter movement jump (NCM) performance and active hip flexion range of movement (ROM) was significantly (p<0.05) associated with increased propensity for hamstring injury. Odds for sustaining an injury increased 1.78X for every 1 year increase in age, 1.47 X for every 1cm increase in NCM and X for every 1 o decrease in active range of hip flexion. Older, more powerful and less flexible soccer players are at greater risk of sustaining a hamstring injury. Prehabilitation and conditioning strategies should target modifiable risk factors to minimise individual potential for injury. 20 Keywords: fitness, multifactorial, preventative strategies 25
5 INTRODUCTION Over the past two decades, injury trends in elite-level soccer have changed [1,2,3], with the hamstring muscle now recognised as the most frequently injured structure, accounting for the 30 most time lost [4,5]. Indeed, the initial Football Association Audit of Injuries [6] found that over a period of two seasons, hamstring strains were the most prevalent injury, accounting for 12% of all injuries in the English Premier League. Additionally, injuries to the hamstring muscles have been shown to have the highest rates of recurrence [6,7,8] with premature return to play [9] and inadequate or inappropriate rehabilitation programs [10] suggested as contributing factors. 35 Logically, injuries sustained by key players competing in elite team sports may result in a negative impact on team performance, success and inevitably, financial well being [11]. A fuller understanding of the mechanisms of hamstring injury and players most at risk will be of great benefit to those working in professional sport. 40 The relationship between the architecture of the hamstring muscle group, its contribution to human locomotion, and its propensity for injury is undeniably complex. Despite the fact that it is widely thought that in many instances the cause of hamstring injury may be multifactorial [12], to our knowledge nearly all studies to date have modelled predictor variables in isolation [1,13]. In an attempt to model multiple intrinsic risk factors with propensity for muscle strain injury, 45 Bradley and Portas [14] identified flexibility as the only modifiable variable to be a significant predictor. To our knowledge, to date, no investigators have attempted to simultaneously model combinations of intrinsic and trainable factors with incidence of hamstring injury to better understand any relationships which may exist. 50 Hence, the aim of this study was to investigate the combined influence of a range of physical characteristics and performance capabilities on propensity for hamstring injury over a period of one full season (10 months) in a squad of English Premier League soccer players.
6 METHODS Thirty six healthy, male, elite, professional footballers (mean ± S.D.; age: 22.6 ± 5.2 years; 55 height 1.81 ± 0.08m; mass 75.8 ± 9.4kg; lean mass 69.0 ± 8.0kg) from an English Premier League soccer club gave written informed consent to participate in the study. Prior to participating in this study, eleven (31%) subjects had experienced at least one incidence of previous hamstring injury. Ethical approval for this study was granted by the University Institutional Review Board. 60 Pre season tests were conducted over a period of 2 days. All players were familiar with protocols used, having undertaken the tests on a minimum of 2 occasions previously. Tests were conducted in the same order, and at the same time of day to limit circadian influences on performance. Following a standardised warm up (consisting of 10mins sub-maximal stationary cycling and 65 light stretching), isokinetic strength for knee flexion and extension was assessed (Biodex System 3; Biodex Medical Systems Inc., Shirley, New York.). Peak torque was determined at angular velocities of 1.05, 3.14 and 5.24 rads.sec -1. All values were corrected for the effects of gravity at 30 degrees of knee flexion [15]. The test protocol consisted of three trial repetitions followed by 3, 5 and 7 recorded repetitions at 1.05, 3.14 and 5.24 rads.sec -1 respectively, with a 70 one minute rest period observed between sets [16]. Peak torque was recorded in absolute terms (N.m) and relative to fat free mass (N.m.kg -1 ). Anaerobic fitness was assessed using previously validated tests of soccer specific agility and speed endurance [17]. Aerobic fitness was assessed using the Yo-Yo Intermittent Endurance Test (YIET, level 2) [18]. 75 Explosive leg power was determined from standing vertical jump protocols. Maximum jump height was recorded both with and without counter-movement. For both techniques data were recorded using electric pressure mat apparatus (Newtest Powertimer Testing System, Newtest Oy, Kiviharjunte, Finland). Subjects stood on the mat with hands on hips and descended until
7 80 knees were at 90 degrees before explosively jumping for maximum height. For the non countermovement jump subjects held the crouch position for 3 seconds prior to jumping. Active and passive range of hip flexion ROM for dominant and non-dominant leg of each player was assessed according to the methods of Reese et. al., [19] using 2-dimensional image-based analysis. A stationary video camera (Panasonic SHM20, Matsushita Electric Corp of America, Secaucus, NJ) operating at a frame rate of 25 Hz was placed perpendicular to the plane of 85 motion at a distance of 10 m. This capture technique has been previously validated by Selfe [20]. To determine the reliability of the ROM protocol, measurements for 12 players were repeated 10 times. This resulted in a coefficient of variation of 1.5% for hip flexion ROM. During the 45 weeks of the competitive season all injuries sustained and requiring medical attention were recorded. For the purposes of this study a hamstring injury was defined as one 90 that would result in a player being unable to participate in general training for a period of 48 hours or more. All injuries were diagnosed clinically by the doctor, physiotherapists and sports therapists employed at the club, and subsequently confirmed by MRI scan. Descriptive statistics were performed on each variable to confirm the assumptions of normality. Following removal of one subject as a significant outlier, forward stepwise logistic regression 95 (block method) was performed to assess the impact of several factors collectively on the likelihood that subjects would sustain a hamstring injury. We chose to model data on the injury propensity for the dominant limb only as there were enough data on this side to permit use of the statistic (n=10). Independent variables (maximum 4) were entered according to logical criteria (based on previous work and deduction). This technique allows data to be modelled as 100 continuous and categorical variables simultaneously and is considered to be the criterion statistical procedure for this kind of research problem [13]. Significance was accepted at the p<0.05 level of confidence and all results reported as mean (SD). Data were analysed using SPSS for Windows (version 10; SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL).
8 105 RESULTS A total of 104 injuries were recorded for all participants (n=36), of which 14 (13.5%) were disruptions to the hamstrings (grade 1, 2 or 3). This is comparable to that reported by others [6] in previous work. Of the 14 incidences of hamstring injury recorded, three were sustained by the same player, the remaining 11 being single incidences for different players. Twelve injuries 110 resulted in less than 14 training days missed and 2 resulted in 14 or more (maximum 37 days missed). Ten of the 12 injuries were to the dominant (favoured kicking) leg. No relationship (p>0.05) between prior injury and injury during this study was observed for either limb. Subjects showed typical anthropometric profiles for professional soccer players [21] characterised by high relative lean mass (69 8kg) and low levels of body fat ( %). 115 Active hip flexion ROM was lower on the dominant limb than the non-dominant (69.3 vs 66.5 degrees, P<0.05). No differences were observed for passive hip flexion ROM between dominant and non-dominant limbs (76.7 o vs 75.1 o, p>0.05, Table 1). Performance in tests of endurance, agility and vertical jump power are detailed in Table 1. YIET scores are typical for adult professional soccer players [22]
9 Table 1. Performance data on pre-season tests. Mean (SD) Isokinetic Data Velocity (rads.sec -1 ) Dominant Non-dominant Target Extension Flexion Extension Flexion Peak torque (PT, N.m -1 ) (37) 162(35) 262(46) 151(27) (28) 121(25) 201(30) 125(21) (23) 104(21) 159(24) 99(21) PT corrected for body mass (N.m -1.kg -1 ) (0.65) 2.17(0.55) 3.49(0.69) 2.03(0.41) (0.52) 1.62(0.35) 2.69(0.55) 1.68(0.35) (0.43) 1.39(0.35) 2.13(0.42) 1.33(0.32) (11) 58(7) 61 HQ ratio (%) (10) 63(11) (9) 62(10) 78 Hip flexion ROM Dominant Non-dominant Active (Deg) 69.3(9.8)* 66.5(10.9) Passive (Deg) 76.7(10.7) 75.1(11.1) Field tests Agility run (s) (0.28) YIET (level 2) (m) 2183 (401) 145 Countermovement jump (cm) 40 (5) Non-countermovement jump 40 (4) (cm) * dominant significantly different to non-dominant
10 Comparison of performance on the agility and jump tests with externally validated norms is not possible due to the fact that protocols used were internally developed and validated [18]. Scores for the jump with counter movement did not differ from those with non-counter movement 150 (p>0.05). When analysed independently, none of the performance measures in this study were found to be related to propensity for hamstring injury in the subsequent season (p>0.05). No differences were found for any of the isokinetic measures of leg strength between dominant and non-dominant limbs for knee flexion or knee extension (p>0.05). Data are similar to that reported from other studies on professional soccer players, both in absolute terms and when 155 adjusted for body mass [23]. As expected, with increasing angular velocity, peak torque values decreased. Again, no differences between dominant and non-dominant limbs were observed (p>0.05). Hamstring:quadriceps strength ratios remain relatively constant (Table 1), at around 60% with increasing angular velocity (p>0.05). This is in contrast to normative values for the general population, where ratios have been shown to rise from 61% at 1.05rads.sec -1 to 78% at rads.sec -1 [24]. The resultant regression model predicting propensity for hamstring injury contained four independent variables (age, active range of movement on the dominant limb (ACTDOM), noncounter movement jump (NCMJUMP) and lean mass) and was statistically significant ( 2 (4, N=35) = 4.38, p<0.05, Table 2) indicating that it could successfully discriminate between 165 subjects who have a higher propensity for hamstring injury in the dominant limb, and those who might have a lower propensity, correctly classifying 88.6% of cases
11 Table 2. Logistic regression model predicting likelihood to sustain a hamstring injury on the dominant 180 limb. B Sig Odds Ratio 95% C.I for Odds Ratio Lower Upper Age ACTDOM NCMJUMP Lean Mass Constant Of the 4 variables in the model, only lean mass did not make a uniquely significant contribution (p=0.068). It would thus appear that propensity for hamstring injury in the dominant (kicking) leg is 185 attenuated with increasing age, increasing non-counter movement jump performance and a decrease in active range of hip flexion. DISCUSSION To our knowledge this study was the first to attempt to simultaneously model the effect of 190 physical and performance characteristics on individual propensity for hamstring injury. When modelled individually, no relationship between any of our variables and injury occurrence was noted. However, using multivariate techniques, a final model containing four independent variables (age, active ROM, explosive power and lean mass) demonstrated a strong combined influence on individual propensity for injury. Indeed, the model had a capacity to correctly 195 classify 88.6% of cases.
12 Of those contributory variables, three of four (active range of movement, non-countermovement jump and lean mass) can be considered as modifiable. Whilst lean mass did not make a statistically significant contribution to the overall model (p=0.068), on a practical level the 95% confidence limits for its inclusion were very close to unity ( ) suggesting that players 200 with lower lean mass are inherently more at risk of injury. The inclusion of age as a significant predictor variable in our model would seem logical for a number of reasons. The population being assessed are professional athletes who expose themselves to extraordinary physical stresses on a daily basis. The likelihood of older athletes having suffered a previous hamstring injury could logically be assumed to be greater than for 205 younger athletes through cumulative training exposure alone. It is therefore not surprising that with each additional year of age, the odds of sustaining an injury increase by 1.78X. These findings add to the already powerful body of evidence [6,8,25] linking age with increased risk of hamstring injury. The results were, however, in contrast to findings from Bradley and Portas [14] who, when modelling intrinsic predictor variables for generic muscle injury in professional soccer 210 players, found age to be a non-significant factor. The difference in findings could be due to the fact that the age profile for the players in their study was more homogeneous than for ours, giving less scope for any association to be identified. The significant contribution of hip flexion active range of motion to the model is supported by the findings of a number of other investigators [1,13,15]. Results from this study add to existing knowledge by showing that for 215 every 1 o decrease in active straight leg raise, propensity for injury is increased 1.29X (1/0.77). We found that the odds of sustaining an injury increased 1.47X with every 1cm extra achieved in the jump test. These findings concur with those of previous work [26] in that explosive power makes a significant contribution to the final model, indicating that athletes who generate most power (those who jumped highest) are at greater risk of injury. On a practical level these results 220 present something of a dilemma in that explosive power is an accepted pre-requisite for
13 successful performance in elite soccer, yet increases in power would also appear to increase propensity for hamstring injury. This study was performed on a group of 35 elite soccer players which is a typical sample size for work of this nature and is similar to that reported in previous work [14,27]. To avoid diluting 225 the homogeneity of the group and the control we maintained over training and conditioning regimes, we purposefully avoided increasing the sample size by using youth players, or players from other clubs. We suggest that practitioners can use the findings of this work to inform training interventions with soccer players. The structure of training programmes for older players should account for 230 their increased susceptibility to hamstring injury and be structured around appropriate preventative elements. We would suggest that in order to minimise the inherent enhanced injury risk in more powerful players, that conditioning programmes focus on increased capacity to control activities where this power is expressed. Flexibility in itself is a complex issue with many interacting factors contributing to range of movement about a joint. We do provide evidence that 235 improvements in active ROM could decrease injury risk, and recommend that limitations in less flexible athletes should be addressed through appropriate static stretching and strengthening regimes [28,29]. It may also be appropriate to incorporate postural assessment into screening programmes as it could help identify restricted range of movement and associated increased injury risk. [30]. 240 CONCLUSION These findings extend the existing knowledge in the area of injury prevention for those involved in the daily training of elite athletes, particularly soccer players and adds quantifiable support to the discussion that mechanisms of hamstring injury are indeed multifactorial. We have 245 demonstrated that older, more powerful athletes with reduced range of motion are potentially at greater risk for hamstring injury. Reduced lean mass, although not significantly contributing to
14 our model should also not be ignored by practitioners as another possible contributor to hamstring injury. Practitioners should consider these results when implementing physical training regimes with elite soccer players. 250 PRACTICAL APPLICATIONS Powerful, older soccer players with reduced active hip flexion range of motion are more susceptible to hamstring injury. Results from screening of players can be used to identify individual physical and 255 performance limitations which could contribute to increased injury susceptibility. Individualised conditioning plans based on screening results should be used to help to minimize risk of hamstring injury. Training for older players should be adapted to allow time to perform activities which will minimize risk of injury. 260 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS There has been no external financial assistance with this project
15 REFERENCES 1. Ekstrand J, Gillquist J. Soccer injuries and their mechanisms: a prospective study. Med Sci Sports Exerc 1983; 15: Lewin G. The incidence of injury in an English professional soccer club during one competitive season. Physiotherapy 1989; 7: Nielsen AB, Yde J. Epidemiology and traumatology of injuries in soccer. Am J Sports Med 1989; 17: Arnason A, Sigurdsson SB, Gudmundsson A, et al. Risk Factors for Injuries in Football. Am J Sports Med 2004a; 32: Walden M, Hagglund M, Ekstrand J. UEFA Champions League study: a prospective study of injuries in professional football during the season. Br J Sports Med 2005; 39: Woods C, Hawkins RD, Maltby S, et al. The Football Association Medical Research Programme: an audit of injuries in professional football-analysis of hamstring injuries. Br J Sports Med 2004; 38: Hawkins, RD, Hulse, MA, Wilkinson C, et al. The association football medical research programme: an audit of injuries in professional football. Br J Sports Med 2001; 35: Verrall GM, Slavotinek JP, Barnes PG. The effect of sport specific training on reducing the incidence of hamstring injuries in professional Australian Rules football players. Br J Sports Med 2005; 39: Crosier JL. Factors Associated with Recurrent Hamstring Injuries. Sports Med 2004; 34: Bennell K, Wajswelner H, Lew P, et al. Isokinetic strength testing does not predict hamstring injury in Australian Rules footballers. Br J Sports Med 1998; 32:
16 11. Arnason A, Sigurdsson SB, Gudmundsson A, et al. Physical Fitness, Injuries, and Team Performance in Soccer. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2004b; 36: Hoskins W, Pollard H. The management of hamstring injury. Part 1: Issues in diagnosis. Man Ther. 2005; 10: Witvrouw E, Danneels L, Asselman P, et al. Muscle flexibility as a risk factor for developing muscle injuries in male professional soccer players: a prospective study. Am J Sports Med 2003; 31: Bradley PS, Portas MD. The relationship between preseason range of motion and muscle strain injury in elite soccer players. J Strength Cond Res. 2007; 21 (4): Perrin D H. Isokinetic exercise and assessment, Human Kinetics, Champaign , Parcell AC, Sawyer RD, Tricoli VA, et al. Minimum rest period for strength recovery during a common Isokinetic testing protocol. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2002; 34(6); Barnes C. Soccer. In Sport and Exercise Physiology Testing Guidelines, The British Association of Sport and Exercise Sciences Guide, Volume One, Sport Testing. Winter EM, Jones AM, Davison RCR, Bromley PD, Mercer TH, eds. London: Routledge , Bangsbo J. YO-YO tests. HO + Strom, Copenhagen, Denmark Reese NB, Bandy W. Joint Range of Motion and Muscle Length Testing. W.B Saunders Company. Philadelphia, Selfe J. Validity and reliability of measurement taken by the peak 5motion analysis system. J Med. Eng. Technol 1998; 22; Strudwick A, Reilly T, Doran D. Anthropometric and fitness profiles of elite players in two football codes. J Sports Med Phys Fitness 2002; 42;
17 22. Castagna C, Impellizzeri FM, Chamari K, et al. Aerobic fitness and yo-yo continuous and intermittent tests performances in soccer players: a correlation study. J Strength Cond Res 2006; 20(2): Davies JG, Kirkendall TD, Leigh HD, et al. Isokinetic characteristics of professional football players: Normative data between quadriceps and hamstrings muscle group and relative to body weight. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1981; 13: Dvir Z, Isokinetics: Muscle Testing, Interpretation and Clinical Applications Elsevier Health Sciences, , Gabbe BJ, Bennell KL, Finch, CF. Why are older Australian football players at greater risk of hamstring injury? J Sci Med Sport 2006a; 9: Jonhagen S, Nemeth G, Eriksson E. Hamstring injuries in sprinters. The role of concentric and eccentric hamstring muscle strength and flexibility. Am J Sports Med 1994; 22: Small K, McNaughton L, Greig M, et al. The effects of multidirectional soccer-specific fatigue on markers of hamstring injury risk. J Sci Med Sport 2008, doi: 10:1016/j.jsams Milliaropoulos N, Papalexandris S, Papalada A, et al. The role of stretching in rehabilitation of hamstring injuries: 80 Athletes Follow-Up. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2004; 36, 5, Arnason A, Andersen TE, Holme I, et al. Prevention of hamstring strains in elite soccer: an intervention study. Scand J Med Sci Sports 2008; 18: Elphinston J, Hardman SL. Effect of an integrated functional stability program on injury rates in an international netball squad. J Sci Med Sport. 2006; 9:
The predictive validity of a single leg bridge test for hamstring injuries in Australian Rules Football Players
 Editor s choice Scan to access more free content 1 Department of Physiotherapy, La Trobe University, Melbourne, Victoria, Australia 2 Department of Medicine, Nursing and Health Sciences, Monash University,
Editor s choice Scan to access more free content 1 Department of Physiotherapy, La Trobe University, Melbourne, Victoria, Australia 2 Department of Medicine, Nursing and Health Sciences, Monash University,
This file was dowloaded from the institutional repository Brage NIH - brage.bibsys.no/nih
 This file was dowloaded from the institutional repository Brage NIH - brage.bibsys.no/nih Engebretsen, A. H., Myklebust, G., Holme, I., Engebretsen, L., Bahr, R. (2010). Intrinsic risk factors for hamstring
This file was dowloaded from the institutional repository Brage NIH - brage.bibsys.no/nih Engebretsen, A. H., Myklebust, G., Holme, I., Engebretsen, L., Bahr, R. (2010). Intrinsic risk factors for hamstring
Hamstring strains and prevention
 Research Center of Movement Science Department of Physiotherapy University of Iceland UIVERSITY OF ICELAD DEPARTMET OF PHYSIOTHERAPY Hamstring strains and prevention Árni Árnason PT, PhD University of
Research Center of Movement Science Department of Physiotherapy University of Iceland UIVERSITY OF ICELAD DEPARTMET OF PHYSIOTHERAPY Hamstring strains and prevention Árni Árnason PT, PhD University of
Change in knee flexor torque after fatiguing exercise identifies previous hamstring injury in football players
 Edith Cowan University Research Online ECU Publications Post 2013 2018 Change in knee flexor torque after fatiguing exercise identifies previous hamstring injury in football players Cameron Lord Edith
Edith Cowan University Research Online ECU Publications Post 2013 2018 Change in knee flexor torque after fatiguing exercise identifies previous hamstring injury in football players Cameron Lord Edith
THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN PRESEASON RANGE OF MOTION AND MUSCLE STRAIN INJURY IN ELITE SOCCER PLAYERS
 Journal i)f Strength and Conditioning Research. 2007, 2H4), 1155-1159 i'} 2007 National Strength & Conditioning Association THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN PRESEASON RANGE OF MOTION AND MUSCLE STRAIN INJURY IN
Journal i)f Strength and Conditioning Research. 2007, 2H4), 1155-1159 i'} 2007 National Strength & Conditioning Association THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN PRESEASON RANGE OF MOTION AND MUSCLE STRAIN INJURY IN
STRENGTH & CONDITIONING
 Introduction to player profiling Introduction We have previously described the demands of the sevens game for both men and women. We noted that conditioning for the game should take into account the increased
Introduction to player profiling Introduction We have previously described the demands of the sevens game for both men and women. We noted that conditioning for the game should take into account the increased
To return-to-play or not to return-to-play: Assessing quadriceps strain in a professional soccer player
 To return-to-play or not to return-to-play: Assessing quadriceps strain in a professional soccer player Hembre, A. 1 and Eriksrud, O. 2 1 Apex klinikken, Oslo, Norway 2 1080 Motion AB, Stockholm, Sweden
To return-to-play or not to return-to-play: Assessing quadriceps strain in a professional soccer player Hembre, A. 1 and Eriksrud, O. 2 1 Apex klinikken, Oslo, Norway 2 1080 Motion AB, Stockholm, Sweden
strength ratios and power in tennis, squash and track athletes
 Br. J. Sp. Med; Vol 24, No. 3 Comparison of hamstring/quadriceps isokinetic strength ratios and power in tennis, squash and track M.T.F. Read, MA, MRCGP and M.J. Bellamy, BSc Sport and Fitness, London
Br. J. Sp. Med; Vol 24, No. 3 Comparison of hamstring/quadriceps isokinetic strength ratios and power in tennis, squash and track M.T.F. Read, MA, MRCGP and M.J. Bellamy, BSc Sport and Fitness, London
A cute hamstring strains are common injuries in sport.1
 4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Type of acute hamstring strain affects flexibility, strength, and time to return to pre-injury level C Askling, T Saartok, A Thorstensson... See end of article for authors affiliations...
4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Type of acute hamstring strain affects flexibility, strength, and time to return to pre-injury level C Askling, T Saartok, A Thorstensson... See end of article for authors affiliations...
A pilot randomised controlled trial of eccentric exercise to prevent hamstring injuries in community-level Australian Football
 Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport (2006) 9, 103 109 ORIGINAL PAPER A pilot randomised controlled trial of eccentric exercise to prevent hamstring injuries in community-level Australian Football
Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport (2006) 9, 103 109 ORIGINAL PAPER A pilot randomised controlled trial of eccentric exercise to prevent hamstring injuries in community-level Australian Football
Asymmetry after Hamstring Injury in English Premier League: Issue Resolved, Or Perhaps Not?
 Asymmetry after Hamstring Injury in English Premier League: Issue Resolved, Or Perhaps Not? Authors P. Barreira 1, B. Drust 2, M. A. Robinson 1, J. Vanrenterghem 3 Affiliations Key words horizontal force
Asymmetry after Hamstring Injury in English Premier League: Issue Resolved, Or Perhaps Not? Authors P. Barreira 1, B. Drust 2, M. A. Robinson 1, J. Vanrenterghem 3 Affiliations Key words horizontal force
Previous injury as a risk factor for injury in elite football: a prospective study over two consecutive seasons
 Previous injury as a risk factor for injury in elite football: a prospective study over two consecutive seasons Martin Hägglund, Markus Waldén and Jan Ekstrand Linköping University Post Print N.B.: When
Previous injury as a risk factor for injury in elite football: a prospective study over two consecutive seasons Martin Hägglund, Markus Waldén and Jan Ekstrand Linköping University Post Print N.B.: When
Reviewed by to be arranged, VIS Sport Science, Victorian Institute of Sport, Melbourne, Australia 3205.
 THE CHANGES IN STRENGTH, POWER AND ASSOCIATED FUNCTIONAL VARIABLES IN THE AUSTRALIAN WOMEN S SOCCER TEAM DURING THE 12 MONTH PREPARATION FOR THE SYDNEY 2000 OLYMPIC GAMES Stuart Cormack Fitness Coach West
THE CHANGES IN STRENGTH, POWER AND ASSOCIATED FUNCTIONAL VARIABLES IN THE AUSTRALIAN WOMEN S SOCCER TEAM DURING THE 12 MONTH PREPARATION FOR THE SYDNEY 2000 OLYMPIC GAMES Stuart Cormack Fitness Coach West
Original article. Muscle injuries in Chilean professional soccer players
 ABSTRACT Muscle injuries in Chilean professional soccer players N. Garcίa 1, C. Sáez 2, J. P. Guarachi 3, J. Rosales 4, M. Verdugo 4, R. Yáñez 2 1Clínica Meds, Santiago, Chile. Sports Medicine Department
ABSTRACT Muscle injuries in Chilean professional soccer players N. Garcίa 1, C. Sáez 2, J. P. Guarachi 3, J. Rosales 4, M. Verdugo 4, R. Yáñez 2 1Clínica Meds, Santiago, Chile. Sports Medicine Department
Can Muscle Power Be Estimated From Thigh Bulk Measurements? A Preliminary Study
 Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 1999, 8.50-59 O 1999 Human Kinetics Publishers, Inc. Can Muscle Power Be Estimated From Thigh Bulk Measurements? A Preliminary Study Eric Maylia, John A. Fairclough, Leonard
Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 1999, 8.50-59 O 1999 Human Kinetics Publishers, Inc. Can Muscle Power Be Estimated From Thigh Bulk Measurements? A Preliminary Study Eric Maylia, John A. Fairclough, Leonard
Neither Stretching nor Postactivation Potentiation Affect Maximal Force and Rate of Force Production during Seven One-Minute Trials
 Neither Stretching nor Postactivation Potentiation Affect Maximal Force and Rate of Force Production during Seven One-Minute Trials David M. Bazett-Jones Faculty Sponsors: Jeffery M. McBride & M. R. McGuigan
Neither Stretching nor Postactivation Potentiation Affect Maximal Force and Rate of Force Production during Seven One-Minute Trials David M. Bazett-Jones Faculty Sponsors: Jeffery M. McBride & M. R. McGuigan
The Reliability of Four Different Methods. of Calculating Quadriceps Peak Torque Angle- Specific Torques at 30, 60, and 75
 The Reliability of Four Different Methods. of Calculating Quadriceps Peak Torque Angle- Specific Torques at 30, 60, and 75 By: Brent L. Arnold and David H. Perrin * Arnold, B.A., & Perrin, D.H. (1993).
The Reliability of Four Different Methods. of Calculating Quadriceps Peak Torque Angle- Specific Torques at 30, 60, and 75 By: Brent L. Arnold and David H. Perrin * Arnold, B.A., & Perrin, D.H. (1993).
NORDIC HAMSTRING PROGRAM
 NORDIC HAMSTRING PROGRAM Injury Prevention Sport Med 18 January 26 Dave Wright CAT(c) University of Guelph Hamstring Injury Prevention Injury Prevention: Evidence Based Literature Hamstring injuries are
NORDIC HAMSTRING PROGRAM Injury Prevention Sport Med 18 January 26 Dave Wright CAT(c) University of Guelph Hamstring Injury Prevention Injury Prevention: Evidence Based Literature Hamstring injuries are
The Effectiveness of Injury-Prevention Programs in Reducing the Incidence of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Sprains in Adolescent Athletes
 Critically Appraised Topics Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 2012, 21, 371-377 2012 Human Kinetics, Inc. The Effectiveness of Injury-Prevention Programs in Reducing the Incidence of Anterior Cruciate Ligament
Critically Appraised Topics Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 2012, 21, 371-377 2012 Human Kinetics, Inc. The Effectiveness of Injury-Prevention Programs in Reducing the Incidence of Anterior Cruciate Ligament
T his review is based on computerised searches
 319 REVIEW Evidence based prevention of hamstring injuries in sport J Petersen, P Hölmich... A common soft tissue injury in sports involving sprinting and jumping is the hamstring strain. A major problem
319 REVIEW Evidence based prevention of hamstring injuries in sport J Petersen, P Hölmich... A common soft tissue injury in sports involving sprinting and jumping is the hamstring strain. A major problem
Effect of cold treatment on the concentric and eccentric torque-velocity relationship of the quadriceps femoris
 Effect of cold treatment on the concentric and eccentric torque-velocity relationship of the quadriceps femoris By: Kerriann Catlaw *, Brent L. Arnold, and David H. Perrin Catlaw, K., Arnold, B.L., & Perrin,
Effect of cold treatment on the concentric and eccentric torque-velocity relationship of the quadriceps femoris By: Kerriann Catlaw *, Brent L. Arnold, and David H. Perrin Catlaw, K., Arnold, B.L., & Perrin,
Fitness components & assessment
 Fitness components & assessment Key terms & definitions: Capacity: The total amount of energy produced by the energy system (e.g. aerobic capacity or anaerobic capacity). Power: The rate of energy production
Fitness components & assessment Key terms & definitions: Capacity: The total amount of energy produced by the energy system (e.g. aerobic capacity or anaerobic capacity). Power: The rate of energy production
Isokinetic Strength Responses to Season-long Training and Competition in Turkish Elite Soccer Players
 Journal of Human Kinetics volume 31/2012, 159-168 DOI: 10.2478/v10078-012-0017-5 159 Section III Sports Training Isokinetic Strength Responses to Season-long Training and Competition in Turkish Elite Soccer
Journal of Human Kinetics volume 31/2012, 159-168 DOI: 10.2478/v10078-012-0017-5 159 Section III Sports Training Isokinetic Strength Responses to Season-long Training and Competition in Turkish Elite Soccer
EFFECTS OF TWO WARM-UP PROGRAMS ON BALANCE AND ISOKINETIC STRENGTH IN MALE HIGH SCHOOL SOCCER PLAYERS ACCEPTED
 Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research Publish Ahead of Print DOI: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000001509 By EFFECTS OF TWO WARM-UP PROGRAMS ON BALANCE AND ISOKINETIC STRENGTH IN MALE HIGH SCHOOL SOCCER PLAYERS
Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research Publish Ahead of Print DOI: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000001509 By EFFECTS OF TWO WARM-UP PROGRAMS ON BALANCE AND ISOKINETIC STRENGTH IN MALE HIGH SCHOOL SOCCER PLAYERS
2014 Athletes Performance inc. Athletic Profiling Discuss the need for athletic profiling and the factors that underpin sports performance
 Athletic Profiling: Testing Models That Transfer to Sport Nick Winkelman, MSc, XPS, CSCS*D Director of Movement and Education nwinkelman@teamexos.com Objectives Athletic Profiling Discuss the need for
Athletic Profiling: Testing Models That Transfer to Sport Nick Winkelman, MSc, XPS, CSCS*D Director of Movement and Education nwinkelman@teamexos.com Objectives Athletic Profiling Discuss the need for
The Risk Factors of Hamstring Strain Injury Induced by High-Speed Running
 Journal of Sports Science and Medicine (2018) 17, 650-655 http://www.jssm.org ` Research article The Risk Factors of Hamstring Strain Injury Induced by High-Speed Running Gaku Tokutake 1, Rieko Kuramochi
Journal of Sports Science and Medicine (2018) 17, 650-655 http://www.jssm.org ` Research article The Risk Factors of Hamstring Strain Injury Induced by High-Speed Running Gaku Tokutake 1, Rieko Kuramochi
CHAPTER 24. Working as a physiologist in professional soccer. Barry Drust The Football Exchange, Liverpool John Moores University, Liverpool, UK
 Working as a physiologist in professional soccer CHAPTER 24 Barry Drust The Football Exchange, Liverpool John Moores University, Liverpool, UK Discussion Soccer is characterised by high-intensity efforts
Working as a physiologist in professional soccer CHAPTER 24 Barry Drust The Football Exchange, Liverpool John Moores University, Liverpool, UK Discussion Soccer is characterised by high-intensity efforts
Title: Hamstring strength and flexibility after hamstring strain injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 Title: Hamstring strength and flexibility after hamstring strain injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 Title: Hamstring strength and flexibility after hamstring strain injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
performance in young jumpers
 BIOLOGY OF EXERCISE VOLUME 5.2, 2009 Isokinetic muscle strength and running long jump performance in young jumpers D.O.I: http:doi.org/10.4127/jbe.2009.0030 YIANNIS KOUTSIORAS, ATHANASIOS TSIOKANOS, DIMITRIOS
BIOLOGY OF EXERCISE VOLUME 5.2, 2009 Isokinetic muscle strength and running long jump performance in young jumpers D.O.I: http:doi.org/10.4127/jbe.2009.0030 YIANNIS KOUTSIORAS, ATHANASIOS TSIOKANOS, DIMITRIOS
The Relationship among Flexibility, Aerobic Fitness, Leg Extension Power and Agility with Lower Extremity Injuries in Footballers
 ISSN 750-983 (print) International Journal of Sports Science and Engineering Vol. 05 (0) No. 0, pp. 05- The Relationship among Flexibility, Aerobic Fitness, Leg Extension Power and Agility with Lower Extremity
ISSN 750-983 (print) International Journal of Sports Science and Engineering Vol. 05 (0) No. 0, pp. 05- The Relationship among Flexibility, Aerobic Fitness, Leg Extension Power and Agility with Lower Extremity
H amstring injuries are common in sprinting, dancing,
 106 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Risk factors for hamstring injuries in community level Australian football B J Gabbe, C F Finch, K L Bennell, H Wajswelner... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence
106 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Risk factors for hamstring injuries in community level Australian football B J Gabbe, C F Finch, K L Bennell, H Wajswelner... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence
In the lower extremity, it is very important to maintain
 PREDICTING ASYMMETRICAL LOWER EXTREMITY STRENGTH DEFICITS IN COLLEGE-AGED MEN AND WOMEN USING COMMON HORIZONTAL AND VERTICAL POWER FIELD TESTS: A POSSIBLE SCREENING MECHANISM DAVID W. KEELEY, HILLARY A.
PREDICTING ASYMMETRICAL LOWER EXTREMITY STRENGTH DEFICITS IN COLLEGE-AGED MEN AND WOMEN USING COMMON HORIZONTAL AND VERTICAL POWER FIELD TESTS: A POSSIBLE SCREENING MECHANISM DAVID W. KEELEY, HILLARY A.
Development of a Functional Movement Screening Tool for Football
 Development of a Functional Movement Screening Tool for Football By Erin Morehead MSc Medicine and Science in Sport and Exercise BSc (Hons) Physiotherapy A thesis submitted in partial fulfilment for the
Development of a Functional Movement Screening Tool for Football By Erin Morehead MSc Medicine and Science in Sport and Exercise BSc (Hons) Physiotherapy A thesis submitted in partial fulfilment for the
Chapter I. Introduction
 Chapter I Introduction 1 Chapter 1 Introduction The body is the temple of the soul and to reach the harmony of the mind, body and spirit, the body must be physically fit (Bucher, 1968) 1.1 Soccer demands
Chapter I Introduction 1 Chapter 1 Introduction The body is the temple of the soul and to reach the harmony of the mind, body and spirit, the body must be physically fit (Bucher, 1968) 1.1 Soccer demands
Chapter 20: Test Administration and Interpretation
 Chapter 20: Test Administration and Interpretation Thought Questions Why should a needs analysis consider both the individual and the demands of the sport? Should test scores be shared with a team, or
Chapter 20: Test Administration and Interpretation Thought Questions Why should a needs analysis consider both the individual and the demands of the sport? Should test scores be shared with a team, or
Rapid hamstrings/quadriceps strength capacity in professional soccer players with different conventional isokinetic muscle strength ratios
 Journal of Sports Science and Medicine (2012) 11, 418-422 http://www.jssm.org Research article Rapid hamstrings/quadriceps strength capacity in professional soccer players with different conventional isokinetic
Journal of Sports Science and Medicine (2012) 11, 418-422 http://www.jssm.org Research article Rapid hamstrings/quadriceps strength capacity in professional soccer players with different conventional isokinetic
Intramachine and intermachine reproducibility of concentric performance: A study of the Con-Trex MJ and the Cybex Norm dynamometers
 Isokinetics and Exercise Science 12 (4) 91 97 91 IOS Press Intramachine and intermachine reproducibility of concentric performance: A study of the Con-Trex MJ and the Cybex Norm dynamometers C. Bardis
Isokinetics and Exercise Science 12 (4) 91 97 91 IOS Press Intramachine and intermachine reproducibility of concentric performance: A study of the Con-Trex MJ and the Cybex Norm dynamometers C. Bardis
The influence of soccer-specific fatigue on functional stability
 ARTICLE IN PRESS Physical Therapy in Sport 8 (2007) 185 190 Original research The influence of soccer-specific fatigue on functional stability Matt Greig a,, Colin Walker-Johnson b a Medical and Exercise
ARTICLE IN PRESS Physical Therapy in Sport 8 (2007) 185 190 Original research The influence of soccer-specific fatigue on functional stability Matt Greig a,, Colin Walker-Johnson b a Medical and Exercise
REHABILITATION PROTOCOL FOLLOWING PCL RECONSTRUCTION USING A TWO TUNNEL GRAFT. Brace E-Z Wrap locked at zero degree extension, sleep in Brace
 Therapist Phone REHABILITATION PROTOCOL FOLLOWING PCL RECONSTRUCTION USING A TWO TUNNEL GRAFT I. IMMEDIATE POST-OPERATIVE PHASE (Week 1) Control Swelling and Inflammation Obtain Full Passive Knee Extension
Therapist Phone REHABILITATION PROTOCOL FOLLOWING PCL RECONSTRUCTION USING A TWO TUNNEL GRAFT I. IMMEDIATE POST-OPERATIVE PHASE (Week 1) Control Swelling and Inflammation Obtain Full Passive Knee Extension
ACL Injury Prevention: Considerations for Children and Adolescents
 ACL Injury Prevention: Considerations for Children and Adolescents Susan Sigward PhD, PT, ATC Human Performance Laboratory University of Southern California 1 ACL Injury Season ending/ Career ending 82%
ACL Injury Prevention: Considerations for Children and Adolescents Susan Sigward PhD, PT, ATC Human Performance Laboratory University of Southern California 1 ACL Injury Season ending/ Career ending 82%
Validity of Data Extraction Techniques on the Kinetic Communicator (KinCom) Isokinetic Device
 Validity of Data Extraction Techniques on the Kinetic Communicator (KinCom) Isokinetic Device By: Laurie L. Tis, PhD, AT,C * and David H. Perrin, PhD, AT,C Tis, L.L., & Perrin, D.H. (1993). Validity of
Validity of Data Extraction Techniques on the Kinetic Communicator (KinCom) Isokinetic Device By: Laurie L. Tis, PhD, AT,C * and David H. Perrin, PhD, AT,C Tis, L.L., & Perrin, D.H. (1993). Validity of
Prevention in Groin Injury
 Prevention in Groin Injury Wennig Louis, PT Radrizzi Laurent, PT Centre de l l Appareil Locomoteur, de Médecine M du Sport et de Prévention Centre Hospitalier de Luxembourg Clinique d Eichd Groin Injury
Prevention in Groin Injury Wennig Louis, PT Radrizzi Laurent, PT Centre de l l Appareil Locomoteur, de Médecine M du Sport et de Prévention Centre Hospitalier de Luxembourg Clinique d Eichd Groin Injury
Protocols for the. Physiological Assessment of. Gaelic Football Development. Squads
 Protocols for the Physiological Assessment of Gaelic Football Development Squads by Eugene Young, Declan Gamble & Paul Boyle 1 Introduction Physical fitness in Gaelic football has been defined by the OTú
Protocols for the Physiological Assessment of Gaelic Football Development Squads by Eugene Young, Declan Gamble & Paul Boyle 1 Introduction Physical fitness in Gaelic football has been defined by the OTú
NATURAL DEVELOPMENT AND TRAINABILITY OF PLYOMETRIC ABILITY DURING CHILDHOOD BY KIRSTY QUERL SPORT SCIENTIST STRENGTH AND CONDITIONING COACH
 NATURAL DEVELOPMENT AND TRAINABILITY OF PLYOMETRIC ABILITY DURING CHILDHOOD BY KIRSTY QUERL SPORT SCIENTIST STRENGTH AND CONDITIONING COACH The truth... Youth are not as active as they used to be, Decline
NATURAL DEVELOPMENT AND TRAINABILITY OF PLYOMETRIC ABILITY DURING CHILDHOOD BY KIRSTY QUERL SPORT SCIENTIST STRENGTH AND CONDITIONING COACH The truth... Youth are not as active as they used to be, Decline
Long-term Training Adaptations in Elite Male Volleyball Players
 Edith Cowan University Research Online ECU Publications 2011 2011 Long-term Training Adaptations in Elite Male Volleyball Players Jeremy Sheppard Edith Cowan University Robert Newton Edith Cowan University
Edith Cowan University Research Online ECU Publications 2011 2011 Long-term Training Adaptations in Elite Male Volleyball Players Jeremy Sheppard Edith Cowan University Robert Newton Edith Cowan University
Applied physiology of female soccer: an update
 TeesRep - Teesside's Research Repository Applied physiology of female soccer: an update Item type Article Authors Datson, N. (Naomi); Hulton, A. (Andrew); Andersson, H. (Helena); Lewis, T. (Tracy); Weston,
TeesRep - Teesside's Research Repository Applied physiology of female soccer: an update Item type Article Authors Datson, N. (Naomi); Hulton, A. (Andrew); Andersson, H. (Helena); Lewis, T. (Tracy); Weston,
Manual or exercise therapy for long-standing adductor-related groin pain: Mid-term follow-up of a randomised controlled clinical trial
 Manual or exercise therapy for long-standing adductor-related groin pain: Mid-term follow-up of a randomised controlled clinical trial Weir A 1, Jansen N 2, Dijkstra SD 3, Backx FJG 4, Tol JL 1 1Aspetar
Manual or exercise therapy for long-standing adductor-related groin pain: Mid-term follow-up of a randomised controlled clinical trial Weir A 1, Jansen N 2, Dijkstra SD 3, Backx FJG 4, Tol JL 1 1Aspetar
Reliability and Validity of the T-Test as a Measure of Agility, Leg Power, and Leg Speed in College-Aged Men and Women
 Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 2000, 14(4), 443 450 2000 National Strength & Conditioning Association Reliability and Validity of the T-Test as a Measure of Agility, Leg Power, and Leg
Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 2000, 14(4), 443 450 2000 National Strength & Conditioning Association Reliability and Validity of the T-Test as a Measure of Agility, Leg Power, and Leg
REHABILITATION PROTOCOL FOLLOWING PCL RECONSTRUCTION USING Allograft
 Sports Medicine and Rehabilitation Center Therapist Phone REHABILITATION PROTOCOL FOLLOWING PCL RECONSTRUCTION USING Allograft I. IMMEDIATE POST-OPERATIVE PHASE (Week 1) Control Swelling and Inflammation
Sports Medicine and Rehabilitation Center Therapist Phone REHABILITATION PROTOCOL FOLLOWING PCL RECONSTRUCTION USING Allograft I. IMMEDIATE POST-OPERATIVE PHASE (Week 1) Control Swelling and Inflammation
The effect of hamstring flexibility on peak hamstring muscle strain in sprinting
 HOSTED BY Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Journal of Sport and Health Science 6 (2017) 283 289 Original article The effect of hamstring flexibility on peak hamstring muscle strain
HOSTED BY Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Journal of Sport and Health Science 6 (2017) 283 289 Original article The effect of hamstring flexibility on peak hamstring muscle strain
Sports Conditioning for the Knee A guide to conditioning and knee injury prevention
 Alex Petruska, PT, SCS, LAT Sports Conditioning for the Knee A guide to conditioning and knee injury prevention This program has been developed to provide a comprehensive guide to the conditioning of the
Alex Petruska, PT, SCS, LAT Sports Conditioning for the Knee A guide to conditioning and knee injury prevention This program has been developed to provide a comprehensive guide to the conditioning of the
Hamstring muscle injuries in professional football: the correlation of MRI findings with return to play
 Hamstring muscle injuries in professional football: the correlation of MRI findings with return to play Jan Ekstrand, Jeremiah C Healy, Markus Waldén, Justin C Lee, Bryan English and Martin Hägglund Linköping
Hamstring muscle injuries in professional football: the correlation of MRI findings with return to play Jan Ekstrand, Jeremiah C Healy, Markus Waldén, Justin C Lee, Bryan English and Martin Hägglund Linköping
The Science of Sustained Excellence
 Theory of Monitoring Annual Training Progression with Physical Testing to Prevent Injury and Improve Performance By Troy Purdom, PhD & Kyle Levers, PhD CSCS The Science of Sustained Excellence July 22,
Theory of Monitoring Annual Training Progression with Physical Testing to Prevent Injury and Improve Performance By Troy Purdom, PhD & Kyle Levers, PhD CSCS The Science of Sustained Excellence July 22,
TRAINING FOR EXPLOSIVE POWER
 TRAINING FOR EXPLOSIVE POWER How fast an athlete can generate power from a stand still. Short sprinters, offensive lineman in football and shot putters are examples of explosive athletes. An athlete s
TRAINING FOR EXPLOSIVE POWER How fast an athlete can generate power from a stand still. Short sprinters, offensive lineman in football and shot putters are examples of explosive athletes. An athlete s
Functional Asymmetry of Lower Limbs in Female Elite Volleyball Players during Jumping - landing
 ISSN No. (Print): 0975-1130 ISSN No. (Online): 2249-3239 Functional Asymmetry of Lower Limbs in Female Elite Volleyball Players during Jumping - landing Doroudian Zohreh* and Jamshidi Ali Ashraf** *College
ISSN No. (Print): 0975-1130 ISSN No. (Online): 2249-3239 Functional Asymmetry of Lower Limbs in Female Elite Volleyball Players during Jumping - landing Doroudian Zohreh* and Jamshidi Ali Ashraf** *College
The Star Excursion Balance Test (SEBT) is a unilateral, UNILATERAL BALANCE PERFORMANCE IN FEMALE COLLEGIATE SOCCER ATHLETES
 UNILATERAL BALANCE PERFORMANCE IN FEMALE COLLEGIATE SOCCER ATHLETES JENNIFER L. THORPE AND KYLE T. EBERSOLE University of Illinois, Department of Kinesiology and Community Health, Urbana, Illinois ABSTRACT
UNILATERAL BALANCE PERFORMANCE IN FEMALE COLLEGIATE SOCCER ATHLETES JENNIFER L. THORPE AND KYLE T. EBERSOLE University of Illinois, Department of Kinesiology and Community Health, Urbana, Illinois ABSTRACT
Hamstring Strain. 43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) Website: philip-bayliss.com.
 43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) 356 1353. Website: philip-bayliss.com Hamstring Strain The hamstring muscles are very susceptible to tears, strains and other common sporting
43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) 356 1353. Website: philip-bayliss.com Hamstring Strain The hamstring muscles are very susceptible to tears, strains and other common sporting
The influence of soccer-specific fatigue on hip range of motion and peak isokinetic hip flexor torque in male soccer players
 Graduate Theses and Dissertations Graduate College 2011 The influence of soccer-specific fatigue on hip range of motion and peak isokinetic hip flexor torque in male soccer players Timothy William Robinson
Graduate Theses and Dissertations Graduate College 2011 The influence of soccer-specific fatigue on hip range of motion and peak isokinetic hip flexor torque in male soccer players Timothy William Robinson
Isokinetic strength testing does not predict hamstring injury in Australian Rules footballers
 Br J Sports Med 1998;32:309 314 309 School of Physiotherapy, University of Melbourne, Australia K Bennell H Wajswelner P Lew A Schall-Riaucour S Leslie J Cirone Department of Physiology D Plant Correspondence
Br J Sports Med 1998;32:309 314 309 School of Physiotherapy, University of Melbourne, Australia K Bennell H Wajswelner P Lew A Schall-Riaucour S Leslie J Cirone Department of Physiology D Plant Correspondence
Descriptive characteristics of NCAA Division I women lacrosse players
 Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport (2007) 10, 334 340 ORIGINAL PAPER Descriptive characteristics of NCAA Division I women lacrosse players Jason D. Vescovi a,b,, Todd D. Brown b, Teena M. Murray
Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport (2007) 10, 334 340 ORIGINAL PAPER Descriptive characteristics of NCAA Division I women lacrosse players Jason D. Vescovi a,b,, Todd D. Brown b, Teena M. Murray
Injury prevention: Which measures are useful? Prof. István Berkes MD., PhD
 Injury prevention: Which measures are useful? Prof. István Berkes MD., PhD Priorities in Sports Medicine Antidoping Prevention of injuries General considerations Increasing number of active athletes and
Injury prevention: Which measures are useful? Prof. István Berkes MD., PhD Priorities in Sports Medicine Antidoping Prevention of injuries General considerations Increasing number of active athletes and
Clinical predictors of time to return to competition and of recurrence following hamstring strain in elite Australian footballers
 Clinical predictors of time to return to competition and of recurrence following hamstring strain in elite Australian footballers Price Warren 1, Belinda J Gabbe 2, Michal SchneiderKolsky 3, Kim L Bennell
Clinical predictors of time to return to competition and of recurrence following hamstring strain in elite Australian footballers Price Warren 1, Belinda J Gabbe 2, Michal SchneiderKolsky 3, Kim L Bennell
CORRELATION PROFILES BETWEEN LOWER EXTREMITY JOINT POWER AND WHOLE BODY POWER DURING THE POWER CLEAN BACKGROUND
 CORRELATION PROFILES BETWEEN LOWER EXTREMITY JOINT POWER AND WHOLE BODY POWER DURING THE POWER CLEAN BACKGROUND The power clean (PC) is one of the essential Olympic weightlifting techniques and technically
CORRELATION PROFILES BETWEEN LOWER EXTREMITY JOINT POWER AND WHOLE BODY POWER DURING THE POWER CLEAN BACKGROUND The power clean (PC) is one of the essential Olympic weightlifting techniques and technically
Isokinetic strength effects of FIFA s The 11+ injury prevention training programme
 Isokinetics and Exercise Science 18 (2010) 211 215 211 DOI 10.3233/IES-2010-0386 IOS Press Isokinetic strength effects of FIFA s The 11+ injury prevention training programme João Brito a,, Pedro Figueiredo
Isokinetics and Exercise Science 18 (2010) 211 215 211 DOI 10.3233/IES-2010-0386 IOS Press Isokinetic strength effects of FIFA s The 11+ injury prevention training programme João Brito a,, Pedro Figueiredo
An investigation into the physical determinants of change of direction speed.
 University of Bolton UBIR: University of Bolton Institutional Repository Sport and Recreation: Journal Articles (Peer- Reviewed) Sport and Recreation 00 An investigation into the physical determinants
University of Bolton UBIR: University of Bolton Institutional Repository Sport and Recreation: Journal Articles (Peer- Reviewed) Sport and Recreation 00 An investigation into the physical determinants
NONOPERATIVE REHABILITATION FOLLOWING ACL INJURY ( Program)
 Therapist: Phone: NONOPERATIVE REHABILITATION FOLLOWING ACL INJURY (3-3-4-4 Program) IMMEDIATE INJURY PHASE (Day 1 to Day 7) Restore full passive knee extension Diminish joint swelling and pain Restore
Therapist: Phone: NONOPERATIVE REHABILITATION FOLLOWING ACL INJURY (3-3-4-4 Program) IMMEDIATE INJURY PHASE (Day 1 to Day 7) Restore full passive knee extension Diminish joint swelling and pain Restore
Prior et al Mar Apr An Evidence-Based Approach to Hamstring Strain Injury: A Systematic Review of the Literature
 [ Athletic Training ] An Evidence-Based Approach to Hamstring Strain Injury: A Systematic Review of the Literature Mathew Prior, B Physiotherapy (Hons),* Michelle Guerin, B Physiotherapy (Hons), and Karen
[ Athletic Training ] An Evidence-Based Approach to Hamstring Strain Injury: A Systematic Review of the Literature Mathew Prior, B Physiotherapy (Hons),* Michelle Guerin, B Physiotherapy (Hons), and Karen
Preventing Joint Injury & Subsequent Osteoarthritis:
 Preventing Joint Injury & Subsequent Osteoarthritis: A Population Health Prospective Carolyn Emery PT, PhD Public Health Burden of Injury in Alberta The leading cause of death and hospitalization in youth
Preventing Joint Injury & Subsequent Osteoarthritis: A Population Health Prospective Carolyn Emery PT, PhD Public Health Burden of Injury in Alberta The leading cause of death and hospitalization in youth
Hams t r ing s t r ain injur ie s: ar e we heading in the right direction?
 Hams t r ing s t r ain injur ie s: ar e we heading in the right direction? Jurd an M endiguchia, 1 Edu ard A len tor n - G eli, 2 M a t t B r ughelli 3 Acute hamstring injuries are the most prevalent muscle
Hams t r ing s t r ain injur ie s: ar e we heading in the right direction? Jurd an M endiguchia, 1 Edu ard A len tor n - G eli, 2 M a t t B r ughelli 3 Acute hamstring injuries are the most prevalent muscle
The relationship between hip internal rotation. and groin pain in elite Australian Rules Football. players. Ngaire McKay. Jenny Hynes.
 The relationship between hip internal rotation and groin pain in elite Australian Rules Football players. Ngaire McKay Jenny Hynes Patrick McLaughlin 1 Abstract A prospective study was performed in order
The relationship between hip internal rotation and groin pain in elite Australian Rules Football players. Ngaire McKay Jenny Hynes Patrick McLaughlin 1 Abstract A prospective study was performed in order
THE YOUTH PHYSICAL DEVELOPMENT MODEL: A New Approach to Long Term Athletic Development
 THE YOUTH PHYSICAL DEVELOPMENT MODEL: A New Approach to Long Term Athletic Development Lindsay Dunn ASA England Programmes Officer and AASE Technical Lead Youth Physical Development Model Alternative to
THE YOUTH PHYSICAL DEVELOPMENT MODEL: A New Approach to Long Term Athletic Development Lindsay Dunn ASA England Programmes Officer and AASE Technical Lead Youth Physical Development Model Alternative to
FIFA 11 + WARM-UP TORONTO HIGH PARK FOOTBALL CLUB
 FIFA 11 + WARM-UP TORONTO HIGH PARK FOOTBALL CLUB OVERVIEW What is the FIFA 11 + Warm-up? Who Developed the FIFA 11 + Warm-up? FIFA 11 + Program 3 Parts FIFA 11 + Field Set-up What are the Advantages of
FIFA 11 + WARM-UP TORONTO HIGH PARK FOOTBALL CLUB OVERVIEW What is the FIFA 11 + Warm-up? Who Developed the FIFA 11 + Warm-up? FIFA 11 + Program 3 Parts FIFA 11 + Field Set-up What are the Advantages of
Fatigue Impact to Mechanical Movement of Maximal Instep Kicking in Soccer
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Fatigue Impact to Mechanical Movement of Maximal Instep Kicking in Soccer To cite this article: A Rusdiana et al 2017 IOP Conf.
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Fatigue Impact to Mechanical Movement of Maximal Instep Kicking in Soccer To cite this article: A Rusdiana et al 2017 IOP Conf.
EVect of stretching duration on active and passive range of motion in the lower extremity
 Br J Sports Med 1999;33:259 263 259 School of Health Sciences, University of Sunderland J M Roberts K Wilson Correspondence to: J M Roberts, School of Health Sciences, University of Sunderland, Chester
Br J Sports Med 1999;33:259 263 259 School of Health Sciences, University of Sunderland J M Roberts K Wilson Correspondence to: J M Roberts, School of Health Sciences, University of Sunderland, Chester
ELECTRICAL MUSCLE STIMULATION (EMS) IMPLEMENTATION IN EXPLOSIVE STRENGTH DEVELOPMENT
 Zoran Đokić, Bojan Međedović Fakultet za sport i turizam, Novi Sad UDK:796.012.11:615.84 ELECTRICAL MUSCLE STIMULATION (EMS) IMPLEMENTATION IN EXPLOSIVE STRENGTH DEVELOPMENT 1. INTRODUCTION Research on
Zoran Đokić, Bojan Međedović Fakultet za sport i turizam, Novi Sad UDK:796.012.11:615.84 ELECTRICAL MUSCLE STIMULATION (EMS) IMPLEMENTATION IN EXPLOSIVE STRENGTH DEVELOPMENT 1. INTRODUCTION Research on
Mechanisms of ACL Injury: Implications for Rehabilitation, Injury Prevention & Return to Sport Decisions. Overarching research theme:
 Mechanisms of ACL Injury: Implications for Rehabilitation, Injury Prevention & Return to Sport Decisions Associate Professor Co Director, Musculoskeletal Biomechanics Research Laboratory University of
Mechanisms of ACL Injury: Implications for Rehabilitation, Injury Prevention & Return to Sport Decisions Associate Professor Co Director, Musculoskeletal Biomechanics Research Laboratory University of
BCLFC Prehab U915 s/17s 3 rd December 2013 Jade Moore and Tim Colledge
 BCLFC Prehab U915 s/17s 3 rd December 2013 Jade Moore and Tim Colledge Objectives Outline the purpose of prehabilitation exercises and its role within football, building on your progress as an athlete
BCLFC Prehab U915 s/17s 3 rd December 2013 Jade Moore and Tim Colledge Objectives Outline the purpose of prehabilitation exercises and its role within football, building on your progress as an athlete
ACL and Knee Injury Prevention. Presented by: Zach Kirkpatrick, PT, MPT, SCS
 ACL and Knee Injury Prevention Presented by: Zach Kirkpatrick, PT, MPT, SCS ACL Anatomy ACL Mechanism of Injury Contact ACL Tear Noncontact ACL Tear ACL MOI and Pathology Common in young individual who
ACL and Knee Injury Prevention Presented by: Zach Kirkpatrick, PT, MPT, SCS ACL Anatomy ACL Mechanism of Injury Contact ACL Tear Noncontact ACL Tear ACL MOI and Pathology Common in young individual who
Game-based conditioning using small-sided games
 ACUTE PHYSIOLOGICAL RESPONSES AND TIME- MOTION CHARACTERISTICS OF TWO SMALL-SIDED TRAINING REGIMES IN YOUTH SOCCER PLAYERS STEPHEN V. HILL-HAAS, 1 GREG J. ROWSELL, 2 BRIAN T. DAWSON, 1 AND AARON J. COUTTS
ACUTE PHYSIOLOGICAL RESPONSES AND TIME- MOTION CHARACTERISTICS OF TWO SMALL-SIDED TRAINING REGIMES IN YOUTH SOCCER PLAYERS STEPHEN V. HILL-HAAS, 1 GREG J. ROWSELL, 2 BRIAN T. DAWSON, 1 AND AARON J. COUTTS
Objectives. Running Analysis: Sprint. The Lost Art. What is Acceleration. Force Velocity Curve 3/6/2017
 Objectives Running Analysis: Sprint Presented by Brenton A Hardy, MEd, ATC, CSCS 1. Understand basic sprinting mechanics and utilization of acceleration training in programs 2. Rehabilitation approach
Objectives Running Analysis: Sprint Presented by Brenton A Hardy, MEd, ATC, CSCS 1. Understand basic sprinting mechanics and utilization of acceleration training in programs 2. Rehabilitation approach
Authors Taylor, J. M.; Macpherson, T. W. (Tom); Spears, I. R. (Iain); Weston, M. (Matthew)
 TeesRep - Teesside's Research Repository Repeated sprints: an independent not dependent variable Item type Article Authors Taylor, J. M.; Macpherson, T. W. (Tom); Spears, I. R. (Iain); Weston, M. (Matthew)
TeesRep - Teesside's Research Repository Repeated sprints: an independent not dependent variable Item type Article Authors Taylor, J. M.; Macpherson, T. W. (Tom); Spears, I. R. (Iain); Weston, M. (Matthew)
What Factors Determine Vertical Jumping Height?
 What Factors Determine Vertical Jumping Height? L. Oddsson University College of Physical Education and Department of Physiology Ill, Karolinska Institute, Stockholm. Sweden. INTRODUCTION The ability to
What Factors Determine Vertical Jumping Height? L. Oddsson University College of Physical Education and Department of Physiology Ill, Karolinska Institute, Stockholm. Sweden. INTRODUCTION The ability to
Carling, C., Le Gall, F., McCall, A., Nedelec, M., and Dupont, G.
 Article Are aerobic fitness and repeated sprint ability linked to fatigue in professional soccer match play? A pilot study Carling, C., Le Gall, F., McCall, A., Nedelec, M., and Dupont, G. Available at
Article Are aerobic fitness and repeated sprint ability linked to fatigue in professional soccer match play? A pilot study Carling, C., Le Gall, F., McCall, A., Nedelec, M., and Dupont, G. Available at
Injury rate, mechanism, and risk factors of hamstring strain injuries in sports: A review of the literature
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Journal of Sport and Health Science 1 (2012) 92e101 Review Injury rate, mechanism, and risk factors of hamstring strain injuries in sports: A review of the literature
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Journal of Sport and Health Science 1 (2012) 92e101 Review Injury rate, mechanism, and risk factors of hamstring strain injuries in sports: A review of the literature
Readiness for Soccer
 Youth Fitness? Readiness for Soccer Readiness for sports is the match between a child s level of growth, maturity and development, and the task demands presented in competitive sports. Robert M. Malina,
Youth Fitness? Readiness for Soccer Readiness for sports is the match between a child s level of growth, maturity and development, and the task demands presented in competitive sports. Robert M. Malina,
STRENGTH MEASUREMENTS IN ATHLETES WITH GROIN PAIN
 STRENGTH MEASUREMENTS IN ATHLETES WITH GROIN PAIN Written by Kristian Thorborg, Denmark INTRODUCTION Hip and groin pain is a common problem often related to physical functioning and sports activities.
STRENGTH MEASUREMENTS IN ATHLETES WITH GROIN PAIN Written by Kristian Thorborg, Denmark INTRODUCTION Hip and groin pain is a common problem often related to physical functioning and sports activities.
This file was dowloaded from the institutional repository Brage NIH - brage.bibsys.no/nih
 This file was dowloaded from the institutional repository Brage NIH - brage.bibsys.no/nih Bahr, R., Thorborg, K., Ekstrand, J. (2015). Evidence-based hamstring injury prevention is not adopted by the majority
This file was dowloaded from the institutional repository Brage NIH - brage.bibsys.no/nih Bahr, R., Thorborg, K., Ekstrand, J. (2015). Evidence-based hamstring injury prevention is not adopted by the majority
Effect of Static Stretching or Foam Rolling on Hamstrings Range of Motion and Strength
 Southern Illinois University Carbondale OpenSIUC Research Papers Graduate School Summer 8-10-2017 Effect of Static Stretching or Foam Rolling on Hamstrings Range of Motion and Strength Grant Wiseman Southern
Southern Illinois University Carbondale OpenSIUC Research Papers Graduate School Summer 8-10-2017 Effect of Static Stretching or Foam Rolling on Hamstrings Range of Motion and Strength Grant Wiseman Southern
CHAPTER 15: KINESIOLOGY OF FITNESS AND EXERCISE
 CHAPTER 15: KINESIOLOGY OF FITNESS AND EXERCISE KINESIOLOGY Scientific Basis of Human Motion, 12th edition Hamilton, Weimar & Luttgens Presentation Created by TK Koesterer, Ph.D., ATC Humboldt State University
CHAPTER 15: KINESIOLOGY OF FITNESS AND EXERCISE KINESIOLOGY Scientific Basis of Human Motion, 12th edition Hamilton, Weimar & Luttgens Presentation Created by TK Koesterer, Ph.D., ATC Humboldt State University
Home-based exercise program 12 weeks following ACL reconstitution Inspired by the FIFA 11+ Injury prevention program
 Home-based exercise program 12 weeks following ACL reconstitution Inspired by the FIFA 11+ Injury prevention program Introduction This homed-based program is suited for rehabilitation at least 12 weeks
Home-based exercise program 12 weeks following ACL reconstitution Inspired by the FIFA 11+ Injury prevention program Introduction This homed-based program is suited for rehabilitation at least 12 weeks
Effect of plyometric and circuit training programme on explosive strength of male basketball players of Punjab
 2016; 2(12): 636-640 ISSN Print: 2394-7500 ISSN Online: 2394-5869 Impact Factor: 5.2 IJAR 2016; 2(12): 636-640 www.allresearchjournal.com Received: 02-10-2016 Accepted: 03-11-2016 Research Scholar Desh
2016; 2(12): 636-640 ISSN Print: 2394-7500 ISSN Online: 2394-5869 Impact Factor: 5.2 IJAR 2016; 2(12): 636-640 www.allresearchjournal.com Received: 02-10-2016 Accepted: 03-11-2016 Research Scholar Desh
Comparative study of two isokinetics dynamometers: CYBEX NORM vs CON-TREX MJ
 Isokinetics and Exercise Science 11 (2003) 37 43 37 IOS Press Comparative study of two isokinetics dynamometers: CYBEX NORM vs CON-TREX MJ T. Cotte and J.-M. Ferret Centre de Médecine du Sport de Lyon
Isokinetics and Exercise Science 11 (2003) 37 43 37 IOS Press Comparative study of two isokinetics dynamometers: CYBEX NORM vs CON-TREX MJ T. Cotte and J.-M. Ferret Centre de Médecine du Sport de Lyon
Rehabilitation Guidelines Following Proximal Hamstring Primary Repair
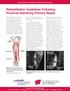 UW HEALTH SPORTS REHABILITATION Rehabilitation Guidelines Following Proximal Hamstring Primary Repair The hamstring muscle group consists of three muscles: the biceps femoris, semitendinosus and semimembranosus.
UW HEALTH SPORTS REHABILITATION Rehabilitation Guidelines Following Proximal Hamstring Primary Repair The hamstring muscle group consists of three muscles: the biceps femoris, semitendinosus and semimembranosus.
Outline 3D Core Training with Rubber Resistance
 Outline 3D Core Training with Rubber Resistance Mike Bracko, Ed.D. CSCS, FACSM Fitness Educator / Sports Physiologist drbrackofitness@aol.com Introduction Rubber resistance was originally used to train
Outline 3D Core Training with Rubber Resistance Mike Bracko, Ed.D. CSCS, FACSM Fitness Educator / Sports Physiologist drbrackofitness@aol.com Introduction Rubber resistance was originally used to train
MEASURING BILATERAL ASYMMETRY IN A LONG TERM ATHLETE MONITORING
 MEASURING BILATERAL ASYMMETRY IN A LONG TERM ATHLETE MONITORING Kimitake Sato Department of Exercise and Sport Science, Center of Excellence for Sport Science and Coach Education, East Tennessee State
MEASURING BILATERAL ASYMMETRY IN A LONG TERM ATHLETE MONITORING Kimitake Sato Department of Exercise and Sport Science, Center of Excellence for Sport Science and Coach Education, East Tennessee State
Prediction of Hamstring injury in professional soccer players by isokinetic measurements
 Prediction of Hamstring injury in professional soccer players by isokinetic measurements Original article Marc Dauty Pierre Menu Alban Fouasson-Chaillou Sophie Ferréol Charles Dubois Department of Pôle
Prediction of Hamstring injury in professional soccer players by isokinetic measurements Original article Marc Dauty Pierre Menu Alban Fouasson-Chaillou Sophie Ferréol Charles Dubois Department of Pôle
Re training Movement Behavior for ACL Injury Prevention and Rehabilitation: A Matter of Strength or Motor Control?
 Re training Movement Behavior for ACL Injury Prevention and Rehabilitation: A Matter of Strength or Motor Control? Christopher M. Powers, PT, PhD, FACSM, FAPTA Beth Fisher, PT, PhD, FAPTA Division of Biokinesiology
Re training Movement Behavior for ACL Injury Prevention and Rehabilitation: A Matter of Strength or Motor Control? Christopher M. Powers, PT, PhD, FACSM, FAPTA Beth Fisher, PT, PhD, FAPTA Division of Biokinesiology
Can Lower Extremity Injuries be Prevented in Soccer?
 Can Lower Extremity Injuries be Prevented in Soccer? Implementing the 11+ Program in Soccer: An Evidence-Informed Discussion Carolyn Emery Professor Faculty of Kinesiology & Medicine University of Calgary
Can Lower Extremity Injuries be Prevented in Soccer? Implementing the 11+ Program in Soccer: An Evidence-Informed Discussion Carolyn Emery Professor Faculty of Kinesiology & Medicine University of Calgary
Open and Closed Chained Activity Effect on Shoulder External Rotation Range of Motion using Whole Body Vibration Therapy
 Open and Closed Chained Activity Effect on Shoulder External Rotation Range of Motion using Whole Body Vibration Therapy Timothy L. Cooley, MS, ATC University of Utah Craig L. Switzler, MS, ATC University
Open and Closed Chained Activity Effect on Shoulder External Rotation Range of Motion using Whole Body Vibration Therapy Timothy L. Cooley, MS, ATC University of Utah Craig L. Switzler, MS, ATC University
