32b. Core stabilisation rediscovered in rehabilitation. Core Strengthening in Lumbar Spinal. Disorders. Anatomy. General Overview
|
|
|
- Brent Bond
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Core Strengthening in Lumbar Spinal 32b Disorders 201 Core stabilisation rediscovered in rehabilitation. The term has come to connote lumbar stabilization and other therapeutic exercise regimens. In essence, all terms describe the muscular control required around the lumbar spine to maintain functional stability. The core has been described as a box with the abdominals in the front, paraspinals and gluteals in the back, the diaphragm as the roof, and the pelvic floor and hip girdle musculature as the bottom. 1 Particular attention has been paid to the core because it serves as a muscular corset that works as a unit to stabilize the body and spine, with and without limb movement. In short, the core serves as the center of the functional kinetic chain. In the alternative medicine world, the core has been referred to as the powerhouse, the foundation or engine of all limb movement. A comprehensive strengthening or facilitation of these core muscles has been advocated as a way to prevent and rehabilitate various lumbar spine and musculoskeletal disorders and as a way to enhance athletic performance. Despite its widespread use, research in core strengthening is meager. The present review was undertaken to describe the available literature using a theoretical framework. Stability of the lumbar spine requires both passive stiffness, through the osseous and ligamentous structures, and active stiffness, through muscles. A bare spine, without muscles attached, is unable to bear much of a compressive load. 2,3 Spinal instability occurs when either of these components is disturbed. Gross instability is true displacement of vertebrae, such as with traumatic disruption of 2 of 3 vertebral columns. On the other hand, functional instability is defined as a relative increase in the range of the neutral zone (the range in which internal resistance from active muscular control is minimal). Active stiffness or stability can be achieved through muscular cocontraction, akin to tightening the guy wires of a tent to unload weight on the center pole. 2,3 Also described as the serape effect, cocontraction further connects the stability of the upper and lower extremities via the abdominal fascial system. The effect becomes particularly important in overhead athletes because that stability acts as a torque-countertorque of diagonally related muscles during throwing. The Queensland research group1 has suggested the differentiation of local and global muscle groups to outline the postural segmental control function and general multisegmental stabilization function for these muscles groups, respectively. Anatomy General Overview Stability and movement are critically dependent on the coordination of all the muscles surrounding
2 202 the lumbar spine. Although it has advocated the importance of a few muscles (in particular, the), all core muscles are needed for optimal stabilization and performance. To acquire this cocontraction, precise neural input and output (which has also been referred to as) are needed. 1,2 Osseous and Ligamentous Structures Passive stiffness is imparted to the lumbar spine by the osseoligamentous structures. Tissue injury to any of these structures may cause functional instability. The posterior elements of the spine include the zygapophyseal (facet) joints, pedicle, lamina, and pars interarticularis. These structures are, in fact, flexible. However, repetitive loading of the inferior articular facets with excessive lumbar flexion and extension causes failure, typically at the pars. The zygapophyseal joints carry little vertical load except in certain positions such as excessive lumbar lordosis. The intervertebral disk is composed of the annulus fibrosis, nucleus pulposus, and the endplates. Compressive and shearing loads can cause injury initially to the endplates and ultimately to the annulus such that posterior disk herniations result. Excessive external loads on the disk may be caused by weak muscular control, thus causing a vicious cycle where the disk no longer provides optimal passive stiffness or stability. The spinal ligaments provide little stability in the neutral zone. Their more important role may be to provide afferent proprioception of the lumbar spine segments. The thoracolumbar fascia acts as nature s back belt. It works as a retinacular strap of the muscles of the lumbar spine. The thoracolumbar fascia consists of 3 layers: the anterior, middle, and posterior layers. Of these layers, the posterior layer has the most important role in supporting the lumbar spine and abdominal musculature. The transversus abdominis has large attachments to the middle and posterior layers of the thoracolumbar fascia The posterior layer consists of 2 laminae: a superficial lamina with fibers passing downward and medially and a deep lamina with fibers passing downward and laterally. The aponeurosis of the latissimus dorsi muscle forms the superficial layer. In essence, the thoracolumbar fascia provides a link between the lower limb and the upper limb. With contraction of the muscular contents, the thoracolumbar fascia acts as an activated proprioceptor, like a back belt providing feedback in lifting activities. Paraspinals There are 2 major groups of the lumbar extensors: the erector spinae The erector spinae in the lumbar region are composed of 2 major muscles: the longissimus and iliocostalis. These are actually primarily thoracic muscles that act on the lumbar via a long tendon that attaches to the pelvis. This long moment arm is ideal for lumbar spine extension and for creating posterior shear with lumbar flexion. 3 Deep and medial to the erector spinae muscles lay the local muscles. The rotators and intertransversi muscles do not have a great moment arm. Likely, they represent length transducers or position sensors of a spinal segment by way of their rich composition of muscle spindles. The multifidi pass along 2 or 3 spinal levels. They are theorized to work as segmental stabilizers. Because of their short moment arms, the multifidi are not involved much in gross movement. Multifidi have been found to atrophy in people with low back pain (LBP). Quadratus Lumborum Quadratus Lumborum is large, thin, and quadrangular shaped muscle that has direct insertions to the lumbar spine. There are 3 major components or muscular fascicles to the quadratus lumborum: the inferior oblique, superior oblique, and longitudinal fascicles. Both the longitudinal and superior oblique fibers have no direct action on the lumbar spine. They are designed as secondary respiratory muscles to stabilize the twelfth rib during respiration. The inferior oblique fibers of the quadratus lumborum are generally thought to be a weak lateral flexor of the lumbar vertebrae. Mc Gill states the quadratus lumborum is a major stabilizer of the spine, typically working isometrically. 4,5 Abdominals The abdominals serve as a vital component of the core. In particular, the transversus abdominis has received attention. Its fibers run horizontally around the abdomen, allowing for hooplike stresses with contraction. Isolated activation of the transversus
3 abdominis is achieved through hollowing in of the abdomen. 6,7 The transversus abdominis has been shown to activate before limb movement in healthy people, theoretically to stabilize the lumbar spine, whereas patients with LBP have a delayed activation of the transversus abdominis. 8 The internal oblique has similar fiber orientation to the transversus abdominis, yet receives much less attention with regard to its creation of hoop stresses. Together, the internal oblique, external oblique, and transversus abdominis increase the intra-abdominal pressure from the hoop created via the thoracolumbar fascia, thus imparting functional stability of the lumbar spine. 3 The external oblique, the largest and most superficial abdominal muscle, acts as a check of anterior pelvic tilt. As well, it acts eccentrically in lumbar extension and lumbar torsion. 5 Finally, the rectus abdominis is a paired, straplike muscle of the anterior abdominal wall. Contraction of this muscle predominantly causes flexion of the lumbar spine. In our opinion, most fitness programs incorrectly overemphasize rectus abdominis and internal oblique development, thus creating an imbalance with the relatively weaker external oblique. The external oblique can be stimulated by some of the exercises described later, particularly those that emphasize isometric or eccentric trunk twists. Hip Girdle Musculature The hip musculature plays a significant role within the kinetic chain, particularly for all ambulatory activities, in sta-bilization of the trunk and pelvis, and in transferring force from the lower extremities to the pelvis and spine. 8,9 Poor endurance and delayed firing of the hip extensor (gluteus maximus) and abductor (gluteus medius) muscles have previously been noted in people with lower-extremity instability or LBP. 10 It has been showed a significant asymmetry in hip extensor strength in female athletes with reported LBP. It has been showed a significant association between hip strength and imbalance of the hip extensors measured during the preparticipation physical and the occurrence of LBP in female athletes over the ensuing year. Overall, the hip appears to play a significant role in transferring forces from the lower extremities to the pelvis and spine, acting as 1 link within the kinetic chain. The Core Strengthening in Lumbar Spinal Disorders psoas major is a long, thick muscle whose primary action is flexion of the hip. However, its attachment sites into the lumbar spine give it the potential to aid in spinal biomechanics. During anatomic dissections, the psoas muscle has been found to have 3 proximal attachment sites: the medial half of the transverse processes from T12 to L5, the intervertebral disk, and the vertebral body adjacent to the disk. 10 The psoas does not likely provide much stability to the lumbar spine except in increased lumbar flexion.3 Increased stability requirements or a tight psoas will concomitantly cause increased, compressive, injurious loads to the lumbar disks. 11 Diaphragm and Pelvic Floor The diaphragm serves as the roof of the core. 12 Stability is imparted on the lumbar spine by contraction of the diaphragm and increasing intra-abdominal pressure. Recent studies have indicated that people with sacroiliac pain have impaired recruitment of the diaphragm and pelvic floor. Likewise, ventilatory challenges on the body may cause further diaphragm dysfunction and lead to more compressive loads on the lumbar spine. Thus, diaphragmatic breathing techniques may be an important part of a core-strengthening program. Furthermore, the pelvic floor musculature is coactivated with transversus abdominis contraction. Exercise of the Core Musculature Exercise of the core musculature is more than trunk strengthening. 13 In fact, motor relearning of inhibited muscles may be more important than strengthening in patients with LBP. In athletic endeavors, muscle endurance appears to be more important than pure muscle strength. 14 The overload principle advocated in sports medicine is a nemesis in the back. In other words, the progressive resistance strengthening of some core muscles, particularly the lumbar extensors, may be unsafe to the back. In fact, many traditional back strengthening exercises may also be unsafe. For example, roman chair exercises or back extensor strengthening machines require at least torso mass as resistance, which is a load often injurious to the lumbar spine.3 Traditional sit-ups are also unsafe because they cause increased compression loads on the lumbar spine. 15 Pelvic tilts are used less often 203
4 204 than in the past because they may increase spinal loading. In addition, all these traditional exercises are nonfunctional.3 In individuals suspected to have instability, stretching exercises should be used with caution, particularly ones encouraging end range lumbar flexion. The risk of lumbar injury is greatly increased 1 when the spine is fully flexed 2 and when it undergoes excessive repetitive torsion. Exercise must progress from training isolated muscles to training as an integrated unit to facilitate functional activity. The neutral spine has been advocated by some as a safe place to begin exercise. 16 The neutral spine position is a pain-free position that should not be confused with assuming a flat back posture nor the biomechanic term neutral zone described and It is touted as the position of power and balance. However, functional activities move through the neutral position, thus exercises should be progressed to nonneutral positions. Decreasing Spinal and Pelvic Viscosity Spinal exercises should not be done in the first hour after awakening because of the increased hydrostatic pressures in the disk during that time. 17 The cat and camel and the pelvic translation exercises are ways to achieve spinal segment and pelvic accessory motion before starting more aggressive exercises. As well, improving hip range of motion can help dissipate forces from the lumbar spine. A short aerobic program may also be implemented to serve as a warmup. Fast walking appears to cause less torque on the lower back than slow walking. Core Training Because sports activity involves movement in the 3 cardinal planes sagittal, frontal, and transverse core musculature must be assessed and trained in these planes. Often, transverse or rotational movements are neglected in core training. Assessment tools for functional evaluation of these movements (lunge, step-down, single leg press, balance, reach) have not been well validated but have proven to be reliable. 18 However, the multidirectional reach test and the star-excursion balance test (multidirectional excursion assessments in all cardinal planes) are both reliable and valid tests of multiplanar excursion. Single-leg squat tests (with or without step downs) also serve as validated tools of assessment. These evaluative tools help one select an individualized core training program, emphasizing areas of weakness and sports-specific movements. Core training programs for sports are widely used by strengthening and conditioning coaches at the collegiate and professional levels. Core strength is an integral component of the complex phenomena that comprise balance. Balance requires a multidimensional interplay between central, peripheral, sensory, and motor systems. Training the domain of balance is important for functional activities. Progression to labile surfaces may improve balance and proprioception. Different fitness programs incorporate various aspects of core strengthening and may be a useful way to maintain compliance in many individuals. 19,20 Physioball Exercises for the Core Abdominal crunch Balancing exercise while seated Superman prone exercise Modified push-up Pelvic bridging Advanced Core Program Body weight and gravitational loading (push-ups, pull-ups, rope climbs) Body blade exercises Medicine ball exercises (throwing, catching) Dumbbell exercises in diagonal patterns Stretch cord exercises Balance training with labile surfaces Squats Lunges Conclusion Core Strengthening for Treatment of Back Pain The core stability program was performed as an uncontrolled prospective trial of dynamic lumbar stabilization for patients with lumbar disk herniations creating radiculopathy. 21 The impact of therapeutic exercise alone was difficult to ascertain because of the offering of other nonsurgical
5 interventions, including medication, epidural steroid injections, and back school. The exercise training program was well outlined and consisted of a flexibility program, joint mobilization of the hip and the thoracolumbar spinal segments, a stabilization and abdominal program, a gym program, and aerobic activity. Successful outcomes were reported in 50 of 52 subjects (96%). The described dynamic lumbar stabilization program resembles the current concept of a core stability program without the higher level sports-specific core training. Work-hardening or functional restoration programs have also been used for the injured worker with back pain. 21 The exercise training program uses Nautilus equipment for progressive resistance strengthening of isolated muscle groups. An emphasis is placed on reaching objective goals. The training program differs from the current concept of core strengthening in that it emphasizes nonfunctional isolation exercises over motor relearning. Core Strengthening in Lumbar Spinal Disorders Although a recent Cochrane review found that exercise is an effective treatment of LBP, no specific exercise programs showed a clear advantage for that application. Stabilization exercises can be progressed from a beginner level to more advanced levels. The beginner level exercises described by McGill. 17 These include the curl-up, side bridge, and the bird dog. The bird dog exercise can progress from 4-point kneeling to 3-point to 2-point kneeling. Advancement to a physioball can be done at this stage. Functional progression is the most important stage in the core-strengthening program. A thorough history of functional activities should be taken to individualize this part of the program. 21 Patients should be given exercises in sitting, standing, and walking. Sitting is often a problematic position, particularly with lumbar disk injury. Sitting with lumbar lordosis totally flattened shifts the center of gravity anteriorly, relative to the standing position. 205
ACE s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals TRUNK
 ACE s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals TRUNK Posture and Balance Posture refers to the biomechanical alignment of the individual body parts and the orientation of the body to the
ACE s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals TRUNK Posture and Balance Posture refers to the biomechanical alignment of the individual body parts and the orientation of the body to the
Training Philosophy. There are numerous views on core conditioning.
 Abs Lab Presented by Helen Vanderburg BKin, ACE, CanFitPro, Yoga and Pilates 2005 IDEA Instructor of the Year 2006/ 1996 CanFitPro Presenter of the Year Nautilus and BOSU Fitness Education Team Introduction
Abs Lab Presented by Helen Vanderburg BKin, ACE, CanFitPro, Yoga and Pilates 2005 IDEA Instructor of the Year 2006/ 1996 CanFitPro Presenter of the Year Nautilus and BOSU Fitness Education Team Introduction
External Obliques Abdominal muscles that attaches at the lower ribs, pelvis, and abdominal fascia.
 The Core The core is where most of the body s power is derived. It provides the foundation for all movements of the arms and legs. The core must be strong, have dynamic flexibility, and function synergistically
The Core The core is where most of the body s power is derived. It provides the foundation for all movements of the arms and legs. The core must be strong, have dynamic flexibility, and function synergistically
Core Stabilization Training in Rehabilitation
 Core Stabilization Training in Rehabilitation Assistant professor of Sports Medicine Department of Sports Medicine Tehran university of Medical Sciences Introduction To develop a comprehensive functional
Core Stabilization Training in Rehabilitation Assistant professor of Sports Medicine Department of Sports Medicine Tehran university of Medical Sciences Introduction To develop a comprehensive functional
Lower Back Pain. Sensory motor function. 1 Principles of Exercise Therapy. Global muscles vs Local muscles. Research in Spine Rehabilitation
 1 Principles of Exercise Therapy Lower Back Pain 1. Facet joint pain 2. Spondylolysis & Spondylisthesis 1. Exercise Therapy turns the patient into an active participant and not just a passive recipient
1 Principles of Exercise Therapy Lower Back Pain 1. Facet joint pain 2. Spondylolysis & Spondylisthesis 1. Exercise Therapy turns the patient into an active participant and not just a passive recipient
The theory and practice of getting fitter and stronger
 The theory and practice of getting fitter and stronger David Docherty, PhD, Professor Emeritus School of Exercise Science, Physical and Health Education University of Victoria All the presentations are
The theory and practice of getting fitter and stronger David Docherty, PhD, Professor Emeritus School of Exercise Science, Physical and Health Education University of Victoria All the presentations are
Role of Lumbar Stabilization Exercise and Spinal Manipulation in Low back pain. Dr. PICHET YIEMSIRI
 Role of Lumbar Stabilization Exercise and Spinal Manipulation in Low back pain Dr. PICHET YIEMSIRI Lumbar Stabilization Exercise Spinal stability Static stability Dynamic stability Stable of the back The
Role of Lumbar Stabilization Exercise and Spinal Manipulation in Low back pain Dr. PICHET YIEMSIRI Lumbar Stabilization Exercise Spinal stability Static stability Dynamic stability Stable of the back The
Functional Anatomy and Exam of the Lumbar Spine. Thomas Hunkele MPT, ATC, NASM-PES,CES Coordinator of Rehabilitation
 Functional Anatomy and Exam of the Lumbar Spine Thomas Hunkele MPT, ATC, NASM-PES,CES Coordinator of Rehabilitation Disclosure Anatomical Review Quick Review of Bony and Ligamentous structures Discal anatomy
Functional Anatomy and Exam of the Lumbar Spine Thomas Hunkele MPT, ATC, NASM-PES,CES Coordinator of Rehabilitation Disclosure Anatomical Review Quick Review of Bony and Ligamentous structures Discal anatomy
The Muscles of the Core
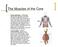 The Muscles of the Core Rectus abdominis - abdominal muscle that attaches at the fifth through seventh ribs, the lower sternum and the front of the pubic bone. This muscle flexes the spine, compresses
The Muscles of the Core Rectus abdominis - abdominal muscle that attaches at the fifth through seventh ribs, the lower sternum and the front of the pubic bone. This muscle flexes the spine, compresses
Pilates instructor final mat exam - ANSWERS
 Balanced Body - Mat EXAM Pilates instructor final mat exam - ANSWERS Name Date Training Location Examiner Total Points - 60 Passing Grade - 42 1) Which of the following are considered Balanced Body Pilates
Balanced Body - Mat EXAM Pilates instructor final mat exam - ANSWERS Name Date Training Location Examiner Total Points - 60 Passing Grade - 42 1) Which of the following are considered Balanced Body Pilates
ULTI BACK FITNESS AND PERFORMANCE STUART MCGILL, PHD FOURTH EDITION. Professor of Spine Biomechanics University of Waterloo Canada
 ULTI BACK FITNESS AND PERFORMANCE FOURTH EDITION STUART MCGILL, PHD Professor of Spine Biomechanics University of Waterloo Canada Backfitpro Inc. (formerly Wabuno Publishers) Waterloo, Ontario, Canada
ULTI BACK FITNESS AND PERFORMANCE FOURTH EDITION STUART MCGILL, PHD Professor of Spine Biomechanics University of Waterloo Canada Backfitpro Inc. (formerly Wabuno Publishers) Waterloo, Ontario, Canada
Main Menu. Trunk and Spinal Column click here. The Power is in Your Hands
 1 The Trunk and Spinal Column click here Main Menu K.9 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes/k9/k9entry.htm[3/27/18, 2:00:55 PM] The Trunk and Spinal Column Vertebral column complex 24 intricate
1 The Trunk and Spinal Column click here Main Menu K.9 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes/k9/k9entry.htm[3/27/18, 2:00:55 PM] The Trunk and Spinal Column Vertebral column complex 24 intricate
Clarification of Terms
 Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Evaluating the Athlete Questionnaire
 Evaluating the Athlete Questionnaire Prior to developing the strength and conditioning training plan the coach should first evaluate factors from the athlete s questionnaire that may impact the strength
Evaluating the Athlete Questionnaire Prior to developing the strength and conditioning training plan the coach should first evaluate factors from the athlete s questionnaire that may impact the strength
Session 4: Exercise Prescription for Musculoskeletal Disorders: Low Back Pain
 Session 4: Exercise Prescription for Musculoskeletal Disorders: Low Back Pain Course: Designing Exercise Prescriptions for Normal/Special Populations Presentation Created by Ken Baldwin, M.ED, ACSM-H/FI
Session 4: Exercise Prescription for Musculoskeletal Disorders: Low Back Pain Course: Designing Exercise Prescriptions for Normal/Special Populations Presentation Created by Ken Baldwin, M.ED, ACSM-H/FI
Thoracolumbar Anatomy Eric Shamus Catherine Patla Objectives
 1 2 Thoracolumbar Anatomy Eric Shamus Catherine Patla Objectives List the muscular and ligamentous attachments of the thoracic and lumbar spine Describe how the muscles affect the spine and upper extremity
1 2 Thoracolumbar Anatomy Eric Shamus Catherine Patla Objectives List the muscular and ligamentous attachments of the thoracic and lumbar spine Describe how the muscles affect the spine and upper extremity
Provide movement Maintain posture/stability Generate heat
 How we move.. What do muscles do for us? Provide movement Maintain posture/stability Generate heat (skeletal muscle accounts for 40% body mass) So looking at skeletal muscles.. What do skeletal muscles
How we move.. What do muscles do for us? Provide movement Maintain posture/stability Generate heat (skeletal muscle accounts for 40% body mass) So looking at skeletal muscles.. What do skeletal muscles
Pilates for Chronic Low Back Pain
 Pilates for Chronic Low Back Pain Julianne Bettencourt March 23, 2015 Course Year: 2014 Integrated Fitness, Visalia, CA Abstract Low back pain is an injury that affects thousands of people every day and
Pilates for Chronic Low Back Pain Julianne Bettencourt March 23, 2015 Course Year: 2014 Integrated Fitness, Visalia, CA Abstract Low back pain is an injury that affects thousands of people every day and
The Trunk and Spinal Column Kinesiology Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University
 The Trunk and Spinal Column Kinesiology Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University The Trunk and Spinal Column Vertebral column 24 articulating vertebrae 31 pairs of spinal nerves Abdominal muscles some
The Trunk and Spinal Column Kinesiology Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University The Trunk and Spinal Column Vertebral column 24 articulating vertebrae 31 pairs of spinal nerves Abdominal muscles some
Rotational Forces. : Their impact; our treatments
 Rotational Forces : Their impact; our treatments Lee Stang, LMT, LMBT, BCTMB NCBTMB Provider: 450217-06 bridgestohealthseminars.com bthseminars@gmail.com 860.985.5834 Facebook.com/BridgesToHealthSeminars
Rotational Forces : Their impact; our treatments Lee Stang, LMT, LMBT, BCTMB NCBTMB Provider: 450217-06 bridgestohealthseminars.com bthseminars@gmail.com 860.985.5834 Facebook.com/BridgesToHealthSeminars
PART ONE. Belly Dance Fitness Technique
 PART ONE Belly Dance Fitness Technique OVERVIEW Understanding belly dance movement The gentle, symmetrical, rhythmic undulations that we practice in Belly dance can help to revitalize almost every part
PART ONE Belly Dance Fitness Technique OVERVIEW Understanding belly dance movement The gentle, symmetrical, rhythmic undulations that we practice in Belly dance can help to revitalize almost every part
The Role of the Rectus Abdominis in Predicting and Preventing Low Back Pain
 The Role of the Rectus Abdominis in Predicting and Preventing Low Back Pain What causes low back pain? The causes of low back pain and complicated and varied, but the pain we feel is in most cases the
The Role of the Rectus Abdominis in Predicting and Preventing Low Back Pain What causes low back pain? The causes of low back pain and complicated and varied, but the pain we feel is in most cases the
Clarification of Terms
 Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Connecting the Core. Rationale. Physiology. Paul J. Goodman, MS, CSCS. Athletes have been inundated with terminology
 Connecting the Core Paul J. Goodman, MS, CSCS Athletes have been inundated with terminology and references to core development in recent years. However, little has been conveyed to these athletes on what
Connecting the Core Paul J. Goodman, MS, CSCS Athletes have been inundated with terminology and references to core development in recent years. However, little has been conveyed to these athletes on what
Clarification of Terms
 Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
The Back. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 9 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Back Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 9 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa The spine has to meet 2 functions Strength Mobility Stability of the vertebral column is provided by: Deep intrinsic muscles of the back Ligaments
The Back Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 9 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa The spine has to meet 2 functions Strength Mobility Stability of the vertebral column is provided by: Deep intrinsic muscles of the back Ligaments
Case Study: Pilates and the Pelvic Instability of. the Hypermobile Dancer
 Case Study: Pilates and the Pelvic Instability of the Hypermobile Dancer Markella Kefallonitou 31/08/2015 Comprehensive Training Program 2015 London Abstract Dancers are well known for their extreme physical
Case Study: Pilates and the Pelvic Instability of the Hypermobile Dancer Markella Kefallonitou 31/08/2015 Comprehensive Training Program 2015 London Abstract Dancers are well known for their extreme physical
# Work your Abs when you re not working your abs: See above When you do all of your other exercises all exercise is an abdominal exercise!!
 #178 Tools for Training Torso Presented by: Alex McMillan President of Northwest Personal Training & Fitness Education 2006 IDEA Program Director of the Year NASM and ACE Certified Personal Trainer Nike,
#178 Tools for Training Torso Presented by: Alex McMillan President of Northwest Personal Training & Fitness Education 2006 IDEA Program Director of the Year NASM and ACE Certified Personal Trainer Nike,
The Biomechanics of the Human Spine. Basic Biomechanics, 6 th edition By Susan J. Hall, Ph.D.
 Chapter 9 The Biomechanics of the Human Spine Structure of the Spine The spine is a curved stack of 33 vertebrae structurally divided into five regions: cervical region - 7 vertebrae thoracic region -
Chapter 9 The Biomechanics of the Human Spine Structure of the Spine The spine is a curved stack of 33 vertebrae structurally divided into five regions: cervical region - 7 vertebrae thoracic region -
An athlete s ability to handle their own
 Training Force Couples for Optimized Sports Performance An athlete s ability to handle their own body weight is foundational to competition-based actions. Thus, strength to weight ratio is a key correlate
Training Force Couples for Optimized Sports Performance An athlete s ability to handle their own body weight is foundational to competition-based actions. Thus, strength to weight ratio is a key correlate
MODULE 4: Stability Training for Riders
 MODULE 4: Stability Training for Riders The most common answer you will get from almost any rider when you ask them what they need more of, in terms of their fitness, is core strength. Indeed, core strength
MODULE 4: Stability Training for Riders The most common answer you will get from almost any rider when you ask them what they need more of, in terms of their fitness, is core strength. Indeed, core strength
Active-Assisted Stretches
 1 Active-Assisted Stretches Adequate flexibility is fundamental to a functional musculoskeletal system which represents the foundation of movement efficiency. Therefore a commitment toward appropriate
1 Active-Assisted Stretches Adequate flexibility is fundamental to a functional musculoskeletal system which represents the foundation of movement efficiency. Therefore a commitment toward appropriate
CORE STABILITY. Contents Understanding your Back... 3
 Contents Understanding your Back........................................................... 3 What is core stability?............................................................... 5 YOUR GUIDE TO CORE
Contents Understanding your Back........................................................... 3 What is core stability?............................................................... 5 YOUR GUIDE TO CORE
Presented by Maureen Hagan BScPT (Physiotherapist), BA PE ACE, Can-Fit-Pro Certified 2006 IDEA Fitness Instructor & 1998 Program Director of the Year
 Presented by Maureen Hagan BScPT (Physiotherapist), BA PE ACE, Can-Fit-Pro Certified 2006 IDEA Fitness Instructor & 1998 Program Director of the Year 1. Overview the most common age-related risk factors
Presented by Maureen Hagan BScPT (Physiotherapist), BA PE ACE, Can-Fit-Pro Certified 2006 IDEA Fitness Instructor & 1998 Program Director of the Year 1. Overview the most common age-related risk factors
Lower Crossed Syndrome
 Lower Crossed Syndrome Sang mi Yun October 23 rd 2017 Costa Mesa 2016 Abstract Lower-Crossed Syndrome (LCS) is also referred to as distal or pelvic crossed syndrome. In LCS, tightness of the thoracolumbar
Lower Crossed Syndrome Sang mi Yun October 23 rd 2017 Costa Mesa 2016 Abstract Lower-Crossed Syndrome (LCS) is also referred to as distal or pelvic crossed syndrome. In LCS, tightness of the thoracolumbar
3 Movements of the Trunk. Flexion Rotation Extension
 3 Movements of the Trunk Flexion Rotation Extension 1 TRUNK FLEXION 2 TRUNK FLEXION: Rectus Abdominalis O: Crest of Pubis & ligaments covering front of symphysis pubis. I: By «3 portions into cartilages
3 Movements of the Trunk Flexion Rotation Extension 1 TRUNK FLEXION 2 TRUNK FLEXION: Rectus Abdominalis O: Crest of Pubis & ligaments covering front of symphysis pubis. I: By «3 portions into cartilages
The vault bones Frontal Parietals Occiput Temporals Sphenoid Ethmoid
 The Vertebral Column Head, Neck and Spine Bones of the head Some consider the bones of the head in terms of the vault bones and the facial bones hanging off the front of them The vault bones Frontal Parietals
The Vertebral Column Head, Neck and Spine Bones of the head Some consider the bones of the head in terms of the vault bones and the facial bones hanging off the front of them The vault bones Frontal Parietals
Balanced Body Movement Principles. How the Body Works and How to Train It Module 2: Trunk Integration. Copyright 2017, Balanced Body Education LLC.
 Balanced Body Movement Principles How the Body Works and How to Train It Module 2: Trunk Integration Trunk Integration Module 2: Key Principles Breathing Core work Transverse Abdominis, Multifidi, Pelvic
Balanced Body Movement Principles How the Body Works and How to Train It Module 2: Trunk Integration Trunk Integration Module 2: Key Principles Breathing Core work Transverse Abdominis, Multifidi, Pelvic
Rehabilitation, Core Stability & Personal Training using the Swiss Ball
 s EDUCATION WORKSHOPS Rehabilitation, Core Stability & Personal Training using the Swiss Ball with B.App.Sc (Physio), Dip.Ed (P.E.) CONTENTS Topic Page 1. Introduction 2. Core Stability Basics 3 3. Core
s EDUCATION WORKSHOPS Rehabilitation, Core Stability & Personal Training using the Swiss Ball with B.App.Sc (Physio), Dip.Ed (P.E.) CONTENTS Topic Page 1. Introduction 2. Core Stability Basics 3 3. Core
Please note. The following notes are 2017 Donna Farhi and Laura Stuart. They are for your personal study only, not for distribution or commercial use.
 Please note The following notes are 2017 Donna Farhi and Laura Stuart. They are for your personal study only, not for distribution or commercial use. Farhi & Stuart Model for Joint Function Form Closure
Please note The following notes are 2017 Donna Farhi and Laura Stuart. They are for your personal study only, not for distribution or commercial use. Farhi & Stuart Model for Joint Function Form Closure
Posture. Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 10 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 Posture Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 10 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Posture = body alignment = the relative arrangement of parts of the body Changes with the positions and movements of the body throughout the day
Posture Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 10 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Posture = body alignment = the relative arrangement of parts of the body Changes with the positions and movements of the body throughout the day
Combating the Ramifications of Extended Sitting
 Combating the Ramifications of Extended Sitting Theresa Cork July, 2018 Chicago - 2015 Abstract Creator and visionary of Contrology, Joseph H. Pilates believed physical fitness was the first requisite
Combating the Ramifications of Extended Sitting Theresa Cork July, 2018 Chicago - 2015 Abstract Creator and visionary of Contrology, Joseph H. Pilates believed physical fitness was the first requisite
Structure and Function of the Vertebral Column
 Structure and Function of the Vertebral Column Posture Vertebral Alignment Does it really matter? Yes it does! Postural Curves The vertebral column has a series of counterbalancing curves posterior anterior
Structure and Function of the Vertebral Column Posture Vertebral Alignment Does it really matter? Yes it does! Postural Curves The vertebral column has a series of counterbalancing curves posterior anterior
Certified Personal Trainer Re-Certification Manual
 Certified Personal Trainer Re-Certification Manual Section II 1 Anatomy & Physiology Terms Anatomy and physiology are closely related fields of study: anatomy is the study of form, and physiology is the
Certified Personal Trainer Re-Certification Manual Section II 1 Anatomy & Physiology Terms Anatomy and physiology are closely related fields of study: anatomy is the study of form, and physiology is the
Introduction. The Inner Core Muscles. Why Train The Inner Core? How Do You Train The Inner Core?
 Introduction Pilates focuses on the deep postural muscles, including the pelvic floor, the transversus abdominis (TA) and the multifidus. These deep postural muscles are also referred to as the core. Improving
Introduction Pilates focuses on the deep postural muscles, including the pelvic floor, the transversus abdominis (TA) and the multifidus. These deep postural muscles are also referred to as the core. Improving
THE ROLE OF THE MID-TORSO IN SPEED DEVELOPMENT
 THE ROLE OF THE MID-TORSO IN SPEED DEVELOPMENT The mid-torso is made up of 4 major muscle groups: 1. Rectus Abdominus Origin Base of sternum and bottom ribs Insertion Pubis bone (as part of the pelvis)
THE ROLE OF THE MID-TORSO IN SPEED DEVELOPMENT The mid-torso is made up of 4 major muscle groups: 1. Rectus Abdominus Origin Base of sternum and bottom ribs Insertion Pubis bone (as part of the pelvis)
It consist of two components: the outer, laminar fibrous container (or annulus), and the inner, semifluid mass (the nucleus pulposus).
 Lumbar Spine The lumbar vertebrae are the last five vertebrae of the vertebral column. They are particularly large and heavy when compared with the vertebrae of the cervical or thoracicc spine. Their bodies
Lumbar Spine The lumbar vertebrae are the last five vertebrae of the vertebral column. They are particularly large and heavy when compared with the vertebrae of the cervical or thoracicc spine. Their bodies
Pilates for Low Back Pain Relief
 Pilates for Low Back Pain Relief Tia Stanley May 14, 2017 Course Year: 2015 One Physical Therapy and Wellness, Bryn Mawr, PA Abstract This paper outlines the research and looks at Pilates as a form of
Pilates for Low Back Pain Relief Tia Stanley May 14, 2017 Course Year: 2015 One Physical Therapy and Wellness, Bryn Mawr, PA Abstract This paper outlines the research and looks at Pilates as a form of
Common Low Back Injuries in Dancers
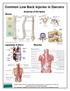 Common Low Back Injuries in Dancers Bones Anatomy of the Spine Ligaments & Discs Muscles Quadratus Lumborum (QL) Muscle Strain or Trigger Point The QL originates from the posterior iliac crest and inserts
Common Low Back Injuries in Dancers Bones Anatomy of the Spine Ligaments & Discs Muscles Quadratus Lumborum (QL) Muscle Strain or Trigger Point The QL originates from the posterior iliac crest and inserts
Principles of Core Stabilization for Athletic Populations
 Principles of Core Stabilization for Athletic Populations R. BARRY DALE, PhD, PT, ATC, CSCS University of South Alabama RYAN LAWRENCE, DC Saraland Chiropractic, Saraland, AL Key Points Core strengthening,
Principles of Core Stabilization for Athletic Populations R. BARRY DALE, PhD, PT, ATC, CSCS University of South Alabama RYAN LAWRENCE, DC Saraland Chiropractic, Saraland, AL Key Points Core strengthening,
Presentation Overview 8/8/12. Muscle Imbalances Revealed Assessment & Exercise for Personal Training
 Presentation Overview Common issues seen in many athletes from different sports Some important assessments that can be used for many varieties of athletes Exercise progressions that can fix imbalances
Presentation Overview Common issues seen in many athletes from different sports Some important assessments that can be used for many varieties of athletes Exercise progressions that can fix imbalances
Outline. Introduction / Epidemiology. Anatomy / Pain generators. Diagnosis. Treatment. Most Important lecture!!
 Acute Low Back Pain Outline Introduction / Epidemiology. Most Important lecture!! Anatomy / Pain generators Diagnosis Treatment Course Objectives Know the RED FLAGS in history taking. Know the Pain Generators
Acute Low Back Pain Outline Introduction / Epidemiology. Most Important lecture!! Anatomy / Pain generators Diagnosis Treatment Course Objectives Know the RED FLAGS in history taking. Know the Pain Generators
Muscles of the Core. PSK 4U Mr. S. Kelly North Grenville DHS
 Muscles of the Core PSK 4U Mr. S. Kelly North Grenville DHS Intercostal Muscles Run between the ribs Provide shape and movement for chest wall External intercostals: aid in both quiet (passive) and forced
Muscles of the Core PSK 4U Mr. S. Kelly North Grenville DHS Intercostal Muscles Run between the ribs Provide shape and movement for chest wall External intercostals: aid in both quiet (passive) and forced
Chapter 3: Applied Kinesiology. ACE Personal Trainer Manual Third Edition
 Chapter 3: Applied Kinesiology ACE Personal Trainer Manual Third Edition Introduction Kinesiology is the study of the body s infinite number of movements, positions, and postures and is grounded in the
Chapter 3: Applied Kinesiology ACE Personal Trainer Manual Third Edition Introduction Kinesiology is the study of the body s infinite number of movements, positions, and postures and is grounded in the
Pilates for Pelvic Lumbar Instability in CrossFit Athletes
 Pilates for Pelvic Lumbar Instability in CrossFit Athletes Emily Von Fange 11/28/2018 Comprehensive Program 2018 Herndon, VA Abstract! Lauren is a CrossFit athlete and coach who injured her lower back
Pilates for Pelvic Lumbar Instability in CrossFit Athletes Emily Von Fange 11/28/2018 Comprehensive Program 2018 Herndon, VA Abstract! Lauren is a CrossFit athlete and coach who injured her lower back
Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Anatomy.
 Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Anatomy www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Thoracic Vertebrae Bodies Pedicles Laminae Spinous Processes Transverse Processes Inferior & Superior Facets Distinguishing Feature Costal Fovea
Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Anatomy www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Thoracic Vertebrae Bodies Pedicles Laminae Spinous Processes Transverse Processes Inferior & Superior Facets Distinguishing Feature Costal Fovea
Your spine is able to create multidirectional movement that gives you the
 Spine C h a p t 2 e r Your spine is able to create multidirectional movement that gives you the ability to execute various dance styles with fluidity and ease. Your spine can portray a resilient elastic
Spine C h a p t 2 e r Your spine is able to create multidirectional movement that gives you the ability to execute various dance styles with fluidity and ease. Your spine can portray a resilient elastic
Contraindicated and High-Risk Exercises
 Contraindicated and High-Risk Exercises Young sub Kwon, Ph.D. ACSM RCEP, NSCA CSCS,*D Exercise Physiology Laboratory The University of New Mexico Albuquerque, NM, USA Introduction Any activity selected
Contraindicated and High-Risk Exercises Young sub Kwon, Ph.D. ACSM RCEP, NSCA CSCS,*D Exercise Physiology Laboratory The University of New Mexico Albuquerque, NM, USA Introduction Any activity selected
Lumbar Stenosis Rehabilitation Using the Resistance Chair
 PRODUCTS HELPING PEOPLE HELP THEMSELVES! Lumbar Stenosis Rehabilitation Using the Resistance Chair a. Description Lumbar spinal stenosis is a term used to describe a narrowing of the spinal canal. The
PRODUCTS HELPING PEOPLE HELP THEMSELVES! Lumbar Stenosis Rehabilitation Using the Resistance Chair a. Description Lumbar spinal stenosis is a term used to describe a narrowing of the spinal canal. The
Intermediate: Lift the elbows off the floor for added difficulty.
 Core Stability Please Note: The postures, techniques, and exercises contained on this web site are solely for the use of patients of our clinic who have been given a prescription to do them. Unauthorized
Core Stability Please Note: The postures, techniques, and exercises contained on this web site are solely for the use of patients of our clinic who have been given a prescription to do them. Unauthorized
Core Stabilization for a Pain- Free Posture
 PAIN-FREE POSTURE PROGRAM Core Stabilization for a Pain- Free Posture with Mary Ann Foster ABOUT MARY ANN FOSTER Massage therapist since 1981 Somatic educator and movement teacher Author of Somatic Patterning
PAIN-FREE POSTURE PROGRAM Core Stabilization for a Pain- Free Posture with Mary Ann Foster ABOUT MARY ANN FOSTER Massage therapist since 1981 Somatic educator and movement teacher Author of Somatic Patterning
 Today we will cover: Exercise for the back L-S spine S-I joint Pelvis www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Toward Developing Scientifically Justified Low Back Rehabilitation Exercises Use evidence to support clinical
Today we will cover: Exercise for the back L-S spine S-I joint Pelvis www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Toward Developing Scientifically Justified Low Back Rehabilitation Exercises Use evidence to support clinical
PILATES CONDITIONING FOR PATHOLOGY OF THE INTERVETEBRAL DISK
 PILATES CONDITIONING FOR PATHOLOGY OF THE INTERVETEBRAL DISK Ashlee Tinken August 12, 2017 Comprehensive Apparatus Program Pilates Denver June 2015 ABSTRACT The pathology of the intervertebral disk is
PILATES CONDITIONING FOR PATHOLOGY OF THE INTERVETEBRAL DISK Ashlee Tinken August 12, 2017 Comprehensive Apparatus Program Pilates Denver June 2015 ABSTRACT The pathology of the intervertebral disk is
CORE STABILIZATION EXERCISE. Vincent J. Hudson, PhD, DPT, MBA, ATC Chief Operating Officer OAA Orthopaedic Specialists Allentown, PA
 CORE STABILIZATION EXERCISE Vincent J. Hudson, PhD, DPT, MBA, ATC Chief Operating Officer OAA Orthopaedic Specialists Allentown, PA Stepping Back What are the goals? What is the value? Is it Sport Specific
CORE STABILIZATION EXERCISE Vincent J. Hudson, PhD, DPT, MBA, ATC Chief Operating Officer OAA Orthopaedic Specialists Allentown, PA Stepping Back What are the goals? What is the value? Is it Sport Specific
Prater Chiropractic Wellness Center 903 W. South St. Kalamazoo, MI PH: (269)
 Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle. Following a well-structured conditioning
Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle. Following a well-structured conditioning
Back Conditioning for the construction worker/tradesperson.
 Back Conditioning for the construction worker/tradesperson. Colina Morrison 10 th June 2018 2017, BASI Australia, Pilates Studio 64 Abstract Australian tradespeople, commonly referred to as tradies are
Back Conditioning for the construction worker/tradesperson. Colina Morrison 10 th June 2018 2017, BASI Australia, Pilates Studio 64 Abstract Australian tradespeople, commonly referred to as tradies are
Pilates For The Mother Runner
 Pilates For The Mother Runner Emma Wagenvelt July 2018 Comprehensive Teacher Training Certification The Woodlands, TX. 1 Abstract Running as a form of exercise has numerous health benefits, including cardiovascular
Pilates For The Mother Runner Emma Wagenvelt July 2018 Comprehensive Teacher Training Certification The Woodlands, TX. 1 Abstract Running as a form of exercise has numerous health benefits, including cardiovascular
Posture and balance. Center of gravity. Dynamic nature of center of gravity. John Milton BIO-39 November 7, 2017
 Posture and balance John Milton BIO-39 November 7, 2017 Center of gravity The center of gravity (COG) of the human body lies approximately at the level of the second sacral vertebrae (S2), anterior to
Posture and balance John Milton BIO-39 November 7, 2017 Center of gravity The center of gravity (COG) of the human body lies approximately at the level of the second sacral vertebrae (S2), anterior to
Ab Fab (abdominal strengthening & core control)
 Ab Fab (abdominal strengthening & core control) By James Bone Are you confused about abdominal strengthening and core control? SIT UPS AND SIX PACKS Is developing a six pack with sit ups good for you or
Ab Fab (abdominal strengthening & core control) By James Bone Are you confused about abdominal strengthening and core control? SIT UPS AND SIX PACKS Is developing a six pack with sit ups good for you or
Fitness Theory Exam Review
 - 1 - Fitness Theory Exam Review 1. Identify the risk factors for cardio-vascular disease Controllable Uncontrollable 2. What health improvements could be made by being physically active? 3. What behaviours
- 1 - Fitness Theory Exam Review 1. Identify the risk factors for cardio-vascular disease Controllable Uncontrollable 2. What health improvements could be made by being physically active? 3. What behaviours
Anatomy - Reconnect with your Spine Muscles by NFPT Idea World 2016 : Session 449 Friday July 15th 9:40-11:30am Beverly Hosford, MA
 Anatomy - Reconnect with your Spine Muscles by NFPT Idea World 2016 : Session 449 Friday July 15th 9:40-11:30am Beverly Hosford, MA Posture Core Anatomy Awareness Action 1. Anatomy *Know the muscle attachments.
Anatomy - Reconnect with your Spine Muscles by NFPT Idea World 2016 : Session 449 Friday July 15th 9:40-11:30am Beverly Hosford, MA Posture Core Anatomy Awareness Action 1. Anatomy *Know the muscle attachments.
Spine Conditioning Program Purpose of Program
 Prepared for: Prepared by: Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle. Following
Prepared for: Prepared by: Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle. Following
Information within the handout. Brief Introduction Anatomy & Biomechanics Assessment & Diagnosis Treatment through Muscle Energy
 Manual Medicine Diagnosis and Treatment for Somatic Dysfunction of the Pelvis Through Muscle Energy Greenman s Priciples of Manual Medicine (5 th Ed.)- Lisa DeStefano,DO Speaker disclosure I declare I
Manual Medicine Diagnosis and Treatment for Somatic Dysfunction of the Pelvis Through Muscle Energy Greenman s Priciples of Manual Medicine (5 th Ed.)- Lisa DeStefano,DO Speaker disclosure I declare I
BIOMECHANICAL INFLUENCES ON THE SOCCER PLAYER. Planes of Lumbar Pelvic Femoral (Back, Pelvic, Hip) Muscle Function
 BIOMECHANICAL INFLUENCES ON THE SOCCER PLAYER Functional performance of the soccer player reflects functional capability of certain specific muscle and muscle groups of the back, pelvis and hip to work
BIOMECHANICAL INFLUENCES ON THE SOCCER PLAYER Functional performance of the soccer player reflects functional capability of certain specific muscle and muscle groups of the back, pelvis and hip to work
Pilates for Low Back Pain
 Pilates for Low Back Pain Sarah Hoffman October 19, 2017 Pilates Body LLC University Place, Washington 1 Abstract Most people will experience Low Back Pain at some point in their life. The most common
Pilates for Low Back Pain Sarah Hoffman October 19, 2017 Pilates Body LLC University Place, Washington 1 Abstract Most people will experience Low Back Pain at some point in their life. The most common
Shoulder Rehabilitation after Dislocation
 Shoulder Rehabilitation after Dislocation John Nyland DPT, SCS, EdD, ATC, CSCS, FACSM Professor Athletic Training Program Director Spalding University Louisville, Kentucky, USA Normal Glenohumeral Capsulo-ligamentous
Shoulder Rehabilitation after Dislocation John Nyland DPT, SCS, EdD, ATC, CSCS, FACSM Professor Athletic Training Program Director Spalding University Louisville, Kentucky, USA Normal Glenohumeral Capsulo-ligamentous
Strength Essentials for Lower Back Problems. Lower Back Problems. Injury and Pain issues. Tim Keeley B.Phty, Cred.MDT, APA Principal Physiotherapist
 for Lower Back Problems Tim Keeley B.Phty, Cred.MDT, APA Principal Physiotherapist 1300 233 300 physiofitness.com.au Lower Back Problems Hyper-lordotic / kyphotic Disc Bulge and Herniation SIJ dysfunction
for Lower Back Problems Tim Keeley B.Phty, Cred.MDT, APA Principal Physiotherapist 1300 233 300 physiofitness.com.au Lower Back Problems Hyper-lordotic / kyphotic Disc Bulge and Herniation SIJ dysfunction
Lumbar/Core Strength and Stability Exercises
 Athletic Medicine Lumbar/Core Strength and Stability Exercises Introduction Low back pain can be the result of many different things. Pain can be triggered by some combination of overuse, muscle strain,
Athletic Medicine Lumbar/Core Strength and Stability Exercises Introduction Low back pain can be the result of many different things. Pain can be triggered by some combination of overuse, muscle strain,
Pilates for Strengthening and Mobilizing the Thoracic Spine
 Pilates for Strengthening and Mobilizing the Thoracic Spine R. Meson 11 March 2017 2016 Course Balanced Bodies, Herndon, VA. Abstract The spine provides the primary movements of the axial skeleton. And
Pilates for Strengthening and Mobilizing the Thoracic Spine R. Meson 11 March 2017 2016 Course Balanced Bodies, Herndon, VA. Abstract The spine provides the primary movements of the axial skeleton. And
Overuse Injuries. Overuse injury defined. Overuse Injuries
 Overuse Injuries Lisa DeStefano, DO Associate Professor and Chair Department of Osteopathic Manipulative Medicine College of Osteopathic Medicine Michigan State University Overuse injury defined Overuse
Overuse Injuries Lisa DeStefano, DO Associate Professor and Chair Department of Osteopathic Manipulative Medicine College of Osteopathic Medicine Michigan State University Overuse injury defined Overuse
Cervical, Thorasic, Lumbar and Sacrum Dysfunction WHERE AND HOW DO I START?
 Cervical, Thorasic, Lumbar and Sacrum Dysfunction WHERE AND HOW DO I START? FAITH CLEMENTS SEPTEMBER 2016 COPENHAGEN 2015 ABSTRACT This paper examines the conditions of the author, Faith Clements and her
Cervical, Thorasic, Lumbar and Sacrum Dysfunction WHERE AND HOW DO I START? FAITH CLEMENTS SEPTEMBER 2016 COPENHAGEN 2015 ABSTRACT This paper examines the conditions of the author, Faith Clements and her
CHAPTER 9: THE SPINAL COLUMN AND THORAX KINESIOLOGY Scientific Basis of Human Motion, 12 th edition Hamilton, Weimar & Luttgens
 CHAPTER 9: THE SPINAL COLUMN AND THORAX KINESIOLOGY Scientific Basis of Human Motion, 12 th edition Hamilton, Weimar & Luttgens Presentation Created by TK Koesterer, Ph.D., ATC Humboldt State University
CHAPTER 9: THE SPINAL COLUMN AND THORAX KINESIOLOGY Scientific Basis of Human Motion, 12 th edition Hamilton, Weimar & Luttgens Presentation Created by TK Koesterer, Ph.D., ATC Humboldt State University
Low Back Health The Benefits of Pilates in Corporate America
 Low Back Health The Benefits of Pilates in Corporate America Laura Ann Piini BASI Teacher Comprehensive Training Course December 16, 2012 Oceanside 1 Abstract The purpose of this research paper and case
Low Back Health The Benefits of Pilates in Corporate America Laura Ann Piini BASI Teacher Comprehensive Training Course December 16, 2012 Oceanside 1 Abstract The purpose of this research paper and case
Stand Tall with Osteoporosis thru Pilates
 Stand Tall with Osteoporosis thru Pilates C A S S I T E R P E N I N G P T, D P T, C S C S, C P I C H R I S R I E G E R P T U P S T A T E U N I V E R S I T Y H O S P I T A L J U N E 1 9, 2 0 1 7 Content
Stand Tall with Osteoporosis thru Pilates C A S S I T E R P E N I N G P T, D P T, C S C S, C P I C H R I S R I E G E R P T U P S T A T E U N I V E R S I T Y H O S P I T A L J U N E 1 9, 2 0 1 7 Content
Improving swimming through Pilates
 Improving swimming through Pilates Cleia Ramsey 10 Mar 2017 2016 BASI Training Class Herndon, VA Introduction As a mother of two swimmers, I spend many hours at the pool deck and have learned a lot about
Improving swimming through Pilates Cleia Ramsey 10 Mar 2017 2016 BASI Training Class Herndon, VA Introduction As a mother of two swimmers, I spend many hours at the pool deck and have learned a lot about
Movement System Diagnoses. Movement System Impairment Syndromes of the Lumbar Spine. MSI Syndrome - Assumptions. Return From Forward Bending
 Movement System Diagnoses Kinesiopathologic Pathokinesiologic Movement System Impairment Syndromes of the Lumbar Spine Shirley Sahrmann, PT, PhD, FAPTA Washington University St. Louis School of Medicine
Movement System Diagnoses Kinesiopathologic Pathokinesiologic Movement System Impairment Syndromes of the Lumbar Spine Shirley Sahrmann, PT, PhD, FAPTA Washington University St. Louis School of Medicine
5/17/2017. Integration of the Kinetic Chain: The Trunk. Stabilizing Systems. Integration of the Kinetic Chain: The Trunk
 Integration of the Kinetic Chain: The Trunk Integration of the Kinetic Chain: The Trunk Michael Higgins PhD, ATC, PT, CSCS University of Virginia Sasha Digges, PT, ATC, CSCS PEAK PHYSICAL THERAPY & SPORTS
Integration of the Kinetic Chain: The Trunk Integration of the Kinetic Chain: The Trunk Michael Higgins PhD, ATC, PT, CSCS University of Virginia Sasha Digges, PT, ATC, CSCS PEAK PHYSICAL THERAPY & SPORTS
Functional Movement Screen (Cook, 2001)
 Functional Movement Screen (Cook, 2001) TEST 1 DEEP SQUAT Purpose - The Deep Squat is used to assess bilateral, symmetrical, mobility of the hips, knees, and ankles. The dowel held overhead assesses bilateral,
Functional Movement Screen (Cook, 2001) TEST 1 DEEP SQUAT Purpose - The Deep Squat is used to assess bilateral, symmetrical, mobility of the hips, knees, and ankles. The dowel held overhead assesses bilateral,
ATHLETIC CONDITIONING ON THE ARC BARREL
 ATHLETIC CONDITIONING ON THE ARC BARREL page 1 INTRODUCTION The STOTT PILATES Athletic Conditioning stream serves as a bridge between STOTT PILATES standard repertoire and the CORE Athletic Conditioning
ATHLETIC CONDITIONING ON THE ARC BARREL page 1 INTRODUCTION The STOTT PILATES Athletic Conditioning stream serves as a bridge between STOTT PILATES standard repertoire and the CORE Athletic Conditioning
Strength Exercises for Improved Running Biomechanics
 2 CHAPTER Strength Exercises for Improved Running Biomechanics ssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssdd s Many gait abnormalities seen
2 CHAPTER Strength Exercises for Improved Running Biomechanics ssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssdd s Many gait abnormalities seen
Pilates for the Endurance Runner With Special Focus on the Hip Joint
 Pilates for the Endurance Runner With Special Focus on the Hip Joint Kellie McGeoy April 11 th, 2014 Aptos, CA 2013 1 Abstract: Endurance running is defined as any distance over 5 kilometers (3.1 miles)
Pilates for the Endurance Runner With Special Focus on the Hip Joint Kellie McGeoy April 11 th, 2014 Aptos, CA 2013 1 Abstract: Endurance running is defined as any distance over 5 kilometers (3.1 miles)
Understanding back pain 2- exercises and stretches for back pain suffere
 Understanding back pain 2- exercises and stretches for back pain suffere Dr James Tang, MBA, BDS, LDS RCS General Dental Practitioner, Level 3 Personal Trainer (REP registration no R1045463), Sports Nutritionist
Understanding back pain 2- exercises and stretches for back pain suffere Dr James Tang, MBA, BDS, LDS RCS General Dental Practitioner, Level 3 Personal Trainer (REP registration no R1045463), Sports Nutritionist
Diagnostic and Treatment Approach to the Active Patient with Complex Spine Pathology
 Physical Therapy Diagnostic and Treatment Approach to the Active Patient with Complex Spine Pathology Scott Behjani, DPT, OCS Introduction Prevalence 1-year incidence of first-episode LBP ranges from
Physical Therapy Diagnostic and Treatment Approach to the Active Patient with Complex Spine Pathology Scott Behjani, DPT, OCS Introduction Prevalence 1-year incidence of first-episode LBP ranges from
Eligibility The NCSF online quizzes are open to any currently certified fitness professional, 18 years or older.
 Eligibility The NCSF online quizzes are open to any currently certified fitness professional, 18 years or older. Deadlines Course completion deadlines correspond with the NCSF Certified Professionals certification
Eligibility The NCSF online quizzes are open to any currently certified fitness professional, 18 years or older. Deadlines Course completion deadlines correspond with the NCSF Certified Professionals certification
PHYSICAL TRAINING INSTRUCTORS MANUAL TABLE OF CONTENT PART 5. Exercise No 31: Reverse Crunch 1. Exercise No 32: Single Hip Flexion 3
 TABLE OF CONTENT PART 5 Exercise No 31: Reverse Crunch 1 Exercise No 32: Single Hip Flexion 3 Exercise No 33: Bicycle Crunch 4 Exercise No 34: Straight Leg U Crunches 5 Exercise No 35: Bent Knee U Crunch
TABLE OF CONTENT PART 5 Exercise No 31: Reverse Crunch 1 Exercise No 32: Single Hip Flexion 3 Exercise No 33: Bicycle Crunch 4 Exercise No 34: Straight Leg U Crunches 5 Exercise No 35: Bent Knee U Crunch
Dean Somerset BSc. Kinesiology, CSCS, MES
 Dean Somerset BSc. Kinesiology, CSCS, MES Today s Webinar will... Show you that core training is more than just crunches Go through how the core works, in normal situations and also in pain Come up with
Dean Somerset BSc. Kinesiology, CSCS, MES Today s Webinar will... Show you that core training is more than just crunches Go through how the core works, in normal situations and also in pain Come up with
GFM Platform Exercise Manual
 GFM Platform Exercise Manual STEPHEN NEWHART, CSCS*D What is Whole Body Vibration? Body vibration is delivered through a variety of machines, including the most recent inclusion of whole body vibration
GFM Platform Exercise Manual STEPHEN NEWHART, CSCS*D What is Whole Body Vibration? Body vibration is delivered through a variety of machines, including the most recent inclusion of whole body vibration
CENTER FOR ORTHOPAEDICS AND SPINE CARE PHYSICAL THERAPY PROTOCOL ACUTE PROXIMAL HAMSTRING TENDON REPAIR BENJAMIN J. DAVIS, MD
 Weeks 0-6 Goal: 1) Protection of the surgical repair Precautions: 1) Non-weight bearing with crutches for 6 weeks with foot flat or with knee Knee flexed to 90 degrees with sitting 2) No active hamstring
Weeks 0-6 Goal: 1) Protection of the surgical repair Precautions: 1) Non-weight bearing with crutches for 6 weeks with foot flat or with knee Knee flexed to 90 degrees with sitting 2) No active hamstring
How to GET RESULTS BETWEEN SESSIONS LumboPelvic Hip Complex HOMEWORK. LPHC Homework Presented by Dr. Bruce Costello
 How to GET RESULTS BETWEEN SESSIONS LumboPelvic Hip Complex HOMEWORK LPHC Homework Presented by Dr. Bruce Costello Spinal Mobilization Reaching for the Stars Side-Bend Modified Karate Punch Session Objectives
How to GET RESULTS BETWEEN SESSIONS LumboPelvic Hip Complex HOMEWORK LPHC Homework Presented by Dr. Bruce Costello Spinal Mobilization Reaching for the Stars Side-Bend Modified Karate Punch Session Objectives
Correcting Muscle Imbalance in Helicopter Pilots with Pilates
 Correcting Muscle Imbalance in Helicopter Pilots with Pilates Tara Businski October 9, 2014 Oceanside/South Pasadena, CA 2013 Abstract Many professions require people to work in imbalanced or unnatural
Correcting Muscle Imbalance in Helicopter Pilots with Pilates Tara Businski October 9, 2014 Oceanside/South Pasadena, CA 2013 Abstract Many professions require people to work in imbalanced or unnatural
