Archived at the Flinders Academic Commons:
|
|
|
- Sophie Lindsey
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Archived at the Flinders Academic Commons: This is the peer reviewed version of the following article: Fox M, Omari T, Rommel N. Supraesophageal Reflux Disease: Solving a Riddle Wrapped in a Mystery Inside an Enigma. Gastroenterology Nov;149(6): which has been published in final form at Copyright 2015 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. This manuscript version is made available under the CC-BY-NC-ND 4.0 license
2 Supra-Esophageal Reflux Disease: Solving a riddle wrapped in a mystery inside an enigma Mark Fox 1,2, Taher Omari 3, Nathalie Rommel 5,6 1 Abdominal Center, Department of Gastroenterology, St. Claraspital, Basel, Switzerland 2 Zürich Neurogastroenterology and Motility Research Group, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, University Hospital Zurich, Switzerland 3 Human Physiology, Medical Science and Technology, School of Medicine Flinders University, Adelaide, South Australia 5 KU Leuven, Neurosciences, ExpORL, Leuven, Belgium 6 KU Leuven, Translational Research Center for Gastrointestinal Diseases (TARGID), Leuven, Belgium 7 University Hospital Leuven, Leuven, Gastroenterology (Neurogastroenterology and Motility), University Hospital Leuven, Leuven, Belgium. Correspondence Address Mark Fox, Abdominal Center, Department of Gastroenterology, Claraspital, Basel, Switzerland dr.mark.fox@gmail.com Tel. +41 (0) /
3 Symptoms referable to irritation and inflammation of the pharynx, larynx and bronchi are very common in the community. Hoarseness, persistent sore throat, globus and chronic cough are present in up to 25% of the primary care population and account for a large number of referrals to gastroenterologists, respiratory physicians and ear, nose and throat (ENT) specialists. 1 Epidemiological research has documented an association between gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and a range of supra-esophageal symptoms and diseases (Table 1). Further clinical studies report a high prevalence of typical reflux symptoms in patients with signs of laryngo-pharyngeal disease 2 and, also, a high frequency of throat and respiratory symptoms among patients with pathological esophageal acid exposure. 3 Based on this evidence, the Montreal classification included so called laryngo-pharyngeal or supra-esophageal reflux disease (SERD) as a subcategory of GERD, 4 and clinical reviews have proposed gastric acid and reflux suppression as empirical treatment for these atypical manifestations of GERD. 5 Notwithstanding this broad based agreement, if reflux of gastric contents is a common cause of supra-esophageal symptoms and disease, then many issues remain unresolved. In many cases the mechanism of disease is a riddle. The inability of current investigations to establish an association between reflux events and symptoms is a mystery. The failure of proton pump inhibitors (PPI) to treat laryngo-pharyngeal symptoms or heal mucosal disease in well-designed clinical trials is an enigma. In this issue of Gastroenterology, Babaei and colleagues applied state-of-the-art physiological measurements to study the pharyngo-esophageal response to simulated reflux events. 6 Their findings identified specific abnormalities in patients with symptoms suggestive of SERD. Moreover their approach to investigation could point the way to promising new clinical diagnostic tests for this condition. Mechanism of disease The simplest mechanism proposed for SERD is microaspiration of gastric contents into the pharynx and larynx. 7 In vivo experiments suggest that minute amounts of acid are sufficient to cause mucosal damage, especially in the 2/
4 presence of pepsin. 8 However, in most cases, ambulatory ph-impedance monitoring detects very few pharyngeal reflux events and this direct mechanism alone cannot explain the frequent symptoms reported by many patients. Other proposals include the possibility that distal esophageal reflux causes laryngopharyngeal symptoms by an indirect mechanism either by triggering an antedromic vasovagal reflex and neurogenic inflammation, or by prompting repetitive swallowing behavior. 7 An additional consideration is that acid exposure to the distal esophagus heightens visceral sensitivity of the whole organ through a central mechanism. 9 If this effect extends to the larynx and pharynx, then this would lower the sensory threshold not only to further reflux events but also to a range of other potential stimuli such as temperature change, cigarette smoke, airborne allergens and ingestion of alcohol or other irritants. 7 Physiological Measurement In patients with heartburn, acid regurgitation and reflux esophagitis the cause of laryngo-pharyngeal symptoms and disease may be obvious. However, the majority of patients with suspected SERD do not have typical reflux symptoms or mucosal disease. 10 In this group, physiological measurements that detect reflux events at, or close to, the site of pathology provide objective evidence to support of the diagnosis. Studies that include pharyngeal ph sensors in addition to esophageal sensors may be more discriminatory of SERD patients. 11 The current standard is ambulatory ph-impedance reflux monitoring. 12 This technology can detect both acid and non-acid reflux and, in principle, establish a causal association between these events and symptoms. Unfortunately, there is little consensus regarding the optimal acquisition, analysis or interpretation of this data. Moreover, in practice, if isolated pharyngeal reflux events are sufficient to cause disease, if symptoms are present all the time, or if there is only an indirect link between reflux and symptoms, then even the most accurate ambulatory reflux monitoring will not establish a definitive SERD diagnosis. These issues are compounded by the fact that symptoms such as hoarseness and chronic cough are very common and have multiple potential causes that may coexist with 3/
5 GERD by chance. These are real and important concerns because treatment decisions, including referral for anti-reflux surgery, are based on this information. Given the limitations of existing tests, new methods to detect SERD are of interest. Measurement of pepsin and bile acids in the saliva have been proposed as an 'office-based' method for detecting reflux. Recent studies indicate that high levels of pepsin provide a specific marker of GERD. 13 The presence of this gastric enzyme in the throat can be explained only by supra-esophageal reflux and, therefore, this approach may be particularly value for SERD diagnosis. 14 The same concept can be applied by nuclear imaging. Scintigraphy is used to detect reflux to the pharynx after ingestion of a radio-labelled drink, with late studies of the lungs obtained to detect aspiration. 15 Both these investigations are well-tolerated and require less expertise to interpret than ph-impedance studies; however, neither provides insight into the mechanism of disease. To address this issue, the current study applied high-resolution impedance manometry (HRiM) to obtain a detailed description of sensory-motor mechanisms that control upper esophageal sphincter (UES) function and how this is disrupted in patients with typical symptoms of GERD and SERD. 6 It is known from the previous work by Reza Shaker s group, 16 that both relaxation and contractile UES responses are present in health, each governed by independent neural circuits that are activated in relation to the rate, magnitude and physical properties of distending stimuli. Relaxation enables venting of gas ( belching ). Contraction guards against reflux of gastric contents into the pharynx. The authors identified the UES relaxation reflex (RR) and contraction reflex (CR) by HRM and SER events using impedance data. These observations revealed that some patients with SERD symptoms have aberrant UES responses to rapid esophageal infusion of liquid (i.e. simulated reflux) that were not seen in patients with GERD symptoms or healthy controls. Specifically, rather than an effective contraction of the UES and proximal esophagus to clear refluxate away from the sensitive laryngo-pharyngeal region, some patients had an inappropriate 4/
6 UESRR and / or ineffective UES and esophageal CR during liquid reflux. The absolute frequency of SER during individual studies and how often SER was associated with each form of dysfunction was not reported and therefore the overall extent to which these aberrant responses are permissive of reflux is unknown; nevertheless, the unique abnormality in patients with SERD symptoms were inappropriate UESRRs. Although failure to initiate UES and esophageal CR also occurred in this group, the latter abnormality was seen also in GERD, and SER was never reported following isolated failure of the protective response. This study provides new insight into the pathophysiology of SERD. The presence of inappropriate UESRR in patients with laryngo-pharyngeal symptoms is consistent with microaspiration as a mechanism of disease. In addition, the technology and methodology used by this group is of interest to clinicians looking for a new, more informative diagnostic test for SERD. HRiM provides a comprehensive, non-radiological assessment of pharyngo-esophageal function. High resolution manometry with spatiotemporal Clouse plots delivers a continuous representation of motor activity from the pharynx to the stomach. Intraluminal impedance detects bolus movement by measuring changes in resistance between multiple pairs of electrodes. To date, this combined technology has been applied most often to study patients with pharyngeal swallowing problems and to assess the risk of aspiration. 17 The findings reported here suggest that HRiM could be applied also to assess the risk of supraesophageal reflux in patients with laryngo-pharyngeal symptoms. Importantly, the HRiM methodology is different to ambulatory ph-impedance monitoring or stationary observations after a test meal because, rather than relying on the detection of spontaneous SER events, a standardized challenge designed to simulate gastro-esophageal reflux (i.e. esophageal infusion) is applied to identify patients at risk of SERD. Further validation is required before HRiM could be used for SERD diagnosis. Surprisingly, the current study did not apply standardized questionnaires, 5/
7 laryngoscopic assessment or physiological studies to define study groups. Not one of these investigations represents a gold standard"; however, symptoms are non-specific and the differential diagnosis for patients with troublesome regurgitation along with at least one supra-esophageal manifestation (the entry criterion used in the study) includes motility disorders, rumination syndrome and a number of ENT or respiratory diseases. 18 This could explain why only 5/19 patients with typical SERD symptoms had the characteristic UESRR abnormality after rapid esophageal saline infusion. Future studies should apply standardized inclusion criteria with either pathological acid exposure or a positive reflux-symptom association on ph-impedance monitoring. Additionally, HRiM data analysis could be optimized. In this paper assessment of impedance was subjective and considered separately to the pressure measurements. Pressure Flow Analysis (PFA) is a semi-automated method which integrates high resolution pressure and impedance signals to obtain objective metrics that cannot be determined by either method alone. 19 Application of PFA in patients with pharyngeal dysfunction identifies biomechanical factors that determine the success or failure of the swallow and defines the risk of aspiration. 19, 20 This includes not only UES relaxation, but also UES opening and the efficacy of pharyngeal clearance. 20 Adapting this approach, UES responses to esophageal infusion could be quantified in terms of flow permissive characteristics to detect factors that determine the risk of supra-esophageal reflux. The success of scientific medicine is based on the identification and treatment of the pathophysiological basis of disease. To date, the diagnosis of SERD has been based as much on subjective assessment as objective physiology. Now, as with the introduction of HRM and the Chicago Classification of esophageal motility disorders a few years ago, new technology and methods is driving progress in the pharyngo-esophageal region. HRiM combined with analysis that utilizes all the information acquired, are now available to describe the causes of SERD, identify individual patients that can benefit from anti-reflux treatment and, in the process, solve this riddle wrapped in a mystery inside an enigma. 6/
8 Table 1 Extraesophageal conditions linked to SERD Symptoms Diseases Acid Regurgitation Dental erosions Voice change Sinusitis Hoarseness Posterior Laryngitis Chronic sore throat Vocal cord ulceration Repetitive throat clearing Laryngeal polyps Globus sensation Cancer of pharynx / larynx Chronic cough Bronchiectasis Recurrent aspiration Non-atopic asthma 7/
9 References 1. Lowden M, McGlashan JA, Steel A, et al. Prevalence of symptoms suggestive of extra-oesophageal reflux in a general practice population in the UK. Logoped Phoniatr Vocol 2009;34: Champion GL, Richter JE. Atypical presentation of gastroesophageal reflux disease: chest pain, pulmonary, and ear, nose, throat manifestations. Gastroenterologist 1993;1: Theodoropoulos DS, Ledford DK, Lockey RF, et al. Prevalence of upper respiratory symptoms in patients with symptomatic gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2001;164: Vakil N, van Zanten SV, Kahrilas P, et al. The Montreal definition and classification of gastroesophageal reflux disease: a global evidence-based consensus. Am J Gastroenterol 2006;101: ; quiz Fox M, Forgacs I. Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. BMJ 2006;332: Babaei A, Venu M, Naini SR, et al. Impaired Upper Esophageal Sphincter (UES) Reflexes in Patients with Supra-Esophageal Reflux Disease (SERD). Gastroenterology Pearson JP, Parikh S, Orlando RC, et al. Review article: reflux and its consequences--the laryngeal, pulmonary and oesophageal manifestations. Conference held in conjunction with the 9th International Symposium on Human Pepsin (ISHP) Kingston-upon-Hull, UK, April Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2011;33 Suppl 1: Bulmer DM, Ali MS, Brownlee IA, et al. Laryngeal mucosa: its susceptibility to damage by acid and pepsin. Laryngoscope 2010;120: Sarkar S, Aziz Q, Woolf CJ, et al. Contribution of central sensitisation to the development of non-cardiac chest pain. Lancet 2000;356: Koufman JA. The otolaryngologic manifestations of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD): a clinical investigation of 225 patients using ambulatory 24-hour ph monitoring and an experimental investigation of the role of acid and pepsin in the development of laryngeal injury. Laryngoscope 1991;101: Merati AL, Lim HJ, Ulualp SO, et al. Meta-analysis of upper probe measurements in normal subjects and patients with laryngopharyngeal reflux. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 2005;114: Sifrim D, Dupont L, Blondeau K, et al. Weakly acidic reflux in patients with chronic unexplained cough during 24 hour pressure, ph, and impedance monitoring. Gut 2005;54: Hayat JO, Gabieta-Somnez S, Yazaki E, et al. Pepsin in saliva for the diagnosis of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Gut 2015;64: Sereg-Bahar M, Jerin A, Jansa R, et al. Pepsin and bile acids in saliva in patients with laryngopharyngeal reflux - a prospective comparative study. Clin Otolaryngol 2015;40: Falk GL, Beattie J, Ing A, et al. Scintigraphy in laryngopharyngeal and gastroesophageal reflux disease: a definitive diagnostic test? World J Gastroenterol 2015;21: /
10 16. Jadcherla S, Hogan W, Shaker R. Physiology and pathophysiology of glottic reflexes and pulmonary aspiration: from neonates to adults. Semin Respir Crit Care Med 2010;31: Omari TI, Dejaeger E, van Beckevoort D, et al. A method to objectively assess swallow function in adults with suspected aspiration. Gastroenterology 2011;140: Vardar R, Sweis R, Anggiansah A, et al. Upper esophageal sphincter and esophageal motility in patients with chronic cough and reflux: assessment by high-resolution manometry. Dis Esophagus 2013;26: Omari TI, Papathanasopoulos A, Dejaeger E, et al. Reproducibility and Agreement of Pharyngeal Automated Impedance Manometry With Videofluoroscopy. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol Omari T, Wiklendt L, Dinning P, et al. Upper esophageal sphincter mechanical states analysis: a novel methodology to describe UES relaxation and opening. Front Syst Neurosci 2015;8:241. 9/
Maximizing Outcome of Extraesophageal Reflux Disease. (GERD) is often accompanied
 ...PRESENTATIONS... Maximizing Outcome of Extraesophageal Reflux Disease Based on a presentation by Peter J. Kahrilas, MD Presentation Summary Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) accompanied by regurgitation
...PRESENTATIONS... Maximizing Outcome of Extraesophageal Reflux Disease Based on a presentation by Peter J. Kahrilas, MD Presentation Summary Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) accompanied by regurgitation
GERD is a condition which develops when the reflux of stomach contents causes troublesome symptoms and/or complications
 GERD is a condition which develops when the reflux of stomach contents causes troublesome symptoms and/or complications Esophageal Syndromes Extra - esophageal Syndromes Symptomatic Syndromes Typical reflux
GERD is a condition which develops when the reflux of stomach contents causes troublesome symptoms and/or complications Esophageal Syndromes Extra - esophageal Syndromes Symptomatic Syndromes Typical reflux
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Infants and Children
 Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Infants and Children 4 Marzo 2017 Drssa Chiara Leoni Drssa Valentina Giorgio pediatriagastro@gmail.com valentinagiorgio1@gmail.com Definitions: GER GER is the passage
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Infants and Children 4 Marzo 2017 Drssa Chiara Leoni Drssa Valentina Giorgio pediatriagastro@gmail.com valentinagiorgio1@gmail.com Definitions: GER GER is the passage
Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Extraesophageal Manifestations
 Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Extraesophageal Manifestations Karen B. Zur, MD Director, Pediatric Voice Program Associate Director, Center for Pediatric Airway Disorders The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia
Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Extraesophageal Manifestations Karen B. Zur, MD Director, Pediatric Voice Program Associate Director, Center for Pediatric Airway Disorders The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia
Refractory GERD: What s a Gastroenterologist To Do?
 Refractory GERD: What s a Gastroenterologist To Do? Philip O. Katz, MD, FACG Chairman, Division of Gastroenterology Einstein Medical Center Clinical Professor of Medicine Jefferson Medical College Philadelphia,
Refractory GERD: What s a Gastroenterologist To Do? Philip O. Katz, MD, FACG Chairman, Division of Gastroenterology Einstein Medical Center Clinical Professor of Medicine Jefferson Medical College Philadelphia,
Review article: identifying the causes of reflux events and symptoms new approaches
 Review article: identifying the causes of reflux events and symptoms new approaches M. Fox Nottingham Digestive Diseases Centre and Biomedical Research Unit, Queen s Medical Centre, University Hospital,
Review article: identifying the causes of reflux events and symptoms new approaches M. Fox Nottingham Digestive Diseases Centre and Biomedical Research Unit, Queen s Medical Centre, University Hospital,
Refractory GERD : case presentation and discussion
 Refractory GERD : case presentation and discussion Ping-Huei Tseng National Taiwan University Hospital May 19, 2018 How effective is PPI based on EGD? With GERD symptom 75% erosive 25% NERD Endoscopy 81%
Refractory GERD : case presentation and discussion Ping-Huei Tseng National Taiwan University Hospital May 19, 2018 How effective is PPI based on EGD? With GERD symptom 75% erosive 25% NERD Endoscopy 81%
GERD: A linical Clinical Clinical Update Objectives
 GERD: A Clinical Update Jeff Gilbert, M.D. University i of Kentucky Gastroenterology 11/6/08 Objectives To review the basic pathophysiology underlying gastroesophageal reflux disease To highlight current
GERD: A Clinical Update Jeff Gilbert, M.D. University i of Kentucky Gastroenterology 11/6/08 Objectives To review the basic pathophysiology underlying gastroesophageal reflux disease To highlight current
Putting Chronic Heartburn On Ice
 Putting Chronic Heartburn On Ice Over the years, gastroesophageal reflux disease has proven to be one of the most common complaints facing family physicians. With quicker diagnosis, this pesky ailment
Putting Chronic Heartburn On Ice Over the years, gastroesophageal reflux disease has proven to be one of the most common complaints facing family physicians. With quicker diagnosis, this pesky ailment
Lansoprazole Treatment of Patients With Chronic Idiopathic Laryngitis: A Placebo-Controlled Trial
 THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF GASTROENTEROLOGY Vol. 96, No. 4, 2001 2001 by Am. Coll. of Gastroenterology ISSN 0002-9270/01/$20.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0002-9270(01)02244-4 Lansoprazole Treatment
THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF GASTROENTEROLOGY Vol. 96, No. 4, 2001 2001 by Am. Coll. of Gastroenterology ISSN 0002-9270/01/$20.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0002-9270(01)02244-4 Lansoprazole Treatment
Management of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Disease. Abdul Aziz J Ashoor, Facharzt fuer Hals Nasen Ohren (H.N.O.)*
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 33, No. 3, September 2011 Management of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Disease Abdul Aziz J Ashoor, Facharzt fuer Hals Nasen Ohren (H.N.O.)* Objective: To evaluate the efficacy
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 33, No. 3, September 2011 Management of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Disease Abdul Aziz J Ashoor, Facharzt fuer Hals Nasen Ohren (H.N.O.)* Objective: To evaluate the efficacy
A Prospective, Randomized, Placebo-controlled, Double-Blind Study of Rabeprazole for Therapeutic Trial in Chronic Idiopathic Laryngitis ABSTRACT
 THAI J 28 GASTROENTEROL Rabeprazole for Therapeutic Trial in Chronic Original Idiopathic Laryngitis Article A Prospective, Randomized, Placebo-controlled, Double-Blind Study of Rabeprazole for Therapeutic
THAI J 28 GASTROENTEROL Rabeprazole for Therapeutic Trial in Chronic Original Idiopathic Laryngitis Article A Prospective, Randomized, Placebo-controlled, Double-Blind Study of Rabeprazole for Therapeutic
ORIGINAL ARTICLES ALIMENTARY TRACT
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2012;10:379 384 ORIGINAL ARTICLES ALIMENTARY TRACT Baclofen Improves Symptoms and Reduces Postprandial Flow Events in Patients With Rumination and Supragastric
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2012;10:379 384 ORIGINAL ARTICLES ALIMENTARY TRACT Baclofen Improves Symptoms and Reduces Postprandial Flow Events in Patients With Rumination and Supragastric
GERD DIAGNOSIS & TREATMENT DISCLOSURES 4/18/2018
 GERD DIAGNOSIS & TREATMENT Subhash Chandra MBBS Assistant Professor CHI Health Clinic Gastroenterology Creighton University, School of Medicine April 28, 2018 DISCLOSURES None 1 OBJECTIVES Review update
GERD DIAGNOSIS & TREATMENT Subhash Chandra MBBS Assistant Professor CHI Health Clinic Gastroenterology Creighton University, School of Medicine April 28, 2018 DISCLOSURES None 1 OBJECTIVES Review update
ENT Manifestations in Gastro - Esophageal Reflux Disease.
 DOI: 10.21276/aimdr.2016.2.6.EN2 Original Article ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-2814 ENT Manifestations in Gastro - Esophageal Reflux Disease. Santhana Krishna Kumar. B 1, Sivasankari. L 1 1 Assistant
DOI: 10.21276/aimdr.2016.2.6.EN2 Original Article ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-2814 ENT Manifestations in Gastro - Esophageal Reflux Disease. Santhana Krishna Kumar. B 1, Sivasankari. L 1 1 Assistant
Esophageal Disorders. Learning Objectives. Introduction. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. Reza Shaker, MD, and Benson T.
 Esophageal Disorders Reza Shaker, MD, and Benson T. Massey, MD, FACP Learning Objectives AFTER COMPLETING THIS CHAPTER, THE LEARNER SHOULD BE ABLE TO: 1. Recognize the typical and atypical presentations
Esophageal Disorders Reza Shaker, MD, and Benson T. Massey, MD, FACP Learning Objectives AFTER COMPLETING THIS CHAPTER, THE LEARNER SHOULD BE ABLE TO: 1. Recognize the typical and atypical presentations
A Case of Severe Neonatal Dysphagia: Experience and Reason
 A Case of Severe Neonatal Dysphagia: Experience and Reason The Contemporary Management of Aerodigestive Disease in Children 2 nd Aerodigestive Meeting Vanderbilt University, Nashville, TN Friday, November
A Case of Severe Neonatal Dysphagia: Experience and Reason The Contemporary Management of Aerodigestive Disease in Children 2 nd Aerodigestive Meeting Vanderbilt University, Nashville, TN Friday, November
Somkiat Wongtim Professor of Medicine Division of Respiratory Disease and Critical Care Chulalongkorn University
 Somkiat Wongtim Professor of Medicine Division of Respiratory Disease and Critical Care Chulalongkorn University Asthma-related Comorbidities Comorbid conditions of the upper airways Rhinitis and Sinusitis
Somkiat Wongtim Professor of Medicine Division of Respiratory Disease and Critical Care Chulalongkorn University Asthma-related Comorbidities Comorbid conditions of the upper airways Rhinitis and Sinusitis
pissn: eissn: Journal of Neurogastroenterology and Motility
 JNM J Neurogastroenterol Motil, Vol. 21 No. 3 July, 2015 pissn: 2093-0879 eissn: 2093-0887 http://dx.doi.org/10.5056/jnm15002 Journal of Neurogastroenterology and Motility Original Article Supragastric
JNM J Neurogastroenterol Motil, Vol. 21 No. 3 July, 2015 pissn: 2093-0879 eissn: 2093-0887 http://dx.doi.org/10.5056/jnm15002 Journal of Neurogastroenterology and Motility Original Article Supragastric
GERD. Gastroesophageal reflux disease, or GERD, occurs when acid from the. stomach backs up into the esophagus. Normally, food travels from the
 GERD What is GERD? Gastroesophageal reflux disease, or GERD, occurs when acid from the stomach backs up into the esophagus. Normally, food travels from the mouth, down through the esophagus and into the
GERD What is GERD? Gastroesophageal reflux disease, or GERD, occurs when acid from the stomach backs up into the esophagus. Normally, food travels from the mouth, down through the esophagus and into the
Outline. Outline. Definition. Asthma, GERD and Laryngeal Pharyngeal Reflux (LPR) Definitions
 Asthma, GERD and Laryngeal Pharyngeal Reflux (LPR) Richard F. Lockey, M.D. Division of Allergy and Immunology Department of Internal Medicine University of South Florida College of Medicine and James A.
Asthma, GERD and Laryngeal Pharyngeal Reflux (LPR) Richard F. Lockey, M.D. Division of Allergy and Immunology Department of Internal Medicine University of South Florida College of Medicine and James A.
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: esophageal_ph_monitoring 4/2011 5/2017 5/2018 5/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Acid reflux is the
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: esophageal_ph_monitoring 4/2011 5/2017 5/2018 5/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Acid reflux is the
The prevalence of upper respiratory symptoms in a cohort of adults presenting with symptoms of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease
 The prevalence of upper respiratory symptoms in a cohort of adults presenting with symptoms of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease D L Amarasiri 1, A Pathmeswaran 2, A S Dassanayake 3, A P de Silva 4, M
The prevalence of upper respiratory symptoms in a cohort of adults presenting with symptoms of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease D L Amarasiri 1, A Pathmeswaran 2, A S Dassanayake 3, A P de Silva 4, M
The Validity and Reliability of the Reflux Finding Score (RFS)
 The Laryngoscope Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia 2001 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. The Validity and Reliability of the Reflux Finding Score (RFS)
The Laryngoscope Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia 2001 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. The Validity and Reliability of the Reflux Finding Score (RFS)
ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
 ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Philip O. Katz MD 1, Lauren B. Gerson MD, MSc 2 and Marcelo F. Vela MD, MSCR 3 1 Division of Gastroenterology, Einstein
ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Philip O. Katz MD 1, Lauren B. Gerson MD, MSc 2 and Marcelo F. Vela MD, MSCR 3 1 Division of Gastroenterology, Einstein
Extraesophageal GERD: Fact or Fiction?
 Transcript Details This is a transcript of an educational program accessible on the ReachMD network. Details about the program and additional media formats for the program are accessible by visiting: https://reachmd.com/programs/gi-insights/extraesophageal-gerd-fact-or-fiction/4157/
Transcript Details This is a transcript of an educational program accessible on the ReachMD network. Details about the program and additional media formats for the program are accessible by visiting: https://reachmd.com/programs/gi-insights/extraesophageal-gerd-fact-or-fiction/4157/
Extraesophageal Manifestations of GERD in Children
 Extraesophageal Manifestations of GERD in Children Jose Luis Martinez, M.D. Associate Professor University of California San Francisco Director Endoscopy Unit Children s Hospital Central California Overview
Extraesophageal Manifestations of GERD in Children Jose Luis Martinez, M.D. Associate Professor University of California San Francisco Director Endoscopy Unit Children s Hospital Central California Overview
Gastroesophageal Reflux Evaluation in Patients Affected by Chronic Cough: Restech Versus Multichannel Intraluminal Impedance/pH Metry
 The Laryngoscope VC 2012 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Gastroesophageal Reflux Evaluation in Patients Affected by Chronic Cough: Restech Versus Multichannel Intraluminal
The Laryngoscope VC 2012 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Gastroesophageal Reflux Evaluation in Patients Affected by Chronic Cough: Restech Versus Multichannel Intraluminal
Obesity Is Associated With Increased Transient Lower Esophageal Sphincter Relaxation. Introduction. Predisposing factor. Introduction.
 Obesity Is Associated With Increased Transient Lower Esophageal Sphincter Relaxation Gastro Esophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) JUSTIN CHE-YUEN WU, et. al. The Chinese University of Hong Kong Gastroenterology,
Obesity Is Associated With Increased Transient Lower Esophageal Sphincter Relaxation Gastro Esophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) JUSTIN CHE-YUEN WU, et. al. The Chinese University of Hong Kong Gastroenterology,
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
 Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) Acid Reflux Acid reflux occurs when acid from the stomach moves backwards into the esophagus. Heartburn Heartburn is a symptom of acid reflux and GERD. It may feel
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) Acid Reflux Acid reflux occurs when acid from the stomach moves backwards into the esophagus. Heartburn Heartburn is a symptom of acid reflux and GERD. It may feel
Combined multichannel intraluminal impedance and. Characteristics of Consecutive Esophageal Motility Diagnoses After a Decade of Change
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Characteristics of Consecutive Esophageal Motility Diagnoses After a Decade of Change Katherine Boland, BS,* Mustafa Abdul-Hussein, MD,* Radu Tutuian, MD,w and Donald O. Castell, MD* Background
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Characteristics of Consecutive Esophageal Motility Diagnoses After a Decade of Change Katherine Boland, BS,* Mustafa Abdul-Hussein, MD,* Radu Tutuian, MD,w and Donald O. Castell, MD* Background
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) Extraesophageal symptoms of GERD
 Extraesophageal symptoms of GERD KENNETH R. DEVAULT, MD ABSTRACT Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) can be the primary cause of, or an aggravating contributor to, a wide variety of conditions affecting
Extraesophageal symptoms of GERD KENNETH R. DEVAULT, MD ABSTRACT Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) can be the primary cause of, or an aggravating contributor to, a wide variety of conditions affecting
Extraesophageal presentations of gastroesophageal reflux disease: the case for aggressive diagnosis and treatment
 JOEL E. RICHTER, MD Dr. Richter is chairman of the Department of Gastroenterology at the Cleveland Clinic Foundation, specializing in esophageal diseases with particular interest in GERD, achalasia, and
JOEL E. RICHTER, MD Dr. Richter is chairman of the Department of Gastroenterology at the Cleveland Clinic Foundation, specializing in esophageal diseases with particular interest in GERD, achalasia, and
Mapping Regional Laryngopharyngeal Mechanoreceptor Response
 Original Article Clinical and Experimental Otorhinolaryngology Vol. 7, No. 4: 319-323, December 2014 http://dx.doi.org/10.3342/ceo.2014.7.4.319 pissn 1976-8710 eissn 2005-0720 Mapping Regional Laryngopharyngeal
Original Article Clinical and Experimental Otorhinolaryngology Vol. 7, No. 4: 319-323, December 2014 http://dx.doi.org/10.3342/ceo.2014.7.4.319 pissn 1976-8710 eissn 2005-0720 Mapping Regional Laryngopharyngeal
The role of the modified barium swallow study & esophagram in patients with GERD/Globus sensation
 The role of the modified barium swallow study & esophagram in patients with GERD/Globus sensation James P. Dworkin, Ph.D. Jayme Dowdall, M.D. Adam Folbe, M.D. Tom Willis, M.S. Richard Culatta, Ph.D. Wayne
The role of the modified barium swallow study & esophagram in patients with GERD/Globus sensation James P. Dworkin, Ph.D. Jayme Dowdall, M.D. Adam Folbe, M.D. Tom Willis, M.S. Richard Culatta, Ph.D. Wayne
GERD. gastroesophageal reflux disease : GERD. Laryngopharyngeal reflux disease : LPRD GERD GERD GERD LPRD GERD. gastroesophageal reflux ; GER GERD
 114114 2011 : GERD gastroesophageal reflux disease : GERD Laryngopharyngeal reflux disease : LPRD GERD GERD GERD GERD LPRD QOL GERD LPRD QOL LPRD : gastroesophageal reflux ; GER gastroesophageal reflux
114114 2011 : GERD gastroesophageal reflux disease : GERD Laryngopharyngeal reflux disease : LPRD GERD GERD GERD GERD LPRD QOL GERD LPRD QOL LPRD : gastroesophageal reflux ; GER gastroesophageal reflux
GERD: Pitfalls and Pearls
 GERD: Pitfalls and Pearls Gary W. Falk, M.D., M.S. Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology Perelman School of Medicine of the University of Pennsylvania Conflicts of Interest Nothing to disclose
GERD: Pitfalls and Pearls Gary W. Falk, M.D., M.S. Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology Perelman School of Medicine of the University of Pennsylvania Conflicts of Interest Nothing to disclose
pat hways Medtech innovation briefing Published: 22 May 2015 nice.org.uk/guidance/mib31
 pat hways Peptest for diagnosing gastro-oesophageal reflux Medtech innovation briefing Published: 22 May 2015 nice.org.uk/guidance/mib31 Summary The Peptest is designed to help diagnose gastro-oesophageal
pat hways Peptest for diagnosing gastro-oesophageal reflux Medtech innovation briefing Published: 22 May 2015 nice.org.uk/guidance/mib31 Summary The Peptest is designed to help diagnose gastro-oesophageal
Clinical Policy Title: Esophageal ph monitoring
 Clinical Policy Title: Esophageal ph monitoring Clinical Policy Number: CCP.1381 Effective Date: August 1, 2018 Initial Review Date: June 5, 2018 Most Recent Review Date: July 3, 2018 Next Review Date:
Clinical Policy Title: Esophageal ph monitoring Clinical Policy Number: CCP.1381 Effective Date: August 1, 2018 Initial Review Date: June 5, 2018 Most Recent Review Date: July 3, 2018 Next Review Date:
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is implicated
 Donald O. Castell, M.D., Series Editor Chronic Laryngitis and Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease by Jonathan A. Schneider and Michael F. Vaezi INTRODUCTION Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is implicated
Donald O. Castell, M.D., Series Editor Chronic Laryngitis and Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease by Jonathan A. Schneider and Michael F. Vaezi INTRODUCTION Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is implicated
Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE)
 Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE) 01.06.2016 EoE: immune-mediated disorder food or environmental antigens => Th2 inflammatory response. Key cytokines: IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 stimulate the production of eotaxin-3
Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE) 01.06.2016 EoE: immune-mediated disorder food or environmental antigens => Th2 inflammatory response. Key cytokines: IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 stimulate the production of eotaxin-3
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. or dysphagia may alert a physician to the possibility of LPR. 1,2 Laryngeal findings
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Clinical Value of Pharyngeal ph Monitoring Using a Double-Probe, Triple-Sensor Catheter in Patients With Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Togay Muderris, MD; M. Kursat Gokcan, MD; Irfan Yorulmaz,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Clinical Value of Pharyngeal ph Monitoring Using a Double-Probe, Triple-Sensor Catheter in Patients With Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Togay Muderris, MD; M. Kursat Gokcan, MD; Irfan Yorulmaz,
ACID REFLUX & GERD: The Unsettling Reality in Canada
 ACID REFLUX & GERD: The Unsettling Reality in Canada gerd fact 1 see page 8 Canadian Society of Intestinal Research On average, ARD patients wait over two years before seeking care 1. 1 gerd fact 2 see
ACID REFLUX & GERD: The Unsettling Reality in Canada gerd fact 1 see page 8 Canadian Society of Intestinal Research On average, ARD patients wait over two years before seeking care 1. 1 gerd fact 2 see
Clearance mechanisms of the aperistaltic esophagus. The pump-gun hypothesis.
 Gut Online First, published on December 14, 2005 as 10.1136/gut.2005.085423 Clearance mechanisms of the aperistaltic esophagus. The pump-gun hypothesis. Radu Tutuian 1, Daniel Pohl 1, Donald O Castell
Gut Online First, published on December 14, 2005 as 10.1136/gut.2005.085423 Clearance mechanisms of the aperistaltic esophagus. The pump-gun hypothesis. Radu Tutuian 1, Daniel Pohl 1, Donald O Castell
Review Article Impact of Laparoscopic Fundoplication for the Treatment of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux: Review of the Literature
 International Otolaryngology Volume 2012, Article ID 291472, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/291472 Review Article Impact of Laparoscopic Fundoplication for the Treatment of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux: Review of
International Otolaryngology Volume 2012, Article ID 291472, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/291472 Review Article Impact of Laparoscopic Fundoplication for the Treatment of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux: Review of
Laryngopharyngeal Reflux
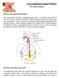 Laryngopharyngeal Reflux The Silent Reflux What is Laryngopharyngeal Reflux? Also called Reflux laryngitis, laryngopharyngeal reflux is a condition where the acid from the stomach reaches the voicebox
Laryngopharyngeal Reflux The Silent Reflux What is Laryngopharyngeal Reflux? Also called Reflux laryngitis, laryngopharyngeal reflux is a condition where the acid from the stomach reaches the voicebox
ORIGINAL ARTICLES ALIMENTARY TRACT
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2012;10:612 619 ORIGINAL ARTICLES ALIMENTARY TRACT Regurgitation Is Less Responsive to Acid Suppression Than Heartburn in Patients With Gastroesophageal Reflux
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2012;10:612 619 ORIGINAL ARTICLES ALIMENTARY TRACT Regurgitation Is Less Responsive to Acid Suppression Than Heartburn in Patients With Gastroesophageal Reflux
Title: Comparison of esophageal motility in gastroesophageal reflux disease with and without globus sensation
 Title: Comparison of esophageal motility in gastroesophageal reflux disease with and without globus sensation Authors: Yuming Tang, Jia Huang, Ying Zhu, Aihua Qian, Bin Xu, Weiyan Yao DOI: 10.17235/reed.2017.4449/2016
Title: Comparison of esophageal motility in gastroesophageal reflux disease with and without globus sensation Authors: Yuming Tang, Jia Huang, Ying Zhu, Aihua Qian, Bin Xu, Weiyan Yao DOI: 10.17235/reed.2017.4449/2016
1. Introduction. Correspondence should be addressed to Wei-Chen Tai; Received 29 May 2013; Accepted 5 July 2013
 Gastroenterology Research and Practice Volume 2013, Article ID 480325, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/480325 Clinical Study The Frequencies of Gastroesophageal and Extragastroesophageal Symptoms
Gastroenterology Research and Practice Volume 2013, Article ID 480325, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/480325 Clinical Study The Frequencies of Gastroesophageal and Extragastroesophageal Symptoms
Review article: the measurement of non-acid gastro-oesophageal reflux
 Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics Review article: the measurement of non-acid gastro-oesophageal reflux A. J. P. M. SMOUT Department of Gastroenterology, University Medical Center Utrecht, Utrecht,
Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics Review article: the measurement of non-acid gastro-oesophageal reflux A. J. P. M. SMOUT Department of Gastroenterology, University Medical Center Utrecht, Utrecht,
Supplementary appendix
 Supplementary appendix This appendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Ang D, Misselwitz B, Hollenstein M, et al.
Supplementary appendix This appendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Ang D, Misselwitz B, Hollenstein M, et al.
Comparison of esophageal motility in gastroesophageal reflux disease with and without globus sensation
 1130-0108/2017/109/12/850-855 Revista Española de Enfermedades Digestivas Copyright 2017. SEPD y ARÁN EDICIONES, S.L. Rev Esp Enferm Dig 2017, Vol. 109, N.º 12, pp. 850-855 ORIGINAL PAPERS Comparison of
1130-0108/2017/109/12/850-855 Revista Española de Enfermedades Digestivas Copyright 2017. SEPD y ARÁN EDICIONES, S.L. Rev Esp Enferm Dig 2017, Vol. 109, N.º 12, pp. 850-855 ORIGINAL PAPERS Comparison of
127 Chapter 1 Chapter 2 Chapter 3
 CHAPTER 8 Summary Summary 127 In Chapter 1, a general introduction on the principles and applications of intraluminal impedance monitoring in esophageal disorders is provided. Intra-esophageal impedance
CHAPTER 8 Summary Summary 127 In Chapter 1, a general introduction on the principles and applications of intraluminal impedance monitoring in esophageal disorders is provided. Intra-esophageal impedance
Original Policy Date 12:2013
 MP 2.01.17 Esophageal ph Monitoring Medical Policy Section Medicine Issue 12:2013 Subsection Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed with literature search/12:2013 Return to Medical
MP 2.01.17 Esophageal ph Monitoring Medical Policy Section Medicine Issue 12:2013 Subsection Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed with literature search/12:2013 Return to Medical
Achalasia is a rare disease with an annual incidence estimated REVIEWS. Erroneous Diagnosis of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Achalasia
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2011;9:1020 1024 REVIEWS Erroneous Diagnosis of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Achalasia BOUDEWIJN F. KESSING, ALBERT J. BREDENOORD, and ANDRÉ J. P. M. SMOUT
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2011;9:1020 1024 REVIEWS Erroneous Diagnosis of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Achalasia BOUDEWIJN F. KESSING, ALBERT J. BREDENOORD, and ANDRÉ J. P. M. SMOUT
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,800 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,800 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Archived at the Flinders Academic Commons:
 Archived at the Flinders Academic Commons: http://dspace.flinders.edu.au/dspace/ This is the peer reviewed version of the following article: Rayyan M, Allegaert K, Omari T, Rommel N. Dysphagia in children
Archived at the Flinders Academic Commons: http://dspace.flinders.edu.au/dspace/ This is the peer reviewed version of the following article: Rayyan M, Allegaert K, Omari T, Rommel N. Dysphagia in children
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Afferent nerves, interactions of, in cough, 20 21 Airway, eosinophilic inflammation of, 124 narrowing of, in asthma, 126 protection of, terms
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Afferent nerves, interactions of, in cough, 20 21 Airway, eosinophilic inflammation of, 124 narrowing of, in asthma, 126 protection of, terms
Review article: pharmacology of esomeprazole and comparisons with omeprazole
 Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2003; 17 (Suppl. 1): 5 9. Review article: pharmacology of esomeprazole and comparisons with omeprazole J. DENT Department of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and General Medicine, Royal
Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2003; 17 (Suppl. 1): 5 9. Review article: pharmacology of esomeprazole and comparisons with omeprazole J. DENT Department of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and General Medicine, Royal
Management of laryngopharyngeal refl ux with proton pump inhibitors
 REVIEW Management of laryngopharyngeal refl ux with proton pump inhibitors Christina Reimer Peter Bytzer Department of Medical Gastroenterology, Køge University Hospital, Denmark Abstract: There is a lack
REVIEW Management of laryngopharyngeal refl ux with proton pump inhibitors Christina Reimer Peter Bytzer Department of Medical Gastroenterology, Køge University Hospital, Denmark Abstract: There is a lack
What can you expect from the lab?
 Role of the GI Motility Lab in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Esophageal Disorders Kenneth R. DeVault MD, FACG, FACP Professor and Chair Department of Medicine Mayo Clinic Florida What can you expect from
Role of the GI Motility Lab in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Esophageal Disorders Kenneth R. DeVault MD, FACG, FACP Professor and Chair Department of Medicine Mayo Clinic Florida What can you expect from
Pressure topography metrics
 Aim: The Chicago Classification (CC) categorizes esophageal motility disorders in high-resolution manometry (HRM) depicted with color pressure topography plots, also known as Clouse plots in honor of Ray
Aim: The Chicago Classification (CC) categorizes esophageal motility disorders in high-resolution manometry (HRM) depicted with color pressure topography plots, also known as Clouse plots in honor of Ray
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease, Paraesophageal Hernias &
 530.81 553.3 & 530.00 43289, 43659 1043432842, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Surgery, UH JABSOM Associate General Surgery Program Director Director of Minimally Invasive & Bariatric Surgery Programs
530.81 553.3 & 530.00 43289, 43659 1043432842, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Surgery, UH JABSOM Associate General Surgery Program Director Director of Minimally Invasive & Bariatric Surgery Programs
Understanding GERD. & Stretta Therapy. GERD (gĕrd): Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
 Understanding GERD & Stretta Therapy GERD (gĕrd): Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease What is GERD? When the muscle between your stomach and esophagus is weak, stomach contents like acid or bile can reflux
Understanding GERD & Stretta Therapy GERD (gĕrd): Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease What is GERD? When the muscle between your stomach and esophagus is weak, stomach contents like acid or bile can reflux
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
 Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) Information for patients UHN Read this handout to learn about: What gastroesohageal reflux (GERD) is Signs and symptoms How your doctor will know if you have it Tests
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) Information for patients UHN Read this handout to learn about: What gastroesohageal reflux (GERD) is Signs and symptoms How your doctor will know if you have it Tests
Oro-pharyngeal and Esophageal Motility and Dysmotility John E. Pandolfino, MD, MSci
 Oro-pharyngeal and Esophageal Department of Medicine Feinberg School of Medicine Northwestern University 1 Oro-pharyngeal and Esophageal Motility Function: Oropharynx Transfer food Prevent aspiration Breathing
Oro-pharyngeal and Esophageal Department of Medicine Feinberg School of Medicine Northwestern University 1 Oro-pharyngeal and Esophageal Motility Function: Oropharynx Transfer food Prevent aspiration Breathing
Surgical aspects of dysphagia
 Dysphagia Why is dysphagia important? Surgery Surgical aspects of dysphagia Adrian P. Ireland aireland@eircom.net Academic RCSI Department of Surgery, Beaumont Hospital Why important Definitons Swallowing
Dysphagia Why is dysphagia important? Surgery Surgical aspects of dysphagia Adrian P. Ireland aireland@eircom.net Academic RCSI Department of Surgery, Beaumont Hospital Why important Definitons Swallowing
Motility characteristics in the transition zone in Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GORD) patients
 Li et al. BMC Gastroenterology (2016) 16:106 DOI 10.1186/s12876-016-0525-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Motility characteristics in the transition zone in Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GORD) patients
Li et al. BMC Gastroenterology (2016) 16:106 DOI 10.1186/s12876-016-0525-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Motility characteristics in the transition zone in Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GORD) patients
JPoelmans,JTack RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL PRACTICE EXTRAOESOPHAGEAL MANIFESTATIONS OF GASTRO- OESOPHAGEAL REFLUX
 1492 See end of article for authors affiliations Correspondence to: Dr J Tack, Centre for Gastroenterological Research, Catholic University of Leuven, Herestraat 49, B-3000 Leuven, Belgium; Jan.Tack@ med.kuleuven.ac.be
1492 See end of article for authors affiliations Correspondence to: Dr J Tack, Centre for Gastroenterological Research, Catholic University of Leuven, Herestraat 49, B-3000 Leuven, Belgium; Jan.Tack@ med.kuleuven.ac.be
Esophageal Motor Abnormalities
 Esophageal Motor Abnormalities Brooks D. Cash, MD, FACP, AGAF, FACG, FASGE Professor of Medicine Gastroenterology Division University of South Alabama Mobile, AL High Resolution Manometry Late Ray Clouse,
Esophageal Motor Abnormalities Brooks D. Cash, MD, FACP, AGAF, FACG, FASGE Professor of Medicine Gastroenterology Division University of South Alabama Mobile, AL High Resolution Manometry Late Ray Clouse,
TBURN TBURN BURN ARTBURN EARTBURN EART HEARTBURN: HOW TO GET IT OFF YOUR CHEST
 TBURN BURN TBURN ARTBURN. EARTBURN EART N EARTBURN HEARTBURN: HOW TO GET IT OFF YOUR CHEST Do you sometimes wake up at night with a sharp, burning sensation in your chest? Does this sometimes happen during
TBURN BURN TBURN ARTBURN. EARTBURN EART N EARTBURN HEARTBURN: HOW TO GET IT OFF YOUR CHEST Do you sometimes wake up at night with a sharp, burning sensation in your chest? Does this sometimes happen during
A Guide to Gastrointestinal Motility Disorders
 A Guide to Gastrointestinal Motility Disorders Albert J. Bredenoord André Smout Jan Tack A Guide to Gastrointestinal Motility Disorders Albert J. Bredenoord Gastroenterology and Hepatology Academic Medical
A Guide to Gastrointestinal Motility Disorders Albert J. Bredenoord André Smout Jan Tack A Guide to Gastrointestinal Motility Disorders Albert J. Bredenoord Gastroenterology and Hepatology Academic Medical
NEGATIVE ENDOSCOPY, What is the Diagnosis and Treatment?
 NEGATIVE ENDOSCOPY, PPI REFRACTORY REFLUX: What is the Diagnosis and Treatment? Michael F. Vaezi, MD, PhD, MSc, FACG Professor of Medicine Clinical Director Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and
NEGATIVE ENDOSCOPY, PPI REFRACTORY REFLUX: What is the Diagnosis and Treatment? Michael F. Vaezi, MD, PhD, MSc, FACG Professor of Medicine Clinical Director Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and
New Directions in the Diagnostic Assessment of Swallowing Disorders in Children
 New Directions in the Diagnostic Assessment of Swallowing Disorders in Children Larissa Kate Noll BAppSc (Speech Pathology) School of Medicine Faculty of Health Sciences Flinders University South Australia
New Directions in the Diagnostic Assessment of Swallowing Disorders in Children Larissa Kate Noll BAppSc (Speech Pathology) School of Medicine Faculty of Health Sciences Flinders University South Australia
Chronic pharyngitis and the association with pepsin detection and reflux disease
 Original Article Page 1 of 8 Chronic pharyngitis and the association with pepsin detection and reflux disease Peter W. Dettmar 1, Qiuping Wang 2, Rachel M. Hodgson 1, Xiu Wang 3, Yifei Li 3, Manjie Jiang
Original Article Page 1 of 8 Chronic pharyngitis and the association with pepsin detection and reflux disease Peter W. Dettmar 1, Qiuping Wang 2, Rachel M. Hodgson 1, Xiu Wang 3, Yifei Li 3, Manjie Jiang
Manometry Conundrums
 Manometry Conundrums Gastroenterology and Hepatology Symposium February 10, 2018 Reena V. Chokshi, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, & Nutrition Department of
Manometry Conundrums Gastroenterology and Hepatology Symposium February 10, 2018 Reena V. Chokshi, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, & Nutrition Department of
Oesophageal Disorders
 Oesophageal Disorders Anatomy Upper sphincter Oesophageal body Diaphragm Lower sphincter Gastric Cardia Symptoms Of Oesophageal Disorders Dysphagia Odynophagia Heartburn Atypical Chest Pain Regurgitation
Oesophageal Disorders Anatomy Upper sphincter Oesophageal body Diaphragm Lower sphincter Gastric Cardia Symptoms Of Oesophageal Disorders Dysphagia Odynophagia Heartburn Atypical Chest Pain Regurgitation
Prevalence and Clinical Characteristics of Refractoriness to Optimal Proton Pump Inhibitor Therapy in Non-erosive Reflux Disease
 www.medscape.com Prevalence and Clinical Characteristics of Refractoriness to Optimal Proton Pump Inhibitor Therapy in Non-erosive Reflux Disease Mentore Ribolsi; Michele Cicala; Patrizia Zentilin; Matteo
www.medscape.com Prevalence and Clinical Characteristics of Refractoriness to Optimal Proton Pump Inhibitor Therapy in Non-erosive Reflux Disease Mentore Ribolsi; Michele Cicala; Patrizia Zentilin; Matteo
Policy #: 138 Latest Review Date: November 2016
 Name of Policy: Ambulatory Esophageal ph Monitoring Policy #: 138 Latest Review Date: November 2016 Category: Medical Policy Grade: B Background/Definitions: As a general rule, benefits are payable under
Name of Policy: Ambulatory Esophageal ph Monitoring Policy #: 138 Latest Review Date: November 2016 Category: Medical Policy Grade: B Background/Definitions: As a general rule, benefits are payable under
Prevention of Esophagopharyngeal Reflux by Augmenting the Upper Esophageal Sphincter Pressure Barrier
 The Laryngoscope VC 2014 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Prevention of Esophagopharyngeal Reflux by Augmenting the Upper Esophageal Sphincter Pressure Barrier Reza
The Laryngoscope VC 2014 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Prevention of Esophagopharyngeal Reflux by Augmenting the Upper Esophageal Sphincter Pressure Barrier Reza
Symptoms such as heartburn, pyrosis, and acid regurgitation
 CLINICAL INVESTIGATIONS 99m Tc-Sulfur Colloid Gastroesophageal Scintigraphy with Late Lung Imaging to Evaluate Patients with Posterior Laryngitis Alberto Bestetti, Federica Carola, PierMarziano Carnevali-Ricci,
CLINICAL INVESTIGATIONS 99m Tc-Sulfur Colloid Gastroesophageal Scintigraphy with Late Lung Imaging to Evaluate Patients with Posterior Laryngitis Alberto Bestetti, Federica Carola, PierMarziano Carnevali-Ricci,
WHAT IS GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD)?
 WHAT IS GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD)? The term gastroesophageal reflux describes the movement (or reflux) of stomach contents back up into the esophagus, the muscular tube that extends from the
WHAT IS GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD)? The term gastroesophageal reflux describes the movement (or reflux) of stomach contents back up into the esophagus, the muscular tube that extends from the
Role of Reflux Symptom Index and Reflux Finding Score in Evaluation of Treatment Outcome in Patients with Laryngopharyngeal Reflux
 Original Article Role of RSI and RFS in Evaluation of Treatment 10.5005/jp-journals-10023-1141 Outcome in Patients with LPR Role of Reflux Symptom Index and Reflux Finding Score in Evaluation of Treatment
Original Article Role of RSI and RFS in Evaluation of Treatment 10.5005/jp-journals-10023-1141 Outcome in Patients with LPR Role of Reflux Symptom Index and Reflux Finding Score in Evaluation of Treatment
Medicine. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. 1. Introduction. 2. Methods OPEN
 Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Medicine Efficacy of acid suppression therapy in gastroesophageal reflux disease-related chronic laryngitis Yue Yang, PhD a,b, Haitao Wu, PhD a,b, Jian Zhou, PhD a,b,
Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Medicine Efficacy of acid suppression therapy in gastroesophageal reflux disease-related chronic laryngitis Yue Yang, PhD a,b, Haitao Wu, PhD a,b, Jian Zhou, PhD a,b,
Reproducibility of multichannel intraluminal electrical impedance monitoring of gastroesophageal reflux
 3 Reproducibility of multichannel intraluminal electrical impedance monitoring of gastroesophageal reflux A.J. Bredenoord B.L.A.M. Weusten R. Timmer A.J.P.M. Smout Dept. of Gastroenterology, St. Antonius
3 Reproducibility of multichannel intraluminal electrical impedance monitoring of gastroesophageal reflux A.J. Bredenoord B.L.A.M. Weusten R. Timmer A.J.P.M. Smout Dept. of Gastroenterology, St. Antonius
GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX
 DR. PHILIP K. BLUSTEIN M.D. F.R.C.P.(C) 415 14 TH ST. NW. CALGARY AB T2N2A1 PHONE (403) 270-9555 FAX (404) 270-7479 GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DEFINITION: *MONTREAL CONSENSUS DEFINED GERD AS A CONDITION WHICH
DR. PHILIP K. BLUSTEIN M.D. F.R.C.P.(C) 415 14 TH ST. NW. CALGARY AB T2N2A1 PHONE (403) 270-9555 FAX (404) 270-7479 GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DEFINITION: *MONTREAL CONSENSUS DEFINED GERD AS A CONDITION WHICH
Primary and secondary esophageal contractions in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (6) 39: 27-31 ISSN -879X 27 Primary and secondary esophageal contractions in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease C.G. Aben-Athar and R.O.
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (6) 39: 27-31 ISSN -879X 27 Primary and secondary esophageal contractions in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease C.G. Aben-Athar and R.O.
J Neurogastroenterol Motil, Vol. 25 No. 1 January, 2019
 JNM J Neurogastroenterol Motil, Vol. 25 No. 1 January, 2019 pissn: 2093-0879 eissn: 2093-0887 https://doi.org/10.5056/jnm18054 Original Article High-resolution Manometry Findings During Solid Swallows
JNM J Neurogastroenterol Motil, Vol. 25 No. 1 January, 2019 pissn: 2093-0879 eissn: 2093-0887 https://doi.org/10.5056/jnm18054 Original Article High-resolution Manometry Findings During Solid Swallows
Characteristics of gastroesophageal reflux in patients with and without excessive gastroesophageal acid exposure
 13 Characteristics of gastroesophageal reflux in patients with and without excessive gastroesophageal acid exposure A.J. Bredenoord B.L.A.M. Weusten R. Timmer A.J.P.M. Smout Dept. of Gastroenterology,
13 Characteristics of gastroesophageal reflux in patients with and without excessive gastroesophageal acid exposure A.J. Bredenoord B.L.A.M. Weusten R. Timmer A.J.P.M. Smout Dept. of Gastroenterology,
The STRETTA Procedure
 THE HEARTBURN AND REFLUX STUDY CENTER The STRETTA Procedure Introduction The STRETTA procedure is an advanced state-of-the-art endoscopic technique for the correction of all forms of reflux disease including:
THE HEARTBURN AND REFLUX STUDY CENTER The STRETTA Procedure Introduction The STRETTA procedure is an advanced state-of-the-art endoscopic technique for the correction of all forms of reflux disease including:
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy with conscious sedation does not interfere with catheter-based 24-h ph monitoring
 Online Submissions: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/ wjg@wjgnet.com doi:10.3748/wjg.v19.i11.1805 World J Gastroenterol 2013 March 21; 19(11): 1805-1810 ISSN 1007-9327 (print) ISSN 2219-2840 (online) 2013 Baishideng.
Online Submissions: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/ wjg@wjgnet.com doi:10.3748/wjg.v19.i11.1805 World J Gastroenterol 2013 March 21; 19(11): 1805-1810 ISSN 1007-9327 (print) ISSN 2219-2840 (online) 2013 Baishideng.
The most widely accepted tool for the diagnosis of
 Evaluation of Gastroesophageal Reflux Events in Children Using Multichannel Intraluminal Electrical Impedance Tobias G. Wenzl, MD The majority of gastroesophageal reflux (GER) episodes in infants and children
Evaluation of Gastroesophageal Reflux Events in Children Using Multichannel Intraluminal Electrical Impedance Tobias G. Wenzl, MD The majority of gastroesophageal reflux (GER) episodes in infants and children
Falk Symposium, , , Portorož. Physiology of Swallowing and Anti-Gastroesophageal. Reflux-Mechanisms. Mechanisms: C.
 Falk Symposium, 15.-16.6.07, 16.6.07, Portorož Physiology of Swallowing and Anti-Gastroesophageal Reflux-Mechanisms Mechanisms: Anything new from a radiologist s view? C.Kulinna-Cosentini Cosentini Medical
Falk Symposium, 15.-16.6.07, 16.6.07, Portorož Physiology of Swallowing and Anti-Gastroesophageal Reflux-Mechanisms Mechanisms: Anything new from a radiologist s view? C.Kulinna-Cosentini Cosentini Medical
An Overview on Pediatric Esophageal Disorders. Annamaria Staiano Department of Translational Medical Sciences University of Naples Federico II
 An Overview on Pediatric Esophageal Disorders Annamaria Staiano Department of Translational Medical Sciences University of Naples Federico II Case report F.C. 3 year old boy Preterm born from emergency
An Overview on Pediatric Esophageal Disorders Annamaria Staiano Department of Translational Medical Sciences University of Naples Federico II Case report F.C. 3 year old boy Preterm born from emergency
Gastroesophageal reflux (GER) Gastroesophageal reflux (GER), the passage of gastric contents into the esophagus, is a normal physiologic process that
 Gastroesophageal reflux (GER) Gastroesophageal reflux (GER), the passage of gastric contents into the esophagus, is a normal physiologic process that may occur daily in healthy infants, children and adults.
Gastroesophageal reflux (GER) Gastroesophageal reflux (GER), the passage of gastric contents into the esophagus, is a normal physiologic process that may occur daily in healthy infants, children and adults.
The effect of dietary intake, physical activity and posture on pepsin concentrations detected in the saliva of free-living, healthy individuals
 The effect of dietary intake, physical activity and posture on pepsin concentrations detected in the saliva of free-living, healthy individuals Authors Richard Khaw 1, Naomi Slater 2, Ellie Smith 2, Chi
The effect of dietary intake, physical activity and posture on pepsin concentrations detected in the saliva of free-living, healthy individuals Authors Richard Khaw 1, Naomi Slater 2, Ellie Smith 2, Chi
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease:
 Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: Introduction Gastroesophageal reflux is the involuntary movement of gastric contents to the esophagus. It is a common disease, occurring in one third of the population
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: Introduction Gastroesophageal reflux is the involuntary movement of gastric contents to the esophagus. It is a common disease, occurring in one third of the population
Related Policies None
 Medical Policy MP 2.01.20 BCBSA Ref. Policy: 2.01.20 Last Review: 11/30/2017 Effective Date: 11/30/2017 Section: Medicine Related Policies None DISCLAIMER Our medical policies are designed for informational
Medical Policy MP 2.01.20 BCBSA Ref. Policy: 2.01.20 Last Review: 11/30/2017 Effective Date: 11/30/2017 Section: Medicine Related Policies None DISCLAIMER Our medical policies are designed for informational
Speech and Language Therapy. Kerrie McCarthy Senior Speech and Language Therapist
 Speech and Language Therapy Kerrie McCarthy Senior Speech and Language Therapist Contents 1. Voice disorders 2. Swallow disorders 3. Videofluroscopy 4. Adult Acquired Communication Disorders 5. How to
Speech and Language Therapy Kerrie McCarthy Senior Speech and Language Therapist Contents 1. Voice disorders 2. Swallow disorders 3. Videofluroscopy 4. Adult Acquired Communication Disorders 5. How to
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Achalasia, barium esophagography for, 57 58 Acid pocket, 18 19 Acid-sensing ion, 20 Acupuncture, 128 Adiponectin, in obesity, 166 ADX10059 metabotropic
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Achalasia, barium esophagography for, 57 58 Acid pocket, 18 19 Acid-sensing ion, 20 Acupuncture, 128 Adiponectin, in obesity, 166 ADX10059 metabotropic
