ENT Manifestations in Gastro - Esophageal Reflux Disease.
|
|
|
- Teresa Eileen Bailey
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DOI: /aimdr EN2 Original Article ISSN (O): ; ISSN (P): ENT Manifestations in Gastro - Esophageal Reflux Disease. Santhana Krishna Kumar. B 1, Sivasankari. L 1 1 Assistant Professor, ENT, Thoothukudi Medical College Hospital, Thoothukudi, Tamilnadu. Received: August 2016 Accepted: September 2016 Copyright: the author(s), publisher. Annals of International Medical and Dental Research (AIMDR) is an Official Publication of Society for Health Care & Research Development. It is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License, which permits unrestricted noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. ABSTRACT Background: Gastro - esophageal reflux disease is a common problem in medical practice. There is increasing evidence that GERD causes laryngeal signs and symptoms. AIM: To identify and study the laryngeal manifestations in symptomatic patients with GERD. Methods: A prospective study was conducted in about 60 patients with GERD in a tertiary care medical college hospital for a period of one year. Results: The study was statistically evaluated using chi square test and there was strong statistical significance for the laryngeal manifestations in GERD.Conclusion: The incidence of laryngeal manifestations of GERD in our study was 68%, the common symptom being hoarseness and the common sign being interarytenoid eythema. Keywords: GERD, Chronic laryngitis, endoscopy, LERD. INTRODUCTION Gastro - esophageal reflux refers to the effortless movement of gastric contents from stomach to the esophagus without associated belching or vomiting. It is a normal physiological process. GERD is a pathological condition with symptoms or with Histopathological alterations. Gastroesophageal reflux may affect the oropharynx, larynx and respiratory tract and has found to be associated with pulmonary, otolaryngologic, dental symptoms. These are collectively called as Atypical or Extra esophageal manifestations of GERD. Laryngopharyngeal reflux (LPR) refers to the backflow of stomach contents in to the laryngopharynx. LPR has been postulated to play a role in up to 50% of laryngeal complaints that are present in otolaryngological practice. Otorhinolaryngologic manifestations of GERD may be non-specific and high index of suspicion is essential for diagnosis and treatment of the condition. In our study, we evaluate the otorhinolaryngologic manifestations in patients who attend the gastoentrology clinic with symptoms of GERD and subjected to upper GI endoscopy. Name & Address of Corresponding Author Dr. Sivasankari. L Assistant Professor, Dept. of ENT, Thoothukudi Medical College Hospital, Thoothukudi, Tamilnadu. Aims and objectives To identify and study about the otorhinolaryngological manifestations of Gastroesophageal reflux disease. MATERIALS AND METHODS A prospective study was conducted in Department of ENT in a tertiary care hospital for a period of one year in about 60 patients. The patients attending Gatro-entrology department between the age years, of both the sexes and with symptoms of GERD such as heart burn, regurgitation, belching, odynophagia, non- cardiac chest pain (at least three out the six symptoms should be present) were included for study. These patients were subjected to upper GI endoscopy and grading of esophagitis was done according to Savary Millar and Demeester classification. The other findings such as lax lower esophageal sphincter, hiatus hernia or gastric mucosal prolapse were also noted. These patients were further evaluated in Department of ENT for symptoms such as sore throat, hoarseness, chronic throat clearing, cough, dysphonia, post-nasal drip, laryngospasm and halitosis and subjected to videolaryngoscopy. The findings such as granular pharyngitis, excessive throat mucus, arytenoid and inter-arytenoid erythema, vocal nodule, laryngeal odema, contact ulcer, subglottic stenosis and granulomas were noted. The patients with gastric outlet obstruction, occlusive lesion of the esophagus, motor disorder of the esophagus, chronic sinusitis, previous gastric surgery, pregnancy, asthmatic and hypertensive s on calcium channel blockers are excluded from the study. The factors such as age, Annals of International Medical and Dental Research, Vol (2), Issue (6) Page 5
2 sex, smoking, alcoholism, obesity were also considered. RESULTS The study consists of 60 symptomatic patients with Gastroesophageal reflux disease who were assessed for the presence of atypical laryngeal manifestations of GERD. There were and 23 male and 37 female patients (M:F ratio 1:1.5) [Table 1]. had hoarseness of voice, chronic throat clearing in 53% and excess mucus in throat and sore throat in half of patients. Approximately 10% of patients had dysphonia and post nasal drip [Figure 2]. Table 1: Number of Cases. Age Male Female No of cases Years Years Years Years Total The mean age was 32.9±10.02 years and ranged between years. About 16 males were found to be alcoholics and 12 males were found to be smokers in the study group. About 7 males were non-alcoholics and 11 males were non smokers. All 37 females were found to be non- alcoholics and non-smokers. In our study, 68.3 percent (24 patients in Class I Obese, 14 in Class II Obese and 3 in Morbid Obese) were in obese category and 16.7 percent (10 patients) were in overweight category. On evaluating the symptoms of GERD, Heartburn was the common presenting complaint in 80% of patients followed by Regurgitation in 66.6%, Belching in 60%, chest pain 56% and dysphagia in 25% and odynophagia in 26% [Figure 1]. Figure 1: Symptoms of GERD. Atypical laryngeal manifestations have been found in 68% of patient with GERD, 19 patients (32%) had no laryngeal symptoms. On symptom analysis, 63% Figure 2: Laryngeal Symptoms. On investigating these patients, in upper GI endoscopy, the features of esophagitis is noted in 66.7%, endoscopy was found to be normal in 20 (33.3%) patients. It was mild, grade I in 28 (47%), grade II in 11(18.3%) and grade III in one patient. Other contributory findings pertaining to GERD include a patulous LES in 20% and gastric mucosal prolapse in 10%. Video- laryngoscopy was performed in all patients and it was normal in 53.3% of patient. In the rest 33.3% had inter-arytenoid erythema, 21% had vocal cord erythema 10% had granular pharyngitis and 1% had vocal nodule. From this analysis, it is found that a significant number of patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease have associated chronic laryngeal symptoms and signs suggesting one of the extra esophageal manifestation of GERD. DISCUSSION GERD is a common gastro intestinal disorder presenting with esophageal and extra esophageal manifestations. These atypical manifestations include bronchial asthma, noncardiac chest pain and otolaryngologic disease. The exact prevalence of extra esophageal symptom is not known; hence, it is very often go unrecognized and poorly managed. Gastroesophageal reflux disease is believed to be associated with a variety of laryngeal conditions and symptoms of which chronic laryngitis is perhaps the most common. Laryngopharyngeal reflux is the terminology used to describe GER that reaches the structure above upper esophageal sphincter. Other terminologies used to describe this disorder are Acid laryngitis, Posterior laryngitis or Reflux laryngitis. Ohmen et al., 1983 noted that 74% of patients with reflux laryngitis, 80% with paroxysmal laryngospasm, 80% with laryngostenosis, had abnormal esophageal ph study suggestive of GERD. Annals of International Medical and Dental Research, Vol (2), Issue (6) Page 6
3 In 1989, Weinert documented double blinded ph findings and was really able to show that there are separate episodes of reflux that goes up to laryngopharynx. The incidence of GER related otolaryngologic symptom and finding in otolaryngologic practice has been estimated as 4-10%. [11] Reflux laryngitis is associated with symptoms of hoarseness, vocal fatigue, chronic throat clearing, excessive throat mucus, chronic cough, dysphagia, globus sensation, halitosis & chronic cough. Laryngeal condition associated with GERD are reflux laryngitis, subglottic stenosis, carcinoma of larynx, contact ulcer and granuloma, paroxysmal laryngospasm, arytenoids fixation, globus pharynges, vocal nodule, pachydermia larynges and recurrent leucoplakia. [9] Two Schools of thought has been put forward to explain the pathophysiology of GERD related otolaryngologic disorder. [9] These are 1. Direct acid peptic injury to the larynx and surrounding tissue via esophago-pharyngeal reflux due to reduced resting tone of UES, especially in night 2. Acid in the distal esophagus stimulates vagally mediated reflux resulting in chronic throat clearing and coughing which eventually leads to laryngeal symptoms and lesions. Several others factors such as esophagogastric junction, esophageal acid clearance, esophageal mucosal resistance, and intactness of UES have been shown to be important in the pathophysiology of GER. In addition to this, functional interaction among pharynx, larynx, lung, and esophagus have also been involved in pathogenesis. [12] Kambic et al., biopsied the larynx in 44 patients and noted thickening of laryngeal epithelium due to hyperplasia of prickle cell layer and in some the epithelium was keratinized. [4] In laryngeal ulcer, there were abundant lymphocyte and plasma cells infiltrating the epithelium. These were similar to esophageal biopsies of reflux esophagitis patients. Jacob et al., found no difference in time between proximal and distal reflux episodes [3], Wo et al., (1997) found no significant differences in the amount of proximal reflux in typical and atypical symptoms group. [15] Warning et al., found that proximal esophageal reflux had no predictive value in identifying patient with atypical reflux symptom and in those who would respond to therapy. [14] It seem therefore the distribution of reflux episode may be different in typical and atypical GER. Esophago pharyngeal reflux can also occur in normal people with a prevalence of 16-21% but the frequency is more in patients with reflux laryngitis. Esophageal dysmotility in reflux laryngitis has been found in some studies and study by Ulualp et al., found that at least secondary peristalsis is preserved in patient with posterior laryngitis versus controls. [13] The presence of heartburn, dysphagia, or regurgitation may indicate the presence of GERD. However because these disorder are so prevalent, it may be difficult to establish a causal relationship without further testing. Persistent symptom with or without GERD in these patients necessitates consultation with an otolaryngologist. Diagnosis in based on 1) careful history and investigation, as many of them have chronic intermittent symptom. Because the differential diagnosis of symptoms of reflux laryngitis is broad, a careful history should include the risk factors like frequent voice use, concurrent tobacco use, ethanol, history of upper respiratory tract infection with coughing, chronic idiopathic cough, vomiting, nocturnal regurgitation, allergic type symptoms, pets, recent air condition use, postnasal drip, new environmental condition containing synthetic materials and medication. Presence of Laryngopharyngeal complaint without a obvious laryngeal or pharyngeal disease should lead to a suspicion of associated GERD. Laryngeal examination can be performed using Indirect laryngoscopy, Fibreoptic laryngoscopy, Videostroboscopy or Microlaryngoscopy can identify an underlying otolaryngologic cause and eliminate a neoplastic process. Indirect laryngoscopy is an inexpensive and invaluable technique to evaluate the hypopharynx and the larynx. A carefully performed IDL provides clue for the diagnosis and should be done in every patient with laryngeal symptom. Video laryngoscopy provides the direct examination of larynx and gives us a better information about laryngeal and laryngopharyngeal pathologies. The finding seen in classic posterior laryngitis is red arytenoids, piled up interarytenoid mucosa and edema of posterior third of vocal cord. The abnormalities are more often on the posterior aspect of larynx, as it is in close proximity to the esophagus and hence may be most exposed to acid peptic refluxate. The other tests used as confirmatory tests are 1. Esophageal endoscopy provides the visualization of the esophageal mucosa and is commonly performed as an initial investigation for the evaluation of traditional reflux symptom. Esophagitis was documented in 50-67% of patient with laryngeal symptom with or without objective finding by endoscopy. [11] 2. Radiologic Techniques Radiographic imaging methods to evaluate include radionuclide scinti scanning and barium esophagogram. Radionuclide scinti scanning using a gamma camera is a simple and noninvasive method with minimal radiation exposure. The fraction of administered radioactive material refluxing into the esophagus is used as GER index. An abnormal GER was seen only in 11% patient with reflux laryngitis Annals of International Medical and Dental Research, Vol (2), Issue (6) Page 7
4 and hence considered as less sensitive compared to esophageal endoscopy and 24 hr intra esophageal ph monitoring and thus has a limited role to demonstrate GER. 3. Ambulatory 24 hour pharyngo esophageal ph monitoring. Ambulatory ph monitoring has been used to diagnosis GER associated otolaryngologic disorders. Dual sensor ph electrodes have been placed to monitor the acid reflux events in the proximal esophagus below the UES, in the pharynx above the UES, in the proximal esophagus and pharynx or at the level of UES. In manometric localization of the UES, the distal ph sensor is placed 5 cm above LES and the proximal sensor placed 2 cm above or immediately below the UES. Each sensor can record events that are analyzed independently. The occurrence of even small amount of acid reflux proximally suggests an association with GERD. Esophageal acid exposure time is the most useful discriminator between physiologic and pathologic reflux. In patient with Laryngopharyngeal reflux the distal esophageal acid exposure time was not significantly different from GERD patients, but the proximal esophageal acid exposure time has been however to be greater to similar to that of GERD patient. [4] Pharyngeal ph monitoring document the pharyngeal acid reflux events in patients with otolaryngologic disorders, and not in normal volunteer or GERD patients. The prevalence of pharyngeal acid reflux events are more in patients with reflux laryngitis. [12] The reproducibility of pharyngeal ph monitoring is 65% in patients with reflux laryngitis. The relative low reproducibility has been attributed to the heterogeneity of the etiology of posterior laryngitis patients and to the episodic and infrequent nature of pharyngeal and reflux events. The threshold ph 5 increase the reproducibility and therefore the use of pharyngeal ph threshold of 5 have been suggested in patients with high suspicion of GER associated otolaryngologic disorder. [13] Due to the non-availability of the advanced radiographic tests and 24 hours ambulatory p H monitoring, we have studied the laryngeal manifestations in patients with the positive endoscopic findings for GERD. Kaufmann et al., reported the estimated prevalence of laryngeal symptoms in GERD was 4-10%. [6] In our present study the prevalence of laryngeal symptom in GERD patients was 68%. Roy et al., reported the commonest laryngeal symptom as hoarseness of voice of more than 4 weeks duration, frequent sore throat, globus sensation, chronic throat clearing, halitosis and chronic cough. Among these hoarseness of voice alone is estimated to be prevalent in 55% of patients in the study conducted by McNally et al., and Koufman et al., In our study 63% of patients had hoarseness. Klanser et al., and Walter et al found heartburn as the commonest gastrointestinal symptom in GERD patients, followed by regurgitation, dysphagia, odynophagia, and belching and chest pain. In our study, heartburn was present in 80% of patients (5). Age was associated with an increase in esophageal acid exposure and its severity is related to degradation of the gastro esophageal junction and impaired esophageal clearance. In our study, most of the patients are in years age group. Reflux disease is more common in men than women in the ratio of 2-3:1. In our study there are 23 male and 37 female patients. (M.F. ratio 1:1.5). GERD is aggravated by factors like alcohol, smoking, fatty food, excess tea, coffee, NSAID abuse Nebel et al., [7]. Locke et al., performed a cross sectional study in age and gender matched controls to ascertain the risk factors associated with development of heart burn and showed its higher incidence in people with BMI >30kg/m 2, family history of heartburn, symptoms of esophageal or gastric disease, h/o smoking, h/o alcohol consumption and high psychosomatic symptoms. These were present in a small proportion of patients in our series -12 were smoker, 16 had a history of chronic alcohol abuse. In our study, 68.3 percent (24 patient in Class I Obese, 14 in Class II Obese and 3 in Morbid Obese) were in obese category and 16.7 percent (10 patient) were in overweight category. Studies showed that obesity plays a role in the pathogenesis of reflux symptoms; a disruption of the esophago-gastric junction could allow reflux to occur. According to Frank K. Friedberg et, al [2]. 53% of patients were obese and 39% were obese by El. Serg et.al.,. [1] Endoscopy with histological evidence of esophagitis is considered as the gold standard in diagnosis when ph monitoring is not available. Endoscopy showed esophagitis in 53.3% and most of them are Grade I&II. Study by Young JL., and others reported endoscopic positivity in 30-40% of patients. [16] Hence all the patients with GERD may not have a endoscopically detectable GERD and is called Endoscopy Negative GERD. This is seen in 33.3 % of people in the present study and is supported by Sami et al., who reported 32-50% of patients having endoscopy negative GERD [10]. Esophagitis was documented in 68.3% of patient in our series. 22.6% of patient had features suggesting acute esophagitis. Video- laryngoscopy helps to confirm the laryngeal manifestation. Findings in the present study includes interarytenoid erythema in 33.3%. These results were similar to reported findings by Roy [9], Fibreoptic laryngoscopy was performed in 40 patients and Wong et al., [16]. In a study by Jacob et al.,with GERD, persistent laryngeal symptoms was seen in 62.5% of them, symptoms include dysphonia, cough, globus sensation and frequent sore Annals of International Medical and Dental Research, Vol (2), Issue (6) Page 8
5 throat (3). Laryngoscopy findings were consistent with reflux laryngitis in 40% of them. In our study, laryngeal manifestations were present in 68% of patients. This high percentage clearly indicates the common occurrence of ENT manifestation as an atypical feature in GERD and necessitates the need to identify and document in reflux disease patients. The commonest laryngeal symptoms included are hoarseness of voice and chronic throat clearing, other symptoms found are globus sensation, cough, post nasal drip, halitosis and laryngeal spasm. Any of these symptoms when present for a significant period of time (>4 wks) should alert a clinician to a causal association of GERD in these Patients. CONCLUSION Gastroesophgeal Reflux Disease (GERD) has varied manifestations in ENT, the most common being in the larynx; Indirect laryngoscopy/ Videolaryngoscopy and Upper GI endoscopy are indicated in these patients. 1. The incidence of laryngeal manifestations in our study is 68%. 2. Most common laryngeal symptom in our study - hoarseness of voice 63%. 3. Most common laryngeal finding in our studyinterarytenoid erythema 33.3%. 4. Laryngeal manifestations are common in the age group years. 5. Obesity, alcoholism, smoking and old age are risk factors, not only for GERD but also for laryngeal manifestations. The study highlights two important facts namely The importance of identifying and documenting atypical manifestations such as hoarseness of voice, recurrent sore throat, chronic throat clearing etc. in patients with symptomatic GERD To consider the possibility of GERD as an etiological factor for chronic laryngitis refractory to routine treatment. Early recognition and treatment for GERD will relieve patients suffering & prevents the development of laryngeal complications. 7. Nebel O, Castell DO. Symptomatic GER: incidence and precipitating factors. Am J Dig Dis. 1976; 21(11): Ohmen L, Olofsson J, Tibbling L, et al., Esophageal dysfunction in patients with contact ulcer of the larynx. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1978; 92: Roy K.H Wonng et al, ENT Manifestation of Gastroesopharyngeal reflux. The American Journal of Gastroenterology. 2000; 95: Sami R, Achem MD. Endoscopy Negative GERD- Gastroenterology. Clinic of North America. 1999; 28(4): Seckin O, Ulnalp and Robert. J Toohil. MD- Laryngopharyngeal reflux state of the Art Diagnosis and Treatment. Otolaryngolgic Clin North Am 2001;12: Ulualp SO, Toohill RJ, Shanker R. Pharyngeal acid reflux events in patients with single and multiple otolaryngologic disorders. Otolaryngol Head and Neck Surg. 1999; 121: Ulualp S, Toohill RJ, Arndorfer R et al., Revalations about 24 hour ambulatory ph monitoring (abstract) Gasteroenterology. 1998; 114:G Warning JP, Hunter J, Katz E, Suwak B et al., Chronic cough and hoarseness in patients with severe GERD. Dig Dis Sci. 1995;40: Wo JM, Hunter JG, Warning JP. Dual- Channel ambulatory esophageal Ph monitoring a useful diagnostic tool. Dig Dis Sci. 1997;42: Young JL, Shaw GY, et al., Laryngeal manifestation of GERD, Endoscopic appearance and management Gastrointest. Endos. 1995; 43:225. How to cite this article: Krishna Kumar SB, Sivasankari L. ENT Manifestations in Gastro - Esophageal Reflux Disease. Ann. Int. Med. Den. Res. 2016; 2(6):EN05-EN09. Source of Support: Nil, Conflict of Interest: None declared REFERENCES 1. El.Serg HB, Graham DY, Satia JA, Rabenc L Amj. Gastroenterol. 2005;100(6): Frank K Fridenberg MD, Melissa Xanthopoulos, Gary D Foster. American J OF Gastroenterol. 2008; Jacob P, Kahrilas PJ, Herzon G, Proximal esophageal ph metre in patients with reflux laryngitis. Gastroenterology. 1991; 100: Kambic V, Radsel Z. Acid posterior Laryngitis. J. Laryngol Otol : Klauser AG, Schindlebeck NE et al., Symptom of GERD Lancet. 1990;335: Koufman JA. The otolaryngologic manifestation of GERD. Laryngoscope. 1991;101:1-78. Annals of International Medical and Dental Research, Vol (2), Issue (6) Page 9
A Prospective, Randomized, Placebo-controlled, Double-Blind Study of Rabeprazole for Therapeutic Trial in Chronic Idiopathic Laryngitis ABSTRACT
 THAI J 28 GASTROENTEROL Rabeprazole for Therapeutic Trial in Chronic Original Idiopathic Laryngitis Article A Prospective, Randomized, Placebo-controlled, Double-Blind Study of Rabeprazole for Therapeutic
THAI J 28 GASTROENTEROL Rabeprazole for Therapeutic Trial in Chronic Original Idiopathic Laryngitis Article A Prospective, Randomized, Placebo-controlled, Double-Blind Study of Rabeprazole for Therapeutic
Maximizing Outcome of Extraesophageal Reflux Disease. (GERD) is often accompanied
 ...PRESENTATIONS... Maximizing Outcome of Extraesophageal Reflux Disease Based on a presentation by Peter J. Kahrilas, MD Presentation Summary Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) accompanied by regurgitation
...PRESENTATIONS... Maximizing Outcome of Extraesophageal Reflux Disease Based on a presentation by Peter J. Kahrilas, MD Presentation Summary Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) accompanied by regurgitation
Lansoprazole Treatment of Patients With Chronic Idiopathic Laryngitis: A Placebo-Controlled Trial
 THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF GASTROENTEROLOGY Vol. 96, No. 4, 2001 2001 by Am. Coll. of Gastroenterology ISSN 0002-9270/01/$20.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0002-9270(01)02244-4 Lansoprazole Treatment
THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF GASTROENTEROLOGY Vol. 96, No. 4, 2001 2001 by Am. Coll. of Gastroenterology ISSN 0002-9270/01/$20.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0002-9270(01)02244-4 Lansoprazole Treatment
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. or dysphagia may alert a physician to the possibility of LPR. 1,2 Laryngeal findings
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Clinical Value of Pharyngeal ph Monitoring Using a Double-Probe, Triple-Sensor Catheter in Patients With Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Togay Muderris, MD; M. Kursat Gokcan, MD; Irfan Yorulmaz,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Clinical Value of Pharyngeal ph Monitoring Using a Double-Probe, Triple-Sensor Catheter in Patients With Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Togay Muderris, MD; M. Kursat Gokcan, MD; Irfan Yorulmaz,
Laryngopharyngeal Reflux
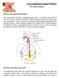 Laryngopharyngeal Reflux The Silent Reflux What is Laryngopharyngeal Reflux? Also called Reflux laryngitis, laryngopharyngeal reflux is a condition where the acid from the stomach reaches the voicebox
Laryngopharyngeal Reflux The Silent Reflux What is Laryngopharyngeal Reflux? Also called Reflux laryngitis, laryngopharyngeal reflux is a condition where the acid from the stomach reaches the voicebox
The Validity and Reliability of the Reflux Finding Score (RFS)
 The Laryngoscope Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia 2001 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. The Validity and Reliability of the Reflux Finding Score (RFS)
The Laryngoscope Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia 2001 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. The Validity and Reliability of the Reflux Finding Score (RFS)
GERD: A linical Clinical Clinical Update Objectives
 GERD: A Clinical Update Jeff Gilbert, M.D. University i of Kentucky Gastroenterology 11/6/08 Objectives To review the basic pathophysiology underlying gastroesophageal reflux disease To highlight current
GERD: A Clinical Update Jeff Gilbert, M.D. University i of Kentucky Gastroenterology 11/6/08 Objectives To review the basic pathophysiology underlying gastroesophageal reflux disease To highlight current
Outline. Outline. Definition. Asthma, GERD and Laryngeal Pharyngeal Reflux (LPR) Definitions
 Asthma, GERD and Laryngeal Pharyngeal Reflux (LPR) Richard F. Lockey, M.D. Division of Allergy and Immunology Department of Internal Medicine University of South Florida College of Medicine and James A.
Asthma, GERD and Laryngeal Pharyngeal Reflux (LPR) Richard F. Lockey, M.D. Division of Allergy and Immunology Department of Internal Medicine University of South Florida College of Medicine and James A.
Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Extraesophageal Manifestations
 Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Extraesophageal Manifestations Karen B. Zur, MD Director, Pediatric Voice Program Associate Director, Center for Pediatric Airway Disorders The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia
Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Extraesophageal Manifestations Karen B. Zur, MD Director, Pediatric Voice Program Associate Director, Center for Pediatric Airway Disorders The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia
Gastroesophageal reflux (GER) Gastroesophageal reflux (GER), the passage of gastric contents into the esophagus, is a normal physiologic process that
 Gastroesophageal reflux (GER) Gastroesophageal reflux (GER), the passage of gastric contents into the esophagus, is a normal physiologic process that may occur daily in healthy infants, children and adults.
Gastroesophageal reflux (GER) Gastroesophageal reflux (GER), the passage of gastric contents into the esophagus, is a normal physiologic process that may occur daily in healthy infants, children and adults.
Oesophageal Disorders
 Oesophageal Disorders Anatomy Upper sphincter Oesophageal body Diaphragm Lower sphincter Gastric Cardia Symptoms Of Oesophageal Disorders Dysphagia Odynophagia Heartburn Atypical Chest Pain Regurgitation
Oesophageal Disorders Anatomy Upper sphincter Oesophageal body Diaphragm Lower sphincter Gastric Cardia Symptoms Of Oesophageal Disorders Dysphagia Odynophagia Heartburn Atypical Chest Pain Regurgitation
GERD is a condition which develops when the reflux of stomach contents causes troublesome symptoms and/or complications
 GERD is a condition which develops when the reflux of stomach contents causes troublesome symptoms and/or complications Esophageal Syndromes Extra - esophageal Syndromes Symptomatic Syndromes Typical reflux
GERD is a condition which develops when the reflux of stomach contents causes troublesome symptoms and/or complications Esophageal Syndromes Extra - esophageal Syndromes Symptomatic Syndromes Typical reflux
Putting Chronic Heartburn On Ice
 Putting Chronic Heartburn On Ice Over the years, gastroesophageal reflux disease has proven to be one of the most common complaints facing family physicians. With quicker diagnosis, this pesky ailment
Putting Chronic Heartburn On Ice Over the years, gastroesophageal reflux disease has proven to be one of the most common complaints facing family physicians. With quicker diagnosis, this pesky ailment
EGD. John M. Wo, M.D. University of Louisville July 3, 2008
 EGD John M. Wo, M.D. University of Louisville July 3, 2008 Different Ways to do an EGD Which scope? Pediatric, regular, jumbo EGD endoscope or pediatric colonoscope Transnasal vs. transoral insertion Sedation
EGD John M. Wo, M.D. University of Louisville July 3, 2008 Different Ways to do an EGD Which scope? Pediatric, regular, jumbo EGD endoscope or pediatric colonoscope Transnasal vs. transoral insertion Sedation
Management of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Disease. Abdul Aziz J Ashoor, Facharzt fuer Hals Nasen Ohren (H.N.O.)*
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 33, No. 3, September 2011 Management of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Disease Abdul Aziz J Ashoor, Facharzt fuer Hals Nasen Ohren (H.N.O.)* Objective: To evaluate the efficacy
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 33, No. 3, September 2011 Management of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Disease Abdul Aziz J Ashoor, Facharzt fuer Hals Nasen Ohren (H.N.O.)* Objective: To evaluate the efficacy
Extraesophageal Manifestations of GERD in Children
 Extraesophageal Manifestations of GERD in Children Jose Luis Martinez, M.D. Associate Professor University of California San Francisco Director Endoscopy Unit Children s Hospital Central California Overview
Extraesophageal Manifestations of GERD in Children Jose Luis Martinez, M.D. Associate Professor University of California San Francisco Director Endoscopy Unit Children s Hospital Central California Overview
SASKATCHEWAN REGISTERED NURSES ASSOCIATION
 DEFINITION Reflux of gastric contents into the esophagus, which results in esophageal irritation or inflammation. IMMEDIATE CONSULTATION REQUIRED IN THE FOLLOWING SITUATIONS Dysphagia (solid food, progressive)
DEFINITION Reflux of gastric contents into the esophagus, which results in esophageal irritation or inflammation. IMMEDIATE CONSULTATION REQUIRED IN THE FOLLOWING SITUATIONS Dysphagia (solid food, progressive)
The role of the modified barium swallow study & esophagram in patients with GERD/Globus sensation
 The role of the modified barium swallow study & esophagram in patients with GERD/Globus sensation James P. Dworkin, Ph.D. Jayme Dowdall, M.D. Adam Folbe, M.D. Tom Willis, M.S. Richard Culatta, Ph.D. Wayne
The role of the modified barium swallow study & esophagram in patients with GERD/Globus sensation James P. Dworkin, Ph.D. Jayme Dowdall, M.D. Adam Folbe, M.D. Tom Willis, M.S. Richard Culatta, Ph.D. Wayne
Review Article Impact of Laparoscopic Fundoplication for the Treatment of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux: Review of the Literature
 International Otolaryngology Volume 2012, Article ID 291472, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/291472 Review Article Impact of Laparoscopic Fundoplication for the Treatment of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux: Review of
International Otolaryngology Volume 2012, Article ID 291472, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/291472 Review Article Impact of Laparoscopic Fundoplication for the Treatment of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux: Review of
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) Extraesophageal symptoms of GERD
 Extraesophageal symptoms of GERD KENNETH R. DEVAULT, MD ABSTRACT Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) can be the primary cause of, or an aggravating contributor to, a wide variety of conditions affecting
Extraesophageal symptoms of GERD KENNETH R. DEVAULT, MD ABSTRACT Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) can be the primary cause of, or an aggravating contributor to, a wide variety of conditions affecting
A Clinical Assessment of Throat Manifestations of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Disease with Special Reference to Video Endoscopic Findings
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 6 Ver. VII (June. 2017), PP 57-62 www.iosrjournals.org A Clinical Assessment of Throat Manifestations
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 6 Ver. VII (June. 2017), PP 57-62 www.iosrjournals.org A Clinical Assessment of Throat Manifestations
Epidemiology Classic Symptoms of GERD
 Definitions LARYNGOPHARYNGEAL REFLUX AND ITS ROLE IN PEDIATRIC OTOLARYNGOLOGY Wendy Mackey, APRN, CORLN SOHN Congress Meeting Washington, DC September 2012 Laryngopharyngeal Reflux (LPR) Retrograde movement
Definitions LARYNGOPHARYNGEAL REFLUX AND ITS ROLE IN PEDIATRIC OTOLARYNGOLOGY Wendy Mackey, APRN, CORLN SOHN Congress Meeting Washington, DC September 2012 Laryngopharyngeal Reflux (LPR) Retrograde movement
Mapping Regional Laryngopharyngeal Mechanoreceptor Response
 Original Article Clinical and Experimental Otorhinolaryngology Vol. 7, No. 4: 319-323, December 2014 http://dx.doi.org/10.3342/ceo.2014.7.4.319 pissn 1976-8710 eissn 2005-0720 Mapping Regional Laryngopharyngeal
Original Article Clinical and Experimental Otorhinolaryngology Vol. 7, No. 4: 319-323, December 2014 http://dx.doi.org/10.3342/ceo.2014.7.4.319 pissn 1976-8710 eissn 2005-0720 Mapping Regional Laryngopharyngeal
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Correlation of Findings at Direct Laryngoscopy and Bronchoscopy With Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Children
 Correlation of Findings at Direct Laryngoscopy and Bronchoscopy With Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Children A Prospective Study ORIGINAL ARTICLE Michele M. Carr, DDS, MD, MEd, FRCSC; Mark L. Nagy,
Correlation of Findings at Direct Laryngoscopy and Bronchoscopy With Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Children A Prospective Study ORIGINAL ARTICLE Michele M. Carr, DDS, MD, MEd, FRCSC; Mark L. Nagy,
The role of 24 h ph-recording in pediatric otolaryngologic gastro-esophageal reflux disease
 International Journal of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology (2003) 67S1, S95 S100 The role of 24 h ph-recording in pediatric otolaryngologic gastro-esophageal reflux disease Thierry van Den Abbeele a, *, Vincent
International Journal of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology (2003) 67S1, S95 S100 The role of 24 h ph-recording in pediatric otolaryngologic gastro-esophageal reflux disease Thierry van Den Abbeele a, *, Vincent
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: esophageal_ph_monitoring 4/2011 5/2017 5/2018 5/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Acid reflux is the
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: esophageal_ph_monitoring 4/2011 5/2017 5/2018 5/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Acid reflux is the
ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
 ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Philip O. Katz MD 1, Lauren B. Gerson MD, MSc 2 and Marcelo F. Vela MD, MSCR 3 1 Division of Gastroenterology, Einstein
ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Philip O. Katz MD 1, Lauren B. Gerson MD, MSc 2 and Marcelo F. Vela MD, MSCR 3 1 Division of Gastroenterology, Einstein
GERD. Gastroesophageal reflux disease, or GERD, occurs when acid from the. stomach backs up into the esophagus. Normally, food travels from the
 GERD What is GERD? Gastroesophageal reflux disease, or GERD, occurs when acid from the stomach backs up into the esophagus. Normally, food travels from the mouth, down through the esophagus and into the
GERD What is GERD? Gastroesophageal reflux disease, or GERD, occurs when acid from the stomach backs up into the esophagus. Normally, food travels from the mouth, down through the esophagus and into the
Extraesophageal presentations of gastroesophageal reflux disease: the case for aggressive diagnosis and treatment
 JOEL E. RICHTER, MD Dr. Richter is chairman of the Department of Gastroenterology at the Cleveland Clinic Foundation, specializing in esophageal diseases with particular interest in GERD, achalasia, and
JOEL E. RICHTER, MD Dr. Richter is chairman of the Department of Gastroenterology at the Cleveland Clinic Foundation, specializing in esophageal diseases with particular interest in GERD, achalasia, and
The Frequency of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Nutcracker Esophagus and the Effect of Acid-Reduction Therapy on the Motor Abnormality
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.22, No.4, December 2000 The Frequency of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Nutcracker Esophagus and the Effect of Acid-Reduction Therapy on the Motor Abnormality Saleh Mohsen
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.22, No.4, December 2000 The Frequency of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Nutcracker Esophagus and the Effect of Acid-Reduction Therapy on the Motor Abnormality Saleh Mohsen
GERD DIAGNOSIS & TREATMENT DISCLOSURES 4/18/2018
 GERD DIAGNOSIS & TREATMENT Subhash Chandra MBBS Assistant Professor CHI Health Clinic Gastroenterology Creighton University, School of Medicine April 28, 2018 DISCLOSURES None 1 OBJECTIVES Review update
GERD DIAGNOSIS & TREATMENT Subhash Chandra MBBS Assistant Professor CHI Health Clinic Gastroenterology Creighton University, School of Medicine April 28, 2018 DISCLOSURES None 1 OBJECTIVES Review update
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease, Paraesophageal Hernias &
 530.81 553.3 & 530.00 43289, 43659 1043432842, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Surgery, UH JABSOM Associate General Surgery Program Director Director of Minimally Invasive & Bariatric Surgery Programs
530.81 553.3 & 530.00 43289, 43659 1043432842, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Surgery, UH JABSOM Associate General Surgery Program Director Director of Minimally Invasive & Bariatric Surgery Programs
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Infants and Children
 Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Infants and Children 4 Marzo 2017 Drssa Chiara Leoni Drssa Valentina Giorgio pediatriagastro@gmail.com valentinagiorgio1@gmail.com Definitions: GER GER is the passage
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Infants and Children 4 Marzo 2017 Drssa Chiara Leoni Drssa Valentina Giorgio pediatriagastro@gmail.com valentinagiorgio1@gmail.com Definitions: GER GER is the passage
WHAT IS GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD)?
 WHAT IS GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD)? The term gastroesophageal reflux describes the movement (or reflux) of stomach contents back up into the esophagus, the muscular tube that extends from the
WHAT IS GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD)? The term gastroesophageal reflux describes the movement (or reflux) of stomach contents back up into the esophagus, the muscular tube that extends from the
EXTRAESOPHAGEAL MANIFESTATIONS OF GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE WITH IMPLICATIONS FOR ORAL CAVITY
 EXTRAESOPHAGEAL MANIFESTATIONS OF GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE WITH IMPLICATIONS FOR ORAL CAVITY Crînguţa Paraschiv*, Cristina Gavrilescu, Irina Cotea, Manea Paloma, Rodica Ghiuru Gr. T. Popa" U.M.Ph.
EXTRAESOPHAGEAL MANIFESTATIONS OF GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE WITH IMPLICATIONS FOR ORAL CAVITY Crînguţa Paraschiv*, Cristina Gavrilescu, Irina Cotea, Manea Paloma, Rodica Ghiuru Gr. T. Popa" U.M.Ph.
Mucosal Changes in Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Prevalence, Sensitivity, Specificity and Assessment
 The Laryngoscope VC 2012 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Contemporary Review Mucosal Changes in Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Prevalence, Sensitivity, Specificity and
The Laryngoscope VC 2012 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Contemporary Review Mucosal Changes in Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Prevalence, Sensitivity, Specificity and
Frequency of Barrett Esophagus in Patients with Symptoms of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
 Original Article Frequency of Barrett Esophagus in Patients with Symptoms of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease From Military Hospital, Rawalpindi Obaid Ullah Khan, Abdul Rasheed Correspondence: Dr. Abdul
Original Article Frequency of Barrett Esophagus in Patients with Symptoms of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease From Military Hospital, Rawalpindi Obaid Ullah Khan, Abdul Rasheed Correspondence: Dr. Abdul
Speaker disclosure. Objectives. GERD: Who and When to Treat 7/21/2015
 GERD: Who and When to Treat Eugenio J Hernandez, MD Gastrohealth, PL Assistant Professor of Clinical Medicine, FIU Herbert Wertheim School of Medicine Speaker disclosure I do not have any relevant commercial
GERD: Who and When to Treat Eugenio J Hernandez, MD Gastrohealth, PL Assistant Professor of Clinical Medicine, FIU Herbert Wertheim School of Medicine Speaker disclosure I do not have any relevant commercial
Dysphagia. Conflicts of Interest
 Dysphagia Bob Kizer MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Creighton University School of Medicine August 25, 2018 Conflicts of Interest None 1 Which patient does not need an EGD as the first test? 1. 50 year
Dysphagia Bob Kizer MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Creighton University School of Medicine August 25, 2018 Conflicts of Interest None 1 Which patient does not need an EGD as the first test? 1. 50 year
Symptoms such as heartburn, pyrosis, and acid regurgitation
 CLINICAL INVESTIGATIONS 99m Tc-Sulfur Colloid Gastroesophageal Scintigraphy with Late Lung Imaging to Evaluate Patients with Posterior Laryngitis Alberto Bestetti, Federica Carola, PierMarziano Carnevali-Ricci,
CLINICAL INVESTIGATIONS 99m Tc-Sulfur Colloid Gastroesophageal Scintigraphy with Late Lung Imaging to Evaluate Patients with Posterior Laryngitis Alberto Bestetti, Federica Carola, PierMarziano Carnevali-Ricci,
Disclosures. Heartburn and Barrett s Esophagus. Heartburn and Barrett s Esophagus. GERD is common in the U.S. None
 Heartburn and Barrett s Esophagus None Disclosures Christian Mathy, MD University of California, San Francisco 2015 Heartburn and Barrett s Esophagus Heartburn and GERD GERD therapy Extraesophageal GERD
Heartburn and Barrett s Esophagus None Disclosures Christian Mathy, MD University of California, San Francisco 2015 Heartburn and Barrett s Esophagus Heartburn and GERD GERD therapy Extraesophageal GERD
Somkiat Wongtim Professor of Medicine Division of Respiratory Disease and Critical Care Chulalongkorn University
 Somkiat Wongtim Professor of Medicine Division of Respiratory Disease and Critical Care Chulalongkorn University Asthma-related Comorbidities Comorbid conditions of the upper airways Rhinitis and Sinusitis
Somkiat Wongtim Professor of Medicine Division of Respiratory Disease and Critical Care Chulalongkorn University Asthma-related Comorbidities Comorbid conditions of the upper airways Rhinitis and Sinusitis
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is implicated
 Donald O. Castell, M.D., Series Editor Chronic Laryngitis and Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease by Jonathan A. Schneider and Michael F. Vaezi INTRODUCTION Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is implicated
Donald O. Castell, M.D., Series Editor Chronic Laryngitis and Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease by Jonathan A. Schneider and Michael F. Vaezi INTRODUCTION Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is implicated
Acid reflux treatment for hoarseness (Protocol)
 Hopkins C, Yousaf U, Pedersen M This is a reprint of a Cochrane protocol, prepared and maintained by The Cochrane Collaboration and published in The Cochrane Library 200, Issue 2 http://www.thecochranelibrary.com
Hopkins C, Yousaf U, Pedersen M This is a reprint of a Cochrane protocol, prepared and maintained by The Cochrane Collaboration and published in The Cochrane Library 200, Issue 2 http://www.thecochranelibrary.com
THE CONNECTIVE TISSUE AND EPITHELIUM
 THE CONNECTIVE TISSUE AND EPITHELIUM The focus of this week s lab will be pathology of connective tissue and epithelium. The lab will introduce you to the four basic tissue types: epithelium, connective
THE CONNECTIVE TISSUE AND EPITHELIUM The focus of this week s lab will be pathology of connective tissue and epithelium. The lab will introduce you to the four basic tissue types: epithelium, connective
Radiology. Gastrointestinal. Transient Intraluminal Diverticulum of the Esophagus: A Significant Flow Artifact. Farooq P. Agha
 Gastrointest Radiol 9:9%103 (1984) Gastrointestinal Radiology 9 Springer-Verlag 1984 Transient Intraluminal Diverticulum of the Esophagus: A Significant Flow Artifact Farooq P. Agha Department of Radiology,
Gastrointest Radiol 9:9%103 (1984) Gastrointestinal Radiology 9 Springer-Verlag 1984 Transient Intraluminal Diverticulum of the Esophagus: A Significant Flow Artifact Farooq P. Agha Department of Radiology,
INFECTIOUS AND INFLAMMATORY DISORDERS
 Chapter 52 INFECTIOUS AND INFLAMMATORY DISORDERS Allen M. Seiden Infection or inflammation of the esophagus typically produces dysphagia and odynophagia, so these patients may frequently present to the
Chapter 52 INFECTIOUS AND INFLAMMATORY DISORDERS Allen M. Seiden Infection or inflammation of the esophagus typically produces dysphagia and odynophagia, so these patients may frequently present to the
Role of Reflux Symptom Index and Reflux Finding Score in Evaluation of Treatment Outcome in Patients with Laryngopharyngeal Reflux
 Original Article Role of RSI and RFS in Evaluation of Treatment 10.5005/jp-journals-10023-1141 Outcome in Patients with LPR Role of Reflux Symptom Index and Reflux Finding Score in Evaluation of Treatment
Original Article Role of RSI and RFS in Evaluation of Treatment 10.5005/jp-journals-10023-1141 Outcome in Patients with LPR Role of Reflux Symptom Index and Reflux Finding Score in Evaluation of Treatment
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Afferent nerves, interactions of, in cough, 20 21 Airway, eosinophilic inflammation of, 124 narrowing of, in asthma, 126 protection of, terms
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Afferent nerves, interactions of, in cough, 20 21 Airway, eosinophilic inflammation of, 124 narrowing of, in asthma, 126 protection of, terms
Extraesophageal GERD: Fact or Fiction?
 Transcript Details This is a transcript of an educational program accessible on the ReachMD network. Details about the program and additional media formats for the program are accessible by visiting: https://reachmd.com/programs/gi-insights/extraesophageal-gerd-fact-or-fiction/4157/
Transcript Details This is a transcript of an educational program accessible on the ReachMD network. Details about the program and additional media formats for the program are accessible by visiting: https://reachmd.com/programs/gi-insights/extraesophageal-gerd-fact-or-fiction/4157/
Refractory GERD : case presentation and discussion
 Refractory GERD : case presentation and discussion Ping-Huei Tseng National Taiwan University Hospital May 19, 2018 How effective is PPI based on EGD? With GERD symptom 75% erosive 25% NERD Endoscopy 81%
Refractory GERD : case presentation and discussion Ping-Huei Tseng National Taiwan University Hospital May 19, 2018 How effective is PPI based on EGD? With GERD symptom 75% erosive 25% NERD Endoscopy 81%
A Multidisciplinary Approach to Esophageal Dysphagia: Role of the SLP. Darlene Graner, M.A., CCC-SLP, BRS-S Sharon Burton, M.D.
 A Multidisciplinary Approach to Esophageal Dysphagia: Role of the SLP Darlene Graner, M.A., CCC-SLP, BRS-S Sharon Burton, M.D. What is the role of the SLP? Historically SLPs the preferred providers for
A Multidisciplinary Approach to Esophageal Dysphagia: Role of the SLP Darlene Graner, M.A., CCC-SLP, BRS-S Sharon Burton, M.D. What is the role of the SLP? Historically SLPs the preferred providers for
9/18/2015. Disclosures. Objectives. Dysphagia Sherri Ekobena PA-C. I have no relevant financial interests to disclose I have no conflicts of interest
 Dysphagia Sherri Ekobena PA-C Disclosures I have no relevant financial interests to disclose I have no conflicts of interest Objectives Define what dysphagia is Define types of dysphagia Define studies
Dysphagia Sherri Ekobena PA-C Disclosures I have no relevant financial interests to disclose I have no conflicts of interest Objectives Define what dysphagia is Define types of dysphagia Define studies
Gastro esophageal reflux disease DR. AMMAR I. ABDUL-LATIF
 Gastro esophageal reflux disease )GERD( DR. AMMAR I. ABDUL-LATIF GERD DEFINITION EPIDEMIOLOGY CAUSES PATHOGENESIS SIGNS &SYMPTOMS COMPLICATIONS DIAGNOSIS TREATMENT Definition Montreal consensus defined
Gastro esophageal reflux disease )GERD( DR. AMMAR I. ABDUL-LATIF GERD DEFINITION EPIDEMIOLOGY CAUSES PATHOGENESIS SIGNS &SYMPTOMS COMPLICATIONS DIAGNOSIS TREATMENT Definition Montreal consensus defined
Obesity Is Associated With Increased Transient Lower Esophageal Sphincter Relaxation. Introduction. Predisposing factor. Introduction.
 Obesity Is Associated With Increased Transient Lower Esophageal Sphincter Relaxation Gastro Esophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) JUSTIN CHE-YUEN WU, et. al. The Chinese University of Hong Kong Gastroenterology,
Obesity Is Associated With Increased Transient Lower Esophageal Sphincter Relaxation Gastro Esophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) JUSTIN CHE-YUEN WU, et. al. The Chinese University of Hong Kong Gastroenterology,
Accuracy of Fiberoptic Nasopharyngoscopy in the Diagnosis of Pharyngolaryngeal Diseases
 FIBEROPTIC THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE NASOPHARYNGOSCOPY MEDICAL JOURNAL Accuracy of Fiberoptic Nasopharyngoscopy in the Diagnosis of Pharyngolaryngeal Diseases Ragheed Turky Miteab ABSTRACT: BACKGROUND: In
FIBEROPTIC THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE NASOPHARYNGOSCOPY MEDICAL JOURNAL Accuracy of Fiberoptic Nasopharyngoscopy in the Diagnosis of Pharyngolaryngeal Diseases Ragheed Turky Miteab ABSTRACT: BACKGROUND: In
ESOPHAGEAL CANCER AND GERD. Prof Salman Guraya FRCS, Masters MedEd
 ESOPHAGEAL CANCER AND GERD Prof Salman Guraya FRCS, Masters MedEd Learning objectives Esophagus anatomy and physiology Esophageal cancer Causes, presentations of esophageal cancer Diagnosis and management
ESOPHAGEAL CANCER AND GERD Prof Salman Guraya FRCS, Masters MedEd Learning objectives Esophagus anatomy and physiology Esophageal cancer Causes, presentations of esophageal cancer Diagnosis and management
Achalasia is a rare disease with an annual incidence estimated REVIEWS. Erroneous Diagnosis of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Achalasia
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2011;9:1020 1024 REVIEWS Erroneous Diagnosis of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Achalasia BOUDEWIJN F. KESSING, ALBERT J. BREDENOORD, and ANDRÉ J. P. M. SMOUT
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2011;9:1020 1024 REVIEWS Erroneous Diagnosis of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Achalasia BOUDEWIJN F. KESSING, ALBERT J. BREDENOORD, and ANDRÉ J. P. M. SMOUT
A CURIOUS CASE OF HYPERTENSIVE LES. Erez Hasnis Department of Gastroenterology Rambam Health Care Campus
 A CURIOUS CASE OF HYPERTENSIVE LES Erez Hasnis Department of Gastroenterology Rambam Health Care Campus CASE DESCRIPTION 63yo, F, single, attending nurse. PMH includes T2DM (Sitagliptin/Metformin), Hyperlipidemia
A CURIOUS CASE OF HYPERTENSIVE LES Erez Hasnis Department of Gastroenterology Rambam Health Care Campus CASE DESCRIPTION 63yo, F, single, attending nurse. PMH includes T2DM (Sitagliptin/Metformin), Hyperlipidemia
Surgical aspects of dysphagia
 Dysphagia Why is dysphagia important? Surgery Surgical aspects of dysphagia Adrian P. Ireland aireland@eircom.net Academic RCSI Department of Surgery, Beaumont Hospital Why important Definitons Swallowing
Dysphagia Why is dysphagia important? Surgery Surgical aspects of dysphagia Adrian P. Ireland aireland@eircom.net Academic RCSI Department of Surgery, Beaumont Hospital Why important Definitons Swallowing
Effect of Proton Pump Inhibitors in the Treatment of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux
 IOSR Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences (IOSR-JPBS) e-issn:2278-3008, p-issn:2319-7676. Volume 13, Issue 4 Ver. III (Jul Aug 2018), PP 54-61 www.iosrjournals.org Effect of Proton Pump Inhibitors
IOSR Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences (IOSR-JPBS) e-issn:2278-3008, p-issn:2319-7676. Volume 13, Issue 4 Ver. III (Jul Aug 2018), PP 54-61 www.iosrjournals.org Effect of Proton Pump Inhibitors
The Throat. Image source:
 The Throat Anatomy Image source: http://anatomyforlayla.blogspot.co.za/2007/04/blog-post.html The Throat consists of three parts: 1. The Nasopharynx is the upper part of the throat and it is situated behind
The Throat Anatomy Image source: http://anatomyforlayla.blogspot.co.za/2007/04/blog-post.html The Throat consists of three parts: 1. The Nasopharynx is the upper part of the throat and it is situated behind
B. Cystic Teratoma: Refer to virtual microscope slide p_223 ovary, teratoma and compare to normal virtual microscope slide 086 ovary.
 LAB 2: THE CONNECTIVE TISSUE AND EPITHELIUM The focus of this week s lab will be pathology of connective tissue and epithelium. The lab will introduce you to the four basic tissue types: epithelium, connective
LAB 2: THE CONNECTIVE TISSUE AND EPITHELIUM The focus of this week s lab will be pathology of connective tissue and epithelium. The lab will introduce you to the four basic tissue types: epithelium, connective
Peptic ulcer disease Disorders of the esophagus
 Peptic ulcer disease Disorders of the esophagus Peptic ulcer disease Burning epigastric pain Exacerbated by fasting Improved with meals Ulcer: disruption of mucosal integrity >5 mm in size, with depth
Peptic ulcer disease Disorders of the esophagus Peptic ulcer disease Burning epigastric pain Exacerbated by fasting Improved with meals Ulcer: disruption of mucosal integrity >5 mm in size, with depth
Definition of GERD American College of Gastroenterology
 Definition of GERD American College of Gastroenterology GERD is defined as chronic symptoms or mucosal damage produced by the abnormal reflux of gastric contents into the esophagus DeVault et al. Am J
Definition of GERD American College of Gastroenterology GERD is defined as chronic symptoms or mucosal damage produced by the abnormal reflux of gastric contents into the esophagus DeVault et al. Am J
GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX
 DR. PHILIP K. BLUSTEIN M.D. F.R.C.P.(C) 415 14 TH ST. NW. CALGARY AB T2N2A1 PHONE (403) 270-9555 FAX (404) 270-7479 GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DEFINITION: *MONTREAL CONSENSUS DEFINED GERD AS A CONDITION WHICH
DR. PHILIP K. BLUSTEIN M.D. F.R.C.P.(C) 415 14 TH ST. NW. CALGARY AB T2N2A1 PHONE (403) 270-9555 FAX (404) 270-7479 GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DEFINITION: *MONTREAL CONSENSUS DEFINED GERD AS A CONDITION WHICH
Hoarseness. Evidence-based Key points for Approach
 Hoarseness Evidence-based Key points for Approach Sasan Dabiri, Assistant Professor Department of otorhinolaryngology Head & Neck Surgery Amir A lam hospital Tehran University of Medial Sciences Definition:
Hoarseness Evidence-based Key points for Approach Sasan Dabiri, Assistant Professor Department of otorhinolaryngology Head & Neck Surgery Amir A lam hospital Tehran University of Medial Sciences Definition:
JMSCR Vol 07 Issue 01 Page January 2019
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v7i1.43 Clinicopathological Study of
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v7i1.43 Clinicopathological Study of
THORACIC SURGERY: Dysphagia. Dr. Robert Zeldin Dr. John Dickie Dr. Carmine Simone. Thoracic Surgery Toronto East General Hospital
 THORACIC SURGERY: Dysphagia Dr. Robert Zeldin Dr. John Dickie Dr. Carmine Simone Thoracic Surgery Toronto East General Hospital Objectives Definitions Common causes Investigations Treatment options Anatomy
THORACIC SURGERY: Dysphagia Dr. Robert Zeldin Dr. John Dickie Dr. Carmine Simone Thoracic Surgery Toronto East General Hospital Objectives Definitions Common causes Investigations Treatment options Anatomy
Nature and Science, 2009;7(5), ISSN ,
 Study of Gastro Esophageal Reflux Disease in COD atients Adel M.Khattab*, Khaled Z. El-Karmouty**,Tamer M. Aly*, Asmaa H. Abdel Azeem* *Chest Department, Faculty of Medicine, Ain Shams University **Internal
Study of Gastro Esophageal Reflux Disease in COD atients Adel M.Khattab*, Khaled Z. El-Karmouty**,Tamer M. Aly*, Asmaa H. Abdel Azeem* *Chest Department, Faculty of Medicine, Ain Shams University **Internal
Refractory GERD: What s a Gastroenterologist To Do?
 Refractory GERD: What s a Gastroenterologist To Do? Philip O. Katz, MD, FACG Chairman, Division of Gastroenterology Einstein Medical Center Clinical Professor of Medicine Jefferson Medical College Philadelphia,
Refractory GERD: What s a Gastroenterologist To Do? Philip O. Katz, MD, FACG Chairman, Division of Gastroenterology Einstein Medical Center Clinical Professor of Medicine Jefferson Medical College Philadelphia,
Laryngopharyngeal reflux disease; how to evaluate
 Open Science Journal of Clinical Medicine 20; (): 5- Published online December 20, 20 (http://www.openscienceonline.com/journal/osjcm) Laryngopharyngeal reflux disease; how to evaluate IRFAN IQBAL, *,
Open Science Journal of Clinical Medicine 20; (): 5- Published online December 20, 20 (http://www.openscienceonline.com/journal/osjcm) Laryngopharyngeal reflux disease; how to evaluate IRFAN IQBAL, *,
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease:
 Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: Introduction Gastroesophageal reflux is the involuntary movement of gastric contents to the esophagus. It is a common disease, occurring in one third of the population
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: Introduction Gastroesophageal reflux is the involuntary movement of gastric contents to the esophagus. It is a common disease, occurring in one third of the population
AGA SECTION. Gastroenterology 2016;150:
 Gastroenterology 2016;150:1026 1030 April 2016 AGA Section 1027 Procedural intervention (3) Upper endoscopy indications 3 6 Non-response of symptoms to a 4 8 week empiric trial of twice-daily PPI Troublesome
Gastroenterology 2016;150:1026 1030 April 2016 AGA Section 1027 Procedural intervention (3) Upper endoscopy indications 3 6 Non-response of symptoms to a 4 8 week empiric trial of twice-daily PPI Troublesome
An Insight into Allergy and Allergen Immunotherapy Co-morbidities of allergic disease
 An Insight into Allergy and Allergen Immunotherapy Co-morbidities of allergic disease Carmen Vidal Athens, September 11, 2014 Pucci S & Incorvaia C, 2008; 153:1-2 1. The major player in driving the immune
An Insight into Allergy and Allergen Immunotherapy Co-morbidities of allergic disease Carmen Vidal Athens, September 11, 2014 Pucci S & Incorvaia C, 2008; 153:1-2 1. The major player in driving the immune
What can you expect from the lab?
 Role of the GI Motility Lab in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Esophageal Disorders Kenneth R. DeVault MD, FACG, FACP Professor and Chair Department of Medicine Mayo Clinic Florida What can you expect from
Role of the GI Motility Lab in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Esophageal Disorders Kenneth R. DeVault MD, FACG, FACP Professor and Chair Department of Medicine Mayo Clinic Florida What can you expect from
JPoelmans,JTack RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL PRACTICE EXTRAOESOPHAGEAL MANIFESTATIONS OF GASTRO- OESOPHAGEAL REFLUX
 1492 See end of article for authors affiliations Correspondence to: Dr J Tack, Centre for Gastroenterological Research, Catholic University of Leuven, Herestraat 49, B-3000 Leuven, Belgium; Jan.Tack@ med.kuleuven.ac.be
1492 See end of article for authors affiliations Correspondence to: Dr J Tack, Centre for Gastroenterological Research, Catholic University of Leuven, Herestraat 49, B-3000 Leuven, Belgium; Jan.Tack@ med.kuleuven.ac.be
Predictors of Outcome in an Open Label, Therapeutic Trial of High-Dose Omeprazole in Laryngitis
 American Journal of Gastroenterology ISSN 0002-9270 C 2004 by Am. Coll. of Gastroenterology doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2004.04151.x Published by Blackwell Publishing ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTIONS Predictors of
American Journal of Gastroenterology ISSN 0002-9270 C 2004 by Am. Coll. of Gastroenterology doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2004.04151.x Published by Blackwell Publishing ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTIONS Predictors of
Understanding GERD. & Stretta Therapy. GERD (gĕrd): Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
 Understanding GERD & Stretta Therapy GERD (gĕrd): Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease What is GERD? When the muscle between your stomach and esophagus is weak, stomach contents like acid or bile can reflux
Understanding GERD & Stretta Therapy GERD (gĕrd): Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease What is GERD? When the muscle between your stomach and esophagus is weak, stomach contents like acid or bile can reflux
Dysphagia after EA repair. Disclosure. Learning objectives 9/17/2013
 Dysphagia after EA repair Christophe Faure, M.D. Professor of Pediatrics, Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Sainte-Justine University Health Center, Université de Montréal, Montréal, QC, Canada christophe.faure@umontreal.ca
Dysphagia after EA repair Christophe Faure, M.D. Professor of Pediatrics, Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Sainte-Justine University Health Center, Université de Montréal, Montréal, QC, Canada christophe.faure@umontreal.ca
LARYNGO-PHARYNGEAL REFLUX A RANDOMIZED CONTROLLED TRIAL
 LARYNGO-PHARYNGEAL REFLUX A RANDOMIZED CONTROLLED TRIAL A randomized, open label, three arm parallel design, single-site study, comparing the effects of esomeprazole and alginate on top of lifestyle guidance
LARYNGO-PHARYNGEAL REFLUX A RANDOMIZED CONTROLLED TRIAL A randomized, open label, three arm parallel design, single-site study, comparing the effects of esomeprazole and alginate on top of lifestyle guidance
Esophageal Disorders. Learning Objectives. Introduction. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. Reza Shaker, MD, and Benson T.
 Esophageal Disorders Reza Shaker, MD, and Benson T. Massey, MD, FACP Learning Objectives AFTER COMPLETING THIS CHAPTER, THE LEARNER SHOULD BE ABLE TO: 1. Recognize the typical and atypical presentations
Esophageal Disorders Reza Shaker, MD, and Benson T. Massey, MD, FACP Learning Objectives AFTER COMPLETING THIS CHAPTER, THE LEARNER SHOULD BE ABLE TO: 1. Recognize the typical and atypical presentations
A Review of Esophageal ph Monitoring for the Diagnosis of Gastroesophageal Reflux in Children
 HK J Paediatr (new series) 2002;7:112-117 A Review of Esophageal ph Monitoring for the Diagnosis of Gastroesophageal Reflux in Children TF TONG, DKK NG Abstract Key words Gastroesophageal reflux (GER)
HK J Paediatr (new series) 2002;7:112-117 A Review of Esophageal ph Monitoring for the Diagnosis of Gastroesophageal Reflux in Children TF TONG, DKK NG Abstract Key words Gastroesophageal reflux (GER)
Myogenic Control. Esophageal Motility. Enteric Nervous System. Alimentary Tract Motility. Determinants of GI Tract Motility.
 Myogenic Control Esophageal Motility David Markowitz, MD Columbia University, College of Physicians and Surgeons Basic Electrical Rythym: intrinsic rhythmic fluctuation of smooth muscle membrane potential
Myogenic Control Esophageal Motility David Markowitz, MD Columbia University, College of Physicians and Surgeons Basic Electrical Rythym: intrinsic rhythmic fluctuation of smooth muscle membrane potential
Esophageal Motility. Alimentary Tract Motility
 Esophageal Motility David Markowitz, MD Columbia University, College of Physicians and Surgeons Alimentary Tract Motility Propulsion Movement of food and endogenous secretions Mixing Allows for greater
Esophageal Motility David Markowitz, MD Columbia University, College of Physicians and Surgeons Alimentary Tract Motility Propulsion Movement of food and endogenous secretions Mixing Allows for greater
The prevalence of upper respiratory symptoms in a cohort of adults presenting with symptoms of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease
 The prevalence of upper respiratory symptoms in a cohort of adults presenting with symptoms of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease D L Amarasiri 1, A Pathmeswaran 2, A S Dassanayake 3, A P de Silva 4, M
The prevalence of upper respiratory symptoms in a cohort of adults presenting with symptoms of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease D L Amarasiri 1, A Pathmeswaran 2, A S Dassanayake 3, A P de Silva 4, M
Gastroenterology. Certification Examination Blueprint. Purpose of the exam
 Gastroenterology Certification Examination Blueprint Purpose of the exam The exam is designed to evaluate the knowledge, diagnostic reasoning, and clinical judgment skills expected of the certified gastroenterologist
Gastroenterology Certification Examination Blueprint Purpose of the exam The exam is designed to evaluate the knowledge, diagnostic reasoning, and clinical judgment skills expected of the certified gastroenterologist
David Markowitz, MD. Physicians and Surgeons
 Esophageal Motility David Markowitz, MD Columbia University, College of Columbia University, College of Physicians and Surgeons Alimentary Tract Motility Propulsion Movement of food and endogenous secretions
Esophageal Motility David Markowitz, MD Columbia University, College of Columbia University, College of Physicians and Surgeons Alimentary Tract Motility Propulsion Movement of food and endogenous secretions
ENDOLUMINAL THERAPIES FOR GERD. University of Colorado Department of Surgery Grand Rounds March 31st, 2008
 ENDOLUMINAL THERAPIES FOR GERD University of Colorado Department of Surgery Grand Rounds March 31st, 2008 Overview GERD Healthcare significance Definitions Treatment objectives Endoscopic options Plication
ENDOLUMINAL THERAPIES FOR GERD University of Colorado Department of Surgery Grand Rounds March 31st, 2008 Overview GERD Healthcare significance Definitions Treatment objectives Endoscopic options Plication
GUIDELINES FOR CLINICIANS. Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux Disease in Adults. Reflux Disease. 4th Edition Digestive Health Foundation
 GUIDELINES FOR CLINICIANS Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux Disease in Adults Reflux Disease 4th Edition 2008 Digestive Health Foundation Digestive Health Foundation Table of contents Page 4 Gastro-oesophageal
GUIDELINES FOR CLINICIANS Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux Disease in Adults Reflux Disease 4th Edition 2008 Digestive Health Foundation Digestive Health Foundation Table of contents Page 4 Gastro-oesophageal
The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2015; 57:
 The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2015; 57: 258-265 Original Evaluation of the likelihood of reflux developing in patients with recurrent upper respiratory infections, recurrent sinusitis or recurrent
The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2015; 57: 258-265 Original Evaluation of the likelihood of reflux developing in patients with recurrent upper respiratory infections, recurrent sinusitis or recurrent
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Patients with Eustachian Tube Catarrh
 IJOPL Original article Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in 10.5005/jp-journals-10023-1107 Patients with Eustachian Tube Catarrh Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Patients with Eustachian Tube Catarrh 1
IJOPL Original article Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in 10.5005/jp-journals-10023-1107 Patients with Eustachian Tube Catarrh Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Patients with Eustachian Tube Catarrh 1
4/24/2015. History of Reflux Surgery. Recent Innovations in the Surgical Treatment of Reflux
 Recent Innovations in the Surgical Treatment of Reflux Scott Carpenter, DO, FACOS, FACS Mercy Hospital Ardmore Ardmore, OK History of Reflux Surgery - 18 th century- first use of term heartburn - 1934-
Recent Innovations in the Surgical Treatment of Reflux Scott Carpenter, DO, FACOS, FACS Mercy Hospital Ardmore Ardmore, OK History of Reflux Surgery - 18 th century- first use of term heartburn - 1934-
A cross-sectional study on prevalence of gastro esophageal reflux disease in regurgitant infant and children with evaluation of IGERQ score
 International Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics Kandaswamy E et al. Int J Contemp Pediatr. 2018 Mar;5(2):395-399 http://www.ijpediatrics.com pissn 2349-3283 eissn 2349-3291 Original Research Article DOI:
International Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics Kandaswamy E et al. Int J Contemp Pediatr. 2018 Mar;5(2):395-399 http://www.ijpediatrics.com pissn 2349-3283 eissn 2349-3291 Original Research Article DOI:
Rings in the esophagus are not always eosinophilic esophagitis: Case series of ring forming lymphocytic esophagitis and review of the literature
 Rings in the esophagus are not always eosinophilic esophagitis: Case series of ring forming lymphocytic esophagitis and review of the literature Authors Julia L. Pleet 1,SofiaTaboada 2, Arvind Rishi 2,
Rings in the esophagus are not always eosinophilic esophagitis: Case series of ring forming lymphocytic esophagitis and review of the literature Authors Julia L. Pleet 1,SofiaTaboada 2, Arvind Rishi 2,
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Achalasia, barium esophagography for, 57 58 Acid pocket, 18 19 Acid-sensing ion, 20 Acupuncture, 128 Adiponectin, in obesity, 166 ADX10059 metabotropic
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Achalasia, barium esophagography for, 57 58 Acid pocket, 18 19 Acid-sensing ion, 20 Acupuncture, 128 Adiponectin, in obesity, 166 ADX10059 metabotropic
Vocal cord dysfunction: what do we know? K. Kenn and R. Balkissoon European Respiratory Journal 2011; 37:
 本檔僅供內部教學使用檔案內所使用之照片之版權仍屬於原期刊公開使用時, 須獲得原期刊之同意授權 Vocal cord dysfunction: what do we know? K. Kenn and R. Balkissoon European Respiratory Journal 2011; 37: 194 200 Introduction Refractory or severe asthma
本檔僅供內部教學使用檔案內所使用之照片之版權仍屬於原期刊公開使用時, 須獲得原期刊之同意授權 Vocal cord dysfunction: what do we know? K. Kenn and R. Balkissoon European Respiratory Journal 2011; 37: 194 200 Introduction Refractory or severe asthma
Archived at the Flinders Academic Commons:
 Archived at the Flinders Academic Commons: http://dspace.flinders.edu.au/dspace/ This is the peer reviewed version of the following article: Fox M, Omari T, Rommel N. Supraesophageal Reflux Disease: Solving
Archived at the Flinders Academic Commons: http://dspace.flinders.edu.au/dspace/ This is the peer reviewed version of the following article: Fox M, Omari T, Rommel N. Supraesophageal Reflux Disease: Solving
Barrett s Esophagus. Abdul Sami Khan, M.D. Gastroenterologist Aurora Healthcare Burlington, Elkhorn, Lake Geneva, WI
 Barrett s Esophagus Abdul Sami Khan, M.D. Gastroenterologist Aurora Healthcare Burlington, Elkhorn, Lake Geneva, WI A 58 year-old, obese white man has had heartburn for more than 20 years. He read a magazine
Barrett s Esophagus Abdul Sami Khan, M.D. Gastroenterologist Aurora Healthcare Burlington, Elkhorn, Lake Geneva, WI A 58 year-old, obese white man has had heartburn for more than 20 years. He read a magazine
Burning Issues in Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
 3:45 4:45pm Burning Issues in GERD SPEAKER Prateek Sharma, MD, FACG, FACP Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Prateek Sharma, MD, FACG, FACP,
3:45 4:45pm Burning Issues in GERD SPEAKER Prateek Sharma, MD, FACG, FACP Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Prateek Sharma, MD, FACG, FACP,
