Allergic fungal rhinosinusitis: an overview on pathogenesis, early diagnosis and management
|
|
|
- Kenneth Malone
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Suri N et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg May;4(3): pissn eissn Original Research Article DOI: Allergic fungal rhinosinusitis: an overview on pathogenesis, early diagnosis and management Neeraj Suri*, Bhavya B. M. Department of ENT, GMERS Medical College and Civil Hospital, Gandhinagar, Gujarat, India Received: 28 February 2018 Accepted: 26 March 2018 *Correspondence: Dr. Neeraj Suri, singhn_16@yahoo.com Copyright: the author(s), publisher and licensee Medip Academy. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License, which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. ABSTRACT Background: The objective of the study was to evaluate the criteria for diagnosing allergic fungal rhinosinusitis and to maintain permanent drainage and ventilation, while preserving the integrity of the mucosa. Methods: This is a prospective study of 50 patients with allergic fungal sinusitis with or without polyposis all of whom were treated with endoscopic debridement. Mucous sample collection, nasal secretion culture, surgical specimen handling, and histological evaluation of surgical specimens are described. All patients treated with endoscopic sinus surgery, debridement, post-operative use of steroids and antifungal therapy. Results: Fungal mucin was found in all 50 cases, histology and fungal cultures confirmed the diagnosis. Out of 50 patients, 29 were females and 21 were males, with a mean age of 32 years. The most common symptom was nasal discharge 41 (82%) cases, nasal obstruction in 38 (76%) cases, headache and facial pain in 32 (72%) cases, 7 (14%) patients had bronchial asthma. Symptoms of nasal obstruction and nasal discharge were improved in 46 (92%) cases. All preoperative versus postoperative changes in AFRS associated complaints reached statistical significance of p value <0.001 except in patients with asthma. Conclusions: Comprehensive management with endoscopic sinus surgery, oral steroids and antifungals reduces the recurrence or need for revision surgery. Long term follow up is very important. Keywords: Allergic fungal rhinosinusitis, Type I hypersensitivity, Oral corticosteroids, Immunotherapy, Endoscopic sinus surgery INTRODUCTION Allergic fungal rhinosinusitis is a distinct clinical entity, which was first reported in 1976, characterized by the presence of allergic fungal mucin, which consists of thick tenacious eosinophilic secretion with characteristic histologic findings. 1 AFRS is a form of non-invasive fungal rhinosinusitis coupled with the clinical entity of fungus ball (mycetoma). It is a unique pathologic entity which has the mucin which is similar to that found in the lungs of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA). This pulmonary correlation helped the researchers to understand the pathogenesis of AFRS over last decade. 2 Earlier it was known as a paranasal sinus tumor. AFRS is now believed to be an IgE mediated allergic reaction to the aerosolized environmental fungi, commonly the dematiaceous species in an immunocompetent host. Aspergillus was the only fungal species recovered in the cultures of AFRS due to lack of culture techniques and knowledge. Plaignaud reported the first case in A detailed clinical description of the causative fungus Aspergillus was given by Schubert in Katzenstein et al, described allergic aspergillus sinusitis as a newly recognized form of sinusitis. 3 Robson et al introduced the terminology allergic fungal sinusitis (AFS). 4 International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery May-June 2018 Vol 4 Issue 3 Page 694
2 Approximately 6-8% of surgically treated chronic rhinosinusitis had fungal elements in their biopsied specimens. Ence et al, identified five different organisms responsible for AFRS. 5 Cody et al simplified the criteria for diagnosis of AFRS which included characteristic allergic mucin, and non-invasive fungal hyphae within the collected mucin or positive fungal cultures. 6 Some studies added, type I hypersensitivity reaction diagnosed by history, positive skin test or serology as other prerequisites for diagnosing AFRS. 7 In 1994, Bent and Kuhn published their diagnostic criteria centered on the histologic, radiographic, and immunologic characteristics of the disease. 8 Others have proposed several sets of criteria that have served to further the discussion of an investigation into this unique disease; however, the Bent and Kuhn criteria (Table 1) are largely regarded as the standard for diagnosis today. Patients must meet all the major criteria for diagnosis, while the minor criteria serve to support the diagnosis and describe individual patients but are not used to make a diagnosis. The major criteria include a history of type I hypersensitivity by history, skin testing, or in vitro testing; nasal polyposis; characteristic computed tomography (CT) scan/mri findings; the presence of eosinophilic mucin without invasion; and a positive fungal stain of sinus contents removed at the time of surgery. The minor criteria include a history of asthma, unilateral predominance of disease, radiographic evidence of bone erosion, fungal cultures, presence of Charcot-Leyden crystals in surgical specimens, and serum eosinophilia. Since its initial description, AFRS has been a topic of debate and controversy regarding its pathogenesis, diagnosis, classification and management. This study was a prospective look into the cases we encountered at our centre. Our aims are: To re-evaluate the diagnostic criteria for AFRS. To reduce the complications by surgically removing the inciting fungal allergic mucin and marsupialisation of the involved sinuses. To provide a comprehensive management for permanent drainage and ventilation of the involved sinuses while preserving the integrity of the mucosa. Table 1: Bent and Kuhn diagnostic criteria. Major Type I hypersensitivity Nasal polyposis Characteristic CT findings Eosinophilic mucin without invasion Positive fungal stain Minor Asthma Unilateral disease Bone erosion Fungal cultures Charcot-Leyden crystals Serum Eosinophilia METHODS A total of 50 patients aged years diagnosed with chronic rhinosinusitis suspected to have AFRS by clinical history and examination were included in the study. All 50 patients were treated surgically between In this study 29 were females and 21 were males, with an average age of 32 years. The essential criteria for diagnosis of AFRS were: 1. Nasal polyposis 2. Presence of thick tenacious allergic mucin. 3. Computed tomographic scan of paranasal sinuses showing opacification of the sinus with areas of hyperattenuation. 4. Positive fungal culture of the surgical specimen. Sample collection and culture technique As the fungus colonises the mucus, a simple non invasive procedure to obtain as much mucin as possible should be done in all patients who present with sinus infections. Xylocaine 10% spray was used (1-2 puffs) in each nostril to anaesthetize the nasal mucosa. After about two to three minutes, each nostril was flushed with 20cc normal saline using sterile disposable syringe and needle, during which the patient was asked to take a deep inspiratory breath and hold just before instillation of the saline and then forcefully exhale. The return fluid was collected in a sterile pan. This sample was sent to the laboratory and inoculated onto inhibitory agar mould (containing ciprofloxacin or chloramphenicol to prevent bacterial growth) or brain heart infusion agar. Fungal culture was usually seen around days. Surgical specimen collection The allergic mucin was manually collected with the inflamed tissue during the surgical procedure while keeping in mind to preserve the normal mucosa. The collected sample was transferred to sterile normal saline solution/ nonstick sheet. Use of suction devices to clear the mucin was minimised to get high yield of the fungal mucin. Specimen was stained using haemotoxylin and eosin (H&E) and Gomori methanamine silver and the microbiologist was asked to look for allergic fungal mucus. Surgical treatment Preoperative workup All patients planned for surgical treatment underwent routine blood and urine investigations, x ray paranasal sinuses water s view and CT paranasal sinuses to know the extent of disease and also to rule out invasive fungal rhinosinusitis. International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery May-June 2018 Vol 4 Issue 3 Page 695
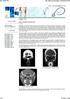
3 To reduce the recurrence of the disease all patients were given a short course of oral prednisolone 0.5mg- 1mg/kg/day for 1 week prior to the surgery. Steroids were given to ameliorate the underlying inflammatory process, to decrease the bulk of nasal polyposis and intraoperative bleeding. Preoperative antibiotics were also given to avoid concomitant post obstructive bacterial sinusitis. Intraoperative details Surgery was aimed to achieve (1) Complete extirpation of the allergic mucin and fungal debris, (2) Provide permanent drainage and ventilation of the affected sinus while preserving the integrity of normal mucosa, and (3) Postoperative access to the diseased operated areas for look up for recurrence during follow up sessions. The surgical procedure was tailored to the extent of the disease, all patients underwent endoscopic sinus surgery. The disease was seen evident as nasal polyp, hypertrophied mucosa, with necrotic avascular blackish or greenish crusts / caseous thick secretions which was debrided. The ethmoid sinuses were involved in about 48% cases. The Inter sinus septa were eroded and seen lying free embedded in the caseous mucin. The expansile nature of AFRS, provides better access for the surgeon to debride the areas which are usually difficult to reach in endoscopic approach. Most of the patients had widened nasal cavity, middle meatus, frontal recess even dehiscence of the frontal sinus due to the disease process. Figure 2: Nasal polyp in a patient with AFRS. Postoperative care Nasal irrigation with normal saline and antifungal solution was started in the immediate post operative period once nasal packing was removed. Antibiotics were given for 1 week. Oral steroids (prednisolone) was given for 2-4 weeks duration in tapered dosage. Orbital extension was seen in 7 cases (14%) which was explored via endoscopic ethmoidectomy. The fungal debris was seen not breaching the orbital periosteum. 2 patients (4%) had the disease extending upto the cribriform plate but not eroding it. No neurosurgical exploration was required. 2 patients (4%) had disease extending to the sphenoid sinus which was cleared by suction and minimal manipulation. Once the debridement was done, all the sinuses were reinspected for any leftover disease, saline irrigation done and wide marsupialisation of the sinuses was achieved. A B C Figure 3: (A) Coronal CT shows soft tissue shadow involving left ethmoids and maxillary sinus with hetergenecity, (B) Axial non-contrast CT of same patient, (C) MRI Axial cut showing signal void on T2W images. Follow-up Figure 1: Shows thick tenacious, dirty white fungal mucin. All patients were followed up at regular intervals, weekly for first 3 months 2 weekly for 6-12 months and monthly for months. The average follow up period was 12 months, with maximum follow up till 36 months. International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery May-June 2018 Vol 4 Issue 3 Page 696
4 On follow up patients were advised 1. Twice daily nasal irrigation with antifungal drops (clotrimazole) 2. Intranasal steroid spray (budesonide 2 puffs in each nostril once a day) for a mean period of months. 3. Oral fluconazole 150 mg once daily for 7 days course. With repeat liver function tests with in normal limits oral antifungals were continued for 7 more days. All patients underwent suction clearance and debridement for retained fungal disease during weekly follow up for 3 months. All were advised for avoidance of allergens. During follow up in the first 3-6 months we observed hypertrophied oedematous mucosa (7 cases), synechiae (3 cases), healing granulations (5 cases), retained fungal debris (8 cases). RESULTS Demographic data Of the 50 patients who were included in the study, 3 patients were lost to follow up. 29 were females and 21 were males, with a mean age of 32 years. Of these, 38 patients belonged to lower socio-ecomonic status, 22 (44%) patients resided in high humid areas. Revision surgery was done in 11 (22%) cases. Symptoms of AFRS In our present study, the most common compliant was nasal discharge 41 (82%) cases, blood stained nasal discharge in 10 (20%) cases, nasal obstruction in 38 (76%) cases, headache and facial pain in 32 (72%) cases, 7 (14%) patients had bronchial asthma, 13 (26%) patients had history of hyposmia. Symptoms of nasal obstruction and nasal discharge were improved in 46 (92%) cases, hyposmia and headache improved in almost all patients. All preoperative versus postoperative changes in AFRS associated complaints reached statistical significance of p<0.001 except in patients with asthma. According to the results 46 patients had improvement. In our study, we observed recurrence of the disease in 4 (8%) cases, which was limited to maxilla and ethmoidal sinuses with no intracranial or orbital extension. This was attributed mainly to irregular follow up, noncompliance with medical and antifungal therapy, discontinuation of nasal irrigation, Non-avoidance of allergens. Nasal airway obstruction in AFRS is a gradual process that many a times patients are unaware about the underlying disease. 7 (14%) patients had proptosis less than 2 mm, 5 (10%) patients had cheek swelling, 7 (14%) patients had eye lid swelling, while none of the patients had diplopia or visual loss. Radiologically, patients with AFRS show high attenuation with in the soft tissue shadow of the involved sinuses on non-contrast CT scan Expansion remodelling or thinning of the sinus wall was noted commonly in our patients. Bony erosion of the sinus wall with extension into adjoining sinuses was noted in 23 (46%) cases. Maxilla and ethmoids were the most commonly affected sinus. Sphenoid was involved only in 2 (4%) patients. Lamina papyracea showed demineralisation in 8 (16%) cases. None of the patients had intracranial extension or orbital extension (Table 2). Table 2: Extension of the disease. Extension of disease No of patients Pansinusitis 26 Unilateral 37 Bilateral 23 Ethmoidal 24 Sphenoid 02 Frontal sinus 04 Orbital extension 07 Cribriform plate involvement 02 DISCUSSION Since the description of the disease in 1970, many studies have been conducted towards the pathogenesis, symptomatology and association, diagnosis and management of AFRS. 12 Many studies evaluating the diagnostic criteria, and treatment regimen have appeared in literature. 6-8,13-14 The diagnostic criteria for AFRS includes (1) chronic rhinosinusitis confirmed radiologically by CT scan of paranasal sinuses; (2) Presence of allergic fungal mucin with predominant eosinophils; (3) Presence of fungus confirmed by the culture of mucin or histology. 15,16 Studies have reported an incidence varying from 40-65%. Relatively higher incidences are seen depending on the geographical regions like high humid areas and occupational differences and also specimen isolation techniques. All patients who were suspected to have fungal infection underwent mucus culture/histology. Chances of positive culture is high with increased volume of mucus sample collected. Suction clearance and microdebrider decreased the amount of the recovered fungal mucin. Studies observed that some patients with AFRS clinical symptoms did not give any history of allergies. This observation led to further research in pathogenesis of AFRS. Ponikau et al proposed an alternative theory, which demonstrated ubiquitous presence of fungi within the nose and paranasal sinuses in 93% of patients undergoing surgery for any form of CRS. 17 This study also showed that fungal-specific allergy was uncommon in these patients and concluded that most CRS is a T-cell mediated response to fungi, resulting in eosinophilic chemotaxis and activation. Collins et al proposed that AFRS is the result of a local, not systemic, hypersensitivity reaction, based on finding International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery May-June 2018 Vol 4 Issue 3 Page 697
5 fungus-specific IgE in the mucin of AFRS as well as non- AFRS patients, evidence for a local type I response entirely localized to the nose and paranasal sinuses without signs of systemic involvement. 18 Pant et al in his study demonstrated the significance of humoral immunity in the pathogenesis of AFRS. 19 He studied patients with eosinophilic mucin CRS, polypoid rhinosinusitis with or without fungal elements. He stated that elevated levels of fungal-specific IgG3, rather than total serum IgE, is more specific in diagnosing AFRS. Histopathologic findings in AFRS are critical to the diagnosis is the striking number of eosinophils. Microscopic review of mucosal specimens on haematoxylin-eosin (H&E) staining will show typical inflammatory infiltrate composed of eosinophils, lymphocytes, and plasma cells. 20 The presence of Charcot -Leyden crystals alone is not specific for AFRS, hence should not be used as a single diagnostic criterion. Other markers like major basic protein which is more specific needs further study. The mucosa will be hypertrophic and hyperplastic but should not have evidence of necrosis, giant cells, granulomas, or invasion into surrounding structures. Such findings would lend support to a diagnosis of a fungal process other than AFRS. Radiologically, computed tomography shows heterogeneous signal intensity characteristic of AFRS. Magnetic resonance imaging has a high specificity for AFRS, especially when combined with CT. 21 The high protein concentration of allergic mucin (greater than 28%) results in crosslinking and slows macromolecular motion, giving rise to T1 central hypointensity and T2 central signal void (Figure 2). Both T1 and T2 series demonstrate peripheral enhancement. Laboratory findings are also helpful in the diagnosis of AFRS. Total immunoglobulin E (IgE) levels are generally elevated, often to more than 1,000 U/mL. Mabry and colleagues demonstrated broad sensitivity to both fungal and nonfungal antigens, emphasizing that AFRS patients are generally atopic. Interestingly, the reactions were not fungal specific, although typically only one fungus was isolated from the culture. This finding could represent a common fungal epitope to explain the broad reactivity, or possibly as Schubert described the presence of a superantigen that could contribute to the nonspecific reactivity of these patients. 25 Manning's work has identified the dematiaceous fungi, namely Bipolaris, in the vast majority of cases. 26 Correct identification of the causative organism has been accompanied by the development of multimodality treatment algorithms, with surgical therapy remaining the cornerstone for this recidivistic disease. Oral corticosteroid and other medical therapies are used in the treatment of AFRS, increased cure rates and decreased recurrence, increased time to revision surgery, reduction in mucosal stage of disease, and reduced systemic IgE levels. 27 Immunotherapy has also been shown to be very efficacious in the treatment of AFRS since it was initiated in Mabry and colleagues have published results on the use of immunotherapy in AFRS, showing that treating reactivity to both fungal and nonfungal antigens resulted in elimination of nasal crusting and mucin deposits. 23,24 He also observed there was decreased need for oral steroid therapy in patients who underwent immunotherapy. Therapy is initiated 4 6 weeks after surgery and is predicated on the removal of all allergic mucin at the time of surgery to reduce the antigenic load and prevent worsening of disease. The optimal length of treatment has not yet been determined. Antifungal therapy initially started because of high rates of recurrence following surgical therapy alone but has largely debated for their efficacy since the advent of oral corticosteroids and immunotherapy. Kennedy and colleagues showed no improvement in the radiographic appearance of the disease or in symptoms in patients treated with oral terbinafine for 6 weeks. Several investigators have evaluated intranasal antifungals with mixed results. 28,29 These findings emphasize the need for further work in this area and underlie the reason why antifungal therapy is not widely employed in the treatment of AFRS. Minimally invasive endoscopic approach but complete surgical debridement of the disease with removal of polyps and marsupialisation of the involved sinuses is mandatory. Schaefer and co-workers in their study reported that an open approach is required if the disease extends to orbit or anterior cranial fossa. 30 However, in our study we have used only endoscopic approach. Due to the expansile nature of disease and destruction of bone, distorted anatomy was potentially disorienting during surgery. Involved paranasal sinus acting as epicentre of fungal mucin for the spread of disease to adjacent tissues. Systemic corticosteroids and antifungal medicines were advised during postoperative period to prevent recurrence with close follow up. Care was taken in teaching the patients for proper nasal irrigation, and avoidance of allergens. Kupferberg et al observed that in his study 19 out of 24 patients developed recurrence owing to discontinuation of steroids, and improper follow up. 31,32 Bent and Kuhn emphasized the importance of follow up to prevent recurrence of the disease. A study done by Rains et al done on 139 patients, suggested that postoperative medical treatment of recurrent AFRS may avoid the need for revision surgery. 33 The endoscopic approach has the potential advantages in being able to do under local anaesthesia, avoiding scars, provides direct access to the disease area, limits tissue damage, preserves integrity of the uninvolved mucosa, reduces morbidity, intraoperative bleeding, can be used International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery May-June 2018 Vol 4 Issue 3 Page 698
6 for post-operative suction clearance to look for retained fungal debris. In our study, with this comprehensive management 92% of patients had symptomatic improvement. None of our patients showed any complications in the form of diplopia, blindness, haemorrhage, CSF leak during follow up. CONCLUSION AFRS is a relatively new clinical entity; diagnosis requires a high index of suspicion. The Bent and Kuhn criteria are generally the most widely accepted diagnostic criteria in use today. Theories on pathogenesis include hypersensitivity and T-cell mediated reactions as well as a humoral immune response. A confirmatory diagnosis is made from characteristics of the fungal mucin, histological findings and CT scan findings. Mainstay of treatment is surgical debridement using endoscopic sinus surgery, along with a strong role for oral corticosteroids and an emerging role for IT. Comprehensive management with steroids and antifungals reduces the recurrence or need for revision surgery. Antifungals, both systemic and topical, currently have a limited role in treatment, although this area needs further study. Long term follow up is very important. Funding: No funding sources Conflict of interest: None declared Ethical approval: The study was approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee REFERENCES 1. Safirstein B. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis with obstruction of the upper respiratory tract. Chest. 1976;70: Kuhn FA, Javer AR. Allergic fungal rhinosinusitis: our experience. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1998;124(10): Katzenstein AL, Sale SR, Greenberger PA. Allergic Apergillus sinusitis: a newly recognized form of sinusitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1983;72: Robson JM, Hogan PG, Benn RA, Gatenby PA. Allergic fungal sinusitis presenting as a paranasal sinus tumour. Aust N Z J Med. 1989;19: Ence BK, Gourley DS, Jorgensen NL, Shagets FW, Parsons DS. Allergic Fungal Sinusitis. Am J Rhinol 1990;4: Cody DT II, Neel HB III, Ferreiro JA, Roberts GD. Allergic fungal sinusitis: the Mayo clinic experience. Laryngoscope 1994;104: Morpeth JF, Rupp NT, Dolen WK, Bent JP, Kuhn FA. Fungal sinusitis: an update. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 1996;76: Bent JP III, Kuhn FA. Diagnosis of allergic fungal sinusitis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1994;111: Zinreich SJ, Kennedy DW, Malat J, Curtin HD, Epstein JI, Huff LC et.al. Fungal sinusitis: diagnosis with CT and MR imaging. Radiology. 1988;169: Manning SC, Mekel M, Kriesel K, Vuitch F, Marple B. Computed Tomography and Magnetic Resonance diagnosis of allergic fungal sinusitis. Laryngoscope. 1997;107: Mukherji SK, Tableueroa RE, Ginsberg LE, Zeifer BA, Marple BF, Alley JG et.al. Allergic fungal sinusitis: CT findings. Radiology. 1998;207: Bent JP III, Kuhn FA. Allergic fungal sinusitis/polyposis. Allergic Asthma Proc. 1996;17: Bent JP III, Kuhn FA. Antifungal activity against Allergic fungal sinusitis organisms. Laryngoscope. 1996;106: Berretini S, Carabelli A, Papini M, Cianca E, Sellari FS. Allergic fungal rhinosinusitis: is this rare disease an allergy or infection? Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 1996;16: deshazo RD, Swain RE. Diagnostic criteria for allergic fungal sinusitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1995;96: deshazo RD, O Brien M, Chapin K, Soto AM, Swain R, Lyons M, et.al. Criteria for the diagnosis of sinus mycetoma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1997;99: Ponikau JU, Sherris DA, Kern EB, et al. The diagnosis and incidence of allergic fungal sinusitis. Mayo Clin Proc. 1999;74(9): Collins M, Nair S, Smith W, Kette F, Gillis D, Wormald PJ. Role of local immunoglobulin E production in the pathophysiology of noninvasive fungal sinusitis. Laryngoscope. 2004;114(7): Pant H, Kette FE, Smith WB, Wormald PJ, Macardle PJ. Fungal-specific humoral response in eosinophilic mucus chronic rhinosinusitis. Laryngoscope. 2005;115(4): Marple BF. Allergic fungal rhinosinusitis: current theories and management strategies. Laryngoscope. 2001;111(6): Zinreich SJ, Kennedy DW, Malat J, Curtin HD, Epstein JI, Huff LC, et al. Fungal sinusitis: diagnosis with CT and MR imaging. Radiology. 1988;169(2): Mabry RL, Manning SC, Mabry CS. Immunotherapy in the treatment of allergic fungal sinusitis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1997;116(1): Mabry RL, Marple BF, Folker RJ, Mabry CS. Immunotherapy for allergic fungal sinusitis: three years' experience. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1998;119(6): Mabry RL, Mabry CS. Allergic fungal sinusitis: the role of immunotherapy. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2000;33(2): Schubert MS. A superantigen hypothesis for the pathogenesis of chronic hypertrophic rhinosinusitis, International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery May-June 2018 Vol 4 Issue 3 Page 699
7 allergic fungal sinusitis, and related disorders. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2001;87(3): Manning SC, Schaefer SD, Close LG, Vuitch F. Culture-positive allergic fungal sinusitis. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1991;117(2): Kuhn FA, Javer AR. Allergic fungal rhinosinusitis: our experience. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1998;124(10): Kennedy DW, Kuhn FA, Hamilos DL, Zinreich SJ, Butler D, Warsi G, et al. Treatment of chronic rhinosinusitis with high-dose oral terbinafine: a double blind, placebo-controlled study. Laryngoscope. 2005;115(10): Stankiewicz JA, Musgrave BK, Scianna JM. Nasal amphotericin irrigation in chronic rhinosinusitis. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2008;16(1): Schaefer SD, Liu JK, Moscatello AL, Cloudwell WT. Neurosurgical implications of allergic fungal sinusitis. J Neurol. 2004;100: Kupferberf SB, Bent JP. Allergic fungal sinusitis in the pediatric population. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1996;122: Kupferberf SB, Bent JP, Kuhn FA. Prognosis for allergic fungal sinusitis. Otolarygol Head Neck Surg. 1997;117: Rains BM III, Mineck CW. Treatment of allergic fungal sinusitis with high dose iatraconazole. Am J Rhinol. 2003;17(1):1-8. Cite this article as: Suri N, Bhavya BM. Allergic fungal rhinosinusitis: an overview on pathogenesis, early diagnosis and management. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2018;4: International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery May-June 2018 Vol 4 Issue 3 Page 700
Mucin-Related Rhinosinusitis YOUSEF ALJATHLANY ORL-HNS RESIDENT
 Mucin-Related Rhinosinusitis YOUSEF ALJATHLANY ORL-HNS RESIDENT Free PPT Click to add title This PowerPoint Template has clean and neutral design that can be adapted to any content and meets various market
Mucin-Related Rhinosinusitis YOUSEF ALJATHLANY ORL-HNS RESIDENT Free PPT Click to add title This PowerPoint Template has clean and neutral design that can be adapted to any content and meets various market
Allergic Fungal Rhinosinusitis Involving Frontal Sinus: A Prospective Study comparing Surgical Modalities
 10.5005/jp-journals-10013-1141 H Verma et al ORIGINAL ARTICLE Allergic Fungal Rhinosinusitis Involving Frontal Sinus: A Prospective Study comparing Surgical Modalities H Verma, Rijuneeta, AK Gupta, A Chakrabarti
10.5005/jp-journals-10013-1141 H Verma et al ORIGINAL ARTICLE Allergic Fungal Rhinosinusitis Involving Frontal Sinus: A Prospective Study comparing Surgical Modalities H Verma, Rijuneeta, AK Gupta, A Chakrabarti
Controversies surrounding categorization of fungal sinusitis
 Controversies surrounding categorization of fungal sinusitis Arunaloke Chakrabarti Professor,Department of Medical Microbiology Center for Advanced Research in Medical Mycology Postgraduate Institute of
Controversies surrounding categorization of fungal sinusitis Arunaloke Chakrabarti Professor,Department of Medical Microbiology Center for Advanced Research in Medical Mycology Postgraduate Institute of
Allergic fungal rhinosinusitis: A review of clinical manifestations and current treatment strategies
 Medical Mycology September 2006, 44, S277 S284 Allergic fungal rhinosinusitis: A review of clinical manifestations and current treatment strategies BRADLEY F. MARPLE Department of Otolaryngology, Head
Medical Mycology September 2006, 44, S277 S284 Allergic fungal rhinosinusitis: A review of clinical manifestations and current treatment strategies BRADLEY F. MARPLE Department of Otolaryngology, Head
Fungal ball.. Clinical and radiological features DR. AHMED ALTUWAIJRI 1/5/2017
 Fungal ball.. Clinical and radiological features DR. AHMED ALTUWAIJRI 1/5/2017 Fungal Rhinosinusitis (FRS) Rhinosinusitis, is a common disorder affecting approximately 20% of the population at some time
Fungal ball.. Clinical and radiological features DR. AHMED ALTUWAIJRI 1/5/2017 Fungal Rhinosinusitis (FRS) Rhinosinusitis, is a common disorder affecting approximately 20% of the population at some time
Rhinosinusitis: Current Concepts. Frederick S. Rosen, MD Matthew Ryan, MD
 Rhinosinusitis: Current Concepts Frederick S. Rosen, MD Matthew Ryan, MD Introduction 2 Introduction The medical condition most commonly reported by US Census Department Major Factors: Facial pain/pressure,
Rhinosinusitis: Current Concepts Frederick S. Rosen, MD Matthew Ryan, MD Introduction 2 Introduction The medical condition most commonly reported by US Census Department Major Factors: Facial pain/pressure,
Allergic Fungal Rhinosinusitis
 10.5005/jp-journals-10013-1124 Ashok K Gupta et al ARTICLE 3 Ashok K Gupta, Nishit Shah, Mohan Kameswaran, Davinder Rai, TN Janakiram, Hemant Chopra, Ravi Nayar Arvind Soni, NK Mohindroo, C Madhu Sudana
10.5005/jp-journals-10013-1124 Ashok K Gupta et al ARTICLE 3 Ashok K Gupta, Nishit Shah, Mohan Kameswaran, Davinder Rai, TN Janakiram, Hemant Chopra, Ravi Nayar Arvind Soni, NK Mohindroo, C Madhu Sudana
Chronic Sinusitis. Acute Sinusitis. Sinusitis. Anatomy of the Paranasal Sinuses. Sinusitis. Medical Topics - Sinusitis
 1 Acute Chronic is the inflammation of the inner lining of the parnasal sinuses due to infection or non-infectious causes such as allergies or environmental pullutants. If the inflammation lasts more than
1 Acute Chronic is the inflammation of the inner lining of the parnasal sinuses due to infection or non-infectious causes such as allergies or environmental pullutants. If the inflammation lasts more than
Presentation of Invasive Fungal Rhinosinusitis in Sudanese Children: A Report of Four Cases
 Volume 13, Issue no. 2, DOI 10.18502/sjms.v13i2.2643 Production and Hosting by Knowledge E Case Report Presentation of Invasive Fungal Rhinosinusitis in Sudanese Children: A Report of Four Cases Faculty
Volume 13, Issue no. 2, DOI 10.18502/sjms.v13i2.2643 Production and Hosting by Knowledge E Case Report Presentation of Invasive Fungal Rhinosinusitis in Sudanese Children: A Report of Four Cases Faculty
Rhinosinusitis. John Ramey, MD Joseph Russell, MD
 Rhinosinusitis John Ramey, MD Joseph Russell, MD Disclosure Statement RSFH as a continuing medical education provider, accredited by the South Carolina Medical Association, it is the policy of RSFH to
Rhinosinusitis John Ramey, MD Joseph Russell, MD Disclosure Statement RSFH as a continuing medical education provider, accredited by the South Carolina Medical Association, it is the policy of RSFH to
Allergic Fungal Rhinosinusitis
 Allergic Fungal Rhinosinusitis My Published Experience 1999-2018 Prof. Surayie H Al Dousary Professor of Rhinology Rhinology research Chair Director KSU Rhinology fellowship Program Director KSU Rhinology
Allergic Fungal Rhinosinusitis My Published Experience 1999-2018 Prof. Surayie H Al Dousary Professor of Rhinology Rhinology research Chair Director KSU Rhinology fellowship Program Director KSU Rhinology
Pathologic Features of Non-Invasive Fungal Rhinosinusitis
 The Open Otorhinolaryngology Journal, 2008, 2, 7-12 7 Pathologic Features of on-invasive Fungal Rhinosinusitis Sarah E. Mowry 1, Sunita Bhuta 2 and Marilene B. Wang *,1,3 1 Division of Head and eck Surgery,
The Open Otorhinolaryngology Journal, 2008, 2, 7-12 7 Pathologic Features of on-invasive Fungal Rhinosinusitis Sarah E. Mowry 1, Sunita Bhuta 2 and Marilene B. Wang *,1,3 1 Division of Head and eck Surgery,
Allergic Fungal Rhinosinusitis in Patients with Nasal Polyposis
 Iraqi JMS Published by Al-Nahrain College of Medicine P-ISSN 1681-6579 E-ISSN 2224-4719 Email: iraqijms@colmed-alnahrain.edu.iq http://www.colmed-alnahrain.edu.iq http://www.iraqijms.net Allergic Fungal
Iraqi JMS Published by Al-Nahrain College of Medicine P-ISSN 1681-6579 E-ISSN 2224-4719 Email: iraqijms@colmed-alnahrain.edu.iq http://www.colmed-alnahrain.edu.iq http://www.iraqijms.net Allergic Fungal
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 4/ Issue 81/ Oct 08, 2015 Page 14240
 INCREASED INCIDENCE OF FUNGAL SINUSITIS IN COASTAL REGION: A CASE SERIES I. Arumugam 1, Jalagandeesh B 2, Ganesh Bala 3, Ishani Borah 4, Sandeep Jith 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: I. Arumugam, Jalagandeesh
INCREASED INCIDENCE OF FUNGAL SINUSITIS IN COASTAL REGION: A CASE SERIES I. Arumugam 1, Jalagandeesh B 2, Ganesh Bala 3, Ishani Borah 4, Sandeep Jith 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: I. Arumugam, Jalagandeesh
Rhinosinusitis: A Prospective Study
 االله الرحمن الرحيم بسم Pathological l & Radiological i l Evidences in the Pathogenesis es s of Chronic Rhinosinusitis: A Prospective Study Prof. Dr. H. ABDEL FATAH, MD A. Prof. Dr. K. NOWEAM, MD Dr. Z.
االله الرحمن الرحيم بسم Pathological l & Radiological i l Evidences in the Pathogenesis es s of Chronic Rhinosinusitis: A Prospective Study Prof. Dr. H. ABDEL FATAH, MD A. Prof. Dr. K. NOWEAM, MD Dr. Z.
Isolated sphenoid inflammatory diseases
 International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2454-5929.ijohns20183688
International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2454-5929.ijohns20183688
Conventional Sinus Surgery Vs Fess
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 7 Ver. III (July. 2017), PP 44-51 www.iosrjournals.org Conventional Sinus Surgery Vs Fess *
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 7 Ver. III (July. 2017), PP 44-51 www.iosrjournals.org Conventional Sinus Surgery Vs Fess *
Nasal Polyposis. DEPARTMENT OF ENT K.S.Hegde Medical Academy Deralakatte, Mangalore
 Nasal Polyposis DEPARTMENT OF ENT K.S.Hegde Medical Academy Deralakatte, Mangalore Def: INTRODUCTION Chronic inflammatory disease of the mucous membrane in the nose & PNS, presenting as pedunculated smooth
Nasal Polyposis DEPARTMENT OF ENT K.S.Hegde Medical Academy Deralakatte, Mangalore Def: INTRODUCTION Chronic inflammatory disease of the mucous membrane in the nose & PNS, presenting as pedunculated smooth
PRESENTATION AND MANAGEMENT OF ALLERGIC FUNGAL SINUSITIS
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE PRESENTATION AND MANAGEMENT OF ALLERGIC FUNGAL SINUSITIS Kalimullah Thahim, Mahboob Afzal Jawaid and M. Saleem Marfani ABSTRACT Objective: To assess the presentation of allergic fungal
ORIGINAL ARTICLE PRESENTATION AND MANAGEMENT OF ALLERGIC FUNGAL SINUSITIS Kalimullah Thahim, Mahboob Afzal Jawaid and M. Saleem Marfani ABSTRACT Objective: To assess the presentation of allergic fungal
Allergic fungal rhinosinusitis is observed to be. Evaluation of Diagnostic Criteria for AFRS: A Hospital Based Study. Main Article
 Main Article Evaluation of Diagnostic Criteria for AFRS: A Hospital Based Study Krishna V Chaitanya, 1 Lakshmi C Kalavathi 2 ABSTRACT Introduction Bent and Kuhn criteria are the most commonly accepted
Main Article Evaluation of Diagnostic Criteria for AFRS: A Hospital Based Study Krishna V Chaitanya, 1 Lakshmi C Kalavathi 2 ABSTRACT Introduction Bent and Kuhn criteria are the most commonly accepted
Is the Classical Classification of Aspergillosis of the Paranasal Sinuses to non invasive and invasive still valid or not?
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.24, No.3, September 2002 Is the Classical Classification of Aspergillosis of the Paranasal Sinuses to non invasive and invasive still valid or not? Abdul Aziz Ashoor (FA-HNO)*
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.24, No.3, September 2002 Is the Classical Classification of Aspergillosis of the Paranasal Sinuses to non invasive and invasive still valid or not? Abdul Aziz Ashoor (FA-HNO)*
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Computed Tomographic Findings in Patients With Invasive Fungal Sinusitis
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Computed Tomographic Findings in Patients With Invasive Fungal Sinusitis John M. DelGaudio, MD; Ron E. Swain Jr, MD; Todd T. Kingdom, MD; Susan Muller, DMD; Patricia A. Hudgins, MD Objective:
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Computed Tomographic Findings in Patients With Invasive Fungal Sinusitis John M. DelGaudio, MD; Ron E. Swain Jr, MD; Todd T. Kingdom, MD; Susan Muller, DMD; Patricia A. Hudgins, MD Objective:
Endoscopic Management Of A Giant Ethmoid Mucocele
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Volume 6 Number 1 S Ceylan, F Bora Citation S Ceylan, F Bora.. The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology. 2006 Volume 6 Number 1. Abstract We present
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Volume 6 Number 1 S Ceylan, F Bora Citation S Ceylan, F Bora.. The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology. 2006 Volume 6 Number 1. Abstract We present
Research Article Allergic Fungal Rhinosinusitis: A Study in a Tertiary Care Hospital in India
 Allergy Volume 2016, Article ID 7698173, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/7698173 Research Article Allergic Fungal Rhinosinusitis: A Study in a Tertiary Care Hospital in India Ravinder Kaur, 1,2
Allergy Volume 2016, Article ID 7698173, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/7698173 Research Article Allergic Fungal Rhinosinusitis: A Study in a Tertiary Care Hospital in India Ravinder Kaur, 1,2
MANAGEMENT OF RHINOSINUSITIS IN ADULTS IN PRIMARY CARE
 PROFESSOR DR SALINA HUSAIN DEPUTY HEAD DEPARTMENT OF OTORHINOLARYNGOLOGY-HEAD NECK SURGERY UKM MEDICAL CENTRE MANAGEMENT OF RHINOSINUSITIS IN ADULTS IN PRIMARY CARE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES ON MANAGEMENT
PROFESSOR DR SALINA HUSAIN DEPUTY HEAD DEPARTMENT OF OTORHINOLARYNGOLOGY-HEAD NECK SURGERY UKM MEDICAL CENTRE MANAGEMENT OF RHINOSINUSITIS IN ADULTS IN PRIMARY CARE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES ON MANAGEMENT
Retrospective Analysis of Patients with Allergy Sinusitis
 Original article: Retrospective Analysis of Patients with Allergy Sinusitis G.S. Thalor Senior Specialist (MS) (department of Oto Rhino Laryngology), Govt. S.K. Hospital, Sikar, Rajasthan, India. Corresponding
Original article: Retrospective Analysis of Patients with Allergy Sinusitis G.S. Thalor Senior Specialist (MS) (department of Oto Rhino Laryngology), Govt. S.K. Hospital, Sikar, Rajasthan, India. Corresponding
Sphenoid rhinosinusitis associated with abducens nerve palsy Case report
 Romanian Journal of Rhinology, Volume 8, No. 30, April-June 2018 CASE REPORT Sphenoid rhinosinusitis associated with abducens nerve palsy Case report Lucian Lapusneanu 1, Marlena Radulescu 1, Florin Ghita
Romanian Journal of Rhinology, Volume 8, No. 30, April-June 2018 CASE REPORT Sphenoid rhinosinusitis associated with abducens nerve palsy Case report Lucian Lapusneanu 1, Marlena Radulescu 1, Florin Ghita
Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery
 WHAT IS FUNCTIONAL ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY (FESS)? The nasal telescope has greatly changes the evaluation and treatment of rhino-sinusitis. This instrument, which provides a view of the structures in
WHAT IS FUNCTIONAL ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY (FESS)? The nasal telescope has greatly changes the evaluation and treatment of rhino-sinusitis. This instrument, which provides a view of the structures in
Histopathology of Nasal Masses
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Histopathology of Nasal Masses 1 Hemant Chopra, 2 Kapil Dua, 3 Neha Chopra, 4 Vikrant Mittal AIJCR Histopathology of Nasal Masses 1 Professor and Head, Dayanand Medical College, Ludhiana,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Histopathology of Nasal Masses 1 Hemant Chopra, 2 Kapil Dua, 3 Neha Chopra, 4 Vikrant Mittal AIJCR Histopathology of Nasal Masses 1 Professor and Head, Dayanand Medical College, Ludhiana,
Mucocele of paranasal sinuses
 From the SelectedWorks of Balasubramanian Thiagarajan March 7, 2012 Mucocele of paranasal sinuses Balasubramanian Thiagarajan Available at: https://works.bepress.com/drtbalu/57/ Mucoceles of paranasal
From the SelectedWorks of Balasubramanian Thiagarajan March 7, 2012 Mucocele of paranasal sinuses Balasubramanian Thiagarajan Available at: https://works.bepress.com/drtbalu/57/ Mucoceles of paranasal
Diagnostic Accuracy in Sinus Fungus Balls: CT Scan and Operative Findings
 tg.jar 200? _A:\ : Di3LiS/;-JESS Diagnostic Accuracy in Sinus Fungus Balls: CT Scan and Operative Findings Hun-Jong Dhong, M.D., Jae-Yun Jung, M.D., and Joo Hyun Park, M.D. ABSTRACT A fungus ball may be
tg.jar 200? _A:\ : Di3LiS/;-JESS Diagnostic Accuracy in Sinus Fungus Balls: CT Scan and Operative Findings Hun-Jong Dhong, M.D., Jae-Yun Jung, M.D., and Joo Hyun Park, M.D. ABSTRACT A fungus ball may be
Fungal Sinusitis: A Ten-Year Experience at King Abdulaziz University Hospital
 JKAU: Med. Sci., Vol. 20 No. 3, pp: 29-41 (2013 A.D. / 1434 A.H.) DOI: 10.4197/Med. 20-3.3 Fungal Sinusitis: A Ten-Year Experience at King Abdulaziz University Hospital Khalid B. Al-Ghamdi, MD, Almoaidbellah
JKAU: Med. Sci., Vol. 20 No. 3, pp: 29-41 (2013 A.D. / 1434 A.H.) DOI: 10.4197/Med. 20-3.3 Fungal Sinusitis: A Ten-Year Experience at King Abdulaziz University Hospital Khalid B. Al-Ghamdi, MD, Almoaidbellah
Disclaimers. Topical Therapy. The Problem. Topical Therapy for Chronic Rhinosinusitis No Disclosures
 Topical Therapy for Chronic Rhinosinusitis No Disclosures Disclaimers Off-label use of multiple steroid and antibiotic medications Large talk, limited time Steven D. Pletcher MD University of California,
Topical Therapy for Chronic Rhinosinusitis No Disclosures Disclaimers Off-label use of multiple steroid and antibiotic medications Large talk, limited time Steven D. Pletcher MD University of California,
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Medical technology guidance SCOPE The XprESS Multi-Sinus Dilation System for the treatment of 1 Technology 1.1 Description of the technology The XprESS
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Medical technology guidance SCOPE The XprESS Multi-Sinus Dilation System for the treatment of 1 Technology 1.1 Description of the technology The XprESS
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines/considerations SINUS & MAXILLOFACIAL AREA CT 70486, 70487, 70488
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines/considerations SINUS & MAXILLOFACIAL AREA CT 70486, 70487, 70488 Date: September 1997 Page 1 of 5 LIMITED OR LOCALIZED FOLLOW UP - SINUS CT 76380 Guideline
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines/considerations SINUS & MAXILLOFACIAL AREA CT 70486, 70487, 70488 Date: September 1997 Page 1 of 5 LIMITED OR LOCALIZED FOLLOW UP - SINUS CT 76380 Guideline
ISSN: Volume 4 Issue CHOLESTEROL GRANULOMA: AN UNCOMMON CLINICAL ENTITY OF THE MAXILLARY SINUS
 ISSN: 2250-0359 Volume 4 Issue 4 2014 CHOLESTEROL GRANULOMA: AN UNCOMMON CLINICAL ENTITY OF THE MAXILLARY SINUS Sunita Singh Sonia Chhabra Pansi Gupta Priya Malik Pt B.D. Sharma PGIMS, Rohtak, Haryana
ISSN: 2250-0359 Volume 4 Issue 4 2014 CHOLESTEROL GRANULOMA: AN UNCOMMON CLINICAL ENTITY OF THE MAXILLARY SINUS Sunita Singh Sonia Chhabra Pansi Gupta Priya Malik Pt B.D. Sharma PGIMS, Rohtak, Haryana
Case Report Chronic Invasive Nongranulomatous Fungal Rhinosinusitis in Immunocompetent Individuals
 Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2016, Article ID 6854121, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6854121 Case Report Chronic Invasive Nongranulomatous Fungal Rhinosinusitis in Immunocompetent Individuals
Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2016, Article ID 6854121, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6854121 Case Report Chronic Invasive Nongranulomatous Fungal Rhinosinusitis in Immunocompetent Individuals
MANAGEMENT OF RHINOSINUSITIS IN ADOLESCENTS AND ADULTS
 MANAGEMENT OF RHINOSINUSITIS IN ADOLESCENTS AND ADULTS Ministry of Health Malaysia Malaysian Society of Otorhinolaryngologist - Head & Neck Surgeons (MS)-HNS) Academy of Medicine Malaysia KEY MESSAGES
MANAGEMENT OF RHINOSINUSITIS IN ADOLESCENTS AND ADULTS Ministry of Health Malaysia Malaysian Society of Otorhinolaryngologist - Head & Neck Surgeons (MS)-HNS) Academy of Medicine Malaysia KEY MESSAGES
Advances in the Surgical Management of Chronic Rhinosinusitis
 Rhinitis and Sinusitis dvances in the Surgical Management of Chronic Rhinosinusitis Erin D. Wright, MDCM, MEd, FRCSC; Saul Frenkiel, MDCM, FRCSC bstract The surgical management of chronic rhinosinusitis
Rhinitis and Sinusitis dvances in the Surgical Management of Chronic Rhinosinusitis Erin D. Wright, MDCM, MEd, FRCSC; Saul Frenkiel, MDCM, FRCSC bstract The surgical management of chronic rhinosinusitis
Prevalence of Fungal Allergy in Patients with Allergic Rhinosinusitis
 Prevalence of Fungal Allergy in Patients with Allergic Rhinosinusitis Kyle Kennedy, M.D. Karen Calhoun,, M.D. June 5, 1999 Hypothesis Subset of patients with signs and symptoms of allergic rhinosinusitis
Prevalence of Fungal Allergy in Patients with Allergic Rhinosinusitis Kyle Kennedy, M.D. Karen Calhoun,, M.D. June 5, 1999 Hypothesis Subset of patients with signs and symptoms of allergic rhinosinusitis
Outline. Sinonasal Endoscopic Surgery 6/1/2011
 Kathleen Kthl T. Montone, M.D. Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Pennsylvania Outline Evaluation of sinonasal ethmoidectomy specimens. Overview of Sinonasal fungal diseases
Kathleen Kthl T. Montone, M.D. Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Pennsylvania Outline Evaluation of sinonasal ethmoidectomy specimens. Overview of Sinonasal fungal diseases
A comprehensive study on complications of endoscopic sinus surgery
 International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Shyras JAD et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2017 Jul;3(3):472-477 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937
International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Shyras JAD et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2017 Jul;3(3):472-477 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937
International Journal of Research and Review E-ISSN: ; P-ISSN:
 International Journal of Research and Review www.ijrrjournal.com E-ISSN: 2349-9788; P-ISSN: 2454-2237 Original Research Article Incidence of Fungal Rhinosinusitis in Bihar and Its Management Shelendra
International Journal of Research and Review www.ijrrjournal.com E-ISSN: 2349-9788; P-ISSN: 2454-2237 Original Research Article Incidence of Fungal Rhinosinusitis in Bihar and Its Management Shelendra
FRONTAL SINUPLASTY P R E P A R E D A N D P R E S E N T E D B Y : D R. Y A H Y A F A G E E H R 4 16/ 12/ 2013
 FRONTAL SINUPLASTY P R E P A R E D A N D P R E S E N T E D B Y : D R. Y A H Y A F A G E E H R 4 16/ 12/ 2013 ANATOMY: FRONTAL SINUS Not present at birth Starts developing at 4 years Radiographically visualized
FRONTAL SINUPLASTY P R E P A R E D A N D P R E S E N T E D B Y : D R. Y A H Y A F A G E E H R 4 16/ 12/ 2013 ANATOMY: FRONTAL SINUS Not present at birth Starts developing at 4 years Radiographically visualized
Recovery of non-invasive Aspergillus sinusitis by endoscopic sinus surgery*
 Rhinology, 35, 84 88, 1997 Recovery of non-invasive Aspergillus sinusitis by endoscopic sinus surgery* Sheen-Yie Fang Department of Otolaryngology, Faculty of Medicine, National Cheng Kung University,
Rhinology, 35, 84 88, 1997 Recovery of non-invasive Aspergillus sinusitis by endoscopic sinus surgery* Sheen-Yie Fang Department of Otolaryngology, Faculty of Medicine, National Cheng Kung University,
Reasons for Failure and Surgical Revisions. Stil Kountakis, MD, PhD Professor and Chief, Division of Rhinology
 Reasons for Failure and Surgical Revisions Stil Kountakis, MD, PhD Professor and Chief, Division of Rhinology Medical College of Georgia of Georgia Regents University Department of Otolaryngology / Head
Reasons for Failure and Surgical Revisions Stil Kountakis, MD, PhD Professor and Chief, Division of Rhinology Medical College of Georgia of Georgia Regents University Department of Otolaryngology / Head
Medical Mycology Case Reports
 Medical Mycology Case Reports 1 (2012) 107 111 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Medical Mycology Case Reports journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/mmcr Granulomatous invasive fungal
Medical Mycology Case Reports 1 (2012) 107 111 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Medical Mycology Case Reports journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/mmcr Granulomatous invasive fungal
EVALUATION OF PATIENT'S OUTCOME AFTER ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY
 Basrah Journal Of Surgery Bas J Surg, September, 16, 2010 EVALUATION OF PATIENT'S OUTCOME AFTER ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY Hiwa A Abdulkareem MB.ChB, FICMS, CABS(ENT); Teaching Hospital; University of Sulaimania.
Basrah Journal Of Surgery Bas J Surg, September, 16, 2010 EVALUATION OF PATIENT'S OUTCOME AFTER ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY Hiwa A Abdulkareem MB.ChB, FICMS, CABS(ENT); Teaching Hospital; University of Sulaimania.
Dr.Adel A. Al Ibraheem
 Rhinology Chair Weekly Activity Dr.Adel A. Al Ibraheem www.rhinologychair.org conference@rhinologychair.org Rhinology Chair Introduction: It is important to classify and stage nasal polyposis. ( decide
Rhinology Chair Weekly Activity Dr.Adel A. Al Ibraheem www.rhinologychair.org conference@rhinologychair.org Rhinology Chair Introduction: It is important to classify and stage nasal polyposis. ( decide
Introduction. Ophthalmic manifestations can result from a myriad of Non Sinogenic and Sinogenic Disease :
 Ophthalmic Manifestations of Paranasal Sinus Disease; A Clinical Grading System Surayie Al Dousary, MD Associate Professor Director Rhinology Research Chair & Fatma Al Anazy, MD Associate Professor Rhinology
Ophthalmic Manifestations of Paranasal Sinus Disease; A Clinical Grading System Surayie Al Dousary, MD Associate Professor Director Rhinology Research Chair & Fatma Al Anazy, MD Associate Professor Rhinology
Orbital cellulitis. Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1992, 9,
 Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1992, 9, 143-148 Orbital cellulitis D. P. MARTIN-HIRSCH, S. HABASHI, A. H. HINTON & B. KOTECHA University Department of ENT Surgery, Manchester Royal Infirmary, Manchester
Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1992, 9, 143-148 Orbital cellulitis D. P. MARTIN-HIRSCH, S. HABASHI, A. H. HINTON & B. KOTECHA University Department of ENT Surgery, Manchester Royal Infirmary, Manchester
Clinical study of fungal sinusitis
 International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Waghray J. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 28 Sep;4():7-32 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 24-929 eissn 24-937 Original Research
International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Waghray J. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 28 Sep;4():7-32 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 24-929 eissn 24-937 Original Research
Actinomycosis and aspergillosis in the nose of a diabetic: A case report
 Volume 2 Issue 3 2012 ISSN 2250-0359 Actinomycosis and aspergillosis in the nose of a diabetic: A case report 1 Meenu Khurana Cherian 1*, Rajarajeswari 2 1 Department of ENT, Gulf Medical College Hospital
Volume 2 Issue 3 2012 ISSN 2250-0359 Actinomycosis and aspergillosis in the nose of a diabetic: A case report 1 Meenu Khurana Cherian 1*, Rajarajeswari 2 1 Department of ENT, Gulf Medical College Hospital
Orbital cellulitis. Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1992, 9,
 Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1992, 9, 143-148 Orbital cellulitis D. P. MARTIN-HIRSCH, S. HABASHI, A. H. HINTON & B. KOTECHA University Department of ENT Surgery, Manchester Royal Infirmary, Manchester
Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1992, 9, 143-148 Orbital cellulitis D. P. MARTIN-HIRSCH, S. HABASHI, A. H. HINTON & B. KOTECHA University Department of ENT Surgery, Manchester Royal Infirmary, Manchester
Variation in frontal cells in relation to chronic frontal sinusitis
 International Journal of Current Research in Medical Sciences ISSN: 244-71 P-ISJN: A472-04, E -ISJN: A472-01 www.ijcrims.com Original Research Article Volume, Issue 1-2019 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.22192/ijcrms.2019.0.01.00
International Journal of Current Research in Medical Sciences ISSN: 244-71 P-ISJN: A472-04, E -ISJN: A472-01 www.ijcrims.com Original Research Article Volume, Issue 1-2019 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.22192/ijcrms.2019.0.01.00
Clinical and imagistic correlations in the inflammatory pathology of nasosinusal cavities
 Romanian Journal of Rhinology, Volume 8, No. 29, January-March 2018 ORIGINAL STUDY DOI: 10.2478/rjr-2018-0003 Clinical and imagistic correlations in the inflammatory pathology of nasosinusal cavities Emilia
Romanian Journal of Rhinology, Volume 8, No. 29, January-March 2018 ORIGINAL STUDY DOI: 10.2478/rjr-2018-0003 Clinical and imagistic correlations in the inflammatory pathology of nasosinusal cavities Emilia
Pathophysiology and Etiology
 Sinusitis Pathophysiology and Etiology Sinusitis is inflammation of the mucosa of one or more sinuses. It can be either acute chronic. Chronic sinusitis is diagnosed if symptoms are present for more than
Sinusitis Pathophysiology and Etiology Sinusitis is inflammation of the mucosa of one or more sinuses. It can be either acute chronic. Chronic sinusitis is diagnosed if symptoms are present for more than
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 07 Page July 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i7.59 A Study of Allergic Fungal Rhinosinusitis
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i7.59 A Study of Allergic Fungal Rhinosinusitis
Chapter Five. 1 of 8 11/3/2008 2:52 PM.
 1 of 8 11/3/2008 2:52 PM Email : myousefmian@hotmail.com Chapter Five FRONT COVER Introduction Acknowledgement CHAPTERS Chapter One Chapter Two Chapter Three Chapter Four Chapter Five Chapter Six Chapter
1 of 8 11/3/2008 2:52 PM Email : myousefmian@hotmail.com Chapter Five FRONT COVER Introduction Acknowledgement CHAPTERS Chapter One Chapter Two Chapter Three Chapter Four Chapter Five Chapter Six Chapter
Chronic Rhinosinusitis-Treatment
 Chronic Rhinosinusitis-Treatment INFECTION INFLAMMATION Predisposing Factors Anatomical variations Allergic rhinitis Acute sinusitis Immune deficiency Rhinosinusitis Non-allergic rhinitis Chronic sinusitis
Chronic Rhinosinusitis-Treatment INFECTION INFLAMMATION Predisposing Factors Anatomical variations Allergic rhinitis Acute sinusitis Immune deficiency Rhinosinusitis Non-allergic rhinitis Chronic sinusitis
A Study of Anatomical Variations in Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis.
 DOI: 10.2127/aimdr.201..2.EN1 Original Article ISSN (O):239-222; ISSN (P):239-21 A Study of Anatomical Variations in Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Smruti Swain 1 1 Associate Professor, Department
DOI: 10.2127/aimdr.201..2.EN1 Original Article ISSN (O):239-222; ISSN (P):239-21 A Study of Anatomical Variations in Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Smruti Swain 1 1 Associate Professor, Department
The prevalence of positive fungal cultures in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis in a high altitude region of Iran
 Iranian Journal of Otorhinolaryngology No.1, Vol.24, Serial No.66, Winter-2012 Original Article The prevalence of positive fungal cultures in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis in a high altitude region
Iranian Journal of Otorhinolaryngology No.1, Vol.24, Serial No.66, Winter-2012 Original Article The prevalence of positive fungal cultures in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis in a high altitude region
Recent advances in diagnosis and management of ABPA. Arindam SR(Pulmonary Medicine)
 Recent advances in diagnosis and management of ABPA Arindam SR(Pulmonary Medicine) Conventional diagnostic criteria for ABPA Primary Episodic bronchial obstruction (asthma) Peripheral blood eosinophilia
Recent advances in diagnosis and management of ABPA Arindam SR(Pulmonary Medicine) Conventional diagnostic criteria for ABPA Primary Episodic bronchial obstruction (asthma) Peripheral blood eosinophilia
RoleofAllergyinNasalPolyposis. Role of Allergy in Nasal Polyposis
 Global Journal of Medical Research: J Dentistry & Otolaryngology Volume 17 Issue 1 Version 1.0 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc. (USA) Online
Global Journal of Medical Research: J Dentistry & Otolaryngology Volume 17 Issue 1 Version 1.0 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc. (USA) Online
Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery (FESS)
 Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery (FESS) Last Review Date: December 12, 2017 Number: MG.MM.SU.56C2 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or
Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery (FESS) Last Review Date: December 12, 2017 Number: MG.MM.SU.56C2 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or
Allergic fungal rhinosinusitis: detection of fungal DNA in sinus aspirate using polymerase chain reaction
 1- Allergic fungal rhinosinusitis: detection of fungal DNA in sinus aspirate using polymerase chain reaction Abstract Objective: This study investigated allergic fungal rhinosinusitis cases, and aimed
1- Allergic fungal rhinosinusitis: detection of fungal DNA in sinus aspirate using polymerase chain reaction Abstract Objective: This study investigated allergic fungal rhinosinusitis cases, and aimed
Pott s Puffy Tumor. Shahad Almohanna 15/1/2018
 Pott s Puffy Tumor Shahad Almohanna R2 15/1/2018 Definition First described in 1760 by Sir Percival Pott. s he originally suggested that trauma of the frontal bone was causative for this lesion, but later,
Pott s Puffy Tumor Shahad Almohanna R2 15/1/2018 Definition First described in 1760 by Sir Percival Pott. s he originally suggested that trauma of the frontal bone was causative for this lesion, but later,
Allergic fungal rhinosinusitis a new staging system*
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Rhinology 49: 318-323, 2011 Allergic fungal rhinosinusitis a new staging system* Carl M. Philpott 1,2, Allan Clark 2, Amin R. Javer 1 1 St Paul s Sinus Centre, Vancouver, British
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Rhinology 49: 318-323, 2011 Allergic fungal rhinosinusitis a new staging system* Carl M. Philpott 1,2, Allan Clark 2, Amin R. Javer 1 1 St Paul s Sinus Centre, Vancouver, British
Signal void and pseudo-pneumatized sinus in fungal rhinosinusitis Case report
 Romanian Journal of Rhinology, Vol. 7, No. 28, October - December 2017 Alexis Vuzitas 1,2, Marian Petrica 1, Claudiu Manea 1,2,3 1 ENT&HNS Department, Sfanta Maria Hospital, Bucharest, Romania 2 Carol
Romanian Journal of Rhinology, Vol. 7, No. 28, October - December 2017 Alexis Vuzitas 1,2, Marian Petrica 1, Claudiu Manea 1,2,3 1 ENT&HNS Department, Sfanta Maria Hospital, Bucharest, Romania 2 Carol
Cholesterol granuloma of the jaws: report of two cases
 Cholesterol granuloma of the jaws: report of two cases Pages with reference to book, From 15 To 17 Alper Alkan, Osman Etoz ( Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Erciyes University, Faculty of
Cholesterol granuloma of the jaws: report of two cases Pages with reference to book, From 15 To 17 Alper Alkan, Osman Etoz ( Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Erciyes University, Faculty of
CHRONIC RHINOSINUSITIS IN ADULTS
 CHRONIC RHINOSINUSITIS IN ADULTS SCOPE OF THE PRACTICE GUIDELINE This clinical practice guideline is for use by the Philippine Society of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery. It covers the diagnosis and
CHRONIC RHINOSINUSITIS IN ADULTS SCOPE OF THE PRACTICE GUIDELINE This clinical practice guideline is for use by the Philippine Society of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery. It covers the diagnosis and
Malignant growth Maxilla management an analysis
 ISSN: 2250-0359 Volume 3 Issue 2 2013 Malignant growth Maxilla management an analysis *Balasubramanian Thiagarajan *Geetha Ramamoorthy *Stanley Medical College Abstract: Malignant tumors involving maxilla
ISSN: 2250-0359 Volume 3 Issue 2 2013 Malignant growth Maxilla management an analysis *Balasubramanian Thiagarajan *Geetha Ramamoorthy *Stanley Medical College Abstract: Malignant tumors involving maxilla
Middleton Chapter 43 (pages ) Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyps Prepared by: Malika Gupta, MD
 FIT Board Review Corner December 2017 Welcome to the FIT Board Review Corner, prepared by Amar Dixit, MD, and Christin L. Deal, MD, senior and junior representatives of ACAAI's Fellows-In- Training (FITs)
FIT Board Review Corner December 2017 Welcome to the FIT Board Review Corner, prepared by Amar Dixit, MD, and Christin L. Deal, MD, senior and junior representatives of ACAAI's Fellows-In- Training (FITs)
OSTEITIS IN CRS. Rhinology Chair Meeting presented by Amal Binhazza a
 OSTEITIS IN CRS Rhinology Chair Meeting presented by Amal Binhazza a ROAD MAP Definition. pathophysiology. Diagnosis. Grading systems. Clinical implications. Management. OSTEITIS Presence of new bone formation,
OSTEITIS IN CRS Rhinology Chair Meeting presented by Amal Binhazza a ROAD MAP Definition. pathophysiology. Diagnosis. Grading systems. Clinical implications. Management. OSTEITIS Presence of new bone formation,
The Nose and Sinuses. Ophir Ilan, MD, PhD Department of Otolaryngology/Head&Neck surgery Hadassah University Hospital
 The Nose and Sinuses Ophir Ilan, MD, PhD Department of Otolaryngology/Head&Neck surgery Hadassah University Hospital Nasal Mucociliary System Function of the Nasal Mucosa warming and humidifying the
The Nose and Sinuses Ophir Ilan, MD, PhD Department of Otolaryngology/Head&Neck surgery Hadassah University Hospital Nasal Mucociliary System Function of the Nasal Mucosa warming and humidifying the
Destructive Giant Maxillary Sinus Mucocele: A Case Report
 Destructive Giant Maxillary Sinus Mucocele: A Vahit Mutlu 1, Ozgur Yoruk 1, Ozalkan Ozkan 2 1 Atatürk University Faculty of Medicine, Department of Ears, Nose and Throat, Erzurum, Turkey 2 Erzincan University
Destructive Giant Maxillary Sinus Mucocele: A Vahit Mutlu 1, Ozgur Yoruk 1, Ozalkan Ozkan 2 1 Atatürk University Faculty of Medicine, Department of Ears, Nose and Throat, Erzurum, Turkey 2 Erzincan University
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 10 Page October 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-45 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/1.18535/jmscr/v5i1.116 Nasal Polyps- Causes and Associated Symptoms-
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-45 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/1.18535/jmscr/v5i1.116 Nasal Polyps- Causes and Associated Symptoms-
Diagnostic And Therapeutic Challenges in IgG4-Related disease in the Sphenoid Sinus
 Diagnostic And Therapeutic Challenges in IgG4-Related disease in the Sphenoid Sinus Omar Abu Suliman, MBBS, SB-ORL Senior Registrar, otolaryngology Head & neck surgery King Abdullah Medical City, Makkah,
Diagnostic And Therapeutic Challenges in IgG4-Related disease in the Sphenoid Sinus Omar Abu Suliman, MBBS, SB-ORL Senior Registrar, otolaryngology Head & neck surgery King Abdullah Medical City, Makkah,
Invasive Fungal Rhinosinusitis: A 15-Year Experience With 29 Patients
 The Laryngoscope VC 2013 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Invasive Fungal Rhinosinusitis: A 15-Year Experience With 29 Patients Marcus M. Monroe, MD; Max McLean, BA;
The Laryngoscope VC 2013 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Invasive Fungal Rhinosinusitis: A 15-Year Experience With 29 Patients Marcus M. Monroe, MD; Max McLean, BA;
Concepts in Rhinosinusitis. Nick Jones University of Nottingham
 Concepts in Rhinosinusitis Nick Jones University of Nottingham Definition of rhinosinusitis Very broad and is based on clinical symptoms, CT and endoscopy NOT on pathology Definition of rhinosinusitis
Concepts in Rhinosinusitis Nick Jones University of Nottingham Definition of rhinosinusitis Very broad and is based on clinical symptoms, CT and endoscopy NOT on pathology Definition of rhinosinusitis
Consumer summary. Endoscopic modified Lothrop procedure for the. treatment of chronic frontal sinusitis
 ASERNIP S Australian Safety and Efficacy Register of New Interventional Procedures Surgical Consumer summary Endoscopic modified Lothrop procedure for the treatment of chronic frontal sinusitis (The report
ASERNIP S Australian Safety and Efficacy Register of New Interventional Procedures Surgical Consumer summary Endoscopic modified Lothrop procedure for the treatment of chronic frontal sinusitis (The report
Chronic Invasive Fungal Granuloma A Diagnostic Dilemma in an Immunocompetent Host
 Case Report Iranian Journal of Otorhinolaryngology, Vol.28(1), Serial No.84, Jan 2016 Chronic Invasive Fungal Granuloma A Diagnostic Dilemma in an Immunocompetent Host Shrinivas S. Chavan 1, K.S. Bhople
Case Report Iranian Journal of Otorhinolaryngology, Vol.28(1), Serial No.84, Jan 2016 Chronic Invasive Fungal Granuloma A Diagnostic Dilemma in an Immunocompetent Host Shrinivas S. Chavan 1, K.S. Bhople
Imaging of the Paranasal Sinuses
 14. Sommerschule Imaging of the Paranasal Sinuses Bettlach 24.08.2018 Christoph Schlegel Conventional Radiology NNH-Status: okzipito-frontal: frontal sinus, anterior ethmoid okzipito-nasal : maxillary
14. Sommerschule Imaging of the Paranasal Sinuses Bettlach 24.08.2018 Christoph Schlegel Conventional Radiology NNH-Status: okzipito-frontal: frontal sinus, anterior ethmoid okzipito-nasal : maxillary
Case Report IgG4-Related Nasal Pseudotumor
 Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2015, Article ID 749890, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/749890 Case Report IgG4-Related Nasal Pseudotumor L. K. Døsen, 1 P. Jebsen, 2 B. Dingsør, 3 and R.
Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2015, Article ID 749890, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/749890 Case Report IgG4-Related Nasal Pseudotumor L. K. Døsen, 1 P. Jebsen, 2 B. Dingsør, 3 and R.
Mr Glenn Watson M.B., B.S., B.Sc. (Hons), F.R.A.C.S. Ear, Nose and Throat Head and Neck Surgeon
 Mr Glenn Watson M.B., B.S., B.Sc. (Hons), F.R.A.C.S. Ear, Nose and Throat Head and Neck Surgeon FUNCTIONAL ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY A guide for Mr Watson s patients During your consultation with Mr Watson,
Mr Glenn Watson M.B., B.S., B.Sc. (Hons), F.R.A.C.S. Ear, Nose and Throat Head and Neck Surgeon FUNCTIONAL ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY A guide for Mr Watson s patients During your consultation with Mr Watson,
ENT Infections. Case 1. Diagnosis. Marlene L. Durand, M.D. Mass. General Hospital Mass. Eye & Ear Infirmary
 ENT Infections Marlene L. Durand, M.D. Mass. General Hospital Mass. Eye & Ear Infirmary Case 1 18 yr-old patient presents with L eyelid swelling, redness, and pain. He was well until 10 days ago, when
ENT Infections Marlene L. Durand, M.D. Mass. General Hospital Mass. Eye & Ear Infirmary Case 1 18 yr-old patient presents with L eyelid swelling, redness, and pain. He was well until 10 days ago, when
SINUSITIS/RHINOSINUSITIS
 1. Medical Condition TUEC Guidelines SINUSITIS/RHINOSINUSITIS Sinusitis refers to inflammation of the sinuses only while the more clinically relevant term should be Rhinosinusitis which is the inflammation
1. Medical Condition TUEC Guidelines SINUSITIS/RHINOSINUSITIS Sinusitis refers to inflammation of the sinuses only while the more clinically relevant term should be Rhinosinusitis which is the inflammation
Congestion, headache, recurrent infection, post-nasal drip, smell problems? We can find the source and offer solutions for relief.
 Sinus Sinus Congestion, headache, recurrent infection, post-nasal drip, smell problems? We can find the source and offer solutions for relief. So what is sinusitis? Although many individuals interpret
Sinus Sinus Congestion, headache, recurrent infection, post-nasal drip, smell problems? We can find the source and offer solutions for relief. So what is sinusitis? Although many individuals interpret
ISSN X (Print) B. G Nagara, Nagamangala Taluk, Mandya District, Karnataka, Karnataka, India
 Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2016; 4(2C):489-493 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2016; 4(2C):489-493 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Spheno-Ethmoidectomy
 Diagnostic and Therapeutic Endoscopy, Vol. 5, pp. 1-8 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only (C) 1998 OPA (Overseas Publishers Association) N.V. Published
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Endoscopy, Vol. 5, pp. 1-8 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only (C) 1998 OPA (Overseas Publishers Association) N.V. Published
Inter-Observer and Intra-Observer Variability In the Assessment of The Paranasal Sinuses Radiographs
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Volume 5 Number 2 Inter-Observer and Intra-Observer Variability In the Assessment of The Paranasal Sinuses Radiographs A Norie, R Ahmad, W Liew, M
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Volume 5 Number 2 Inter-Observer and Intra-Observer Variability In the Assessment of The Paranasal Sinuses Radiographs A Norie, R Ahmad, W Liew, M
Provider Led Entity. CDI Quality Institute PLE Rhinosinusitis AUC 12/04/2018
 Provider Led Entity CDI Quality Institute PLE Rhinosinusitis AUC 12/04/2018 Appropriateness of advanced imaging procedures* in patients with rhinosinusitis and the following clinical presentations or diagnoses:
Provider Led Entity CDI Quality Institute PLE Rhinosinusitis AUC 12/04/2018 Appropriateness of advanced imaging procedures* in patients with rhinosinusitis and the following clinical presentations or diagnoses:
Computerised tomographic profile of ethmoid roof on basis of keros classification among ethnic Kashmiri s
 International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Salroo IN et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2016 Jan;2(1):1-5 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937 Research
International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Salroo IN et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2016 Jan;2(1):1-5 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937 Research
SINUSITIS. HAVAS ENT CLINICS Excellence in otolaryngology
 JULY 2015 SINUSITIS WHAT IS IT? WHAT SHOULD YOU DO? WHAT WORKS? THOMAS E HAVAS MBBS (SYD) MD (UNSW) FRCSE, FRACS, FACS CONJOINT ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR UNSW OTOLARNGOLOGY HEAD AND NECK SURGERY HAVAS ENT CLINICS
JULY 2015 SINUSITIS WHAT IS IT? WHAT SHOULD YOU DO? WHAT WORKS? THOMAS E HAVAS MBBS (SYD) MD (UNSW) FRCSE, FRACS, FACS CONJOINT ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR UNSW OTOLARNGOLOGY HEAD AND NECK SURGERY HAVAS ENT CLINICS
SINUS SURGERY. Dr Zenia Chow MBBS(hons), FRACS
 SINUS SURGERY Dr Zenia Chow MBBS(hons), FRACS Facial Plastic & Reconstructive Surgeon Otolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgeon ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY/FESS What are sinuses The sinuses are a connected system
SINUS SURGERY Dr Zenia Chow MBBS(hons), FRACS Facial Plastic & Reconstructive Surgeon Otolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgeon ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY/FESS What are sinuses The sinuses are a connected system
Journal of American Science 2017;13(1) Identification of Allergic Fungal Sinusitis (AFs) by MDCT and MR Imaging
 Identification of Allergic Fungal Sinusitis (AFs) by MDCT and MR Imaging Nadia Abd El Sater Metwally 1 ; Hoda Mohammed Abd El Wahab 1 ; Bothina Ahmed Mohammed 2 1 Radiodiagnosis Department, Faculty of
Identification of Allergic Fungal Sinusitis (AFs) by MDCT and MR Imaging Nadia Abd El Sater Metwally 1 ; Hoda Mohammed Abd El Wahab 1 ; Bothina Ahmed Mohammed 2 1 Radiodiagnosis Department, Faculty of
Epidemiology of nasal polyps in hilly areas and its risk factors
 International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Nanda MS et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2017 Jan;3(1):77-81 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937 Original
International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Nanda MS et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2017 Jan;3(1):77-81 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937 Original
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 09 Page September 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i9.52 Relationship of Agger Nasi Cell and Uncinate
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i9.52 Relationship of Agger Nasi Cell and Uncinate
Role of Modified Endoscopic Medial Maxillectomy in Persistent Chronic Maxillary Sinusitis
 THIEME Original Research 159 Role of Modified Endoscopic Medial Maxillectomy in Persistent Chronic Maxillary Sinusitis Ponnaiah Thulasidas 1 Venkatraman Vaidyanathan 2 1 Department of Otolaryngology Head
THIEME Original Research 159 Role of Modified Endoscopic Medial Maxillectomy in Persistent Chronic Maxillary Sinusitis Ponnaiah Thulasidas 1 Venkatraman Vaidyanathan 2 1 Department of Otolaryngology Head
Dose-dependent effects of tobramycin in an animal model of Pseudomonas sinusitis Am J Rhino Jul-Aug; 21(4):423-7
 AMINOGLYCOSIDES Dose-dependent effects of tobramycin in an animal model of Pseudomonas sinusitis Am J Rhino. 2007 Jul-Aug; 21(4):423-7 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17882910 Evaluation of the in-vivo
AMINOGLYCOSIDES Dose-dependent effects of tobramycin in an animal model of Pseudomonas sinusitis Am J Rhino. 2007 Jul-Aug; 21(4):423-7 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17882910 Evaluation of the in-vivo
