Anatomy and Physiology. Neurological Topics. Common Signs and Symptoms
|
|
|
- Dustin Dalton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Anatomy and Physiology Neurological Topics HIHIM 409 Nervous system: brain, spinal cord, nerves Central Nervous System (CNS) and Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) CNS: brain and spinal cord PNS: autonomic nervous system, cranial and spinal nerves Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 2 Common Signs and Symptoms Common signs and symptoms Headache Nausea and vomiting Weakness Mood swings Fever Common Signs and Symptoms Symptoms specific to CNS Stiffness in neck, back, or extremities Inability to move any part of the body Seizures or convulsion Paralysis Visual difficulties Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 3 Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 4 Common Signs and Symptoms Symptoms specific to CNS Inability to speak Paralysis Extreme or prolongeddrowsinessdrowsiness Stupor, unconsciousness, amnesia, extreme forgetfulness Common Signs and Symptoms Common diagnostic tests Cerebrospinal fluid Measuring intracranial pressure X rays of skull and vertebralcolumn Myelogram Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 5 Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 6 1
2 Common Signs and Symptoms Common diagnostic tests Angiogram Electroencephlogram CAT Scan MRI Encephalitis Inflammation of brain tissue caused by bacteria and viruses : Headache, stiff neck and back Fever and lethargy Confusion and even coma Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 7 Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 8 Encephalitis : Supportive Antiviral medication may be effective Meningitis Inflammation of meninges or coverings of brain and spinal cord Causes: Bacterial and viral Fungi Toxins such as lead and arsenic Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 9 Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 10 Meningitis High fever Severe headaches Photophobia Meningitis Stiffness and resistance in neck (nuchal rigidity) Drowsiness Stupor Seizures Coma Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 11 Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 12 2
3 Meningitis Diagnosis: collect spinal fluid to find cause Antibiotics for bacterial infection Antipyretics Anticonvulsants Quiet dark environment Poliomyelitis Viral infection affecting brain and spinal cord Vaccine has eliminated the disease in the United States Virus is spread by oropharyngeal secretions and infected feces Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 13 Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 14 Poliomyelitis Muscle weakness Neck stiffness Nausea and vomiting Poliomyelitis Diagnosis: clinical examination, throat, feces, and spinal fluid culture : supportive therapy including analgesics and bedrest during acute phase Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 15 Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 16 Poliomyelitis Long term physical therapy and braces may be needed If respiratory system involved, mechanical ventilation may be needed Tetanus Highly fatal infection of nerve tissue caused by bacteria Clostridium tetani First symptom is stiffness of the jaw, commonly called lockjaw Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 17 Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 18 3
4 Rabies Caused by virus Primarily affects animals such as dogs, cats, raccoons, squirrels Transmitted to humans through bite of an infected animal Rabies Fever and pain Convulsions and rage Spasms and paralysis of muscles for swallowing Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 19 Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 20 Rabies Throat spasms leading to hydrophobia Inability to swallow; drooling of frothy saliva Clean infection site and rabies vaccine injections No cure Shingles Viral disease caused by herpes zoster Itching, painful red rash, and small vesicles on sensory nerve paths last ten days to several weeks Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 21 Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 22 Shingles Diagnosis Appearance of lesions Viral culture test Shingles Antiviral medications Analgesics Antipyretics Antipruritic medications Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 23 Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 24 4
5 Transient Ischemic Attacks TIAs or mini strokes Insufficient blood to brain Symptoms Weakness of arm and/or leg Dizziness Slurred speech Mild loss of consciousness Transient Ischemic Attacks Symptoms last few minutes to an hour Diagnosis is made by angiogram Surgery to improve blood flow Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 25 Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 26 Degenerative Disk Disease Headache Epilepsy Bell s Palsy Degenerative Disk Disease Degeneration or wearing away of the intervertebral disk Wearing away allows vertebrae to bump or rub against each other Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 27 Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 28 Degenerative Disk Disease : Difficulty walking Radiating pain in back and in one or both legs Degenerative Disk Disease Diagnosis: X ray Myelogram CAT or MRI Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 29 Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 30 5
6 Degenerative Disk Disease Rest back and legs Back brace Analgesics and anti inflammatory drugs Exercise to ease pain Surgery Headaches one of the most common disorders in humans Caused by two mechanisms Tension on facial, neck, and scalp muscles Vascular changes in arterial size of vessels inside head Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 31 Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 32 Headaches Contributing factors Stress Toxic fumes Noise Lack of sleep Alcohol consumption Headaches May be acute or chronic Pain may be constant, pressure, throbbing, stabbing, intermittent Tension, cluster, following lumbar puncture, migraine Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 33 Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 34 Headaches Diagnosis History and physical examination X ray EEG, MRI, and CAT Headaches Analgesics Bedrestandmuscle massage Muscle relaxants Warm baths Biofeedback Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 35 Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 36 6
7 Epilepsy Chronic disease of brain Intermittent episodes of abnormal electrical activity in brain Most common symptom is seizure Convulsions include petit mal, grand mal Epilepsy Diagnosis EEG CAT scan Cerebral angiogram Blood tests Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 37 Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 38 Epilepsy Anticonvulsive medications Close monitoring and adjusting of medications Bell s Palsy Affects facial nerve (7 th cranial), causing unilateral paralysis Affects individuals 20 to 60 years of age Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 39 Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 40 Bell s Palsy Drooping weakness of eye Drooling of saliva Unable to whistle or smile Distorted facial appearance Bell s Palsy Diagnosis History and symptoms Analgesics and anti inflammatory medication Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 41 Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 42 7
8 Dementia Loss of mental ability due to loss of neurons or brain cells Most common dementiais is senility Most common cause of senile dementia is Alzheimer's disease Alzheimer's Disease Form of dementia Affects individuals 70 and older Early symptoms Short term memory loss Inability to concentrate Slight changes in personality Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 43 Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 44 Alzheimer's Disease of disease progression Diminished communication skills Meaningless words Inability to form sentences Increased forgetfulness Irritability and agitation Alzheimer's Disease Positive diagnosis: autopsy Initially may be made by ruling out other brain diseases is supportive No cure Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 45 Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 46 Vascular Dementia Atrophy and death of brain cells due to decreased blood flow Atherosclerotic plaque can cause decreased blood flow and is common with aging Vascular Dementia Changes in memory, personality, and judgment Irritability, depression, and sleeplessness Lacks personal hygiene Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 47 Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 48 8
9 Vascular Dementia Diagnosis Blood flow testing and history and physical Increasing blood flow to brain Carotid endarterectomy Head Dementia Death of brain cells due to head trauma Decrease in mental intellect andcognitive function Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 49 Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 50 Head Dementia Diagnosis History Cranial X rays MRI and CT Correct damage if possible Substance Induced Dementia Brain cell death from drug toxicity and toxins Causes mental impairment and decreased cognitive ability Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 51 Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 52 Sleep Disorders Insomnia Inability to fall or stay asleep Related to stress, pain, fear, depression, caffeine, alcohol, nicotine, and bronchodilators Identifying and removing cause Sleep Apnea Sleep disorder characterized by periods of breathlessness Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 53 Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 54 9
10 Symptoms Daytime sleepiness Extreme snoring Personality changes Depression Impotence Sleep Apnea Sleep Apnea Diagnosis Monitor affected individual during sleep for apnea and low blood oxygen levels Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 55 Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 56 Sleep Apnea Based on cause Sleep Disorders Weight loss Surgery to correct nasal obstruction Oxygen during sleep Medications to stimulate breathing Tumors Primary and secondary Benign and malignant Symptoms Headache Vomiting and seizures Mood and personality changes Visual disturbance and loss of memory Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 57 Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 58 Tumors Diagnosis Clinical symptoms X ray, CT, and MRI Biopsy Treatment: surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy Concussions and Contusions Blow to head by an object, fall, or other trauma such as an automobile accident Disruptionof of normalelectricalactivity activity in brain Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 59 Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
11 Concussions and Contusions Causes immediate unconsciousness May last a few seconds to several hours Concussionis is less serious than a contusion Concussions and Contusions Contusion is bruising of the brain Outcomes: Canlead to a hematoma Increased intracranial pressure (ICP) Permanent brain damage Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 61 Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 62 Concussions and Contusions Diagnosis History of injury Neurologic examination Cranial X ray CT and MRI Concussions and Contusions Bedrest and direct observation Individual should be checked every 2 to 4 hours Monitor changes in consciousness, eye pupil size, mood, and behavior Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 63 Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 64 Concussion and Contusions Analgesics, stimulants, and sedatives should not be given to individuals with a head injury Medications may mask the symptoms and make assessment difficult Skull Fracture Greatest danger is brain tissue damage from bony fragments Potential of cutting brain, severing a vessel, and causing a hematoma Brain damage may be temporary or permanent Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 65 Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
12 Skull Fracture Fracture near base of skull may injure respiratory center and impair breathing Infection of brain tissue may be a problem Skull Fracture Dependent on type and position of fracture Craniotomymay may be necessary to relieve ICP Protective headgear may be necessary until fracture is healed Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 67 Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 68 Epidural and Subdural Hematoma Blood vessels rupture and hemorrhage Blood seeps between bony skull and outer meninges Pushes dura mater away from inner bony skull Epidural and Subdural Hematoma Epidural Hematoma symptoms Headache Dilated pupils Nausea, vomiting, and dizziness Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 69 Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 70 Epidural and Subdural Hematoma Subdural Hematoma Usually the result of head hitting a stationary object Blood collects betweenthe the dura mater and arachnoid layer Epidural and Subdural Hematoma Subdural Hematoma Develops slowly over period of days Hemiparesis Nausea, vomiting, dizziness Convulsions and loss of consciousness Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 71 Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
13 Epidural and Subdural Hematoma Diagnosis Clinical history Cranial X ray, CT or MRI Decrease intracranial pressure Craniotomy called bur holes Spinal Cord Injury Quadriplegia and Paraplegia Injury to spinal cord Results in varying degrees of loss of movement Results in varying degrees of loss of feeling below the area of injury Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 73 Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 74 Spinal Cord Injury Quadriplegia and Paraplegia Quadriplegia Loss of movement and feeling in the trunk and all four extremities Lossof of bowel, bladder, and sexual function Spinal Cord Injury Quadriplegia and Paraplegia Paraplegia Loss of movement and feeling in trunk and both legs Lossof of bladder, bowel, and sexual function Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 75 Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 76 Spinal Cord Injury Quadriplegia and Paraplegia Emergency treatment Immediate treatment is necessary Do not move the victim unless surroundings are unsafe Maintain position of spine with special collars and backboards Spinal Cord Injury Quadriplegia and Paraplegia Diagnosis History of injury Neurologic exam Spinal X rays, MRI, and CAT scan Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 77 Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
14 Spinal Cord Injury Quadriplegia and Paraplegia Treatment Realignment and stabilization of the bony spinal column Decompression or release of pressure on spinal cord Prevent further injury Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) Lou Gehrig s disease Destructive disease of motor or movement neurons Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 79 Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 80 Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) Atrophy of muscles leading to progressive loss of movement of hands, arms, and legs is supportive No cure Guillian Barré Syndrome Acute, progressive disease affecting the spinal nerves Begins 10 to 21 days after febrile illness Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 81 Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 82 Guillian Barré Syndrome Early symptoms include nausea, fever, and malaise Within 24 to 72 hours paresthesia, muscle weakness, and paralysis usually begins Guillian Barré Syndrome may progress for several days to weeks Once progression ceases, recovery begins is supportive Recovery is usually complete Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 83 Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
15 Huntington s Chorea Inherited disease Appears during middle age Progressive degenerativediseasedisease of brain Huntington s Chorea Loss of muscle control and chorea Leads to mental deterioration Personality change, moody behavior, loss of memory, dementia is supportive No cure Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 85 Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 86 Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Causes: Demyelination of the nerves of the CNS Allows information to leak from the nerve pathway Leads to poor or absent nerve transmission Multiple Sclerosis (MS) : Muscle weakness and lack of coordination Paresthesia Speech difficulty Loss of bladder function Visual disturbance especially diplopia Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 87 Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 88 Multiple Sclerosis Affects adults between ages 20 and 40 Periods of remission and exacerbation Physical therapy Muscle relaxants in order to maintain muscle tone and reduce spastic movement Parkinson s Disease Slow, progressive brain degeneration Develops between ages 50 and 60 Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 89 Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
16 Parkinson s Disease Classic symptoms Rigidity and immobility of hand Very slow speech pattern Pill rolling motion of fingers Expressionless facial appearance Parkinson s Disease Abnormal bent forward posture Short, fast running steps, shuffling appearance Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 91 Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 92 Parkinson s Disease Symptomatic Dopamine replacement Physical and psychological therapy Learning. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
DISORDERS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
 DISORDERS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Bell Work What s your reaction time? Go to this website and check it out: https://www.justpark.com/creative/reaction-timetest/ Read the following brief article and summarize
DISORDERS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Bell Work What s your reaction time? Go to this website and check it out: https://www.justpark.com/creative/reaction-timetest/ Read the following brief article and summarize
Vascular Disorders. Nervous System Disorders (Part B-1) Module 8 -Chapter 14. Cerebrovascular disease S/S 1/9/2013
 Nervous System Disorders (Part B-1) Module 8 -Chapter 14 Overview ACUTE NEUROLOGIC DISORDERS Vascular Disorders Infections/Inflammation/Toxins Metabolic, Endocrinologic, Nutritional, Toxic Neoplastic Traumatic
Nervous System Disorders (Part B-1) Module 8 -Chapter 14 Overview ACUTE NEUROLOGIC DISORDERS Vascular Disorders Infections/Inflammation/Toxins Metabolic, Endocrinologic, Nutritional, Toxic Neoplastic Traumatic
Workbook Answers Chapter 13. Neurologic Diseases and Conditions
 Workbook Answers Chapter 13 Neurologic Diseases and Conditions Short Answer 1. Afferent nerves transmit impulses from parts of the body to the spinal cord; efferent nerves transmit impulses away from the
Workbook Answers Chapter 13 Neurologic Diseases and Conditions Short Answer 1. Afferent nerves transmit impulses from parts of the body to the spinal cord; efferent nerves transmit impulses away from the
Central nervous system
 Central nervous system By Dr. Mohsen Dashti Clinical Medicine & Pathology 316 7 th Lecture Lecture outline Review of structure & function. Symptoms, signs & tests. Specific diseases. Review of structure
Central nervous system By Dr. Mohsen Dashti Clinical Medicine & Pathology 316 7 th Lecture Lecture outline Review of structure & function. Symptoms, signs & tests. Specific diseases. Review of structure
Injuries to the head and spine
 Injuries to the head and spine Aaron J. Katz, AEMT-P, CIC www.es26medic.net 2013 Nervous System Two sub-systems Central Nervous System ( CNS ) Brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System 12 cranial
Injuries to the head and spine Aaron J. Katz, AEMT-P, CIC www.es26medic.net 2013 Nervous System Two sub-systems Central Nervous System ( CNS ) Brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System 12 cranial
The Nervous System. The Central Nervous System. School of Social Work
 School of Social Work The Nervous System Undergraduate researchers: Kate Decoste, Lauren Degrange, Liz Miller, Sean Mortenson, Batool Qweider, and Kaylie Reese (2009). Co-edited by Nancy D. Bergerson (2010).
School of Social Work The Nervous System Undergraduate researchers: Kate Decoste, Lauren Degrange, Liz Miller, Sean Mortenson, Batool Qweider, and Kaylie Reese (2009). Co-edited by Nancy D. Bergerson (2010).
Chapter 26 Head and Spine Trauma The Nervous System The nervous system controls virtually all of our body activities including reflex, voluntary and
 1 2 3 4 5 Chapter 26 Head and Spine Trauma The Nervous System The nervous system controls virtually all of our body activities including reflex, voluntary and involuntary activities Voluntary activities
1 2 3 4 5 Chapter 26 Head and Spine Trauma The Nervous System The nervous system controls virtually all of our body activities including reflex, voluntary and involuntary activities Voluntary activities
Chapter 15 Neurological Emergencies Stroke (1 of 2) Stroke (2 of 2) Seizures Altered Mental Status (AMS)
 1 2 3 4 5 Chapter 15 Neurological Emergencies Stroke (1 of 2) Stroke is the leading cause of death in the United States. After heart disease and cancer It is common in geriatric patients. More than women
1 2 3 4 5 Chapter 15 Neurological Emergencies Stroke (1 of 2) Stroke is the leading cause of death in the United States. After heart disease and cancer It is common in geriatric patients. More than women
Chapter 15 Neurological Emergencies Stroke (1 of 2) Stroke (2 of 2) Seizures Altered Mental Status (AMS) Brain Structure and Function
 1 Chapter 15 Neurological Emergencies 2 Stroke (1 of 2) Stroke is the leading cause of death in the United States. After heart disease and cancer It is common in geriatric patients. More than women have
1 Chapter 15 Neurological Emergencies 2 Stroke (1 of 2) Stroke is the leading cause of death in the United States. After heart disease and cancer It is common in geriatric patients. More than women have
FORM ID. Patient's Personal Details. SECTION A : Medical Record of the Patient. Name. Policy Number. NRIC/Old IC/Passport/Birth Cert/Others
 CRITICAL ILLNESS CLAIM - DOCTOR'S STATEMENT Brain and Nerve Related Conditions Note: This form is to be completed at the Patient s expense by the Attending Physician/ Surgeon who treated the patient. Patient's
CRITICAL ILLNESS CLAIM - DOCTOR'S STATEMENT Brain and Nerve Related Conditions Note: This form is to be completed at the Patient s expense by the Attending Physician/ Surgeon who treated the patient. Patient's
Nervous System. Unit 6.6 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.6 (7 th Edition)
 Nervous System Unit 6.6 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.6 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the main parts (anatomy) of a neuron. Identify the 2 divisions of nervous system. Classify the major types
Nervous System Unit 6.6 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.6 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the main parts (anatomy) of a neuron. Identify the 2 divisions of nervous system. Classify the major types
Chapter Fifteen. Neurological Disorders
 Chapter Fifteen Neurological Disorders Causes of Neurological Disorders Head Injuries Tumors Seizures Drugs (primary effects, side effects, and withdrawal) Circulation Issues Circulation Issues STROKES!
Chapter Fifteen Neurological Disorders Causes of Neurological Disorders Head Injuries Tumors Seizures Drugs (primary effects, side effects, and withdrawal) Circulation Issues Circulation Issues STROKES!
Chapter 57: Nursing Management: Acute Intracranial Problems
 Chapter 57: Nursing Management: Acute Intracranial Problems NORMAL INTRACRANIAL PRESSURE Intracranial pressure (ICP) is the hydrostatic force measured in the brain CSF compartment. Normal ICP is the total
Chapter 57: Nursing Management: Acute Intracranial Problems NORMAL INTRACRANIAL PRESSURE Intracranial pressure (ICP) is the hydrostatic force measured in the brain CSF compartment. Normal ICP is the total
Biology 3201 Nervous System # 7: Nervous System Disorders
 Biology 3201 Nervous System # 7: Nervous System Disorders Alzheimer's Disease first identified by German physician, Alois Alzheimer, in 1906 most common neurodegenerative disease two thirds of cases of
Biology 3201 Nervous System # 7: Nervous System Disorders Alzheimer's Disease first identified by German physician, Alois Alzheimer, in 1906 most common neurodegenerative disease two thirds of cases of
LOSS OF CONSCIOUSNESS & ASSESSMENT. Sheba Medical Center Acute Medicine Department MATTHEW WRIGHT
 LOSS OF CONSCIOUSNESS & ASSESSMENT Sheba Medical Center Acute Medicine Department MATTHEW WRIGHT OUTLINE Causes Head Injury Clinical Features Complications Rapid Assessment Glasgow Coma Scale Classification
LOSS OF CONSCIOUSNESS & ASSESSMENT Sheba Medical Center Acute Medicine Department MATTHEW WRIGHT OUTLINE Causes Head Injury Clinical Features Complications Rapid Assessment Glasgow Coma Scale Classification
Neurological Emergencies. Aaron J. Katz, AEMT-P, CIC
 Neurological Emergencies Aaron J. Katz, AEMT-P, CIC www.es26medic.net 2013 1 Stroke ( CVA ) CerebroVascular Accident Brain Attack Brain damage caused by a blockage of blood to a specific area of the brain
Neurological Emergencies Aaron J. Katz, AEMT-P, CIC www.es26medic.net 2013 1 Stroke ( CVA ) CerebroVascular Accident Brain Attack Brain damage caused by a blockage of blood to a specific area of the brain
Disorders of the Nervous System. Disorders of the Neurological System. General Endpoints of CNS Disease. General Endpoints of CNS Disease
 HD in Nursing-Pathophysiology Disorders of the Nervous System What are some disorders of the nervous system? Disorders of the Neurological System Dr. C.H. Lai The nervous system is vulnerable to various
HD in Nursing-Pathophysiology Disorders of the Nervous System What are some disorders of the nervous system? Disorders of the Neurological System Dr. C.H. Lai The nervous system is vulnerable to various
Brain Injuries. Presented By Dr. Said Said Elshama
 Brain Injuries Presented By Dr. Said Said Elshama Types of head injuries 1- Scalp injuries 2- Skull injuries 3- Intra Cranial injuries ( Brain ) Anatomical structure of meninges Intra- Cranial Injuries
Brain Injuries Presented By Dr. Said Said Elshama Types of head injuries 1- Scalp injuries 2- Skull injuries 3- Intra Cranial injuries ( Brain ) Anatomical structure of meninges Intra- Cranial Injuries
Alterations of Neurologic Function
 Pathophysiology JP Advis DVM, Ph.D. Bartlett Hall, Animal Sciences, Cook, 932-9240, advis@aesop.rutgers.edu 08 Course website: rci.rutgers.edu/~advis Lectures, tests, grades, office hours, textbook, Material
Pathophysiology JP Advis DVM, Ph.D. Bartlett Hall, Animal Sciences, Cook, 932-9240, advis@aesop.rutgers.edu 08 Course website: rci.rutgers.edu/~advis Lectures, tests, grades, office hours, textbook, Material
Essentials of Human Diseases and Conditions
 Essentials of Human Diseases and Conditions 6 th edition Margaret Schell Frazier Jeanette Wist Drzymkowski Copyright 2010 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Copyright 2016,
Essentials of Human Diseases and Conditions 6 th edition Margaret Schell Frazier Jeanette Wist Drzymkowski Copyright 2010 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Copyright 2016,
Chapter 15. Neurologic Emergencies
 Chapter 15 Neurologic Emergencies Introduction (1 of 4) Stroke is the third leading cause of death in the United States. After heart disease and cancer It is common in geriatric patients. More men than
Chapter 15 Neurologic Emergencies Introduction (1 of 4) Stroke is the third leading cause of death in the United States. After heart disease and cancer It is common in geriatric patients. More men than
Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Unit 7b
 Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Unit 7b Chetek High School Mrs. Michaelsen 9.12 Meninges A. Meninges 1. The organs of the CNS are covered by membranes a. The meninges are divided into 3 layers:
Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Unit 7b Chetek High School Mrs. Michaelsen 9.12 Meninges A. Meninges 1. The organs of the CNS are covered by membranes a. The meninges are divided into 3 layers:
Nervous System. Unit 6.6 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.6 (7 th Edition)
 Nervous System Unit 6.6 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.6 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the main parts (anatomy) of a neuron. Identify the 2 divisions of nervous system. Classify the major types
Nervous System Unit 6.6 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.6 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the main parts (anatomy) of a neuron. Identify the 2 divisions of nervous system. Classify the major types
Appendix 2 (as supplied by the authors): ICD codes to identify high-risk children
 Appendix 2 (as supplied by the authors): ICD codes to identify high-risk children ICD-9 codes to identify high risk children in physician claims database Category of condition Condition ICD-9 code Bacterial
Appendix 2 (as supplied by the authors): ICD codes to identify high-risk children ICD-9 codes to identify high risk children in physician claims database Category of condition Condition ICD-9 code Bacterial
Traumatic brain injuries are caused by external mechanical forces such as: - Falls - Transport-related accidents - Assault
 PP2231 Brain injury Cerebrum consists of frontal, parietal, occipital and temporal lobes Diencephalon consists of thalamus, hypothalamus Cerbellum Brain stem consists of midbrain, pons, medulla Central
PP2231 Brain injury Cerebrum consists of frontal, parietal, occipital and temporal lobes Diencephalon consists of thalamus, hypothalamus Cerbellum Brain stem consists of midbrain, pons, medulla Central
Tutorials. By Dr Sharon Truter
 Tutorials By Dr Sharon Truter To the Tutorials By Dr Sharon Truter What to expect from the Tutorials What to expect from these tutorials Outlines, structure, guided reading, explanations, mnemonics Begin
Tutorials By Dr Sharon Truter To the Tutorials By Dr Sharon Truter What to expect from the Tutorials What to expect from these tutorials Outlines, structure, guided reading, explanations, mnemonics Begin
The Nervous System PART C. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7 PART C Protection of the Central Nervous System Scalp and skin Skull and vertebral
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7 PART C Protection of the Central Nervous System Scalp and skin Skull and vertebral
Hockey New South Wales Head Injury Guidelines Effective November
 Hockey New South Wales Effective November 2011 1 Table of Contents Part 1: Guidelines Statement 3 Head Injuries 3 Two Types of Head Injuries 3 Symptoms of Head Injuries 3 Head Injury Notifications 3 Important
Hockey New South Wales Effective November 2011 1 Table of Contents Part 1: Guidelines Statement 3 Head Injuries 3 Two Types of Head Injuries 3 Symptoms of Head Injuries 3 Head Injury Notifications 3 Important
Problems of Neurological Function
 Problems of Neurological Function Unit 10 Independent Student Review Brain Anatomy and physiology of cerebral hemispheres, diencephalon, brain stem, and cerebellum Meninges, ventricles, flow of CSF Blood
Problems of Neurological Function Unit 10 Independent Student Review Brain Anatomy and physiology of cerebral hemispheres, diencephalon, brain stem, and cerebellum Meninges, ventricles, flow of CSF Blood
P1: OTA/XYZ P2: ABC c01 BLBK231-Ginsberg December 23, :43 Printer Name: Yet to Come. Part 1. The Neurological Approach COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL
 Part 1 The Neurological Approach COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL 1 2 Chapter 1 Neurological history-taking The diagnosis and management of diseases of the nervous system have been revolutionized in recent years by
Part 1 The Neurological Approach COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL 1 2 Chapter 1 Neurological history-taking The diagnosis and management of diseases of the nervous system have been revolutionized in recent years by
Neurology Clerkship Learning Objectives
 Neurology Clerkship Learning Objectives Clinical skills Perform a neurological screening examination of the cranial nerves, motor system, reflexes, and sensory system under the observation and guidance
Neurology Clerkship Learning Objectives Clinical skills Perform a neurological screening examination of the cranial nerves, motor system, reflexes, and sensory system under the observation and guidance
Coastal Carolina University Athletic Training Department Policy and Procedure Manual Concussion Management Revised/Reviewed 6/2012
 Coastal Carolina University Athletic Training Department Policy and Procedure Manual Concussion Management Revised/Reviewed 6/2012 INTRODUCTION: Concussion classification, management, and protocols have
Coastal Carolina University Athletic Training Department Policy and Procedure Manual Concussion Management Revised/Reviewed 6/2012 INTRODUCTION: Concussion classification, management, and protocols have
By Mr. Danilo Villar Rogayan Jr.
 The Nervous System By Mr. Danilo Villar Rogayan Jr. Instructor I, Department of Natural Sciences College of Agriculture & Veterinary Medicine RMTU San Marcelino Introduction Highly complex system of two
The Nervous System By Mr. Danilo Villar Rogayan Jr. Instructor I, Department of Natural Sciences College of Agriculture & Veterinary Medicine RMTU San Marcelino Introduction Highly complex system of two
Bellringer. What type of neuron carries messages from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles and glands?
 Bellringer What type of neuron carries messages from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles and glands? a. Sensory b. Motor c. Associative d. Afferent Which part of the brain stem controls respiration?
Bellringer What type of neuron carries messages from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles and glands? a. Sensory b. Motor c. Associative d. Afferent Which part of the brain stem controls respiration?
Trauma Life Support Pre-Hospital (TLS-P) Preparatory Materials
 Trauma Life Support Pre-Hospital (TLS-P) Preparatory Materials 1 1. A high-risk bodily fluid for spreading infection is blood. 2. Items that can reduce the spread of infection include masks, gloves, and
Trauma Life Support Pre-Hospital (TLS-P) Preparatory Materials 1 1. A high-risk bodily fluid for spreading infection is blood. 2. Items that can reduce the spread of infection include masks, gloves, and
Head Injury Guidelines POL 5700
 Issued by: WHS Effective Date: 1 st Oct 13 Rev: A Page 1 of 5 1. PURPOSE Concussion - Important information What is a concussion? A concussion is an injury to the brain. A blow to the head usually causes
Issued by: WHS Effective Date: 1 st Oct 13 Rev: A Page 1 of 5 1. PURPOSE Concussion - Important information What is a concussion? A concussion is an injury to the brain. A blow to the head usually causes
Seizures. What is a seizure? How does it occur?
 Seizures What is a seizure? A seizure is a symptom, not a disease. It happens when nerve cells in the brain function abnormally and there is a sudden abnormal electrical signal in the brain. The seizure
Seizures What is a seizure? A seizure is a symptom, not a disease. It happens when nerve cells in the brain function abnormally and there is a sudden abnormal electrical signal in the brain. The seizure
Chapter 15. Nervous System and Behavioral Health. Copyright 2018, Elsevier Inc. All Rights Reserved.
 Chapter 15 Nervous System and Behavioral Health Chapter 15 Objective 1: Pronounce organs and anatomic structures of the nervous system. Central Nervous System: Brain and Spinal Cord Simplified View of
Chapter 15 Nervous System and Behavioral Health Chapter 15 Objective 1: Pronounce organs and anatomic structures of the nervous system. Central Nervous System: Brain and Spinal Cord Simplified View of
Brisbin Family Chiropractic
 Information reviewed with patient: Dr. Initials Today s Date Brisbin Family Chiropractic Name: Sex: Male Female Address: City: Postal Code: Home Ph# Work# Ext# Cell# Preferred number (circle one) Home
Information reviewed with patient: Dr. Initials Today s Date Brisbin Family Chiropractic Name: Sex: Male Female Address: City: Postal Code: Home Ph# Work# Ext# Cell# Preferred number (circle one) Home
Disclosure Statement. Dr. Kadish has no relevant financial relationships with any commercial interests mentioned in this talk.
 Disclosure Statement Dr. Kadish has no relevant financial relationships with any commercial interests mentioned in this talk. Head Trauma Evaluation Primary and secondary injury Disposition Sports related
Disclosure Statement Dr. Kadish has no relevant financial relationships with any commercial interests mentioned in this talk. Head Trauma Evaluation Primary and secondary injury Disposition Sports related
Covered Critical Illness Conditions Appendix Effective Date: March 1, 2010
 Covered Critical Illness Conditions Appendix Effective Date: March 1, 2010 This Appendix contains definitions for those Conditions that are covered under the Manulife Financial s Group Critical Illness
Covered Critical Illness Conditions Appendix Effective Date: March 1, 2010 This Appendix contains definitions for those Conditions that are covered under the Manulife Financial s Group Critical Illness
Spinal Cord Injury Transection Injury, Spinal Shock, and Hermiated Disc. Copyright 2014, 2011, 2006 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc.
 Spinal Cord Injury Transection Injury, Spinal Shock, and Hermiated Disc 1 Spinal Cord Injury Results from fracture and/or dislocation of vertebrae // Compresses, stretches, or tears spinal cord Cervical
Spinal Cord Injury Transection Injury, Spinal Shock, and Hermiated Disc 1 Spinal Cord Injury Results from fracture and/or dislocation of vertebrae // Compresses, stretches, or tears spinal cord Cervical
Problems of Neurological Function. Unit 10
 Problems of Neurological Function Unit 10 Independent Student Review Brain Anatomy and physiology of cerebral hemispheres, diencephalon, brain stem, and cerebellum Meninges, ventricles, flow of CSF Blood
Problems of Neurological Function Unit 10 Independent Student Review Brain Anatomy and physiology of cerebral hemispheres, diencephalon, brain stem, and cerebellum Meninges, ventricles, flow of CSF Blood
8th Annual NKY TBI Conference 3/28/2014
 Closed Head Injury: Headache to Herniation A N T H O N Y T. K R A M E R U N I V E R S I T Y O F C I N C I N N A T I B L U E A S H E M S T E C H N O L O G Y P R O G R A M Objectives Describe the pathological
Closed Head Injury: Headache to Herniation A N T H O N Y T. K R A M E R U N I V E R S I T Y O F C I N C I N N A T I B L U E A S H E M S T E C H N O L O G Y P R O G R A M Objectives Describe the pathological
Head, Face, Eyes, Ears, Nose and Throat. Neurological Exam. Eye Function 12/11/2017. Oak Ridge High School Conroe, Texas
 Head, Face, Eyes, Ears, Nose and Throat Oak Ridge High School Conroe, Texas Neurological Exam Consists of Five Major Areas: 1. cerebral testing cognitive functioning 2. Cranial nerve testing 3. Cerebellar
Head, Face, Eyes, Ears, Nose and Throat Oak Ridge High School Conroe, Texas Neurological Exam Consists of Five Major Areas: 1. cerebral testing cognitive functioning 2. Cranial nerve testing 3. Cerebellar
InterQual Level of Care 2018 Index
 InterQual Level of Care 2018 Index Rehabilitation Criteria Index Words by Subset The Index is an alphabetical listing of conditions and/or diagnoses designed to guide the user to the criteria subset where
InterQual Level of Care 2018 Index Rehabilitation Criteria Index Words by Subset The Index is an alphabetical listing of conditions and/or diagnoses designed to guide the user to the criteria subset where
10/6/2017. Notice. Traumatic Brain Injury & Head Trauma
 Notice All EMS Live@Nite presentations will be recorded (both audio and video) and available for public viewing online. By participating in EMS Live@Nite, you consent to audio and video recording and its/their
Notice All EMS Live@Nite presentations will be recorded (both audio and video) and available for public viewing online. By participating in EMS Live@Nite, you consent to audio and video recording and its/their
Headache Assessment In Primary Eye Care
 Headache Assessment In Primary Eye Care Spencer Johnson, O.D., F.A.A.O. Northeastern State University Oklahoma College of Optometry johns137@nsuok.edu Course Objectives Review headache classification Understand
Headache Assessment In Primary Eye Care Spencer Johnson, O.D., F.A.A.O. Northeastern State University Oklahoma College of Optometry johns137@nsuok.edu Course Objectives Review headache classification Understand
SPRINGFIELD CLINIC S
 SPRINGFIELD CLINIC S HEAD INJURY MANAGEMENT GUIDE FOR PARENTS Given the complexities of concussion management, Springfield Clinic recognizes the importance of managing concussions on an individualized
SPRINGFIELD CLINIC S HEAD INJURY MANAGEMENT GUIDE FOR PARENTS Given the complexities of concussion management, Springfield Clinic recognizes the importance of managing concussions on an individualized
Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1
 Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 31.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 13 15, 17, 19, 28 31.2 Describe the components and function of the nervous system and the anatomy
Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 31.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 13 15, 17, 19, 28 31.2 Describe the components and function of the nervous system and the anatomy
TBI are twice as common in males High potential for poor outcome Deaths occur at three points in time after injury
 Head Injury Any trauma to (closed vs. open) Skull Scalp Brain Traumatic brain injury (TBI) High incidence Most common causes Falls Motor vehicle accidents Other causes Firearm- related injuries Assaults
Head Injury Any trauma to (closed vs. open) Skull Scalp Brain Traumatic brain injury (TBI) High incidence Most common causes Falls Motor vehicle accidents Other causes Firearm- related injuries Assaults
PET Scans. External Appearance. The Brain: Anatomy & Functions. Cerebral Hemispheres
 PET Scans The Brain: Anatomy & Functions Click for PET Scan video Cerebral Hemispheres External Appearance a pattern of ridges and shallow grooves ridges - gyri (sing. gyrus) grooves - sulci (sing. sulcus)
PET Scans The Brain: Anatomy & Functions Click for PET Scan video Cerebral Hemispheres External Appearance a pattern of ridges and shallow grooves ridges - gyri (sing. gyrus) grooves - sulci (sing. sulcus)
Overview. Overview. Chapter 30. Injuries to the Head and Spine 9/11/2012. Review of the Nervous and Skeletal Systems. Devices for Immobilization
 Chapter 30 Injuries to the Head and Spine Slide 1 Overview Review of the Nervous and Skeletal Systems The Nervous System The Skeletal System Devices for Immobilization Cervical Spine Short Backboards Long
Chapter 30 Injuries to the Head and Spine Slide 1 Overview Review of the Nervous and Skeletal Systems The Nervous System The Skeletal System Devices for Immobilization Cervical Spine Short Backboards Long
Angiostrongyliasis - Rat Lungworm Disease
 Hawaii Island Rat Lungworm Working Group Daniel K. Inouye College of Pharmacy University of Hawaii, Hilo Rat Lungworm IPM RLWL-10 Angiostrongyliasis - Rat Lungworm Disease Standards Addressed: Life Science
Hawaii Island Rat Lungworm Working Group Daniel K. Inouye College of Pharmacy University of Hawaii, Hilo Rat Lungworm IPM RLWL-10 Angiostrongyliasis - Rat Lungworm Disease Standards Addressed: Life Science
Subspecialty Rotation: Child Neurology at SUNY (KCHC and UHB) Residents: Pediatric residents at the PL1, PL2, PL3 level
 Subspecialty Rotation: Child Neurology at SUNY (KCHC and UHB) Residents: Pediatric residents at the PL1, PL2, PL3 level Prerequisites: Any prior pediatric rotations and experience Primary Goals for this
Subspecialty Rotation: Child Neurology at SUNY (KCHC and UHB) Residents: Pediatric residents at the PL1, PL2, PL3 level Prerequisites: Any prior pediatric rotations and experience Primary Goals for this
Depress consciousness by destroying or encroaching upon the substance of the brain Examples: Brain tumor ( ) disease Intracranial Parasites Trauma
 1 Chapter 29 Neurology 2 Pathophysiology CNS Disorders: Alterations in mental status in the sign of central nervous system disorder Alterations may range from a loss in the thought process to totally unconscious
1 Chapter 29 Neurology 2 Pathophysiology CNS Disorders: Alterations in mental status in the sign of central nervous system disorder Alterations may range from a loss in the thought process to totally unconscious
CHAPTER 6 NERVOUS SYSTEM G00-G99. Presented by Jan Halloran
 CHAPTER 6 NERVOUS SYSTEM G00-G99 Presented by Jan Halloran 1 LEARNING OUTCOMES After studying this chapter you should be able to: Explain the difference between the central and peripheral nervous systems
CHAPTER 6 NERVOUS SYSTEM G00-G99 Presented by Jan Halloran 1 LEARNING OUTCOMES After studying this chapter you should be able to: Explain the difference between the central and peripheral nervous systems
Head Trauma Inservice (October)
 John Tramell - Head Trauma Inservice, October 2005.doc Page 1 Head Trauma Inservice (October) Head trauma is the leading cause of death in trauma patients. Having a basic understanding of the anatomy and
John Tramell - Head Trauma Inservice, October 2005.doc Page 1 Head Trauma Inservice (October) Head trauma is the leading cause of death in trauma patients. Having a basic understanding of the anatomy and
Epilepsy. Epilepsy can be defined as:
 Epilepsy Epilepsy can be defined as: A neurological condition causing the tendency for repeated seizures of primary cerebral origin Epilepsy is currently defined as a tendency to have recurrent seizures
Epilepsy Epilepsy can be defined as: A neurological condition causing the tendency for repeated seizures of primary cerebral origin Epilepsy is currently defined as a tendency to have recurrent seizures
Advanced Concept of Nursing- II
 In The Name of God (A PROJECT OF NEW LIFE HEALTH CARE SOCIETY, KARACHI) Advanced Concept of Nursing- II UNIT- VIII Advance Nursing Management Of neurovascular Diseases. Shahzad Bashir RN, BScN, DCHN,MScN
In The Name of God (A PROJECT OF NEW LIFE HEALTH CARE SOCIETY, KARACHI) Advanced Concept of Nursing- II UNIT- VIII Advance Nursing Management Of neurovascular Diseases. Shahzad Bashir RN, BScN, DCHN,MScN
McCance: Pathophysiology, 6th Edition
 McCance: Pathophysiology, 6th Edition Chapter 17: Disorders of the Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems and the Neuromuscular Junction Key Points Print SUMMARY REVIEW Central Nervous System Disorders
McCance: Pathophysiology, 6th Edition Chapter 17: Disorders of the Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems and the Neuromuscular Junction Key Points Print SUMMARY REVIEW Central Nervous System Disorders
Identification number: TÁMOP /1/A
 Manifestation of Novel Social Challenges of the European Union in the Teaching Material of Medical Biotechnology Master s Programmes at the University of Pécs and at the University of Debrecen Identification
Manifestation of Novel Social Challenges of the European Union in the Teaching Material of Medical Biotechnology Master s Programmes at the University of Pécs and at the University of Debrecen Identification
THE LUMBAR SPINE (BACK)
 THE LUMBAR SPINE (BACK) At a glance Chronic back pain, especially in the area of the lumbar spine (lower back), is a widespread condition. It can be assumed that 75 % of all people have it sometimes or
THE LUMBAR SPINE (BACK) At a glance Chronic back pain, especially in the area of the lumbar spine (lower back), is a widespread condition. It can be assumed that 75 % of all people have it sometimes or
387
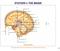 http://images.tutorvista.com/content/control5coordination/human5brain.jpeg!! 387! 388! http://my.fresnounified.org/personal/lygonza/gonzalez/neuron/neuron5synapse%20communication.png!! http://www.urbanchildinstitute.org/sites/all/files/databooks/2011/ch15fg25communication5between5neurons.jpg!!
http://images.tutorvista.com/content/control5coordination/human5brain.jpeg!! 387! 388! http://my.fresnounified.org/personal/lygonza/gonzalez/neuron/neuron5synapse%20communication.png!! http://www.urbanchildinstitute.org/sites/all/files/databooks/2011/ch15fg25communication5between5neurons.jpg!!
Meningitis. A fact sheet for patients and carers
 A fact sheet for patients and carers Meningitis This fact sheet provides information on meningitis. Our fact sheets are designed as general introductions to each subject and are intended to be concise.
A fact sheet for patients and carers Meningitis This fact sheet provides information on meningitis. Our fact sheets are designed as general introductions to each subject and are intended to be concise.
The CNS Part II pg
 The CNS Part II pg. 455-474 Protection of the Brain Objectives Describe how the meninges, cerebrospinal fluid, and the blood brain barrier protect the CNS. Explain how Cerebrospinal fluid is formed, and
The CNS Part II pg. 455-474 Protection of the Brain Objectives Describe how the meninges, cerebrospinal fluid, and the blood brain barrier protect the CNS. Explain how Cerebrospinal fluid is formed, and
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program. Primary Goals for Rotation. Neurology
 The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Neurology 1. GOAL: Understand the role of the pediatrician in preventing neurological diseases, and in counseling and screening
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Neurology 1. GOAL: Understand the role of the pediatrician in preventing neurological diseases, and in counseling and screening
Spinal injury. Structure of the spine
 Spinal injury Structure of the spine Some understanding of the structure of the spine (spinal column) and the spinal cord is important as it helps your Neurosurgeon explain about the part of the spine
Spinal injury Structure of the spine Some understanding of the structure of the spine (spinal column) and the spinal cord is important as it helps your Neurosurgeon explain about the part of the spine
Neurology. Learning Outcomes. Cognitive Domain. Psychomotor Domain. ABHES Competencies. Affective Domain
 CHAPTER 33 Neurology Learning Outcomes Cognitive Domain 1. Spell and define key terms 2. Identify common diseases of the nervous system 3. Describe the physical and emotional effects of degenerative nervous
CHAPTER 33 Neurology Learning Outcomes Cognitive Domain 1. Spell and define key terms 2. Identify common diseases of the nervous system 3. Describe the physical and emotional effects of degenerative nervous
E X P L A I N I N G STROKE
 EXPLAINING STROKE Introduction Explaining Stroke is a practical step-by-step booklet that explains how a stroke happens, different types of stroke and how to prevent a stroke. Many people think a stroke
EXPLAINING STROKE Introduction Explaining Stroke is a practical step-by-step booklet that explains how a stroke happens, different types of stroke and how to prevent a stroke. Many people think a stroke
Pain Management Questionnaire
 In order to make the most of your visit, we require this form to be completed to the best of your ability and sent to the Pain Management Clinic a copy should be shared with your Primary Care Provider
In order to make the most of your visit, we require this form to be completed to the best of your ability and sent to the Pain Management Clinic a copy should be shared with your Primary Care Provider
American Board of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation. Part I Curriculum & Weights
 American Board of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation Part I Curriculum & Weights Neurologic Disorders 30% Stroke Spinal Cord Injury Traumatic Brain Injury Neuropathies a) Mononeuropathies b) Polyneuropathies
American Board of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation Part I Curriculum & Weights Neurologic Disorders 30% Stroke Spinal Cord Injury Traumatic Brain Injury Neuropathies a) Mononeuropathies b) Polyneuropathies
Cascadia Chiropractic Centre
 Name: Cascadia Chiropractic Centre New Patient Information & Clinical Record Date: Date of Birth: Your age: Care Card #: Address: City/Prov: Postal Code: Phone: Cell: Work Phone: E-mail Address: Marital
Name: Cascadia Chiropractic Centre New Patient Information & Clinical Record Date: Date of Birth: Your age: Care Card #: Address: City/Prov: Postal Code: Phone: Cell: Work Phone: E-mail Address: Marital
Common Causes of Brain Damage Cerebrovascular Disorders = Stroke Arteriosclerosis Ischemia and Excitotoxicity
 1 2 Common Causes of Brain Damage Cerebrovascular Disorders = Stroke Tumors Closed-head injuries Infections Neurotoxins Genetic Factors Cerebrovascular Disorders = Stroke May result from: Cerebral hemorrhage
1 2 Common Causes of Brain Damage Cerebrovascular Disorders = Stroke Tumors Closed-head injuries Infections Neurotoxins Genetic Factors Cerebrovascular Disorders = Stroke May result from: Cerebral hemorrhage
Meningococcal Infections Management Procedure
 Meningococcal Infections Management Procedure (IPC Policy Manual) DOCUMENT CONTROL: Version: v1 Ratified by: Clinical Policies Review and Approval Group Date ratified: 4 September 2018 Name of originator/author:
Meningococcal Infections Management Procedure (IPC Policy Manual) DOCUMENT CONTROL: Version: v1 Ratified by: Clinical Policies Review and Approval Group Date ratified: 4 September 2018 Name of originator/author:
Epilepsy 101. Recognition and Care of Seizures and Emergencies Patricia Osborne Shafer RN, MN. American Epilepsy Society
 Epilepsy 101 Recognition and Care of Seizures and Emergencies Patricia Osborne Shafer RN, MN American Epilepsy Society Objectives Recognize generalized and partial seizures. Demonstrate basic first aid
Epilepsy 101 Recognition and Care of Seizures and Emergencies Patricia Osborne Shafer RN, MN American Epilepsy Society Objectives Recognize generalized and partial seizures. Demonstrate basic first aid
CONSULTATION ADMITTANCE FORM
 CONSULTATION ADMITTANCE FORM Last Name: First Name: Address: City Postal Code: Home Phone: Work Phone: Age: Birth date (dd/mm/yr): Sex: M / F Height Weight Occupation: Alberta Health Care #: PLEASE CHECK
CONSULTATION ADMITTANCE FORM Last Name: First Name: Address: City Postal Code: Home Phone: Work Phone: Age: Birth date (dd/mm/yr): Sex: M / F Height Weight Occupation: Alberta Health Care #: PLEASE CHECK
Lyme Disease Specific Symptoms
 Did you have: Please indicate yes or no (Y / N) and/or date month/year tick bite spotted rash over large area circular or bull-eye rash linear red streaks Lyme test date(s) mm/year Results: (positive +,
Did you have: Please indicate yes or no (Y / N) and/or date month/year tick bite spotted rash over large area circular or bull-eye rash linear red streaks Lyme test date(s) mm/year Results: (positive +,
Learn about Leptomeningeal Disease
 Learn about Leptomeningeal Disease Information for patients and caregivers Princess Margaret Read this resource to learn: What is leptomeningeal disease What are the symptoms of leptomeningeal disease
Learn about Leptomeningeal Disease Information for patients and caregivers Princess Margaret Read this resource to learn: What is leptomeningeal disease What are the symptoms of leptomeningeal disease
Spinal Cord Injury. The nerves that go from the spinal cord to the arms, legs, chest, and abdomen are called peripheral nerves.
 Spinal Cord Injury Introduction Spinal cord injuries can be very devastating. More than 10,000 Americans experience spinal cord injuries each year, mainly due to auto or falling accidents. More than 200,000
Spinal Cord Injury Introduction Spinal cord injuries can be very devastating. More than 10,000 Americans experience spinal cord injuries each year, mainly due to auto or falling accidents. More than 200,000
Extended Health Care Company Do you need any help retaining information about your health insurance coverage? Yes No
 PATIENT ENTRANCE FORM Date Circle: Male Female Name Birth Date (dd/mm/yy) Age Address Apt # City Province Postal Code Home # Cell # Work # E-MAIL Occupation Employer Name of Emergency Contact Contact #
PATIENT ENTRANCE FORM Date Circle: Male Female Name Birth Date (dd/mm/yy) Age Address Apt # City Province Postal Code Home # Cell # Work # E-MAIL Occupation Employer Name of Emergency Contact Contact #
Your guide to recovery. Treating concussions
 Your guide to recovery Treating concussions About concussions A concussion is a condition, usually caused when a blow to the head or body causes the brain to move rapidly within the skull, that can temporarily
Your guide to recovery Treating concussions About concussions A concussion is a condition, usually caused when a blow to the head or body causes the brain to move rapidly within the skull, that can temporarily
Chapter 12b. Overview
 Chapter 12b Spinal Cord Overview Spinal cord gross anatomy Spinal meninges Sectional anatomy Sensory pathways Motor pathways Spinal cord pathologies 1 The Adult Spinal Cord About 18 inches (45 cm) long
Chapter 12b Spinal Cord Overview Spinal cord gross anatomy Spinal meninges Sectional anatomy Sensory pathways Motor pathways Spinal cord pathologies 1 The Adult Spinal Cord About 18 inches (45 cm) long
Brain and Central Nervous System Cancers
 Brain and Central Nervous System Cancers NICE guidance link: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ta121 Clinical presentation of brain tumours History and Examination Consider immediate referral Management
Brain and Central Nervous System Cancers NICE guidance link: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ta121 Clinical presentation of brain tumours History and Examination Consider immediate referral Management
Paraparesis. Differential Diagnosis. Ran brauner, Tel Aviv university
 Paraparesis Differential Diagnosis Ran brauner, Tel Aviv university Definition Loss of motor power to both legs Paraparesis (paraplegia) refers to partial (- paresis) or complete (-plegia) loss of voluntary
Paraparesis Differential Diagnosis Ran brauner, Tel Aviv university Definition Loss of motor power to both legs Paraparesis (paraplegia) refers to partial (- paresis) or complete (-plegia) loss of voluntary
Seizures and strokes: Teaching plan
 Seizures and strokes: Teaching plan To use this lesson for self-study, the learner should read the material, do the activity, and take the test. For group study, the leader may give each learner a copy
Seizures and strokes: Teaching plan To use this lesson for self-study, the learner should read the material, do the activity, and take the test. For group study, the leader may give each learner a copy
Provide specific counseling to parents and patients with neurological disorders, addressing:
 Neurology Description: The Pediatric Neurology elective will give the resident the opportunity to learn how to obtain an appropriate history and perform a complete neurologic exam. Four to five half days
Neurology Description: The Pediatric Neurology elective will give the resident the opportunity to learn how to obtain an appropriate history and perform a complete neurologic exam. Four to five half days
FIRST COAST SERVICE OPTIONS FLORIDA MEDICARE PART B LOCAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION
 FIRST COAST SERVICE OPTIONS FLORIDA MEDICARE PART B LOCAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION CPT/HCPCS Codes 70450 Computed tomography, head or brain; without contrast material 70460 with contrast material(s) 70470
FIRST COAST SERVICE OPTIONS FLORIDA MEDICARE PART B LOCAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION CPT/HCPCS Codes 70450 Computed tomography, head or brain; without contrast material 70460 with contrast material(s) 70470
Pre-hospital Response to Trauma and Brain Injury. Hans Notenboom, M.D. Asst. Medical Director Sacred Heart Medical Center
 Pre-hospital Response to Trauma and Brain Injury Hans Notenboom, M.D. Asst. Medical Director Sacred Heart Medical Center Traumatic Brain Injury is Common 235,000 Americans hospitalized for non-fatal TBI
Pre-hospital Response to Trauma and Brain Injury Hans Notenboom, M.D. Asst. Medical Director Sacred Heart Medical Center Traumatic Brain Injury is Common 235,000 Americans hospitalized for non-fatal TBI
Vague Neurological Disorders
 Vague Neurological Disorders Dr. Philip Smalley MD FRCPC SVP & Global Chief Medical Officer RGA International Rose Conference, September 17, 2015 Agenda Vague neurological symptoms associated with: Alzheimer
Vague Neurological Disorders Dr. Philip Smalley MD FRCPC SVP & Global Chief Medical Officer RGA International Rose Conference, September 17, 2015 Agenda Vague neurological symptoms associated with: Alzheimer
History of Present Condition
 Name: Date: Address: City: Province: Postal Code: Home Phone: Cell Phone: Work Phone: Email: Marital Status: Name Of Family Physician (MD): Age: Occupation: Employer: Extended Health Care Company: Policy
Name: Date: Address: City: Province: Postal Code: Home Phone: Cell Phone: Work Phone: Email: Marital Status: Name Of Family Physician (MD): Age: Occupation: Employer: Extended Health Care Company: Policy
/ / / / / / Hospital Abstraction: Stroke/TIA. Participant ID: Hospital Code: Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis
 Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis Participant ID: Hospital Code: Hospital Abstraction: Stroke/TIA History and Hospital Record 1. Was the participant hospitalized as an immediate consequence of this
Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis Participant ID: Hospital Code: Hospital Abstraction: Stroke/TIA History and Hospital Record 1. Was the participant hospitalized as an immediate consequence of this
Traumatic Brain Injury TBI Presented by Bill Masten
 1 2 Cerebrum two hemispheres and four lobes. Cerebellum (little brain) coordinates the back and forth ballet of motion. It judges the timing of every movement precisely. Brainstem coordinates the bodies
1 2 Cerebrum two hemispheres and four lobes. Cerebellum (little brain) coordinates the back and forth ballet of motion. It judges the timing of every movement precisely. Brainstem coordinates the bodies
COPYRIGHT 2012 THE TRANSVERSE MYELITIS ASSOCIATION. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
 The Transverse Myelitis Association...advocating for those with acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, neuromyelitis optica, optic neuritis and transverse myelitis ACUTE DISSEMINATED ENCEPHALOMYELITIS (ADEM)
The Transverse Myelitis Association...advocating for those with acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, neuromyelitis optica, optic neuritis and transverse myelitis ACUTE DISSEMINATED ENCEPHALOMYELITIS (ADEM)
IMPAIRMENT OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
 IMPAIRMENT OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM The following information provides criteria for the evaluation of permanent impairment resulting from dysfunction brain, spinal cord and cranial nerves and certain peripheral
IMPAIRMENT OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM The following information provides criteria for the evaluation of permanent impairment resulting from dysfunction brain, spinal cord and cranial nerves and certain peripheral
May He Rest in Peace
 May He Rest in Peace Neurologic Complications of AIDS Medical Knowledge Fiesta 2012 Paul K. King MD pkingmd@yahoo.com Objectives definition of HIV/AIDS what are the neurologic complications of AIDS how
May He Rest in Peace Neurologic Complications of AIDS Medical Knowledge Fiesta 2012 Paul K. King MD pkingmd@yahoo.com Objectives definition of HIV/AIDS what are the neurologic complications of AIDS how
Medical Emergencies. Emergency Medical Response
 Medical Emergencies Lesson 23: Medical Emergencies You Are the Emergency Medical Responder You are the emergency medical responder (EMR) responding to a scene on a downtown street involving a male who
Medical Emergencies Lesson 23: Medical Emergencies You Are the Emergency Medical Responder You are the emergency medical responder (EMR) responding to a scene on a downtown street involving a male who
HEADACHE. Dr Nick Pendleton. September Headache
 HEADACHE Dr Nick Pendleton September 2017 Headache Tension Type Headache Cranial Nerve Examination Migraine Migraine Treatment Medication Overuse Headache Headache Red Flags Sinusitis Headache Raised ICP
HEADACHE Dr Nick Pendleton September 2017 Headache Tension Type Headache Cranial Nerve Examination Migraine Migraine Treatment Medication Overuse Headache Headache Red Flags Sinusitis Headache Raised ICP
The Nervous System PART B
 7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Central Nervous System
7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Central Nervous System
Intracranial hypotension secondary to spinal CSF leak: diagnosis
 Intracranial hypotension secondary to spinal CSF leak: diagnosis Spinal cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak is an important and underdiagnosed cause of new onset headache that is treatable. Cerebrospinal fluid
Intracranial hypotension secondary to spinal CSF leak: diagnosis Spinal cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak is an important and underdiagnosed cause of new onset headache that is treatable. Cerebrospinal fluid
